Unit Objectives. Legis= Latin root for law
|
|
|
- Hilda McCoy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name Block Teacher Legis= Latin root for law Legislation= laws that are made Legislative= to make laws Legislature= government body that makes laws Legislator= people who make the laws Unit Objectives Describe the structure of Congress Identify the roles and powers of Congress Explain the lawmaking process at the national level 117
2 118
3 Legislative Branch Vocabulary Interest Group Levy (ies) Budget Annual Bill Legislature Revenue Trade Debate Impeach Lobbyist Veto Constituent Implied powers Override Legislation Majority Party Law Expressed Powers Directions: Use the words from the word bank and match to the definitions below. A group of people who meet to make the laws (Example- Congress) In Congress, the political party to which more than half of the members belong A person from a legislator s district Powers of Congress that are listed (or enumerated) in the Constitution Powers that Congress has that are NOT specifically listed in the Constitution To apply or establish a tax To accuse a government official of misconduct while in office A plan for making and spending money Income (money) that the government collects for public use To vote against a presidential veto A representative of an interest group that contacts lawmakers in order to influence their policymaking Yearly To exchange goods and services A rule made by a legislature for all people to follow Refusal to sign a bill or law An idea or a draft for a new law A group of people who share a point of view about an issue and unite to promote their belief To discuss and argue over different viewpoints Laws made by a governing body 119
4 National Government- Legislative Branch The Constitution of the United States defines and outlines the structure and the powers of the national government. The powers held by the government are split between the national government in Washington, D.C. and the governments of the 50 states. These powers are distributed among three distinct and independent branches of the national government. They are the legislative branch, the executive branch, and the judicial branch. LEGISLATIVE BRANCH The Legislative branch is called the Congress. Congress is a bicameral, or two chamber, legislature. The first chamber is made up of the House of Representatives with 435 members who are elected based on the population of each state. The official Census that is conducted every 10 years for the purpose of counting all citizens in every state is the way in which each state is allocated, or given its share of representatives. The second chamber is called the Senate with 100 members. There are two senators from each state. (50 states x 2 senators = 100 total senators) The Constitution gives the Congress certain powers: making the laws of the nation; approving the annual national budget; raising revenue through taxes and other levies; confirming presidential appointments; regulating interstate and foreign trade; and declaring war against other hostile nations. 1. Explain why Congress is a bicameral legislature? 2. Name the powers of Congress and the Legislative Branch. The Legislative Branch- Separation of powers & checks and balances At the legislative branch, there are two ways Congress checks the President, or executive branch. First, Congress can override, or reverse a presidential veto of legislation. A veto is the power of one branch of government to reject the legislation of another branch. Second, Congress can impeach and convict a President of violating or disobeying the laws of the land. To impeach means to remove somebody such as the President from public office. 120
5 The Congress also checks the judicial branch, or the courts. One way Congress does this is by confirming or refusing to confirm the nominated judges or justices of federal courts. Another way Congress checks the courts is by impeaching and convicting judges or justices of violating, or disobeying the laws of the land. 1. How can the legislative branch check the executive branch? 2. How can the legislative branch check the judicial branch? The Lawmaking Process ~ National Level The voters elect officials to serve in Congress, our national legislature, on our behalf and make the laws for us. It is important to remember that the formal powers of Congress are limited by the Constitution of the United States. Congress has a number of expressed and implied legislative powers. Expressed legislative powers are those powers specifically listed in the Constitution of the United States. Implied legislative powers are those used to carry out expressed powers. (Example: The Constitution spells out how to become a citizen of the United States. You remember there are 2 ways: birth and naturalization. These are expressed powers. These are stated in the Constitution. However, regulating and controlling immigration is an implied power. These are not specifically written in the Constitution but are necessary to enforce, or carry out naturalization laws. ) How does Congress make laws? The process of lawmaking in Congress begins with a Senator or a Representative who introduces a bill. The bill is then referred or moved to a committee for review. Next it is debated on the floor of both houses (the Senate and the House of Representatives). Then the bill is voted on by both houses. If passed, the bill is sent to the President who can sign the bill into law. Senators and Representatives write laws and take action in response to problems or issues that affect their voters. In some cases, individuals or interest groups may help shape how the bill is written and thereby influence public policy. 1. What is the difference between an implied power and an expressed power? 2. List the steps (in order) of how a bill becomes a law. 3. Who influences the Senators and Representatives to make laws? 121
6 Homework- Write a friendly letter Pretend you have a pen pal or friend in another country. He/she wants to know how our Congress is structured for a school project. Write a letter back giving with as much detail as possible to help your friend. Use the space below. 122
7 Topic: Date: Essential Question: Main Ideas/ Connections to Notes: Notes: 123
8 Summary : 124
9 TITLE: DATE: Essential Question: Congress has 2 legislative power granted by the Constitution 1. Expressed Powers are listed in the Constitution: Makes Example- Approves Example- Confirms Example- Raises Example- Regulates Example- Declares Example- 2. Implied Powers are used to carry out the expressed powers: This power is NOT This power is hinted at or implied by the Expands Examples- Checks and Balances Congress (the Legislative Branch) can check the powers of the other 2 branches: 1. Congress checks the Executive Branch and the President when Overrides a president 125
10 2. Congress checks the Judicial Branch and the Supreme Court Confirm or refuse federal judges The Powers of Congress are limited 1. The powers of Congress are NOT. 2. The limits the power of Congress. CONCLUSION Homework- Powers of Congress Matching Directions- The following items are the main powers of Congress. Match the pictures below to each item by writing the number of the power beneath the picture. 1-makes the laws for the nation 2- approves an annual budget 3- confirms presidential appointments 4- raises revenue through taxes and other levies 5- regulates interstate and foreign trade 6- declares war 126
11 Topic: Date: Essential Question: Main Ideas/ Connections to Notes: Notes: 127
12 The Legislative Branch How a Bill Becomes a Law House of Representatives House STEP 1: Senate STEP 1: Senate House STEP 2: House STEP 3: House STEP 4: A bill is a written idea or proposal for a law. If it goes through all steps in each house of Congress and gets approved by the president, it becomes an official law! Senate STEP 2: Senate STEP 3: Senate STEP 4: STEP 5: Summary : 128
13 Homework- Legislative Process (how a bill becomes a law) Directions- Cut out the steps in how a bill becomes a law provided to you on class and paste them on the comic strip below in the correct order of the steps. 129
14 Vocabulary Legislative Branch Study Guide Define all 19 of the vocab words on the Legislative Branch list Recognize all of the vocab words when used in the context of a question or answer Concepts to know: 1. Name the two houses in Congress- Senate and House of Representatives 2. The Legislative Branch is outlined in Article I (one) of the Constitution 3. The main role of Congress is to - make laws 4. Title of the leader of the House of Representatives- Speaker of the House 5. Title of the acting leader of the Senate- President Pro Temp 6. Representation in the House is based on the state s- population 7. Representation in the Senate is- equal (2 per state) 8. There are 100 members of the Senate and 435 members of the House 9. Name the two types of powers the Constitution gives to Congress ( recognize examples) expressed- listed in the Constitution (enumerated) o o o o o o declare war makes the laws of the nation approves annual budget confirms presidential appointments raises revenue through taxes and other levies regulates interstate and foreign trade implied- not listed, but used to carry out the expressed powers by the "necessary and proper clause 10. How can Congress check the other 2 branches- Checks the Executive Branch- override presidential vetoes, impeach and convict a president Checks the Judicial Branch- confirm or refuse the confirm presidential appointments of officials, impeach and convict a federal judge/justice 11. Understand the steps in the legislative process (how a bill becomes a law) idea bill is written with the idea by a sponsor in Congress bill introduced to the house the sponsor belongs to bill sent to a committee for review and editing bill comes back to the floor for a debate Congress can override presidential veto by 2/3 vote in favor of the bill if bill passes in both housed- goes to the president to 1) sign 2) veto if it passes on one house, bill has to go to the other house to be introduced, committee work, debate and vote vote on the bill (must pass with a majority) 12. Explain how groups and/or individuals can influence the legislative (or policymaking) process the media can help set the public agenda by: 1. focus public attention on certain issues 2. offer a forum (meeting place) for opposing viewpoints to be communicated 3. hold officials accountable to the public individuals can have influence on public policy: 1. participate in politics (voting, campaigning, holding office) 2. express opinions (lobby, protesting, write letters) 3. join interest groups interest groups (because of their size and money) can influence our lawmakers (legislators) by: 1. identify issues (for the public agenda) 2. make political contributions (donate money) 3. lobby government officials (the people who do the lobbying are called lobbyists) 130
The Legislative Branch
 The Legislative Branch Congress Legislative Branch of National Government Established in Article I of the Constitution Makes laws, ratifies treaties, impeachment, confirm presidential appointments, controls
The Legislative Branch Congress Legislative Branch of National Government Established in Article I of the Constitution Makes laws, ratifies treaties, impeachment, confirm presidential appointments, controls
Exceptions to Symmetry. Congress: The Legislative Branch. In comparative perspective, Congress is unusual.
 Congress: The Legislative Branch In comparative perspective, Congress is unusual. Most legislatures, particularly in parliamentary systems, are relatively weak. Congress exhibits symmetric bicameralism:
Congress: The Legislative Branch In comparative perspective, Congress is unusual. Most legislatures, particularly in parliamentary systems, are relatively weak. Congress exhibits symmetric bicameralism:
Unit Test. Procedure: Warm Up/Attendance (5 min) While students enter the room, they will be able to study while I take attendance.
 Unit Test Objective: Standards: LWBBAT articulate what happens in the legislative branch. C2.1.3 Explain how the Declaration of Independence, Constitution and Bill of Rights reflected political principles
Unit Test Objective: Standards: LWBBAT articulate what happens in the legislative branch. C2.1.3 Explain how the Declaration of Independence, Constitution and Bill of Rights reflected political principles
PRINCIPLES OF THE CONSTITUTION
 PRINCIPLES OF THE CONSTITUTION The Constitution of the United States is based on such fundamental principles of government as representative democracy, separation of powers, checks and balances, and federalism.
PRINCIPLES OF THE CONSTITUTION The Constitution of the United States is based on such fundamental principles of government as representative democracy, separation of powers, checks and balances, and federalism.
Unit #11: The National Government
 Unit #11: The National Government 1. What document defines the current structure and powers of the national government? A. Magna Carta B. Articles of Confederation C. Constitution of the United States
Unit #11: The National Government 1. What document defines the current structure and powers of the national government? A. Magna Carta B. Articles of Confederation C. Constitution of the United States
Standard CE.6a - Structure and Powers of National Government
 Standard CE.6a - Structure and Powers of National Government The Constitution of the United States defines the structure and powers of the government. The powers held by government are divided between
Standard CE.6a - Structure and Powers of National Government The Constitution of the United States defines the structure and powers of the government. The powers held by government are divided between
Legislative Branch Unit Day Section Standard(s) Focus
 Day Section Standard(s) Focus 1 Congressional Membership LWBBAT understand a rough outline of Congress. LWBBAT describe the similarities and differences of the House and Senate. on historical background
Day Section Standard(s) Focus 1 Congressional Membership LWBBAT understand a rough outline of Congress. LWBBAT describe the similarities and differences of the House and Senate. on historical background
CONGRESSIONAL ELECTIONS
 CONGRESS CONGRESSIONAL ELECTIONS Who Wins Elections? Incumbent: Those already holding office. Figure 12.1 CONGRESSIONAL ELECTIONS The Role of Party Identification Most members represent the majority party
CONGRESS CONGRESSIONAL ELECTIONS Who Wins Elections? Incumbent: Those already holding office. Figure 12.1 CONGRESSIONAL ELECTIONS The Role of Party Identification Most members represent the majority party
Chapter 6 Congress 9/28/2015. Roots of the U.S. Congress 6.1. Bicameral legislature. TABLE 6.1 What are the powers of Congress? 6.
 Chapter 6 Congress Roots of the U.S. Congress 6.1 Bicameral legislature House Representatives based on population Two-year term Senate Two from each state Six-year term TABLE 6.1 What are the powers of
Chapter 6 Congress Roots of the U.S. Congress 6.1 Bicameral legislature House Representatives based on population Two-year term Senate Two from each state Six-year term TABLE 6.1 What are the powers of
CHAPTER 6: The legislative branch NAME
 CHAPTER 6: The legislative branch NAME VOCAB 1. CONSTITUENT : voters represented by someone in a political office 2. CENSUS : government count of the population every 10 years 3. GERRYMANDER : drawing
CHAPTER 6: The legislative branch NAME VOCAB 1. CONSTITUENT : voters represented by someone in a political office 2. CENSUS : government count of the population every 10 years 3. GERRYMANDER : drawing
Chapter Three Assignment
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter Three Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The Constitution is based on the concept
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter Three Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The Constitution is based on the concept
American History 11R
 American History 11R 3 Branches of Government Legislative Branch To Make the Laws Executive Branch To Enforce the Laws Judicial Branch To Interpret the Laws Legislative Branch Article I of the Constitution.
American History 11R 3 Branches of Government Legislative Branch To Make the Laws Executive Branch To Enforce the Laws Judicial Branch To Interpret the Laws Legislative Branch Article I of the Constitution.
HIST-CE SOL CE 6 Unit Test Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions
 HIST-CE SOL CE 6 Unit Test Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:4W9T4A 1 In America, who makes the laws? A People elected to serve in the legislature B Cabinet members C People elected
HIST-CE SOL CE 6 Unit Test Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:4W9T4A 1 In America, who makes the laws? A People elected to serve in the legislature B Cabinet members C People elected
The Executive Branch
 The Executive Branch Each state has its own constitution based on its unique history, needs, philosophy, and geography. Just like the national government, each state's constitution separates power between
The Executive Branch Each state has its own constitution based on its unique history, needs, philosophy, and geography. Just like the national government, each state's constitution separates power between
UNIT 3: THE LEGISLATIVE BRANCH
 UNIT 3: THE LEGISLATIVE BRANCH POWERS OF THE LEGISLATIVE BRANCH E X P R E S S E D OR IMPLIED EXPRESSED POWERS Powers that are specifically listed in the Constitution (Article 1 Section 8) Coin money Impeach
UNIT 3: THE LEGISLATIVE BRANCH POWERS OF THE LEGISLATIVE BRANCH E X P R E S S E D OR IMPLIED EXPRESSED POWERS Powers that are specifically listed in the Constitution (Article 1 Section 8) Coin money Impeach
The Legislative Branch
 Chapter 5 The Legislative Branch Section 1: Section 2: Section 3: Section 4: The Senate and the House of Representatives How Congress Is Organized The Powers of Congress How a Bill Becomes a Law Section
Chapter 5 The Legislative Branch Section 1: Section 2: Section 3: Section 4: The Senate and the House of Representatives How Congress Is Organized The Powers of Congress How a Bill Becomes a Law Section
Unit III: The Federal Government / + 1 for each Chapter completed. + 3 possible. Name: Date: Period: Chapter 8: The Legislative Branch
 Unit Review Guide Unit III: The Federal Government / + 1 for each Chapter completed. + 3 possible. Name: Date: Period: Chapter 8: The Legislative Branch Section 1: Members of Congress 1. Policy 2. Constituents
Unit Review Guide Unit III: The Federal Government / + 1 for each Chapter completed. + 3 possible. Name: Date: Period: Chapter 8: The Legislative Branch Section 1: Members of Congress 1. Policy 2. Constituents
Name: 2) political party 3) They require large majorities of Congress and of state legislatures.
 Name: Directions (1 50): For each statement or question, record on your separate answer sheet the number of the word or expression that, of those given, best completes the statement or answers the question.
Name: Directions (1 50): For each statement or question, record on your separate answer sheet the number of the word or expression that, of those given, best completes the statement or answers the question.
The Powers of Congress. The Work of Congress (HA)
 The Work of Congress (HA) Members of Congress have two distinct but interrelated jobs. They must represent their constituents in their districts or states, and they must perform their constitutional duties
The Work of Congress (HA) Members of Congress have two distinct but interrelated jobs. They must represent their constituents in their districts or states, and they must perform their constitutional duties
GOVERNMENT IN THE U.S.
 GOVERNMENT IN THE U.S. 1. Main parts of the U. S. Constitution a. Preamble: goals of the gov t. 1. form a more perfect union, 2. establish justice 3. insure domestic tranquility 4. provide for the common
GOVERNMENT IN THE U.S. 1. Main parts of the U. S. Constitution a. Preamble: goals of the gov t. 1. form a more perfect union, 2. establish justice 3. insure domestic tranquility 4. provide for the common
Chapter 24: Governing the States Section 2
 Chapter 24: Governing the States Section 2 Objectives 1. Describe State legislatures. 2. Explain the election, terms, and compensation of legislators. 3. Examine the powers and organizations of State legislatures.
Chapter 24: Governing the States Section 2 Objectives 1. Describe State legislatures. 2. Explain the election, terms, and compensation of legislators. 3. Examine the powers and organizations of State legislatures.
LAW-MAKING FEDERAL, STATE AND LOCAL LEVEL SS.7.C.3.9
 LAW-MAKING FEDERAL, STATE AND LOCAL LEVEL SS.7.C.3.9 Use the PowerPoint to complete the work. By the end of this lesson I will be able to SS.7.C.3.9 Illustrate the lawmaking process at the local, state
LAW-MAKING FEDERAL, STATE AND LOCAL LEVEL SS.7.C.3.9 Use the PowerPoint to complete the work. By the end of this lesson I will be able to SS.7.C.3.9 Illustrate the lawmaking process at the local, state
9.3. The Legislative Branch Makes Laws For the framers of the Constitution,
 9.3. The Legislative Branch Makes Laws For the framers of the Constitution, the first step in building a trusted government was to create a fair way to make laws. Article I of the Constitution gives the
9.3. The Legislative Branch Makes Laws For the framers of the Constitution, the first step in building a trusted government was to create a fair way to make laws. Article I of the Constitution gives the
Unit 2 - Know Your Role: Federalism a love story. Statement of Inquiry
 Unit 2 - Know Your Role: Federalism a love story Key Concept: Form Related Concepts: Authority and Cooperation Global Context: Identities and Relationships Statement of Inquiry Federalism is a form of
Unit 2 - Know Your Role: Federalism a love story Key Concept: Form Related Concepts: Authority and Cooperation Global Context: Identities and Relationships Statement of Inquiry Federalism is a form of
The Structure and Functions of the Government
 The Structure and Functions of the Government The United States of America is a democratic republic or an indirect government. In definition, it means that when the people vote, they give the power to
The Structure and Functions of the Government The United States of America is a democratic republic or an indirect government. In definition, it means that when the people vote, they give the power to
Three Branches of the American Government Packet
 Name: Three es of the American Government Packet THREE BRANCHES OF GOVERNMENT Directions: Use the Civics in Action section in your book to complete the flow chart below by filling in the blanks with words
Name: Three es of the American Government Packet THREE BRANCHES OF GOVERNMENT Directions: Use the Civics in Action section in your book to complete the flow chart below by filling in the blanks with words
The Six Basic Principles
 The Constitution The Six Basic Principles The Constitution is only about 7000 words One of its strengths is that it does not go into great detail. It is based on six principles that are embodied throughout
The Constitution The Six Basic Principles The Constitution is only about 7000 words One of its strengths is that it does not go into great detail. It is based on six principles that are embodied throughout
The Constitution: A More Perfect Union
 The Constitution: A More Perfect Union How has the Constitution created a more perfect Union? P R E V I E W Read the quotation and answer the questions that follow. If men were angels, no government would
The Constitution: A More Perfect Union How has the Constitution created a more perfect Union? P R E V I E W Read the quotation and answer the questions that follow. If men were angels, no government would
Popular Sovereignty. Limited Government. Separation of Powers. Checks and Balances. Judicial Review. Federalism
 U.S. Constitution distributes the powers of the National Government among Congress: the legislative branch makes laws President: the executive branch enforces laws Courts: the judicial branch interprets
U.S. Constitution distributes the powers of the National Government among Congress: the legislative branch makes laws President: the executive branch enforces laws Courts: the judicial branch interprets
Federal Constitution Test Review & Study Guide
 Name: AP GOPO 2018-2019 AP United States Government & Politics (AP GOPO) Sumer Work Federal Constitution Test Review & Study Guide AP Government will require you to do a high level of work and to have
Name: AP GOPO 2018-2019 AP United States Government & Politics (AP GOPO) Sumer Work Federal Constitution Test Review & Study Guide AP Government will require you to do a high level of work and to have
The Legislative Branch UNIT 2
 The Legislative Branch UNIT 2 I. Congress A. The House of Representatives 1. Size and Terms - 435 members - 2- yr terms - Qualifications: 25 yrs old, citizen for 7 yrs, resident of state A. The House of
The Legislative Branch UNIT 2 I. Congress A. The House of Representatives 1. Size and Terms - 435 members - 2- yr terms - Qualifications: 25 yrs old, citizen for 7 yrs, resident of state A. The House of
UNITED STATES CONSTITUTION TEST REVIEW
 UNITED STATES CONSTITUTION TEST REVIEW The following questions will help you study for the U.S. Constitution Test. All questions on the test are not necessarily covered on these review sheets. Make sure
UNITED STATES CONSTITUTION TEST REVIEW The following questions will help you study for the U.S. Constitution Test. All questions on the test are not necessarily covered on these review sheets. Make sure
US Constitution. Articles I-VII
 US Constitution Articles I-VII Quick Questions What is the Constitution? What is the Preamble? What are the Articles and their purpose? Preamble Six Purposes are Listed -> What are they? We the people
US Constitution Articles I-VII Quick Questions What is the Constitution? What is the Preamble? What are the Articles and their purpose? Preamble Six Purposes are Listed -> What are they? We the people
Congress, Lobbyist, and the Legislative. Ch. 6 &7 SSCG 10 &11
 Congress, Lobbyist, and the Legislative process Ch. 6 &7 SSCG 10 &11 Constitutional Powers Article 1, Section 8 of the Constitution spells out the powers of Congress. Congress has expressed powers, or
Congress, Lobbyist, and the Legislative process Ch. 6 &7 SSCG 10 &11 Constitutional Powers Article 1, Section 8 of the Constitution spells out the powers of Congress. Congress has expressed powers, or
Constitutional Underpinnings of the U.S. Government
 U.S. Government What is the constitutional basis of separation of powers? It can be found in several principles, such as the separation of government into three branches, the conception that each branch
U.S. Government What is the constitutional basis of separation of powers? It can be found in several principles, such as the separation of government into three branches, the conception that each branch
Chapter 13 Congress. Congress. Know the terms/names (especially with FRQs) House of Representatives. Senate
 Chapter 13 Congress Know the terms/names (especially with FRQs) Congress House of Representatives Senate Almost always referred to as Congress A term of Congress is 2 years Term begins on January 3 rd
Chapter 13 Congress Know the terms/names (especially with FRQs) Congress House of Representatives Senate Almost always referred to as Congress A term of Congress is 2 years Term begins on January 3 rd
Advanced Placement U.S. Comparative Government Extra Credit Assignment
 Name Pd. Advanced Placement U.S. Comparative Government Extra Credit Assignment Directions: Read the U.S. Constitution (available at many websites including http://www.usconstitution.net) and complete
Name Pd. Advanced Placement U.S. Comparative Government Extra Credit Assignment Directions: Read the U.S. Constitution (available at many websites including http://www.usconstitution.net) and complete
Unit: The Legislative Branch
 - two houses. Name: Date: Period: Unit: The Legislative Branch Part One: How Congress is Organized Gerrymandering- to a state into an odd-shaped district for reasons. - people in a representative s district.
- two houses. Name: Date: Period: Unit: The Legislative Branch Part One: How Congress is Organized Gerrymandering- to a state into an odd-shaped district for reasons. - people in a representative s district.
Separation of Powers
 Separation of Powers Separation of Powers: The Legislative Branch The legislative branch of government is Congress. Congress consists of the House of Representatives and the Senate Members of the House
Separation of Powers Separation of Powers: The Legislative Branch The legislative branch of government is Congress. Congress consists of the House of Representatives and the Senate Members of the House
Congress. Congress STEP BY STEP. through the first reading page with the class. one Primary Document Activity and Review Activity to each student.
 Teacher s Guide Congress Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Copy Instructions: Reading (2 pages; class set) Primary Document Activity (1 page; class set) Review Activity
Teacher s Guide Congress Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Copy Instructions: Reading (2 pages; class set) Primary Document Activity (1 page; class set) Review Activity
Congress. Congress STEP BY STEP. one Congress in a FLASH reading page to each student. students to complete the activities in the review worksheet.
 Teacher s Guide Congress Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Copy Instructions: Reading (2 pages; class set) Primary Document Activity (1 page; class set) Review Worksheet
Teacher s Guide Congress Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Copy Instructions: Reading (2 pages; class set) Primary Document Activity (1 page; class set) Review Worksheet
Rabalais AP Government Review Vocabulary List
 Rabalais AP Government Review Vocabulary List Chapter 2 The Constitution Democracy Government by the people, both directly or indirectly, with free and frequent elections. Direct democracy Government in
Rabalais AP Government Review Vocabulary List Chapter 2 The Constitution Democracy Government by the people, both directly or indirectly, with free and frequent elections. Direct democracy Government in
AP Government and Politics THE US CONSTITUTION STUDY GUIDE Available at:
 Name Class Period AP Government and Politics THE US CONSTITUTION STUDY GUIDE Available at: www.constitutioncenter.org PART I: THE OVERALL STRUCTURE OF THE CONSTITUTION A. Read each article of the Constitution.
Name Class Period AP Government and Politics THE US CONSTITUTION STUDY GUIDE Available at: www.constitutioncenter.org PART I: THE OVERALL STRUCTURE OF THE CONSTITUTION A. Read each article of the Constitution.
HOW OUR LAWS ARE MADE
 HOW OUR LAWS ARE MADE 52 nd LEGISLATURE of LIBERIA Joint Legislative Modernization Committee This program is made possible by the generous support of the American people through the United States Agency
HOW OUR LAWS ARE MADE 52 nd LEGISLATURE of LIBERIA Joint Legislative Modernization Committee This program is made possible by the generous support of the American people through the United States Agency
4) Once every decade, the Constitution requires that the population be counted. This is called the 4)
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The Founders intended that the House of Representatives be 1) A) professional. B) electorally insulated.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The Founders intended that the House of Representatives be 1) A) professional. B) electorally insulated.
S8CG2 The student will analyze the role of the legislative branch in Georgia state government. a. Explain the qualifications, term, election, and
 S8CG2 The student will analyze the role of the legislative branch in Georgia state government. a. Explain the qualifications, term, election, and duties of members of the General Assembly. b. Describe
S8CG2 The student will analyze the role of the legislative branch in Georgia state government. a. Explain the qualifications, term, election, and duties of members of the General Assembly. b. Describe
American Government Unit 3 Rules were made to be broken or at least interpreted
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary for the American Government course. American Government
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary for the American Government course. American Government
Class Period THE US CONSTITUTION. 2. Compare Article I with Article II. Which article is longer and more detailed? WHY do you suppose it s longer?
 Name Class Period AP GOVERNMENT there s a copy of the Constitution online at http://bit.ly/1j4mbqa or http://bit.ly/1dlarv1 THE US CONSTITUTION 1. Read each article of the Constitution. Summarize the general
Name Class Period AP GOVERNMENT there s a copy of the Constitution online at http://bit.ly/1j4mbqa or http://bit.ly/1dlarv1 THE US CONSTITUTION 1. Read each article of the Constitution. Summarize the general
The Legislative Branch
 The Legislative Branch What you need to know Differences between the House of Representatives and the Senate The legislative process Influence of lobbyists How a bill becomes a law The National Legislature
The Legislative Branch What you need to know Differences between the House of Representatives and the Senate The legislative process Influence of lobbyists How a bill becomes a law The National Legislature
1. What are the requirements for becoming a Representative? How long do they serve?
 20 th /Raffel Constitution Study Questions Directions: To complete these questions, you need to read an online version of the constitution, available from the class website (select Online Constitution
20 th /Raffel Constitution Study Questions Directions: To complete these questions, you need to read an online version of the constitution, available from the class website (select Online Constitution
AP US Government & Politics Summer Assignment 2017
 Name Date: AP US Government & Politics Summer Assignment 2017 This summer assignment will analyze the US Constitution which will prepare you for the first unit of study in the course. The first unit explores
Name Date: AP US Government & Politics Summer Assignment 2017 This summer assignment will analyze the US Constitution which will prepare you for the first unit of study in the course. The first unit explores
Nine of the 13 states had to approve the Constitution in. order for it to be the law of the land. This happened on June 21,
 Task 1: Read Nine of the 13 states had to approve the Constitution in order for it to be the law of the land. This happened on June 21, 1788 when New Hampshire ratified it. The government of the United
Task 1: Read Nine of the 13 states had to approve the Constitution in order for it to be the law of the land. This happened on June 21, 1788 when New Hampshire ratified it. The government of the United
Guided Notes: Articles of the Constitution. Name: Date: Per: Score: /5
 Name: Date: Per: Score: /5 Directions: Complete the outline of Article 1 of the U.S. Constitution in groups. Then report to the class on your section. ARTICLE 1: The Legislative Branch Article 1: The Legislative
Name: Date: Per: Score: /5 Directions: Complete the outline of Article 1 of the U.S. Constitution in groups. Then report to the class on your section. ARTICLE 1: The Legislative Branch Article 1: The Legislative
Student Reading. American Indian Tribal Governments
 Student Reading American Indian Tribal Governments American Indians who live on reservations are citizens of the United States but they are also citizens of their reservation. They live on federally protected
Student Reading American Indian Tribal Governments American Indians who live on reservations are citizens of the United States but they are also citizens of their reservation. They live on federally protected
9.1 Introduction When the delegates left Independence Hall in September 1787, they each carried a copy of the Constitution. Their task now was to
 9.1 Introduction When the delegates left Independence Hall in September 1787, they each carried a copy of the Constitution. Their task now was to convince their states to approve the document that they
9.1 Introduction When the delegates left Independence Hall in September 1787, they each carried a copy of the Constitution. Their task now was to convince their states to approve the document that they
Government Final Exam Study Guide
 Mrs. Toxqui Government Government Final Exam Study Guide Assigned: Due: Part 1: Articles of the Constitution Directions: Write the name of the branch that gets its power from the corresponding article
Mrs. Toxqui Government Government Final Exam Study Guide Assigned: Due: Part 1: Articles of the Constitution Directions: Write the name of the branch that gets its power from the corresponding article
MIX AND MATCH-PRINCIPLES OF THE CONSTITUTION
 MIX AND MATCH- OF THE CONSTITUTION Learning Objective: The student will A. Identify examples of the Seven Principles of the U.S. Constitution TEKS: 8.15 D; GOVT. 7 D Materials Needed: 1 set of the cards
MIX AND MATCH- OF THE CONSTITUTION Learning Objective: The student will A. Identify examples of the Seven Principles of the U.S. Constitution TEKS: 8.15 D; GOVT. 7 D Materials Needed: 1 set of the cards
CHAPTER 5: CONGRESS: THE LEGISLATIVE BRANCH
 CHAPTER 5: CONGRESS: THE LEGISLATIVE BRANCH 1 Section 1: Congress Section 2: The Powers of Congress Section 3: The House of Representative Section 4: The Senate Section 5: Congress At Work SECTION 1: CONGRESS
CHAPTER 5: CONGRESS: THE LEGISLATIVE BRANCH 1 Section 1: Congress Section 2: The Powers of Congress Section 3: The House of Representative Section 4: The Senate Section 5: Congress At Work SECTION 1: CONGRESS
AP Government THE US CONSTITUTION STUDY GUIDE
 AP Government THE US CONSTITUTION STUDY GUIDE Directions: Read the US Constitution and complete the following questions directly on this handout. PART I: THE OVERALL STRUCTURE OF THE CONSTITUTION 1. Read
AP Government THE US CONSTITUTION STUDY GUIDE Directions: Read the US Constitution and complete the following questions directly on this handout. PART I: THE OVERALL STRUCTURE OF THE CONSTITUTION 1. Read
The Legislative Branch: The United States of America in Congress Assembled
 The Legislative Branch: The United States of America in Congress Assembled Basic Structure Bicameral Legislature House: Terms and qualifications Reapportionment, Redistricting Senate Election of Senators
The Legislative Branch: The United States of America in Congress Assembled Basic Structure Bicameral Legislature House: Terms and qualifications Reapportionment, Redistricting Senate Election of Senators
Unit 4 The Legislative Branch Study Guide Explain all the following: 1. Bi-Cameral 2. Congress: - Office - term - Number of members - Selection -
 Unit 4 The Legislative Branch Study Guide Explain all the following: 1. Bi-Cameral 2. Congress: - Office - term - Number of members - Selection - Requirements 3. 17 th Amendment 4. 20 th amendment 5. 27
Unit 4 The Legislative Branch Study Guide Explain all the following: 1. Bi-Cameral 2. Congress: - Office - term - Number of members - Selection - Requirements 3. 17 th Amendment 4. 20 th amendment 5. 27
Teacher s Guide. S.M.A.R.T.box. How a Bill Becomes a Law CURRICULUM MEDIA GROUP. Standards-based MediA Resource for Teachers
 CURRICULUM MEDIA GROUP S.M.A.R.T.box Standards-based MediA Resource for Teachers TM How a Bill Becomes a Law Teacher s Guide 30821 A DIVISION OF FILMS MEDIA GROUP INTRODUCTION This Teacher s Guide provides
CURRICULUM MEDIA GROUP S.M.A.R.T.box Standards-based MediA Resource for Teachers TM How a Bill Becomes a Law Teacher s Guide 30821 A DIVISION OF FILMS MEDIA GROUP INTRODUCTION This Teacher s Guide provides
The Legislative Branch and Domestic Policy. POLS 103 Unit 2 Week 7-8
 The Legislative Branch and Domestic Policy POLS 103 Unit 2 Week 7-8 The Institutional Design of Congress Unit 2 BICAMERAL Legislature! The House of Representatives Elected Via Popular vote. 2 year term
The Legislative Branch and Domestic Policy POLS 103 Unit 2 Week 7-8 The Institutional Design of Congress Unit 2 BICAMERAL Legislature! The House of Representatives Elected Via Popular vote. 2 year term
Chapter 1: How Effectively Does Canada s Federal Political System Govern Canada for all Canadians?
 Chapter 1: How Effectively Does Canada s Federal Political System Govern Canada for all Canadians? In this section you will be looking for: 1) How governance* in Canada creates opportunities and challenges
Chapter 1: How Effectively Does Canada s Federal Political System Govern Canada for all Canadians? In this section you will be looking for: 1) How governance* in Canada creates opportunities and challenges
SS.7.C.2.4 Evaluate rights contained in the Bill of Rights and other amendments to the Constitution
 Civics 2 nd Quarter Exam Study Guide Use your worksheet reading pages and the following chapters in the workbook to complete this study guide. Refer to past tests and progress checks for additional review.
Civics 2 nd Quarter Exam Study Guide Use your worksheet reading pages and the following chapters in the workbook to complete this study guide. Refer to past tests and progress checks for additional review.
Teacher s Guide LAWCRAFT EXTENSION PACK STEP BY STEP INSTRUCTIONS
 Teacher s Guide Time Needed: Approx. 3 class periods Materials/Equipment: Microsoft PowerPoint Access to icivics.org for game play Interactive white board (optional but ideal) Teaching bundle PowerPoint
Teacher s Guide Time Needed: Approx. 3 class periods Materials/Equipment: Microsoft PowerPoint Access to icivics.org for game play Interactive white board (optional but ideal) Teaching bundle PowerPoint
Why Was Congress Created?
 Chapter 13: Congress Why Was Congress Created? Fear that power in the hands of a single individual would be abused and the people would suffer. The national legislative power that was vested in Congress
Chapter 13: Congress Why Was Congress Created? Fear that power in the hands of a single individual would be abused and the people would suffer. The national legislative power that was vested in Congress
Voting. Name. Lesson 8
 Name Voting Lesson 8 ACROSS CLUES: 1. The people vote for the candidates in this type of election. 3. a special election in which voters approve or reject a law 5. This type of government allows its people
Name Voting Lesson 8 ACROSS CLUES: 1. The people vote for the candidates in this type of election. 3. a special election in which voters approve or reject a law 5. This type of government allows its people
Chapter 9 - The Constitution: A More Perfect Union
 Chapter 9 - The Constitution: A More Perfect Union 9.1 - Introduction When the delegates left Independence Hall in September 1787, they each carried a copy of the Constitution. Their task now was to convince
Chapter 9 - The Constitution: A More Perfect Union 9.1 - Introduction When the delegates left Independence Hall in September 1787, they each carried a copy of the Constitution. Their task now was to convince
EOC Civics Unit #4 Review. Organization and Function of Government
 EOC Civics Unit #4 Review Organization and Function of Government Forms of Government SS.7.C.3.1 Democracy = We The People = Self-Government Direct Democracy Everyone makes decisions Florida is a DD for
EOC Civics Unit #4 Review Organization and Function of Government Forms of Government SS.7.C.3.1 Democracy = We The People = Self-Government Direct Democracy Everyone makes decisions Florida is a DD for
Constitution Quest PART I - THE OVERALL STRUCTURE OF THE CONSTITUTION
 Constitution Quest Directions : Read the U.S. Constitution and complete the following questions directly on this handout legibly. This is due on the second week of class and you will be responsible for
Constitution Quest Directions : Read the U.S. Constitution and complete the following questions directly on this handout legibly. This is due on the second week of class and you will be responsible for
Name: Date: 1. Like most other national legislatures, Congress is (comprising two houses ). A) bicameral B) bilateral C) binary D) bicentenary
 Name: Date: 1. Like most other national legislatures, Congress is (comprising two houses ). A) bicameral B) bilateral C) binary D) bicentenary 2. A House member represents a district of about people. A)
Name: Date: 1. Like most other national legislatures, Congress is (comprising two houses ). A) bicameral B) bilateral C) binary D) bicentenary 2. A House member represents a district of about people. A)
State Legislatures. State & Local Government. Ch. 7
 State Legislatures State & Local Government Ch. 7 Legislature in some states is the dominant branch of govt. Highlights State Legislatures have 4 clear functions: 1. Making laws 2. Represent their constituents
State Legislatures State & Local Government Ch. 7 Legislature in some states is the dominant branch of govt. Highlights State Legislatures have 4 clear functions: 1. Making laws 2. Represent their constituents
FIRST MARKING PERIOD Quarterly Assessment Study Guide
 FIRST MARKING PERIOD Quarterly Assessment Study Guide CITIZENSHIP (CHAPTER 3) IMPTANT VOCABULARY 1. Citizen A person with certain rights and duties under a government. 2. Aliens a citizen of one country
FIRST MARKING PERIOD Quarterly Assessment Study Guide CITIZENSHIP (CHAPTER 3) IMPTANT VOCABULARY 1. Citizen A person with certain rights and duties under a government. 2. Aliens a citizen of one country
The Federalist, No. 51
 The Legislative Branch Fall, 2015 In republican government, the legislative authority necessarily predominates. The remedy for this inconveniency is to divide the legislature into different branches; and
The Legislative Branch Fall, 2015 In republican government, the legislative authority necessarily predominates. The remedy for this inconveniency is to divide the legislature into different branches; and
Unit One: Quarter Three. Name:
 SS.7.C.3.3 Structure and Function of the LEGISLATIVE BRANCH ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: recognize the structure of the legislative, executive, and judicial branches.
SS.7.C.3.3 Structure and Function of the LEGISLATIVE BRANCH ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: recognize the structure of the legislative, executive, and judicial branches.
Chapter 5: Congress: The Legislative Branch
 Chapter 5: Congress: The Legislative Branch Section 1: Congress Section 2: The Powers of Congress Section 3: The House of Representatives Section 4: The Senate Section 5: Congress at Work Congress Main
Chapter 5: Congress: The Legislative Branch Section 1: Congress Section 2: The Powers of Congress Section 3: The House of Representatives Section 4: The Senate Section 5: Congress at Work Congress Main
The Constitution: A More Perfect Union
 The Constitution: A More Perfect Union How has the Constitution created a more perfect Union? P R E V I E W Read the quotation and answer the questions that follow. If men were angels, no government would
The Constitution: A More Perfect Union How has the Constitution created a more perfect Union? P R E V I E W Read the quotation and answer the questions that follow. If men were angels, no government would
Name Due Date: September 9, AP US Government & Politics Unit I: Constitutional Underpinnings and Federalism THE US CONSTITUTION STUDY GUIDE
 Name Due Date: September 9, 2016 AP US Government & Politics Unit I: Constitutional Underpinnings and Federalism THE US CONSTITUTION STUDY GUIDE Unit Focus: Using your annotated guide to the US Constitution
Name Due Date: September 9, 2016 AP US Government & Politics Unit I: Constitutional Underpinnings and Federalism THE US CONSTITUTION STUDY GUIDE Unit Focus: Using your annotated guide to the US Constitution
UNIT II: THE U.S. CONSTITUTION
 UNIT II: THE U.S. CONSTITUTION Seven Articles Separation of Powers Principles of Federalism Ilovesocialstudies.com SEVEN ARTICLES Article I Establishes the Legislative Branch Article II Establishes the
UNIT II: THE U.S. CONSTITUTION Seven Articles Separation of Powers Principles of Federalism Ilovesocialstudies.com SEVEN ARTICLES Article I Establishes the Legislative Branch Article II Establishes the
The Legislative Process and You. Influencing Public Policy
 The Legislative Process and You Influencing Public Policy Overview of the legislative process How decisions are made Why get involved How to get involved make an impact Your State Government Massachusetts
The Legislative Process and You Influencing Public Policy Overview of the legislative process How decisions are made Why get involved How to get involved make an impact Your State Government Massachusetts
Organization. -Great Compromise of branches of government Bicameral legislature. -House. -Senate Upper house
 Organization -Great Compromise of 1787 3 branches of government Bicameral legislature -House Lower house -Senate Upper house The House of Representatives is based on population The Senate is based on equal
Organization -Great Compromise of 1787 3 branches of government Bicameral legislature -House Lower house -Senate Upper house The House of Representatives is based on population The Senate is based on equal
2015 ICCB and CAIT i-pathways.org 1 The GED Mark is a registered trademark of the American Council on Education.
 LESSON 1: MODERN AND HISTORICAL GOVERNMENTS This lesson covers the following information: The different government systems in the world Political ideologies Highlights include the following: Every nation
LESSON 1: MODERN AND HISTORICAL GOVERNMENTS This lesson covers the following information: The different government systems in the world Political ideologies Highlights include the following: Every nation
Congress. AP US Government Spring 2017
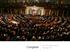 Congress AP US Government Spring 2017 Congressional Elections: House vs Senate Constituent: citizen who is represented by a member of Congress House is closer to constitutents House members come from individual
Congress AP US Government Spring 2017 Congressional Elections: House vs Senate Constituent: citizen who is represented by a member of Congress House is closer to constitutents House members come from individual
1. States must meet certain requirements in drawing district boundaries. Identify one of these requirements.
 Multiple Choice 1. States must meet certain requirements in drawing district boundaries. Identify one of these requirements. a. A person's vote in the largest district of a state must have only half the
Multiple Choice 1. States must meet certain requirements in drawing district boundaries. Identify one of these requirements. a. A person's vote in the largest district of a state must have only half the
How Congress Is Organized. Chapter 6.1 P
 How Congress Is Organized Chapter 6.1 P138-144 Terms of Congress The Framers of the U.S. Constitution intended the legislative branch to be the most powerful branch. Terms of Congress Each term starts
How Congress Is Organized Chapter 6.1 P138-144 Terms of Congress The Framers of the U.S. Constitution intended the legislative branch to be the most powerful branch. Terms of Congress Each term starts
Chapter 12: Congress. American Democracy Now, 4/e
 Chapter 12: Congress American Democracy Now, 4/e Congress Where Do You Stand? How would you rate the overall performance of Congress today? a. Favorably b. Unfavorably c. Neither favorably nor unfavorably
Chapter 12: Congress American Democracy Now, 4/e Congress Where Do You Stand? How would you rate the overall performance of Congress today? a. Favorably b. Unfavorably c. Neither favorably nor unfavorably
Going Over the LEJ. Analyzing the Legislative, Executive, and Judicial Branches. Benchmarks
 Going Over the LEJ Analyzing the Legislative, Executive, and Judicial Branches Benchmarks SS.7.C.3.8 Analyze the structure, functions, and processes of the legislative, executive, and judicial branches.
Going Over the LEJ Analyzing the Legislative, Executive, and Judicial Branches Benchmarks SS.7.C.3.8 Analyze the structure, functions, and processes of the legislative, executive, and judicial branches.
Article I. Article III. Article IV. Article V. Article VI. Article VII
 Directions: Read the U.S. Constitution and complete the following questions directly on this handout. Be sure to identify the location of each answer in the Constitution (example: Article I, Section 3,
Directions: Read the U.S. Constitution and complete the following questions directly on this handout. Be sure to identify the location of each answer in the Constitution (example: Article I, Section 3,
US Government Module 3 Study Guide
 US Government Module 3 Study Guide There are 3 branches of government. Module 3 will cover the legislative and execute and module 4 will cover the judicial. 3.01 The Legislative Branch aka Congress Established
US Government Module 3 Study Guide There are 3 branches of government. Module 3 will cover the legislative and execute and module 4 will cover the judicial. 3.01 The Legislative Branch aka Congress Established
AP Government THE US CONSTITUTION Available at: Wilson text pages A4-A20 (Appendix at the end of the book)
 AP Government THE US CONSTITUTION Available at: www.constitutioncenter.org Wilson text pages A4-A20 (Appendix at the end of the book) Directions: Read the US Constitution and complete the following questions
AP Government THE US CONSTITUTION Available at: www.constitutioncenter.org Wilson text pages A4-A20 (Appendix at the end of the book) Directions: Read the US Constitution and complete the following questions
STRUCTURE, POWERS, AND ROLES OF CONGRESS
 American Government Semester 1, Chapter 4 STRUCTURE, POWERS, AND ROLES OF CONGRESS STRUCTURE In our government, Congress has two parts, or houses. This type of legislature is known as bicameral. One half
American Government Semester 1, Chapter 4 STRUCTURE, POWERS, AND ROLES OF CONGRESS STRUCTURE In our government, Congress has two parts, or houses. This type of legislature is known as bicameral. One half
A copy of the US Constitution is available at: or in the textbook
 Name Class Period AP Government : THE US CONSTITUTION STUDY GUIDE A copy of the US Constitution is available at: www.constitutioncenter.org or in the textbook Directions: Read the US Constitution and complete
Name Class Period AP Government : THE US CONSTITUTION STUDY GUIDE A copy of the US Constitution is available at: www.constitutioncenter.org or in the textbook Directions: Read the US Constitution and complete
GUIDE TO BEING AN EFFECTIVE CITIZEN LOBBYIST
 GUIDE TO BEING AN EFFECTIVE CITIZEN LOBBYIST Citizen Lobbyist Training Agenda What is a Citizen Lobbyist? Understanding the Legislative Process How an Idea Becomes Law How to Track a Bill or Issue Being
GUIDE TO BEING AN EFFECTIVE CITIZEN LOBBYIST Citizen Lobbyist Training Agenda What is a Citizen Lobbyist? Understanding the Legislative Process How an Idea Becomes Law How to Track a Bill or Issue Being
Child Advocacy 101: Speaking Out for Kids from your Community to the Capitol
 Child Advocacy 101: Speaking Out for Kids from your Community to the Capitol Ruth Ehresman Vision for Children at Risk Missouri Alliance for Children, Youth, & Families Child Advocacy Day April 6, 2017
Child Advocacy 101: Speaking Out for Kids from your Community to the Capitol Ruth Ehresman Vision for Children at Risk Missouri Alliance for Children, Youth, & Families Child Advocacy Day April 6, 2017
Warm-Up: can you answer these questions? ( L)
 Legislative Branch Warm-Up: can you answer these questions? ( L) What is the purpose of the legislative branch? Which party has the majority in the House? In the Senate? What are the names of the two Senators
Legislative Branch Warm-Up: can you answer these questions? ( L) What is the purpose of the legislative branch? Which party has the majority in the House? In the Senate? What are the names of the two Senators
STUDY GUIDE Three Branches Test
 STUDY GUIDE Three Branches Test NAME (Remember to review your notes and class materials as well as this guide.) 1 Circle, highlight, check, or underline the correct answers, or fill in the blanks. 1. The
STUDY GUIDE Three Branches Test NAME (Remember to review your notes and class materials as well as this guide.) 1 Circle, highlight, check, or underline the correct answers, or fill in the blanks. 1. The
AP U.S. Government and Politics: 1999 Exam
 AP U.S. Government and Politics: 1999 Exam 1. Which of the following is an example of checks and balances, as established by the Constitution? A) A requirement that states lower their legal drinking age
AP U.S. Government and Politics: 1999 Exam 1. Which of the following is an example of checks and balances, as established by the Constitution? A) A requirement that states lower their legal drinking age
Civics Study Guide: Final 2015
 Creation of the Constitution: Virginia Plan: Proposal for how the American government should look. Requested 3 branches of government (executive, judicial, legislative) and wanted the legislative branch
Creation of the Constitution: Virginia Plan: Proposal for how the American government should look. Requested 3 branches of government (executive, judicial, legislative) and wanted the legislative branch
The Legislative Branch
 The Legislative Branch Representative body Congress Law-making body Creating a Bi-Cameral Legislature Virginia Plan New Jersey Plan Connecticut Compromise Differences Between The Chambers HOUSE SENATE
The Legislative Branch Representative body Congress Law-making body Creating a Bi-Cameral Legislature Virginia Plan New Jersey Plan Connecticut Compromise Differences Between The Chambers HOUSE SENATE
