BTI 2012 Côte d Ivoire Country Report
|
|
|
- Camilla Stafford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BTI 01 Côte d Ivoire Country Report Status Index # 11 of 18 Political Transformation # 118 of 18 Economic Transformation # 114 of 18 Management Index # 14 of 18 scale: 1 (lowest) to 10 (highest) score rank trend This report is part of the Bertelsmann Stiftung s Transformation Index (BTI) 01. The BTI is a global assessment of transition processes in which the state of democracy and market economy as well as the quality of political management in 18 transformation and developing countries are evaluated. More on the BTI at Please cite as follows: Bertelsmann Stiftung, BTI 01 Côte d Ivoire Country Report. Gütersloh: Bertelsmann Stiftung, Bertelsmann Stiftung, Gütersloh
2 BTI 01 Côte d Ivoire Key Indicators Population mn HDI GDP p.c. $ 1899 Pop. growth 1 % p.a..0 HDI rank of Gini Index 41.5 Life expectancy years 54 UN Education Index Poverty 3 % 46.3 Urban population % 50.1 Gender inequality Aid per capita $ 11.3 Sources: The World Bank, World Development Indicators 011 UNDP, Human Development Report 011. Footnotes: (1) Average annual growth rate. () Gender Inequality Index (GII). (3) Percentage of population living on less than $ a day. Executive Summary Côte d Ivoire does not meet the minimum criteria for democracy. The country s civil war and its subsequent political division have since negated the limited progress made during the 1990s in political participation and the establishment of the rule of law. The presidential elections in late 010 plunged the country into even deeper chaos as the loser of the election clung to power, while the international community acknowledged that the elected government and citizens had to be supported by United Nations peacekeepers. As the shape of the political landscape and citizenship in general remains contested, the political and social integration of Côte d Ivoire has reached a historic low. Some sense of economic order has been maintained despite the country s general instability. Overall, macroeconomic performance slightly recovered in the period under review, mainly due to the cocoa and oil industries. The division of the country, although formally completed in January 009, has led to a weakening of traditional markets and the birth of more informal economies in both parts of the country. As violent conflicts resumed and the country was ruled by two partly competing, partly overlapping, de facto regimes, political elites have struggled to maintain stability and to ensure the continued functioning of the cocoa and oil industries. The establishment of a seemingly stable power-sharing government in Abidjan with former rebel leader Guillaume Soro as prime minister was seen as a sign of hope, especially as the government was considered in its decisionmaking as more pragmatic and also more consensual. This government, however, neither inspired trust within the political elite nor, as became evident in late 010, offered a departure from violence as an exit option, a strategy to which all political parties still held in case the elections did not work in their favor. Under these circumstances, structural economic reform was neither realistic nor a government priority (notwithstanding negotiations with international donors over reforms).
3 BTI 01 Côte d Ivoire 3 In sum, Côte d Ivoire could represent a case of how a country with a sound economic basis and much potential should not be managed, as well as a country where considerable responsibility for its failures resides with the political elite. The not very obvious but possibly only available solution to the political stalemate in early 011 would be the establishment of a minimum of consensus, commitment and steering capacity among Ivorian political actors. History and Characteristics of Transformation Political and economic transformation have followed different paths: After independence in August 1960, the country s first president, Félix Houphouet-Boigny, came to dominate the country s political life and economic decision-making, and in the 1960s and 1970s presided over Côte d Ivoire s emergence as one of Africa s few stable and economically successful countries. A broadly liberal economic system with active integration into the world market was combined with a basically authoritarian mode of political regulation. Côte d Ivoire s success as an exporter of cocoa (as the world s top producer) and coffee was a major factor in its stability, as these exports quickly enabled the country to achieve an enviable level of prosperity and social development. There was both an increased presence of French people working in the administration and in business, and a large influx of immigrant workers from the neighboring Sahel countries, including Burkina Faso, Mali and Guinea, mainly for seasonal work on the cocoa and coffee plantations. When commodity prices fell in the 1980s, Côte d Ivoire began to face serious economic and social problems. The established model of political and economic regulation, which denied political participation but guaranteed social advancement for elites and fixed producer prices for planters, had become unsustainable. Popular dissent increased and by the beginning of the 1990s, multiparty rule was introduced. Along with political liberalization came an attempt of economic reform headed by a technocratic team under Prime Minister Alassane Ouattara. He conducted an economic reform program in the face of significant resistance within the ruling party, the Parti Démocratique de la Côte d Ivoire (PDCI), particularly from the president of the National Assembly, Henri Konan Bedié. Upon Houphouet-Boigny s death in December 1993, both Ouattara and Bedié vied for the succession, which Bedié eventually won by invoking a constitutional provision transferring interim power to the president of parliament in the event of the president s death. Bedié subsequently consolidated his own power by sidelining those sympathetic to Ouattara. A pro- Ouattara party, the Rassemblement des Républicains (RDR), broke away from the PDCI. The 1995 presidential elections saw the victory of Bedié with both RDR and the other historical opposition party, Front Populaire Ivoirien (FPI), boycotting the polls on the grounds that the electoral code excluded Ouattara from standing due to his dubious Ivorian nationality.
4 BTI 01 Côte d Ivoire 4 Support for President Bedié, who initially benefited from the positive effects of the CFA franc devaluation in January 1994, waned rapidly after 1998 due to a growing economic recession and a lack of structural reforms as well as the rise in radical political nationalism intended to systematically disenfranchise Ouattara and his northern supporters. President Bedié was eventually overthrown in a bloodless coup in December 1999 which was generally greeted with relief by the population, and also, albeit less openly, by international donors who had stopped financial support for the government on growing concerns over fraud and corruption. Initial hopes of a more thorough political democratization were soon disappointed when it became clear that the coup leader General Robert Guei would stand in the 000 elections; the eternal opposition party FPI then joined the PDCI in their nationalist policy stance, which led anew to the exclusion of Ouattara. A popular uprising thwarted the rigged election of October 000, forcing General Guei, after losing the support of the army, into hiding. Laurent Gbagbo was declared the winner against the protests of RDR supporters. Clashes between RDR militants and FPI supporters turned violent with many civilian northerners (i.e., pro-rdr) as victims. Despite substantial misgivings, France and the international community eventually endorsed Gbagbo s election. Developments in 001 seemed to presage an easing of tensions starting with local elections and a forum of national reconciliation held in Abidjan between the four main political leaders, Gbagbo, Bedié, Ouattara and Guei, in late 001. A government of national unity, including the RDR among others, was established in August 00. The September 00 coup attempt and the ensuing descent into civil war took the country thus by surprise. The mutineers swiftly took control of the entire northern half of the country, a move welcomed by the local population who felt marginalized by the nationalist policies of the Guei and Gbagbo administrations. In response to the growing prospect of a civil war, the French government stepped up its military presence in Côte d Ivoire, agreeing to police the ceasefire line following the agreement of a truce on 19 October 00. The main political parties and rebel groups reached a political settlement during negotiations in Marcoussis, France, in January 003. In March 003 a national reconciliation government took office, which included both the parties of the governing coalition, the PDCI, the RDR and representatives of the armed rebel groups, known as the New Forces. Ongoing political conflicts hampered the government s ability to function and led component parties to withdraw for periods of time. Implementation of the peace accords, including disarmament, territorial reintegration and a menu of significant political reforms, were halting. A new peace agreement, brokered by Burkina Faso s President Blaise Compaoré in early 007, allowed for a power-sharing government with former rebel leader Soro as prime minister. This government eventually made the formal reunification of the country possible and led the way to presidential elections, eventually held in October-November 010. All hopes that this election would represent a first but decisive step toward solving the conflict were soon dashed.
5 BTI 01 Côte d Ivoire 5 The BTI combines text analysis and numerical assessments. The score for each question is provided below its respective title. The scale ranges from 10 (best) to 1 (worst). Transformation Status I. Political Transformation 1 Stateness The presidential elections of October-November 010 were supposed to bring an end to the territorial division of an official government zone in the south and a rebel New Forces-held zone in the north (which occurred in the wake of the failed coup of September 00). The installation of a new transitional government with the March 007 peace accord allowed for an incremental process of reunification. The state s monopoly on the use of force is, however, still only partially established in the northern part of the country. Many former commanders of the rebel forces maintain their lucrative zones of influence and state governors are still powerless in the face of the rebel s military influence and the incomplete cantonment of former combatants. Demobilization of combatants and their integration into the national army has been terribly slow. Citizenship rights is one important among several root causes of the current political-military conflict. Significant aspects of citizenship (if not citizenship tout court) were withheld from northerners as well as from migrant workers who lived in Côte d Ivoire over the past few decades. Fuelled by politicians, the nationalistic concept of Ivoirité encouraged southerners, who are, in the main, Christian or animist, to regard themselves as true Ivorians and whipped up xenophobic sentiment and action against northerners (whether they were of Ivorian nationality or not). Since the 007 Ouagadougou peace accord and with the help of the international community, an identification exercise (forensic audits) by mobile legal teams was launched and eventually the parties in conflict were made to agree on an electoral roll for the 010 elections. The general question of citizenship rights, which also refers to economic rights, is nevertheless far from being resolved. Recent events clearly demonstrate that the election winner Alassane Ouattara is still not perceived as Ivorian by Laurent Gbagbo s southern supporters. Question Score Monopoly on the use of force State identity
6 BTI 01 Côte d Ivoire 6 The separation of church and state is guaranteed by the French-style secular constitution, and religious extremists command little political influence. Conflicts among the different ethnic groups and immigrant groups have lately gained religious overtones. However, political discrimination (and violence) is related to ethnocultural stereotypes and linguistic cleavages and targets all northerners, independent of their religious affiliation (although most Muslims live in the northern part of Côte d Ivoire). Since 009, substantial progress has been achieved in restoring state administration throughout the country. Civil servants have been successively redeployed to the north, although their operational capacity and full authority remains limited. While many schools and hospitals have reopened, law enforcement, courts and correctional institutions were still not functional in the north. In many instances rebel New Forces commanders still control tax collection and often local administration functions as well. No interference of religious dogmas 7 Basic administration 5 Political Participation Universal suffrage, the right to campaign for office and the right to elections are in principle assured. The October 000 elections that installed the current Gbagbo-FPI government was marred by irregularities. Since then no elections were until October 010; the various governments in power since early 003 have been established by international agreements. Although Gbagbo s constitutional term as president ended October 005, new elections were repeatedly postponed. With considerable logistical support from United Nations organizations, new presidential elections were organized in late 010. The electoral management bodies worked professionally yet tried to avoid political interference. As the incumbent president did not comply with the established rules, management bodies could not allow the elected government to be formed. This task has now been left to regional and international policymakers. Until the October 010 elections, there was no democratically elected government; instead, the government was legitimized through international negotiations. The effective capacity of this transitional government to govern was limited by the tenuous control of New Forces leader Soro over various former rebel commanders in the north and the unclear role of militias in the south which, however, seemed to remain under the control of President Gbagbo and his supporters. The situation after the presidential elections was different, as the newly elected president was hindered not only by the incumbent president but also by the army leadership from assuming office. His rule was de facto restricted to an international hotel in Abidjan. Free and fair elections 4 Effective power to govern
7 BTI 01 Côte d Ivoire 7 The freedom of civil society groups and opposition parties to operate has been largely constrained since the 00 coup attempt, both due to repressive policy measures (prohibition of public demonstrations for extended periods) and the activities of youth activist groups ( young patriots ) in the south, and a general lack of the rule of law in the north. When the Soro government came to power in mid- 007, the situation improved gradually yet mainly in the south. Association / assembly rights 6 In the run-up to the elections of 010, assembly rights were maintained yet supervised by the United Nations. Union activity has continued without disruption. The country s political division and subsequent instability has made access to balanced information very difficult. National and international media remain subject to threats and pressure from both the government and rebel forces. Constitutional provisions for freedom of expression are rarely respected in practice and journalists remain vulnerable to physical and other abuse by police. There were fewer reports of harassment and violence against journalists in 009 and 010 than in previous years. However, during and after the elections, there were instances of widespread defamation, and thus there has in effect been a substantial decrease in freedom of expression particularly after the contested elections and subsequent violence. Côte d Ivoire ranks 146th out of 196 countries ( not free ) in the Global Press Freedom Survey 010 by Freedom House. Freedom of expression 3 3 Rule of Law Côte d Ivoire has a long history of complete presidential control of the political process. Political liberalization during the 1990s did not lead to any meaningful political empowerment of parliament. The installment of a former opposition party in power has not significantly modified the power balance, as incumbent President Gbagbo simply shifted government decision-making to a close group of consultants, including his own wife, Simone. Even opposition party ministers who took part in various national unity governments since 003 cannot control their senior civil servants or heads of state agencies in their remit, most of whom they have inherited from their predecessors or were appointed without consultation by the president. The establishment in 007 of a power-sharing government worked to weaken presidential omnipotence by establishing a strong prime minister, but neglected to establish separation of powers. The structural annihilation of parliamentary oversight has been officially justified since 00 by the country s prolonged state of emergency. Separation of powers The 010 presidential elections did not change this overall picture; new parliamentary elections have been postponed to a later date.
8 BTI 01 Côte d Ivoire 8 Formally, the judiciary is institutionally distinct but its decisions and doctrines have always been subordinated to the current government. Both the constitutional and the regular judiciary branch are vulnerable to executive intervention, lack adequate resources (especially outside Abidjan) and are riddled with corruption. Prior to the civil war, a series of major judicial reforms were announced (installation of a Council of State, a Supreme Court of Appeal and of an Audit Office) but have yet to be implemented. Independent judiciary 3 The independence of the Constitutional Court was severely questioned by the behavior of its president in the electoral crisis of November 010. Financial malpractice plagued previous government administrations, and the transitional government, encouraged by the absence of auditing, was implicated in a number of new scandals. In the current context, corrupt officeholders do not face adverse publicity from civil society, in the media or from opposition parties, nor prosecution under the law. The sacking of 5 top managers in the cocoa sector (among them a former election campaign manager of President Gbagbo and a trade union leader) and their arrest in June 008 on massive corruption charges does not alter this general assessment. While the trial was suspended amid the country s political upheaval, out of the 5 accused were released in January 010. Since the outbreak of civil war in 00, most civil liberties are not secure, not only because of the state s inability to centralize the use of force but also from a lack of political will and judicial control. In the run-up to the presidential elections and in the unrest following the second round, more than 300 persons were killed by security forces or militia groups. Human rights abuses occur, including genderspecific rights violations, in all parts of the country. The perpetrators of mass murder and other serious violations of human rights committed since the first coup in 1999 have not been yet brought to justice. The United Nations Security Council enacted formal sanctions against certain individuals (two militia leaders from the south, and one from the north) in February 006, which are still in force. Prosecution of office abuse 3 Civil rights 4 Stability of Democratic Institutions A transitional government was the product of international negotiations and not of popular will. Parliamentarians elected in 000 continue to sit in parliament but have no control over legislative activity or governmental activities. At the end of 010, the country maintained two parallel governments which both claimed to have democratic legitimacy. Even though the constitution provides for a democratic regime, and one could argue that the elections were instrumental in establishing a new government, these democratic institutions can hardly be said to work at all. Performance of democratic institutions
9 BTI 01 Côte d Ivoire 9 Most elite actors have shown little interest in reviving the democratic process. This is certainly the case of the incumbent president and his party, which have postponed elections for many years and have hindered the successful completion of a democratic change of power. They have defended a narrow and legalistic interpretation of democratic rule that may have actually brought democracy into thorough discredit with large segments of the population. The political opposition to Gbagbo claims to guarantee a return to democratic rule, but neither Bedié nor Ouattara had ever shown particular respect for democracy when they were in power. Northern military officers who fought against Gbagbo s elected government in 00 cannot be considered as supportive of democratic institutions however willing one might be in accepting their moral case for the fairer treatment of northern populations. Commitment to democratic institutions 5 Political and Social Integration Three political parties have dominated political life since the mid-1990s: the Front Populaire Ivoirien (FPI), the Rassemblement des Républicains (RDR) and the Parti Démocratique de la Côte d Ivoire (PDCI). Leaders of these parties still dominate political life as of 010. Both the FPI and the PDCI have a long tradition of political participation and used to be strongly rooted in society. To an extent, violent conflict has stymied the party system and prevented the formation of new parties. Although the rebel New Forces participate in government, they have yet to transform into a political party, despite former rebel leader Soro becoming Ouattara s prime minister following the 010 elections. Amid the highly polarized and violent political atmosphere since 00 political parties have had limited opportunities to organize and consequently have not had any meaningful role in forming or moderating social interests. While interest groups exist (cocoa planters associations and student unions, as two examples) they seldom cooperate (many new cocoa planters associations have been formed since 005) and have no or even negative influence on the political process. Important social interests remain underrepresented (especially religious and ethnically cross-cutting interest groups that were much more active in the 1990s). The creation of a loosely coordinated civil society body (Convention de la Société Civile Ivoirienne, CSCI) in 005 was enthusiastically welcomed but still did not help to manage the election crises or general rebel demobilization. While no reliable survey data exist, support for democracy has always been moderate, as the tradition of benign authoritarian rule (l houphouëtisme) or exclusionary varieties of nationalism (FPI and Gbagbo) are more characteristic of Ivorian political culture. Party system 3 Interest groups 3 Approval of democracy n/a
10 BTI 01 Côte d Ivoire 10 On the other hand, voter turnout was very high at over 80% of the electorate in the 010 elections. This is, however, not a conclusive sign of the approval of democratic elections per se, but rather a sign of the de facto political relevance of the elections and the extent of political mobilization. The lack of trust within ethnically mixed neighborhoods (also the practice of setting indigenous and migrant populations against each other) has been identified since the 1990s as a major root cause of social conflict. Civil war and mass evictions of migrant workers have aggravated the problem. Violent clashes continue, among migrant workers from Mali or Burkina Faso and Ivorians supporting Gbagbo s regime and between Baoule and Bete ethnic groups in the cocoa belt. Although many local peace-building activities (often through external funding) have been implemented, there is little indication of generalized (i.e., not only bonding) social capital within the social fabric of Côte d Ivoire. Social capital II. Economic Transformation 6 Level of Socioeconomic Development As one of the world s least developed countries (ranked 149th of 169 on the Human Development Index 010), Côte d Ivoire exhibits social marginalization that is quantitatively and qualitatively extensive and structurally ingrained. Almost all relevant indicators point to severe problems, although violent conflict has made collection of valid data difficult or impossible. Life expectancy is 58.4 years (010). According to World Bank data, the percentage of people living under a poverty line of $1.5 per day has increased to 49% of the population (008). The civil war has led to more informal economic activities and to growing socioeconomic disparities between the north and south. Although some socioeconomic problems have been clearly linked to the civil war and its consequences (i.e., a lack of administrative structures in the north) many barriers are structurally ingrained. Question Score Socioeconomic barriers Economic indicators GDP $ mn GDP growth % Inflation (CPI) % Unemployment %
11 BTI 01 Côte d Ivoire 11 Economic indicators Foreign direct investment % of GDP Export growth % Import growth % Current account balance $ mn Public debt % of GDP External debt $ mn Total debt service $ mn Cash surplus or deficit % of GDP Tax revenue % of GDP Government consumption % of GDP Public expnd. on edu. % of GDP Public expnd. on health % of GDP R&D expenditure % of GDP Military expenditure % of GDP Sources: The World Bank, World Development Indicators 011 International Monetary Fund (IMF), World Economic Outlook 011 Stockholm International Pease Research Institute (SIPRI), Military Expenditure Database Organization of the Market and Competition Although Côte d Ivoire used to be hailed as a model of capitalism in Africa, the institutional setting for free markets or competition has never been sufficient, especially in the vital cocoa sector where uncertainty over both economic fundamentals and regulations persists a decade after the disbanding of the central agricultural marketing board with its marketing monopoly. Côte d Ivoire ranks 1nd out of 179 countries ( mostly unfree ) on the 011 Index of Economic Freedom. In the context of military and political conflict, the informal economic sector has gained in importance, with the increase of smuggling and other illicit activities. Donors have made considerable investments toward creating a more nurturing environment for small and medium-sized enterprises. Monopolies and oligopolies are neither regulated consistently nor considered a policy issue of major importance, and even less so since 00. In several sectors such as electricity, water, and transport, foreign-owned companies hold de facto monopolies. The inefficiency of the Ivorian Electric Company (Compagnie Market-based competition 4 Anti-monopoly policy
12 BTI 01 Côte d Ivoire 1 Ivoirienne d Electricité) and a lack of new investments over the last decade have led to the first power cuts in recent history in early 010. Conflict has seriously affected the free circulation of goods and services over the last decade. The reestablishment of a national customs service was still not finished at the end of 010. Côte d Ivoire used to be a regional hub, and will certainly again attract much trade (and investment) once political stability is regained. Foreign trade follows non-discrimination principles (as provided for in the West African Economic and Monetary Union (WAEMU) and ECOWAS regional schemes), but numerous rules, barriers and informal intervention by officeholders constrain the actual liberalization of foreign trade. Since 1995, no WTO Trade Policy Review has been conducted. Liberalization of foreign trade 5 The cocoa and coffee trade is to a large extent run by multinational companies, and as still the world s largest producer of cocoa, the country s economy is, against all odds, strongly integrated into the world economy. Alassane Ouattara, the president-elect of Côte d Ivoire, called for a ban on cocoa exports in an attempt to starve incumbent President Laurent Gbagbo of funds as he refused to give up office. The suggested ban inspired a rise in the price of the country s cash crop. The banking sector has survived the politico-military conflict relatively well, but has suffered from the increase in government arrears to the private sector and from the temporary closure of banks in the north and west. A legal framework for the banking system and capital markets exists; the West African regional stock exchange (Bourse Régionale des Valeurs Mobilières, BRVM) is located in Abidjan and lists 39 companies (010), having continued with its activities throughout the crisis. Banking system 5 The BCEAO crisis of early 011 led to a closure of all Central Bank of the West African States (BCEAO) branches in Côte d Ivoire. The BVRM also suspended all trading in Abidjan after troops supporting incumbent president Gbagbo seized the building in February 011. The banking system has been threatened as seven major international commercial banks have suspended operations and other banks have been overwhelmed by customers trying to withdraw savings. The closures stem from insecurity following the closure of the BCEAO and an international sanctions effort to squeeze Gbagbo of funds and force him to stand down after U.N.-certified results of the 8 November 010 vote showed his rival Ouattara as the winner. Gbagbo s government decreed that major banks such as the Ivorian branches of Societe Generale and BNP Paribas that suspended their operations would be nationalized.
13 BTI 01 Côte d Ivoire 13 8 Currency and Price Stability As a member of the CFA-franc monetary union, Côte d Ivoire cannot pursue an independent policy on currency and foreign-exchange rates. The currency is pegged to the euro (formerly pegged to the French franc), and the BCEAO is fully independent and targets inflation as its main priority. With some exceptions, such as a spurt of inflation after the CFA franc was devalued in 1994 (at a temporary peak of 6.3% in 008 amid a surge in international food prices), this has led to relatively low inflation. Inflation was between 1% and 4.3% throughout the last decade and, according to Economist Intelligence Unit estimates, 0.9% and 1.1% in 009 and 010. Despite the political unrest following the presidential election, there was no discernible increase in the inflation rate. As the country has tended to quickly accumulate both domestic and external payment arrears, fiscal policy used to be the main source of disagreement with the IMF. Programs have been negotiated, suspended and resumed since Since 00 the country has lapsed in its performance commitments and programs suspended with the outbreak of civil war in September 00 were only resumed in 009. Despite some fiscal shortfalls and extra-budgetary expenditures, the IMF awarded a PRGF in March 009 and was quite optimistic about further prospects. The government was also optimistic about reaching the completion point under the HIPC initiative, which would allow the write-off of large multilateral and bilateral debt. Anti-inflation / forex policy 9 Macrostability 3 Various World Bank reports have raised concerns about public financial management although capacities have been strengthened over recent years. Since the disputed elections, the fiscal situation has been thrown into chaos. Donors have suspended payments; the rival government(s) has stopped honoring interest payments; the BCEAO has cut off Gbagbo s access to state accounts. 9 Private Property Property rights are adequately defined but cannot be considered satisfactorily safeguarded by law (certainly not in the north). The main problem with property rights is land tenure and especially the rights of immigrants to secure property rights on the land they farm. Private companies represent the backbone of the economy, but there are still some important state companies and strong market concentrations. Property rights 4 Private enterprise 5
14 BTI 01 Côte d Ivoire 14 The IMF has been increasingly concerned about the poor business operating environment. Côte d Ivoire occupied a miserable 168th out of 183 countries listed in the Doing Business Index 010. The establishment of a privately run price stabilization system for the cocoa sector in the wake of the liberalization of prices by the government in 1999 has led to unsatisfactory results. With world cocoa prices at a 33-year high in 010, most farmers did not benefit and increased profits were absorbed by middlemen and exporters with ties to the government. Most observers expected the creation of a new state-controlled cocoa marketing body following the establishment of a democratically elected government. 10 Welfare Regime The government has committed itself to alleviate poverty, but this has been undermined by political instability and the de facto division of the country since 00. Negotiations concerning a PRSP, originally expected in 00, were suspended over many years, but a PRGF was eventually concluded in 009. The World Bank presented in October 010 a new interim PRSP, the execution of which was linked, however, to the successful outcome of the presidential elections. Social services have deteriorated amid a lack of funding, confirmed by the latest UNDP indices for education (54.6% literacy) and life expectancy (58.4 years). The large informal economic sector contributes to poverty reduction, albeit to an unknown extent. Public expenditure for health stood at 1.0% of GDP, the second lowest value across sub-saharan Africa. Women lack adequate access to public office and to educational institutions, as shown by the low percentage of women in parliament and a significantly low female literacy rate of 44.3% (64.% for men). Female enrollment in the educational system is among the lowest worldwide (ratio of female enrollment at the primary level is 79.4%, and at the secondary level, 55.1%). While equality of opportunity is protected by the constitution and by other legal norms, since the mid- 1990s people from the north have been discriminated against in the education system and in the job market. Social safety nets Equal opportunity 11 Economic Performance The political-military standoff since 1999, the civil war and 00 division of the country have all contributed to a severe economic crisis and subsequent negative growth rates. It has to be stressed that the economy managed to not collapse, despite infrastructure problems and business disruption. But the country s modest macroeconomic growth so far can be contributed to cocoa-growing areas (and Output strength 4
15 BTI 01 Côte d Ivoire 15 cocoa s extraordinarily high world price) and especially oil exploration in the Gulf of Guinea, efforts which have been largely unaffected by the ongoing conflict. Inflation is low and growth rates in 009 and 010 stood at 4.% and 3.6% respectively, according to Economist Intelligence Unit estimates. In 009 there was real growth of per capita income for the first time since Employment has fallen in both the north and south and outstanding debts cannot be rescheduled or written off before the completion point is reached (HIPC status). The overall potential for further growth is seen to be strong but still heavily dependent on the settlement of the conflict between incumbent President Gbagbo and election-winner Ouattara and the severity of economic sanctions. Until October 010 all donors had agreed upon a relatively optimistic assessment, always arguing that further developments would depend on the outcome of elections. If we take into account the situation since November 010, however, the picture is quite bleak. 1 Sustainability Environmentally sustainable growth receives only sporadic consideration and has only a rudimentary framework (Environmental Performance Index score 54.3, rank 10). The country depends more than ever on commodity exports, but the fiscal squeeze being passed on producers is leading them to use extensive and extreme cultivation methods; for example, most virgin forest has been completely destroyed despite strict regulations established in the 1990s restricting commercial logging and agricultural encroachment. The lax and irresponsible handling of environmental issues was revealed by a toxic waste disaster in late August 006. In the north, environmental regulations have not been enforced since 00. Côte d Ivoire has a poor record in supporting educational infrastructure. The country has since independence put more emphasis on importing skilled people than on developing and training its own. Expenditure for education stood at around 4.6% over the last decade (and also in 008, the last year when data was available). The quality of education seems, however, rather poor, as shown by a low enrollment rate (74.5%) and a still very low literacy rate of 54.6% (both figures for 010). For over six years students in the north have lacked proper schooling, with probably catastrophic consequences in the mid- to long-term. Environmental policy 3 Education policy / R&D 3
16 BTI 01 Côte d Ivoire 16 Transformation Management I. Level of Difficulty It is difficult to distinguish between constraints that are structural and those that are man-made and result from actions of the current political leadership. The current government inherited an already impoverished country, a highly polarized political process and violent conflict as the norm. The country s division has been a terrific obstacle to governance. Côte d Ivoire previously had the most developed economic infrastructure in West Africa and the fact that production in the cocoa sector could be increased in comparison to pre-00 levels shows that the country can and still does benefit from its favorable climatic, geographical and structural conditions. There are also still unexploited further mineral resources (such as oil and gas). Traditions of civil society are few and have further been weakened throughout the civil conflict. The landscape of voluntary organizations concentrates on the economic sector where independent planter associations have existed since colonial times. These activities lack, however, a component of civic or public engagement. The climate of intimidation and the militarization of public life since the coup d état of 1999 have crushed much of the potential for civic participation in public life. There are more than 50 different ethnic groups in Côte d Ivoire. After years of social harmony and the promotion of migrant work from neighboring countries by the late President Houphouet-Boigny, successor governments have fully exploited ethnic resentments to their narrow political advantage. The country thus plunged into violent conflict with overt ethnic dimensions. Although the open military conflict was halted in late 004, inter-community violence continued to occur, especially in the villages of the western cocoa belt. Structural constraints 8 Civil society traditions 8 Conflict intensity 8 Following the electoral crisis and the establishment of two parallel governments in December 010, the country is verging on new violent ethnic conflict.
17 BTI 01 Côte d Ivoire 17 II. Management Performance 14 Steering Capability The Ouagadougou peace agreement (March 007) set a reduced number of clear priorities for the period until the presidential elections, including the demobilization of various armed forces and the preparation of an acceptable electoral list. In addition the government was supposed to restart cooperation with donors, especially assuring the execution of the PRGF, with the goal of putting the economy back on track. While both the Gbagbo government and former rebels previously showed an impressive capability in doing everything possible to avoid a smooth transformation, things somehow changed; although the sincerity of the actors in pursuing these objectives remains unclear. There is a lot of speculation about the presidency spending considerable sums of money off budget (especially from cocoa and oil) to equip and train the army. The former rebels have resisted effective demobilization over the years and have maintained their grip on the north without any international recognition or formalized economic system. The economy has recovered despite, and not because of, governmental action. Question Score Prioritization 1 The electoral conflict clearly reveals the total lack of steering capability of both incumbent President Gbagbo and President-elect Ouattara. Economic policy has focused simply on keeping the main functions of government operating and on collecting sufficient revenue to pay civil service wages. The government has tried to boost revenue by any and all means, thereby neglecting structural and qualitative reforms such as judicial reform, reorganization of the cocoa and coffee market and forgoing investment in basic health care, primary education, roads and rural electrification in accordance with the PRSP. Further democratization is clearly not on the agenda, as was shown after the election. Unpopular measures such as the incremental scrapping of fuel subsidies since 008 were reversed only days later after massive transport strikes. Implementation The successful organization of relatively fair elections in 010 was an achievement of the international community and of dedicated leaders from civil society and political parties. The very notion of policy learning assumes a minimum of coherent policy-making, which seems to have been restricted to the management of macroeconomic policies under the finance minister who established good relations with IFIs by improving fiscal management. Policy learning
18 BTI 01 Côte d Ivoire 18 The whole electoral crisis can be seen as a grandiose example of policy learning by the incumbent president, but such learning obviously does not correspond with the normative framework of this survey. 15 Resource Efficiency In the country s current political context, it is difficult to determine the government s efficient use of assets. We lack reliable information on how resources are spent within the context of an unrealistic and opaque budget (as criticized by IMF) and without an independent audit of the cocoa and oil sector. There are few doubts that the political elites (both in the north and the south) have consumed most state resources themselves to a large extent over recent years. There is no indication to assume that the government has been able to seriously coordinate conflicting objectives or interests. The Ouagadougou formula consisted of an individual veto from both President Gbagbo and Prime Minister Soro over all policy decisions, so there was effectively a minimum of coordination between these two men. The country s toxic waste scandal or the corruption case against top managers from the cocoa sector revealed both the chaotic state of affairs and the general lack of a coherent policy response. The severe economic downturn since the military conflict erupted in 00 seems to have led to higher levels of generalized corruption and venality at all levels of public administration in the south, especially in judicial proceedings, contract awards, customs and tax issues. The highly publicized arrest of managers from the cocoa sector did not result from any systematic anti-corruption policies. It is telling that the state was unable to present sufficient evidence, and the managers were temporarily released in January 011 after more than two years in prison without any charges brought against them, while the legal process was repeatedly postponed. Efficient use of assets Policy coordination 1 Anti-corruption policy Similarly, two heads of the then ruling party, FPI, accused each other of corruption in 009, but an investigation led by President Gbagbo did not find any evidence to support the accusations. 16 Consensus-Building The country s political leadership does not hold democratic and economic transformation as a goal. The main political actors struggled to implement the minimum consensus on reforms reached at Ouagadougou, but the elections showed that this consensus was hollow. There is no fundamental conflict among the most relevant actors regarding the goal of a market-based economy; however, the political and military crisis since 1999 has made political survival the top priority Consensus on goals
19 BTI 01 Côte d Ivoire 19 and allowed military leaders to fill their pockets in the meantime. Much of the Ivoirité debate stemmed from different notions of democracy, for example, a narrow and exclusionary definition based on family lines, the rights of native Ivorians and the majority principle, versus a more tolerant and inclusionary notion of citizenship. There are plenty of anti-democratic actors in Côte d Ivoire, both within and outside the government. Many of these actors have benefited from the continued state of affairs, that is, an unelected government that still maintains direct access to the country s economic resources. These anti-democratic actors have full control over the reform process, which is in this case the normalization of the political process through the holding of acceptably fair and free elections. Anti-democratic actors It certainly makes sense to see Alassane Ouattara as the winner of the 010 presidential election, but whether he is indeed a reformer remains to be seen. Both the Gbagbo government and the northern New Forces have done little to mend ethnic cleavages, and Côte d Ivoire could be seen as a textbook example of ethnic politicization taken to its violent extreme. Between 001 and 006, death squads harassed or killed based on ethnic and linguistic affiliation, violence that was tolerated or even underhandedly promoted by government circles. The apparent drop in the number of killings and of instances of ethnic violence has to do with the massive international military presence in the country and not with any change in local political management. Ethnic cleavages remain salient in most parts of the country, and there are still internally displaced refugees; the political-military division of the country, although formally ended in late 008, is the physical manifestation of socio-cultural cleavages. Cleavage / conflict management 1 Faced with electoral defeat, incumbent President Gbagbo has used state media and his militia to clearly exacerbate ethnic and social cleavages. The already very limited participation of civil society in the political process was weakened by the Ouagadougou peace process, which consisted of the marginalization of external actors, traditional political parties and civil society actors to the benefit of the tandem power holders President Gbagbo and Prime Minister Soro. Civil society participation 3 Civil society actors were more strongly involved in the electoral process, especially in electoral observation. They have, however, been unable to fight growing political polarization. Economic associations still try to influence policy-making in the cocoa sector but without any meaningful impact.
20 BTI 01 Côte d Ivoire 0 In the period under review, conflict parties continue to commit acts of injustice and murder is still rife. The establishment of a stable political dispensation is a necessary condition to initiate, again, a process of reconciliation which started initially between 000 and 00 when the civil war first broke out. The electoral campaign appeared to represent a tepid reconciliation of leaders (for example, during a television debate between Gbagbo and Ouattara), but elections are seldom a good time to bring about reconciliation. Reconciliation 17 International Cooperation Côte d Ivoire s political crisis remains internationalized with the presence of French military forces (Operation Unicorn) and the deployment of the U.N. peacekeeping mission (United Nations Operation in Côte d Ivoire, UNOCI) both covered by mandates from the U.N. Security Council. Relations with donors have been strained since the late 1990s, but particularly so since 00. Effective use of support 3 Given the past history of relations between donors and Côte d Ivoire, which has seen funds suspended for prolonged periods of time over corruption concerns, the unwillingness of donors to offer substantial support until a political agreement seems well-established is understandable. The current power-sharing government has certainly improved relations with donors and formal resumption of IFI lending occurred in July-August 007. The government was very clever in using the international support for elections by organizing the most expensive election campaign ever experienced on African soil, as well as by engineering a rapprochement with the IMF to obtain a write-off of outstanding debts. President Gbagbo knew very well, however, that his desperate constitutional coup was going to compromise all these previous efforts. The Gbagbo presidency has certainly lost its international reputation as a credible partner with international organizations, bilateral donors and regional partners. Credibility It is true that the transitional Soro government established some credibility which helped to re-establish a connection to the World Bank and the IMF in April 006. The country s relationship with France has gone through various stages. The former colonial power remains a main trading partner, foreign investor and bilateral donor and maintains a permanent military base in Abidjan. The French community has shrunk to around 8,000 residents, but French-controlled business still accounts for a considerable share of the country s tax base. At various times since 00, President Gbagbo has threatened French residents directly or indirectly, and the French government has declared that it would pull its troops if asked to do so. French
BTI 2010 Côte d Ivoire Country Report
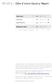 BTI 2010 Côte d Ivoire Country Report Status Index 1-10 3.53 # 115 of 128 Democracy 1-10 3.20 # 116 of 128 Market Economy 1-10 3.86 # 109 of 128 Management Index 1-10 2.91 # 116 of 128 scale: 1 (lowest)
BTI 2010 Côte d Ivoire Country Report Status Index 1-10 3.53 # 115 of 128 Democracy 1-10 3.20 # 116 of 128 Market Economy 1-10 3.86 # 109 of 128 Management Index 1-10 2.91 # 116 of 128 scale: 1 (lowest)
BTI 2018 Country Report. Côte d Ivoire
 BTI 2018 Country Report Côte d Ivoire This report is part of the Bertelsmann Stiftung s Transformation Index (BTI) 2018. It covers the period from February 1, 2015 to January 31, 2017. The BTI assesses
BTI 2018 Country Report Côte d Ivoire This report is part of the Bertelsmann Stiftung s Transformation Index (BTI) 2018. It covers the period from February 1, 2015 to January 31, 2017. The BTI assesses
Côte d Ivoire. Efforts to End the Political-Military Stalemate
 January 2009 country summary Côte d Ivoire At the end of 2008, hopes that a March 2007 peace accord would end the six-year political and military stalemate between government forces and northern-based
January 2009 country summary Côte d Ivoire At the end of 2008, hopes that a March 2007 peace accord would end the six-year political and military stalemate between government forces and northern-based
Polity IV Country Report 2010: Ivory Coast
 Polity IV Country Report 2010: Ivory Coast Score: 2009 2010 Change Polity: -88-88 x Democ: -88-88 x Autoc: -88-88 x Durable: 0 Tentative: No SCODE IVO CCODE 437 Date of Report 1 June 2011 Polity IV Component
Polity IV Country Report 2010: Ivory Coast Score: 2009 2010 Change Polity: -88-88 x Democ: -88-88 x Autoc: -88-88 x Durable: 0 Tentative: No SCODE IVO CCODE 437 Date of Report 1 June 2011 Polity IV Component
Ethiopian National Movement (ENM) Program of Transition Towards a Sustainable Democratic Order in Ethiopia
 Ethiopian National Movement (ENM) Program of Transition Towards a Sustainable Democratic Order in Ethiopia January 2018 1 I. The Current Crisis in Ethiopia and the Urgent need for a National Dialogue Ethiopia
Ethiopian National Movement (ENM) Program of Transition Towards a Sustainable Democratic Order in Ethiopia January 2018 1 I. The Current Crisis in Ethiopia and the Urgent need for a National Dialogue Ethiopia
Under-five chronic malnutrition rate is critical (43%) and acute malnutrition rate is high (9%) with some areas above the critical thresholds.
 May 2014 Fighting Hunger Worldwide Democratic Republic of Congo: is economic recovery benefiting the vulnerable? Special Focus DRC DRC Economic growth has been moderately high in DRC over the last decade,
May 2014 Fighting Hunger Worldwide Democratic Republic of Congo: is economic recovery benefiting the vulnerable? Special Focus DRC DRC Economic growth has been moderately high in DRC over the last decade,
JANUARY 2018 COUNTRY SUMMARY. Côte d Ivoire
 JANUARY 2018 COUNTRY SUMMARY Côte d Ivoire Cote d Ivoire continued the process of moving away from the successive and bloody political crises of 2000-11, with the United Nations ending a 13-year peacekeeping
JANUARY 2018 COUNTRY SUMMARY Côte d Ivoire Cote d Ivoire continued the process of moving away from the successive and bloody political crises of 2000-11, with the United Nations ending a 13-year peacekeeping
CÔTE D IVOIRE. Insecurity and Lack of Disarmament Progress JANUARY 2013
 JANUARY 2013 COUNTRY SUMMARY CÔTE D IVOIRE Ongoing socio-political insecurity, failure to deliver impartial justice for past crimes, and inadequate progress in addressing the root causes of recent political
JANUARY 2013 COUNTRY SUMMARY CÔTE D IVOIRE Ongoing socio-political insecurity, failure to deliver impartial justice for past crimes, and inadequate progress in addressing the root causes of recent political
AFRICAN DEVELOPMENT BANK GROUP
 AFRICAN DEVELOPMENT BANK GROUP Ministerial Round Table Discussions PANEL 1: The Global Financial Crisis and Fragile States in Africa The 2009 African Development Bank Annual Meetings Ministerial Round
AFRICAN DEVELOPMENT BANK GROUP Ministerial Round Table Discussions PANEL 1: The Global Financial Crisis and Fragile States in Africa The 2009 African Development Bank Annual Meetings Ministerial Round
Cote d'ivoire: No Peace in Sight
 INTERNATIONAL CRISIS GROUP - NEW REPORT Cote d'ivoire: No Peace in Sight Dakar/Brussels, 12 July 2004: Lack of good faith on the part of all sides in the Côte d'ivoire peace process is jeopardising the
INTERNATIONAL CRISIS GROUP - NEW REPORT Cote d'ivoire: No Peace in Sight Dakar/Brussels, 12 July 2004: Lack of good faith on the part of all sides in the Côte d'ivoire peace process is jeopardising the
FACT SHEET: 25 October 2010
 FACT SHEET: 25 October 2010 The first round of presidential elections in Côte d Ivoire is scheduled to take place on 31 October 2010. The national institution in charge of organizing and conducting the
FACT SHEET: 25 October 2010 The first round of presidential elections in Côte d Ivoire is scheduled to take place on 31 October 2010. The national institution in charge of organizing and conducting the
Adopted by the Security Council at its 4918th meeting, on 27 February 2004
 United Nations S/RES/1528 (2004) Security Council Distr.: General 27 February 2004 04-25320 (E) *0425320* Resolution 1528 (2004) Adopted by the Security Council at its 4918th meeting, on 27 February 2004
United Nations S/RES/1528 (2004) Security Council Distr.: General 27 February 2004 04-25320 (E) *0425320* Resolution 1528 (2004) Adopted by the Security Council at its 4918th meeting, on 27 February 2004
3.3. Côte d Ivoire. Background
 3.3 Côte d Ivoire Sustained stability in Côte d Ivoire during 2009 contributed to the alteration of the peacekeeping operations in the country. The Frenchled Operation Licorne halved its presence, and
3.3 Côte d Ivoire Sustained stability in Côte d Ivoire during 2009 contributed to the alteration of the peacekeeping operations in the country. The Frenchled Operation Licorne halved its presence, and
Helen Clark: Opening Address to the International Conference on the Emergence of Africa
 Helen Clark: Opening Address to the International Conference on the Emergence of Africa 18 Mar 2015 It is a pleasure to join the President of Cote d Ivoire, H.E. Alassane Ouattara, in welcoming you to
Helen Clark: Opening Address to the International Conference on the Emergence of Africa 18 Mar 2015 It is a pleasure to join the President of Cote d Ivoire, H.E. Alassane Ouattara, in welcoming you to
VENEZUELA: Oil, Inflation and Prospects for Long-Term Growth
 VENEZUELA: Oil, Inflation and Prospects for Long-Term Growth Melody Chen and Maggie Gebhard 9 April 2007 BACKGROUND The economic history of Venezuela is unique not only among its neighbors, but also among
VENEZUELA: Oil, Inflation and Prospects for Long-Term Growth Melody Chen and Maggie Gebhard 9 April 2007 BACKGROUND The economic history of Venezuela is unique not only among its neighbors, but also among
Letter dated 20 December 2006 from the Chairman of the Peacebuilding Commission addressed to the President of the Security Council
 United Nations S/2006/1050 Security Council Distr.: General 26 December 2006 Original: English Letter dated 20 December 2006 from the Chairman of the Peacebuilding Commission addressed to the President
United Nations S/2006/1050 Security Council Distr.: General 26 December 2006 Original: English Letter dated 20 December 2006 from the Chairman of the Peacebuilding Commission addressed to the President
INFORMATION NOTE ON POST-ELECTION CRISIS IN THE IVORY COAST
 INFORMATION NOTE ON POST-ELECTION CRISIS IN THE IVORY COAST (October-December 2010) 1. BACKGROUND 1. December 24th, 1999: Military coup d'etat against President Henri Konan Bedie 2. October 26th, 2000:
INFORMATION NOTE ON POST-ELECTION CRISIS IN THE IVORY COAST (October-December 2010) 1. BACKGROUND 1. December 24th, 1999: Military coup d'etat against President Henri Konan Bedie 2. October 26th, 2000:
BTI 2010 Burkina Faso Country Report
 BTI 2010 Burkina Faso Country Report Status Index 1-10 4.74 # 87 of 128 Democracy 1-10 5.17 # 74 of 128 Market Economy 1-10 4.32 # 96 of 128 Management Index 1-10 4.88 # 68 of 128 scale: 1 (lowest) to
BTI 2010 Burkina Faso Country Report Status Index 1-10 4.74 # 87 of 128 Democracy 1-10 5.17 # 74 of 128 Market Economy 1-10 4.32 # 96 of 128 Management Index 1-10 4.88 # 68 of 128 scale: 1 (lowest) to
Côte d Ivoire. Country Overview Politics. Economy. Social/Human Development
 Côte d Ivoire Country Overview Politics Côte d Ivoire is a democratic republic in West Africa. In October 2015, President Alassane Outarra was re elected in elections judged to be credible by the international
Côte d Ivoire Country Overview Politics Côte d Ivoire is a democratic republic in West Africa. In October 2015, President Alassane Outarra was re elected in elections judged to be credible by the international
Strategy for Sweden s development cooperation with Zimbabwe
 Strategy for Sweden s development cooperation with Zimbabwe 2017 2021 Strategy for Sweden s development cooperation with Zimbabwe 1 1. Focus The objective of Sweden s international development cooperation
Strategy for Sweden s development cooperation with Zimbabwe 2017 2021 Strategy for Sweden s development cooperation with Zimbabwe 1 1. Focus The objective of Sweden s international development cooperation
DRAFT REPORT. EN United in diversity EN 2014/2230(INI) on the current political situation in Afghanistan (2014/2230(INI))
 EUROPEAN PARLIAMT 2014-2019 Committee on Foreign Affairs 2014/2230(INI) 6.3.2015 DRAFT REPORT on the current political situation in Afghanistan (2014/2230(INI)) Committee on Foreign Affairs Rapporteur:
EUROPEAN PARLIAMT 2014-2019 Committee on Foreign Affairs 2014/2230(INI) 6.3.2015 DRAFT REPORT on the current political situation in Afghanistan (2014/2230(INI)) Committee on Foreign Affairs Rapporteur:
Adopted by the Security Council at its 7681st meeting, on 28 April 2016
 United Nations S/RES/2284 (2016) Security Council Distr.: General 28 April 2016 Resolution 2284 (2016) Adopted by the Security Council at its 7681st meeting, on 28 April 2016 The Security Council, Recalling
United Nations S/RES/2284 (2016) Security Council Distr.: General 28 April 2016 Resolution 2284 (2016) Adopted by the Security Council at its 7681st meeting, on 28 April 2016 The Security Council, Recalling
Country Summary January 2005
 Country Summary January 2005 Afghanistan Despite some improvements, Afghanistan continued to suffer from serious instability in 2004. Warlords and armed factions, including remaining Taliban forces, dominate
Country Summary January 2005 Afghanistan Despite some improvements, Afghanistan continued to suffer from serious instability in 2004. Warlords and armed factions, including remaining Taliban forces, dominate
Security Council. United Nations S/2007/144. Letter dated 13 March 2007 from the Secretary-General addressed to the President of the Security Council
 United Nations S/2007/144 Security Council Distr.: General 13 March 2007 Original: English Letter dated 13 March 2007 from the Secretary-General addressed to the President of the Security Council I have
United Nations S/2007/144 Security Council Distr.: General 13 March 2007 Original: English Letter dated 13 March 2007 from the Secretary-General addressed to the President of the Security Council I have
Letter dated 12 September 2005 from the Secretary-General addressed to the President of the Security Council
 United Nations Security Council Distr.: General 13 September 2005 Original: English S/2005/584 Letter dated 12 September 2005 from the Secretary-General addressed to the President of the Security Council
United Nations Security Council Distr.: General 13 September 2005 Original: English S/2005/584 Letter dated 12 September 2005 from the Secretary-General addressed to the President of the Security Council
About the. ground ers AFRICAPORTAL. The Root Causes of the. Backgrounder NO. 5 April By Tom Ogwang
 AFRICAPORTAL a project of the africa initiative Backgrounder NO. 5 April 2011 About the Portal Back ground ers The Africa Portal backgrounder series offers brief background information and commentary on
AFRICAPORTAL a project of the africa initiative Backgrounder NO. 5 April 2011 About the Portal Back ground ers The Africa Portal backgrounder series offers brief background information and commentary on
COUNTRY REPORT. by Andrei V. Sonin 1 st Secretary, Ministry of Foreign Affairs
 Regional Workshop on Capacity-Building in Governance and Public Administration for Sustainable Development Thessaloniki, 29-31 July 2002 Ladies and Gentlemen, Dear colleagues, COUNTRY REPORT B E L A R
Regional Workshop on Capacity-Building in Governance and Public Administration for Sustainable Development Thessaloniki, 29-31 July 2002 Ladies and Gentlemen, Dear colleagues, COUNTRY REPORT B E L A R
ACP-EU JOINT PARLIAMENTARY ASSEMBLY
 ACP-EU JOINT PARLIAMTARY ASSEMBLY Committee on Political Affairs 23 September 2003 DRAFT REPORT on conflict prevention, the peace process and post-conflict management Co-Rapporteurs: Philippe Morillon
ACP-EU JOINT PARLIAMTARY ASSEMBLY Committee on Political Affairs 23 September 2003 DRAFT REPORT on conflict prevention, the peace process and post-conflict management Co-Rapporteurs: Philippe Morillon
IMPACT OF GLOBALIZATION ON POVERTY: CASE STUDY OF PAKISTAN
 Romain Pison Prof. Kamal NYU 03/20/06 NYU-G-RP-A1 IMPACT OF GLOBALIZATION ON POVERTY: CASE STUDY OF PAKISTAN INTRODUCTION The purpose of this paper is to examine the effect of globalization in Pakistan
Romain Pison Prof. Kamal NYU 03/20/06 NYU-G-RP-A1 IMPACT OF GLOBALIZATION ON POVERTY: CASE STUDY OF PAKISTAN INTRODUCTION The purpose of this paper is to examine the effect of globalization in Pakistan
Inclusive growth and development founded on decent work for all
 Inclusive growth and development founded on decent work for all Statement by Mr Guy Ryder, Director-General International Labour Organization International Monetary and Financial Committee Washington D.C.,
Inclusive growth and development founded on decent work for all Statement by Mr Guy Ryder, Director-General International Labour Organization International Monetary and Financial Committee Washington D.C.,
Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, of the United Nations Population Fund
 United Nations DP/DCP/BEN/2 Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, of the United Nations Population Fund and of the United Nations Office for Project Services Distr.: General 15 March
United Nations DP/DCP/BEN/2 Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, of the United Nations Population Fund and of the United Nations Office for Project Services Distr.: General 15 March
African Local Governments and the Global Economic and Financial Crisis
 Second Conference of African and European Regional and Local Authorities on the theme of The Impact of the Economic and Financial Crisis on Decentralized Governance in Africa: the Response of Local Authorities
Second Conference of African and European Regional and Local Authorities on the theme of The Impact of the Economic and Financial Crisis on Decentralized Governance in Africa: the Response of Local Authorities
Central African Republic
 JANUARY 2014 COUNTRY SUMMARY Central African Republic A rebel coalition known as the Seleka took control of Bangui, the capital of the Central African Republic (CAR), on March 24, 2013, forcing out the
JANUARY 2014 COUNTRY SUMMARY Central African Republic A rebel coalition known as the Seleka took control of Bangui, the capital of the Central African Republic (CAR), on March 24, 2013, forcing out the
POLI 12D: International Relations Sections 1, 6
 POLI 12D: International Relations Sections 1, 6 Spring 2017 TA: Clara Suong Chapter 10 Development: Causes of the Wealth and Poverty of Nations The realities of contemporary economic development: Billions
POLI 12D: International Relations Sections 1, 6 Spring 2017 TA: Clara Suong Chapter 10 Development: Causes of the Wealth and Poverty of Nations The realities of contemporary economic development: Billions
Congo's Elections: Making or Breaking the Peace <http://www.crisisgroup.org/home >Congo s Elections: Making or Breaking the Peace,*
 INTERNATIONAL CRISIS GROUP - NEW REPORT Congo's Elections: Making or Breaking the Peace Congo s Elections: Making or Breaking the Peace,* Nairobi/Brussels, 27 April 2006:
INTERNATIONAL CRISIS GROUP - NEW REPORT Congo's Elections: Making or Breaking the Peace Congo s Elections: Making or Breaking the Peace,* Nairobi/Brussels, 27 April 2006:
HOW ECONOMIES GROW AND DEVELOP Macroeconomics In Context (Goodwin, et al.)
 Chapter 17 HOW ECONOMIES GROW AND DEVELOP Macroeconomics In Context (Goodwin, et al.) Chapter Overview This chapter presents material on economic growth, such as the theory behind it, how it is calculated,
Chapter 17 HOW ECONOMIES GROW AND DEVELOP Macroeconomics In Context (Goodwin, et al.) Chapter Overview This chapter presents material on economic growth, such as the theory behind it, how it is calculated,
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS. Issued by the Center for Civil Society and Democracy, 2018 Website:
 ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The Center for Civil Society and Democracy (CCSD) extends its sincere thanks to everyone who participated in the survey, and it notes that the views presented in this paper do not necessarily
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The Center for Civil Society and Democracy (CCSD) extends its sincere thanks to everyone who participated in the survey, and it notes that the views presented in this paper do not necessarily
Key Trade and Development Policy challenges in post-conflict countries: the case of Liberia and Sierra Leone
 Key Trade and Development Policy challenges in post-conflict countries: the case of Liberia and Sierra Leone Conflict in the study countries Development frameworks in Liberia & Sierra Leone Trade and Development
Key Trade and Development Policy challenges in post-conflict countries: the case of Liberia and Sierra Leone Conflict in the study countries Development frameworks in Liberia & Sierra Leone Trade and Development
Lebanon. Lebanon: the largest per capita recipient of refugees in the world
 October 2014 Fighting Hunger Worldwide Is the Syrian crisis jeopardizing the economy and food security in Lebanon? Special Focus Lebanon The crisis in Syria now already in its third year has had an immense
October 2014 Fighting Hunger Worldwide Is the Syrian crisis jeopardizing the economy and food security in Lebanon? Special Focus Lebanon The crisis in Syria now already in its third year has had an immense
How s Life in New Zealand?
 How s Life in New Zealand? November 2017 On average, New Zealand performs well across the different well-being indicators and dimensions relative to other OECD countries. It has higher employment and lower
How s Life in New Zealand? November 2017 On average, New Zealand performs well across the different well-being indicators and dimensions relative to other OECD countries. It has higher employment and lower
MEETING OF THE SUPPORT AND FOLLOW UP GROUP ON THE SITUATION IN MALI BRUSSELS, BELGIUM 5 FEBRUARY 2013 CONCLUSIONS
 MEETING OF THE SUPPORT AND FOLLOW UP GROUP ON THE SITUATION IN MALI BRUSSELS, BELGIUM 5 FEBRUARY 2013 CONCLUSIONS Page 1 CONCLUSIONS 1. The Support and Follow up Group on the Situation in Mali held its
MEETING OF THE SUPPORT AND FOLLOW UP GROUP ON THE SITUATION IN MALI BRUSSELS, BELGIUM 5 FEBRUARY 2013 CONCLUSIONS Page 1 CONCLUSIONS 1. The Support and Follow up Group on the Situation in Mali held its
General Assembly Security Council
 United Nations PBC/3/BDI/3 General Assembly Security Council Distr.: General 9 February 2009 Original: English Peacebuilding Commission Third session Burundi configuration 6 February 2009 Conclusions of
United Nations PBC/3/BDI/3 General Assembly Security Council Distr.: General 9 February 2009 Original: English Peacebuilding Commission Third session Burundi configuration 6 February 2009 Conclusions of
How s Life in France?
 How s Life in France? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, France s average performance across the different well-being dimensions is mixed. While household net adjusted disposable income stands
How s Life in France? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, France s average performance across the different well-being dimensions is mixed. While household net adjusted disposable income stands
E#IPU th IPU ASSEMBLY AND RELATED MEETINGS. Sustaining peace as a vehicle for achieving sustainable development. Geneva,
 138 th IPU ASSEMBLY AND RELATED MEETINGS Geneva, 24 28.03.2018 Sustaining peace as a vehicle for achieving sustainable development Resolution adopted unanimously by the 138 th IPU Assembly (Geneva, 28
138 th IPU ASSEMBLY AND RELATED MEETINGS Geneva, 24 28.03.2018 Sustaining peace as a vehicle for achieving sustainable development Resolution adopted unanimously by the 138 th IPU Assembly (Geneva, 28
Ghana Lower-middle income Sub-Saharan Africa (developing only) Source: World Development Indicators (WDI) database.
 Knowledge for Development Ghana in Brief October 215 Poverty and Equity Global Practice Overview Poverty Reduction in Ghana Progress and Challenges A tale of success Ghana has posted a strong growth performance
Knowledge for Development Ghana in Brief October 215 Poverty and Equity Global Practice Overview Poverty Reduction in Ghana Progress and Challenges A tale of success Ghana has posted a strong growth performance
and with support from BRIEFING NOTE 1
 and with support from BRIEFING NOTE 1 Inequality and growth: the contrasting stories of Brazil and India Concern with inequality used to be confined to the political left, but today it has spread to a
and with support from BRIEFING NOTE 1 Inequality and growth: the contrasting stories of Brazil and India Concern with inequality used to be confined to the political left, but today it has spread to a
MIDDLE EAST NORTH AFRICA
 MIDDLE EAST NORTH AFRICA MIDDLE EAST AND NORTH AFRICA Stretching from Morocco s Atlantic shores to Iran and Yemen s beaches on the Arabian Sea, the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region remains central
MIDDLE EAST NORTH AFRICA MIDDLE EAST AND NORTH AFRICA Stretching from Morocco s Atlantic shores to Iran and Yemen s beaches on the Arabian Sea, the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region remains central
SIXTY-SEVENTH ORDINARY SESSION OF THE ECOWAS COUNCIL OF MINISTERS. Abidjan, 20 & 21 June 2013
 COMMUNAUTE ECONOMIQUE DES ETATS DE L AFRIQUE DE L OUEST ECONOMIC COMMUNITY OF WEST AFRICAN STATES SIXTY-SEVENTH ORDINARY SESSION OF THE ECOWAS COUNCIL OF MINISTERS Abidjan, 20 & 21 June 2013 ADDRESS BY
COMMUNAUTE ECONOMIQUE DES ETATS DE L AFRIQUE DE L OUEST ECONOMIC COMMUNITY OF WEST AFRICAN STATES SIXTY-SEVENTH ORDINARY SESSION OF THE ECOWAS COUNCIL OF MINISTERS Abidjan, 20 & 21 June 2013 ADDRESS BY
Ivory Coast: New Vision or Same Old Story? First Published: March 2000 in Africana.com
 Ivory Coast: New Vision or Same Old Story? First Published: March 2000 in Africana.com By Zachariah Mampilly Despite the fervent hopes of eternal optimists, the recent collapse of the democratic regime
Ivory Coast: New Vision or Same Old Story? First Published: March 2000 in Africana.com By Zachariah Mampilly Despite the fervent hopes of eternal optimists, the recent collapse of the democratic regime
Côte d Ivoire s Political Stalemate: A Symptom of Africa s Weak Electoral Institutions
 UNITED STates institute of peace peacebrief 80 United States Institute of Peace www.usip.org Tel. 202.457.1700 Fax. 202.429.6063 February 7, 2011 Dorina Bekoe E-mail: dbekoe@usip.org Phone: 202.429.4708
UNITED STates institute of peace peacebrief 80 United States Institute of Peace www.usip.org Tel. 202.457.1700 Fax. 202.429.6063 February 7, 2011 Dorina Bekoe E-mail: dbekoe@usip.org Phone: 202.429.4708
Adopted by the Security Council at its 6792nd meeting, on 27 June 2012
 United Nations S/RES/2053 (2012) Security Council Distr.: General 27 June 2012 Resolution 2053 (2012) Adopted by the Security Council at its 6792nd meeting, on 27 June 2012 The Security Council, Recalling
United Nations S/RES/2053 (2012) Security Council Distr.: General 27 June 2012 Resolution 2053 (2012) Adopted by the Security Council at its 6792nd meeting, on 27 June 2012 The Security Council, Recalling
Security and Sustainable Development: an African Perspective
 Security and Sustainable Development: an African Perspective Funmi Olonisakin A consensus has emerged in recent years among security thinkers and development actors alike, that security is a necessary
Security and Sustainable Development: an African Perspective Funmi Olonisakin A consensus has emerged in recent years among security thinkers and development actors alike, that security is a necessary
How s Life in Ireland?
 How s Life in Ireland? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Ireland s performance across the different well-being dimensions is mixed. While Ireland s average household net adjusted disposable
How s Life in Ireland? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Ireland s performance across the different well-being dimensions is mixed. While Ireland s average household net adjusted disposable
Hungary. Basic facts The development of the quality of democracy in Hungary. The overall quality of democracy
 Hungary Basic facts 2007 Population 10 055 780 GDP p.c. (US$) 13 713 Human development rank 43 Age of democracy in years (Polity) 17 Type of democracy Electoral system Party system Parliamentary Mixed:
Hungary Basic facts 2007 Population 10 055 780 GDP p.c. (US$) 13 713 Human development rank 43 Age of democracy in years (Polity) 17 Type of democracy Electoral system Party system Parliamentary Mixed:
Conference on What Africa Can Do Now To Accelerate Youth Employment. Organized by
 Conference on What Africa Can Do Now To Accelerate Youth Employment Organized by The Olusegun Obasanjo Foundation (OOF) and The African Union Commission (AUC) (Addis Ababa, 29 January 2014) Presentation
Conference on What Africa Can Do Now To Accelerate Youth Employment Organized by The Olusegun Obasanjo Foundation (OOF) and The African Union Commission (AUC) (Addis Ababa, 29 January 2014) Presentation
Afternoon Keynote Speech at Harvard University s 9th Annual African Development Conference
 Afternoon Keynote Speech at Harvard University s 9th Annual African Development Conference Antoinette Monsio Sayeh Distinguished Visiting Fellow, Center for Global Development March 24, 2018 Opening Thank
Afternoon Keynote Speech at Harvard University s 9th Annual African Development Conference Antoinette Monsio Sayeh Distinguished Visiting Fellow, Center for Global Development March 24, 2018 Opening Thank
French Election Result: Macron Wins, But Can He Deliver?
 French Election Result: Macron Wins, But Can He Deliver? May 8, 2017 by Philippe Brugere-Trelat, David Zahn, Dylan Ball, Emilie Esposito, Uwe Zoellner of Franklin Templeton Investments New President Will
French Election Result: Macron Wins, But Can He Deliver? May 8, 2017 by Philippe Brugere-Trelat, David Zahn, Dylan Ball, Emilie Esposito, Uwe Zoellner of Franklin Templeton Investments New President Will
BTI 2012 Zambia Country Report
 BTI 2012 Zambia Country Report Status Index 1-10 5.96 # 54 of 128 Political Transformation 1-10 6.5 # 42 of 128 Economic Transformation 1-10 5.18 # 5 of 128 Management Index 1-10 5.50 # 4 of 128 scale:
BTI 2012 Zambia Country Report Status Index 1-10 5.96 # 54 of 128 Political Transformation 1-10 6.5 # 42 of 128 Economic Transformation 1-10 5.18 # 5 of 128 Management Index 1-10 5.50 # 4 of 128 scale:
How s Life in Australia?
 How s Life in Australia? November 2017 In general, Australia performs well across the different well-being dimensions relative to other OECD countries. Air quality is among the best in the OECD, and average
How s Life in Australia? November 2017 In general, Australia performs well across the different well-being dimensions relative to other OECD countries. Air quality is among the best in the OECD, and average
15-1. Provisional Record
 International Labour Conference Provisional Record 105th Session, Geneva, May June 2016 15-1 Fifth item on the agenda: Decent work for peace, security and disaster resilience: Revision of the Employment
International Labour Conference Provisional Record 105th Session, Geneva, May June 2016 15-1 Fifth item on the agenda: Decent work for peace, security and disaster resilience: Revision of the Employment
Situation in Mali. Mali is an African nation located on the Western region of the continent. Since Mali s
 Situation in Mali Background: Mali is an African nation located on the Western region of the continent. Since Mali s independence from France in 1960, it has experienced tremendous political turmoil as
Situation in Mali Background: Mali is an African nation located on the Western region of the continent. Since Mali s independence from France in 1960, it has experienced tremendous political turmoil as
MEXICO: ECONOMIC COUNTRY REPORT
 MEXICO: ECONOMIC COUNTRY REPORT 2018-2020 By Eduardo Loria 1 Center of Modeling and Economic Forecasting School of Economics National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM) Mexico Prepared for the Fall
MEXICO: ECONOMIC COUNTRY REPORT 2018-2020 By Eduardo Loria 1 Center of Modeling and Economic Forecasting School of Economics National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM) Mexico Prepared for the Fall
Executive summary. Strong records of economic growth in the Asia-Pacific region have benefited many workers.
 Executive summary Strong records of economic growth in the Asia-Pacific region have benefited many workers. In many ways, these are exciting times for Asia and the Pacific as a region. Dynamic growth and
Executive summary Strong records of economic growth in the Asia-Pacific region have benefited many workers. In many ways, these are exciting times for Asia and the Pacific as a region. Dynamic growth and
Italy s average level of current well-being: Comparative strengths and weaknesses
 How s Life in Italy? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Italy s average performance across the different well-being dimensions is mixed. The employment rate, about 57% in 2016, was among the
How s Life in Italy? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Italy s average performance across the different well-being dimensions is mixed. The employment rate, about 57% in 2016, was among the
Southern Sudan: Overcoming obstacles to durable solutions now building stability for the future
 Southern Sudan: Overcoming obstacles to durable solutions now building stability for the future Briefing paper - August 2010 After two and a half decades of war, the 2005 Comprehensive Peace Agreement
Southern Sudan: Overcoming obstacles to durable solutions now building stability for the future Briefing paper - August 2010 After two and a half decades of war, the 2005 Comprehensive Peace Agreement
How s Life in Greece?
 How s Life in Greece? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Greece has a mixed performance across the different well-being dimensions. Material conditions in Greece are generally below the OECD
How s Life in Greece? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Greece has a mixed performance across the different well-being dimensions. Material conditions in Greece are generally below the OECD
How s Life in Germany?
 How s Life in Germany? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Germany performs well across most well-being dimensions. Household net adjusted disposable income is above the OECD average, but household
How s Life in Germany? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Germany performs well across most well-being dimensions. Household net adjusted disposable income is above the OECD average, but household
Tell us about your role within the Syrian Opposition Coalition (SOC).
 An Interview with Osama Kadi Tell us about your role within the Syrian Opposition Coalition (SOC). Kadi: I am not a Coalition member, but I was nominated to head the Friends of Syria (FoS) platform addressing
An Interview with Osama Kadi Tell us about your role within the Syrian Opposition Coalition (SOC). Kadi: I am not a Coalition member, but I was nominated to head the Friends of Syria (FoS) platform addressing
How to Generate Employment and Attract Investment
 How to Generate Employment and Attract Investment Beatrice Kiraso Director UNECA Subregional Office for Southern Africa 1 1. Introduction The African Economic Outlook (AEO) is an annual publication that
How to Generate Employment and Attract Investment Beatrice Kiraso Director UNECA Subregional Office for Southern Africa 1 1. Introduction The African Economic Outlook (AEO) is an annual publication that
How s Life in the United Kingdom?
 How s Life in the United Kingdom? November 2017 On average, the United Kingdom performs well across a number of well-being indicators relative to other OECD countries. At 74% in 2016, the employment rate
How s Life in the United Kingdom? November 2017 On average, the United Kingdom performs well across a number of well-being indicators relative to other OECD countries. At 74% in 2016, the employment rate
THE BROOKINGS INSTITUTION
 THE BROOKINGS INSTITUTION Divi 1775 Massachusetts Avenue, NW Washington, DC 20036-2188 Tel: 202-797-6000 Fax: 202-797-6004 www.brookings.edu U.S.-FRANCE ANALYSIS SERIES March 2003 The Crisis in Côte d'ivoire
THE BROOKINGS INSTITUTION Divi 1775 Massachusetts Avenue, NW Washington, DC 20036-2188 Tel: 202-797-6000 Fax: 202-797-6004 www.brookings.edu U.S.-FRANCE ANALYSIS SERIES March 2003 The Crisis in Côte d'ivoire
SIEPR policy brief. Turkish Economic Successes and Challenges. By Anne O. Krueger. Stanford University September 2014.
 SIEPR policy brief Stanford University September 214 Stanford Institute for Economic Policy Research on the web: http://siepr.stanford.edu Turkish Economic Successes and Challenges By Anne O. Krueger Turkey
SIEPR policy brief Stanford University September 214 Stanford Institute for Economic Policy Research on the web: http://siepr.stanford.edu Turkish Economic Successes and Challenges By Anne O. Krueger Turkey
The Era of Reconstruction
 The Era of Reconstruction 1 www.heartpunchstudio.com/.../reconstruction.jpg 2 Learning Objectives 3 Define the major problems facing the South and the nation after the Civil War. Analyze the differences
The Era of Reconstruction 1 www.heartpunchstudio.com/.../reconstruction.jpg 2 Learning Objectives 3 Define the major problems facing the South and the nation after the Civil War. Analyze the differences
Globalisation and Open Markets
 Wolfgang LEHMACHER Globalisation and Open Markets July 2009 What is Globalisation? Globalisation is a process of increasing global integration, which has had a large number of positive effects for nations
Wolfgang LEHMACHER Globalisation and Open Markets July 2009 What is Globalisation? Globalisation is a process of increasing global integration, which has had a large number of positive effects for nations
G8 MIYAZAKI INITIATIVES FOR CONFLICT PREVENTION I. EFFORTS FOR CONFLICT PREVENTION -- A BASIC CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK --
 G8 MIYAZAKI INITIATIVES FOR CONFLICT PREVENTION I. EFFORTS FOR CONFLICT PREVENTION -- A BASIC CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK -- The G8 Heads of State and Government announced last June in Cologne, and we, Foreign
G8 MIYAZAKI INITIATIVES FOR CONFLICT PREVENTION I. EFFORTS FOR CONFLICT PREVENTION -- A BASIC CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK -- The G8 Heads of State and Government announced last June in Cologne, and we, Foreign
How s Life in Austria?
 How s Life in Austria? November 2017 Austria performs close to the OECD average in many well-being dimensions, and exceeds it in several cases. For example, in 2015, household net adjusted disposable income
How s Life in Austria? November 2017 Austria performs close to the OECD average in many well-being dimensions, and exceeds it in several cases. For example, in 2015, household net adjusted disposable income
How s Life in Belgium?
 How s Life in Belgium? November 2017 Relative to other countries, Belgium performs above or close to the OECD average across the different wellbeing dimensions. Household net adjusted disposable income
How s Life in Belgium? November 2017 Relative to other countries, Belgium performs above or close to the OECD average across the different wellbeing dimensions. Household net adjusted disposable income
Japan s average level of current well-being: Comparative strengths and weaknesses
 How s Life in Japan? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Japan s average performance across the different well-being dimensions is mixed. At 74%, the employment rate is well above the OECD
How s Life in Japan? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Japan s average performance across the different well-being dimensions is mixed. At 74%, the employment rate is well above the OECD
How s Life in Canada?
 How s Life in Canada? November 2017 Canada typically performs above the OECD average level across most of the different well-indicators shown below. It falls within the top tier of OECD countries on household
How s Life in Canada? November 2017 Canada typically performs above the OECD average level across most of the different well-indicators shown below. It falls within the top tier of OECD countries on household
South Sudan. Political and Legislative Developments JANUARY 2012
 JANUARY 2012 COUNTRY SUMMARY South Sudan Following an overwhelming vote for secession from Sudan in the January 2011 referendum, South Sudan declared independence on July 9. The new nation faces major
JANUARY 2012 COUNTRY SUMMARY South Sudan Following an overwhelming vote for secession from Sudan in the January 2011 referendum, South Sudan declared independence on July 9. The new nation faces major
UNCTAD Public Symposium June, A Paper on Macroeconomic Dimensions of Inequality. Contribution by
 UNCTAD Public Symposium 18-19 June, 2014 A Paper on Macroeconomic Dimensions of Inequality Contribution by Hon. Hamad Rashid Mohammed, MP Member of Parliament United Republic of Tanzania Disclaimer Articles
UNCTAD Public Symposium 18-19 June, 2014 A Paper on Macroeconomic Dimensions of Inequality Contribution by Hon. Hamad Rashid Mohammed, MP Member of Parliament United Republic of Tanzania Disclaimer Articles
Women Waging Peace PEACE IN SUDAN: WOMEN MAKING THE DIFFERENCE RECOMMENDATIONS I. ADDRESSING THE CRISIS IN DARFUR
 Women Waging Peace PEACE IN SUDAN: WOMEN MAKING THE DIFFERENCE RECOMMENDATIONS October 8-15, 2004, Women Waging Peace hosted 16 Sudanese women peace builders for meetings, presentations, and events in
Women Waging Peace PEACE IN SUDAN: WOMEN MAKING THE DIFFERENCE RECOMMENDATIONS October 8-15, 2004, Women Waging Peace hosted 16 Sudanese women peace builders for meetings, presentations, and events in
African Democracy Simulation
 Boston University College of Arts & Sciences African Studies Center Outreach Program 232 Bay State Road Boston, Massachusetts 02215 (617) 353-7303 African Democracy Simulation Professor Timothy Longman
Boston University College of Arts & Sciences African Studies Center Outreach Program 232 Bay State Road Boston, Massachusetts 02215 (617) 353-7303 African Democracy Simulation Professor Timothy Longman
Africa Integrity Indicators Country Findings
 Africa Integrity Indicators Country Findings Who is Global Integrity? Global Integrity supports progress toward open and accountable governance in countries and communities around the world. We focus on
Africa Integrity Indicators Country Findings Who is Global Integrity? Global Integrity supports progress toward open and accountable governance in countries and communities around the world. We focus on
How s Life in the Netherlands?
 How s Life in the Netherlands? November 2017 In general, the Netherlands performs well across the OECD s headline well-being indicators relative to the other OECD countries. Household net wealth was about
How s Life in the Netherlands? November 2017 In general, the Netherlands performs well across the OECD s headline well-being indicators relative to the other OECD countries. Household net wealth was about
Sixteenth progress report of the Secretary-General on the United Nations Operation in Côte d Ivoire I. Introduction
 United Nations S/2008/250 Security Council Distr.: General 15 April 2008 Original: English Sixteenth progress report of the Secretary-General on the United Nations Operation in Côte d Ivoire I. Introduction
United Nations S/2008/250 Security Council Distr.: General 15 April 2008 Original: English Sixteenth progress report of the Secretary-General on the United Nations Operation in Côte d Ivoire I. Introduction
How s Life in Norway?
 How s Life in Norway? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Norway performs very well across the OECD s different well-being indicators and dimensions. Job strain and long-term unemployment are
How s Life in Norway? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Norway performs very well across the OECD s different well-being indicators and dimensions. Job strain and long-term unemployment are
COUNTRY REPORT ON SIERRA LEONE
 COUNTRY REPORT ON SIERRA LEONE Sierra Leone Labour Congress Sierra Leone is situated along the West Coast of Africa and shares boundaries with Liberia on the South and Guinea on the North. The area of
COUNTRY REPORT ON SIERRA LEONE Sierra Leone Labour Congress Sierra Leone is situated along the West Coast of Africa and shares boundaries with Liberia on the South and Guinea on the North. The area of
UNITED NATIONS SECURITY COUNCIL
 UNITED NATIONS SECURITY COUNCIL INTRODUCTION The United Nations Security Council is the primary body of the organization in maintaining international peace and security, as defined by the UN Charter. The
UNITED NATIONS SECURITY COUNCIL INTRODUCTION The United Nations Security Council is the primary body of the organization in maintaining international peace and security, as defined by the UN Charter. The
A Putin policy without Putin after 2008? Putin s legacy: achievements
 A Putin policy without Putin after 08? Vladimir Popov, Professor, New Economic School On October 1, 0, two months before the parliamentary elections (December 2, 0) and less than half a year before the
A Putin policy without Putin after 08? Vladimir Popov, Professor, New Economic School On October 1, 0, two months before the parliamentary elections (December 2, 0) and less than half a year before the
Economic Development and Transition
 Economic Development and Transition Developed Nations and Less Developed Countries Developed Nations Developed nations are nations with higher average levels of material well-being. Less Developed Countries
Economic Development and Transition Developed Nations and Less Developed Countries Developed Nations Developed nations are nations with higher average levels of material well-being. Less Developed Countries
II. The role of indicators in monitoring implementation of Security Council resolution 1325 (2000)
 United Nations S/2010/173 Security Council Distr.: General 6 April 2010 Original: English Women and peace and security Report of the Secretary-General I. Introduction 1. On 5 October 2009, the Security
United Nations S/2010/173 Security Council Distr.: General 6 April 2010 Original: English Women and peace and security Report of the Secretary-General I. Introduction 1. On 5 October 2009, the Security
Chapter 7 Institutions and economics growth
 Chapter 7 Institutions and economics growth 7.1 Institutions: Promoting productive activity and growth Institutions are the laws, social norms, traditions, religious beliefs, and other established rules
Chapter 7 Institutions and economics growth 7.1 Institutions: Promoting productive activity and growth Institutions are the laws, social norms, traditions, religious beliefs, and other established rules
Transparency, Accountability and Citizen s Engagement
 Distr.: General 13 February 2012 Original: English only Committee of Experts on Public Administration Eleventh session New York, 16-20 April 2011 Transparency, Accountability and Citizen s Engagement Conference
Distr.: General 13 February 2012 Original: English only Committee of Experts on Public Administration Eleventh session New York, 16-20 April 2011 Transparency, Accountability and Citizen s Engagement Conference
Throughout its history, Pakistan has been plagued by cycles of
 IDA at Work Pakistan: Achieving Results in a Challenging Environment Throughout its history, Pakistan has been plagued by cycles of high growth interrupted by shocks and crises and followed by relative
IDA at Work Pakistan: Achieving Results in a Challenging Environment Throughout its history, Pakistan has been plagued by cycles of high growth interrupted by shocks and crises and followed by relative
Economic and Social Council
 United Nations Economic and Social Council Distr.: General 23 April 2018 Original: English English, French, Russian and Spanish only Committee on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights List of issues in
United Nations Economic and Social Council Distr.: General 23 April 2018 Original: English English, French, Russian and Spanish only Committee on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights List of issues in
Nepal. Implementing the Comprehensive Peace Agreement
 January 2008 country summary Nepal Implementation of the November 2006 Comprehensive Peace Agreement (CPA) to end the 1996-2006 civil war progressed with the promulgation of an interim constitution, and
January 2008 country summary Nepal Implementation of the November 2006 Comprehensive Peace Agreement (CPA) to end the 1996-2006 civil war progressed with the promulgation of an interim constitution, and
THE POLITICAL ECONOMY OF HYDROCARBON REVENUE CYCLING IN TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO
 THE POLITICAL ECONOMY OF HYDROCARBON REVENUE CYCLING IN TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO Richard Auty (Lancaster University) 1. Rent Cycling Theory and Growth Collapses 2. Initial Conditions Render T+T Vulnerable 3.
THE POLITICAL ECONOMY OF HYDROCARBON REVENUE CYCLING IN TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO Richard Auty (Lancaster University) 1. Rent Cycling Theory and Growth Collapses 2. Initial Conditions Render T+T Vulnerable 3.
How s Life in Sweden?
 How s Life in Sweden? November 2017 On average, Sweden performs very well across the different well-being dimensions relative to other OECD countries. In 2016, the employment rate was one of the highest
How s Life in Sweden? November 2017 On average, Sweden performs very well across the different well-being dimensions relative to other OECD countries. In 2016, the employment rate was one of the highest
Mid-Term Assessment of the Quality of Democracy in Pakistan
 SoD Summary Mid-Term Assessment of the Quality of Democracy in Pakistan 2008-10 Pakistan Institute of Legislative Development and Transparency (PILDAT) Pakistan, 2010 Ingress Since the end of the military
SoD Summary Mid-Term Assessment of the Quality of Democracy in Pakistan 2008-10 Pakistan Institute of Legislative Development and Transparency (PILDAT) Pakistan, 2010 Ingress Since the end of the military
