May, 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania ~Independence Hall~ Leader: George Washington
|
|
|
- Esther Cook
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 May, 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania ~Independence Hall~ Leader: George Washington
2 -May 1787 Philadelphia Met in Independence Hall in Philadelphia George Washington leader -12 of 13 states Rhode Island absent Feared a strong central government -55 Delegates Many leaders missing In May 1787, delegates from all the states except Rhode Island gathered at the Philadelphia State House in the same room in which the Declaration of Independence had been signed 11 years earlier. Most of the 55 delegates were lawyers, merchants, or planters. Most were rich, well-educated men in their thirties and forties. They included some of the most influential leaders at the time, such as Ben Franklin, Alexander Hamilton, and George Washington. George Washington was elected presiding officer by a unanimous vote.
3 -rewrite gov t Meant to revise articles Threw AOC away, started over -1 vote per state -keep meeting a secret In spite of the sweltering heat, the windows were tightly sealed to prevent outsiders from eavesdropping on the discussions. The delegates wanted to feel free to speak their minds without causing alarm or opposition among the general public. They agreed to keep whatever was said in the meeting room a secret until their work was done. Speak freely without public influence -majority rules Delegates divided on where power should come from - people or states?
4 -representation Should representation be equal or based on population? large states Want rep. based on population small states Want equal rep. from each state -slavery Should the U.S. keep it? Do slaves count in population? -economics Can the gov. tax? How to pay off debts Key Issue: Should states with more people have more representatives, or should every state be represented equally? What about slaves? Do they count?
5 PLANS PROPOSED -Virginia Plan -James Madison - Father of the Constitution -3 branches (strong national government) -bicameral Congress James Madison is known as the Father of the Constitution not only for his proposal of the Virginia Plan, but also for his actions during the convention. He addressed the convention more than 200 times, and when he was not speaking, he took notes. Sitting near the front of the room so that he could hear everything that was said, Madison wrote down nearly every word. From this record, we know what happened at the convention every day. (2 houses) -population based Number of lawmakers depends on states population Favors LARGE states
6 New Jersey Plan -small state plan 3 branches, 1 house Congress -equal voting Keep small states from being taken over by large states -group executive William Paterson proposed the New Jersey Plan, which promoted states rights for the small states. -promoted state s rights
7 -Great Compromise Roger Sherman (Conn.) -Agreement made at the Convention of 1787 that created a two house legislature with one house based on population and the other based on state equality - House To represent people, based on population -Senate To represent state, equal representation Roger Sherman proposed the Great Compromise, which became our U.S. Constitution
8 Representation based on population raised the question of whether slaves should be counted as people. Southern delegates, whose states had many slaves, wanted slaves included in the population count that determined the number of representatives in the House. Northern delegates, whose states had few slaves, disagreed. Not counting Southern slaves would give the Northern states more representatives. The delegates finally agreed to the Three-Fifths Compromise. This settled the political issue, but not the economic issue of slavery. Slaveholders, especially in the South, worried that if Congress were given power to regulate foreign trade, it might do away with the slave trade. To resolve this issue, the convention gave Congress the power to regulate trade but prevented it from interfering with the slave trade for 20 years. -3/5 Compromise -Agreement made at the convention of 1787 that slaves would count as 3/5 a person for the census to determine the population of each state 3 of every 5 slaves count -Slave Trade Compromise -Agreement at the convention of 1787 that Congress would not tax exports and slave trading could be banned in 20 years
9 -much stronger than Articles of Confederation -power to tax Congress and states -regulate trade Congress controls interstate trade -strong executive Called a President 1 term = 4 years -needed 9 of 13 to ratify Pass/approve September 17, 1787, delegates at the Constitutional Convention declared the new constitution complete. Now it would be sent to the states for ratification.
10
11 The framers set up a procedure for ratification that called for each state to hold a special convention. The voters would elect delegates to the convention, who would then vote to accept or reject the Constitution. Those in favor called themselves Federalists. Those opposed called themselves Anti-Federalists. They divided the powers, that each might be a check upon the other and I presume that every reasonable man will agree to it. ~Federalist Alexander Hamilton You are not to inquire how your trade may be increased, nor how you are to become a great and powerful people, but how your liberties can be secured ~Anti-Federalist Patrick Henry -Federalists -Political group who supported the passage of the new Constitution and its stronger government Hamilton, Madison -Anti-Federalist -Political group who opposed the new Constitution and thought it lacked a specific list of people s rights Wanted to protect the people against federal government
12 -Federalist Papers support the new government Convince Americans to adopt the new Constitution -written by Hamilton, Madison, and Jay Both sides waged a war of words in the public debate over ratification. The Federalist, a series of 85 essays defending the Constitution, appeared in New York newspapers between 1787 and The Federalist provided an explanation of Constitutional provisions, such as the separation of powers and limits on the power of majorities, that remain important today. -Bill of Rights promised Rights of the people Bill of Rights won the states needed for ratification
13
The Constitutional Convention
 The Constitutional Convention Problems like Shay s Rebellion revealed the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation This event convinced many U.S. citizens that our 1 st written plan of government needed
The Constitutional Convention Problems like Shay s Rebellion revealed the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation This event convinced many U.S. citizens that our 1 st written plan of government needed
The Constitutional Convention. Chapter 2 Section 4
 The Constitutional Convention Chapter 2 Section 4 Constitutional Convention May 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 74 delegates allowed, 55 attended, 39 signed final Delegates to the Convention Had lots of
The Constitutional Convention Chapter 2 Section 4 Constitutional Convention May 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 74 delegates allowed, 55 attended, 39 signed final Delegates to the Convention Had lots of
The Constitutional Convention
 The Constitutional Convention Problems like Shay s Rebellion revealed the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation This event convinced many U.S. citizens that our 1 st written plan of government needed
The Constitutional Convention Problems like Shay s Rebellion revealed the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation This event convinced many U.S. citizens that our 1 st written plan of government needed
Chapter 5, Section 3 Creating the Constitution. Pages
 Chapter 5, Section 3 Creating the Constitution Pages 163-168 It didn t take long for people to realize that the Articles of Confederation had many weaknesses. By the mid-1780s most political leaders agreed
Chapter 5, Section 3 Creating the Constitution Pages 163-168 It didn t take long for people to realize that the Articles of Confederation had many weaknesses. By the mid-1780s most political leaders agreed
The American Revolution is over but now the colonists have to decide how they want to frame their government. Take the first 5 minutes of class and
 The American Revolution is over but now the colonists have to decide how they want to frame their government. Take the first 5 minutes of class and imagine that you were a colonist that just fought against
The American Revolution is over but now the colonists have to decide how they want to frame their government. Take the first 5 minutes of class and imagine that you were a colonist that just fought against
 Everybody hated this thing. While observing that it was too weak is an oversimplification. The variety of reasons why people were so miserable in the 1780s have everything to do with this document (until
Everybody hated this thing. While observing that it was too weak is an oversimplification. The variety of reasons why people were so miserable in the 1780s have everything to do with this document (until
Constitutional Convention. May 1787
 Constitutional Convention May 1787 Annapolis Convention September 11 to September 14, 1786 Annapolis, Maryland Purpose - How to fix the articles of confederation Alexander Hamilton (New York) MUST resolve
Constitutional Convention May 1787 Annapolis Convention September 11 to September 14, 1786 Annapolis, Maryland Purpose - How to fix the articles of confederation Alexander Hamilton (New York) MUST resolve
the states. decisions within its own borders) 1. A central government that would represent all 2. State sovereignty (the power to make
 The United States has operated under two constitutions. The first, The Articles of Confederation, was in effect from March 1, 1781. The Articles tried to balance two very different ideas: 1. A central
The United States has operated under two constitutions. The first, The Articles of Confederation, was in effect from March 1, 1781. The Articles tried to balance two very different ideas: 1. A central
Chapter 25 Section 1. Section 1. Terms and People
 Chapter 25 Terms and People republic a government in which the people elect their representatives unicameral legislature a lawmaking body with a single house whose representatives are elected by the people
Chapter 25 Terms and People republic a government in which the people elect their representatives unicameral legislature a lawmaking body with a single house whose representatives are elected by the people
Establishing A New Government: Creating a Government. Chapter 4 Concept 2
 Establishing A New Government: Creating a Government Chapter 4 Concept 2 4.2 Creating a Government How did the decisions made at the Constitutional Convention affect the balance of power in the new nation?
Establishing A New Government: Creating a Government Chapter 4 Concept 2 4.2 Creating a Government How did the decisions made at the Constitutional Convention affect the balance of power in the new nation?
Constitutional Convention
 Constitutional Convention How did the United States overcome the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation and provide for the organization of the new government? What role did compromise play in the
Constitutional Convention How did the United States overcome the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation and provide for the organization of the new government? What role did compromise play in the
Why do you think the Framers organized the new country as a republic, when most countries in the world (in 1783) were ruled by a king or queen?
 NAME: Date: U.S. History CHAPTER 7 PACKET ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: 1. What is a constitution? 2. What is a republic? 3. What was the Articles of Confederation? 4. How was state and national power divided under
NAME: Date: U.S. History CHAPTER 7 PACKET ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: 1. What is a constitution? 2. What is a republic? 3. What was the Articles of Confederation? 4. How was state and national power divided under
Ch.8, Sec.2 Creating the Constitution
 ü A al Convention Is Called - during the summer of 1787, 12 states sent delegates to Philadelphia to discuss amending the Articles of Confederation - the example set by Shays Rebellion proved our young
ü A al Convention Is Called - during the summer of 1787, 12 states sent delegates to Philadelphia to discuss amending the Articles of Confederation - the example set by Shays Rebellion proved our young
Chapter 5 section 3: Creating the Constitution textbook pages
 Chapter 5 section 3: Creating the Constitution textbook pages 163-168 The Big Idea A new constitution provided a framework for a stronger national government. Main Idea 1:The Constitutional Convention
Chapter 5 section 3: Creating the Constitution textbook pages 163-168 The Big Idea A new constitution provided a framework for a stronger national government. Main Idea 1:The Constitutional Convention
Jeopardy Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400
 Jeopardy 2013-14 Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $500 Q $500 Q $500 Q $500 Final Jeopardy
Jeopardy 2013-14 Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $500 Q $500 Q $500 Q $500 Final Jeopardy
Articles of Confederation
 Articles of Confederation What was the nation facing after the Revolutionary War? -An agrarian or agricultural nation (Farmland) -A Confederate Nation-joined by an agreement or treaty -Debt -Major economic
Articles of Confederation What was the nation facing after the Revolutionary War? -An agrarian or agricultural nation (Farmland) -A Confederate Nation-joined by an agreement or treaty -Debt -Major economic
Major Problem. Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government.
 The Constitution Major Problem Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government. Why? Feared a government like King George The Constitutional
The Constitution Major Problem Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government. Why? Feared a government like King George The Constitutional
The Constitutional Convention formed the plan of government that the United States still has today.
 2 Creating the Constitution MAIN IDEA The states sent delegates to a convention to solve the problems of the Articles of Confederation. WHY IT MATTERS NOW The Constitutional Convention formed the plan
2 Creating the Constitution MAIN IDEA The states sent delegates to a convention to solve the problems of the Articles of Confederation. WHY IT MATTERS NOW The Constitutional Convention formed the plan
Creating the Constitution 2.2, 2.3, 2.4
 Creating the Constitution 2.2, 2.3, 2.4 Struggle for Government The creation and signing of the Declaration of Independence did not create a government The founding fathers had many problems Declaration
Creating the Constitution 2.2, 2.3, 2.4 Struggle for Government The creation and signing of the Declaration of Independence did not create a government The founding fathers had many problems Declaration
Section 4 at a Glance The Constitutional Convention
 Section 4 at a Glance The Constitutional Convention At the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia, delegates debated competing plans the Virginia Plan and the New Jersey Plan for how the new government
Section 4 at a Glance The Constitutional Convention At the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia, delegates debated competing plans the Virginia Plan and the New Jersey Plan for how the new government
The United States Constitution. The Supreme Law of the Land
 The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land The Articles Prove Unstable Federal gov t could declare war and other foreign affairs Federal gov t have no power to collect taxes, relying only
The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land The Articles Prove Unstable Federal gov t could declare war and other foreign affairs Federal gov t have no power to collect taxes, relying only
Constitutional Convention
 2014 Delegates Remember a delegate is someone who is chosen to speak for others, or to represent them. The delegates represented each of the states and consisted of: Wealthy and educated landowners, business
2014 Delegates Remember a delegate is someone who is chosen to speak for others, or to represent them. The delegates represented each of the states and consisted of: Wealthy and educated landowners, business
CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION
 CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Objectives Why did the Constitutional Convention draft a new plan for government? How did the rival plans for the new government differ? What other conflicts required the Framers
CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Objectives Why did the Constitutional Convention draft a new plan for government? How did the rival plans for the new government differ? What other conflicts required the Framers
2:Forging a New Constitution. Essential Question How do new ideas change the way people live?
 2:Forging a New Constitution Essential Question How do new ideas change the way people live? The Need for Change Bold action helped the nation overcome the serious shortcomings of the Articles of Confederation.
2:Forging a New Constitution Essential Question How do new ideas change the way people live? The Need for Change Bold action helped the nation overcome the serious shortcomings of the Articles of Confederation.
2. Divided Convention. 3. Inside the Constitution. Constitution replaced the Articles---becomes the law of the land.
 2. Divided Convention notes7 9/13 states needed to ratify (to approve) Political parties begin Federalists: supported the Constitution The Federalist ---essays support Constitution Anti-Federalists: against
2. Divided Convention notes7 9/13 states needed to ratify (to approve) Political parties begin Federalists: supported the Constitution The Federalist ---essays support Constitution Anti-Federalists: against
Vocabulary Match-Up. Name Date Period Workbook Activity
 Name Date Period Workbook Activity Vocabulary Match-Up Chapter 2, Lesson 1 7 Part A Directions Match the vocabulary word in Column 1 with its definition in Column 2. Write the correct letter on each line.
Name Date Period Workbook Activity Vocabulary Match-Up Chapter 2, Lesson 1 7 Part A Directions Match the vocabulary word in Column 1 with its definition in Column 2. Write the correct letter on each line.
Creating the Constitution
 Creating the Constitution 1776-1791 US Timeline 1777-1791 1777 Patriots win Battles of Saratoga. Continental Congress passes the Articles of Confederation. 1781 Articles of Confederation go into effect.
Creating the Constitution 1776-1791 US Timeline 1777-1791 1777 Patriots win Battles of Saratoga. Continental Congress passes the Articles of Confederation. 1781 Articles of Confederation go into effect.
Shays. Daniel Shay 1784 to 1785, unfair taxes, debt and foreclosure Farmer s rebellion to overthrow Mass. Govt.
 Shays Daniel Shay 1784 to 1785, unfair taxes, debt and foreclosure Farmer s rebellion to overthrow Mass. Govt. 1. Constitutional Convention: May to Sept. 1787 2. Divided Convention 9/13 states needed to
Shays Daniel Shay 1784 to 1785, unfair taxes, debt and foreclosure Farmer s rebellion to overthrow Mass. Govt. 1. Constitutional Convention: May to Sept. 1787 2. Divided Convention 9/13 states needed to
CREATING A GOVERNMENT
 Let us not be afraid to view with a steady eye the dangers with which we are surrounded. Are we not on the eve of a war, which is only to be prevented by the hopes from this convention? CREATING A GOVERNMENT
Let us not be afraid to view with a steady eye the dangers with which we are surrounded. Are we not on the eve of a war, which is only to be prevented by the hopes from this convention? CREATING A GOVERNMENT
HIST 1301 Part Two. 6: The Republican Experiment
 HIST 1301 Part Two 6: The Republican Experiment The States and the Confederation 1776-1788 During the Revolution, state Governments formed first. 2 min. 40 sec. Each state had a written constitution. Each
HIST 1301 Part Two 6: The Republican Experiment The States and the Confederation 1776-1788 During the Revolution, state Governments formed first. 2 min. 40 sec. Each state had a written constitution. Each
Ratification of the Constitution. Issues
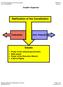 Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
What were the Articles of Confederation? What did America do to create a stronger government in the 1780s?
 2.3 Articles of Confederation What were the Articles of Confederation? Why were the 1780s a critical period in United States history? What did America do to create a stronger government in the 1780s? Section:
2.3 Articles of Confederation What were the Articles of Confederation? Why were the 1780s a critical period in United States history? What did America do to create a stronger government in the 1780s? Section:
Warm Up. 1 Explain how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to Shays Rebellion:
 Warm Up 1 Explain how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to Shays Rebellion: 2 What was the primary concern of soldier/farmers who supported Daniel Shays? 3 Explain how Shays Rebellion
Warm Up 1 Explain how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to Shays Rebellion: 2 What was the primary concern of soldier/farmers who supported Daniel Shays? 3 Explain how Shays Rebellion
Beginnings of a New Nation
 The period between the Treaty of Paris and the writing of the Constitution, the states were united only by a rope of sand. George Washington Beginnings of a New Nation Officers were disgusted with Congress
The period between the Treaty of Paris and the writing of the Constitution, the states were united only by a rope of sand. George Washington Beginnings of a New Nation Officers were disgusted with Congress
WARM UP. 1 Using the information from yesterday or new information collected using your ipad create a bubble map on the Constitutional Convention
 WARM UP 1 Using the information from yesterday or new information collected using your ipad create a bubble map on the Constitutional Convention 2 Include people, dates, locations, facts and other information
WARM UP 1 Using the information from yesterday or new information collected using your ipad create a bubble map on the Constitutional Convention 2 Include people, dates, locations, facts and other information
1 st United States Constitution. A. loose alliance of states. B. Congress lawmaking body. C. 9 states had to vote to pass laws
 1 st United States Constitution A. loose alliance of states B. Congress lawmaking body C. 9 states had to vote to pass laws D. each state had 1 vote in Congress Northwest Ordinance / Land Ordinance division
1 st United States Constitution A. loose alliance of states B. Congress lawmaking body C. 9 states had to vote to pass laws D. each state had 1 vote in Congress Northwest Ordinance / Land Ordinance division
THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION. Compromises Federalists v. Anti-Federalists
 THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Compromises Federalists v. Anti-Federalists QUICK REVIEW: FIND SOMEONE WHO Second Continental Congress Drafting of the Articles of Confederation Weaknesses International Relations
THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Compromises Federalists v. Anti-Federalists QUICK REVIEW: FIND SOMEONE WHO Second Continental Congress Drafting of the Articles of Confederation Weaknesses International Relations
Ch. 6 Creating the Constitution /EQ:
 Ch. 6 Creating the Constitution /EQ: 6.1 Introduction Like Washington, most Americans did not want to be ruled by a monarch. What they did want, though, was an effective government. Articles of Confederation,
Ch. 6 Creating the Constitution /EQ: 6.1 Introduction Like Washington, most Americans did not want to be ruled by a monarch. What they did want, though, was an effective government. Articles of Confederation,
SS.7.C.1.5. Identify how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing of the Constitution
 SS.7.C.1.5. Identify how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing of the Constitution SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the
SS.7.C.1.5. Identify how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing of the Constitution SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the
Ratifying the Constitution
 Ratifying the Constitution Signing the Constitution Once the debate ended, Governor Morris of New Jersey put the Constitution in its final form. He competed the task of hand-writing 4,300 words in two
Ratifying the Constitution Signing the Constitution Once the debate ended, Governor Morris of New Jersey put the Constitution in its final form. He competed the task of hand-writing 4,300 words in two
A More Perfect Union. Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation
 A More Perfect Union Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation 1. Eleven of the thirteen states adopted state constitutions. Connecticut and Rhode Island kept its colonial charter as its constitution
A More Perfect Union Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation 1. Eleven of the thirteen states adopted state constitutions. Connecticut and Rhode Island kept its colonial charter as its constitution
It was decided that delegates from the different states would meet during the summer of 1787 in Philadelphia.
 It was decided that delegates from the different states would meet during the summer of 1787 in Philadelphia. Philadelphia has a rich history, as it was at one time America s largest city and former capital.
It was decided that delegates from the different states would meet during the summer of 1787 in Philadelphia. Philadelphia has a rich history, as it was at one time America s largest city and former capital.
Warm Up 12/3. Why did Shays Rebellion occur? What did it prove to many people? What did Alexander Hamilton and James Madison call for?
 Warm Up 12/3 Why did Shays Rebellion occur? What did it prove to many people? What did Alexander Hamilton and James Madison call for? 1. How did many Americans feel about the Articles of Confederation?
Warm Up 12/3 Why did Shays Rebellion occur? What did it prove to many people? What did Alexander Hamilton and James Madison call for? 1. How did many Americans feel about the Articles of Confederation?
Creating a Nation Test Review
 Creating a Nation Test Review Question #1: Multiple Choice The Northwest ordinance of 1787 is important because. A. It sent troops to the Northwest to protect the colonies from Native Americans. B. It
Creating a Nation Test Review Question #1: Multiple Choice The Northwest ordinance of 1787 is important because. A. It sent troops to the Northwest to protect the colonies from Native Americans. B. It
Organization & Agreements
 Key Players Key Players Key Players George Washington unanimously chosen to preside over the meetings. Benjamin Franklin now 81 years old. Gouverneur Morris wrote the final draft. James Madison often called
Key Players Key Players Key Players George Washington unanimously chosen to preside over the meetings. Benjamin Franklin now 81 years old. Gouverneur Morris wrote the final draft. James Madison often called
OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS
 CHAPTER 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS The colonists brought with them to North America knowledge of the English political system, including three key ideas about government.
CHAPTER 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS The colonists brought with them to North America knowledge of the English political system, including three key ideas about government.
Chapter 2:4 Constitutional Convention
 Chapter 2:4 Constitutional Convention Psa_119:165 Great peace have they which love thy law: and nothing shall offend them. Objectives: 2:4 Our Political Beginnings o Students will examine the process that
Chapter 2:4 Constitutional Convention Psa_119:165 Great peace have they which love thy law: and nothing shall offend them. Objectives: 2:4 Our Political Beginnings o Students will examine the process that
The U.S. Constitution: Who, What, Where, When, Why & How
 The U.S. Constitution: Who, What, Where, When, Why & How 'a ^Va&o/z Fighting between the American colonists and British forces under King George III was in its second year when the Declaration of Independence
The U.S. Constitution: Who, What, Where, When, Why & How 'a ^Va&o/z Fighting between the American colonists and British forces under King George III was in its second year when the Declaration of Independence
CHAPTER 7 CREATING A GOVERNMENT
 CHAPTER 7 CREATING A GOVERNMENT The Constitution set out our rules for government. It explains what our government can and cannot do. It reflects are experience as a colony as well as ideas from Europe
CHAPTER 7 CREATING A GOVERNMENT The Constitution set out our rules for government. It explains what our government can and cannot do. It reflects are experience as a colony as well as ideas from Europe
U.S. Constitution PSCI 1040
 PSCI 1040 Purposes of a Constitution Organize and empower the government Limit the powers of government. Many consider limited government to be the essence of constitutional government. 2 Articles of Confederation
PSCI 1040 Purposes of a Constitution Organize and empower the government Limit the powers of government. Many consider limited government to be the essence of constitutional government. 2 Articles of Confederation
New Nation. establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s
 New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
What types of things did the new states do to make the governments more democratic?
 Chapter 8 Confederation to Constitution pg. 218 241 8 1 The Confederation Era pg. 221 225 Moving West and New State Governments Into which areas did American settlement expand in the late 1700s? What types
Chapter 8 Confederation to Constitution pg. 218 241 8 1 The Confederation Era pg. 221 225 Moving West and New State Governments Into which areas did American settlement expand in the late 1700s? What types
THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION. Ch 3-2
 THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Ch 3-2 By the end, the Constitutional Convention of 1787 had replaced the Articles of Confederation The new U.S. Constitution created a stronger, more complex national government
THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Ch 3-2 By the end, the Constitutional Convention of 1787 had replaced the Articles of Confederation The new U.S. Constitution created a stronger, more complex national government
Who attended the Philadelphia Convention? How was it organized? We the People, Unit 3 Lesson 12
 Who attended the Philadelphia Convention? How was it organized? We the People, Unit 3 Lesson 12 A convention has been called to rewrite Redwood school constitution. We need some delegates (representatives).
Who attended the Philadelphia Convention? How was it organized? We the People, Unit 3 Lesson 12 A convention has been called to rewrite Redwood school constitution. We need some delegates (representatives).
Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings. Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings. Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings. Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings
 Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings The US government has its roots in English history Limited Government The concept that government is limited in what it can and cannot do Representative Government Government
Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings The US government has its roots in English history Limited Government The concept that government is limited in what it can and cannot do Representative Government Government
Creating the Constitution
 Creating the Constitution Constitutional Convention Philadelphia 1787 Met in Secret Goal: Alter or abolish fix the old system or create a new one Needed to tweak the articles Focus of Convention Meeting
Creating the Constitution Constitutional Convention Philadelphia 1787 Met in Secret Goal: Alter or abolish fix the old system or create a new one Needed to tweak the articles Focus of Convention Meeting
Constitutional Convention
 Constitutional Convention Members Principles Agreements and compromises The Constitutional Convention, 1787 u 55 delegates attended but on a typical day 35 were present u 29 held college degrees u 34 were
Constitutional Convention Members Principles Agreements and compromises The Constitutional Convention, 1787 u 55 delegates attended but on a typical day 35 were present u 29 held college degrees u 34 were
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton
 Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
3: A New Plan of Government. Essential Question: How Do Governments Change?
 3: A New Plan of Government Essential Question: How Do Governments Change? The Constitution s Source Guiding Question: From where did the Framers of the Constitution borrow their ideas about government?
3: A New Plan of Government Essential Question: How Do Governments Change? The Constitution s Source Guiding Question: From where did the Framers of the Constitution borrow their ideas about government?
understanding CONSTITUTION
 understanding the CONSTITUTION Contents The Articles of Confederation The Constitutional Convention The Principles of the Constitution The Preamble The Legislative Branch The Executive Branch The Judicial
understanding the CONSTITUTION Contents The Articles of Confederation The Constitutional Convention The Principles of the Constitution The Preamble The Legislative Branch The Executive Branch The Judicial
Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation
 Name: Date: Chapter 8 Study Guide Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation 1. A constitution is a set of basic principles and laws, usually in written form, that state the powers and duties of a government.
Name: Date: Chapter 8 Study Guide Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation 1. A constitution is a set of basic principles and laws, usually in written form, that state the powers and duties of a government.
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes
 Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
Articles of Confederation
 Articles of Confederation Do Now How is power divided in our country today? SWBAT Analyze government problems under the Articles of Confederation Activity Review the Articles of Confederation chart and
Articles of Confederation Do Now How is power divided in our country today? SWBAT Analyze government problems under the Articles of Confederation Activity Review the Articles of Confederation chart and
American History 11R
 American History 11R Setting of the Philadelphia Convention Early decision to re-write, rather than tinker with the Articles of Confederation Open agreement secretly arrived at--washington's plea Intent
American History 11R Setting of the Philadelphia Convention Early decision to re-write, rather than tinker with the Articles of Confederation Open agreement secretly arrived at--washington's plea Intent
Magruder s American Government
 Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 Our Political Beginnings
Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 Our Political Beginnings
The United States Constitution. The Supreme Law of the Land
 The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land Standards SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States
The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land Standards SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States
The Critical Period The early years of the American Republic
 The Critical Period 1781-1789 The early years of the American Republic America after the War New Political Ideas: - Greater power for the people Republic: Represent the Public America after the War State
The Critical Period 1781-1789 The early years of the American Republic America after the War New Political Ideas: - Greater power for the people Republic: Represent the Public America after the War State
Debating the Constitution
 SECTION 3 A Bill of Rights A bill of rights is what the people are entitled to against every government on earth, general or particular; and what no just government should refuse or rest on inference.
SECTION 3 A Bill of Rights A bill of rights is what the people are entitled to against every government on earth, general or particular; and what no just government should refuse or rest on inference.
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Articles of Confederation. Essential Question:
 Articles of Confederation Essential Question: Why was the central government s power too weak under the Articles of Confederation? Objectives Discuss the ideas that guided the new state governments. Describe
Articles of Confederation Essential Question: Why was the central government s power too weak under the Articles of Confederation? Objectives Discuss the ideas that guided the new state governments. Describe
Chapter 2 TEST Origins of American Government
 US Government - Ried Chapter 2 TEST Origins of American Government 1)The Magna Carta was originally intended to protect the rights of which group? A. religious leaders B. kings and queens C. common people
US Government - Ried Chapter 2 TEST Origins of American Government 1)The Magna Carta was originally intended to protect the rights of which group? A. religious leaders B. kings and queens C. common people
Articles of Confederation September 18, 2007
 Articles of Confederation September 18, 2007 Powers Given to Congress under the Articles Weaknesses under the Articles Results of the Articles during the Critical Period Use Page 44-46 to analyze the effects
Articles of Confederation September 18, 2007 Powers Given to Congress under the Articles Weaknesses under the Articles Results of the Articles during the Critical Period Use Page 44-46 to analyze the effects
Four reasons we need government
 Four reasons we need government 1. Need for Law and Order - Government makes laws to protect citizens, and punishes those who break the law. Laws provide order in a society. This allows citizens to live
Four reasons we need government 1. Need for Law and Order - Government makes laws to protect citizens, and punishes those who break the law. Laws provide order in a society. This allows citizens to live
Test Day. October 3-4
 Test Day October 3-4 Sit Wherever Turn in your Study Guide to me When done with test, Turn in to the correct area up front (follow sticky notes) Pick up outline for Unit 3 Pick up a survey for Unit 3 Pick
Test Day October 3-4 Sit Wherever Turn in your Study Guide to me When done with test, Turn in to the correct area up front (follow sticky notes) Pick up outline for Unit 3 Pick up a survey for Unit 3 Pick
American Government. Unit 2 Study Guide
 American Government Unit 2 Study Guide Events leading up the Declaration of Independence: 1) Stamp Act- a tax placed on all printed material a. An attempt to earn money lost in the French and Indian War
American Government Unit 2 Study Guide Events leading up the Declaration of Independence: 1) Stamp Act- a tax placed on all printed material a. An attempt to earn money lost in the French and Indian War
AIM: How did the Articles of Confederation impact the U.S.?
 AIM: How did the Articles of Confederation impact the U.S.? Do Now: How do you think Hale Charter Academy would function if we got rid of the assistant principal, and the dean, and we allowed the individual
AIM: How did the Articles of Confederation impact the U.S.? Do Now: How do you think Hale Charter Academy would function if we got rid of the assistant principal, and the dean, and we allowed the individual
Chapter 3 Constitution. Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook
 Chapter 3 Constitution Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on www.pknock.com Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from
Chapter 3 Constitution Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on www.pknock.com Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from
The End of the Confederation Era
 The End of the Confederation Era By 1786 it became clear that the Articles were not working The Philadelphia Convention of 1787 brought leaders from the 12 states (Rhode Island did not attend) to address
The End of the Confederation Era By 1786 it became clear that the Articles were not working The Philadelphia Convention of 1787 brought leaders from the 12 states (Rhode Island did not attend) to address
The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783!
 Creating a Republic The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783! The treaty ending the war with Britain, more than doubled the territory of the United States!
Creating a Republic The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783! The treaty ending the war with Britain, more than doubled the territory of the United States!
The Beginnings of a New American Government
 The Constitution The Beginnings of a New American Government Dissatisfaction grew with the Articles of Confederation as disagreements over control of waterways and trade developed. In 1785 the first meeting
The Constitution The Beginnings of a New American Government Dissatisfaction grew with the Articles of Confederation as disagreements over control of waterways and trade developed. In 1785 the first meeting
Chapter 8 Section Review Packet
 Name: Date: Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation Chapter 8 Section Review Packet 1. Constitution 2. Republicanism 3. Limited government 4. Suffrage 5. Articles of Confederation 6. Ratification 7.
Name: Date: Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation Chapter 8 Section Review Packet 1. Constitution 2. Republicanism 3. Limited government 4. Suffrage 5. Articles of Confederation 6. Ratification 7.
How Shall We Govern Ourselves?
 How Shall We Govern Ourselves? The Articles of Confederation America s First Constitution What kind of government would the FREEDOM loving Americans create to balance LIBERTY with enough AUTHORITY to get
How Shall We Govern Ourselves? The Articles of Confederation America s First Constitution What kind of government would the FREEDOM loving Americans create to balance LIBERTY with enough AUTHORITY to get
Standard Indicator SOUTH CAROLINA AND THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION IN PHILADELPHIA
 Standard Indicator 8-3.2 SOUTH CAROLINA AND THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION IN PHILADELPHIA ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION First plan of government for US Adopted during Revolutionary War Weak plan of government
Standard Indicator 8-3.2 SOUTH CAROLINA AND THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION IN PHILADELPHIA ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION First plan of government for US Adopted during Revolutionary War Weak plan of government
AKS M 49 C 30 a-d D 32 a-c D 33 a-c D 34 a-b BUILDING A NEW NATION
 AKS M 49 C 30 a-d D 32 a-c D 33 a-c D 34 a-b BUILDING A NEW NATION The official end of the Revolutionary War was the signing of the Treaty of Paris in 1783. The newly independent US and GA now faced the
AKS M 49 C 30 a-d D 32 a-c D 33 a-c D 34 a-b BUILDING A NEW NATION The official end of the Revolutionary War was the signing of the Treaty of Paris in 1783. The newly independent US and GA now faced the
VUS. 5 (pt.1): Building a New Nation: The Constitutional Convention
 Name: Date: Period: VUS 5 (pt1): Building a New Nation: The Constitutional Convention Notes US 5 (pt1): Building a New Nation: The Constitutional Convention 1 Objectives about VUS5: Building a New Nation
Name: Date: Period: VUS 5 (pt1): Building a New Nation: The Constitutional Convention Notes US 5 (pt1): Building a New Nation: The Constitutional Convention 1 Objectives about VUS5: Building a New Nation
[ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals
![[ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals [ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals](/thumbs/77/76341976.jpg) [ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals [ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals Key Terms limited government representative government due process bicameral unicameral [ 2.1 ] Origins of American
[ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals [ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals Key Terms limited government representative government due process bicameral unicameral [ 2.1 ] Origins of American
The Constitution I. Considerations that influenced the formulation and adoption of the Constitution A. Roots 1. Religious Freedom a) Puritan
 The Constitution I. Considerations that influenced the formulation and adoption of the Constitution A. Roots 1. Religious Freedom a) Puritan Theocracy (1) 9 of 13 had state church b) Rhode Island (1) Roger
The Constitution I. Considerations that influenced the formulation and adoption of the Constitution A. Roots 1. Religious Freedom a) Puritan Theocracy (1) 9 of 13 had state church b) Rhode Island (1) Roger
The Articles of Confederation
 1 The Articles of Confederation Approved by Congress on November 15, 1777, Congress sent to the states for ratification the Articles of Confederation. This was the first governing constitution for the
1 The Articles of Confederation Approved by Congress on November 15, 1777, Congress sent to the states for ratification the Articles of Confederation. This was the first governing constitution for the
Charles de Montesquieu
 Unit III He first created the idea of consent of the governed where people have a vote in who leads them (democracy). Every person has the right to life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness. John Locke
Unit III He first created the idea of consent of the governed where people have a vote in who leads them (democracy). Every person has the right to life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness. John Locke
The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783!
 Creating a Republic The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783! The treaty ending the war with Britain, more than doubled the territory of the United States!
Creating a Republic The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783! The treaty ending the war with Britain, more than doubled the territory of the United States!
Vocabulary for Evolution of Government
 Vocabulary for Evolution of Government Directions Students will make a flash card for each word The flash card must include all the information on the screen (cards will be stamped for completeness) The
Vocabulary for Evolution of Government Directions Students will make a flash card for each word The flash card must include all the information on the screen (cards will be stamped for completeness) The
Constitutional Convention
 Constitutional Convention I INTRODUCTION Constitutional Convention, meeting during the summer of 1787 at which delegates from 12 states wrote the Constitution of the United States. At the convention in
Constitutional Convention I INTRODUCTION Constitutional Convention, meeting during the summer of 1787 at which delegates from 12 states wrote the Constitution of the United States. At the convention in
Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50
 Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50 The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from religious persecution Economic opportunity Independent
Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50 The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from religious persecution Economic opportunity Independent
Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution
 Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution The Articles of Confederation After declaring independence from Britain in 1776, Congress tried to unite the states under one national government. However, many feared
Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution The Articles of Confederation After declaring independence from Britain in 1776, Congress tried to unite the states under one national government. However, many feared
Basic Concepts of Government The English colonists brought 3 ideas that loom large in the shaping of the government in the United States.
 Civics Honors Chapter Two: Origins of American Government Section One: Our Political Beginnings Limited Government Representative government Magna Carta Petition of Right English Bill of Rights Charter
Civics Honors Chapter Two: Origins of American Government Section One: Our Political Beginnings Limited Government Representative government Magna Carta Petition of Right English Bill of Rights Charter
Unit 7 Our Current Government
 Unit 7 Our Current Government Name Date Period Learning Targets (What I need to know): I can describe the Constitutional Convention and two compromises that took place there. I can describe the structure
Unit 7 Our Current Government Name Date Period Learning Targets (What I need to know): I can describe the Constitutional Convention and two compromises that took place there. I can describe the structure
The States: Experiments in Republicanism State constitutions served as experiments in republican government The people demand written constitutions
 The States: Experiments in Republicanism State constitutions served as experiments in republican government The people demand written constitutions provide clear definition of rights describe clear limits
The States: Experiments in Republicanism State constitutions served as experiments in republican government The people demand written constitutions provide clear definition of rights describe clear limits
End of American Revolution and Creation of American government
 End of American Revolution and Creation of American government American Revolution concludes, an independent nation develops, 1781. Articles of Confederation ratified by states March 1781 - framework for
End of American Revolution and Creation of American government American Revolution concludes, an independent nation develops, 1781. Articles of Confederation ratified by states March 1781 - framework for
BEGINNINGS: Political essentials and foundational ideas
 BEGINNINGS: Political essentials and foundational ideas 1689 LOCKE S SECOND TREATISE ON GOVERNMENT: Natural Rights: Life, Liberty & Property which existed before government Legitimate government depends
BEGINNINGS: Political essentials and foundational ideas 1689 LOCKE S SECOND TREATISE ON GOVERNMENT: Natural Rights: Life, Liberty & Property which existed before government Legitimate government depends
The U.S. Constitution. Ch. 2.4 Ch. 3
 The U.S. Constitution Ch. 2.4 Ch. 3 The Constitutional Convention Philadelphia Five months, from May until September 1787 Secret Meeting, closed to outside. Originally intent to revise the Articles of
The U.S. Constitution Ch. 2.4 Ch. 3 The Constitutional Convention Philadelphia Five months, from May until September 1787 Secret Meeting, closed to outside. Originally intent to revise the Articles of
America: The Last Best Hope Chapter 4 Reflection and Choice
 America: The Last Best Hope Chapter 4 Reflection and Choice 1. Under the Articles of Confederation, Congress had all of the following powers EXCEPT A settle disputes between the states B borrow money C
America: The Last Best Hope Chapter 4 Reflection and Choice 1. Under the Articles of Confederation, Congress had all of the following powers EXCEPT A settle disputes between the states B borrow money C
