Quarter One: Unit Four
|
|
|
- Beverly Pierce
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will identify the weaknesses of the government under the Articles of Confederation (i.e., Congress had no power to tax, to regulate trade, or to enforce its laws; the national government lacked a national court system [judicial branch] and central leadership [executive branch]; and changes to the Articles required unanimous consent of the 13 states). **** Terms I need to know at the end of this lesson. Articles of Confederation (weaknesses) Shay s Rebellion Debt Key Events: Year Event 1775 Revolutionary War begins (the 13 Colonies revolt against the British) Constitutional Convention 1776 Declaration of Independence written and approved by the Continental Congress 1781 Ratification of the Articles of Confederation by all 13 states March 1, The Articles created a loose confederation of independent states and a weak central government, leaving most of the power with the state governments Revolutionary War Ends Britain recognizes the independence of the USA (Treaty of Paris) US Constitution written at the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia, PA [May 25 - Sept. 17] US Constitution ratified by 9 states [June 22] and becomes the supreme law of the USA Critical Background Information: Mark the text with a purpose! (NUMBER PARAGRAPHS) 1. The core parts of the Articles of Confederation The first government of the United States following the Declaration of Independence was the Articles of Confederation ( ). A confederation is a statecentered, form of government where the power is held at the state level. The Declaration of Independence spoke of the many abuses of King George III, who, as a king ruled over the executive, legislative and judicial powers of the government in the colonies. In the Declaration, Thomas Jefferson stated that both King George III and the form of government in place at the time both failed to protect the colonists life, liberty and pursuit of happiness..aka natural rights. What did John Locke say that citizens could do if their government did not protect their rights? The colonists decided to create a government that was quite different from a unitary system where the powers of government were concentrated in a single person, the king. This confederal system reflected the colonists fear of a powerful central government or a king that held all the power. Under the Articles of Confederation, states kept their freedom and independence. Each of the 13 states had a vote in the weak national Congress (appointed by the state governments), a unanimous vote of all 13 states was required for the Articles to be amended. That was difficult when each state was looking out for 1
2 themselves. The national Congress was also denied the power to tax, so it could not pay for the army and navy needed to defend the nation. The national Congress also lacked the power to regulate trade. As for the other powers of government, there was no national court system nor was there a national executive. The result of this system was that each state acted in many ways as an independent country. The lack of a national court system meant that criminals committing crimes in one state would often flee to another state where they could not be punished. Without a national military, states that were attacked from outside forces or from inside forces (like a rebellion) could not turn to the national government for support or resources for their defense. The result of these state actions was that the states, despite being part of the same country, did not function as a nation. For instance, fears emerged that the 13 states functioning as independent countries would make the nation vulnerable to attack by Spain, France, by Native Americans. Responding to Shay s Rebellion Shay s Rebellion was a citizen rebellion that began in Two thousand western Massachusetts farmers marched on county courthouses to prevent their homes and land from being foreclosed upon and taken from them. The farmers land was threatened with foreclosure because they were assured that they did not have to pay taxes and other debts on their land during the Revolutionary War. These promises were not kept, which prompted the farmers to revolt. Congress would not respond because it was too weak and did not collect federal taxes therefore it did not have its own army. Shay s Rebellion made it very clear that big changes needed to be made. The federal government needed the power to collect taxes to be able to form a United States military. **What did Shay s Rebellion make obvious? The lack of a weak national Congress along with each state s independent and often conflicting actions, raised concerns that the Articles of Confederation were not designed in a way to protect the new nation. The Articles of Confederation definitely did not UNITE the states. In February 1787, Alexander Hamilton called for a constitutional convention, a Meeting of Commissioners to Remedy Defects of the Federal Government to take place the following May. The original purpose was to amend or tweak the Articles of Confederation. In May 1787, 12 of the 13 states met in Philadelphia, PA for this purpose. It became apparent that tweaking the Articles of Confederation would not do and the outcome of the Constitutional Convention was the U.S. Constitution which was completed on September 17, 1787 and sent to the states for their review and ratification or approval. Purpose ***Why did they meet at the Constitutional Convention? ***What was the outcome of the Constitutional Convention? Outcome 2
3 SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation Triple D! Define Describe Draw Word/Term Articles of Confederation Paragraph # in the reading Definition/Describe/Draw Define: Describe in your own words: Draw: Confederation (or confederal system of government) Define: Describe in your own words: Draw: Weaknesses in the Articles of Confederation Define: Describe in your own words: Draw: 3
4 Constitutional Convention Define: Describe in your own words: Draw: debt Define: Describe in your own words: Draw: Shay s Rebellion Define: Describe in your own words: Draw: 4
5 SS.7.C.1.5 Constitution Fixes Weakness in Articles of Confederation 1. There was no central leadership (executive branch) 2. Congress had no power to tax 3. Congress had no power to regulate trade 4. The national government lacked a national court system (judicial branch) 5. Changes to the Articles required unanimous consent of the 13 states. 6. Congress Excerpts had no power of the to enforce U.S. Constitution its laws Directions: Below are six excerpts from the U.S. Constitution. Summarize the excerpts in your own words. Then, compare the excerpt to the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation and determine which weakness is related to the excerpt. US Constitution: Article I, Section 8: The Congress shall have Power To lay and collect Taxes, Duties, Imposts, and Excises, to pay the Debts and provide for the common Defence and general Welfare of the Unites States; but all Duties, Imposts and Excises shall be uniform throughout the United States. What does this mean? Which weakness does this fix? US Constitution: Article I, Section 8: The Congress shall have Power To regulate Commerce foreign Nations, and among the several States What does this mean? Which weakness does this fix? US Constitution: Article II, Section 3:.he shall take Care that the Laws be faithfully executed What does this mean? Which weakness does this fix? US Constitution: Article III, Section 1: The judicial Power of the United States, shall be vested in one supreme Court, and in such inferior Courts as the Congress may from time to time ordain and establish. What does this mean? Which weakness does this fix? US Constitution: Article II, Section 1: The executive Power shall be vested in a President of the United States of America. What does this mean? Which weakness does this fix? US Constitution: Article V: The Congress, whenever two thirds of both Houses shall deem it necessary, shall propose Amendments to this Constitution What does this mean? Which weakness does this fix? 5
6 NOTES: 6
7 SS.7.C.1.6 Preamble Introduction and Unscramble the Preamble ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will explain how the Preamble serves as an introduction to the U.S. Constitution, establishing the goals and purposes of government. Students will identify the SIX goals and purposes of government as set forth in the Preamble of the U.S. Constitution (i.e., 1. form a more perfect union, 2. establish justice, 3. ensure domestic tranquility, 4. provide for the common defense, 5. promote the general welfare, and 6. secure the blessings of liberty to ourselves and our posterity). Students will recognize that the intention of the phrase We the People means that government depends on the people for its power and exists to serve them. **** Terms I need to know at the end of this lesson. Union Justice Domestic Tranquility Welfare Posterity Ordain Defense The Preamble of the U.S. Constitution We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defence, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings of Liberty to ourselves and our Posterity, do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America. What is a synonym for preamble? Following are some words that will help you UNSCRAMBLE the PREAMBLE: 1. union something formed by combining 6. defense method of protecting oneself parts, such as states into one country 2. justice a system of establishing what is 7. welfare well-being legal and illegal by fair rules, legal system 3. insure ensure, to make sure 8. future generations posterity 4. domestic referring to something at home, not 9. ordain to establish something by law foreign, within the country 5. tranquility peace 10. liberty Freedom from, independence Circle the text from this statement that answers the question: Where does the government s power come from? We the People of the United States do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America 7
8 What are the goals and purposes of government? Translate the goals and purposes of government. List the goals and purposes of government: Translate the goals and purposes of government: 8
9 SS.7.C.1.8 Federalists and Anti-Federalists We need a strong central government! We need a bill of rights! ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: identify the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists about the ratification of the U.S. Constitution. compare the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists about the ratification of the U.S. Constitution. recognize the Anti-Federalists reasons for the inclusion of a bill of rights in the U.S. Constitution. **** Terms I need to know at the end of this lesson. Federalist Viewpoints Federalist Papers Anti-Federalist Viewpoints Anti-Federalist Papers Bill of Rights Ratification Background Reading: Mark the text with a purpose! During the period from the drafting and proposal of the Constitution between May and September, 1787, to its ratification or approval in 1788 there was an intense debate on ratification. During this period, people basically divided into two groups, the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists. People opposed to the ratification of the Constitution were called the Anti-Federalists. They were concerned that the Constitution gave too much power to the federal, or national, government at the expense of the state governments. They were also concerned that, within the federal government, the legislative and executive branches were too powerful. Specifically, the Anti-Federalists were concerned that the necessary and proper clause in Article I, Section 8 of the Constitution, which allows Congress to do what it believes is necessary and proper in order to carry out its other responsibilities, was too broad and would give Congress too much power. Anti-Federalists were also concerned that the Constitution lacked a specific listing of rights or a bill of rights. They believed that a bill of rights was essential to protect the people from the federal government. The Revolutionary War had just been fought because the American people needed to defend their rights. With the war experience still in mind, the Anti-Federalists did not want a powerful national government taking away those rights. The lack of a bill of rights became the focus of the Anti-Federalist campaign against ratification. To communicate their concerns, Anti-Federalists such as Patrick Henry wrote essays and newspaper articles to spread their point of view and these writings became known as the Anti-Federalist Papers. Other Anti- Federalists were George Mason and Thomas Jefferson. 9
10 The supporters of the proposed Constitution called themselves Federalists. For the Federalists, the Constitution was necessary in order to protect the liberty and independence that was gained from the American Revolution. The main arguments in favor of ratifying the Constitution were stated in a series of essays published in newspapers written by James Madison, George Washington, Alexander Hamilton, and John Jay called the Federalist Papers. They believed that the three branches of the national government separated the powers and protected the rights of the people. Each branch represents a different aspect of the people, and because all three branches are equal, no one group can assume control over another. They also believed that a listing of rights can be a dangerous thing. If the federal government were to protect specific listed rights, what would stop it from violating or abusing rights that were not listed? Since they cannot list all the rights, the Federalists argued that it is better to list no rights at all. Overall, the Federalists were more organized in their efforts. By June of 1788, the Constitution was close to ratification. Nine states had voted to ratify it (eight voted yes and New York at first voted no ), and only one more (New Hampshire) was needed. To achieve this, the Federalists agreed that once Congress met, it would draft a bill of rights. Finally, New York and Virginia approved, and the Constitution was a reality. Interestingly, the Bill of Rights (1 st Ten Amendments) was not originally a part of the Constitution, and yet it has proved to be highly important to protecting the rights of the people. Bill of Rights Video: Take Notes from reading and video: Federalist Anti- Federalist Beliefs 10
11 People What papers did they write? View Points of the Federalist and Anti Federalist From the video and the background reading tell me what you know. Question: Answer in a complete, well-developed sentence. What were the Federalist viewpoints? Who were some Federalists? What were the Federalist papers? What were the Anti-Federalist viewpoints? Who were some Anti-Federalists? What were the Anti-Federalist papers? What is the Bill of Rights? What does ratification mean? Paragraph # 11
12 SS.7.C.1.7 Separation of Powers and Checks and Balances ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will explain the concept of limited government as set forth in the U.S. Constitution. Students will describe and distinguish between the concepts of separation of powers and checks and balances. Students will analyze how government power is limited by separation of powers and/or checks and balances. Students will be able to recognize examples of separation of powers and checks and balances. **** Terms I need to know at the end of this lesson. Limited Government Separation of Powers Checks and Balances Constitutional Government ************************************************************************************* The framers of the Constitution feared too much centralized power. Therefore at the national level, they created three different branches of government to administer three different types of power. (Which Enlightenment thinker came up with this idea? ) The legislative branch made the laws through a Congress of two houses, the Senate and the House of Representatives. The executive branch enforced the laws through a president and many advisors called cabinet members. And the judicial branch interpreted the laws through a Supreme Court and other lower courts. In the words of James Madison: The accumulation of all powers, legislative, executive, and judiciary, in the same hands, whether of one, a few, or many, and whether hereditary, self-appointed, or elective, may justly be pronounced the very definition of tyranny. (What does Madison mean? ) Within the separation of powers, each of the three branches of government has checks and balances over the other two. For instance, Congress makes the laws, but the President can veto them and the Supreme Court can declare them unconstitutional. The President enforces the law, but Congress must approve executive appointments and the Supreme Court rules whether executive action is constitutional. The Supreme Court can strike down actions by both the legislative and executive branches, but the President nominates Supreme Court justices and the Senate confirms or denies their nominations. ************************************************************************************* Complete: The legislative branch is made up of, comprised of the House of and the. The executive branch is made up of the and his. The judicial branch is made up of the and lower federal courts. 12
13 SS.7.C.3.3 Structure of the US Constitution PREAMBLE (Introduction) the six goals and purposes of government ARTICLE I - Establishes the Legislative Branch (House of Representatives and the Senate). This branch makes laws ARTICLE II - Establishes the Executive Branch (headed by the President). This branch enforces laws ARTICLE III - Establishes the Judicial Branch (a system of courts and judges). This branch interprets laws ARTICLE IV - Establishes the relationship between the states and the federal government. Describes how to admit new states to the Union. ARTICLE V - Describes how to amend the Constitution. ARTICLE VI - Establishes the Constitution as the supreme law of the USA. Authorizes the national debt (Congress can borrow money). Public officials must take an oath to support the Constitution. ARTICLE VII - Lists the requirements for ratification of the Constitution. AMENDMENTS 1-27 (1-10 THE BILL OF RIGHTS) Complete 13
14 SS.7.C.3.5 The Amendment Process ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: recognize the methods used to propose and ratify amendments to the U.S. Constitution. identify the correct sequence of each amendment process. identify the importance of a formal amendment process. recognize the significance of the difficulty of formally amending the U.S. Constitution. **** Terms I need to know at the end of this lesson. Amendment Process Caucus Ratify Amending the U.S. Constitution Article V (FIVE) of the U.S. Constitution outlines two methods for introducing amendments to the U.S. Constitution. One method of amending the Constitution is for 2/3 of each house of CONGRESS (287 of the 435-member House of Representatives, and 66 of the 100 Senators. That is a total of 353!) to pass a proposed amendment and send it to the states legislatures. It takes 3/4 (38) states approval of the amendment in order for it to be added to the Constitution What is Congress? ****We the People do not directly vote on new amendments, and the President does not vote on or veto any amendment. **** Another method for amending the Constitution is a Constitutional Convention to be called for by 2/3 (33) of the state legislatures. At such a convention, one or more amendments can be proposed and then sent to the state legislatures (or state conventions) for approval again, 3/4 of the state legislatures must approve. (This method has not been used successfully). The Constitution has been amended 27 times; the first 10 amendments, the Bill of Rights, were ratified in The Constitution was last amended in Questions: Define Amendment: Define Caucus: How many amendments to the Constitution have been ratiftied? What are the first 10 Amendments to the Constitution called? Which Article of the Constitution states the process for amending the Constitution? True or False: The President directly votes on amendments to the Constitution? Remember the song..2/3s of both houses, 3/4s of all states! 14
Quarter One: Unit Four
 SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will identify the weaknesses of the government under the Articles of Confederation (i.e.,
SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will identify the weaknesses of the government under the Articles of Confederation (i.e.,
FEDERALISTS, ANTI-FEDERALISTS AND THE CONSTITUTION SS.7.C.1.8
 FEDERALISTS, ANTI-FEDERALISTS AND THE CONSTITUTION SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the ratification of the Constitution and inclusion of a bill of
FEDERALISTS, ANTI-FEDERALISTS AND THE CONSTITUTION SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the ratification of the Constitution and inclusion of a bill of
The Articles of Confederation
 The Articles of Confederation The Articles of Confederation was the first government of the United States following the Declaration of Independence. A confederation is a state-centered, decentralized government
The Articles of Confederation The Articles of Confederation was the first government of the United States following the Declaration of Independence. A confederation is a state-centered, decentralized government
SS.7.C.1.5. Identify how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing of the Constitution
 SS.7.C.1.5. Identify how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing of the Constitution SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the
SS.7.C.1.5. Identify how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing of the Constitution SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the
understanding CONSTITUTION
 understanding the CONSTITUTION Contents The Articles of Confederation The Constitutional Convention The Principles of the Constitution The Preamble The Legislative Branch The Executive Branch The Judicial
understanding the CONSTITUTION Contents The Articles of Confederation The Constitutional Convention The Principles of the Constitution The Preamble The Legislative Branch The Executive Branch The Judicial
10/6/11. A look at the history and organization of US Constitution
 A look at the history and organization of US Constitution During Revolution, the states created a confederation. Loose association of states. Continental Congress responsible to war effort during the Revolution.
A look at the history and organization of US Constitution During Revolution, the states created a confederation. Loose association of states. Continental Congress responsible to war effort during the Revolution.
1 st United States Constitution. A. loose alliance of states. B. Congress lawmaking body. C. 9 states had to vote to pass laws
 1 st United States Constitution A. loose alliance of states B. Congress lawmaking body C. 9 states had to vote to pass laws D. each state had 1 vote in Congress Northwest Ordinance / Land Ordinance division
1 st United States Constitution A. loose alliance of states B. Congress lawmaking body C. 9 states had to vote to pass laws D. each state had 1 vote in Congress Northwest Ordinance / Land Ordinance division
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of American Government
 Chapter 2: The Beginnings of American Government United States Government Fall, 2017 Origins of American Political Ideals Colonial Period Where did ideas for government in the colonies come from? Largely,
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of American Government United States Government Fall, 2017 Origins of American Political Ideals Colonial Period Where did ideas for government in the colonies come from? Largely,
The Articles of Confederation
 The Articles of Confederation 1777-1787 During the American Revolution States organized their governments and adopted their own state constitutions. But, Americans needed to establish their own national
The Articles of Confederation 1777-1787 During the American Revolution States organized their governments and adopted their own state constitutions. But, Americans needed to establish their own national
Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation
 Name: Date: Chapter 8 Study Guide Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation 1. A constitution is a set of basic principles and laws, usually in written form, that state the powers and duties of a government.
Name: Date: Chapter 8 Study Guide Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation 1. A constitution is a set of basic principles and laws, usually in written form, that state the powers and duties of a government.
Civics Learning Goals for the 2 nd Quarter
 Civics Learning Goals for the 2 nd Quarter Unit: The Founding From Colonies to the United States C.1.1 Recognize how Enlightenment ideas including Montesquieu s view of separation of powers and John Locke
Civics Learning Goals for the 2 nd Quarter Unit: The Founding From Colonies to the United States C.1.1 Recognize how Enlightenment ideas including Montesquieu s view of separation of powers and John Locke
THE CONSTITUTION. How do societies balance individual and community rights? How does social change influence government?
 CHAPTER 5 THE CONSTITUTION NGSSS SS.7.C.1.7 Describe how the Constitution limits the powers of government through separation of powers and checks and balances. ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why do people create,
CHAPTER 5 THE CONSTITUTION NGSSS SS.7.C.1.7 Describe how the Constitution limits the powers of government through separation of powers and checks and balances. ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why do people create,
Chapter 3 Constitution. Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook
 Chapter 3 Constitution Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on www.pknock.com Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from
Chapter 3 Constitution Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on www.pknock.com Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from
3: A New Plan of Government. Essential Question: How Do Governments Change?
 3: A New Plan of Government Essential Question: How Do Governments Change? The Constitution s Source Guiding Question: From where did the Framers of the Constitution borrow their ideas about government?
3: A New Plan of Government Essential Question: How Do Governments Change? The Constitution s Source Guiding Question: From where did the Framers of the Constitution borrow their ideas about government?
AIM: How did the Articles of Confederation impact the U.S.?
 AIM: How did the Articles of Confederation impact the U.S.? Do Now: How do you think Hale Charter Academy would function if we got rid of the assistant principal, and the dean, and we allowed the individual
AIM: How did the Articles of Confederation impact the U.S.? Do Now: How do you think Hale Charter Academy would function if we got rid of the assistant principal, and the dean, and we allowed the individual
2. Divided Convention. 3. Inside the Constitution. Constitution replaced the Articles---becomes the law of the land.
 2. Divided Convention notes7 9/13 states needed to ratify (to approve) Political parties begin Federalists: supported the Constitution The Federalist ---essays support Constitution Anti-Federalists: against
2. Divided Convention notes7 9/13 states needed to ratify (to approve) Political parties begin Federalists: supported the Constitution The Federalist ---essays support Constitution Anti-Federalists: against
Analyze the maps in Setting the Stage. Then answer the following questions and fill out the map as directed.
 Geography Challenge G e o G r a p h y C h a l l e n G e Geography Skills Analyze the maps in Setting the Stage. Then answer the following questions and fill out the map as directed. 1. Label each state
Geography Challenge G e o G r a p h y C h a l l e n G e Geography Skills Analyze the maps in Setting the Stage. Then answer the following questions and fill out the map as directed. 1. Label each state
The U.S. Constitution. Ch. 2.4 Ch. 3
 The U.S. Constitution Ch. 2.4 Ch. 3 The Constitutional Convention Philadelphia Five months, from May until September 1787 Secret Meeting, closed to outside. Originally intent to revise the Articles of
The U.S. Constitution Ch. 2.4 Ch. 3 The Constitutional Convention Philadelphia Five months, from May until September 1787 Secret Meeting, closed to outside. Originally intent to revise the Articles of
Shays. Daniel Shay 1784 to 1785, unfair taxes, debt and foreclosure Farmer s rebellion to overthrow Mass. Govt.
 Shays Daniel Shay 1784 to 1785, unfair taxes, debt and foreclosure Farmer s rebellion to overthrow Mass. Govt. 1. Constitutional Convention: May to Sept. 1787 2. Divided Convention 9/13 states needed to
Shays Daniel Shay 1784 to 1785, unfair taxes, debt and foreclosure Farmer s rebellion to overthrow Mass. Govt. 1. Constitutional Convention: May to Sept. 1787 2. Divided Convention 9/13 states needed to
i n t e r a C t i v e s t u d e n t n o t e b o o k Mapping Activity 11/02/17
 Mapping Activity 11/02/17 Geography Skills Analyze the maps in Setting the Stage. Then answer the following questions and fill out the map as directed. 1. Label each state on the map. Which two states
Mapping Activity 11/02/17 Geography Skills Analyze the maps in Setting the Stage. Then answer the following questions and fill out the map as directed. 1. Label each state on the map. Which two states
Close Read: Articles of Confederation vs. Constitution
 Close Read: vs. CR Objective CR Introduction What are the differences between the governing systems and structures established by the and the? The were written in, and ratified in. Following a turbulent
Close Read: vs. CR Objective CR Introduction What are the differences between the governing systems and structures established by the and the? The were written in, and ratified in. Following a turbulent
Guided Reading Activity
 Guided Reading Activity Lesson 1 Government in Colonial America Review Questions Directions: Read each main idea. Use your text to supply the details that support or explain each main idea. A. Main Idea:
Guided Reading Activity Lesson 1 Government in Colonial America Review Questions Directions: Read each main idea. Use your text to supply the details that support or explain each main idea. A. Main Idea:
Section One. A) The Leviathan B) Two Treatises of Government C) Spirit of the Laws D) The Social Contract
 Government Exam Study Guide You will need to be prepared to answer/discuss any of these questions on the exam in various formats. We will complete this study guide in class and review it. Section One 1)
Government Exam Study Guide You will need to be prepared to answer/discuss any of these questions on the exam in various formats. We will complete this study guide in class and review it. Section One 1)
Weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation 1. Congress could not levy or collect taxes
 Virginia Plan New Jersey Plan The Great Compromise UNIT 2 TEST REVIEW SHEET Strengths of A of C 1- Established Federalism - A system of government where power is divided between a national government and
Virginia Plan New Jersey Plan The Great Compromise UNIT 2 TEST REVIEW SHEET Strengths of A of C 1- Established Federalism - A system of government where power is divided between a national government and
UNIT 2 TEST REVIEW SHEET. Weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation 1. Congress could not levy or collect taxes
 Virginia Plan New Jersey Plan The Great Compromise UNIT 2 TEST REVIEW SHEET Strengths of A of C 1- Established Federalism - A system of government where power is divided between a national government and
Virginia Plan New Jersey Plan The Great Compromise UNIT 2 TEST REVIEW SHEET Strengths of A of C 1- Established Federalism - A system of government where power is divided between a national government and
The Constitution: A More Perfect Union
 The Constitution: A More Perfect Union How has the Constitution created a more perfect Union? P R E V I E W Read the quotation and answer the questions that follow. If men were angels, no government would
The Constitution: A More Perfect Union How has the Constitution created a more perfect Union? P R E V I E W Read the quotation and answer the questions that follow. If men were angels, no government would
United States Constitution 101
 Constitution 101: An Introduction & Overview to the US Constitution United States Constitution 101 This PPT can be used alone or in conjunction with the Consortium s Goal 1 & 2 lessons, available in the
Constitution 101: An Introduction & Overview to the US Constitution United States Constitution 101 This PPT can be used alone or in conjunction with the Consortium s Goal 1 & 2 lessons, available in the
The Coming of Independence. Ratifying the Constitution
 C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government 1 SECTION 1 SECTION 2 SECTION 3 SECTION 4 SECTION 5 Our Political Beginnings The Coming of Independence The Critical Period Creating the Constitution Ratifying
C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government 1 SECTION 1 SECTION 2 SECTION 3 SECTION 4 SECTION 5 Our Political Beginnings The Coming of Independence The Critical Period Creating the Constitution Ratifying
The Constitution I. Considerations that influenced the formulation and adoption of the Constitution A. Roots 1. Religious Freedom a) Puritan
 The Constitution I. Considerations that influenced the formulation and adoption of the Constitution A. Roots 1. Religious Freedom a) Puritan Theocracy (1) 9 of 13 had state church b) Rhode Island (1) Roger
The Constitution I. Considerations that influenced the formulation and adoption of the Constitution A. Roots 1. Religious Freedom a) Puritan Theocracy (1) 9 of 13 had state church b) Rhode Island (1) Roger
How Shall We Govern Ourselves?
 How Shall We Govern Ourselves? The Articles of Confederation America s First Constitution What kind of government would the FREEDOM loving Americans create to balance LIBERTY with enough AUTHORITY to get
How Shall We Govern Ourselves? The Articles of Confederation America s First Constitution What kind of government would the FREEDOM loving Americans create to balance LIBERTY with enough AUTHORITY to get
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Articles of Confederation. Essential Question:
 Articles of Confederation Essential Question: Why was the central government s power too weak under the Articles of Confederation? Objectives Discuss the ideas that guided the new state governments. Describe
Articles of Confederation Essential Question: Why was the central government s power too weak under the Articles of Confederation? Objectives Discuss the ideas that guided the new state governments. Describe
Name Class Date. MATCHING In the space provided, write the letter of the term or person that matches each description. Some answers will not be used.
 Origins of American Government Section 1 MATCHING In the space provided, write the letter of the term or person that matches each description. Some answers will not be used. 1. Idea that people should
Origins of American Government Section 1 MATCHING In the space provided, write the letter of the term or person that matches each description. Some answers will not be used. 1. Idea that people should
Articles of Confederation vs. Constitution
 Articles of Confederation vs. Analysis Objective What kind of government was set up by the Articles of Confederation? How does this compare to the US? Directions: Analyze the timeline below to understand
Articles of Confederation vs. Analysis Objective What kind of government was set up by the Articles of Confederation? How does this compare to the US? Directions: Analyze the timeline below to understand
US Government Module 2 Study Guide
 US Government Module 2 Study Guide 2.01 Revolutionary Ideas The Declaration of Independence contains an introduction, list of grievances, and formal statement of independence. The principle of natural
US Government Module 2 Study Guide 2.01 Revolutionary Ideas The Declaration of Independence contains an introduction, list of grievances, and formal statement of independence. The principle of natural
The Constitution. Chapter 2 O Connor and Sabato American Government: Continuity and Change
 The Constitution Chapter 2 O Connor and Sabato American Government: Continuity and Change The Constitution In this chapter we will cover 1. The Origins of a New Nation 2. The Declaration of Independence
The Constitution Chapter 2 O Connor and Sabato American Government: Continuity and Change The Constitution In this chapter we will cover 1. The Origins of a New Nation 2. The Declaration of Independence
FEDERAL GOVERNMENT GOVT Limited Government & Representative Government September 18, Dr. Michael Sullivan. MoWe 5:30-6:50 MoWe 7-8:30
 Limited Government & Representative Government September 18, 2017 FEDERAL GOVERNMENT GOVT 2305 MoWe 5:30-6:50 MoWe 7-8:30 Dr. Michael Sullivan TODAY S AGENDA Current Events Limited Government Representative
Limited Government & Representative Government September 18, 2017 FEDERAL GOVERNMENT GOVT 2305 MoWe 5:30-6:50 MoWe 7-8:30 Dr. Michael Sullivan TODAY S AGENDA Current Events Limited Government Representative
THE CONSTITUTION. Chapter 2
 THE CONSTITUTION Chapter 2 ROOTS OF THE CONSTITUTION 2.1 TRADE AND TAXATION 2.1 Mercantilism Strict import/export controls Widely ignored Costly French and Indian War New taxes on sugar and paper items
THE CONSTITUTION Chapter 2 ROOTS OF THE CONSTITUTION 2.1 TRADE AND TAXATION 2.1 Mercantilism Strict import/export controls Widely ignored Costly French and Indian War New taxes on sugar and paper items
The Constitution. Karen H. Reeves
 The Constitution Karen H. Reeves Toward a New Union Annapolis Convention (Sept. 1786) Met to determine commercial regulation Nationalists called for Constitutional Convention Constitutional Convention
The Constitution Karen H. Reeves Toward a New Union Annapolis Convention (Sept. 1786) Met to determine commercial regulation Nationalists called for Constitutional Convention Constitutional Convention
Name: 8 th Grade U.S. History. STAAR Review. Constitution
 8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Constitution FORT BURROWS 2018 VOCABULARY Confederation - A group of loosely connected nations or states that work together for mutual benefit. Republic - A system
8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Constitution FORT BURROWS 2018 VOCABULARY Confederation - A group of loosely connected nations or states that work together for mutual benefit. Republic - A system
From Revolution to Government
 From Revolution to Government The Second Continental Congress declared independence from Britain in 1776. The Revolutionary War lasted from 1775 to 1783. Congress developed a new government for America:
From Revolution to Government The Second Continental Congress declared independence from Britain in 1776. The Revolutionary War lasted from 1775 to 1783. Congress developed a new government for America:
Anatomy of the Constitution
 We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defense, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings
We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defense, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings
Charles de Montesquieu
 Unit III He first created the idea of consent of the governed where people have a vote in who leads them (democracy). Every person has the right to life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness. John Locke
Unit III He first created the idea of consent of the governed where people have a vote in who leads them (democracy). Every person has the right to life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness. John Locke
A More Perfect Union. Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation
 A More Perfect Union Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation 1. Eleven of the thirteen states adopted state constitutions. Connecticut and Rhode Island kept its colonial charter as its constitution
A More Perfect Union Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation 1. Eleven of the thirteen states adopted state constitutions. Connecticut and Rhode Island kept its colonial charter as its constitution
4 th Grade U.S. Government Study Guide
 4 th Grade U.S. Government Study Guide Big Ideas: Imagine trying to make a new country from scratch. You ve just had a war with the only leaders you ve ever known, and now you have to step up and lead.
4 th Grade U.S. Government Study Guide Big Ideas: Imagine trying to make a new country from scratch. You ve just had a war with the only leaders you ve ever known, and now you have to step up and lead.
BEGINNINGS: Political essentials and foundational ideas
 BEGINNINGS: Political essentials and foundational ideas 1689 LOCKE S SECOND TREATISE ON GOVERNMENT: Natural Rights: Life, Liberty & Property which existed before government Legitimate government depends
BEGINNINGS: Political essentials and foundational ideas 1689 LOCKE S SECOND TREATISE ON GOVERNMENT: Natural Rights: Life, Liberty & Property which existed before government Legitimate government depends
Why do you think the Framers organized the new country as a republic, when most countries in the world (in 1783) were ruled by a king or queen?
 NAME: Date: U.S. History CHAPTER 7 PACKET ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: 1. What is a constitution? 2. What is a republic? 3. What was the Articles of Confederation? 4. How was state and national power divided under
NAME: Date: U.S. History CHAPTER 7 PACKET ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: 1. What is a constitution? 2. What is a republic? 3. What was the Articles of Confederation? 4. How was state and national power divided under
Constitutional Democracy: Promoting Liberty and Self-Government. Chapter 2
 Constitutional Democracy: Promoting Liberty and Self-Government Chapter 2 Before the Constitution: Colonial and Revolutionary Experiences The Rights of Englishmen Life, liberty and property to which all
Constitutional Democracy: Promoting Liberty and Self-Government Chapter 2 Before the Constitution: Colonial and Revolutionary Experiences The Rights of Englishmen Life, liberty and property to which all
Magruder s American Government
 Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 Our Political Beginnings
Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 Our Political Beginnings
The Articles of!confederation
 The Articles of Confederation Our New Nation s First Constitution The Articles of Confederation When the Second Continental Congress appointed a committee to write a Declaration of Independence in 1776,
The Articles of Confederation Our New Nation s First Constitution The Articles of Confederation When the Second Continental Congress appointed a committee to write a Declaration of Independence in 1776,
OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS
 CHAPTER 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS The colonists brought with them to North America knowledge of the English political system, including three key ideas about government.
CHAPTER 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS The colonists brought with them to North America knowledge of the English political system, including three key ideas about government.
Chapter 25 Section 1. Section 1. Terms and People
 Chapter 25 Terms and People republic a government in which the people elect their representatives unicameral legislature a lawmaking body with a single house whose representatives are elected by the people
Chapter 25 Terms and People republic a government in which the people elect their representatives unicameral legislature a lawmaking body with a single house whose representatives are elected by the people
History Of American Justice P R E S E N T E D T O F A C U L T Y O F L A W B E L G R A D E M A R C H, BY J U D G E D A L E A.
 History Of American Justice P R E S E N T E D T O F A C U L T Y O F L A W B E L G R A D E M A R C H, 2 0 1 1 BY J U D G E D A L E A. C R A W F O R D 1492-1774 Colonists-Wanted their own land and wanted
History Of American Justice P R E S E N T E D T O F A C U L T Y O F L A W B E L G R A D E M A R C H, 2 0 1 1 BY J U D G E D A L E A. C R A W F O R D 1492-1774 Colonists-Wanted their own land and wanted
Creating the Constitution
 Creating the Constitution 1776-1791 US Timeline 1777-1791 1777 Patriots win Battles of Saratoga. Continental Congress passes the Articles of Confederation. 1781 Articles of Confederation go into effect.
Creating the Constitution 1776-1791 US Timeline 1777-1791 1777 Patriots win Battles of Saratoga. Continental Congress passes the Articles of Confederation. 1781 Articles of Confederation go into effect.
The Articles vs. the Constitution Articles of Confederation. U.S. Constitution A Firm League of Friendship
 USHC 1.4 Analyze how dissatisfactions with the government under the Articles of Confederation were addressed with the writing of the Constitution of 1787, including the debates and compromises reached
USHC 1.4 Analyze how dissatisfactions with the government under the Articles of Confederation were addressed with the writing of the Constitution of 1787, including the debates and compromises reached
We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, provide for the common defense, promote the general Welfare,
 We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defense, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings
We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defense, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings
Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50
 Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50 The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from religious persecution Economic opportunity Independent
Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50 The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from religious persecution Economic opportunity Independent
Early US. Unit 3 Visuals
 Early US Unit 3 Visuals 1 st US Government Articles of Confederation Articles of Confederation 1 st form of national Gov t Powerful State Gov t Weak Central Gov t No Taxes Couldn t enforce laws No President
Early US Unit 3 Visuals 1 st US Government Articles of Confederation Articles of Confederation 1 st form of national Gov t Powerful State Gov t Weak Central Gov t No Taxes Couldn t enforce laws No President
Articles of Confederation
 Articles of Confederation Do Now How is power divided in our country today? SWBAT Analyze government problems under the Articles of Confederation Activity Review the Articles of Confederation chart and
Articles of Confederation Do Now How is power divided in our country today? SWBAT Analyze government problems under the Articles of Confederation Activity Review the Articles of Confederation chart and
Chapter 6. APUSH Mr. Muller
 Chapter 6 APUSH Mr. Muller Aim: How is the New Republic tested? Do Now: Thus I consent, sir, to this Constitution, because I expect no better, and because I am not sure that it is not the best. The opinions
Chapter 6 APUSH Mr. Muller Aim: How is the New Republic tested? Do Now: Thus I consent, sir, to this Constitution, because I expect no better, and because I am not sure that it is not the best. The opinions
1. STUDENTS WILL BE ABLE TO IDENTIFY AND EXPLAIN THE WEAKNESSES OF THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION
 SOUTHWESTERN CHRISTIAN SCHOOL UNITED STATES HISTORY STUDY GUIDE # 7 : CREATING A NEW NATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES STUDENTS WILL BE ABLE TO IDENTIFY AND EXPLAIN THE WEAKNESSES OF THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION
SOUTHWESTERN CHRISTIAN SCHOOL UNITED STATES HISTORY STUDY GUIDE # 7 : CREATING A NEW NATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES STUDENTS WILL BE ABLE TO IDENTIFY AND EXPLAIN THE WEAKNESSES OF THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION
America: The Last Best Hope Chapter 4 Reflection and Choice
 America: The Last Best Hope Chapter 4 Reflection and Choice 1. Under the Articles of Confederation, Congress had all of the following powers EXCEPT A settle disputes between the states B borrow money C
America: The Last Best Hope Chapter 4 Reflection and Choice 1. Under the Articles of Confederation, Congress had all of the following powers EXCEPT A settle disputes between the states B borrow money C
Chapter 02 The Constitution
 Chapter 02 The Constitution Multiple Choice Questions 1. (p. 34) Which of these countries employs an unwritten constitution? A. the United States B. Great Britain C. France D. Sweden E. Germany Difficulty:
Chapter 02 The Constitution Multiple Choice Questions 1. (p. 34) Which of these countries employs an unwritten constitution? A. the United States B. Great Britain C. France D. Sweden E. Germany Difficulty:
Citizenship in American History and Government. Unit 6
 Citizenship in American History and Government Unit 6 Chapter 1 You the People Citizenship Skills Lesson 1 The Preamble What You Will Learn to Do Examine the Preamble to the American Constitution Linked
Citizenship in American History and Government Unit 6 Chapter 1 You the People Citizenship Skills Lesson 1 The Preamble What You Will Learn to Do Examine the Preamble to the American Constitution Linked
Unit 4 Writing the Constitution Concepts to Review
 Unit 4 Writing the Constitution Concepts to Review CAUSE AND EFFECTS OF MAJOR ERAS AND EVENTS IN U.S. HISTORY THROUGH 1877 Writing the Constitution Shays Rebellion Philadelphia Convention 1787 Great Compromise
Unit 4 Writing the Constitution Concepts to Review CAUSE AND EFFECTS OF MAJOR ERAS AND EVENTS IN U.S. HISTORY THROUGH 1877 Writing the Constitution Shays Rebellion Philadelphia Convention 1787 Great Compromise
How is the Constitution structured?
 How is the structured? Lesson 14 Objectives You will be able to identify and analyze the U.S. s structure. The Facts and Characteristics provides a framework for the U.S. government is the basic law of
How is the structured? Lesson 14 Objectives You will be able to identify and analyze the U.S. s structure. The Facts and Characteristics provides a framework for the U.S. government is the basic law of
Vocabulary Match-Up. Name Date Period Workbook Activity
 Name Date Period Workbook Activity Vocabulary Match-Up Chapter 2, Lesson 1 7 Part A Directions Match the vocabulary word in Column 1 with its definition in Column 2. Write the correct letter on each line.
Name Date Period Workbook Activity Vocabulary Match-Up Chapter 2, Lesson 1 7 Part A Directions Match the vocabulary word in Column 1 with its definition in Column 2. Write the correct letter on each line.
Ch. 6 Creating the Constitution /EQ:
 Ch. 6 Creating the Constitution /EQ: 6.1 Introduction Like Washington, most Americans did not want to be ruled by a monarch. What they did want, though, was an effective government. Articles of Confederation,
Ch. 6 Creating the Constitution /EQ: 6.1 Introduction Like Washington, most Americans did not want to be ruled by a monarch. What they did want, though, was an effective government. Articles of Confederation,
CREATING A GOVERNMENT
 Let us not be afraid to view with a steady eye the dangers with which we are surrounded. Are we not on the eve of a war, which is only to be prevented by the hopes from this convention? CREATING A GOVERNMENT
Let us not be afraid to view with a steady eye the dangers with which we are surrounded. Are we not on the eve of a war, which is only to be prevented by the hopes from this convention? CREATING A GOVERNMENT
The Constitution CHAPTER 5. Table of Contents
 CHAPTER 5 The Constitution ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: Why do people, create, structure, and change governments? How do societies balance individual and community rights? How does social change influence government?
CHAPTER 5 The Constitution ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: Why do people, create, structure, and change governments? How do societies balance individual and community rights? How does social change influence government?
NEW GOVERNMENT: CONFEDERATION TO CONSTITUTION FLIP CARD
 NEW GOVERNMENT: CONFEDERATION TO CONSTITUTION FLIP CARD Big Ideas: Imagine trying to make a new country from scratch. You ve just had a war with the only leaders you ve ever known, and now you have to
NEW GOVERNMENT: CONFEDERATION TO CONSTITUTION FLIP CARD Big Ideas: Imagine trying to make a new country from scratch. You ve just had a war with the only leaders you ve ever known, and now you have to
The Critical Period The early years of the American Republic
 The Critical Period 1781-1789 The early years of the American Republic America after the War New Political Ideas: - Greater power for the people Republic: Represent the Public America after the War State
The Critical Period 1781-1789 The early years of the American Republic America after the War New Political Ideas: - Greater power for the people Republic: Represent the Public America after the War State
The first fighting in the American Revolution happened in in early 1775
 The chief objective of the First Continental Congress was to establish trade relations with foreign powers like France and Germany. select a commander for the Continental Army. draft the U.S. Constitution.
The chief objective of the First Continental Congress was to establish trade relations with foreign powers like France and Germany. select a commander for the Continental Army. draft the U.S. Constitution.
Ratification of the Constitution. Issues
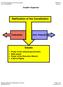 Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
Ratifying the Constitution
 Ratifying the Constitution Signing the Constitution Once the debate ended, Governor Morris of New Jersey put the Constitution in its final form. He competed the task of hand-writing 4,300 words in two
Ratifying the Constitution Signing the Constitution Once the debate ended, Governor Morris of New Jersey put the Constitution in its final form. He competed the task of hand-writing 4,300 words in two
Ch. 1 Principles of Government
 Ch. 1 Principles of Government Objectives: 1. Identify the four main purposes of government. 2. Identify and explain the four theories that explain the origin of government. I. What is government? A. Government-
Ch. 1 Principles of Government Objectives: 1. Identify the four main purposes of government. 2. Identify and explain the four theories that explain the origin of government. I. What is government? A. Government-
What were the Articles of Confederation? What did America do to create a stronger government in the 1780s?
 2.3 Articles of Confederation What were the Articles of Confederation? Why were the 1780s a critical period in United States history? What did America do to create a stronger government in the 1780s? Section:
2.3 Articles of Confederation What were the Articles of Confederation? Why were the 1780s a critical period in United States history? What did America do to create a stronger government in the 1780s? Section:
Constitution Day September 17
 Constitution Day September 17 Articles of Confederation March 1, 1781- goes into effect No Executive Branch-No single leader No Judicial Branch-No national courts No power to collect taxes No power to
Constitution Day September 17 Articles of Confederation March 1, 1781- goes into effect No Executive Branch-No single leader No Judicial Branch-No national courts No power to collect taxes No power to
Learning Goal. Main Points 10/24/2012. Discuss the philosophical underpinnings of the U.S. Constitution.
 Learning Goal Discuss the philosophical underpinnings of the U.S. Constitution. Main Points The weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the adoption of a new form of government Federalism becomes
Learning Goal Discuss the philosophical underpinnings of the U.S. Constitution. Main Points The weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the adoption of a new form of government Federalism becomes
LESSON TWO: THE FEDERALIST PAPERS
 LESSON TWO: THE FEDERALIST PAPERS OVERVIEW OBJECTIVES Students will be able to: Identify the Articles of Confederation and explain why it failed. Explain the argument over the need for a bill of rights
LESSON TWO: THE FEDERALIST PAPERS OVERVIEW OBJECTIVES Students will be able to: Identify the Articles of Confederation and explain why it failed. Explain the argument over the need for a bill of rights
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes
 Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
During the, the majority of delegates voted to declare independence from Britain. What is known as the official beginning of the America Revolution?
 What is known as the official beginning of the America Revolution? A. The Stamp Act B. Boston Tea Party C. Quartering Act D. Battle of Lexington and Concord During the, the majority of delegates voted
What is known as the official beginning of the America Revolution? A. The Stamp Act B. Boston Tea Party C. Quartering Act D. Battle of Lexington and Concord During the, the majority of delegates voted
The U.S. Constitution: Who, What, Where, When, Why & How
 The U.S. Constitution: Who, What, Where, When, Why & How 'a ^Va&o/z Fighting between the American colonists and British forces under King George III was in its second year when the Declaration of Independence
The U.S. Constitution: Who, What, Where, When, Why & How 'a ^Va&o/z Fighting between the American colonists and British forces under King George III was in its second year when the Declaration of Independence
[ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals
![[ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals [ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals](/thumbs/77/76341976.jpg) [ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals [ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals Key Terms limited government representative government due process bicameral unicameral [ 2.1 ] Origins of American
[ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals [ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals Key Terms limited government representative government due process bicameral unicameral [ 2.1 ] Origins of American
The Constitution: A More Perfect Union
 The Constitution: A More Perfect Union How has the Constitution created a more perfect Union? P R E V I E W Read the quotation and answer the questions that follow. If men were angels, no government would
The Constitution: A More Perfect Union How has the Constitution created a more perfect Union? P R E V I E W Read the quotation and answer the questions that follow. If men were angels, no government would
HIST 1301 Part Two. 6: The Republican Experiment
 HIST 1301 Part Two 6: The Republican Experiment The States and the Confederation 1776-1788 During the Revolution, state Governments formed first. 2 min. 40 sec. Each state had a written constitution. Each
HIST 1301 Part Two 6: The Republican Experiment The States and the Confederation 1776-1788 During the Revolution, state Governments formed first. 2 min. 40 sec. Each state had a written constitution. Each
Unit 7 Our Current Government
 Unit 7 Our Current Government Name Date Period Learning Targets (What I need to know): I can describe the Constitutional Convention and two compromises that took place there. I can describe the structure
Unit 7 Our Current Government Name Date Period Learning Targets (What I need to know): I can describe the Constitutional Convention and two compromises that took place there. I can describe the structure
Structure of the Constitution
 American History I Unit 2 Confederation, Constitution, and Compromise Structure of the Constitution Journal: What document created our government before the Constitution? Why did we change it? Remember:
American History I Unit 2 Confederation, Constitution, and Compromise Structure of the Constitution Journal: What document created our government before the Constitution? Why did we change it? Remember:
New Nation. establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s
 New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
3. Popular sovereignty - Rule by the people - People give their consent to be governed by government officials - People have the right to revolution
 Unit I Notes Purposes of Government - Maintain social order - Provide public services - Provide security and defense - Provide for the economy - Governments get authority from: o Their legitimacy o Ability
Unit I Notes Purposes of Government - Maintain social order - Provide public services - Provide security and defense - Provide for the economy - Governments get authority from: o Their legitimacy o Ability
American Democracy Now Chapter 2: The Constitution
 American Democracy Now Chapter 2: The Constitution Multiple-Choice Questions: 1. Which of these countries employs an unwritten constitution? a. the United States b. Great Britain c. Venezuela d. Kenya
American Democracy Now Chapter 2: The Constitution Multiple-Choice Questions: 1. Which of these countries employs an unwritten constitution? a. the United States b. Great Britain c. Venezuela d. Kenya
The Constitution: From Ratification to Amendments. US Government Fall, 2014
 The Constitution: From Ratification to Amendments US Government Fall, 2014 Origins of American Government Colonial Period Where did ideas for government in the colonies come from? Largely, from England
The Constitution: From Ratification to Amendments US Government Fall, 2014 Origins of American Government Colonial Period Where did ideas for government in the colonies come from? Largely, from England
The Relationship between Britain and its American Colonies Changes
 Packet 3: Page 1 The Relationship between Britain and its American Colonies Changes What were the differing interests of the colonial regions? How and why did the relationship between Britain and the colonies
Packet 3: Page 1 The Relationship between Britain and its American Colonies Changes What were the differing interests of the colonial regions? How and why did the relationship between Britain and the colonies
Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution
 Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution The Articles of Confederation After declaring independence from Britain in 1776, Congress tried to unite the states under one national government. However, many feared
Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution The Articles of Confederation After declaring independence from Britain in 1776, Congress tried to unite the states under one national government. However, many feared
The constitution supercedes ordinary law even when the law represents the wishes of a majority of citizens.
 AP Government Chapter 2 The Constitution The constitution supercedes ordinary law even when the law represents the wishes of a majority of citizens. The Constitution is this nation s basic law: It creates
AP Government Chapter 2 The Constitution The constitution supercedes ordinary law even when the law represents the wishes of a majority of citizens. The Constitution is this nation s basic law: It creates
SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States Constitution.
 Standards SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States Constitution. a. Explain how weaknesses in the Articles of
Standards SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States Constitution. a. Explain how weaknesses in the Articles of
Life was good in the colonies (Slaves excepted, of
 1. The Origins of the Constitution 2. The Government That Failed: 1776 1787 3. Making a Constitution: The Philadelphia Convention 4. Critical Issues at the Convention 5. The Madisonian System 6. Ratifying
1. The Origins of the Constitution 2. The Government That Failed: 1776 1787 3. Making a Constitution: The Philadelphia Convention 4. Critical Issues at the Convention 5. The Madisonian System 6. Ratifying
The Articles of Confederation
 The Articles of Confederation Our New Nation s First Constitution The Articles of Confederation When the Second Continental Congress appointed a committee to write a Declaration of Independence in 1776,
The Articles of Confederation Our New Nation s First Constitution The Articles of Confederation When the Second Continental Congress appointed a committee to write a Declaration of Independence in 1776,
Major Problem. Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government.
 The Constitution Major Problem Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government. Why? Feared a government like King George The Constitutional
The Constitution Major Problem Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government. Why? Feared a government like King George The Constitutional
The Founding of American Democracy By Jessica McBirney 2016
 Name: Class: The Founding of American Democracy By Jessica McBirney 2016 The American colonies rose up in 1776 against Britain with the goal of becoming an independent state. They sent the King of England
Name: Class: The Founding of American Democracy By Jessica McBirney 2016 The American colonies rose up in 1776 against Britain with the goal of becoming an independent state. They sent the King of England
Constitution Unit Test
 Constitution Unit Test Eighth Amendment Excessive fines cannot be imposed. Excessive bail cannot be required. 1. Which sentence completes this diagram? A. People cannot be forced to be witnesses against
Constitution Unit Test Eighth Amendment Excessive fines cannot be imposed. Excessive bail cannot be required. 1. Which sentence completes this diagram? A. People cannot be forced to be witnesses against
