James Madison's Defense of the Constitution at the Virginia Convention (1788)
|
|
|
- Rudolf Hampton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 James Madison's Defense of the Constitution at the Virginia Convention (1788) James Madison, a slight, soft-spoken, and studious man well versed in history, philosophy, and law, was a principal advocate of a stronger central government at both the Federal Convention and then in the Virginia ratifying convention. He had arrived at the former fully prepared both to prosecute the Articles of Confederation for weaknesses dangerous to the well-being of the nation and to present an innovative form of government to replace them. Madison's fellow delegates at the Philadelphia convention accepted many of his ideas, such as allowing the new government to act directly on the people and giving it the right to veto state legislation, and used these ideas to form the foundation of the Constitution. His compatriots did, however, compromise on or reject, as in the matter of representation in the legislative branch, some of his other proposals. Although he initially feared that the compromises had fatally weakened the new Constitution, Madison remained a firm advocate for change. He needed that resolution when the proposed Constitution was attacked by Patrick Henry and others at the Virginia convention, where Madison was forced from his role of prosecutor into that of defender. [Friday, 6 June 1788] Mr. MADISON... [P]rofessions of attachment to the public good, and comparisons of parties, ought not to govern or influence us now. We ought, sir, to examine the Constitution on its own merits solely: we are to inquire whether it will promote the public happiness: its aptitude to produce this desirable object ought to be the exclusive subject of our present researches. In this pursuit, we ought not to address our arguments to the feelings and passions, but to those understandings and judgments which were selected by the people of this country, to decide this great question by a calm and rational investigation. I hope that gentlemen, in displaying their abilities on this occasion, instead of giving opinions and making assertions, will condescend to prove and demonstrate, by a fair and regular discussion.... He [Henry] told us that this Constitution ought to be rejected because it endangered the public liberty, in his opinion, in many instances. Give me leave to make one answer to that observation: Let the dangers which this system is supposed to be replete with be clearly pointed out: if any dangerous and unnecessary powers be given to the general legislature, let them be plainly demonstrated, and let us not rest satisfied with general assertions of danger, without examination. If powers be necessary, apparent danger is not a sufficient reason against conceding them.... I must confess I have not been able to find his usual consistency in the gentleman's argument on this occasion. He informs us that the people of the country are at perfect repose, that is, every man enjoys the fruits of his labor peaceably and securely, and that every thing is in perfect tranquillity and safety. I wish sincerely, sir, this were true. If this be their happy situation, why has every state acknowledged the contrary? Why were deputies from all the states sent to the general Convention? Why have complaints of national and individual distresses been echoed and reechoed throughout the continent? Why has our general government been so shamefully
2 disgraced, and our Constitution violated? Wherefore have laws been made to authorize a change, and wherefore are we now assembled here? A federal government is formed for the protection of its individual members. Ours has attacked itself with impunity. Its authority has been disobeyed and despised. I think I perceive a glaring inconsistency in another of his arguments. He complains of this Constitution, because it requires the consent of at least three fourths of the states to introduce amendments which shall be necessary for the happiness of the people. The assent of so many he urges as too great an obstacle to the admission of salutary amendments, which, he strongly insists, ought to be at the will of a bare majority. We hear this argument, at the very moment we are called upon to assign reasons for proposing a constitution which puts it in the power of nine states to abolish the present inadequate, unsafe, and pernicious Confederation! In the first case, he asserts that a majority ought to have the power of altering the government, when found to be inadequate to the security of public happiness. In the last case, he affirms that even three fourths of the community have not a right to alter a government which experience has proved to be subversive of national felicity! nay, that the most necessary and urgent alterations cannot be made without the absolute unanimity of all the states! Does not the thirteenth article of the Confederation expressly require that no alteration shall be made without the unanimous consent of all the states? Could any thing in theory be more perniciously improvident and injudicious than this submission of the will of the majority to the most trifling minority? Have not experience and practice actually manifested this theoretical inconvenience to be extremely impolite? Let me mention one fact, which I conceive must carry conviction to the mind of any one: the smallest state in the Union has obstructed every attempt to reform the government; that little member has repeatedly disobeyed and counteracted the general authority; nay, has even supplied the enemies of its country with provisions. Twelve states had agreed to certain improvements which were proposed, being thought absolutely necessary to preserve the existence of the general government; but as these improvements, though really indispensable, could not, by the Confederation, be introduced into it without the consent of every state, the refractory dissent of that little state prevented their adoption. The inconveniences resulting from this requisition, of unanimous concurrence in alterations in the Confederation, must be known to every member in this Convention; it is therefore needless to remind them of them. Is it not selfevident that a trifling minority ought not to bind the majority? Would not foreign influence be exerted with facility over a small minority? Would the honorable gentleman agree to continue the most radical defects in the old system, because the petty state of Rhode Island would not agree to remove them? Give me leave to say something of the nature of the government, and to show that it is safe and just to vest it with the power of taxation. There are a number of opinions; but the principal question is, whether it be a federal or consolidated government. In order to judge properly of the question before us, we must consider it minutely in its principal parts. I conceive myself that it is of a mixed nature; it is in a manner unprecedented; we cannot find one express example in the experience of the world. It stands by itself. In some respects it is a government of a federal nature; in others, it is of a consolidated nature. Even if we attend to the manner in which the Constitution is investigated, ratified, and made the act of the people of America, I can say, notwithstanding what the honorable gentleman has alleged, that this government is not completely consolidated, nor is it entirely federal. Who are parties to it? The people but not the people as composing one great body; but the people as composing thirteen sovereignties. Were
3 it, as the gentleman asserts, a consolidated government, the assent of a majority of the people would be sufficient for its establishment; and, as a majority have adopted it already, the remaining states would be bound by the act of the majority, even if they unanimously reprobated it. Were it such a government as is suggested, it would be now binding on the people of this state, without having had the privilege of deliberating upon it. But, sir, no state is bound by it, as it is, without its own consent. Should all the states adopt it, it will be then a government established by the thirteen states of America, not through the intervention of the legislatures, but by the people at large. In this particular respect, the distinction between the existing and proposed governments is very material. The existing system has been derived from the dependent derivative authority of the legislatures of the states; whereas this is derived from the superior power of the people. If we look at the manner in which alterations are to be made in it, the same idea is, in some degree, attended to. By the new system, a majority of the states cannot introduce amendments; nor are all the states required for that purpose; three fourths of them must concur in alterations; in this there is a departure from the federal idea. The members to the national House of Representatives are to be chosen by the people at large, in proportion to the numbers in the respective districts. When we come to the Senate, its members are elected by the states in their equal and political capacity. But had the government been completely consolidated, the Senate would have been chosen by the people in their individual capacity, in the same manner as the members of the other house. Thus it is of a complicated nature; and this complication, I trust, will be found to exclude the evils of absolute consolidation, as well as of a mere confederacy. If Virginia was separated from all the states, her power and authority would extend to all cases: in like manner, were all powers vested in the general government, it would be a consolidated government; but the powers of the federal government are enumerated; it can only operate in certain cases; it has legislative powers on defined and limited objects, beyond which it cannot extend its jurisdiction. But the honorable member has satirized, with peculiar acrimony, the powers given to the general government by this Constitution. I conceive that the first question on this subject is, whether these powers be necessary; if they be, we are reduced to the dilemma of either submitting to the inconvenience or losing the Union. Let us consider the most important of these reprobated powers; that of direct taxation is most generally objected to. With respect to the exigencies of government, there is no question but the most easy mode of providing for them will be adopted. When, therefore, direct taxes are not necessary, they will not be recurred to. It can be of little advantage to those in power to raise money in a manner oppressive to the people. To consult the conveniences of the people will cost them nothing, and in many respects will be advantageous to them. Direct taxes will only be recurred to for great purposes. What has brought on other nations those immense debts, under the pressure of which many of them labor? Not the expenses of their governments, but war. If this country should be engaged in war, and I conceive we ought to provide for the possibility of such a case, how would it be carried on? By the usual means provided from year to year? As our imports will be necessary for the expenses of government and other common exigencies, how are we to carry on the means of defence? How is it possible a war could be supported without money or credit? And would it be possible for a government to have credit without having the power of raising money? No; it would be impossible for any government, in such a case, to defend itself. Then, I say, sir, that it is necessary to establish funds for extraordinary exigencies, and to give this power to the general government; for the utter inutility of previous requisitions on the states is too well known.... This must be obvious to
4 every member here; I think, therefore, that it is necessary, for the preservation of the Union, that this power shall be given to the general government. But it is urged that its consolidated nature, joined to the power of direct taxation, will give it a tendency to destroy all subordinate authority; that its increasing influence will speedily enable it to absorb the state governments. I cannot think this will be the case. If the general government were wholly independent of the governments of the particular states, then, indeed, usurpation might be expected to the fullest extent. But, sir, on whom does this general government depend? It derives its authority from these governments, and from the same sources from which their authority is derived. The members of the federal government are taken from the same men from whom those of the state legislatures are taken. If we consider the mode in which the federal representatives will be chosen, we shall be convinced that the general will never destroy the individual governments;... [Saturday, 7 June 1788] Mr. MADISON. I agree with the honorable gentleman (Mr. Henry) that national splendor and glory are not our objects; but does he distinguish between what will render us secure and happy at home, and what will render us respectable abroad? If we be free and happy at home, we shall be respectable abroad. The Confederation is so notoriously feeble, that foreign nations are unwilling to form any treaties with us; they are apprized that our general government cannot perform any of its engagements, but that they may be violated at pleasure by any of the states. Our violation of treaties already entered into proves this truth unequivocally.... [Tuesday, 24 June 1788] Mr. MADISON. When we consider this government, we ought to make great allowances. We must calculate the impossibility that every state should be gratified in its wishes, and much less that every individual should receive this gratification. It has never been denied, by the friends of the paper on the table, that it has defects; but they do not think that it contains any real danger. They conceive that they will, in all probability, be removed, when experience will show it to be necessary. I beg that gentlemen, in deliberating on this subject, would consider the alternative. Either nine states shall have ratified it, or they will not. If nine states will adopt it, can it be reasonably presumed, or required, that nine states, having freely and fully considered the subject, and come to an affirmative decision, will, upon the demand of a single state, agree that they acted wrong, and could not see its defects tread back the steps which they have taken, and
5 come forward, and reduce it to uncertainty whether a general system shall be adopted or not? Virginia has always heretofore spoken the language of respect to the other states, and she has always been attended to. Will it be that language to call on a great majority of the states to acknowledge that they have done wrong? Is it the language of confidence to say that we do not believe that amendments for the preservation of the common liberty, and general interests, of the states, will be consented to by them? This is the language neither of confidence nor respect.... [From Jonathan Elliot, ed., The Debates in the Several State Conventions on the Adoption of the Federal Constitution, vol. 3 (1836; New York: Burt Franklin Reprints, 1974), pp , 93 96, , 135, [Editorial insertions appear in square brackets Ed.]]
The Constitution. Karen H. Reeves
 The Constitution Karen H. Reeves Toward a New Union Annapolis Convention (Sept. 1786) Met to determine commercial regulation Nationalists called for Constitutional Convention Constitutional Convention
The Constitution Karen H. Reeves Toward a New Union Annapolis Convention (Sept. 1786) Met to determine commercial regulation Nationalists called for Constitutional Convention Constitutional Convention
James Wilson s Speech in the State House Yard, Philadelphia, 6 October 1787
 James Wilson s Speech in the State House Yard, Philadelphia, 6 October 1787 Mr. Wilson then rose, and delivered a long and eloquent speech upon the principles of the Federal Constitution proposed by the
James Wilson s Speech in the State House Yard, Philadelphia, 6 October 1787 Mr. Wilson then rose, and delivered a long and eloquent speech upon the principles of the Federal Constitution proposed by the
Excerpt From Brutus Essay #1
 Excerpt From Brutus Essay #1 Among the most important of the Anti-Federalist essays is those of Brutus, whose essays were first published in the New York Journal. Brutus, whose identity has never been
Excerpt From Brutus Essay #1 Among the most important of the Anti-Federalist essays is those of Brutus, whose essays were first published in the New York Journal. Brutus, whose identity has never been
AP American Government
 AP American Government WILSON, CHAPTER 2 The Constitution OVERVIEW The Framers of the Constitution sought to create a government capable of protecting liberty and preserving order. The solution they chose
AP American Government WILSON, CHAPTER 2 The Constitution OVERVIEW The Framers of the Constitution sought to create a government capable of protecting liberty and preserving order. The solution they chose
The Constitution CHAPTER 2 CHAPTER OUTLINE WITH KEYED-IN RESOURCES
 CHAPTER 2 The Constitution CHAPTER OUTLINE WITH KEYED-IN RESOURCES I. The problem of liberty (THEME A: THE POLITICAL PHILOSOPHY OF THE FOUNDERS) A. Colonists were focused on traditional liberties 1. The
CHAPTER 2 The Constitution CHAPTER OUTLINE WITH KEYED-IN RESOURCES I. The problem of liberty (THEME A: THE POLITICAL PHILOSOPHY OF THE FOUNDERS) A. Colonists were focused on traditional liberties 1. The
Document Based Essay Grade 7 The Constitution
 Document Based Essay Grade 7 The Constitution Directions: The following question is based on the accompanying documents (1-5). This question is designed to test your ability to work with historic documents.
Document Based Essay Grade 7 The Constitution Directions: The following question is based on the accompanying documents (1-5). This question is designed to test your ability to work with historic documents.
CONTROLLING LEGAL PRINCIPLES Free Exercise Clause Decision The Contemplation of Justice McCulloch v. Maryland, 17 U.S. 4 Wheat.
 CONTROLLING LEGAL PRINCIPLES Free Exercise Clause Decision The Contemplation of Justice McCulloch v. Maryland, 17 U.S. 4 Wheat. 316 316 (1819) The Government of the Union, though limited in its powers,
CONTROLLING LEGAL PRINCIPLES Free Exercise Clause Decision The Contemplation of Justice McCulloch v. Maryland, 17 U.S. 4 Wheat. 316 316 (1819) The Government of the Union, though limited in its powers,
Excerpts from Brutus No. 1
 DOCUMENTS of FREEDOM History, Government & Economics through Primary Sources Primary Source: Excerpts from Brutus No. 1, Annotated Excerpts from Brutus No. 1 18 October 1787 To the Citizens of the State
DOCUMENTS of FREEDOM History, Government & Economics through Primary Sources Primary Source: Excerpts from Brutus No. 1, Annotated Excerpts from Brutus No. 1 18 October 1787 To the Citizens of the State
HIST 1301 Part Two. 6: The Republican Experiment
 HIST 1301 Part Two 6: The Republican Experiment The States and the Confederation 1776-1788 During the Revolution, state Governments formed first. 2 min. 40 sec. Each state had a written constitution. Each
HIST 1301 Part Two 6: The Republican Experiment The States and the Confederation 1776-1788 During the Revolution, state Governments formed first. 2 min. 40 sec. Each state had a written constitution. Each
Learning Goal. Main Points 10/24/2012. Discuss the philosophical underpinnings of the U.S. Constitution.
 Learning Goal Discuss the philosophical underpinnings of the U.S. Constitution. Main Points The weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the adoption of a new form of government Federalism becomes
Learning Goal Discuss the philosophical underpinnings of the U.S. Constitution. Main Points The weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the adoption of a new form of government Federalism becomes
Federalist 55 James Madison
 FEDERALIST 319 Federalist James Madison Under the Constitution s original formula, the House would have sixtyfive members. This number was too small according to Anti-Federalists. Publius employs a number
FEDERALIST 319 Federalist James Madison Under the Constitution s original formula, the House would have sixtyfive members. This number was too small according to Anti-Federalists. Publius employs a number
South Carolina s Exposition Against the Tariff of 1828 By John C. Calhoun (Anonymously)
 As John C. Calhoun was Vice President in 1828, he could not openly oppose actions of the administration. Yet he was moving more and more toward the states rights position which in 1832 would lead to nullification.
As John C. Calhoun was Vice President in 1828, he could not openly oppose actions of the administration. Yet he was moving more and more toward the states rights position which in 1832 would lead to nullification.
May, 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania ~Independence Hall~ Leader: George Washington
 May, 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania ~Independence Hall~ Leader: George Washington -May 1787 Philadelphia Met in Independence Hall in Philadelphia George Washington leader -12 of 13 states Rhode Island
May, 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania ~Independence Hall~ Leader: George Washington -May 1787 Philadelphia Met in Independence Hall in Philadelphia George Washington leader -12 of 13 states Rhode Island
James Madison Debates a Bill of Rights
 James Madison Debates a Bill of Rights Framing Question What doubts, concerns, and misgivings arose during the development of the Bill of Rights? Understanding The Bill of Rights, considered today a foundation
James Madison Debates a Bill of Rights Framing Question What doubts, concerns, and misgivings arose during the development of the Bill of Rights? Understanding The Bill of Rights, considered today a foundation
The Constitution. Chapter 2 O Connor and Sabato American Government: Continuity and Change
 The Constitution Chapter 2 O Connor and Sabato American Government: Continuity and Change The Constitution In this chapter we will cover 1. The Origins of a New Nation 2. The Declaration of Independence
The Constitution Chapter 2 O Connor and Sabato American Government: Continuity and Change The Constitution In this chapter we will cover 1. The Origins of a New Nation 2. The Declaration of Independence
Please note: Each segment in this Webisode has its own Teaching Guide
 Please note: Each segment in this Webisode has its own Teaching Guide The Articles of Confederation created a union in which the states had the power to pursue their own self-interests, and the central
Please note: Each segment in this Webisode has its own Teaching Guide The Articles of Confederation created a union in which the states had the power to pursue their own self-interests, and the central
OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS
 CHAPTER 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS The colonists brought with them to North America knowledge of the English political system, including three key ideas about government.
CHAPTER 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS The colonists brought with them to North America knowledge of the English political system, including three key ideas about government.
Articles of Confederation vs. Constitution
 Articles of Confederation vs. Analysis Objective What kind of government was set up by the Articles of Confederation? How does this compare to the US? Directions: Analyze the timeline below to understand
Articles of Confederation vs. Analysis Objective What kind of government was set up by the Articles of Confederation? How does this compare to the US? Directions: Analyze the timeline below to understand
Selections from the Ratification debates in Virginia, June 1788:
 The following selection from the Virginia ratification debates of the U.S. Constitution were take from volume 3: Source: Jonathan Elliot, The debates in the several state conventions on the adoption of
The following selection from the Virginia ratification debates of the U.S. Constitution were take from volume 3: Source: Jonathan Elliot, The debates in the several state conventions on the adoption of
Creating Our. Constitution. Key Terms. delegates equal representation executive federal system framers House of Representatives judicial
 Lesson 2 Creating Our Constitution Key Terms delegates equal representation executive federal system framers House of Representatives judicial What You Will Learn to Do Explain how the Philadelphia Convention
Lesson 2 Creating Our Constitution Key Terms delegates equal representation executive federal system framers House of Representatives judicial What You Will Learn to Do Explain how the Philadelphia Convention
Brutus No. 1. Brutus October 18, To the Citizens of the State of New-York.
 Brutus No. 1 Brutus October 18, 1787 To the Citizens of the State of New-York. [1] When the public is called to investigate and decide upon a question in which not only the present members of the community
Brutus No. 1 Brutus October 18, 1787 To the Citizens of the State of New-York. [1] When the public is called to investigate and decide upon a question in which not only the present members of the community
The first question made in the cause is, has Congress power to incorporate a bank?...
 The Federal Government Is Supreme over the States (1819) -John Marshall (1755-1835) In the case now to be determined, the defendant, a sovereign State, denies the obligation of a law enacted by the legislature
The Federal Government Is Supreme over the States (1819) -John Marshall (1755-1835) In the case now to be determined, the defendant, a sovereign State, denies the obligation of a law enacted by the legislature
Four reasons we need government
 Four reasons we need government 1. Need for Law and Order - Government makes laws to protect citizens, and punishes those who break the law. Laws provide order in a society. This allows citizens to live
Four reasons we need government 1. Need for Law and Order - Government makes laws to protect citizens, and punishes those who break the law. Laws provide order in a society. This allows citizens to live
Lesson 13 Writing and Ratifying the Constitution
 Lesson 13 Writing and Ratifying the Constitution Doct r. FRANKLIN looking towards the Presidents Chair, at the back of which a rising sun happened to be painted, observed to a few members near him, that
Lesson 13 Writing and Ratifying the Constitution Doct r. FRANKLIN looking towards the Presidents Chair, at the back of which a rising sun happened to be painted, observed to a few members near him, that
Handout B: Madison EXCERPTS FROM FEDERALIST NO. 47 BY JAMES MADISON. DOCUMENTS of FREEDOM History, Government & Economics through Primary Sources
 DOCUMENTS of FREEDOM History, Government & Economics through Primary Sources Unit 2: The Purpose of Government Reading: Separation of Powers and Checks and Balances Activity: Montesquieu and Madison Handout
DOCUMENTS of FREEDOM History, Government & Economics through Primary Sources Unit 2: The Purpose of Government Reading: Separation of Powers and Checks and Balances Activity: Montesquieu and Madison Handout
Close Read: Articles of Confederation vs. Constitution
 Close Read: vs. CR Objective CR Introduction What are the differences between the governing systems and structures established by the and the? The were written in, and ratified in. Following a turbulent
Close Read: vs. CR Objective CR Introduction What are the differences between the governing systems and structures established by the and the? The were written in, and ratified in. Following a turbulent
The Critical Period The early years of the American Republic
 The Critical Period 1781-1789 The early years of the American Republic America after the War New Political Ideas: - Greater power for the people Republic: Represent the Public America after the War State
The Critical Period 1781-1789 The early years of the American Republic America after the War New Political Ideas: - Greater power for the people Republic: Represent the Public America after the War State
10/6/11. A look at the history and organization of US Constitution
 A look at the history and organization of US Constitution During Revolution, the states created a confederation. Loose association of states. Continental Congress responsible to war effort during the Revolution.
A look at the history and organization of US Constitution During Revolution, the states created a confederation. Loose association of states. Continental Congress responsible to war effort during the Revolution.
STANDARD: CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION. Philadelphia, PA- May 25-September 17, 1787
 STANDARD: 8-3.2 CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Philadelphia, PA- May 25-September 17, 1787 Let s Think? Reasons for a Convention Called to address problems in governing the U.S. In 1787- U.S. was operating
STANDARD: 8-3.2 CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Philadelphia, PA- May 25-September 17, 1787 Let s Think? Reasons for a Convention Called to address problems in governing the U.S. In 1787- U.S. was operating
Objectives: Students will be able to explain that the success and failures of the articles of confederation and be able to give some examples of each.
 Day 1 Objectives: Students will be able to explain that the success and failures of the articles of confederation and be able to give some examples of each. Procedure: Do Now: Why is it important to have
Day 1 Objectives: Students will be able to explain that the success and failures of the articles of confederation and be able to give some examples of each. Procedure: Do Now: Why is it important to have
U.S. Constitution PSCI 1040
 PSCI 1040 Purposes of a Constitution Organize and empower the government Limit the powers of government. Many consider limited government to be the essence of constitutional government. 2 Articles of Confederation
PSCI 1040 Purposes of a Constitution Organize and empower the government Limit the powers of government. Many consider limited government to be the essence of constitutional government. 2 Articles of Confederation
Chapter 5 section 3: Creating the Constitution textbook pages
 Chapter 5 section 3: Creating the Constitution textbook pages 163-168 The Big Idea A new constitution provided a framework for a stronger national government. Main Idea 1:The Constitutional Convention
Chapter 5 section 3: Creating the Constitution textbook pages 163-168 The Big Idea A new constitution provided a framework for a stronger national government. Main Idea 1:The Constitutional Convention
Key Constitutional Concepts: Creating a Constitution
 Key Constitutional Concepts: Creating a Constitution Author: A Project of: The Annenberg Foundation Trust at Sunnylands About this Lesson The first section of the film Key Constitutional Concepts examines
Key Constitutional Concepts: Creating a Constitution Author: A Project of: The Annenberg Foundation Trust at Sunnylands About this Lesson The first section of the film Key Constitutional Concepts examines
American Political History, Topic 4: The United States Constitution and Jefferson to Madison (1787)
 Background: The United States Constitution is the God-inspired rubber-and-metal vehicle that carries the American ideals of life, liberty, the pursuit of happiness, equality, justice, and republican government
Background: The United States Constitution is the God-inspired rubber-and-metal vehicle that carries the American ideals of life, liberty, the pursuit of happiness, equality, justice, and republican government
the states. decisions within its own borders) 1. A central government that would represent all 2. State sovereignty (the power to make
 The United States has operated under two constitutions. The first, The Articles of Confederation, was in effect from March 1, 1781. The Articles tried to balance two very different ideas: 1. A central
The United States has operated under two constitutions. The first, The Articles of Confederation, was in effect from March 1, 1781. The Articles tried to balance two very different ideas: 1. A central
National Endowment for the Humanities Summer Seminars and Institutes for School Teachers
 National Endowment for the Humanities Summer Seminars and Institutes for School Teachers George Washington and His Legacy: Myths, Symbols, and Reality A Federal Man: George Washington at the Constitutional
National Endowment for the Humanities Summer Seminars and Institutes for School Teachers George Washington and His Legacy: Myths, Symbols, and Reality A Federal Man: George Washington at the Constitutional
Essay 1. Brutus ESSAY I
 ESSAY I 221 Essay 1 Brutus Supporters of the Constitution dubbed their opponents Anti-Federalists. Opponents resented the label, but it stuck. The Anti-Federalist author Brutus most likely New York lawyer
ESSAY I 221 Essay 1 Brutus Supporters of the Constitution dubbed their opponents Anti-Federalists. Opponents resented the label, but it stuck. The Anti-Federalist author Brutus most likely New York lawyer
Constitution Unit Test
 Constitution Unit Test Eighth Amendment Excessive fines cannot be imposed. Excessive bail cannot be required. 1. Which sentence completes this diagram? A. People cannot be forced to be witnesses against
Constitution Unit Test Eighth Amendment Excessive fines cannot be imposed. Excessive bail cannot be required. 1. Which sentence completes this diagram? A. People cannot be forced to be witnesses against
US Government Module 2 Study Guide
 US Government Module 2 Study Guide 2.01 Revolutionary Ideas The Declaration of Independence contains an introduction, list of grievances, and formal statement of independence. The principle of natural
US Government Module 2 Study Guide 2.01 Revolutionary Ideas The Declaration of Independence contains an introduction, list of grievances, and formal statement of independence. The principle of natural
American History 11R
 American History 11R Setting of the Philadelphia Convention Early decision to re-write, rather than tinker with the Articles of Confederation Open agreement secretly arrived at--washington's plea Intent
American History 11R Setting of the Philadelphia Convention Early decision to re-write, rather than tinker with the Articles of Confederation Open agreement secretly arrived at--washington's plea Intent
The States: Experiments in Republicanism State constitutions served as experiments in republican government The people demand written constitutions
 The States: Experiments in Republicanism State constitutions served as experiments in republican government The people demand written constitutions provide clear definition of rights describe clear limits
The States: Experiments in Republicanism State constitutions served as experiments in republican government The people demand written constitutions provide clear definition of rights describe clear limits
Federalists and Antifederalists January 25, 2011 Biographies of the Nation Danice Toyias,
 Constitution Debate, pg. 1 of 1 Federalists and Antifederalists January 25, 2011 Biographies of the Nation Danice Toyias, danice.toyias@mchce.net Lesson Topic and Focus This lesson utilizes what I call
Constitution Debate, pg. 1 of 1 Federalists and Antifederalists January 25, 2011 Biographies of the Nation Danice Toyias, danice.toyias@mchce.net Lesson Topic and Focus This lesson utilizes what I call
Ratification of the US Constitution in New York, 1788
 Introduction Ratification of the US Constitution in New York, 1788 This unique copy of the US Constitution was printed by Claxton and Babcock in Albany, New York, between February 11 and March 21, 1788.
Introduction Ratification of the US Constitution in New York, 1788 This unique copy of the US Constitution was printed by Claxton and Babcock in Albany, New York, between February 11 and March 21, 1788.
US History, Ms. Brown Website: dph7history.weebly.com
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #70 Aims: SWBAT understand and explain the debate over representation SWBAT identify and explain the Virginia Plan and
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #70 Aims: SWBAT understand and explain the debate over representation SWBAT identify and explain the Virginia Plan and
1 st United States Constitution. A. loose alliance of states. B. Congress lawmaking body. C. 9 states had to vote to pass laws
 1 st United States Constitution A. loose alliance of states B. Congress lawmaking body C. 9 states had to vote to pass laws D. each state had 1 vote in Congress Northwest Ordinance / Land Ordinance division
1 st United States Constitution A. loose alliance of states B. Congress lawmaking body C. 9 states had to vote to pass laws D. each state had 1 vote in Congress Northwest Ordinance / Land Ordinance division
Chapter 3 The Age of Constitution Writing
 Page 21 Chapter 3 The Age of Constitution Writing ven before independence was declared, seven colonies had begun writing new constitutions. Four Eothers followed shortly after July 4,1776. At the same
Page 21 Chapter 3 The Age of Constitution Writing ven before independence was declared, seven colonies had begun writing new constitutions. Four Eothers followed shortly after July 4,1776. At the same
America: The Last Best Hope Chapter 4 Reflection and Choice
 America: The Last Best Hope Chapter 4 Reflection and Choice 1. Under the Articles of Confederation, Congress had all of the following powers EXCEPT A settle disputes between the states B borrow money C
America: The Last Best Hope Chapter 4 Reflection and Choice 1. Under the Articles of Confederation, Congress had all of the following powers EXCEPT A settle disputes between the states B borrow money C
Shays. Daniel Shay 1784 to 1785, unfair taxes, debt and foreclosure Farmer s rebellion to overthrow Mass. Govt.
 Shays Daniel Shay 1784 to 1785, unfair taxes, debt and foreclosure Farmer s rebellion to overthrow Mass. Govt. 1. Constitutional Convention: May to Sept. 1787 2. Divided Convention 9/13 states needed to
Shays Daniel Shay 1784 to 1785, unfair taxes, debt and foreclosure Farmer s rebellion to overthrow Mass. Govt. 1. Constitutional Convention: May to Sept. 1787 2. Divided Convention 9/13 states needed to
Letters from the Federal Farmer, No December 1787
 Letters from the Federal Farmer, No. 7 31 December 1787 Among the hundreds of pamphlets, newspaper articles, and published speeches opposing the new Constitution, a few were judged especially outstanding
Letters from the Federal Farmer, No. 7 31 December 1787 Among the hundreds of pamphlets, newspaper articles, and published speeches opposing the new Constitution, a few were judged especially outstanding
Table Annexed to Article: Why is March the Fourth March the Fourth? Excerpts from the Journals of the Continental Congress
 Purdue University From the SelectedWorks of Peter J. Aschenbrenner January, 2015 Table Annexed to Article: Why is March the Fourth March the Fourth? Excerpts from the Journals of the Continental Congress
Purdue University From the SelectedWorks of Peter J. Aschenbrenner January, 2015 Table Annexed to Article: Why is March the Fourth March the Fourth? Excerpts from the Journals of the Continental Congress
The Clay Compromise Measures by John C. Calhoun March 4, 1850
 The Clay Compromise Measures by John C. Calhoun March 4, 1850 John C. Calhoun This is among John C. Calhoun's most famous speeches. He was too ill to deliver it himself, so it was read by another senator
The Clay Compromise Measures by John C. Calhoun March 4, 1850 John C. Calhoun This is among John C. Calhoun's most famous speeches. He was too ill to deliver it himself, so it was read by another senator
Vocabulary Match-Up. Name Date Period Workbook Activity
 Name Date Period Workbook Activity Vocabulary Match-Up Chapter 2, Lesson 1 7 Part A Directions Match the vocabulary word in Column 1 with its definition in Column 2. Write the correct letter on each line.
Name Date Period Workbook Activity Vocabulary Match-Up Chapter 2, Lesson 1 7 Part A Directions Match the vocabulary word in Column 1 with its definition in Column 2. Write the correct letter on each line.
The U.S. Constitution: Who, What, Where, When, Why & How
 The U.S. Constitution: Who, What, Where, When, Why & How 'a ^Va&o/z Fighting between the American colonists and British forces under King George III was in its second year when the Declaration of Independence
The U.S. Constitution: Who, What, Where, When, Why & How 'a ^Va&o/z Fighting between the American colonists and British forces under King George III was in its second year when the Declaration of Independence
understanding CONSTITUTION
 understanding the CONSTITUTION Contents The Articles of Confederation The Constitutional Convention The Principles of the Constitution The Preamble The Legislative Branch The Executive Branch The Judicial
understanding the CONSTITUTION Contents The Articles of Confederation The Constitutional Convention The Principles of the Constitution The Preamble The Legislative Branch The Executive Branch The Judicial
Constitutional Convention
 The Constitution LT#1: Explain the important decisions and compromises made at the Constitutional Convention. LT#2: Explain the set up and operation of the Federal government. LT#3: Identify and discuss
The Constitution LT#1: Explain the important decisions and compromises made at the Constitutional Convention. LT#2: Explain the set up and operation of the Federal government. LT#3: Identify and discuss
The Debates in the Several State Conventions on the Adoption of the Federal Constitution [Elliot's Debates, Volume 3]
![The Debates in the Several State Conventions on the Adoption of the Federal Constitution [Elliot's Debates, Volume 3] The Debates in the Several State Conventions on the Adoption of the Federal Constitution [Elliot's Debates, Volume 3]](/thumbs/94/119857644.jpg) The Debates in the Several State Conventions on the Adoption of the Federal Constitution [Elliot's Debates, Volume 3] Monday, June 16, 1788. Mr. GEORGE MASON still thought that there ought to be some express
The Debates in the Several State Conventions on the Adoption of the Federal Constitution [Elliot's Debates, Volume 3] Monday, June 16, 1788. Mr. GEORGE MASON still thought that there ought to be some express
CONSTITUTIONAL DOCUMENTS OF THE REIGN OF JAMES I A D WITH AN HISTORICAL COMMENTARY
 CONSTITUTIONAL DOCUMENTS OF THE REIGN OF JAMES I A D 1603 1625 WITH AN HISTORICAL COMMENTARY CONSTITUTIONAL DOCUMENTS OF THE PDF THE CONSTITUTION OF THE UNITED STATES THE CONSTITUTION OF THE UNITED STATES:
CONSTITUTIONAL DOCUMENTS OF THE REIGN OF JAMES I A D 1603 1625 WITH AN HISTORICAL COMMENTARY CONSTITUTIONAL DOCUMENTS OF THE PDF THE CONSTITUTION OF THE UNITED STATES THE CONSTITUTION OF THE UNITED STATES:
Perspectives from FSF Scholars May 24, 2018 Vol. 13, No. 19
 Perspectives from FSF Scholars May 24, 2018 Vol. 13, No. 19 The Framers Establish an Administrative Constitution Introduction and Summary by Joseph Postell* Does the Constitution provide any guiding principles
Perspectives from FSF Scholars May 24, 2018 Vol. 13, No. 19 The Framers Establish an Administrative Constitution Introduction and Summary by Joseph Postell* Does the Constitution provide any guiding principles
Name: 8 th Grade U.S. History. STAAR Review. Constitution
 8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Constitution FORT BURROWS 2018 VOCABULARY Confederation - A group of loosely connected nations or states that work together for mutual benefit. Republic - A system
8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Constitution FORT BURROWS 2018 VOCABULARY Confederation - A group of loosely connected nations or states that work together for mutual benefit. Republic - A system
Constitutional Convention. May 1787
 Constitutional Convention May 1787 Annapolis Convention September 11 to September 14, 1786 Annapolis, Maryland Purpose - How to fix the articles of confederation Alexander Hamilton (New York) MUST resolve
Constitutional Convention May 1787 Annapolis Convention September 11 to September 14, 1786 Annapolis, Maryland Purpose - How to fix the articles of confederation Alexander Hamilton (New York) MUST resolve
4.6. AP American Government and Politics. John Locke Précis
 John Locke Précis After reading John Locke s Second Treatise of Civil Government, write a précis (a summary of the main ideas and points) about the treatise in 150 words or less. Final product must be
John Locke Précis After reading John Locke s Second Treatise of Civil Government, write a précis (a summary of the main ideas and points) about the treatise in 150 words or less. Final product must be
Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution
 Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution The Articles of Confederation After declaring independence from Britain in 1776, Congress tried to unite the states under one national government. However, many feared
Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution The Articles of Confederation After declaring independence from Britain in 1776, Congress tried to unite the states under one national government. However, many feared
Congress had the power over relations, foreign, with the capacity to create alliance and form
 Surname 1 Name: Course: Instructor: Date: The Articles of Confederation were the first written constitution of the United States. These Articles created a legislature where there was equal representation
Surname 1 Name: Course: Instructor: Date: The Articles of Confederation were the first written constitution of the United States. These Articles created a legislature where there was equal representation
Quarter One: Unit Four
 SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will identify the weaknesses of the government under the Articles of Confederation (i.e.,
SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will identify the weaknesses of the government under the Articles of Confederation (i.e.,
The College Board Advanced Placement Examination. AMERICAN HISTORY SECTION I1 (Suggested writing time-40 minutes)
 The College Board Advanced Placement Examination AMERICAN HISTORY SECTION I1 (Suggested writing time-40 minutes) Directions: The following question requires you to construct a coherent essay that integrates
The College Board Advanced Placement Examination AMERICAN HISTORY SECTION I1 (Suggested writing time-40 minutes) Directions: The following question requires you to construct a coherent essay that integrates
Organization & Agreements
 Key Players Key Players Key Players George Washington unanimously chosen to preside over the meetings. Benjamin Franklin now 81 years old. Gouverneur Morris wrote the final draft. James Madison often called
Key Players Key Players Key Players George Washington unanimously chosen to preside over the meetings. Benjamin Franklin now 81 years old. Gouverneur Morris wrote the final draft. James Madison often called
Charles de Montesquieu
 Unit III He first created the idea of consent of the governed where people have a vote in who leads them (democracy). Every person has the right to life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness. John Locke
Unit III He first created the idea of consent of the governed where people have a vote in who leads them (democracy). Every person has the right to life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness. John Locke
Creating the Constitution. Complete the InQuizitive exercises for Chapter 2 as you work through this outline.
 Creating the Constitution The road to the ruling document Complete the InQuizitive exercises for Chapter 2 as you work through this outline. Knowing the exact dates of the events below is not essential,
Creating the Constitution The road to the ruling document Complete the InQuizitive exercises for Chapter 2 as you work through this outline. Knowing the exact dates of the events below is not essential,
Magruder s American Government
 Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 Our Political Beginnings
Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 Our Political Beginnings
Name: Section: Date:
 Directions: Answer the following multiple choice questions. 1. In 1774, the first Continental Congress took place in what city? a. New York City b. Jamestown c. Philadelphia d. Boston I. The deteriorating
Directions: Answer the following multiple choice questions. 1. In 1774, the first Continental Congress took place in what city? a. New York City b. Jamestown c. Philadelphia d. Boston I. The deteriorating
We The People Packet. Chapter 12- Objective (8.1A,B,C): Describe who attended the Philadelphia Convention & how it was organized.
 We The People Packet Chapter 12- Objective (8.1A,B,C): Describe who attended the Philadelphia Convention & how it was organized. When was the Philadelphia Convention held? What was the intended goal of
We The People Packet Chapter 12- Objective (8.1A,B,C): Describe who attended the Philadelphia Convention & how it was organized. When was the Philadelphia Convention held? What was the intended goal of
Establishing A New Government: Creating a Government. Chapter 4 Concept 2
 Establishing A New Government: Creating a Government Chapter 4 Concept 2 4.2 Creating a Government How did the decisions made at the Constitutional Convention affect the balance of power in the new nation?
Establishing A New Government: Creating a Government Chapter 4 Concept 2 4.2 Creating a Government How did the decisions made at the Constitutional Convention affect the balance of power in the new nation?
Ratification of the Constitution. Issues
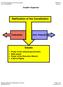 Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
Creating a Nation Test Review
 Creating a Nation Test Review Question #1: Multiple Choice The Northwest ordinance of 1787 is important because. A. It sent troops to the Northwest to protect the colonies from Native Americans. B. It
Creating a Nation Test Review Question #1: Multiple Choice The Northwest ordinance of 1787 is important because. A. It sent troops to the Northwest to protect the colonies from Native Americans. B. It
Do not copy, post, or distribute. Ladies and gentlemen, the presidents of the United States. JAMES MADISON S NOTES OF THE FEDERAL CONVENTION* (1787)
 CHAPTER 1 JAMES MADISON S NOTES OF THE FEDERAL CONVENTION* (1787) Ladies and gentlemen, the presidents of the United States. A typographical error, right? Not if certain delegates to the Constitutional
CHAPTER 1 JAMES MADISON S NOTES OF THE FEDERAL CONVENTION* (1787) Ladies and gentlemen, the presidents of the United States. A typographical error, right? Not if certain delegates to the Constitutional
How does the U.S. Constitution reflect both the founders distrust of government AND democracy?
 How does the U.S. Constitution reflect both the founders distrust of government AND democracy? Alexander Hamilton All communities divide themselves into the few and the many. The first are the rich and
How does the U.S. Constitution reflect both the founders distrust of government AND democracy? Alexander Hamilton All communities divide themselves into the few and the many. The first are the rich and
Articles of Confederation
 Articles of Confederation What was the nation facing after the Revolutionary War? -An agrarian or agricultural nation (Farmland) -A Confederate Nation-joined by an agreement or treaty -Debt -Major economic
Articles of Confederation What was the nation facing after the Revolutionary War? -An agrarian or agricultural nation (Farmland) -A Confederate Nation-joined by an agreement or treaty -Debt -Major economic
Section 4 at a Glance The Constitutional Convention
 Section 4 at a Glance The Constitutional Convention At the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia, delegates debated competing plans the Virginia Plan and the New Jersey Plan for how the new government
Section 4 at a Glance The Constitutional Convention At the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia, delegates debated competing plans the Virginia Plan and the New Jersey Plan for how the new government
How Shall We Govern Ourselves?
 How Shall We Govern Ourselves? The Articles of Confederation America s First Constitution What kind of government would the FREEDOM loving Americans create to balance LIBERTY with enough AUTHORITY to get
How Shall We Govern Ourselves? The Articles of Confederation America s First Constitution What kind of government would the FREEDOM loving Americans create to balance LIBERTY with enough AUTHORITY to get
: Objections to the Constitution, George Mason
 : We would sooner submit to a foreign power Records of the Federal Convention of 1787 Resolution Proposed by Mr. Patterson (New Jersey), June 15, 1787 At the onset of the Constitutional Convention, Governor
: We would sooner submit to a foreign power Records of the Federal Convention of 1787 Resolution Proposed by Mr. Patterson (New Jersey), June 15, 1787 At the onset of the Constitutional Convention, Governor
Chapter 3 Constitution. Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook
 Chapter 3 Constitution Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on www.pknock.com Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from
Chapter 3 Constitution Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on www.pknock.com Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from
Judicial Veto and the Ohio Plan
 Washington University Law Review Volume 9 Issue 1 January 1923 Judicial Veto and the Ohio Plan Edward Selden Follow this and additional works at: http://openscholarship.wustl.edu/law_lawreview Part of
Washington University Law Review Volume 9 Issue 1 January 1923 Judicial Veto and the Ohio Plan Edward Selden Follow this and additional works at: http://openscholarship.wustl.edu/law_lawreview Part of
A More Perfect Union Listening Guide Key Questions for A More Perfect Union lesson one:
 Questions for A More Perfect Union lesson one: 1.The US Constitution was written in what year? 1787 2.Who was the country s first president? George Washington 3.Who was the driving force behind the development
Questions for A More Perfect Union lesson one: 1.The US Constitution was written in what year? 1787 2.Who was the country s first president? George Washington 3.Who was the driving force behind the development
Federalist 62 James Madison
 FEDERALIST 62 331 Federalist 62 James Madison The Senate, with its equal representation of each state and members selected by state legislatures, was at once a concession to small states and a bulwark
FEDERALIST 62 331 Federalist 62 James Madison The Senate, with its equal representation of each state and members selected by state legislatures, was at once a concession to small states and a bulwark
During the, the majority of delegates voted to declare independence from Britain. What is known as the official beginning of the America Revolution?
 What is known as the official beginning of the America Revolution? A. The Stamp Act B. Boston Tea Party C. Quartering Act D. Battle of Lexington and Concord During the, the majority of delegates voted
What is known as the official beginning of the America Revolution? A. The Stamp Act B. Boston Tea Party C. Quartering Act D. Battle of Lexington and Concord During the, the majority of delegates voted
Creating the Constitution
 Creating the Constitution Constitutional Convention Philadelphia 1787 Met in Secret Goal: Alter or abolish fix the old system or create a new one Needed to tweak the articles Focus of Convention Meeting
Creating the Constitution Constitutional Convention Philadelphia 1787 Met in Secret Goal: Alter or abolish fix the old system or create a new one Needed to tweak the articles Focus of Convention Meeting
What is Compromise? My friend wanted a boat more than anything. His wife kept refusing, but he bought one anyway. "I'll tell you what," he told her,
 What is Compromise? My friend wanted a boat more than anything. His wife kept refusing, but he bought one anyway. "I'll tell you what," he told her, "In the spirit of compromise, why don't you name the
What is Compromise? My friend wanted a boat more than anything. His wife kept refusing, but he bought one anyway. "I'll tell you what," he told her, "In the spirit of compromise, why don't you name the
Major Problem. Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government.
 The Constitution Major Problem Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government. Why? Feared a government like King George The Constitutional
The Constitution Major Problem Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government. Why? Feared a government like King George The Constitutional
The Coming of Independence. Ratifying the Constitution
 C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government 1 SECTION 1 SECTION 2 SECTION 3 SECTION 4 SECTION 5 Our Political Beginnings The Coming of Independence The Critical Period Creating the Constitution Ratifying
C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government 1 SECTION 1 SECTION 2 SECTION 3 SECTION 4 SECTION 5 Our Political Beginnings The Coming of Independence The Critical Period Creating the Constitution Ratifying
The House of Representatives shall be composed of Members chosen every second Year by the People of the several States.
 Guiding Principles of the Constitution (HA) Over the years, the Constitution has acquired an almost sacred status for Americans. Part of the reason for that is its durability: the Constitution has survived,
Guiding Principles of the Constitution (HA) Over the years, the Constitution has acquired an almost sacred status for Americans. Part of the reason for that is its durability: the Constitution has survived,
Module 1.2 U.S. Constitutional Framework. Constitutional Trivia! Overview of Lecture 6/4/2008
 Module 1.2 U.S. Constitutional Framework Prof. Bryan McQuide University of Idaho Summer 2008 Constitutional Trivia! Which of the following Presidents signed the U.S. Constitution? George Washington John
Module 1.2 U.S. Constitutional Framework Prof. Bryan McQuide University of Idaho Summer 2008 Constitutional Trivia! Which of the following Presidents signed the U.S. Constitution? George Washington John
Antifederalist No. 84. On the Lack of a Bill of Rights
 Antifederalist No. 84 On the Lack of a Bill of Rights By "Brutus." When a building is to be erected which is intended to stand for ages, the foundation should be firmly laid. The Constitution proposed
Antifederalist No. 84 On the Lack of a Bill of Rights By "Brutus." When a building is to be erected which is intended to stand for ages, the foundation should be firmly laid. The Constitution proposed
Constitutional Convention
 Constitutional Convention I INTRODUCTION Constitutional Convention, meeting during the summer of 1787 at which delegates from 12 states wrote the Constitution of the United States. At the convention in
Constitutional Convention I INTRODUCTION Constitutional Convention, meeting during the summer of 1787 at which delegates from 12 states wrote the Constitution of the United States. At the convention in
Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50
 Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50 The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from religious persecution Economic opportunity Independent
Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50 The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from religious persecution Economic opportunity Independent
Learning Check. You CAN use your notes. You CAN NOT use your neighbor!
 Learning Check You CAN use your notes. You CAN NOT use your neighbor! Constitution and Bill of Rights QC Standards B.1.i. Interpret the ideas and principles expressed in the U.S. Constitution B.1.j. Explain
Learning Check You CAN use your notes. You CAN NOT use your neighbor! Constitution and Bill of Rights QC Standards B.1.i. Interpret the ideas and principles expressed in the U.S. Constitution B.1.j. Explain
2. Divided Convention. 3. Inside the Constitution. Constitution replaced the Articles---becomes the law of the land.
 2. Divided Convention notes7 9/13 states needed to ratify (to approve) Political parties begin Federalists: supported the Constitution The Federalist ---essays support Constitution Anti-Federalists: against
2. Divided Convention notes7 9/13 states needed to ratify (to approve) Political parties begin Federalists: supported the Constitution The Federalist ---essays support Constitution Anti-Federalists: against
ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION TO THE CONSTITUTION
 ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION TO THE CONSTITUTION Articles of Confederation The representatives of the thirteen states agree to create a confederacy called the United States of America, in which each state
ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION TO THE CONSTITUTION Articles of Confederation The representatives of the thirteen states agree to create a confederacy called the United States of America, in which each state
Chapter 2 The Politics of the American Founding
 Multiple Choice Chapter 2 The Politics of the American Founding 1. Early colonists came to America: a. for a wide range of economic and political agendas as well as for religious and philosophical reasons
Multiple Choice Chapter 2 The Politics of the American Founding 1. Early colonists came to America: a. for a wide range of economic and political agendas as well as for religious and philosophical reasons
By the mid-1780s many people in the United States recognized that the Articles of
 Constitutional Convention By the mid-1780s many people in the United States recognized that the Articles of Confederation were not taking the country in a desirable direction. Because of this, a convention
Constitutional Convention By the mid-1780s many people in the United States recognized that the Articles of Confederation were not taking the country in a desirable direction. Because of this, a convention
Federalists versus Anti-Federalists
 Federalists versus Anti-Federalists Overview In this lesson, students will explore the Articles of Confederation and the revisions that created the Constitution of 1787. Students will analyze and assume
Federalists versus Anti-Federalists Overview In this lesson, students will explore the Articles of Confederation and the revisions that created the Constitution of 1787. Students will analyze and assume
