US History, Ms. Brown Website: dph7history.weebly.com
|
|
|
- Alice Quinn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #69 Aims: SWBAT identify and evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation DO NOW Directions: Answer the following questions in complete and historically accurate sentences. Use your notes and knowledge of history. You MUST annotate your answers, which means cross off the question stem, capitalize the first letter, and cross off the question mark. 1. What were the Articles of Confederation? 2. Following the American Revolution, what did Congress fear about a strong central government? 3. Why is Shay s Rebellion an important event in US History? 4. What were the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation? Use specific examples from yesterday s case studies to support your answers. 1
2 I. The Purpose of the Convention The Articles of Confederation have more power to the states than to the federal government (also known as the national government). This was done because many Americans were suspicious of a strong national government. However, after Shay s Rebellion, many Americans knew that the government needed to change. The Articles of Confederation were just not working. The Constitutional Convention was called in Philadelphia. The purpose was to create a new government that would better serve Americans. 1. How did Shay s Rebellion lead to the Constitutional Convention? II. Opening the Constitutional Convention Philadelphia was already hot and humid when delegates began drifting into the city. On May 25, 1787, the Constitutional Convention1 met for the first time in the East room of the Pennsylvania State House (now known as Independence Hall). The Declaration of Independence had been debated in this very room 11 years earlier. The delegates would meet in the east room all summer. On some days temperatures rose well into the nineties. Benjamin Franklin, the oldest delegate to the Constitutional Convention, had doubts about the drafting of he Constitution. However, he said, The older I grow, the more apt I am to doubt my judgment and pay more respect to the judgment of others. The delegates first action was to elect George Washington president of the Convention. No man was more admired and respected than the former Commander and Chief of the Continental Army. When the war ended, Washington could have used his popularity and power to make himself a king. Instead, he went home to Virginia to resume his life as an ordinary citizen. But despite his reluctance to return to public life, Washington would play a key role by presiding over the convention and lending it his prestige. 1 Constitutional Convention: a meeting held in Philadelphia in 1787 at which delegates from the states wrote 2
3 The Delegates Fifty-five delegates from 12 states attended the Constitutional Convention. Rhode Island, which prided itself as the home of the otherwise minded and feared a strong national government, boycotted the meeting. Some leaders of the revolution were missing. John Adams and Thomas Jefferson were representing the United States in Great Britain and France, respectively. Others who did not attend included Samuel Adams, John Hancock and Patrick Henry. They feared that a strong national government would endanger the rights of the states. As a group, the delegates were, in the words of a modern historian, the well-bred, the well-fed, the well-read, and the well-wed. Their average age was 42. At 81, Benjamin Franklin of Pennsylvania was the oldest. He arrived at the convention each day in a sedan chair carried by four good-natured prisoners from a nearby jail. Most of the delegates brought extensive political experience to the meeting. More than two-thirds (2/3) were lawyers. Most had served in their state legislatures or held a state office. Thomas Jefferson was so impressed by the experience of these men that he called the convention an assembly of demi-gods. The Father of the Constitution The best prepared of the delegates was James Madison of Virginia. One delegate wrote of Madison, In management of every great question he evidently took the lead in the Convention. Indeed, Madison s influence was so great that later he would called the Father of the Constitution. Madison addressed the convention numerous times. When he was not speaking, he took notes. Sitting near the front of the room so that he could hear everything that was said. Madison wrote down The delegates to the Constitutional Convention met on May 25, 1787, in the same hall where the Declaration of Independence was signed. Today, the building is called Independence Hall. nearly every word. All together, his notes covered more than 600 printed pages. From this remarkable record, we know what went on inside the convention day by day. The Rule of Secrecy At the time, however, no one outside the convention knew what was happening. After choosing a president, the delegates voted on rules for the convention. The most important of these was the rule of secrecy. The delegates wanted to feel free to speak their minds without causing alarm or opposition among the general public. They agreed to keep secret whatever was said in the meeting room until their work was done. The delegates took the rule of secrecy seriously. During that long summer, not a word of the convention debates appeared in any newspaper. 3
4 Shared Beliefs and Clashing Views Once the convention was organized, the delegates got down to business. As a group the delegates had much in common. But they also had very different views on many issues facing the new nation. To be sure, all the delegates were committed2 to the ideals of the Declaration of Independence. The basic purpose of government, they believed, was to protect the rights to life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness. And they agreed, in the words of the Declaration, that the just powers of government came from the consent of the government. Human institutions these liberal3 thinkers had argued, should be based on laws of nature. Among these laws were the rights to liberty and equality. The best way to protect these rights, the delegates agreed was through some form of republic4. Delegates with opposing views were Pennsylvania s James Wilson (left) and New Jersey s William Paterson (right). Wilson, one of the most vocal delegates at the constitution, argued for a strong national government. Paterson tried to protect state rights of the states. Many delegates of small states shared his fear of being swallowed up by the larger states. From New England s town meetings to lawmaking bodies like the Virginia House of Burgesses, Americans had a long tradition of participating in their own government. After the American Revolution, all the states had adopted constitutions5 that embraced republican ideals. Despite many differences in details, every state had a form of representative government. States had also expanded the rights to vote and hold office. The states constitutions helped to shape the delegates thinking. Despite the delegates broad agreement on a government of the people many questions were left unanswered. For example, who exactly should have a say in a truly representative government? Even in liberal Pennsylvania, only free, white males could vote. Some states allowed only wealthier citizens to vote or hold office. Women could not vote in any state except New Jersey. (New Jersey women would lose the right to vote in1807). Perhaps the most troubling question of all was how powerful the national government should be. Many delegates wanted to keep government close to the people by preserving the rights of the states. They feared that a strong national government would threaten individual liberty. Others, including Madison, argued the opposite. Look at what has happened under the Articles of Confederation, they said, referring to events like Shay s Rebellion. If the central government is too weak, it cannot do its job of protecting liberty and property. As they met behind closed doors, the delegates wrestled with this and other issues. Tempers often flared and at times it seemed the convention might collapse in failure. But in the end delegates found ways to save the convention and the nation. 2 Committed: to agree or pledge to support someone or something Liberal: supporting ideas of freedom, change and progress 4 Republic: a country governed by elected representatives 5 Constitutions: a written plan that provides the basic framework of a government 3 4
5 5
6 6
7 HOMEWORK /10 Mastered/Passing/Not Mastered The Important People in the Convention James Madison Madison is known as the Father of the Constitution. His influence over the convention was great. This was partly because Madison brought with him a plan for a stronger national government. Madison s ideas were the basis for discussing how to structure a new government. Much of what we know about the Constitutional Convention comes from Madison s notes. Question: What is Madison known as? Why did he earn this title? George Washington Washington was probably the most honored and respected man in American at this time. This was mainly due to the fact that he ad been the Commanderin-Chief of the Continental Army. He was convinced that a stronger national government was necessary, but did not want to speak about it publically. He did not want to become involved in politics. He preferred to return to Mount Vernon, Virginia, his home, to be a farmer. At first, Washington refused to come to the convention. He later changed his mind. Washington was afraid if he did not attend, people would think that he had lost faith in republican government. Washington served as presiding officer at the proceedings. This made the convention more respectable and prestigious in citizens minds. 7
8 Question: Why did Washington decide to join the Constitutional Convention? What was his role in the Convention? Benjamin Franklin Franklin was eighty-one years old and in poor health. He attended the convention as a delegate for Pennsylvania. Franklin was one of the most respected men in America. He had a long and distinguished career as a printer, writer, revolutionary, peacemaker and diplomat. He had organized the Albany Plan of Union, and helped to write the Treaty of Paris after the Revolutionary War. Franklin s primary role during the convention was to encourage the delegates to cooperate when they disagreed. Question: What was Franklin s primary (main) role in the Constitutional Convention? Governor Morris Morris was a delegate from New York. He had served in the state militia and in the New York State legislature. Morris had also been a member of the Continental Congress. He was an exceptionally good speaker during the Convention he played an important role in writing the Constitution and prepared its final draft. 8
9 Question: What was Morris role in the Constitutional Convention? Who Am I? 1. I was a famous and well-respected man from Virginia. I had gained this respect as the Commander-inChief of the Continental Army. While I was reluctant to join the convention, I later changed my mind. Who Am I? 2. I was a famous man, known for my various careers, such as peacemaker, inventor, and negotiator. I gained my reputation from organizing the Albany Plan of Union and the peace treaty after the Revolution. I served as a negotiator and mediator during the Constitutional Convention. Who Am I? 3. I was the delegate from New York. I played an important role in writing and preparing the final draft of the Constitution. Who Am I? 4. I am known as the Father of the Constitution. I wrote much of the Constitution and later wrote important papers supporting the Constitution, known as the Federalist Papers. Who Am I? 9
10 10
11 The Constitutional Convention EXIT TICKET /5 Mastered/Passing/Not Mastered 1. What was the original purpose of the convention in May 1787? a. to write the US Constitution b. to end the conflict in Massachusetts c. to revise the Articles of Confederation d. to rewrite the Declaration of Independence 2. Why is James Madison known as the Father of the Constitution? a. He wrote the first draft of the Constitution b. He knew more about government than anyone else c. He was the oldest delegate to the Constitutional Convention d. He was well prepared to lead the discussion at the convention 3. The delegates to the Constitutional Convention agreed to establish a republic. Which of these best describes a republic? a. a country led by a president b. a government led by a powerful few c. a parliamentary form of government d. a country led by elected representatives 4. Which information on the Writing of the Constitution is considered a primary source? a. a newspaper written in 1887 b. an encyclopedia article on the Constitution c. the book, An Economic Interpretation of the Constitution d. notes from the Constitutional Convention taken by James Madison 11
Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution
 Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution The Articles of Confederation After declaring independence from Britain in 1776, Congress tried to unite the states under one national government. However, many feared
Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution The Articles of Confederation After declaring independence from Britain in 1776, Congress tried to unite the states under one national government. However, many feared
US History, Ms. Brown Website: dph7history.weebly.com
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #70 Aims: SWBAT understand and explain the debate over representation SWBAT identify and explain the Virginia Plan and
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #70 Aims: SWBAT understand and explain the debate over representation SWBAT identify and explain the Virginia Plan and
Creating Our. Constitution. Key Terms. delegates equal representation executive federal system framers House of Representatives judicial
 Lesson 2 Creating Our Constitution Key Terms delegates equal representation executive federal system framers House of Representatives judicial What You Will Learn to Do Explain how the Philadelphia Convention
Lesson 2 Creating Our Constitution Key Terms delegates equal representation executive federal system framers House of Representatives judicial What You Will Learn to Do Explain how the Philadelphia Convention
Setting the Stage - Forming a New Nation
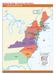 Setting the Stage - Forming a New Nation The 13 states that independence brought together to form the United States of America had very different physical and human geographic features. Most of the Southern
Setting the Stage - Forming a New Nation The 13 states that independence brought together to form the United States of America had very different physical and human geographic features. Most of the Southern
Creating the Constitution
 Creating the Constitution 1776-1791 US Timeline 1777-1791 1777 Patriots win Battles of Saratoga. Continental Congress passes the Articles of Confederation. 1781 Articles of Confederation go into effect.
Creating the Constitution 1776-1791 US Timeline 1777-1791 1777 Patriots win Battles of Saratoga. Continental Congress passes the Articles of Confederation. 1781 Articles of Confederation go into effect.
Chapter 25 Section 1. Section 1. Terms and People
 Chapter 25 Terms and People republic a government in which the people elect their representatives unicameral legislature a lawmaking body with a single house whose representatives are elected by the people
Chapter 25 Terms and People republic a government in which the people elect their representatives unicameral legislature a lawmaking body with a single house whose representatives are elected by the people
US History, Ms. Brown Website: dph7history.weebly.com
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #68 Aims: SWBAT identify and evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation DO NOW Directions:
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #68 Aims: SWBAT identify and evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation DO NOW Directions:
Section 1 - Introduction
 Section 1 - Introduction When the American war for independence ended, no one was happier than a serious Virginia Patriot named James Madison. And no one was more worried about the future of the United
Section 1 - Introduction When the American war for independence ended, no one was happier than a serious Virginia Patriot named James Madison. And no one was more worried about the future of the United
Basic Concepts of Government The English colonists brought 3 ideas that loom large in the shaping of the government in the United States.
 Civics Honors Chapter Two: Origins of American Government Section One: Our Political Beginnings Limited Government Representative government Magna Carta Petition of Right English Bill of Rights Charter
Civics Honors Chapter Two: Origins of American Government Section One: Our Political Beginnings Limited Government Representative government Magna Carta Petition of Right English Bill of Rights Charter
Why do you think the Framers organized the new country as a republic, when most countries in the world (in 1783) were ruled by a king or queen?
 NAME: Date: U.S. History CHAPTER 7 PACKET ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: 1. What is a constitution? 2. What is a republic? 3. What was the Articles of Confederation? 4. How was state and national power divided under
NAME: Date: U.S. History CHAPTER 7 PACKET ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: 1. What is a constitution? 2. What is a republic? 3. What was the Articles of Confederation? 4. How was state and national power divided under
May, 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania ~Independence Hall~ Leader: George Washington
 May, 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania ~Independence Hall~ Leader: George Washington -May 1787 Philadelphia Met in Independence Hall in Philadelphia George Washington leader -12 of 13 states Rhode Island
May, 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania ~Independence Hall~ Leader: George Washington -May 1787 Philadelphia Met in Independence Hall in Philadelphia George Washington leader -12 of 13 states Rhode Island
US History, Ms. Brown Website: dph7history.weebly.com
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #80 Aims: SWBAT identify and describe the difference in the Federalists and Anti-Federalists perspective of government
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #80 Aims: SWBAT identify and describe the difference in the Federalists and Anti-Federalists perspective of government
The Constitutional Convention formed the plan of government that the United States still has today.
 2 Creating the Constitution MAIN IDEA The states sent delegates to a convention to solve the problems of the Articles of Confederation. WHY IT MATTERS NOW The Constitutional Convention formed the plan
2 Creating the Constitution MAIN IDEA The states sent delegates to a convention to solve the problems of the Articles of Confederation. WHY IT MATTERS NOW The Constitutional Convention formed the plan
What types of things did the new states do to make the governments more democratic?
 Chapter 8 Confederation to Constitution pg. 218 241 8 1 The Confederation Era pg. 221 225 Moving West and New State Governments Into which areas did American settlement expand in the late 1700s? What types
Chapter 8 Confederation to Constitution pg. 218 241 8 1 The Confederation Era pg. 221 225 Moving West and New State Governments Into which areas did American settlement expand in the late 1700s? What types
From VOA Learning English, welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in Special English. I m Steve Ember.
 From VOA Learning English, welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in Special English. I m Steve Ember. Today, we continue our story of the United States Constitution. In recent weeks, we told
From VOA Learning English, welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in Special English. I m Steve Ember. Today, we continue our story of the United States Constitution. In recent weeks, we told
Wednesday, February 15 th
 Anticipating Constitutional Reform 1 Wednesday, February 15 th Midterm #1: February 14-17 in the Testing Center Monday and Tuesday: No late fee Wednesday: $5 late fee Thursday: $7 late fee and test must
Anticipating Constitutional Reform 1 Wednesday, February 15 th Midterm #1: February 14-17 in the Testing Center Monday and Tuesday: No late fee Wednesday: $5 late fee Thursday: $7 late fee and test must
Chapter 2. Government
 Chapter 2 Government The way the United States government is organized, its powers, and its limitations, are based on ideas about government that were brought to these shores by the English colonist. Three
Chapter 2 Government The way the United States government is organized, its powers, and its limitations, are based on ideas about government that were brought to these shores by the English colonist. Three
The Convention Leaders
 The Convention Leaders When Thomas Jefferson heard who was attending the Constitutional Convention, he called it an assembly of demigods because the members were so rich in education and political experience.
The Convention Leaders When Thomas Jefferson heard who was attending the Constitutional Convention, he called it an assembly of demigods because the members were so rich in education and political experience.
What were the Articles of Confederation? What did America do to create a stronger government in the 1780s?
 2.3 Articles of Confederation What were the Articles of Confederation? Why were the 1780s a critical period in United States history? What did America do to create a stronger government in the 1780s? Section:
2.3 Articles of Confederation What were the Articles of Confederation? Why were the 1780s a critical period in United States history? What did America do to create a stronger government in the 1780s? Section:
Ratifying the Constitution
 Ratifying the Constitution Signing the Constitution Once the debate ended, Governor Morris of New Jersey put the Constitution in its final form. He competed the task of hand-writing 4,300 words in two
Ratifying the Constitution Signing the Constitution Once the debate ended, Governor Morris of New Jersey put the Constitution in its final form. He competed the task of hand-writing 4,300 words in two
Lesson 8 - Creating the Constitution
 Lesson 8 - Creating the Constitution Setting the Stage - Forming a New Nation The 13 states that independence brought together to form the United States of America had very different physical and human
Lesson 8 - Creating the Constitution Setting the Stage - Forming a New Nation The 13 states that independence brought together to form the United States of America had very different physical and human
T H E C O N F E D E R A T I O N A N D T H E C O N S T I T U T I O N C H A P T E R 7 A P U S H I S T O R Y
 T H E C O N F E D E R A T I O N A N D T H E C O N S T I T U T I O N C H A P T E R 7 A P U S H I S T O R Y LEARNING GOAL: Students will be able to explain the growth of the new governing systems in the
T H E C O N F E D E R A T I O N A N D T H E C O N S T I T U T I O N C H A P T E R 7 A P U S H I S T O R Y LEARNING GOAL: Students will be able to explain the growth of the new governing systems in the
Origins of American Government Guided Reading Activity Section 1
 Section 1 Read each of the following descriptions, and write who or what is speaking in the space provided. 1. My theories that a republic could only survive if its citizens actively participated in government
Section 1 Read each of the following descriptions, and write who or what is speaking in the space provided. 1. My theories that a republic could only survive if its citizens actively participated in government
the states. decisions within its own borders) 1. A central government that would represent all 2. State sovereignty (the power to make
 The United States has operated under two constitutions. The first, The Articles of Confederation, was in effect from March 1, 1781. The Articles tried to balance two very different ideas: 1. A central
The United States has operated under two constitutions. The first, The Articles of Confederation, was in effect from March 1, 1781. The Articles tried to balance two very different ideas: 1. A central
US History, Ms. Brown Need Help? or Call
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #76 Aims: SWBAT define Separation of powers and checks and balances SWBAT identify and explain how each branch of government
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #76 Aims: SWBAT define Separation of powers and checks and balances SWBAT identify and explain how each branch of government
Creating a Nation Test Review
 Creating a Nation Test Review Question #1: Multiple Choice The Northwest ordinance of 1787 is important because. A. It sent troops to the Northwest to protect the colonies from Native Americans. B. It
Creating a Nation Test Review Question #1: Multiple Choice The Northwest ordinance of 1787 is important because. A. It sent troops to the Northwest to protect the colonies from Native Americans. B. It
CHAPTER 7 CREATING A GOVERNMENT
 CHAPTER 7 CREATING A GOVERNMENT The Constitution set out our rules for government. It explains what our government can and cannot do. It reflects are experience as a colony as well as ideas from Europe
CHAPTER 7 CREATING A GOVERNMENT The Constitution set out our rules for government. It explains what our government can and cannot do. It reflects are experience as a colony as well as ideas from Europe
The Articles of Confederation
 1 The Articles of Confederation Approved by Congress on November 15, 1777, Congress sent to the states for ratification the Articles of Confederation. This was the first governing constitution for the
1 The Articles of Confederation Approved by Congress on November 15, 1777, Congress sent to the states for ratification the Articles of Confederation. This was the first governing constitution for the
Name Class Date. MATCHING In the space provided, write the letter of the term or person that matches each description. Some answers will not be used.
 Origins of American Government Section 1 MATCHING In the space provided, write the letter of the term or person that matches each description. Some answers will not be used. 1. Idea that people should
Origins of American Government Section 1 MATCHING In the space provided, write the letter of the term or person that matches each description. Some answers will not be used. 1. Idea that people should
OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS
 CHAPTER 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS The colonists brought with them to North America knowledge of the English political system, including three key ideas about government.
CHAPTER 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS The colonists brought with them to North America knowledge of the English political system, including three key ideas about government.
Ch. 1 Principles of Government
 Ch. 1 Principles of Government Objectives: 1. Identify the four main purposes of government. 2. Identify and explain the four theories that explain the origin of government. I. What is government? A. Government-
Ch. 1 Principles of Government Objectives: 1. Identify the four main purposes of government. 2. Identify and explain the four theories that explain the origin of government. I. What is government? A. Government-
The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783!
 Creating a Republic The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783! The treaty ending the war with Britain, more than doubled the territory of the United States!
Creating a Republic The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783! The treaty ending the war with Britain, more than doubled the territory of the United States!
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes
 Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
Magruder s American Government
 Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 Our Political Beginnings
Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 Our Political Beginnings
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton
 Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
understanding CONSTITUTION
 understanding the CONSTITUTION Contents The Articles of Confederation The Constitutional Convention The Principles of the Constitution The Preamble The Legislative Branch The Executive Branch The Judicial
understanding the CONSTITUTION Contents The Articles of Confederation The Constitutional Convention The Principles of the Constitution The Preamble The Legislative Branch The Executive Branch The Judicial
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes
 Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
The Critical Period The early years of the American Republic
 The Critical Period 1781-1789 The early years of the American Republic America after the War New Political Ideas: - Greater power for the people Republic: Represent the Public America after the War State
The Critical Period 1781-1789 The early years of the American Republic America after the War New Political Ideas: - Greater power for the people Republic: Represent the Public America after the War State
Once a year, each state would select a delegation to send to the capital city.
 In November 1777, the Continental Congress adopted the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union. This was a plan for a loose union of the states under Congress. Once a year, each state would select
In November 1777, the Continental Congress adopted the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union. This was a plan for a loose union of the states under Congress. Once a year, each state would select
Constitutional Convention
 Constitutional Convention I INTRODUCTION Constitutional Convention, meeting during the summer of 1787 at which delegates from 12 states wrote the Constitution of the United States. At the convention in
Constitutional Convention I INTRODUCTION Constitutional Convention, meeting during the summer of 1787 at which delegates from 12 states wrote the Constitution of the United States. At the convention in
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Articles of Confederation. Essential Question:
 Articles of Confederation Essential Question: Why was the central government s power too weak under the Articles of Confederation? Objectives Discuss the ideas that guided the new state governments. Describe
Articles of Confederation Essential Question: Why was the central government s power too weak under the Articles of Confederation? Objectives Discuss the ideas that guided the new state governments. Describe
During the, the majority of delegates voted to declare independence from Britain. What is known as the official beginning of the America Revolution?
 What is known as the official beginning of the America Revolution? A. The Stamp Act B. Boston Tea Party C. Quartering Act D. Battle of Lexington and Concord During the, the majority of delegates voted
What is known as the official beginning of the America Revolution? A. The Stamp Act B. Boston Tea Party C. Quartering Act D. Battle of Lexington and Concord During the, the majority of delegates voted
LESSON TWO: THE FEDERALIST PAPERS
 LESSON TWO: THE FEDERALIST PAPERS OVERVIEW OBJECTIVES Students will be able to: Identify the Articles of Confederation and explain why it failed. Explain the argument over the need for a bill of rights
LESSON TWO: THE FEDERALIST PAPERS OVERVIEW OBJECTIVES Students will be able to: Identify the Articles of Confederation and explain why it failed. Explain the argument over the need for a bill of rights
AIM: How did the Articles of Confederation impact the U.S.?
 AIM: How did the Articles of Confederation impact the U.S.? Do Now: How do you think Hale Charter Academy would function if we got rid of the assistant principal, and the dean, and we allowed the individual
AIM: How did the Articles of Confederation impact the U.S.? Do Now: How do you think Hale Charter Academy would function if we got rid of the assistant principal, and the dean, and we allowed the individual
US History, Ms. Brown Website: dph7history.weebly.com
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #72 Aims: SWBAT identify and explain the different perspectives of the Northern states and the Southern states SWBAT identify
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #72 Aims: SWBAT identify and explain the different perspectives of the Northern states and the Southern states SWBAT identify
The Coming of Independence. Ratifying the Constitution
 C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government 1 SECTION 1 SECTION 2 SECTION 3 SECTION 4 SECTION 5 Our Political Beginnings The Coming of Independence The Critical Period Creating the Constitution Ratifying
C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government 1 SECTION 1 SECTION 2 SECTION 3 SECTION 4 SECTION 5 Our Political Beginnings The Coming of Independence The Critical Period Creating the Constitution Ratifying
4. After some negotiating, mostly with the promise of the Bill of Rights, the Constitution was ratified.
 Chapter #9: The Confederation and the Constitution Big Picture Ideas 1. The Articles of Confederation, the first government set up after the American Revolution, was structured out of fear of a too-strong
Chapter #9: The Confederation and the Constitution Big Picture Ideas 1. The Articles of Confederation, the first government set up after the American Revolution, was structured out of fear of a too-strong
The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783!
 Creating a Republic The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783! The treaty ending the war with Britain, more than doubled the territory of the United States!
Creating a Republic The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783! The treaty ending the war with Britain, more than doubled the territory of the United States!
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of American Government
 Chapter 2: The Beginnings of American Government United States Government Fall, 2017 Origins of American Political Ideals Colonial Period Where did ideas for government in the colonies come from? Largely,
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of American Government United States Government Fall, 2017 Origins of American Political Ideals Colonial Period Where did ideas for government in the colonies come from? Largely,
The Federalist Papers
 The Federalist Papers If men were angels, no government would be necessary. James Madison During the Revolutionary War, Americans set up a new national government. They feared a strong central government.
The Federalist Papers If men were angels, no government would be necessary. James Madison During the Revolutionary War, Americans set up a new national government. They feared a strong central government.
VUS. 5 (pt.1): Building a New Nation: The Constitutional Convention
 Name: Date: Period: VUS 5 (pt1): Building a New Nation: The Constitutional Convention Notes US 5 (pt1): Building a New Nation: The Constitutional Convention 1 Objectives about VUS5: Building a New Nation
Name: Date: Period: VUS 5 (pt1): Building a New Nation: The Constitutional Convention Notes US 5 (pt1): Building a New Nation: The Constitutional Convention 1 Objectives about VUS5: Building a New Nation
US History, Ms. Brown Website: dph7history.weebly.com
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #67 Aims: SWBAT identify the key parts of the Patriot s philosophy SWBAT identify and evaluate the strengths and weaknesses
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #67 Aims: SWBAT identify the key parts of the Patriot s philosophy SWBAT identify and evaluate the strengths and weaknesses
Who attended the Philadelphia Convention? How was it organized? We the People, Unit 3 Lesson 12
 Who attended the Philadelphia Convention? How was it organized? We the People, Unit 3 Lesson 12 A convention has been called to rewrite Redwood school constitution. We need some delegates (representatives).
Who attended the Philadelphia Convention? How was it organized? We the People, Unit 3 Lesson 12 A convention has been called to rewrite Redwood school constitution. We need some delegates (representatives).
Ch.8, Sec.2 Creating the Constitution
 ü A al Convention Is Called - during the summer of 1787, 12 states sent delegates to Philadelphia to discuss amending the Articles of Confederation - the example set by Shays Rebellion proved our young
ü A al Convention Is Called - during the summer of 1787, 12 states sent delegates to Philadelphia to discuss amending the Articles of Confederation - the example set by Shays Rebellion proved our young
7 th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #55
 Name Date: Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7 th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #55 Aims: SWBAT identify the purpose of the First Continental Congress, and describe two actions they took
Name Date: Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7 th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #55 Aims: SWBAT identify the purpose of the First Continental Congress, and describe two actions they took
Constitutional Convention. May 1787
 Constitutional Convention May 1787 Annapolis Convention September 11 to September 14, 1786 Annapolis, Maryland Purpose - How to fix the articles of confederation Alexander Hamilton (New York) MUST resolve
Constitutional Convention May 1787 Annapolis Convention September 11 to September 14, 1786 Annapolis, Maryland Purpose - How to fix the articles of confederation Alexander Hamilton (New York) MUST resolve
Wednesday, September 28 th
 Wednesday, September 28 th Midterm #1: Monday, Sept. 26 th to Thursday, Sept. 29 th Wednesday ($5 late fee) Thursday ($7 late fee) Must have test in hand by 11 am Exam in Testing Center. Be sure to go
Wednesday, September 28 th Midterm #1: Monday, Sept. 26 th to Thursday, Sept. 29 th Wednesday ($5 late fee) Thursday ($7 late fee) Must have test in hand by 11 am Exam in Testing Center. Be sure to go
Unit 7. Our First Government. Bellwork. Essential Questions (What I need to know):
 Unit 7 Our First Government Name Date Period Essential Questions (What I need to know): Date Bellwork Answer(s) 1. What is government? 2. How did the first United States government operate? 3. How did
Unit 7 Our First Government Name Date Period Essential Questions (What I need to know): Date Bellwork Answer(s) 1. What is government? 2. How did the first United States government operate? 3. How did
Practice Basic Civics Test
 Practice Basic Civics Test Here is a practice test using 50 of the 100 United States Customs and Immigration Services (USCIS) Civics Test questions. The multiple-choice questions and answers were selected
Practice Basic Civics Test Here is a practice test using 50 of the 100 United States Customs and Immigration Services (USCIS) Civics Test questions. The multiple-choice questions and answers were selected
1 st United States Constitution. A. loose alliance of states. B. Congress lawmaking body. C. 9 states had to vote to pass laws
 1 st United States Constitution A. loose alliance of states B. Congress lawmaking body C. 9 states had to vote to pass laws D. each state had 1 vote in Congress Northwest Ordinance / Land Ordinance division
1 st United States Constitution A. loose alliance of states B. Congress lawmaking body C. 9 states had to vote to pass laws D. each state had 1 vote in Congress Northwest Ordinance / Land Ordinance division
Creating the Constitution 2.2, 2.3, 2.4
 Creating the Constitution 2.2, 2.3, 2.4 Struggle for Government The creation and signing of the Declaration of Independence did not create a government The founding fathers had many problems Declaration
Creating the Constitution 2.2, 2.3, 2.4 Struggle for Government The creation and signing of the Declaration of Independence did not create a government The founding fathers had many problems Declaration
The Beginnings of a New American Government
 The Constitution The Beginnings of a New American Government Dissatisfaction grew with the Articles of Confederation as disagreements over control of waterways and trade developed. In 1785 the first meeting
The Constitution The Beginnings of a New American Government Dissatisfaction grew with the Articles of Confederation as disagreements over control of waterways and trade developed. In 1785 the first meeting
Four reasons we need government
 Four reasons we need government 1. Need for Law and Order - Government makes laws to protect citizens, and punishes those who break the law. Laws provide order in a society. This allows citizens to live
Four reasons we need government 1. Need for Law and Order - Government makes laws to protect citizens, and punishes those who break the law. Laws provide order in a society. This allows citizens to live
Ch. 6 Creating the Constitution /EQ:
 Ch. 6 Creating the Constitution /EQ: 6.1 Introduction Like Washington, most Americans did not want to be ruled by a monarch. What they did want, though, was an effective government. Articles of Confederation,
Ch. 6 Creating the Constitution /EQ: 6.1 Introduction Like Washington, most Americans did not want to be ruled by a monarch. What they did want, though, was an effective government. Articles of Confederation,
Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation
 Name: Date: Chapter 8 Study Guide Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation 1. A constitution is a set of basic principles and laws, usually in written form, that state the powers and duties of a government.
Name: Date: Chapter 8 Study Guide Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation 1. A constitution is a set of basic principles and laws, usually in written form, that state the powers and duties of a government.
Unit 2 Part 2 Articles of Confederation
 Unit 2 Part 2 Articles of Confederation Explain how the states new constitutions reflected republican ideals. Describe the structure and powers of the national government under the Articles of Confederation.
Unit 2 Part 2 Articles of Confederation Explain how the states new constitutions reflected republican ideals. Describe the structure and powers of the national government under the Articles of Confederation.
Forming a New Government
 Forming a New Government Why Independent in the First Place? Citizens wanted to limit the power of government Lack of representation No taxation without representation Protect personal freedoms Desired
Forming a New Government Why Independent in the First Place? Citizens wanted to limit the power of government Lack of representation No taxation without representation Protect personal freedoms Desired
New Nation. establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s
 New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
Was the Constitutional Convention a coup d etat?
 Was the Constitutional Convention a coup d etat? The Federal Convention ( known now as the Constitutional Convention ) is understood by most Americans as the historic meeting place of the most patriotic
Was the Constitutional Convention a coup d etat? The Federal Convention ( known now as the Constitutional Convention ) is understood by most Americans as the historic meeting place of the most patriotic
The Constitutional Convention
 The Constitutional Convention Problems like Shay s Rebellion revealed the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation This event convinced many U.S. citizens that our 1 st written plan of government needed
The Constitutional Convention Problems like Shay s Rebellion revealed the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation This event convinced many U.S. citizens that our 1 st written plan of government needed
Chapter 2 TEST Origins of American Government
 US Government - Ried Chapter 2 TEST Origins of American Government 1)The Magna Carta was originally intended to protect the rights of which group? A. religious leaders B. kings and queens C. common people
US Government - Ried Chapter 2 TEST Origins of American Government 1)The Magna Carta was originally intended to protect the rights of which group? A. religious leaders B. kings and queens C. common people
The American Revolution is over but now the colonists have to decide how they want to frame their government. Take the first 5 minutes of class and
 The American Revolution is over but now the colonists have to decide how they want to frame their government. Take the first 5 minutes of class and imagine that you were a colonist that just fought against
The American Revolution is over but now the colonists have to decide how they want to frame their government. Take the first 5 minutes of class and imagine that you were a colonist that just fought against
THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION. Compromises Federalists v. Anti-Federalists
 THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Compromises Federalists v. Anti-Federalists QUICK REVIEW: FIND SOMEONE WHO Second Continental Congress Drafting of the Articles of Confederation Weaknesses International Relations
THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Compromises Federalists v. Anti-Federalists QUICK REVIEW: FIND SOMEONE WHO Second Continental Congress Drafting of the Articles of Confederation Weaknesses International Relations
From Revolution to Government
 From Revolution to Government The Second Continental Congress declared independence from Britain in 1776. The Revolutionary War lasted from 1775 to 1783. Congress developed a new government for America:
From Revolution to Government The Second Continental Congress declared independence from Britain in 1776. The Revolutionary War lasted from 1775 to 1783. Congress developed a new government for America:
Name: Section: Date:
 Directions: Answer the following multiple choice questions. 1. In 1774, the first Continental Congress took place in what city? a. New York City b. Jamestown c. Philadelphia d. Boston I. The deteriorating
Directions: Answer the following multiple choice questions. 1. In 1774, the first Continental Congress took place in what city? a. New York City b. Jamestown c. Philadelphia d. Boston I. The deteriorating
CREATING A GOVERNMENT
 Let us not be afraid to view with a steady eye the dangers with which we are surrounded. Are we not on the eve of a war, which is only to be prevented by the hopes from this convention? CREATING A GOVERNMENT
Let us not be afraid to view with a steady eye the dangers with which we are surrounded. Are we not on the eve of a war, which is only to be prevented by the hopes from this convention? CREATING A GOVERNMENT
Vocabulary Match-Up. Name Date Period Workbook Activity
 Name Date Period Workbook Activity Vocabulary Match-Up Chapter 2, Lesson 1 7 Part A Directions Match the vocabulary word in Column 1 with its definition in Column 2. Write the correct letter on each line.
Name Date Period Workbook Activity Vocabulary Match-Up Chapter 2, Lesson 1 7 Part A Directions Match the vocabulary word in Column 1 with its definition in Column 2. Write the correct letter on each line.
Articles of Confederation
 Articles of Confederation What was the nation facing after the Revolutionary War? -An agrarian or agricultural nation (Farmland) -A Confederate Nation-joined by an agreement or treaty -Debt -Major economic
Articles of Confederation What was the nation facing after the Revolutionary War? -An agrarian or agricultural nation (Farmland) -A Confederate Nation-joined by an agreement or treaty -Debt -Major economic
Colonies Become States
 Colonies Become States Colonies already had their own individual governments before the 1776 Declaration 11 of 13 colonies had State Constitutions Constitution a document that states rules under which
Colonies Become States Colonies already had their own individual governments before the 1776 Declaration 11 of 13 colonies had State Constitutions Constitution a document that states rules under which
Reading and Learning the U.S. Constitution
 Reading and Learning the U.S. Constitution Class 1 History Pre-Constitution - Class 2-3 Article 1 - Congress Class 3-4 Article 2 - Presidency Class 4-5 Article 3 - Courts Class 6: Bill of Rights - Amendments
Reading and Learning the U.S. Constitution Class 1 History Pre-Constitution - Class 2-3 Article 1 - Congress Class 3-4 Article 2 - Presidency Class 4-5 Article 3 - Courts Class 6: Bill of Rights - Amendments
It was decided that delegates from the different states would meet during the summer of 1787 in Philadelphia.
 It was decided that delegates from the different states would meet during the summer of 1787 in Philadelphia. Philadelphia has a rich history, as it was at one time America s largest city and former capital.
It was decided that delegates from the different states would meet during the summer of 1787 in Philadelphia. Philadelphia has a rich history, as it was at one time America s largest city and former capital.
CHAPTER 2 ORIGINS OF AMERICAN GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS
 CHAPTER 2 ORIGINS OF AMERICAN GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS Basic Concepts of Government Early settlers brought ideas of government or political systems with them.
CHAPTER 2 ORIGINS OF AMERICAN GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS Basic Concepts of Government Early settlers brought ideas of government or political systems with them.
Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings. Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings. Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings. Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings
 Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings The US government has its roots in English history Limited Government The concept that government is limited in what it can and cannot do Representative Government Government
Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings The US government has its roots in English history Limited Government The concept that government is limited in what it can and cannot do Representative Government Government
US History, Ms. Brown Need Help? or Call
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #88 Aims: SWBAT explain two conflicts the new government was faced with SWBAT explain Washington s idea of neutrality DO
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #88 Aims: SWBAT explain two conflicts the new government was faced with SWBAT explain Washington s idea of neutrality DO
 Everybody hated this thing. While observing that it was too weak is an oversimplification. The variety of reasons why people were so miserable in the 1780s have everything to do with this document (until
Everybody hated this thing. While observing that it was too weak is an oversimplification. The variety of reasons why people were so miserable in the 1780s have everything to do with this document (until
4 th Grade U.S. Government Study Guide
 4 th Grade U.S. Government Study Guide Big Ideas: Imagine trying to make a new country from scratch. You ve just had a war with the only leaders you ve ever known, and now you have to step up and lead.
4 th Grade U.S. Government Study Guide Big Ideas: Imagine trying to make a new country from scratch. You ve just had a war with the only leaders you ve ever known, and now you have to step up and lead.
Name Per. 2. Identify the important principles and issues debated at the Constitutional Convention and describe how they were resolved.
 Name Per CHAPTER 2 THE CONSTITUTION LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying Chapter 2, you should be able to: 1. Discuss the importance of the English philosophical heritage, the colonial experience, the Articles
Name Per CHAPTER 2 THE CONSTITUTION LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying Chapter 2, you should be able to: 1. Discuss the importance of the English philosophical heritage, the colonial experience, the Articles
Major Problem. Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government.
 The Constitution Major Problem Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government. Why? Feared a government like King George The Constitutional
The Constitution Major Problem Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government. Why? Feared a government like King George The Constitutional
New Nation. establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s
 New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
1- England Became Great Britain in the early 1700s. 2- Economic relationships Great Britain imposed strict control over trade.
 1- England Became Great Britain in the early 1700s 2- Economic relationships Great Britain imposed strict control over trade. Great Britain taxed the colonies after the French and Indian War Colonies traded
1- England Became Great Britain in the early 1700s 2- Economic relationships Great Britain imposed strict control over trade. Great Britain taxed the colonies after the French and Indian War Colonies traded
America: The Last Best Hope Chapter 4 Reflection and Choice
 America: The Last Best Hope Chapter 4 Reflection and Choice 1. Under the Articles of Confederation, Congress had all of the following powers EXCEPT A settle disputes between the states B borrow money C
America: The Last Best Hope Chapter 4 Reflection and Choice 1. Under the Articles of Confederation, Congress had all of the following powers EXCEPT A settle disputes between the states B borrow money C
The Constitutional Convention. Chapter 2 Section 4
 The Constitutional Convention Chapter 2 Section 4 Constitutional Convention May 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 74 delegates allowed, 55 attended, 39 signed final Delegates to the Convention Had lots of
The Constitutional Convention Chapter 2 Section 4 Constitutional Convention May 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 74 delegates allowed, 55 attended, 39 signed final Delegates to the Convention Had lots of
Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 2
 Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 2 Objectives 1. Explain how Britain s colonial policies contributed to the growth of self-government in the colonies. 2. Identify the major steps that
Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 2 Objectives 1. Explain how Britain s colonial policies contributed to the growth of self-government in the colonies. 2. Identify the major steps that
i n t e r a C t i v e s t u d e n t n o t e b o o k Mapping Activity 11/02/17
 Mapping Activity 11/02/17 Geography Skills Analyze the maps in Setting the Stage. Then answer the following questions and fill out the map as directed. 1. Label each state on the map. Which two states
Mapping Activity 11/02/17 Geography Skills Analyze the maps in Setting the Stage. Then answer the following questions and fill out the map as directed. 1. Label each state on the map. Which two states
I. SSUSH1: The student will describe European settlement in North America during the 17th century
 Unit I Review Sheet I. SSUSH1: The student will describe European settlement in North America during the 17th century 1. The Virginia Company A joint stock company. A group of investors share the risk
Unit I Review Sheet I. SSUSH1: The student will describe European settlement in North America during the 17th century 1. The Virginia Company A joint stock company. A group of investors share the risk
Chapter 7 Creating a Republic Powerpoint Questions ( ) Instructions:
 Chapter 7 Creating a Republic Powerpoint Questions (1776-1790) Instructions: Use the Creating a Republic class notes and American Nation textbook, Pages 198-219 and your class notes to answer these questions.
Chapter 7 Creating a Republic Powerpoint Questions (1776-1790) Instructions: Use the Creating a Republic class notes and American Nation textbook, Pages 198-219 and your class notes to answer these questions.
The United States Constitution. The Supreme Law of the Land
 The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land The Articles Prove Unstable Federal gov t could declare war and other foreign affairs Federal gov t have no power to collect taxes, relying only
The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land The Articles Prove Unstable Federal gov t could declare war and other foreign affairs Federal gov t have no power to collect taxes, relying only
Conceived in Liberty. 5th Grade Social Studies Textbook
 Conceived in Liberty 5th Grade Social Studies Textbook Chapter 9 Creating the Constitution Chapter 9 Creating the Constiution When the American people won their independence, they had to decide what kind
Conceived in Liberty 5th Grade Social Studies Textbook Chapter 9 Creating the Constitution Chapter 9 Creating the Constiution When the American people won their independence, they had to decide what kind
Articles of Confederation
 Articles of Confederation Do Now How is power divided in our country today? SWBAT Analyze government problems under the Articles of Confederation Activity Review the Articles of Confederation chart and
Articles of Confederation Do Now How is power divided in our country today? SWBAT Analyze government problems under the Articles of Confederation Activity Review the Articles of Confederation chart and
The Constitutional Convention
 The Constitutional Convention Problems like Shay s Rebellion revealed the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation This event convinced many U.S. citizens that our 1 st written plan of government needed
The Constitutional Convention Problems like Shay s Rebellion revealed the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation This event convinced many U.S. citizens that our 1 st written plan of government needed
