The Effect of New Turkish Foreign Policy on International Trade
|
|
|
- Eric James
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE EFFECT OF NEW TURKISH FOREIGN POLICY ON INTERNATIONAL TRADE The Effect of New Turkish Foreign Policy on International Trade ABDÜLKADİR CİVAN *, SAVAŞ GENÇ **, DAVUT TAŞER *** and SİNEM ATAKUL **** ABSTRACT Turkish foreign policy has changed substantially within the last decade. Even though its relationship with the West still has significance, relations with neighboring countries and other countries in Africa, the Middle East, and Asia have improved. This new foreign policy incorporates Turkey s political and economic aspirations. Its aim is to utilize the country s economic strength in order to reach political goals while simultaneously using political tools to obtain economic benefits. This study analyzes the effects of the recent change in foreign policy on Turkey s international trade. Specifically, we investigate the influence of Turkish Prime Minister Erdoğan s foreign visits on international trade by using a standard trade gravity model. Statistical analyses imply that Erdoğan s visits help increase Turkish international trade. Economic interests have always been one of the most important elements of foreign policy. In today s globalizing world, the significance of economic relations in foreign policy has increased even more, and the success of specific foreign policies is now measured by their economic impact. International trade has become the leading factor in international policy making, especially since the Cold War. In recent decades, policy makers of both developed and developing countries have been able to appreciate the mutual benefits of international trade to importing and exporting countries. In addition, the establishment of the World Trade Organization (WTO) and other developments in international law have liberalized and greatly reduced the barriers to international trade, thus increasing its volume and importance. By contrast, after the foundation of the Republic in the 1920s, security concerns were the focus of Turkey s foreign policies. The decision-makers gave priority to policies that would strengthen the regime and reinforce the reforms. Turkish foreign policy continued to follow this approach even long after the establishment of the Republic. However, after the Cold War, Turkey became much more * Gediz University, Department of Economics ** Fatih University, Department of International Relations *** Bilkent University, Department of Economics **** Fatih University, Department of Economics Insight Turkey Vol. 15 / No. 3 / 2013, pp Summer 107
2 ABDÜLKADİR CİVAN, SAVAŞ GENÇ, DAVUT TAŞER and SİNEM ATAKUL open to broad structural changes in its foreign policy framework. With Turgut Özal s new government in the 1980s, Turkey started to put economic interests at the forefront of its foreign policy decisions. Özal decided to reshape foreign policy in Turkey when the country could only pay for its petrol import with its export revenues. His primary concern was to ensure Turkey s productivity, and then establish a country that could sell its products in the world market. Özal, who could read the signs of globalization very well, knew that Turkey had to cover a large distance to meet these goals, and he prioritized trade development by first improving relations with neighboring countries. Özal s foreign policy was an instrument of development model based on exports. He wanted to undo economy policies based on import substitution, and continued global initiative policies by opening up relations with the Soviet Union. Preferring an aesthetic and pragmatic foreign policy, Özal established the Black Sea Economic Cooperation Organization with the region s countries after the dissolution of the Soviet Union, and also showed interest in the republics of Middle Asia. By expanding the trade volume mutually with neighbors in the region, Özal defended the view that regional conflicts could be solved easily and with lower risks. He emphasized that to be a regional power, it is necessary to have a strong economy and substantial economic relationships, and he attempted to reach these goals through regional peace. As can be seen, most of the successful foreign and economic policies that are on the agenda of the Justice and Development party (the AK Party) were also on Özal s agenda. This kind of change prevents a nation s foreign policy from remaining too restricted.in order to be a more effective state in its region, Turkey has started to follow a relatively more independent and multidimensional foreign policy by putting more emphasis on bilateral relationships. However, even though there is great support for the new Turkish foreign policy, there are also critics who claim that Turkey is making an axis shift toward the East, and that the policy makers are driven by neo-ottomanism rather than by Turkish national interests. 1 But approaches based on identity like Islamist preferences and ideological definitions are insufficient in explaining the present situation and can be deceptive. With the phrase order establishing country in Ottoman geography, Ahmet Davutoğlu refers to the transformation of those countries into stabilized and competitive polities; and though he objects to the ideological concept of neo-ottomanism. 2 Turkey s new regional role cannot be explained only by the identity preferences of the AK Party; instead, an interest-based approach with a perspective of economic and geopolitical acquisitions is relevant here Turkey s economy is becoming increasingly dynamic, as shown by an increase in foreign visits from decision makers and top-level leaders, as well as an in- 108 Insight Turkey
3 THE EFFECT OF NEW TURKISH FOREIGN POLICY ON INTERNATIONAL TRADE crease in competition over shares in regional and world markets between Turkish investors and industrialists. Under this new and active foreign policy, the international trade of Turkey has increased significantly in the relevant period. Turkey s total international trade volume increased from $72 billion in 2001 to $389 billion in In this study, the interaction between Turkish foreign policy and international trade is analyzed. It is argued that as in many other modern countries, an important dimension of the new Turkish foreign policy is that of economic benefits to the country. It is shown that this new foreign policy has benefited Turkey economically; specifically, the positive effects of diplomatic activities on international trade are estimated by using a standard trade gravity model. The rest of the paper is organized as follows: Background information is given about Turkish foreign policy and the changes in its structure during the AK Party governments. Then a brief literature review and the empirical methodology is presented, followed by a discussion of the results. New Turkish Foreign Policy Turkey s new regional role embodied by Ankara, cannot be explained only by the identity preferences of the AK Party; instead, an interest-based approach with a perspective of economic and geopolitical acquisitions is relevant here. After Turkey gained the legal status of full membership in the EU, its economy began to be defined as safe and consistent, with the ability to make investments. Ankara, which prefers a rational foreign policy in parallel with identity-based approaches, started to form a foreign policy that gradually adopted the concept of a trade state. 4 The AK Party, which came into power with great hopes after the economic crisis of 2001, focused on rational preferences, as it knew it would be impossible to sustain economic success using identity politics. The AK Party shaped Turkish foreign policy with these rational goals in mind as well as the new paradigms of EU policies, emphasized above. The new foreign policy preferences of Ankara, aimed at establishing unproblematic relationships with peripheral countries, have always been economic benefits. Turkey accepted the dialogue with peripheral countries as a driving force for its economy, security policy and new image, and removed foreign policy from its priorities. By abolishing visas with most Middle East countries, Turkey s aim was to influence the culture of Arabic society while concurrently increasing foreign trade volume. Because of the Islamist background of the AK Party government, there are analyses that interpret these preferences as idealist as well as analyses that prioritize economic rationality which is the focus of this article Summer 109
4 ABDÜLKADİR CİVAN, SAVAŞ GENÇ, DAVUT TAŞER and SİNEM ATAKUL Turkish Foreign Minister Ahmet Davutoglu, (R) Shakes Hands With Deputy Prime Minister Ali Babacan AFP / Adem Altan Why does Turkey prefer an active foreign policy? Does the Turkish Ministry of Foreign Affairs, which added success in foreign trade to its performance criteria, use foreign policy as an instrument to increase trade? Are trust-based policy preferences reflected positively in Ankara s tourism and export volumes? Apart from its Western identity, Turkey discovers new markets with the help of the relationships it establishes through its Muslim counterparts; and in these new markets, it finds new zones of influence and bilateral relations. International trade is one of the leading instruments of Turkish foreign policy. This is not merely an incidental issue; it forms a new platform that accelerates bilateral relations on a real political field. Increasing mutual dependence through trade has enabled Turkey to establish more predictable and sustainable relations with other countries. 5 The biggest risk that threatens this new and major preference of Turkish foreign policy is the presence of many regional conflicts in the Middle East and African countries. Parallel to these risks, Turkey s industrial substructure is quite weak, while the industrial and economic substructure of China its rival in regions such as the Middle East and Africa is developed and strong; this leads to many discussions and doubts about when and how much Turkey should rely on foreign trade. For Turkey to be able to exist in the asymmetric competition of the region, the status of a trade state should be widely accepted, supported on different levels, and practiced efficiently. 110 Insight Turkey
5 THE EFFECT OF NEW TURKISH FOREIGN POLICY ON INTERNATIONAL TRADE Given this environment, western neighbors of Turkey will face numerous problems due to financial crises, while the eastern neighbors will face problems due to political instabilities. These problems will not be solved in the near future in Europe or the Arabic world, either. This can mean a shrinking of the market for a productive economy. Security issues caused by the movement of political fault lines are as much a threat for Ankara as losing markets. Thus, Ankara turning to Africa as an alternative market, can be evaluated as a consequence of rising conflicts in the Middle East. In 2001, EU and North American countries were making 60 percent of the total Turkish international trade volume; that ratio decreased to 44 percent in 2012 However, the governments have followed a proactive diplomacy. Being at the center of its region requires Turkey to balance both South-North and East-West relations. As a necessity of proactive diplomacy, it is indispensable for Turkey to establish close relationships with all the countries in the region. Turkey started to demonstrate an interest in events in the region by pushing variety of foreign policy instruments through diplomatic processes. 6 By focusing on past competitors such as Russia, Greece, Armenia, Iran, Iraq and Syria, Ankara has replaced the Cold War strategy of static polarization and regional isolation with a multidimensional foreign policy, embracing the new role of regional leadership. The principle of good neighborly relations began before the AK Party came to power. For instance, relations with Greece had already been easing due to mutual aid attempts after earthquakes hit both countries in However, the support of the Annan Plan in Cyprus was the result of the new foreign policy of the AK Party. Turkey also exerted considerable effort to bring about more normalized relations with Armenia. Moreover, in spite of international political criticism and UN sanctions, Turkey enjoys a positive relationship with Iran. Similarly, relations with Iraq (not only the Central Government but also the Regional Kurdish Government) have improved. A democratized Middle East means more predictable neighbor relations, long-term investment plans, and an expansion in the scope of regional cooperation projects for Turkey. 7 In terms of foreign policy, Turkey has made the largest investment in Syria, accepting the country as a significant market and route for both security policies and foreign trade. With the Arab awakening, Turkey has distanced itself from the Assad regime; but because of this, the foreign trade volume of Turkey has decreased in many Arab countries that are reached by land. Parallel to these positive political relationships that emerged before the Arab Spring, economic ties with neighboring countries have also improved. Even if we exclude energy imports, the growth in trade (exports as well as imports) with neighboring 2013 Summer 111
6 ABDÜLKADİR CİVAN, SAVAŞ GENÇ, DAVUT TAŞER and SİNEM ATAKUL states is remarkable. This alone suggests that Turkey s zero problem policy has created some economic benefits. Another distinctive point of the AK Party s foreign policy is the attempt to abandon the single-axle concept, which is more accepted in the West. Even though Turkey s relationship with the West remains important, the strength of Turkey s relationships with neighboring countries and other countries in Africa, the Middle East and Asia has increased. According to Davutoğlu, Turkey currently has an opportunity to redefine its position in Afro-Eurasia as a geopolitically important country. He presents this vision in his book Strategic Depth: Turkey is a country at the epicenter of the Balkans, the Middle East, and the Caucasus, the center of Eurasia in general and is in the middle of the Rimland belt cutting across the Mediterranean to the Pacific. The AK Party s policy makers argue that rather than being peripheral, Turkey is a central international player and a regional power. Turkey has attempted to gain observer status to organizations such as Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), the U.N. Security Council, the African Union and the Shanghai Cooperation Organization. Regions that were regarded as distant and irrelevant before the AK Party governments are now considered hotspots. A large area from Africa to Far Asia and Latin America is included in the sphere of interest of new foreign policy. Moreover, in purely economic terms, the axis is rapidly shifting toward developing countries. While the economic weight of industrialized countries such as the United States, Japan, Germany, England, Canada, France, Italy and Belgium is decreasing, developing countries such as China, India, South Korea, Indonesia, Thailand and Malaysia, are becoming bigger players in the world economy. As a result, a five-polar (at least) world is forming. Taking into account this new balance of economic power, Turkey s newly constructed foreign policy and its regional involvement have expanded the economic horizons or Ankara. Casual observation suggests that trade volume has increased more with those countries where Turkish foreign policy makers have developed greater interactions Looking at the international trade flows of Turkey, the consequences of these connections with non-western countries can easily be identified. Table 1 presents the trade data of Turkey with different country groups and how it changed between In 2001, EU and North American countries were making 60 percent of the total Turkish international trade volume; that ratio decreased 112 Insight Turkey
7 THE EFFECT OF NEW TURKISH FOREIGN POLICY ON INTERNATIONAL TRADE to 44 percent in Similarly, countries within the Organization of Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) saw trade decrease from 66 percent to 46 percent. (Note: most EU countries are also members of OECD.) On the other hand, the share of Asian, Near and Middle East countries, members of Black Sea Economic Cooperation, and Organization of the Islamic Conference has increased substantially. We observe a 20 to 30 percent increase - in some countries, it s even close to 50 percent - in annual trade volume. Although those growth rates cannot continue indefinitely, they are nevertheless related to Turkey s new foreign policy. However, Ankara s attempt at multidimensional foreign policy is not as simple as it looks, especially when conflicts of interests are taken into consideration. On the one hand, Turkey tries to balance between the EU-United States and the Middle East-Eurasia; on the other, it searches for harmony between the North and the South, and the policies that give importance to both Russia and Africa involve risks. Thus, multidimensional foreign policy generates new rivalries in different centers and involves new risks 5. While some experts consider Turkey s new foreign policy to be a proactive expansion, others accuse of Davutoğlu of being unrealistic and irrational. They interpret the policy conducted by Davutoglu to be neo-ottomanist. As the data in Table 1 clearly shows, not only has trade with geographically close countries like Iran, Lebanon and Israel increased during the last decade, but so too has trade with other Asian, African, European, and Muslim countries. Casual observation suggests that trade volume has increased more with those countries where Turkish foreign policy makers have developed greater interactions. Specifically, we observe that trade has increased with the countries where the Prime Minister, President and Ministry of State have made frequent visits. It shows that the new foreign policy has generated positive economic results. In the next section we will statistically test the hypothesis that Turkish foreign policy activities have indeed had a beneficial impact on the country s trade. Data and Methodology In order to understand the influence of diplomatic activities on the international trade of Turkey, we use a standard gravity model. This framework predicts the trade flows between two countries by their economic sizes and geographic distances between them. The model, first proposed by Jan Tibergen (1962) 8, has been used frequently in empirical trade flow studies. The underlying concept is simple and attractive: bigger countries (per capita income and population) trade more, and the further away from each other the higher the costs of trade, and thus, the lower the trade flow. The basic model is defined by the following formula, which is similar to the Newtonian gravity equation: 2013 Summer 113
8 ABDÜLKADİR CİVAN, SAVAŞ GENÇ, DAVUT TAŞER and SİNEM ATAKUL [(Size] i [ ) (Size] j ) Trade ij = Distance ij Where Trade ij : The trade flow between countries i and j, Size i : The economic size of country i, Size j : The economic size of country j, Distance ij : The geographic distance between countries i and j. There have been many theoretical justifications and adjustments to the basic model. Alan Deardoff (1998) 9 provided a good theoretical assessment of the model and concluded that a gravity specification is consistent with many types of trade models. Generally, it has been observed that the gravity model is indeed a good predictor of bilateral trade flows. Later empirical studies added many other variables to the basic gravity model, such as the existence of common borders, language, currency and colonial links. Those additional explanatory variables both improve the predictive power of the model and help to clarify the impact of specific factors on trade. However, since the goal of this paper is not to accurately describe all factors affecting trade between Turkey and other countries, the gravity model is kept as simple as possible and only the most basic explanatory variables are used. Keeping the model simple allows us to use almost all countries in this statistical analysis, since the required income and population data are available for virtually all countries. Thus we estimate the following panel gravity equation: 10 [(TRD] it ) = β 0 + β 1 [(Y] Tt ) + β 2 [(Y] it ) + β 3 [(Pop] Tt ) + β 4 [(Pop] it ) + β 5 (D it ) + ε it (1) [(MPRT] it ) = β 0 + β 1 [(Y] Tt ) + β 2 [(Y] it ) + β 3 [(Pop] Tt ) + β 4 [(Pop] it ) + β 5 (D it ) + ε it (2) [(XPRT] it ) = β 0 + β 1 [(Y] Tt ) + β 2 [(Y] it ) + β 3 [(Pop] Tt ) + β 4 [(Pop] it ) + β 5 (D it ) + ε it (3) Where TRD it : The total trade between country i and Turkey in year t, XPRT it : The export of Turkey to country i in year t, MPRT it : The import of Turkey from country i in year t, Y Tt : The real income per capita in Turkey in year t, Y it : The real income per capita in country i in year t, Pop Tt : The population of Turkey in year t, Pop it : The population of country i in year t, D it : The geographical distance between country i and Turkey. The aim of this study is to understand the influence of diplomatic activities of the government on Turkey s international trade. Therefore, the diplomatic activities of the government in these estimations could be included. A positive 114 Insight Turkey
9 THE EFFECT OF NEW TURKISH FOREIGN POLICY ON INTERNATIONAL TRADE coefficient would represent a positive relationship between diplomatic activities and international trade. However, if the government concentrates on its diplomatic activities in those countries where there are already strong trade links, we would see a positive relationship between trade volume and diplomatic activities. This is the typical question of whether there is causation or mere correlation between two events which causes what? Do diplomatic missions cause more trade, or does trade cause an increase in diplomatic missions? As stated before, endogeneity can be a serious problem in econometric analysis. There are two possible ways to handle this problem: IV-estimation and the differences-in-differences (diff-diff) method. Since it is difficult to find a strong instrumental variable, the diff-diff method is more common than IV. Also, the diff-diff method is used mostly for panel data while IV is used for cross-sectional data. Andrew Rose (2007) 11 uses IV to overcome the causality problem in cross-sectional data for whether foreign missions are in fact systematically linked to exports or not. He links exports from 22 important countries to 200 destination countries and uses data averaged between On the other hand, Volker Nitsch (2007) 12 studies whether visits from heads of state from France, Germany and the U.S. from promoted exports. Nitsch applies a long-run differences-in-differences specification. Specifically, he regresses the annual growth rates of Our hypothesis is that if more diplomatic missions occurred between Turkey and any country, we should expect a higher increase in trade with that country bilateral exports on a dummy variable that takes the value of 1 when a country in his sample has ever received an official visit from the exporting nation, and another dummy that is equal to 1 when an actual visit has taken place. The method used in this paper, explained below, is similar. What we do is regress differences between actual trade and predicted trade by the number of visitations. In this aspect, it operates like the diff-diff method. To analyze the possible effects of diplomatic missions on trade, we use a simple two-step strategy. In the first step, we estimate a standard gravity trade model using the Equations 1-3. In these estimations, we use the annual international trade data of Turkey with more than 150 countries in the years of 1998, 1999 and By using these estimation results we predict the trade of Turkey with other countries in We compare those predicted values with the actual trade volume in Then, we look at whether there is any relationship between diplomatic missions in the related period and any unpredicted increase in the trade volume. Essentially, we simulate trade between Turkey and the relevant country in 2008, assuming that only per-capita incomes and populations of these two countries changed after Obviously many other things have 2013 Summer 115
10 ABDÜLKADİR CİVAN, SAVAŞ GENÇ, DAVUT TAŞER and SİNEM ATAKUL A positive relationship between the residual of actual and predicted values of trade volume and diplomatic missions can be loosely interpreted as diplomatic missions helping (and thus, causing) the increase in international trade changed in the relevant period; but the one thing we are interested in is the diplomatic missions. Our hypothesis is that if more diplomatic missions occurred between Turkey and any country, we should expect a higher increase in trade with that country. In other words, the actual change in the trade volume would be higher than the expected change due to the increase in income and population of Turkey and the other country. In short, a positive relationship between the residual of actual and predicted values of trade volume and diplomatic missions can be loosely interpreted as diplomatic missions helping (and thus, causing) the increase in international trade. The standard gravity model explains the trade volume between two countries by the incomes and populations of two trading countries and the distance between them. Therefore, we expect the trade volume between Turkey and other countries to have increased from 2001 to 2008, since the populations and incomes of both Turkey and the trading partner countries increased. However, if the diplomatic missions of the Prime Minister were successful in encouraging trade, the actual increase in trade volume would have been bigger than the rise in trade volume because of the rise in income and population. In order to test this hypothesis we estimated the following equations. UTRDD i = β 1 + β 2 DM i + ε i (4) UMPRTD i = β 1 + β 2 DM i + ε i (5) UXPRTD i = β 1 + β 2 DM i + ε i (6) Where UTRDD i UMPRT i UXPRT i DM i : The difference between actual trade between Turkey and country i and predicted trade between Turkey and country i in 2008, : The difference between actual imports of Turkey from country i and predicted imports of Turkey from country i in 2008, : The difference between actual exports of Turkey to country i and predicted exports of Turkey to country i in 2008, : The number of formal visitations of the Prime Minister of Turkey (Recep Tayyip Erdogan) to country i between 2003 and A positive β 2 coefficient can be interpreted as the fact that diplomatic visitations from Turkish officials (the Prime Minister in this case) increase the 116 Insight Turkey
11 THE EFFECT OF NEW TURKISH FOREIGN POLICY ON INTERNATIONAL TRADE trade between two countries. Obviously many other government officials, including the President of the Republic, the Minister of Trade, other ministers and lower-level public officials, also make formal visitations to the other countries. Naturally those visitations also have an effect on trade. However, categorizing and weighting the different officials formal visitations would require a lot more data and some ad hoc assumptions, so we use only the Prime Minister s visitations. In fact we can presume that the visitations of the Prime Minister and other public officials are highly correlated. We obtained data on formal visitations from the Prime Minister s General Office through private communication. Income and population data were obtained from The World Bank s World Development Indicators Database. Export and import data were obtained from the Turkish Statistical Office s (TUIK) website. 3 The distances between Turkey and other trading partner countries were obtained from data software EU Gene version by Bennett Scott and Stam Allan. 13 Results and Discussion Table 2 presents the estimation results of Equations 1-3 using data from We omitted the 2001 and 2002 data in our estimations to avoid the distortionary effects of the 2001 financial crisis. On the other hand, we do not want to go too far from today in our estimations, as we rely on the presumption that the Turkish economy and global economy are not too different today than in the years on which we do our estimations. By using these three years of data we have a relatively reasonable number of observations (between 414 and 445 on different specifications) in the estimations. All coefficients on the estimations have the expected signs and almost all of them are statistically significant at conventional levels. In column 1, the estimation results of Equation 1 are presented. Here the dependent variable is total trade between Turkey and the other country. The positive sign on the coefficient of Turkish per capita income variable means that as the per capita income in Turkey increases the total trade between Turkey and the other country rises. The estimated elasticity is presented in brackets. Elasticity is a measurement that indicates the changes in one variable in response to a change in another variable. In this case elasticity is defined as: ΔY Tt Y Income elasticity of total trade = Tt ΔTRDit TRD it 2013 Summer 117
12 ABDÜLKADİR CİVAN, SAVAŞ GENÇ, DAVUT TAŞER and SİNEM ATAKUL Elasticities with respect to other variables are calculated similarly. A coefficient of 3.9 in the first row of the first column indicates that a 10 percent increase in the per capita income of Turkey increases the trade volume by 39 percent. Similarly, an increase in the per capita income of the corresponding country increases the total trade between Turkey and the other country. The populations of both countries (Turkey and its trading partner) also positively affect the trade volume between them. Similar to other studies on the subject, we also find a negative relationship between trade volume and geographical distance. If a country is 10 percent farther away from Turkey than another country, ceteris paribus, its total trade with Turkey is 7.9 percent less than the other one. There could be many explanations for that negative effect of distance, but the most basic and significant one is that transportation and communication costs are higher for faraway places. In the second column, the dependent variable is the import of Turkey from the other country. 14 Similar to total trade estimation, all coefficients have the expected signs and they are all significant. The third column presents the estimation results of Equation 3, where the dependent variable is the export of Turkey to the other country. In this estimation many coefficients are insignificant, though they have the correct sign. Turkish per capita and the population values do not seem to be affecting the exports of Turkey to the other country. That result is not surprising, since we do not expect those variables to be very important for Turkish exports to the other country. The other country s per capita income and population are more important explanatory variables. Table 3 presents our main estimations. In this table, the dependent variable is the unexplained increase in trade between Turkey and other countries. The dependent variable in the first column is the trade (due to the change in the income and population) between Turkey and the other country from The explanatory variable is the number of formal visitations of the Turkish Prime Minister Erdoğan to each country from We use the total number of visitations in that period since we presume that it is very unlikely that diplomatic visitations would increase trade immediately. It will take time to launch and increase the trade, so there will be latency. There is no theoretical basis to choose a specific latency period, and there is not enough empirical data to choose a latency period by using quantitative methods, either. Hence, we choose to analyze the cumulative effect of diplomatic visitations on the trade in The positive coefficient on the diplomacy variable suggests that there is a very strong and positive relationship between the Prime Minister s visits and an increase in the trade. Since the dependent variable is the unexplained increase in trade due to the change in standard gravity model explanatory variables, there is no straightforward interpretation of the coefficient. It tells us that a 10 percent increase in the formal visitations of the Prime Minister would increase 118 Insight Turkey
13 THE EFFECT OF NEW TURKISH FOREIGN POLICY ON INTERNATIONAL TRADE the trade by 21 percent, if there is no other change in the factors affecting the trade. According to that estimation, the Prime Minister s visits are highly effective in promoting trade relations. The second and third columns of Table 3 suggest that international visits of the Prime Minister increase both the imports and exports of Turkey. Conclusion During the Cold War, Turkey had practically no room for practicing its own independent foreign policy, since it was a member of NATO. Turkey had developed a concept of foreign policy and security in a bipolar world, and believed for years that its importance derived solely from its geopolitical position. Changing regional and global circumstances are now providing new opportunities for Ankara. Thus, experimentation with different foreign policy approaches should be expected. Turkey has thus turned into a country that can make flexible political decisions for its own benefit in the world and the region. Emiliano Alessandri (2010) expresses this perspective in following statement: Turkey, it is stressed, has in recent years come to adopt a soft-power as opposed to a hard-power approach to foreign policy. Economic opportunity and peace have become the driving forces of its external action, allowing Turkey to greatly expand its trading relations and to act as facilitator of dialogue in such realms as the Caucasus and the Arab-Israeli peace process. To European countries subscribing to this view, Turkey s activism in the Middle East is nothing to be afraid of. It is, on the contrary, a clear demonstration that Turkey would be a critical asset for the EU 15. The new foreign policy concept involves close interaction between the political and economic aspirations of Turkey. Its aim is to utilize its economic strength in order to reach political goals, while concurrently using political tools to obtain economic benefits. However, when Turkey s economic and military capacities are critically assessed, it is obvious that they are not sufficient for Turkey to meet its very ambitious political goals. The relatively ineffective role played by Turkey in the latest Middle East crisis has only made that point clearer. On the other hand, Turkey s somewhat reluctant attitude toward the latest crisis in Libya may be attributed to economic ties that sometimes become barriers, rather than instruments in political processes. Is the new foreign policy associated with Davutoğlu a sustainable concept? Whether or not the same line of new foreign policy can be maintained under a different government is a question that can only be answered in time. Yet, very fast and significant changes in the region show that Turkey cannot afford 2013 Summer 119
14 ABDÜLKADİR CİVAN, SAVAŞ GENÇ, DAVUT TAŞER and SİNEM ATAKUL to be closed to regional and global progress. It can be argued that peace, democratization, and the maintenance of economic stability will bear positive results not only for its own subjects, but for other countries in the region and for international security. When we analyze Turkish foreign policy from a perspective that takes into account its historical roots, we see that sometimes an interest-seeking foreign policy has been dominant while at other times a value-based foreign policy has emerged. Even if Turkey seems to have developed a new foreign policy line in which certain values are in the foreground, it can t be claimed that these values are distinct from Turkey s interests. Turkey, as the only liberal, democratic, secular and Muslim country in the region, will be active in the Middle East. 16 The increasing interest of Turkish foreign policy in Muslim areas, and especially in the Middle East, should not be perceived as an opposition to traditional Western-oriented foreign policy; nor should it be described as an axis shift or as neo-ottomanism. A stable Middle East in the process of democratization and normalization presents Turkey with a golden opportunity for better security and improved economy policies. Table 1. The Change in Trade Structure of Turkey between 2001 and % to % to Total Export Import Trade Total Export Import Trade Trade Export Import Trade Trade Country Groups (Million $) (Million $) (Million $) (%) (Million $) (Million $) (Million $) (%) EU (27 Countries) 17,546 19,823 37, ,201 87, , Other Europe ,368 37,416 51, Africa , ,279 4 North America ,084 21,746 6 Central America South America Near and Middle East ,452 21,410 63, Other Asia ,575 49,601 60, OECD 21,307 26,886 48, , ,723 18, Black Sea Economic Cooperation Organization ,793 41,509 60, Commonwealth of Independent States ,075 35,248 50, Organization of the Islamic Conference ,220 31,690 86, Total 31,334 41,399 72, , , , Insight Turkey
15 THE EFFECT OF NEW TURKISH FOREIGN POLICY ON INTERNATIONAL TRADE Table 2. International Trade Gravity Model. This table reports results from estimation of equation 1, 2 and 3 by random effects generalized least squares using heteroskedastic structure. The t statistics are reported in parentheses. ***, ** and * denotes significance levels at the 1%, 5% and 10% levels, respectively. The numbers in brackets represent the elasticity values. Dependent Variables Total Trade between Imports of Exports of Turkey and the Turkey from the Turkey to the Other Country Other Country Other Country Exogenous Variables Model 1 Model 2 Model 3 Intercept -3.27e+9*** -3.66e+9*** 1.94e+8 (-3.93) (-4.78) (0.57) [3.90] *** [5.82] Per capita income in Turkey *** [0.33] (3.90) (4.26) (0.50) Per capita income in the other country [0.79] *** [0.77] 36040*** [0.89] ** (2.99) (3.53) (2.54) [3.87] 27.97*** [6.61] Population in Turkey 31.63*** [-0.67] (3.31) (3.59) (-0.42.) [0.17] 1.93** [0.17] Population in the other Country 1.33** [0.12] 0.52 (2.20) (2.54) (1.32) Distance between Turkey and the other country [-0.79] *** [-0.69] *** [-0.88] *** (-2,72) (-2.70) (-2.62) # of Obs Table 3. Effects of Diplomatic Visitations on Trade. This table reports results from estimation of Equation 1 and 2 by ordinary least squares using heteroskedastic structure. The t statistics are reported in parentheses. ***, ** and * denote significance levels at the 1%, 5% and 10% levels, respectively. These are estimation results of equations 4, 5 and 6. The numbers in brackets represent the elasticity values. The dependent variable is the difference between the predicted value of trade in 2008 (import, export) using the coefficients from estimations of equations 1-3 using data and actual trade volume. Dependent Variables Difference in Difference in Difference in Trade between Imports of Exports of Turkey and the Turkey from the Turkey to Other Country Other Country Other Country Exogenous Variables Model 1 Model 2 Model 3 Intercept -8.63E+08**** -8.51e+8*** 3.36e+8*** (-3.63) (-4.87) (3.96) [2.10] 1.93e+9*** [6.35] Diplomacy 1.20e+9*** [0.63] 7.38e+8*** (4.46) (3.97) (4.37) R # of Obs Summer 121
16 ABDÜLKADİR CİVAN, SAVAŞ GENÇ, DAVUT TAŞER and SİNEM ATAKUL Endnotes 1. Şaban Kardaş, Türk Diş Politikasında Eksen Kayması mı? Akademik Orta Doğu, Vol. 5, No. 2, (2011). 2. Speech of Ahmet Davutoğlu at Şehir University 3. The data is obtained from Turkish Statistical Institute s website, do?alt_id=12 (accessed on ). 4. Ahmet Davutoğlu, Stratejik Derinlik, Turkiye nin Uluslararasi Konumu (Istanbul: Küre Yayınları, 2001) 5. Bülent Aras, The Davutoğlu Era in Turkish Foreign Policy, Insight Turkey, Vol. 11, No. 3, (2009), p Savaş Genç, Perception of Turkey s Foreign Policy Among the Elite of Its Neighbors, Turkish Review, Vol. 1 (June 2011), p Gülistan Gürbey, Changes in Turkish Foreign Policy under AK Party Government? Foreign Minister Da vutoğlu s Concept of Strategic Depth, Südosteuropa Mitteilungen, Vol. 2 (2010). 8. Jan Tinbergen, Shaping the World Economy: Suggestions for an International Economic Policy (New York: Twentieth Century Fund, 1962). 9. Alan Deardoff, Determinants of Bilateral Trade: Does Gravity Work in a Neoclassical Framework? In J. A. Frankel (ed.), The Regionalization of the World Economy. (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1998), p See following articles for more details about gravity models and specific examples. James Anderson and Eric van Wincoop, Gravity with Gravitas: A Solution to the Border Puzzle, American Economic Review, Vol. 93, No. 1 (2003), p Peter Egger, An Econometric View on the Estimation of Gravity Models and the Calculation of Trade Potentials, World Economy, Vol. 25 (2002), p Andrew Rose, The Foreign Service and Foreign Trade: Embassies as Export Promotion, World Economy, Vol. 30, No. 1 (2007), p Volker Nitsch, State Visits and International Trade, The World Economy, vol. 30, No. 12 (2007), p Scott Bennett and Allan Stam, EU Gene Software (accessed on ). 14. One critic has suggested that since oil and natural markets are different than others (prices change substantially and demand price elasticies are very low), we should exclude those from our analysis but include only non-energy trade. So we exclude six countries where Turkey imports substantial amount of oil and/or natural gas from our analysis: Algeria, Iran, Iraq, Kazakhstan, Russia and Saudi Arabia. The results were qualitatively the same and quantitatively very similar. 15. Emiliano Alessandri, The New Turkish Foreign Policy and the Future of Turkey-EU Relations, Istituto Affari Internazionali, retrieved , from Şaban Kardaş, Turkey and the Arab Spring: Coming to Terms with Democracy Promotion? Foreign Policy Program Policy Brief (October 27, 2011). 122 Insight Turkey
Turkish Foreign Policy and Russian-Turkish Relations. Dr. Emre Erşen Marmara University, Istanbul, Turkey
 Turkish Foreign Policy and Russian-Turkish Relations Dr. Emre Erşen Marmara University, Istanbul, Turkey E-mail: eersen@marmara.edu.tr Domestic Dynamics --- 2002 elections --- (general) Only two parties
Turkish Foreign Policy and Russian-Turkish Relations Dr. Emre Erşen Marmara University, Istanbul, Turkey E-mail: eersen@marmara.edu.tr Domestic Dynamics --- 2002 elections --- (general) Only two parties
Davutoglu as Turkey's PM and Future Challenges
 Position Papers Davutoglu as Turkey's PM and Future Challenges AlJazeera Centre for Studies Al Jazeera Center for Studies Tel: +974-44663454 jcforstudies-en@aljazeera.net 28 August 2014 [AlJazeera] Abstract
Position Papers Davutoglu as Turkey's PM and Future Challenges AlJazeera Centre for Studies Al Jazeera Center for Studies Tel: +974-44663454 jcforstudies-en@aljazeera.net 28 August 2014 [AlJazeera] Abstract
TURKISH FOREIGN POLICY IN A GLOBALIZING WORLD
 TURKISH FOREIGN POLICY IN A GLOBALIZING WORLD In Turkey there is currently a lack of trust and an increasing feeling of ambiguity and insecurity about the future of Turkey-EU relations. However, this article
TURKISH FOREIGN POLICY IN A GLOBALIZING WORLD In Turkey there is currently a lack of trust and an increasing feeling of ambiguity and insecurity about the future of Turkey-EU relations. However, this article
ISTANBUL SECURITY CONFERENCE 2017 New Security Ecosystem and Multilateral Cost
 VISION DOCUMENT ISTANBUL SECURITY CONFERENCE 2017 New Security Ecosystem and Multilateral Cost ( 01-03 November 2017, Istanbul ) The controversies about who and how to pay the cost of security provided
VISION DOCUMENT ISTANBUL SECURITY CONFERENCE 2017 New Security Ecosystem and Multilateral Cost ( 01-03 November 2017, Istanbul ) The controversies about who and how to pay the cost of security provided
Size of Regional Trade Agreements and Regional Trade Bias
 Size of Regional Trade Agreements and Regional Trade Bias Michele Fratianni * and Chang Hoon Oh** *Indiana University and Università Politecnica delle Marche **Indiana University Abstract We test the relationship
Size of Regional Trade Agreements and Regional Trade Bias Michele Fratianni * and Chang Hoon Oh** *Indiana University and Università Politecnica delle Marche **Indiana University Abstract We test the relationship
TURKISH FOREIGN POLICY AND IRAN
 TURKISH FOREIGN POLICY AND IRAN This article elaborates upon Turkey s foreign policy with a specific focus on relations with Iran. Turkish foreign policy is predicated on its unique historical experience
TURKISH FOREIGN POLICY AND IRAN This article elaborates upon Turkey s foreign policy with a specific focus on relations with Iran. Turkish foreign policy is predicated on its unique historical experience
The Egyptian Cabinet Information and Decision Support Center
 1 Fourth Think Tanks Forum of the OIC Countries Economic Integration within the OIC Countries: Prospects and Challenges Concept Note 26-26 March, 2013 Cairo - Egypt 2 1. About the Forum of Think Tanks
1 Fourth Think Tanks Forum of the OIC Countries Economic Integration within the OIC Countries: Prospects and Challenges Concept Note 26-26 March, 2013 Cairo - Egypt 2 1. About the Forum of Think Tanks
An Empirical Analysis of Pakistan s Bilateral Trade: A Gravity Model Approach
 103 An Empirical Analysis of Pakistan s Bilateral Trade: A Gravity Model Approach Shaista Khan 1 Ihtisham ul Haq 2 Dilawar Khan 3 This study aimed to investigate Pakistan s bilateral trade flows with major
103 An Empirical Analysis of Pakistan s Bilateral Trade: A Gravity Model Approach Shaista Khan 1 Ihtisham ul Haq 2 Dilawar Khan 3 This study aimed to investigate Pakistan s bilateral trade flows with major
The Trade Liberalization Effects of Regional Trade Agreements* Volker Nitsch Free University Berlin. Daniel M. Sturm. University of Munich
 December 2, 2005 The Trade Liberalization Effects of Regional Trade Agreements* Volker Nitsch Free University Berlin Daniel M. Sturm University of Munich and CEPR Abstract Recent research suggests that
December 2, 2005 The Trade Liberalization Effects of Regional Trade Agreements* Volker Nitsch Free University Berlin Daniel M. Sturm University of Munich and CEPR Abstract Recent research suggests that
Impact of Trade blocs on Agricultural Trade and Policy Implications. for China: Gravity Model Study. Lin SUN
 Impact of Trade blocs on Agricultural Trade and Policy Implications for China: Gravity Model Study Lin SUN Department of Economics, College of Business Administration Zhejiang University of Technology
Impact of Trade blocs on Agricultural Trade and Policy Implications for China: Gravity Model Study Lin SUN Department of Economics, College of Business Administration Zhejiang University of Technology
What s the problem with economic integration in the MED?
 tepav The Economic Policy Research Foundation of Turkey What s the problem with economic integration in the MED? Güven Sak Washington DC, 11 June 2013 Connectivity in the Mediterranean Slide 2 Jenin Industrial
tepav The Economic Policy Research Foundation of Turkey What s the problem with economic integration in the MED? Güven Sak Washington DC, 11 June 2013 Connectivity in the Mediterranean Slide 2 Jenin Industrial
EU S FOREIGN POLICY TOWARDS THE BALKANS AND FUTURE PROSPECTS OF TURKEY S MEMBERSHIP OF EU FOR THE REGION. Göknil ERBAŞ *
 EU S FOREIGN POLICY TOWARDS THE BALKANS AND FUTURE PROSPECTS OF TURKEY S MEMBERSHIP OF EU FOR THE REGION Abstract Göknil ERBAŞ * It is well known that there is a strong historical link between Turkey and
EU S FOREIGN POLICY TOWARDS THE BALKANS AND FUTURE PROSPECTS OF TURKEY S MEMBERSHIP OF EU FOR THE REGION Abstract Göknil ERBAŞ * It is well known that there is a strong historical link between Turkey and
Turkey s Rise as a Regional Power and its Role in the European Neighbourhood (ARI)
 Turkey s Rise as a Regional Power and its Role in the European Neighbourhood (ARI) Deniz Devrim and Evelina Schulz * Theme: Turkey has a growing strategic role in its overlapping neighbourhood with the
Turkey s Rise as a Regional Power and its Role in the European Neighbourhood (ARI) Deniz Devrim and Evelina Schulz * Theme: Turkey has a growing strategic role in its overlapping neighbourhood with the
Germany and the Middle East
 Working Paper Research Unit Middle East and Africa Stiftung Wissenschaft und Politik German Institute for International and Security Affairs Volker Perthes Germany and the Middle East (Contribution to
Working Paper Research Unit Middle East and Africa Stiftung Wissenschaft und Politik German Institute for International and Security Affairs Volker Perthes Germany and the Middle East (Contribution to
PRICING BEHAVIOUR OF KAZAKH, RUSSIAN AND UKRAINIAN EXPORTERS IN THE INTERNATIONAL WHEAT MARKET
 PRICING BEHAVIOUR OF KAZAKH, RUSSIAN AND UKRAINIAN EXPORTERS IN THE INTERNATIONAL WHEAT MARKET Gulmira Gafarova*, Oleksandr Perekhozhuk**, Thomas Glauben*** *Gulmira Gafarova PhD Student at the Leibniz
PRICING BEHAVIOUR OF KAZAKH, RUSSIAN AND UKRAINIAN EXPORTERS IN THE INTERNATIONAL WHEAT MARKET Gulmira Gafarova*, Oleksandr Perekhozhuk**, Thomas Glauben*** *Gulmira Gafarova PhD Student at the Leibniz
Revealed Comparative Advantage and Competitiveness: A Case Study for Turkey towards the EU
 Journal of Economic and Social Research 10(2) 2008, 25-41 Revealed Comparative Advantage and Competitiveness: Vildan Serin * & Abdulkadir Civan ** Abstract. This paper seeks to quantify the extent to which
Journal of Economic and Social Research 10(2) 2008, 25-41 Revealed Comparative Advantage and Competitiveness: Vildan Serin * & Abdulkadir Civan ** Abstract. This paper seeks to quantify the extent to which
Poverty Reduction and Economic Growth: The Asian Experience Peter Warr
 Poverty Reduction and Economic Growth: The Asian Experience Peter Warr Abstract. The Asian experience of poverty reduction has varied widely. Over recent decades the economies of East and Southeast Asia
Poverty Reduction and Economic Growth: The Asian Experience Peter Warr Abstract. The Asian experience of poverty reduction has varied widely. Over recent decades the economies of East and Southeast Asia
AVİM UZBEKISTAN'S REGIONAL POLICIES UNDER NEW PRESIDENT: A NEW ERA? Özge Nur ÖĞÜTCÜ. Analyst. Analysis No : 2017 /
 UZBEKISTAN'S REGIONAL POLICIES UNDER NEW PRESIDENT: A NEW ERA? Özge Nur ÖĞÜTCÜ Analyst Analysis No : 2017 / 26 18.08.2017 On 11th of August a conference organized by the Foreign Ministry of Uzbekistan
UZBEKISTAN'S REGIONAL POLICIES UNDER NEW PRESIDENT: A NEW ERA? Özge Nur ÖĞÜTCÜ Analyst Analysis No : 2017 / 26 18.08.2017 On 11th of August a conference organized by the Foreign Ministry of Uzbekistan
TURKEY- HORN OF AFRICA ISTANBUL MEETING
 TURKEY- HORN OF AFRICA ISTANBUL MEETING FINAL REPORT (DRAFT) Istanbul Meeting, the first event of Turkey - Horn of Africa Strategic Dialogue Program that has the main theme of Turkey - Horn of Africa Countries:
TURKEY- HORN OF AFRICA ISTANBUL MEETING FINAL REPORT (DRAFT) Istanbul Meeting, the first event of Turkey - Horn of Africa Strategic Dialogue Program that has the main theme of Turkey - Horn of Africa Countries:
GENDER EQUALITY IN THE LABOUR MARKET AND FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT
 THE STUDENT ECONOMIC REVIEWVOL. XXIX GENDER EQUALITY IN THE LABOUR MARKET AND FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT CIÁN MC LEOD Senior Sophister With Southeast Asia attracting more foreign direct investment than
THE STUDENT ECONOMIC REVIEWVOL. XXIX GENDER EQUALITY IN THE LABOUR MARKET AND FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT CIÁN MC LEOD Senior Sophister With Southeast Asia attracting more foreign direct investment than
Benefit levels and US immigrants welfare receipts
 1 Benefit levels and US immigrants welfare receipts 1970 1990 by Joakim Ruist Department of Economics University of Gothenburg Box 640 40530 Gothenburg, Sweden joakim.ruist@economics.gu.se telephone: +46
1 Benefit levels and US immigrants welfare receipts 1970 1990 by Joakim Ruist Department of Economics University of Gothenburg Box 640 40530 Gothenburg, Sweden joakim.ruist@economics.gu.se telephone: +46
THE GLOBAL FINANCIAL CRISIS AND ECONOMIC INTEGRATION: EVIDENCE ON ASEAN-5 COUNTRIES 1
 Journal of Indonesian Economy and Business Volume 24, Number 3, 2009, 291 300 THE GLOBAL FINANCIAL CRISIS AND ECONOMIC INTEGRATION: EVIDENCE ON ASEAN-5 COUNTRIES 1 Lukman Hakim Faculty of Economics Universitas
Journal of Indonesian Economy and Business Volume 24, Number 3, 2009, 291 300 THE GLOBAL FINANCIAL CRISIS AND ECONOMIC INTEGRATION: EVIDENCE ON ASEAN-5 COUNTRIES 1 Lukman Hakim Faculty of Economics Universitas
Curriculum Vitae (Updated February 2018)
 Curriculum Vitae (Updated February 2018) Seyed Masoud Mousavi Shafaee, Ph.D. Associate Professor of International Relations Department of International Relations Tarbiat Modares University Tehran, Iran
Curriculum Vitae (Updated February 2018) Seyed Masoud Mousavi Shafaee, Ph.D. Associate Professor of International Relations Department of International Relations Tarbiat Modares University Tehran, Iran
CIVIL GLOBAL PROGRAM Economy & Ecosystem of the Future Discovering the Potential
 STRATEGIC VISION DOCUMENT CIVIL GLOBAL PROGRAM Economy & Ecosystem of the Future Discovering the Potential NEW ECOSYSTEM Looking at the basic trends in the world, global competition in the new era of economy
STRATEGIC VISION DOCUMENT CIVIL GLOBAL PROGRAM Economy & Ecosystem of the Future Discovering the Potential NEW ECOSYSTEM Looking at the basic trends in the world, global competition in the new era of economy
Immigration and Internal Mobility in Canada Appendices A and B. Appendix A: Two-step Instrumentation strategy: Procedure and detailed results
 Immigration and Internal Mobility in Canada Appendices A and B by Michel Beine and Serge Coulombe This version: February 2016 Appendix A: Two-step Instrumentation strategy: Procedure and detailed results
Immigration and Internal Mobility in Canada Appendices A and B by Michel Beine and Serge Coulombe This version: February 2016 Appendix A: Two-step Instrumentation strategy: Procedure and detailed results
The Gravity Model on EU Countries An Econometric Approach
 European Journal of Sustainable Development (2014), 3, 3, 149-158 ISSN: 2239-5938 Doi: 10.14207/ejsd.2014.v3n3p149 The Gravity Model on EU Countries An Econometric Approach Marku Megi 1 ABSTRACT Foreign
European Journal of Sustainable Development (2014), 3, 3, 149-158 ISSN: 2239-5938 Doi: 10.14207/ejsd.2014.v3n3p149 The Gravity Model on EU Countries An Econometric Approach Marku Megi 1 ABSTRACT Foreign
European Neighbourhood Policy
 European Neighbourhood Policy Page 1 European Neighbourhood Policy Introduction The EU s expansion from 15 to 27 members has led to the development during the last five years of a new framework for closer
European Neighbourhood Policy Page 1 European Neighbourhood Policy Introduction The EU s expansion from 15 to 27 members has led to the development during the last five years of a new framework for closer
China s role in G20 / BRICS and Implications
 China s role in G20 / BRICS and Implications By Gudrun Wacker, German Institute for International and Security Affairs, Berlin 1 Introduction The main objective of this article is to assess China s roles
China s role in G20 / BRICS and Implications By Gudrun Wacker, German Institute for International and Security Affairs, Berlin 1 Introduction The main objective of this article is to assess China s roles
Migratory pressures in the long run: international migration projections to 2050
 ECONOMIC BULLETIN 4/2017 ANALYTICAL ARTICLES Migratory pressures in the long run: international migration projections to 2050 Rodolfo Campos 5 December 2017 This article presents bilateral international
ECONOMIC BULLETIN 4/2017 ANALYTICAL ARTICLES Migratory pressures in the long run: international migration projections to 2050 Rodolfo Campos 5 December 2017 This article presents bilateral international
report THE ROLE OF RUSSIA IN THE MIDDLE EAST AND NORTH AFRICA: STRATEGY OR OPPORTUNISM? Milan, 12 October 2018 from the Dialogue Workshop
 THE ROLE OF RUSSIA IN THE MIDDLE EAST AND NORTH AFRICA: STRATEGY OR OPPORTUNISM? Milan, 12 October 2018 report from the Dialogue Workshop REPORT No. 23 November 2018 www.euromesco.net report from the Dialogue
THE ROLE OF RUSSIA IN THE MIDDLE EAST AND NORTH AFRICA: STRATEGY OR OPPORTUNISM? Milan, 12 October 2018 report from the Dialogue Workshop REPORT No. 23 November 2018 www.euromesco.net report from the Dialogue
Newsletter. The Outlook for the Tri-polar World and the Japan-China Relationship 1
 Newsletter 2004. 8.1(No.4, 2004,) The Outlook for the Tri-polar World and the Japan-China Relationship 1 Toyoo Gyohten President Institute for International Monetary Affairs With the coming of the 21 st
Newsletter 2004. 8.1(No.4, 2004,) The Outlook for the Tri-polar World and the Japan-China Relationship 1 Toyoo Gyohten President Institute for International Monetary Affairs With the coming of the 21 st
The Flow Model of Exports: An Introduction
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive The Flow Model of Exports: An Introduction Jiri Mazurek School of Business Administration in Karviná 13. January 2014 Online at http://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/52920/
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive The Flow Model of Exports: An Introduction Jiri Mazurek School of Business Administration in Karviná 13. January 2014 Online at http://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/52920/
Policy Brief. Turkey between Syria and Israel: Turkey s Rising Soft Power. May 2008, No.15. Bülent ARAS
 Policy Brief, No.15 Turkey between Syria and Israel: Turkey s Rising Soft Power Bülent ARAS Summary Turkish policymakers exhibit a high degree of selfconfidence and willingness to pursue intensive diplomatic
Policy Brief, No.15 Turkey between Syria and Israel: Turkey s Rising Soft Power Bülent ARAS Summary Turkish policymakers exhibit a high degree of selfconfidence and willingness to pursue intensive diplomatic
Global Scenarios until 2030: Implications for Europe and its Institutions
 January 2013 DPP Open Thoughts Papers 3/2013 Global Scenarios until 2030: Implications for Europe and its Institutions Source: Global Trends 2030: Alternative Worlds, a publication of the National Intelligence
January 2013 DPP Open Thoughts Papers 3/2013 Global Scenarios until 2030: Implications for Europe and its Institutions Source: Global Trends 2030: Alternative Worlds, a publication of the National Intelligence
TURKEY AND THE EUROPEAN NEIGHBORHOOD POLICY
 TURKEY AND THE EUROPEAN NEIGHBORHOOD POLICY There is clear scope for Turkey and the EU to further develop cooperation and to intensify policy coordination in the Southern Mediterranean and Black Sea regions.
TURKEY AND THE EUROPEAN NEIGHBORHOOD POLICY There is clear scope for Turkey and the EU to further develop cooperation and to intensify policy coordination in the Southern Mediterranean and Black Sea regions.
The Asia-Pacific as a Strategic Region for the European Union Tallinn University of Technology 15 Sep 2016
 The Asia-Pacific as a Strategic Region for the European Union Tallinn University of Technology 15 Sep 2016 By Dr Yeo Lay Hwee Director, EU Centre in Singapore The Horizon 2020 (06-2017) The Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific as a Strategic Region for the European Union Tallinn University of Technology 15 Sep 2016 By Dr Yeo Lay Hwee Director, EU Centre in Singapore The Horizon 2020 (06-2017) The Asia-Pacific
The EU & the United States
 The EU & the United States Page 1 The EU & the United States Summary The United States supported European integration from its beginnings after the Second World War despite domestic concerns that Europe
The EU & the United States Page 1 The EU & the United States Summary The United States supported European integration from its beginnings after the Second World War despite domestic concerns that Europe
The Future of Saudi Price Discrimination: The Effect of Russian Production Increases
 The Future of Saudi Price Discrimination: The Effect of Russian Production Increases Amy Myers Jaffe Wallace Wilson Fellow for Energy Studies James A. Baker III Institute for Public Policy Ronald Soligo
The Future of Saudi Price Discrimination: The Effect of Russian Production Increases Amy Myers Jaffe Wallace Wilson Fellow for Energy Studies James A. Baker III Institute for Public Policy Ronald Soligo
The Dispensability of Allies
 The Dispensability of Allies May 17, 2017 Trump brings unpredictability to his talks with Middle East leaders, but some things we already know. By George Friedman U.S. President Donald Trump hosted Turkish
The Dispensability of Allies May 17, 2017 Trump brings unpredictability to his talks with Middle East leaders, but some things we already know. By George Friedman U.S. President Donald Trump hosted Turkish
REGIONAL INTEGRATION AND TRADE IN AFRICA: AUGMENTED GRAVITY MODEL APPROACH
 REGIONAL INTEGRATION AND TRADE IN AFRICA: AUGMENTED GRAVITY MODEL APPROACH Edris H. Seid The Horn Economic & Social Policy Institute (HESPI) 2013 African Economic Conference Johannesburg, South Africa
REGIONAL INTEGRATION AND TRADE IN AFRICA: AUGMENTED GRAVITY MODEL APPROACH Edris H. Seid The Horn Economic & Social Policy Institute (HESPI) 2013 African Economic Conference Johannesburg, South Africa
Examinator s guidance POL1005, Fall 2017
 Examinator s guidance POL1005, Fall 2017 All tasks and sub-tasks must be performed. Task 1 (counts 70 %) (A) As a newly-hired employee of Eurasia Group, you are tasked with the responsibility of preparing
Examinator s guidance POL1005, Fall 2017 All tasks and sub-tasks must be performed. Task 1 (counts 70 %) (A) As a newly-hired employee of Eurasia Group, you are tasked with the responsibility of preparing
Investigating the Geology and Geography of Oil
 S t u d e n t H a n d o u t a Investigating the Geology and Geography of Oil Land Area of Oil Countries of Southwest Asia Examine the map at right. It shows the locations of 10 oil countries in Southwest
S t u d e n t H a n d o u t a Investigating the Geology and Geography of Oil Land Area of Oil Countries of Southwest Asia Examine the map at right. It shows the locations of 10 oil countries in Southwest
International Journal of Humanities & Applied Social Sciences (IJHASS)
 Governance Institutions and FDI: An empirical study of top 30 FDI recipient countries ABSTRACT Bhavna Seth Assistant Professor in Economics Dyal Singh College, New Delhi E-mail: bhavna.seth255@gmail.com
Governance Institutions and FDI: An empirical study of top 30 FDI recipient countries ABSTRACT Bhavna Seth Assistant Professor in Economics Dyal Singh College, New Delhi E-mail: bhavna.seth255@gmail.com
IPIS & Aleksanteri Institute Roundtable 11 April 2016 IPIS Tehran, Iran
 IPIS & Aleksanteri Institute Roundtable 11 April 2016 IPIS Tehran, Iran The joint roundtable between the Institute for Political and International Studies (IPIS) and Aleksanteri Institute from Finland
IPIS & Aleksanteri Institute Roundtable 11 April 2016 IPIS Tehran, Iran The joint roundtable between the Institute for Political and International Studies (IPIS) and Aleksanteri Institute from Finland
Asian Economic and Financial Review THE DETERMINANTS OF FDI IN TUNISIA: AN EMPIRICAL STUDY THROUGH A GRAVITY MODEL
 Asian Economic and Financial Review ISSN(e): 2222-6737/ISSN(p): 2305-2147 URL: www.aessweb.com THE DETERMINANTS OF FDI IN TUNISIA: AN EMPIRICAL STUDY THROUGH A GRAVITY MODEL Souad BANNOUR Ep SFAR 1 ---
Asian Economic and Financial Review ISSN(e): 2222-6737/ISSN(p): 2305-2147 URL: www.aessweb.com THE DETERMINANTS OF FDI IN TUNISIA: AN EMPIRICAL STUDY THROUGH A GRAVITY MODEL Souad BANNOUR Ep SFAR 1 ---
Science and Technology Diplomacy in Asia
 Summary of the 3 rd Annual Neureiter Science Diplomacy Roundtable Science and Technology Diplomacy in Asia Date: Tuesday, November 11, 2014 Venue: National Graduate Institute for Policy Studies (GRIPS),
Summary of the 3 rd Annual Neureiter Science Diplomacy Roundtable Science and Technology Diplomacy in Asia Date: Tuesday, November 11, 2014 Venue: National Graduate Institute for Policy Studies (GRIPS),
INTERNATIONAL MULTILATERAL ASSISTANCE FOR SOCIO-ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT OF THE POOREST COUNTRIES OF SOUTH-EAST ASIA
 Journal of International Development J. Int. Dev. 29, 249 258 (2017) Published online 19 March 2014 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com).2999 INTERNATIONAL MULTILATERAL ASSISTANCE FOR SOCIO-ECONOMIC
Journal of International Development J. Int. Dev. 29, 249 258 (2017) Published online 19 March 2014 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com).2999 INTERNATIONAL MULTILATERAL ASSISTANCE FOR SOCIO-ECONOMIC
Trade, Border Effects, and Regional Integration between Russia s Far East and Northeast Asia
 Trade, Border Effects, and Regional Integration between Russia s Far East and Northeast Asia Russia s Far East (RFE) is set to benefit from Russia s growing economic cooperation with China in the face
Trade, Border Effects, and Regional Integration between Russia s Far East and Northeast Asia Russia s Far East (RFE) is set to benefit from Russia s growing economic cooperation with China in the face
Katerina Dalacoura A new phase in Turkish foreign policy: expediency and AKP survival
 Katerina Dalacoura A new phase in Turkish foreign policy: expediency and AKP survival Report Original citation: Dalacoura, Katerina (2017) A new phase in Turkish foreign policy: expediency and AKP survival.
Katerina Dalacoura A new phase in Turkish foreign policy: expediency and AKP survival Report Original citation: Dalacoura, Katerina (2017) A new phase in Turkish foreign policy: expediency and AKP survival.
Migration and Tourism Flows to New Zealand
 Migration and Tourism Flows to New Zealand Murat Genç University of Otago, Dunedin, New Zealand Email address for correspondence: murat.genc@otago.ac.nz 30 April 2010 PRELIMINARY WORK IN PROGRESS NOT FOR
Migration and Tourism Flows to New Zealand Murat Genç University of Otago, Dunedin, New Zealand Email address for correspondence: murat.genc@otago.ac.nz 30 April 2010 PRELIMINARY WORK IN PROGRESS NOT FOR
REGIONAL AND INTERNATIONAL TRADE OF ARMENIA: PERSPECTIVES AND POTENTIALS
 ISSN 1561-2422 REGIONAL AND INTERNATIONAL TRADE OF ARMENIA: PERSPECTIVES AND POTENTIALS Grigor Hayrapetyan Viktoriya Hayrapetyan Policy brief No11/14E This project (No R10-0421) was supported by the Economics
ISSN 1561-2422 REGIONAL AND INTERNATIONAL TRADE OF ARMENIA: PERSPECTIVES AND POTENTIALS Grigor Hayrapetyan Viktoriya Hayrapetyan Policy brief No11/14E This project (No R10-0421) was supported by the Economics
Does the G7/G8 Promote Trade? Volker Nitsch Freie Universität Berlin
 February 20, 2006 Does the G7/G8 Promote Trade? Volker Nitsch Freie Universität Berlin Abstract The Group of Eight (G8) is an unofficial forum of the heads of state of the eight leading industrialized
February 20, 2006 Does the G7/G8 Promote Trade? Volker Nitsch Freie Universität Berlin Abstract The Group of Eight (G8) is an unofficial forum of the heads of state of the eight leading industrialized
TURKEY OUTLOOK Jan., 2016
 TURKEY OUTLOOK 2016 06 Jan., 2016 Editor s Note Following note is a forward-looking assessment by StratejiCo. team based on information gathered from publicly available sources. StratejiCo. does not ensure
TURKEY OUTLOOK 2016 06 Jan., 2016 Editor s Note Following note is a forward-looking assessment by StratejiCo. team based on information gathered from publicly available sources. StratejiCo. does not ensure
Trends in inequality worldwide (Gini coefficients)
 Section 2 Impact of trade on income inequality As described above, it has been theoretically and empirically proved that the progress of globalization as represented by trade brings benefits in the form
Section 2 Impact of trade on income inequality As described above, it has been theoretically and empirically proved that the progress of globalization as represented by trade brings benefits in the form
Joshua W. Walker Turkey's global strategy: introduction: the sources of Turkish grand strategy - strategic depth and zero-problems in context
 Joshua W. Walker Turkey's global strategy: introduction: the sources of Turkish grand strategy - strategic depth and zero-problems in context Report Original citation: Walker, Joshua W. (2011) Turkey's
Joshua W. Walker Turkey's global strategy: introduction: the sources of Turkish grand strategy - strategic depth and zero-problems in context Report Original citation: Walker, Joshua W. (2011) Turkey's
Gender preference and age at arrival among Asian immigrant women to the US
 Gender preference and age at arrival among Asian immigrant women to the US Ben Ost a and Eva Dziadula b a Department of Economics, University of Illinois at Chicago, 601 South Morgan UH718 M/C144 Chicago,
Gender preference and age at arrival among Asian immigrant women to the US Ben Ost a and Eva Dziadula b a Department of Economics, University of Illinois at Chicago, 601 South Morgan UH718 M/C144 Chicago,
Chinese Views of Post-2014 Afghanistan
 Chinese Views of Post-2014 Afghanistan Zhao Huasheng Asia Policy, Number 17, January 2014, pp. 54-58 (Article) Published by National Bureau of Asian Research DOI: https://doi.org/10.1353/asp.2014.0008
Chinese Views of Post-2014 Afghanistan Zhao Huasheng Asia Policy, Number 17, January 2014, pp. 54-58 (Article) Published by National Bureau of Asian Research DOI: https://doi.org/10.1353/asp.2014.0008
Economic Effects of the Syrian War and the Spread of the Islamic State on the Levant
 Economic Effects of the Syrian War and the Spread of the Islamic State on the Levant Elena Ianchovichina and Maros Ivanic The World Bank Group 10th Defence and Security Economics Workshop Carleton University,
Economic Effects of the Syrian War and the Spread of the Islamic State on the Levant Elena Ianchovichina and Maros Ivanic The World Bank Group 10th Defence and Security Economics Workshop Carleton University,
INVESTIGATING THE TRENDS IN GROWTH OF HIGHER EDUCATION ACROSS THE WORLD WITH REGARD TO INTERNATIONALIZATION FACTORS AND POPULATION CHANGE
 INVESTIGATING THE TRENDS IN GROWTH OF HIGHER EDUCATION ACROSS THE WORLD WITH REGARD TO INTERNATIONALIZATION FACTORS AND POPULATION CHANGE Mahsa Tavan 1 and Shokoufe Sadat Mirarabshahi 2 1 Department of
INVESTIGATING THE TRENDS IN GROWTH OF HIGHER EDUCATION ACROSS THE WORLD WITH REGARD TO INTERNATIONALIZATION FACTORS AND POPULATION CHANGE Mahsa Tavan 1 and Shokoufe Sadat Mirarabshahi 2 1 Department of
Prospects for future economic cooperation between China and Belt & Road countries
 www.pwccn.com Prospects for future economic cooperation between China and Belt & Road countries Top ten Belt & Road (B&R) economies account for 64% of overall GDP of B&R countries Content 1 Overview of
www.pwccn.com Prospects for future economic cooperation between China and Belt & Road countries Top ten Belt & Road (B&R) economies account for 64% of overall GDP of B&R countries Content 1 Overview of
International Economics, 10e (Krugman/Obstfeld/Melitz) Chapter 2 World Trade: An Overview. 2.1 Who Trades with Whom?
 International Economics, 10e (Krugman/Obstfeld/Melitz) Chapter 2 World Trade: An Overview 2.1 Who Trades with Whom? 1) Approximately what percent of all world production of goods and services is exported
International Economics, 10e (Krugman/Obstfeld/Melitz) Chapter 2 World Trade: An Overview 2.1 Who Trades with Whom? 1) Approximately what percent of all world production of goods and services is exported
Economic Growth, Foreign Investments and Economic Freedom: A Case of Transition Economy Kaja Lutsoja
 Economic Growth, Foreign Investments and Economic Freedom: A Case of Transition Economy Kaja Lutsoja Tallinn School of Economics and Business Administration of Tallinn University of Technology The main
Economic Growth, Foreign Investments and Economic Freedom: A Case of Transition Economy Kaja Lutsoja Tallinn School of Economics and Business Administration of Tallinn University of Technology The main
IS CHINA S SOFT POWER DOMINATING SOUTHEAST ASIA? VIEWS FROM THE CITIZENS
 Briefing Series Issue 44 IS CHINA S SOFT POWER DOMINATING SOUTHEAST ASIA? VIEWS FROM THE CITIZENS Zhengxu WANG Ying YANG October 2008 International House University of Nottingham Wollaton Road Nottingham
Briefing Series Issue 44 IS CHINA S SOFT POWER DOMINATING SOUTHEAST ASIA? VIEWS FROM THE CITIZENS Zhengxu WANG Ying YANG October 2008 International House University of Nottingham Wollaton Road Nottingham
The Role of Internet Adoption on Trade within ASEAN Countries plus People s Republic of China
 The Role of Internet Adoption on Trade within ASEAN Countries plus People s Republic of China Wei Zhai Prapatchon Jariyapan Faculty of Economics, Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai University, 239 Huay Kaew
The Role of Internet Adoption on Trade within ASEAN Countries plus People s Republic of China Wei Zhai Prapatchon Jariyapan Faculty of Economics, Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai University, 239 Huay Kaew
Introductory Remarks. Michael Schaefer, Chairman of the Board, BMW Foundation. Check against delivery!
 Introductory Remarks Michael Schaefer, Chairman of the Board, BMW Foundation Check against delivery! A very warm welcome to the 1st Berlin Global Forum in this wonderful old grain silo in Berlin s largest
Introductory Remarks Michael Schaefer, Chairman of the Board, BMW Foundation Check against delivery! A very warm welcome to the 1st Berlin Global Forum in this wonderful old grain silo in Berlin s largest
SHOULD THE UNITED STATES WORRY ABOUT LARGE, FAST-GROWING ECONOMIES?
 Chapter Six SHOULD THE UNITED STATES WORRY ABOUT LARGE, FAST-GROWING ECONOMIES? This report represents an initial investigation into the relationship between economic growth and military expenditures for
Chapter Six SHOULD THE UNITED STATES WORRY ABOUT LARGE, FAST-GROWING ECONOMIES? This report represents an initial investigation into the relationship between economic growth and military expenditures for
myworld Geography Eastern Hemisphere 2011
 A Correlation of to the Pennsylvania Assessment Anchor Standards Civics and Government Economics Geography History Grades 6-8 INTRODUCTION This document demonstrates how 2011 meets the objectives of the
A Correlation of to the Pennsylvania Assessment Anchor Standards Civics and Government Economics Geography History Grades 6-8 INTRODUCTION This document demonstrates how 2011 meets the objectives of the
Relief Situation of Foreign Economic Relations and Geopolitical Prospects of Azerbaijan
 Relief Situation of Foreign Economic Relations and Geopolitical Prospects of Azerbaijan Dr. Daqbeyi Abdullayev; Department of Globalization and International Economic Relations of the Institute of Economics
Relief Situation of Foreign Economic Relations and Geopolitical Prospects of Azerbaijan Dr. Daqbeyi Abdullayev; Department of Globalization and International Economic Relations of the Institute of Economics
IMF Governance and the Political Economy of a Consolidated European Seat
 10 IMF Governance and the Political Economy of a Consolidated European Seat LORENZO BINI SMAGHI During recent years, IMF governance has increasingly become a topic of public discussion. 1 Europe s position
10 IMF Governance and the Political Economy of a Consolidated European Seat LORENZO BINI SMAGHI During recent years, IMF governance has increasingly become a topic of public discussion. 1 Europe s position
Supplementary Material for Preventing Civil War: How the potential for international intervention can deter conflict onset.
 Supplementary Material for Preventing Civil War: How the potential for international intervention can deter conflict onset. World Politics, vol. 68, no. 2, April 2016.* David E. Cunningham University of
Supplementary Material for Preventing Civil War: How the potential for international intervention can deter conflict onset. World Politics, vol. 68, no. 2, April 2016.* David E. Cunningham University of
Working Together as a Global Company
 Working Together as a Global Company Thomas R. Pickering Senior VP International Relations The Boeing Company September 17, 2004 The Global Economy Bright global economic outlook: strong 2004 World GDP
Working Together as a Global Company Thomas R. Pickering Senior VP International Relations The Boeing Company September 17, 2004 The Global Economy Bright global economic outlook: strong 2004 World GDP
A Global Perspective on Socioeconomic Differences in Learning Outcomes
 2009/ED/EFA/MRT/PI/19 Background paper prepared for the Education for All Global Monitoring Report 2009 Overcoming Inequality: why governance matters A Global Perspective on Socioeconomic Differences in
2009/ED/EFA/MRT/PI/19 Background paper prepared for the Education for All Global Monitoring Report 2009 Overcoming Inequality: why governance matters A Global Perspective on Socioeconomic Differences in
Report. Iran's Foreign Policy Following the Nuclear Argreement and the Advent of Trump: Priorities and Future Directions.
 Report Iran's Foreign Policy Following the Nuclear Argreement and the Advent of Trump: Priorities and Future Directions Fatima Al-Smadi* 20 May 2017 Al Jazeera Centre for Studies Tel: +974 40158384 jcforstudies@aljazeera.net
Report Iran's Foreign Policy Following the Nuclear Argreement and the Advent of Trump: Priorities and Future Directions Fatima Al-Smadi* 20 May 2017 Al Jazeera Centre for Studies Tel: +974 40158384 jcforstudies@aljazeera.net
REMITTANCE PRICES WORLDWIDE
 REMITTANCE PRICES WORLDWIDE THE WORLD BANK PAYMENT SYSTEMS DEVELOPMENT GROUP FINANCIAL AND PRIVATE SECTOR DEVELOPMENT VICE PRESIDENCY ISSUE NO. 3 NOVEMBER, 2011 AN ANALYSIS OF TRENDS IN THE AVERAGE TOTAL
REMITTANCE PRICES WORLDWIDE THE WORLD BANK PAYMENT SYSTEMS DEVELOPMENT GROUP FINANCIAL AND PRIVATE SECTOR DEVELOPMENT VICE PRESIDENCY ISSUE NO. 3 NOVEMBER, 2011 AN ANALYSIS OF TRENDS IN THE AVERAGE TOTAL
2009 Diplomatic White Paper
 2009 Diplomatic White Paper Minister s Message The year 2008 was indeed a meaningful year. It marked not only the 60th anniversary of the establishment of the Republic of Korea but also the launch of the
2009 Diplomatic White Paper Minister s Message The year 2008 was indeed a meaningful year. It marked not only the 60th anniversary of the establishment of the Republic of Korea but also the launch of the
SECTION THREE BENEFITS OF THE JSEPA
 SECTION THREE BENEFITS OF THE JSEPA 1. Section Two described the possible scope of the JSEPA and elaborated on the benefits that could be derived from the proposed initiatives under the JSEPA. This section
SECTION THREE BENEFITS OF THE JSEPA 1. Section Two described the possible scope of the JSEPA and elaborated on the benefits that could be derived from the proposed initiatives under the JSEPA. This section
Online Appendix for. Home Away From Home? Foreign Demand and London House Prices
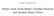 Online Appendix for Home Away From Home? Foreign Demand and London House Prices List of Tables A.1 Summary statistics across wards..................... 14 A.2 Robustness of the results.........................
Online Appendix for Home Away From Home? Foreign Demand and London House Prices List of Tables A.1 Summary statistics across wards..................... 14 A.2 Robustness of the results.........................
A Post-2014 Vision for Turkey-Africa Relations
 Turkish Cooperation and Coordination Agency (TIKA) From the SelectedWorks of Mehmet OZKAN Fall December, 2014 A Post-2014 Vision for Turkey-Africa Relations Mehmet OZKAN, Turkish National Police Academy
Turkish Cooperation and Coordination Agency (TIKA) From the SelectedWorks of Mehmet OZKAN Fall December, 2014 A Post-2014 Vision for Turkey-Africa Relations Mehmet OZKAN, Turkish National Police Academy
Differences in National IQs behind the Eurozone Debt Crisis?
 3 Differences in National IQs behind the Eurozone Debt Crisis? Tatu Vanhanen * Department of Political Science, University of Helsinki The purpose of this article is to explore the causes of the European
3 Differences in National IQs behind the Eurozone Debt Crisis? Tatu Vanhanen * Department of Political Science, University of Helsinki The purpose of this article is to explore the causes of the European
Arab Spring vs. Zero Problems Policy. Impact of the Arab Spring on the Trade Expansion of Turkey
 International Journal of Research in Business and Social Science IJRBS Vol.2 No.4, 2013 ISSN: 2147-4478 available online at www.ssbfnet.com Arab Spring vs. Zero Problems Policy Impact of the Arab Spring
International Journal of Research in Business and Social Science IJRBS Vol.2 No.4, 2013 ISSN: 2147-4478 available online at www.ssbfnet.com Arab Spring vs. Zero Problems Policy Impact of the Arab Spring
Leangkollen Conference, 3 February, 2014 Speech by Foreign Minister Børge Brende
 1 av 16 Leangkollen Conference, 3 February, 2014 Speech by Foreign Minister Børge Brende The Rise of East Asia and Transatlantic Relations Check against delivery Let me first thank Kjell Engebretsen, Kate
1 av 16 Leangkollen Conference, 3 February, 2014 Speech by Foreign Minister Børge Brende The Rise of East Asia and Transatlantic Relations Check against delivery Let me first thank Kjell Engebretsen, Kate
Impact of Human Rights Abuses on Economic Outlook
 Digital Commons @ George Fox University Student Scholarship - School of Business School of Business 1-1-2016 Impact of Human Rights Abuses on Economic Outlook Benjamin Antony George Fox University, bantony13@georgefox.edu
Digital Commons @ George Fox University Student Scholarship - School of Business School of Business 1-1-2016 Impact of Human Rights Abuses on Economic Outlook Benjamin Antony George Fox University, bantony13@georgefox.edu
China s Aid Approaches in the Changing International Aid Architecture
 China s Aid Approaches in the Changing International Aid Architecture Mao Xiaojing Deputy Director, Associate Research Fellow Chinese Academy of International Trade and Economic Cooperation (CAITEC) MOFCOM,
China s Aid Approaches in the Changing International Aid Architecture Mao Xiaojing Deputy Director, Associate Research Fellow Chinese Academy of International Trade and Economic Cooperation (CAITEC) MOFCOM,
Table A.2 reports the complete set of estimates of equation (1). We distinguish between personal
 Akay, Bargain and Zimmermann Online Appendix 40 A. Online Appendix A.1. Descriptive Statistics Figure A.1 about here Table A.1 about here A.2. Detailed SWB Estimates Table A.2 reports the complete set
Akay, Bargain and Zimmermann Online Appendix 40 A. Online Appendix A.1. Descriptive Statistics Figure A.1 about here Table A.1 about here A.2. Detailed SWB Estimates Table A.2 reports the complete set
Quantitative Analysis of Migration and Development in South Asia
 87 Quantitative Analysis of Migration and Development in South Asia Teppei NAGAI and Sho SAKUMA Tokyo University of Foreign Studies 1. Introduction Asia is a region of high emigrant. In 2010, 5 of the
87 Quantitative Analysis of Migration and Development in South Asia Teppei NAGAI and Sho SAKUMA Tokyo University of Foreign Studies 1. Introduction Asia is a region of high emigrant. In 2010, 5 of the
The WTO Trade Effect and Political Uncertainty: Evidence from Chinese Exports
 Abstract: The WTO Trade Effect and Political Uncertainty: Evidence from Chinese Exports Yingting Yi* KU Leuven (Preliminary and incomplete; comments are welcome) This paper investigates whether WTO promotes
Abstract: The WTO Trade Effect and Political Uncertainty: Evidence from Chinese Exports Yingting Yi* KU Leuven (Preliminary and incomplete; comments are welcome) This paper investigates whether WTO promotes
Econometric Estimation of a Gravity Model for the External Trade of Romania
 IBIMA Publishing Journal of Eastern Europe Research in Business & Economics http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/jeerbe/jeerbe.html Vol. 0 (0), Article ID 854058, 9 pages DOI: 0.57/0.854058 Econometric
IBIMA Publishing Journal of Eastern Europe Research in Business & Economics http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/jeerbe/jeerbe.html Vol. 0 (0), Article ID 854058, 9 pages DOI: 0.57/0.854058 Econometric
BBVA EAGLEs. Emerging And Growth Leading Economies Economic Outlook. Annual Report 2014 Cross-Country Emerging Markets, BBVA Research March 2014
 BBVA EAGLEs Emerging And Growth Leading Economies Economic Outlook Annual Report 2014 Cross-Country Emerging Markets, BBVA Research March 2014 Index Key takeaways in 2013 Rethinking EAGLEs for the next
BBVA EAGLEs Emerging And Growth Leading Economies Economic Outlook Annual Report 2014 Cross-Country Emerging Markets, BBVA Research March 2014 Index Key takeaways in 2013 Rethinking EAGLEs for the next
Shake Hands or Shake Apart? Pre-war Global Trade and Currency. Blocs: the Role of the Japanese Empire
 HEI Working Paper No: 05/2006 Shake Hands or Shake Apart? Pre-war Global Trade and Currency Blocs: the Role of the Japanese Empire Toshihiro Okubo Graduate Institute of International Studies Abstract Despite
HEI Working Paper No: 05/2006 Shake Hands or Shake Apart? Pre-war Global Trade and Currency Blocs: the Role of the Japanese Empire Toshihiro Okubo Graduate Institute of International Studies Abstract Despite
Remittance Prices Worldwide Issue n. 19, September 2016
 An analysis of trends in cost of remittance services Remittance Prices Worldwide Issue n. 19, September This Report reflects the latest trends observed in the data published in September. Remittance Prices
An analysis of trends in cost of remittance services Remittance Prices Worldwide Issue n. 19, September This Report reflects the latest trends observed in the data published in September. Remittance Prices
Does Korea Follow Japan in Foreign Aid? Relationships between Aid and FDI
 Does Korea Follow Japan in Foreign Aid? Relationships between Aid and FDI Japan and the World Economy (Forthcoming) Sung Jin Kang, Korea Univ. Hongshik Lee, Korea Univ. Bokyeong Park, KIEP 1 Korea and
Does Korea Follow Japan in Foreign Aid? Relationships between Aid and FDI Japan and the World Economy (Forthcoming) Sung Jin Kang, Korea Univ. Hongshik Lee, Korea Univ. Bokyeong Park, KIEP 1 Korea and
Prospects for Inclusive Growth in the MENA Region: A Comparative Approach
 Prospects for Inclusive Growth in the MENA Region: A Comparative Approach Hassan Hakimian London Middle East Institute SOAS, University of London Email: HH2@SOAS.AC.UK International Parliamentary Conference
Prospects for Inclusive Growth in the MENA Region: A Comparative Approach Hassan Hakimian London Middle East Institute SOAS, University of London Email: HH2@SOAS.AC.UK International Parliamentary Conference
The 2018 Israeli Foreign Policy Index of the Mitvim Institute
 The 2018 Israeli Foreign Policy Index of the Mitvim Institute October 2018 The Israeli Institute for Regional Foreign Policies The 2018 Israeli Foreign Policy Index Findings of the Mitvim Institute Poll
The 2018 Israeli Foreign Policy Index of the Mitvim Institute October 2018 The Israeli Institute for Regional Foreign Policies The 2018 Israeli Foreign Policy Index Findings of the Mitvim Institute Poll
Migration in the Turkish Republic
 Migration in the Turkish Republic Turkey has historically been a country of both emigration and immigration. Internal dynamics, bilateral agreements, conflicts and war, and political and economic interests
Migration in the Turkish Republic Turkey has historically been a country of both emigration and immigration. Internal dynamics, bilateral agreements, conflicts and war, and political and economic interests
Trade and Security: The Two Sides of US-Indian Relations
 Trade and Security: The Two Sides of US-Indian Relations New Delhi is a valuable partner to Washington on one but not the other. Allison Fedirka August 13, 2018 Trade and Security: The Two Sides of US-Indian
Trade and Security: The Two Sides of US-Indian Relations New Delhi is a valuable partner to Washington on one but not the other. Allison Fedirka August 13, 2018 Trade and Security: The Two Sides of US-Indian
Is Corruption Anti Labor?
 Is Corruption Anti Labor? Suryadipta Roy Lawrence University Department of Economics PO Box- 599, Appleton, WI- 54911. Abstract This paper investigates the effect of corruption on trade openness in low-income
Is Corruption Anti Labor? Suryadipta Roy Lawrence University Department of Economics PO Box- 599, Appleton, WI- 54911. Abstract This paper investigates the effect of corruption on trade openness in low-income
ISAF GROWS THIS YEAR, TOO.
 ISAF GROWS THIS YEAR, TOO. 17 th ISAF was held in a total area of 17.150m 2 in the 9 th, 10 th, and 11 th halls at The Istanbul Expo Center from September 19 th, 2013 to September 22 nd, 2013. ISAF that
ISAF GROWS THIS YEAR, TOO. 17 th ISAF was held in a total area of 17.150m 2 in the 9 th, 10 th, and 11 th halls at The Istanbul Expo Center from September 19 th, 2013 to September 22 nd, 2013. ISAF that
Ignacio Molina and Iliana Olivié May 2011
 Ignacio Molina and Iliana Olivié May 2011 What is the IEPG? The Elcano Global Presence Index (IEPG after its initials in Spanish) is a synthetic index that orders, quantifies and aggregates the external
Ignacio Molina and Iliana Olivié May 2011 What is the IEPG? The Elcano Global Presence Index (IEPG after its initials in Spanish) is a synthetic index that orders, quantifies and aggregates the external
The Political Economy of Governance in the Euro-Mediterranean Partnership
 The Political Economy of Governance in the Euro-Mediterranean Partnership Deliverable No. 10 Working Package 8 New Challenges: Regional Integration Working Package Summary: Working Package 8 New Challenges:
The Political Economy of Governance in the Euro-Mediterranean Partnership Deliverable No. 10 Working Package 8 New Challenges: Regional Integration Working Package Summary: Working Package 8 New Challenges:
HOW TO NEGOTIATE WITH THE EU? THEORIES AND PRACTICE
 HOW TO NEGOTIATE WITH THE EU? THEORIES AND PRACTICE In the European Union, negotiation is a built-in and indispensable dimension of the decision-making process. There are written rules, unique moves, clearly
HOW TO NEGOTIATE WITH THE EU? THEORIES AND PRACTICE In the European Union, negotiation is a built-in and indispensable dimension of the decision-making process. There are written rules, unique moves, clearly
