2014 Cam mpaign Finance Upda ate
|
|
|
- Shawn Stewart
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 C O G E L B L U E B O O K 2014 Cam mpaign Finance Upda ate Edited by: Jason D. Kaune Darrin Lim With assistance from: Erin Lama and Michael R. Kelly Nielsen Merksamer Parrinello Gross & Leoni, LLP 2350 Kerner Blvd., Suite 250 San Rafael, CA (415) Contributors: Kevin Deeley and Adav Noti, Federal Election Commission Paul S. Ryan, Campaign Legal Center Nola Western, Elections BC
2 About the Editors JASON D. KAUNE is a partner with Nielsen Merksamer Parrinello Gross & Leoni, LLP. He specializes in political law and ethics, lobbying, election and campaign finance laws in the 50 states, and on the local and federal levels. He advises corporations, advocacy groups, individuals and governments, with a focus on establishing and maintaining multi-jurisdictional compliance systems. He has co-authored this annual 50 state compendium of campaign finance law developments for the Council on Governmental Ethics Laws (COGEL) since Additionally, Mr. Kaune has contributed to the Practising Law Institute s Corporate Political Activities course book since He has served as a speechwriter in Washington D.C., a policy advisor for a state governor, and in the non-profit sector. He earned advanced degrees from Harvard University, John F. Kennedy School of Government and University of California, Hastings College of the Law and graduated with honors from Yale College. DARRIN LIM is a partner with Nielsen Merksamer Parrinello Gross & Leoni, LLP, where he specializes in national political law compliance matters. Specifically, he advises corporations with the development and administration of comprehensive compliance programs for corporate and federal PAC campaign contribution activity, federal and state lobbying work, and federal, state and local ethics/gift compliance. This is Mr. Lim s tenth year co-authoring this annual 50 state compendium of campaign finance law developments for COGEL. He is also the Co-Chair of this year s COGEL Conference Program Committee. Mr. Lim serves on the Editorial Board of Public Integrity, an academic journal of the American Society for Public Administration. He is a frequent speaker on political law matters at conferences around the country. He previously served as the Communications Director for a state legislator in California. Before that he was the main anchor and reporter for a station in Southern California. Mr. Lim received his BA in Broadcast Journalism and Political Science from the University of Southern California and graduated with honors from the University of the Pacific, McGeorge School of Law. ERIN LAMA is an attorney with Nielsen Merksamer Parrinello Gross & Leoni, LLP. She received her BA from the University of San Francisco and graduated from the University of California, Hastings College of the Law. MICHAEL R. KELLY is a research attorney at Nielsen Merksamer Parrinello Gross & Leoni, LLP. He previously was a Principal Deputy in the California Office of the Legislative Counsel. He received his B.A. at the University of California, Davis, and his J.D. from the University of the Pacific, McGeorge School of Law.
3 About the Contributors KEVIN DEELEY is the Acting Associate General Counsel for Litigation at the Federal Election Commission. Previously, he served as the Acting Associate General Counsel for Policy and as an Assistant General Counsel for the Litigation Division. He received his bachelors from Boston College and his law degree from Harvard Law School. ADAV NOTI is the Acting Associate General Counsel for Policy at the Federal Election Commission. Previously, he served as the Acting Assistant General Counsel for Litigation. Mr. Noti also worked as a Special Assistant United States Attorney. He began his legal career as an Associate at Paul, Weiss, Rifkind, Wharton & Garrison. He received his bachelors from the University of Pennsylvania, his law degree from New York University School of Law and his masters from Georgetown University. PAUL S. RYAN of the Campaign Legal Center authored the Local Government Campaign Finance Update with the generous assistance of Campaign Legal Center intern Max Hechl. Mr. Ryan is Senior Counsel at the Campaign Legal Center and regularly represents the Campaign Legal Center before the Federal Election Commission, as well as state and local campaign finance and ethics commissions. Mr. Ryan litigates campaign finance issues before federal and state courts throughout the United States and speaks frequently on the topics of campaign finance and ethics laws at conferences around the nation. He is a graduate of the University of California, Los Angeles School of Law s Program in Public Interest Law and Policy and the University of Montana. NOLA WESTERN is the Deputy Chief Electoral Officer, Funding and Disclosure at Elections British Columbia. She joined Elections BC in 1996 and is responsible for both the financial, human resource and administrative functions of the office and the administration of the campaign financing provisions of the election Act and the Recall and Initiative Act. Prior to joining Elections BC, Ms. Western was the Manager, Financial Services for the Vancouver Island Region of the Ministry of Transportation and Highways and worked as an auditor for the Office of the Auditor General of British Columbia. Ms. Western graduated from the University of British Columbia in 1985 and is a Chartered Accountant. She is currently the Vice-Chair of the Professional Development Review Committee of the Institute of Chartered Accountants of BC (ICABC) and has served on several other ICABC committees. Ms. Western is a former President of COGEL and serves as Co-Chair of this year s COGEL Conference Program Committee.
4 Table of Contents ABOUT THE EDITORS ABOUT THE CONTRIBUTORS I N T R O D U C T I O N i ii Louisiana 61 Maine 63 Maryland 64 Massachusetts 66 Michigan 69 Minnesota 70 United States: The State of the States and Federal Law Developments 1 Federal Litigation Digest 12 Federal Policy Digest 17 Local Gov. Campaign Finance Update 19 The Canadian Update 25 Mississippi 72 Missouri 73 Montana 75 Nebraska 76 Nevada 77 New Hampshire 78 New Jersey 79 New Mexico 82 New York 83 S T A T E S U M M A R I E S Alabama 28 Alaska 29 Arizona 31 Arkansas 32 California 34 Colorado 39 Connecticut 42 Delaware 46 District of Columbia 48 Florida 49 Georgia 50 Hawaii 51 Idaho 53 Illinois 54 Indiana 56 Iowa 57 Kansas 58 North Carolina 84 North Dakota 86 Ohio 88 Oklahoma 89 Oregon 90 Pennsylvania 91 Rhode Island 93 South Carolina 94 South Dakota 95 Tennessee 96 Texas 97 Utah 99 Vermont 100 Virginia 102 Washington 103 West Virginia 104 Wisconsin 105 Wyoming 107 Kentucky 59
5 The State of the States and Federal Law Developments in 2014 Campaign Finance Litigation and Legislation in the United States W e applaud all of the participating states and local jurisdictions that shared important developments for this year s compendium. On behalf of the Council on Governmental Ethics Laws ( COGEL ), we are again pleased to report that virtually all states are included in this COGEL BLUE BOOK: Campaign Finance Update 2014 with new information and developments. As is tradition, we outline what we see as significant trends in federal, state and local campaign finance laws since our last meeting in Quebec City, Canada roughly from November 2013 to October This compendium provides a vast array of information and perspectives including federal highlights from Kevin Deeley and Adav Noti of the Federal Election Commission; local city and county changes to campaign finance law from Paul S. Ryan of the Campaign Legal Center; and the latest developments in campaign finance in Canada from Nola Western of Elections BC. Each jurisdiction begins with an At a Glance capsule, as seen to the left, to provide a preview of the changes included in each jurisdiction. To A T A G L A N C E facilitate the discussion, during the separate sessions at this Enforcement data year s conference, we provide two overviews below concerning key developments in litigation and key updates in Disclosure changes legislation and other regulatory trends. $ Limit changes Special thanks to Erin Lama and Michael R. Kelly of Nielsen Merksamer for their hard work with this year s COGEL BLUE BOOK: Campaign Finance Update Jason Kaune and Darrin Lim Nielsen Merksamer Parrinello Gross & Leoni, LLP December
6 Part I: Federal and State Litigation Update Jason Kaune of Nielsen Merksamer presents this overview of federal and state litigation developments. Each year, we identify prominent trends in campaign finance litigation based on responses to BLUE BOOK surveys and with the participation of COGEL conference attendees. Campaign finance litigation on the state, local and federal levels in the United States has continued to trend in broad patterns of reaction and action. This year our panel will once again join with COGEL conference participants to discuss five trends and contrast them with the relative lack of litigation in Canada. Another landmark U.S. Supreme Court case has forced states and localities to react by abandoning aggregate limits on individual or corporate contributions. We will consider if the same may be in store for pay to play laws that limit the contributions of government contractors, their executives and sometimes their immediately family members. Meanwhile, states and localities continue to find ways to act while the Federal Election Commission (FEC) and federal campaign finance law generally remain largely deadlocked. Seventeen states reported litigation in this year s survey, including unique cases concerning waiting periods, electioneering and the use of public resources. Continued Fallout from Federal Decisions in 2014 A review of the last year must start with the U.S. Supreme Court. On April 2, 2014, the Court, in McCutcheon v. Federal Election Commission, 572 U.S., No (S. Ct. Apr. 2, 2014), struck down federal law that limited the aggregate amount of money a person may contribute in a federal election. Although the process took several months, many jurisdictions responded to the court s ruling. The responses varied and will be described in our two panels. Nearly all states (and cities such as San Francisco and Los Angeles) with aggregate contribution limits chose to respond unilaterally via advisory opinions, statements or other guidance, as detailed further in this BLUE BOOK. Four states reported developments via litigation: The Wyoming Secretary of State s Office initially indicated that it would defer to a legislative solution to revise its aggregate contribution limits. The matter was ultimately decided in court and Wyoming no longer limits an individual s total contributions to candidates and political parties. 2
7 The Wisconsin Government Accountability Board issued a statement on May 22, 2014 following an order in a case pending in federal court in Milwaukee. The order, in Young v. Vocke, struck down the state s annual aggregate limit on individual campaign contributions. In Minnesota, a U.S. District Court enjoined the enforcement of a state statute that placed aggregate contribution limits on large givers. In Louisiana, a $100,000 limit on an individual s contributions to PACs in a 4 year period was found unconstitutional as applied to PACs that make independent expenditures. More Fallout from a New Federal Decision in 2015? This year we will again discuss a case arising from federal law, which could have an impact on state laws similar to McCutcheon. On September 30, 2014 the D.C. Circuit, sitting en banc, heard oral argument for Wagner v. FEC. This is a First Amendment and equal protection challenge to the prohibition on federal contractors making campaign contributions. The court has not issued an opinion as of the publishing of this writing. Kevin Deeley, Acting Associate General for Litigation at the FEC, shared his perspective of the case when arguing it at the District Court level. He provides a summary of the case in this BLUE BOOK and will provide his perspective of the appellate litigation in Pittsburgh. We will discuss the potential impact on the states and cities that have adopted pay-to-play laws and ordinances. As summarized in past years and by other COGEL panels, jurisdictions across the nation have adopted pay-to-play restrictions and disclosure requirements. A Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) rule, which impacts contributions to governors running for state and federal office among others, is currently being challenged in New York State Republican Committee v. SEC, 14-cv-1345, U.S. District Court, District of Columbia. States Defend Varied Challenges to Campaign Finance Laws Numerous challenges to contribution limits, disclosure requirements and reporting thresholds are making their way through various state and federal courts. Those filing these cases hope to expand the decisions in Citizens United and McCutcheon to reach other types of restrictions and requirements. 3
8 Hawaii continues to defend its law in the 9th Circuit, following a District Court holding that invalidated a $1,000 per election contribution limit applicable to noncandidate committees that solely make independent expenditures. (Yamada v. Snipes, et al., Civil No. CV ) Litigation continues in Illinois, where the U.S. District Court, must rule on First Amendment and Equal Protection challenges to contribution limits imposed by the state as they apply to political party committees and PACs. (Illinois Liberty PAC v. Madigan, No. 12 C 5811.) The 5th Circuit found that a Texas law requiring a committee to have ten separate contributors to qualify as a general purpose committee and a sixty day waiting period before the committee can exceed $500 in expenditures was unconstitutional. (Catholic Leadership Coalition of Tex. v. Reisman, 764 F.3d 409 (5th Cir ) In a similar vein, a constitutional challenge to Washington s requirement that political committees must obtain contributions from ten registered voters of at least $10 or more prior to the political committee contributing to another political committee is pending before the Superior Court. (State v. Grocery Manufacturers Association, Thurston County Superior Court No ) Following a comprehensive challenge to Wisconsin s campaign-finance law in the wake of Citizens United, the 7th Circuit found the state s ban on corporate political spending unconstitutional. (Wisconsin Right to Life v. Barland, 751 F.3d 804, 809 (7th Cir ) California once again stands in the forefront of defending, and compelling, campaign finance disclosure. In ProtectMarriage.Com et al. v. Bowen et al., 752 F.3d 827 (9th Cir. 2014), the plaintiff political committee stated that their donors had been harassed as a result of the state s campaign disclosure laws. The 9th Circuit upheld the state s disclosure requirements, finding that Californian s had a right to know the origin of campaign funding. Finally, Colorado continues to litigate a spectrum of issues with respect to the State s campaign laws and regulations. Last year, the Colorado Court of Appeals invalidated rules capping penalties for campaign finance violations, requirements for groups to file campaign finance reports only if 30% of their spending was for or against a ballot issue, a major purpose test for political committees, and a bright line test for registration requirements of an issue committee. (Colo. Ethics Watch v. Gessler, (Colo. Ct. App. 2013).) This year, the Colorado Supreme Court found that the Secretary of State exceeded his authority when he enacted a regulation which set a $5,000 contribution and expenditure threshold for registration of issue committees. (Gessler v. Colo. Common Cause, 327 P.3d 232 (Colo ) 4
9 The Federal Litigation Digest also includes cases involving waiting periods, preelection limits, and committees maintaining multiple accounts. Another Target: Electioneering Provisions With the narrowed ability to limit contributions, about half of the states and numerous localities are shifting their focus to disclosure or reporting requirements related to pre-election activity, specifically electioneering communications. Twenty-five states maintain some form of electioneering communication statute or regulation. A summary of these statutes is available through the Brennan Center for Justice. (Brennan Center For Justice, published February 7, 2013, In Delaware, litigation is pending in Delaware Strong Families v. Biden (No. 1:2013- cv-01746) where the federal Third Circuit Court of Appeals will decide the constitutionality of the state s law requiring entities engaging in electioneering communication to disclose their contributors. In Idaho, the Secretary of State took action against an organization that ran advertisements which qualified as electioneering communications, but failed to submit any disclosure reports. The action arose following the organization s dissemination of radio advertisements supporting two legislators that did not expressly advocate for their reelection, however, under state law would be considered electioneering communications. The Federal Litigation Digest also provides updates on the ongoing litigation concerning federal electioneering communication disclosure, Van Hollen v. FEC, No (D.D.C.) and a new case challenging the application of the requirements to an issue advertisement that did not attack a referenced federal candidate, Independence Institute _ F. Supp. 3d, 2014 WL (D.D.C. Oct. 6, 2014.) Use of Public Resources and Campaign Funds Finally, cases involving the improper use of public resources and impermissible uses of campaign funds continue to proliferate. The Federal Litigation Digest reports on a case concerning former United States Senator Larry Craig, FEC v. Craig for U.S. Senate, F. Supp. 3d, 2014 WL (D.D.C. Sept. 30, 2014). 5
10 In Alaska, two mayors were found to have improperly used public resources for campaign purposes. In Gilbert v. Eberhart, Fairbanks Mayor, John Eberhart illegally used city assets, in the form of the city s system, for campaign purposes. (14-01-CD.) Anchorage Mayor, Dan Sullivan also used city resources for his campaign when the mayor s office issued a press release clarifying remarks made at a candidate forum. (14-03-CD.) In Arkansas, two state politicians resigned following investigations and actions against them due to their use of public resources for personal purposes. Following an Ethics Commission investigation into State Senator Paul Bookout s use of campaign funds to buy personal items, Bookout was fined $8,000 and resigned from the Legislature. (Arkansas Ethics Commission Case No CO-014.) Former Lieutenant Governor Mark Darr also was fined $11,000 and resigned from office when he was found to have used $31,000 in campaign contributions for personal expenses. (Arkansas Ethics Commission Case Nos CO-025 and 2013-CO-026.) Additionally, former Arkansas State Treasure Martha Shoffner was convicted in federal court of 14 counts of extortion and bribery for taking cash payments from an investment broker handling state funds. She is awaiting trial on 10 counts of mail fraud for allegedly using campaign contributions to make payments on her personal credit card. 6
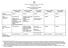
11 Part II: Legislation and Other Trends Darrin Lim of Nielsen Merksamer leads the roundtable discussion on legislative and regulatory developments by highlighting broad trends apparent from the legislation, administrative regulations, advice letters, and enforcements provided in this year s annual survey responses. Joining Mr. Lim for this discussion will again be Paul S. Ryan and Nola Western. In addition, Adav Noti, Acting Associate General Counsel, Policy Division, Federal Election Commission will share federal advisory opinion and rulemaking developments. To facilitate a lively and engaging discussion, Mr. Lim will encourage those attending the session to share additional insights about their jurisdictions. This context is often helpful to better understand the particular developments in a jurisdiction. McCutcheon s State and Local Domino Effect For many states across the country, 2014 was already going to be a busy year with statewide elections in many jurisdictions. The election year got even busier with the U.S. Supreme Court s ruling in McCutcheon v. Federal Election Commission. The decision, which struck down the federal limit on the aggregate amount of money individuals could contribute in federal races, immediately called into question many state and local campaign finance laws with similar restrictions. States and local jurisdictions responded to the court s decision with varying degrees of urgency. The Maryland State of Board of Elections was one of the first offices to immediately issue guidance on the subject. Several other jurisdictions followed with board decisions and guidance. The following chart provides an overview of how state and local agencies responded to McCutcheon through legislative and regulatory action. Connecticut District of Columbia California - Los Angeles California San Francisco Maine Maryland Massachusetts New York Rhode Island Vermont Advisory Opinion Issued Attorney General Advice Issued Commission Vote Commission Vote Commission Vote Guidance Issued Guidance Issued Commission Vote Commission Vote Legislation Approved 7
12 Shining Light on Dark Money States continue to report the influence of dark money in elections and face the challenge of enforcing existing laws or crafting new requirements to expose undisclosed campaign contribution activity from tax-exempt political advocacy groups and trade associations. This year brought a variety of developments including a new law in California and a new mandate in Massachusetts. In California, Governor Jerry Brown signed SB 27, which changed the reporting rules for nonprofit organizations that spend money to influence candidate and ballot measure elections in the state. In short, organizations that spend more than $50,000 in election activity in a 12-month period or more than $100,000 in four consecutive years must register and file reports as PACs. The legislation was approved with an urgency clause, which meant that the change was effective throughout the 2014 General Election season. In Massachusetts, the Office of Campaign & Political Finance will now be required to adopt regulations concerning the disclosure of any transfers of money to make independent expenditures or electioneering communications. Coordination Challenges The line in the sand separating a candidate from an independent expenditure effort featuring the candidate continues to be a challenging issue for states. Several jurisdictions tackled the issue with new advice this year. In Maryland, the State Board of Elections issued guidelines including factors to be considered when determining if a candidate, campaign finance entity, or a person making independent expenditures is cooperating and coordinating activity with another candidate or committee. In Massachusetts, the Office of Campaign & Political Finance issued an advisory opinion on coordination where a common vendor provided services to both a candidate and an entity making independent expenditures. A candidate s involvement in fundraising efforts for an independent expenditure committee was the subject of an advisory opinion in Minnesota. In that opinion, the Campaign Finance and Public Disclosure Board opined that a candidate s involvement in fundraising efforts for the I.E. destroyed the independence of the ultimate expenditure. Coordination was also the subject of two enforcement actions in Minnesota, which concerned photo shoots involving candidates that ultimately developed into independent expenditures. 8
13 Will the Top Supporters Please Stand Up States are sharpening their focus on the top supporters behind ballot measure campaigns and independent expenditures and imposing new disclosure requirements. In California, legislation was approved this year requiring committees that raise $1 million or more to maintain an accurate list of the committee s top 10 contributors of $10,000 or more. These lists must be submitted to the Fair Political Practices Commission and are posted on the agency s website. In Massachusetts, the disclaimers for independent expenditures and electioneering communications got longer with the passage of legislation requiring that television, internet and print acts include a listing of the top five contributors of $5,000 or more. Apps = Access to Information Hawaii continues to lead in the development of new and innovative ways to post campaign finance data. The Hawaii Campaign Spending Commission expanded its data visualization applications this year. First introduced in 2013, these apps display campaign finance data using pie charts and graphs to provide users with a better big picture view of state campaign activity. This year, the apps were expanded to display non-candidate activity, previously the apps focused on candidate activity alone. Hawaii also hosted a civic competition this year to challenge coders and developers to create new apps using the state s open source campaign finance data. The goal is to provide the public with new and different ways to understand campaign finance data. Texas may be the next state to develop new tools for campaign finance data. The state is in the midst of developing a new electronic filing system with $3.5 million in new state funding, which will include new forms and ways of reporting information. Innovative Fundraising Prompts Questions As innovative fundraising techniques continue to develop, jurisdictions are challenged to apply their campaign finance laws to these new methods. The Kansas Governmental Ethics Commission opined that political action committees registered in the state may receive contributions derived from a portion of sales transactions that occur with a third party. The Commission advised that a Florida company that sells goods on the Internet may contribute a portion of each sale to a PAC designated by the customer. Meanwhile in Kentucky, the Registry of Election Finance advised that a candidate is permitted to loan copies of his self-published book to his campaign for distribution to supporters and requires the candidate to report the cost of the books as a candidate 9
14 loan. Repayment from the campaign must be made to the candidate personally instead of being paid to the candidate s self-owned publishing company. Truth in Advertising During the election season, it is not uncommon to see political advertisements featuring so-called experts recommending that voters support a particular position. In California, a new law expands the disclosure requirements for paid spokespersons. Specifically, committees must now disclose any time a paid spokesperson appears in an advertisement and the disclaimer must note if the individual is not employed in the occupation portrayed in the advertisement. Election Surprise in Arkansas To the surprise of some campaign watchers, the passage of a ballot measure in Arkansas, immediately ended corporate contributions in the state. The Arkansas Elected Officials Ethics, Transparency and Financial Reform Amendment, Issue 3, was a legislatively-referred constitutional amendment, which voters approved in the November General Election. Among other things, the measure bans corporate contributions to statewide candidates and legislators. It is currently unclear if the corporate contributions are still allowed to PACs and political parties. Other Developments The following is a sampling of other developments worth highlighting: In Minnesota, legislation was approved this year that requires the Campaign Finance and Public Disclosure Board to conduct audits and investigations of reports filed with the office and develop applicable rules. In California, it may be a bit harder for candidates to make politics a family business. Legislation was approved to prohibit a spouse or domestic partner of an elected official or a candidate for elective office to receive compensation from the campaign for any services rendered. Efforts to tackle campaign finance and disclosure issues are now extending beyond state boundaries. A nonpartisan group consisting of 10 states and cities, including, New York State and City, California, Alaska, Idaho, Maine, Montana, Maryland, Massachusetts, Washington, and Iowa, launched the "States' Unified Network (SUN) Center," a web presence aimed at providing campaign disclosure nationwide and collaborative enforcement of campaign finance rules. The group is nonpartisan and informal, but connects regularly to bring best practices and coordination to campaign disclosure efforts in individual states and at the national level. 10
15 The states of California and New Jersey celebrated major milestones in Both jurisdictions held 40 th Anniversary events honoring political reform and good government efforts in the states. 11
16 Federal Litigation Digest in 2014 Summary of Key Federal Election Commission Cases Aggregate contribution limits: McCutcheon v. FEC, 134 S. Ct (Apr. 2, 2014) The Supreme Court invalidated the federal aggregate contribution limits, which restricted how much money a donor may contribute in total to all candidates or committees Regarding the constitutional standard of review for contribution limits, the Court concluded that there was no need... to revisit Buckley [v. Valeo] s distinction between contributions and expenditures and the corollary distinction in the applicable standards of review. The opinion noted the governmental interest in preventing quid pro corruption would satisfy either strict scrutiny or the closely drawn test described in Buckley, and that a substantial mismatch between the Government s stated objective and the means selected to achieve it would render the aggregate limits unconstitutional under either standard. The Court concluded that Buckley s short section upholding FECA s original aggregate limit was not controlling. The Court found relevant that other statutory and regulatory safeguards against circumvention have been strengthened since Buckley was decided: Congress s 1976 enactment of limits on contributions to noncandidate political committees and an antiproliferation rule preventing donors from creating multiple affiliated political rules, as well as the FEC s addition of regulations that define earmarking broadly. Addressing associational rights, the Court found that the aggregate limits prohibit an individual from fully contributing to all the candidates of a contributor s choosing, and that there were impediments to individuals being able to find other ways of expressing support for a number of candidates. Aggregate limits do not prevent actual or apparent quid pro quo corruption in any meaningful way, the opinion concluded, because circumvention scenarios are either illegal or divorced from reality. Finally, regarding concerns about the potential for officeholders to solicit and receive large contributions for a number of candidates and committees at once, the Court concluded the statute s restrictions were overbroad. Government Contractor Contributions: Wagner v. FEC, No (D.C. Cir.) As explained at the last several conferences, Wagner is a First Amendment and equal protection challenge to the prohibition on federal contractors making campaign contributions. Pursuant to a special judicial review provision, it is before the District of 12
17 Columbia Circuit Court of Appeals sitting en banc. Oral argument was held on September 30, Independent Expenditure Accounts for Political Party Committees: Rufer v. FEC / Republican National Committee v. FEC, F. Supp. 2d, 2014 WL (D.D.C. Aug. 19, 2014) Committees of the Libertarian and Republican parties and persons associated with those parties challenge limits on contributions to the parties as applied to accounts they propose to use solely for expenditures that are not coordinated with candidates. The court denied the Rufer/Libertarian Party plaintiffs motion for a preliminary injunction, finding them unlikely to succeed given past Supreme Court cases upholding limits on contributions to political parties. The court also held that granting the injunction was not equitable or in the public interest because it would alter the campaign finance rules only a few months prior to the next federal general election date. The court also considered requests by plaintiffs to proceed pursuant to two special judicial review provisions and found the case inappropriate for one provision that provides for a direct appeal to the Supreme Court. The court found the case appropriate for another special procedure, concluding that the challenges presented substantial, nonfrivolous questions. The constitutional questions are scheduled to be argued before the en banc Court of Appeals on February 27, Independent Expenditure Accounts for Connected PACs: Stop This Insanity, Inc. v. FEC, 761 F.3d 10 (D.C. Cir. Aug. 5, 2014) Stop This Insanity, Inc. sought to establish an independent-expenditure account within its corporate PAC, which would solicit unlimited contributions from a variety of persons, including individuals who were not members of the restricted class of persons associated with the corporation freely solicitable under federal law. The account would have been used to fund independent expenditures. The Court of Appeals rejected the plaintiffs First Amendment challenge. The Court noted that there are solicitation restrictions on corporate PACs, and that corporations are permitted to fund the establishment, administration, and solicitation costs of their PACs without disclosure. The court also noted that PACs are no longer necessary for corporate involvement in independent expenditures; following Citizens United, corporations are permitted to make such expenditures with their general treasury funds. By seeking to finance independent expenditures through its separate segregated fund rather than directly with corporate funds, the court concluded that Stop This Insanity, Inc. was voluntarily choosing a more burdensome alternative. Because of the substantial overlap between the political speech of Stop This Insanity, Inc. and its separate segregated fund, the court held there was no substantial burden on the entities First Amendment rights. In its review of solicitation restrictions, the court declined to apply strict scrutiny. 13
18 In the alternative, even assuming a separate segregated fund s First Amendment rights should be viewed in isolation from its sponsoring organization, the Court found that disclosure requirements for solicitations furthered the governmental interest in preventing quid pro quo corruption. A petition for certiorari is pending. Contribution-Limit Waiting Period: Stop Reckless Economic Instability Caused By Democrats v. FEC, No (E.D. Va. complaint filed Apr. 4, 2014) A group of plaintiffs claim that federal law violates the First Amendment and equal protection principles by requiring political committees that are not connected to candidates or parties to be registered with the Commission for six months before they may qualify as multicandidate committees entitled to make higher contributions to candidates. Plaintiffs also claim that the limit on contributions from multicandidate committees to national and state political parties violate equal protection because other committees may contribute larger amounts to those political parties. A hearing was held on cross-motions for summary judgment on October 31, Per-Election Contribution Limits: Holmes v. FEC, F. Supp. 3d, 2014 WL (D.D.C. Oct. 20, 2014) Two contributors to candidates contended that the $2600, per-election contribution limit in federal law violated their First and Fifth Amendment rights by preventing them from donating $5,200 to candidates after primary elections for use only in connection with general-election campaigns. The court denied plaintiffs motion for a preliminary injunction, finding that they were unlikely to succeed on their First Amendment claim because they could have contributed $2600 to their preferred candidates before those candidates primary elections, and the per-election limits are closely drawn to reduce corruption or its appearance. The court also found that federal law does not treat contributors to candidates who ran in uncontested primaries differently from other contributors. Plaintiffs contended that contributors in the former situation can effectively give $5200 for general elections because the candidates to whom they give can use the $2600 contributed before the primary towards the general election, as well as $2600 contributed after the primary. The court disagreed, noting that it is candidates, rather than contributors, who determine how primary-election funds will be spent. The contribution limits are the same for all candidates based on the number of elections in which they run. The court thus found plaintiffs unlikely to succeed on their claim that they had been denied equal protection. The court has sent constitutional questions to the D.C. Circuit en banc pursuant to a special judicial review provision. Contribution Limits Applied to Bequests: Libertarian National Committee v. FEC, 2014 WL (D.C. Cir. Feb. 7, 2014) This case was a First Amendment challenge to FECA s limits on contributions to national party committees as they apply 14
19 to bequests (property given through the will of a deceased person). FECA permits the distribution of bequests through an escrow account up to the contribution limit each year, but the Libertarian National Committee sought to accept bequests in amounts above the applicable annual limit as single payments. A three-judge panel in the D.C. Circuit Court of Appeals summarily affirmed the district court s ruling that bequests, like other contributions addressed by the Supreme Court, generally do pose a danger of corruption and its appearance. A separate part of the case addressing one particular bequest was dismissed after it became moot. Major Purpose Determinations: Public Citizen v. FEC, No (D.D.C.) / No (D.C. Cir.) Two nonprofit organizations, as well as individuals associated with those organizations, sued the FEC to challenge its dismissal of their administrative complaint alleging certain campaign-finance violations by Crossroads Grassroots Political Strategies, an entity organized under section 501(c)(4) of the Internal Revenue Code. They contend that the group should have registered with the FEC and filed periodic disclosure reports because it meets federal statutory requirements and has as its major purpose federal campaign activity. The issues in the case include whether it is reasonable to decline to count ads that do not expressly advocate for the election or defeat of candidates when determining major purpose. Another issue regarding that determination is whether it is reasonable to examine the spending of an entity according to its fiscal year rather than by calendar year. Crossroads Grassroots Political Strategies moved to intervene as a defendant in the case. The district court denied that motion. The D.C. Circuit has stayed all proceedings in the district court pending briefing and decision on the appeal of the intervention denial. Oral argument for the intervention appeal will occur in February Citizens for Responsibility and Ethics in Washington v.fec, No (D.D.C. complaint filed Aug. 20, 2014) Citizens for Responsibility and Ethics in Washington and its executive director bring an action similar to Public Citizen, above. They challenge the FEC s dismissal of two administrative complaints contending that American Action Network and Americans for Job Security, respectively, violated federal law by failing to register and file reports with the FEC. They also seek to have the court generally enjoin the FEC from taking the challenged positions regarding major purpose in other matters. Disclosure Regarding Electioneering Communications: Independence Institute, F. Supp. 3d, 2014 WL (D.D.C. Oct. 6, 2014) The Independence Institute, a nonprofit organization, challenged the application of federal disclosure requirements for electioneering communications to a radio advertisement it planned to air that it contended was a genuine issue ad 15
20 which did not attack the referenced federal candidate. The court awarded judgment to the Commission, finding that the Supreme Court had rejected an attempt to limit application of the disclosure requirements to express advocacy and its functional equivalent in Citizens United. Even though the Supreme Court noted that the ads at issue in Citizens United advocated a commercial transaction and may have spoken pejoratively about a candidate, the court found the holding in that case still governs Independence Institute s noncommercial ad, which did not on its face say anything positive or negative about a candidate. Citizens United also controlled, the court concluded, even though Independence Institute is organized under section 501(c)(3) of the Internal Revenue Code and Citizens United was organized section 501(c)(4). Independence Institute has appealed. Van Hollen v. FEC, No (D.D.C.) This challenge to an FEC regulation governing the disclosure of persons who give funds to corporations and unions that make electioneering communications has been discussed at past conferences. The D.C. Circuit remanded it in 2012 and it has remained pending with the district court throughout this past year. Personal Use of Campaign Funds: FEC v. Craig for U.S. Senate, F. Supp. 3d, 2014 WL (D.D.C. Sept. 30, 2014) The court found that former United States Senator Larry E. Craig and his campaign committee converted nearly $200,000 of campaign contributions to the personal use of Senator Craig. The funds were used to pay for legal expenses associated with his attempt to withdraw a guilty plea of disorderly conduct. The court ordered Senator Craig to disgorge the funds to the U.S. Treasury and, in addition, pay a civil penalty of $45,
21 Federal Policy Digest in 2014 Summary of Key Federal Election Commission Policy Actions Candidate Books and Reality Shows: The FEC issued two advisory opinions regarding books written by congressional candidates. In each opinion, the FEC concluded that the candidate s campaign was permitted to purchase copies of the candidate s book in bulk for distribution to supporters, provided that the book s publisher donated the royalties accruing from such sales to charity rather than paying them to the candidate. In one of these advisory opinions, the FEC also concluded that a campaign committee was permitted to place a small amount of promotional material about the candidate s book on the campaign s website and social media pages, as long as the cost of doing so was de minimis. In a third advisory opinion request, the FEC considered a proposal for a television production company to pay a congressional candidate to appear on a reality television show regarding candidates running in races considered unwinnable. The FEC released two draft advisory opinions, each of which would have concluded that the production company was not permitted to pay the candidate to appear on a television show about his campaign. The candidate then withdrew his request for an advisory opinion. Rulemaking in Response to Citizens United v. FEC: In October 2014, the FEC published final rules in response to the Supreme Court s decision in Citizens United v. FEC. These rules removed from the FEC s regulations the general prohibitions on independent expenditures and electioneering communications by corporations and unions. The rules also clarified regulations regarding certain categories of corporate and union expenditures, such as voter registration and GOTV activity. The rules did not address super PACs or hybrid PACs, reserving those issues for a later rulemaking. Rulemakings in Response to McCutcheon v. FEC: In October 2014, the FEC published final rules in response to the Supreme Court s decision in McCutcheon v. FEC. These rules deleted the FEC regulations that had implemented the aggregate contribution limits that were struck down in McCutcheon. Along with these final rules, the FEC also published an advance notice of proposed rulemaking that seeks comment on other regulatory changes that might be appropriate in response to the McCutcheon decision, including changes in areas such as earmarking, disclosure, affiliation, and joint fundraising. The comment period on this notice remains open until January 15, 2015, and the FEC will hold a hearing on the matter in February
22 Federal Preemption of State Law: The FEC considered three advisory opinions in 2014 regarding preemption of state law by federal campaign finance law. The first opinion concerned whether FEC regulations regarding the use of voluntary payroll deductions to administer contributions to a corporation s PAC preempted New York prohibitions on the use of payroll deductions for political purposes. The second opinion concerned whether an FEC regulation that permits a corporate PAC to solicit contributions from certain employees of the corporation s subsidiaries preempted a Michigan law that does not permit such solicitations. In each of these matters, the relevant state enforcement agency had indicated that the state provision at issue did not apply to federal political committees. The FEC relied on these statements and found that it would not reach the preemption issues presented in the requests in light of the states assurances that they would not seek to apply their law to federal committees. In a third advisory opinion request, a state political party asked whether federal law and regulations that require a state political party to finance certain activity with federal funds preempted Connecticut state laws that require state political parties to finance such activity with state funds. Before the FEC had released any draft advisory opinions, the requesting political party was sued in state court by the opposing political party, which sought to enjoin the conduct that was at issue in the advisory opinion request. The requesting party then withdrew its request. Bitcoins: In May 2014, the FEC issued an advisory opinion regarding political committees acceptance of contributions in bitcoins, a privately issued digital currency. The FEC approved a political committee s proposal to accept bitcoin contributions in amounts up to $100 per contributor, provided that the recipients take certain measures to ensure the legality of these contributions. The FEC also provided guidance regarding how committees should report transactions involving bitcoins and determine their value. The advisory opinion did not reach a conclusion as to whether committees may receive bitcoin contributions of more than $100 per contributor. 18
23 Local Government Campaign Finance Update in 2014 Campaign Finance Legislation and Litigation in Local U.S. Jurisdictions Colorado Springs, CO Legislation/Policy: In November 2014, the City of Colorado Springs launched an electronic campaign finance filing and disclosure system for city elections. The new system will be fully operational for the upcoming April 2015 city elections. Houston, TX Litigation: In Gordon v. City of Houston, No. 4:14-cv (S.D. Tex. 2014), a candidate for at-large Houston City Council in the November 2015 election, Trebor Gordon, filed a First Amendment challenge in federal district court to the city s fundraising blackout period, which prohibits candidates from soliciting or receiving contributions except during a period commencing on the 1st day of February prior to the day of the election, and ending on the 4th day of March following the election date for the race that the candidate has entered. Gordon filed a motion for preliminary injunction on November 4, The case is pending before the district court. Los Angeles, CA Legislation/Policy: In April 2014, in the wake of the Supreme Court decision in McCutcheon v. FEC and on the advice of the City Attorney s office, the Los Angeles City Ethics Commission adopted a resolution stating that the city s aggregate contribution limits would not be enforced in this year s city elections. Legislation/Policy: In April 2014, new Los Angeles City Ethics Commission regulations pertaining to advisory opinions, investigations and enforcement processes became effective. Among the changes to these processes, the Ethics Commission may now initiate advisory opinions on behalf of classes of regulated persons. The new regulations also clarify and streamline the procedures for investigations and enforcement matters and enhance the Commission s ability to work with other City agencies that have investigative authority. The new regulations also authorize the Commission to seek sanctions from a civil court when a person interferes with the investigative or enforcement processes and to enter a default order when a respondent fails to communicate with the Commission in an enforcement matter. 19
24 Legislation/Policy: In September 2014, the City of Los Angeles enacted two new campaign finance ordinances (Ordinances Nos and ) amending many aspects of the city s campaign finance laws. The amendments include: modification of the Consumer Price Index adjustments to contribution limits, modification of provisions regarding aggregation of contributions for the purpose of contribution limits, application of fundraising window provisions to special elections, modification of pre-election reporting requirements, extension of the reproduction of campaign materials provisions to non-candidate committees and addition of a substantial part requirement, adjustments and clarification of public matching funds provisions and related spending limits, and clarification of the independent expenditure disclosure requirements. Legislation/Policy: In August, the Los Angeles City Ethics Commission unanimously approved recommendations to the city council for amendments of city law pertaining to officeholder and legal defense committees, including adjusting contribution limits for such committees to reflect changes in the Consumer Price Index, clarifying ordinance provisions related to allowable officeholder expenditures, prohibiting fundraising for an officeholder committee while the officeholder is running for reelection, creation of a behested payment disclosure report. Litigation: In Dickranian v. City of Los Angeles, No. 2:12-cv (C.D. Cal.), on appeal No (9th Cir.), plaintiff Laurel Dickranian filed suit in U.S. District Court challenging Los Angeles disclaimer and disclosure requirements as unconstitutional, and seeking declaratory and injunctive relief as well as damages. The city s law requires those making independent expenditures above certain thresholds in city candidate or ballot measure elections to file a campaign finance report and a copy of the communication. Dickranian spent nearly $8,000 sending letters to more than 17,000 Los Angeles voters urging them to elect a particular candidate for the office of City Attorney. The district court summarily dismissed Dickranian s complaint and upheld the city s disclosure law. Dickranian appealed the district court s dismissal to the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals, which scheduled oral argument for Nov. 19, On November 7, 2014, counsel to plaintiff-appellant filed a letter with the Ninth Circuit indicating that the parties had reached a settlement in advance of the November 19 argument though the details of the settlement had not been finalized or disclosed at that time. Montgomery County, MD Legislation/Policy: In October 2014, the Montgomery County Council unanimously enacted a bill (Bill 16-14) that creates a voluntary matching public financing system for candidates for County Council and County Executive, which will take effect for the county s 2018 elections. The new law establishes a Public Election Fund and requires participating candidates to accept only individual 20
Limitations on Contributions to Political Committees
 Limitations on Contributions to Committees Term for PAC Individual PAC Corporate/Union PAC Party PAC PAC PAC Transfers Alabama 10-2A-70.2 $500/election Alaska 15.13.070 Group $500/year Only 10% of a PAC's
Limitations on Contributions to Committees Term for PAC Individual PAC Corporate/Union PAC Party PAC PAC PAC Transfers Alabama 10-2A-70.2 $500/election Alaska 15.13.070 Group $500/year Only 10% of a PAC's
Campaign Finance E-Filing Systems by State WHAT IS REQUIRED? WHO MUST E-FILE? Candidates (Annually, Monthly, Weekly, Daily).
 Exhibit E.1 Alabama Alabama Secretary of State Mandatory Candidates (Annually, Monthly, Weekly, Daily). PAC (annually), Debts. A filing threshold of $1,000 for all candidates for office, from statewide
Exhibit E.1 Alabama Alabama Secretary of State Mandatory Candidates (Annually, Monthly, Weekly, Daily). PAC (annually), Debts. A filing threshold of $1,000 for all candidates for office, from statewide
Lobbying: 10 Answers you need to know Venable LLP
 Lobbying: 10 Answers you need to know 2013 Venable LLP 1 Faculty Ronald M. Jacobs Co-chair, political law practice, Venable LLP, Washington, DC Government and campaign experience Counsel to corporations,
Lobbying: 10 Answers you need to know 2013 Venable LLP 1 Faculty Ronald M. Jacobs Co-chair, political law practice, Venable LLP, Washington, DC Government and campaign experience Counsel to corporations,
Matthew Miller, Bureau of Legislative Research
 Matthew Miller, Bureau of Legislative Research Arkansas (reelection) Georgia (reelection) Idaho (reelection) Kentucky (reelection) Michigan (partisan nomination - reelection) Minnesota (reelection) Mississippi
Matthew Miller, Bureau of Legislative Research Arkansas (reelection) Georgia (reelection) Idaho (reelection) Kentucky (reelection) Michigan (partisan nomination - reelection) Minnesota (reelection) Mississippi
Sunlight State By State After Citizens United
 Sunlight State By State After Citizens United How state legislation has responded to Citizens United Corporate Reform Coalition June 2012 www.corporatereformcoalition.org About the Author Robert M. Stern
Sunlight State By State After Citizens United How state legislation has responded to Citizens United Corporate Reform Coalition June 2012 www.corporatereformcoalition.org About the Author Robert M. Stern
Should Politicians Choose Their Voters? League of Women Voters of MI Education Fund
 Should Politicians Choose Their Voters? 1 Politicians are drawing their own voting maps to manipulate elections and keep themselves and their party in power. 2 3 -The U.S. Constitution requires that the
Should Politicians Choose Their Voters? 1 Politicians are drawing their own voting maps to manipulate elections and keep themselves and their party in power. 2 3 -The U.S. Constitution requires that the
Background Information on Redistricting
 Redistricting in New York State Citizens Union/League of Women Voters of New York State Background Information on Redistricting What is redistricting? Redistricting determines the lines of state legislative
Redistricting in New York State Citizens Union/League of Women Voters of New York State Background Information on Redistricting What is redistricting? Redistricting determines the lines of state legislative
Case dismissed as moot by Seventh Circuit on 9/1/11. 1st Circuit dismissed as moot on 7/21/11.
 Case Type Financing Financing State of Origin Wisconsin Maine Case Name Current Status Brief Description Wisconsin Right to Life v. Brennan; Koschnick v. Doyle Cushing v. McKee New York NOM v. Walsh Case
Case Type Financing Financing State of Origin Wisconsin Maine Case Name Current Status Brief Description Wisconsin Right to Life v. Brennan; Koschnick v. Doyle Cushing v. McKee New York NOM v. Walsh Case
Redistricting in Michigan
 Dr. Martha Sloan of the Copper Country League of Women Voters Redistricting in Michigan Should Politicians Choose their Voters? Politicians are drawing their own voting maps to manipulate elections and
Dr. Martha Sloan of the Copper Country League of Women Voters Redistricting in Michigan Should Politicians Choose their Voters? Politicians are drawing their own voting maps to manipulate elections and
NOTICE TO MEMBERS No January 2, 2018
 NOTICE TO MEMBERS No. 2018-004 January 2, 2018 Trading by U.S. Residents Canadian Derivatives Clearing Corporation (CDCC) maintains registrations with various U.S. state securities regulatory authorities
NOTICE TO MEMBERS No. 2018-004 January 2, 2018 Trading by U.S. Residents Canadian Derivatives Clearing Corporation (CDCC) maintains registrations with various U.S. state securities regulatory authorities
530 East Montecito Street, Santa Barbara, CA
 11/7/17 Ohio: The Ohio legislature has passed O.R.C. 5741.01 (I). This legislation provides tax collection on out-of-state retailers who enter into agreements with one or more residents of Ohio under which
11/7/17 Ohio: The Ohio legislature has passed O.R.C. 5741.01 (I). This legislation provides tax collection on out-of-state retailers who enter into agreements with one or more residents of Ohio under which
PREVIEW 2018 PRO-EQUALITY AND ANTI-LGBTQ STATE AND LOCAL LEGISLATION
 PREVIEW 08 PRO-EQUALITY AND ANTI-LGBTQ STATE AND LOCAL LEGISLATION Emboldened by the politics of hate and fear spewed by the Trump-Pence administration, state legislators across the nation have threatened
PREVIEW 08 PRO-EQUALITY AND ANTI-LGBTQ STATE AND LOCAL LEGISLATION Emboldened by the politics of hate and fear spewed by the Trump-Pence administration, state legislators across the nation have threatened
Oregon enacts statute to make improper patent license demands a violation of its unlawful trade practices law
 ebook Patent Troll Watch Written by Philip C. Swain March 14, 2016 States Are Pushing Patent Trolls Away from the Legal Line Washington passes a Patent Troll Prevention Act In December, 2015, the Washington
ebook Patent Troll Watch Written by Philip C. Swain March 14, 2016 States Are Pushing Patent Trolls Away from the Legal Line Washington passes a Patent Troll Prevention Act In December, 2015, the Washington
PERMISSIBILITY OF ELECTRONIC VOTING IN THE UNITED STATES. Member Electronic Vote/ . Alabama No No Yes No. Alaska No No No No
 PERMISSIBILITY OF ELECTRONIC VOTING IN THE UNITED STATES State Member Conference Call Vote Member Electronic Vote/ Email Board of Directors Conference Call Vote Board of Directors Electronic Vote/ Email
PERMISSIBILITY OF ELECTRONIC VOTING IN THE UNITED STATES State Member Conference Call Vote Member Electronic Vote/ Email Board of Directors Conference Call Vote Board of Directors Electronic Vote/ Email
FEDERAL ELECTION COMMISSION [NOTICE ] Price Index Adjustments for Contribution and Expenditure Limitations and
![FEDERAL ELECTION COMMISSION [NOTICE ] Price Index Adjustments for Contribution and Expenditure Limitations and FEDERAL ELECTION COMMISSION [NOTICE ] Price Index Adjustments for Contribution and Expenditure Limitations and](/thumbs/76/74112431.jpg) This document is scheduled to be published in the Federal Register on 02/03/2015 and available online at http://federalregister.gov/a/2015-01963, and on FDsys.gov 6715-01-U FEDERAL ELECTION COMMISSION
This document is scheduled to be published in the Federal Register on 02/03/2015 and available online at http://federalregister.gov/a/2015-01963, and on FDsys.gov 6715-01-U FEDERAL ELECTION COMMISSION
2016 Voter Registration Deadlines by State
 2016 Voter s by Alabama 10/24/2016 https://www.alabamavotes.gov/electioninfo.aspx?m=vote rs Alaska 10/9/2016 (Election Day registration permitted for purpose of voting for president and Vice President
2016 Voter s by Alabama 10/24/2016 https://www.alabamavotes.gov/electioninfo.aspx?m=vote rs Alaska 10/9/2016 (Election Day registration permitted for purpose of voting for president and Vice President
Campaign Finance Options: Public Financing and Contribution Limits
 Campaign Finance Options: Public Financing and Contribution Limits Wendy Underhill Program Manager Elections National Conference of State Legislatures prepared for Oregon s Joint Interim Task Force on
Campaign Finance Options: Public Financing and Contribution Limits Wendy Underhill Program Manager Elections National Conference of State Legislatures prepared for Oregon s Joint Interim Task Force on
Of the People, By the People, For the People
 January 2010 Of the People, By the People, For the People A 2010 Report Card on Statewide Voter Initiative Rights Executive Summary For over a century, the initiative and referendum process has given voters
January 2010 Of the People, By the People, For the People A 2010 Report Card on Statewide Voter Initiative Rights Executive Summary For over a century, the initiative and referendum process has given voters
Official Voter Information for General Election Statute Titles
 Official Voter Information for General Election Statute Titles Alabama 17-6-46. Voting instruction posters. Alaska Sec. 15.15.070. Public notice of election required Sec. 15.58.010. Election pamphlet Sec.
Official Voter Information for General Election Statute Titles Alabama 17-6-46. Voting instruction posters. Alaska Sec. 15.15.070. Public notice of election required Sec. 15.58.010. Election pamphlet Sec.
Judicial Selection in the States
 Judicial S in the States Appellate and General Jurisdiction Courts Initial S, Retention, and Term Length INITIAL Alabama Supreme Court X 6 Re- (6 year term) Court of Civil App. X 6 Re- (6 year term) Court
Judicial S in the States Appellate and General Jurisdiction Courts Initial S, Retention, and Term Length INITIAL Alabama Supreme Court X 6 Re- (6 year term) Court of Civil App. X 6 Re- (6 year term) Court
Security Breach Notification Chart
 Security Breach Notification Chart Perkins Coie's Privacy & Security practice maintains this comprehensive chart of state laws regarding security breach notification. The chart is for informational purposes
Security Breach Notification Chart Perkins Coie's Privacy & Security practice maintains this comprehensive chart of state laws regarding security breach notification. The chart is for informational purposes
State Limits on Contributions to Candidates Election Cycle. PAC Candidate Contributions. Unlimited Unlimited Unlimited Unlimited Unlimited
 State Limits on to Candidates 2015-2016 Election Cycle Individual Candidate Alabama Ala. Code 17-5-1 et seq. Unlimited Unlimited Unlimited Unlimited Unlimited Alaska 15.13.070 and 15.13.074(f) $500//year
State Limits on to Candidates 2015-2016 Election Cycle Individual Candidate Alabama Ala. Code 17-5-1 et seq. Unlimited Unlimited Unlimited Unlimited Unlimited Alaska 15.13.070 and 15.13.074(f) $500//year
State Trial Courts with Incidental Appellate Jurisdiction, 2010
 ALABAMA: G X X X de novo District, Probate, s ALASKA: ARIZONA: ARKANSAS: de novo or on the de novo (if no ) G O X X de novo CALIFORNIA: COLORADO: District Court, Justice of the Peace,, County, District,
ALABAMA: G X X X de novo District, Probate, s ALASKA: ARIZONA: ARKANSAS: de novo or on the de novo (if no ) G O X X de novo CALIFORNIA: COLORADO: District Court, Justice of the Peace,, County, District,
POLITICAL CONTRIBUTIONS. OUT-OF- STATE DONORS. INITIATIVE STATUTE.
 University of California, Hastings College of the Law UC Hastings Scholarship Repository Initiatives California Ballot Propositions and Initiatives 3-13-2015 POLITICAL CONTRIBUTIONS. OUT-OF- STATE DONORS.
University of California, Hastings College of the Law UC Hastings Scholarship Repository Initiatives California Ballot Propositions and Initiatives 3-13-2015 POLITICAL CONTRIBUTIONS. OUT-OF- STATE DONORS.
Class Actions and the Refund of Unconstitutional Taxes. Revenue Laws Study Committee Trina Griffin, Research Division April 2, 2008
 Class Actions and the Refund of Unconstitutional Taxes Revenue Laws Study Committee Trina Griffin, Research Division April 2, 2008 United States Supreme Court North Carolina Supreme Court Refunds of Unconstitutional
Class Actions and the Refund of Unconstitutional Taxes Revenue Laws Study Committee Trina Griffin, Research Division April 2, 2008 United States Supreme Court North Carolina Supreme Court Refunds of Unconstitutional
If you have questions, please or call
 SCCE's 17th Annual Compliance & Ethics Institute: CLE Approvals By State The SCCE submitted sessions deemed eligible for general CLE credits and legal ethics CLE credits to most states with CLE requirements
SCCE's 17th Annual Compliance & Ethics Institute: CLE Approvals By State The SCCE submitted sessions deemed eligible for general CLE credits and legal ethics CLE credits to most states with CLE requirements
Security Breach Notification Chart
 Security Breach Notification Chart Perkins Coie's Privacy & Security practice maintains this comprehensive chart of state laws regarding security breach notification. The chart is for informational purposes
Security Breach Notification Chart Perkins Coie's Privacy & Security practice maintains this comprehensive chart of state laws regarding security breach notification. The chart is for informational purposes
Political Contributions Report. Introduction POLITICAL CONTRIBUTIONS
 Political Contributions Report January 1, 2009 December 31, 2009 Introduction At CCA, we believe that participation in the political process is an important and appropriate part of our partnership relations
Political Contributions Report January 1, 2009 December 31, 2009 Introduction At CCA, we believe that participation in the political process is an important and appropriate part of our partnership relations
Case 3:15-md CRB Document 4700 Filed 01/29/18 Page 1 of 5
 Case 3:15-md-02672-CRB Document 4700 Filed 01/29/18 Page 1 of 5 Michele D. Ross Reed Smith LLP 1301 K Street NW Suite 1000 East Tower Washington, D.C. 20005 Telephone: 202 414-9297 Fax: 202 414-9299 Email:
Case 3:15-md-02672-CRB Document 4700 Filed 01/29/18 Page 1 of 5 Michele D. Ross Reed Smith LLP 1301 K Street NW Suite 1000 East Tower Washington, D.C. 20005 Telephone: 202 414-9297 Fax: 202 414-9299 Email:
NATIONAL SOCIETY OF BLACK ENGINEERS CONSTITUTION MARCH 1988 APRIL Approved March 30, 2013 Revised August, 2015
 NATIONAL SOCIETY OF BLACK MARCH 1988 APRIL 2016 ENGINEERS National Society of Black Engineers CONSTITUTION www.nsbe.org 1 Think Green! Please do not print unless absolutely necessary TABLE OF CONTENTS
NATIONAL SOCIETY OF BLACK MARCH 1988 APRIL 2016 ENGINEERS National Society of Black Engineers CONSTITUTION www.nsbe.org 1 Think Green! Please do not print unless absolutely necessary TABLE OF CONTENTS
CONSTITUTION of the ASSOCIATION OF STATE CORRECTIONAL ADMINISTRATORS. ARTICLE I Name
 CONSTITUTION of the ASSOCIATION OF STATE CORRECTIONAL ADMINISTRATORS ARTICLE I Name The name of this organization shall be the Association of State Correctional Administrators. ARTICLE II Objective The
CONSTITUTION of the ASSOCIATION OF STATE CORRECTIONAL ADMINISTRATORS ARTICLE I Name The name of this organization shall be the Association of State Correctional Administrators. ARTICLE II Objective The
Delegates: Understanding the numbers and the rules
 Delegates: Understanding the numbers and the rules About 4,051 pledged About 712 unpledged 2472 delegates Images from: https://ballotpedia.org/presidential_election,_2016 On the news I hear about super
Delegates: Understanding the numbers and the rules About 4,051 pledged About 712 unpledged 2472 delegates Images from: https://ballotpedia.org/presidential_election,_2016 On the news I hear about super
o Yes o No o Under 18 o o o o o o o o 85 or older BLW YouGov spec
 BLW YouGov spec This study is being conducted by John Carey, Gretchen Helmke, Brendan Nyhan, and Susan Stokes, who are professors at Dartmouth College (Carey and Nyhan), the University of Rochester (Helmke),
BLW YouGov spec This study is being conducted by John Carey, Gretchen Helmke, Brendan Nyhan, and Susan Stokes, who are professors at Dartmouth College (Carey and Nyhan), the University of Rochester (Helmke),
NORTH CAROLINA GENERAL ASSEMBLY Legislative Services Office
 NORTH CAROLINA GENERAL ASSEMBLY Legislative Services Office Kory Goldsmith, Interim Legislative Services Officer Research Division 300 N. Salisbury Street, Suite 545 Raleigh, NC 27603-5925 Tel. 919-733-2578
NORTH CAROLINA GENERAL ASSEMBLY Legislative Services Office Kory Goldsmith, Interim Legislative Services Officer Research Division 300 N. Salisbury Street, Suite 545 Raleigh, NC 27603-5925 Tel. 919-733-2578
MEMORANDUM JUDGES SERVING AS ARBITRATORS AND MEDIATORS
 Knowledge Management Office MEMORANDUM Re: Ref. No.: By: Date: Regulation of Retired Judges Serving as Arbitrators and Mediators IS 98.0561 Jerry Nagle, Colleen Danos, and Anne Endress Skove October 22,
Knowledge Management Office MEMORANDUM Re: Ref. No.: By: Date: Regulation of Retired Judges Serving as Arbitrators and Mediators IS 98.0561 Jerry Nagle, Colleen Danos, and Anne Endress Skove October 22,
ASSOCIATES OF VIETNAM VETERANS OF AMERICA, INC. BYLAWS (A Nonprofit Corporation)
 Article I Name The name of the corporation is Associates of Vietnam Veterans of America, Inc., as prescribed by the Articles of Incorporation, hereinafter referred to as the Corporation. Article II Purposes
Article I Name The name of the corporation is Associates of Vietnam Veterans of America, Inc., as prescribed by the Articles of Incorporation, hereinafter referred to as the Corporation. Article II Purposes
THE PROCESS TO RENEW A JUDGMENT SHOULD BEGIN 6-8 MONTHS PRIOR TO THE DEADLINE
 THE PROCESS TO RENEW A JUDGMENT SHOULD BEGIN 6-8 MONTHS PRIOR TO THE DEADLINE STATE RENEWAL Additional information ALABAMA Judgment good for 20 years if renewed ALASKA ARIZONA (foreign judgment 4 years)
THE PROCESS TO RENEW A JUDGMENT SHOULD BEGIN 6-8 MONTHS PRIOR TO THE DEADLINE STATE RENEWAL Additional information ALABAMA Judgment good for 20 years if renewed ALASKA ARIZONA (foreign judgment 4 years)
INTRODUCTION AND SUMMARY
 Gender Parity Index INTRODUCTION AND SUMMARY - 2017 State of Women's Representation Page 1 INTRODUCTION As a result of the 2016 elections, progress towards gender parity stalled. Beyond Hillary Clinton
Gender Parity Index INTRODUCTION AND SUMMARY - 2017 State of Women's Representation Page 1 INTRODUCTION As a result of the 2016 elections, progress towards gender parity stalled. Beyond Hillary Clinton
STATUS OF 2002 REED ACT DISTRIBUTION BY STATE
 STATUS OF 2002 REED ACT DISTRIBUTION BY STATE Revised January 2003 State State Reed Act Reed Act Funds Appropriated* (as of November 2002) Comments on State s Reed Act Activity Alabama $110,623,477 $16,650,000
STATUS OF 2002 REED ACT DISTRIBUTION BY STATE Revised January 2003 State State Reed Act Reed Act Funds Appropriated* (as of November 2002) Comments on State s Reed Act Activity Alabama $110,623,477 $16,650,000
Chart 12.7: State Appellate Court Divisions (Cross-reference ALWD Rule 12.6(b)(2))
 Chart 12.7: State Appellate Court (Cross-reference ALWD Rule 12.6(b)(2)) Alabama Divided Court of Civil Appeals Court of Criminal Appeals Alaska Not applicable Not applicable Arizona Divided** Court of
Chart 12.7: State Appellate Court (Cross-reference ALWD Rule 12.6(b)(2)) Alabama Divided Court of Civil Appeals Court of Criminal Appeals Alaska Not applicable Not applicable Arizona Divided** Court of
Committee Consideration of Bills
 Committee Procedures 4-79 Committee Consideration of ills It is not possible for all legislative business to be conducted by the full membership; some division of labor is essential. Legislative committees
Committee Procedures 4-79 Committee Consideration of ills It is not possible for all legislative business to be conducted by the full membership; some division of labor is essential. Legislative committees
Governance State Boards/Chiefs/Agencies
 Governance State Boards/Chiefs/Agencies Education Commission of the States 700 Broadway, Suite 1200 Denver, CO 80203-3460 303.299.3600 Fax: 303.296.8332 www.ecs.org Qualifications for Chief State School
Governance State Boards/Chiefs/Agencies Education Commission of the States 700 Broadway, Suite 1200 Denver, CO 80203-3460 303.299.3600 Fax: 303.296.8332 www.ecs.org Qualifications for Chief State School
Security Breach Notification Chart
 Security Breach Notification Chart Perkins Coie's Privacy & Security practice maintains this comprehensive chart of state laws regarding security breach notification. The chart is for informational purposes
Security Breach Notification Chart Perkins Coie's Privacy & Security practice maintains this comprehensive chart of state laws regarding security breach notification. The chart is for informational purposes
Race to the White House Drive to the 2016 Republican Nomination. Ron Nehring California Chairman, Ted Cruz for President
 Race to the White House Drive to the 2016 Republican Nomination Ron Nehring California Chairman, Ted Cruz for President July 18 21, 2016 2016 Republican National Convention Cleveland, Ohio J ul y 18 21,
Race to the White House Drive to the 2016 Republican Nomination Ron Nehring California Chairman, Ted Cruz for President July 18 21, 2016 2016 Republican National Convention Cleveland, Ohio J ul y 18 21,
PROFESSIONAL STANDARDS POLICY. Table of Contents Page
 PROFESSIONAL STANDARDS POLICY Title: REGIONAL COORDINATOR ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES Doc ID: PS6008 Revision: 0.09 Committee: Professional Standards Written by: C. Wilson, R. Anderson, J. Smith Date Established:
PROFESSIONAL STANDARDS POLICY Title: REGIONAL COORDINATOR ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES Doc ID: PS6008 Revision: 0.09 Committee: Professional Standards Written by: C. Wilson, R. Anderson, J. Smith Date Established:
2008 Changes to the Constitution of International Union UNITED STEELWORKERS
 2008 Changes to the Constitution of International Union UNITED STEELWORKERS MANUAL ADOPTED AT LAS VEGAS, NEVADA July 2008 Affix to inside front cover of your 2005 Constitution CONSTITUTIONAL CHANGES Constitution
2008 Changes to the Constitution of International Union UNITED STEELWORKERS MANUAL ADOPTED AT LAS VEGAS, NEVADA July 2008 Affix to inside front cover of your 2005 Constitution CONSTITUTIONAL CHANGES Constitution
28 USC 152. NB: This unofficial compilation of the U.S. Code is current as of Jan. 4, 2012 (see
 TITLE 28 - JUDICIARY AND JUDICIAL PROCEDURE PART I - ORGANIZATION OF COURTS CHAPTER 6 - BANKRUPTCY JUDGES 152. Appointment of bankruptcy judges (a) (1) Each bankruptcy judge to be appointed for a judicial
TITLE 28 - JUDICIARY AND JUDICIAL PROCEDURE PART I - ORGANIZATION OF COURTS CHAPTER 6 - BANKRUPTCY JUDGES 152. Appointment of bankruptcy judges (a) (1) Each bankruptcy judge to be appointed for a judicial
ACCESS TO STATE GOVERNMENT 1. Web Pages for State Laws, State Rules and State Departments of Health
 1 ACCESS TO STATE GOVERNMENT 1 Web Pages for State Laws, State Rules and State Departments of Health LAWS ALABAMA http://www.legislature.state.al.us/codeofalabama/1975/coatoc.htm RULES ALABAMA http://www.alabamaadministrativecode.state.al.us/alabama.html
1 ACCESS TO STATE GOVERNMENT 1 Web Pages for State Laws, State Rules and State Departments of Health LAWS ALABAMA http://www.legislature.state.al.us/codeofalabama/1975/coatoc.htm RULES ALABAMA http://www.alabamaadministrativecode.state.al.us/alabama.html
12B,C: Voting Power and Apportionment
 12B,C: Voting Power and Apportionment Group Activities 12C Apportionment 1. A college offers tutoring in Math, English, Chemistry, and Biology. The number of students enrolled in each subject is listed
12B,C: Voting Power and Apportionment Group Activities 12C Apportionment 1. A college offers tutoring in Math, English, Chemistry, and Biology. The number of students enrolled in each subject is listed
7-45. Electronic Access to Legislative Documents. Legislative Documents
 Legislative Documents 7-45 Electronic Access to Legislative Documents Paper is no longer the only medium through which the public can gain access to legislative documents. State legislatures are using
Legislative Documents 7-45 Electronic Access to Legislative Documents Paper is no longer the only medium through which the public can gain access to legislative documents. State legislatures are using
The remaining legislative bodies have guides that help determine bill assignments. Table shows the criteria used to refer bills.
 ills and ill Processing 3-17 Referral of ills The first major step in the legislative process is to introduce a bill; the second is to have it heard by a committee. ut how does legislation get from one
ills and ill Processing 3-17 Referral of ills The first major step in the legislative process is to introduce a bill; the second is to have it heard by a committee. ut how does legislation get from one
Campaigns & Elections November 6, 2017 Dr. Michael Sullivan. FEDERAL GOVERNMENT GOVT 2305 MoWe 5:30 6:50 MoWe 7 8:30
 Campaigns & Elections November 6, 2017 Dr. Michael Sullivan FEDERAL GOVERNMENT GOVT 2305 MoWe 5:30 6:50 MoWe 7 8:30 Current Events, Recent Polls, & Review Background influences on campaigns Presidential
Campaigns & Elections November 6, 2017 Dr. Michael Sullivan FEDERAL GOVERNMENT GOVT 2305 MoWe 5:30 6:50 MoWe 7 8:30 Current Events, Recent Polls, & Review Background influences on campaigns Presidential
Nominating Committee Policy
 Nominating Committee Policy February 2014 Revision to include clarification on candidate qualifications. Mission Statement: The main purpose of the nominating committee is to present the Board of Directors
Nominating Committee Policy February 2014 Revision to include clarification on candidate qualifications. Mission Statement: The main purpose of the nominating committee is to present the Board of Directors
VOL. XV No. 12 Dec. 3, 2018
 VOL. XV No. 12 Dec. 3, 2018 Election Update CSBS Fintech Lawsuit Seattle Releases Public Bank Feasibility Study Appraisal Thresholds Raised ALEC States and Nation Policy Summit Council of State Governments
VOL. XV No. 12 Dec. 3, 2018 Election Update CSBS Fintech Lawsuit Seattle Releases Public Bank Feasibility Study Appraisal Thresholds Raised ALEC States and Nation Policy Summit Council of State Governments
NATIONAL SCHOOL TRANSPORTATION ASSOCIATION, INC. BYLAWS WITH CHANGES
 NATIONAL SCHOOL TRANSPORTATION ASSOCIATION, INC. BYLAWS WITH CHANGES Second... July 1969 Third Revision... July 1970 Fourth Revision... January 1972 (Proposed) Fifth Revision... July 1973 (Proposed) Sixth
NATIONAL SCHOOL TRANSPORTATION ASSOCIATION, INC. BYLAWS WITH CHANGES Second... July 1969 Third Revision... July 1970 Fourth Revision... January 1972 (Proposed) Fifth Revision... July 1973 (Proposed) Sixth
Case 1:14-cv Document 1-1 Filed 06/17/14 Page 1 of 61 IN THE UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE DISTRICT OF COLUMBIA
 Case 1:14-cv-01028 Document 1-1 Filed 06/17/14 Page 1 of 61 IN THE UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE DISTRICT OF COLUMBIA UNITED STATES OF AMERICA, et al., 555 4th Street, NW Washington, D.C. 20530
Case 1:14-cv-01028 Document 1-1 Filed 06/17/14 Page 1 of 61 IN THE UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE DISTRICT OF COLUMBIA UNITED STATES OF AMERICA, et al., 555 4th Street, NW Washington, D.C. 20530
CONSTITUTION of the NATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR THE PROFESSIONAL ADVANCEMENT OF BLACK CHEMISTS AND CHEMICAL ENGINEERS. (Adopted April 11, 1975)
 CONSTITUTION of the NATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR THE PROFESSIONAL ADVANCEMENT OF BLACK CHEMISTS AND CHEMICAL ENGINEERS (Adopted April 11, 1975) Amended April 12, 1990 Amended January 21, 2006 ARTICLE I Name
CONSTITUTION of the NATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR THE PROFESSIONAL ADVANCEMENT OF BLACK CHEMISTS AND CHEMICAL ENGINEERS (Adopted April 11, 1975) Amended April 12, 1990 Amended January 21, 2006 ARTICLE I Name
Constitution of Future Business Leaders of America-Phi Beta Lambda University of California, San Diego
 Constitution of Future Business Leaders of America-Phi Beta Lambda University of California, San Diego Revised 2015 Article I Name The name of this division of FBLA-PBL, Inc. shall be Phi Beta Lambda and
Constitution of Future Business Leaders of America-Phi Beta Lambda University of California, San Diego Revised 2015 Article I Name The name of this division of FBLA-PBL, Inc. shall be Phi Beta Lambda and
BYLAWS THE ASSOCIATION OF PUBLIC-SAFETY COMMUNICATIONS OFFICIALS- INTERNATIONAL, INC. AS ADOPTED BY THE MEMBERSHIP QUORUM AUGUST 19, 2009
 BYLAWS OF THE ASSOCIATION OF PUBLIC-SAFETY COMMUNICATIONS OFFICIALS- INTERNATIONAL, INC. AS ADOPTED BY THE MEMBERSHIP QUORUM AUGUST 19, 2009 VERIFIED AS ACCURATE BY THE BYLAWS COMMITTEE NOVEMBER 10, 2009
BYLAWS OF THE ASSOCIATION OF PUBLIC-SAFETY COMMUNICATIONS OFFICIALS- INTERNATIONAL, INC. AS ADOPTED BY THE MEMBERSHIP QUORUM AUGUST 19, 2009 VERIFIED AS ACCURATE BY THE BYLAWS COMMITTEE NOVEMBER 10, 2009
INSTITUTE of PUBLIC POLICY
 INSTITUTE of PUBLIC POLICY Harry S Truman School of Public Affairs University of Missouri ANALYSIS OF STATE REVENUES AND EXPENDITURES Andrew Wesemann and Brian Dabson Summary This report analyzes state
INSTITUTE of PUBLIC POLICY Harry S Truman School of Public Affairs University of Missouri ANALYSIS OF STATE REVENUES AND EXPENDITURES Andrew Wesemann and Brian Dabson Summary This report analyzes state
State Campaign Finance Disclosure Requirements Election Cycle
 State Campaign Finance Disclosure Requirements 2015-2016 Election Cycle State/Statute Who Needs to Disclose What Needs to be Disclosed When is it Disclosed Electronic Alabama Ala. Code 1975 17-5-8 Alaska
State Campaign Finance Disclosure Requirements 2015-2016 Election Cycle State/Statute Who Needs to Disclose What Needs to be Disclosed When is it Disclosed Electronic Alabama Ala. Code 1975 17-5-8 Alaska
Election Year Restrictions on Mass Mailings by Members of Congress: How H.R Would Change Current Law
 Election Year Restrictions on Mass Mailings by Members of Congress: How H.R. 2056 Would Change Current Law Matthew Eric Glassman Analyst on the Congress August 20, 2010 Congressional Research Service CRS
Election Year Restrictions on Mass Mailings by Members of Congress: How H.R. 2056 Would Change Current Law Matthew Eric Glassman Analyst on the Congress August 20, 2010 Congressional Research Service CRS
ACTION: Notice announcing addresses for summons and complaints. SUMMARY: Our Office of the General Counsel (OGC) is responsible for processing
 This document is scheduled to be published in the Federal Register on 02/23/2017 and available online at https://federalregister.gov/d/2017-03495, and on FDsys.gov 4191-02U SOCIAL SECURITY ADMINISTRATION
This document is scheduled to be published in the Federal Register on 02/23/2017 and available online at https://federalregister.gov/d/2017-03495, and on FDsys.gov 4191-02U SOCIAL SECURITY ADMINISTRATION
Security Breach Notification Chart
 Security Breach Notification Chart Perkins Coie's Privacy & Security practice maintains this comprehensive chart of state laws regarding security breach notification. The chart is for informational purposes
Security Breach Notification Chart Perkins Coie's Privacy & Security practice maintains this comprehensive chart of state laws regarding security breach notification. The chart is for informational purposes
ABOUT THE LSD The HNBA-LSD is a national organization of law students governed by its members. The mission of the HNBA-LSD is to increase the number
 ABOUT THE LSD The HNBA-LSD is a national organization of law students governed by its members. The mission of the HNBA-LSD is to increase the number of Latino/a law students involved with the HNBA and
ABOUT THE LSD The HNBA-LSD is a national organization of law students governed by its members. The mission of the HNBA-LSD is to increase the number of Latino/a law students involved with the HNBA and
CONSTITUTION OF THE NATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF BIOLOGY TEACHERS, INC.
 CONSTITUTION OF THE NATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF BIOLOGY TEACHERS, INC. ARTICLE I. NAME The name of this organization shall be The National Association of Biology Teachers, Incorporated, hereafter referred
CONSTITUTION OF THE NATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF BIOLOGY TEACHERS, INC. ARTICLE I. NAME The name of this organization shall be The National Association of Biology Teachers, Incorporated, hereafter referred
Rhoads Online State Appointment Rules Handy Guide
 Rhoads Online Appointment Rules Handy Guide ALABAMA Yes (15) DOI date approved 27-7-30 ALASKA Appointments not filed with DOI. Record producer appointment in SIC register within 30 days of effective date.
Rhoads Online Appointment Rules Handy Guide ALABAMA Yes (15) DOI date approved 27-7-30 ALASKA Appointments not filed with DOI. Record producer appointment in SIC register within 30 days of effective date.
ARTICLES OF INCORPORATION AND BYLAWS OF THE ASSOCIATION
 ARTICLES OF INCORPORATION AND BYLAWS OF THE ASSOCIATION ARTICLES OF INCORPORATION OF THE NATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF SECONDARY SCHOOL PRINCIPALS Filed with District of Columbia on April 3, 1970 FIFTH: SIXTH:
ARTICLES OF INCORPORATION AND BYLAWS OF THE ASSOCIATION ARTICLES OF INCORPORATION OF THE NATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF SECONDARY SCHOOL PRINCIPALS Filed with District of Columbia on April 3, 1970 FIFTH: SIXTH:
Branches of Government
 What is a congressional standing committee? Both houses of Congress have permanent committees that essentially act as subject matter experts on legislation. Both the Senate and House have similar committees.
What is a congressional standing committee? Both houses of Congress have permanent committees that essentially act as subject matter experts on legislation. Both the Senate and House have similar committees.
2016 us election results
 1 of 6 11/12/2016 7:35 PM 2016 us election results All News Images Videos Shopping More Search tools About 243,000,000 results (0.86 seconds) 2 WA OR NV CA AK MT ID WY UT CO AZ NM ND MN SD WI NY MI NE
1 of 6 11/12/2016 7:35 PM 2016 us election results All News Images Videos Shopping More Search tools About 243,000,000 results (0.86 seconds) 2 WA OR NV CA AK MT ID WY UT CO AZ NM ND MN SD WI NY MI NE
Results and Criteria of BGA/NFOIC survey
 Results and Criteria of BGA/NFOIC survey State Response Time Appeals Expedited Review Fees Sanctions Total Points Percent Grade By grade Out of 4 Out of 2 Out of 2 Out of 4 Out of 4 Out of 16 Out of 100
Results and Criteria of BGA/NFOIC survey State Response Time Appeals Expedited Review Fees Sanctions Total Points Percent Grade By grade Out of 4 Out of 2 Out of 2 Out of 4 Out of 4 Out of 16 Out of 100
U.S. Sentencing Commission Preliminary Crack Retroactivity Data Report Fair Sentencing Act
 U.S. Sentencing Commission Preliminary Crack Retroactivity Data Report Fair Sentencing Act July 2013 Data Introduction As part of its ongoing mission, the United States Sentencing Commission provides Congress,
U.S. Sentencing Commission Preliminary Crack Retroactivity Data Report Fair Sentencing Act July 2013 Data Introduction As part of its ongoing mission, the United States Sentencing Commission provides Congress,
at New York University School of Law A 50 state guide to redistricting
 at New York University School of Law A 50 state guide to redistricting ABOUT THE BRENNAN CENTER FOR JUSTICE The Brennan Center for Justice at New York University School of Law is a non-partisan public
at New York University School of Law A 50 state guide to redistricting ABOUT THE BRENNAN CENTER FOR JUSTICE The Brennan Center for Justice at New York University School of Law is a non-partisan public
The Victim Rights Law Center thanks Catherine Cambridge for her research assistance.
 The Victim Rights Law Center thanks Catherine Cambridge for her research assistance. Privilege and Communication Between Professionals Summary of Research Findings Question Addressed: Which jurisdictions
The Victim Rights Law Center thanks Catherine Cambridge for her research assistance. Privilege and Communication Between Professionals Summary of Research Findings Question Addressed: Which jurisdictions
Case 1:16-cv Document 3 Filed 02/05/16 Page 1 of 66 IN THE UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE DISTRICT OF COLUMBIA ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) )
 Case 1:16-cv-00199 Document 3 Filed 02/05/16 Page 1 of 66 IN THE UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE DISTRICT OF COLUMBIA UNITED STATES OF AMERICA, et al., v. Plaintiffs, HSBC NORTH AMERICA HOLDINGS INC.,
Case 1:16-cv-00199 Document 3 Filed 02/05/16 Page 1 of 66 IN THE UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE DISTRICT OF COLUMBIA UNITED STATES OF AMERICA, et al., v. Plaintiffs, HSBC NORTH AMERICA HOLDINGS INC.,
PREAMBLE Article I-Name Article II-Purpose Article III-Membership Article IV-Officers Article V- Regions...
 Table of Contents PREAMBLE... 2 Article I-Name... 2 Article II-Purpose... 2 Article III-Membership... 2 Article IV-Officers... 3 Article V- Regions... 4 Article VI-Duties of Officers... 6 Article VII-
Table of Contents PREAMBLE... 2 Article I-Name... 2 Article II-Purpose... 2 Article III-Membership... 2 Article IV-Officers... 3 Article V- Regions... 4 Article VI-Duties of Officers... 6 Article VII-
Notice N HCFB-1. March 25, Subject: FEDERAL-AID HIGHWAY PROGRAM OBLIGATION AUTHORITY FISCAL YEAR (FY) Classification Code
 Notice Subject: FEDERAL-AID HIGHWAY PROGRAM OBLIGATION AUTHORITY FISCAL YEAR (FY) 2009 Classification Code N 4520.201 Date March 25, 2009 Office of Primary Interest HCFB-1 1. What is the purpose of this
Notice Subject: FEDERAL-AID HIGHWAY PROGRAM OBLIGATION AUTHORITY FISCAL YEAR (FY) 2009 Classification Code N 4520.201 Date March 25, 2009 Office of Primary Interest HCFB-1 1. What is the purpose of this
Soybean Promotion and Research: Amend the Order to Adjust Representation on the United Soybean Board
 This document is scheduled to be published in the Federal Register on 07/06/08 and available online at https://federalregister.gov/d/08-507, and on FDsys.gov DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE Agricultural Marketing
This document is scheduled to be published in the Federal Register on 07/06/08 and available online at https://federalregister.gov/d/08-507, and on FDsys.gov DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE Agricultural Marketing
and Ethics: Slope Lisa Sommer Devlin
 Hotel Sales and Ethics: Avoiding the Slippery Slope Steve Rudner Steve Rudner Lisa Sommer Devlin States t Adopting the ABA Model Rules Alabama Alaska Arizona Arkansas Colorado Connecticut Delaware District
Hotel Sales and Ethics: Avoiding the Slippery Slope Steve Rudner Steve Rudner Lisa Sommer Devlin States t Adopting the ABA Model Rules Alabama Alaska Arizona Arkansas Colorado Connecticut Delaware District
National State Law Survey: Statute of Limitations 1
 National State Law Survey: Limitations 1 Alabama Alaska Arizona Arkansas California Colorado Connecticut Delaware DC Florida Georgia Hawaii limitations Trafficking and CSEC within 3 limit for sex trafficking,
National State Law Survey: Limitations 1 Alabama Alaska Arizona Arkansas California Colorado Connecticut Delaware DC Florida Georgia Hawaii limitations Trafficking and CSEC within 3 limit for sex trafficking,
Subcommittee on Design Operating Guidelines
 Subcommittee on Design Operating Guidelines Adopted March 1, 2004 Revised 6-14-12; Revised 9-24-15 These Operating Guidelines are adopted by the Subcommittee on Design to ensure proper and consistent operation
Subcommittee on Design Operating Guidelines Adopted March 1, 2004 Revised 6-14-12; Revised 9-24-15 These Operating Guidelines are adopted by the Subcommittee on Design to ensure proper and consistent operation
UNIFORM NOTICE OF REGULATION A TIER 2 OFFERING Pursuant to Section 18(b)(3), (b)(4), and/or (c)(2) of the Securities Act of 1933
 Item 1. Issuer s Identity UNIFORM NOTICE OF REGULATION A TIER 2 OFFERING Pursuant to Section 18(b)(3), (b)(4), and/or (c)(2) of the Securities Act of 1933 Name of Issuer Previous Name(s) None Entity Type
Item 1. Issuer s Identity UNIFORM NOTICE OF REGULATION A TIER 2 OFFERING Pursuant to Section 18(b)(3), (b)(4), and/or (c)(2) of the Securities Act of 1933 Name of Issuer Previous Name(s) None Entity Type
GUIDING PRINCIPLES THE NATIONAL COUNCIL ON ELECTRICITY POLICY (NCEP)
 GUIDING PRINCIPLES THE NATIONAL COUNCIL ON ELECTRICITY POLICY (NCEP) Adopted April 1, 2016 Adopted as Revised July 18, 2017, May 8, 2018, and November 13, 2018 ARTICLE I PURPOSE AND OBJECTIVES The National
GUIDING PRINCIPLES THE NATIONAL COUNCIL ON ELECTRICITY POLICY (NCEP) Adopted April 1, 2016 Adopted as Revised July 18, 2017, May 8, 2018, and November 13, 2018 ARTICLE I PURPOSE AND OBJECTIVES The National
THE CALIFORNIA LEGISLATURE: SOME FACTS AND FIGURES. by Andrew L. Roth
 THE CALIFORNIA LEGISLATURE: SOME FACTS AND FIGURES by Andrew L. Roth INTRODUCTION The following pages provide a statistical profile of California's state legislature. The data are intended to suggest who
THE CALIFORNIA LEGISLATURE: SOME FACTS AND FIGURES by Andrew L. Roth INTRODUCTION The following pages provide a statistical profile of California's state legislature. The data are intended to suggest who
BYLAWS OF THE NATIONAL FEDERATION OF DEMOCRATIC WOMEN (Revisions 2015; 2016)
 BYLAWS OF THE NATIONAL FEDERATION OF DEMOCRATIC WOMEN (Revisions 2015; 2016) ARTICLE I: NAME The organization shall be known as The National Federation of Democratic Women (NFDW.) ARTICLE II: OBJECTIVES
BYLAWS OF THE NATIONAL FEDERATION OF DEMOCRATIC WOMEN (Revisions 2015; 2016) ARTICLE I: NAME The organization shall be known as The National Federation of Democratic Women (NFDW.) ARTICLE II: OBJECTIVES
National Home Page About FBLA-PBL Membership Conferences Community Service News and Events Multimedia Gallery MarketPlace FBLA-PBL Blog E-Learning
 National Home Page About FBLA-PBL Membership Conferences Community Service News and Events Multimedia Gallery MarketPlace FBLA-PBL Blog E-Learning Center Contact Us PBL National Officers Membership Benefits
National Home Page About FBLA-PBL Membership Conferences Community Service News and Events Multimedia Gallery MarketPlace FBLA-PBL Blog E-Learning Center Contact Us PBL National Officers Membership Benefits
Democratic Convention *Saturday 1 March 2008 *Monday 25 August - Thursday 28 August District of Columbia Non-binding Primary
 Presidential Primaries, Caucuses, and s Chronologically http://www.thegreenpapers.com/p08/events.phtml?s=c 1 of 9 5/29/2007 2:23 PM Presidential Primaries, Caucuses, and s Chronologically Disclaimer: These
Presidential Primaries, Caucuses, and s Chronologically http://www.thegreenpapers.com/p08/events.phtml?s=c 1 of 9 5/29/2007 2:23 PM Presidential Primaries, Caucuses, and s Chronologically Disclaimer: These
Survey of State Laws on Credit Unions Incidental Powers
 Survey of State Laws on Credit Unions Incidental Powers Alabama Ala. Code 5-17-4(10) To exercise incidental powers as necessary to enable it to carry on effectively the purposes for which it is incorporated
Survey of State Laws on Credit Unions Incidental Powers Alabama Ala. Code 5-17-4(10) To exercise incidental powers as necessary to enable it to carry on effectively the purposes for which it is incorporated
Constitution of The National Alumnae Association of Spelman College (NAASC)
 Constitution of The National Alumnae Association of Spelman College (NAASC) (Ratified: May 14, 1977 - Revised: May 17, 1986; May 21, 1988) (Amended: May 18, 1991) REVISED MAY 18, 1994 Amended July 1, 1997
Constitution of The National Alumnae Association of Spelman College (NAASC) (Ratified: May 14, 1977 - Revised: May 17, 1986; May 21, 1988) (Amended: May 18, 1991) REVISED MAY 18, 1994 Amended July 1, 1997
Electronic Access? State. Court Rules on Public Access? Materials/Info on the web?
 ALABAMA State employs dial-up access program similar to Maryland. Public access terminals are available in every county. Remote access sites are available for a monthly fee. New rule charges a fee for
ALABAMA State employs dial-up access program similar to Maryland. Public access terminals are available in every county. Remote access sites are available for a monthly fee. New rule charges a fee for
Electronic Notarization
 Electronic Notarization Legal Disclaimer: Although a good faith attempt has been made to make this table as complete as possible, it is still subject to human error and constantly changing laws. It should
Electronic Notarization Legal Disclaimer: Although a good faith attempt has been made to make this table as complete as possible, it is still subject to human error and constantly changing laws. It should
Overview. Strategic Imperatives. Our Organization. Finance and Budget. Path to Victory
 Overview Strategic Imperatives Our Organization Finance and Budget Path to Victory Strategic Imperatives Strategic Imperatives 1. Prove to voters that Hillary Clinton will be a President who fights for
Overview Strategic Imperatives Our Organization Finance and Budget Path to Victory Strategic Imperatives Strategic Imperatives 1. Prove to voters that Hillary Clinton will be a President who fights for
2015 ANNUAL OUTCOME GOAL PLAN (WITH FY 2014 OUTCOMES) Prepared in compliance with Government Performance and Results Act
 Administration for Children & Families 370 L Enfant Promenade, S.W. Washington, D.C. 20447 Office of Refugee Resettlement www.acf.hhs.gov 2015 ANNUAL OUTCOME GOAL PLAN (WITH FY 2014 OUTCOMES) Prepared
Administration for Children & Families 370 L Enfant Promenade, S.W. Washington, D.C. 20447 Office of Refugee Resettlement www.acf.hhs.gov 2015 ANNUAL OUTCOME GOAL PLAN (WITH FY 2014 OUTCOMES) Prepared
Soil and Water Conservation Society Bylaws
 Soil and Water Conservation Society Bylaws ARTICLE I - Name ARTICLE II - Purposes and Objectives ARTICLE III - Members ARTICLE IV - Society Meetings ARTICLE V - Board of Directors ARTICLE VI - Officers
Soil and Water Conservation Society Bylaws ARTICLE I - Name ARTICLE II - Purposes and Objectives ARTICLE III - Members ARTICLE IV - Society Meetings ARTICLE V - Board of Directors ARTICLE VI - Officers
December 30, 2008 Agreement Among the States to Elect the President by National Popular Vote
 STATE OF VERMONT HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES STATE HOUSE 115 STATE STREET MONTPELIER, VT 05633-5201 December 30, 2008 Agreement Among the States to Elect the President by National Popular Vote To Members
STATE OF VERMONT HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES STATE HOUSE 115 STATE STREET MONTPELIER, VT 05633-5201 December 30, 2008 Agreement Among the States to Elect the President by National Popular Vote To Members
The name of this division of FBLA-PBL, Inc. shall be Phi Beta Lambda and may be referred to as PBL.
 Phi Beta Lambda National Bylaws Revised 2008 ARTICLE I Name The name of this division of FBLA-PBL, Inc. shall be Phi Beta Lambda and may be referred to as PBL. ARTICLE II Purpose Section 1. The purpose
Phi Beta Lambda National Bylaws Revised 2008 ARTICLE I Name The name of this division of FBLA-PBL, Inc. shall be Phi Beta Lambda and may be referred to as PBL. ARTICLE II Purpose Section 1. The purpose
Federal Rate of Return. FY 2019 Update Texas Department of Transportation - Federal Affairs
 Federal Rate of Return FY 2019 Update Texas Department of Transportation - Federal Affairs Texas has historically been, and continues to be, the biggest donor to other states when it comes to federal highway
Federal Rate of Return FY 2019 Update Texas Department of Transportation - Federal Affairs Texas has historically been, and continues to be, the biggest donor to other states when it comes to federal highway
CenturyLink Political Contributions Report. July 1, 2017 December 31, 2017
 CenturyLink Political Contributions Report July 1, 2017 December 31, 2017 1 Participation in the Political Process As one of the nation s leading communications companies, CenturyLink plays a key role
CenturyLink Political Contributions Report July 1, 2017 December 31, 2017 1 Participation in the Political Process As one of the nation s leading communications companies, CenturyLink plays a key role
Appointment of Committees
 Alabama: Credit committee and supervisory committee determined at annual meeting. Credit union bylaws may indicate that the board of directors may carry out duties of the credit committee. Alaska: Board
Alabama: Credit committee and supervisory committee determined at annual meeting. Credit union bylaws may indicate that the board of directors may carry out duties of the credit committee. Alaska: Board
BYLAWS. Mission Providing visionary leadership in nursing education to improve the health and wellbeing of our communities.
 BYLAWS Article I Name This organization shall be known as the Organization for Associate Degree Nursing (OADN). The name of the organization shall officially be abbreviated as OADN. Article II Vision and
BYLAWS Article I Name This organization shall be known as the Organization for Associate Degree Nursing (OADN). The name of the organization shall officially be abbreviated as OADN. Article II Vision and
