FREE CAT ALO NIA [EN] SPREAD THE WORD! The struggle for the independence of Catalonia in 4 languages
|
|
|
- Oliver Harvey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FREE CAT ALO NIA [EN] SPREAD THE WORD! The struggle for the independence of Catalonia in 4 languages
2 FREECATALONIA The Catalan nation s struggle for freedom You may have heard of Catalan culture: the Romanesque art of Boí and Taüll; avant-garde artists Joan Miró, Joan Tàpies or Salvador Dalí; Architects Rafael Guastavino and Antoni Gaudí; musicians Enric Granados and Jordi Savall; authors Quim Monzó, Mercè Rodoreda or the novel Tirant lo Blanc. In sports, you will know Barça (Barcelona Football Club), the successful century-old club of the Catalan capital, and USAP, Perpignan (in Catalan, Perpinyà)
3 well-known rugby club. You may enjoy the festivities of Ibiza (in Catalan, Eivissa) the Fallas (in Catalan, Falles) of Valencia, the Costa Brava, and our cuisine - chefs and restaurants selected by the Michelin Guide as being among the best in the world. But maybe you did not know that all these places and their people are part of a great nation dating back a thousand years that yearns for freedom, and is striving for independence.
4 STORY The story of a people that refuses to disappear Catalonia is an ancient nation. It was born politically over a thousand years ago, in 988, on the emancipation in the so-called Marca Hispanica territories between the line of borders of the Muslim and Christian worlds, to the south, and the Frankish kingdom some way north of the Pyrenees. It expanded down the Iberian Peninsula and across the Mediterranean, from the kernel of the territories set up as sovereign counties. Its independence was always based on its sovereign institutions. In 1640, the Principality of Catalonia suffered its first serious conflict within the Hispanic Kingdom, against Castile and its French ally, in the so-called Reapers War. Catalonia fought against French annexation to the north and against the centralism of Castile impo-
5 sed by its army on Catalan territory. Catalonia s defeat in that war led to the French annexation - through the Treaty of the Pyrenees (1659) - of the Catalan counties north of the Pyrenees: Roussillon, Conflent, Vallespir and Alta Cerdanya, and the public administration of what at that time was the second largest city in the country, Perpignan, was stripped of any Catalan vestige from that moment on. In 1705, rival claims to the thrones of Castile and Catalonia- Aragon again confronted the two countries and their allies in a trans-european war: the War of Spanish Succession. Catalonia confronted the Franco-Spanish Bourbon king Philip V, who defeated those supporting the other pretender, Charles of Austria. Catalonia s defeat in this war meant the de facto annexation of Catalonia to the Kingdom of Castile, by the abolishment of its institutions and its historic rights; it lost its freedom and independence. The Nueva Planta Decree was enacted, Castilian-model legislation for all the Catalan, Valencian, Balearic and Aragonese territories with the aim of turning the country into a barren colony subject to the Kingdom of Castile. The impact of that episode was so great that it is remembered every year on April 25th and September 11th, the dates on which the war was lost, respectively, in Valencia and in Catalonia, where it is the National Holiday. After that war, however, the Catalan struggle against the Bourbons did not end. Resistance began just after the war, although it was not until over a hundred years later that Cata-
6 lonia began to really reorganize itself in order to recover its liberties by any possible means, including popular uprisings and revolts. In 1873, 1931 and 1934 the Catalan Republic was proclaimed three times. After a 1936 Fascist military coup which had been crushed in Catalonia but led to a three-year civil war in Spain, the leader of the coup, General Francisco Franco, won the war in 1939 with the support of Hitler and Mussolini, and his dictatorship once again abolished Catalonia s liberties and all Catalan institutions. The dictatorship began a brutal repression against Catalan culture and language and civil rights in general, and all areas of the new occupying administration were governed directly by military officers for the first decades. The persecution against every sign of Catalanness was extremely harsh; it was a repression that has been defined as an attempted cultural genocide. Spanish, referred to as the language of the empire or simply Christian, (in contrast to Catalan, which was regarded as being well nigh heretical), was imposed in all public services as the only official language, in a clear attempt to systematically replace the language. Anyone who showed the slightest sign of Catalan-ness ran the risk of being fined, imprisoned... or worse. The epitomy and main symbol of that repression was the torture and execution in Barcelona of the exiled president of Catalonia Lluís Companys, after being captured in France by the Gestapo, in the summer of 1940.
7 economic drainage Colonial economic drainage acknowledged by the metropolis After the death of dictator Franco, in Catalonia the democratic struggle restored the Generalitat and the Parliament of Catalonia as legitimate governing bodies. Thus began a convoluted path to recover institutions and to decriminalize Catalan culture, as part of Spain s new framework of the parliamentary monarchy of Bourbon king Juan Carlos (whom Franco had appointed to be his heir in 1969). Catalonia is, it is claimed, currently living in a democratic state. However, the design of a falsely decentralised political model hides not only legislative constraints and supervision outside Catalonia (Constitutional Court) but also a net tax outflow from Catalonia, admitted by the Spanish Government, which has be calculated to amount to 16 billion every year. This scale of financial blood-letting affects all citizens indiscriminately, whether or not they support independence. It is a true spoliation that impoverishes the present and the future of generations of Catalonia s citizens.
8 Self-determination Self-determination, a right denied by Spain The Catalan nation has a natural right to its independence, as it is a society with its own culture and language, within a geographically defined territory. It has also a historic right, thanks to the persistence of its people over the centuries, and a political right, given the will of a majority to decide its future democratically through a representative government and with the willingness to set up relations with other nations. The Parliament of Catalonia adopted a resolution in 1989 in which it proclaimed that it would never forego its right to selfdetermination. In 2006 and 2007, two large demonstrations in Barcelona, preceding the centenary year of the pro-independence flag, or l estelada (2008), claimed against a clearly pro-independence backdrop - the right to decide on their own territory. In 2009, a process of popular participation began in the Principality in which local referenda on self-determination were organized. These local referenda led up
9 to the November 9, 2014 participatory process which became the final step before the decision to hold a referendum on independence. Spain s legal proceedings against the 2014 non-binding referendum ended up with those responsible being barred from public office and receiving heavy fines ( 5,200,000 to date). After an election in Catalonia, in which the pro-independence members won a majority in the Catalan Parliament, with almost two million votes, efforts progressed to hold a referendum on the independence of Catalonia, which was eventually held on October 1, On September 20, 2017 the Spanish government, which had already usurped control of the finances of the Generalitat, began an offensive to prevent the referendum by force. The Civil Guard, a militarized Spanish police force, began to violate civil rights of freedom of the press and opinion, closing websites, censoring publications, searching warehouses and presses, and threatening reporters and public and private media. At the institutional level, it called in for questioning mayors and public representatives, and even arrested and gaoled some of the political leaders accused of organizing the referendum. Meanwhile about ten thousand riot police officers and various military detachments arrived in Catalonia, after leaving their barracks amidst cries of revenge and hatred chanted by their neighbours and relatives. On October 1, in spite of being officially banned, the referendum was finally held, thanks to the determined defence, by the civilian population, of the polling stations throughout the weekend. The participatory success of more than two million voters - 43% of the census - and a victory of 90% for independence were the irrefutable proof. However, the Spanish State
10 repressed it fiercely with its police forces, who tried to break through with extreme violence, beating thousands of voters, regardless of their age. In all, with court orders, the Spanish police closed 92 polling stations and thanks to their brutality 1,066 people received medical attention, while they caused widespread damage in schools and local council property. More than double that number of polling stations were closed or prevented from opening by the Catalan police, without any incidents. On October 10, President Carles Puigdemont announced the results of the referendum in Parliament, but instead of proposing the declaration of independence established by law, and at the request of European high-ranking presidents, he gave the State the opportunity to open a period of negotiations that were to lead to a peaceful and democratic solution for the pro-independence issue. Jordi Cuixart and Jordi Sànchez, leaders of Òmnium Cultural (a cultural organisation with 99,000 members, devoted to the promotion of Catalan culture) and the Assemblea Nacional Catalana (an association with more than 80,000 members and followers, that works for the independence of Catalonia) were detained without bail, accused of sedition and rebellion, and sent to a gaol near Madrid. Given that the Spanish government refused any possibility of dialogue and negotiation and was prepared to activate all its mechanisms of repression, on October 27 the absolute majority of the Parliament of Catalonia resolved to implement the Catalan Republic. The Spanish government had already decided to take full political control of the country, and under Article 155 of the Constitution, arrested ministers of the Catalan Government, while other ministers stayed in Belgium, in exile; and dissolved the Parliament of Catalonia. Hundreds of public servants were dismissed, criminal charges were brought against many democratic leaders, and public and private media were silenced with new threats and reprisals. Under pressure from Europe, the Spanish State called supervised elections, in the hope of toppling pro-independence parties from power. But with a record 82% turnout, the results once again gave the victory to the pro-independence parties with a renewed outright majority. The Spanish government has not accepted this result, and has tried to block selfgovernment again. The struggle of the citizens of Catalonia, for the freedom and the Republic that have already been declared, continues.
11
12 SYMBOLS Catalonia s symbols of identity The Catalan flag, the ancient ensign The coat of arms of the Catalan Count-Kings of Barcelona became, over time, the royal flag of the nine yellow and red stripes, recently documented as one of the oldest in Europe. It first appeared in a coin showing the coat of arms of Count Ramon Berenguer IV (12th century). Its colours were flown for centuries throughout the Mediterranean,
13 and are present to this day far, far away, such as in Sicily, where they still glitter proudly. Closer to home, the Spanish flag itself drew its inspiration from the Catalan flag. Over time, the ensign of the Barcelona royal dynasty became the official flag of the country and today it is fully accepted by all, without distinction. Nevertheless, the flag was forbidden and persecuted by various Spanish totalitarian reigns and governments for many years, as it was seen, correctly, as a differentiated mark of national identity. The estelada flag of freedom The estelada is the Catalan flag with a blue triangle - representing humanity at one end - with a five-pointed white star in the middle, representing the yearning for freedom. It was created at the beginning of the last century by the Catalan at the time clandestine - independence movement, and symbolizes the struggle for the independence of Catalonia. freedom and democracy that they represented. Cuba was one of the last Spanish colonies to achieve emancipation and where the first explicitly pro-independence Catalan publication appeared in The flag s massive presence in the streets of Catalonia is a good example of the majority sentiment, more present than ever, which clamours for our own State. Right now, in violation of the freedom of expression of any democracy, the star is banned de facto in most Spanish sports stadiums. The Spanish police often confiscate such flags but, nevertheless, fans of Catalan clubs still brandish them to support their teams. It was originally inspired by the Cuban flag which in turn had been inspired by the U.S. Stars and Stripes, for the values of
14 The black flag: the banner for fighting to the bitter end The Catalan black flag represents the attitude of mourning and of either living in liberty or dying. It is documented as early as the 13th century in Ramon Muntaner s Crònica, and reappeared in the 18th century, in the War of Succession, during the sieges of Barcelona and Cardona. During the three-hundredth anniversary of the War of the Succession (2014), it was redesigned and became the symbol of non-surrender.
15 languages Catalan and Occitan, Catalonia s own and official languages Catalan and Occitan (or Aranese, from the Aran valley) are the expression of the national and cultural reality of Catalonia. They come from vulgar Latin and in the 13th century they became consolidated in all domains. In the case of Catalan, the earliest documented source are the Homilies d Organyà (12th century). From the reign of James I, Catalan spread to its present-day linguistic domain, as it did across the Mediterranean, though there is only one extant testimony, in Alghero (Sardinia). For centuries, the Catalan language was the only private, public and official language throughout the country. Its history of success was cut short by its persecution by Spain and France, through hundreds of regulations and decrees by all kinds of government. This obsessive desire to persecute it aims simply to eliminate any public trace of the language, in the knowledge that it poses a dangerous cognitive mechanism to rationalize a differentiated way of thinking in the face of uniformization. Catalan continues to be the object of negative politicization by the Spanish State and by political Unionist parties in Catalonia, that use it as a handy weapon to try to create linguistic divisiveness in the country, with Spanish reigning supreme.
16 The referendum The referendum on independence in figures The Spanish police were mobilized for months to try to forestall the referendum; more than 10,000 policemen took part, that is to say, this was a military invasion with all its effects. In addition, various groups of Fascists acted with impunity by attacking citizens, and a few of them were identified as policemen out of uniform. The cost of this operation was 87 million. The Civil Guard closed more than 144 websites related to the organization of the referendum. The Spanish police visited the headquarters of various Catalan media to identify journalists. Despite the presence of the Spanish police forces and the army, 10,000 ballot boxes entered across the border with France into
17 the interior of Catalonia thanks to anonymous volunteers, and were later distributed and hidden until the day of the vote. Of all the necessary material to hold the vote, after the Spanish police searched various companies, 11,500,000 ballots and 100 ballot boxes were seized, as well as notifications for 45,000 election officials. The Spanish Data Protection Agency threatened the members of the voting tables with fines of up to 600,000. In spite of this, on the weekend in which the polling stations were occupied until the day of the voting, around hundred of thousands people were mobilized in order to defend them. The turn-out was 2,286,217 voters, and the result was: 2,044,038 YES votes, 177,547 NO votes, 44,913 blank votes and 19,719 invalid votes. Until now, the Spanish judicial system has called in for questioning dozens of teachers, only because the issue of Spanish police brutality arose in their classes the day after the referendum; some of these schools had been savagely assailed, leaving hundreds of casualties and material damage. Up to now, Spanish courts have summoned dozens of school teachers to be questioned, merely because they dealt with police violence in schools the day after the referendum; some schools had been savagely assaulted, leaving hundreds of injured and plenty of damage to school property. Over 700 Catalan mayors have been threatened with court or police summons, for having allowed municipal premises to be used as polling stations for the democratic voting exercise. President Carles Puigdemont, along with three other Catalan ministers, is in exile in Belgium, where they are working to build the Catalan Republic from their new base in Waterloo. Exiled Catalan Minister Clara Ponsatí has gone back to her former university post in Scotland. Political leaders Marta Rovira and Anna Gabriel are also in exile, in Switzerland. In spite of this, Rajoy s government is still chasing Puigdemont, by sending the Spanish secret services to track him unbeknown to the authorities of each country, and have him captured. The latest episode was when they tipped off the German police about Sr. Puigdemont s presence in Germany, on his way from Finland to Belgium. Today, Sr. Puigdemont awaits a German court decision on a European Arrest Warrant and his possible extradition to Spain.
18 The Spanish government has already locked in jail - without bail and ahead of the trial - six other Catalan ministers: vicepresident Oriol Junqueras amb ministers Joaquim Forn, Jordi Turull, Josep Rull, Raül Romeva and Dolors Bassa, together with former Speaker of Parlament Carme Forcadell MP and the Òmnium Cultural and Assemblea Nacional Catalana chairmen Jordi Cuixart and Jordi Sànchez. None of them has yet been tried, nor have any of them ever condoned violence. They face charges of rebellion, a crime that only appears in Spanish and European legislation when accompanied by violence. Violence has only been exercised in Catalonia by Spanish policemen and groups of Fascist thugs. Amnesty International has accused Spain of violating human rights, and several cases are before the UN Humans Rights Committee. So no-one in Spain (except the Government) can deny that there are political prisoners in Europe today.
Catalan Independence 2018
 Catalan Independence 2018 On October 1, 2017, the Catalan Government headed by Carles Puigdemont of the Junts per Catalunya parliamentary alliance held a referendum on the future independence of Catalonia.
Catalan Independence 2018 On October 1, 2017, the Catalan Government headed by Carles Puigdemont of the Junts per Catalunya parliamentary alliance held a referendum on the future independence of Catalonia.
An international mediation for Catalonia
 Conference by the President of Catalonia at the University of Geneva: An international mediation for Catalonia University of Geneva, October 17 th 2018 Welcome and memories of the Catalan exile(s) Ladies
Conference by the President of Catalonia at the University of Geneva: An international mediation for Catalonia University of Geneva, October 17 th 2018 Welcome and memories of the Catalan exile(s) Ladies
BALLOT FRAUD IN THE CATALAN ELECTIONS: COULD IT HAPPEN?
 BALLOT FRAUD IN THE CATALAN ELECTIONS: COULD IT HAPPEN? Matthew Parish Catalonia has regional elections on 21 December 2017: in barely a week s time. The circumstances of those elections are that after
BALLOT FRAUD IN THE CATALAN ELECTIONS: COULD IT HAPPEN? Matthew Parish Catalonia has regional elections on 21 December 2017: in barely a week s time. The circumstances of those elections are that after
PRELIMINARY STATEMENT. Introduction. Executive Summary. 3 October 2017 Barcelona, Spain
 PRELIMINARY STATEMENT 3 October 2017 Barcelona, Spain Introduction Since early September, the International Limited Observation Mission (ILOM), a team of independent international election experts, facilitated
PRELIMINARY STATEMENT 3 October 2017 Barcelona, Spain Introduction Since early September, the International Limited Observation Mission (ILOM), a team of independent international election experts, facilitated
Fascism is Alive and Well in Spain The Case of Judge Garzon
 February 22, 2010 Fascism is Alive and Well in Spain The Case of Judge Garzon By VINCENT NAVARRO Barcelona The fascist regime led by General Franco was one of the most repressive regimes in Europe in the
February 22, 2010 Fascism is Alive and Well in Spain The Case of Judge Garzon By VINCENT NAVARRO Barcelona The fascist regime led by General Franco was one of the most repressive regimes in Europe in the
Catalonia: A Stateless Nation with Deep Social Divisions
 Catalonia: A Stateless Nation with Deep Social Divisions POLICY PAPER / NOVEMBER 2017 AUTHOR: SAMUEL ROSIN Catalonia: A Stateless Nation with Deep Social Divisions Policy Paper Samuel Rosin, November 2017
Catalonia: A Stateless Nation with Deep Social Divisions POLICY PAPER / NOVEMBER 2017 AUTHOR: SAMUEL ROSIN Catalonia: A Stateless Nation with Deep Social Divisions Policy Paper Samuel Rosin, November 2017
Spanish police crack down on Catalonia's referendum voting
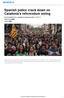 Spanish police crack down on Catalonia's referendum voting By Associated Press, adapted by Newsela staff on 10.05.17 Word Count 868 Level 1160L Independence supporters march during a demonstration in Barcelona,
Spanish police crack down on Catalonia's referendum voting By Associated Press, adapted by Newsela staff on 10.05.17 Word Count 868 Level 1160L Independence supporters march during a demonstration in Barcelona,
Catalonia Independence Bid Pushes Spain Toward Crisis
 https://nyti.ms/2esaoga EUROPE Catalonia Independence Bid Pushes Spain Toward Crisis Leer en español By RAPHAEL MINDER SEPT. 8, 2017 BARCELONA The accelerating battle over Catalonia s status hit warp speed
https://nyti.ms/2esaoga EUROPE Catalonia Independence Bid Pushes Spain Toward Crisis Leer en español By RAPHAEL MINDER SEPT. 8, 2017 BARCELONA The accelerating battle over Catalonia s status hit warp speed
The Rise of Dictators
 The Rise of Dictators DICTATORS THREATEN WORLD PEACE For many European countries the end of World War I was the beginning of revolutions at home, economic depression and the rise of powerful dictators
The Rise of Dictators DICTATORS THREATEN WORLD PEACE For many European countries the end of World War I was the beginning of revolutions at home, economic depression and the rise of powerful dictators
C atalà. Legal situation of Catalan. Basic concepts for understanding the legal situation of the Catalan. Legal framework
 C atalà Parliament of Catalonia (Barcelona. Catalonia) Basic concepts for understanding the legal situation of the Catalan Legal framework Linguistic codes in the public administration Linguistic codes
C atalà Parliament of Catalonia (Barcelona. Catalonia) Basic concepts for understanding the legal situation of the Catalan Legal framework Linguistic codes in the public administration Linguistic codes
Optional Protocol to the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights
 Optional Protocol to the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights Application against Spain by Carles Puigdemont, President-Elect of Catalonia Lodged 1 March 2018 PUIGDEMONT -v- SPAIN SUMMARY:
Optional Protocol to the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights Application against Spain by Carles Puigdemont, President-Elect of Catalonia Lodged 1 March 2018 PUIGDEMONT -v- SPAIN SUMMARY:
The Falange Espanola: Spanish Fascism
 Spanish Civil War The Falange Espanola: Spanish Fascism Fascism reared its ugly head. Similar to Nazi party and Italian Fascist party. Anti-parliamentary and sought one-party rule. Not racist but attached
Spanish Civil War The Falange Espanola: Spanish Fascism Fascism reared its ugly head. Similar to Nazi party and Italian Fascist party. Anti-parliamentary and sought one-party rule. Not racist but attached
Unit 16 Spain at the Beginning of the 20 th Century. Social Studies ESO-4
 Unit 16 Spain at the Beginning of the 20 th Century Social Studies ESO-4 Introduction Alfonso XIII's constitutional reign (1902-1923) The Second Republic Bienio Reformista (1931-1933) Opposition to these
Unit 16 Spain at the Beginning of the 20 th Century Social Studies ESO-4 Introduction Alfonso XIII's constitutional reign (1902-1923) The Second Republic Bienio Reformista (1931-1933) Opposition to these
Section 1: Dictators and War
 Section 1: Dictators and War Objectives: Explain how dictators and militarist regimes arose in several countries in the 1930s. Summarize the actions taken by aggressive regimes in Europe and Asia. Analyze
Section 1: Dictators and War Objectives: Explain how dictators and militarist regimes arose in several countries in the 1930s. Summarize the actions taken by aggressive regimes in Europe and Asia. Analyze
The French Revolution Absolutism monarchs didn t share power with a counsel or parliament--
 The French Revolution Absolutism monarchs didn t share power with a counsel or parliament-- The Seigneurial System method of land ownership and organization Peasant labor Louis XIV Ruled from 1643 1715
The French Revolution Absolutism monarchs didn t share power with a counsel or parliament-- The Seigneurial System method of land ownership and organization Peasant labor Louis XIV Ruled from 1643 1715
Judeo-Christian and Greco-Roman Perspectives
 STANDARD 10.1.1 Judeo-Christian and Greco-Roman Perspectives Specific Objective: Analyze the similarities and differences in Judeo-Christian and Greco-Roman views of law, reason and faith, and duties of
STANDARD 10.1.1 Judeo-Christian and Greco-Roman Perspectives Specific Objective: Analyze the similarities and differences in Judeo-Christian and Greco-Roman views of law, reason and faith, and duties of
INTERIM REPORT. Catalonia Regional Elections 21st December 2017
 INTERIM REPORT Catalonia Regional Elections 21st December 2017 Dr John Ault 22 nd December 2017 Catalonia Regional Elections 21 st December 2017 Interim Report on Election Research Objectives 1. To objectively
INTERIM REPORT Catalonia Regional Elections 21st December 2017 Dr John Ault 22 nd December 2017 Catalonia Regional Elections 21 st December 2017 Interim Report on Election Research Objectives 1. To objectively
GA-4:SPECIAL POLITICAL AND DECOLONIZATION COMMITTEE
 KALMUN 2018 CHAIR REPORT GA-4:SPECIAL POLITICAL AND DECOLONIZATION COMMITTEE AGENDA ITEM 1: Measures to combat separatist movements based on ethnicity with a special emphasis on the question of people
KALMUN 2018 CHAIR REPORT GA-4:SPECIAL POLITICAL AND DECOLONIZATION COMMITTEE AGENDA ITEM 1: Measures to combat separatist movements based on ethnicity with a special emphasis on the question of people
Declaration by Spain on Democracy and the Rule of Law in Spain Session of the OSCE Permanent Council Vienna, 5 October 2017
 MINISTERIO DE ASUNTOS EXTERIORES Y DE COOPERACIÓN REPRESENTACIÓN PERMANENTE DE ESPAÑA ANTE LA OSCE, VIENA Declaration by Spain on Democracy and the Rule of Law in Spain Session of the OSCE Permanent Council
MINISTERIO DE ASUNTOS EXTERIORES Y DE COOPERACIÓN REPRESENTACIÓN PERMANENTE DE ESPAÑA ANTE LA OSCE, VIENA Declaration by Spain on Democracy and the Rule of Law in Spain Session of the OSCE Permanent Council
Content Statement/Learning Goal:
 Ch 6-3 Questions Content Statement/Learning Goal: Explain how Enlightenment ideas influenced the American Revolution, French Revolution and Latin American wars for Independence. Napoleon Bonaparte Coup
Ch 6-3 Questions Content Statement/Learning Goal: Explain how Enlightenment ideas influenced the American Revolution, French Revolution and Latin American wars for Independence. Napoleon Bonaparte Coup
Napoleon. Global History and Geography II
 Global History and Geography II Napoleon Name: Date: In 1799, a thirty-year-old general named Napoleon Bonaparte forced the Directory to resign. He took control of the government with the backing of the
Global History and Geography II Napoleon Name: Date: In 1799, a thirty-year-old general named Napoleon Bonaparte forced the Directory to resign. He took control of the government with the backing of the
Nationalism movement wanted to: UNIFICATION: peoples of common culture from different states were joined together
 7-3.2 Analyze the effects of the Napoleonic Wars on the development and spread of nationalism in Europe, including the Congress of Vienna, the revolutionary movements of 1830 and 1848, and the unification
7-3.2 Analyze the effects of the Napoleonic Wars on the development and spread of nationalism in Europe, including the Congress of Vienna, the revolutionary movements of 1830 and 1848, and the unification
Spain feels Franco's legacy 40 years after his death
 Cookies on the BBC website The BBC has updated its cookie policy. We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. This includes cookies from third party social media websites
Cookies on the BBC website The BBC has updated its cookie policy. We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. This includes cookies from third party social media websites
Ascent of the Dictators. Mussolini s Rise to Power
 Ascent of the Dictators Mussolini s Rise to Power Benito Mussolini was born in Italy in 1883. During his early life he worked as a schoolteacher, bricklayer, and chocolate factory worker. In December 1914,
Ascent of the Dictators Mussolini s Rise to Power Benito Mussolini was born in Italy in 1883. During his early life he worked as a schoolteacher, bricklayer, and chocolate factory worker. In December 1914,
A Brief History of the Spanish Civil War
 A Brief History of the Spanish Civil War The Spanish Civil War (1936-39), pitted the right wing Nationalists, who received support from Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany, against the leftist Republicans,
A Brief History of the Spanish Civil War The Spanish Civil War (1936-39), pitted the right wing Nationalists, who received support from Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany, against the leftist Republicans,
Obtaining Information About Totalitarian States in Europe
 STUDENT HANDOUT A 1. Carefully read the secret information below. It relates to Placard A in the exhibit. During the A. Say yes and secretly give them the information below without letting the government
STUDENT HANDOUT A 1. Carefully read the secret information below. It relates to Placard A in the exhibit. During the A. Say yes and secretly give them the information below without letting the government
The Spanish Political System
 POL 3107 COMPARATIVE GOVERNMENT AND POLITICS The Spanish Political System Dr. Miguel A. Martínez City University of Hong Kong FROM DICTATORSHIP TO DEMOCRACY: REGIME CHANGE AND INSTITUTIONAL DESIGN General
POL 3107 COMPARATIVE GOVERNMENT AND POLITICS The Spanish Political System Dr. Miguel A. Martínez City University of Hong Kong FROM DICTATORSHIP TO DEMOCRACY: REGIME CHANGE AND INSTITUTIONAL DESIGN General
The French Revolution THE EUROPEAN MOMENT ( )
 The French Revolution THE EUROPEAN MOMENT (1750 1900) Quick Video 1 The French Revolution In a Nutshell Below is a YouTube link to a very short, but very helpful introduction to the French Revolution.
The French Revolution THE EUROPEAN MOMENT (1750 1900) Quick Video 1 The French Revolution In a Nutshell Below is a YouTube link to a very short, but very helpful introduction to the French Revolution.
Lecture Outline, The French Revolution,
 Lecture Outline, The French Revolution, 1789-1799 A) Causes growth of "liberal" public opinion the spread of Enlightenment ideas re. rights, liberty, limited state power, need for rational administrative
Lecture Outline, The French Revolution, 1789-1799 A) Causes growth of "liberal" public opinion the spread of Enlightenment ideas re. rights, liberty, limited state power, need for rational administrative
The Rise of Fascism. AP World History Chapter 21 The Collapse and Recovery of Europe ( s)
 The Rise of Fascism AP World History Chapter 21 The Collapse and Recovery of Europe (1914-1970s) New Forms of Government After WWI: Germany, Italy, and Russia turned to a new form of dictatorship = totalitarianism
The Rise of Fascism AP World History Chapter 21 The Collapse and Recovery of Europe (1914-1970s) New Forms of Government After WWI: Germany, Italy, and Russia turned to a new form of dictatorship = totalitarianism
Name Class Date. The French Revolution and Napoleon Section 3
 Name Class Date Section 3 MAIN IDEA Napoleon Bonaparte rose through military ranks to become emperor over France and much of Europe. Key Terms and People Napoleon Bonaparte ambitious military leader who
Name Class Date Section 3 MAIN IDEA Napoleon Bonaparte rose through military ranks to become emperor over France and much of Europe. Key Terms and People Napoleon Bonaparte ambitious military leader who
Prelude to War. The Causes of World War II
 Prelude to War The Causes of World War II The Treaty of Versailles Harsh, bitter treaty that ended WWI Germany must: Accept responsibility for WWI Pay war reparations to Allies Demilitarize the Rhineland
Prelude to War The Causes of World War II The Treaty of Versailles Harsh, bitter treaty that ended WWI Germany must: Accept responsibility for WWI Pay war reparations to Allies Demilitarize the Rhineland
FROM THE PARLIAMENTARY BUREAU RESOLUTION MOTIONS. Declaration of the representatives of Catalonia
 FROM THE PARLIAMENTARY BUREAU Lluís M. Corominas i Díaz, president del Grup Parlamentari de Junts pel Sí, Mar- ta Rovira i Vergés, portaveu del Grup Parlamentari de Junts pel Sí, Mireia Boya e Busquet,
FROM THE PARLIAMENTARY BUREAU Lluís M. Corominas i Díaz, president del Grup Parlamentari de Junts pel Sí, Mar- ta Rovira i Vergés, portaveu del Grup Parlamentari de Junts pel Sí, Mireia Boya e Busquet,
The French Revolution and Napoleon. ( ) Chapter 11
 The French Revolution and Napoleon (1789-1815) Chapter 11 Main Ideas Social inequality & economic problems contributed to the French Revolution Radical groups controlled the Revolution Revolution allowed
The French Revolution and Napoleon (1789-1815) Chapter 11 Main Ideas Social inequality & economic problems contributed to the French Revolution Radical groups controlled the Revolution Revolution allowed
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The Age of Napoleon
 The Age of Napoleon Objectives Understand Napoleon s rise to power and why the French strongly supported him. Explain how Napoleon built an empire and what challenges the empire faced. Analyze the events
The Age of Napoleon Objectives Understand Napoleon s rise to power and why the French strongly supported him. Explain how Napoleon built an empire and what challenges the empire faced. Analyze the events
Obtaining Information About Totalitarian States in Europe
 STUDENT HANDOUT A 1. Carefully read the secret information below. It relates to Placard A in the exhibit. During the A. Say yes and secretly give them the information below without letting the government
STUDENT HANDOUT A 1. Carefully read the secret information below. It relates to Placard A in the exhibit. During the A. Say yes and secretly give them the information below without letting the government
Extra Credit. 1. What Estate held high offices in army, government & courts? 2. Besides the French Revolution, what other event took place in 1789?
 Extra Credit 1. What Estate held high offices in army, government & courts? 2. Besides the French Revolution, what other event took place in 1789? 3. Identify the three groups of people that made up the
Extra Credit 1. What Estate held high offices in army, government & courts? 2. Besides the French Revolution, what other event took place in 1789? 3. Identify the three groups of people that made up the
The French Revolution and Napoleon Section 4. Napoleon s Fall
 Main Idea Napoleon s Fall After defeating Napoleon, the European allies sent him into exile and held a meeting in Vienna to restore order and stability to Europe. 1) Disaster and Defeat /The Russian Campaign
Main Idea Napoleon s Fall After defeating Napoleon, the European allies sent him into exile and held a meeting in Vienna to restore order and stability to Europe. 1) Disaster and Defeat /The Russian Campaign
Briefing Note on the situation in Catalonia (Part III)
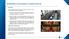 Summary Since the illegal referendum in Catalonia took place, in October 1 st, there have been relevant news along this week: 1) A strike was called in Catalonia to protest against the violent actions
Summary Since the illegal referendum in Catalonia took place, in October 1 st, there have been relevant news along this week: 1) A strike was called in Catalonia to protest against the violent actions
European Parliament resolution of 16 February 2012 on the situation in Syria (2012/2543(RSP)) The European Parliament,
 European Parliament resolution of 16 February 2012 on the situation in Syria (2012/2543(RSP)) The European Parliament, having regard to its previous resolutions on Syria, having regard to the Foreign Affairs
European Parliament resolution of 16 February 2012 on the situation in Syria (2012/2543(RSP)) The European Parliament, having regard to its previous resolutions on Syria, having regard to the Foreign Affairs
MIGRATORY MOVEMENTS IN SPAIN, CATALONIA AND BARCELONA
 MIGRATORY MOVEMENTS IN SPAIN, CATALONIA AND BARCELONA Prepared by: Núria Salvador, Paula Díaz, Laura Alcalá, Paula Saloni and Flors Riera Oral exposition by: Mariona Martínez, Oriol Gaviño, Laura Herrero,
MIGRATORY MOVEMENTS IN SPAIN, CATALONIA AND BARCELONA Prepared by: Núria Salvador, Paula Díaz, Laura Alcalá, Paula Saloni and Flors Riera Oral exposition by: Mariona Martínez, Oriol Gaviño, Laura Herrero,
Ch. 6.3 Radical Period of the French Revolution. leader of the Committee of Public Safety; chief architect of the Reign of Terror
 the right to vote Ch. 6.3 Radical Period of the French Revolution leader of the Committee of Public Safety; chief architect of the Reign of Terror period from September 1793 to July 1794 when those who
the right to vote Ch. 6.3 Radical Period of the French Revolution leader of the Committee of Public Safety; chief architect of the Reign of Terror period from September 1793 to July 1794 when those who
After the French Revolution
 Warm Up In your spiral (page ), answer the following prompt. After the French Revolution (think of the video from last class), what would the people of France be looking for? Napoleon, the Napoleonic Wars,
Warm Up In your spiral (page ), answer the following prompt. After the French Revolution (think of the video from last class), what would the people of France be looking for? Napoleon, the Napoleonic Wars,
AGGRESSORS INVADE NATIONS SECTION 4, CH 15
 AGGRESSORS INVADE NATIONS SECTION 4, CH 15 VOCAB TO KNOW... APPEASEMENT GIVING IN TO AN AGGRESSOR TO KEEP PEACE PUPPET GOVERNMENT - A STATE THAT IS SUPPOSEDLY INDEPENDENT BUT IS IN FACT DEPENDENT UPON
AGGRESSORS INVADE NATIONS SECTION 4, CH 15 VOCAB TO KNOW... APPEASEMENT GIVING IN TO AN AGGRESSOR TO KEEP PEACE PUPPET GOVERNMENT - A STATE THAT IS SUPPOSEDLY INDEPENDENT BUT IS IN FACT DEPENDENT UPON
SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions.
 SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions. a. Examine absolutism through a comparison of the rules of Louis XIV, Tsar Peter the Great, and Tokugawa Ieyasu. Known as the Sun
SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions. a. Examine absolutism through a comparison of the rules of Louis XIV, Tsar Peter the Great, and Tokugawa Ieyasu. Known as the Sun
Department for Legal Affairs
 Emerika Bluma 1, 71000 Sarajevo Tel. 28 35 00 Fax. 28 35 01 Department for Legal Affairs CONSTITUTION OF THE WESTERN- HERZEGOVINA CANTON Official Gazette of the West Herzegovina Canton, 1/96, 2/99, 14/00,
Emerika Bluma 1, 71000 Sarajevo Tel. 28 35 00 Fax. 28 35 01 Department for Legal Affairs CONSTITUTION OF THE WESTERN- HERZEGOVINA CANTON Official Gazette of the West Herzegovina Canton, 1/96, 2/99, 14/00,
Catalonia, a New State within Europe?
 Catalonia, a New State within Europe? October 14, 2015 by Kaisa Stucke of Confluence Investment Management Catalonia, a New State within Europe? Catalonia, a new state within Europe is the slogan of the
Catalonia, a New State within Europe? October 14, 2015 by Kaisa Stucke of Confluence Investment Management Catalonia, a New State within Europe? Catalonia, a new state within Europe is the slogan of the
Fascism is a nationalistic political philosophy which is anti-democratic, anticommunist, and anti-liberal. It puts the importance of the nation above
 1939-1945 Fascism is a nationalistic political philosophy which is anti-democratic, anticommunist, and anti-liberal. It puts the importance of the nation above the rights of the individual. The word Fascism
1939-1945 Fascism is a nationalistic political philosophy which is anti-democratic, anticommunist, and anti-liberal. It puts the importance of the nation above the rights of the individual. The word Fascism
CAUSES OF THE FRENCH REVOLUTION
 REVOLUTIONS CAUSES OF THE FRENCH REVOLUTION During the reign of Louis XIV. A political system known as the Old Regime Divided France into 3 social classes- Estates First Estate Catholic clergy own 10 percent
REVOLUTIONS CAUSES OF THE FRENCH REVOLUTION During the reign of Louis XIV. A political system known as the Old Regime Divided France into 3 social classes- Estates First Estate Catholic clergy own 10 percent
Terrill: World Criminal Justice Systems, 8th Edition
 Terrill: World Criminal Justice Systems, 8th Edition Chapter 2 Multiple Choice 1. The French Constitution contains a Bill of Rights. 2. The president of France is limited to two consecutive terms in office.
Terrill: World Criminal Justice Systems, 8th Edition Chapter 2 Multiple Choice 1. The French Constitution contains a Bill of Rights. 2. The president of France is limited to two consecutive terms in office.
The Rise of Dictators Ch 23-1
 The Rise of Dictators Ch 23-1 The Main Idea The shattering effects of World War I helped set the stage for a new, aggressive type of leader in Europe and Asia. Content Statement/Learning Goal Analyze the
The Rise of Dictators Ch 23-1 The Main Idea The shattering effects of World War I helped set the stage for a new, aggressive type of leader in Europe and Asia. Content Statement/Learning Goal Analyze the
Jordan. Freedom of Expression JANUARY 2012
 JANUARY 2012 COUNTRY SUMMARY Jordan International observers considered voting in the November 2010 parliamentary elections a clear improvement over the 2007 elections, which were widely characterized as
JANUARY 2012 COUNTRY SUMMARY Jordan International observers considered voting in the November 2010 parliamentary elections a clear improvement over the 2007 elections, which were widely characterized as
Absolutism Activity 1
 Absolutism Activity 1 Who is in the painting? What do you think is going on in the painting? Take note of the background. What is the message of the painting? For example, why did the author paint this?
Absolutism Activity 1 Who is in the painting? What do you think is going on in the painting? Take note of the background. What is the message of the painting? For example, why did the author paint this?
Welcome to the World, the Country of Catalonia?
 Welcome to the World, the Country of Catalonia? October 7, 2014 by Bill O'Grady, Kaisa Stucke of Confluence Investment Management On November 9, the Catalonia region of Spain is due to hold a referendum
Welcome to the World, the Country of Catalonia? October 7, 2014 by Bill O'Grady, Kaisa Stucke of Confluence Investment Management On November 9, the Catalonia region of Spain is due to hold a referendum
John Locke Natural Rights- Life, Liberty, and Property Two Treaties of Government
 Enlightenment Enlightenment 1500s Enlightenment was the idea that man could use logic and reason to solve the social problems of the day. Philosophers spread this idea of logic and reason to the people
Enlightenment Enlightenment 1500s Enlightenment was the idea that man could use logic and reason to solve the social problems of the day. Philosophers spread this idea of logic and reason to the people
CHAPTER 23- THE RISE OF FASCISM AND TOTALITARIAN STATES
 CHAPTER 23- THE RISE OF FASCISM AND TOTALITARIAN STATES The world must be made safe for democracy, President Woodrow Wilson declared as the United States entered World War I in 1917. However, the Central
CHAPTER 23- THE RISE OF FASCISM AND TOTALITARIAN STATES The world must be made safe for democracy, President Woodrow Wilson declared as the United States entered World War I in 1917. However, the Central
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The American Revolution and the Constitution
 The American Revolution and the Constitution Objectives Describe characteristics of Britain and its 13 American colonies in the mid-1700s. Outline the events that led to the American Revolution. Summarize
The American Revolution and the Constitution Objectives Describe characteristics of Britain and its 13 American colonies in the mid-1700s. Outline the events that led to the American Revolution. Summarize
Unit 5, SSWH 14 b Parliament & the English Monarchy
 Unit 5, SSWH 14 b Parliament & the English Monarchy What effect did the Age of Revolution have on Global Society? SSWH 14 b Identify the causes and results of the revolutions in England (1689), United
Unit 5, SSWH 14 b Parliament & the English Monarchy What effect did the Age of Revolution have on Global Society? SSWH 14 b Identify the causes and results of the revolutions in England (1689), United
The Rise of Dictators Ch 23-1
 The Rise of Dictators Ch 23-1 The Main Idea The shattering effects of World War I helped set the stage for a new, aggressive type of leader in Europe and Asia. Content Statement/Learning Goal Analyze the
The Rise of Dictators Ch 23-1 The Main Idea The shattering effects of World War I helped set the stage for a new, aggressive type of leader in Europe and Asia. Content Statement/Learning Goal Analyze the
B. Directions: Use the words from the sentences to fill in the words in this puzzle. The letters in the box reading down name a part of nationalism.
 Name Date Period Nationalism Puzzle Chapter 22 Activity 64 A. Directions: Write the correct word from the Word Bank to complete each sentence. 1) Customs, religion, music, beliefs, and way of life make
Name Date Period Nationalism Puzzle Chapter 22 Activity 64 A. Directions: Write the correct word from the Word Bank to complete each sentence. 1) Customs, religion, music, beliefs, and way of life make
Explain how dictators and militarist regimes arose in several countries in the 1930s.
 Objectives Explain how dictators and militarist regimes arose in several countries in the 1930s. Summarize the actions taken by aggressive regimes in Europe and Asia. Analyze the responses of Britain,
Objectives Explain how dictators and militarist regimes arose in several countries in the 1930s. Summarize the actions taken by aggressive regimes in Europe and Asia. Analyze the responses of Britain,
Nationalism in Europe Section 1
 Preview Italian Unification Starting Points Map: Europe,1815 Main Idea / Reading Focus Stirrings of Nationalism Quick Facts: Elements of Nationalism The Path Toward Unity Garibaldi and the Red Shirts Preview,
Preview Italian Unification Starting Points Map: Europe,1815 Main Idea / Reading Focus Stirrings of Nationalism Quick Facts: Elements of Nationalism The Path Toward Unity Garibaldi and the Red Shirts Preview,
Vicenç Villatoro The International Significance of Catalan Culture?* 26 May 2011
 Vicenç Villatoro The International Significance of Catalan Culture?* 26 May 2011 Before I begin, may I just briefly tell you about two things that are essential in any conversation: what it is that I want
Vicenç Villatoro The International Significance of Catalan Culture?* 26 May 2011 Before I begin, may I just briefly tell you about two things that are essential in any conversation: what it is that I want
Map: Conversi, Daniele. Ibid. Page XVIII. Chronology:
 PLEASE DO NOT QUOTE OR USE IN ANY FORM. THIS CHAPTER IS COPYRIGHTED. ==================================================== Nations and Nationalisms in Global Perspective: An Encyclopedia of Origins, Development
PLEASE DO NOT QUOTE OR USE IN ANY FORM. THIS CHAPTER IS COPYRIGHTED. ==================================================== Nations and Nationalisms in Global Perspective: An Encyclopedia of Origins, Development
Background Information
 Background Information 1791 The seating of these representatives gives us our modern political terms of Right Wing or Left Wing Legislative Assembly rules France Members with similar political views sat
Background Information 1791 The seating of these representatives gives us our modern political terms of Right Wing or Left Wing Legislative Assembly rules France Members with similar political views sat
Revolutionary France. Legislative Assembly to the Directory ( )
 Revolutionary France Legislative Assembly to the Directory (1791-1798) The Legislative Assembly (1791-92) Consisted of brand new deputies because members of the National Assembly, led by Robespierre, passed
Revolutionary France Legislative Assembly to the Directory (1791-1798) The Legislative Assembly (1791-92) Consisted of brand new deputies because members of the National Assembly, led by Robespierre, passed
Causes of the American Revolution. The American Revolution
 1 Causes of the American Revolution The American Revolution The American Colonists developed 2 A strong sense of autonomy from 1607-1763 a strong sense of self government a different understanding of key
1 Causes of the American Revolution The American Revolution The American Colonists developed 2 A strong sense of autonomy from 1607-1763 a strong sense of self government a different understanding of key
Dictators and Publics
 History 104 Europe from Napoleon to the PRESENT 17 March 2008 Dictators and Publics Olympic Stadium Berlin (1936) Introduction Historians of Europe often refer to the 1930s as a period of democracy in
History 104 Europe from Napoleon to the PRESENT 17 March 2008 Dictators and Publics Olympic Stadium Berlin (1936) Introduction Historians of Europe often refer to the 1930s as a period of democracy in
French Revolution. II. Louis XVI A. Supported the American Revolution 1. This caused hardship on the economy
 1 French Revolution I. 3 estates A. 1 st estate 1. Clergy 5-10% of the land B. 2 nd estate 1. Nobles 25% of the land C. 3 rd estate 1. Peasants 40-60% of the land 2. Artisans 3. Bourgeoisie (Middle Class)
1 French Revolution I. 3 estates A. 1 st estate 1. Clergy 5-10% of the land B. 2 nd estate 1. Nobles 25% of the land C. 3 rd estate 1. Peasants 40-60% of the land 2. Artisans 3. Bourgeoisie (Middle Class)
From 1789 to 1804, France experienced revolutionary changes that transformed France from an absolute monarchy to a republic to an empire
 From 1789 to 1804, France experienced revolutionary changes that transformed France from an absolute monarchy to a republic to an empire The success of the American Revolution & Enlightenment ideas such
From 1789 to 1804, France experienced revolutionary changes that transformed France from an absolute monarchy to a republic to an empire The success of the American Revolution & Enlightenment ideas such
Dictators and their Publics
 History 104 Europe from Napoleon to the PRESENT 23 March 2009 Dictators and their Publics Olympic Stadium Berlin (1936) Introduction Historians of Europe often refer to the 1930s as a period of democracy
History 104 Europe from Napoleon to the PRESENT 23 March 2009 Dictators and their Publics Olympic Stadium Berlin (1936) Introduction Historians of Europe often refer to the 1930s as a period of democracy
Catalonia and eastern Europe: A false comparison?
 Carme Arenas, Jordi Arrufat, Tomas Kavaliauskas Catalonia and eastern Europe: A false comparison? Published 8 November 2017 Original in Lithuanian First published in Kulturos barai 10/2017 (Lithuanian
Carme Arenas, Jordi Arrufat, Tomas Kavaliauskas Catalonia and eastern Europe: A false comparison? Published 8 November 2017 Original in Lithuanian First published in Kulturos barai 10/2017 (Lithuanian
Chapter 15. Years of Crisis
 Chapter 15 Years of Crisis Section 2 A Worldwide Depression Setting the Stage European nations were rebuilding U.S. gave loans to help Unstable New Democracies A large number of political parties made
Chapter 15 Years of Crisis Section 2 A Worldwide Depression Setting the Stage European nations were rebuilding U.S. gave loans to help Unstable New Democracies A large number of political parties made
JANUARY 2017 COUNTRY SUMMARY. Gambia
 JANUARY 2017 COUNTRY SUMMARY Gambia The December 2106 presidential election, won by opposition coalition leader Adama Barrow, brought hope for improved respect for human rights and the rule of law. Barrow
JANUARY 2017 COUNTRY SUMMARY Gambia The December 2106 presidential election, won by opposition coalition leader Adama Barrow, brought hope for improved respect for human rights and the rule of law. Barrow
Law 19/2017, of 6 September, on the Referendum on Selfdetermination
 Only the official text in Catalan language is authentic Law 19/2017, of 6 September, on the Referendum on Selfdetermination Procedure 202-00065/11 Passed by: Plenary Assembly Session 42, 06.09.2017, DSPC-P
Only the official text in Catalan language is authentic Law 19/2017, of 6 September, on the Referendum on Selfdetermination Procedure 202-00065/11 Passed by: Plenary Assembly Session 42, 06.09.2017, DSPC-P
Bowie State University Police Department General Order
 Bowie State University Police Department General Order Subject: Laws and Rules of Arrest Number: 2 Effective Date: July 2003 Rescinds: N/A Approved: Acting Director Roderick C. Pullen This article contains
Bowie State University Police Department General Order Subject: Laws and Rules of Arrest Number: 2 Effective Date: July 2003 Rescinds: N/A Approved: Acting Director Roderick C. Pullen This article contains
The Spanish American-War 4 Causes of the War: Important Events 1/7/2018. Effects of the Spanish American War
 The Spanish American-War 4 Causes of the War: Sugar (Economic) Spanish Cruelties (Humanitarian) The Sinking of the USS Maine (Self-Defense/National Pride) Spanish Brutalities and Yellow Journalism (Political
The Spanish American-War 4 Causes of the War: Sugar (Economic) Spanish Cruelties (Humanitarian) The Sinking of the USS Maine (Self-Defense/National Pride) Spanish Brutalities and Yellow Journalism (Political
The French Revolution establishes a new political order, Napoleon Bonaparte gains and loses an empire, and European states forge a balance of power.
 SLIDE 1 Chapter 23 The French Revolution and Napoleon, 1789 1815 The French Revolution establishes a new political order, Napoleon Bonaparte gains and loses an empire, and European states forge a balance
SLIDE 1 Chapter 23 The French Revolution and Napoleon, 1789 1815 The French Revolution establishes a new political order, Napoleon Bonaparte gains and loses an empire, and European states forge a balance
AMERICA AND THE WORLD. Chapter 13 Section 1 US History
 AMERICA AND THE WORLD Chapter 13 Section 1 US History AMERICA AND THE WORLD THE RISE OF DICTATORS MAIN IDEA Dictators took control of the governments of Italy, the Soviet Union, Germany, and Japan End
AMERICA AND THE WORLD Chapter 13 Section 1 US History AMERICA AND THE WORLD THE RISE OF DICTATORS MAIN IDEA Dictators took control of the governments of Italy, the Soviet Union, Germany, and Japan End
(3) parliamentary democracy (2) ethnic rivalries
 1) In the Soviet Union, Joseph Stalin governed by means of secret police, censorship, and purges. This type of government is called (1) democracy (2) totalitarian 2) The Ancient Athenians are credited
1) In the Soviet Union, Joseph Stalin governed by means of secret police, censorship, and purges. This type of government is called (1) democracy (2) totalitarian 2) The Ancient Athenians are credited
Catalonia s Troubled Relationship with Spain
 A PREMIER UNDERGRADUATE THINK-TANK www.queensglobalmarkets.ca NOVEMBER 2017 Contributors Dirong Wen Grant Kavanagh Gavrilo Randjelovic Ethan Urbankiewicz Simone Aria Queen s Global Markets (QGM) is a premier
A PREMIER UNDERGRADUATE THINK-TANK www.queensglobalmarkets.ca NOVEMBER 2017 Contributors Dirong Wen Grant Kavanagh Gavrilo Randjelovic Ethan Urbankiewicz Simone Aria Queen s Global Markets (QGM) is a premier
Georgia High School Graduation Test Tutorial. World History from World War I to World War II
 Georgia High School Graduation Test Tutorial World History from World War I to World War II Causes of World War I 1. Balkan Nationalism Causes of World War I 2. Entangled Alliances Causes of World War
Georgia High School Graduation Test Tutorial World History from World War I to World War II Causes of World War I 1. Balkan Nationalism Causes of World War I 2. Entangled Alliances Causes of World War
Mariano Rajoy s People s Party emerges strengthened after the parliamentary elections in Spain.
 parliamentary elections in spain European Elections monitor SUMMARY 1) Analysis : Page 01 2) Résults : Page 03 Mariano Rajoy s People s Party emerges strengthened after the parliamentary elections in Spain.
parliamentary elections in spain European Elections monitor SUMMARY 1) Analysis : Page 01 2) Résults : Page 03 Mariano Rajoy s People s Party emerges strengthened after the parliamentary elections in Spain.
Introduction to World War II By USHistory.org 2017
 Name: Class: Introduction to World War II By USHistory.org 2017 World War II was the second global war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. The war involved a majority of the world s countries, and it is considered
Name: Class: Introduction to World War II By USHistory.org 2017 World War II was the second global war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. The war involved a majority of the world s countries, and it is considered
Chapter 16: Attempts at Liberty
 Chapter 16: Attempts at Liberty 18 th Century Few people enjoyed such rights as, and the pursuit of ; and absolutism was the order of the day. The desire for personal and political liberty prompted a series
Chapter 16: Attempts at Liberty 18 th Century Few people enjoyed such rights as, and the pursuit of ; and absolutism was the order of the day. The desire for personal and political liberty prompted a series
Revolution and Nationalism
 Revolution and Nationalism 1900-1939 Revolutions in Russia Section 1 Long-term social unrest in Russia exploded in revolution, and ushered in the first Communist government. Czars Resist Change Romanov
Revolution and Nationalism 1900-1939 Revolutions in Russia Section 1 Long-term social unrest in Russia exploded in revolution, and ushered in the first Communist government. Czars Resist Change Romanov
RISE OF DICTATORSHIP IN EUROPE
 7 RISE OF DICTATORSHIP IN EUROPE Q.1. (A) Complete the following statements by choosing appropriate alternatives from those given in the brackets : *1. Italy had a hope of acquiring the Italian speaking
7 RISE OF DICTATORSHIP IN EUROPE Q.1. (A) Complete the following statements by choosing appropriate alternatives from those given in the brackets : *1. Italy had a hope of acquiring the Italian speaking
WW II. The Rise of Dictators. Stalin in USSR 2/9/2016
 WW II The Rise of Dictators Benito Mussolini: founder of the Fascist Party in Italy. Fascism is an intense form of nationalism, the nation before the individual. Anti-communist Blackshirts, fascist militia
WW II The Rise of Dictators Benito Mussolini: founder of the Fascist Party in Italy. Fascism is an intense form of nationalism, the nation before the individual. Anti-communist Blackshirts, fascist militia
What is Totalitarianism?
 What is Totalitarianism? A form of government in which all social, political, economic, intellectual, cultural, and spiritual activities are controlled by the rulers. The ruler is an absolute dictator.
What is Totalitarianism? A form of government in which all social, political, economic, intellectual, cultural, and spiritual activities are controlled by the rulers. The ruler is an absolute dictator.
Situation of human rights in the Islamic Republic of Iran
 United Nations A/C.3/70/L.45 General Assembly Distr.: Limited 2 November 2015 Original: English Seventieth session Third Committee Agenda item 72 (c) Promotion and protection of human rights: human rights
United Nations A/C.3/70/L.45 General Assembly Distr.: Limited 2 November 2015 Original: English Seventieth session Third Committee Agenda item 72 (c) Promotion and protection of human rights: human rights
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Chapter 12, Section 2 For use with textbook pages 371 376 REACTION AND REVOLUTION KEY TERMS conservatism a political philosophy based on tradition and social stability (page 372) principle of intervention
Chapter 12, Section 2 For use with textbook pages 371 376 REACTION AND REVOLUTION KEY TERMS conservatism a political philosophy based on tradition and social stability (page 372) principle of intervention
Speech by the President of the Government of Catalonia, Carles Puigdemont
 Speech by the President of the Government of Catalonia, Carles Puigdemont Brussels, 24 January 2017 Just like Minister Romeva and Vice-president Junqueras, I would like to thank you for being here with
Speech by the President of the Government of Catalonia, Carles Puigdemont Brussels, 24 January 2017 Just like Minister Romeva and Vice-president Junqueras, I would like to thank you for being here with
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 3 The Rise of Napoleon and the Napoleonic Wars ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What causes revolution? How does revolution change society? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary capable having or showing ability
Lesson 3 The Rise of Napoleon and the Napoleonic Wars ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What causes revolution? How does revolution change society? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary capable having or showing ability
to support an independent and comprehensive investigation into the Violation of Human Rights that took place in Spain on October 1, 2017,
 Barcelona, December 29, 2017 The present complaint, carried out by Col lectiu Praga 1, is signed by 628 Jurists to demonstrate to the various International Mechanisms for the Protection of Human Rights,
Barcelona, December 29, 2017 The present complaint, carried out by Col lectiu Praga 1, is signed by 628 Jurists to demonstrate to the various International Mechanisms for the Protection of Human Rights,
The Internal Conflict in Spain: The case of Catalonia
 The Internal Conflict in Spain: The case of Catalonia Christos Anastasios Tzagkas Aristotle University of Thessaloniki Historical Background ºCatalonia is one of the autonomous regions of the Spanish state.
The Internal Conflict in Spain: The case of Catalonia Christos Anastasios Tzagkas Aristotle University of Thessaloniki Historical Background ºCatalonia is one of the autonomous regions of the Spanish state.
Section 1: Dictators & Wars
 Chapter 23: The Coming of War (1931-1942) Section 1: Dictators & Wars Objectives Explain how dictators and militarist regimes arose in several countries in the 1930s. Summarize the actions taken by aggressive
Chapter 23: The Coming of War (1931-1942) Section 1: Dictators & Wars Objectives Explain how dictators and militarist regimes arose in several countries in the 1930s. Summarize the actions taken by aggressive
The Rise of Dictators. The totalitarian states did away with individual freedoms.
 The Rise of Dictators The totalitarian states did away with individual freedoms. The Rise of Dictators (cont.) Many European nations became totalitarian states in which governments controlled the political,
The Rise of Dictators The totalitarian states did away with individual freedoms. The Rise of Dictators (cont.) Many European nations became totalitarian states in which governments controlled the political,
Essential Question: What were the important causes & effects of the French Revolution?
 Essential Question: What were the important causes & effects of the French Revolution? Do Now On your ipad or blank piece of paper write down one example on what is needed to consider a revolution as successful.
Essential Question: What were the important causes & effects of the French Revolution? Do Now On your ipad or blank piece of paper write down one example on what is needed to consider a revolution as successful.
On your own paper create the following layout LEADER PROBLEMS MAJOR REFORMS
 On your own paper create the following layout LEADER PROBLEMS MAJOR REFORMS EXAMPLES OF TOTALITARIAN RULE Joseph Stalin Benito Mussolini Adolph Hitler Hideki Tojo Francisco Franco Rise of Totalitarianism
On your own paper create the following layout LEADER PROBLEMS MAJOR REFORMS EXAMPLES OF TOTALITARIAN RULE Joseph Stalin Benito Mussolini Adolph Hitler Hideki Tojo Francisco Franco Rise of Totalitarianism
NATIONALISM CASE STUDIES: ITALY AND GERMANY
 NATIONALISM CASE STUDIES: ITALY AND GERMANY NATIONALISM Nationalism is the belief that one s greatest loyalty should not be to a king or an empire but to a nation of people who share a common culture and
NATIONALISM CASE STUDIES: ITALY AND GERMANY NATIONALISM Nationalism is the belief that one s greatest loyalty should not be to a king or an empire but to a nation of people who share a common culture and
