The Federalist, #47 (by James Madison)
|
|
|
- Irene Nelson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
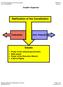
1 READING NO. 2 The Federalist, #47 (by James Madison) Questions to consider while reading Why does Madison go to great lengths to chronicle the examples of state constitutions in his argument in favor of the Constitution? 2. Why is the British Constitution, according to Montesquieu, considered the mirror of political liberty? 3. What is the criticism levied against this Constitution that Madison seeks to defend? 4. What points does Madison make to argue that the proposed Constitution does indeed have a separation of powers? 5. Does Madison generally agree or disagree with the Anit-federalist point of view there there needs to be a separation of powers in the Constitution? Having reviewed the general form of the proposed government and the general mass of power allotted to it, I proceed to examine the particular structure of this government, and the distribution of this mass of power among its constituent parts. One of the principal objections inculcated by the more respectable adversaries to the Constitution is its supposed violation of the political maxim that the legislative, executive, and judiciary departments ought to be separate and distinct. In the structure of the federal government no regard, it is said, seems to have been paid to this essential precaution in favor of liberty. The several departments of power are distributed and blended in such a manner as at once to destroy all symmetry and beauty of form, and to expose some of the essential parts of the edifice to the danger of being crushed by the disproportionate weight of other parts. No political truth is certainly of greater intrinsic value, or is stamped with the authority of more enlightened patrons of liberty than that on which 9 the objection is founded. The accumulation of all powers, legislative, executive, and judiciary, in the same hands, whether of one, a few, or many, and whether hereditary, self-appointed, or elective, may justly be pronounced the very definition of tyranny. Were the federal Constitution,
2 therefore, really chargeable with this accumulation of power, or with a mixture of powers, having a dangerous tendency to such an accumulation, no further arguments would be necessary to inspire a universal reprobation of the system. I persuade myself, however, that it will be made apparent to everyone that the charge cannot be supported, and that the maxim on which it relies has been totally misconceived and misapplied. In order to form correct ideas on this important subject it will be proper to investigate the sense in which the preservation of liberty requires that the three great departments of power should be separate and distinct. The oracle who is always consulted and cited on this subject is the celebrated Montesquieu. If he be not the author of this invaluable precept in the science of politics, he has the merit at least of displaying and recommending it most effectually to the attention of mankind. Let us endeavor, in the first place, to ascertain his meaning on this point. The British Constitution was to Montesquieu what Homer has been to the didactic writers on epic poetry. As the latter have considered the work of the immortal bard as the perfect model from which the principles and rules of the epic art were to be drawn, and by which all similar works were to be judged, so this great political critic appears to have viewed the Constitution of England as the standard, or to use his own expression, as the mirror of political liberty; and to have delivered, in the form of elementary truths, the several characteristic principles of that particular system. That we may be sure, then, not to mistake his meaning in this case, let us recur to the source from which the maxim was drawn. On the slightest view of the British Constitution, we must perceive that the legislative, executive, and judiciary departments are by no means totally separate and distinct from each other. The executive magistrate forms an integral part of the legislative authority. He alone has the prerogative of making treaties with foreign sovereigns which, when made, have, under certain limitations, the force of legislative acts. All the members of the judiciary department are appointed by him, can be removed by him on the address of the two Houses of Parliament, and form, when he pleases to consult them, one of his constitutional councils. One branch of the legislative department forms also a great constitutional council to the executive chief, as, on another hand, it is the sole depositary of judicial power in cases of impeachment, and is invested with the supreme appellate jurisdiction in all other cases. The judges, again, are so far connected with the legislative department as often to attend and participate in its deliberations, though not admitted to a legislative vote. From these facts, by which Montesquieu was guided, it may clearly be inferred that in saying "There can be no liberty where the legislative and executive powers are united in the same person, or body of magistrates," or, "if the power of judging be not separated from the legislative and executive powers," he did not mean that these departments ought to have no partial agency in, or no control over, the acts of each other. His meaning, as his own words import, and still more conclusively as illustrated by the example in his eye, can amount to no more than this, that where the whole power of one department is exercised by the same hands which possess the whole power of another department, the fundamental principles of a free constitution are subverted. This would have been the case in the constitution examined by him, if the king, who is the sole execu- 10
3 tive magistrate, had possessed also the complete legislative power, or the supreme administration of justice; or if the entire legislative body had possessed the supreme judiciary, or the supreme executive authority. This, however, is not among the vices of that constitution. The magistrate in whom the whole executive power resides cannot of himself make a law, though he can put a negative on every law; nor administer justice in person, though he has the appointment of those who do administer it. The judges can exercise no executive prerogative, though they are shoots from the executive stock; nor any legislative function, though they may be advised by the legislative councils. The entire legislature can perform no judiciary act, though by the joint act of two of its branches the judges may be removed from their offices, and though one of its branches is possessed of the judicial power in the last resort. The entire legislature, again, can exercise no executive prerogative, though one of its branches constitutes the supreme executive magistracy, and another, on the impeachment of a third, can try and condemn all the subordinate officers in the executive department. The reasons on which Montesquieu grounds his maxim are a further demonstration of his meaning. "When the legislative and executive powers are united in the same person or body," says he, "there can be no liberty, because apprehensions may arise lest the same monarch or senate should enact tyrannical laws to execute them in a tyrannical manner." Again: "Were the power of judging joined with the legislative, the life and liberty of the subject would be exposed to arbitrary control, for the judge would then be the legislator. Were it joined to the executive power, the judge might behave with all the violence of an oppressor." Some of these reasons are more fully explained in other passages; but briefly stated as they are here they sufficiently establish the meaning which we have put on this celebrated maxim of this celebrated author. If we look into the constitutions of the several States we find that, notwithstanding the emphatical and, in some instances, the unqualified terms in which this axiom has been laid down, there is not a single instance in which the several departments of power have been kept absolutely separate and distinct. New Hampshire, whose constitution was the last formed, seems to have been fully aware of the impossibility and inexpediency of avoiding any mixture whatever of these departments, and has qualified the doctrine by declaring "that the legislative, executive, and judiciary powers ought to be kept as separate from, and independent of, each other as the nature of a free government will admit; or as is consistent with that chain of connection that binds the whole fabric of the constitution in one indissoluble bond of unity and amity. "Her constitution accordingly mixes these departments in several respects. The Senate, which is a branch of the legislative department, is also a judicial tribunal for the trial of impeachments. The President, who is the head of the executive department, is the presiding member also of the Senate; and, besides an equal vote in all cases, has a casting vote in case of a tie. The executive head is himself eventually elective every year by the legislative department, and his council is every year chosen by and from the members of the same department. Several of the officers of state are also appointed by the legislature. And the members of the judiciary department are appointed by the executive department. The constitution of Massachusetts has observed a sufficient though less pointed caution in expressing this fundamental article of liberty. It declares "that the legislative department shall never exercise 11
4 the executive and judicial powers, or either of them; the executive shall never exercise the legislative and judicial powers, or either of them; the judicial shall never exercise the legislative and executive powers, or either of them. "This declaration corresponds precisely with the doctrine of Montesquieu, as it has been explained, and is not in a single point violated by the plan of the convention. It goes no farther than to prohibit any one of the entire departments from exercising the powers of another department. In the very Constitution to which it is prefixed, a partial mixture of powers has been admitted. The executive magistrate has a qualified negative on the legislative body, and the Senate, which is a part of the legislature, is a court of impeachment for members both of the executive and judiciary departments. The members of the judiciary department, again, are appointable by the executive department, and removable by the same authority on the address of the two legislative branches. Lastly, a number of the officers of government are annually appointed by the legislative department. As the appointment to offices, particularly executive offices, is in its nature an executive function; the compilers of the Constitution have, in this last point at least, violated the rule established by themselves. I pass over the constitutions of Rhode Island and Connecticut, because they were formed prior to the Revolution and even before the principle under examination had become an object of political attention. The constitution of New York contains no declaration on this subject, but appears very clearly to have been framed with an eye to the danger of improperly blending the different departments. It gives, nevertheless, to the executive magistrate, a partial control over the legislative department; and, what is more, gives a like control to the judiciary department; and even blends the executive and judiciary departments in the exercise of this control. In its council of appointment members of the legislative are associated with the executive authority, in the appointment of officers, both executive and judiciary. And its court for the trial of impeachments and correction of errors is to consist of one branch of the legislature and the principal members of the judiciary department. The constitution of New Jersey has blended the different powers of government more than any of the preceding. The governor, who is the executive magistrate, is appointed by the legislature; is chancellor and ordinary, or surrogate of the State; is a member of the Supreme Court of Appeals, and president, with a casting vote, of one of the legislative branches. The same legislative branch acts again as executive council to the governor, and with him constitutes the Court of Appeals. The members of the judiciary department are appointed by the legislative department, and removable by one branch of it, on the impeachment of the other. According to the constitution of Pennsylvania, the president, who is the head of the executive department, is annually elected by a vote in which the legislative department predominates. In conjunction with an executive council, he appoints the members of the judiciary department and forms a court of impeachment for trial of all officers, judiciary as well as executive. The judges of the Supreme Court and justices of the peace seem also to be removable by the legislature; and the executive power of pardoning, in certain cases, to be referred to the same department. The members of the executive council are made EX OFFICIO justices of peace throughout the State. 12
5 In Delaware, the chief executive magistrate is annually elected by the legislative department. The speakers of the two legislative branches are vice-presidents in the executive department. The executive chief, with six others appointed, three by each of the legislative branches, constitutes the Supreme Court of Appeals; he is joined with the legislative department in the appointment of the other judges. Throughout the States it appears that the members of the legislature may at the same time be justices of the peace; in this State, the members of one branch of it are EX OFFICIO justices of the peace; as are also the members of the executive council. The principal officers of the executive department are appointed by the legislative; and one branch of the latter forms a court of impeachments. All officers may be removed on address of the legislature. Maryland has adopted the maxim in the most unqualified terms; declaring that the legislative, executive, and judicial powers of government ought to be forever separate and distinct from each other. Her constitution, notwithstanding, makes the executive magistrate appointable by the legislative department; and the members of the judiciary by the executive department. The language of Virginia is still more pointed on this subject. Her constitution declares "that the legislative, executive, and judiciary departments shall be separate and distinct; so that neither exercises the powers properly belonging to the other; nor shall any person exercise the powers of more than one of them at the same time, except that the justices of county courts shall be eligible to either House of Assembly. "Yet we find not only this express exception with respect to the members of the inferior courts, but that the chief magistrate, with his executive council, are appointable by the legislature; that two members of the latter are triennially displaced at the pleasure of the legislature; and that all the principal offices, both executive and judiciary, are filled by the same department. The executive prerogative of pardon, also, is in one case vested in the legislative department. The constitution of North Carolina, which declares "that the legislative, executive, and supreme judicial powers of government ought to be forever separate and distinct from each other," refers, at the same time, to the legislative department, the appointment not only of the executive chief, but all the principal officers within both that and the judiciary department. In South Carolina, the constitution makes the executive magistracy eligible by the legislative department. It gives to the latter, also, the appointment of the members of the judiciary department, including even justices of the peace and sheriffs; and the appointment of officers in the executive department, down to captains in the army and navy of the State. In the constitution of Georgia where it is declared "that the legislative, executive, and judiciary departments shall be separate and distinct, so that neither exercise the powers properly belonging to the other," we find that the executive department is to be filled by appointments of the legislature; and the executive prerogative of pardon to be finally exercised by the same authority. Even justices of the peace are to be appointed by the legislature. In citing these cases, in which the legislative, executive, and judiciary departments have not been kept totally separate and distinct, I wish not to be regarded as an advocate for the particular organizations of the several State governments. I am fully aware that among the many excellent principles which they exemplify they 13
6 carry strong marks of the haste, and still stronger of the inexperience, under which they were framed. It is but too obvious that in some instances the fundamental principle under consideration has been violated by too great a mixture, and even an actual consolidation of the different powers; and that in no instance has a competent provision been made for maintaining in practice the separation delineated on paper. What I have wished to evince is that the charge brought against the proposed Constitution of violating the sacred maxim of free government is warranted neither by the real meaning annexed to that maxim by its author, nor by the sense in which it has hitherto been understood in America. This interesting subject will be resumed in the ensuing paper. Publius 14
7 Federalist No. 51 Teaching American History 1 of 5 9/8/2015 1:14 PM Publius (James Madison) February 6, 1788 To what expedient then shall we finally resort, for maintaining in practice the necessary partition of power among the several departments, as laid down in the constitution? The only answer that can be given is, that as all these exterior provisions are found to be inadequate, the defect must be supplied, by so contriving the interior structure of the government, as that its several constituent parts may, by their mutual relations, be the means of keeping each other in their proper places. Without presuming to undertake a full developement of this important idea, I will hazard a few general observations, which may perhaps place it in a clearer light, and enable us to form a more correct judgment of the principles and structure of the government planned by the convention. In order to lay a due foundation for that separate and distinct exercise of the different powers of government, which, to a certain extent, is admitted on all hands to be essential to the preservation of liberty, it is evident that each department should have a will of its own; and consequently should be so constituted, that the members of each should have as little agency as possible in the appointment of the members of the others. Were this principle rigorously adhered to, it would require that all the appointments for the supreme executive, legislative, and judiciary magistracies, should be drawn from the same fountain of authority, the people, through channels having no communication whatever with one another. Perhaps such a plan of constructing the several departments, would be less difficult in practice, than it may in contemplation appear. Some difficulties, however, and some additional expense, would attend the execution of it. Some deviations, therefore, from the principle must be admitted. In the constitution of the judiciary department in particular, it might be inexpedient to insist rigorously on the principle; first, because peculiar qualifications being essential in the members, the primary consideration ought to be to select that mode of choice which best secures these
8 Federalist No. 51 Teaching American History 2 of 5 9/8/2015 1:14 PM qualifications; secondly, because the permanent tenure by which the appointments are held in that department, must soon destroy all sense of dependence on the authority conferring them. It is equally evident, that the members of each department should be as little dependent as possible on those of the others, for the emoluments annexed to their offices. Were the executive magistrate, or the judges, not independent of the legislature in this particular, their independence in every other, would be merely nominal. But the great security against a gradual concentration of the several powers in the same department, consists in giving to those who administer each department, the necessary constitutional means, and personal motives, to resist encroachments of the others. The provision for defence must in this, as in all other cases, be made commensurate to the danger of attack. Ambition must be made to counteract ambition. The interest of the man, must be connected with the constitutional rights of the place. It may be a reflection on human nature, that such devices should be necessary to control the abuses of government. But what is government itself, but the greatest of all reflections on human nature? If men were angels, no government would be necessary. If angels were to govern men, neither external nor internal controls on government would be necessary. In framing a government which is to be administered by men over men, the great difficulty lies in this: you must first enable the government to control the governed; and in the next place oblige it to control itself. A dependence on the people is, no doubt, the primary control on the government; but experience has taught mankind the necessity of auxiliary precautions. This policy of supplying, by opposite and rival interests, the defect of better motives, might be traced through the whole system of human affairs, private as well as public. We see it particularly displayed in all the subordinate distributions of power; where the constant aim is, to divide and arrange the several offices in such a manner as that each may be a check on the other; that the private interest of every individual may be a centinel over the public rights. These inventions of prudence cannot be less requisite in the distribution of the supreme powers of the state. But it is not possible to give to each department an equal power of self-defence. In republican government, the legislative authority necessarily predominates. The remedy for this inconveniency is, to divide the legislature into different branches; and to render them, by different modes of election, and different principles of action, as little connected with each other, as the nature of their common functions, and their common dependence on the society, will admit. It may even be necessary to guard against dangerous encroachments by still further precautions. As the weight of the legislative authority requires that it should be thus divided, the weakness of the executive may require, on the other hand, that it should be fortified. An absolute negative on the legislature, appears, at first view, to be the natural defence with which the executive magistrate should be armed. But perhaps it would be neither altogether safe, nor alone sufficient. On ordinary occasions, it might not be exerted with the requisite firmness; and on extraordinary occasions, it might be perfidiously abused. May not this defect of an absolute negative be supplied by some qualified connexion between this weaker
9 Federalist No. 51 Teaching American History 3 of 5 9/8/2015 1:14 PM department, and the weaker branch of the stronger department, by which the latter may be led to support the constitutional rights of the former, without being too much detached from the rights of its own department? If the principles on which these observations are founded be just, as I persuade myself they are, and they be applied as a criterion to the several state constitutions, and to the federal constitution, it will be found, that if the latter does not perfectly correspond with them, the former are infinitely less able to bear such a test. There are moreover two considerations particularly applicable to the federal system of America, which place that system in a very interesting point of view. First. In a single republic, all the power surrendered by the people, is submitted to the administration of a single government; and the usurpations are guarded against, by a division of the government into distinct and separate departments. In the compound republic of America, the power surrendered by the people, is first divided between two distinct governments, and then the portion allotted to each subdivided among distinct and separate departments. Hence a double security arises to the rights of the people. The different governments will control each other; at the same time that each will be controled by itself. Second. It is of great importance in a republic, not only to guard the society against the oppression of its rulers; but to guard one part of the society against the injustice of the other part. Different interests necessarily exist in different classes of citizens. If a majority be united by a common interest, the rights of the minority will be insecure. There are but two methods of providing against this evil: the one, by creating a will in the community independent of the majority, that is, of the society itself; the other, by comprehending in the society so many separate descriptions of citizens, as will render an unjust combination of a majority of the whole very improbable, if not impracticable. The first method prevails in all governments possessing an hereditary or self-appointed authority. This, at best, is but a precarious security; because a power independent of the society may as well espouse the unjust views of the major, as the rightful interests of the minor party, and may possibly be turned against both parties. The second method will be exemplified in the federal republic of the United States. Whilst all authority in it will be derived from, and dependent on the society, the society itself will be broken into so many parts, interests, and classes of citizens, that the rights of individuals, or of the minority, will be in little danger from interested combinations of the majority. In a free government, the security for civil rights must be the same as that for religious rights. It consists in the one case in the multiplicity of interests, and in the other, in the multiplicity of sects. The degree of security in both cases will depend on the number of interests and sects; and this may be presumed to depend on the extent of country and number of people comprehended under the same government. This view of the subject must particularly recommend a proper federal system to all the sincere and considerate friends of republican government: since it shows, that in exact proportion as the territory of the union may be formed into more circumscribed confederacies, or states, oppressive combinations of a majority will be facilitated; the best security under the republican form, for the rights of every class of citizens, will be diminished; and consequently, the
10 Federalist No. 51 Teaching American History 4 of 5 9/8/2015 1:14 PM stability and independence of some member of the government, the only other security, must be proportionally increased. Justice is the end of government. It is the end of civil society. It ever has been, and ever will be, pursued, until it be obtained, or until liberty be lost in the pursuit. In a society, under the forms of which the stronger faction can readily unite and oppress the weaker, anarchy may as truly be said to reign, as in a state of nature, where the weaker individual is not secured against the violence of the stronger: and as, in the latter state, even the stronger individuals are prompted, by the uncertainty of their condition, to submit to a government which may protect the weak, as well as themselves: so, in the former state, will the more powerful factions or parties be gradually induced, by a like motive, to wish for a government which will protect all parties, the weaker as well as the more powerful. It can be little doubted, that if the state of Rhode Island was separated from the confederacy, and left to itself, the insecurity of rights under the popular form of government within such narrow limits, would be displayed by such reiterated oppressions of factious majorities, that some power altogether independent of the people, would soon be called for by the voice of the very factions whose misrule had proved the necessity of it. In the extended republic of the United States, and among the great variety of interests, parties, and sects, which it embraces, a coalition of a majority of the whole society could seldom take place upon any other principles, than those of justice and the general good: whilst there being thus less danger to a minor from the will of the major party, there must be less pretext also, to provide for the security of the former, by introducing into the government a will not dependent on the latter: or, in other words, a will independent of the society itself. It is no less certain than it is important, notwithstanding the contrary opinions which have been entertained, that the larger the society, provided it lie within a practicable sphere, the more duly capable it will be of self-government. And happily for the republican cause, the practicable sphere may be carried to a very great extent, by a judicious modification and mixture of the federal principle. PUBLIUS Source: The Federalist: The Gideon Edition, eds. George W. Carey and James McClellan (Indianapolis: Liberty Fund, 2001),
11 Federalist No. 51 Teaching American History 5 of 5 9/8/2015 1:14 PM TeachingAmericanHistory.org TeachingAmericanHistory.org is a project of the Ashbrook Center at Ashland University 401 College Avenue Ashland, Ohio (419) (877) (Toll Free) info@teachingamericanhistory.org Ashbrook Center Design by CiV Digital
12 Federalist #51 Discussion questions 1. What are the three branches of government? 2. Which branch did Madison think would be the weakest? 3. Which methods does Madison suggest to check the powers of government? 4. How is the separation of powers between the three branches assured? 5. Give two examples of the "checks and balances" in the U.S. constitutional system. 6. Which branch appears as an exception to the separation of powers norm? Why is this exception not dangerous? 7. What is federalism? 8. What are the two great advantages of federalism, according to Madison? 9. What is the "end" (supreme goal) of government, according to Madison? 10. What is Madison's view of human nature and how does it affect his prescriptions for the republic?
Handout B: Madison EXCERPTS FROM FEDERALIST NO. 47 BY JAMES MADISON. DOCUMENTS of FREEDOM History, Government & Economics through Primary Sources
 DOCUMENTS of FREEDOM History, Government & Economics through Primary Sources Unit 2: The Purpose of Government Reading: Separation of Powers and Checks and Balances Activity: Montesquieu and Madison Handout
DOCUMENTS of FREEDOM History, Government & Economics through Primary Sources Unit 2: The Purpose of Government Reading: Separation of Powers and Checks and Balances Activity: Montesquieu and Madison Handout
Federalist 47, 48, 51
 James Madison 41 Limitation of Governmental Power and of Majority Rule The most accurate and helpful way to characterize our political system is to call it a constitutional democracy. The term implies
James Madison 41 Limitation of Governmental Power and of Majority Rule The most accurate and helpful way to characterize our political system is to call it a constitutional democracy. The term implies
Unit #1: Constitutional Underpinnings AP US Government & Politics Mr. Coia
 Unit #1: Constitutional Underpinnings AP US Government & Politics Mr. Coia Name: Date: Period: Since this is the first unit guide, let me explain a few items. Each unit guide will cover anywhere from one-four
Unit #1: Constitutional Underpinnings AP US Government & Politics Mr. Coia Name: Date: Period: Since this is the first unit guide, let me explain a few items. Each unit guide will cover anywhere from one-four
POPULAR SOVEREIGNTY. 1. Underline the 2 fragments that address Popular Sovereignty s foundation. 2. Both fragments contain which word?
 POPULAR SOVEREIGNTY If we resort for a criterion to the different principles on which different forms of government are established, we may define a republic to be, or at least may bestow that name on,
POPULAR SOVEREIGNTY If we resort for a criterion to the different principles on which different forms of government are established, we may define a republic to be, or at least may bestow that name on,
Madison s Theory: Self-Interest & Ambition as the Solution
 Madison s Theory: Self-Interest & Ambition as the Solution Carlos Algara calgara@ucdavis.edu October 5, 2017 Solution: Ambition must be made to counteract ambition. Meeting Agenda: 1 Problem of Human Nature
Madison s Theory: Self-Interest & Ambition as the Solution Carlos Algara calgara@ucdavis.edu October 5, 2017 Solution: Ambition must be made to counteract ambition. Meeting Agenda: 1 Problem of Human Nature
We The People Packet. Chapter 12- Objective (8.1A,B,C): Describe who attended the Philadelphia Convention & how it was organized.
 We The People Packet Chapter 12- Objective (8.1A,B,C): Describe who attended the Philadelphia Convention & how it was organized. When was the Philadelphia Convention held? What was the intended goal of
We The People Packet Chapter 12- Objective (8.1A,B,C): Describe who attended the Philadelphia Convention & how it was organized. When was the Philadelphia Convention held? What was the intended goal of
How Did the Constitution Guard Against Tyranny?
 How Did the Constitution Guard Against Tyranny? Overview: In the summer of 1787, fifty-five delegates representing twelve of the thirteen states met in Philadelphia to fix the national government. The
How Did the Constitution Guard Against Tyranny? Overview: In the summer of 1787, fifty-five delegates representing twelve of the thirteen states met in Philadelphia to fix the national government. The
OPINION OFFICIAL OPINION NO. did thereby become a mefuber of that Board, and thereby vacate his Senate seat.
 Hon. Marlin K. McDaniel OPINION OFFICIAL OPINION NO. State Senator 34 South Seventh Street Richmond, Indiana Dear Senator McDaniel: June 4, 1970 This is in response to your request for my Offcial Opinion
Hon. Marlin K. McDaniel OPINION OFFICIAL OPINION NO. State Senator 34 South Seventh Street Richmond, Indiana Dear Senator McDaniel: June 4, 1970 This is in response to your request for my Offcial Opinion
Excerpt From Brutus Essay #1
 Excerpt From Brutus Essay #1 Among the most important of the Anti-Federalist essays is those of Brutus, whose essays were first published in the New York Journal. Brutus, whose identity has never been
Excerpt From Brutus Essay #1 Among the most important of the Anti-Federalist essays is those of Brutus, whose essays were first published in the New York Journal. Brutus, whose identity has never been
How Does the Constitution Guard Against Having a Ruler that is too
 Constitution MiniQ How Does the Constitution Guard Against Having a Ruler that is too Powerful? Overview: In the summer of 1787, fiftyfive delegates representing twelve of the thirteen states met in Philadelphia
Constitution MiniQ How Does the Constitution Guard Against Having a Ruler that is too Powerful? Overview: In the summer of 1787, fiftyfive delegates representing twelve of the thirteen states met in Philadelphia
Blackman High School AP Government & Politics Summer Assignment M. Giacobbi Room D School Year
 Blackman High School AP Government & Politics Summer Assignment M. Giacobbi Room D-02 2017-2018 School Year This college-level course is a challenging course that is meant to be the equivalent of a freshman
Blackman High School AP Government & Politics Summer Assignment M. Giacobbi Room D-02 2017-2018 School Year This college-level course is a challenging course that is meant to be the equivalent of a freshman
2 approaches to curb mischiefs
 Federalist Papers 85 essays by Hamilton, Jay, Madison Published anonymously (Publius) in New York Packet and Independent Journal between October, 1787 and May, 1788 Address insufficiency of the present
Federalist Papers 85 essays by Hamilton, Jay, Madison Published anonymously (Publius) in New York Packet and Independent Journal between October, 1787 and May, 1788 Address insufficiency of the present
Federalist 55 James Madison
 FEDERALIST 319 Federalist James Madison Under the Constitution s original formula, the House would have sixtyfive members. This number was too small according to Anti-Federalists. Publius employs a number
FEDERALIST 319 Federalist James Madison Under the Constitution s original formula, the House would have sixtyfive members. This number was too small according to Anti-Federalists. Publius employs a number
Separation of Powers: History and Theory
 Separation of Powers: History and Theory James E. Hanley Published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International license. This work may be freely reproduced for non-commercial
Separation of Powers: History and Theory James E. Hanley Published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International license. This work may be freely reproduced for non-commercial
James Madison's Defense of the Constitution at the Virginia Convention (1788)
 James Madison's Defense of the Constitution at the Virginia Convention (1788) James Madison, a slight, soft-spoken, and studious man well versed in history, philosophy, and law, was a principal advocate
James Madison's Defense of the Constitution at the Virginia Convention (1788) James Madison, a slight, soft-spoken, and studious man well versed in history, philosophy, and law, was a principal advocate
Publius: The Federalist 69, New York Packet, 14 March 1788
 Publius: The Federalist 69, New York Packet, 14 March 1788 To the People of the State of New-York. I proceed now to trace the real characters of the proposed executive as they are marked out in the plan
Publius: The Federalist 69, New York Packet, 14 March 1788 To the People of the State of New-York. I proceed now to trace the real characters of the proposed executive as they are marked out in the plan
Social Studies Lesson Plan Template 1
 Social Studies Lesson Plan Template 1 Title: Debate over the Ratification of the Constitution Lesson Author: Tommy George, Gina Rumbolo Key Words: Federalists, Anti-federalists, Ratification, Constitution,
Social Studies Lesson Plan Template 1 Title: Debate over the Ratification of the Constitution Lesson Author: Tommy George, Gina Rumbolo Key Words: Federalists, Anti-federalists, Ratification, Constitution,
Publius: The Federalist 81, New York, 28 May 1788
 Publius: The Federalist 81, New York, 28 May 1788 A further View of the Judicial Department, in Relation to the Distribution of its Authority. Let us now return to the partition of the judiciary authority
Publius: The Federalist 81, New York, 28 May 1788 A further View of the Judicial Department, in Relation to the Distribution of its Authority. Let us now return to the partition of the judiciary authority
Key Questions. Organization. Federalist Papers: Institutions, policy-making, and the public interest
 Federalist Papers: Institutions, policy-making, and the public interest Sept 22, 2004 11.002/17.30j Public Policy 1 Key Questions What does it mean to say, Institutions matter? What design do policy-making
Federalist Papers: Institutions, policy-making, and the public interest Sept 22, 2004 11.002/17.30j Public Policy 1 Key Questions What does it mean to say, Institutions matter? What design do policy-making
AP Government and Politics Basic Vocabulary. Political Culture Political Efficacy (Low) Constituency/Constituents Reverse Discrimination
 AP Government and Politics Basic Vocabulary Adversarial System Interest Group Affirmative Action Jim Crow Laws Balance of Trade Lame Duck Bandwagon Effect Litigation Bicameral Legislature Non-Government
AP Government and Politics Basic Vocabulary Adversarial System Interest Group Affirmative Action Jim Crow Laws Balance of Trade Lame Duck Bandwagon Effect Litigation Bicameral Legislature Non-Government
South Carolina s Exposition Against the Tariff of 1828 By John C. Calhoun (Anonymously)
 As John C. Calhoun was Vice President in 1828, he could not openly oppose actions of the administration. Yet he was moving more and more toward the states rights position which in 1832 would lead to nullification.
As John C. Calhoun was Vice President in 1828, he could not openly oppose actions of the administration. Yet he was moving more and more toward the states rights position which in 1832 would lead to nullification.
Chief Justice John Marshall Marbury v. Madison (1803) [Abridged]
![Chief Justice John Marshall Marbury v. Madison (1803) [Abridged] Chief Justice John Marshall Marbury v. Madison (1803) [Abridged]](/thumbs/77/74509333.jpg) Chief Justice John Marshall Marbury v. Madison (1803) [Abridged] Chief Justice Marshall delivered the opinion of the Court. At the last term on the affidavits then read and filed with the clerk, a rule
Chief Justice John Marshall Marbury v. Madison (1803) [Abridged] Chief Justice Marshall delivered the opinion of the Court. At the last term on the affidavits then read and filed with the clerk, a rule
Ratification of the US Constitution in New York, 1788
 Introduction Ratification of the US Constitution in New York, 1788 This unique copy of the US Constitution was printed by Claxton and Babcock in Albany, New York, between February 11 and March 21, 1788.
Introduction Ratification of the US Constitution in New York, 1788 This unique copy of the US Constitution was printed by Claxton and Babcock in Albany, New York, between February 11 and March 21, 1788.
Under these impressions, it has been my object to turn your attention to the principal defects in this system.
 Brutus III Brutus November 15, 1787 To the Citizens of the State of New-York. In the investigation of the constitution, under your consideration, great care should be taken, that you do not form your opinions
Brutus III Brutus November 15, 1787 To the Citizens of the State of New-York. In the investigation of the constitution, under your consideration, great care should be taken, that you do not form your opinions
The Federalist No. 10. The Utility of the Union as a Safeguard Against Domestic Faction and Insurrection (continued)
 1 The Federalist No. 10 The Utility of the Union as a Safeguard Against Domestic Faction and Insurrection (continued) To the People of the State of New York: Daily Advertiser Thursday, November 22, 1787
1 The Federalist No. 10 The Utility of the Union as a Safeguard Against Domestic Faction and Insurrection (continued) To the People of the State of New York: Daily Advertiser Thursday, November 22, 1787
LETTER XIV. January 17, Dear sir,
 1 of 5 11/4/2007 1:11 PM From the Constitution Society http://www.constitution.org/ LETTER XIV. Dear sir, January 17, 1788. To continue the subject of appointments: Officers, in the fifth place, may be
1 of 5 11/4/2007 1:11 PM From the Constitution Society http://www.constitution.org/ LETTER XIV. Dear sir, January 17, 1788. To continue the subject of appointments: Officers, in the fifth place, may be
Quarter One: Unit Four
 SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will identify the weaknesses of the government under the Articles of Confederation (i.e.,
SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will identify the weaknesses of the government under the Articles of Confederation (i.e.,
The Constitution: From Ratification to Amendments. US Government Fall, 2014
 The Constitution: From Ratification to Amendments US Government Fall, 2014 Origins of American Government Colonial Period Where did ideas for government in the colonies come from? Largely, from England
The Constitution: From Ratification to Amendments US Government Fall, 2014 Origins of American Government Colonial Period Where did ideas for government in the colonies come from? Largely, from England
US History, Ms. Brown Website: dph7history.weebly.com
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #70 Aims: SWBAT understand and explain the debate over representation SWBAT identify and explain the Virginia Plan and
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #70 Aims: SWBAT understand and explain the debate over representation SWBAT identify and explain the Virginia Plan and
James Wilson s Speech in the State House Yard, Philadelphia, 6 October 1787
 James Wilson s Speech in the State House Yard, Philadelphia, 6 October 1787 Mr. Wilson then rose, and delivered a long and eloquent speech upon the principles of the Federal Constitution proposed by the
James Wilson s Speech in the State House Yard, Philadelphia, 6 October 1787 Mr. Wilson then rose, and delivered a long and eloquent speech upon the principles of the Federal Constitution proposed by the
Antifederalist No. 84. On the Lack of a Bill of Rights
 Antifederalist No. 84 On the Lack of a Bill of Rights By "Brutus." When a building is to be erected which is intended to stand for ages, the foundation should be firmly laid. The Constitution proposed
Antifederalist No. 84 On the Lack of a Bill of Rights By "Brutus." When a building is to be erected which is intended to stand for ages, the foundation should be firmly laid. The Constitution proposed
Federalist No. 78. The Judiciary Department. Author: Alexander Hamilton. To the People of the State of New York:
 Federalist No. 78 The Judiciary Department Author: Alexander Hamilton To the People of the State of New York: WE PROCEED now to an examination of the judiciary department of the proposed government. In
Federalist No. 78 The Judiciary Department Author: Alexander Hamilton To the People of the State of New York: WE PROCEED now to an examination of the judiciary department of the proposed government. In
Quarter One: Unit Four
 SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will identify the weaknesses of the government under the Articles of Confederation (i.e.,
SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will identify the weaknesses of the government under the Articles of Confederation (i.e.,
Federalist 63. James Madison
 337 Federalist 63 James Madison To the Anti-Federalists, the Senate s six-year term and smaller number seemed too aristocratic. But to Publius, the selection of senators by state legislatures was a built-in
337 Federalist 63 James Madison To the Anti-Federalists, the Senate s six-year term and smaller number seemed too aristocratic. But to Publius, the selection of senators by state legislatures was a built-in
If men were angels, no government would be necessary. - James Madison
 If men were angels, no government would be necessary. - James Madison Knowing what you know about the Causes of the American Revolution and the principle of Separation of Powers, agree or disagree with
If men were angels, no government would be necessary. - James Madison Knowing what you know about the Causes of the American Revolution and the principle of Separation of Powers, agree or disagree with
American Political History, Topic 4: The United States Constitution and Jefferson to Madison (1787)
 Background: The United States Constitution is the God-inspired rubber-and-metal vehicle that carries the American ideals of life, liberty, the pursuit of happiness, equality, justice, and republican government
Background: The United States Constitution is the God-inspired rubber-and-metal vehicle that carries the American ideals of life, liberty, the pursuit of happiness, equality, justice, and republican government
The Federalist Papers. Day 1: Constitutional Convention 2/9/2018. In Search of Original Intent
 The Federalist Papers In Search of Original Intent Day 1: Background 10of Constitutional Convention; Purpose of Federalist Papers; Federalist No. 1 Constitutional Convention 1 Facts about the Constitutional
The Federalist Papers In Search of Original Intent Day 1: Background 10of Constitutional Convention; Purpose of Federalist Papers; Federalist No. 1 Constitutional Convention 1 Facts about the Constitutional
Brutus No. 1. Brutus October 18, To the Citizens of the State of New-York.
 Brutus No. 1 Brutus October 18, 1787 To the Citizens of the State of New-York. [1] When the public is called to investigate and decide upon a question in which not only the present members of the community
Brutus No. 1 Brutus October 18, 1787 To the Citizens of the State of New-York. [1] When the public is called to investigate and decide upon a question in which not only the present members of the community
CONTROLLING LEGAL PRINCIPLES Free Exercise Clause Decision The Contemplation of Justice McCulloch v. Maryland, 17 U.S. 4 Wheat.
 CONTROLLING LEGAL PRINCIPLES Free Exercise Clause Decision The Contemplation of Justice McCulloch v. Maryland, 17 U.S. 4 Wheat. 316 316 (1819) The Government of the Union, though limited in its powers,
CONTROLLING LEGAL PRINCIPLES Free Exercise Clause Decision The Contemplation of Justice McCulloch v. Maryland, 17 U.S. 4 Wheat. 316 316 (1819) The Government of the Union, though limited in its powers,
The Constitution. Karen H. Reeves
 The Constitution Karen H. Reeves Toward a New Union Annapolis Convention (Sept. 1786) Met to determine commercial regulation Nationalists called for Constitutional Convention Constitutional Convention
The Constitution Karen H. Reeves Toward a New Union Annapolis Convention (Sept. 1786) Met to determine commercial regulation Nationalists called for Constitutional Convention Constitutional Convention
TEACHING AMERICAN HISTORY PROJECT The Constitution, Article I Kyra Kasperson
 TEACHING AMERICAN HISTORY PROJECT The Constitution, Article I Kyra Kasperson Grade 7 Length of class period 42 minutes Inquiry What is the composition of the legislative branch under the Constitution and
TEACHING AMERICAN HISTORY PROJECT The Constitution, Article I Kyra Kasperson Grade 7 Length of class period 42 minutes Inquiry What is the composition of the legislative branch under the Constitution and
Ratification of the Constitution. Issues
 Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
Essay 1. Brutus ESSAY I
 ESSAY I 221 Essay 1 Brutus Supporters of the Constitution dubbed their opponents Anti-Federalists. Opponents resented the label, but it stuck. The Anti-Federalist author Brutus most likely New York lawyer
ESSAY I 221 Essay 1 Brutus Supporters of the Constitution dubbed their opponents Anti-Federalists. Opponents resented the label, but it stuck. The Anti-Federalist author Brutus most likely New York lawyer
No. 17 Federalist Power Will Ultimately Subvert State Authority
 No. 17 Federalist Power Will Ultimately Subvert State Authority The "necessary and proper" clause has, from the beginning, been a thorn in the side of those seeking to reduce federal power, but its attack
No. 17 Federalist Power Will Ultimately Subvert State Authority The "necessary and proper" clause has, from the beginning, been a thorn in the side of those seeking to reduce federal power, but its attack
Do not copy, post, or distribute. Ladies and gentlemen, the presidents of the United States. JAMES MADISON S NOTES OF THE FEDERAL CONVENTION* (1787)
 CHAPTER 1 JAMES MADISON S NOTES OF THE FEDERAL CONVENTION* (1787) Ladies and gentlemen, the presidents of the United States. A typographical error, right? Not if certain delegates to the Constitutional
CHAPTER 1 JAMES MADISON S NOTES OF THE FEDERAL CONVENTION* (1787) Ladies and gentlemen, the presidents of the United States. A typographical error, right? Not if certain delegates to the Constitutional
Federalists versus Anti-Federalists
 Federalists versus Anti-Federalists Overview In this lesson, students will explore the Articles of Confederation and the revisions that created the Constitution of 1787. Students will analyze and assume
Federalists versus Anti-Federalists Overview In this lesson, students will explore the Articles of Confederation and the revisions that created the Constitution of 1787. Students will analyze and assume
Letters from the Federal Farmer, No December 1787
 Letters from the Federal Farmer, No. 7 31 December 1787 Among the hundreds of pamphlets, newspaper articles, and published speeches opposing the new Constitution, a few were judged especially outstanding
Letters from the Federal Farmer, No. 7 31 December 1787 Among the hundreds of pamphlets, newspaper articles, and published speeches opposing the new Constitution, a few were judged especially outstanding
3: A New Plan of Government. Essential Question: How Do Governments Change?
 3: A New Plan of Government Essential Question: How Do Governments Change? The Constitution s Source Guiding Question: From where did the Framers of the Constitution borrow their ideas about government?
3: A New Plan of Government Essential Question: How Do Governments Change? The Constitution s Source Guiding Question: From where did the Framers of the Constitution borrow their ideas about government?
Excerpts from Brutus No. 1
 DOCUMENTS of FREEDOM History, Government & Economics through Primary Sources Primary Source: Excerpts from Brutus No. 1, Annotated Excerpts from Brutus No. 1 18 October 1787 To the Citizens of the State
DOCUMENTS of FREEDOM History, Government & Economics through Primary Sources Primary Source: Excerpts from Brutus No. 1, Annotated Excerpts from Brutus No. 1 18 October 1787 To the Citizens of the State
We the People of the United States,
 We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defence, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings
We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defence, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings
James Madison Debates a Bill of Rights
 James Madison Debates a Bill of Rights Framing Question What doubts, concerns, and misgivings arose during the development of the Bill of Rights? Understanding The Bill of Rights, considered today a foundation
James Madison Debates a Bill of Rights Framing Question What doubts, concerns, and misgivings arose during the development of the Bill of Rights? Understanding The Bill of Rights, considered today a foundation
Blackman High School AP Government & Politics Summer Assignment M. Giacobbi Room D School Year
 Blackman High School AP Government & Politics Summer Assignment M. Giacobbi Room D-02 2018-2019 School Year This college-level course is a challenging course that is meant to be the equivalent of a freshman
Blackman High School AP Government & Politics Summer Assignment M. Giacobbi Room D-02 2018-2019 School Year This college-level course is a challenging course that is meant to be the equivalent of a freshman
Creating Our. Constitution. Key Terms. delegates equal representation executive federal system framers House of Representatives judicial
 Lesson 2 Creating Our Constitution Key Terms delegates equal representation executive federal system framers House of Representatives judicial What You Will Learn to Do Explain how the Philadelphia Convention
Lesson 2 Creating Our Constitution Key Terms delegates equal representation executive federal system framers House of Representatives judicial What You Will Learn to Do Explain how the Philadelphia Convention
Federalist 62 James Madison
 FEDERALIST 62 331 Federalist 62 James Madison The Senate, with its equal representation of each state and members selected by state legislatures, was at once a concession to small states and a bulwark
FEDERALIST 62 331 Federalist 62 James Madison The Senate, with its equal representation of each state and members selected by state legislatures, was at once a concession to small states and a bulwark
I. Making the Constitution: (includes The Articles of Confederation, Preamble, and Federalists vs. Antifederalists )
 Civics 3 rd Quarter Civics Study Guide Page 1 Student Name: Civics 3 rd Quarter Civics Study Guide Date: In completing this study guide, you will need to draw on your knowledge from throughout the 3 rd
Civics 3 rd Quarter Civics Study Guide Page 1 Student Name: Civics 3 rd Quarter Civics Study Guide Date: In completing this study guide, you will need to draw on your knowledge from throughout the 3 rd
The Clay Compromise Measures by John C. Calhoun March 4, 1850
 The Clay Compromise Measures by John C. Calhoun March 4, 1850 John C. Calhoun This is among John C. Calhoun's most famous speeches. He was too ill to deliver it himself, so it was read by another senator
The Clay Compromise Measures by John C. Calhoun March 4, 1850 John C. Calhoun This is among John C. Calhoun's most famous speeches. He was too ill to deliver it himself, so it was read by another senator
4.6. AP American Government and Politics. John Locke Précis
 John Locke Précis After reading John Locke s Second Treatise of Civil Government, write a précis (a summary of the main ideas and points) about the treatise in 150 words or less. Final product must be
John Locke Précis After reading John Locke s Second Treatise of Civil Government, write a précis (a summary of the main ideas and points) about the treatise in 150 words or less. Final product must be
The House of Representatives shall be composed of Members chosen every second Year by the People of the several States.
 Guiding Principles of the Constitution (HA) Over the years, the Constitution has acquired an almost sacred status for Americans. Part of the reason for that is its durability: the Constitution has survived,
Guiding Principles of the Constitution (HA) Over the years, the Constitution has acquired an almost sacred status for Americans. Part of the reason for that is its durability: the Constitution has survived,
Constitution of the United States. Article. I.
 Constitution of the United States Article. I. Section. 1. All legislative Powers herein granted shall be vested in a Congress of the United States, which shall consist of a Senate and House of Representatives.
Constitution of the United States Article. I. Section. 1. All legislative Powers herein granted shall be vested in a Congress of the United States, which shall consist of a Senate and House of Representatives.
Copyright 2014 Organic Laws Institute
 1 The United States In this part of this lesson, we explore the different meanings of the phrases, United States and United States of America used in the Organic Laws of the United States of America. Article
1 The United States In this part of this lesson, we explore the different meanings of the phrases, United States and United States of America used in the Organic Laws of the United States of America. Article
Anti-Federalists Supporters. 18 October, To the citizens of the State of New York
 Anti-Federalists Supporters 18 October, 1787 To the citizens of the State of New York This government is to possess absolute and uncontroulable power, legislative, executive and judicial, with respect
Anti-Federalists Supporters 18 October, 1787 To the citizens of the State of New York This government is to possess absolute and uncontroulable power, legislative, executive and judicial, with respect
1. According to Washington, what is needed to prevent an uprising like Shays Rebellion? [1]
![1. According to Washington, what is needed to prevent an uprising like Shays Rebellion? [1] 1. According to Washington, what is needed to prevent an uprising like Shays Rebellion? [1]](/thumbs/83/87708147.jpg) Part A Short-Answer Questions Directions: Analyze the documents and answer the short-answer questions that follow each document in the space provided. Document 1 We are fast verging to anarchy and confusion!
Part A Short-Answer Questions Directions: Analyze the documents and answer the short-answer questions that follow each document in the space provided. Document 1 We are fast verging to anarchy and confusion!
Wednesday, October 12 th
 Wednesday, October 12 th Draft of Essay #1 Due TODAY! Final Essay #1 Due Wednesday, Oct. 26 th Federalism NATIONAL L J E STATE L J E The Founders on Government Government is not reason; it is not eloquent;
Wednesday, October 12 th Draft of Essay #1 Due TODAY! Final Essay #1 Due Wednesday, Oct. 26 th Federalism NATIONAL L J E STATE L J E The Founders on Government Government is not reason; it is not eloquent;
The Critical Period The early years of the American Republic
 The Critical Period 1781-1789 The early years of the American Republic America after the War New Political Ideas: - Greater power for the people Republic: Represent the Public America after the War State
The Critical Period 1781-1789 The early years of the American Republic America after the War New Political Ideas: - Greater power for the people Republic: Represent the Public America after the War State
Publius: The Federalist 32 33, New York Independent Journal, 2 January 1788
 Publius: The Federalist 32 33, New York Independent Journal, 2 January 1788 This essay, written by Alexander Hamilton, was number 31 in the newspapers, but was divided into two parts and became numbers
Publius: The Federalist 32 33, New York Independent Journal, 2 January 1788 This essay, written by Alexander Hamilton, was number 31 in the newspapers, but was divided into two parts and became numbers
Rattfying the Constitution
 Handout 4 (page 1) Part A. Rattfying the Constitution Read the fact sheet, and answer the questions. The Articles of Confederation failed to address several problems confronting the newly formed United
Handout 4 (page 1) Part A. Rattfying the Constitution Read the fact sheet, and answer the questions. The Articles of Confederation failed to address several problems confronting the newly formed United
Chinmay Sridhar, Angel Weng, Benjamin Zhang APUS, Buggé, Period 1 Chapter 7, Topic 2: Newburgh Conspiracy
 Chinmay Sridhar, Angel Weng, Benjamin Zhang APUS, Buggé, Period 1 Chapter 7, Topic 2: Newburgh Conspiracy Land Grants Land Ordinance (1785) Northwest Ordinance (1787) Who Made by Congress under Articles
Chinmay Sridhar, Angel Weng, Benjamin Zhang APUS, Buggé, Period 1 Chapter 7, Topic 2: Newburgh Conspiracy Land Grants Land Ordinance (1785) Northwest Ordinance (1787) Who Made by Congress under Articles
Perspectives from FSF Scholars May 24, 2018 Vol. 13, No. 19
 Perspectives from FSF Scholars May 24, 2018 Vol. 13, No. 19 The Framers Establish an Administrative Constitution Introduction and Summary by Joseph Postell* Does the Constitution provide any guiding principles
Perspectives from FSF Scholars May 24, 2018 Vol. 13, No. 19 The Framers Establish an Administrative Constitution Introduction and Summary by Joseph Postell* Does the Constitution provide any guiding principles
The Politics of Constitution Building: An Overview of the American Political System
 The Politics of Constitution Building: An Overview of the American Political System 1. THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION: NEITHER FIT FOR WAR, NOR PEACE When the representatives of the colonies meeting in
The Politics of Constitution Building: An Overview of the American Political System 1. THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION: NEITHER FIT FOR WAR, NOR PEACE When the representatives of the colonies meeting in
ALEXANDER LIBRARY has recently acquired a 1775 edition
 EDMUND BURKE AND THE "PRESENT DISCONTENTS 55 BY NANCY HARPER Dr. Harper is an assistant professor of communication in Rutgers College ALEXANDER LIBRARY has recently acquired a 1775 edition of Edmund Burke's
EDMUND BURKE AND THE "PRESENT DISCONTENTS 55 BY NANCY HARPER Dr. Harper is an assistant professor of communication in Rutgers College ALEXANDER LIBRARY has recently acquired a 1775 edition of Edmund Burke's
Unit One Reading Guide DEFINING DEMOCRACY
 Name Period Textbook: Chapter One Unit One Reading Guide DEFINING DEMOCRACY Direct Democracy Representative Democracy Core Beliefs of American Democracy Individual liberty Popular consent Equality of opportunity
Name Period Textbook: Chapter One Unit One Reading Guide DEFINING DEMOCRACY Direct Democracy Representative Democracy Core Beliefs of American Democracy Individual liberty Popular consent Equality of opportunity
The Constitution I. Considerations that influenced the formulation and adoption of the Constitution A. Roots 1. Religious Freedom a) Puritan
 The Constitution I. Considerations that influenced the formulation and adoption of the Constitution A. Roots 1. Religious Freedom a) Puritan Theocracy (1) 9 of 13 had state church b) Rhode Island (1) Roger
The Constitution I. Considerations that influenced the formulation and adoption of the Constitution A. Roots 1. Religious Freedom a) Puritan Theocracy (1) 9 of 13 had state church b) Rhode Island (1) Roger
Wednesday, February 29 th
 Ratification & New Government 1 Wednesday, February 29 th Final version of Essay 1 and Change Memo: due March 8 th or 9 th at the beginning of lab. Post a digital copy of final version of Essay 1 to Turn-It-In
Ratification & New Government 1 Wednesday, February 29 th Final version of Essay 1 and Change Memo: due March 8 th or 9 th at the beginning of lab. Post a digital copy of final version of Essay 1 to Turn-It-In
The Federalist Papers
 Questions What did the Federalists believe in? Name two important Federalist leaders. Why did they write the Federalist Papers? What were the Federalist Papers? The Federalist Papers Written from 1787-1788
Questions What did the Federalists believe in? Name two important Federalist leaders. Why did they write the Federalist Papers? What were the Federalist Papers? The Federalist Papers Written from 1787-1788
The first question made in the cause is, has Congress power to incorporate a bank?...
 The Federal Government Is Supreme over the States (1819) -John Marshall (1755-1835) In the case now to be determined, the defendant, a sovereign State, denies the obligation of a law enacted by the legislature
The Federal Government Is Supreme over the States (1819) -John Marshall (1755-1835) In the case now to be determined, the defendant, a sovereign State, denies the obligation of a law enacted by the legislature
The Social Contract 1600s
 The Constitution History! European Influence! European Enlightenment Scientific Revolution of the 16 th and 17 th centuries, basis of modern science.! European philosophers were strongly criticizing governments
The Constitution History! European Influence! European Enlightenment Scientific Revolution of the 16 th and 17 th centuries, basis of modern science.! European philosophers were strongly criticizing governments
Red, white, and blue. One for each state. Question 1 What are the colors of our flag? Question 2 What do the stars on the flag mean?
 1 What are the colors of our flag? Red, white, and blue 2 What do the stars on the flag mean? One for each state 3 How many stars are there on our flag? There are 50 stars on our flag. 4 What color are
1 What are the colors of our flag? Red, white, and blue 2 What do the stars on the flag mean? One for each state 3 How many stars are there on our flag? There are 50 stars on our flag. 4 What color are
Articles of Confederation [first printing, first edition] Lancaster, Pennsylvania, 1777 Book, 26 pages. ARTICLES. OF [Illegible] 1777 CONFEDERATION
![Articles of Confederation [first printing, first edition] Lancaster, Pennsylvania, 1777 Book, 26 pages. ARTICLES. OF [Illegible] 1777 CONFEDERATION Articles of Confederation [first printing, first edition] Lancaster, Pennsylvania, 1777 Book, 26 pages. ARTICLES. OF [Illegible] 1777 CONFEDERATION](/thumbs/79/78892399.jpg) Articles of Confederation [first printing, first edition] Lancaster, Pennsylvania, 1777 Book, 26 pages. [2] ARTICLES OF [Illegible] 1777 CONFEDERATION AND Perpetual Union BETWEEN THE S T A T E S OF NEW-HAMPSHIRE,
Articles of Confederation [first printing, first edition] Lancaster, Pennsylvania, 1777 Book, 26 pages. [2] ARTICLES OF [Illegible] 1777 CONFEDERATION AND Perpetual Union BETWEEN THE S T A T E S OF NEW-HAMPSHIRE,
Name Per. 2. Identify the important principles and issues debated at the Constitutional Convention and describe how they were resolved.
 Name Per CHAPTER 2 THE CONSTITUTION LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying Chapter 2, you should be able to: 1. Discuss the importance of the English philosophical heritage, the colonial experience, the Articles
Name Per CHAPTER 2 THE CONSTITUTION LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying Chapter 2, you should be able to: 1. Discuss the importance of the English philosophical heritage, the colonial experience, the Articles
TEACHING AMERICAN HISTORY PROJECT Lesson Title -The Constitutional Convention- Role-Playing Kyra Kasperson
 Grade 7 TEACHING AMERICAN HISTORY PROJECT Lesson Title -The Constitutional Convention- Role-Playing Kyra Kasperson Length of class period Two 42-minute periods Inquiry What were the opposing views regarding
Grade 7 TEACHING AMERICAN HISTORY PROJECT Lesson Title -The Constitutional Convention- Role-Playing Kyra Kasperson Length of class period Two 42-minute periods Inquiry What were the opposing views regarding
Why do you think the Framers organized the new country as a republic, when most countries in the world (in 1783) were ruled by a king or queen?
 NAME: Date: U.S. History CHAPTER 7 PACKET ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: 1. What is a constitution? 2. What is a republic? 3. What was the Articles of Confederation? 4. How was state and national power divided under
NAME: Date: U.S. History CHAPTER 7 PACKET ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: 1. What is a constitution? 2. What is a republic? 3. What was the Articles of Confederation? 4. How was state and national power divided under
The Constitution: WHO WE ARE (and how it came to be)
 The Constitution: WHO WE ARE (and how it came to be) WHERE ARE WE GOING? Examine your home grown Constitutions Discuss the problems doing it from scratch Look at the First Government of the United States
The Constitution: WHO WE ARE (and how it came to be) WHERE ARE WE GOING? Examine your home grown Constitutions Discuss the problems doing it from scratch Look at the First Government of the United States
The Debates in the Several State Conventions on the Adoption of the Federal Constitution [Elliot's Debates, Volume 3]
![The Debates in the Several State Conventions on the Adoption of the Federal Constitution [Elliot's Debates, Volume 3] The Debates in the Several State Conventions on the Adoption of the Federal Constitution [Elliot's Debates, Volume 3]](/thumbs/94/119857644.jpg) The Debates in the Several State Conventions on the Adoption of the Federal Constitution [Elliot's Debates, Volume 3] Monday, June 16, 1788. Mr. GEORGE MASON still thought that there ought to be some express
The Debates in the Several State Conventions on the Adoption of the Federal Constitution [Elliot's Debates, Volume 3] Monday, June 16, 1788. Mr. GEORGE MASON still thought that there ought to be some express
5. Which of the following documents created a compromise that led to the formation of a bicameral legislature
 AP Government & Politics Ch. 1 & 2 Unit Exam 1. In a republic, usurpations are guarded against by a division of the government into distinct branches. This is an example of: (A) Federalism (D) A system
AP Government & Politics Ch. 1 & 2 Unit Exam 1. In a republic, usurpations are guarded against by a division of the government into distinct branches. This is an example of: (A) Federalism (D) A system
Attached are letters from the following distinguished professionals against a convention:
 Opposition to HJR 7 or SJR 5 (Calling for an Article V convention) Dave Black, Willoughby Ohio 11/9/13 Attached are letters from the following distinguished professionals against a convention: Supreme
Opposition to HJR 7 or SJR 5 (Calling for an Article V convention) Dave Black, Willoughby Ohio 11/9/13 Attached are letters from the following distinguished professionals against a convention: Supreme
Judicial Veto and the Ohio Plan
 Washington University Law Review Volume 9 Issue 1 January 1923 Judicial Veto and the Ohio Plan Edward Selden Follow this and additional works at: http://openscholarship.wustl.edu/law_lawreview Part of
Washington University Law Review Volume 9 Issue 1 January 1923 Judicial Veto and the Ohio Plan Edward Selden Follow this and additional works at: http://openscholarship.wustl.edu/law_lawreview Part of
Learning Check. You CAN use your notes. You CAN NOT use your neighbor!
 Learning Check You CAN use your notes. You CAN NOT use your neighbor! Constitution and Bill of Rights QC Standards B.1.i. Interpret the ideas and principles expressed in the U.S. Constitution B.1.j. Explain
Learning Check You CAN use your notes. You CAN NOT use your neighbor! Constitution and Bill of Rights QC Standards B.1.i. Interpret the ideas and principles expressed in the U.S. Constitution B.1.j. Explain
The constitution supercedes ordinary law even when the law represents the wishes of a majority of citizens.
 AP Government Chapter 2 The Constitution The constitution supercedes ordinary law even when the law represents the wishes of a majority of citizens. The Constitution is this nation s basic law: It creates
AP Government Chapter 2 The Constitution The constitution supercedes ordinary law even when the law represents the wishes of a majority of citizens. The Constitution is this nation s basic law: It creates
AP American Government
 AP American Government WILSON, CHAPTER 2 The Constitution OVERVIEW The Framers of the Constitution sought to create a government capable of protecting liberty and preserving order. The solution they chose
AP American Government WILSON, CHAPTER 2 The Constitution OVERVIEW The Framers of the Constitution sought to create a government capable of protecting liberty and preserving order. The solution they chose
The Doctrine of Judicial Review and Natural Law
 Catholic University Law Review Volume 6 Issue 2 Article 3 1956 The Doctrine of Judicial Review and Natural Law Charles N. R. McCoy Follow this and additional works at: http://scholarship.law.edu/lawreview
Catholic University Law Review Volume 6 Issue 2 Article 3 1956 The Doctrine of Judicial Review and Natural Law Charles N. R. McCoy Follow this and additional works at: http://scholarship.law.edu/lawreview
17. Who becomes President of the United States if the President should die? 22. How many changes or Amendments are there to the Constitution?
 The following are 100 sample U.S. History and Government Questions that may be asked during the Naturalization Exam. 100 Typical Questions 1. What are the colors of our flag? 2. How many stars are there
The following are 100 sample U.S. History and Government Questions that may be asked during the Naturalization Exam. 100 Typical Questions 1. What are the colors of our flag? 2. How many stars are there
The Constitution CHAPTER 2 CHAPTER OUTLINE WITH KEYED-IN RESOURCES
 CHAPTER 2 The Constitution CHAPTER OUTLINE WITH KEYED-IN RESOURCES I. The problem of liberty (THEME A: THE POLITICAL PHILOSOPHY OF THE FOUNDERS) A. Colonists were focused on traditional liberties 1. The
CHAPTER 2 The Constitution CHAPTER OUTLINE WITH KEYED-IN RESOURCES I. The problem of liberty (THEME A: THE POLITICAL PHILOSOPHY OF THE FOUNDERS) A. Colonists were focused on traditional liberties 1. The
Colorado and U.S. Constitutions
 Courts in the Community Colorado Judicial Branch Office of the State Court Administrator Updated January 2013 Lesson: Objective: Activities: Outcomes: Colorado and U.S. Constitutions Students understand
Courts in the Community Colorado Judicial Branch Office of the State Court Administrator Updated January 2013 Lesson: Objective: Activities: Outcomes: Colorado and U.S. Constitutions Students understand
Federalists and anti-federalists The power of subtleties
 Federalists and anti-federalists The power of subtleties The ratification of the Constitution exemplifies the power of subtleties. The two sides in the debate, the Federalists and the Anti-federalists,
Federalists and anti-federalists The power of subtleties The ratification of the Constitution exemplifies the power of subtleties. The two sides in the debate, the Federalists and the Anti-federalists,
Constitution Day: Federalists vs. Anti-Federalists Introduction Massachusetts History and Social Science Curriculum Frameworks Content Standards
 Constitution Day: Federalists vs. Anti-Federalists Adapted from the Stanford History Education Group s Federalists and Anti-Federalists Lesson Plan https://sheg.stanford.edu/history-lessons/federalists-and-anti-federalists
Constitution Day: Federalists vs. Anti-Federalists Adapted from the Stanford History Education Group s Federalists and Anti-Federalists Lesson Plan https://sheg.stanford.edu/history-lessons/federalists-and-anti-federalists
C H A P T E R 3 The US Constitution
 C H A P T E R 3 The US Constitution SECTION 1 The Six Basic Principles SECTION 2 Formal Amendment SECTION 3 Informal Amendment What are the important elements of the Constitution? What are the six basic
C H A P T E R 3 The US Constitution SECTION 1 The Six Basic Principles SECTION 2 Formal Amendment SECTION 3 Informal Amendment What are the important elements of the Constitution? What are the six basic
Chapter 7. Multiple-Choice Questions
 Chapter 7 Multiple-Choice Questions 1a. No. None of the three definitions of republicanism specifically held that republics should be large and have a diverse population. In fact, the definition of republicanism
Chapter 7 Multiple-Choice Questions 1a. No. None of the three definitions of republicanism specifically held that republics should be large and have a diverse population. In fact, the definition of republicanism
Close Read: Articles of Confederation vs. Constitution
 Close Read: vs. CR Objective CR Introduction What are the differences between the governing systems and structures established by the and the? The were written in, and ratified in. Following a turbulent
Close Read: vs. CR Objective CR Introduction What are the differences between the governing systems and structures established by the and the? The were written in, and ratified in. Following a turbulent
Constitutional Convention
 Constitutional Convention 1 The Framers were delegates who went to the Constitutional Convention at the Pennsylvania State House in Philadelphia to draft a new vision of America s system of government.
Constitutional Convention 1 The Framers were delegates who went to the Constitutional Convention at the Pennsylvania State House in Philadelphia to draft a new vision of America s system of government.
Four reasons we need government
 Four reasons we need government 1. Need for Law and Order - Government makes laws to protect citizens, and punishes those who break the law. Laws provide order in a society. This allows citizens to live
Four reasons we need government 1. Need for Law and Order - Government makes laws to protect citizens, and punishes those who break the law. Laws provide order in a society. This allows citizens to live
