FACULTY OF LAW LAW 211. Contract Law. Section 2. Professor Biukovié TOTAL MARKS: 100. minutes reading time
|
|
|
- Miranda Gray
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NOTE: PLEASE ENSURE THAT YOU HAVE A COMPLETE PAPER LAW 211 DECEMBER 2014 EXAMINATION 1. This is a LIMITED OPEN BOOK examination. You may use 3. Please write legibly. Professor Biukovié minutes reading time they are necessary. to you in the exam. TOTAL MARKS: 100 Section 2 Contract Law any question fully, please state those facts and explain why only a CLEAN copy of the syllabus and case chart provided FACULTY OF LAW THIS EXAMINATION CONSISTS OF THREE (3) PAGES THE UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA TIME ALLOWED: 1 HOUR and If you think that additional facts are necessary to answer THIS EXAMINATION CONSISTS OF ONE QUESTION.
2 LAW 211, Section 002 Page 2/3 Marks: Marcia is a 76 year old widow and a retired UBC librarian. She has a big house in East Vancouver, in Mount Pleasant. She is quite lonely since her husband died and her children moved to interior BC to live with their own families. Most of the days she thinks about selling her house and moving to a smaller place. Marcia relies on other people to maintain the house and to keep up with her daily routine. One of Marcia s neighbours, Tony, a 1L at UBC Law, cleans her house monthly and runs small errands twice a month, for which she pays him $ every month. Even though Marcia and Tony never signed a contract, Marcia gave him a pair of keys to her house and let him use her car to go shopping for her. On April 1, 2014, Marcia mentions to Tony that she is worried about her wonderful garden because her hands are not strong enough to maintain it: Sadly, that s my only hobby, Tony, and I am now too old for it. Marcia, don t worry, replies Tony. I ll work on your garden when I have a bit more time. I am very busy now because I have several final exams and I really want to do well. The following day, Marcia went to Kamloops, BC, to visit her son and to celebrate her grandson s third birthday. When she returns home to Vancouver on May 8, 2014, she finds that Tony not only cleaned her house, but also did a lot of gardening. She notices several new plants in the front yard. Even her boxwood looks completely new, although Tony just gave it a little boost with a new layer of fertilizer. Marcia is both stunned by Tony s skilled gardening and happy with the results of his work and promises to pay him $ for the work on the garden in addition to her usual monthly payment to him for cleaning and shopping for her. On May 15, 2014, Marcia receives in the mail an invoice from Green Wonder Nursery asking her to pay almost $ for all the supplies Tony took for her garden. She immediately phones Tony to ask about an invoice but only manages to reach his voice mail and to leave a message. Without returning Marcia s call at all, Tony mails her back her home and car keys. Marcia decides not to pay Tony for any work he did in May while she was in Kamloops.
3 will be happy to continue cleaning her home for $ per to return her keys as soon as possible. Apparently, she has hired a THE END OF EXAMINATION pay Tony for any work done in May while she was away. Explain nursery? Wonder Nursery. Do you think that she needs to pay Tony and the Wonder Nursery with his own money and phones Marcia asking to Tony his position vis-à-vis Marcia and Green Wonder Nursery. reimburse him. However, he only manages to leave her a voic Considering only the common law rules that you have studied in your Contract Law class: explaining that she owes him almost $ He also says that he month. Marcia calls back only to leave him a voice mail asking him company that provides services to senior citizens and will not need to bother Tony with her problems anymore. She refuses to LAW 211, Section 002 Page 3/3 A) advise Marcia regarding her relations with Tony and Green B) Imagine the following scenario: Tony buys supplies from Green
4 LAW : Contract Law Syllabus and Outline 2014/2015 Professor: Ljiljana Biukovié Class schedule: Tuesdays & Thursdays 11:00 13:30 Classroom: #122 AlIard Hall Office: #454 Allard Hall Office hours: Mondays & Wednesdays 1-2 pm (other times by appointment) Telephone: Secretary: Iris Lee Course description and objectives: The aim of this course is to introduce the basic concepts that underlie contractual obligations and to examine contract law in Canada in its social and political context. While the focus is primarily on common law, different ideas on which contract law is founded in civil law in Quebec are also discussed. The main objective of the course is to enable students to acquire basic legal skills to competently identify, analyze, synthesize and apply the law of contract. Students will learn to analyze and evaluate judicial opinions, statutory provisions and contractual clauses. In the first term (September-December 2014), the objectives are to help students understand the relationship between contract law and other categories of obligations recognized by the common law (tort and restitution), to familiarize them with different functions of contract law, and to introduce them to the key concepts of contract formation, such as an agreement between the parties, certainty, intention to create legal obligation, consideration, and privity. In the second term (January-April 2015), the focus is on interpretation of contractual obligations and on remedies for breach of contract. The objectives are to enable students to distinguish terms of the contracts from representations and puffs, to understand the importance and consequences of classification of terms of the contract, to learn when and why terms will be implied into a contract, and to understand consequences of nonperformance of contractual obligations. Course materials (required): Stephanie Ben-Ishai and David Percy, Contracts: Cases and Commentaries, 8th ed. (Toronto: Carswell, 2009) Biukovic, Supplementary Materials (Connect course web page TBA) NOTE: CASES AND READINGS ARE SUBJECT TO ADDITIONS, DELETIONS AND REORDERING WHICH WILL BE ANNOUNCED IN CLASS
5 B. MacDougall, Introduction to Contracts (LexisfNexis Canada, 2012) McCamus, The Law of Contracts, 2m1 ed. (Toronto: Irwin Law, 2012) Waddams, McCamus, Waidron, Neyers and Girgis, Cases and Materials on Swan, Canadian Contract Law, 2d ed. (Lexis/Nexis Canada, 2010) The Law Library collection related to common law of contracts includes many valuable casebooks and textbooks which could be used for further readings (Anson s Law of based on primarily US case law, the Restatement of Contracts and Uniform Commercial Treitel on Law of Contract). NOTE: The US materials available in the Law Library are Institute and they summarize in statute-like form the major common law rules on applicable only in the US. Key dates: September 2, 2014 contracts. The UCC is statutory law that covers contracts for the sale of goods and is January 6, 2015 April 9, 2015 April 22, 2015 Code (UCC). The Restatements (Second) of Contracts were drafted by the American Law Contract, Cheshire, Ffoot and Furmston s Law of Contract, Chitly on Contract, or November 27, 2014 December 17, 2014 February 16-20, 2015 Last Contracts class I term Final examination (1:30 pm) NOTE: CASES AND READINGS ARE SUBJECT TO ADDITIONS, 2 DELETIONS AND REORDERING WHICH WILL BE ANNOUNCED IN CLASS First Contracts class I term December examination (1:30 pm) First Contracts class II term Midterm break Last Contracts class II term Contracts, 5 ed. (Toronto: Edmond Montgomery Publications, 2014) Other sources (Law Library):
6 Note: All cases are available in Ben-Ishal & Percy (8th edition) and the on-line Goldthorpe v. Logan 30 Double N Earthmovers Ltd v. City of Edmonton, 2007 SCC 3 Livingstone v. Evans Acceptance, communication of acceptance, electronic contracts R. v. Clarke 51 M.J.B. Enterprises Ltd. v. Defence Construction (1951) Ltd. 38 Williams v. Carwardine 50 R. v. Ron Engineering & Construction (Eastern) Ltd. 35 Canadian Dyers Ass. Ltd. v. Burton 18 Carlill v. Carbolic Smoke Ball Co Offer, invitation to treat, tenders, communication of offer Supplement Boyle&Percy 1-15 INTRODUCTION TO THE STUDY OF THE LAW OF CONTRACT II. FORMATION OF THE CONTRACT COURSE SYLLABUS Pharmaceutical Society v. Boots 20 Harvela Investments Ltd. v. Royal Trust Co of Canada 33 Carlill v. Carbolic Smoke Ball Co. 25 NOTE: CASES AND READINGS ARE SUBJECT TO ADDITIONS, 3 DELETIONS AND REORDERING WHICH WILL BE ANNOUNCED IN CLASS httn://wwwhc1wsc)ept ihrries/hc1aws newk1nciimenrjtfl/freeside/ Dawson v. Helicopter Exploration Co. 66 Timberwolf Log Trading Ltd v Columbia National Investments Ltd. 11/08/2011 BCSCO864corI.htm Hoiwell Securities v. Hughes 85 Brinkibon v. Stahag Stahl 88 Century 21 Canada Ltd. v Rogers Communications Inc., 2011 BCSC 1196 httjx// ii.org/en/bc/bcsc/doc/20 11/201 I bcsc 1196/2011 bcsc html Butler Machine Tool v. Ex-cell-o Corp. 56 Felthouse v. Bindley 72 Household Fire v. Grant 81 Saint John Tug Boat Co. v. Irving Refinery Ltd. 75 Rudder v. Microsoft Corp. 93 Electronic Transaction Act [SBC 2001] C & 15 ss.
7 3. Termination of Offer: revocation, rejection and counter-offer, lapse of time; problems with unilateral contracts Dickinson v. Dodds 97 Byrne v. Van Tienhoven 100 Errington v. Errington and Woods 102 Carlill v. Carbolic Smoke Ball Co. 25 Livingstone v. Evans 54 Dawson v. Helicopter Exploration Co. 66 Barrick v. Clark Certainty of Terms; vagueness, incompleteness, agreements to negotiate, anticipation of formalization R. v. CAE Industries Ltd. 114 May &Butcherv.R. 119 Hillas v. Arcos 122 Foley v. Classique Coaches Ltd. 126 Sale of GoodsAct ss. 12 & 13 - Ascertainment of price new/document/id/freeside/ Empress v. Bank ofnova Scotia 131 Mannpar Enterprises Ltd. v. Canada 134 Bawitko Investments Ltd v. Kernels Popcorn Ltd. 145 Wallace v. Allen, 2009 ONCA Consideration: nature of consideration, past consideration, forbearance, pre-existing duty The Governors of Daihousie College v. the Estate ofarthur Boutilier 156 Thomas v. Thomas 169 Eastwood v. Kenyon 166 Lampleigh v. Brathwait 168 Pao On v. Lau Yiu Long 173 Stilk v. Myrick 177 Gilbert Steel v. University Construction Ltd. 178 Williams v. Roffey Bros. 182 Greater Fredericton Airport Authority Inc. v. NAV Canada 186 Foakes v. Beer 192 Re Selectmove 195 Foot v. Rawlings 197 Law and EquityAct (R.S.B.C. 1996, c. 253)s new/documentlld/freeside/ Waiver and Promissory Estoppel Hughes v. Metropolitan Railway Company 201 Central London Property v. High Trees House 203 John Burrows v. Subsurface Surveys 205 D &CBuilders v. Rees 208 NOTE: CASES AND READINGS ARE SUBJECT TO ADDITIONS, 4 DELETIONS AND REORDERING WHICH WILL BE ANNOUNCED IN CLASS
8 Combe v. Combe 224 Walton Stores v. Maher 230 M.(N.) v.a.(t.a.) Intention to Create Legal Obligation Balfour v. Balfour 243 Rose and Frank v. JR. Crompton Bros. 246 TD Bank v. Leigh Instruments Ltd Formality: The Requirement of Writing Dynamic Transport Ltd. v. O.K Detailing Ltd. 258 Deglman v. Guaranty Trust Co. 262 III. PRIVITY OF CONTRACT Tweddle v. Atkinson 276 Dunlop PneumaticTyre Co. v. Selfridge & Co. Ltd. 277 Besweck v. Beswick 283 London Drugs Ltd. v. Kuehne & Nagel International Ltd. 298 Fraser River Pile & Dredge Ltd. v. Can-Dive Services 310 IV. CONTENT OF THE CONTRACT 1. Representations and Terms: 1 lisrepresentation and Rescission: Parol Evidence Rule and Rectification; Classification of Terms Redgrave v. Hurd 355 Smith v. Land & House Property Corporation 359 Kupchak v. Dayson Holdings 363 Hielbut, Symons & Co. v. Buck!eton 371 Leaf v. International Galleries 378 Sodd Corp. v. N. Tessis 392 B.G. Checo Int l Ltd. v. B.C. Hydro 395 No Taurus Ventures Ltd. V. Intrawest Corp. gov.bc.caljdb-txt/cajo7/02/2007bcca0228.htm Hawrish v. Bank ofmontreal 412 Bauer v. Bank ofmontreal 415 Gallen v. Butterley 422 Hong Kong Fir v. Kawasaki Kisen Kaisha Ltd 436 Wickman v. Schuler 443 Business Practice and Consumer Protection Act 2. Discharge by Performance or Breach Jedfro Investments (USA) Ltd. V. Jacyk NOTE: CASES AND READINGS ARE SUBJECT TO ADDITIONS, 5 DELETIONS AND REORDERING WHICH WILL BE ANNOUNCED IN CLASS
9 Fairbanks v. Sheppard 450 Sumpter v. Hedges 454 Howe v. Smith 455 Stevenson v. Colonial Homes Ltd Standard Form Contracts; Interpretation; Incorporation of Terms; Exclusion and Limitation of Liability Clauses Machtinger v. Hoj Industries Ltd. 463 Thornton v. Shoe Lane Parking Ltd. 478 McCutcheon v. David MacBrayene Ltd. 488 Tilden Rent-A-Car CO. v. Clendenning 492 Karroll v. Star Mountain Resorts Ltd. 496 Kanitz v. Rogers Cable Inc. ii.or/en/on/onsc/doc/2002/2002can1ii /2002can11i htmlSilver Tercon Contractors Ltd. v. BC (Transportation and Highways) Loychuk v. Cougar Mountain Adventures [2012] BCCA ii.calen/bc/bccaldoc/20 12/201 2bcca 122/201 2bcca I 22.html V. EXCUSES FOR NON-PERFORMANCE 1. Mistake (TBC) Smith v. Hughes 546 Bell v. Lever Brothers Ltd. 560 McRae v. Commonwealth Disposals Commission 565 Solle v. Butcher 571 Great Peace Shipping v. Tsavliris Salvage Ltd. 574 Miller Paving v. Gottardo 579 Sylvan Lake Golf & Tennis Club v. Performance Industries Ltd Frustration (TBC) Paradine v. Jane 620 Taylor v. Caldwell 621 KBKNo. 138 Ventures Ltd. v. Canada Safeway Ltd. 636 VI. THE PROTECTION OF WEAKER PARTIES: DURESS, UNDUE INFLUENCE, UNCONSIONABILITY Pao On v. Lau Yiu Long 173 Greater Fredericton Airport Authority Inc. v. NAV Canada 666 Geffen v. Goodman Estate 680 Royal Bank of Scotland Plc. v. Etridge (no. 2) 688 Morrison v. Coast Finance Ltd. 697 Marshall v. Can. Permanent Trust Co. 701 Harry v. Kreutziger 709 Business Practices and Consumer Protection Act (S.B.C. 2004, c.2) ss new/document/id/freeside/ NOTE: CASES AND READINGS ARE SUBJECT TO ADDITIONS, 6 DELETIONS AND REORDERING WHICH WILL BE ANNOUNCED IN CLASS
10 VII. ILLEGALITY AND PUBLIC POLICY Still v. Minister of National Revenue 762 Shafron v. KRG Insurance Brokers (Western) Inc. 730 VIII. REMEDIES Damages: interest protected, quantification, certainty, causation and remoteness, mitigation, time of measurement McRae v. Commonwealth Disposals Commission 793 Sunshine Vacation Villas Ltd. v. Hudson Bay Co. 801 Attorney General v. Blake 805 Chaplin v. Hinks 814 Groves v. John Wunder Co. 816 New West Homes Ltd. v. Thunderbird Petroleums Ltd. 821 Jarvis v. Swans Tours 825 Hadley v. Baxendale 858 Victoria Lzundiy v. Newman 861 Koufos v. Czarnikow (The Heron II) 868 Semeihago v. Paramadevan 879 Southcott Estates Inc. v. Toronto Catholic District School Board lexurn.org/decisia-scc-csc/scc-csc/scc-csc/enhi 2612/1 /document.do 2. Aggravated and Punitive Damages Whiten v. Pilot Insurance Co. 846 Fidler v. Sun Life Assurance Honda v. Keays RBC Dominion Securities Inc. v. Merrill Lynch Canada Inc. pdf 3. Liquidated Damages, Deposits and Forfeitures Shatilla v. Feinstein 885 H.F. Clarke Ltd. v. Thermadaire Corporation Ltd. 889 J. G. Collins Insurance Agencies Ltd. v. Esley 896 Stockloser v. Johnson 898 Super Save Disposal Inc. v. Blazin Auto Ltd. 1/17/2011 BCSC I 784.htm 4. Equitable Remedies (Specific Performance, Injunctions, Rectification) John E. Dodge Holdings Ltd. v Ontario Ltd. 904 Warner Bros. v. Nelson 910 NOTE: CASES AND READINGS ARE SUBJECT TO ADDITIONS, 7 DELETIONS AND REORDERING WHICH WILL BE ANNOUNCED IN CLASS
11 NOTE: CASES ANTI READINGS ARE SUBJECT TO ADDITIONS, 8 DELETIONS AND REORDERING WHICH WILL BE ANNOUNCED IN CLASS Shafron v. KRG Insurance Brokers (Western) Inc. 730 Zipper Transportation v. Korstrom 916 Zipper Transportation v. Korstrom 917
12 1 Lai Contracts Case Rule Topic Biukovic. There can be no contract of sale unless there can be found an offer to sell and an [1] acceptance of the offer.. A mere quotation of price does not constitute an offer to sell; it is no more than an. Canadian Dyers Ass. Ltd. v. Burton. invitation to treat. (1920) 47 O.L.R. 259 (H.L.). The courts will look at the lan uae used in the light of the circumstances in which it is Formation: Offer & Invitation to Treat [2] used and into the subsequent actions of both parties to determine whether what is said by the_seller_is_a_mere_quotation_of price_or an offer to sell.. The general assumption in the case of retail self-service sales is that placing goods on Pharmaceutical Society v. Boots shelves is an invitation to treat. [1953] 1 Q.B. 401, [1953] All E.R. An offer and acceptance take place at the cashier when a customer offers to buy and a 482 (C.A.) cashier_accepts_the_offer. Formation: Offer & Invitation to Treat (retail sale). The general assumption is that advertisements published in newspapers are invitations to Goldthorpe v. Logan treat, not offers. Formation: Public [4] [1943] O.W.N 215, [1943] 2 D.L.R. However, the court looked at the surrounding circumstances, the actions ofboth parties offer or invitation 519 (C.A.) (direct contact, consultation, examination, etc.) and the language used in the ad and held to treat that Logan s electrolysis ad was an offer to the public at large. [6] Carlill v. Carbolic Smoke Ball Co. [1893] 1 Q.B. 256 (C.A.). An ad was held to be an offer for a unilateral contract, an offer to the public at large to Formation: everyone who does something (a guarantee in an ad was held to be an indication of the Communication of intention to create legal obligations). Offer public offer An ordinary rule of law is that acceptance of an offer requires the offeror to be notified in to anyone who does order that the two minds may come together. something; However, in the case of a unilateral contract, an offer is made to the public but the Communication of contract is not concluded with everybody (all the world). It is only formed with that Acceptance; limited portion of the public who come forward and perform the condition on the faith of Unilateral the advertisement (following the indicated method of acceptance). Contracts The court held that in the case of rewards (or an offer to anyone who can give the Formation: Williams v. Carwardine information requested) the defendant is entitled to the reward regardless of her motives Communication of [7] (1883) 4 B. & Ad. 621, 110 E.R. (fear of God s punishment) because she knew ofthe reward and she performed the act in Offer public offer 590 (K.B.) question. to anyone who does The case does not give offer-acceptance analysis but deals with human motives, something In contrast with Williams v. Carwardine, the court held that the defendant was not entitled Formation: R. v. Clarke to the reward because he did not act in reliance on the offer but for other reasons (to clear Communication of [8] (1927) 40 C.L.R. 227 (Aust. H.C.) himself from a false accusation). Offer public offer Reconcile with Williams v. Carwardine by noting that in a bi-lateral contract knowledge is to anyone who does required (to enable meeting of the minds), but motive is irrelevant, something
13 2 Law 2 11,02 Contracts Biukovic [9] Case Rule Topic Harvela Investments Ltd. v. Royal Trust Co. of Canada [1986] A.C. 207, [1985] 2 All E.R. 966 (H.L.) R. v. Ron Engineering & [10] Construction (Eastern) Ltd. [1981] 1 S.C.R. 111, 13 B.L.R. 72. Whether an invitation from a seller to prospective buyers was to be construed as an invitation to participate in a fixed bidding sale or in an auction sale depended on the presumed intention of the seller as deduced from the express provisions of the invitation to bid (an invitation for the submission of offers was held to be an invitation for a fixed Formation: Offer & bid). Invitation to Treat The leral nature of the invitation was that of unilateral contracts; if an offer was received - tenders from both Harvela and Sir Leonard, the obligation of the bank (the vendors) was to sell the shares to the promisor whose offer was the highest and any obligation to the other tenderer under the other unilateral contract came to an end.. Analyses the tender process a 2 phase process which includes formation of two contracts (A and B). This changed the traditional analysis of a call for tenders as an invitation to potential tenderers to make offers. The tender call is the offer and the bid submission is the acceptance of that offer which leads to formation of contract A; the consideration is the preparation of the bid; consequence of formation of contract A is the imposition of contractual liability on the tenderer (not to withdraw from the bid) and the owner (to treat tenderers fairly and in good faith).. Contract B is the construction contract to be formed between the owner and the successful tenderer. The submission of a tender in response to an invitation to tender may give rise to contractual oblinations (contract A), quite apart from the obligations associated with the construction contract to be entered into upon the acceptance of a tender (contract B). But it is always possible that contract A does not arise upon the submission of a tender (if the tender is invalid). Formation: Offer & Invitation to Treat M.J.B. Enterprises Ltd. v. Defence The invitation for tenders may be characterized as an offer to consider a tender, if that Formation: Offer & [11] Construction (1951) Ltd) tender is valid. Invitation to Treat [1999] 1 S.C.R. 619 The submission of the tender is good consideration of the owner s promise, as the tender was of benefit to the owner, prepared at a not an insignificant cost and accompanied by the bid security. The privile e clause is only one term of contract A and must be read in harmony with the rest of the tender documents it does not override the obligation to only accept compliwit - - tenders tenders Double N. Earthmovers Ltd. City [12] of Edmonton, 2007 SCC 3 [13] The owner does not have a duty to investigate as to whether a submitted bid is compliant or to look beyond the face of the bid to ensure compliance; it only has a duty to treat all bids fairly and equally. When an owner accepts a compliant bid and enters into Contract B on the terms set out in the tender documents, Contract A is fully discharged and an owner has no any further obligations_to_unsuccessful_bidders Fotion: Offer & Invitation to Treat - tenders Livingstone v. Evans An offer that has been rejected is thereby ended and it cannot be afterwards accepted Formation: [1925] 3 W.W.R. 453, [1925] 4 without the consent of the one who made it. Acceptance
14 3 [Law [fijtkovic [141 [15] Case I Rule Topic D.L.R. 769 (Alta S.C.) A counter-offer is a rejection of the ori inal offer. a mere inquiry is not, counter-offer; If an offeror replies to the rejection, the reply ( cannot reduce price ) may amount to a rejection and renewal of the offer. The answer is dependent upon considering all surrounding counter offer circumstances. In order to avoid problems with contract formation (and revocation of offer) courts should treat offers as calling for bilateral rather than unilateral action when the language can be fairly so construed. Where acceptance is not expressly given the question of whether the language used Formation: offer Dawson v. Helicopter Exploration amounts to acceptance will be a matter of construction of the court which may include and acceptance; Co. [1955] S.C.R. 868 taking into consideration conduct of the acceptor Unilateral and Although in theory an offer for a unilateral contract can be revoked any time before the bilateral contracts acceptance, such as offer could be interpreted to have an implied term that an offeror who controls conditions of cooperation of an offeree would not be allowed to prevent performance/acceptance of an offeree. Lord Denning restated the traditional last shot formula for the resolution of the battle of the forms, identifying several possibilities for courts: Butler Machine Tool v. Ex-cell-o 1. Last shot: a contract is concluded upon the terms of the last document sent by one of the Formation: Corp. parties that was not objected to; 2. First shot: a contract is concluded upon the terms of the Acceptance [1979] 1 W.L.R. 401, 1 All E.R. first document; 3. All shots count and the court must discover its terms on an objective counter-offer; 965 (C.A.) basis: A) a contract is concluded upon terms drawn from all the documents that have battle of forms passed between the parties when the terms can be reconciled as to give a harmonious result, or B)_a_contract_is_not concluded_since_the_differences_are_irreconcilable.. Silence does not amount to acceptance. Feithouse v. Bindley Even though the nephew (seller) might have intended to sell, he never communicated this Formation: [17] (1962) 11 C.B. (N.S. 869, 142 E.R. intention to his uncle (buyer). Communication of [18] 1037 (Ex. Cli.) In general, the offeror is in control of the mode of acceptance but the courts are reluctant to Acceptance Saint John Tug Boat Co... V. Irving Refinery Ltd. [1964] S.C.R. 614 allow silence to be specified as the mode of acceptance. The conduct of an offeree, unaccompanied by any verbal or written undertaking, could Formation:..... under certam circumstances (for example, contmumg serviced on terms previously agreed) Communication of be reasonably constructed as valid acceptance Acceptance. When there was no written contract between the parties the court had to review all communications between them to see if they made an oral agreement, as well as to consider Timberwolf Log Trading Ltd V. their conducts over the relevant period of time and in the context of a particular industry Formation: [19] Columbia National Investments Ltd. (BC logging industry) Communication of 2011 BCSC 864 Held that where one party represents through conduct and silence that a contract has been Acceptance.. formed so as to lead the other party to reasonably conclude that such is the case, that the law_fmds a contract_to_have_been formed._[para._116] Brinkinbon v. Stahag Stahl The mailbox rule (the contract is concluded where and when the acceptance is mailed) [21] [1983] 2 A.C. 34 [1982] 1. All E.R. applies only if acceptance by mail is required or if that has been a regular business practice 293 (H.L.) of the parties or if the offer is made by mail and no acceptance requirements are specified... Formation: Of
15 4 Law Contracts Bi,ektjvic [22] [23] [1974] [25] [26] [27] [28] Household Fire Case Rule Topic The receipt rule (the contract is made when and where the acceptance is received) applies communication to_instantaneous_communications_such_as_phone_or telex_or facsimile. The court upheld the Reneral mailbox rule in situations where the acceptance is lost in the Formation: v. Grant p and as a consequence the offeror was bound by the offer even though acceptance was Communication of (1879) 4 Ex. D, 216 (C.A.) not received. The majority held the post office to be the agent of both parties. The dissent Acceptance Hoiwell Securities v. Hughes 161 Rudder [29] [1952] 1 W.L.R. 155, 1 (C.A.) All E.R rejected this and applied the recipient rule. mailed acceptance The postal rule should only apply if it does not lead to manifest inconvenience and Formation: absurdity. Communication of The postal rule does not apply if the express terms of the offer specify that the acceptance Acceptance must reach the offeror. The requirement for notice was held to invoke the recipient rule. mailed acceptance. Terms of a contract entered into on the internet can be displayed on multiple pages. Users v. Microsoft Corp.are expected to follow the links and become familiar with all terms before accepting the [1999] O.J (Ont. S.C.J.) terms of the contract. v.. Clicking the I agree button results in formation of a valid contract. The court defmes the browse wrap agreement the one that does not require that the Formation: COnuUUniC1tiOn of Acceptance purchaser indicate their agreement by clicking on an I Agree button. All that is required Formation: is that they use the product after being made aware of the product s Terms of Use. [92] Acceptance by Rogers The act of browsing could constitute the acceptance of terms (of use) of the web agreement Browsing; Century 21 Canada Communications Inc. and the formation of contract as long as a user of the web site continues to browse after Terms of Contract 2011 BCSC 1196 reading the terms posted Exclusion Clauses in. The court found that there was an enforceable browse wrap agreement on the Century 21 web posted contracts web site and that terms of use were properly incorporated because the terms of use were (browse wrap clear and a person who browsed the web site had enough time to read them prior to agreements) accepting them Byrne v. Van Tienhoven The mailbox rule does not apply to revocation revocation must be received by the offeree (1880) C.P.D. 344 to be effective. The general principle is that if a person who makes an offer dies, the offer cannot be accepted after they are dead. The court held that an offer could be revoked by indirect communication applying the same Dickinson v. Dodds general rule logic that is, once the person to whom the offer was made knows that the (1876) 2 Ch. D. 463 (CA.) property has been sold to someone else, it is too late for them to accept the offer and the contract is impossible to make. A promise to hold an offer open is not binding unless have consideration or a deed. Equity cannot be applied_when_a third party has_acquired rights. Legal consequences of family arrangements are difficult to ascertain. Errington v. Errington and Woods Unilateral contracts are formed when all conditions of the offer are met. 1 K.B. 290, [1952] 1 All In general, offers for unilateral contracts can be revoked any time prior to complete E.R. 149 (C.A.) fulfillment by the offeree, but the court held that in this case an offer for a unilateral contract could_not be_revoked_by_the_promisor_once_the_promesee_entered_on performance Formation: Termination of Offer Formation: - Revocation TelilIlmation of Offer Formation: - Revocation Termination of Offer contracts Unilateral
16 5 Law Contracts Biukovic Barrick v. Clark [30] [1951] S.C.R. 177, [ D.L.R. Case Rule Topic of the act (but it would cease to bind the offeror if performance was left incomplete and unperformed). An offer will lapse if it is not accepted within a tune limit determined by the offeror, or if a time limit is not specified, then it will lapse within a reasonable time. Formation: The court will determine what is a reasonable time using the rule of construction Termination of 529 (objective test) it will depend upon the nature and character of the item being sold, on the Offer Lapse normal or usual course of business in negotiations as well as the circumstances of the offer, Time including the conduct of the parties in the course of negotiation. R. v. CAE industries Ltd.. The court dealt with vagueness of a best efforts term by constructing its reasonable meaning in the context of the language used by the parties and the overall purpose of the Formation: [33] contract which has also been partly performed Vagueness of [35] [36] [1986] 1 F.C. 129 (F.C.A.) Preliminary issue was if the contract was intended and the court held that it could be Terms answered by analyzing the surrounding circumstances as well as the letter itself To be a good contract there must be a concluded bargain which settles everything that is necessary to be settled and leaves nothing to be settled by later agreement between the parties. May & Butcher v. R. It has long been a well-recognized principle of contract law that an agreement in which Formation: of [1934] 2 K.B. 17 (H.L.) some critical part of the contract matter is left undetermined is no contract at all. Certainty of Terms Hi/las v. Arcos (1932) 40 Lloyd s Rep. (C.A.) Hi/las v. Arcos It is perfectly possible to contract to sign a document which will contain all the relevant terms, but it is not acceptable to agree that the parties will in the future agree upon a matter which is vital to the contract. Court of Appeal with great regret upheld May & Butcher s general rule that if there are any essential terms of a contract of sale undetermined, and therefore to be determined by a subsequent contract, there is no enforceable contract. House of Lords took a more modern approach: Business men often record the most important agreements in crude and summary fashion; modes of expression sufficient and [37] clear to them in the course of their business that are far from complete or precise. [38] [40] Formation: Certainty of Terms Formation: (1932) 147 L.T. 503 (H.L.) Certainty of Terms It is the duty of the court to construe such documents fairly and broadly, without being too astute or subtle in finding defects.. Interpreted the general principles of H.L. s decision in Hi/las to mean that each case should be decided on the construction of the particular document. Foley v. Classique Coaches Ltd. Held that an agreement to agree on price from time to time was certain enough since the Formation: [1934] 2 K.B. 1 Empress v. Bank ofnova Scotia [1991] (C.A.) parties believed they had a contract and had acted for 3 years as if they did i.e. there was Certainty of Terms 1 W.W.R. 537 (B.C.C.A.) already partial performance: The land had been transferred and a portion of the sale of gas agreement had been performed. The court will try, wherever possible, to give the proper legal effect to any clause that the parties understood and intended to have legal effect. Agreements to agree cannot be enforced. When the parties stated a formula (e.g. market rental) to ascertain a clause, but did not supply_machinery_(e.g._arbitration)_for applying the_formula,_the courts_will_supply_(be)_the Formation: Certainty of Terms
17 6 Lall Contracts Bizikovic [41] Mannpar Enterprises Ltd. v. Case Rule Topic machinery and apply the formulae so long as the formulae is not defective.. Where the formula is set out but is defective, and machinery is provided for applying the formula, the machinery may be used to cure the defect in the formula.. While there is no common law obligation to negotiate in good faith (because it is unworkable), in this case there was an implied term requiring good faith negotiations for the renewal of the rental agreement. Canada The court held that the renewal clause in the rental contract was a mere agreement to Formation: [1999] 173 D.L.R. (4th) 243 agree the contract did not provide a formula or objective measure to determine rent (such Certainty of Terms (B.C.C.A.) as fair market value) or a mechanism to apply the formula. Bawitko Investment Ltd. v. Kernels The oral agreement in contemplation of a formal written agreement not enforceable due to [42] Popocorn Ltd (1991) 79 D.L.R. (4th) the lack of certainty; it is a contract to make a contract 97(Ont. C.A.) Wallace v. Allen, 2009 ONCA 36. Letter of intent could amount to an enforceable contract if the parties clearly express their intention to be bound by the terms of LOl which were later to be incorporated into a main [44] contract, if the terms of LOT are precise and complete, and if the parties after signing LOl [46] conducted themselves as if the deal is completed. Fontion: Certainty of Terms Formation: Certainty of Terms and letters of intent. Atkin L.J.: the common law does not regulate agreements between spouses...the Enforcement of Balfour v. Balfour consideration that really obtains from them is that natural love and affection. Promises: Intention [1919] 2 K.B. 571 There is a strong presumption that family agreements are not intended to produce legal to Create Legal Rose and Frank v. J.R. Crompton [471 Bros., [ K.B. 261 (C.A.) consequences. Obligation. There is a strong presumption that business agreements are intended to produce legal consequences. However, if there is a clear and definite expression of the business parties that they do not intend to be subject to legal jurisdiction, there is no reason in public policy why effect should not be given to_their intention. Enforcement of Promises: Intention to Cte Legal Obligation Enforcement of [491 Toronto Dominion Bank v. Leigh Promises: Intention Instruments (1999) 178 D.L.R. (4th) A comfort letter is a form of undertaking that is deliberately designed with the intention not to Create Legal to create enforceable obligations. 634 (Ont. C. A.) Obligation The Governors ofdaihousie Enforcement of [50] College at Halifax v. The Estate of Arthur Boutilier, Deceased [1934] S.C.R For a promise to be binding as a contract it has to be supported by a good and sufficient consideration which moves from the promisee at the time of and in exchange for the promise which is sought to be enforced Promises: Consideration Eastwood v. Kenyon Moral obligation is nudum pactum, a voluntary promise without any consideration. Enforcement of [51] (1840) 11 Ad. & E. 438, 113 E.R. Past consideration is not a good consideration for a new promise made after a benefit was Promises: Past [ (Q.B.) conferred and when the benefit was not conferred at the request of the promisor. Consideration Lainpleigh v. Brathwait, (1615) Past consideration may be a good consideration for a subsequent promise if the benefit was Enforcement: Past Hobart 105, 80 E.R. 255 (K.B.) conferred at the request of the promisor. Consideration
18 Topic of 7 Law Contracts Biukovic Case Rule J Thomas v. Thomas [531 (1842) 2 Q.B. 851, 114 E.R. 330 Consideration is something which is of some value in the eyes of the law. Enforcement of Consideration must move from the promise. Promises: Nature.. Consideration must be sufficient but need not be adequate. Consideration [57] [581 [591 Past consideration can sometimes be good consideration if: 1. The act was done at the promisor s request; 2. The parties understood that the act was to be remunerated; and 3. Enforcement of Promises: Pre to Stilk Enforcement of Payment would have been legally enforceable had it been promised in advance. A promise to perform, or the performance a pre-existing contractual obligation to a third On v. Lou Yiu Long party can be valid consideration. isting Duty Duty Owed [1980] A.C. 614 (P.C.) Duress, whatever form it takes, is a coercion of the will so as to vitiate consent; duress may render a contract voidable, but this must be claimed promptly. to Economic Duress; The commercial pressure alleged to constitute duress must be such that the victim entered the contract against their will, they had no alternative course open to them, and they were confronted with coercive acts by the party exerting the pressure. A unilateral promise to increase price is unenforceable because there is no clear agreement to rescind the existing contract the new provisions were unilaterally imported into the Enforcement of document and accordingly, consideration of the oral agreement was not found in a mutual Promises: Pre Gilbert Steel v. University agreement to abandon the earlier written contract and assume the obligations under the new existing Legal Construction Ltd. oral one. Duty Duty Owed (1976) 12 O.R. 19, 67 D.L.R. In Sulk v. Myrick (1809), when two out of 11 sailors deserted the ship, the captain to (3d) 606 (C.A.) promised to pay the remaining sailors extra money they sailed the ship back. However, he later refused to pay that extra money. The court held that the captain was not obliged to v. Myrick (1809) pay the extra money because the obligation to sail the ship back was not a valid 170 E.R consideration for the subsequent agreement which varied the original one. Pre-existing legal duty owed to the promisor may be a valid consideration for a subsequent Promises: Williams v. Roffey Bros. Pre promise if the promisor derives practical benefit from the agreement and if the subsequent existing Legal [ All E.R. 512 (C.A.) promise is not given under economic duress (note Glidewell s 6 point test). Duty Duty Owed Pao (2.).... of if iegai a Third Party; Past Consideration the Promisor Reference to the Promisor Robertson J.A. held that it is time to build upon UK decision in Williams v. Roffey and accepted that post-contractual modification, unsupported by consideration, may be Enforcement enforceable so long as it is established that the variation of contracts was not procured of Promises: under economic duress. Pre [60] Authority Inc. v. NAY Canada existing Commercial reality needs to be recognized and considered that is, that the parties Legal [2008] N.B.J. No. 108 (N.B.C.A.) frequently varied and modified their contractual obligations and that the law has to protect to their legitimate expectations that the modifications or variations will be regarded as enforceable. The to pay a sum which the to pay was good Enforcement of [61] Re Selectmove Ltd. [1995] 2 All (confirms Foakes v. Beer) Promises: Duty E.R. 531 (C.A.) Williams v. Roffey principle not applicable where the existing obligation is to pay money Owed to the Greater Fredericton Airport promise consideration debtor was already bound not Duty Duty Owed the Promisor
19 8 Law Contracts Biukovic Case Rule Topic but rather only where the existing obligation is to supply goods or services Promisor Enforcement of Foakes V. Beer The traditional common law position is that an agreement to accept a smaller sum in Promises: Pre [62] satisfaction of a debt of a larger sum is not a good consideration, existing Legal (1884) 9 App. Cas. 605 (H.L.). This case has been overruled in B.C. by s.43 of the Law and Equity Act. Duty Duty Owed to the Promisor [631. In the case of the debtor who owed the creditor a large sum under a series of promissory Enforcement of Foot v. Rawlings [1963] S.C.R. 197 notes as full payment of the debt, as long as the debtor continued to perform his obligation Promises: and kept paying by post-dated cheques as subsequently agreed between the two, the Part payment of creditor s right to sue on the notes was suspended. debt Hughes v. Metropolitan Railway [64] Co. (1877) 2 A.C. 439 (HI.) [65] [661 [67] [lit is the first principle upon which all Courts of Equity proceed, that if parties who have entered into defmite and distinct terms involving certain legal results certain penalties or legal forfeiture afterwards by their own act or with their own consent enter upon a course Enforcement of of negotiation which has the effect of leading one of the parties to suppose that the strict Promises: Waiver rights arising under the contract will not be enforced, or will be kept in suspense, or held in and Promissory abeyance, the person who otherwise might have enforced those rights will not be allowed Estoppel to enforce them where it would be inequitable having regard to the dealings which have thus taken place between the parties Central London Property v. High A promise intended to be binding, intended to be acted on and in fact acted on, is binding Trees House even if there is no consideration (Lord Denning relied on the doctrine of promissory [1947] 1 K.B. 130, [1956] 1 All estoppel). E.R. 256 Estoppel was used as a shield by tenants against the landlord who wanted to enforce a higher rent. Enforcement of Promises: Waiver and Promissory Estoppel John Burrows v. Subsurface The passive conduct of the appellant was not taken by the court as a waiver of his rights to Enforcement of Surveys seek enforcement of the contract, but only as friendly indulgences. Promises: Waiver [1968] S.C.R. 607, 68 D.L.R. (2 ). When there is no consideration or deed, any relaxation of terms must be clear and and Promissory 354 unequivocal. Estoppel D.C. Builders v. Rees [1966] 2 Q.B. 617 A creditor is barred from enforcing their legal rights only when it would be inequitable for the creditor to insist on them. Where there has been a true accord, under which the creditor voluntarily agrees to accept a lesser sum in satisfaction, and the debtor acts on that accord by paying the lesser sum and the creditor accepts it, then it is inequitable for the creditor afterwards to insist on the balance, but they are not bound if there was no true accord. A promise made under duress should not be estopped. Lord Denning explained his own principle set out in High Trees: a) promissory estoppel Combe v. Coinbe cannot be used as a sword, to create new causes of action where none existed before, b) [681 [1951] 2 K.B. 215, 1 All E.R. 767 promissory estoppel can only be used as a shield, as a part of a cause of action, to prevent a (C.A.) party from insisting upon his strict legal rights when it would be unjust to allow him to enforce them. Enforcement of Promises: Waiver and Promissory Estoppel Enforcement of Promises: Waiver and Promissory Estoppel [69] Walton Stores (Interstate) Ltd. v.. Australian court made an exception to the general rule that promissory estoppel cannot be Enforcement of
20 9 Law Contracts Biukovic Case Rule Topic Maher used in the absence of a pre-existing legal relationship. Promises: Waiver (1988) 62 A.L.J.R. (H.C.) The court held that the doctrine can be used in the absence of a pre-existing legal relation if and Promissory N.M. v. A.TA. (2003), 13 B.C.L.R. [70] (4th) 73 (B.C.C.A.) Tweddle v. Atkinson (1861) 1 B & there was a reliance on the promise that was a reasonable expectation and if a departure Estoppel from the promise is unconscionable behavior. B.C.C.A found little evidence in Canadian authorities to indicate a move toward a more generous approach to promissory estoppel and distinguished the case from Walton iii which there was a reasonable expectation of a legal obligation. Enforcement of Promises: Waiver and Promissory Estoppel A person who is not engaged in a coniract (a third party) can generally neither sue nor be Privity of Contract: [77] sued on that contract. Third Party. Love and affection are not sufficient consideration. Beneficiaries. Only a person who is a party to a contract can sue on it. Dunlop PneumaticTyre Co. V. Even if a contract provides a third party with an enforceable right, there still must be Privily of Contract: [78] Seifridge & Co. Ltd. [1915] A.C. consideration. Third Party 847(H.L.) A principal not named in the contract, however, may sue upon it if the promisee really Beneficiaries Besweck v. Beswick [1966] 1 Ch. 538; [ A11E.R. 1 (C.A.) [79] [1968] A.C. 58;[1967] 2 All ER. 119 (H.L.) contracted as his agent.. C.A: Lord Denning MR fmds an equitable exception to general rule of privity where the third party is in a trustee relationship - in this case the widow sued in her capacity as executrix of the estate, and also in her personal capacity (Denning for C.A. held that she Privity of Contract: could make a joint claim and that a personal claim was good as well but I{L disagreed with Ways for Third him on the point of a personal claim see below). Parties to Acquire. H.L.: Lord Reid found that although the widow in her personal capacity had no right to sue, Benefits (choice of she had a right as adminisiratrix of her husband s estate to sue and seek for specific remedy) performance of a contract (rather than damages); the widow is in that way enforcing the contract in her benefit. lacobucci I held employees were protected from clause limiting their liability even though they were not parties to the contract. London Drugs Ltd. v. Kuehne & The employee could rely on the limitation of liability clause if such clause expressly or Privity of Contract: [80] Nagel International Ltd. implicitly extends its benefits to the employees and if the employees have been acting in Exceptions [82] [1992] 3 S.C.R. 299 the course of their employment and performing the very services provided for in the Employees Fraser River Pile & Dredge Lt. v. Can-Dive Services. [ B.C.L.R. (3d) 187 (B.C.C.A.) contract between their employer and the customer when the loss occurred Limited Exception to privity, employees may use as shields.. Followed London Drugs analysis re: application of limitation of liability clause on employees in order to enforce the insurer s waiver of its tights of subrogation against the charterer Privity of Contract: Does not modify the test of London Drugs but extends its application on contracts other Exceptions other than employment contracts as long as the contract explicitly or implicitly extends its than Employees benefits to the third party and if the third party has been performing the activities contemplated_in the contract [83] Dynamic Transportation Ltd. v. Statutory requirement that a contract be in writing has been satisfied with a memorandum Requirement of
21 10 Law 2c.cts Birikovic I [84] Case Rule Topic O.K Detailing Ltd. [ S.C.R. evidencing the agreement (that is, description of land) with a sufficient certainty of Writing 1072 description that enables the property to be identified Degiman v. Brunet Estate,, [1954] S.C.R 725 (s.c.c.). Equitable doctrine of part performance could be used to enforce an (oral) agreement for transfer of land which is non-compliant with a statutory requirement of form if an oral agreement is partially performed (part performance relevant to an oral agreement, not Requirement of wholly neutral and it would be unjust to refuse enforcement of an agreement writing: effects of. If the doctrine of part performance is not applicable, the plamtiff could still have a claim in non-compliance quantum meruit based on the reasonable value of services rendered, if those services would otherwise unjustly enriched the defendant
THE UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA FACULTY OF LAW DECEMBER 2015 EXAMINATION. LAW 211 Contract Law. Section 2 Professor Biukovh TOTAL MARKS: 100
 r THIS EXAMINATION CONSISTS OF THREE (3) PAGES PLEASE ENSURE THAT YOU HAVE A COMPLETE PAPER THE UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA FACULTY OF LAW DECEMBER 2015 EXAMINATION LAW 211 Contract Law Section 2 Professor
r THIS EXAMINATION CONSISTS OF THREE (3) PAGES PLEASE ENSURE THAT YOU HAVE A COMPLETE PAPER THE UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA FACULTY OF LAW DECEMBER 2015 EXAMINATION LAW 211 Contract Law Section 2 Professor
Was there a counter offer? Was there silence? Is it by mail or an instantaneous mode?
 FORMATION OF A VALID CONTRACT 1 Is there intent to create legal obligations? 2 Is there communication of the offer? 3 Is there acceptance of the offer? 4 Is there a certainty of terms? Is there a social
FORMATION OF A VALID CONTRACT 1 Is there intent to create legal obligations? 2 Is there communication of the offer? 3 Is there acceptance of the offer? 4 Is there a certainty of terms? Is there a social
LAW 110 Contracts. Section 2 Professor Biukoviá TOTAL MARKS: 100
 THIS EXAMINATION CONSISTS OF 5 PAGES PLEASE ENSURE THAT YOU HAVE A COMPLETE PAPER THE UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA FACULTY OF LAW FINAL EXAMINATION LAW 110 - APRIL 2012 Section 2 Professor Biukoviá TOTAL
THIS EXAMINATION CONSISTS OF 5 PAGES PLEASE ENSURE THAT YOU HAVE A COMPLETE PAPER THE UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA FACULTY OF LAW FINAL EXAMINATION LAW 110 - APRIL 2012 Section 2 Professor Biukoviá TOTAL
The Kinds of Promises Legally Enforced
 The Kinds of Promises Legally Enforced Offers There can be serious consequences if an offer is found to be legally binding. In Denton a railway schedule was found to be a unilateral contract, and thus
The Kinds of Promises Legally Enforced Offers There can be serious consequences if an offer is found to be legally binding. In Denton a railway schedule was found to be a unilateral contract, and thus
Consideration sits alongside, offer and acceptance to form a legally binding contract.
 CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG Consideration and Estoppel Refer to Richards Law of Contract Chapter 3 A Introduction Background and function Consideration sits alongside, offer and acceptance to form a legally
CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG Consideration and Estoppel Refer to Richards Law of Contract Chapter 3 A Introduction Background and function Consideration sits alongside, offer and acceptance to form a legally
Privity: Third party to K can t enforce its obligations b/c they haven t contributed consideration for its promises ( Tweddle ); Principal not named
 Privity: Third party to K can t enforce its obligations b/c they haven t contributed consideration for its promises ( Tweddle ); Principal not named in K can sue if promisee was contracted as principal
Privity: Third party to K can t enforce its obligations b/c they haven t contributed consideration for its promises ( Tweddle ); Principal not named in K can sue if promisee was contracted as principal
CONTRACTS. Fall 2015 JENNA DAVIS THOMPSON RIVERS UNIVERSITY LAW 3030
 CONTRACTS Fall 2015 JENNA DAVIS THOMPSON RIVERS UNIVERSITY LAW 3030 1 1 Is there an intention to create legal obligations? 2 Is there communication of an offer? 3 Is there acceptance of the offer? 4 Is
CONTRACTS Fall 2015 JENNA DAVIS THOMPSON RIVERS UNIVERSITY LAW 3030 1 1 Is there an intention to create legal obligations? 2 Is there communication of an offer? 3 Is there acceptance of the offer? 4 Is
Contracts: Kinds of Contracts: Offer: Communication of Offer:
 Contracts: Kinds of Contracts: - Executory Contract - Obligations are not enforceable immediately - Executed Contract - Immediately fulfilled upon entry - Partly Executed Contract - Some obligations fulfilled,
Contracts: Kinds of Contracts: - Executory Contract - Obligations are not enforceable immediately - Executed Contract - Immediately fulfilled upon entry - Partly Executed Contract - Some obligations fulfilled,
CONTRACT LAWS 3003A/B Of the Bars of Ontario and Nova Scotia Department of Law Loeb D Ext. 3672
 CONTRACT LAWS 3003A/B 2017-2018 INSTRUCTOR: Professor M.H. Ogilvie Of e Bars of Ontario a Nova Scotia Department of Law Loeb D596 613-520-2600 Ext. 3672 OFFICE HOURS: Wednesday 2:30-5:00 or by appointment
CONTRACT LAWS 3003A/B 2017-2018 INSTRUCTOR: Professor M.H. Ogilvie Of e Bars of Ontario a Nova Scotia Department of Law Loeb D596 613-520-2600 Ext. 3672 OFFICE HOURS: Wednesday 2:30-5:00 or by appointment
MLL111- Exam Notes Contract Law (All Topics + Cases)
 1 MLL111- Exam Notes Contract Law (All Topics + Cases) 2 Contents Page Page 8: Formation of Contracts Offer and Acceptance Page 9: Acceptance Communication of Acceptance: Waiver Silence Page 10: Acceptance
1 MLL111- Exam Notes Contract Law (All Topics + Cases) 2 Contents Page Page 8: Formation of Contracts Offer and Acceptance Page 9: Acceptance Communication of Acceptance: Waiver Silence Page 10: Acceptance
the parties had dealt with each other before and were well acquainted with the timber industry
 Formation of a Contract To start with it needs to be identified whether and which party is alleging a contract. For a contract to be valid it must be: 1.! An agreement 2.! Contractual intention 3.! Consideration
Formation of a Contract To start with it needs to be identified whether and which party is alleging a contract. For a contract to be valid it must be: 1.! An agreement 2.! Contractual intention 3.! Consideration
FORMATION OF A VALID CONTRACT 4 1. Offer and Invitations to Treat 4 Canadian Dyers Assn v. Burton (1920, H.L.) 4 Pharmaceutical Society v.
 FORMATION OF A VALID CONTRACT 4 1. Offer and Invitations to Treat 4 Canadian Dyers Assn v. Burton (1920, H.L.) 4 Pharmaceutical Society v. Boots Cash Chemists (1953, C.A.) 4 Carlill v. Carbolic Smoke Ball
FORMATION OF A VALID CONTRACT 4 1. Offer and Invitations to Treat 4 Canadian Dyers Assn v. Burton (1920, H.L.) 4 Pharmaceutical Society v. Boots Cash Chemists (1953, C.A.) 4 Carlill v. Carbolic Smoke Ball
CONTRACT LAW SUMMARY
 CONTRACT LAW SUMMARY LAWSKOOL UK CONTENTS INTRODUCTION TO CONTRACT LAW 6 DEFINITION OF CONTRACT LAW 6 1) The Classical Model of Contract Law 6 INTENTION TO CREATE LEGAL RELATIONS 8 INTRODUCTION TO INTENTION
CONTRACT LAW SUMMARY LAWSKOOL UK CONTENTS INTRODUCTION TO CONTRACT LAW 6 DEFINITION OF CONTRACT LAW 6 1) The Classical Model of Contract Law 6 INTENTION TO CREATE LEGAL RELATIONS 8 INTRODUCTION TO INTENTION
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 9084 LAW
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 9084 LAW 9084/31 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 9084 LAW 9084/31 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers
Contracts Final Exam Notes Formation of a contract What is a contract MUST Offer REASONABLE PERSON Acceptance
 Contracts Final Exam Notes Formation of a contract What is a contract - Binding promise between two or more parties, reliant upon several important factors - Offer - Acceptance - Consideration - Certainty
Contracts Final Exam Notes Formation of a contract What is a contract - Binding promise between two or more parties, reliant upon several important factors - Offer - Acceptance - Consideration - Certainty
CONTRACT LAW. Elements of a Contract
 CONTRACT LAW Contracts: Types and Sources in Australia CONTRACT: An agreement concerning promises made between two or more parties with the intention of creating certain legal rights and obligations upon
CONTRACT LAW Contracts: Types and Sources in Australia CONTRACT: An agreement concerning promises made between two or more parties with the intention of creating certain legal rights and obligations upon
Table of Content - Commercial Law. Year End Examination Notes
 Table of Content - Commercial Law Year End Examination Notes Chapter 4: Contract: Offer & Acceptance... 2 Chapter 5: Intention & Consideration... 7 Chapter 6: Express Terms of the Contract... 12 Chapter
Table of Content - Commercial Law Year End Examination Notes Chapter 4: Contract: Offer & Acceptance... 2 Chapter 5: Intention & Consideration... 7 Chapter 6: Express Terms of the Contract... 12 Chapter
LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS - JUNE 2011
 Note to Candidates and Tutors: LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS - JUNE 2011 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students
Note to Candidates and Tutors: LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS - JUNE 2011 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students
LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS - JANUARY 2013
 Note to Candidates and Tutors: LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS - JANUARY 2013 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students
Note to Candidates and Tutors: LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS - JANUARY 2013 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students
Contents. Table of Statutes. Table of Secondary Legislation. Table of Cases. The Agreement to Contract
 Contents Table of Statutes Table of Secondary Legislation Table of Cases Chapter 1: The Agreement to Contract 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Elements required for a valid simple contract 1.3 The phenomenon of agreement
Contents Table of Statutes Table of Secondary Legislation Table of Cases Chapter 1: The Agreement to Contract 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Elements required for a valid simple contract 1.3 The phenomenon of agreement
CONTRACTS LAW. Fall 2015 CAN IQRA AZHAR
 CONTRACTS LAW Fall 2015 CAN IQRA AZHAR Contracts CANs Fall 2015 Iqra Azhar 1 1. Table of Contents 1. FORMATION OF A VALID CONTRACT... 5 Offer and Invitation to Treat... 5 Canadian Dryers Association v
CONTRACTS LAW Fall 2015 CAN IQRA AZHAR Contracts CANs Fall 2015 Iqra Azhar 1 1. Table of Contents 1. FORMATION OF A VALID CONTRACT... 5 Offer and Invitation to Treat... 5 Canadian Dryers Association v
!"#$%&'(&)'*+%*+,& /G$+:'($"0B",E$"#'8E,",0"?$+%'9*,$"..."HH" I'('9B0+%*,'09"..."H>" ?E$")*+02"/4'&$9:$"#J2$"..."HK"
 !#$%&'(&)'*+%*+,& #$%$&'$()*+,-...- /(,011$2...3 )+'4',5678$9:5*9&7(('89%$9,(;< +& )*+,'$(=...>?$+%(*9&@9,$+1+$,*,'09...A @9,$+1+$,*,'090BC09,+*:,(...-- )$+B0+%*9:$*9&?$+%'9*,'09...-3?$+%'9*,'09B0+D+$*:E...-F
!#$%&'(&)'*+%*+,& #$%$&'$()*+,-...- /(,011$2...3 )+'4',5678$9:5*9&7(('89%$9,(;< +& )*+,'$(=...>?$+%(*9&@9,$+1+$,*,'09...A @9,$+1+$,*,'090BC09,+*:,(...-- )$+B0+%*9:$*9&?$+%'9*,'09...-3?$+%'9*,'09B0+D+$*:E...-F
LEVEL 4 - UNIT 1 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS JANUARY 2015
 Note to Candidates and Tutors: LEVEL 4 - UNIT 1 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS JANUARY 2015 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students
Note to Candidates and Tutors: LEVEL 4 - UNIT 1 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS JANUARY 2015 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students
Contents. Table of cases. Introduction
 Table of cases Contents Introduction 1. The Making of a Contract 17 The nature of contracts-unilateral and bi-lateral ` 18 The notion of offer and acceptance 18 The invitation to treat 19 Offers of sale
Table of cases Contents Introduction 1. The Making of a Contract 17 The nature of contracts-unilateral and bi-lateral ` 18 The notion of offer and acceptance 18 The invitation to treat 19 Offers of sale
Business Law - Contract Law Study Notes
 Business Law - Contract Law Study Notes Comprehensive unit study notes as per Victoria University. 1 Table of Contents Note topic Content page Full semester notes 3-49 How to write IRAC 50-51 response
Business Law - Contract Law Study Notes Comprehensive unit study notes as per Victoria University. 1 Table of Contents Note topic Content page Full semester notes 3-49 How to write IRAC 50-51 response
7/23/2010. The. Contract. Sources of contractual obligations
 Law for Spatial Designers Introduction to the Law of Contract Module 3 Topic 1 Sources of contractual obligations Obligations imposed by law and equity The Contract Statutory obligations The obligations
Law for Spatial Designers Introduction to the Law of Contract Module 3 Topic 1 Sources of contractual obligations Obligations imposed by law and equity The Contract Statutory obligations The obligations
Negligence 1. Duty of Care 2. Breach of duty of care p 718 c) p 724
 Negligence 1. Duty of Care Donoghue v Stevenson [1932] AC 562 - a duty of care could exist in any situation where loss, damage or injury to one party was reasonable foreseeable (foreseeable harm) - the
Negligence 1. Duty of Care Donoghue v Stevenson [1932] AC 562 - a duty of care could exist in any situation where loss, damage or injury to one party was reasonable foreseeable (foreseeable harm) - the
LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 LAW OF CONTRACT SUGGESTED ANSWERS - JUNE 2014
 Note to Candidates and Tutors: LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 LAW OF CONTRACT SUGGESTED ANSWERS - JUNE 2014 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students
Note to Candidates and Tutors: LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 LAW OF CONTRACT SUGGESTED ANSWERS - JUNE 2014 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students
9084 LAW. 9084/32 Paper 3 (Paper 3), maximum raw mark 75
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2015 series 9084 LAW 9084/32 Paper 3 (Paper 3), maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme is published
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2015 series 9084 LAW 9084/32 Paper 3 (Paper 3), maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme is published
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level. Published
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level LAW 9084/31 Paper 3 October/November 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 75 Published This mark scheme is
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level LAW 9084/31 Paper 3 October/November 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 75 Published This mark scheme is
CHAPTER 1. The question requires a discussion of the law with regard to offer an acceptance. For a contract to be valid it must be:
 CHAPTER 1 property of 1stclasslawnotes lawstoreuk Formation Formation of Contract The question requires a discussion of the law with regard to offer an acceptance. For a contract to be valid it must be:
CHAPTER 1 property of 1stclasslawnotes lawstoreuk Formation Formation of Contract The question requires a discussion of the law with regard to offer an acceptance. For a contract to be valid it must be:
Emily M. Weitzenboeck, 2012 Norwegian Research Center for Computers & Law
 What is acceptance? i. The final and unconditional expression of consent to offer ii. made in response to offer iii. exactly matching terms of offer iv. communicated to offeror. Element (i): final and
What is acceptance? i. The final and unconditional expression of consent to offer ii. made in response to offer iii. exactly matching terms of offer iv. communicated to offeror. Element (i): final and
Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Spring Contract Formation
 Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Contract Formation I. Foundations A. Mutual Assent: Each party to a contract manifests its assent to the
Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Contract Formation I. Foundations A. Mutual Assent: Each party to a contract manifests its assent to the
Business Law & Ethics notes Lec Lecture topic Topic s covered Text book refs. constitution expansion of power interpreting power
 Business Law & Ethics notes Lec Lecture topic Topic s covered Text book refs 1 law, morality and philosophical views of ch 1 meaning of eithics law 2 the source of laws governing constitution expansion
Business Law & Ethics notes Lec Lecture topic Topic s covered Text book refs 1 law, morality and philosophical views of ch 1 meaning of eithics law 2 the source of laws governing constitution expansion
Contents. Table of Statutes. Table of Secondary Legislation. Table of Cases. The Agreement to Contract
 Contents Table of Statutes Table of Secondary Legislation Table of Cases Chapter 1: The Agreement to Contract 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Elements required for a valid simple contract 1.3 The phenomenon of agreement
Contents Table of Statutes Table of Secondary Legislation Table of Cases Chapter 1: The Agreement to Contract 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Elements required for a valid simple contract 1.3 The phenomenon of agreement
PRINCIPLES OF CONTRACTUAL LIABILITY 1.1. AGREEMENT TEMPLATE: CERTAINTY TEMPLATE:... Error! Bookmark not defined.
 PRINCIPLES OF CONTRACTUAL LIABILITY 1. FORMATION OF CONTRACT:... 2 1.1. AGREEMENT TEMPLATE:... 2 1.2. CAPACITY TEMPLATE:... = Error! Bookmark not defined. 1.3. INTENTION TEMPLATE: (objective test)... Error!
PRINCIPLES OF CONTRACTUAL LIABILITY 1. FORMATION OF CONTRACT:... 2 1.1. AGREEMENT TEMPLATE:... 2 1.2. CAPACITY TEMPLATE:... = Error! Bookmark not defined. 1.3. INTENTION TEMPLATE: (objective test)... Error!
Company Law: Conwest Exploration Company Limited et al. v. Letain, (1964) S.C.R. 20
 Osgoode Hall Law Journal Volume 3, Number 3 (October 1965) Article 3 Company Law: Conwest Exploration Company Limited et al. v. Letain, (1964) S.C.R. 20 Burton B. C. Tait Follow this and additional works
Osgoode Hall Law Journal Volume 3, Number 3 (October 1965) Article 3 Company Law: Conwest Exploration Company Limited et al. v. Letain, (1964) S.C.R. 20 Burton B. C. Tait Follow this and additional works
Please distribute and reproduce these notes freely
 Course: Law of Contracts Date: Fall/Winter (2000-2001) Professor: Berryman (Fall) & Whiteside (Winter) Textbook: Contract Law in Canada Please distribute and reproduce these notes freely Although great
Course: Law of Contracts Date: Fall/Winter (2000-2001) Professor: Berryman (Fall) & Whiteside (Winter) Textbook: Contract Law in Canada Please distribute and reproduce these notes freely Although great
CONTRACT LAW. What is a contract? A promise or set of promises that is legally binding. Why is contract so important? Contract forms the basis for
 CONTRACT LAW What is a contract? A promise or set of promises that is legally binding Why is contract so important? Contract forms the basis for - Commercial transactions - Consumer transactions; and o
CONTRACT LAW What is a contract? A promise or set of promises that is legally binding Why is contract so important? Contract forms the basis for - Commercial transactions - Consumer transactions; and o
Do you have a contract checklist? 3 How do you get out of the contract? 5. Remedies Checklist 12
 Do you have a contract checklist? 3 How do you get out of the contract? 5 Hunter, Tercon, Bhasin. 5 Misrepresentation (voidable) 5 Mistake (void)(cl) 6 ( ) Test for rectification (Sylvan): 7 Duress 8 Undue
Do you have a contract checklist? 3 How do you get out of the contract? 5 Hunter, Tercon, Bhasin. 5 Misrepresentation (voidable) 5 Mistake (void)(cl) 6 ( ) Test for rectification (Sylvan): 7 Duress 8 Undue
9084 LAW 9084/03 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2009 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9084 LAW 9084/03 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2009 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9084 LAW 9084/03 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark
CONTRACT LAW IN THE SOUTH PACIFIC
 CONTRACT LAW IN THE SOUTH PACIFIC Jennifer Corrin Care Senior Lecturer TC Beirne School of Law University of Queensland Cavendish Publishing Limited London Sydney CONTENTS Preface Table of Cases Table
CONTRACT LAW IN THE SOUTH PACIFIC Jennifer Corrin Care Senior Lecturer TC Beirne School of Law University of Queensland Cavendish Publishing Limited London Sydney CONTENTS Preface Table of Cases Table
Contracts Summary Notes
 Contracts Summary Notes TOPIC ONE: AGREEMENT- OFFER AND ACCEPTANCE There are 4 elements of a contract: Agreement, consideration, intention to create legal relations and certainty The above are all required
Contracts Summary Notes TOPIC ONE: AGREEMENT- OFFER AND ACCEPTANCE There are 4 elements of a contract: Agreement, consideration, intention to create legal relations and certainty The above are all required
The Objective Principle of a Promise... 2 Intention to Create Legal Relations... 4 Offer and Acceptance... 5
 1 Contents The Objective Principle of a Promise... 2 Intention to Create Legal Relations... 4 Offer and Acceptance... 5 Offer vs. Invitation to Treat... 5 Termination/Lapse of Offer... 6 Acceptance of
1 Contents The Objective Principle of a Promise... 2 Intention to Create Legal Relations... 4 Offer and Acceptance... 5 Offer vs. Invitation to Treat... 5 Termination/Lapse of Offer... 6 Acceptance of
TABLE OF CONTENTS. Preface... iii Preface to the First Edition... v Table of Cases... TC-1 Table of Statutes... TS-1
 TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE Preface... iii Preface to the First Edition... v Table of Cases... TC-1 Table of Statutes... TS-1 PART I. INTRODUCTION... 1-17 CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION... 1 PART II. ENFORCEABILITY...
TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE Preface... iii Preface to the First Edition... v Table of Cases... TC-1 Table of Statutes... TS-1 PART I. INTRODUCTION... 1-17 CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION... 1 PART II. ENFORCEABILITY...
Law 410 CONTRACTS BUCKWOLD
 Law 410 CONTRACTS BUCKWOLD 1 FORMATION: Is there a contract? In order to have a contract, you must have: o Capacity to contract: Note that minors can enforce a contract against adults, but adults cannot
Law 410 CONTRACTS BUCKWOLD 1 FORMATION: Is there a contract? In order to have a contract, you must have: o Capacity to contract: Note that minors can enforce a contract against adults, but adults cannot
a) The body of law as made by judges through the determination of cases. d) The system of law that emerged following the Norman Conquest in 1066.
 1. Who of the following was NOT a proponent of natural law? a) Aristotle b) Jeremy Bentham c) St Augustine d) St Thomas Aquinas 2. The term 'common law' has three different meanings. Which of the following
1. Who of the following was NOT a proponent of natural law? a) Aristotle b) Jeremy Bentham c) St Augustine d) St Thomas Aquinas 2. The term 'common law' has three different meanings. Which of the following
CONTRACTS. Miscellaneous applications of ACL for Contracts:! 6 PROMISSORY ESTOPPEL! Assumption! Detrimental Reliance!...
 CONTRACTS Miscellaneous applications of ACL for Contracts:! 6 PROMISSORY ESTOPPEL! 7 1. Assumption!... 7 2. Detrimental Reliance!... 7 3. Unconscionability!... 8 Remedy of Promissory Estoppel!... 8 PRIVITY!
CONTRACTS Miscellaneous applications of ACL for Contracts:! 6 PROMISSORY ESTOPPEL! 7 1. Assumption!... 7 2. Detrimental Reliance!... 7 3. Unconscionability!... 8 Remedy of Promissory Estoppel!... 8 PRIVITY!
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 9084 LAW. 9084/33 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 9084 LAW 9084/33 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme is published
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 9084 LAW 9084/33 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme is published
9084 LAW. 9084/32 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2014 series 9084 LAW 9084/32 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and candidates,
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2014 series 9084 LAW 9084/32 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and candidates,
MBE WORKSHOP: CONTRACTS PROFESSOR LISA MCELROY DREXEL UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF LAW
 MBE WORKSHOP: CONTRACTS PROFESSOR LISA MCELROY DREXEL UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF LAW CHAPTER 1: CONTRACTS Editor's Note 1: The below outline is taken from the National Conference of Bar Examiners' website. NOTE:
MBE WORKSHOP: CONTRACTS PROFESSOR LISA MCELROY DREXEL UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF LAW CHAPTER 1: CONTRACTS Editor's Note 1: The below outline is taken from the National Conference of Bar Examiners' website. NOTE:
TOPIC 1: AGREEMENT Lucy v Zehmer (1954) 84 SE 2d 516). ACCC v CG Berbatis Holdings Pty Ltd (2003) 214 CLR 51) However: Smith v Hughes
 1 TOPIC 1: AGREEMENT An agreement is an understanding between two parties that one of them will do something, or will promise to do, in return for the other doing something, or promising to do so Requires
1 TOPIC 1: AGREEMENT An agreement is an understanding between two parties that one of them will do something, or will promise to do, in return for the other doing something, or promising to do so Requires
Termination of an Offer
 Termination of an Offer Lapse! If the offer contains a time limit, then it lapses according to the explicit provisions! Offer must be accepted by midnight tonight.! If the offer does not contain a time
Termination of an Offer Lapse! If the offer contains a time limit, then it lapses according to the explicit provisions! Offer must be accepted by midnight tonight.! If the offer does not contain a time
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 9084 LAW. 9084/31 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 9084 LAW 9084/31 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme is published
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 9084 LAW 9084/31 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme is published
Offer: Has a valid offer been made?
 Agreement Offer and acceptance based can exist between 2 or more (Clarke v Dunraven) May be necessary to look at whole agreement rather than isolate offer and acceptance (Empirnall Holdings v Machon Paul
Agreement Offer and acceptance based can exist between 2 or more (Clarke v Dunraven) May be necessary to look at whole agreement rather than isolate offer and acceptance (Empirnall Holdings v Machon Paul
OVERVIEW OF CONTRACT LAW
 OVERVIEW OF CONTRACT LAW Liability is generally the key issue in regards to contractual disputes. Purpose of K law is to provide the rules which determine when one party is liable to another under or in
OVERVIEW OF CONTRACT LAW Liability is generally the key issue in regards to contractual disputes. Purpose of K law is to provide the rules which determine when one party is liable to another under or in
University of Miami School of Law. CONTRACTS PROFESSOR ROBERT ROSEN Fall Syllabus 1
 University of Miami School of Law CONTRACTS PROFESSOR ROBERT ROSEN Fall 2007 Syllabus 1 [Unless otherwise indicated, all page # s refer to MACAULEY, ET.AL. CONTRACTS: LAW IN ACTION (2 ND ED., 2003)]. YOU
University of Miami School of Law CONTRACTS PROFESSOR ROBERT ROSEN Fall 2007 Syllabus 1 [Unless otherwise indicated, all page # s refer to MACAULEY, ET.AL. CONTRACTS: LAW IN ACTION (2 ND ED., 2003)]. YOU
LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS - JUNE 2013
 Note to Candidates and Tutors: LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS - JUNE 2013 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students
Note to Candidates and Tutors: LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS - JUNE 2013 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students
Sample. 2.1 Introduction. 2.2 Types of consideration
 Chapter 2: Consideration Outline 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Types of consideration 2.3 Consideration must move from the promisee 2.4 Consideration must be of some value 2.5 Summary 2.1 Introduction As noted
Chapter 2: Consideration Outline 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Types of consideration 2.3 Consideration must move from the promisee 2.4 Consideration must be of some value 2.5 Summary 2.1 Introduction As noted
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level. Published
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level LAW 9084/32 Paper 3 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 75 Published This mark scheme is published as an aid to
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level LAW 9084/32 Paper 3 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 75 Published This mark scheme is published as an aid to
UNIT 2 - CONTRACT LAW. Suggested Answers January 2009
 Note to Candidates and Tutors: UNIT 2 - CONTRACT LAW Suggested Answers January 2009 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students should
Note to Candidates and Tutors: UNIT 2 - CONTRACT LAW Suggested Answers January 2009 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students should
Is there a contract?
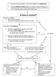 1. te whether this transaction is governed by UCC or the Restatement. 2. Does the Statute of Frauds apply? The contract must be in writing if it is in regard to land, if by its nature it takes more than
1. te whether this transaction is governed by UCC or the Restatement. 2. Does the Statute of Frauds apply? The contract must be in writing if it is in regard to land, if by its nature it takes more than
LAW OF CONTRACT (PART I) Shanila H. Gunawardena LL.B. (Hons.) (Colombo) Attorney-at-Law, CTA (CASL)
 LAW OF CONTRACT (PART I) Shanila H. Gunawardena LL.B. (Hons.) (Colombo) Attorney-at-Law, CTA (CASL) 30-07-2017 MAIN COMPONENTS OF A CONTRACT 1. Intention to create legal relations 2. Agreement between
LAW OF CONTRACT (PART I) Shanila H. Gunawardena LL.B. (Hons.) (Colombo) Attorney-at-Law, CTA (CASL) 30-07-2017 MAIN COMPONENTS OF A CONTRACT 1. Intention to create legal relations 2. Agreement between
Contracts. 2. Parties to the contract a) Capacity b) Privity
 Contracts 1. Formation of a contract a) Agreement Offer b) Agreement Acceptance c) Consideration d) Intention e) Certainty/completeness f) Promissory estoppel 2. Parties to the contract a) Capacity b)
Contracts 1. Formation of a contract a) Agreement Offer b) Agreement Acceptance c) Consideration d) Intention e) Certainty/completeness f) Promissory estoppel 2. Parties to the contract a) Capacity b)
The plaintiff must show that his loss was one which resulted from a breach of contract by the defendant (a direct causal link).
 1. CAUSATION The plaintiff must show that his loss was one which resulted from a breach of contract by the defendant (a direct causal link). An act of the defendant in a sequence of events leading to a
1. CAUSATION The plaintiff must show that his loss was one which resulted from a breach of contract by the defendant (a direct causal link). An act of the defendant in a sequence of events leading to a
Foundation Level LAW PRACTICE MANUAL
 Part: - 1 The Indian Contract Act, 1872 Chapter 1:- Nature and Kinds of Contracts 5. The general principles of law of contract applied to all kinds of contract irrespective of their nature. (a) True, as
Part: - 1 The Indian Contract Act, 1872 Chapter 1:- Nature and Kinds of Contracts 5. The general principles of law of contract applied to all kinds of contract irrespective of their nature. (a) True, as
CONTRACT LAW EXAM NOTES
 What is a contract? CONTRACT LAW EXAM NOTES Topic 1: The Nature and Importance of Contract Law A contract is a legally binding promise or agreement. A promise of agreement is not legally binding and enforceable
What is a contract? CONTRACT LAW EXAM NOTES Topic 1: The Nature and Importance of Contract Law A contract is a legally binding promise or agreement. A promise of agreement is not legally binding and enforceable
PAPER: LAW MARK AWARDED: 73% The overriding objective was recently modified in the Jackson reforms and recites as follows.
 PAPER: LAW MARK AWARDED: 73% Question 1 The overriding objective was recently modified in the Jackson reforms and recites as follows. 1) These rules are a new procedural code with the overriding objective
PAPER: LAW MARK AWARDED: 73% Question 1 The overriding objective was recently modified in the Jackson reforms and recites as follows. 1) These rules are a new procedural code with the overriding objective
Simple. CONTRACTS & UCC Outline. NINETY PERCENT of the LAW in NINETY PAGES. Tim Tyler, Ph.D., Attorney at Law
 NAILING THE BAR Simple CONTRACTS & UCC Outline Tim Tyler, Ph.D., Attorney at Law NINETY PERCENT of the LAW in NINETY PAGES NAILING THE BAR Simple CONTRACTS & UCC Outline Table of Contents CHAPTER 1: CONTRACT
NAILING THE BAR Simple CONTRACTS & UCC Outline Tim Tyler, Ph.D., Attorney at Law NINETY PERCENT of the LAW in NINETY PAGES NAILING THE BAR Simple CONTRACTS & UCC Outline Table of Contents CHAPTER 1: CONTRACT
MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9084 LAW. 9084/31 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9084 LAW 9084/31 Paper 3, maximum
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9084 LAW 9084/31 Paper 3, maximum
California Bar Examination
 California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question On May 1, Owner asked Builder
California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question On May 1, Owner asked Builder
MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2008 question paper 9084 LAW. 9084/03 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2008 question paper 9084 LAW 9084/03 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2008 question paper 9084 LAW 9084/03 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme
Opening Assignment. The Bargain. Contracts. Elements of Contract. Ending an Offer. What is an Offer 10/31/2017
 Opening Assignment Should the shopkeeper have been allowed to continue increasing the price of the vase? Explain. The Bargain Contracts What is a contract? Legally binding agreement Who may enter into
Opening Assignment Should the shopkeeper have been allowed to continue increasing the price of the vase? Explain. The Bargain Contracts What is a contract? Legally binding agreement Who may enter into
SAMPLE NOTES FROM OUR LLB CORE GUIDE:
 SAMPLE NOTES FROM OUR LLB CORE GUIDE: CONTRACT LAW PRIVITY CHAPTER LLB Answered is a comprehensive, first-class set of exam-focused study notes for the Undergraduate Law Degree. Please visit LLBanswered.com
SAMPLE NOTES FROM OUR LLB CORE GUIDE: CONTRACT LAW PRIVITY CHAPTER LLB Answered is a comprehensive, first-class set of exam-focused study notes for the Undergraduate Law Degree. Please visit LLBanswered.com
MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2007 question paper 9084 LAW
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2007 question paper 9084 LAW 9084/03 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme is published as an
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2007 question paper 9084 LAW 9084/03 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme is published as an
CONTRACTS TOPIC OUTLINE1
 CONTRACTS TOPIC OUTLINE1 1. OFFER AND ACCEPTANCE a. offer defined b. preliminary negotiations c. advertisements d. unilateral offer e. who may accept an offer f. irrevocable offer g. material terms h.
CONTRACTS TOPIC OUTLINE1 1. OFFER AND ACCEPTANCE a. offer defined b. preliminary negotiations c. advertisements d. unilateral offer e. who may accept an offer f. irrevocable offer g. material terms h.
1.2 Explain the legal requirements for the formation of an enforceable contract. 1.3 Explain the factual indicators of the existence of agreement.
 Unit 2 Title: Contract Law Level: 3 Credit Value: 7 Learning outcomes The learner will: 1 Understand the concept of contract. 2 Understand the rules for establishing whether a valid offer and acceptance
Unit 2 Title: Contract Law Level: 3 Credit Value: 7 Learning outcomes The learner will: 1 Understand the concept of contract. 2 Understand the rules for establishing whether a valid offer and acceptance
Unconscionability in Canadian Contract Law
 Loyola Marymount University and Loyola Law School Digital Commons at Loyola Marymount University and Loyola Law School Loyola of Los Angeles International and Comparative Law Review Law Reviews 7-1-1992
Loyola Marymount University and Loyola Law School Digital Commons at Loyola Marymount University and Loyola Law School Loyola of Los Angeles International and Comparative Law Review Law Reviews 7-1-1992
Class B.Com. I Sem. (Hons.)
 SYLLABUS Class B.Com. I Sem. (Hons.) Subject Business Regulatory Framework UNIT I UNIT II UNIT III UNIT IV UNIT V Contract Act 1872 Definition nature of contract, offer and acceptances capacity of parties
SYLLABUS Class B.Com. I Sem. (Hons.) Subject Business Regulatory Framework UNIT I UNIT II UNIT III UNIT IV UNIT V Contract Act 1872 Definition nature of contract, offer and acceptances capacity of parties
Question If CapCo files a lawsuit against the Bears seeking damages for breach of contract, who is likely to prevail? Discuss.
 Question 2 CapCo sells baseball caps to youth leagues and recently approached two new teams, the Bears and the Lions. Uncertain how many caps the team would require, the Bears team manager signed a written
Question 2 CapCo sells baseball caps to youth leagues and recently approached two new teams, the Bears and the Lions. Uncertain how many caps the team would require, the Bears team manager signed a written
BAREXAMDOCTOR.COM UNLIMITED ESSAYS AND PTS ONLINE! ESSAY APPROACH. Bar Exam Doctor. CONTRACTS ESSAY
 ESSAY APPROACH www.barexamdoctor.com CONTRACTS ESSAY I. DOES THE UCC APPLY? a. The UCC governs all Ks for the sale of goods b. The UCC also has special rule governing transactions between merchants c.
ESSAY APPROACH www.barexamdoctor.com CONTRACTS ESSAY I. DOES THE UCC APPLY? a. The UCC governs all Ks for the sale of goods b. The UCC also has special rule governing transactions between merchants c.
An Introduction to the Law of CONTRACT STEPHEN GRAW
 An Introduction to the Law of CONTRACT by STEPHEN GRAW B.Com., LL.B. (Qld) Solicitor of the Supreme Court of Queensland Associate Professor of Business Law, James Cook University of North Queensland SECOND
An Introduction to the Law of CONTRACT by STEPHEN GRAW B.Com., LL.B. (Qld) Solicitor of the Supreme Court of Queensland Associate Professor of Business Law, James Cook University of North Queensland SECOND
Foundation Level LAW PRACTICE MANUAL
 Chapter 2:- Offer and Acceptance 2.1 Definition And Essential Elements Of A VALID OFFER 1. The term 'offer or proposal' in legal terms, is defined in (a) Section 2 (a) (b) Section 2 (b) (c) Section 2 (i)
Chapter 2:- Offer and Acceptance 2.1 Definition And Essential Elements Of A VALID OFFER 1. The term 'offer or proposal' in legal terms, is defined in (a) Section 2 (a) (b) Section 2 (b) (c) Section 2 (i)
QUESTION 1. Carl said, Let me think a moment.
 QUESTION 1 Zena placed an advertisement in a local newspaper: Wanted: Someone to clean my four-bedroom, four-bath house (2500 square feet) once a week for the next month; pay $35 per hour. No interview
QUESTION 1 Zena placed an advertisement in a local newspaper: Wanted: Someone to clean my four-bedroom, four-bath house (2500 square feet) once a week for the next month; pay $35 per hour. No interview
TITLE 7 CONTRACTS TABLE OF CONTENTS
 TITLE 7 CONTRACTS TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 7.01 General Provisions 7.0101 Definition 1 7.0102 Essential elements of a contract 1 7.0103 Law of place applied to contracts 1 7.0104 Time of performance 1
TITLE 7 CONTRACTS TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 7.01 General Provisions 7.0101 Definition 1 7.0102 Essential elements of a contract 1 7.0103 Law of place applied to contracts 1 7.0104 Time of performance 1
LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS JANUARY 2016
 Note to Candidates and Tutors: LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS JANUARY 2016 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students
Note to Candidates and Tutors: LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS JANUARY 2016 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students
CHAPTER 2 CONTRACT LAWS INDIAN CONTRACT ACT, A contract is an agreement made between two or more parties which the law will enforce.
 CHAPTER 2 CONTRACT LAWS INDIAN CONTRACT ACT, 1872 Definition of Contract A contract is an agreement made between two or more parties which the law will enforce. Sec 2(h) defines contract as an agreement
CHAPTER 2 CONTRACT LAWS INDIAN CONTRACT ACT, 1872 Definition of Contract A contract is an agreement made between two or more parties which the law will enforce. Sec 2(h) defines contract as an agreement
LAW5005: PRINCIPLES OF CONTRACT LAW B EXAM NOTES
 LAW5005: PRINCIPLES OF CONTRACT LAW B EXAM NOTES Table of Contents Overview of Contracts B... 1 Termination... 3 Express termination... 3 Termination for breach of contract... 3 Repudiation... 4 Unwillingness
LAW5005: PRINCIPLES OF CONTRACT LAW B EXAM NOTES Table of Contents Overview of Contracts B... 1 Termination... 3 Express termination... 3 Termination for breach of contract... 3 Repudiation... 4 Unwillingness
A breach of contract occurs where a party does not comply with one or more of the terms of contract, express or implied.
 CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG Breach and Remedy Refer to Richards, P. Law of Contract Chapters 16-18 Uff, J. Construction Law 9 th Edition Chapter 9 BREACH OF CONTRACT A breach of contract occurs where
CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG Breach and Remedy Refer to Richards, P. Law of Contract Chapters 16-18 Uff, J. Construction Law 9 th Edition Chapter 9 BREACH OF CONTRACT A breach of contract occurs where
Contract Law. 2. Contract formation: a) mutual assent: offer & acceptance b) consideration: need to have an exchange of something.
 Contract Law Jan 18th, 2012: 1. Sources of law: -statutory law: United Commercial Code, uniformed state law; (only for sales of goods, does not require parties to be merchants) -common law; -restatement:
Contract Law Jan 18th, 2012: 1. Sources of law: -statutory law: United Commercial Code, uniformed state law; (only for sales of goods, does not require parties to be merchants) -common law; -restatement:
Creation of the K a. Statute of Frauds land part performance one year debt 500 b. Offer master of the offer revoke mailbox rule absence of terms
 Contracts outline I. Creation of the K a. Statute of Frauds requires that a sufficient writing, signed by the party to be charged be in existence for the following subject-matter (doesn t apply to restitution
Contracts outline I. Creation of the K a. Statute of Frauds requires that a sufficient writing, signed by the party to be charged be in existence for the following subject-matter (doesn t apply to restitution
California Bar Examination
 California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question PC manufactures computers. Mart
California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question PC manufactures computers. Mart
HENTHORN v FRASER [1892] 2 Ch. 27 (C.A. 1892)
![HENTHORN v FRASER [1892] 2 Ch. 27 (C.A. 1892) HENTHORN v FRASER [1892] 2 Ch. 27 (C.A. 1892)](/thumbs/74/70566874.jpg) HENTHORN v FRASER [1892] 2 Ch. 27 (C.A. 1892) In 1891 the Plaintiff was desirous of purchasing from the Huskisson Benefit Building Society certain houses in Flamank Street, Birkenhead. In May he, at the
HENTHORN v FRASER [1892] 2 Ch. 27 (C.A. 1892) In 1891 the Plaintiff was desirous of purchasing from the Huskisson Benefit Building Society certain houses in Flamank Street, Birkenhead. In May he, at the
Contract Law. Contract law. Kacper Szkalej 1. Structure. Law and regulation. Media Law, KTH
 Contract Law Media Law, KTH Kacper Szkalej, LL.M. kacper.szkalej@jur.uu.se Structure Law and regulation of society Basics of contract law Functions Creation Freedom of contract Privity of contract Contract
Contract Law Media Law, KTH Kacper Szkalej, LL.M. kacper.szkalej@jur.uu.se Structure Law and regulation of society Basics of contract law Functions Creation Freedom of contract Privity of contract Contract
BUSINESS LAW GUIDEBOOK
 BUSINESS LAW GUIDEBOOK SECOND EDITION CHARLES YC CHEW CHAPTER 4: CONTRACT: TERMS AND REMEDIES FOR BREACH TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE 1. The terms of a contract may be either express or implied. Explain what is
BUSINESS LAW GUIDEBOOK SECOND EDITION CHARLES YC CHEW CHAPTER 4: CONTRACT: TERMS AND REMEDIES FOR BREACH TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE 1. The terms of a contract may be either express or implied. Explain what is
Is there really any question about the test for part performance in Alberta? by Jonnette Watson Hamilton
 Is there really any question about the test for part performance in Alberta? by Jonnette Watson Hamilton G 400 Holdings Ltd. v. Yeoman Development Company Limited, 2008 ABQB 667 http://www.albertacourts.ab.ca/jdb%5c2003-%5cqb%5ccivil%5c2008%5c2008abqb0667.pdf
Is there really any question about the test for part performance in Alberta? by Jonnette Watson Hamilton G 400 Holdings Ltd. v. Yeoman Development Company Limited, 2008 ABQB 667 http://www.albertacourts.ab.ca/jdb%5c2003-%5cqb%5ccivil%5c2008%5c2008abqb0667.pdf
Waiver, Estoppel and Election in the context of adjudication applications
 1 Waiver, Estoppel and Election in the context of adjudication applications Adjudication Forum 13 November 2012 Max Tonkin The Pareto Principal Italian economist Vilfredo Pareto observed in 1906 that 80%
1 Waiver, Estoppel and Election in the context of adjudication applications Adjudication Forum 13 November 2012 Max Tonkin The Pareto Principal Italian economist Vilfredo Pareto observed in 1906 that 80%
Spring 2018 Business Law Fundamentals O'Hara 2018 D
 Page 1 of 7 as your signature PRINT your name EXAM #2 Business Law Fundamentals LAWS 3930 sections -001, -002-003 Chapters 1-4, 24, 6, 7, 9-19 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Affix your printed name as your signature
Page 1 of 7 as your signature PRINT your name EXAM #2 Business Law Fundamentals LAWS 3930 sections -001, -002-003 Chapters 1-4, 24, 6, 7, 9-19 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Affix your printed name as your signature
DOCTRINE OF ULTRA VIRES-EFFECTS AND EXCEPTIONS
 CONCEPT DOCTRINE OF ULTRA VIRES-EFFECTS AND EXCEPTIONS The object clause of the Memorandum of the company contains the object for which the company is formed. An act of the company must not be beyond the
CONCEPT DOCTRINE OF ULTRA VIRES-EFFECTS AND EXCEPTIONS The object clause of the Memorandum of the company contains the object for which the company is formed. An act of the company must not be beyond the
LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS - JANUARY 2014
 Note to Candidates and Tutors: LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS - JANUARY 2014 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students
Note to Candidates and Tutors: LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS - JANUARY 2014 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students
