Active Viewing: 1877: The Grand Army of Starvation
|
|
|
- Primrose Clark
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Active Viewing: 1877: The Grand Army of Starvation In this activity, you will watch a short clip from the ASHP documentary 1877: The Grand Army of Starvation to learn about the impact of railroad expansion on Americans and the nation as a whole. After watching the clip, you will complete the Technological Turning Points and their Impact worksheet in order to examine the positive and negative effects of the railroad. Essential Questions What was the impact of the railroad on the United States, including which people benefitted from it and which did not? How and why was the completion of the transcontinental railroad considered a major turning point? For what reasons did the railroad workers decide to go on strike in Instructions 1. Step 1. Please locate the 1877 Viewer s Guide we will read the 3 paragraphs of text on page 1 under What was The Great Strike of 1877? You are going to watch a clip from a documentary about the causes of this national uprising. a. Please locate the 1877 Vocabulary list.
2 2. Step 2. We will view the first seven minutes of the film to provide an overview of the transcontinental railroad. In groups, think about two things; a. What is the overall tone of this documentary (ie. what is the attitude of this film towards the railroad during the Gilded Age?). b. Please locate the Technological Turning Points worksheet and in your groups (after viewing the excerpt), check off any of the effects that you think apply to the railroad. We will review the Part 1 list as a class. 3. Step 3. Complete Part II of the worksheet individually. Then, with a partner, you should identify: the top 2 positive effects and top 2 negative effects who benefited the most, and who was harmed the most o Share out group responses. 4. Step 5. I am going to play the remainder of the film, with the Viewers Guide pages interspersed as follows: a. Clip 2: 7:00 to 19:50 b. Read p. 2-6 in Viewers Guide. c. Play Clip 3-19:50 to 24:30 d. Read p. 7-9 in Viewers Guide (using info from p. 4-7 in viewers guide, please complete 1877 Viewer s Guide: Close Reading Worksheet. e. Play Clip 4-24:30 to 29:00. f. P in Viewers Guide
3 1877 Viewer s Guide: Close Reading Worksheet Write down two details and describe one illustration (drawing/photo) from your reading (1877 Viewer s Guide pages 4-7) that help to answer each question. What was it like to work on the railroad? 1: 2: Illustration: How did railroads change American society? 1: 2: Illustration:
4 What happened during the Depression of ? 1: 2: Illustration: How did unions try to protect workers and solve their problems? 1: 2: Illustration:
5 1877: The Grand Army of Starvation Vocabulary (for chapters on "The Centennial Exposition" and "The Railroad") This is a vocabulary list for chapters on "The Centennial Exposition" and "The Railroad" in the 1877: The Grand Army of Starvation documentary. amassed: accumulated anvil: a heavy metal block used by blacksmiths to hammer out other metal brakeman: railroad worker who operates, repairs, or inspects train brakes centennial exposition: celebration to mark the 100th anniversary of America s Declaration of Independence corporate: having to do with large companies or big business cylindric: shaped like a tube dividends: money paid to people who own stock in a company domination: complete control emblem: a symbol of some idea or thing flocked: gathered in a group Great Uprising: national strike by 80,000 railroad workers, also known as the Great Strike of 1877 manipulated: controlled or influenced, usually to one s own benefit militia: military force of civilians that supports regular army, especially in an emergency resilience: the ability to recover quickly from illness or misfortune sultry: hot and damp spike: large nail used to construct railroad tracks territorial expansion: adding new lands to an existing country, often by force transcontinental railroad: a railroad that crosses and connects a continent
6 1877: The Grand Army of Starvation Script (for chapters on "The Centennial Exposition" and "The Railroad") This is a partial script, for chapters on "The Centennial Exposition" and "The Railroad" in the documentary 1877: The Grand Army of Starvation produced by the American Social History Project/Center for Media and Learning. In bold are vocabulary words defined on a vocabulary sheet linked to this script. [1876] NARRATOR: Philadelphia. One hundred years after America declared its independence its citizensflocked to the centennial exposition. Thousands gathered to mark the republic s resilience following a bitter civil war They came to admire the country's technological triumphs and its territorial expansion. At the center of this century of progress the American railway system. The railroad had promised to unite the one divided nation and benefit all citizens. Chinese and Irish immigrants as well as Civil War veterans were set to work as the country enthusiastically committed itself to railroad construction. AMERICAN WORKER #1: When me and my mates get our sturdy sledge hammers going, we make a kinda grand anvil chorus 'cross the plains. Three strokes to a spike; ten spikes to a rail. Let's see I've got it figured out 400 rails to a mile miles to bloody San Francisco. That makes, by my reckonin', some 20 million or so times we'll swing these sledges before this great work of modern America is done. NARRATOR: In 1869 the Golden Spike was finally hammered into place. The transcontinental railroad system unified America. The poet Walt Whitman sang its praises: Thy black cylindric body, golden brass and silvery steel Type of the modern emblem of motion and power pulse of the continent The railroad connected farm lands towns cities. It moved goods, information, and people. In ten short years railroad mileage doubled. Federal and state governments sponsored railroad expansion, giving the railroads nearly 200 million acres of public land as well as millions of dollars in loans and tax breaks. Railroad owners, notably New York Central president Cornelius Vanderbilt, amassed staggering wealth. His son William inherited $100 million upon Vanderbilt's death in In that year of economic depression, a decent day's wage was a dollar fifty. Railroad owners' wealth translated into unimagined power. Tom Scott ran the Pennsylvania Railroad, the nation's largest business enterprise. From his Philadelphia headquarters, Scott controlled the lives of workers and communities
7 across the country. He manipulated state and federal legislatures and even presidential elections. Such domination led Charles Francis Adams, son and grandson of Presidents, to observe: C.F. ADAMS: The system of corporate life is a new power for which our language contains no name; we have no word to express government by monied corporations. NARRATOR: In June, Scott, Vanderbilt and other executives secretly met. They agreed to cut their employees' wages even as they announced substantial dividends for their stockholders. John Garrett, President of the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad, explained: GARRETT: The great principle upon which we joined to act was to earn more and spend less. NARRATOR: On July 15th the B & O announced a 10% wage cut. Dick Zepp, a brakeman on the B & O lines, decides this action is too much to take. On the hot, sultry afternoon of July 16th, Zepp steps down from his locomotive. He and his fellow workers stop trains in the Martinsburg, West Virginia rail yards. CROWD: We're all working men, ain't we? No train's goinna move 'til we get a living wage! We're on strike! We might as well starve without work as with it! Here comes the damn militia! You wouldn't fire on your brother? Stop that blackleg! Don't let him throw the switch! NARRATOR: This is the spark that ignites the Great Uprising.
8 TECHNOLOGICAL TURNINGPOINTS AND THEIR IMPACT Use the following list to evaluate the impact of a particular kind of technology (eg. the railroad, the internet). Part 1: Identify the Effects Economic Effects Creates new jobs Eliminates some jobs Creates new industries or products Makes work faster, safe, and/or easier Creates big profits for owners + investors Social + Environmental Effects Makes communication, faster, cheaper and/or easier Makes transportation faster, cheaper, and/or easier Consumes lots of natural resources (eg. land, water, energy) Pollutes or harms the natural environment Endangers workers or consumers Creates social and/or economic inequality Creates leisure time Political Effects Receives assistance from federal or local government (eg. tax breaks, loans, favorable laws) Creates big businesses that influence government policies and elected officials Allows for greater participation in democracy Builds national pride
9 Part I1: Analyze the Effects 1) What are the positive effects of this technology? 2) What are the negative effects of this technology? 3) Who benefits and who might be harmed?
10 An African-American Socialist Lends His Support to Railroad Strikers A nationwide rebellion brought the United States to a standstill in the summer of Eighty thousand railroad workers walked off the job, joined by hundreds of thousands of Americans outraged by the excesses of the railroad companies and the misery of a four-year economic depression. Peter H. Clark, an African-American school principal and member of the Workingmen's (Socialist) Party, gave the keynote address at a mass meeting in support of the railroad strikers that was held on July 22, 1877 in Cincinnati, Ohio. But when [workers] see high railroad officials receiving the salary of princes, when they hear of dividends in stock and railroad bonds, they cannot understand why there is no money for the man whose labor earns these vast sums...when they complain, they are told that they are at liberty to quit and take their services elsewhere. This is equivalent to telling them that they are at liberty to go and starve...hence they make the effort to obtain an increase in wages and to retain their places at the same time. Understanding their motive, and the dire necessity by which they are driven, I pity, but I cannot condemn them... Then too, the door of justice seems shut in their faces. They have no representation on the Board of Directors. Every state has laws punishing conspiracy, punishing riot and unlawful assemblages, but no state has laws providing for the examination and redress of the grievances of which these men complain. The whole force of the State and National Governments may be invoked by the railroad managers, but the laborer has nothing. SOURCE The Cincinnati Commerical, July 23, CREATOR Peter H. Clark ITEM TYPE Speech
Industrial Development
 Industrial Development Rapid growth 1865 1914 Abundance of cheap natural resources Large pools of labor immigrants Largest free trade market in the world Capital, no government regulation New technological
Industrial Development Rapid growth 1865 1914 Abundance of cheap natural resources Large pools of labor immigrants Largest free trade market in the world Capital, no government regulation New technological
Chinese-Americans on track to learn history of railroad-worker ancestors
 Chinese-Americans on track to learn history of railroad-worker ancestors By Los Angeles Times, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.30.15 Word Count 933 A crowd gathered on May 10, 1869, to celebrate the completion
Chinese-Americans on track to learn history of railroad-worker ancestors By Los Angeles Times, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.30.15 Word Count 933 A crowd gathered on May 10, 1869, to celebrate the completion
Industry Comes of Age Chapter 24
 Industry Comes of Age 1865-1900 Chapter 24 The Iron Colt Becomes an Iron Horse Is there more power in BUSINESS or POLITICS? Surge in railroad development 1865 35,000 miles of track 1900 over 192,000 miles
Industry Comes of Age 1865-1900 Chapter 24 The Iron Colt Becomes an Iron Horse Is there more power in BUSINESS or POLITICS? Surge in railroad development 1865 35,000 miles of track 1900 over 192,000 miles
Part III DOCUMENT-BASED QUESTION
 NAME SCHOOL In developing your answer to Part III, be sure to keep this general definition in mind: discuss means to make observations about something using facts, reasoning, and argument; to present in
NAME SCHOOL In developing your answer to Part III, be sure to keep this general definition in mind: discuss means to make observations about something using facts, reasoning, and argument; to present in
SSUSH11A thru E and 12B & D Industrialization
 SSUSH11A thru E and 12B & D Industrialization Causes of U.S. Industrialization The earliest forms of industrialization in the U.S. began in the late 1700 s with the development of the transportation and
SSUSH11A thru E and 12B & D Industrialization Causes of U.S. Industrialization The earliest forms of industrialization in the U.S. began in the late 1700 s with the development of the transportation and
Chapter 13 Section 4 T H E G R E A T S T R I K E S
 Chapter 13 Section 4 T H E G R E A T S T R I K E S Gulf Between Rich and Poor In 1890, the richest 9% of Americans held nearly 75% of the nation s wealth The average worker could earn only a few hundred
Chapter 13 Section 4 T H E G R E A T S T R I K E S Gulf Between Rich and Poor In 1890, the richest 9% of Americans held nearly 75% of the nation s wealth The average worker could earn only a few hundred
I-The Age of Industry
 STRIKE ONE! { Learning Target: I can describe the working conditions that an individual faced when working in factories and why Unions were created to help workers. I-The Age of Industry A-People began
STRIKE ONE! { Learning Target: I can describe the working conditions that an individual faced when working in factories and why Unions were created to help workers. I-The Age of Industry A-People began
Chapter 18 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 18 Lecture Outline Big Business and Organized Labor 2013 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Chapter 18 Lecture Outline Big Business and Organized Labor 2013 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Robber Barons
Chapter 18 Lecture Outline Big Business and Organized Labor 2013 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Chapter 18 Lecture Outline Big Business and Organized Labor 2013 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Robber Barons
netw rks Reading Essentials and Study Guide Growth and Division, Lesson 2 Early Industry ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Reading HELPDESK
 and Study Guide Lesson 2 Early Industry ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How did the nation s economy help shape its politics? How did the economic differences between the North and the South cause tension? Reading
and Study Guide Lesson 2 Early Industry ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How did the nation s economy help shape its politics? How did the economic differences between the North and the South cause tension? Reading
Industrialism. Sophia Wright, David Suescun, Oliver Santos, Kayla Gardner
 Industrialism Sophia Wright, David Suescun, Oliver Santos, Kayla Gardner Industrialism- What is It? Before industrialism, mainly farming and agriculture took place in the United States, despite Alexander
Industrialism Sophia Wright, David Suescun, Oliver Santos, Kayla Gardner Industrialism- What is It? Before industrialism, mainly farming and agriculture took place in the United States, despite Alexander
Guided Reading Activity 25-1
 Guided Reading Activity 25-1 DIRECTIONS: Filling in the Blanks Use your textbook to fill in the blanks using the words in the box. Use another sheet of paper if necessary. Reconstruction Finance Corporation
Guided Reading Activity 25-1 DIRECTIONS: Filling in the Blanks Use your textbook to fill in the blanks using the words in the box. Use another sheet of paper if necessary. Reconstruction Finance Corporation
The Constitutional Convention formed the plan of government that the United States still has today.
 2 Creating the Constitution MAIN IDEA The states sent delegates to a convention to solve the problems of the Articles of Confederation. WHY IT MATTERS NOW The Constitutional Convention formed the plan
2 Creating the Constitution MAIN IDEA The states sent delegates to a convention to solve the problems of the Articles of Confederation. WHY IT MATTERS NOW The Constitutional Convention formed the plan
Industrialization, Urbanization, and Immigration Overview
 Industrialization, Urbanization, and Immigration Overview Demographic Expansion In 1840, where we began our studies, the US population stood at 17.1 million and by 1920 it was 106 million. Chart made in
Industrialization, Urbanization, and Immigration Overview Demographic Expansion In 1840, where we began our studies, the US population stood at 17.1 million and by 1920 it was 106 million. Chart made in
UNIT 4: EXPANSION & REFORM LESSON 4.1: EFFECTS OF MANIFEST DESTINY & INDUSTRIALIZATION
 UNIT 4: EXPANSION & REFORM LESSON 4.1: EFFECTS OF MANIFEST DESTINY & INDUSTRIALIZATION ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does expansion and industrialization contribute to growing sectionalism within the United States
UNIT 4: EXPANSION & REFORM LESSON 4.1: EFFECTS OF MANIFEST DESTINY & INDUSTRIALIZATION ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does expansion and industrialization contribute to growing sectionalism within the United States
Yick Wo: Equal Justice Under Law
 Yick Wo: Equal Justice Under Law Compelling Question o How can you promote justice for yourself and others? Virtue: Justice Definition Justice is the capacity to determine and preserve our common rights.
Yick Wo: Equal Justice Under Law Compelling Question o How can you promote justice for yourself and others? Virtue: Justice Definition Justice is the capacity to determine and preserve our common rights.
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Articles of Confederation. Essential Question:
 Articles of Confederation Essential Question: Why was the central government s power too weak under the Articles of Confederation? Objectives Discuss the ideas that guided the new state governments. Describe
Articles of Confederation Essential Question: Why was the central government s power too weak under the Articles of Confederation? Objectives Discuss the ideas that guided the new state governments. Describe
1880s Agricultural Nation: Foods and Families on the Move (subtheme: immigrant and migrant workers) Historical Thinking Skills Used
 Unit One 1880s Agricultural Nation: Foods and Families on the Move (subtheme: immigrant and migrant workers) Each Unit Contains To the Teacher Instructions for Use Image Cards Six primary sources, and
Unit One 1880s Agricultural Nation: Foods and Families on the Move (subtheme: immigrant and migrant workers) Each Unit Contains To the Teacher Instructions for Use Image Cards Six primary sources, and
Deflation deflation,
 Unions Deflation Between 1865 and 1897, the United States experienced deflation, or a rise in the value of money Deflation caused prices to fall and companies to cut wages To the workers, it seemed their
Unions Deflation Between 1865 and 1897, the United States experienced deflation, or a rise in the value of money Deflation caused prices to fall and companies to cut wages To the workers, it seemed their
Chapter 5: DEFINING AMERICAN WAR AIMS
 Chapter 5: DEFINING AMERICAN WAR AIMS Objectives: Identify the major debates in the Second Continental Congress, and their outcomes. Assess the impact of Thomas Paine s Common Sense on the colonial view
Chapter 5: DEFINING AMERICAN WAR AIMS Objectives: Identify the major debates in the Second Continental Congress, and their outcomes. Assess the impact of Thomas Paine s Common Sense on the colonial view
Labor Response to. Industrialism
 Labor Response to Industrialism Was the rise of industry good for American workers? 1. Introduction Rose Schneiderman Organized Uprising of 20,000 1000 s of women in shirtwaist industry strike Higher wages,
Labor Response to Industrialism Was the rise of industry good for American workers? 1. Introduction Rose Schneiderman Organized Uprising of 20,000 1000 s of women in shirtwaist industry strike Higher wages,
The Declaration of Independence
 The Declaration of Independence N1: This is the story N2: of the birth of the Adapted by Timothy Rasinski The Promise of America A reader s theater for six voices: three narrators (N) and three readers
The Declaration of Independence N1: This is the story N2: of the birth of the Adapted by Timothy Rasinski The Promise of America A reader s theater for six voices: three narrators (N) and three readers
Mr. Saccullo 8 th Grade Social Studies Review Sheet IV
 Mr. Saccullo 8 th Grade Social Studies Review Sheet IV Key Points of the Time Period Word Bank mass production poorly northern wages machines working western unions rural urban southern Europe eastern
Mr. Saccullo 8 th Grade Social Studies Review Sheet IV Key Points of the Time Period Word Bank mass production poorly northern wages machines working western unions rural urban southern Europe eastern
Working conditions Monotonous same job day after day hour shifts, 6 days a week Dangerous machinery with no safety precautions Workers frequentl
 Labor Unions Working conditions Monotonous same job day after day 12 16 hour shifts, 6 days a week Dangerous machinery with no safety precautions Workers frequently lost fingers, limbs, eyesight, & hearing
Labor Unions Working conditions Monotonous same job day after day 12 16 hour shifts, 6 days a week Dangerous machinery with no safety precautions Workers frequently lost fingers, limbs, eyesight, & hearing
The Rise of Smokestack America
 18 The Rise of Smokestack America (1) CHAPTER OUTLINE Thomas O'Donnell's testimony highlights the marginal existence of many workingclass Americans in the late nineteenth century. The responses of congressional
18 The Rise of Smokestack America (1) CHAPTER OUTLINE Thomas O'Donnell's testimony highlights the marginal existence of many workingclass Americans in the late nineteenth century. The responses of congressional
Name Class Date. Forging the New Republic Section 1
 Name Class Date Section 1 MAIN IDEA President Washington and other leaders tried to solve the new nation s economic problems. This led to the rise of political parties. Key Terms and People cabinet heads
Name Class Date Section 1 MAIN IDEA President Washington and other leaders tried to solve the new nation s economic problems. This led to the rise of political parties. Key Terms and People cabinet heads
The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783!
 Creating a Republic The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783! The treaty ending the war with Britain, more than doubled the territory of the United States!
Creating a Republic The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783! The treaty ending the war with Britain, more than doubled the territory of the United States!
Visit the ASHP website for more information:
 Viewer s Guide to the 30-minute documentary by the American Social History Project A nationwide rebellion brought the United States to a standstill in the summer of 1877. Eighty thousand railroad workers
Viewer s Guide to the 30-minute documentary by the American Social History Project A nationwide rebellion brought the United States to a standstill in the summer of 1877. Eighty thousand railroad workers
Textile workers win a hard-fought victory during hard times
 March 1879 It required many years of struggle, but the United States now officially recognizes March as Women s History Month. The commemoration was born out of a terrible workplace tragedy a fire in a
March 1879 It required many years of struggle, but the United States now officially recognizes March as Women s History Month. The commemoration was born out of a terrible workplace tragedy a fire in a
Rise of American Industrialization,
 Rise of American Industrialization, 1860-1900 Thesis: Between 1861 and 1900, manufacturing replaced agriculture as the country s leading source of economic growth and gave rise to large cities, immigration,
Rise of American Industrialization, 1860-1900 Thesis: Between 1861 and 1900, manufacturing replaced agriculture as the country s leading source of economic growth and gave rise to large cities, immigration,
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century)
 The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 6: TELESCOPING THE TIMES A New Industrial Age CHAPTER OVERVIEW Technological innovations and the growth of the railroad industry help fuel an
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 6: TELESCOPING THE TIMES A New Industrial Age CHAPTER OVERVIEW Technological innovations and the growth of the railroad industry help fuel an
LOREM IPSUM. Book Title DOLOR SET AMET
 LOREM IPSUM Book Title DOLOR SET AMET CHAPTER 3 INDUSTRY IN THE GILDED AGE In 1865, the United States was a second-rate economic power behind countries like Great Britain and France. But over the course
LOREM IPSUM Book Title DOLOR SET AMET CHAPTER 3 INDUSTRY IN THE GILDED AGE In 1865, the United States was a second-rate economic power behind countries like Great Britain and France. But over the course
Central Historical Question: What factors contributed to the Chinese Exclusion Act?
 Central Historical Question: What factors contributed to the Chinese Exclusion Act? Materials: Instructions: Railroad PPT (one slide) Video Segment: Perilous Endeavor (from The West: The Grandest Enterprise
Central Historical Question: What factors contributed to the Chinese Exclusion Act? Materials: Instructions: Railroad PPT (one slide) Video Segment: Perilous Endeavor (from The West: The Grandest Enterprise
Analyze the maps in Setting the Stage. Then answer the following questions and fill out the map as directed.
 Geography Challenge G e o G r a p h y C h a l l e n G e Geography Skills Analyze the maps in Setting the Stage. Then answer the following questions and fill out the map as directed. 1. Label each state
Geography Challenge G e o G r a p h y C h a l l e n G e Geography Skills Analyze the maps in Setting the Stage. Then answer the following questions and fill out the map as directed. 1. Label each state
Chapter 14, Section 1 I. The United States Industrializes (pages ) A. With the end of the Civil War, American industry expanded and millions
 Chapter 14, Section 1 I. The United States Industrializes (pages 436 437) A. With the end of the Civil War, American industry expanded and millions of people left their farms to work in mines and factories.
Chapter 14, Section 1 I. The United States Industrializes (pages 436 437) A. With the end of the Civil War, American industry expanded and millions of people left their farms to work in mines and factories.
Farmers and the Populist Movement
 Farmers and the Populist Movement Farmers Unite In the late 1800 s a vicious economic cycle was especially harmful to farmers. Prices for their products was falling while the cost of seeds and tools was
Farmers and the Populist Movement Farmers Unite In the late 1800 s a vicious economic cycle was especially harmful to farmers. Prices for their products was falling while the cost of seeds and tools was
Chapter 13: The Expansion of American Industry ( )
 Name: Period Page# Chapter 13: The Expansion of American Industry (1850 1900) Section 1: A Technological Revolution Why did people s daily lives change in the decades following the Civil War? How did advances
Name: Period Page# Chapter 13: The Expansion of American Industry (1850 1900) Section 1: A Technological Revolution Why did people s daily lives change in the decades following the Civil War? How did advances
U.S. INDUSTRIALISM. Chap 9
 U.S. INDUSTRIALISM Chap 9 How did the US industrialize? Plenty of raw materials needed for industry: water, wood, coal, iron, copper Large workforce: population tripled between 1860-1910 Technology and
U.S. INDUSTRIALISM Chap 9 How did the US industrialize? Plenty of raw materials needed for industry: water, wood, coal, iron, copper Large workforce: population tripled between 1860-1910 Technology and
Unit 3 Section 1 Articles and Early Government.notebook. January 18, Vocabulary. Westward Ho! Need for State and National Government
 8.1 Vocabulary Wilderness Road Republic Articles of Confederation Land Ordinance of 1785 Northwest Territory Northwest Ordinance Shays's Rebellion Chapter Connection: Articles of Confederation were not
8.1 Vocabulary Wilderness Road Republic Articles of Confederation Land Ordinance of 1785 Northwest Territory Northwest Ordinance Shays's Rebellion Chapter Connection: Articles of Confederation were not
UNIONS CHAPTER 3 US HISTORY (EOC)
 UNIONS CHAPTER 3 US HISTORY (EOC) ESSENTIAL QUESTION: WHAT IMPACT DID SCIENTIFIC DISCOVERIES AND MANUFACTURING PROCESSES HAVE ON THE NATURE OF WORK, THE AMERICAN LABOR MOVEMENT, AND AMERICAN BUSINESSES?
UNIONS CHAPTER 3 US HISTORY (EOC) ESSENTIAL QUESTION: WHAT IMPACT DID SCIENTIFIC DISCOVERIES AND MANUFACTURING PROCESSES HAVE ON THE NATURE OF WORK, THE AMERICAN LABOR MOVEMENT, AND AMERICAN BUSINESSES?
US History, Ms. Brown Website: dph7history.weebly.com
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #69 Aims: SWBAT identify and evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation DO NOW Directions:
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #69 Aims: SWBAT identify and evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation DO NOW Directions:
Chapter 13: The Expansion of American Industry ( )
 Name: Period Page# Chapter 13: The Expansion of American Industry (1850 1900) Section 1: A Technological Revolution Why did people s daily lives change in the decades following the Civil War? How did advances
Name: Period Page# Chapter 13: The Expansion of American Industry (1850 1900) Section 1: A Technological Revolution Why did people s daily lives change in the decades following the Civil War? How did advances
Colonies Become States
 Colonies Become States Colonies already had their own individual governments before the 1776 Declaration 11 of 13 colonies had State Constitutions Constitution a document that states rules under which
Colonies Become States Colonies already had their own individual governments before the 1776 Declaration 11 of 13 colonies had State Constitutions Constitution a document that states rules under which
S apt ect er ion 25 1 Section 1 hnology nd Industrial Growth
 Chapter 13 Objectives Analyze the factors that led to the industrialization of the United States in the late 1800s. Explain how new inventions and innovations changed Americans lives. Describe the impact
Chapter 13 Objectives Analyze the factors that led to the industrialization of the United States in the late 1800s. Explain how new inventions and innovations changed Americans lives. Describe the impact
The Industrialization of America:
 The Industrialization of America: 1865-1900 1 Learning Objectives 2 Explain how the transcontinental railroad network provided the basis for the great post- Civil War industrial transformation. Identify
The Industrialization of America: 1865-1900 1 Learning Objectives 2 Explain how the transcontinental railroad network provided the basis for the great post- Civil War industrial transformation. Identify
INDUSTRY AND MIGRATION/THE NORTH AND THE SOUTH. pp
 INDUSTRY AND MIGRATION/THE NORTH AND THE SOUTH pp 382-405 What drives history? Table Talk: Brainstorm some things that have driven history forward What do these things have in common? What changes have
INDUSTRY AND MIGRATION/THE NORTH AND THE SOUTH pp 382-405 What drives history? Table Talk: Brainstorm some things that have driven history forward What do these things have in common? What changes have
The Birth of Unions SE: US 3B. By Brad Harris, Grand Prairie HS
 The Birth of Unions SE: US 3B By Brad Harris, Grand Prairie HS What is a Labor Union? A labor union is an organization of workers who unite to protect the rights of the workers from abusive practices of
The Birth of Unions SE: US 3B By Brad Harris, Grand Prairie HS What is a Labor Union? A labor union is an organization of workers who unite to protect the rights of the workers from abusive practices of
Activity Documents and Handouts
 STUDENTS INVESTIGATING PRIMARY SOURCES Immigration Inquiry A Closer Look at Chinese Immigration to the United States How did the U.S. treatment toward Chinese immigrants compare with treatment toward European
STUDENTS INVESTIGATING PRIMARY SOURCES Immigration Inquiry A Closer Look at Chinese Immigration to the United States How did the U.S. treatment toward Chinese immigrants compare with treatment toward European
The First President. Guide to Reading
 The First President Main Idea President Washington and the first Congress tackled the work of establishing a new government. Key Terms precedent, cabinet, national debt, bond, speculator, unconstitutional,
The First President Main Idea President Washington and the first Congress tackled the work of establishing a new government. Key Terms precedent, cabinet, national debt, bond, speculator, unconstitutional,
US History The End of Prosperity The Big Idea Main Ideas
 The End of Prosperity The Big Idea The collapse of the stock market in 1929 helped lead to the start of the Great Depression. Main Ideas The U.S. stock market crashed in 1929. The economy collapsed after
The End of Prosperity The Big Idea The collapse of the stock market in 1929 helped lead to the start of the Great Depression. Main Ideas The U.S. stock market crashed in 1929. The economy collapsed after
Industrialization Spreads
 3 Industrialization Spreads MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW TERMS & NAMES EMPIRE BUILDING The industrialization that began in Great Britain spread to other parts of the world. The Industrial Revolution set
3 Industrialization Spreads MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW TERMS & NAMES EMPIRE BUILDING The industrialization that began in Great Britain spread to other parts of the world. The Industrial Revolution set
INDUSTRY COMES OF AGE CHAPTER 24
 INDUSTRY COMES OF AGE CHAPTER 24 Railroad Boom By 1900 the U.S. had more track than all of Europe combined 1890 Govt. Help for Railroads The U.S. govt encouraged railroad building in a # of ways Gave RR
INDUSTRY COMES OF AGE CHAPTER 24 Railroad Boom By 1900 the U.S. had more track than all of Europe combined 1890 Govt. Help for Railroads The U.S. govt encouraged railroad building in a # of ways Gave RR
Chapter 17: THE GREAT RAILROAD STRIKES:
 Chapter 17: THE GREAT RAILROAD STRIKES: Objectives: o We will study the growing conflict between labor and ownership during this era. o We will examine the rise of organized labor in attempting to address
Chapter 17: THE GREAT RAILROAD STRIKES: Objectives: o We will study the growing conflict between labor and ownership during this era. o We will examine the rise of organized labor in attempting to address
THE ELECTION OF 1896
 THE ELECTION OF 1896 Gilded Age Politics Politics focused on personalities and patronage. Fierce party loyalty Stalemate and inactivity Close elections Timid presidents Laissez-faire Rapid industrialization
THE ELECTION OF 1896 Gilded Age Politics Politics focused on personalities and patronage. Fierce party loyalty Stalemate and inactivity Close elections Timid presidents Laissez-faire Rapid industrialization
U.S. History / Geography I Final Exam Review
 U.S. History / Geography I Final Exam Review 1. Laissez-faire relies on to regulate prices and wages. 2. A shortage of workers in California forced the Central-Pacific railroad while building the Trans-Continental
U.S. History / Geography I Final Exam Review 1. Laissez-faire relies on to regulate prices and wages. 2. A shortage of workers in California forced the Central-Pacific railroad while building the Trans-Continental
CHAPTER 24 The Industrial Age,
 CHAPTER 24 The Industrial Age, 1865 1900 1. Railroad Expansion (pp. 528-536) a. The government gave away land bigger than the state of to various railroad companies. What benefits did the government get
CHAPTER 24 The Industrial Age, 1865 1900 1. Railroad Expansion (pp. 528-536) a. The government gave away land bigger than the state of to various railroad companies. What benefits did the government get
Politics in the Gilded Age
 Politics in the Gilded Age Setting the Scene Jay Gould never formally learned how to run a railroad, but he understood the stock market. By 1871, he had become the most powerful railroad man in New York.
Politics in the Gilded Age Setting the Scene Jay Gould never formally learned how to run a railroad, but he understood the stock market. By 1871, he had become the most powerful railroad man in New York.
The Building of Modern America, Part 2. The Big Business Era and Organized Labor Movement
 The Building of Modern America, Part 2 The Big Business Era and Organized Labor Movement SSUSH11 The student will describe the growth of big business and technological innovations after Reconstruction.
The Building of Modern America, Part 2 The Big Business Era and Organized Labor Movement SSUSH11 The student will describe the growth of big business and technological innovations after Reconstruction.
3.2 Hamilton s Economic Plan. American History I Unit 3 The New Nation Day 2 Alexander Hamilton s Economic Plan
 3.2 Hamilton s Economic Plan American History I Unit 3 The New Nation Day 2 Alexander Hamilton s Economic Plan Five parts of Hamilton s Economic Plan 1. Funding 2. State Debt Assumption 3. National Bank
3.2 Hamilton s Economic Plan American History I Unit 3 The New Nation Day 2 Alexander Hamilton s Economic Plan Five parts of Hamilton s Economic Plan 1. Funding 2. State Debt Assumption 3. National Bank
The Effects of the 1930s HOLC Redlining Maps
 The Effects of the 1930s HOLC Redlining Maps Daniel Aaronson Daniel Hartley Bhashkar Mazumder Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago Minneapolis Fed, October 26, 2017 The views expressed are those of the authors
The Effects of the 1930s HOLC Redlining Maps Daniel Aaronson Daniel Hartley Bhashkar Mazumder Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago Minneapolis Fed, October 26, 2017 The views expressed are those of the authors
Section 3: The Organized Labor Movement
 Chapter 13: The Triumph of Industry (1865-1914) Section 3: The Organized Labor Movement Objectives Assess the problems that workers faced in the late 1800s. Compare the goals and strategies of different
Chapter 13: The Triumph of Industry (1865-1914) Section 3: The Organized Labor Movement Objectives Assess the problems that workers faced in the late 1800s. Compare the goals and strategies of different
Student Reading 10.6: How Can Citizens Influence Their Government? Introduction
 Student Reading 10.6: How Can Citizens Influence Their Government? Introduction The United States of America is a very large country compared to many other countries in the world. Many citizens live hundreds
Student Reading 10.6: How Can Citizens Influence Their Government? Introduction The United States of America is a very large country compared to many other countries in the world. Many citizens live hundreds
CHAPTER 2 -Defining and Debating America's Founding Ideals What are America's founding ideals, and why are they important?
 CHAPTER 2 -Defining and Debating America's Founding Ideals What are America's founding ideals, and why are they important? On a June day in 1776, Thomas Jefferson set to work in a rented room in Philadelphia.
CHAPTER 2 -Defining and Debating America's Founding Ideals What are America's founding ideals, and why are they important? On a June day in 1776, Thomas Jefferson set to work in a rented room in Philadelphia.
SSUSH17 The student will analyze the causes and consequences of the Great Depression.
 SSUSH17 The student will analyze the causes and consequences of the Great Depression. Overview: Though the U.S. economy appeared to be prosperous during the 1920 s, the conditions that led to the Great
SSUSH17 The student will analyze the causes and consequences of the Great Depression. Overview: Though the U.S. economy appeared to be prosperous during the 1920 s, the conditions that led to the Great
Social Studies Grade 5
 (1) History. The student understands the causes and effects of European colonization in the United States beginning in 1565, the founding of St. Augustine. The student is expected to: (A) explain when,
(1) History. The student understands the causes and effects of European colonization in the United States beginning in 1565, the founding of St. Augustine. The student is expected to: (A) explain when,
The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783!
 Creating a Republic The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783! The treaty ending the war with Britain, more than doubled the territory of the United States!
Creating a Republic The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783! The treaty ending the war with Britain, more than doubled the territory of the United States!
Declaring Independence. ESSENTIAL QUESTION: What motivates people to act?
 Declaring Independence ESSENTIAL QUESTION: What motivates people to act? The Second Continental Congress The decision to declare independence came only after all other options had been exhausted. Guiding
Declaring Independence ESSENTIAL QUESTION: What motivates people to act? The Second Continental Congress The decision to declare independence came only after all other options had been exhausted. Guiding
The Articles of Confederation
 1 The Articles of Confederation Approved by Congress on November 15, 1777, Congress sent to the states for ratification the Articles of Confederation. This was the first governing constitution for the
1 The Articles of Confederation Approved by Congress on November 15, 1777, Congress sent to the states for ratification the Articles of Confederation. This was the first governing constitution for the
US Early Test #1 TEST A
 US Early Test #1 TEST A Matching A. Boston Tea Party B. Bill of Rights C. George Washington D. Railroads E. 13 th Amendment AB. Robert E Lee AC. Nueces AD. Dred Scott AE. Crop Lien BC. Sharecropping BD.
US Early Test #1 TEST A Matching A. Boston Tea Party B. Bill of Rights C. George Washington D. Railroads E. 13 th Amendment AB. Robert E Lee AC. Nueces AD. Dred Scott AE. Crop Lien BC. Sharecropping BD.
Document A: Newark Anniversary Guide (Excerpt)
 Document A: Newark Anniversary Guide (Excerpt) In 1916, Newark celebrated the 250th anniversary of its founding. For the occasion, the Newark Sales and Advertising Company published 250,000 copies of the
Document A: Newark Anniversary Guide (Excerpt) In 1916, Newark celebrated the 250th anniversary of its founding. For the occasion, the Newark Sales and Advertising Company published 250,000 copies of the
The New Deal. President Franklin Delano Roosevelt sitting in the Oval Office.
 The New Deal President Franklin D. Roosevelt s New Deal programs stimulate the economy and the arts. The New Deal leaves a lasting, yet controversial mark on American government. President Franklin Delano
The New Deal President Franklin D. Roosevelt s New Deal programs stimulate the economy and the arts. The New Deal leaves a lasting, yet controversial mark on American government. President Franklin Delano
Chapter Introduction. Section 1: Causes of the Depression Section 2: Americans Face Hard Times Section 3: Hoover s Response Fails
 Chapter Introduction Chapter Introduction This chapter will cover the causes of the Great Depression, its impact on Americans, and Herbert Hoover s unsuccessful attempts to deal with the crisis. Section
Chapter Introduction Chapter Introduction This chapter will cover the causes of the Great Depression, its impact on Americans, and Herbert Hoover s unsuccessful attempts to deal with the crisis. Section
LESSON WRITER: Bryan Bettis LESSON EDITOR: Karen Hodges / Wendy Schanberger DATE: June 2010
 LESSON WRITER: Bryan Bettis LESSON EDITOR: Karen Hodges / Wendy Schanberger DATE: June 2010 COURSE/GRADE: United States History, Grade 9-12 UNIT: Reconstruction and an Expanding America (Reconstruction-1897);
LESSON WRITER: Bryan Bettis LESSON EDITOR: Karen Hodges / Wendy Schanberger DATE: June 2010 COURSE/GRADE: United States History, Grade 9-12 UNIT: Reconstruction and an Expanding America (Reconstruction-1897);
Grade 5 Integrated Social Studies Scope and Sequence TEKS Timeline. Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills
 Cypress-Fairbanks I. S. D. 1 5.1 History. The student understands the causes and effects of European colonization in the United States beginning in 1565, the founding of St. Augustine. The A Explain when,
Cypress-Fairbanks I. S. D. 1 5.1 History. The student understands the causes and effects of European colonization in the United States beginning in 1565, the founding of St. Augustine. The A Explain when,
SSWH 15 Presentation. Describe the impact of industrialization and urbanization.
 SSWH 15 Presentation Describe the impact of industrialization and urbanization. Vocabulary Industrial Revolution Industrialization Adam Smith Capitalism Laissiez-Faire Wealth of Nations Karl Marx Communism
SSWH 15 Presentation Describe the impact of industrialization and urbanization. Vocabulary Industrial Revolution Industrialization Adam Smith Capitalism Laissiez-Faire Wealth of Nations Karl Marx Communism
Lecture to the New York Telephone Company December 1933
 Lecture to the New York Telephone Company December 1933 Page, A. W. (1933, December 18). Our Public Relations Today and the Outlook for the Future. Speech presented at a Public Relations Course, New York
Lecture to the New York Telephone Company December 1933 Page, A. W. (1933, December 18). Our Public Relations Today and the Outlook for the Future. Speech presented at a Public Relations Course, New York
Chapter 6, Lesson 3. The Wilson Years
 Chapter 6, Lesson 3 The Wilson Years VOCAB: income tax, unfair trade practices, unconstitutional ESSENTIAL QUESTION: Can politics fix social problems? [ANSWER NOW] Was the Progressive Movement a success?
Chapter 6, Lesson 3 The Wilson Years VOCAB: income tax, unfair trade practices, unconstitutional ESSENTIAL QUESTION: Can politics fix social problems? [ANSWER NOW] Was the Progressive Movement a success?
Modern America Assessment Settling the West and Industrialization
 Modern America Assessment Settling the West and Industrialization NAME: 1. During the 1870s, the principal agricultural product of the shaded region on this map was A. poultry B. rice C. cattle D. cotton
Modern America Assessment Settling the West and Industrialization NAME: 1. During the 1870s, the principal agricultural product of the shaded region on this map was A. poultry B. rice C. cattle D. cotton
Settling the Western Frontier
 Settling the Western Frontier 1860-1890 Library of Congress America Moves West America s desire to expand meant that thousands would migrate to western lands (Manifest Destiny). What are some pull factors?
Settling the Western Frontier 1860-1890 Library of Congress America Moves West America s desire to expand meant that thousands would migrate to western lands (Manifest Destiny). What are some pull factors?
AP UNITED STATES HISTORY SECTION II, Part B Time 55 minutes DOCUMENT-BASED QUESTION
 P a g e 1 AP UNITED STATES HISTORY SECTION II, Part B Time 55 minutes DOCUMENT-BASED QUESTION Prompt: Some historians have characterized the industrial and business leaders of 1865 to 1900 as robber barons
P a g e 1 AP UNITED STATES HISTORY SECTION II, Part B Time 55 minutes DOCUMENT-BASED QUESTION Prompt: Some historians have characterized the industrial and business leaders of 1865 to 1900 as robber barons
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Causes of the Great Depression
 Causes of the Great Depression Objectives Discuss the weaknesses in the economy of the 1920s. Explain how the stock market crash contributed to the coming of the Great Depression. Describe how the Great
Causes of the Great Depression Objectives Discuss the weaknesses in the economy of the 1920s. Explain how the stock market crash contributed to the coming of the Great Depression. Describe how the Great
Nationalism, Economic Revolution, and Social Change
 Nationalism, Economic Revolution, and Social Change 1800-1860 Nationalism and Economic Growth By 1815, following the end of The War of 1812, America had shown: That it could defend its sovereignty against
Nationalism, Economic Revolution, and Social Change 1800-1860 Nationalism and Economic Growth By 1815, following the end of The War of 1812, America had shown: That it could defend its sovereignty against
THE archival program of Bank of America was an outgrowth
 Bank of America's Archival Program By O. G. WILSON Bank of America N.T. fcf S.A. THE archival program of Bank of America was an outgrowth of the desire to have a factual and readable history written by
Bank of America's Archival Program By O. G. WILSON Bank of America N.T. fcf S.A. THE archival program of Bank of America was an outgrowth of the desire to have a factual and readable history written by
Period 6 The Gilded Age and Imperialism Study Guide Chapters 23-26
 Period 6 The Gilded Age and Imperialism Study Guide Chapters 23-26 Chapter #23 Political Paralysis in the Gilded Age Big Picture Themes Name: Date: Hour: 1. President Ulysses S. Grant s administration
Period 6 The Gilded Age and Imperialism Study Guide Chapters 23-26 Chapter #23 Political Paralysis in the Gilded Age Big Picture Themes Name: Date: Hour: 1. President Ulysses S. Grant s administration
Welcome to Class! February 8, 2018
 Welcome to Class! February 8, 2018 On this day in history 1887, President Cleveland signs the Dawes Act Bell-Ringer #7 Title: Immigration Pick up the worksheet from the table. Fold it to make a booklet
Welcome to Class! February 8, 2018 On this day in history 1887, President Cleveland signs the Dawes Act Bell-Ringer #7 Title: Immigration Pick up the worksheet from the table. Fold it to make a booklet
Hey, there! My name is (Name), and I ve got some kinda heavy stuff on my mind.
 Government's Response HS623 Activity Introduction Hey, there! My name is (Name), and I ve got some kinda heavy stuff on my mind. During the nineteen-thirties, the United States suffered through one of
Government's Response HS623 Activity Introduction Hey, there! My name is (Name), and I ve got some kinda heavy stuff on my mind. During the nineteen-thirties, the United States suffered through one of
Wonder and Woe The Rise of Industrial America CHAPTER 18
 Wonder and Woe The Rise of Industrial America 1865-1900 CHAPTER 18 World s Fair Chicago 1892 Results of American industrial, culture, and commerce dominance. AC/DC debate Chicago World s Fair: display
Wonder and Woe The Rise of Industrial America 1865-1900 CHAPTER 18 World s Fair Chicago 1892 Results of American industrial, culture, and commerce dominance. AC/DC debate Chicago World s Fair: display
1: Population* and urbanisation for want of more hands
 1: Population* and urbanisation for want of more hands *Remember that the study of population is called Demographics By 1900 there were nearly five times as many people in Britain as there were in 1750.
1: Population* and urbanisation for want of more hands *Remember that the study of population is called Demographics By 1900 there were nearly five times as many people in Britain as there were in 1750.
The March of Millions
 The March of Millions Around 1850 the population was doubling every 25 years. By 186 there were 33 states. America was the fourth most populous nation in the world. Cities were rapidly developing as were
The March of Millions Around 1850 the population was doubling every 25 years. By 186 there were 33 states. America was the fourth most populous nation in the world. Cities were rapidly developing as were
THE RECONSTRUCTION ERA
 THE RECONSTRUCTION ERA 1865-1877 ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS I. What problems faced the nation during Reconstruction? II. How well did Reconstruction governments in the South succeed? III. What factors promoted
THE RECONSTRUCTION ERA 1865-1877 ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS I. What problems faced the nation during Reconstruction? II. How well did Reconstruction governments in the South succeed? III. What factors promoted
i n t e r a C t i v e s t u d e n t n o t e b o o k Mapping Activity 11/02/17
 Mapping Activity 11/02/17 Geography Skills Analyze the maps in Setting the Stage. Then answer the following questions and fill out the map as directed. 1. Label each state on the map. Which two states
Mapping Activity 11/02/17 Geography Skills Analyze the maps in Setting the Stage. Then answer the following questions and fill out the map as directed. 1. Label each state on the map. Which two states
Thousands Join Beijing March for Democracy
 Thousands Join Beijing March for Democracy Los Angeles Times April 22, 1989 This article from the Los Angeles Times describes protests in Beijing's Tian'an Men (here spelled Tian An Men ) Square in the
Thousands Join Beijing March for Democracy Los Angeles Times April 22, 1989 This article from the Los Angeles Times describes protests in Beijing's Tian'an Men (here spelled Tian An Men ) Square in the
IRISH PRIDE Page 1 HCHS
 Chapter 6 Section 2 What are some characteristics of cities? Large populations, density of buildings, noise, pollution, traffic, cultural amenities, access to public services. Main Idea Important Rural
Chapter 6 Section 2 What are some characteristics of cities? Large populations, density of buildings, noise, pollution, traffic, cultural amenities, access to public services. Main Idea Important Rural
Visual 1: No Chief Executive. Brainstorm Possible Problems
 Visual 1: No Chief Executive Brainstorm Possible Problems Visual 2: Laws needed 9/13 of the colonies votes to be approved. Brainstorm Possible Problems Visual 3: The legislative branch (Congress) did not
Visual 1: No Chief Executive Brainstorm Possible Problems Visual 2: Laws needed 9/13 of the colonies votes to be approved. Brainstorm Possible Problems Visual 3: The legislative branch (Congress) did not
Industrial Revolution
 Chapter 9 Economic Transformation Industrial Revolution Division of Labor Industry in America 1790 1820 aided by transportation Industrial Revolution outwork system work done outside of shop modern factory
Chapter 9 Economic Transformation Industrial Revolution Division of Labor Industry in America 1790 1820 aided by transportation Industrial Revolution outwork system work done outside of shop modern factory
APUSH Reading Quizzes
 APUSH Reading Quizzes 6.5-6.6 (Bailey, Chapters 23 & 26) The Great West, the Agricultural Revolution & Politics in the Gilded Age, Part 3 (1865-1896) *with Replace Lowest Unit 6 RQ Score option! 1. Which
APUSH Reading Quizzes 6.5-6.6 (Bailey, Chapters 23 & 26) The Great West, the Agricultural Revolution & Politics in the Gilded Age, Part 3 (1865-1896) *with Replace Lowest Unit 6 RQ Score option! 1. Which
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction Commerce, which ought naturally to be, among nations, as among individuals, a bond of union and friendship, has become the most fertile source of discord and animosity. Adam Smith,
Chapter 1 Introduction Commerce, which ought naturally to be, among nations, as among individuals, a bond of union and friendship, has become the most fertile source of discord and animosity. Adam Smith,
We re Free Let s Grow!
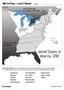 Atlantic Ocean Find Those States! The United States started out with just thirteen states. Use the list below to correctly identify each one on the map. Watch out: Things were a little different back then!
Atlantic Ocean Find Those States! The United States started out with just thirteen states. Use the list below to correctly identify each one on the map. Watch out: Things were a little different back then!
Big Picture Matrix for Fifth Grade Social Studies
 Big Picture Matrix for Fifth Grade Social Studies (1) History. The student understands the causes and effects of European colonization in the United States beginning in 1565, the founding of St. Augustine.
Big Picture Matrix for Fifth Grade Social Studies (1) History. The student understands the causes and effects of European colonization in the United States beginning in 1565, the founding of St. Augustine.
Industrialization Spreads. Section 9.3
 Industrialization Spreads Section 9.3 England First country to industrialize on huge scale Inspired other countries to industrialize Copy the British miracle Class structure becomes more rigid Raises the
Industrialization Spreads Section 9.3 England First country to industrialize on huge scale Inspired other countries to industrialize Copy the British miracle Class structure becomes more rigid Raises the
The 19th Century. Its Place in the Flow of History. Sunday, February 17, 13
 The 19th Century Its Place in the Flow of History Industrialization Industrial Revolution By the 1830s writers began using the Industrial revolution to refer to the extraordinary changes in their economic
The 19th Century Its Place in the Flow of History Industrialization Industrial Revolution By the 1830s writers began using the Industrial revolution to refer to the extraordinary changes in their economic
