Auditing Income Inequality Data in Models of Capitalism, Development and Democracy
|
|
|
- Homer McKinney
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Boise State University ScholarWorks Political Science Faculty Publications and Presentations Department of Political Science Auditing Income Inequality Data in Models of Capitalism, Development and Democracy Ross E. Burkhart Boise State University This document was originally published by Social Science Electronic Publishing, Inc. in Conference Papers - American Political Science Association. Copyright restrictions may apply.
2 AUDITING INCOME INEQUALITY DATA IN MODELS OF CAPITALISM, DEVELOPMENT AND DEMOCRACY Ross E. Burkhart Department of Political Science Boise State University 1910 University Drive Boise, ID USA Telephone: Fax: Internet: For presentation at the annual meeting of the American Political Science Association, Toronto, 5 September I would like to express my sincere thanks to Paige Fetzer and Trish Stack for their research assistance.
3 AUDITING INCOME INEQUALITY DATA IN MODELS OF CAPITALISM, DEVELOPMENT AND DEMOCRACY ABSTRACT It is appropriate to take stock of extant measures of income inequality as they pertain to their utility in cross-national models of political and economic performance. Are some measures more reliable and valid than others? What about data coverage, conceptual mapping of similar indicators, functional form specification matters? This paper specifies models of cross-national democratic and economic performance, with common, industry-standard variables such as economic growth and development level, globalization, political culture (colonialism, ethnicity, religion), and economic type (world-system), and insert various measures of income inequality (Hoover, Deininger and Squire, Galbraith, and UNU-WIDER). The intent is to compare and contrast model robustness under conditions of variable country coverage, inequality definitions, and measurement strategies. With both practical and conceptual matters in mind, the hope is to become better acquainted with the consequences of variable choice in income inequality data usage and modeling techniques. 1
4 INTRODUCTION This paper is a brief discussion of how measures of income inequality affect measures of democracy, controlling for capitalism, economic development, and other factors. The literature is replete with varying income inequality measures, some based on household income, others on wages. Some utilize the Gini coefficient, while others divide the earnings population into quintiles and analyze those at the top 10%, or the top 20%. Which measures of inequality provide the most useful results to academics and policymakers? The intent of this paper is to examine the properties and performance of four measures of income inequality in models of democratic performance: Hoover (1989), Galbraith (1993), Deininger and Squire (1996), and the UNU-WIDER World Income Inequality Database (2008). Each measure is an attempt to improve the data collection of income inequality. This analysis will discover, unsurprisingly, that each has virtues and drawbacks, but that each can be used depending on the overall purpose of the research endeavor. Hoover (1989) was an early effort to capture in more systematic fashion the concept of income inequality, creating measures from It is of the second generation of income inequality measures, the first being Paukert (1973). The second generation improved on the first by directing more attention to the quality of the measure. Hoover created an early standard, though the measure was not frequently employed. Exceptions include Burkhart (1997, 2007) and Crenshaw (1993). Better publicized were the datasets created by Galbraith (1993) and Deininger and Squire (1996). They take the measurement in opposite directions. Unlike the Hoover 2
5 and the Deininger and Squire income-based measures, Galbraith forms his inequality measure from wage data, believing it best captures the concept of inequality. Deininger and Squire comb through extant inequality measures and create their own standard of quality. Under the auspices of the World Bank, it has become a popular measure of inequality in this literature. A later entrant in the catalog of income inequality measures is that of the United Nations University World Institute for Development Economics Research project, or UNU-WIDER (2008). It is an overlap of other databases, including Deininger and Squire as well as the Luxembourg Income Study and the Transmonee data from UNICEF. The UNU-WIDER dataset has gained a reputation for reliability. Which measure is best? The answer depends on what one wishes to accomplish. The definitional question becomes important. Does one believe that household income is a sufficient measure of inequality? What is the role of consumption in the inequality measure? Or is it wages that one should focus upon for a better grasp of inequality? It is both a matter of taste and definitional belief. The Pearson product-moment correlations demonstrate the stark contrast. They are as follows: r (Hoover, Galbraith) =.10, N = 140 r (Hoover, Deininger and Squire) =.88, N = 120 r (Hoover, UNU-WIDER) =.83, N = 50 r (Galbraith, Deininger and Squire) =.08, N = 110 r (Galbraith, UNU-WIDER) = -.01, N = 42 r (Deininger and Squire, UNU-WIDER) =.85, N = 386 3
6 It is clear from the correlation analysis that the measures are measuring different aspects of inequality. It is also quite possible that the measures are not valid in comparison to one another, if validity is understood to be a measure that measures what it is supposed to measure according to definitional criteria. This paper is also a brief empirical excursion into the world of political economy, utilizing these measures of inequality as a main control variable. These models build on the work of Burkhart (2007) on exploring the utility of assessment measures of capitalism (such as those put forth by the Fraser Institute) in models of cross-national democracy. As with measures of income inequality, a major concern is that there are limitations in the amount of data available for these assessment measures. While a seemingly important theoretical variable to include, assessment measures of capitalism may well have to be excluded due to data limitations and be proxied by other variables such as wealth. The underlying purpose of this exercise is to find ways to balance the issue of country coverage in the cross-national models, without sacrificing too much in the way of failing to capture concepts such as inequality or capitalism by using proxy variables. These are important questions to consider for model specification, theoretical perspectives, and empirical procedure. Sound statistical analysis is dependent on strong theory buttressing a plausibly parsimonious, well-specified model with sufficient data to estimate it. As just suggested, an answer to the question posed above is obvious: most any concept can be proxied. Wealth, for instance, is meant to signify a lengthy series of conditions that are largely associated with quality of life : ownership of property, good nutrition, highly educated, resources to invest, among others. Wealth can either substitute well or poorly for quality of life, avoiding inevitable problems of collinearity 4
7 among the potential independent variables that signify quality of life. Indeed, the real question is to what degree one can proxy complex concepts such as quality of life with a single variable. In part, answering that question is an empirical exercise, one that I largely engage in throughout this essay, focusing on the concept of economic structure MODELS OF CONCERN My concern with this issue arises from two papers I have published over the past decade (Burkhart 1997, Burkhart 2007). In these papers, I have attempted to account for variation in democracy and income inequality in countries around the world using a baseline model: (1) Dem = a + b1 Ineq + b2 Econ + b3 Econ x Semiper + b4 Econ x Per + b5 Eth + b6 Prot + b7 Brit + e Where Dem = democracy, Ineq = income inequality, Econ = economic development, Econ x Semiper = economic development multiplied by semiperipheral world-system position, Econ x Per = economic development multiplied by peripheral world-system position, Eth = ethnolinguistic fractionalization, Prot = percentage of population Protestant, Brit = former British colony, a = intercept, b1 b6 = slope coefficients, e = error. This baseline model of democracy attempts to bring several theoretical factors to the forefront. These include the effect of increased income inequality leading to a falling middle class and consequent political inequality (Aristotle 1905, Bollen and Jackman 1985), the positive effect of wealth on democracy through a rising middle class and increased power (Arat 1988, Bollen 1979, Bollen 1983, Burkhart and Lewis-Beck 1994, Gonick and Rosh 1988, Jackman 1973, Lipset 1959, Londregan and Poole 1996, 5
8 Przeworski and Limongi 1997, Przeworski et al. 2000), the negative impact of distance from the core of the global economic world-system on democracy due to the apparent concentration of economic power in countries that rely on primary products (Bollen 1983, Burkhart and Lewis-Beck 1994, Wallerstein 1974), the negative impact of an ethnically heterogeneous society on political unity leading to division and power concentration (Burkhart 1997), the positive impact of Protestantism and its encouragement of an individualistic work ethic on democratic formation (Lipset 1959, Bollen 1979), and the ameliorating effects of British colonial history on encouragement of local control and democratic development (Smith 1978, Bollen 1979, Burkhart 1997). These variables thus have the backing of many literature sources. I should add that this model does not pretend to be exhaustive, as there are other possible independent variables: globalization effects such as composition of labor force (Rudra 2005), trade (Reuveny and Li 2003) foreign direct investment (Reuveny and Li 2003, de Soysa 2003), as well as the impact of rentier state behaviors in the petroleum export business (Ross 2001). Nor do I estimate a multiequation system to ascertain the effect of democracy on income inequality, an exercise I have performed in previous work (Burkhart 1997, Burkhart 2007). However, I am concerned with the issue of country coverage in my research. Using the best data available, I still could only use 50 countries in the main dataset in both articles. While the countries represented in the dataset are from all world regions, some regions are less well represented. There are only three countries from Sub-Saharan Africa, for instance. There is much interesting variation thus left in the error term from countries that are not included in the analysis. 6
9 Where does the extent to which a country is capitalist fit in this discussion? As an independent variable, it has potential in accounting for variation in democracy, economic development, and income inequality. Previous studies have examined its performance in such models and found it to be statistically significant in explaining democracy (Brunk, Caldeira and Lewis-Beck 1987; Burkhart 2000) and income distribution (Burkhart 2007). Capitalism appears to be a variable that should be seriously considered for model inclusion, whether measured as government expenditure as a percentage of total economic product, or using a subjective scale as developed by an organization like Freedom House (Burkhart 2000, Freedom House 1996). With this serious consideration come serious concerns, both in terms of theoretical overlap with measures of economic development such as GNP per capita, and data coverage. I focus on the latter in this paper. The development and democracy literature regularly employs variables with lengthy time series. GNP per capita and the POLITY democracy scale come to mind. The largest extant subjective measurement of capitalism, the Fraser Institute capitalism index (Gwartney, Lawson and Block 1996), has coverage that extends back to 1970 only. This misses a substantial time period. As well, its coverage of countries is more scattered than that of more objective political economy measures. While the benefits of a comprehensive assessment of capitalist conditions in countries has its theoretical and conceptual merits, in the end, if sufficient data is lacking for robust parameter estimation, then its statistical usefulness is questionable. This is the fundamental source of this paper s motivation. Are there enough data to warrant capitalism s inclusion in cross-national models? Are there alternative variables capable of proxying capitalism? What are the results of using such alternatives? 7
10 DATA The newly constructed dataset that I employ covers 50 countries for the years These countries also cover the major world regions. I use the Fraser Institute s summary measure of capitalism that encompasses several characteristics:! Size of government, including expenditures, taxes, and enterprises! Legal structures and security of property rights! Access to sound money! Freedom to trade internationally! Regulation of credit, labor and business (Fraser Institute 2006) The democracy variable is the Freedom House measure of political rights, uncorrected, meaning that a score of 1 represents the country that is least respectful of political rights and a score of 7 represents the country that is most respectful of political rights. The economic development variable is energy consumption per capita, logged to the base 10, from Burkhart (1997). Countries that are in the semiperiphery and periphery in the world-system are coded by rules established in Burkhart and Lewis Beck (1994). British colonial status comes from the historical record. The measures of income inequality are Hoover s household inequality measure (1989, as reported in Burkhart 1997, 2007), Deininger and Squire s household inequality measure (1996, high-quality accept data points only), the Gini coefficient as reported by the UNU-WIDER project, and the measurement of within-country wage inequality from Galbraith s University of Texas Inequality Project, Theil s t statistic. 8
11 ESTIMATED MODEL (2) Dem = a + b1 Econ + b2 Econ x Semper + b3 Econ x Per + b4 Brit + b5 Capital + b6 Ineq + e Where variables are defined as in the above sections, I deviate from model (1) above in that I take just one historical measurement into account in the model, British colonial status, a consistent performer in previous models, so that the direct measure of capitalism has every opportunity to shine in these models. I provide both OLS regression results and, to account for an unbalanced pooled time-series element to the data, the xtreg procedure in Stata 10, random effects. MAIN RESULTS AND DISCUSSION [TABLE ONE ABOUT HERE] On balance, the main variables of interest, the impact of the various measures of income and wage inequality and the Fraser Institute capitalism on democracy, do not show impressive strength. In no model does inequality achieve conventional levels of statistical significance. In models 2.1 and 2.2., the Galbraith measure of inequality approach significance at the.05 level, but in a one-tailed test which may be appropriate considering the directional aspect of inequality s influence on democracy. Since the Galbraith coefficients are negative, it suggests that as wage inequality increases, the country s democratic performance decreases, keeping in mind that the smaller the Freedom House democracy score, the more democratic the country. And the Deininger and Squire income inequality measure in model 3.2 shows promise, in the expected direction. Neither the UNU-WIDER nor the Hoover measures of income inequality come close to statistical significance. 9
12 The capitalism variable is fully significant in the Deininger and Squire model (3.2), and is positive, meaning that more capitalism leads to less democracy. But capitalism is not significant at conventional levels in any of the other models. Instead, perhaps we should consider the constancy in both the OLS and the xtreg estimates of the statistically significant logged gross national product per capita variable. The coefficients are in the expected direction, positively affecting democratic performance regardless of the inequality measure presented. This leaves one with the impression that there is less value added from the inclusion of income inequality and capitalism in these models to our knowledge about the variation of democracy. CONCLUSION Should inequality and capitalism be left out of models explaining variation in cross-national democracy? For a definitive answer, this very short exercise needs empirical expansion. Country coverage needs expansion. Additionally, other functional forms of capitalism, such as the second-order polynomial and logarithmic, remain untried in these models. Lagging democracy by one year may also make the model be more robust. Clearly, more fine-tuning needs to take place. For now, if one is willing to believe that inequality is a rather static phenomenon (Firebaugh 2000), that the four measures of income and wage inequality considered in this paper represent well the variety of extant measures, and that capitalism is adequately captured by gross domestic product per capita, then there appears to be little urgency in adding income inequality and direct, assessment-based measures of capitalism as main explanatory variables in cross-national democracy models, other than as reasonable control variables. Their explanatory power falls short of ideal, but this story is not over. 10
13 REFERENCES Arat, Zehra F Democracy and Economic Development: Modernization Theory Revisited. Comparative Politics 21: Aristotle Aristotle s Politics. Benjamin Jowett, trans. Oxford: Clarendon Press. Bollen, Kenneth A Political Democracy and the Timing of Development. American Sociological Review 44: World System Position, Dependency, and Democracy: The Cross-National Evidence. American Sociological Review 48: Bollen, Kenneth A., and Robert W. Jackman Political Democracy and the Size Distribution of Income. American Sociological Review 50: Brunk, Gregory G., Gregory A. Caldeira, and Michael S. Lewis-Beck Capitalism, Socialism, and Democracy: An Empirical Inquiry. European Journal of Political Research 15: Burkhart, Ross E Comparative Democracy and Income Distribution: Shape and Direction of the Causal Arrow. Journal of Politics 59: Economic Freedom and Democracy: Post-Cold War Tests. European Journal of Political Research 37: Democracy, Capitalism, and Income Inequality: Seeking Causal Directions. Comparative Sociology 36:4. Burkhart, Ross E., and Michael S. Lewis-Beck Comparative Democracy: The Economic Development Thesis. American Political Science Review 88: Crenshaw, Edward M Polity, Economy and Technoecology: Alternative Explanations for Income Inequality. Social Forces 71:
14 Deininger, Klaus, and Lyn Squire A New Data Set Measuring Income Inequality. World Bank Economic Review 10: de Soysa, Indra Foreign Direct Investment, Democracy, and Development: Assessing Contours, Correlates, and Concomitants of Globalization. London: Routledge. Firebaugh, Glenn The Trend in Between-Nation Income Inequality. Annual Review of Sociology 26: Fraser Institute Economic Freedom of the World. Dataset downloaded 6 July Freedom House Nations and Markets: The World Survey of Economic Freedom. New York: Freedom House. Freedom House Freedom in the World New York: Freedom House. Gonick, Lev S., and Robert M. Rosh The Structural Constraints of the World- Economy on National Political Development. Comparative Political Studies 21: Gwartney, James, Robert Lawson, and Walter Block Economic Freedom of the World Vancouver, BC: Fraser Institute. Hoover, Greg A Intranational Inequality: A Cross-National Dataset. Social Forces 67: Jackman, Robert W On the Relationship of Economic Development to Political Performance. American Journal of Political Science 17:
15 Lewis-Beck, Michael S Applied Regression. Sage University Paper series on Quantitative Applications in the Social Sciences Series Beverly Hills: Sage Publications. Lipset, Seymour M Some Social Requisites of Democracy. American Political Science Review 53: Londregan, John, and Kenneth Poole Does High Income Promote Democracy? World Politics 49:1-30. Przeworski, Adam, and Fernando Limongi Modernization: Theories and Facts. World Politics 49: Przeworski, Adam, Michael E. Alvarez, José Antonio Cheibub, and Fernando Limongi Democracy and Development: Political Institutions and Well-Being in the World, New York: Cambridge University Press. Reuveny, Rafael, and Quan Li "Economic Openness, Democracy, and Income Inequality: An Empirical Analysis." Comparative Political Studies 36: Ross, Michael L Does Oil Hinder Democracy? World Politics 53: Rudra, Nita Globalization and the Strengthening of Democracy in the Developing World. American Journal of Political Science 49: Smith, Tony A Comparative Study of French and British Decolonization. Comparative Studies in Society and History 20: UNU-WIDER World Income Inequality Database Version 2.0c. May. Wallerstein, Immanuel The Rise and Future Demise of the World-Capitalist System: Concepts for Comparative Analysis. Comparative Studies in Society and History 16:
16 TABLE ONE: CAPITALISM, DEMOCRACY AND INEQUALITY Dependent Variable = Democracy (Freedom House political rights scale, scored 1=most respecting of political rights to 7=least respecting of political rights). Estimated with Stata 10, OLS and xtreg. IVs" Model 1.1 Model 1.2 Model 2.1 Model 2.2 Model 3.1 Model 3.2 Model 4.1 Model 4.2 OLS, Random- OLS, Random OLS, Random OLS, Random Hoover Effects Galbraith Effects Deininger Effects UNU- Effects GLS, GLS, and Squire GLS, WIDER GLS, Hoover Galbraith Deininger UNU- and Squire WIDER Econ (3.97) (3.63) (5.16) (2.72) (1.6) (.45) (.77) (1.87) Econ x Semi (.01) (.16) (.73) (.51) (1.09) (.34) (1.27) (.60) Econ x Per (.35) (.26) (1.16) (.22) (.33) (2.33) (.47) (.01) Brit (1.58) (.38) (2.38) (.23) (.81) (1.50) (1.86) (1.08) Ineq (.27) (.77) (1.56) (1.69) (.42) (1.64) (.94) (.27) Capital (.04) (.63) (.42) (.91) (1.21) (2.17) (1.72) (1.00) Intercept (4.74) (3.82) (5.78) (3.91) (1.85) (1.02) (.92) (2.38) R square Number of cases Figures in parentheses are either absolute t-ratios (OLS estimations). 14
Democracy and Income Inequality: Measurement and Modeling of the Western Hemispheric Experience
 Boise State University ScholarWorks Political Science Faculty Publications and Presentations Department of Political Science 1-1-2011 Democracy and Income Inequality: Measurement and Modeling of the Western
Boise State University ScholarWorks Political Science Faculty Publications and Presentations Department of Political Science 1-1-2011 Democracy and Income Inequality: Measurement and Modeling of the Western
Differences Lead to Differences: Diversity and Income Inequality Across Countries
 Illinois State University ISU ReD: Research and edata Master's Theses - Economics Economics 6-2008 Differences Lead to Differences: Diversity and Income Inequality Across Countries Michael Hotard Illinois
Illinois State University ISU ReD: Research and edata Master's Theses - Economics Economics 6-2008 Differences Lead to Differences: Diversity and Income Inequality Across Countries Michael Hotard Illinois
Comparative Democracy: the Economic Development Thesis
 Department of Political Science Publications 12-1-1994 Comparative Democracy: the Economic Development Thesis Ross E. Burkhart Michael S. Lewis-Beck University of Iowa Copyright 1994 American Political
Department of Political Science Publications 12-1-1994 Comparative Democracy: the Economic Development Thesis Ross E. Burkhart Michael S. Lewis-Beck University of Iowa Copyright 1994 American Political
Income inequality, Redistribution, and Democracy
 Income inequality, Redistribution, and Democracy Linda de Jongh Supervisor: Prof. K. Thomsson Many economists, and more generally institutions are concerned with the development of poor countries. Not
Income inequality, Redistribution, and Democracy Linda de Jongh Supervisor: Prof. K. Thomsson Many economists, and more generally institutions are concerned with the development of poor countries. Not
RELIGIOUS FREEDOM AND ECONOMIC PROSPERITY Ilan Alon and Gregory Chase
 RELIGIOUS FREEDOM AND ECONOMIC PROSPERITY Ilan Alon and Gregory Chase Let there be no compulsion in religion. The Qu ran, Surah 2, verse 256 The basic notion that an individual s freedom to choose will
RELIGIOUS FREEDOM AND ECONOMIC PROSPERITY Ilan Alon and Gregory Chase Let there be no compulsion in religion. The Qu ran, Surah 2, verse 256 The basic notion that an individual s freedom to choose will
Level of Economic Development and Political Democracy Revisited
 Level of Economic Development and Political Democracy Revisited YONG U. GLASURE,* AIE-RIE LEE,** AND JAMES NORRIS** This article reassesses a democracy-economic development linkage for the period 1972
Level of Economic Development and Political Democracy Revisited YONG U. GLASURE,* AIE-RIE LEE,** AND JAMES NORRIS** This article reassesses a democracy-economic development linkage for the period 1972
Is Corruption Anti Labor?
 Is Corruption Anti Labor? Suryadipta Roy Lawrence University Department of Economics PO Box- 599, Appleton, WI- 54911. Abstract This paper investigates the effect of corruption on trade openness in low-income
Is Corruption Anti Labor? Suryadipta Roy Lawrence University Department of Economics PO Box- 599, Appleton, WI- 54911. Abstract This paper investigates the effect of corruption on trade openness in low-income
THE IMPACT OF OIL DEPENDENCE ON DEMOCRACY
 THE IMPACT OF OIL DEPENDENCE ON DEMOCRACY A Thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences of Georgetown University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
THE IMPACT OF OIL DEPENDENCE ON DEMOCRACY A Thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences of Georgetown University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
GLOBALIZATION AND THE GREAT U-TURN: INCOME INEQUALITY TRENDS IN 16 OECD COUNTRIES. Arthur S. Alderson
 GLOBALIZATION AND THE GREAT U-TURN: INCOME INEQUALITY TRENDS IN 16 OECD COUNTRIES by Arthur S. Alderson Department of Sociology Indiana University Bloomington Email aralders@indiana.edu & François Nielsen
GLOBALIZATION AND THE GREAT U-TURN: INCOME INEQUALITY TRENDS IN 16 OECD COUNTRIES by Arthur S. Alderson Department of Sociology Indiana University Bloomington Email aralders@indiana.edu & François Nielsen
Exploring the Impact of Democratic Capital on Prosperity
 Exploring the Impact of Democratic Capital on Prosperity Lisa L. Verdon * SUMMARY Capital accumulation has long been considered one of the driving forces behind economic growth. The idea that democratic
Exploring the Impact of Democratic Capital on Prosperity Lisa L. Verdon * SUMMARY Capital accumulation has long been considered one of the driving forces behind economic growth. The idea that democratic
The Effect of Globalization on National Income Inequality*
 The Effect of Globalization on National Income Inequality* MARGIT BUSSMANN, INDRA DE SOYSA AND JOHN R. ONEAL ABSTRACT We assess the effect of globalization on income inequality within countries, focusing
The Effect of Globalization on National Income Inequality* MARGIT BUSSMANN, INDRA DE SOYSA AND JOHN R. ONEAL ABSTRACT We assess the effect of globalization on income inequality within countries, focusing
Volume 35, Issue 1. An examination of the effect of immigration on income inequality: A Gini index approach
 Volume 35, Issue 1 An examination of the effect of immigration on income inequality: A Gini index approach Brian Hibbs Indiana University South Bend Gihoon Hong Indiana University South Bend Abstract This
Volume 35, Issue 1 An examination of the effect of immigration on income inequality: A Gini index approach Brian Hibbs Indiana University South Bend Gihoon Hong Indiana University South Bend Abstract This
Poverty Reduction and Economic Growth: The Asian Experience Peter Warr
 Poverty Reduction and Economic Growth: The Asian Experience Peter Warr Abstract. The Asian experience of poverty reduction has varied widely. Over recent decades the economies of East and Southeast Asia
Poverty Reduction and Economic Growth: The Asian Experience Peter Warr Abstract. The Asian experience of poverty reduction has varied widely. Over recent decades the economies of East and Southeast Asia
Abstract. research studies the impacts of four factors on inequality income level, emigration,
 Abstract Using a panel data of China that covers the time period from 1997 to 2011, this research studies the impacts of four factors on inequality income level, emigration, public spending on education,
Abstract Using a panel data of China that covers the time period from 1997 to 2011, this research studies the impacts of four factors on inequality income level, emigration, public spending on education,
The Impact of the Interaction between Economic Growth and Democracy on Human Development: Cross-National Analysis
 Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications 2012 2012 The Impact of the Interaction between Economic Growth and Democracy on Human Development: Cross-National Analysis Shrabani Saha Edith Cowan
Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications 2012 2012 The Impact of the Interaction between Economic Growth and Democracy on Human Development: Cross-National Analysis Shrabani Saha Edith Cowan
Appendix: Uncovering Patterns Among Latent Variables: Human Rights and De Facto Judicial Independence
 Appendix: Uncovering Patterns Among Latent Variables: Human Rights and De Facto Judicial Independence Charles D. Crabtree Christopher J. Fariss August 12, 2015 CONTENTS A Variable descriptions 3 B Correlation
Appendix: Uncovering Patterns Among Latent Variables: Human Rights and De Facto Judicial Independence Charles D. Crabtree Christopher J. Fariss August 12, 2015 CONTENTS A Variable descriptions 3 B Correlation
Does Democracy Promote Transnational Terrorist Incidents?
 Does Democracy Promote Transnational Terrorist Incidents? QUAN LI Assistant Professor Department of Political Science The Pennsylvania State University 107 Burrowes Building University Park, PA 16802 Email:
Does Democracy Promote Transnational Terrorist Incidents? QUAN LI Assistant Professor Department of Political Science The Pennsylvania State University 107 Burrowes Building University Park, PA 16802 Email:
Powersharing, Protection, and Peace. Scott Gates, Benjamin A. T. Graham, Yonatan Lupu Håvard Strand, Kaare W. Strøm. September 17, 2015
 Powersharing, Protection, and Peace Scott Gates, Benjamin A. T. Graham, Yonatan Lupu Håvard Strand, Kaare W. Strøm September 17, 2015 Corresponding Author: Yonatan Lupu, Department of Political Science,
Powersharing, Protection, and Peace Scott Gates, Benjamin A. T. Graham, Yonatan Lupu Håvard Strand, Kaare W. Strøm September 17, 2015 Corresponding Author: Yonatan Lupu, Department of Political Science,
EFFECTS OF PROPERTY RIGHTS AND CORRUPTION ON GENDER DEVELOPMENT
 EFFECTS OF PROPERTY RIGHTS AND CORRUPTION ON GENDER DEVELOPMENT A Thesis submitted to the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences at Georgetown University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the
EFFECTS OF PROPERTY RIGHTS AND CORRUPTION ON GENDER DEVELOPMENT A Thesis submitted to the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences at Georgetown University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the
Poverty and Inequality
 Chapter 4 Poverty and Inequality Problems and Policies: Domestic After completing this chapter, you will be able to 1. Measure poverty across countries using different approaches and explain how poverty
Chapter 4 Poverty and Inequality Problems and Policies: Domestic After completing this chapter, you will be able to 1. Measure poverty across countries using different approaches and explain how poverty
Corruption and business procedures: an empirical investigation
 Corruption and business procedures: an empirical investigation S. Roy*, Department of Economics, High Point University, High Point, NC - 27262, USA. Email: sroy@highpoint.edu Abstract We implement OLS,
Corruption and business procedures: an empirical investigation S. Roy*, Department of Economics, High Point University, High Point, NC - 27262, USA. Email: sroy@highpoint.edu Abstract We implement OLS,
Errata Summary. Comparison of the Original Results with the New Results
 Errata for Karim and Beardsley (2016), Explaining Sexual Exploitation and Abuse in Peacekeeping Missions: The Role of Female Peacekeepers and Gender Equality in Contributing Countries, Journal of Peace
Errata for Karim and Beardsley (2016), Explaining Sexual Exploitation and Abuse in Peacekeeping Missions: The Role of Female Peacekeepers and Gender Equality in Contributing Countries, Journal of Peace
Uncovering patterns among latent variables: human rights and de facto judicial independence
 605343RAP0010.1177/2053168015605343Research & PoliticsCrabtree and Fariss research-article2015 Research Article Uncovering patterns among latent variables: human rights and de facto judicial independence
605343RAP0010.1177/2053168015605343Research & PoliticsCrabtree and Fariss research-article2015 Research Article Uncovering patterns among latent variables: human rights and de facto judicial independence
Figure 2: Proportion of countries with an active civil war or civil conflict,
 Figure 2: Proportion of countries with an active civil war or civil conflict, 1960-2006 Sources: Data based on UCDP/PRIO armed conflict database (N. P. Gleditsch et al., 2002; Harbom & Wallensteen, 2007).
Figure 2: Proportion of countries with an active civil war or civil conflict, 1960-2006 Sources: Data based on UCDP/PRIO armed conflict database (N. P. Gleditsch et al., 2002; Harbom & Wallensteen, 2007).
DISCUSSION PAPERS IN ECONOMICS
 DISCUSSION PAPERS IN ECONOMICS No. 2009/4 ISSN 1478-9396 IS THERE A TRADE-OFF BETWEEN INCOME INEQUALITY AND CORRUPTION? EVIDENCE FROM LATIN AMERICA Stephen DOBSON and Carlyn RAMLOGAN June 2009 DISCUSSION
DISCUSSION PAPERS IN ECONOMICS No. 2009/4 ISSN 1478-9396 IS THERE A TRADE-OFF BETWEEN INCOME INEQUALITY AND CORRUPTION? EVIDENCE FROM LATIN AMERICA Stephen DOBSON and Carlyn RAMLOGAN June 2009 DISCUSSION
The Correlates of Wealth Disparity Between the Global North & the Global South. Noelle Enguidanos
 The Correlates of Wealth Disparity Between the Global North & the Global South Noelle Enguidanos RESEARCH QUESTION/PURPOSE STATEMENT: What explains the economic disparity between the global North and the
The Correlates of Wealth Disparity Between the Global North & the Global South Noelle Enguidanos RESEARCH QUESTION/PURPOSE STATEMENT: What explains the economic disparity between the global North and the
262 Index. D demand shocks, 146n demographic variables, 103tn
 Index A Africa, 152, 167, 173 age Filipino characteristics, 85 household heads, 59 Mexican migrants, 39, 40 Philippines migrant households, 94t 95t nonmigrant households, 96t 97t premigration income effects,
Index A Africa, 152, 167, 173 age Filipino characteristics, 85 household heads, 59 Mexican migrants, 39, 40 Philippines migrant households, 94t 95t nonmigrant households, 96t 97t premigration income effects,
Institutions, Human Capital, and Diversification of Rentier Economies
 Prepared for Workshop on Transforming Authoritarian Rentier Economies at the Friedrich Ebert Foundation in Bonn 21-24 September 2005. Institutions, Human Capital, and Diversification of Rentier Economies
Prepared for Workshop on Transforming Authoritarian Rentier Economies at the Friedrich Ebert Foundation in Bonn 21-24 September 2005. Institutions, Human Capital, and Diversification of Rentier Economies
Does Inequality Matter for Poverty Reduction? Evidence from Pakistan s Poverty Trends
 The Pakistan Development Review 45 : 3 (Autumn 2006) pp. 439 459 Does Inequality Matter for Poverty Reduction? Evidence from Pakistan s Poverty Trends HAROON JAMAL * The paper explores the linkages between
The Pakistan Development Review 45 : 3 (Autumn 2006) pp. 439 459 Does Inequality Matter for Poverty Reduction? Evidence from Pakistan s Poverty Trends HAROON JAMAL * The paper explores the linkages between
Liberté, Egalité, Fraternité!
 Laboratory for Comparative Social Studies Research Project: Liberté, Egalité, Fraternité! The Impact of Inequality on Support for Democracy and Redistribution Yegor Lazarev Department of Political Science
Laboratory for Comparative Social Studies Research Project: Liberté, Egalité, Fraternité! The Impact of Inequality on Support for Democracy and Redistribution Yegor Lazarev Department of Political Science
Democracy and government spending
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Democracy and government Pavlos Balamatsias 6 March 2018 Online at https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/86905/ MPRA Paper No. 86905, posted 23 May 2018 19:21 UTC Democracy
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Democracy and government Pavlos Balamatsias 6 March 2018 Online at https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/86905/ MPRA Paper No. 86905, posted 23 May 2018 19:21 UTC Democracy
GOVERNANCE RETURNS TO EDUCATION: DO EXPECTED YEARS OF SCHOOLING PREDICT QUALITY OF GOVERNANCE?
 GOVERNANCE RETURNS TO EDUCATION: DO EXPECTED YEARS OF SCHOOLING PREDICT QUALITY OF GOVERNANCE? A Thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences of Georgetown University in
GOVERNANCE RETURNS TO EDUCATION: DO EXPECTED YEARS OF SCHOOLING PREDICT QUALITY OF GOVERNANCE? A Thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences of Georgetown University in
Democracy and Economic Development: A Simultaneous Equation Analysis
 Democracy and Economic Development: A Simultaneous Equation Analysis Uk Heo Department of Political Science University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee P.O.Box 413 Milwaukee, WI 53201 heouk@uwm.edu Abstract Despite
Democracy and Economic Development: A Simultaneous Equation Analysis Uk Heo Department of Political Science University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee P.O.Box 413 Milwaukee, WI 53201 heouk@uwm.edu Abstract Despite
University of Groningen. Corruption and governance around the world Seldadyo, H.
 University of Groningen Corruption and governance around the world Seldadyo, H. IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
University of Groningen Corruption and governance around the world Seldadyo, H. IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
The Impact of Unionization on the Wage of Hispanic Workers. Cinzia Rienzo and Carlos Vargas-Silva * This Version, December 2014.
 The Impact of Unionization on the Wage of Hispanic Workers Cinzia Rienzo and Carlos Vargas-Silva * This Version, December 2014 Abstract This paper explores the role of unionization on the wages of Hispanic
The Impact of Unionization on the Wage of Hispanic Workers Cinzia Rienzo and Carlos Vargas-Silva * This Version, December 2014 Abstract This paper explores the role of unionization on the wages of Hispanic
REMITTANCES, POVERTY AND INEQUALITY
 JOURNAL OF ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT 127 Volume 34, Number 1, June 2009 REMITTANCES, POVERTY AND INEQUALITY LUIS SAN VICENTE PORTES * Montclair State University This paper explores the effect of remittances
JOURNAL OF ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT 127 Volume 34, Number 1, June 2009 REMITTANCES, POVERTY AND INEQUALITY LUIS SAN VICENTE PORTES * Montclair State University This paper explores the effect of remittances
Immigrant-native wage gaps in time series: Complementarities or composition effects?
 Immigrant-native wage gaps in time series: Complementarities or composition effects? Joakim Ruist Department of Economics University of Gothenburg Box 640 405 30 Gothenburg, Sweden joakim.ruist@economics.gu.se
Immigrant-native wage gaps in time series: Complementarities or composition effects? Joakim Ruist Department of Economics University of Gothenburg Box 640 405 30 Gothenburg, Sweden joakim.ruist@economics.gu.se
The Journal of Developing Areas, Volume 48, Number 1, Winter 2014, pp (Article) DOI: /jda
 Th D l P l t l ff t f F r n D r t nv t nt n D v l p n ntr Feng Sun The Journal of Developing Areas, Volume 48, Number 1, Winter 2014, pp. 107-125 (Article) P bl h d b T nn t t n v r t ll f B n DOI: 10.1353/jda.2014.0020
Th D l P l t l ff t f F r n D r t nv t nt n D v l p n ntr Feng Sun The Journal of Developing Areas, Volume 48, Number 1, Winter 2014, pp. 107-125 (Article) P bl h d b T nn t t n v r t ll f B n DOI: 10.1353/jda.2014.0020
Beyond Gini: Income Distribution and Economic Development. Pushan Dutt INSEAD, Corresponding author
 Working Paper Series 2015/99/EPS/DSC Beyond Gini: Income Distribution and Economic Development Pushan Dutt INSEAD, pushan.dutt@insead.edu Corresponding author Ilia Tsetlin INSEAD, ilia.tsetlin@insead.edu
Working Paper Series 2015/99/EPS/DSC Beyond Gini: Income Distribution and Economic Development Pushan Dutt INSEAD, pushan.dutt@insead.edu Corresponding author Ilia Tsetlin INSEAD, ilia.tsetlin@insead.edu
Happiness and economic freedom: Are they related?
 Happiness and economic freedom: Are they related? Ilkay Yilmaz 1,a, and Mehmet Nasih Tag 2 1 Mersin University, Department of Economics, Mersin University, 33342 Mersin, Turkey 2 Mersin University, Department
Happiness and economic freedom: Are they related? Ilkay Yilmaz 1,a, and Mehmet Nasih Tag 2 1 Mersin University, Department of Economics, Mersin University, 33342 Mersin, Turkey 2 Mersin University, Department
LABOUR-MARKET INTEGRATION OF IMMIGRANTS IN OECD-COUNTRIES: WHAT EXPLANATIONS FIT THE DATA?
 LABOUR-MARKET INTEGRATION OF IMMIGRANTS IN OECD-COUNTRIES: WHAT EXPLANATIONS FIT THE DATA? By Andreas Bergh (PhD) Associate Professor in Economics at Lund University and the Research Institute of Industrial
LABOUR-MARKET INTEGRATION OF IMMIGRANTS IN OECD-COUNTRIES: WHAT EXPLANATIONS FIT THE DATA? By Andreas Bergh (PhD) Associate Professor in Economics at Lund University and the Research Institute of Industrial
Corruption and quality of public institutions: evidence from Generalized Method of Moment
 Document de travail de la série Etudes et Documents E 2008.13 Corruption and quality of public institutions: evidence from Generalized Method of Moment Gbewopo Attila 1 University Clermont I, CERDI-CNRS
Document de travail de la série Etudes et Documents E 2008.13 Corruption and quality of public institutions: evidence from Generalized Method of Moment Gbewopo Attila 1 University Clermont I, CERDI-CNRS
Poverty, Income Inequality, and Growth in Pakistan: A Pooled Regression Analysis
 The Lahore Journal of Economics 17 : 2 (Winter 2012): pp. 137 157 Poverty, Income Inequality, and Growth in Pakistan: A Pooled Regression Analysis Ahmed Raza Cheema * and Maqbool H. Sial ** Abstract This
The Lahore Journal of Economics 17 : 2 (Winter 2012): pp. 137 157 Poverty, Income Inequality, and Growth in Pakistan: A Pooled Regression Analysis Ahmed Raza Cheema * and Maqbool H. Sial ** Abstract This
The Socioeconomic Effects of Economic Liberalization Revisited: A Case for Democracy Andrew Dawson AUGUST Series #2005-3
 The Socioeconomic Effects of Economic Liberalization Revisited: A Case for Democracy Andrew Dawson AUGUST 31 2005 Series #2005-3 ABSTRACT This study empirically investigates the theoretical doctrines of
The Socioeconomic Effects of Economic Liberalization Revisited: A Case for Democracy Andrew Dawson AUGUST 31 2005 Series #2005-3 ABSTRACT This study empirically investigates the theoretical doctrines of
Natural Resources & Income Inequality: The Role of Ethnic Divisions
 DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS OxCarre (Oxford Centre for the Analysis of Resource Rich Economies) Manor Road Building, Manor Road, Oxford OX1 3UQ Tel: +44(0)1865 281281 Fax: +44(0)1865 281163 reception@economics.ox.ac.uk
DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS OxCarre (Oxford Centre for the Analysis of Resource Rich Economies) Manor Road Building, Manor Road, Oxford OX1 3UQ Tel: +44(0)1865 281281 Fax: +44(0)1865 281163 reception@economics.ox.ac.uk
Volume 36, Issue 1. Impact of remittances on poverty: an analysis of data from a set of developing countries
 Volume 6, Issue 1 Impact of remittances on poverty: an analysis of data from a set of developing countries Basanta K Pradhan Institute of Economic Growth, Delhi Malvika Mahesh Institute of Economic Growth,
Volume 6, Issue 1 Impact of remittances on poverty: an analysis of data from a set of developing countries Basanta K Pradhan Institute of Economic Growth, Delhi Malvika Mahesh Institute of Economic Growth,
Comments on Ansell & Samuels, Inequality & Democracy: A Contractarian Approach. Victor Menaldo University of Washington October 2012
 Comments on Ansell & Samuels, Inequality & Democracy: A Contractarian Approach Victor Menaldo University of Washington October 2012 There s a lot to like here Robustness to Dependent Variable (Regime Type)
Comments on Ansell & Samuels, Inequality & Democracy: A Contractarian Approach Victor Menaldo University of Washington October 2012 There s a lot to like here Robustness to Dependent Variable (Regime Type)
Quantitative Analysis of Migration and Development in South Asia
 87 Quantitative Analysis of Migration and Development in South Asia Teppei NAGAI and Sho SAKUMA Tokyo University of Foreign Studies 1. Introduction Asia is a region of high emigrant. In 2010, 5 of the
87 Quantitative Analysis of Migration and Development in South Asia Teppei NAGAI and Sho SAKUMA Tokyo University of Foreign Studies 1. Introduction Asia is a region of high emigrant. In 2010, 5 of the
Income Inequality and Trade Protection
 Income Inequality and Trade Protection Does the Sector Matter? Amanda Bjurling August 2015 Master s Programme in Economics Supervisor: Joakim Gullstrand Abstract According to traditional trade theory,
Income Inequality and Trade Protection Does the Sector Matter? Amanda Bjurling August 2015 Master s Programme in Economics Supervisor: Joakim Gullstrand Abstract According to traditional trade theory,
The Impact of Unionization on the Wage of Hispanic Workers. Cinzia Rienzo and Carlos Vargas-Silva * This Version, May 2015.
 The Impact of Unionization on the Wage of Hispanic Workers Cinzia Rienzo and Carlos Vargas-Silva * This Version, May 2015 Abstract This paper explores the role of unionization on the wages of Hispanic
The Impact of Unionization on the Wage of Hispanic Workers Cinzia Rienzo and Carlos Vargas-Silva * This Version, May 2015 Abstract This paper explores the role of unionization on the wages of Hispanic
WORKING PAPER SERIES
 DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS UNIVERSITY OF MILAN - BICOCCA WORKING PAPER SERIES Inequality, Political Systems and Public Spending Enrico Longoni, Filippo Gregorini No. 159 April 2009 Dipartimento di Economia
DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS UNIVERSITY OF MILAN - BICOCCA WORKING PAPER SERIES Inequality, Political Systems and Public Spending Enrico Longoni, Filippo Gregorini No. 159 April 2009 Dipartimento di Economia
Immigration and Its Effect on Economic Freedom: An Empirical Approach
 Immigration and Its Effect on Economic Freedom: An Empirical Approach Ryan H. Murphy Many concerns regarding immigration have arisen over time. The typical worry is that immigrants will displace native
Immigration and Its Effect on Economic Freedom: An Empirical Approach Ryan H. Murphy Many concerns regarding immigration have arisen over time. The typical worry is that immigrants will displace native
Luxembourg Income Study Working Paper Series
 Luxembourg Income Study Working Paper Series Working Paper No. 385 Economic Inequality and Democratic Political Engagement Frederick Solt July 2004 Luxembourg Income Study (LIS), asbl Abstract Economic
Luxembourg Income Study Working Paper Series Working Paper No. 385 Economic Inequality and Democratic Political Engagement Frederick Solt July 2004 Luxembourg Income Study (LIS), asbl Abstract Economic
Direction of trade and wage inequality
 This article was downloaded by: [California State University Fullerton], [Sherif Khalifa] On: 15 May 2014, At: 17:25 Publisher: Routledge Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number:
This article was downloaded by: [California State University Fullerton], [Sherif Khalifa] On: 15 May 2014, At: 17:25 Publisher: Routledge Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number:
U.S. Family Income Growth
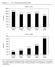 Figure 1.1 U.S. Family Income Growth Growth 140% 120% 100% 80% 60% 115.3% 1947 to 1973 97.1% 97.7% 102.9% 84.0% 40% 20% 0% Lowest Fifth Second Fifth Middle Fifth Fourth Fifth Top Fifth 70% 60% 1973 to
Figure 1.1 U.S. Family Income Growth Growth 140% 120% 100% 80% 60% 115.3% 1947 to 1973 97.1% 97.7% 102.9% 84.0% 40% 20% 0% Lowest Fifth Second Fifth Middle Fifth Fourth Fifth Top Fifth 70% 60% 1973 to
ANALYSIS OF THE EFFECT OF REMITTANCES ON ECONOMIC GROWTH USING PATH ANALYSIS ABSTRACT
 ANALYSIS OF THE EFFECT OF REMITTANCES ON ECONOMIC GROWTH USING PATH ANALYSIS Violeta Diaz University of Texas-Pan American 20 W. University Dr. Edinburg, TX 78539, USA. vdiazzz@utpa.edu Tel: +-956-38-3383.
ANALYSIS OF THE EFFECT OF REMITTANCES ON ECONOMIC GROWTH USING PATH ANALYSIS Violeta Diaz University of Texas-Pan American 20 W. University Dr. Edinburg, TX 78539, USA. vdiazzz@utpa.edu Tel: +-956-38-3383.
Does Paternity Leave Matter for Female Employment in Developing Economies?
 Policy Research Working Paper 7588 WPS7588 Does Paternity Leave Matter for Female Employment in Developing Economies? Evidence from Firm Data Mohammad Amin Asif Islam Alena Sakhonchik Public Disclosure
Policy Research Working Paper 7588 WPS7588 Does Paternity Leave Matter for Female Employment in Developing Economies? Evidence from Firm Data Mohammad Amin Asif Islam Alena Sakhonchik Public Disclosure
Development, Politics, and Inequality in Latin America and East Asia
 Institutions in Context: Inequality Development, Politics, and Inequality in Latin America and East Asia Inyoung Cho DPhil student Department of Politics and International Relations University of Oxford
Institutions in Context: Inequality Development, Politics, and Inequality in Latin America and East Asia Inyoung Cho DPhil student Department of Politics and International Relations University of Oxford
Determinants of Democracy
 Determinants of Democracy The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published Version Accessed Citable Link Terms
Determinants of Democracy The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published Version Accessed Citable Link Terms
Economic Freedom and Mass Migration: Evidence from Israel
 Economic Freedom and Mass Migration: Evidence from Israel Benjamin Powell The economic case for free immigration is nearly identical to the case for free trade. They both rely on a greater division of
Economic Freedom and Mass Migration: Evidence from Israel Benjamin Powell The economic case for free immigration is nearly identical to the case for free trade. They both rely on a greater division of
Industrial & Labor Relations Review
 Industrial & Labor Relations Review Volume 60, Issue 3 2007 Article 5 Labor Market Institutions and Wage Inequality Winfried Koeniger Marco Leonardi Luca Nunziata IZA, University of Bonn, University of
Industrial & Labor Relations Review Volume 60, Issue 3 2007 Article 5 Labor Market Institutions and Wage Inequality Winfried Koeniger Marco Leonardi Luca Nunziata IZA, University of Bonn, University of
Welfare State and Local Government: the Impact of Decentralization on Well-Being
 Welfare State and Local Government: the Impact of Decentralization on Well-Being Paolo Addis, Alessandra Coli, and Barbara Pacini (University of Pisa) Discussant Anindita Sengupta Associate Professor of
Welfare State and Local Government: the Impact of Decentralization on Well-Being Paolo Addis, Alessandra Coli, and Barbara Pacini (University of Pisa) Discussant Anindita Sengupta Associate Professor of
Unequal Recovery, Labor Market Polarization, Race, and 2016 U.S. Presidential Election. Maoyong Fan and Anita Alves Pena 1
 Unequal Recovery, Labor Market Polarization, Race, and 2016 U.S. Presidential Election Maoyong Fan and Anita Alves Pena 1 Abstract: Growing income inequality and labor market polarization and increasing
Unequal Recovery, Labor Market Polarization, Race, and 2016 U.S. Presidential Election Maoyong Fan and Anita Alves Pena 1 Abstract: Growing income inequality and labor market polarization and increasing
Urban income inequality in China revisited,
 Urban income inequality in China revisited, 1988-2002 Sylvie Démurger, Martin Fournier, Shi Li To cite this version: Sylvie Démurger, Martin Fournier, Shi Li. Urban income inequality in China revisited,
Urban income inequality in China revisited, 1988-2002 Sylvie Démurger, Martin Fournier, Shi Li To cite this version: Sylvie Démurger, Martin Fournier, Shi Li. Urban income inequality in China revisited,
APPENDIX - Table A1: Countries Used in the Analysis Models 1a,2a*,3a*
 APPENDIX - Table A1: Countries Used in the Analysis Country Models 1a,2a*,3a* Models 1c, 2c, 3c Models 1d, 2d,3d Models 1b,2b,3b VAR Case studies Argentina X* X X X X Australia X* X X X Austria X* X X
APPENDIX - Table A1: Countries Used in the Analysis Country Models 1a,2a*,3a* Models 1c, 2c, 3c Models 1d, 2d,3d Models 1b,2b,3b VAR Case studies Argentina X* X X X X Australia X* X X X Austria X* X X
Labour Market Reform, Rural Migration and Income Inequality in China -- A Dynamic General Equilibrium Analysis
 Labour Market Reform, Rural Migration and Income Inequality in China -- A Dynamic General Equilibrium Analysis Yinhua Mai And Xiujian Peng Centre of Policy Studies Monash University Australia April 2011
Labour Market Reform, Rural Migration and Income Inequality in China -- A Dynamic General Equilibrium Analysis Yinhua Mai And Xiujian Peng Centre of Policy Studies Monash University Australia April 2011
When Does Legal Origin Matter? Mohammad Amin * World Bank. Priya Ranjan ** University of California, Irvine. December 2008
 When Does Legal Origin Matter? Mohammad Amin * World Bank Priya Ranjan ** University of California, Irvine December 2008 Abstract: This paper takes another look at the extent of business regulation in
When Does Legal Origin Matter? Mohammad Amin * World Bank Priya Ranjan ** University of California, Irvine December 2008 Abstract: This paper takes another look at the extent of business regulation in
Do People Pay More Attention to Earthquakes in Western Countries?
 2nd International Conference on Advanced Research Methods and Analytics (CARMA2018) Universitat Politècnica de València, València, 2018 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.4995/carma2018.2018.8315 Do People Pay
2nd International Conference on Advanced Research Methods and Analytics (CARMA2018) Universitat Politècnica de València, València, 2018 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.4995/carma2018.2018.8315 Do People Pay
Occupation and Growing Wage Inequality in the United States,
 Occupation and Growing Wage Inequality in the United States, 1983-2002. PRC-Brown Bag ä ù Changhwan Kim Department of Sociology University of Texas at Austin Feb 4, 2005 - p. 1/43 Presentation about...
Occupation and Growing Wage Inequality in the United States, 1983-2002. PRC-Brown Bag ä ù Changhwan Kim Department of Sociology University of Texas at Austin Feb 4, 2005 - p. 1/43 Presentation about...
VULNERABILITY STUDY IN KAKUMA CAMP
 EXECUTIVE BRIEF VULNERABILITY STUDY IN KAKUMA CAMP In September 2015, the World Food Programme (WFP) and the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) commissioned Kimetrica to undertake an
EXECUTIVE BRIEF VULNERABILITY STUDY IN KAKUMA CAMP In September 2015, the World Food Programme (WFP) and the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) commissioned Kimetrica to undertake an
Inequality and Corruption
 Inequality and Corruption Sanjeev Khagram i and You, Jong-Song ii December 9, 2003 Abstract Sociological theorizing and research on the relationship between inequality and corruption is surprisingly rare
Inequality and Corruption Sanjeev Khagram i and You, Jong-Song ii December 9, 2003 Abstract Sociological theorizing and research on the relationship between inequality and corruption is surprisingly rare
Institute for Public Policy and Economic Analysis. Spatial Income Inequality in the Pacific Northwest, By: Justin R. Bucciferro, Ph.D.
 Institute for Public Policy and Economic Analysis Spatial Income Inequality in the Pacific Northwest, 1970 2010 By: Justin R. Bucciferro, Ph.D. May, 2014 Spatial Income Inequality in the Pacific Northwest,
Institute for Public Policy and Economic Analysis Spatial Income Inequality in the Pacific Northwest, 1970 2010 By: Justin R. Bucciferro, Ph.D. May, 2014 Spatial Income Inequality in the Pacific Northwest,
Proxies for Economic Freedom: A Critique of the Hanson Critique
 Southern Economic Journal 2005, 72(2), 492 501 Proxies for Economic Freedom: A Critique of the Hanson Critique Jac C. Heckelman* Economic freedom indicators have become quite popular recently as a useful
Southern Economic Journal 2005, 72(2), 492 501 Proxies for Economic Freedom: A Critique of the Hanson Critique Jac C. Heckelman* Economic freedom indicators have become quite popular recently as a useful
Economic Growth, Foreign Investments and Economic Freedom: A Case of Transition Economy Kaja Lutsoja
 Economic Growth, Foreign Investments and Economic Freedom: A Case of Transition Economy Kaja Lutsoja Tallinn School of Economics and Business Administration of Tallinn University of Technology The main
Economic Growth, Foreign Investments and Economic Freedom: A Case of Transition Economy Kaja Lutsoja Tallinn School of Economics and Business Administration of Tallinn University of Technology The main
Abdurohman Ali Hussien,,et.al.,Int. J. Eco. Res., 2012, v3i3, 44-51
 THE IMPACT OF TRADE LIBERALIZATION ON TRADE SHARE AND PER CAPITA GDP: EVIDENCE FROM SUB SAHARAN AFRICA Abdurohman Ali Hussien, Terrasserne 14, 2-256, Brønshøj 2700; Denmark ; abdurohman.ali.hussien@gmail.com
THE IMPACT OF TRADE LIBERALIZATION ON TRADE SHARE AND PER CAPITA GDP: EVIDENCE FROM SUB SAHARAN AFRICA Abdurohman Ali Hussien, Terrasserne 14, 2-256, Brønshøj 2700; Denmark ; abdurohman.ali.hussien@gmail.com
Rainfall, Economic Shocks and Civil Conflicts in the Agrarian Countries of the World
 Xiao 1 Yan Xiao Final Draft: Thesis Proposal Junior Honor Seminar May 10, 2004 Rainfall, Economic Shocks and Civil Conflicts in the Agrarian Countries of the World Introduction Peace and prosperity are
Xiao 1 Yan Xiao Final Draft: Thesis Proposal Junior Honor Seminar May 10, 2004 Rainfall, Economic Shocks and Civil Conflicts in the Agrarian Countries of the World Introduction Peace and prosperity are
Crime and Corruption: An International Empirical Study
 Proceedings 59th ISI World Statistics Congress, 5-3 August 13, Hong Kong (Session CPS111) p.985 Crime and Corruption: An International Empirical Study Huaiyu Zhang University of Dongbei University of Finance
Proceedings 59th ISI World Statistics Congress, 5-3 August 13, Hong Kong (Session CPS111) p.985 Crime and Corruption: An International Empirical Study Huaiyu Zhang University of Dongbei University of Finance
The Determinants of Low-Intensity Intergroup Violence: The Case of Northern Ireland. Online Appendix
 The Determinants of Low-Intensity Intergroup Violence: The Case of Northern Ireland Online Appendix Laia Balcells (Duke University), Lesley-Ann Daniels (Institut Barcelona d Estudis Internacionals & Universitat
The Determinants of Low-Intensity Intergroup Violence: The Case of Northern Ireland Online Appendix Laia Balcells (Duke University), Lesley-Ann Daniels (Institut Barcelona d Estudis Internacionals & Universitat
The interaction effect of economic freedom and democracy on corruption: A panel cross-country analysis
 The interaction effect of economic freedom and democracy on corruption: A panel cross-country analysis Author Saha, Shrabani, Gounder, Rukmani, Su, Jen-Je Published 2009 Journal Title Economics Letters
The interaction effect of economic freedom and democracy on corruption: A panel cross-country analysis Author Saha, Shrabani, Gounder, Rukmani, Su, Jen-Je Published 2009 Journal Title Economics Letters
Economists have long posited that institutions matter for economic success,
 Culture and Freedom 83 Culture and Freedom Claudia R. Williamson and Rachel L. Coyne 1 1. Introduction Economists have long posited that institutions matter for economic success, but how they matter is
Culture and Freedom 83 Culture and Freedom Claudia R. Williamson and Rachel L. Coyne 1 1. Introduction Economists have long posited that institutions matter for economic success, but how they matter is
Corruption, Income Inequality, and Subsequent Economic Growth
 Undergraduate Economic Review Volume 11 Issue 1 Article 3 2014 Corruption, Income Inequality, and Subsequent Economic Growth Josh Matti Indiana Wesleyan University, josh.matti@myemail.indwes.edu Recommended
Undergraduate Economic Review Volume 11 Issue 1 Article 3 2014 Corruption, Income Inequality, and Subsequent Economic Growth Josh Matti Indiana Wesleyan University, josh.matti@myemail.indwes.edu Recommended
Labor versus capital in trade-policy: The role of ideology and inequality
 Journal of International Economics 69 (2006) 310 320 www.elsevier.com/locate/econbase Labor versus capital in trade-policy: The role of ideology and inequality Pushan Dutt a,1, Devashish Mitra b,c, * a
Journal of International Economics 69 (2006) 310 320 www.elsevier.com/locate/econbase Labor versus capital in trade-policy: The role of ideology and inequality Pushan Dutt a,1, Devashish Mitra b,c, * a
Classification and Rating of Democracy. A Comparison. John Högström. Abstract
 Taiwan Journal of Democracy, Volume 9, No. 2: 33-54 Classification and Rating of Democracy A Comparison John Högström Abstract This study compares three indexes of democracy, the EIU, Freedom House, and
Taiwan Journal of Democracy, Volume 9, No. 2: 33-54 Classification and Rating of Democracy A Comparison John Högström Abstract This study compares three indexes of democracy, the EIU, Freedom House, and
THE ECONOMIC EFFECT OF CORRUPTION IN ITALY: A REGIONAL PANEL ANALYSIS (M. LISCIANDRA & E. MILLEMACI) APPENDIX A: CORRUPTION CRIMES AND GROWTH RATES
 THE ECONOMIC EFFECT OF CORRUPTION IN ITALY: A REGIONAL PANEL ANALYSIS (M. LISCIANDRA & E. MILLEMACI) APPENDIX A: CORRUPTION CRIMES AND GROWTH RATES Figure A1 shows an apparently negative correlation between
THE ECONOMIC EFFECT OF CORRUPTION IN ITALY: A REGIONAL PANEL ANALYSIS (M. LISCIANDRA & E. MILLEMACI) APPENDIX A: CORRUPTION CRIMES AND GROWTH RATES Figure A1 shows an apparently negative correlation between
BEYOND GNP: ECONOMIC FREEDOM AS A DETERMINANT OF BASIC HUMAN NEEDS. Eric Juenke, B.A. Thesis Prepared for the Degree of MASTER OF ARTS
 BEYOND GNP: ECONOMIC FREEDOM AS A DETERMINANT OF BASIC HUMAN NEEDS Eric Juenke, B.A. Thesis Prepared for the Degree of MASTER OF ARTS UNIVERSITY OF NORTH TEXAS December 2002 APPROVED: Alexander Tan, Major
BEYOND GNP: ECONOMIC FREEDOM AS A DETERMINANT OF BASIC HUMAN NEEDS Eric Juenke, B.A. Thesis Prepared for the Degree of MASTER OF ARTS UNIVERSITY OF NORTH TEXAS December 2002 APPROVED: Alexander Tan, Major
Remittances and the Brain Drain: Evidence from Microdata for Sub-Saharan Africa
 Remittances and the Brain Drain: Evidence from Microdata for Sub-Saharan Africa Julia Bredtmann 1, Fernanda Martinez Flores 1,2, and Sebastian Otten 1,2,3 1 RWI, Rheinisch-Westfälisches Institut für Wirtschaftsforschung
Remittances and the Brain Drain: Evidence from Microdata for Sub-Saharan Africa Julia Bredtmann 1, Fernanda Martinez Flores 1,2, and Sebastian Otten 1,2,3 1 RWI, Rheinisch-Westfälisches Institut für Wirtschaftsforschung
Remittances and Poverty. in Guatemala* Richard H. Adams, Jr. Development Research Group (DECRG) MSN MC World Bank.
 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Remittances and Poverty in Guatemala* Richard H. Adams, Jr. Development Research Group
Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Remittances and Poverty in Guatemala* Richard H. Adams, Jr. Development Research Group
What Can We Learn about Financial Access from U.S. Immigrants?
 What Can We Learn about Financial Access from U.S. Immigrants? Una Okonkwo Osili Indiana University Purdue University Indianapolis Anna Paulson Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago *These are the views of the
What Can We Learn about Financial Access from U.S. Immigrants? Una Okonkwo Osili Indiana University Purdue University Indianapolis Anna Paulson Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago *These are the views of the
L8: Inequality, Poverty and Development: The Evidence
 L8: Inequality, Poverty and Development: The Evidence Dilip Mookherjee Ec320 Lecture 8, Boston University Sept 25, 2014 DM (BU) 320 Lect 8 Sept 25, 2014 1 / 1 RECAP: Measuring Inequality and Poverty We
L8: Inequality, Poverty and Development: The Evidence Dilip Mookherjee Ec320 Lecture 8, Boston University Sept 25, 2014 DM (BU) 320 Lect 8 Sept 25, 2014 1 / 1 RECAP: Measuring Inequality and Poverty We
An Analysis of Rural to Urban Labour Migration in India with Special Reference to Scheduled Castes and Schedules Tribes
 International Journal of Interdisciplinary and Multidisciplinary Studies (IJIMS), 2015, Vol 2, No.10,53-58. 53 Available online at http://www.ijims.com ISSN: 2348 0343 An Analysis of Rural to Urban Labour
International Journal of Interdisciplinary and Multidisciplinary Studies (IJIMS), 2015, Vol 2, No.10,53-58. 53 Available online at http://www.ijims.com ISSN: 2348 0343 An Analysis of Rural to Urban Labour
Natural Disasters and Poverty Reduction:Do Remittances matter?
 Natural Disasters and Poverty Reduction:Do Remittances matter? Linguère Mously Mbaye and Alassane Drabo + AfDB, Abidjan and IZA, Bonn and + FERDI, Clermont-Ferrand UNU-Wider and ARUA: Migration and Mobility-New
Natural Disasters and Poverty Reduction:Do Remittances matter? Linguère Mously Mbaye and Alassane Drabo + AfDB, Abidjan and IZA, Bonn and + FERDI, Clermont-Ferrand UNU-Wider and ARUA: Migration and Mobility-New
Is the Great Gatsby Curve Robust?
 Comment on Corak (2013) Bradley J. Setzler 1 Presented to Economics 350 Department of Economics University of Chicago setzler@uchicago.edu January 15, 2014 1 Thanks to James Heckman for many helpful comments.
Comment on Corak (2013) Bradley J. Setzler 1 Presented to Economics 350 Department of Economics University of Chicago setzler@uchicago.edu January 15, 2014 1 Thanks to James Heckman for many helpful comments.
Immigration and Internal Mobility in Canada Appendices A and B. Appendix A: Two-step Instrumentation strategy: Procedure and detailed results
 Immigration and Internal Mobility in Canada Appendices A and B by Michel Beine and Serge Coulombe This version: February 2016 Appendix A: Two-step Instrumentation strategy: Procedure and detailed results
Immigration and Internal Mobility in Canada Appendices A and B by Michel Beine and Serge Coulombe This version: February 2016 Appendix A: Two-step Instrumentation strategy: Procedure and detailed results
A Comment on Measuring Economic Freedom: A Comparison of Two Major Sources
 The Journal of Private Enterprise 31(3), 2016, 69 91 A Comment on Measuring Economic Freedom: A Comparison of Two Major Sources Ryan H. Murphy Southern Methodist University Abstract Do social scientists
The Journal of Private Enterprise 31(3), 2016, 69 91 A Comment on Measuring Economic Freedom: A Comparison of Two Major Sources Ryan H. Murphy Southern Methodist University Abstract Do social scientists
Does Horizontal Inequality Matter in Vietnam?
 Soc Indic Res https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-018-1896-1 Does Horizontal Inequality Matter in Vietnam? Thi Thu Hoai Dang 1 Accepted: 31 March 2018 Springer Science+Business Media B.V., part of Springer
Soc Indic Res https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-018-1896-1 Does Horizontal Inequality Matter in Vietnam? Thi Thu Hoai Dang 1 Accepted: 31 March 2018 Springer Science+Business Media B.V., part of Springer
The Impact of Licensing Decentralization on Firm Location Choice: the Case of Indonesia
 The Impact of Licensing Decentralization on Firm Location Choice: the Case of Indonesia Ari Kuncoro 1 I. Introduction Spatial centralization of resources and spatial concentration of manufacturing in a
The Impact of Licensing Decentralization on Firm Location Choice: the Case of Indonesia Ari Kuncoro 1 I. Introduction Spatial centralization of resources and spatial concentration of manufacturing in a
Remittances and Taxation in Developing Countries
 Remittances and Taxation in Developing Countries Biniam Bedasso Woodrow Wilson School, Princeton University July 2017 Biniam Bedasso (Princeton) Remittances & Taxation - UNU-WIDER 07/2017 1 / 1 Introduction
Remittances and Taxation in Developing Countries Biniam Bedasso Woodrow Wilson School, Princeton University July 2017 Biniam Bedasso (Princeton) Remittances & Taxation - UNU-WIDER 07/2017 1 / 1 Introduction
Brain Drain and Emigration: How Do They Affect Source Countries?
 The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Honors Research Projects The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College Spring 2019 Brain Drain and Emigration: How Do They Affect Source Countries? Nicholas
The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Honors Research Projects The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College Spring 2019 Brain Drain and Emigration: How Do They Affect Source Countries? Nicholas
According to standard trade theory (i.e., the
 Globalization, Government Ideology, and Income Inequality in Developing Countries Eunyoung Ha Claremont Graduate University This article examines how globalization, government ideology, and their interaction
Globalization, Government Ideology, and Income Inequality in Developing Countries Eunyoung Ha Claremont Graduate University This article examines how globalization, government ideology, and their interaction
The UK Policy Agendas Project Media Dataset Research Note: The Times (London)
 Shaun Bevan The UK Policy Agendas Project Media Dataset Research Note: The Times (London) 19-09-2011 Politics is a complex system of interactions and reactions from within and outside of government. One
Shaun Bevan The UK Policy Agendas Project Media Dataset Research Note: The Times (London) 19-09-2011 Politics is a complex system of interactions and reactions from within and outside of government. One
