Business Law Fundamentals COMPREHENSIVE FINAL Exam Page 1 of 20
|
|
|
- Shawn Kennedy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Business Law Fundamentals COMPREHENSIVE FINAL Exam Page 1 of 20 PRINT name as your signature 1. This Final Exam must be completed within allocated time (i.e., 120 minutes). Audible time warnings of 2 minutes, 1 minute, and 30 seconds will be given. 2. It is a closed book and open mind exam. It is a closed mouth exam. All team work is academic dishonesty. Any electronic device of any kind for any purpose is academic dishonesty. 3. Recall the material dference between i.e. (that is) versus e.g. (for example). 4. If you finish early, to not disturb others, remain in your seat for 60 minutes. When you are done, turn over your exam papers, STAY IN YOUR SEAT until invited to depart. Students taking their Final Exam on Tuesday shall turn in both [1] white copy of exam; and [2] completed blue answer sheet. Students taking their Final Exam on Wednesday shall turn in the completed blue answer sheet, and will receive in exchange an answer key; you may keep your white copy exam. Students taking their Final Exam on Tuesday may, after 7:00 PM Wednesday, retrieve their white copy exam and an answer key from Professor O'Hara in the MH 321 exam room. 5. This Final Exam is worth 500 points of a course total of 1,000 points. There are 130 questions graded as there only are 125. Accordingly, each correct answer on Final Exam is worth 4.0 course points. 6. All appeals of this exam s questions must be: [6A] typed; [6B] signed by the student in three ways, typed name, handwritten signature, and typed university identication number; [6C] immediately following the signature, list in sequence, solely by number, each of the questions being appealed; [6D] since this exam's design (i.e., 130 as 125) presumes five errors, harmless error exists with five flawed questions; thus, an appeal must appeal SIX or more questions and must prove at least SIX questions to be objectively ambiguous for there to be one non-harmless error; [6E] after the [6C] list, argue each question, one at a time; [6F] at the beginning of each question s [6E] appeal, identy at least two reasonable meanings that the question could have had; [6G] in each [6E] appeal, argue why one or more of the [6F] identied reasonable meanings is as appropriate or is more appropriate than the meaning used for the answer key answer; and [6H] the signed appeal must be personally handed to the instructor (or to the instructor's suite secretary in MH 228) no later than 3:59 PM (i.e., minute before 4PM) Friday, May 9th, time is of the essence. Course grades will be posted following resolution of all appeals of the grading of this Final Exam.
2 Business Law Fundamentals COMPREHENSIVE FINAL Exam Page 2 of 20 NOTES: A. Recall the material dference between i.e. (that is) versus e.g. (for example). B. Use bubble A for TRUE and use bubble B for FALSE. C. If a question contains a number (e.g., Amendment IX), then the truth or falsity of that question never depends upon that number. This is not a test of trivia recall. This test is an objective demonstration of your subjective knowledge. D. For clarity in distinguishing a "principal" from a principal as well as distinguishing an "agent" from an agent, quote marks will be used for the generic words "principal" and "agent" and no quote marks will be used for the specic words principal and agent. That is, "principal" and "agent" refer to all three relationships (i.e., principal and agent; and principal and independent contractor; and employer and employee). E. For clarity in distinguishing enforceable from unenforceable transactions, the word contract is not in quotes for an enforceable contract (e.g., a voidable contract elected to be enforced), whereas the word "contract" is in quotes for a transaction that is not an enforceable contract (e.g., a voidable contract that has been voided and now is a void "contract"). F. The quote marks described in D. and in E. may be the very essence of the question's truth or falsity. For example, it is true to say "An employee is one of the three relationships in "agent"."; and it is false to say "An employee is an agent.". G. Dferent students have dferent versions of this Final Exam. For a student's blue bubble sheet to be correctly scored requires that student to record that student's version of this Final Exam. AT THE BOTTOM RIGHT OF THIS PAGE, WHAT LETTER FOLLOWS THE YEAR 2014? RECORD THAT LETTER AS YOUR ANSWER TO QUESTION 131. Failure to correctly record your version shall earn you a score of zero on Final Exam.
3 Business Law Fundamentals COMPREHENSIVE FINAL Exam Page 3 of 20 QUESTIONS: 1. T F The Law has two subsets: one is law and the other is equity. Both The Law's subset law and its subset equity tend to assign liability to those persons whose actions both are knowing and are voluntary. Both The Law's subset law and subset equity favor using the objective over using the subjective. 2. T F Objective either is express or is implied. Express is in written words. Implied is in acts, words, and/or circumstances. Thus, everything that is implied is express. 3 T F Knowing that is objective comes in two forms: receipt of notice and reason to know. 4. T F The Law recognizes multiple forms of person. Typically, a natural person has more rights than a mere legal person. Most often, however, The Law uses neither a natural person nor a legal person for judging behavior for the purposes of assigning liability. Instead, The Law tends to assign liability to those persons whose actions are less than the reasonably expected actions of the Reasonable Person. 5. T F The separation of powers between the three branches of government (i.e., legislative v. executive v. judicial) in the USA Constitution is implied, but is express in Nebraska's Constitution. 6. T F Judicial review is at its strongest when the court is using substantive due process to actively protect a citizen's fundamental rights from a government's infringement. 7. T F Procedural due process requires both notice and hearing, both proportional to the interests involved. 8. T F The federal government's Commerce Clause expands in the federal government's power beyond its Police Power. 9. T F All authoritative precedence is binding. All non-binding precedence merely is persuasive.
4 Business Law Fundamentals COMPREHENSIVE FINAL Exam Page 4 of T F A plaintf has standing to sue the plaintf suffers an injury in fact and the plaintf is within the zone of protected interests. 11. T F The defendant's answer must include the defendant's alleging a cause of action (e.g., defamation); alleging the court's jurisdiction; and praying for a remedy the court has the power to grant. 12. T F The appellate court will affirm the trial court unless the trial court makes a material error (e.g., any error of law). 13. T F The alternative dispute resolution (ADR) techniques of negotiation, facilitation, mediation, and arbitration each always involves a third party neutral. To be constitutional, that ADR third party neutral must be no less neutral than is a trial court judge. 14. T F The federal government has no power unless the USA Constitution grants that power to the federal government. 15. T F Preemption is favored, and shall be implemented either: [i] Congress' intent is express and national interests outweigh State interests; or [ii] Congress' intent is implied and a need for unormity. 16. T F The Police Power is a power of every USA State government to regulate health, safety, morals, and general welfare. 17. T F Powers within the separation of powers are routinely evaluated using the concepts of core, penumbra, and emanations. An express grant of power to a government is one type of core. An example of an emanation is the authority to do indirectly that which is not expressly prohibited.
5 Business Law Fundamentals COMPREHENSIVE FINAL Exam Page 5 of T F Domestically, Congress has the authority to regulate commerce within the several States (i.e., close and substantial affect on commerce between the several States). 19. T F The federal Commerce Clause power has a core, penumbra, and emanations. The core of the Commerce Clause is transportation (e.g., internet). 20. T F Each USA State has all powers of any sovereign nation unless, in the USA Constitution, the USA States gave that power to the federal government or the USA States took that power from the USA States; or the People of that State took that power away from that State in that State's own Constitution. 21. T F All unfunded mandates in the form of regulation are unconstitutional because to be constitutional all governmental regulation of business must be accomplished using due process of law, must be for a public purpose, and the government must pay the regulated firm just compensation for the costs caused by that regulation. 22. T F The Article IV section 1 Full Faith and Credit clause of the USA Constitution is an express commitment of each USA State government to grant comity to all sister USA State governments. 23. T F Amendment I of the USA Constitution expressly protects the right of free speech. However, all USA governments may reasonably regulate speech. All reasonable regulation of the time, place, manner, and content of speech is constitutional. 24. T F All USA courts strongly prefer constraining their decisions to procedural due process and avoiding making decisions using substantive due process. 25. T F A fundamental federal constitutional right must be expressly listed in the Bill of Rights for a mere legal person; but may be implied for a natural person.
6 Business Law Fundamentals COMPREHENSIVE FINAL Exam Page 6 of T F Courts are far more likely to provide substantive due process when a constitutional right is a fundamental constitutional right. 27. T F Every government has sovereign immunity (until it surrenders it). However, sovereign immunity only exists for that government's Acts of State. 28. T F All fault-based torts are civil 1 wrongs. 29. T F All torts have the same five elements: [i] defendant owes a duty of care to the plaintf; [ii] defendant breaches that duty of care; [iii] plaintf suffers an injury in fact resulting in damages; [iv] defendant's breach is the proximate cause of the damages; and [v] the defendant has no defenses. 30. T F Common law fraud exists the defendant knowingly misrepresents a material fact thereby inducing the plaintf's reliance and proximately causing the plaintf's damages. 31. T F Legally, proximate cause is a fraction of actual cause. 32. T F The defendant has the tort defense of Assumption of the Risk the plaintf knowingly and voluntarily exposes the plaintf to the risk of the defendant's breach of the tort duty. 33 T F An item is material changing that item would change the mind of the Reasonable Person. Parties, time, consideration, and subject matter each is for common law contract is a material term. 1 Civil law as contrasted with criminal law; not civil law as contrasted with common law.
7 Business Law Fundamentals COMPREHENSIVE FINAL Exam Page 7 of T F Each USA State's legislature has broad powers to classy persons as similarly situated and as to similar treatment. The State legislature is at the core of its power when regulating social and economic issues. The State legislature is in the penumbra of its power when regulating suspect classes (e.g., gender, legitimacy, or handicap). The State legislature is in the emanations of its power when regulating topics over which it has no direct authority (i.e., race, national origin, or citizenship). 35. T F Because the specic controls the general, the capacity of a voluntary intoxicated person is greater than the capacity of an adjudicated insane person. 36. T F Preemption is not favored, but, it will be allowed there is Congressional finding either that national interests outweigh State interests or that there is a need for unormity. 37. T F The Police Power is a power of every USA State government to regulate for the People's health, safety, morals, and general welfare. 38. T F All fundamental federal constitutional rights of a legal person are expressly listed in the Bill of Rights or are implied from the Bill of Rights. 39. T F Negotiation is the alternative dispute resolution (ADR) technique that requires participation of a court appointed third party neutral. 40. T F USA Constitution Amendment IX addresses sovereign immunity of the USA State governments relative to the USA federal government. Per Amendment IX the USA States have sovereign immunity as against federal legislative power, executive power, and judicial power. 41. T F The Law has two subsets: one is law and the other is equity. To exit The Law's subset law and enter The Law's subset equity it is necessary to answer "No." to the question "Do you have an adequate remedy at law?".
8 Business Law Fundamentals COMPREHENSIVE FINAL Exam Page 8 of T F An "agent" acts instead of and on behalf of the "agent's" "principal" when that "agent" acts. RECALL exam instruction F. 43. T F Only the legislature has the authority to create a crime. The legislature must clearly define the crime's elements. The criminal statute will be void for vagueness either the crime's bad deed (i.e., actus rea) or bad thought (i.e., mens rea) is not sufficiently clear that the Reasonable Person knows what is prohibited. 44. T F Knowing can be subjective or can be objective. Capacity is an objective measure one's ability to grasp the natural consequences of one's actions. The Law requires more capacity for a will than for a crime. 45. T F Because contract relationships are specic while tort relationships are general, tort damages are mere economic losses in the context of contracts. 46. T F If both parties have capacity and they reach an agreement with genuineness of assent to achieve a legal subject matter, and that agreement is supported by consideration then the parties have a contract. 47. T F A quasi "contract" is enforceable in The Law's subset law. 48. T F A unilateral contract upon its formation is executed on one side. A bilateral contract upon its formation is executory on both sides. 49. T F The Mirror Image Rule requires the offeree's acceptance of the offeror's offer to be an unequivocal "Yes.". 50. T F The offeree, not the offeror, holds and exercises the power to create a contract. This is the prime motive for the Mail Box Rule.
9 Business Law Fundamentals COMPREHENSIVE FINAL Exam Page 9 of T F Contract consideration objectively manests each party's intent to be bound. To be consideration it must be a bargained for exchange of legally sufficient value. 52. T F The common law assumes the parties do not want a contract. Accordingly, the common law requires a modication, a novation, as well as an accord and satisfaction each to satisfy all of the requirements of a new contract. But, the law goes further to require the consideration supporting each of those three be a good faith dispute. 53. T F To be a common law contract, the parties' agreement must be sufficiently definite that the court can enforce the parties objective agreement. Quantity must be specied, both for a common law contract and a UCC Article 2 Sale of Goods contract. Both for a common law output contract and a requirements contract to achieve the required quantity specicity the parties' use the production processes of one of the parties. 54. T F The Law's subset law typically enforces freedom from contract while The Law's subset equity often provides freedom of contract. 55. T F If a court of law opens the door to the court of equity, then, depending upon the jurisdiction, the court of equity either will reform the contract or void the "contract". 56. T F Liquidated, in the law, means made certain. Liquidated damages are those damages made certain by a material breach as contrasted with the far less certain damages of substantial performance. 57. T F Promissory estopple can be either an equitable or a legal remedy. To be a legal remedy the promissory estopple requires both consideration and capacity. 58. T F The offeror may revoke the offer. The offeree may reject the offer.
10 Business Law Fundamentals COMPREHENSIVE FINAL Exam Page 10 of T F The Law's subset law requires all contracts be for a legal subject matter. As a subject matter of a contract insurance often is legal subject matter and gambling rarely is legal subject matter. 60. T F Nebraska voids a covenant not to compete unless that covenant both is a contract whose terms are limited both to reasonable time and reasonable area and that contract's consideration is good will. 61. T F A defendant commits common law fraud the defendant knowingly and intentionally omits a material fact that induces the plaintf's reliance and proximately causes the plaintf's injury. 62. T F A unilateral mistake exists non-mistaking party knows that the mistaking party is making a material mistake of fact. 63. T F A mutual mistake exists both parties suffer from the same material mistake of fact. 64. T F A term is material changing that term would alter the mind of the Reasonable Person. 65. T F Duress is a legally objectionable amount of force that prevents an agreement from having genuineness (a.k.a., reality) of assent. Predatory economic duress involves a force created by the wrongful party. Privileged economic duress involves a force used by, but not created by, the wrongful party. 66. Half way through the final. Time for a free question. Answer E. 67. T F The Parole Evidence Rule prohibits all oral testimony on all written contracts.
11 Business Law Fundamentals COMPREHENSIVE FINAL Exam Page 11 of T F The Statute of Frauds governs the form of a contract. For example, the Statute of Frauds requires all of the contract terms are written, then the contract must be signed by both parties. 69. T F The Statute of Frauds governs contracts in consideration of marriage. 70. T F The Equal Dignity Rule requires the "principal's" authorization of the "agent" satisfy the requirements of the Statute of Frauds that "agent" is to execute a contract governed by the Statute of Frauds. 71. T F A signature is any mark with the current intent to authenticate the document. A guarantor owes nothing unless and until the co-signer breaches. 72. T F A competent businessperson making a signicant purchase of goods always includes both an incorporation clause for the seller's marketing materials as well as a merger clause for the parties' agreement. 73. T F The old common law governing assignments and delegations prohibited the parties from granting any assignment of rights or to make any delegation of duties. 74. T F The new common law governing assignments and delegations focuses upon the parties' reasonable expectations. The new common law of contracts, accordingly, prohibits all assignments of rights and all delegations of duties that materially alter either party's reasonable expectations. 75. T F An assignment of all rights is enforceable as an assignment of all rights coupled with a delegation of all duties made by and to a legal person (e.g., a corporation); but is not enforceable made by and to a natural person.
12 Business Law Fundamentals COMPREHENSIVE FINAL Exam Page 12 of T F The only third party that can vest is an intended creditor. Additionally, only the original parties to a contract intended for that creditor third party to be able to vest may that intended creditor third party vest. 77. T F Ready, willing, and able is a condition concurrent. 78. T F Substantial performance, at the election of the non-breaching party, either discharges the duty to perform the contract or creates the obligation of compensatory damages. 79. T F A party who delivers an anticipatory repudiation to the other contracting party creates in the receiving party the duty to mitigate damages. 80. T F The common law provides for discharge of a contract by operation of law when performance becomes a commercial impossibility (e.g., a ten fold change in market price). The legislature, by statutory law, has changed that common law rule to discharge due to commercial impracticability (e.g., a three fold change in market price). 81. T F A Force Majeure is a force not controlled by either party that imposes a material change in circumstances on the parties, and thus discharges their contractual duties. The parties may by contract expand and define the set such forces. 82. T F Both tort law and contract law award compensatory damages. In both tort law and contract law compensatory damages are to make the plaintf whole. However, because the specic controls the general, in contract law what would be tort damages are a mere economic loss. In contract law compensatory damages are measured by the dference between the contract price and the market price for substitute performance (i.e., loss of the benefit of the bargain).
13 Business Law Fundamentals COMPREHENSIVE FINAL Exam Page 13 of T F In common law of contracts all consequential damages merely are incidental damages: and thus a part of compensatory damages. 84. T F In the common law of contracts lost profits are part of consequential damages. 85. T F Punitive damages are tort damages. However, a bad faith breach of an employment contract or a bad faith breach of an insurance contract will expose the breaching defendant to being ordered to pay punitive damages. 86. T F The breaching party has the duty to mitigate damages. 87. T F A party who receives performance that is a breach may waive the breach. Silence in reply to a breach can be an acceptance. 88. T F The Unorm Commercial Code Article 2, Sale of Goods is a law of the individual USA State governments that governs the sale of goods (i.e., tangible and movable personal property). As long as the predominate nature of the transaction is a sale of goods any amount of services may be included in that contract. 89. T F The UCC Art. 2 reverses many of the assumptions that drive the common law of contracts. For example, by imposing a non-disclaimable obligation of good faith on the parties the UCC Art. 2 can simultaneously allow open terms (instead of using the Mirror Image Rule) while assuming that the parties want a contract. 90. T F Both a consumer (i.e., legal person buying for personal or household use) and a merchant (e.g., deals in goods of that kind) are bound by identically phrased, but materially dferent in effect, UCC Art. 2 obligations of good faith (i.e., honesty in fact and commercially reasonable).
14 Business Law Fundamentals COMPREHENSIVE FINAL Exam Page 14 of T F The UCC Art. 2 shts the focus from title to identication. The goods are identied when the goods are in existence. 92. T F Upon the identication of the goods the buyer has an insurable interest (i.e., the risk of loss). 93. T F A UCC Art. 2 sale requires delivery of the goods. The UCC species that physical delivery will occur at the seller's front door the buyer is a consumer; and at seller's back door the buyer is a merchant. 94. T F The parties to a UCC Art. 2 sale of goods contract may disclaim all provisions of the UCC Art. 2 except the obligation of good faith. 95. T F In a transportation contract the parties choose physical delivery not at the seller's place of business, and the shipper acts as an agent of one of the parties. A shipment contract has the shipper as the agent of the buyer. 96. T F The entrustment rule empowers a merchant with void title to transfer good title. 97. T F A perfect tender will achieve a seller's cure. 98. T F The buyer's exercise of the buyer's Right of Assurance is a condition precedent to a non-breaching buyer's right to cover. 99. T F Only under the UCC Art. 2 does the mere act offering for sale create implied warranties of good title, no liens, and no infringements T F A UCC Art. 2 express warranty exists the seller makes an affirmation of fact that is the basis of the bargain.
15 Business Law Fundamentals COMPREHENSIVE FINAL Exam Page 15 of T F Both the common law of contracts and the UCC Art. 2 recognize that a statement of value ordinarily is puffery rather than part of an express warranty T F Both the UCC Art. 2 implied warranty of merchantability and the UCC Art. 2 implied warranty of fitness for a particular purpose require the seller to know that the buyer is relying on the seller and, at that quality level, the goods will pass without objection in the market T F The UCC Art. 2 creates an election of remedies with respect to warranties that is similar to the election of remedies for pleading in the alternative and to the election of remedies for responding to an anticipatory breach T F A UCC Art. 2 seller may disclaim liability for personal injury from consumer goods only the disclaimer is both express and conspicuous T F The federal Magnuson-Moss Warranty Act requires all sellers of consumer products in interstate commerce to grant a written warranty, but permits that warranty to be either full or limited T F The Restatement of Law, Torts, section 402A defines the public policy choice of the USA States that their tort law impose strict liability on many manufacturers seeking profit from retail sales of consumer products. Thus, consumer injuries are a cost of doing business, not profit.
16 Business Law Fundamentals COMPREHENSIVE FINAL Exam Page 16 of T F The old common law of product liability had very limited manufacturer liability because most products were simple and most risk was under the control of the buyer. The new common law of product liability has greatly expanded manufacturer liability because today many products tend to be complex and most risk is under the control of the seller (e.g., design defects, manufacturing defects, labeling defects) T F The U.N. Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods (CISG) reflects that most of the world uses civil law instead of common law. CISG does, however, follow the UCC Art. 2 rules regarding the Statute of Frauds T F As graphed, both supply and demand solely are functions of quantity and price. As graphed, the non-price determinants are held constant even though, obviously, the non-price determinants very frequently change. This is an example of attempting to tell a moral lie T F Capitalism is an example of making an ethical choice based on the criteria of the ends justy the means. The ends of Capitalism are its functions (e.g., embody self interest) whereas the means of Capitalism are its elements (e.g., private property).
17 Business Law Fundamentals COMPREHENSIVE FINAL Exam Page 17 of T F All markets always generate incorrect results because all markets always contain erroneous supply curves (i.e., spillover costs) and erroneous demand curves (i.e., spillover benefits). Spillovers (a.k.a., externalities) always are present because the market supply and the market demand curves only include market participants who are both willing and able. However, just because it is broken does not mean you can fix it T F Accordingly to economic theory all firms in any market are at the Minimum Efficient Size (MES). Accordingly, it is not surprising that a firm might be a natural monopolist T F As graphed, the market is competitive (i.e., a "large number of buyers, a "large" number of sellers, and all with free entry and free exit), then the industry price is set by the industry's equilibrium; which in turn prompts each competitive firm's demand curve to be flat and thus its demand curve equals its marginal revenue (MR) curve so that the competitive firm's equilibrium exists at its own profit maximizing price and quantity T F A monopolist sets price. Thus, a monopoly is bad because the consumers must pay more and get less than what consumers would have obtained under competition T F The Sherman Act makes it a felony to destroy competition. The court's use the Rule of Reason to interpret that federal statute. Under the Rule of Reason any restraint of trade is lawful as long as that restraint is proportional to the restraining firm's(s') legitimate business interest.
18 Business Law Fundamentals COMPREHENSIVE FINAL Exam Page 18 of T F The proportionality of a restraint of trade is measured across four dimensions: purpose, intent, effect on the market, and power conferred T F If experience with a restraint indicates that a restraint consistently is used in a disproportionate manner, then the courts use the Per Se Unreasonable standard. Four restraints are evaluated using the Per Se Unreasonable standard: price fixing, divisions of territories or customers; group boycotts; and tying (i.e., transfer of monopoly power) T F Application of the Sherman Act's criminal provisions to specic, complex business fact patterns prompted the courts to often rule that the Sherman Act was void for vagueness. In response, Congress adopted some subsequent legislation (e.g., Clayton Act). In those subsequent statutes, Congress specically made unlawful actions that the general Sherman Act could not (e.g., interlocking directorships) T F A defendant in an antitrust lawsuit may be sued either or both criminally or civilly. When sued in civil court the successful plaintf is awarded treble (i.e., times three) damages. This is an example of the government facilitating competition by setting transaction costs T F Noerr-Pennington Doctrine enforces the right to free speech. Because of the legal person's free speech rights it is not possible to violate the antitrust laws when petitioning government in any branch of government T F For an insurance contract all risk is material. Because the essence of insurance is to pool identical risks for the purpose a average pricing of that pooled risk, all insurance contracts must be adhesion contracts. However, unlike most adhesion contracts all ambiguities in all insurance contracts always are interpreted against the insurer.
19 Business Law Fundamentals COMPREHENSIVE FINAL Exam Page 19 of T F To be legal subject matter the insured must have an insurable interest. Accordingly, for all insurance contracts the insured must have the insurable interest at the time of contract T F InsurERs seek profit via inverse adverse selection. This creates in the insurer a strong incentive to promptly discover insured errors regarding the insured's disclosure of risk factors. Legislatures routinely create incontestability periods after which the insurer's discovery of the insured's error does not affect the enforceability of the insurance contract. Thus, the incontestability clause acts as a statute of limitations T F The moral hazard exists when those most likely to need the insurance coverage also are the most likely to purchase insurance coverage (e.g., those with pre-existing medical condition buy health insurance). In reaction to the moral hazard, all jurisdictions that regulate insurance require the policy to require the insured self-insure a deductible for the first dollars of loss as well as require the insured to self-insure a co-pay for a percentage of the loss above the policy limits T F An insurance company may issue a binder. A binder is a temporary insurance contract that provides coverage between the time of issuance of the binder and the time of issuance of the formal insurance contract. Either an insurance agent or an insurance broker may obtain a binder. A not infrequent set of errors are for no binder to be obtained or for the wrong binder to be obtained, both of which materially and adversely alter the insured's coverage. The principal of an agent bears the burden of the agent's error. An insurance agent is an agent of the insured. An insurance broker is an agent of the insurer T F Legal capacity is the ability to grasp the natural consequences of one's actions. For a will, the required capacity is knowledge of one's property and the natural objects of one's bounty. Because of the need to know one's property, the capacity required for a will is great.
20 Business Law Fundamentals COMPREHENSIVE FINAL Exam Page 20 of T F A will is a creature of statute. Thus, the requirements for a will vary by jurisdiction. However, all jurisdictions require some features of a will. For example, all jurisdictions require witnesses who witness the testator's capacity and signature T F The scope of authority of some "agents" is very broad. A power of attorney is a broad grant of authority for the agent to act instead of and on behalf of the principal. Some powers of attorney are for financial matters; some are for medical decisions (e.g., when under general anesthesia). A living will can be, but need not be, in the form of a power of attorney. A living will is a declaration of that person's current intent for how to handle that person's end of le decisions when at that future time that person lacks the capacity to communicate that person's then current intent T F Like a bailment, a trust is a transfer of possession (i.e., from the grantor to the trustee) without the transfer of ownership. The trustee holds the corpus of the trust so as to provide some benefit of the beneficiary of the trust T F In a trust the grantor owes a fiduciary's duty of utmost good faith to the beneficiary of the trust VERSION E.
Business Law Fundamentals Exam #1 Page 1 of 7
 Business Law Fundamentals Exam #1 Page 1 of 7 PRINT name as your signature 1. This Exam #1 must be completed within the allocated time (i.e., 75 minutes). Audible time warnings of 2 minutes, 1 minute,
Business Law Fundamentals Exam #1 Page 1 of 7 PRINT name as your signature 1. This Exam #1 must be completed within the allocated time (i.e., 75 minutes). Audible time warnings of 2 minutes, 1 minute,
Spring 2018 Business Law Fundamentals O'Hara 2018 D
 Page 1 of 7 as your signature PRINT your name EXAM #2 Business Law Fundamentals LAWS 3930 sections -001, -002-003 Chapters 1-4, 24, 6, 7, 9-19 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Affix your printed name as your signature
Page 1 of 7 as your signature PRINT your name EXAM #2 Business Law Fundamentals LAWS 3930 sections -001, -002-003 Chapters 1-4, 24, 6, 7, 9-19 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Affix your printed name as your signature
NEGATIVE TEN COURSE POINTS
 Page 1 of 9 as your signature PRINT your name comprehensive EXAM #3 Business Law Fundamentals LAWS 3930 sections -001, -002-003 Chapters 1-4, 24, 6, 7, 9, 10 through 23, 43, 44, 46, 50, & 51 INSTRUCTIONS:
Page 1 of 9 as your signature PRINT your name comprehensive EXAM #3 Business Law Fundamentals LAWS 3930 sections -001, -002-003 Chapters 1-4, 24, 6, 7, 9, 10 through 23, 43, 44, 46, 50, & 51 INSTRUCTIONS:
Page 1 of 7. Fall 2015 Business Law Fundamentals O'Hara 2015 E
 Page 1 of 7 print name as your signature EXAM #2 Business Law Fundamentals LAWS 3930 sections -001-003 Chapters 1-4, 24, 6, 7, 9-18 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Affix your printed name as your signature in the space
Page 1 of 7 print name as your signature EXAM #2 Business Law Fundamentals LAWS 3930 sections -001-003 Chapters 1-4, 24, 6, 7, 9-18 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Affix your printed name as your signature in the space
on your blue computer graded bubble sheet in the appropriate location.
 as your signature PRINT your name EXAM #1 Business Law Fundamentals LAWS 3930 sections -001, -002 and -003 Chapters 1-4, 24, 6, 7, and 9 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Affix your printed name as your signature in the
as your signature PRINT your name EXAM #1 Business Law Fundamentals LAWS 3930 sections -001, -002 and -003 Chapters 1-4, 24, 6, 7, and 9 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Affix your printed name as your signature in the
Legal & Ethical Applications: Exam #1: Review LAWS 3930 & FoE 1, 3, 4, 9, and 11 & Microecon. & Chapters 5, Page 1 of 8
 Review LAWS 3930 & FoE 1, 3, 4, 9, and 11 & Microecon. & Chapters 5, Page 1 of 8 print name on the line above as your signature INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This Exam #1 must be completed within the allocated time
Review LAWS 3930 & FoE 1, 3, 4, 9, and 11 & Microecon. & Chapters 5, Page 1 of 8 print name on the line above as your signature INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This Exam #1 must be completed within the allocated time
Exam #2 LAWS 3930 Page 1 of 6
 Exam #2 LAWS 3930 Page 1 of 6 print name on the line above as your signature INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This Exam #2 must be completed within the allocated time (i.e., 20 minutes). The start time the end time will
Exam #2 LAWS 3930 Page 1 of 6 print name on the line above as your signature INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This Exam #2 must be completed within the allocated time (i.e., 20 minutes). The start time the end time will
CONTRACTS. A contract is a legally enforceable agreement between two or more parties whereby they make the future more predictable.
 CONTRACTS LESE Spring 2002 O'Hara 1 A contract is a legally enforceable agreement between two or more parties whereby they make the future more predictable. Contracts are in addition to the preexisting,
CONTRACTS LESE Spring 2002 O'Hara 1 A contract is a legally enforceable agreement between two or more parties whereby they make the future more predictable. Contracts are in addition to the preexisting,
 1 of 5 8/27/2014 2:11 PM Units: Teacher: LawandJustice, CORE Course: LawandJustice Year: 2012-13 Constitutional Law and Justice process of ethical decision-making and how does this process relate to law?
1 of 5 8/27/2014 2:11 PM Units: Teacher: LawandJustice, CORE Course: LawandJustice Year: 2012-13 Constitutional Law and Justice process of ethical decision-making and how does this process relate to law?
A. SOURCES OF THE LAW
 COURSE: Business Law GRADE(S): 9-12 UNIT: Basics of Law NATIONAL STANDARDS Achievement Standard: Analyze the relationship between ethics and the law and describe sources of the law, the structure of the
COURSE: Business Law GRADE(S): 9-12 UNIT: Basics of Law NATIONAL STANDARDS Achievement Standard: Analyze the relationship between ethics and the law and describe sources of the law, the structure of the
QUESTION What contract rights and remedies, if any, does Olivia have against Juan? Discuss.
 QUESTION 1 Olivia is a florist who specializes in roses. She has a five-year written contract with Juan to sell him as many roses as he needs for his wedding chapel. Over the past three years, Olivia sold
QUESTION 1 Olivia is a florist who specializes in roses. She has a five-year written contract with Juan to sell him as many roses as he needs for his wedding chapel. Over the past three years, Olivia sold
BAREXAMDOCTOR.COM UNLIMITED ESSAYS AND PTS ONLINE! ESSAY APPROACH. Bar Exam Doctor. CONTRACTS ESSAY
 ESSAY APPROACH www.barexamdoctor.com CONTRACTS ESSAY I. DOES THE UCC APPLY? a. The UCC governs all Ks for the sale of goods b. The UCC also has special rule governing transactions between merchants c.
ESSAY APPROACH www.barexamdoctor.com CONTRACTS ESSAY I. DOES THE UCC APPLY? a. The UCC governs all Ks for the sale of goods b. The UCC also has special rule governing transactions between merchants c.
Course Outline Credits Class Hours Laboratory Hours
 1 Mercer County Community College Course Outline BUS 107 Course Number Business Law I Course Title 3 3 0 Credits Class Hours Laboratory Hours Online Alternate Delivery Method Texts: Title: Introduction
1 Mercer County Community College Course Outline BUS 107 Course Number Business Law I Course Title 3 3 0 Credits Class Hours Laboratory Hours Online Alternate Delivery Method Texts: Title: Introduction
Simple. CONTRACTS & UCC Outline. NINETY PERCENT of the LAW in NINETY PAGES. Tim Tyler, Ph.D., Attorney at Law
 NAILING THE BAR Simple CONTRACTS & UCC Outline Tim Tyler, Ph.D., Attorney at Law NINETY PERCENT of the LAW in NINETY PAGES NAILING THE BAR Simple CONTRACTS & UCC Outline Table of Contents CHAPTER 1: CONTRACT
NAILING THE BAR Simple CONTRACTS & UCC Outline Tim Tyler, Ph.D., Attorney at Law NINETY PERCENT of the LAW in NINETY PAGES NAILING THE BAR Simple CONTRACTS & UCC Outline Table of Contents CHAPTER 1: CONTRACT
Question If CapCo files a lawsuit against the Bears seeking damages for breach of contract, who is likely to prevail? Discuss.
 Question 2 CapCo sells baseball caps to youth leagues and recently approached two new teams, the Bears and the Lions. Uncertain how many caps the team would require, the Bears team manager signed a written
Question 2 CapCo sells baseball caps to youth leagues and recently approached two new teams, the Bears and the Lions. Uncertain how many caps the team would require, the Bears team manager signed a written
Is there a contract?
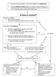 1. te whether this transaction is governed by UCC or the Restatement. 2. Does the Statute of Frauds apply? The contract must be in writing if it is in regard to land, if by its nature it takes more than
1. te whether this transaction is governed by UCC or the Restatement. 2. Does the Statute of Frauds apply? The contract must be in writing if it is in regard to land, if by its nature it takes more than
Shanghai Jiao Tong University. LA200 Business Law
 Shanghai Jiao Tong University LA200 Business Law Instructor: Email: Home Institution: Office: Office Hours: Term: 28 May-28 June, 2018 Credits: 4 units Classroom: Teaching Assistant(s): Class Hours: Discussion
Shanghai Jiao Tong University LA200 Business Law Instructor: Email: Home Institution: Office: Office Hours: Term: 28 May-28 June, 2018 Credits: 4 units Classroom: Teaching Assistant(s): Class Hours: Discussion
MBE WORKSHOP: CONTRACTS PROFESSOR LISA MCELROY DREXEL UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF LAW
 MBE WORKSHOP: CONTRACTS PROFESSOR LISA MCELROY DREXEL UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF LAW CHAPTER 1: CONTRACTS Editor's Note 1: The below outline is taken from the National Conference of Bar Examiners' website. NOTE:
MBE WORKSHOP: CONTRACTS PROFESSOR LISA MCELROY DREXEL UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF LAW CHAPTER 1: CONTRACTS Editor's Note 1: The below outline is taken from the National Conference of Bar Examiners' website. NOTE:
List of Figures. Acknowledgments About the Author
 Contents List of Figures Preface Acknowledgments About the Author xxi xxiii xxvii xxix PART A LAWS AND COURTS CHAPTER 1. OUR LEGAL SYSTEM 3 1.1 Common Law versus Civil Law 4 1.1.1 Common Law 4 1.1.2 Civil
Contents List of Figures Preface Acknowledgments About the Author xxi xxiii xxvii xxix PART A LAWS AND COURTS CHAPTER 1. OUR LEGAL SYSTEM 3 1.1 Common Law versus Civil Law 4 1.1.1 Common Law 4 1.1.2 Civil
Question 2. Delta has not yet paid for any of the three Model 100 presses despite repeated demands by Press.
 Question 2 Delta Print Co. ( Delta ) ordered three identical Model 100 printing presses from Press Manufacturer Co. ( Press ). Delta s written order form described the items ordered by model number. Delta
Question 2 Delta Print Co. ( Delta ) ordered three identical Model 100 printing presses from Press Manufacturer Co. ( Press ). Delta s written order form described the items ordered by model number. Delta
CHAPTER 8: GENUINE AGREEMENT
 CHAPTER 8: GENUINE AGREEMENT GENUINE AGREEMENT AND RESCISSION A valid offer and valid acceptance generally results in an enforceable contract. If one of the parties used physical threats to acquire the
CHAPTER 8: GENUINE AGREEMENT GENUINE AGREEMENT AND RESCISSION A valid offer and valid acceptance generally results in an enforceable contract. If one of the parties used physical threats to acquire the
COURSE OUTLINE. Business Administration 120 (C-ID Number: BUS 125) Business Law I (C-ID Title: Business Law)
 Degree Applicable Glendale Community College May 2014 COURSE OUTLINE Business Administration 120 (C-ID Number: BUS 125) Business Law I (C-ID Title: Business Law) I. Catalog Statement Business Administration
Degree Applicable Glendale Community College May 2014 COURSE OUTLINE Business Administration 120 (C-ID Number: BUS 125) Business Law I (C-ID Title: Business Law) I. Catalog Statement Business Administration
Law of Contracts. Determining Contractual Intent. Offer. 6 Elements of Legally Enforceable Contracts
 6 Elements of Legally Enforceable Contracts Law of Contracts 1. Offer and Acceptance 2. Genuine Assent 3. Legal Purpose Business Law Chapters 6-11 4. Consideration (Exchange of value) 5. Capacity to Contract
6 Elements of Legally Enforceable Contracts Law of Contracts 1. Offer and Acceptance 2. Genuine Assent 3. Legal Purpose Business Law Chapters 6-11 4. Consideration (Exchange of value) 5. Capacity to Contract
CHAPTER 2 CONTRACT LAWS INDIAN CONTRACT ACT, A contract is an agreement made between two or more parties which the law will enforce.
 CHAPTER 2 CONTRACT LAWS INDIAN CONTRACT ACT, 1872 Definition of Contract A contract is an agreement made between two or more parties which the law will enforce. Sec 2(h) defines contract as an agreement
CHAPTER 2 CONTRACT LAWS INDIAN CONTRACT ACT, 1872 Definition of Contract A contract is an agreement made between two or more parties which the law will enforce. Sec 2(h) defines contract as an agreement
Twomey Jennings: Anderson s Business Law, 23 e End of Chapter: CPA Questions and Answers
 March 17, 2016 Twomey Jennings: Anderson s Business Law, 23 e End of Chapter: CPA Questions and Answers CORRECT ANSWERS IN BOLDFACE. Chapter 9: Intellectual Property Rights and the Internet 1. Multicomp
March 17, 2016 Twomey Jennings: Anderson s Business Law, 23 e End of Chapter: CPA Questions and Answers CORRECT ANSWERS IN BOLDFACE. Chapter 9: Intellectual Property Rights and the Internet 1. Multicomp
Although the costs of materials and labor are roughly equal, the primary purpose of the
 Claim 1: Acme Flooring Applicable Law: Although the costs of materials and labor are roughly equal, the primary purpose of the contract was for rendering services because the service component of installation
Claim 1: Acme Flooring Applicable Law: Although the costs of materials and labor are roughly equal, the primary purpose of the contract was for rendering services because the service component of installation
MISTAKE. (1) the other party to the contract knew or should have known of the mistake; or
 MISTAKE Mistake of Fact: The parties entered into a contract with different understandings of one or more material facts relating to the contract s performance. Mutual Mistake: A mistake by both contracting
MISTAKE Mistake of Fact: The parties entered into a contract with different understandings of one or more material facts relating to the contract s performance. Mutual Mistake: A mistake by both contracting
Date Revised: 8/12 COURSE SYLLABUS. Syllabus for: BUS 2610 LEGAL ENVIRONMENT OF BUSINESS. Former Quarter Course(s):
 Date last reviewed: Date Approved: COURSE SYLLABUS Syllabus for: Date Revised: 8/12 Former Quarter Course(s): Catalog Description: This course is a study of the legal and regulatory environment of business.
Date last reviewed: Date Approved: COURSE SYLLABUS Syllabus for: Date Revised: 8/12 Former Quarter Course(s): Catalog Description: This course is a study of the legal and regulatory environment of business.
PART 2 FORMATION, TERMS, AND READJUSTMENT OF CONTRACT. (a) A contract or modification thereof is enforceable,
 1 PART 2 FORMATION, TERMS, AND READJUSTMENT OF CONTRACT SECTION 2-201. NO FORMAL REQUIREMENTS. (a) A contract or modification thereof is enforceable, whether or not there is a record signed by a party
1 PART 2 FORMATION, TERMS, AND READJUSTMENT OF CONTRACT SECTION 2-201. NO FORMAL REQUIREMENTS. (a) A contract or modification thereof is enforceable, whether or not there is a record signed by a party
California Bar Examination
 California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question Berelli Co., the largest single
California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question Berelli Co., the largest single
Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Spring Contract Formation
 Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Contract Formation I. Foundations A. Mutual Assent: Each party to a contract manifests its assent to the
Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Contract Formation I. Foundations A. Mutual Assent: Each party to a contract manifests its assent to the
Creation of the K a. Statute of Frauds land part performance one year debt 500 b. Offer master of the offer revoke mailbox rule absence of terms
 Contracts outline I. Creation of the K a. Statute of Frauds requires that a sufficient writing, signed by the party to be charged be in existence for the following subject-matter (doesn t apply to restitution
Contracts outline I. Creation of the K a. Statute of Frauds requires that a sufficient writing, signed by the party to be charged be in existence for the following subject-matter (doesn t apply to restitution
Answer A to Question 1
 Answer A to Question 1 The issue is whether Pat has a valid contract with Danco and whether Danco has breached such contract, and what damages Pat is entitled to as a result. Service Contract Contracts
Answer A to Question 1 The issue is whether Pat has a valid contract with Danco and whether Danco has breached such contract, and what damages Pat is entitled to as a result. Service Contract Contracts
Study Notes & Practice Questions. Updated 2018 Exams
 Orea Real Estate Exam Course Study Notes & Practice Questions Updated 2018 Exams All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, transmitted or stored in any material form (including
Orea Real Estate Exam Course Study Notes & Practice Questions Updated 2018 Exams All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, transmitted or stored in any material form (including
Define genuine agreement and rescission. Identify when duress occurs. Describe how someone may exercise undue influence.
 Define genuine agreement and rescission Identify when duress occurs Describe how someone may exercise undue influence. Genuine Agreement/Assent: meeting of the minds Must be willful and voluntary Must
Define genuine agreement and rescission Identify when duress occurs Describe how someone may exercise undue influence. Genuine Agreement/Assent: meeting of the minds Must be willful and voluntary Must
District > Intermediate > Business Education > Business Law ( ) (District) > Juett, David
 Granite School District Business Law (52.0441) (District) District > Intermediate > Business Education > Business Law (52.0441) (District) > Juett, David Unit Essential Questions Content Skills Vocabulary
Granite School District Business Law (52.0441) (District) District > Intermediate > Business Education > Business Law (52.0441) (District) > Juett, David Unit Essential Questions Content Skills Vocabulary
Prufrex USA, Inc. TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF PURCHASE
 Prufrex USA, Inc. TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF PURCHASE 1 Contract Formation: These Terms and Conditions of Purchase (the "Terms and Conditions") apply to any purchases by Prufrex USA, Inc., its subsidiaries,
Prufrex USA, Inc. TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF PURCHASE 1 Contract Formation: These Terms and Conditions of Purchase (the "Terms and Conditions") apply to any purchases by Prufrex USA, Inc., its subsidiaries,
NEGOTIABLE INSTRUMENTS TRANSLATION. Portatore, Possessore. Effetti e Titoli di Credito Negoziabili
 NEGOTIABLE INSTRUMENTS TRANSLATION English Italian Bearer Portatore, Possessore Certificate of Deposit Certificato di Deposito Check Assegno Commercial Paper Effetti e Titoli di Credito Negoziabili Discharge
NEGOTIABLE INSTRUMENTS TRANSLATION English Italian Bearer Portatore, Possessore Certificate of Deposit Certificato di Deposito Check Assegno Commercial Paper Effetti e Titoli di Credito Negoziabili Discharge
BAILMENT AGREEMENT FOR EQUIPMENT, TOOLING, CAPITAL AND PACKAGING Minth Purchasing Policy and WI Terms and Conditions of Bailment
 BAILMENT AGREEMENT FOR EQUIPMENT, TOOLING, CAPITAL AND PACKAGING Minth Purchasing Policy and WI 3.1.15 Terms and Conditions of Bailment This Bailment Agreement for Equipment, Tooling, Capital or Packaging
BAILMENT AGREEMENT FOR EQUIPMENT, TOOLING, CAPITAL AND PACKAGING Minth Purchasing Policy and WI 3.1.15 Terms and Conditions of Bailment This Bailment Agreement for Equipment, Tooling, Capital or Packaging
California Bar Examination
 California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question On April 1, Pat, a computer software
California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question On April 1, Pat, a computer software
Chapter 9: Contract Formation. Copyright 2009 South-Western Legal Studies in Business, a part of South-Western Cengage Learning.
 Chapter 9: Contract Formation a Copyright part of South-Western 2009 South-Western Cengage Legal Learning. Studies Business, Introduction is a declaration that something will or will not happen in the
Chapter 9: Contract Formation a Copyright part of South-Western 2009 South-Western Cengage Legal Learning. Studies Business, Introduction is a declaration that something will or will not happen in the
UNIDROIT PRINCIPLES OF INTERNATIONAL COMMERCIAL CONTRACTS 2004 (I)
 UNIDROIT PRINCIPLES OF INTERNATIONAL COMMERCIAL CONTRACTS 2004 (I) PREAMBLE (Purpose of the Principles) These Principles set forth general rules for international commercial contracts. They shall be applied
UNIDROIT PRINCIPLES OF INTERNATIONAL COMMERCIAL CONTRACTS 2004 (I) PREAMBLE (Purpose of the Principles) These Principles set forth general rules for international commercial contracts. They shall be applied
United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods
 United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods ACC International Legal Affairs Committee Legal Quick Hit: November 13, 2014 Presented by: Jeffrey S. Dunn Michael Best & Friedrich
United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods ACC International Legal Affairs Committee Legal Quick Hit: November 13, 2014 Presented by: Jeffrey S. Dunn Michael Best & Friedrich
Index. References are to sections.
 Index References are to sections. A Abandonment Anticipatory breach or repudiation, ground for, 12.35 Damages, 12.35, 14.3 Distinguished from rescission, 14.3 Material breach, ground for, 12.37 Mutual,
Index References are to sections. A Abandonment Anticipatory breach or repudiation, ground for, 12.35 Damages, 12.35, 14.3 Distinguished from rescission, 14.3 Material breach, ground for, 12.37 Mutual,
CONTRACT LAW. Elements of a Contract
 CONTRACT LAW Contracts: Types and Sources in Australia CONTRACT: An agreement concerning promises made between two or more parties with the intention of creating certain legal rights and obligations upon
CONTRACT LAW Contracts: Types and Sources in Australia CONTRACT: An agreement concerning promises made between two or more parties with the intention of creating certain legal rights and obligations upon
Contract Law Final Exam Version C
 Contract Law Final Exam Version C True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Compliance and excuse are valid defenses to a breach of contract action. 2. To have a constructive or implied
Contract Law Final Exam Version C True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Compliance and excuse are valid defenses to a breach of contract action. 2. To have a constructive or implied
FULL OUTLINE. Bar Exam Doctor BAREXAMDOCTOR.COM. CONTRACTS
 FULL OUTLINE www.barexamdoctor.com CONTRACTS I. VOCABULARY a. K = legally enforceable agreement (or legally enforceable promise) b. Quasi-K = equitable remedy. NOT K law. i. Elements: 1. P has conferred
FULL OUTLINE www.barexamdoctor.com CONTRACTS I. VOCABULARY a. K = legally enforceable agreement (or legally enforceable promise) b. Quasi-K = equitable remedy. NOT K law. i. Elements: 1. P has conferred
A) Preliminaries B) Formation
 Contracts Page 1 of 12 A) Preliminaries 1) Governing law The Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) governs transactions that are predominantly for goods (movable property, identifiable to the contract at formation),
Contracts Page 1 of 12 A) Preliminaries 1) Governing law The Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) governs transactions that are predominantly for goods (movable property, identifiable to the contract at formation),
Business Law PRECISION EXAMS
 PRECISION EXAMS Business Law EXAM INFORMATION Items 64 Points 71 Prerequisites NONE Grade Level 10-12 Course Length ONE SEMESTER Career Cluster BUSINESS MANAGEMENT AND ADMINISTRATION DESCRIPTION Students
PRECISION EXAMS Business Law EXAM INFORMATION Items 64 Points 71 Prerequisites NONE Grade Level 10-12 Course Length ONE SEMESTER Career Cluster BUSINESS MANAGEMENT AND ADMINISTRATION DESCRIPTION Students
TYPES OF MONETARY DAMAGES
 TYPES OF MONETARY DAMAGES A breach of contract entitles the non-breaching party to sue for money damages, including: Compensatory Damages: Damages that compensate the non-breaching party for the injuries
TYPES OF MONETARY DAMAGES A breach of contract entitles the non-breaching party to sue for money damages, including: Compensatory Damages: Damages that compensate the non-breaching party for the injuries
California Bar Examination
 California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question On May 1, Owner asked Builder
California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question On May 1, Owner asked Builder
DRAFTING AND ANALYZING CONTRACTS
 0001 VERSACOMP (4.2 ) COMPOSE2 (4.43) NEW LAW SCH. Front Matter SAMPLE for PERFECTBOUND Pubs J:\VRS\DAT\03037\FM.GML --- r3037_fm.sty --- POST DRAFTING AND ANALYZING CONTRACTS A Guide to the Practical
0001 VERSACOMP (4.2 ) COMPOSE2 (4.43) NEW LAW SCH. Front Matter SAMPLE for PERFECTBOUND Pubs J:\VRS\DAT\03037\FM.GML --- r3037_fm.sty --- POST DRAFTING AND ANALYZING CONTRACTS A Guide to the Practical
Equity Investment Agreement
 Equity Investment Agreement THIS EQUITY INVESTMENT AGREEMENT (the "Agreement") is dated as of DATE (the "Effective Date") by and between, a Delaware business corporation, having an address at ("Company")
Equity Investment Agreement THIS EQUITY INVESTMENT AGREEMENT (the "Agreement") is dated as of DATE (the "Effective Date") by and between, a Delaware business corporation, having an address at ("Company")
Glossary of Terms for Business Law and Ethics
 Glossary of Terms for Business Law and Ethics MBA 625, Patten University Abusive/Intimidating Behavior Physical threats, false accusations, being annoying, profanity, insults, yelling, harshness, ignoring
Glossary of Terms for Business Law and Ethics MBA 625, Patten University Abusive/Intimidating Behavior Physical threats, false accusations, being annoying, profanity, insults, yelling, harshness, ignoring
CONTRACT LAW (2) Il est précisé que le thème «CONTRACT LAW» est abordé à travers 2 fiches, cette fiche étant la seconde. I. VALIDITY OF THE CONTRACT
 CONTRACT LAW (2) Il est précisé que le thème «CONTRACT LAW» est abordé à travers 2 fiches, cette fiche étant la seconde. Plan : I. VALIDITY OF THE CONTRACT II. LEGALITY OF THE SUBJECT MATTER III. REALITY
CONTRACT LAW (2) Il est précisé que le thème «CONTRACT LAW» est abordé à travers 2 fiches, cette fiche étant la seconde. Plan : I. VALIDITY OF THE CONTRACT II. LEGALITY OF THE SUBJECT MATTER III. REALITY
One Hundred Fifth Congress of the United States of America
 S. 2392 One Hundred Fifth Congress of the United States of America AT THE SECOND SESSION Begun and held at the City of Washington on Tuesday, the twenty-seventh day of January, one thousand nine hundred
S. 2392 One Hundred Fifth Congress of the United States of America AT THE SECOND SESSION Begun and held at the City of Washington on Tuesday, the twenty-seventh day of January, one thousand nine hundred
Contents. Table of Statutes. Table of Secondary Legislation. Table of Cases. The Agreement to Contract
 Contents Table of Statutes Table of Secondary Legislation Table of Cases Chapter 1: The Agreement to Contract 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Elements required for a valid simple contract 1.3 The phenomenon of agreement
Contents Table of Statutes Table of Secondary Legislation Table of Cases Chapter 1: The Agreement to Contract 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Elements required for a valid simple contract 1.3 The phenomenon of agreement
MLL111- Exam Notes Contract Law (All Topics + Cases)
 1 MLL111- Exam Notes Contract Law (All Topics + Cases) 2 Contents Page Page 8: Formation of Contracts Offer and Acceptance Page 9: Acceptance Communication of Acceptance: Waiver Silence Page 10: Acceptance
1 MLL111- Exam Notes Contract Law (All Topics + Cases) 2 Contents Page Page 8: Formation of Contracts Offer and Acceptance Page 9: Acceptance Communication of Acceptance: Waiver Silence Page 10: Acceptance
IN THE CIRCUIT COURT OF THE SECOND JUDICIAL CIRCUIT IN AND FOR LEON COUNTY, FLORIDA SETTLEMENT AGREEMENT
 IN THE CIRCUIT COURT OF THE SECOND JUDICIAL CIRCUIT IN AND FOR LEON COUNTY, FLORIDA STATE OF FLORIDA, OFFICE OF THE ATTORNEY GENERAL, Plaintiff, v. Case No. 2008 CA 000199 IMERGENT. INC., and STORESONLINE,
IN THE CIRCUIT COURT OF THE SECOND JUDICIAL CIRCUIT IN AND FOR LEON COUNTY, FLORIDA STATE OF FLORIDA, OFFICE OF THE ATTORNEY GENERAL, Plaintiff, v. Case No. 2008 CA 000199 IMERGENT. INC., and STORESONLINE,
NC General Statutes - Chapter 20 Article 12A 1
 Article 12A. Motor Vehicle Captive Finance Source Law. 20-308.13. Regulation of motor vehicle captive finance sources. The General Assembly finds and declares that the distribution of motor vehicles in
Article 12A. Motor Vehicle Captive Finance Source Law. 20-308.13. Regulation of motor vehicle captive finance sources. The General Assembly finds and declares that the distribution of motor vehicles in
DEALER/AGENT/RESELLER/LIEN HOLDER SERVICE PROVIDER AGREEMENT
 DEALER/AGENT/RESELLER/LIEN HOLDER SERVICE PROVIDER AGREEMENT This DEALER/AGENT/RESELLER/LIEN HOLDER AGREEMENT (the Agreement ), effective as of the day of, 20, by and between Crossbow Group Inc. (CGI )
DEALER/AGENT/RESELLER/LIEN HOLDER SERVICE PROVIDER AGREEMENT This DEALER/AGENT/RESELLER/LIEN HOLDER AGREEMENT (the Agreement ), effective as of the day of, 20, by and between Crossbow Group Inc. (CGI )
LAW OFFICE OF MARK ROYSNER Mulholland Highway, Suite 382 Calabasas, CA
 WHAT DOES THAT MEAN? Definitions of Legal Terms Typically Found in Meetings and Exhibition Industry Contracts. By Mark Roysner, Esq. This is a glossary of legal terms and phrases commonly found in hotel,
WHAT DOES THAT MEAN? Definitions of Legal Terms Typically Found in Meetings and Exhibition Industry Contracts. By Mark Roysner, Esq. This is a glossary of legal terms and phrases commonly found in hotel,
SITE LICENSE AGREEMENT FOR ISO 9001 EXPLAINED
 SITE LICENSE AGREEMENT FOR ISO 9001 EXPLAINED Per the ISO 9000 Checklist web site at the internet address iso9000checklist.com, placement of an order and purchase of this product indicates that you have
SITE LICENSE AGREEMENT FOR ISO 9001 EXPLAINED Per the ISO 9000 Checklist web site at the internet address iso9000checklist.com, placement of an order and purchase of this product indicates that you have
SEVES USA INC. PPC Insulators Division North America Purchase Order Terms & Conditions. Title and risk of loss. Governing Terms & Conditions.
 SEVES USA INC. PPC Insulators Division North America Purchase Order Terms & Conditions Governing Terms & Conditions This Purchase Order ( Order ) constitutes the offer of Seves USA Inc. USA, Inc. ( Seves
SEVES USA INC. PPC Insulators Division North America Purchase Order Terms & Conditions Governing Terms & Conditions This Purchase Order ( Order ) constitutes the offer of Seves USA Inc. USA, Inc. ( Seves
TERMS AND CONDITIONS
 This Contract comprises the Sales Confirmation overleaf and these terms and conditions to the exclusion of all other terms and conditions (including any terms or conditions which Buyer purports to apply
This Contract comprises the Sales Confirmation overleaf and these terms and conditions to the exclusion of all other terms and conditions (including any terms or conditions which Buyer purports to apply
Exam Approach: I. CONTRACT FORMATION
 Exam Approach: 1. On scrap paper, write out all main topics (the purple enumerated topics in this outline) look back at them after reading through the fact pattern to MAKE SURE I haven t missed spotting
Exam Approach: 1. On scrap paper, write out all main topics (the purple enumerated topics in this outline) look back at them after reading through the fact pattern to MAKE SURE I haven t missed spotting
California Bar Examination
 California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question PC manufactures computers. Mart
California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question PC manufactures computers. Mart
CONTRACTS TOPIC OUTLINE1
 CONTRACTS TOPIC OUTLINE1 1. OFFER AND ACCEPTANCE a. offer defined b. preliminary negotiations c. advertisements d. unilateral offer e. who may accept an offer f. irrevocable offer g. material terms h.
CONTRACTS TOPIC OUTLINE1 1. OFFER AND ACCEPTANCE a. offer defined b. preliminary negotiations c. advertisements d. unilateral offer e. who may accept an offer f. irrevocable offer g. material terms h.
Material Transfer Agreement
 PARTIES UNSW Recipient The University of New South Wales ABN 57 195 873 179, a body corporate established pursuant to the University of New South Wales Act 1989 (NSW of UNSW Sydney NSW 2052, Australia
PARTIES UNSW Recipient The University of New South Wales ABN 57 195 873 179, a body corporate established pursuant to the University of New South Wales Act 1989 (NSW of UNSW Sydney NSW 2052, Australia
Professional Services are provided subject to the terms and conditions of the Mercury Professional Services Agreement.
 Mercury Systems, Inc. Terms & Conditions of Sale The following terms shall govern the sale of Mercury Systems, Inc. ( Mercury ) products that are ordered by customer ( Buyer ), including all hardware (the
Mercury Systems, Inc. Terms & Conditions of Sale The following terms shall govern the sale of Mercury Systems, Inc. ( Mercury ) products that are ordered by customer ( Buyer ), including all hardware (the
3/12/14. TERMS AND CONDITIONS TO SUPPLY and SALES AGREEMENTS
 1 Universal Environmental Services LLC, 411 Dividend Drive Peachtree City, GA. 30269 3/12/14 TERMS AND CONDITIONS TO SUPPLY and SALES AGREEMENTS Acceptance of Terms: Seller's acceptance of Buyer's order
1 Universal Environmental Services LLC, 411 Dividend Drive Peachtree City, GA. 30269 3/12/14 TERMS AND CONDITIONS TO SUPPLY and SALES AGREEMENTS Acceptance of Terms: Seller's acceptance of Buyer's order
Terms of Use. 1. Limited Use
 Terms of Use The eaccountservices.com/gmfinancialrightnotes Internet site domain name and all materials located at and under that domain name (collectively, this Site ) and any services available on this
Terms of Use The eaccountservices.com/gmfinancialrightnotes Internet site domain name and all materials located at and under that domain name (collectively, this Site ) and any services available on this
I, Accept this proposal and make a payment of $ to confirm my commitment.
 This Solar Home Improvement Agreement (this Agreement ) is between Golden Gate Green Finance dba Golden Gate Power, California General and Electrical Contractor license number 1002922 ( Golden Gate Power,
This Solar Home Improvement Agreement (this Agreement ) is between Golden Gate Green Finance dba Golden Gate Power, California General and Electrical Contractor license number 1002922 ( Golden Gate Power,
CONTRACT LAW IN THE SOUTH PACIFIC
 CONTRACT LAW IN THE SOUTH PACIFIC Jennifer Corrin Care Senior Lecturer TC Beirne School of Law University of Queensland Cavendish Publishing Limited London Sydney CONTENTS Preface Table of Cases Table
CONTRACT LAW IN THE SOUTH PACIFIC Jennifer Corrin Care Senior Lecturer TC Beirne School of Law University of Queensland Cavendish Publishing Limited London Sydney CONTENTS Preface Table of Cases Table
BUSINESS LAW FOR THE ENTREPRENEUR AND MANAGER
 BUSINESS LAW FOR THE ENTREPRENEUR AND MANAGER Chapter Introduction and Summaries and Discussion Questions Frank J. Cavico Bahaudin G. Mujtaba Reference: 1. Cavico, F. & Mujtaba, B. G., (2008). Business
BUSINESS LAW FOR THE ENTREPRENEUR AND MANAGER Chapter Introduction and Summaries and Discussion Questions Frank J. Cavico Bahaudin G. Mujtaba Reference: 1. Cavico, F. & Mujtaba, B. G., (2008). Business
Opening Assignment. The Bargain. Contracts. Elements of Contract. Ending an Offer. What is an Offer 10/31/2017
 Opening Assignment Should the shopkeeper have been allowed to continue increasing the price of the vase? Explain. The Bargain Contracts What is a contract? Legally binding agreement Who may enter into
Opening Assignment Should the shopkeeper have been allowed to continue increasing the price of the vase? Explain. The Bargain Contracts What is a contract? Legally binding agreement Who may enter into
Genuineness of Assent
 Genuineness of Assent A party who demonstrates that she did not genuinely assent to the terms of a contract may avoid an otherwise valid contract. Genuine assent may be lacking due to mistake, fraudulent
Genuineness of Assent A party who demonstrates that she did not genuinely assent to the terms of a contract may avoid an otherwise valid contract. Genuine assent may be lacking due to mistake, fraudulent
NON-EXCLUSIVE LICENSE FOR USE OF SCHOOL WORDMARKS AND LOGOS
 NON-EXCLUSIVE LICENSE FOR USE OF SCHOOL WORDMARKS AND LOGOS THIS LICENSE AGREEMENT (hereinafter "Agreement") is entered into by and between Greenville Independent School District, an independent school
NON-EXCLUSIVE LICENSE FOR USE OF SCHOOL WORDMARKS AND LOGOS THIS LICENSE AGREEMENT (hereinafter "Agreement") is entered into by and between Greenville Independent School District, an independent school
TURKS AND CAICOS ISLANDS TRUSTS BILL 2015 ARRANGEMENT OF CLAUSES
 TURKS AND CAICOS ISLANDS TRUSTS BILL 2015 ARRANGEMENT OF CLAUSES PART I PRELIMINARY CLAUSE 1. Short title and commencement 2. Interpretation 3. Meaning of insolvent 4. Meaning of personal relationship
TURKS AND CAICOS ISLANDS TRUSTS BILL 2015 ARRANGEMENT OF CLAUSES PART I PRELIMINARY CLAUSE 1. Short title and commencement 2. Interpretation 3. Meaning of insolvent 4. Meaning of personal relationship
Ownership of Site; Agreement to Terms of Use
 Ownership of Site; Agreement to Terms of Use These Terms and Conditions of Use (the Terms of Use ) apply to the Volta Career Resource Center, being a web site located at www.voltapeople.com (the Site ).
Ownership of Site; Agreement to Terms of Use These Terms and Conditions of Use (the Terms of Use ) apply to the Volta Career Resource Center, being a web site located at www.voltapeople.com (the Site ).
Arbitration of Distribution and Franchise Disputes
 Arbitration of Distribution and Franchise Disputes Gerald Saltarelli Abstract: Manufacturers and other sellers of goods and services reach their markets through a variety of means, including distributor
Arbitration of Distribution and Franchise Disputes Gerald Saltarelli Abstract: Manufacturers and other sellers of goods and services reach their markets through a variety of means, including distributor
Genuine Agreement (Genuine Assent)
 Chapter 7 Genuine Agreement (Genuine Assent) Business Law Ms. Turner Genuine Agreement (Genuine Assent) Agreement to enter into a contract that is evidenced by words or conduct between parties If there
Chapter 7 Genuine Agreement (Genuine Assent) Business Law Ms. Turner Genuine Agreement (Genuine Assent) Agreement to enter into a contract that is evidenced by words or conduct between parties If there
a) test the strength of the opposing positions and encourage the parties to reach a compromise b) ensure that all documents are in order before trial
 Question 1 The purpose of discovery is to a) test the strength of the opposing positions and encourage the parties to reach a compromise b) ensure that all documents are in order before trial c) ensure
Question 1 The purpose of discovery is to a) test the strength of the opposing positions and encourage the parties to reach a compromise b) ensure that all documents are in order before trial c) ensure
Contents. Gillette, Clayton The UN Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods. digitalisiert durch: IDS Basel Bern
 Preface page xi ι The CISG: history, methodology, and construction ι I The CISG as a set of commercial default rules ι II The history and structure of the CISG 4 III CISG methodology and the limits of
Preface page xi ι The CISG: history, methodology, and construction ι I The CISG as a set of commercial default rules ι II The history and structure of the CISG 4 III CISG methodology and the limits of
ROGERS CORPORATION - TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF PURCHASE
 ROGERS CORPORATION - TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF PURCHASE THE FOLLOWING TERMS AND CONDITIONS, AND THOSE SPECIFIED ON THE FACE OF THIS PURCHASE ORDER, SHALL EXCLUSIVELY GOVERN THE PURCHASE OF ALL MATERIALS
ROGERS CORPORATION - TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF PURCHASE THE FOLLOWING TERMS AND CONDITIONS, AND THOSE SPECIFIED ON THE FACE OF THIS PURCHASE ORDER, SHALL EXCLUSIVELY GOVERN THE PURCHASE OF ALL MATERIALS
GREEN ELECTRONICS COUNCIL UL ECOLOGO/EPEAT JOINT CERTIFICATION LICENSE AND PARTICIPATING MANUFACTURER AGREEMENT
 GREEN ELECTRONICS COUNCIL UL ECOLOGO/EPEAT JOINT CERTIFICATION LICENSE AND PARTICIPATING MANUFACTURER AGREEMENT THIS AGREEMENT, including all Schedules and Exhibits attached hereto (this Agreement ), is
GREEN ELECTRONICS COUNCIL UL ECOLOGO/EPEAT JOINT CERTIFICATION LICENSE AND PARTICIPATING MANUFACTURER AGREEMENT THIS AGREEMENT, including all Schedules and Exhibits attached hereto (this Agreement ), is
PATENT PURCHASE AGREEMENT
 PATENT PURCHASE AGREEMENT This PATENT PURCHASE AGREEMENT (the Agreement ) is entered into by and between Google Inc., a Delaware corporation with its principal place of business at 1600 Amphitheatre Parkway,
PATENT PURCHASE AGREEMENT This PATENT PURCHASE AGREEMENT (the Agreement ) is entered into by and between Google Inc., a Delaware corporation with its principal place of business at 1600 Amphitheatre Parkway,
S A BILL. Calendar No To encourage the disclosure and exchange of information 105TH CONGRESS 2D SESSION
 Calendar No. 0TH CONGRESS D SESSION S. A BILL To encourage the disclosure and exchange of information about computer processing problems and related matters in connection with the transition to the year
Calendar No. 0TH CONGRESS D SESSION S. A BILL To encourage the disclosure and exchange of information about computer processing problems and related matters in connection with the transition to the year
Contract of Sale [Lot * on RP******] Page 1
![Contract of Sale [Lot * on RP******] Page 1 Contract of Sale [Lot * on RP******] Page 1](/thumbs/84/90570785.jpg) [Lot * on RP******] Page 1 PART 1 REFERENCE PARTICULARS Item 1 Formation of Agreement Date: 2015 Item 2 Seller Identity: Address for Notices: Name: Delivery: Larmaq Regional Council Post: Facsimile: Item
[Lot * on RP******] Page 1 PART 1 REFERENCE PARTICULARS Item 1 Formation of Agreement Date: 2015 Item 2 Seller Identity: Address for Notices: Name: Delivery: Larmaq Regional Council Post: Facsimile: Item
University of Miami School of Law. CONTRACTS PROFESSOR ROBERT ROSEN Fall Syllabus 1
 University of Miami School of Law CONTRACTS PROFESSOR ROBERT ROSEN Fall 2007 Syllabus 1 [Unless otherwise indicated, all page # s refer to MACAULEY, ET.AL. CONTRACTS: LAW IN ACTION (2 ND ED., 2003)]. YOU
University of Miami School of Law CONTRACTS PROFESSOR ROBERT ROSEN Fall 2007 Syllabus 1 [Unless otherwise indicated, all page # s refer to MACAULEY, ET.AL. CONTRACTS: LAW IN ACTION (2 ND ED., 2003)]. YOU
Principles of European Contract Law
 Article 1:101: Application of the Principles Principles of European Contract Law CHAPTER 1: GENERAL PROVISIONS Section 1: Scope of the Principles (1) These Principles are intended to be applied as general
Article 1:101: Application of the Principles Principles of European Contract Law CHAPTER 1: GENERAL PROVISIONS Section 1: Scope of the Principles (1) These Principles are intended to be applied as general
SUPPLY AGREEMENT TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF PURCHASE (INFLIGHT SERVICES) SELLER IS ADVISED TO READ THESE TERMS & CONDITIONS CAREFULLY
 SUPPLY AGREEMENT TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF PURCHASE (INFLIGHT SERVICES) SELLER IS ADVISED TO READ THESE TERMS & CONDITIONS CAREFULLY THIS SUPPLY AGREEMENT (the Agreement ) is made on the applicable dates
SUPPLY AGREEMENT TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF PURCHASE (INFLIGHT SERVICES) SELLER IS ADVISED TO READ THESE TERMS & CONDITIONS CAREFULLY THIS SUPPLY AGREEMENT (the Agreement ) is made on the applicable dates
PURCHASE ORDER TERMS AND CONDITIONS
 PURCHASE ORDER TERMS AND CONDITIONS 1. SERVICES & DELIVERABLES. Seller agrees to provide to CORTEC PRECISION SHEETMETAL (or its subsidiaries, if such subsidiaries are designated as the contracting parties
PURCHASE ORDER TERMS AND CONDITIONS 1. SERVICES & DELIVERABLES. Seller agrees to provide to CORTEC PRECISION SHEETMETAL (or its subsidiaries, if such subsidiaries are designated as the contracting parties
LISTING AGREEMENT STANDARD TERMS AND CONDITIONS Date: March 1, 2016
 LISTING AGREEMENT STANDARD TERMS AND CONDITIONS Date: March 1, 2016 ARTICLE 1 Definition 1.1 Definitions. In this Agreement, the following words shall have the following meanings: Agreement means this
LISTING AGREEMENT STANDARD TERMS AND CONDITIONS Date: March 1, 2016 ARTICLE 1 Definition 1.1 Definitions. In this Agreement, the following words shall have the following meanings: Agreement means this
IN THE UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE SOUTHERN DISTRICT OF TEXAS GALVESTON DIVISION
 Case 3:10-cv-00252 Document 1 Filed in TXSD on 06/29/10 Page 1 of 16 IN THE UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE SOUTHERN DISTRICT OF TEXAS GALVESTON DIVISION HUNG MICHAEL NGUYEN NO. an individual; On
Case 3:10-cv-00252 Document 1 Filed in TXSD on 06/29/10 Page 1 of 16 IN THE UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE SOUTHERN DISTRICT OF TEXAS GALVESTON DIVISION HUNG MICHAEL NGUYEN NO. an individual; On
Home Foundation Subcontractor Services Agreement
 Home Foundation Subcontractor Services Agreement This Packet Includes: 1. General Information 2. Instructions and Checklist 3. Step-by-Step Instructions 4. Home Foundation Subcontractor Services Agreement
Home Foundation Subcontractor Services Agreement This Packet Includes: 1. General Information 2. Instructions and Checklist 3. Step-by-Step Instructions 4. Home Foundation Subcontractor Services Agreement
Concord University School of Law Practice Essay
 Concord University School of Law Practice Essay Instructions: This is a timed practice, and you should take no more than one hour to complete this exercise. Set a timer and allow no interruptions. Before
Concord University School of Law Practice Essay Instructions: This is a timed practice, and you should take no more than one hour to complete this exercise. Set a timer and allow no interruptions. Before
CONTRACTS AND SALES QUESTION 1
 CONTRACTS AND SALES QUESTION Peter responded to an advertisement placed by Della, a dentist, seeking a dental hygienist. After an interview, Della offered Peter the job and said she would either: () pay
CONTRACTS AND SALES QUESTION Peter responded to an advertisement placed by Della, a dentist, seeking a dental hygienist. After an interview, Della offered Peter the job and said she would either: () pay
Law of the United States
 Law of the United States An Overview by Peter Hay L. Q. C. Lamar Professor of Law Emory University, Atlanta Universitatsprofessor (ret.), Dresden Third Edition C.H.BECK Bruylant, Brussels 2010 Preface
Law of the United States An Overview by Peter Hay L. Q. C. Lamar Professor of Law Emory University, Atlanta Universitatsprofessor (ret.), Dresden Third Edition C.H.BECK Bruylant, Brussels 2010 Preface
Purchase Agreement TERMS AND CONDITIONS PRICES PAYMENT AND PAYMENT TERMS. Bright Ideas. Better Solutions. Benchmark is Branch Automation.
 Purchase Agreement The following terms and conditions shall apply to the sale of goods or products ( goods or products ) associated with your invoice: TERMS AND CONDITIONS The obligations and rights of
Purchase Agreement The following terms and conditions shall apply to the sale of goods or products ( goods or products ) associated with your invoice: TERMS AND CONDITIONS The obligations and rights of
