Farmers refuse to pay Whiskey tax to US Govt. Mobocracy
|
|
|
- Gabriel Lloyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. Washington s Presidency Served 2 terms to 1797/VP: John Adams 2. US Problems = Solutions Government on paper but not in practice Precedents Develops first Cabinet----Hamilton vs Jefferson Supreme Court Debt Excise taxes and tariffs Bank of United States (BUS) in 1792 Confidence in new Constitution Whiskey Rebellion 1. Successfully put down by Washington, 1794 Farmers refuse to pay Whiskey tax to US Govt. Mobocracy notes1
2 The Possibility of War Jay s Treaty Great Britain notes2 Forts for debts Picnkney s Treaty Spain Open up the Mississippi River French Revolution to US US asked to help France in war with England Neutrality Act---Washington warns US to stay neutral and not side with the French. 4. Washington s Farewell Speech: 1796 Two ways the US can stay unified Avoid political parties Military alliances with Europe Neutrality----Isolation Achievements: Sound economic foundation westward expansion Kept us out of war
3 Wash inaugural New Constitution and Government take effect on April 30, Washington begins his presidency in New York City and alternates between there and Philadelphia. Capital city at this time was New York City.
4 Precedents are models, examples or influences other Presidents would follow What to call the President? Mr. President President sets their own personal style Cabinet appointed by President and advises him VP has no official duties President acts independent from Congress Congress relies on the advice of the President Served 2 terms and stepped aside for someone else edents prec
5 cabinet Cabinet advises the President and heads up an agency of the government Department of State Foreign affairs Thomas Jefferson----Secretary of State Department of Treasury Financial affairs Alexander Hamilton Secretary of the Treasury Department of War Military affairs Henry Knox----Secretary of War Attorney General Legal affairs Edmund Randolph Department of Justice Postmaster General Postal system Samuel Osgood
6 Alexander Hamilton and Thomas Jefferson played a valuable role in the beginning of our nation. Both were visionaries and influenced the direction our country would go economically, politically and socially. President Washington was stuck in the middle of these two men as they argued over our country s beginnings.
7 political Federalist Beliefs Leader Appealed to Ideas of Government Alexander Hamilton John Adams Manufacturers, merchants, wealthy and educated; Favored seaboard cities Strong government over states Loose Construction of Constitution; Implied powers; Wealthy and educated involved; Limit freedoms of speech & press; Preferred govt. similar to a king Democratic-Republicans Thomas Jefferson James Madison Farmers and Planters common man; Favored the South and West State s rights over National Govt. Strict construction of Constitution; Expressed/Enumerated powers; Common man but educated; Bill of Rights is sacred; Lesser government the better Domestic Policy Supported National Bank BUS; Supported excise tax; National debt good for country; National govt. assume state debts; Tariffs should be high Against National Bank BUS; Against excise tax ; Against National debt; States pay their own debts; Tariffs should be low Foreign Policy Opposed French Revolution Wanted war with French Favored the British Supported French Revolution Opposed war with French Favored the French
8 President Washington appoints 6 justices to the Supreme Court 3 from North and 3 from South Judiciary Act of 1789, Congress created lower courts to assist the Supreme Court. John Jay first Chief Justice of the Supreme Court
9 precedents President Washington faced several Indian problems. British were supplying the tribes with arms and ammunition to attack US settlers. Washington sent General Mad Anthony Wayne to defeat the Indian tribes.
10 War in the Old Northwest Territory Several tribes, led by Little Turtle of the Miamis, scored early victories ( ) The Miamis were defeated at Fallen Timbers by General Mad Anthony Wayne (1794)
11 War in the Old Northwest Territory Treaty of Greenville (1795) gave USA right to settle most of Ohio First formal recognition of Indian sovereignty over land not ceded by treaty
12 Map 13 of 45
13 British forts on U.S. soil. Still haven t removed troops and supplying Indians with weapons Disputed land claims with Spain; Cut off Mississippi River
14 Jay s Treaty with England.. British made neutrality difficult: maintained trading posts on US soil, sold firearms to Indians; Collaborated with Indians to check US expansion to frontier. Jays
15 Conflicts with Britain British made neutrality difficult: maintained trading posts on US soil, sold firearms to Indians. Collaborated with Indians to check US expansion to frontier.
16 Conflicts with Britain British expected Americans to defend French West Indies, so attacked US merchant ships, seizing about 300 Impressed and imprisoned American sailors. Jeffersonians called for war Federalists resisted (financial system).
17 Jay s Treaty To avoid war, Washington sent Chief Justice John Jay to London (1794). Jeffersonian s concerned about Jay s loyalty. Hamilton feared war with England, secretly supplied British with US bargaining strategy.
18 Jay s Treaty John Jay is burnt in effigy because Americans believed he sold out to the British. British remove forts from US soil British agreed but required US to pay old debts on pre-revolution accounts. Allowed US to negotiate separate treaties with Indian tribes Opened westward expansion for US settlers.
19 Jay s Treaty British agree to pay some damages, but required US to pay old debts on pre-revolution accounts. John Jay is burnt in effigy because Americans believed he sold out to the British. Jeffersonian s felt treaty was surrender to Britain, betrayal of South (who had debts). Did not stop impressment.
20 Jay s Treaty Jay s Treaty gave life to new Democratic-Republican party, tarnished Wash. s popularity. Spain, fearing US-British alliance, gives US free use of Mississippi, disputed territory north of FL.
21 Spain cut off our farmers right to use the Mississippi River and deposit their crops in New Orleans. Picnkneys Pinckney s Treaty: Spain gave US the free use of the Mississippi River for 5 yrs. and the boundary was set at 31st parallel between Spanish Florida and US
22 Foreign Debt Congress & Sec. of Treasury Alexander Hamilton solve debt problems: $11,710,000 Federal Domestic Debt $42,414,000 State Debt $21,500,000 Misc. Revenue Excise Tax on Whiskey Custom Duties (Tariffs) Compromise with Thomas Jefferson called the Assumption Act led to the creationdebtof Pay off $80 million debt Excise tax: Taxes placed on manufactured products Tariff: a tax on imports Establish good credit with foreign nations Create a national bank with a national currency Raise money for govt backed by gold silver
23 BUS HAMILTON JEFFERSON Safe place to deposit and transfer money Against the Constitution Provide loans to government and state banks State banks would collapse A national currency---$$$$$ An investment by people to buy stock into US bank Constitution did not forbid a national bank.loose construction of Constitution National debt good for country Only wealthy could invest in bank and would control bank than control the government Hurt the common man Strict construction If it is not mentioned in the Constitution than there can t be a national bank. Against a national debt
24 Whiskey Rebellion Whiskey Rebels refused to pay the excise tax that was passed by Congress and signed into law by President Washington.Believed this tax was unfair because it was taxing their income whiskeymap
25 Farmer s revolt in western Pennsylvania. Refused to pay Hamilton s excise tax Believed it was an unfair tax. Were called the Whiskey Rebels
26 Whiskey Issue at hand was testing the power of the new Constitution Outcome: Demonstrated to the people that this new constitution was powerful enough to put down domestic rebellions, mobocracy Showed the power of the national government President Washington reviews 13,000 troops of the Western Army assembled at Fort Cumberland, Maryland, to crush the Whiskey Rebellion.
27 impressment Impressment: an act of kidnapping a ship, its contents, men and forcing them into your navy----the British and French were doing this to us.
28 French Rev Began in 1790 s, unfair taxation and inequality---worldwide crisis Overthrow King Louis 16th and Marie Antoniete; similar to King George Americans believed we should help the French----similar to ours
29 French Rev Executions of King Louis the 16th and Marie Antoniette in Begins Reign of Terror during French Revolution where 40,000 opponents of the new govt. were beheaded. France goes to war against European kings France requested US ships to block West Indies from the British President Washington declared Neutrality and ordered Americans to avoid this war
30 farewell Whereas it appears that a state of war exists between Austria, Prussia, Sardinia, Great Britain and the United Netherlands, of the one part and France on the other; and the duty and interest of the U.S. require, that they should with sincerity and good faith adopt and pursue a conduct friendly and impartial toward the belligerent powers.
31 farewell neutrality I have therefore thought fit by these presents to declare the disposition of the U.S. to observe the conduct aforesaid towards those Powers respectfully; and to exhort and warn the citizens of the U.S. carefully to avoid all acts and proceedings whatsoever, which may in any manner tend to contravene such disposition.april 1793 President Washington s response to the French was to warn Americans to stay out these European conflicts and remain neutral or avoid.
32 Most Americans (Jefferson and Paine) were upset with Washington s Neutrality. Washington s Neutrality decision was based on the long term U.S. self interest. Preserve and protect the infant nation Thomas Paine On Washington s Neutrality And as to you, sir, treacherous in private friendship (for so you have been to me, and that in the day of danger) and a hypocrite in public life, the world will be puzzled to decide, whether you are an apostate or an importer; whether you have abandoned good principles, or whether you ever had any.
33 farewell Washington warned of the dangers of political parties and permanent alliances with other nations. Washington s warning against entangling alliances became a principle of U.S. foreign policy. Europe has a set of primary interests which to us have none or a very remote relation.our detached and distant situation invites and enables us to pursue a different course..it is our true policy to steer clear of permanent alliances with any portion of the foreign world Taking care always to keep ourselves by suitable establishments on a respectable defensive posture, we may safely trust to temporary alliances for extraordinary emergencies..1796
34 Washington is convinced that Americans must stay neutral and avoid foreign affairs associated with all the British and foreign continents--- GOOD HISTORIAN Washington displayed this in 1793 by the Proclamation of Neutrality and his Farewell Address in No entangling alliances.us should avoid military alliances with Europe.continue to trade with Europe Neutrality = Isolation
35
36 1. Washington s Presidency Served 2 terms to 1797; VP: John Adams 2. Problems facing US Debt Government on paper but not in practice British, Spain and Indians Confidence in new government 3. Accomplishments Political achievements Precedents Develops first: Cabinet----Hamilton vs Jefferson; Supreme Court---Judiciary Act of 1789; Treaties notes1
37 Domestic Achievements: Secures westward expansion Jay s Treaty Great Britain Picnkney s Treaty Spain Debt solutions Excise taxes and tariffs Bank of United States (BUS) Enforced Constitution Whiskey Rebellion Demonstrated strength of new government Foreign Achievements No war with Great Britain or Spain French Revolution to US response notes2
38 French Revolution to US response Neutrality Act---Washington warns = stay out Cornerstone of US foreign policy = isolationism Washington s Farewell Speech Two ways the US can stay unified and strong Avoid political parties military alliances with European countries notes2
39 Indian land
40 political Federalist Beliefs Leader Appealed to Ideas of Government Alexander Hamilton John Adams Manufacturers, merchants, wealthy and educated; Favored seaboard cities Strong government over states Loose Construction of Constitution; Implied powers; Wealthy and educated involved; Limit freedoms of speech & press; Preferred govt. similar to a king Democratic-Republicans Thomas Jefferson James Madison Farmers and Planters common man; Favored the South and West State s rights over National Govt. Strict construction of Constitution; Expressed/Enumerated powers; Common man but educated; Bill of Rights is sacred; Lesser government the better Domestic Policy Supported National Bank BUS; Supported excise tax; National debt good for country; National govt. assume state debts; Tariffs should be high Against National Bank BUS; Against excise tax ; Against National debt; States pay their own debts; Tariffs should be low Foreign Policy Opposed French Revolution Wanted war with French Favored the British Supported French Revolution Opposed war with French Favored the French
41 Adams 2nd president---jefferson VP Serves 1 term to Possible war with France Why? French: US neutrality US: impressment of our ships Kidnapped our ships 3. Adams tries to avoid war XYZ Affair French bribed the US US wants war with France Undeclared naval war Adams prepares US for war. Alien and Sedition Act 1798 No immigrants and silenced 1. free speech notes3
42 5. VP Jefferson against these laws Violated Bill of Rights the states can refuse to obey it--- nullify 6. Adams vs. French kept US out of war Agreement: Napoleon Bonaparte agreed to abandon US responsibility to the Franco/American Treaty of 1778 notes4
43 Adams Becomes President 1796 campaign Adams was supported by New England and Federalists Defeated Jefferson in Electoral College Jefferson becomes VP France and US close to war. Jay s Treaty US not honoring the Franco-American Treaty of 1778
44 politicalparties FEDERALISTS 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) Alexander Hamilton/John Adams Led by merchants, bankers and lawyers living primarily in New England. Favored a strong central government. Interpreted the Constitution loosely--- implied powers Believed in a government by the elite, educated and wealthy. Pro-England. Favored Hamilton's financial policies----support BUS Vision for US: Trade center, industry and self-sufficient. DEMOCRATIC-REPUBLICANS 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) Thomas Jefferson/James Madison. Led by planters, farmers and wage earners living primarily in the South and West. Favored strong state governments over national government. Interpreted the Constitution strictly-- enumerated powers Rule by the educated masses. Pro-France. Opposed Hamilton's financial policies---against BUS Vision for US: Agricultural society, little trade and industry
45 impressment Impressment An act of kidnapping a ship, its contents, men and forcing them into your navy France began impressing our ships and sailors because of our Neutrality Proclamation. France upset because we violated the Franco American Treaty of 1778.
46 Fighting with France French upset by US violation of France-US treaty of 1778 Upset with Jay s Treaty toward alliance with England French warships impressed over 300 US merchant ships by 1797
47 xyz To avoid war with France, President Adams sent 3 US representatives (John Marshall, Charles Pinckney and John Jay) to negotiate a peace agreement.. US representatives were snubbed by the French government Adams Tallyrand President Adams on the XYX Affair. I will never send another minister to France without assurances that he will be received, respected, and honored as the representative of a great, free, powerful and independent nation. Eventually, 3 French representatives (known as X, Y and Z because they refused to give their names) XYZ demanded a bribe of $250,000 to merely talk with Tallyrand Insulted, we refused the demands and left France US & French begin to fight an undeclared naval war.
48 XYZ Affair French demanded an apology Demanded a $12 million loan.
49 The French government would permit us to remain at Paris and we should be received by Talleyrand one of us could go to American and consult our government on the subject of the loan. We had no reason to believe that a possible benefit could result from it. And we desired him to tell his government that we would not give a shilling unless American property unjustly captured was previously restored and further hostilities suspended Unless this was done, we did not think that we could even consult our government concerning a loan..
50 Fighting with France Americans wanted war and were heard to say millions for defense, but not one cent for tribute US prepares for war, expands navy, creates the US Marine Corps.
51 Fighting with France : In undeclared hostilities, mostly around West Indies US captured over 80 French ships but lost several hundred to France. Needed only slight push for war.
52 Federalist Witch Hunt 1798: Using anti-french hysteria, Federalists in Congress passed the Alien & Sedition Acts Alien Laws: raised residency required for citizenship to 14 years (from 5), resulting in fewer Democratic-Republican voters
53 ISSUE: Does the United States Govt have the right to suspend your rights (Bill of Rights) in time of crisis (such as war) to protect the national security of the country? ALIEN ACT: Congress gave President Adams the power to deport any immigrant who was considered a risk to national security.also, changed naturalization (immigrants who want to become citizens) from 5 years to 14 yrs SEDITION ACT: Congress gave President Adams special powers to arrest anyone who spoke out against the war effort.primarily against Jefferson s Democratic/Republicans and newspaper editors who opposed the war.. Alien/sedition
54 That if any person shall write, print, utter, or publish, or shall cause or procure to be written, printed, uttered or published, or shall knowingly and willingly assist in any false, Scandalous and malicious writing or writings against the government of the United States, or either house of Congress or the President of the United States, Then such person, being thereof convicted before any court of the United States, shall be punished by a fine not exceeding two thousand dollars and by imprisonment not exceeding two years
55 Federalist Witch Hunt Alien Laws also gave President authority to deport (peace) or imprison (wartime) foreigners Sedition Act: prohibited impeding policies of government or falsely defaming officials ~ aimed at Jeffersonian newspapers
56 Federalist Witch Hunt Sedition Act violated Constitution, but Federalist SC would not overturn Law wrote to expire in 1801 in case Federalists lost election Despite violation of freedoms, Acts were very popular
57 Kty/va resolutions Jefferson s and Madison s response to the Sedition Act.. Believed Sedition Act violated freedom of speech and press. They tried to convince the other states not to support the Sedition Act. It failed and the Sedition Act remained the law until DOCTRINE OF NULLIFICATION: Since the States created the National Government, they have the right to nullify, cancel or decide not to obey a law they believed was unconstitutional.
58 That the General Assembly protests against the alarming infractions of the Constitution, in the "Alien and Sedition Acts" passed at the last session of Congress. That this state having by its Convention, expressly declared, that among other essential rights, "the Liberty of Conscience and of the Press cannot be cancelled, abridged, restrained, or modified by any authority of the United States," The General Assembly appeals to the other states, in confidence that they will concur that the acts are unconstitutional and that the necessary and proper measures will be taken by each in maintaining the Authorities, Rights, and Liberties, referred to the States respectively, or to the people.
59 Kty/va resolutions Jefferson s and Madison s response to the Sedition Act..They tried to convince the other states not to support the Sedition Act.It failed and the Sedition Act remained the law until DOCTRINE OF NULLIFICATION: Since the States created the National Government, they have the right to nullify, cancel or decide not to obey a law they believed was unconstitutional. COMPACT THEORY: Belief Jefferson and Madison held that since the states created the National Govt. and the states entered into this compact voluntarily, they have the right to refuse to obey any law they believe is unconstitutional
60 VA & KY Resolutions As a result, states could nullify federal laws ~ specifically the Alien & Sedition Acts Federalist response: it s people, not states, that formed union
61 Patriotism Above Party New French leader, Napoleon and Talleyrand did not want war, or to push the US to Britain French send back-channel message that new US minister would be received properly 1799: Adams submits to Senate new minister to France
62 Adams Napoleon To prevent a war with France, in 1800, President Adams sent representatives to France to meet with Napoleon and Tallyrand to negotiate a peace agreement.. Tallyrand guarantees France would accept our representatives and treat them with respect. The agreement was as follows: France dropped our responsibility to the treaty of 1778 U.S. would drop the claims (lawsuits brought against the French Govt. for the recovery of private ships and cargo) for the impressment of our merchant ships. President Adams sacrificed his re-election and lost to Thomas Jefferson in Adams/napoleon
63 Adams Napoleon Convention of 1800 signed: ended Franco-American alliance Adams deserves credit: Avoided war Unknowingly laid foundation for LA Purchase Adams sacrificed his re-election in 1800 to keep US out of war Patriotism above self-interest Adams/napoleon
64 Patriotism Above Party Hamilton and the war-hawk Federalists enraged, but most Americans agreeable to try for peace 1800: new US envoys come to find Napoleon as new dictator Wants to resolve US conflict
65 Democratic 1. Federalist Election of 1796 Republican Rise of Political parties Adams 2nd president---jefferson VP Serves 1 term to Foreign relations----possible war with France Why? US neutrality, treaty of 1778 and Jay s Treaty US upset---- impressment of our ships Adams negotiates with France to keep US out of war Congress creates the XYZ Affair Dept. of the Navy and US apologize US Marines Loan France money $250,0000 bribe Americans demand war with France Undeclared naval war---us vs France notes3
66 4. VP Jefferson & Madison against these laws.. Responses Kentucky and Virginia Resolutions if US law violates the Constitution, the states can refuse to obey it. nullification Why? Compact theory: States created national government and have the right to nullify any law they believe is unconstitutional State s rights vs national govt. conflict 5. Adams vs. Napoleon Bonaparte to keep US out of war Treaty agreement Abandon treaty of 1778 US drop the claims against France Adam s accomplishment: Kept US neutral and out of war notes4
67 1. Election of 1796 Rise of Political parties Adams 2nd president---jefferson VP Serves 1 term to 1801 Federalist Democratic Republican 2. Foreign relations----possible war with France Why? US neutrality, treaty of 1778 and Jay s Treaty US upset---- impressment of our ships Adams negotiates with France to keep US out of war XYZ Affair US apologize Loan France money $250,000 bribe Americans demand war with France notes3
68 4. VP Jefferson & Madison against these laws.. Responses Kentucky and Virginia Resolutions if US law violates the Constitution, the states can refuse to obey it. nullification 5. Adams vs. French keep us out of war Treaty agreement Abandon treaty of 1778 US drop the claims against France Adam s accomplishment: Kept US neutral and out of war Sacrifices his presidency and not be re-elected Why? Went against people and Federalists notes4
Slide 1 Essential Question. Slide 2 Timeline. Slide 3
 Slide 1 Essential Question What problems were facing America when George Washington became president? What lasting effects can we see from Washington's presidency? Particularly cabinet, political parties,
Slide 1 Essential Question What problems were facing America when George Washington became president? What lasting effects can we see from Washington's presidency? Particularly cabinet, political parties,
The Confederation and the Constitution
 Art. 5, 6, 7 Unit #3 Chapters 9, 10, 11 The Confederation and the Constitution Presented by: Mr. Anderson, M.Ed., J.D. 1 United States Constitution = Some delegates feared the central government would
Art. 5, 6, 7 Unit #3 Chapters 9, 10, 11 The Confederation and the Constitution Presented by: Mr. Anderson, M.Ed., J.D. 1 United States Constitution = Some delegates feared the central government would
Adams Becomes President
 John Adams Adams Becomes President 1796 campaign Adams was supported by New England and Federalists Defeated Jefferson 71-68 by Electoral College Jefferson becomes VP France and US close to war Jay s Treaty
John Adams Adams Becomes President 1796 campaign Adams was supported by New England and Federalists Defeated Jefferson 71-68 by Electoral College Jefferson becomes VP France and US close to war Jay s Treaty
The New Nation Takes Form
 The New Nation Takes Form 1789-1800 Why Washington? You must be this tall to ride. Aside from being a slam up decorator.? Was he the hottest founding father? Chick Magnet? Hero John Adams Vice-President
The New Nation Takes Form 1789-1800 Why Washington? You must be this tall to ride. Aside from being a slam up decorator.? Was he the hottest founding father? Chick Magnet? Hero John Adams Vice-President
Launching a New Ship of State Part American Pageant Chapter 10
 Launching a New Ship of State Part 2 1789-1800 American Pageant Chapter 10 The Emergence of Political Parties At the start--political parties not in existence or planned for Organized resistance: Anti-federalists
Launching a New Ship of State Part 2 1789-1800 American Pageant Chapter 10 The Emergence of Political Parties At the start--political parties not in existence or planned for Organized resistance: Anti-federalists
THE FEDERALIST ERA, : FOREIGN POLICY
 THE FEDERALIST ERA, 1789-1801: FOREIGN POLICY I. Impact of the French Revolution A. popular overthrow of French monarchy and aristocracy, beginning in July 1789 1. France proclaimed itself a republic (similar
THE FEDERALIST ERA, 1789-1801: FOREIGN POLICY I. Impact of the French Revolution A. popular overthrow of French monarchy and aristocracy, beginning in July 1789 1. France proclaimed itself a republic (similar
Ruthie García Vera APUSH
 Ruthie García Vera APUSH April 30, 1789 George Washington from Virginia is sworn in as President. John Adams from Massachusetts becomes the Vice-President. Both served two terms from 1789-1797. George
Ruthie García Vera APUSH April 30, 1789 George Washington from Virginia is sworn in as President. John Adams from Massachusetts becomes the Vice-President. Both served two terms from 1789-1797. George
Chapter 9: The Confederation and the Constitution,
 APUSH CH 9+10 Lecture Name: Hour: Chapter 9: The Confederation and the Constitution, 1776-1790 I. From Confederation to Constitution A. The Articles of Confederation: An Attempt at Constitution-Making
APUSH CH 9+10 Lecture Name: Hour: Chapter 9: The Confederation and the Constitution, 1776-1790 I. From Confederation to Constitution A. The Articles of Confederation: An Attempt at Constitution-Making
US History. Washington Leads a New Nation. The Big Idea. Main Ideas
 Washington Leads a New Nation The Big Idea President Washington and members of Congress established a new national government. Main Ideas In 1789 George Washington became the first president of the United
Washington Leads a New Nation The Big Idea President Washington and members of Congress established a new national government. Main Ideas In 1789 George Washington became the first president of the United
Welcome Work. Use the paper provided and create a circle map of what you KNOW about George Washington.
 Welcome Work Use the paper provided and create a circle map of what you KNOW about George Washington. Essential Question How did George Washington s presidency influence the New Nation? SS.8.A.3.1 GEORGE
Welcome Work Use the paper provided and create a circle map of what you KNOW about George Washington. Essential Question How did George Washington s presidency influence the New Nation? SS.8.A.3.1 GEORGE
End of Federalists. & Age of Jefferson. Change for the new country.
 End of Federalists. & Age of Jefferson Change for the new country. War & Terror: Does the US Govt have the power to take away your rights in time of crisis (ie. war) to protect the security of the country?
End of Federalists. & Age of Jefferson Change for the new country. War & Terror: Does the US Govt have the power to take away your rights in time of crisis (ie. war) to protect the security of the country?
The Federalist Period
 The Federalist Period Washington as President Washington set several precedents for future presidents 2 terms & the first cabinet Jefferson, Hamilton, Knox, & Randolph fledgling govt faced several domestic
The Federalist Period Washington as President Washington set several precedents for future presidents 2 terms & the first cabinet Jefferson, Hamilton, Knox, & Randolph fledgling govt faced several domestic
Launching the New Ship of State CHAPTER 10
 Launching the New Ship of State CHAPTER 10 Growing Pains Land was very sparsely populated, many forests 4 million people, but population doubled every 25 years Cities Only 6 over 8,000 Philadelphia largest
Launching the New Ship of State CHAPTER 10 Growing Pains Land was very sparsely populated, many forests 4 million people, but population doubled every 25 years Cities Only 6 over 8,000 Philadelphia largest
Chapter 10 Section Review Packet
 Name: Date: Chapter 10 Section Review Packet Section 10-1: Laying the Foundations of Government 1. George Washington 2. Martha Washington 3. Electoral college 4. John Adams 5. New York City 6. Precedent
Name: Date: Chapter 10 Section Review Packet Section 10-1: Laying the Foundations of Government 1. George Washington 2. Martha Washington 3. Electoral college 4. John Adams 5. New York City 6. Precedent
US History Refresher
 US History Refresher US History Refresher video Objective 1.01: Identify the major domestic issues and conflicts experienced by the nation during the Federalist Period. Objective 1.02: Analyze the political
US History Refresher US History Refresher video Objective 1.01: Identify the major domestic issues and conflicts experienced by the nation during the Federalist Period. Objective 1.02: Analyze the political
Washington Leads a New Nation. Chapter 7 Section 1
 Washington Leads a New Nation Chapter 7 Section 1 The First President In January 1789 each of the 11 states that had passed the Constitution sent electors to choose the first president. These delegates
Washington Leads a New Nation Chapter 7 Section 1 The First President In January 1789 each of the 11 states that had passed the Constitution sent electors to choose the first president. These delegates
Washington s Presidency
 !CHAPTER 9 SECTION 1 REVIEW Washington s Presidency Specific Objective Learn that George Washington and his advisers faced many challenges during his Presidency. Directions: Read the summary below to answer
!CHAPTER 9 SECTION 1 REVIEW Washington s Presidency Specific Objective Learn that George Washington and his advisers faced many challenges during his Presidency. Directions: Read the summary below to answer
GEORGE WASHINGTON
 GEORGE WASHINGTON 1732-1799 GEORGE WASHINGTON George Washington was the first president of the United States. He served two terms from 1789-1797. He is called the Father of Our Country. REVOLUTIONARY WAR
GEORGE WASHINGTON 1732-1799 GEORGE WASHINGTON George Washington was the first president of the United States. He served two terms from 1789-1797. He is called the Father of Our Country. REVOLUTIONARY WAR
The Washington Presidency and Political Rivalaries. Chapter 6 Sections 1 & 2
 Bell Ringer: Take out paper for notes. On your paper, answer the following review questions: Name the 4 executive departments established by Congress. Name the 4 people that headed each department. Match
Bell Ringer: Take out paper for notes. On your paper, answer the following review questions: Name the 4 executive departments established by Congress. Name the 4 people that headed each department. Match
Level 2 NEW GOVERNMENT IN OPERATION ESTABLISHING STABILITY
 Level 2 NEW GOVERNMENT IN OPERATION ESTABLISHING STABILITY Vocabulary Precedent: an act that results in a tradition Economics: science that deals with the production, distribution, and consumption of goods
Level 2 NEW GOVERNMENT IN OPERATION ESTABLISHING STABILITY Vocabulary Precedent: an act that results in a tradition Economics: science that deals with the production, distribution, and consumption of goods
netw rks Where in the world? When did it happen? The Federalist Era Lesson 1 The First President ESSENTIAL QUESTION Terms to Know GUIDING QUESTIONS
 Lesson 1 The First President ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the characteristics of a leader? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. What decisions did Washington and the new Congress have to make about the new government?
Lesson 1 The First President ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the characteristics of a leader? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. What decisions did Washington and the new Congress have to make about the new government?
Federalist Era APUSH 2017
 Federalist Era 1789-1801 APUSH 2017 Domestic Policy (What do we do with all the crap going on at home?) Overview Pop. doubling every 25 years New states: KY, TN, OH, VT Finances in disarray Debt, low revenue,
Federalist Era 1789-1801 APUSH 2017 Domestic Policy (What do we do with all the crap going on at home?) Overview Pop. doubling every 25 years New states: KY, TN, OH, VT Finances in disarray Debt, low revenue,
Launching the New Ship of State C H A P T E R 1 0
 Launching the New Ship of State 1789-1800 C H A P T E R 1 0 Growing Pains After 1789, American population continues to grow at an amazing rate Population about 90% rural 95% of population still lives east
Launching the New Ship of State 1789-1800 C H A P T E R 1 0 Growing Pains After 1789, American population continues to grow at an amazing rate Population about 90% rural 95% of population still lives east
Section 1: Washington Leads a New Nation Section 2: Hamilton & National Finances Section 3: Challenges for a New Nation Section 4: John Adams s
 Section 1: Washington Leads a New Nation Section 2: Hamilton & National Finances Section 3: Challenges for a New Nation Section 4: John Adams s Presidency This image cannot currently be displayed. In
Section 1: Washington Leads a New Nation Section 2: Hamilton & National Finances Section 3: Challenges for a New Nation Section 4: John Adams s Presidency This image cannot currently be displayed. In
Chapter 7 Test Review
 Chapter 7 Test Review Be sure to review Washington and Adams Reading Notes as well as the Resource Activity packet, along with the chapter review activity and Primetimes. Precedents The traditions established
Chapter 7 Test Review Be sure to review Washington and Adams Reading Notes as well as the Resource Activity packet, along with the chapter review activity and Primetimes. Precedents The traditions established
Washington decided to create cabinet
 Unit 5 Section 1 Washington decided to create cabinet Not in Constitution 3 Departments Treasury Alexander Hamilton State - Thomas Jefferson War Henry Knox John Adams was VP but not in cabinet Spelled
Unit 5 Section 1 Washington decided to create cabinet Not in Constitution 3 Departments Treasury Alexander Hamilton State - Thomas Jefferson War Henry Knox John Adams was VP but not in cabinet Spelled
Chapter 9: The Confederation and the Constitution,
 APUSH CH 9+10 Lecture Name: Hour: Chapter 9: The Confederation and the Constitution, 1776-1790 I. From Confederation to Constitution A. The Articles of Confederation: An Attempt at Constitution-Making
APUSH CH 9+10 Lecture Name: Hour: Chapter 9: The Confederation and the Constitution, 1776-1790 I. From Confederation to Constitution A. The Articles of Confederation: An Attempt at Constitution-Making
LAUNCHING THE NEW SHIP OF STATE
 CHAPTER 10 LAUNCHING THE NEW SHIP OF STATE GROWING PAINS THERE WAS VERY LITTLE TRUST IN THE NEW GOVERNMENT VIRTUALLY NO REVENUE ($) WAS COMING IN INFLATION WAS RAMPANT DUE TO THE PRINTING OF PAPER MONEY
CHAPTER 10 LAUNCHING THE NEW SHIP OF STATE GROWING PAINS THERE WAS VERY LITTLE TRUST IN THE NEW GOVERNMENT VIRTUALLY NO REVENUE ($) WAS COMING IN INFLATION WAS RAMPANT DUE TO THE PRINTING OF PAPER MONEY
9.1 The First President
 9.1 The First President Washington Takes Ofice precedent: tradition, or something done or said that may serve as an example or rule to follow later April 30, 1789 Geo. Wash. 1st pres, John Adams VP The
9.1 The First President Washington Takes Ofice precedent: tradition, or something done or said that may serve as an example or rule to follow later April 30, 1789 Geo. Wash. 1st pres, John Adams VP The
(c s) Challenges of the First Five Presidents
 (c. 1800-1820 s) Challenges of the First Five Presidents Washington & Adams Washington as President George Washington unanimously elected President by the Electoral College in 1789 and 1792. Set many
(c. 1800-1820 s) Challenges of the First Five Presidents Washington & Adams Washington as President George Washington unanimously elected President by the Electoral College in 1789 and 1792. Set many
Issues Facing the New Government
 Issues Facing the New Government George Washington s Presidency 1789-1797 No political party affiliation Won 100% of electoral vote in both elections Established precedent of serving only 2 terms as president
Issues Facing the New Government George Washington s Presidency 1789-1797 No political party affiliation Won 100% of electoral vote in both elections Established precedent of serving only 2 terms as president
Chapter 6. Launching a New Nation
 Chapter 6 Launching a New Nation 6.1 Laying the foundations of government The United States needed a president that the people already trusted. Washington s Cabinet Currently, there are 14 executive departments
Chapter 6 Launching a New Nation 6.1 Laying the foundations of government The United States needed a president that the people already trusted. Washington s Cabinet Currently, there are 14 executive departments
The election of George Washington as the first president under the Constitution was not exactly unanimous
 The election of George Washington as the first president under the Constitution was not exactly unanimous -2 electors from VA and 2 electors from MD did not vote -NY was entitled to 8 electoral votes but
The election of George Washington as the first president under the Constitution was not exactly unanimous -2 electors from VA and 2 electors from MD did not vote -NY was entitled to 8 electoral votes but
Practice & Review, Monday, 12/4. Practice & Review, Tuesday, 12/5
 Practice & Review, Monday, 12/4 1. The group of advisers who helped Washington run the executive branch was known as.. Cabinet 2. What office did Thomas Jefferson hold in Washington s administration? Secretary
Practice & Review, Monday, 12/4 1. The group of advisers who helped Washington run the executive branch was known as.. Cabinet 2. What office did Thomas Jefferson hold in Washington s administration? Secretary
LOREM IPSUM. Book Title DOLOR SET AMET
 LOREM IPSUM Book Title DOLOR SET AMET Chapter 8 The Federalist Era With a new constitution in place, George Washington would take the reigns of a fledgling nation. He, along with John Adams and Thomas
LOREM IPSUM Book Title DOLOR SET AMET Chapter 8 The Federalist Era With a new constitution in place, George Washington would take the reigns of a fledgling nation. He, along with John Adams and Thomas
Evaluate how our first Constitution Or The Articles of Confederation were our country look weak? Why make it weak?
 U.S. History Mr. Boothby 10/10/2017 The Learning Target : CH 10 Launching a New Ship of State pt2 Whiskey Rebellion and the XYZ Affair/ SHIFT IN STRENGTH! Reaction (2 full page minimum): Hint on page(s)
U.S. History Mr. Boothby 10/10/2017 The Learning Target : CH 10 Launching a New Ship of State pt2 Whiskey Rebellion and the XYZ Affair/ SHIFT IN STRENGTH! Reaction (2 full page minimum): Hint on page(s)
A. True or False Where the statement is true, mark T. Where it is false, mark F, and correct it in the space immediately below.
 AP U.S. History Mr. Mercado Name Chapter 10 Launching the New Ship of State, 1789-1800 A. True or False Where the statement is true, mark T. Where it is false, mark F, and correct it in the space immediately
AP U.S. History Mr. Mercado Name Chapter 10 Launching the New Ship of State, 1789-1800 A. True or False Where the statement is true, mark T. Where it is false, mark F, and correct it in the space immediately
Chapter 7: Democracy and Dissent The Violence of Party Politics ( )
 Chapter 7: Democracy and Dissent The Violence of Party Politics (1788-1800) AP United States History Week of October 19, 2015 Establishing a New Government Much of George Washington s first administration
Chapter 7: Democracy and Dissent The Violence of Party Politics (1788-1800) AP United States History Week of October 19, 2015 Establishing a New Government Much of George Washington s first administration
The Founding Fathers wanted to make sure they did things correctly. They even spent 3 weeks deciding what to call the President!!!
 The Founding Fathers wanted to make sure they did things correctly. They even spent 3 weeks deciding what to call the President!!! His Excellency, and His Highness were suggested, but Washington was simply
The Founding Fathers wanted to make sure they did things correctly. They even spent 3 weeks deciding what to call the President!!! His Excellency, and His Highness were suggested, but Washington was simply
Level 1 NEW GOVERNMENT IN OPERATION ESTABLISHING STABILITY
 Level 1 NEW GOVERNMENT IN OPERATION ESTABLISHING STABILITY Vocabulary Precedent: an act that results in a tradition Economics: science that deals with the production, distribution, and consumption of goods
Level 1 NEW GOVERNMENT IN OPERATION ESTABLISHING STABILITY Vocabulary Precedent: an act that results in a tradition Economics: science that deals with the production, distribution, and consumption of goods
Chapter Eight. The United States of North America
 Chapter Eight The United States of North America 1786-1800 Part One Introduction The United States of North America 1786-1800 What does the drawing say about life in the United States in 1799? 3 Chapter
Chapter Eight The United States of North America 1786-1800 Part One Introduction The United States of North America 1786-1800 What does the drawing say about life in the United States in 1799? 3 Chapter
Ch. 7 Launching a Nation Study Guide
 Ch. 7 Launching a Nation Study Guide Short Answer 1. As secretary of state Thomas Jefferson criticized U.S. policy toward France because he 2. In general, Congress created departments in the executive
Ch. 7 Launching a Nation Study Guide Short Answer 1. As secretary of state Thomas Jefferson criticized U.S. policy toward France because he 2. In general, Congress created departments in the executive
7/10/2009. By Mr. Cegielski WARM UP:
 By Mr. Cegielski WARM UP: 1 PREVIEW: George Washington Presidential Accomplishments Washington voluntarily resigned as Commander-in-Chief of the Continental Army in 1783. Because of his victories in the
By Mr. Cegielski WARM UP: 1 PREVIEW: George Washington Presidential Accomplishments Washington voluntarily resigned as Commander-in-Chief of the Continental Army in 1783. Because of his victories in the
The election of George Washington as the first president under the Constitution was not exactly unanimous
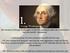 The election of George Washington as the first president under the Constitution was not exactly unanimous -2 electors from VA and 2 electors from MD did not vote -NY was entitled to 8 electoral votes but
The election of George Washington as the first president under the Constitution was not exactly unanimous -2 electors from VA and 2 electors from MD did not vote -NY was entitled to 8 electoral votes but
Washington s Administration
 Washington s Administration Life of George Washington Born Feb. 22, 1732 in Tidewater, VA Limited education - Tutored - Interested in math First political office Surveyor general for Fairfax County, VA
Washington s Administration Life of George Washington Born Feb. 22, 1732 in Tidewater, VA Limited education - Tutored - Interested in math First political office Surveyor general for Fairfax County, VA
Name Class Date. Forging the New Republic Section 1
 Name Class Date Section 1 MAIN IDEA President Washington and other leaders tried to solve the new nation s economic problems. This led to the rise of political parties. Key Terms and People cabinet heads
Name Class Date Section 1 MAIN IDEA President Washington and other leaders tried to solve the new nation s economic problems. This led to the rise of political parties. Key Terms and People cabinet heads
George Washington s Presidency
 George Washington s Presidency 1789-1796 CA 8 th Grade US History Standard 8.4.1, 8.4.2, 8.5.3 George Washington George Washington was sworn in as the first President on April 30, 1789 George Washington
George Washington s Presidency 1789-1796 CA 8 th Grade US History Standard 8.4.1, 8.4.2, 8.5.3 George Washington George Washington was sworn in as the first President on April 30, 1789 George Washington
Political Developments in the early republic. Chapter 12. Foreign Policy in the Young Nation
 Chapter 11 Political Developments in the early republic Chapter 12 Foreign Policy in the Young Nation 1. Inauguration Terms 2. Election of 1800 3. Embargo 4. War hawks 5. Tribute 6. Impressment 7. Isolationism
Chapter 11 Political Developments in the early republic Chapter 12 Foreign Policy in the Young Nation 1. Inauguration Terms 2. Election of 1800 3. Embargo 4. War hawks 5. Tribute 6. Impressment 7. Isolationism
VUS. 5 (pt. 2): Building a New Nation: Ratifying the Constitution
 Name: Date: Period: VUS 5 (pt 2): Building a New Nation: Ratifying the Constitution Notes VUS 5 (pt 2): Building a New Nation: Ratifying the Constitution 1 Objectives about Title VUS5 The student will
Name: Date: Period: VUS 5 (pt 2): Building a New Nation: Ratifying the Constitution Notes VUS 5 (pt 2): Building a New Nation: Ratifying the Constitution 1 Objectives about Title VUS5 The student will
THE NEW REPUBLIC. Chapter 1 Section 4
 THE NEW REPUBLIC Chapter 1 Section 4 Historical Context Constitution Bill of Rights was finally ratified in 1791. During 1790 s and 1800 s the New Republic faced internal political issues and international
THE NEW REPUBLIC Chapter 1 Section 4 Historical Context Constitution Bill of Rights was finally ratified in 1791. During 1790 s and 1800 s the New Republic faced internal political issues and international
Vice President: John Adams. CABINET Secretary of State: Thomas Jefferson Secretary of War: Henry Knox Secretary of Treasury: Alexander Hamilton
 James Madison Amendment I: Freedom of religion, speech, press, assembly, petition. Amendment II: Right to bear arms (for militia). Amendment III: no quartering in peacetime Amendment IV: No unreasonable
James Madison Amendment I: Freedom of religion, speech, press, assembly, petition. Amendment II: Right to bear arms (for militia). Amendment III: no quartering in peacetime Amendment IV: No unreasonable
Washington & Adams U.S. HISTORY CH 7: LAUNCHING THE NATION
 Washington & Adams U.S. HISTORY CH 7: LAUNCHING THE NATION 1.The Constitution: A Brief Review At the Constitutional Convention, the Virginia Plan included a proposal for separation of powers into three
Washington & Adams U.S. HISTORY CH 7: LAUNCHING THE NATION 1.The Constitution: A Brief Review At the Constitutional Convention, the Virginia Plan included a proposal for separation of powers into three
Read the excerpt from George Washington s Farewell Address. What are 3 things Washington warns about as he leaves office?
 Read the excerpt from George Washington s Farewell Address. What are 3 things Washington warns about as he leaves office? Ms. Luco IB History What led to the rise of political parties in the 1790s? President:
Read the excerpt from George Washington s Farewell Address. What are 3 things Washington warns about as he leaves office? Ms. Luco IB History What led to the rise of political parties in the 1790s? President:
Study Guide: Sunshine State Standards
 å È É Ê Ë Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Í É Î Ë Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ï Ð É Ñ Ñ Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Study Guide: Chapter
å È É Ê Ë Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Í É Î Ë Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ï Ð É Ñ Ñ Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Study Guide: Chapter
Section 1 Quiz: Government and Party Politics *Please respond to all questions on your separate answer sheet.
 U.S. History 1 CP Mr. Mulry Chapter 6: The New Republic 1789-1816 Section Quizzes Section 1 Quiz: Government and Party Politics Directions: From I below, choose the term that best fits each description.
U.S. History 1 CP Mr. Mulry Chapter 6: The New Republic 1789-1816 Section Quizzes Section 1 Quiz: Government and Party Politics Directions: From I below, choose the term that best fits each description.
The First Five Presidents. Domestic and Foreign Policy
 The First Five Presidents Domestic and Foreign Policy 1789-1827 Domestic and Foreign Policy Domestic Policy: Actions that happen within the USA. Foreign Policy: Actions that happen overseas. George Washington:
The First Five Presidents Domestic and Foreign Policy 1789-1827 Domestic and Foreign Policy Domestic Policy: Actions that happen within the USA. Foreign Policy: Actions that happen overseas. George Washington:
Constitutional Era Washington & Adams
 Constitutional Era Washington & Adams Federalist Era SOL: VUS. 6A SWBAT The student will apply social science skills to understand the development of the American political system by: a) examining founding
Constitutional Era Washington & Adams Federalist Era SOL: VUS. 6A SWBAT The student will apply social science skills to understand the development of the American political system by: a) examining founding
2) In what century did George Washington take the office as President? 3) Why was President Washington so grave and serious on the day he took office?
 We are in a wilderness without a The Federalist Era (1789-1825) The minority possess their equal single footstep to guide us. Review Sheet 2 rights, which equal law must protect -J. Madison We are all
We are in a wilderness without a The Federalist Era (1789-1825) The minority possess their equal single footstep to guide us. Review Sheet 2 rights, which equal law must protect -J. Madison We are all
Era. Chapter 5 Section 1 The First President. The Nation s First President. The First Congress. President Washington
 Section 1 The First President *Precedent: *cabinet: *national debt: *bond: *speculator: *unconstitutional: *tariff: with relief and enthusiasm. All that was needed was a leader to guide the new nation.
Section 1 The First President *Precedent: *cabinet: *national debt: *bond: *speculator: *unconstitutional: *tariff: with relief and enthusiasm. All that was needed was a leader to guide the new nation.
6. Why did Hamilton suggest moving the nation s capital from New York to the District of Columbia?
 Chapter 6 Short Study Guide Vocabulary 1. Judiciary Act of 1789 2. Alexander Hamilton 3. sectionalism 4. Alien and Sedition Acts 5. Nullification 6. Lewis and Clark Expedition 7. Judiciary Act of 1801
Chapter 6 Short Study Guide Vocabulary 1. Judiciary Act of 1789 2. Alexander Hamilton 3. sectionalism 4. Alien and Sedition Acts 5. Nullification 6. Lewis and Clark Expedition 7. Judiciary Act of 1801
VUS. 5: Building a New Nation: Ratifying the Constitution
 Name: Date: Period: VUS 5: Building a New Nation: Ratifying the Constitution Notes VUS #: Title 1 Objectives about Title VUS5 The student will demonstrate knowledge of the issues involved in the creation
Name: Date: Period: VUS 5: Building a New Nation: Ratifying the Constitution Notes VUS #: Title 1 Objectives about Title VUS5 The student will demonstrate knowledge of the issues involved in the creation
Politics In An Age Of Passion
 Name: Give Me Liberty!, Chapter 8 Video Guide Big Idea Questions What was Washington s view of political parties? What is impressment? Guided Notes Politics In An Age Of Passion Hamilton s Program Hamilton
Name: Give Me Liberty!, Chapter 8 Video Guide Big Idea Questions What was Washington s view of political parties? What is impressment? Guided Notes Politics In An Age Of Passion Hamilton s Program Hamilton
The Young Republic: The Early Years. The Young Republic Test Packet due & test day:
 The Young Republic: The Early Years The Young Republic Test Packet due & test day: The Early Nation Vocabulary Name: Define each of the following words in regards to the early development of the nation:
The Young Republic: The Early Years The Young Republic Test Packet due & test day: The Early Nation Vocabulary Name: Define each of the following words in regards to the early development of the nation:
Washington s Presidency
 Q3 Vocab Washington s Presidency George Washington: 1st President of the US New York City: 1st capital of the US Precedent: an action or decision that serves as a later example Inaugural: the beginning,
Q3 Vocab Washington s Presidency George Washington: 1st President of the US New York City: 1st capital of the US Precedent: an action or decision that serves as a later example Inaugural: the beginning,
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton
 Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: Washington Takes Office Section 2: Creating a Foreign Policy Section 3: Political Parties Emerge Section 4: The Second President Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Cornell
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: Washington Takes Office Section 2: Creating a Foreign Policy Section 3: Political Parties Emerge Section 4: The Second President Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Cornell
8th - EXAM - CHAPTER 6 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The new federal government in America took actions that would set an example for the future. In George
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The new federal government in America took actions that would set an example for the future. In George
APUSH- Unit 4: Early Federal Period
 APUSH- Unit 4: Early Federal Period Launching the New Ship of State, 1789-1800 (Chapter 10) I can explain why George Washington was pivotal to inaugurating the new federal government. (Pages 190-193) Cabinet
APUSH- Unit 4: Early Federal Period Launching the New Ship of State, 1789-1800 (Chapter 10) I can explain why George Washington was pivotal to inaugurating the new federal government. (Pages 190-193) Cabinet
SWBAT. Explain George Washington s implementation of the new Constitution Compare problems Washington faced with those of Obama
 George Washington George Washington DO NOW: With a partner answer the following: 1.Would our current president be able to successfully lead a new nation? Why/Why not? 2.What types of problems would the
George Washington George Washington DO NOW: With a partner answer the following: 1.Would our current president be able to successfully lead a new nation? Why/Why not? 2.What types of problems would the
The Articles vs. the Constitution Articles of Confederation. U.S. Constitution A Firm League of Friendship
 USHC 1.4 Analyze how dissatisfactions with the government under the Articles of Confederation were addressed with the writing of the Constitution of 1787, including the debates and compromises reached
USHC 1.4 Analyze how dissatisfactions with the government under the Articles of Confederation were addressed with the writing of the Constitution of 1787, including the debates and compromises reached
The Early Republic
 The Early Republic 1789-1828 Essential Questions What challenges faced the new nation under the Constitution? How did the first American political parties emerge? How did the Supreme Court establish its
The Early Republic 1789-1828 Essential Questions What challenges faced the new nation under the Constitution? How did the first American political parties emerge? How did the Supreme Court establish its
Chalkboard Splash: Name and describe the Amendments in the Bill of Rights
 Chalkboard Splash: Name and describe the Amendments in the Bill of Rights UNIT III: EXPANSION, NATIONALISM, SECTIONALISM THE FIRST PRESIDENT KING? HIGHNESS? MAJESTY? April 30, 1789: Washington was unanimously
Chalkboard Splash: Name and describe the Amendments in the Bill of Rights UNIT III: EXPANSION, NATIONALISM, SECTIONALISM THE FIRST PRESIDENT KING? HIGHNESS? MAJESTY? April 30, 1789: Washington was unanimously
Overview: Launching the New Ship of State
 Overview: Launching the New Ship of State Chapter 10 (Note quiz Friday!) Test Corrections due Tuesday 10/28 FEDERALIST ERA Theme 1 Led by George Washington and Alexander Hamilton, the first administration
Overview: Launching the New Ship of State Chapter 10 (Note quiz Friday!) Test Corrections due Tuesday 10/28 FEDERALIST ERA Theme 1 Led by George Washington and Alexander Hamilton, the first administration
A New Republic and the Rise of Parties A New Republic and the Rise of Parties Washington s America The Uniformity of New England
 1 2 3 4 5 A New Republic and the Rise of Parties 1789 1800 Washington s America What were the distinguishing features of the early republic s four major regions? Forging a New Government What challenges
1 2 3 4 5 A New Republic and the Rise of Parties 1789 1800 Washington s America What were the distinguishing features of the early republic s four major regions? Forging a New Government What challenges
The Presidency of John Adams
 The Presidency of John Adams 1797-1801 A Contentious Beginning Political parties had developed into powerful forces in the states States control electoral college, electors cast two votes each for President
The Presidency of John Adams 1797-1801 A Contentious Beginning Political parties had developed into powerful forces in the states States control electoral college, electors cast two votes each for President
US History Module 1 (A) Lesson 3. A New Nation
 US History Module 1 (A) Lesson 3 A New Nation Forming a New Government Fears and concerns about the form of government affects planning of new government Experimenting with Confederation 1781 Congress
US History Module 1 (A) Lesson 3 A New Nation Forming a New Government Fears and concerns about the form of government affects planning of new government Experimenting with Confederation 1781 Congress
The First Constitutional Government. April 30, 1789
 The First Constitutional Government April 30, 1789 Standard SSUSH6: Analyze the challenges faced by the first Presidents and how they responded. Washington s Cabinet Washington was sworn in on Wall Street,
The First Constitutional Government April 30, 1789 Standard SSUSH6: Analyze the challenges faced by the first Presidents and how they responded. Washington s Cabinet Washington was sworn in on Wall Street,
SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States Constitution.
 Standards SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States Constitution. a. Explain how weaknesses in the Articles of
Standards SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States Constitution. a. Explain how weaknesses in the Articles of
New Nation. establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s
 New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
The United States Begins. Mr. Baker Humane Letters I
 The United States Begins Mr. Baker Humane Letters I Reading Quiz 1. What did George Washington decide to do concerning calls for America to get involved militarily in the French Revolution? 2. Who was
The United States Begins Mr. Baker Humane Letters I Reading Quiz 1. What did George Washington decide to do concerning calls for America to get involved militarily in the French Revolution? 2. Who was
Launching the New Nation
 Launching the New Nation George Washington becomes the first president. President Thomas Jefferson doubles U.S. territory with the Louisiana Purchase. The U.S. fights the British in the War of 1812. Launching
Launching the New Nation George Washington becomes the first president. President Thomas Jefferson doubles U.S. territory with the Louisiana Purchase. The U.S. fights the British in the War of 1812. Launching
Chapter 7 Quiz. 1. The stalemate over the assumption of state debts was broken when
 You will find the quizzes for Chapters 7 and 8 below. Use two separate scantrons to mark your answers. Both quizzes are due at our next class meeting on Thursday (11/20/14). EXAM 2 WILL BE ON 11/20/14.
You will find the quizzes for Chapters 7 and 8 below. Use two separate scantrons to mark your answers. Both quizzes are due at our next class meeting on Thursday (11/20/14). EXAM 2 WILL BE ON 11/20/14.
Unit 3- Hammering Out a Federal Republic
 Name: Class Period: Unit 3- Hammering Out a Federal Republic Key Concepts FOR PERIOD 3: Key Concept 3.2: The American Revolution s democratic and republican ideals inspired new experiments with different
Name: Class Period: Unit 3- Hammering Out a Federal Republic Key Concepts FOR PERIOD 3: Key Concept 3.2: The American Revolution s democratic and republican ideals inspired new experiments with different
Washington and Adams Administrations
 Washington and Adams Administrations 1788 1800 1. Hamilton s Financial Plan: Report on the Public Credit. Credit Pay all debts in full at face value ( Assumption of Debts }; create a Bank of the U.S. (BUS)
Washington and Adams Administrations 1788 1800 1. Hamilton s Financial Plan: Report on the Public Credit. Credit Pay all debts in full at face value ( Assumption of Debts }; create a Bank of the U.S. (BUS)
LAUNCHING A NEW NATION
 LAUNCHING A NEW NATION 1789-1815 REMEMBER The U.S. had gained its independence but it had to prove to the world that it was a STRONG country Step 1: Organize the government so the country is internally
LAUNCHING A NEW NATION 1789-1815 REMEMBER The U.S. had gained its independence but it had to prove to the world that it was a STRONG country Step 1: Organize the government so the country is internally
Name: 8 th Grade U.S. History. STAAR Review. Early Republic
 8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Early Republic FORT BURROWS 2018 VOCABULARY Rebellion- an effort by many people to change the government or leader of a country by the use of protest or violence Excise
8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Early Republic FORT BURROWS 2018 VOCABULARY Rebellion- an effort by many people to change the government or leader of a country by the use of protest or violence Excise
A - STRUCTURE OF THE EXECUTIVE BRANCH
 A - STRUCTURE OF THE EXECUTIVE BRANCH The executive branch of government took shape during the summer of 1789. Congress set up three departments and two offices within the executive branch. Washington
A - STRUCTURE OF THE EXECUTIVE BRANCH The executive branch of government took shape during the summer of 1789. Congress set up three departments and two offices within the executive branch. Washington
Chapter 7 Politics and Society in the New Republic,
 Chapter 7 Politics and Society in the New Republic, 1787-1820 The Political Crisis of the 1790s Thomas Jefferson vs. Alexander Hamilton The Federalist Implement the Constitution Swept the election of 1788
Chapter 7 Politics and Society in the New Republic, 1787-1820 The Political Crisis of the 1790s Thomas Jefferson vs. Alexander Hamilton The Federalist Implement the Constitution Swept the election of 1788
George Washington s Presidency. ch?v=obupqgv8ybm
 George Washington s Presidency http://www.youtube.com/wat ch?v=obupqgv8ybm Foreign Policy The French Revolution Americans, in general, support the French people wanting a Republic Most are horrified by
George Washington s Presidency http://www.youtube.com/wat ch?v=obupqgv8ybm Foreign Policy The French Revolution Americans, in general, support the French people wanting a Republic Most are horrified by
Washington, Jefferson, Madison, Monroe, Jackson, and Polk Presidencies
 Washington, Jefferson, Madison, Monroe, Jackson, and Polk Presidencies 1. George Washington (1789-1797) - Created a cabinet of advisors 1. Secretary of War - Henry Knox 2. Secretary of the Treasury - Alexander
Washington, Jefferson, Madison, Monroe, Jackson, and Polk Presidencies 1. George Washington (1789-1797) - Created a cabinet of advisors 1. Secretary of War - Henry Knox 2. Secretary of the Treasury - Alexander
Unit 3: Building the New Nation FRQ Outlines. Prompt:Analyze the reasons for the Anti-Federalists opposition to ratifying the Constitution.
 Prompt:Analyze the reasons for the Anti-Federalists opposition to ratifying the Constitution. Re-written as a Question: What were the reasons for the Anti-Federalist opposition to ratifying the constitution?
Prompt:Analyze the reasons for the Anti-Federalists opposition to ratifying the Constitution. Re-written as a Question: What were the reasons for the Anti-Federalist opposition to ratifying the constitution?
Chapter 7 practice test
 Chapter 7 practice test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Many Americans wanted George Washington to be president because he a. was seen
Chapter 7 practice test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Many Americans wanted George Washington to be president because he a. was seen
1. Chapter Eight 2. Columbus discovered America in Jefferson wrote the Declaration of Independence in Washington became President
 1. Chapter Eight 2. Columbus discovered America in 1492. 3. Jefferson wrote the Declaration of Independence in 1776. 4. Washington became President and our US Constitution went into effect in 1789. 5.
1. Chapter Eight 2. Columbus discovered America in 1492. 3. Jefferson wrote the Declaration of Independence in 1776. 4. Washington became President and our US Constitution went into effect in 1789. 5.
Ch. 11: Political Developments in the Early Republic
 Ch. 11: Political Developments in the Early Republic Alexander Hamilton Thomas Jefferson President George Washington On April 30, 1789, George Washington became our nation s first president. His first
Ch. 11: Political Developments in the Early Republic Alexander Hamilton Thomas Jefferson President George Washington On April 30, 1789, George Washington became our nation s first president. His first
Early Challenges. Chapter 5, Section 2 California State Standards - 8.3, 8.4, 8.3.5, 8.4.1,8.4.2,
 Early Challenges Chapter 5, Section 2 California State Standards - 8.3, 8.4, 8.3.5, 8.4.1,8.4.2, Looking Back, Looking Ahead The United States needed money to pay its war debts and to finance national
Early Challenges Chapter 5, Section 2 California State Standards - 8.3, 8.4, 8.3.5, 8.4.1,8.4.2, Looking Back, Looking Ahead The United States needed money to pay its war debts and to finance national
Understanding Washington s Domestic and Foreign Policies
 1783: Treaty of Paris ended the American Revolution Despite the treaty, Britain: Continued to maintain frontier forts along the Great Lakes Continued their alliances with Native American tribes 1787: The
1783: Treaty of Paris ended the American Revolution Despite the treaty, Britain: Continued to maintain frontier forts along the Great Lakes Continued their alliances with Native American tribes 1787: The
What was the Treaty of Greenville? Why did the call Anthony Wayne Mad? What did the Democratic-Republicans believe in?
 What was the Treaty of Greenville? Why did the call Anthony Wayne Mad? What did the Democratic-Republicans believe in? 1. Elastic Clause- 2. Revolution- 3. Privateer- 4. Strict Construction- 5. Loose Construction-
What was the Treaty of Greenville? Why did the call Anthony Wayne Mad? What did the Democratic-Republicans believe in? 1. Elastic Clause- 2. Revolution- 3. Privateer- 4. Strict Construction- 5. Loose Construction-
Forming a New Government
 Forming a New Government Why Independent in the First Place? Citizens wanted to limit the power of government Lack of representation No taxation without representation Protect personal freedoms Desired
Forming a New Government Why Independent in the First Place? Citizens wanted to limit the power of government Lack of representation No taxation without representation Protect personal freedoms Desired
The first political parties emerged
 John Adams 1 The first political parties emerged During the debate over ratification of the Constitution, two organized groups emerged, the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists. Washington opposed political
John Adams 1 The first political parties emerged During the debate over ratification of the Constitution, two organized groups emerged, the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists. Washington opposed political
HERE WAS BURIED THOMAS JEFFERSON AUTHOR OF THE DECLARATION OF AMERICAN INDEPENDENCE OF THE STATUTE OF VIRGINIA FOR RELIGIOUS FREEDOM AND FATHER OF
 HERE WAS BURIED THOMAS JEFFERSON AUTHOR OF THE DECLARATION OF AMERICAN INDEPENDENCE OF THE STATUTE OF VIRGINIA FOR RELIGIOUS FREEDOM AND FATHER OF THE UNIVERSITY OF VIRGINIA BORN APRIL 13, 1743 DIED JULY
HERE WAS BURIED THOMAS JEFFERSON AUTHOR OF THE DECLARATION OF AMERICAN INDEPENDENCE OF THE STATUTE OF VIRGINIA FOR RELIGIOUS FREEDOM AND FATHER OF THE UNIVERSITY OF VIRGINIA BORN APRIL 13, 1743 DIED JULY
George Washington. Information to be included:
 George Washington Information to be included: 2 Facts (ONLY) BEFORE Washington was President, including place of Election facts events of and surrounding his nomination and election to the office of President,
George Washington Information to be included: 2 Facts (ONLY) BEFORE Washington was President, including place of Election facts events of and surrounding his nomination and election to the office of President,
