FEDERALISM SS.7.C.3.4 Identify the relationship and division of powers between the federal government and state governments.
|
|
|
- Jack Taylor
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FEDERALISM SS.7.C.3.4 Identify the relationship and division of powers between the federal government and state governments. TABLE OF CONTENTS Lesson Summary... 2 Suggested Student Activity Sequence... 3 Student Activity Sheets & Reading Materials... 5 Sources... 8 Answer Keys... 9 Civics Content Vocabulary Essential Teacher Content Background Information SS.7.C.3.4 Updated 8/17 1
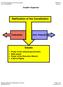
2 Lesson Summary Essential Questions What is federalism? How is power divided between the federal and state governments? NGSSS Benchmark SS.7.C.3.4 Identify the relationship and division of powers between the federal government and state governments. Florida Standards LAFS.68.RH.1.2 LAFS.68.RH.2.4 LAFS.68.WHST.1.2 LAFS.68.WHST.3.9 LAFS.68.WHST.4.10 LAFS.7.SL.1.1 MAFS.K12.MP.1.1 Overview In this lesson, students will be introduced to the concept of federalism by reading text, examining the U.S. Constitution and applying their understanding to various examples and scenarios. Learning Goals/Benchmark Clarifications Students will define the system of federalism. Students will analyze how federalism limits government power. Students will compare concurrent powers, enumerated powers, reserved powers, and delegated powers as they relate to state and federal government. Students will analyze the issues related to the Tenth Amendment of the U.S. Constitution. Benchmark Content Limits Items will not ask students to evaluate the efficacy of the Tenth Amendment. Civics EOC Reporting Category Reporting Category 4 Organization and Function of Government Suggested Time Frame Two minute class periods Civics Content Vocabulary concurrent powers, delegated powers, enumerated powers, federalism, reserved powers, Supremacy Clause, and Tenth Amendment Instructional Strategies Direct instruction Reading of complex text Cooperative learning Materials Copies of the U.S. Constitution for student use and to be projected on the board for the whole class: ( Student activity sheets and reading materials: Federalism Who Has the Power? Lesson Activities and Daily Schedule Please use the chart below to track activity completion. Day Task # Steps in Lesson Day One Day Two Description Task Hook Activity Task Federalism Activity Sheet Task Tenth Amendment Activity Task Who Has the Power? Activity Task Who Has the Power? Activity (continued) Task Tenth Amendment Scenarios and the Supremacy Clause Task Federalism and Limited Government Task 7 28 Checking for Understanding Completed? Yes/No SS.7.C.3.4 Updated 8/17 2
3 Suggested Student Activity Sequence 1. To begin this lesson, list the following civics content vocabulary terms with definitions on the board: federal government, state government and local government. 2. Pass out the Federalism student activity sheet and review the three terms as a whole class. 3. Instruct students to work independently to create a visual representation for each of the vocabulary terms. 4. Have students share out. 5. Instruct students to return their attention back to the activity sheet. 6. Read aloud the definition of federalism. 7. Explain to students the following points about federalism and instruct students to take notes on their activity sheet. Federalism is a core democratic principle of our government. In a federal system, the power of the government is distributed to different levels of government: national (federal), state, and local. The national government is also referred to as the federal government. 8. Project the flow chart from page one of the activity sheet. Instruct students to read aloud the next two paragraphs on the activity sheet and discuss key points to ensure student understanding. 9. Review the graphic organizer on page two of the activity sheet as a whole class. 10. Instruct students to work independently to define federalism in their own words on page two of the activity sheet. Teacher Note: Monitor student work to confirm student understanding or misconceptions. 11. Ask students to place their copies of the U.S. Constitution on their desk. 12. Remind students that state powers are referred to as reserved powers. States have the powers that are not granted to the federal government in the U.S. Constitution. Teacher Note: A helpful way for students to remember that reserved powers are for state governments is to point out that the word reserved has the letter s in it and the word state begins with the letter s. 13. Instruct students to turn to the Tenth Amendment of the U.S. Constitution, and have a student read it aloud. The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people. 14. Explain to students the following points about the Tenth Amendment. The Tenth Amendment was included in the Bill of Rights to further define the balance of power between the federal government and the states. The amendment says that the federal government has only those powers specifically granted by the U.S. Constitution. Some of the powers of the federal government are the power to declare war, collect taxes, and regulate interstate business activities. According to the amendment, any power not listed is left to the states or the people. Although the amendment does not specify what the state powers are, the U.S. Supreme Court has ruled that laws affecting marriage, divorce, adoption, commerce that occurs within a state s borders, and local law enforcement are among the powers specifically reserved to the states or the people. 15. Pass out the Who Has the Power? student activity sheet. 16. Explain to students that citizens in the community have been asking questions and they aren t sure which level of government they should approach to have their questions answered. Their task is to identify the level of government (local, state, and/or federal) and the type of power that level of government has to solve each of the questions on the list. 17. Provide time for students to work with their partner or in a small group to complete the activity sheet. SS.7.C.3.4 Updated 8/17 3
4 18. Review the activity sheet as a whole class. 19. Ask the students to share out any answers they were surprised by or they have questions about. 20. Pose the following questions to the class for reflection and discussion: Why is it important for citizens to know the powers of each level of government? Why do you think different levels of government are responsible for different things? What would be different if there was only a federal (national) government and no state or local entities? Or vice versa? 21. Discuss some contemporary issues related to the Tenth Amendment. Propose the following scenarios to the students and ask them to determine if a federal, state, or concurrent power is being expressed After Superstorm Sandy in October 2012, President Obama worked with Governor Chris Christie of New Jersey and pledged federal support to help repair the massive storm damage throughout the state. What is this an example of? (concurrent power) Why is this an example of a concurrent power? Why is assisting with storm repair in New Jersey of interest to the federal government? Each state has its own rules and regulations for obtaining a teaching certificate. If a teacher living in Florida would like to move and teach in Texas, he or she would need to pass one or more exams in order to be certified to teach in Texas. What is this an example of? (reserved power) Why do you think teaching certification requirements are a state decision? The state of Montana borders Canada. If a conflict occurs between Montana and Canada, can Montana declare war on Canada? (no) Why not? (Declaring war is an enumerated or delegated power.) What is the benefit of the federal government having the sole power to declare war rather than it being a concurrent or reserved power? 22. Ask students to consider the following question: What happens if a state or local government writes a law which conflicts with the U.S. Constitution or a federal law? 23. Allow students to brainstorm and share out. Lead students to the understanding that the U.S. Constitution is the supreme law of the land and that a state or local government cannot make laws that conflict with the U.S. Constitution or with laws passed by Congress. This is because of the Supremacy Clause. 24. Return student attention back to the Federalism activity sheet and have students turn to page two. 25. Read aloud the two paragraphs on page two as a whole class. 26. Instruct students to answer the question at the bottom of the page. 27. Have students share out. 28. Checking for Understanding (Formative Assessment): Instruct students to write a well-crafted informative response using the following prompt: Prompt Your friend in 6 th grade has not taken a civics class yet and doesn t understand what you mean when you say you are learning about federalism. Write an informative paragraph to your friend to explain the concept of federalism. Include the following terms in your paragraph: concurrent powers, enumerated powers, reserved powers, and delegated powers. SS.7.C.3.4 Updated 8/17 4
5 Federalism Term Definition Visual Representation Federal Government the organization through which political authority is exercised at the national level, government of the State Government Local Government United States the organization through which political authority is exercised at the state level, government of a specific state the governing body of a municipality or county N O T E S Federalism is a system of government where power is divided and shared between the federal (national) government, the state governments and the local governments. U.S. Constitution Federal Government Federal & State Governments State Governments State Constitution Local Governments Enumerated (Delegated) Powers Concurrent Powers Reserved Powers Federalism is found in the U.S. Constitution. In the Constitution, there are powers specifically listed for the federal government and an amendment about state government powers. Powers set aside specifically for the federal government are called enumerated or delegated powers. Powers for each branch of the federal government are located in Articles I, II, and III. Powers for state governments are called reserved powers and are listed in the Tenth Amendment. Some powers belong to both the federal and state governments. These powers are called concurrent powers. Local governments get their powers from state constitutions. The Florida Constitution outlines the organization and powers of county and city governments. The powers of each level of government relates to the types of issues each level deals with. The federal government has the power to handle issues the entire nation is concerned about. The state governments have the power to handle issues that concern citizens of particular states. Similarly, local governments have the power to address issues that concern citizens in towns, cities and counties. SS.7.C.3.4 Updated 8/17 5
6 Type of Power Definition Examples Enumerated or Delegated Powers Reserved Powers Concurrent Powers Local Government Powers powers specifically listed in the U.S. Constitution for the federal (national) government only powers that are given to the states by the Tenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution powers shared by the federal (national) and state governments powers given to towns, cities and counties by the Florida Constitution 1. The power to raise and support an army and navy. 2. The power to coin money. 3. The power to declare war. 4. The power to conduct foreign policy. 5. The power to regulate trade between states and internationally. 1. The power to run elections. 2. The power to set up and run schools. 3. The power to establish local governments 4. The power to regulate business in the state. 1. The power to levy taxes (tax the people). 2. The power to establish courts. 3. The ability to borrow money. 1. The power to create speed limits. 2. The power to protect citizens from crime. 3. The power to provide services related to garbage, sewage, fire protection, and traffic control. Define the term federalism in your own words: Before the U.S. Constitution, the United States had the Articles of Confederation and was organized with a confederal system. A confederal system is a system of government where power is held by independent states and there is little power in the federal (national) government. The U.S. Constitution was written because of concerns about the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation. The federal government had very little power and the states acted as independent nations with too much power. Government power was unbalanced and there was no sense of national unity (togetherness). To solve these problems, the U.S. Constitution was written and the United States moved from a confederal system to a system of federalism. The Founding Fathers had a big goal. They needed to limit state power because states had too much power under the Articles of Confederation. They also needed to create a federal government with limited power. As a solution, the Founding Fathers created a system of federalism. This means that power is shared between the federal, state, and local governments. The federal government has its own powers, shares some powers with the states, and gives states some of their own powers. By dividing power between different levels, this limits the power of each level of government and one level of government cannot become too powerful. How does federalism limit government power? Highlight the relevant passages in the text that helped you answer this question. Adapted from: Ben s Guide to Government for Kids - SS.7.C.3.4 Updated 8/17 6
7 Who Has the Power? Directions: Work in small groups to decide which level or levels (federal, state, or local) of government has the power to deal with each of the questions on the list and what type of power they have to deal with the issue (enumerated/delegated, reserved, concurrent or local). Write the level or levels and their associated power in the blank space underneath the question. Be prepared to explain your answers to the class. 1. Who is going to keep people safe from speeding cars (speed limits)? 2. Who is going to protect us from foreign invasion or threats? 3. There is a pothole in the street outside my house. Who should I talk to? 4. A group of people want to establish a new city. Who should they talk to? 5. Who decides who might get married legally? 6. Who resolves conflicts between states? 7. My garbage hasn t been picked up in two weeks, who do I talk to about this issue? 8. Who makes sure that the country s economy is safe and stable? 9. My taxes keep going up! Who can I talk to about this? 10. Who is in charge of passing laws around here? SS.7.C.3.4 Updated 8/17 7
8 Sources Oakland (Michigan) School District Middle School Social Studies Curriculum, The United States Constitution as a Living Document : Accessed November 16, 2012 The Democracy Project at the University of Delaware, Figuring Out Federalism : School Improvement in Maryland, Government Lesson Plan 1: Ben s Guide to Government for Kids: Adapted from: SS.7.C.3.4 Updated 8/17 8
9 Who Has the Power? Sample Answers Directions: Work in small groups to decide which level or levels (federal, state, or local) of government has the power to deal with each of the questions on the list and what type of power they have to deal with the issue (enumerated/delegated, reserved, concurrent or local). Write the level or levels and their associated power in the blank space underneath the question. Be prepared to explain your answers to the class. 1. Who is going to keep people safe from speeding cars (speed limits)? (Local) 2. Who is going to protect us from foreign invasion or threats? (Federal, Enumerated/Delegated) 3. There is a pothole in the street outside my house. Who should I talk to? (Local) 4. A group of people want to establish a new city. Who should they talk to? (State, Reserved) 5. Who decides who might get married legally? (State, Reserved) 6. Who resolves conflicts between states? (Federal, Enumerated/Delegated) 7. My garbage hasn t been picked up in two weeks, who do I talk to about this issue? (Local) 8. Who makes sure that the country s economy is safe and stable? (Federal, Enumerated/Delegated) 9. My taxes keep going up! Who can I talk to about this? (Federal, State and Local, Concurrent) 10. Who is in charge of passing laws around here? (Federal, State, and Local, Concurrent) SS.7.C.3.4 Updated 8/17 9
10 Civics Content Vocabulary Word/Term Part of Definition Speech concurrent noun powers shared by the national, state, and/or local government powers delegated powers noun the powers specifically named and assigned to the federal government or prohibited to be exercised by the states under the U.S. Constitution, also known as enumerated powers enumerated powers noun the powers specifically named and assigned to the federal government or prohibited to be exercised by the states under the U.S. Constitution, also known as delegated powers federal government noun the national level of government; the government of the United States federalism noun a system of government in which power is divided and shared between national, state, and local governments local government noun the government of a municipality (city) or county reserved powers noun powers that are not granted to the federal government that belong to (are reserved for) the states and the people, see Tenth Amendment state government noun the government of an individual state Supremacy Clause proper noun Tenth Amendment proper noun the clause that states that the U.S. Constitution is the supreme law of the land, and that national laws are supreme over state laws, found in Article VI (six) the final amendment in the Bill of Rights, it states: The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people. SS.7.C.3.4 Updated 8/17 10
11 This section addresses the following issues: 1. Federalism in the U.S. Constitution 2. Federal and state powers in the U.S. Constitution 3. The Tenth Amendment 4. A note on tax policy 1. Federalism in the U.S. Constitution Essential Teacher Content Background Information The framing of the U.S. Constitution was organized around the power of the national and state governments. The first national government formed by the colonists following independence in 1776 was the Articles of Confederation, which focused power at the state level giving little power to the national government. The problems experienced under the Articles of Confederation became evident soon afterward: no unified foreign policy, state governments working against one another when facing common concerns, and a lack of coordination among states and between the states and the central government. Adding to these concerns is that most of those attending the Constitutional Convention attended for the purpose of retaining the confederal system while addressing and fixing those factors that weakened it. James Madison worked with George Washington and Alexander Hamilton to shift the direction and purpose of the convention such that the final document, the U.S. Constitution, presented a federal structure. Federalism is a system of government in which power is divided and shared between the national, state, and local governments. This division of powers extends exclusive powers to the national government only (enumerated, also known as delegated), the state governments only (reserved), or to both (concurrent). Federalism is found throughout the U.S. Constitution. In the section that follows, specific powers relating to federalism found in the U.S. Constitution are presented and discussed. 2. Federal and state powers in the U.S. Constitution Article and Section in the U.S. Constitution Article I, Section 4 (The Legislative Branch; elections) Article I, Section 8 (The Legislative Branch; powers of Congress) Article I, Section 10 (The Legislative Branch; Explanation of Power Example of Power Type of Power States organize elections although the federal government may set national standards Congress, as the national legislature, enjoys specific powers. The states are forbidden from engaging in certain The national government sets the date for presidential and congressional elections; the states may determine the date for scheduling primaries Core powers of Congress include: Laying and collecting taxes Providing for the common defense Borrowing money on the credit of the U.S. Regulating commerce Establishing a uniform rule of naturalization Coining money Declaring war Concurrent Enumerated or delegated Raising and supporting armies and navies State may not (partial list): N/A; Article I, Enter into treaties Section 10 SS.7.C.3.4 Updated 8/17 11
12 Article and Section in the U.S. Constitution restrictions on state power) Article II, Section 1 (Executive Branch; Electoral College) Article III, Section 1 (Judicial Branch; creation of courts) Article VI (Supremacy Clause) 3. The Tenth Amendment Explanation of Power Example of Power Type of Power activities State legislatures determine the rules for appointing members of the Electoral College (the Electoral College elects the president). Congress establishes courts inferior to the U.S. Supreme Court State law may not conflict with federal law Coin money Keep troops during peacetime State legislatures give to each political party the power to select Electors from that party; all Electors are assigned to the party of the presidential candidate earning the most votes in that state (except Maine and Nebraska). Congress created the federal appellate court system. Federal law mandates that no state may require residency exceeding 30 days for purposes of voter registration. restricts power; it does not extend power. Reserved Enumerated or delegated The Tenth Amendment was added to the U.S. Constitution as part of the Bill of Rights, which is comprised of the first ten amendments. The Tenth Amendment reads: The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people. It is in the Tenth Amendment where one finds the reserved powers that extend to the states powers that are not granted to the national government. An interesting contrast is found between the powers extended to the national government and the state governments. In the U.S. Constitution, the powers that are granted to Congress are listed out, or enumerated. This suggests that, because the framers were concerned about giving too much power to the national government, they gave specific powers (noted above) to Congress. Critics, including the Anti-Federalists, argued that the last phrase in Article I, Section 8, called the elastic or necessary and proper clause ( To make all Laws which shall be necessary and proper for carrying into Execution the foregoing Powers, and all other Powers vested by this Constitution in the Government of the United States, or in any Department or Officer thereof. ), extended so much power to Congress that it violated the concept of enumerating congressional powers. By comparison, the Tenth Amendment does not identify any powers. Instead, the Tenth Amendment extends to the states and by extension, the people, powers that are not specifically granted to Congress or denied to the states. 4. A note on tax policy One of the best known powers of government is the power to tax. The power to lay and collect taxes is a power of Congress, as found in Article I, Section 8. However, state and local governments are also permitted to lay and collect taxes because these powers are not forbidden in Article I, Section 10. Consequently, even though the power to lay and collect taxes is enumerated in Article I, Section 8 among the powers delegated to Congress, the power to tax is a concurrent power because it is not forbidden to the states. N/A SS.7.C.3.4 Updated 8/17 12
Highlights: The Relationship and Division of Powers between the Federal and State Governments SS.7.C.3.4
 Highlights: The Relationship and Division of Powers between the Federal and State Governments SS.7.C.3.4 Identify the relationship and division of powers between the federal government and state governments.
Highlights: The Relationship and Division of Powers between the Federal and State Governments SS.7.C.3.4 Identify the relationship and division of powers between the federal government and state governments.
FEDERALISTS, ANTI-FEDERALISTS AND THE CONSTITUTION SS.7.C.1.8
 FEDERALISTS, ANTI-FEDERALISTS AND THE CONSTITUTION SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the ratification of the Constitution and inclusion of a bill of
FEDERALISTS, ANTI-FEDERALISTS AND THE CONSTITUTION SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the ratification of the Constitution and inclusion of a bill of
Unit One: Quarter Three. Name:
 SS.7.C.3.3 Structure and Function of the LEGISLATIVE BRANCH ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: recognize the structure of the legislative, executive, and judicial branches.
SS.7.C.3.3 Structure and Function of the LEGISLATIVE BRANCH ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: recognize the structure of the legislative, executive, and judicial branches.
The Articles of Confederation
 The Articles of Confederation The Articles of Confederation was the first government of the United States following the Declaration of Independence. A confederation is a state-centered, decentralized government
The Articles of Confederation The Articles of Confederation was the first government of the United States following the Declaration of Independence. A confederation is a state-centered, decentralized government
Social Studies Lesson Plan Give examples of powers granted to the federal government and those reserved for the states.
 Teacher s Name: Employee Number: School: Social Studies Lesson Plan Give examples of powers granted to the federal government and those reserved for the states. 1. Title: Federal and State Powers 2. Overview
Teacher s Name: Employee Number: School: Social Studies Lesson Plan Give examples of powers granted to the federal government and those reserved for the states. 1. Title: Federal and State Powers 2. Overview
Clay County Civics Review
 Clay County Civics Review Units 4 and 5: The Legislative and Executive Branches C3.4, C3.8, C4.1, C4.2, C4.3 Review content provided by Florida Joint Center for Citizenship Review tasks created by Kelly
Clay County Civics Review Units 4 and 5: The Legislative and Executive Branches C3.4, C3.8, C4.1, C4.2, C4.3 Review content provided by Florida Joint Center for Citizenship Review tasks created by Kelly
Social Studies Grade 5 Optional
 The School District of Palm Beach County Social Studies Grade 5 Optional Standard 3: Structure and Functions of Government SS.5.C.3.3 Give examples of powers granted to the federal government and those
The School District of Palm Beach County Social Studies Grade 5 Optional Standard 3: Structure and Functions of Government SS.5.C.3.3 Give examples of powers granted to the federal government and those
The Six Basic Principles
 The Constitution The Six Basic Principles The Constitution is only about 7000 words One of its strengths is that it does not go into great detail. It is based on six principles that are embodied throughout
The Constitution The Six Basic Principles The Constitution is only about 7000 words One of its strengths is that it does not go into great detail. It is based on six principles that are embodied throughout
Warm-Up. 1. What is judicial review? 2. Do you think judicial review gives the judicial branch too much power? Why or why not?
 Warm-Up 1. What is judicial review? 2. Do you think judicial review gives the judicial branch too much power? Why or why not? Objectives Identify and explain the powers that are divided and shared amongst
Warm-Up 1. What is judicial review? 2. Do you think judicial review gives the judicial branch too much power? Why or why not? Objectives Identify and explain the powers that are divided and shared amongst
McCulloch vs. Maryland
 McCulloch vs. Maryland Background of the Case: After the War of 1812, the U.S. government needed additional funds to pay off the debts of the war. Instead of being able to borrow money from one institution,
McCulloch vs. Maryland Background of the Case: After the War of 1812, the U.S. government needed additional funds to pay off the debts of the war. Instead of being able to borrow money from one institution,
The Constitution CHAPTER 5. Table of Contents
 CHAPTER 5 The Constitution ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: Why do people, create, structure, and change governments? How do societies balance individual and community rights? How does social change influence government?
CHAPTER 5 The Constitution ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: Why do people, create, structure, and change governments? How do societies balance individual and community rights? How does social change influence government?
SS.7.C.1.5. Identify how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing of the Constitution
 SS.7.C.1.5. Identify how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing of the Constitution SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the
SS.7.C.1.5. Identify how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing of the Constitution SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the
EOC Civics Unit #4 Review. Organization and Function of Government
 EOC Civics Unit #4 Review Organization and Function of Government Forms of Government SS.7.C.3.1 Democracy = We The People = Self-Government Direct Democracy Everyone makes decisions Florida is a DD for
EOC Civics Unit #4 Review Organization and Function of Government Forms of Government SS.7.C.3.1 Democracy = We The People = Self-Government Direct Democracy Everyone makes decisions Florida is a DD for
US Government Review 4.1
 Class: Date: US Government Review 4.1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The Constitution grants these powers to the national government.
Class: Date: US Government Review 4.1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The Constitution grants these powers to the national government.
The Scope of Congressional Powers. Congressional Power. Strict Versus Liberal Construction
 The Scope of Congressional Powers What are the three types of congressional power? How does strict construction of the U.S. Constitution on the subject of congressional power compare to liberal construction?
The Scope of Congressional Powers What are the three types of congressional power? How does strict construction of the U.S. Constitution on the subject of congressional power compare to liberal construction?
Civics EOC Exam Preparation
 Civics EOC Exam Preparation Welcome! Sit in groups of four at each table. Presenter Mr. Regnier Do not doodle on the dry erase boards. The U.S. System of Federalism Federal State Local Benchmark Identify
Civics EOC Exam Preparation Welcome! Sit in groups of four at each table. Presenter Mr. Regnier Do not doodle on the dry erase boards. The U.S. System of Federalism Federal State Local Benchmark Identify
Civics Learning Goals for the 3 rd Quarter
 Civics Learning Goals for the 3 rd Quarter 2017-18 Unit: The U.S. and the World C.4.1 Differentiate concepts related to U.S. domestic and foreign policy. - Students will recognize the difference between
Civics Learning Goals for the 3 rd Quarter 2017-18 Unit: The U.S. and the World C.4.1 Differentiate concepts related to U.S. domestic and foreign policy. - Students will recognize the difference between
JWJ Civics Remediation
 STANDARD 1: Demonstrate an understanding of the origins and purposes of government, law, and the American political system. TESTED BENCHMARK BENCHMARK SS.7.C.1.1 Recognize how Enlightenment ideas including
STANDARD 1: Demonstrate an understanding of the origins and purposes of government, law, and the American political system. TESTED BENCHMARK BENCHMARK SS.7.C.1.1 Recognize how Enlightenment ideas including
UNDERSTANDING U.S. DOMESTIC AND FOREIGN POLICY SS.7.C.4.1 Differentiate concepts related to U.S. domestic and foreign policy.
 UNDERSTANDING U.S. DOMESTIC AND FOREIGN POLICY SS.7.C.4.1 Differentiate concepts related to U.S. domestic and foreign policy. TABLE OF CONTENTS Lesson Summary... 2 Suggested Student Activity Sequence...
UNDERSTANDING U.S. DOMESTIC AND FOREIGN POLICY SS.7.C.4.1 Differentiate concepts related to U.S. domestic and foreign policy. TABLE OF CONTENTS Lesson Summary... 2 Suggested Student Activity Sequence...
Georgia Standards of Excellence American Government and Civics 2016
 A Correlation of 2016 To the Georgia Standards of Excellence American Government and Civics 2016 FORMAT FOR CORRELATION TO THE GEORGIA STANDARDS OF EXCELLENCE (GSE) GRADES K-12 SOCIAL STUDIES AND SCIENCE
A Correlation of 2016 To the Georgia Standards of Excellence American Government and Civics 2016 FORMAT FOR CORRELATION TO THE GEORGIA STANDARDS OF EXCELLENCE (GSE) GRADES K-12 SOCIAL STUDIES AND SCIENCE
A Correlation of. Prentice Hall Magruder s American Government To the. Nevada Social Studies Standards Social Studies Skills & Civics
 A Correlation of Prentice Hall American Government 2011 To the Social Studies Skills & Civics Grades 9-12 Prentice Hall,, Grades 9-12 Introduction This document demonstrates how American Government 2010
A Correlation of Prentice Hall American Government 2011 To the Social Studies Skills & Civics Grades 9-12 Prentice Hall,, Grades 9-12 Introduction This document demonstrates how American Government 2010
Magruder s American Government
 Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 11 Powers of Congress 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 11 Powers of Congress SECTION 1 The Scope of Congressional Powers SECTION 2
Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 11 Powers of Congress 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 11 Powers of Congress SECTION 1 The Scope of Congressional Powers SECTION 2
Division of powers between national government and state governments
 3A Reading Division of powers between national government and state governments 10 th amendment: rights and powers are reserved to the states by the 10 th amendment Necessary and Proper Clause: Federal
3A Reading Division of powers between national government and state governments 10 th amendment: rights and powers are reserved to the states by the 10 th amendment Necessary and Proper Clause: Federal
American Government. C H A P T E R 11 Powers of Congress
 American Government C H A P T E R 11 Powers of Congress C H A P T E R 11 Powers of Congress SECTION 1 The Scope of Congressional Powers SECTION 2 The Expressed Powers of Money and Commerce SECTION 3 Other
American Government C H A P T E R 11 Powers of Congress C H A P T E R 11 Powers of Congress SECTION 1 The Scope of Congressional Powers SECTION 2 The Expressed Powers of Money and Commerce SECTION 3 Other
Ratification of the Constitution. Issues
 Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 1 Dividing and Sharing Power ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why and how is power divided and shared among national, state, and local governments? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary authority the right to
Lesson 1 Dividing and Sharing Power ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why and how is power divided and shared among national, state, and local governments? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary authority the right to
The S e cope o e f f Congressi essi nal al P ower w s
 The Scope of Congressional Powers What are the three types of congressional power? How does strict construction of the U.S. Constitution on the subject of congressional power compare to liberal construction?
The Scope of Congressional Powers What are the three types of congressional power? How does strict construction of the U.S. Constitution on the subject of congressional power compare to liberal construction?
Quarter One: Unit Four
 SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will identify the weaknesses of the government under the Articles of Confederation (i.e.,
SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will identify the weaknesses of the government under the Articles of Confederation (i.e.,
The Federal in Federalism STEP BY STEP
 Teacher s Guide Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student Worksheets Projector (optional) Tape Copy Instructions: Reading (3 pages; class set) Federal Power Cheat Sheet (1 page; class set)
Teacher s Guide Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student Worksheets Projector (optional) Tape Copy Instructions: Reading (3 pages; class set) Federal Power Cheat Sheet (1 page; class set)
Social Studies Lesson Plan Analyze how the Constitution has expanded voting rights from our nation's early history to today
 Teacher s Name: Employee Number: School: Social Studies Lesson Plan Analyze how the Constitution has expanded voting rights from our nation's early history to today 1. Title: Voting and the Constitution
Teacher s Name: Employee Number: School: Social Studies Lesson Plan Analyze how the Constitution has expanded voting rights from our nation's early history to today 1. Title: Voting and the Constitution
Social Studies Lesson Plan- SS.4.C.2.2 Identify ways citizens work together to influence government and help solve community and state problems
 Teacher s Name: Employee Number: School: Social Studies Lesson Plan- SS.4.C.2.2 Identify ways citizens work together to 1. Title: HOW A Bill Becomes a Law - 4 th Grade 2. Overview - Big Ideas: Enduring
Teacher s Name: Employee Number: School: Social Studies Lesson Plan- SS.4.C.2.2 Identify ways citizens work together to 1. Title: HOW A Bill Becomes a Law - 4 th Grade 2. Overview - Big Ideas: Enduring
The U.S. Constitution. Ch. 2.4 Ch. 3
 The U.S. Constitution Ch. 2.4 Ch. 3 The Constitutional Convention Philadelphia Five months, from May until September 1787 Secret Meeting, closed to outside. Originally intent to revise the Articles of
The U.S. Constitution Ch. 2.4 Ch. 3 The Constitutional Convention Philadelphia Five months, from May until September 1787 Secret Meeting, closed to outside. Originally intent to revise the Articles of
The Federal System. Chapter 4
 The Federal System Chapter 4 National and State Powers Section 1 Pages 95-102 The Division of Powers The Constitution divided power in the following ways: 1) The national government received certain specified
The Federal System Chapter 4 National and State Powers Section 1 Pages 95-102 The Division of Powers The Constitution divided power in the following ways: 1) The national government received certain specified
JUDGE CHATS. Lesson Plan. Independence Mall 525 Arch Street Philadelphia, PA 19106
 JUDGE CHATS Lesson Plan Independence Mall 525 Arch Street Philadelphia, PA 19106 JUDGE CHATS LESSON PLAN 2 Judge Chats Lesson Plan Grade Levels: 6th, 8th, 12th Number of class periods: 1 (approximately
JUDGE CHATS Lesson Plan Independence Mall 525 Arch Street Philadelphia, PA 19106 JUDGE CHATS LESSON PLAN 2 Judge Chats Lesson Plan Grade Levels: 6th, 8th, 12th Number of class periods: 1 (approximately
C H A P T E R 3 The US Constitution
 C H A P T E R 3 The US Constitution SECTION 1 The Six Basic Principles SECTION 2 Formal Amendment SECTION 3 Informal Amendment What are the important elements of the Constitution? What are the six basic
C H A P T E R 3 The US Constitution SECTION 1 The Six Basic Principles SECTION 2 Formal Amendment SECTION 3 Informal Amendment What are the important elements of the Constitution? What are the six basic
Comparing the U.S. Constitution & The Florida State Constitution. Mr. Raymond s Civics EOC Academy
 Comparing the U.S. Constitution & The Florida State Constitution Mr. Raymond s Civics EOC Academy Last time: Federalism the National, State & Local Governments working together Benchmark: SS.7.C.3.13 Compare
Comparing the U.S. Constitution & The Florida State Constitution Mr. Raymond s Civics EOC Academy Last time: Federalism the National, State & Local Governments working together Benchmark: SS.7.C.3.13 Compare
Constitution Detectives
 Understanding the Constitution of the United States Constitution Detectives ANSWER KEY Directions: Answer the questions below about the Constitution. Make sure to use complete sentences. What events led
Understanding the Constitution of the United States Constitution Detectives ANSWER KEY Directions: Answer the questions below about the Constitution. Make sure to use complete sentences. What events led
Student Performance Q&A:
 Student Performance Q&A: 2014 AP United States Government and Politics Free-Response Questions The following comments on the 2014 free-response questions for AP United States Government and Politics were
Student Performance Q&A: 2014 AP United States Government and Politics Free-Response Questions The following comments on the 2014 free-response questions for AP United States Government and Politics were
We the People.. The Failings of the Articles of Confederation and the Solutions of the Constitutional Convention Unit Two- BD
 We the People.. The Failings of the Articles of Confederation and the Solutions of the Constitutional Convention Unit Two- BD Sorting Out the Problems: Article One * Two plans are put forth to address
We the People.. The Failings of the Articles of Confederation and the Solutions of the Constitutional Convention Unit Two- BD Sorting Out the Problems: Article One * Two plans are put forth to address
Branching Out. The Structure and Function of the Federal Government. Benchmarks
 Branching Out The Structure and Function of the Federal Government Benchmarks SS.7.C.3.3 Illustrate the structure and function (three branches of government established in Articles I, II, and III with
Branching Out The Structure and Function of the Federal Government Benchmarks SS.7.C.3.3 Illustrate the structure and function (three branches of government established in Articles I, II, and III with
Unit 2 Learning Objectives
 AP AMERICAN GOVERNMENT Unit Two Part 2 The Constitution, and Federalism 2 1 Unit 2 Learning Objectives Structure of the Constitution 2.4 Describe the basic structure of the Constitution and its Bill of
AP AMERICAN GOVERNMENT Unit Two Part 2 The Constitution, and Federalism 2 1 Unit 2 Learning Objectives Structure of the Constitution 2.4 Describe the basic structure of the Constitution and its Bill of
Congress had the power over relations, foreign, with the capacity to create alliance and form
 Surname 1 Name: Course: Instructor: Date: The Articles of Confederation were the first written constitution of the United States. These Articles created a legislature where there was equal representation
Surname 1 Name: Course: Instructor: Date: The Articles of Confederation were the first written constitution of the United States. These Articles created a legislature where there was equal representation
THE CONSTITUTION. How do societies balance individual and community rights? How does social change influence government?
 CHAPTER 5 THE CONSTITUTION NGSSS SS.7.C.1.7 Describe how the Constitution limits the powers of government through separation of powers and checks and balances. ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why do people create,
CHAPTER 5 THE CONSTITUTION NGSSS SS.7.C.1.7 Describe how the Constitution limits the powers of government through separation of powers and checks and balances. ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why do people create,
UNIT II: THE U.S. CONSTITUTION
 UNIT II: THE U.S. CONSTITUTION Seven Articles Separation of Powers Principles of Federalism Ilovesocialstudies.com SEVEN ARTICLES Article I Establishes the Legislative Branch Article II Establishes the
UNIT II: THE U.S. CONSTITUTION Seven Articles Separation of Powers Principles of Federalism Ilovesocialstudies.com SEVEN ARTICLES Article I Establishes the Legislative Branch Article II Establishes the
The American Revolution is over but now the colonists have to decide how they want to frame their government. Take the first 5 minutes of class and
 The American Revolution is over but now the colonists have to decide how they want to frame their government. Take the first 5 minutes of class and imagine that you were a colonist that just fought against
The American Revolution is over but now the colonists have to decide how they want to frame their government. Take the first 5 minutes of class and imagine that you were a colonist that just fought against
OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS
 CHAPTER 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS The colonists brought with them to North America knowledge of the English political system, including three key ideas about government.
CHAPTER 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS The colonists brought with them to North America knowledge of the English political system, including three key ideas about government.
Federal System at Work
 The Federal System Federal System at Work Early in American history, South Carolina refused to comply with the tariff of 1828. It nullified, or rejected, this law, which hurt agricultural exports. However,
The Federal System Federal System at Work Early in American history, South Carolina refused to comply with the tariff of 1828. It nullified, or rejected, this law, which hurt agricultural exports. However,
U.S. Government Unit 1 Notes
 Name Period Date / / U.S. Government Unit 1 Notes C H A P T E R 1 Principles of Government, p. 1-24 1 Government and the State What Is Government? Government is the through which a makes and enforces its
Name Period Date / / U.S. Government Unit 1 Notes C H A P T E R 1 Principles of Government, p. 1-24 1 Government and the State What Is Government? Government is the through which a makes and enforces its
Week # Date Benchmark # s to Complete 1 3/30 4/4 Citizen You! SS.7.C.2.1; SS.7.C.2.2; SS.7.C.2.3; SS.7.C.2.14; SS.7.C.1.9
 Name: Date: Per.: Civics End of Course Exam Online Benchmark Review 1. Visit civics360.org. First time only follow the prompts to create an account using your school email. 2. Scroll down to see a list
Name: Date: Per.: Civics End of Course Exam Online Benchmark Review 1. Visit civics360.org. First time only follow the prompts to create an account using your school email. 2. Scroll down to see a list
Federalism: the division of power.
 Federalism: the division of power. key terms Federalism: a system of government in which a written constitution divides the power between a central, or national, government and several regional governments.
Federalism: the division of power. key terms Federalism: a system of government in which a written constitution divides the power between a central, or national, government and several regional governments.
The House of Representatives shall be composed of Members chosen every second Year by the People of the several States.
 Guiding Principles of the Constitution (HA) Over the years, the Constitution has acquired an almost sacred status for Americans. Part of the reason for that is its durability: the Constitution has survived,
Guiding Principles of the Constitution (HA) Over the years, the Constitution has acquired an almost sacred status for Americans. Part of the reason for that is its durability: the Constitution has survived,
A Correlation of. To the. Louisiana High School Civics Standards 2011
 A Correlation of 2016 To the Civics Standards 2011 Introduction This document demonstrates how Pearson American Government, 2016 meets the Civics Standards, 2011. Hailed as a stellar educational resource
A Correlation of 2016 To the Civics Standards 2011 Introduction This document demonstrates how Pearson American Government, 2016 meets the Civics Standards, 2011. Hailed as a stellar educational resource
AP AMERICAN GOVERNMENT. Chapter 3 Outline and Learning Objective
 AP AMERICAN GOVERNMENT Unit Two Part 2 The Constitution, and Federalism 2 1 Chapter 3 Outline and Learning Objective Defining Federalism 2.8 Interpret the definitions of federalism, and assess the advantages
AP AMERICAN GOVERNMENT Unit Two Part 2 The Constitution, and Federalism 2 1 Chapter 3 Outline and Learning Objective Defining Federalism 2.8 Interpret the definitions of federalism, and assess the advantages
I. The Division of Powers
 TOPIC 5: FEDERALISM Objectives p. 02 In the course of reading this chapter and participating in the classroom activity, students will a. explaining the relationship of the state governments to the national
TOPIC 5: FEDERALISM Objectives p. 02 In the course of reading this chapter and participating in the classroom activity, students will a. explaining the relationship of the state governments to the national
Unit 7 Our Current Government
 Unit 7 Our Current Government Name Date Period Learning Targets (What I need to know): I can describe the Constitutional Convention and two compromises that took place there. I can describe the structure
Unit 7 Our Current Government Name Date Period Learning Targets (What I need to know): I can describe the Constitutional Convention and two compromises that took place there. I can describe the structure
US Constitution. Articles I-VII
 US Constitution Articles I-VII Quick Questions What is the Constitution? What is the Preamble? What are the Articles and their purpose? Preamble Six Purposes are Listed -> What are they? We the people
US Constitution Articles I-VII Quick Questions What is the Constitution? What is the Preamble? What are the Articles and their purpose? Preamble Six Purposes are Listed -> What are they? We the people
Constitution Test Study Guide
 Constitution Test Study Guide Part One: Development of the Constitution Articles of Confederation: America's first government. The 13 states were loosely unified but the government was very weak, with
Constitution Test Study Guide Part One: Development of the Constitution Articles of Confederation: America's first government. The 13 states were loosely unified but the government was very weak, with
9.1 Introduction When the delegates left Independence Hall in September 1787, they each carried a copy of the Constitution. Their task now was to
 9.1 Introduction When the delegates left Independence Hall in September 1787, they each carried a copy of the Constitution. Their task now was to convince their states to approve the document that they
9.1 Introduction When the delegates left Independence Hall in September 1787, they each carried a copy of the Constitution. Their task now was to convince their states to approve the document that they
APG Unit 1: Foundations of Government Problem Set Packet #1 Packet Due Date:
 APG Unit 1: Foundations of Government Problem Set Packet #1 Packet Due Date: Name Date Period Chapter Title Status/Point Value 1 1 The Four Theories of Democracy (must use the internet) 2 2 Four Political
APG Unit 1: Foundations of Government Problem Set Packet #1 Packet Due Date: Name Date Period Chapter Title Status/Point Value 1 1 The Four Theories of Democracy (must use the internet) 2 2 Four Political
The Structure and Functions of the Government
 The Structure and Functions of the Government The United States of America is a democratic republic or an indirect government. In definition, it means that when the people vote, they give the power to
The Structure and Functions of the Government The United States of America is a democratic republic or an indirect government. In definition, it means that when the people vote, they give the power to
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 2 The Three Branches of Government ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does the U.S. Constitution structure government and divide power between the national and state governments? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary
Lesson 2 The Three Branches of Government ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does the U.S. Constitution structure government and divide power between the national and state governments? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary
Quarter One: Unit Four
 SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will identify the weaknesses of the government under the Articles of Confederation (i.e.,
SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will identify the weaknesses of the government under the Articles of Confederation (i.e.,
SSS- Social Sciences Stimuli. Embedding the Florida Standards in Social Sciences (E.S. Administrators)
 SSS- Social Sciences Stimuli Embedding the Florida Standards in Social Sciences (E.S. Administrators) Session Title: SSS- Social Studies Stimuli: Embedding the Florida Standards in Social Sciences Audience:
SSS- Social Sciences Stimuli Embedding the Florida Standards in Social Sciences (E.S. Administrators) Session Title: SSS- Social Studies Stimuli: Embedding the Florida Standards in Social Sciences Audience:
Social Studies Lesson Plan- SS.3.C.3.3. Recognize that every state has a state constitution
 Teacher s Name: Employee Number: School: Social Studies Lesson Plan- SS.3.C.3.3 Recognize that every state has a state 1. Title: Every State Has a State Constitution 2. Overview - Big Ideas: Enduring Understandings
Teacher s Name: Employee Number: School: Social Studies Lesson Plan- SS.3.C.3.3 Recognize that every state has a state 1. Title: Every State Has a State Constitution 2. Overview - Big Ideas: Enduring Understandings
Civics EOC. Assembled by the Citrus County Research & Accountability Department
 Civics EOC All 35 of the questions on this Civics EOC are from the Florida Civics EOC Test Item Specifications. An electronic copy of the Item Specifications can be found at http://fcat.fldoe.org/eoc/pdf/fl12spiscivicswtr2g.pdf
Civics EOC All 35 of the questions on this Civics EOC are from the Florida Civics EOC Test Item Specifications. An electronic copy of the Item Specifications can be found at http://fcat.fldoe.org/eoc/pdf/fl12spiscivicswtr2g.pdf
Part Two Print out the Elected Officials Sheet and complete questions. Make sure you pay attention to state officials and national officials.
 Honors Civics Summer Work 2013-2014 Part One Print off the web quest, and complete all assignments and place in a folder/notebook. Make sure your answers are complete with details (the more detail the
Honors Civics Summer Work 2013-2014 Part One Print off the web quest, and complete all assignments and place in a folder/notebook. Make sure your answers are complete with details (the more detail the
1. What are the requirements for becoming a Representative? How long do they serve?
 20 th /Raffel Constitution Study Questions Directions: To complete these questions, you need to read an online version of the constitution, available from the class website (select Online Constitution
20 th /Raffel Constitution Study Questions Directions: To complete these questions, you need to read an online version of the constitution, available from the class website (select Online Constitution
Federalism. A system of shared power between two or more levels of government
 Federalism A system of shared power between two or more levels of government Not A unitary government All power in central government Example? A confederation Most power is in the hands of components Example?
Federalism A system of shared power between two or more levels of government Not A unitary government All power in central government Example? A confederation Most power is in the hands of components Example?
Constitution Day September 17
 Constitution Day September 17 Articles of Confederation March 1, 1781- goes into effect No Executive Branch-No single leader No Judicial Branch-No national courts No power to collect taxes No power to
Constitution Day September 17 Articles of Confederation March 1, 1781- goes into effect No Executive Branch-No single leader No Judicial Branch-No national courts No power to collect taxes No power to
understanding CONSTITUTION
 understanding the CONSTITUTION Contents The Articles of Confederation The Constitutional Convention The Principles of the Constitution The Preamble The Legislative Branch The Executive Branch The Judicial
understanding the CONSTITUTION Contents The Articles of Confederation The Constitutional Convention The Principles of the Constitution The Preamble The Legislative Branch The Executive Branch The Judicial
12 th Grade U.S. Government Curriculum Map FL Literacy Standards (See final pages)
 12 th Grade U.S. Government Curriculum Map FL Literacy Standards (See final pages) Grading Standard Description Unit/Chapter Pacing Chapter Vocab/Resources Period 1 SS 912.C13 SS 912.C4.1 SS912.C2.8 SS912.C2.7
12 th Grade U.S. Government Curriculum Map FL Literacy Standards (See final pages) Grading Standard Description Unit/Chapter Pacing Chapter Vocab/Resources Period 1 SS 912.C13 SS 912.C4.1 SS912.C2.8 SS912.C2.7
State and Local Government in the United States
 State and Local Government in the United States www.whitehouse.gov The United States have three levels of government; a federal level, a state level and a local level. Each one has its own features and
State and Local Government in the United States www.whitehouse.gov The United States have three levels of government; a federal level, a state level and a local level. Each one has its own features and
3.1c- Layer Cake Federalism
 3.1c- Layer Cake Federalism Defining Federalism The United States encompasses many governments over 83,000 separate units. These include municipal, county, regional, state, and federal governments as well
3.1c- Layer Cake Federalism Defining Federalism The United States encompasses many governments over 83,000 separate units. These include municipal, county, regional, state, and federal governments as well
Why do you think the Framers organized the new country as a republic, when most countries in the world (in 1783) were ruled by a king or queen?
 NAME: Date: U.S. History CHAPTER 7 PACKET ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: 1. What is a constitution? 2. What is a republic? 3. What was the Articles of Confederation? 4. How was state and national power divided under
NAME: Date: U.S. History CHAPTER 7 PACKET ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: 1. What is a constitution? 2. What is a republic? 3. What was the Articles of Confederation? 4. How was state and national power divided under
Vocabulary Match-Up. Name Date Period Workbook Activity
 Name Date Period Workbook Activity Vocabulary Match-Up Chapter 2, Lesson 1 7 Part A Directions Match the vocabulary word in Column 1 with its definition in Column 2. Write the correct letter on each line.
Name Date Period Workbook Activity Vocabulary Match-Up Chapter 2, Lesson 1 7 Part A Directions Match the vocabulary word in Column 1 with its definition in Column 2. Write the correct letter on each line.
Unit: The Legislative Branch
 - two houses. Name: Date: Period: Unit: The Legislative Branch Part One: How Congress is Organized Gerrymandering- to a state into an odd-shaped district for reasons. - people in a representative s district.
- two houses. Name: Date: Period: Unit: The Legislative Branch Part One: How Congress is Organized Gerrymandering- to a state into an odd-shaped district for reasons. - people in a representative s district.
15-16 yr olds Practice Constitution Bee Name:
 15-16 yr olds Practice Constitution Bee Name: Assignment #1 Make sure that you are scoring in the 90% range on all 6 regular quizzes and on the Bonus Questions before moving on to this Practice Constitution
15-16 yr olds Practice Constitution Bee Name: Assignment #1 Make sure that you are scoring in the 90% range on all 6 regular quizzes and on the Bonus Questions before moving on to this Practice Constitution
Early US. Unit 3 Visuals
 Early US Unit 3 Visuals 1 st US Government Articles of Confederation Articles of Confederation 1 st form of national Gov t Powerful State Gov t Weak Central Gov t No Taxes Couldn t enforce laws No President
Early US Unit 3 Visuals 1 st US Government Articles of Confederation Articles of Confederation 1 st form of national Gov t Powerful State Gov t Weak Central Gov t No Taxes Couldn t enforce laws No President
AP American Government
 AP American Government WILSON, CHAPTER 2 The Constitution OVERVIEW The Framers of the Constitution sought to create a government capable of protecting liberty and preserving order. The solution they chose
AP American Government WILSON, CHAPTER 2 The Constitution OVERVIEW The Framers of the Constitution sought to create a government capable of protecting liberty and preserving order. The solution they chose
Civics and Economics Point Review
 Civics and Economics Point Review Inside you will find a variety of review activities. Each activity has a different point value. You must choose the activities you want to do. Your total point value must
Civics and Economics Point Review Inside you will find a variety of review activities. Each activity has a different point value. You must choose the activities you want to do. Your total point value must
How Did the Constitution Guard Against Tyranny?
 How Did the Constitution Guard Against Tyranny? Overview: In the summer of 1787, fifty-five delegates representing twelve of the thirteen states met in Philadelphia to fix the national government. The
How Did the Constitution Guard Against Tyranny? Overview: In the summer of 1787, fifty-five delegates representing twelve of the thirteen states met in Philadelphia to fix the national government. The
Federalism - Balance Between Federal and State
 While the constitution continues to be read, and its principles known, the states, must, by every rational man, be considered as essential component parts of the union; and therefore the idea of sacrificing
While the constitution continues to be read, and its principles known, the states, must, by every rational man, be considered as essential component parts of the union; and therefore the idea of sacrificing
Social Studies Curriculum Guide Ninth Grade AMERICAN GOVERNMENT
 Social Studies Curriculum Guide Ninth Grade AMERICAN GOVERNMENT It is the policy of the Fulton County School System not to discriminate on the basis of race, color, sex, religion, national origin, age,
Social Studies Curriculum Guide Ninth Grade AMERICAN GOVERNMENT It is the policy of the Fulton County School System not to discriminate on the basis of race, color, sex, religion, national origin, age,
The Constitution CHAPTER 2 CHAPTER OUTLINE WITH KEYED-IN RESOURCES
 CHAPTER 2 The Constitution CHAPTER OUTLINE WITH KEYED-IN RESOURCES I. The problem of liberty (THEME A: THE POLITICAL PHILOSOPHY OF THE FOUNDERS) A. Colonists were focused on traditional liberties 1. The
CHAPTER 2 The Constitution CHAPTER OUTLINE WITH KEYED-IN RESOURCES I. The problem of liberty (THEME A: THE POLITICAL PHILOSOPHY OF THE FOUNDERS) A. Colonists were focused on traditional liberties 1. The
Chapter Six Test Review
 Chapter Six Test Review Which feature of the Constitution prevents one branch of the national government from becoming too powerful? Checks and Balances At the Constitutional Convention (1787), the Great
Chapter Six Test Review Which feature of the Constitution prevents one branch of the national government from becoming too powerful? Checks and Balances At the Constitutional Convention (1787), the Great
Magruder s American Government
 Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 4 Federalism 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 4 Federalism SECTION 1 Federalism: The Division of Power SECTION 2 The National Government
Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 4 Federalism 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 4 Federalism SECTION 1 Federalism: The Division of Power SECTION 2 The National Government
Social Studies Enduring Issues
 Social Studies Enduring Issues A Workshop by GED Testing Service 2 1 Session Objectives Explore thinking and reading skills in social studies Identify strategies and activities to build social studies
Social Studies Enduring Issues A Workshop by GED Testing Service 2 1 Session Objectives Explore thinking and reading skills in social studies Identify strategies and activities to build social studies
US Government Module 2 Study Guide
 US Government Module 2 Study Guide 2.01 Revolutionary Ideas The Declaration of Independence contains an introduction, list of grievances, and formal statement of independence. The principle of natural
US Government Module 2 Study Guide 2.01 Revolutionary Ideas The Declaration of Independence contains an introduction, list of grievances, and formal statement of independence. The principle of natural
HUMAN RIGHTS AND THE AMERICAN CONSTITUTION
 HUMAN RIGHTS AND THE AMERICAN CONSTITUTION PROFESSOR DELAINE R. SWENSON CLASS MATERIALS n Pracownik.kul.pl/dswenson/dydaktyka 1 The use of Precedent in the United States Source of law Written sources are
HUMAN RIGHTS AND THE AMERICAN CONSTITUTION PROFESSOR DELAINE R. SWENSON CLASS MATERIALS n Pracownik.kul.pl/dswenson/dydaktyka 1 The use of Precedent in the United States Source of law Written sources are
Unit One: Quarter Three. Name:
 SS.7.C.3.3 Structure and Function of the LEGISLATIVE BRANCH ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: recognize the structure of the legislative, executive, and judicial branches.
SS.7.C.3.3 Structure and Function of the LEGISLATIVE BRANCH ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: recognize the structure of the legislative, executive, and judicial branches.
Amarillo ISD Social Studies Curriculum
 Amarillo Independent School District follows the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS). All of AISD curriculum and documents and resources are aligned to the TEKS. The State of Texas State Board
Amarillo Independent School District follows the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS). All of AISD curriculum and documents and resources are aligned to the TEKS. The State of Texas State Board
Jeopardy Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400
 Jeopardy 2013-14 Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $500 Q $500 Q $500 Q $500 Final Jeopardy
Jeopardy 2013-14 Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $500 Q $500 Q $500 Q $500 Final Jeopardy
The US Constitution. Articles of the Constitution
 The US Constitution Articles of the Constitution Article I delegates all legislative power to the bicameral Congress. The two chambers differ in the qualifications required of their members, the term of
The US Constitution Articles of the Constitution Article I delegates all legislative power to the bicameral Congress. The two chambers differ in the qualifications required of their members, the term of
Chapter 03: Federalism Multiple Choice
 Multiple Choice 1. The great issue that provoked the Civil War (1861 1865) was the future of. a. slavery b. education c. religion d. immigration e. the electoral college 2. Which of the following is an
Multiple Choice 1. The great issue that provoked the Civil War (1861 1865) was the future of. a. slavery b. education c. religion d. immigration e. the electoral college 2. Which of the following is an
Civics Curriculum Guide
 Civics Curriculum Guide 2015-2016 Column 1: Standards The standards are the benchmarks that our state decides as what must be taught by teachers and learned by students in a given grade level and content
Civics Curriculum Guide 2015-2016 Column 1: Standards The standards are the benchmarks that our state decides as what must be taught by teachers and learned by students in a given grade level and content
To the whole Constitution -Gives the purposes and goals of government
 Preamble -An Introduction To the whole Constitution -Gives the purposes and goals of government -We, the people of the United States, in Order to from a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic
Preamble -An Introduction To the whole Constitution -Gives the purposes and goals of government -We, the people of the United States, in Order to from a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic
THE CONSTITUTION OF THE UNITED STATES
 Chapter 1 THE CONSTITUTION OF THE UNITED STATES CHAPTER REVIEW Learning Objectives After studying Chapter 1, you should be able to do the following: 1. Explain the nature and functions of a constitution.
Chapter 1 THE CONSTITUTION OF THE UNITED STATES CHAPTER REVIEW Learning Objectives After studying Chapter 1, you should be able to do the following: 1. Explain the nature and functions of a constitution.
Chapter 3 Constitution. Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook
 Chapter 3 Constitution Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on www.pknock.com Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from
Chapter 3 Constitution Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on www.pknock.com Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from
Unit 3: The Constitution
 Unit 3: The Constitution Essential Question: How do the structures of the US and NC Constitutions balance the power of the government with the will of the people? Content and Main Ideas: Constitutional
Unit 3: The Constitution Essential Question: How do the structures of the US and NC Constitutions balance the power of the government with the will of the people? Content and Main Ideas: Constitutional
D1 Constitution. Revised. The Constitution (1787) Timeline 2/28/ Declaration of Independence Articles of Confederation (in force 1781)
 Revised D1 Constitution Timeline 1776 Declaration of Independence 1777 Articles of Confederation (in force 1781) 1789 United States Constitution (replacing the Articles of Confederation) The Constitution
Revised D1 Constitution Timeline 1776 Declaration of Independence 1777 Articles of Confederation (in force 1781) 1789 United States Constitution (replacing the Articles of Confederation) The Constitution
