World Conflicts: Asia and the Middle East Afghanistan
|
|
|
- Lora Goodman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 World Conflicts: Asia and the Middle East Afghanistan A country long plagued by foreign occupations, repressive governments, political instability, and warfare, Afghanistan became a center of international attention at the beginning of the twenty-first century. During the 1970's, the Soviet Union established a puppet regime in Afghanistan. After the Soviets withdrew all their military forces in 1989, a communist president stayed in power, while tribal guerrillas continued to fight for the freedom of their country. In 1992 an Islamic government replaced the puppet regime, hut internal strife continued and intensified. The Muslim Taliban controlled most of the country by the beginning of 2001, but resistance forces survived in some areas, chiefly in the north. During the struggle against Soviet occupation, Muslim fighters from other countries had become heavily involved in Afghanistan and the Taliban government was allied with the international radical Muslim group known as al-qaeda, which was led by wealthy Saudi Arabian Osama bin Laden. Terrorists believed to be members of al-qaeda conducted devastating attacks on the United States on September 11, Afterward, when Afghanistan's Taliban regime refused to deliver Osama bin Laden to the United States, large-scale military forces led by the United States invaded Afghanistan and made common cause with the anti-taliban resistance forces within the country. This resulted in the defeat of the Taliban and the establishment of a new government. However, Taliban fighters kept the war going, and the country continued to suffer from political and economic disorder. Afghanistan is strategically situated with Iran on its western border and Pakistan to the east and south. Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, and Tajikistan border Afghanistan on the north. The northeastern tip of Afghanistan touches China. A landlocked country covering 250,000 square miles, Afghanistan has been overrun by foreign armies since antiquity. North of Kabul, the Afghan capital, the Hindu Kush Mountains, reaching altitudes of more than 21,000 feet, provide many safe locations for guerrilla forces. Trade with Pakistan flows through the thirty-five-mile-long Khyber Pass. The Pakistani border region has provided a haven for munitions smuggling throughout the years of warfare. Kabul, which had an estimated population of 1.5 million people at the end of 2001, has been the capital of Afghanistan since When the Soviet forces left Afghanistan in 1989, the city was still whole and beautiful. As most of the fighting up until then had occurred in the countryside, Kabul remained relatively untouched. Afterward, however, fighting became concentrated in and around Kabul, as guerrilla leaders fought for control of the capital. The city started to be ravaged by bombings, gunfire, and constant bombardment. By 1998 Kabul was divided into sections that represented different controlling factions. Virtually no area of Kabul escaped attack. In late 2001 the city began suffering further damage in the war between the Taliban and forces allied with the United States. Half of Afghanistan's people speak Dari (Afghan Persian), 35 percent Pushtu, 11 percent Turkic languages (primarily Uzbek and Turkmen), and 4 percent more than thirty other, minor languages (primarily Baluohi and Pashai). Bilingualism is prevalent throughout the country. With so many different languages and tribal allegiances, it has been difficult for the Afghan people to unite under one government.
2 Although no fully accurate census of the Afghan population has ever been taken, the estimated population of the country in 2002 was 22,813,000, not including approximately 2,000,000 Afghan refugees believed to be in Pakistan and another 2,000,000 refugees in Iran. Approximately 38 percent of Afghanistan's population was Pashtun, 25 percent Tajiki, 6 percent Uzbek, and 19 percent Hazara, with other minor ethnic groups making up the rest. The country's predominant religion is Islam, with 84 percent of the people practicing Sunni Muslims and 15 percent Shiite Muslims. Early History Known in ancient times as Ariana or Bactria and in the Middle Ages as Khorasan, Afghanistan was long used as an invasion route by outsiders. Darius I, the Persian emperor, conquered parts of what is now Afghanistan in the sixth century b.c.e. Alexander the Great of Macedonia conquered the country three centuries later on his march to India. Foreign empires, local emirs, and kings ruled until the eighteenth century. The classical Bactria was the home of the prophet Zoroaster. The seventh century rise of Islam and the subsequent Muslim conquests changed the ancient world. Several powerful kingdoms disappeared. An Arab army invaded Afghanistan in 652, and many people converted to Islam. In 1219 Genghis Khan invaded Afghanistan. Several other conquerors came to the country over the next few centuries. Afghanistan also saw the rise of some ethnic rulers during these centuries. Although no boundaries were established for Afghanistan until the nineteenth century, modern united Afghanistan was created in 1747, when the Afghans assembled at Kandahar and chose Ahmad Khan Sadozai as their shah. Ahmad Shah had a vision of uniting the Pushtu speaking tribes, and he changed his tribal name from Abdalie to Durrani. His reign and that of most of his successors was plagued by uprisings by the various chieftains. The Sadozai kingdom came to an end in the nineteenth century. International Domination Afghanistan became the focus of international conflict in the nineteenth century. The British sought to protect India from the Russians. In an effort to stop the Russians, Britain brought pressure on Afghanistan, which resulted in two British-Afghan wars, one from 1839 to 1842 and the other from 1878 to British forces first pushed into Afghanistan in 1839, taking Kandahar and Kabul. Tribal opposition led to the withdrawal of the troops in During this withdrawal, almost all the British troops were killed by Afghan tribal warriors. The Second Afghan War erupted in 1878 over British concerns about negotiations between Shir Ali Khan, who ruled Afghanistan from 1863 to 1878, and the Russians. Once again, Great Britain was afraid of Russian interference with the Indian border. The conflict ended when Abdur Rahman Khan became Afghanistan's ruler in He ruled until 1901, promoting the idea of national unity and diminishing the power of the warlike tribes. In 1893 he talked with the British and established the Durand Line, the boundary between Afghanistan and Pakistan that remained into the late twentieth century. Habibullah Khan reigned next. He succeeded in keeping Afghanistan neutral during
3 World War I. The British retained control over Afghanistan's foreign relations until Modern Afghanistan The Third Afghan War with Britain occurred in At this time Britain gave up any interest in Afghanistan's external or internal relations. Amanullah Khan, who reigned from , promoted many reforms in Afghanistan. He wanted a more efficient administration, a constitution, and a modern social structure. His plans outraged many of the traditional religious and tribal leaders. Kabul was seized by Afghan rebels in 1929, and Amanullah abdicated and left the country. Nadir Shah Ghazi became the new ruler. A constitution was adopted, but internal strife resulted in his assassination in Mohammed Zahir Shah, Nadir Shah Ghazi's oldest son, was declared king upon Nadir's death. Mohammed's uncles and cousins were influential throughout the country during this time. The traditional policy of isolation was abandoned, and the first factories, roads, and irrigation projects were begun. Afghanistan remained neutral in World War II, but the resulting lack of trade in the country strained the economy. Mohammed Daud became premier in During the next decade, the government was run by Mohammed Zahir Shah, Mohammed Daud, and Mohammed Naim. By the late 1950's, new social and political reforms had been instituted. In 1963 Mohammed Daud resigned and was replaced by Mohammed Yusuf, the first nonroyal premier in office. A new constitution was adopted in This constitution provided for parliamentary government and the basic rights of the people. The government functioned inefficiently during this democratic period, because no political parties were established. Soviet Occupation A military coup led by Mohammed Daud ushered in a republic in Daud was named president and premier of the new republic. He declared the 1964 constitution invalid and replaced it with a new constitution in 1977 that supported the presidential form of government in a one-party state. Daud's control over the army weakened, and in April, 1978, another military revolt overthrew his government. Daud was killed. The days of April 27-28, 1978, known as the Great Saur Revolution, established the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan and nullified the 1977 constitution. The People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan (PDPA) became the only legal party. Nur Mohammed Taraki became president of the council and premier. The Soviet Union extended its support, and a treaty of friendship was signed in December, The Muslim tribal communities were not happy with the new government, and they soon revolted. The Soviet Union airlifted guns and military equipment into the capital. Infighting also occurred in the PDPA. In September, 1979, Taraki was ousted from power and replaced by Hafizullah Amin. At that time the Soviet Union intervened when it became obvious that the new ruler was no more effective than the last. Thirty thousand Soviet troops invaded Afghanistan in December, Amin was executed, and the Soviet Union gained control of the government. Babrak Karmal was installed as president on December 27, Afghan resistance
4 to Soviet domination was widespread. Eventually the Soviet troops numbered 115,000. Over five million Afghans left the country; three million sought refuge in Pakistan and two million fled to Iran. The rebel guerrillas, known as mujaheddin, or "holy warriors," represented independent tribes with centuries of antagonism toward one another. The main strength of the guerrilla fighters was their knowledge of the countryside. The United States and China provided arms to the Afghan guerrilla forces through Pakistan to assist with their fight against the Soviet Union. However, guerrilla leadership and the power of the field commanders grew more quickly than the power of the political leaders. By 1986 the Soviets desired to withdraw from the country. At this time the question of leadership within the country was unanswered. Karmal's faction of the PDPA, Parcham (flag), struggled for control of the party against the Khalq (masses). The Khalq had been the dominant force before the Great Saur Revolution. A new constitution was introduced in 1985 to ensure Parcham's grip on the party. Political Shifts In May, 1986, another Parcham supporter, Major General Mohammad Najibullah, became general secretary of the PDPA and later Afghanistan's president. Karmal was relieved of his position. Najibullah, the former head of the Afghan secret police, attempted to bring about national reconciliation but failed. The mujaheddin continued their attacks against the Soviet-backed regime in the Afghan countryside, where the guerrillas still had the advantage. In November, 1987, another constitution was adopted that greatly increased Najibullah's power. He was granted the command of the armed forces, the right of approval or veto over all laws, the ability to appoint all high-ranking officials, and the power to convene or dissolve the national assembly. The country was also renamed the Republic of Afghanistan. In April, 1988, the United Nations (U.N.) mediated an agreement, providing for the withdrawal of Soviet troops, an end to Pakistan's rebel support, and the repatriation of refugees. Although the Soviets completed their troop withdrawal in February, 1989, the divisions between the rebels continued to cause fighting against the government of Najibullah. Assisted by weapons left by the departing Soviet troops, the Najibullah government managed to stay in power for three more years. In response to an attempted coup and declining Soviet support, Najibullah and his government proposed a series of constitutional amendments. These amendments were adopted in May, The power of the PDPA was reduced, and the socialist orientation of the country was lessened. Post-Soviet Conflict Communist president Najibullah resigned on April 16, The guerrilla forces, headed by the Tajik war hero Ahmed Shah Masood, were advancing on Kabul. On April 28, the rebels gained control, ending fourteen years of Soviet-backed regimes. Since 1979, more than two million Afghans had been killed while six million had left the country. Clashes between moderates and Islamic fundamentalist forces began to occur soon
5 after the takeover. Each mujaheddin guerrilla leader wanted to succeed Najibullah. The mujaheddin leaders established a fifty-one member ruling council. The ruling council chose the interim president Sibghatullah Mujaddidi to run the government from April to June. One of the Islamic factions, Hizbi Islamic Gulbuddin, led by Gulbuddin Hikmatyar would not participate in the new Islamic government. Hikmatyar maintained that too many of Najibullah's officers had been pardoned. Hikmatyar took his troops to the south and proceeded to attack Kabul. General Abdul Rashid Dostam, a defector from Najibullah's army and leader of the Hizbi Wahdat Islami, withdrew from the ruling council and also began to attack Kabul. On June 28, 1992, Burhanuddin Rabbani, one of the guerrilla leaders and founder of the Jamiat-I Islami political party, became president. The mujaheddin had retaken Afghanistan from the political leaders who were backed by the Soviet Union. Although the Muslim fighters had conquered the capital, fierce fighting continued around Kabul and other places in the country. At least nine different rebel groups began fighting each other. An attempt at peace was made on March 7, 1993, when President Rabbani and Gulbuddin Hikmatyar signed an agreement. Hikmatyar was made prime minister designate. The Taliban In 1994 the Muslim student group Taliban became the most powerful group in the war-torn country. The Taliban, consisting of Muslim fundamentalist students and clerics, believed that the ruling Rabbani government was too lenient toward the dissident guerrilla organizations and thought that the continued fighting by these guerrilla organizations stalled any peacekeeping efforts. The Taliban also believed that the government and the people of Afghanistan strayed too far from classic Islamic teachings. Thus, Taliban members believed that they were rescuing their country from both a corrupt government and a false religious orientation. In 1994 the Taliban began a military campaign that resulted in their occupation of half the country by February, They insisted that Afghanistan become an Islamic fundamentalist state and gained increasing control. On September 6, 1995, the city of Herat fell to Taliban forces. The same day that Herat fell, the state controlled Radio Afghanistan announced that Pakistan had financed, directed, and led the Taliban forces into the city. Pakistan had never hidden its involvement in the Afghan civil war. During President Najibullah's term, the United States sent money and arms to the mujaheddin through Pakistan. When the Cold War ended in the early 1990's, Western policy changed. The United States began to seek a peaceful solution to the Afghan unrest. Pakistan continued to support the mujaheddin. By 1996 the Taliban had established a government in Kabul. The Taliban executed former President Najibullah. Strict Islamic rule was imposed and the laws were strictly enforced by armed police. Local Islamic judges handled judicial matters. Punishments were given according to traditional practices, including public executions and amputations of hands and feet. Burhanuddin Rabbani fled to northern Afghanistan, where anti-taliban forces known as the Northern Alliance launched a rebellion. The Taliban continued to receive aid, monetary backing, and moral support from
6 Pakistan. Much of the Taliban philosophy had been developed by Afghan refugees in Pakistan during the years 1979 to Saudi Arabia and some of the Arab Gulf states had also backed the Taliban forces. In the southern Pashtun areas of Afghanistan, the Taliban regime was welcomed because it brought some prospect of peace. The Pashtun people also supported the Taliban as a way to stop the increasing political power of the Tajiks, the Uzbeks, and other non-pashtun controlled parties. The strict Islamic policies enforced by the Taliban in Kabul and Herat outraged the urban population but did not particularly affect the conservative southern Pashtun villages. Iran backed the political leaders of the Northern Alliance who were fighting the Taliban. Other countries that supported the Northern Alliance included Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Russia, and India. The United States continued to distance itself from the Taliban. Western interests and involvement in Afghan affairs had flagged when the Soviet threat was removed. The high cost of maintaining its military forces in Afghanistan played a significant role in the downfall of the Soviet Union. Another problem that Afghans had to overcome was the loss of some foreign aid because of the planting and cultivation of opium poppies. Jalalabad, located east of Kabul near the Pakistani border, was well known for its poppy orchards and misuse of foreign funds throughout the 1990's. In 1993 more than 58,000 acres of poppies were sighted by satellite. Afghanistan became established as a major supplier of heroin. Many countries wanted to see a government emerge that would attempt to control the drug problem. In 1997 the United Nations made a plea to all nations to stop interfering in Afghanistan's internal affairs. Reference was made to the fact that the continuing internal conflict provided a safe haven for international terrorists and criminals. As long as the war continued, the promotion, production, and distribution of heroin would continue unchecked. Afghan violations of human rights were also addressed by the United nations. A special envoy was sent to Afghanistan to assess peacemaking efforts and activities. The strict Taliban regime continued. As an example of the control of the organization, on May 7, 1997, the Taliban announced the criminalization of the use of paper bags, claiming that the bags could contain recycled Korans. The Islamic Sharia law imposed by the Taliban prohibited alcohol, videotapes, music, television, and social activities between the sexes. Women in Afghanistan were not allowed many basic civil liberties and rights. By October, 1997, they had practically been removed from public life. No woman could take a job outside the home or leave the home without a male relative as an escort. Afghan women did not receive adequate medical attention, because they were barred from the main hospitals in Kabul. The despair felt by most Afghan women could not adequately be assessed or expressed as the Taliban's strict rule continued. By January, 1998, Taliban had lost much of its power in the north of the county. The bitter military struggle continued with the return from exile of General Abdul Rashid Dostam from Turkey, who established his former power base. Because of the strict Taliban blockade, many people north of Kabul faced famine conditions in The northern resistance to Taliban control remained intense. The Shiite elements of the Northern Alliance continued to be the most committed to destroying the regime of the Taliban. Burhanuddin Rabbani remained as president.
A Historical Timeline of Afghanistan
 A Historical Timeline of Afghanistan Soviet soldiers in Afghanistan The land that is now Afghanistan has a long history of domination by foreign conquerors and strife among internally warring factions.
A Historical Timeline of Afghanistan Soviet soldiers in Afghanistan The land that is now Afghanistan has a long history of domination by foreign conquerors and strife among internally warring factions.
Islamic Republic of Afghanistan
 National name: Jomhuri-ye Eslami-ye Afghanestan President: Hamid Karzai (2002) Total area: 647,500 sq km Population (2007 est.): 31,889,923 (growth rate: 2.6%); birth rate: 46.2/1000; infant mortality
National name: Jomhuri-ye Eslami-ye Afghanestan President: Hamid Karzai (2002) Total area: 647,500 sq km Population (2007 est.): 31,889,923 (growth rate: 2.6%); birth rate: 46.2/1000; infant mortality
Afghanistan. A Country Profile. Compiled by: Hima Bindu, Intern, CAS
 Afghanistan A Country Profile Compiled by: Hima Bindu, Intern, CAS 2017 Political Geography Afghanistan is a landlocked multi-ethnic country located at the crossroads of South and Central Asia. It lies
Afghanistan A Country Profile Compiled by: Hima Bindu, Intern, CAS 2017 Political Geography Afghanistan is a landlocked multi-ethnic country located at the crossroads of South and Central Asia. It lies
Soviet Afghan Insurgency. Humanitarian Issues Quelling the Insurgency. By: Ansh Patel, McKenna Gillard, and Amruta Ponugupati
 Soviet Afghan Insurgency Humanitarian Issues Quelling the Insurgency By: Ansh Patel, McKenna Gillard, and I. History of the Soviet-Afghan Insurgency The Soviet Afghan Insurgency was centralized in Afghanistan
Soviet Afghan Insurgency Humanitarian Issues Quelling the Insurgency By: Ansh Patel, McKenna Gillard, and I. History of the Soviet-Afghan Insurgency The Soviet Afghan Insurgency was centralized in Afghanistan
ANNEX 5. Public. Chronology of relevant events
 ICC-02/17-7-Anx5 20-11-2017 1/6 NM PT ANNEX 5 Public Chronology of relevant events ICC-02/17-7-Anx5 20-11-2017 2/6 NM PT CHRONOLOGY OF RELEVANT EVENTS In accordance with Regulation 49(3), the Prosecution
ICC-02/17-7-Anx5 20-11-2017 1/6 NM PT ANNEX 5 Public Chronology of relevant events ICC-02/17-7-Anx5 20-11-2017 2/6 NM PT CHRONOLOGY OF RELEVANT EVENTS In accordance with Regulation 49(3), the Prosecution
Who, Where,And When : USSR vs Afghanistan resistance group (80% mujahideen) Front: Mainland of Afghanistan December 1979-February 1989
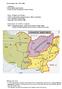 Soviet-Afghan War (1979-1989) Vocabulary: KHAD (Afghan secret police) LCOSF (Limited Contingent of Soviet Forces) Who, Where,And When : USSR vs Afghanistan resistance group (80% mujahideen) Front: Mainland
Soviet-Afghan War (1979-1989) Vocabulary: KHAD (Afghan secret police) LCOSF (Limited Contingent of Soviet Forces) Who, Where,And When : USSR vs Afghanistan resistance group (80% mujahideen) Front: Mainland
International Journal of Multicultural and Multireligious Understanding. Afghanistan: A Study in Internal Conflict and National Cohesion
 Comparative Study of Post-Marriage Nationality Of Women in Legal Systems of Different Countries International Journal of Multicultural and Multireligious Understanding http://ijmmu.com editor@ijmmu.com
Comparative Study of Post-Marriage Nationality Of Women in Legal Systems of Different Countries International Journal of Multicultural and Multireligious Understanding http://ijmmu.com editor@ijmmu.com
Committee: Historical Security Council Topic: The Soviet Invasion of Afghanistan (1979) Committee Directors: Janset Nil Genç, Süha Nurhat
 Committee: Historical Security Council Topic: The Soviet Invasion of Afghanistan (1979) Committee Directors: Janset Nil Genç, Süha Nurhat I. Introduction Wars and conflicts, when looked into, mainly are
Committee: Historical Security Council Topic: The Soviet Invasion of Afghanistan (1979) Committee Directors: Janset Nil Genç, Süha Nurhat I. Introduction Wars and conflicts, when looked into, mainly are
The War Against Terrorism
 The War Against Terrorism Part 2 Dr. János Radványi Radványi Chair in International Security Studies Mississippi State University with Technical Assistance by Tan Tsai, Research Associate Diplomacy and
The War Against Terrorism Part 2 Dr. János Radványi Radványi Chair in International Security Studies Mississippi State University with Technical Assistance by Tan Tsai, Research Associate Diplomacy and
AFGHANISTAN. The Trump Plan R4+S. By Bill Conrad, LTC USA (Ret) October 6, NSF Presentation
 AFGHANISTAN The Trump Plan R4+S By Bill Conrad, LTC USA (Ret) October 6, 2017 --NSF Presentation Battle Company 2 nd of the 503 rd Infantry Regiment 2 Battle Company 2 nd of the 503 rd Infantry Regiment
AFGHANISTAN The Trump Plan R4+S By Bill Conrad, LTC USA (Ret) October 6, 2017 --NSF Presentation Battle Company 2 nd of the 503 rd Infantry Regiment 2 Battle Company 2 nd of the 503 rd Infantry Regiment
Center for Strategic & Regional Studies
 Center for Strategic & Regional Studies Kabul Weekly Analysis-Issue Number 164 (May 7-14, 2016) Weekly Analysis is one of CSRS publications, which significantly analyses weekly economic and political events
Center for Strategic & Regional Studies Kabul Weekly Analysis-Issue Number 164 (May 7-14, 2016) Weekly Analysis is one of CSRS publications, which significantly analyses weekly economic and political events
HUMAN RIGHTS DEFENDERS IN AFGHANISTAN: Civil society destroyed
 HUMAN RIGHTS DEFENDERS IN AFGHANISTAN: Civil society destroyed Two decades of conflict, repression and neglect have had a devastating effect on civil society in Afghanistan. With the virtual collapse of
HUMAN RIGHTS DEFENDERS IN AFGHANISTAN: Civil society destroyed Two decades of conflict, repression and neglect have had a devastating effect on civil society in Afghanistan. With the virtual collapse of
HUMAN RIGHTS DEFENDERS IN AFGHANISTAN:
 HUMAN RIGHTS DEFENDERS IN AFGHANISTAN: Civil society destroyed Costs of war The social costs of two decades of civil war in Afghanistan have been enormous. More than one million civilians are believed
HUMAN RIGHTS DEFENDERS IN AFGHANISTAN: Civil society destroyed Costs of war The social costs of two decades of civil war in Afghanistan have been enormous. More than one million civilians are believed
CultureGram: Afghanistan 2016
 CultureGram: Afghanistan 2016 Land and Climate Located in central Asia, Afghanistan is roughly half the size of Peru and a little smaller than the U.S. state of Texas. Afghanistan is a landlocked country
CultureGram: Afghanistan 2016 Land and Climate Located in central Asia, Afghanistan is roughly half the size of Peru and a little smaller than the U.S. state of Texas. Afghanistan is a landlocked country
World History (Survey) Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present
 World History (Survey) Chapter 33: Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present Section 1: Two Superpowers Face Off The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February
World History (Survey) Chapter 33: Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present Section 1: Two Superpowers Face Off The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February
Unit 7 Station 2: Conflict, Human Rights Issues, and Peace Efforts. Name: Per:
 Name: Per: Station 2: Conflicts, Human Rights Issues, and Peace Efforts Part 1: Vocab Directions: Use the reading below to locate the following vocab words and their definitions. Write their definitions
Name: Per: Station 2: Conflicts, Human Rights Issues, and Peace Efforts Part 1: Vocab Directions: Use the reading below to locate the following vocab words and their definitions. Write their definitions
Putin s Predicament: Russia and Afghanistan after 2014
 Putin s Predicament: Russia and Afghanistan after 2014 Mark N. Katz Asia Policy, Number 17, January 2014, pp. 13-17 (Article) Published by National Bureau of Asian Research DOI: https://doi.org/10.1353/asp.2014.0009
Putin s Predicament: Russia and Afghanistan after 2014 Mark N. Katz Asia Policy, Number 17, January 2014, pp. 13-17 (Article) Published by National Bureau of Asian Research DOI: https://doi.org/10.1353/asp.2014.0009
The new constitution, as adopted on January 4, 2004, At-a-Glance. Official name Islamic Republic of Afghanistan
 At-a-Glance Official name Islamic Republic of Afghanistan Capital Kabul Population 28,513,677 (July 2004 est.) Size 250,001 sq. mi. (647,500 sq. km) Languages Official languages: Pashtu and Dari. Other
At-a-Glance Official name Islamic Republic of Afghanistan Capital Kabul Population 28,513,677 (July 2004 est.) Size 250,001 sq. mi. (647,500 sq. km) Languages Official languages: Pashtu and Dari. Other
Letter from the Director. security council, 1979
 Letter from the Director acronym Soviet security council, 1979 II Position Paper Guidelines Position Paper Guidelines What s it all about? The purpose of a position paper is to display your understanding
Letter from the Director acronym Soviet security council, 1979 II Position Paper Guidelines Position Paper Guidelines What s it all about? The purpose of a position paper is to display your understanding
Resolved: The U.S. should withdraw all regular combat forces from Afghanistan.
 The Final Round 1 Everett Rutan Xavier High School everett.rutan@moodys.com or ejrutan3@acm.org Connecticut Debate Association Darien High School and Glastonbury High School March 7, 2009 Resolved: The
The Final Round 1 Everett Rutan Xavier High School everett.rutan@moodys.com or ejrutan3@acm.org Connecticut Debate Association Darien High School and Glastonbury High School March 7, 2009 Resolved: The
CONFLICT FORMATION AND TRANSFORMATION
 Conflict Formation and Transformation 1 CONFLICT FORMATION AND TRANSFORMATION IN AFGHANISTAN SINCE 1973 DR. MOONIS AHMAR Abstract This paper will examine conflict conflagration in Afghanistan in the light
Conflict Formation and Transformation 1 CONFLICT FORMATION AND TRANSFORMATION IN AFGHANISTAN SINCE 1973 DR. MOONIS AHMAR Abstract This paper will examine conflict conflagration in Afghanistan in the light
Weekly Geopolitical Report
 August 17, 2009 Pakistan and the Death of Baitullah Mehsud Reports indicated that on Aug. 5, Baitullah Mehsud, the notorious leader of the Taliban in Pakistan, died from a U.S. missile strike. In this
August 17, 2009 Pakistan and the Death of Baitullah Mehsud Reports indicated that on Aug. 5, Baitullah Mehsud, the notorious leader of the Taliban in Pakistan, died from a U.S. missile strike. In this
CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web
 Order Code RL30588 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Afghanistan: Current Issues and U.S. Policy Concerns Updated November 15, 2001 Kenneth Katzman Specialist in Middle Eastern Affairs
Order Code RL30588 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Afghanistan: Current Issues and U.S. Policy Concerns Updated November 15, 2001 Kenneth Katzman Specialist in Middle Eastern Affairs
CRS Report for Congress
 Order Code RL30588 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Afghanistan: Post-War Governance, Security, and U.S. Policy Updated April 21, 2005 Kenneth Katzman Specialist in Middle Eastern Affairs
Order Code RL30588 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Afghanistan: Post-War Governance, Security, and U.S. Policy Updated April 21, 2005 Kenneth Katzman Specialist in Middle Eastern Affairs
AFGHANISTAN: THE PAST, THE PRESENT, AND OUR FUTURE
 AFGHANISTAN: THE PAST, THE PRESENT, AND OUR FUTURE Table of Content 1. Afghanistan In the Heart of Asia 2. Demographic Facts about Afghanistan 3. Afghanistan s Historical Timeline 4. From Transition to
AFGHANISTAN: THE PAST, THE PRESENT, AND OUR FUTURE Table of Content 1. Afghanistan In the Heart of Asia 2. Demographic Facts about Afghanistan 3. Afghanistan s Historical Timeline 4. From Transition to
Interview with Ali Ahmad Jalali*
 Volume 93 Number 882 June 2011 Interview with Ali Ahmad Jalali* Distinguished Professor at the National Defense University, Washington, DC. For this issue on understanding armed groups, the Review considered
Volume 93 Number 882 June 2011 Interview with Ali Ahmad Jalali* Distinguished Professor at the National Defense University, Washington, DC. For this issue on understanding armed groups, the Review considered
Afghan Peace Accord (Islamabad Accord) Recalling the glorious success of the epic Jehad waged by the valiant Afghan people against foreign occupation,
 Afghan Peace Accord (Islamabad Accord) Given our submission to the will of Allah Almighty and commitment to seeking guidance from the Holy Quran and Sunnah, Recalling the glorious success of the epic Jehad
Afghan Peace Accord (Islamabad Accord) Given our submission to the will of Allah Almighty and commitment to seeking guidance from the Holy Quran and Sunnah, Recalling the glorious success of the epic Jehad
1. What nineteenth century state was known as the Middle Kingdom to its populace? a. a) China b. b) Japan c. d) Iran d.
 1. What nineteenth century state was known as the Middle Kingdom to its populace? a. a) China b) Japan c. d) Iran d. c) Ottoman Empire 2. Which of the following was a factor in creating China s internal
1. What nineteenth century state was known as the Middle Kingdom to its populace? a. a) China b) Japan c. d) Iran d. c) Ottoman Empire 2. Which of the following was a factor in creating China s internal
Chapter 21: United Nations Good Offices Mission in Afghanistan and Pakistan (UNGOMAP) Adam Baczko and Gilles Dorronsoro
 Chapter 21: United Nations Good Offices Mission in Afghanistan and Pakistan (UNGOMAP) Adam Baczko and Gilles Dorronsoro Introduction On 27 December 1979, Soviet forces invaded Afghanistan, assassinating
Chapter 21: United Nations Good Offices Mission in Afghanistan and Pakistan (UNGOMAP) Adam Baczko and Gilles Dorronsoro Introduction On 27 December 1979, Soviet forces invaded Afghanistan, assassinating
CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web
 Order Code RL30588 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Afghanistan: Current Issues and U.S. Policy Concerns Updated November 15, 2001 Kenneth Katzman Specialist in Middle Eastern Affairs
Order Code RL30588 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Afghanistan: Current Issues and U.S. Policy Concerns Updated November 15, 2001 Kenneth Katzman Specialist in Middle Eastern Affairs
States & Types of States
 States & Types of States Political Geography Nation: a group of people with a common culture - Tightly knit group of people possessing shared cultural beliefs & unity: genous - Ancestry or historical events
States & Types of States Political Geography Nation: a group of people with a common culture - Tightly knit group of people possessing shared cultural beliefs & unity: genous - Ancestry or historical events
CRS Report for Congress
 Order Code RL30588 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Afghanistan: Post-War Governance, Security, and U.S. Policy Updated December 28, 2004 Kenneth Katzman Specialist in Middle Eastern
Order Code RL30588 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Afghanistan: Post-War Governance, Security, and U.S. Policy Updated December 28, 2004 Kenneth Katzman Specialist in Middle Eastern
CRS Report for Congress
 Order Code RL30588 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Afghanistan: Post-War Governance, Security, and U.S. Policy Updated December 16, 2004 Kenneth Katzman Specialist in Middle Eastern
Order Code RL30588 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Afghanistan: Post-War Governance, Security, and U.S. Policy Updated December 16, 2004 Kenneth Katzman Specialist in Middle Eastern
Report for Congress. Afghanistan: Challenges and Options for Reconstructing a Stable and Moderate State. April 24, 2002
 Order Code RL31389 Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Afghanistan: Challenges and Options for Reconstructing a Stable and Moderate State April 24, 2002 Richard P. Cronin Specialist in Asian
Order Code RL31389 Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Afghanistan: Challenges and Options for Reconstructing a Stable and Moderate State April 24, 2002 Richard P. Cronin Specialist in Asian
Positive Vote, Future of Taliban & the Challenges Ahead
 Innovative Research Independent Analysis Informed Opinion Afghanistan Elections 2014 Positive Vote, Future of Taliban & the Challenges Ahead D. Suba Chandran IPCS Special Report # 161 April 2014 AFGHANISTAN
Innovative Research Independent Analysis Informed Opinion Afghanistan Elections 2014 Positive Vote, Future of Taliban & the Challenges Ahead D. Suba Chandran IPCS Special Report # 161 April 2014 AFGHANISTAN
UNITED NATIONS SECURITY COUNCIL
 UNITED NATIONS SECURITY COUNCIL DESCRIPTION OF THE COMMITTEE Under the United Nations Charter, the Security Council is charged with the responsibility of maintaining international peace and security. While
UNITED NATIONS SECURITY COUNCIL DESCRIPTION OF THE COMMITTEE Under the United Nations Charter, the Security Council is charged with the responsibility of maintaining international peace and security. While
26 OCTOBER 2005 culmination of the Bonn process
 Afghanistan: the 26 OCTOBER 2005 culmination of the Bonn process The Afghan parliamentary elections of 18 September 2005 marked the final step in the political process set out in the Bonn Agreement of
Afghanistan: the 26 OCTOBER 2005 culmination of the Bonn process The Afghan parliamentary elections of 18 September 2005 marked the final step in the political process set out in the Bonn Agreement of
Conference Reader. Conference on asylum related questions regarding Afghanistan
 This is project is co-funded by the European Refugee Fund and the Austrian Federal Ministry of the Interior Conference Reader Conference on asylum related questions regarding Afghanistan Vienna, 31.03/01.04.2011
This is project is co-funded by the European Refugee Fund and the Austrian Federal Ministry of the Interior Conference Reader Conference on asylum related questions regarding Afghanistan Vienna, 31.03/01.04.2011
The Reconstruction of Afghanistan: From War to a Dependent Democracy?
 Eurasia R. James Ferguson 2007 Lecture 10: The Reconstruction of Afghanistan: From War to a Dependent Democracy? Topics: - 1. Lessons Unlearnt from Afghanistan s Civil and Proxy Wars (1978-2001) 2. The
Eurasia R. James Ferguson 2007 Lecture 10: The Reconstruction of Afghanistan: From War to a Dependent Democracy? Topics: - 1. Lessons Unlearnt from Afghanistan s Civil and Proxy Wars (1978-2001) 2. The
Clash of Philosophies: 11/10/2010
 1. Notebook Entry: Nationalism Vocabulary 2. What does nationalism look like? EQ: What role did Nationalism play in 19 th century political development? Common Language, Romanticism, We vs. They, Irrational
1. Notebook Entry: Nationalism Vocabulary 2. What does nationalism look like? EQ: What role did Nationalism play in 19 th century political development? Common Language, Romanticism, We vs. They, Irrational
Report for Congress. Afghanistan: Current Issues and U.S. Policy. Updated January 28, 2003
 Order Code RL30588 Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Afghanistan: Current Issues and U.S. Policy Updated January 28, 2003 Kenneth Katzman Specialist in Middle Eastern Affairs Foreign Affairs,
Order Code RL30588 Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Afghanistan: Current Issues and U.S. Policy Updated January 28, 2003 Kenneth Katzman Specialist in Middle Eastern Affairs Foreign Affairs,
The Hot Days of the Cold War
 The Hot Days of the Cold War Brian Frydenborg History 321, Soviet Russia 3/18/02 On my honor, I have neither given nor received any unacknowledged aid on this paper. The origins of the cold war up to 1953
The Hot Days of the Cold War Brian Frydenborg History 321, Soviet Russia 3/18/02 On my honor, I have neither given nor received any unacknowledged aid on this paper. The origins of the cold war up to 1953
Afghanistan: Rebuilding Infrastructure in a Post-Conflict State
 Afghanistan: Rebuilding Infrastructure in a Post-Conflict State GORDON WEYNAND Energy Team Leader Office of Infrastructure & Engineering USAID Bureau for Economic Growth, Agriculture, & Trade [on behalf
Afghanistan: Rebuilding Infrastructure in a Post-Conflict State GORDON WEYNAND Energy Team Leader Office of Infrastructure & Engineering USAID Bureau for Economic Growth, Agriculture, & Trade [on behalf
President Najibullah and the National Reconciliation Policy
 President Najibullah and the National Reconciliation Policy Objectives, operations and obstacles Heela Najibullah Heela Najibullah is a peace and conflict researcher whose book Reconciliation and Social
President Najibullah and the National Reconciliation Policy Objectives, operations and obstacles Heela Najibullah Heela Najibullah is a peace and conflict researcher whose book Reconciliation and Social
Report of the Secretary-General I. INTRODUCTION
 UNITED NATIONS A S General Assembly Security Council Distr. GENERAL A/51/838 16 March 1997 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH GENERAL ASSEMBLY Fifty-first session Agenda item 39 THE SITUATION IN AFGHANISTAN AND ITS IMPLICATIONS
UNITED NATIONS A S General Assembly Security Council Distr. GENERAL A/51/838 16 March 1997 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH GENERAL ASSEMBLY Fifty-first session Agenda item 39 THE SITUATION IN AFGHANISTAN AND ITS IMPLICATIONS
RUSSIA. This issue is for your personal use only. Published monthly in Russian and in English by Trialogue Company Ltd.
 RUSSIA The circulation of this report has been strictly limited to the members of the Trialogue Club International and of the Centre russe d etudes politiques, Geneve. This issue is for your personal use
RUSSIA The circulation of this report has been strictly limited to the members of the Trialogue Club International and of the Centre russe d etudes politiques, Geneve. This issue is for your personal use
Establishment of peace and stability in Afghanistan
 Forum: Issue: Student Officer: Position: The Security Council Establishment of peace and stability in Afghanistan Woo Seong Yoon Deputy President Introduction Afghanistan is situated in the high mountains
Forum: Issue: Student Officer: Position: The Security Council Establishment of peace and stability in Afghanistan Woo Seong Yoon Deputy President Introduction Afghanistan is situated in the high mountains
In 2001, Afghanistan embarked upon a new beginning with the overthrow of the Taliban
 Introduction In 2001, Afghanistan embarked upon a new beginning with the overthrow of the Taliban regime, recognizing anew the contribution of the female half of its society. After years of minimal involvement
Introduction In 2001, Afghanistan embarked upon a new beginning with the overthrow of the Taliban regime, recognizing anew the contribution of the female half of its society. After years of minimal involvement
Afghanistan has become terrain for India-Pakistan proxy war
 Afghanistan has become terrain for India-Pakistan proxy war Ramananda Sengupta* March 2010 Al Jazeera Centre for Studies Tel: +974-4930181 Fax: +974-4831346 jcforstudies@aljazeera.net www.aljazeera.net/studies
Afghanistan has become terrain for India-Pakistan proxy war Ramananda Sengupta* March 2010 Al Jazeera Centre for Studies Tel: +974-4930181 Fax: +974-4831346 jcforstudies@aljazeera.net www.aljazeera.net/studies
Chapter 18: The Colonies Become New Nations: 1945-Present The Indian Subcontinent Achieves Freedom (Section 1) Congress Party Muslim League
 Chapter 18: The Colonies Become New Nations: 1945-Present I. The Indian Subcontinent Achieves Freedom (Section 1) a. A Movement Toward Independence i. Struggling Against British Rule 1. Indian intensifies
Chapter 18: The Colonies Become New Nations: 1945-Present I. The Indian Subcontinent Achieves Freedom (Section 1) a. A Movement Toward Independence i. Struggling Against British Rule 1. Indian intensifies
Security Council Distr. GENERAL
 UNITED NATIONS s Security Council Distr. GENERAL S/25435 19 March 1993 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH LETTER DATED 17 MARCH 1993 FROM THE CHARGE D'AFFAIRES A.I. OF THE PERMANENT MISSION OF AFGHANISTAN TO THE UNITED
UNITED NATIONS s Security Council Distr. GENERAL S/25435 19 March 1993 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH LETTER DATED 17 MARCH 1993 FROM THE CHARGE D'AFFAIRES A.I. OF THE PERMANENT MISSION OF AFGHANISTAN TO THE UNITED
Report for Congress. Afghanistan: Current Issues and U.S. Policy. Updated April 1, 2003
 Order Code RL30588 Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Afghanistan: Current Issues and U.S. Policy Updated April 1, 2003 Kenneth Katzman Specialist in Middle Eastern Affairs Foreign Affairs,
Order Code RL30588 Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Afghanistan: Current Issues and U.S. Policy Updated April 1, 2003 Kenneth Katzman Specialist in Middle Eastern Affairs Foreign Affairs,
IR History Post John Lee Department of Political Science Florida State University
 IR History Post-1950 John Lee Department of Political Science Florida State University World War II Germany initially expands, no one stops them. Allied v/s Axis Powers. USSR/Germany reach initial compromise,
IR History Post-1950 John Lee Department of Political Science Florida State University World War II Germany initially expands, no one stops them. Allied v/s Axis Powers. USSR/Germany reach initial compromise,
AFGHANISTAN. Reports of torture, ill-treatment and extrajudicial execution of prisoners, late April - early May 1992
 AFGHANISTAN Reports of torture, ill-treatment and extrajudicial execution of prisoners, late April - early May 1992 Recent political developments On 16 April 1992, former president Najibullah was replaced
AFGHANISTAN Reports of torture, ill-treatment and extrajudicial execution of prisoners, late April - early May 1992 Recent political developments On 16 April 1992, former president Najibullah was replaced
Center for Strategic & Regional Studies
 Center for Strategic & Regional Studies Kabul Weekly Analysis-Issue Number 174 (September 24 - October 1, 2016) Weekly Analysis is one of CSRS publications, which significantly analyses weekly economic
Center for Strategic & Regional Studies Kabul Weekly Analysis-Issue Number 174 (September 24 - October 1, 2016) Weekly Analysis is one of CSRS publications, which significantly analyses weekly economic
From Nationalisms to Partition: India and Pakistan ( ) Inter War World: Independence of India
 From Nationalisms to Partition: India and Pakistan (1917-1948) Inter War World: Independence of India India: the turn to resistance Post Amritsar India: post war disillusionment articulated in Amritsar
From Nationalisms to Partition: India and Pakistan (1917-1948) Inter War World: Independence of India India: the turn to resistance Post Amritsar India: post war disillusionment articulated in Amritsar
What is Global Governance? Domestic governance
 Essay Outline: 1. What is Global Governance? 2. The modern international order: Organizations, processes, and norms. 3. Western vs. post-western world 4. Central Asia: Old Rules in a New Game. Source:
Essay Outline: 1. What is Global Governance? 2. The modern international order: Organizations, processes, and norms. 3. Western vs. post-western world 4. Central Asia: Old Rules in a New Game. Source:
Center for Strategic & Regional Studies
 Center for Strategic & Regional Studies Kabul Weekly Analysis-Issue Number 272 (Oct 20-27, 2018) Weekly Analysis is one of CSRS publications, which significantly analyses weekly economic and political
Center for Strategic & Regional Studies Kabul Weekly Analysis-Issue Number 272 (Oct 20-27, 2018) Weekly Analysis is one of CSRS publications, which significantly analyses weekly economic and political
President Jimmy Carter
 President Jimmy Carter E. America Enters World War II (1945-Present) g. Analyze the origins of the Cold War, foreign policy developments, and major events of the administrations from Truman to present
President Jimmy Carter E. America Enters World War II (1945-Present) g. Analyze the origins of the Cold War, foreign policy developments, and major events of the administrations from Truman to present
Afghanistan. capitol. size. population. kabul. 647,500 square kilometers slightly less than texas million
 Afghanistan capitol kabul size 647,500 square kilometers slightly less than texas population 32.7 million eradicating extreme poverty and hunger 17,351,339 Afghans live below the poverty line each spot
Afghanistan capitol kabul size 647,500 square kilometers slightly less than texas population 32.7 million eradicating extreme poverty and hunger 17,351,339 Afghans live below the poverty line each spot
AFGHANISTAN: TRANSITION UNDER THREAT WORKSHOP REPORT
 AFGHANISTAN: TRANSITION UNDER THREAT WORKSHOP REPORT On December 17-18, 2006, a workshop was held near Waterloo, Ontario Canada to assess Afghanistan s progress since the end of the Taliban regime. Among
AFGHANISTAN: TRANSITION UNDER THREAT WORKSHOP REPORT On December 17-18, 2006, a workshop was held near Waterloo, Ontario Canada to assess Afghanistan s progress since the end of the Taliban regime. Among
The Geography of Terrorism
 The Geography of Terrorism More than 80 percent of last year's terrorism fatalities occurred in just five countries. KATHY GILSINANNOV 18 2014, 6:08 PM ET Institute for Economics and Peace Of the 17,958
The Geography of Terrorism More than 80 percent of last year's terrorism fatalities occurred in just five countries. KATHY GILSINANNOV 18 2014, 6:08 PM ET Institute for Economics and Peace Of the 17,958
AFGHANISTAN ASSESSMENT
 AFGHANISTAN ASSESSMENT April 2001 Country Information and Policy Unit 1 CONTENTS I SCOPE OF DOCUMENT 1.1-1.5 II GEOGRAPHY General Languages Economy III HISTORY 1973 Coup d' État 1978-1992 1992-1994: Mujahidin
AFGHANISTAN ASSESSMENT April 2001 Country Information and Policy Unit 1 CONTENTS I SCOPE OF DOCUMENT 1.1-1.5 II GEOGRAPHY General Languages Economy III HISTORY 1973 Coup d' État 1978-1992 1992-1994: Mujahidin
THE EARLY COLD WAR YEARS. US HISTORY Chapter 15 Section 2
 THE EARLY COLD WAR YEARS US HISTORY Chapter 15 Section 2 THE EARLY COLD WAR YEARS CONTAINING COMMUNISM MAIN IDEA The Truman Doctrine offered aid to any nation resisting communism; The Marshal Plan aided
THE EARLY COLD WAR YEARS US HISTORY Chapter 15 Section 2 THE EARLY COLD WAR YEARS CONTAINING COMMUNISM MAIN IDEA The Truman Doctrine offered aid to any nation resisting communism; The Marshal Plan aided
OVERCOMING THE OBSTACLES TO ESTABLISHING A DEMOCRATIC STATE IN AFGHANISTAN
 USAWC STRATEGY RESEARCH PROJECT OVERCOMING THE OBSTACLES TO ESTABLISHING A DEMOCRATIC STATE IN AFGHANISTAN by Colonel Dennis O. Young United States Army Dr. David L. Perry Project Adviser This SRP is submitted
USAWC STRATEGY RESEARCH PROJECT OVERCOMING THE OBSTACLES TO ESTABLISHING A DEMOCRATIC STATE IN AFGHANISTAN by Colonel Dennis O. Young United States Army Dr. David L. Perry Project Adviser This SRP is submitted
Engaging Regional Players in Afghanistan Threats and Opportunities
 Engaging Regional Players in Afghanistan Threats and Opportunities A Report of the CSIS Post-Conflict Reconstruction Project author Shiza Shahid codirectors Rick Barton Karin von Hippel November 2009 CSIS
Engaging Regional Players in Afghanistan Threats and Opportunities A Report of the CSIS Post-Conflict Reconstruction Project author Shiza Shahid codirectors Rick Barton Karin von Hippel November 2009 CSIS
General Overview of Communism & the Russian Revolution. AP World History Chapter 27b The Rise and Fall of World Communism (1917 Present)
 General Overview of Communism & the Russian Revolution AP World History Chapter 27b The Rise and Fall of World Communism (1917 Present) Communism: A General Overview Socialism = the belief that the economy
General Overview of Communism & the Russian Revolution AP World History Chapter 27b The Rise and Fall of World Communism (1917 Present) Communism: A General Overview Socialism = the belief that the economy
STABLE AFGHANISTAN: SUGGESTED GOVERNMENT MODELS FOR AFGHANISTAN IN POST AFGHAN WAR SCENARIO Ms. Afshan Sajid Introduction Traditionally, Afghan
 STABLE AFGHANISTAN: SUGGESTED GOVERNMENT MODELS FOR AFGHANISTAN IN POST AFGHAN WAR SCENARIO Ms. Afshan Sajid Introduction Traditionally, Afghan society is the collection of several ethnic groups. These
STABLE AFGHANISTAN: SUGGESTED GOVERNMENT MODELS FOR AFGHANISTAN IN POST AFGHAN WAR SCENARIO Ms. Afshan Sajid Introduction Traditionally, Afghan society is the collection of several ethnic groups. These
Afghanistan: Post-Taliban Governance, Security, and U.S. Policy
 Afghanistan: Post-Taliban Governance, Security, and U.S. Policy Kenneth Katzman Specialist in Middle Eastern Affairs February 17, 2016 Congressional Research Service 7-5700 www.crs.gov RL30588 Summary
Afghanistan: Post-Taliban Governance, Security, and U.S. Policy Kenneth Katzman Specialist in Middle Eastern Affairs February 17, 2016 Congressional Research Service 7-5700 www.crs.gov RL30588 Summary
Dynamics of Political Development in Afghanistan
 Dynamics of Political Development in Afghanistan Dynamics of Political Development in Afghanistan The British, Russian, and American Invasions Hafizullah Emadi dynamics of political development in afghanistan
Dynamics of Political Development in Afghanistan Dynamics of Political Development in Afghanistan The British, Russian, and American Invasions Hafizullah Emadi dynamics of political development in afghanistan
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Cold War Tensions (Chapter 30 Quiz)
 Cold War Tensions (Chapter 30 Quiz) What were the military and political consequences of the Cold War in the Soviet Union, Europe, and the United States? After World War II ended, the United States and
Cold War Tensions (Chapter 30 Quiz) What were the military and political consequences of the Cold War in the Soviet Union, Europe, and the United States? After World War II ended, the United States and
2. The State Department asked the American Embassy in Moscow to explain Soviet behavior.
 1. The Americans become increasingly impatient with the Soviets. 2. The State Department asked the American Embassy in Moscow to explain Soviet behavior. 3. On February 22, 1946, George Kennan an American
1. The Americans become increasingly impatient with the Soviets. 2. The State Department asked the American Embassy in Moscow to explain Soviet behavior. 3. On February 22, 1946, George Kennan an American
Afghanistan: Post-Taliban Governance, Security, and U.S. Policy
 Afghanistan: Post-Taliban Governance, Security, and U.S. Policy Kenneth Katzman Specialist in Middle Eastern Affairs March 28, 2017 Congressional Research Service 7-5700 www.crs.gov RL30588 Summary The
Afghanistan: Post-Taliban Governance, Security, and U.S. Policy Kenneth Katzman Specialist in Middle Eastern Affairs March 28, 2017 Congressional Research Service 7-5700 www.crs.gov RL30588 Summary The
Country Summary January 2005
 Country Summary January 2005 Afghanistan Despite some improvements, Afghanistan continued to suffer from serious instability in 2004. Warlords and armed factions, including remaining Taliban forces, dominate
Country Summary January 2005 Afghanistan Despite some improvements, Afghanistan continued to suffer from serious instability in 2004. Warlords and armed factions, including remaining Taliban forces, dominate
Great Power Withdrawals from Afghanistan
 Great Power Withdrawals from Afghanistan by Colonel Patrick L. Gaydon United States Army United States Army War College Class of 2014 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT: A Approved for Public Release Distribution
Great Power Withdrawals from Afghanistan by Colonel Patrick L. Gaydon United States Army United States Army War College Class of 2014 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT: A Approved for Public Release Distribution
NOREF Policy Brief. Afghanistan and the regional powers: history not repeating itself? Stina Torjesen
 Oktober 2012 NOREF Policy Brief Afghanistan and the regional powers: history not repeating itself? Stina Torjesen Executive summary This brief surveys Afghanistan s links to four key regional powers: India,
Oktober 2012 NOREF Policy Brief Afghanistan and the regional powers: history not repeating itself? Stina Torjesen Executive summary This brief surveys Afghanistan s links to four key regional powers: India,
AFGHANISTAN: THE PROBLEM OF PASHTUN ALIENATION
 AFGHANISTAN: THE PROBLEM OF PASHTUN ALIENATION 5 August 2003 ICG Asia Report N 62 Kabul/Brussels TABLE OF CONTENTS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY AND RECOMMENDATIONS...i I. INTRODUCTION...1 II. BACKGROUND...3 A. STATE
AFGHANISTAN: THE PROBLEM OF PASHTUN ALIENATION 5 August 2003 ICG Asia Report N 62 Kabul/Brussels TABLE OF CONTENTS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY AND RECOMMENDATIONS...i I. INTRODUCTION...1 II. BACKGROUND...3 A. STATE
SSUSH25 The student will describe changes in national politics since 1968.
 SSUSH25 The student will describe changes in national politics since 1968. a. Describe President Richard M. Nixon s opening of China, his resignation due to the Watergate scandal, changing attitudes toward
SSUSH25 The student will describe changes in national politics since 1968. a. Describe President Richard M. Nixon s opening of China, his resignation due to the Watergate scandal, changing attitudes toward
AFGHANISTAN. 7 November 2006
 o 7 November 2006 AFGHANISTAN TABLE OF CONTENTS Background...1 Multilateral Efforts...4 General Assembly...4 Secretary-General...4 UNGOMAP...5 OSGAP...5 UNSMA...5 Changes in Int l Response after 9/11...6
o 7 November 2006 AFGHANISTAN TABLE OF CONTENTS Background...1 Multilateral Efforts...4 General Assembly...4 Secretary-General...4 UNGOMAP...5 OSGAP...5 UNSMA...5 Changes in Int l Response after 9/11...6
Afghanistan: Post-Taliban Governance, Security, and U.S. Policy
 Afghanistan: Post-Taliban Governance, Security, and U.S. Policy Kenneth Katzman Specialist in Middle Eastern Affairs November 8, 2016 Congressional Research Service 7-5700 www.crs.gov RL30588 Summary The
Afghanistan: Post-Taliban Governance, Security, and U.S. Policy Kenneth Katzman Specialist in Middle Eastern Affairs November 8, 2016 Congressional Research Service 7-5700 www.crs.gov RL30588 Summary The
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 3 The Rise of Napoleon and the Napoleonic Wars ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What causes revolution? How does revolution change society? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary capable having or showing ability
Lesson 3 The Rise of Napoleon and the Napoleonic Wars ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What causes revolution? How does revolution change society? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary capable having or showing ability
By Encyclopedia Brittanica, adapted by Newsela staff on Word Count 1,286
 The Arab Spring By Encyclopedia Brittanica, adapted by Newsela staff on 04.14.17 Word Count 1,286 Egyptians wave the national flag in Cairo's Tahrir Square during a rally marking the anniversary of the
The Arab Spring By Encyclopedia Brittanica, adapted by Newsela staff on 04.14.17 Word Count 1,286 Egyptians wave the national flag in Cairo's Tahrir Square during a rally marking the anniversary of the
Understanding War in Afghanistan. by Joseph J. Collins
 Understanding War in Afghanistan by Joseph J. Collins Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for the collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour
Understanding War in Afghanistan by Joseph J. Collins Report Documentation Page Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for the collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour
Chapter 5: National Interest and Foreign Policy. domestic policy
 Chapter 5: National Interest and Foreign Policy Key Terms: national interest peacemaking policy foreign policy peacekeepers continental shelf domestic policy gross domestic product Aspects of National
Chapter 5: National Interest and Foreign Policy Key Terms: national interest peacemaking policy foreign policy peacekeepers continental shelf domestic policy gross domestic product Aspects of National
The reasons for the existence of fundamentalism in Afghanistan. Fatemeh Rajabi
 The reasons for the existence of fundamentalism in Afghanistan Fatemeh Rajabi Fatemehrajabi21@gmx.com Abstract: After the Soviet war in Afghanistan, fundamentalists, issues were raised by the global media
The reasons for the existence of fundamentalism in Afghanistan Fatemeh Rajabi Fatemehrajabi21@gmx.com Abstract: After the Soviet war in Afghanistan, fundamentalists, issues were raised by the global media
Round Table Discussion on Pak-Afghan Relations: Future Prospects
 Phone: +92 51 2514555 Email: info@muslim-institute.org www.muslim-institute.org Round Table Discussion on Pak-Afghan Relations: Future Prospects Organized by MUSLIM Institute MUSLIM Institute organized
Phone: +92 51 2514555 Email: info@muslim-institute.org www.muslim-institute.org Round Table Discussion on Pak-Afghan Relations: Future Prospects Organized by MUSLIM Institute MUSLIM Institute organized
Chapter 34 Crisis, Realignment, and the Dawn of the Post Cold War World
 Chapter 34 Crisis, Realignment, and the Dawn of the Post Cold War World 1975 1991 Postcolonial Crises and Asian Economic Expansion, 1975 1990 Islamic Revolutions in Iran and Afghanistan Crises in Iran
Chapter 34 Crisis, Realignment, and the Dawn of the Post Cold War World 1975 1991 Postcolonial Crises and Asian Economic Expansion, 1975 1990 Islamic Revolutions in Iran and Afghanistan Crises in Iran
The French Revolution establishes a new political order, Napoleon Bonaparte gains and loses an empire, and European states forge a balance of power.
 SLIDE 1 Chapter 23 The French Revolution and Napoleon, 1789 1815 The French Revolution establishes a new political order, Napoleon Bonaparte gains and loses an empire, and European states forge a balance
SLIDE 1 Chapter 23 The French Revolution and Napoleon, 1789 1815 The French Revolution establishes a new political order, Napoleon Bonaparte gains and loses an empire, and European states forge a balance
APPENDIX - 2: Local administrations set up by Mujahideen commanders 11
 Table of contents 1. Introduction 1 2. The political crisis in Afghanistan 2 3. Educated Afghan women 5 4. Afghan academics and other professionals 5 5. Members of some ethnic and religious minorities
Table of contents 1. Introduction 1 2. The political crisis in Afghanistan 2 3. Educated Afghan women 5 4. Afghan academics and other professionals 5 5. Members of some ethnic and religious minorities
US involvement in Afghanistan: Implications for the future. Shri Prakash*
 Journal of Peace Studies Vol. 10, Issue 1, January-March 2003 US involvement in Afghanistan: Implications for the future Shri Prakash* [*Professor Shri Prakash is teaching in Academy of Third World Studies,
Journal of Peace Studies Vol. 10, Issue 1, January-March 2003 US involvement in Afghanistan: Implications for the future Shri Prakash* [*Professor Shri Prakash is teaching in Academy of Third World Studies,
Chapter 33 Summary/Notes
 Chapter 33 Summary/Notes Unit 8 Perspectives on the Present Chapter 33 Section 1. The Cold War Superpowers Face off We learned about the end of WWII. Now we learn about tensions that followed the war.
Chapter 33 Summary/Notes Unit 8 Perspectives on the Present Chapter 33 Section 1. The Cold War Superpowers Face off We learned about the end of WWII. Now we learn about tensions that followed the war.
Afghanistan. Afghanistan
 12 Afghanistan 2 Afghanistan Synopsis By the time the US-led international coalition intervened militarily to remove the Taliban regime in October 2001, and the United Nations (UN)
12 Afghanistan 2 Afghanistan Synopsis By the time the US-led international coalition intervened militarily to remove the Taliban regime in October 2001, and the United Nations (UN)
Afghanistan: The Consolidation of a Rogue State
 Afghanistan: The Consolidation of a Rogue State Zalmay Khalilzad, Daniel Byman The Washington Quarterly, Volume 23, Number 1, Winter 2000, pp. 65-78 (Article) Published by The MIT Press For additional
Afghanistan: The Consolidation of a Rogue State Zalmay Khalilzad, Daniel Byman The Washington Quarterly, Volume 23, Number 1, Winter 2000, pp. 65-78 (Article) Published by The MIT Press For additional
Guided Reading Activity 32-1
 Guided Reading Activity 32-1 DIRECTIONS: Recalling the Facts Use the information in your textbook to answer the questions below. Use another sheet of paper if necessary. 1. What conservative view did many
Guided Reading Activity 32-1 DIRECTIONS: Recalling the Facts Use the information in your textbook to answer the questions below. Use another sheet of paper if necessary. 1. What conservative view did many
Thirty Years of War: Soviet Legacies and Today s Challenges in Afghanistan
 Thirty Years of War: Soviet Legacies and Today s Challenges in Afghanistan Nathaniel Powell* The United States recent reassessment of its strategy in Afghanistan occurs at a critical time. A spreading
Thirty Years of War: Soviet Legacies and Today s Challenges in Afghanistan Nathaniel Powell* The United States recent reassessment of its strategy in Afghanistan occurs at a critical time. A spreading
Afghanistan: Post-Taliban Governance, Security, and U.S. Policy
 Afghanistan: Post-Taliban Governance, Security, and U.S. Policy Kenneth Katzman Specialist in Middle Eastern Affairs June 6, 2016 Congressional Research Service 7-5700 www.crs.gov RL30588 Summary The United
Afghanistan: Post-Taliban Governance, Security, and U.S. Policy Kenneth Katzman Specialist in Middle Eastern Affairs June 6, 2016 Congressional Research Service 7-5700 www.crs.gov RL30588 Summary The United
Afghanistan: Post-Taliban Governance, Security, and U.S. Policy
 Afghanistan: Post-Taliban Governance, Security, and U.S. Policy Kenneth Katzman Specialist in Middle Eastern Affairs Clayton Thomas Analyst in Middle Eastern Affairs December 13, 2017 Congressional Research
Afghanistan: Post-Taliban Governance, Security, and U.S. Policy Kenneth Katzman Specialist in Middle Eastern Affairs Clayton Thomas Analyst in Middle Eastern Affairs December 13, 2017 Congressional Research
Section 1: Nixon and the Watergate Scandal
 Chapter 25 Review Section 1 Chapter Summary Section 1: Nixon and the Watergate Scandal Richard Nixon was reelected in 1972 by a landslide due in part to his southern strategy. The Watergate scandal caused
Chapter 25 Review Section 1 Chapter Summary Section 1: Nixon and the Watergate Scandal Richard Nixon was reelected in 1972 by a landslide due in part to his southern strategy. The Watergate scandal caused
Report. Iran's Foreign Policy Following the Nuclear Argreement and the Advent of Trump: Priorities and Future Directions.
 Report Iran's Foreign Policy Following the Nuclear Argreement and the Advent of Trump: Priorities and Future Directions Fatima Al-Smadi* 20 May 2017 Al Jazeera Centre for Studies Tel: +974 40158384 jcforstudies@aljazeera.net
Report Iran's Foreign Policy Following the Nuclear Argreement and the Advent of Trump: Priorities and Future Directions Fatima Al-Smadi* 20 May 2017 Al Jazeera Centre for Studies Tel: +974 40158384 jcforstudies@aljazeera.net
Afghanistan: Post-Taliban Governance, Security, and U.S. Policy
 Afghanistan: Post-Taliban Governance, Security, and U.S. Policy Kenneth Katzman Specialist in Middle Eastern Affairs April 27, 2015 Congressional Research Service 7-5700 www.crs.gov RL30588 Summary As
Afghanistan: Post-Taliban Governance, Security, and U.S. Policy Kenneth Katzman Specialist in Middle Eastern Affairs April 27, 2015 Congressional Research Service 7-5700 www.crs.gov RL30588 Summary As
