11/30 What are some things we need now that we are our own Nation? List as many things as you can. Moves on the chart.
|
|
|
- Beverly Mason
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 11/30 What are some things we need now that we are our own Nation? List as many things as you can. Moves on the chart.
2 12/1 Predict some problems moving forward under one gov t: (Think back to some issues we faced when trying to create one gov t) Why might Americans be worried about having a president? How did states already balance power in their local state gov t? ALL FOR MOVES ON THE CHART!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
3 Warm Up 1/6 1.Why did Americans not want to give too much power to one person? 2.How did the states attempt to balance power? 3.What were the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation? Strengths?
4 1. What part of the Treaty of Paris did Britain ignore? The British kept troops at frontier posts in American Territory.
5 It s a plan of Government. 2. Define Constitution-
6 3. Why were Americans worried about giving too much power to one ruler? Their experience with British rule made Americans cautious about giving power to one person.
7 4. What did most states establish to help balance power? Most states had a Governor and a legislative body. Some states further balanced power by creating a bicameral legislature (two house)
8 5. Who was allowed to vote for these state legislatures? Males who were at least 21 years old and owned land.
9 6. What did Americans agree on about their central Gov t? That it should be a Republic! A Gov t in which citizens rule through elected representatives.
10 7. What did most Americans want the Central Gov t to be? WEAK! They wanted the colonies to act like small independent countries.
11 8. When would the colonies work together through their Central Gov t? Only to wage war and handle relations with other nations.
12 9. When were the Articles of Confederation adopted? November 1777
13 10. How much power did the States give up under the Articles of Confederation? Very Little. Firm League of Friendship.
14 11. What powers did Congress get under the Articles? Conduct Foreign Affairs. Maintain Armed Forces. Borrow Money. Issue Currency.
15 12. What couldn t the Congress do? Couldn t regulate trade. Force citizens to join Army. Impose taxes. If the Congress needed money or troops they had to ask the States! Also lacked a Chief Executive.
16 13. What business did the Confederation Gov t conduct? Selling Western Lands through Congressional Committees.
17 14. How many votes did each state get under the Articles? One, regardless of its population. All states had to approve the Articles as well as amendments.
18 15. Had did the larger states feel about having one vote? They felt they should have more than one vote due to their larger population.
19 16. When did the Articles of Confederation formally become the Gov t of the United States? March 1, 1781.
20 17. Were the Articles of Confederation effective? NO! They did not provide America a strong enough Gov t to face the problems it had.
21 18. Why was it difficult for the Congress to pass laws? Nine states needed to approve the law. Any attempt to change the Articles required all 13 states.
22 19. What things did the Confederation Congress Accomplish? Won their independence! Expanded Foreign Trade. Settling and Governing the nation s western territories.
23 Warm Up 1/7 4. How many people now lived west of the Appalachian Mountains? 5. What two ordinances attempted to help settlers settle the area peacefully? 6. List problems occurring with Britain? List problems occurring with Spain?
24 20. How many people lived west of the Appalachian Mountains by 1790? 120,000 These settlers wanted to join the Union. Articles of Confederation had no procedure for adding new states.
25 21. How could these new districts become states eventually? When the population of a district reached the population of the smallest state, then that district could petition for statehood.
26 22. What did the Confederation Congress pass in 1785? An ordinance, or law, that established a procedure for surveying and selling the western lands north of the Ohio River.
27 23. Why did Richard Henry Lee want property rights clearly defined? He did not want lawless people moving into the new territory and taking lands unfairly.
28 24. What did the Northwest ordinance create? A single Northwest Territory out of the lands north of the Ohio River and East of the Mississippi.
29 25. When could the territories here apply for statehood? When the population reached 60,000 people.
30 26. What was the one thing the new territories could not have? Slavery! 1 st time the United States attempt to stop slavery.
31 27. What happened to the money printed during the Revolutionary War? It depreciated. Fallen in value it was almost worthless.
32 28. What was not backing up these bills? No gold or silver backed up the money.
33 29. What did the Continental Congress rack up during the war? A HUGE DEBT! And then didn t have the power to tax people to pay for the debt! IRONY
34 30. Summarize the problems facing the Confederation at the end of this section? Couldn t pass a law to tax imported goods. Britain closed the West Indies to American Merchants. Couldn t repay Loyalists money for their lands. Spain closed the Mississippi River to the Americans.
Unit 2 Part 2 Articles of Confederation
 Unit 2 Part 2 Articles of Confederation Explain how the states new constitutions reflected republican ideals. Describe the structure and powers of the national government under the Articles of Confederation.
Unit 2 Part 2 Articles of Confederation Explain how the states new constitutions reflected republican ideals. Describe the structure and powers of the national government under the Articles of Confederation.
The Articles of Confederation: Chapter 3, Section 1
 The Articles of Confederation: Chapter 3, Section 1 Political ideas and major events shape how people form governments. When the American colonies broke their political ties with Great Britain, they faced
The Articles of Confederation: Chapter 3, Section 1 Political ideas and major events shape how people form governments. When the American colonies broke their political ties with Great Britain, they faced
How Shall We Govern Ourselves?
 How Shall We Govern Ourselves? The Articles of Confederation America s First Constitution What kind of government would the FREEDOM loving Americans create to balance LIBERTY with enough AUTHORITY to get
How Shall We Govern Ourselves? The Articles of Confederation America s First Constitution What kind of government would the FREEDOM loving Americans create to balance LIBERTY with enough AUTHORITY to get
Articles of Confederation
 Articles of Confederation 1. The Founders had to deal with a number of difficult questions. a. What type of national government should they create? i. Weak or strong b. How much power should they give
Articles of Confederation 1. The Founders had to deal with a number of difficult questions. a. What type of national government should they create? i. Weak or strong b. How much power should they give
The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783!
 Creating a Republic The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783! The treaty ending the war with Britain, more than doubled the territory of the United States!
Creating a Republic The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783! The treaty ending the war with Britain, more than doubled the territory of the United States!
The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783!
 Creating a Republic The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783! The treaty ending the war with Britain, more than doubled the territory of the United States!
Creating a Republic The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783! The treaty ending the war with Britain, more than doubled the territory of the United States!
The First Government: How it Worked
 IQ S 1. Describe the role of government in securing freedom, opportunity, prosperity, and security (FOP S) for the people. 2. Without FOP S, can a government of the people be successful? 3. Is there a
IQ S 1. Describe the role of government in securing freedom, opportunity, prosperity, and security (FOP S) for the people. 2. Without FOP S, can a government of the people be successful? 3. Is there a
The Articles of Confederation
 The Articles of Confederation U.S.A. s First Govt. I. Following the end of the American Revolution the newly created U.S.A. needed a government A. Previous government was Great Britain B. Independence
The Articles of Confederation U.S.A. s First Govt. I. Following the end of the American Revolution the newly created U.S.A. needed a government A. Previous government was Great Britain B. Independence
SS7 Civics Ch 3.1: Early State Governments
 SS7 Civics Ch 3.1: Early State Governments I. State Constitutions A. Even before the Declaration of Independence was signed, American colonists thought about independence. Independence would mean an end
SS7 Civics Ch 3.1: Early State Governments I. State Constitutions A. Even before the Declaration of Independence was signed, American colonists thought about independence. Independence would mean an end
A More Perfect Union. Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation
 A More Perfect Union Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation 1. Eleven of the thirteen states adopted state constitutions. Connecticut and Rhode Island kept its colonial charter as its constitution
A More Perfect Union Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation 1. Eleven of the thirteen states adopted state constitutions. Connecticut and Rhode Island kept its colonial charter as its constitution
The Critical Period The early years of the American Republic
 The Critical Period 1781-1789 The early years of the American Republic America after the War New Political Ideas: - Greater power for the people Republic: Represent the Public America after the War State
The Critical Period 1781-1789 The early years of the American Republic America after the War New Political Ideas: - Greater power for the people Republic: Represent the Public America after the War State
The Articles of Confederation
 The Articles of Confederation 1781-1789 The United States was the first nation in modern times to have a government designed and run according to democratic principles. During the Revolutionary War the
The Articles of Confederation 1781-1789 The United States was the first nation in modern times to have a government designed and run according to democratic principles. During the Revolutionary War the
Battle of Saratoga. British troops reached Saratoga from Quebec and were surrounded and severely outnumbered = Surrendered
 Battle of Saratoga British troops reached Saratoga from Quebec and were surrounded and severely outnumbered = Surrendered Huge military victory, and boosted morale Convinced the French & Spain to enter
Battle of Saratoga British troops reached Saratoga from Quebec and were surrounded and severely outnumbered = Surrendered Huge military victory, and boosted morale Convinced the French & Spain to enter
LECTURE 3-3: THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION AND THE CONSTITUTION
 LECTURE 3-3: THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION AND THE CONSTITUTION The American Revolution s democratic and republican ideals inspired new experiments with different forms of government. I. Allegiances A.
LECTURE 3-3: THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION AND THE CONSTITUTION The American Revolution s democratic and republican ideals inspired new experiments with different forms of government. I. Allegiances A.
Unit 7. Our First Government. Bellwork. Essential Questions (What I need to know):
 Unit 7 Our First Government Name Date Period Essential Questions (What I need to know): Date Bellwork Answer(s) 1. What is government? 2. How did the first United States government operate? 3. How did
Unit 7 Our First Government Name Date Period Essential Questions (What I need to know): Date Bellwork Answer(s) 1. What is government? 2. How did the first United States government operate? 3. How did
The Search for a National Government by Alan Brinkley
 The Search for a National Government by Alan Brinkley This reading is excerpted from Chapter Five of Brinkley s American History: A Survey (12th ed.). I wrote the footnotes. If you use the questions below
The Search for a National Government by Alan Brinkley This reading is excerpted from Chapter Five of Brinkley s American History: A Survey (12th ed.). I wrote the footnotes. If you use the questions below
Articles of Confederation and Constitutional Conventions
 Articles of Confederation and Constitutional Conventions The Declaration of Independence Recognized changes taking place in colonies; colonies becoming states subject to no higher authority Colonies begin
Articles of Confederation and Constitutional Conventions The Declaration of Independence Recognized changes taking place in colonies; colonies becoming states subject to no higher authority Colonies begin
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century)
 The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 2: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Revolution and the Early Republic CHAPTER OVERVIEW Colonists declare their independence and win a war to gain the right
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 2: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Revolution and the Early Republic CHAPTER OVERVIEW Colonists declare their independence and win a war to gain the right
How did the Articles of Confederation organize the first. 11national government? What are the Articles of Confederation?
 11national government? How did the Articles of Confederation organize the first LESSON PURPOSE Our first government, the Continental Congress, drew up a constitution stating its powers. This constitution
11national government? How did the Articles of Confederation organize the first LESSON PURPOSE Our first government, the Continental Congress, drew up a constitution stating its powers. This constitution
Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation
 Name: Date: Chapter 8 Study Guide Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation 1. A constitution is a set of basic principles and laws, usually in written form, that state the powers and duties of a government.
Name: Date: Chapter 8 Study Guide Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation 1. A constitution is a set of basic principles and laws, usually in written form, that state the powers and duties of a government.
The Confederation Era
 1 The Confederation Era MAIN IDEA The Articles of Confederation were too weak to govern the nation after the war ended. WHY IT MATTERS NOW The weakness of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing
1 The Confederation Era MAIN IDEA The Articles of Confederation were too weak to govern the nation after the war ended. WHY IT MATTERS NOW The weakness of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing
11 1 THE BIG QUESTION: WHO WILL BE IN CHARGE? SHIFTING BALANCE OF POWER: AN OVERVIEW
 11 1 THE BIG QUESTION: WHO WILL BE IN CHARGE? SHIFTING BALANCE OF POWER: AN OVERVIEW 152 11 2 ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION: 13 SOVEREIGN STATES sovereign supreme power; independent THE CONFEDERATION GOVERNMENT
11 1 THE BIG QUESTION: WHO WILL BE IN CHARGE? SHIFTING BALANCE OF POWER: AN OVERVIEW 152 11 2 ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION: 13 SOVEREIGN STATES sovereign supreme power; independent THE CONFEDERATION GOVERNMENT
The Origins of the Constitution
 The Origins of the Constitution Before the colonies signed the Treaty of Paris ending the Revolutionary War in 1783, they ratified the Articles of Confederation in 1781, The Articles provided a weak union
The Origins of the Constitution Before the colonies signed the Treaty of Paris ending the Revolutionary War in 1783, they ratified the Articles of Confederation in 1781, The Articles provided a weak union
Land Ordinance of 1785
 Unit 3 SSUSH5 Investigate specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States Constitution. a. Examine the strengths of the Articles of Confederation,
Unit 3 SSUSH5 Investigate specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States Constitution. a. Examine the strengths of the Articles of Confederation,
Indirect representation: when elected officials elect higher officials Interstate commerce: trade between states Legislature: a law making body of
 Level 2 Indirect representation: when elected officials elect higher officials Interstate commerce: trade between states Legislature: a law making body of government Tariff: a tax on imports Amendment:
Level 2 Indirect representation: when elected officials elect higher officials Interstate commerce: trade between states Legislature: a law making body of government Tariff: a tax on imports Amendment:
Chapter 25 Section 1. Section 1. Terms and People
 Chapter 25 Terms and People republic a government in which the people elect their representatives unicameral legislature a lawmaking body with a single house whose representatives are elected by the people
Chapter 25 Terms and People republic a government in which the people elect their representatives unicameral legislature a lawmaking body with a single house whose representatives are elected by the people
Early Challenges. Chapter 5, Section 2 California State Standards - 8.3, 8.4, 8.3.5, 8.4.1,8.4.2,
 Early Challenges Chapter 5, Section 2 California State Standards - 8.3, 8.4, 8.3.5, 8.4.1,8.4.2, Looking Back, Looking Ahead The United States needed money to pay its war debts and to finance national
Early Challenges Chapter 5, Section 2 California State Standards - 8.3, 8.4, 8.3.5, 8.4.1,8.4.2, Looking Back, Looking Ahead The United States needed money to pay its war debts and to finance national
Colonies Become States
 Colonies Become States Colonies already had their own individual governments before the 1776 Declaration 11 of 13 colonies had State Constitutions Constitution a document that states rules under which
Colonies Become States Colonies already had their own individual governments before the 1776 Declaration 11 of 13 colonies had State Constitutions Constitution a document that states rules under which
US History, Ms. Brown Website: dph7history.weebly.com
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #68 Aims: SWBAT identify and evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation DO NOW Directions:
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #68 Aims: SWBAT identify and evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation DO NOW Directions:
Chapter 6. APUSH Mr. Muller
 Chapter 6 APUSH Mr. Muller Aim: How is the New Republic tested? Do Now: Thus I consent, sir, to this Constitution, because I expect no better, and because I am not sure that it is not the best. The opinions
Chapter 6 APUSH Mr. Muller Aim: How is the New Republic tested? Do Now: Thus I consent, sir, to this Constitution, because I expect no better, and because I am not sure that it is not the best. The opinions
Constitutional Principles (4).notebook. October 08, 2014
 Bell Ringers Mrs. Salasney Homework Objective: Students will describe the conflicts facing the governing of the new nation 2 Which action by the British government was considered by American colonists
Bell Ringers Mrs. Salasney Homework Objective: Students will describe the conflicts facing the governing of the new nation 2 Which action by the British government was considered by American colonists
From Revolution to Government
 From Revolution to Government The Second Continental Congress declared independence from Britain in 1776. The Revolutionary War lasted from 1775 to 1783. Congress developed a new government for America:
From Revolution to Government The Second Continental Congress declared independence from Britain in 1776. The Revolutionary War lasted from 1775 to 1783. Congress developed a new government for America:
SSUSH5 A, B, C & D Creating a New Government
 SSUSH5 A, B, C & D Creating a New Government The Articles of Confederation Formally called the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union, this agreement was created by the leaders of the original thirteen
SSUSH5 A, B, C & D Creating a New Government The Articles of Confederation Formally called the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union, this agreement was created by the leaders of the original thirteen
A More Perfect Union
 A More Perfect Union 1777 1790 Why It Matters When the American colonies broke their political ties with Great Britain, they faced the task of forming independent governments at both the state and national
A More Perfect Union 1777 1790 Why It Matters When the American colonies broke their political ties with Great Britain, they faced the task of forming independent governments at both the state and national
It s to late to apologize uzfrawatbvg&feature=player_de tailpage#t=4s
 It s to late to apologize http://www.youtube.com/watch?v= uzfrawatbvg&feature=player_de tailpage#t=4s War effectively comes to an end in October 1781 with the defeat of the British at Yorktown. Washington
It s to late to apologize http://www.youtube.com/watch?v= uzfrawatbvg&feature=player_de tailpage#t=4s War effectively comes to an end in October 1781 with the defeat of the British at Yorktown. Washington
Unit 3: Building the New Nation FRQ Outlines. Prompt:Analyze the reasons for the Anti-Federalists opposition to ratifying the Constitution.
 Prompt:Analyze the reasons for the Anti-Federalists opposition to ratifying the Constitution. Re-written as a Question: What were the reasons for the Anti-Federalist opposition to ratifying the constitution?
Prompt:Analyze the reasons for the Anti-Federalists opposition to ratifying the Constitution. Re-written as a Question: What were the reasons for the Anti-Federalist opposition to ratifying the constitution?
Once a year, each state would select a delegation to send to the capital city.
 In November 1777, the Continental Congress adopted the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union. This was a plan for a loose union of the states under Congress. Once a year, each state would select
In November 1777, the Continental Congress adopted the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union. This was a plan for a loose union of the states under Congress. Once a year, each state would select
US History, Ms. Brown Website: dph7history.weebly.com
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #67 Aims: SWBAT identify the key parts of the Patriot s philosophy SWBAT identify and evaluate the strengths and weaknesses
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #67 Aims: SWBAT identify the key parts of the Patriot s philosophy SWBAT identify and evaluate the strengths and weaknesses
Study Guide for Test representative government system of government in which voters elect representatives to make laws for them
 Study Guide for Test 4 1. In general, who could vote in the English colonies? Free men, over 21 years old, who owned a certain amount of land. Sometimes had to be church members. 2. representative government
Study Guide for Test 4 1. In general, who could vote in the English colonies? Free men, over 21 years old, who owned a certain amount of land. Sometimes had to be church members. 2. representative government
Ratification. By March 1781, all 13 Colonies had ratified the Articles of Confederation, making it the official written plan of government.
 The Goal To form a confederation of states - A Firm League of Friendship To continue the form of government established by the Second Continental Congress Ratification By March 1781, all 13 Colonies had
The Goal To form a confederation of states - A Firm League of Friendship To continue the form of government established by the Second Continental Congress Ratification By March 1781, all 13 Colonies had
Creating the Constitution
 Creating the Constitution 1776-1791 US Timeline 1777-1791 1777 Patriots win Battles of Saratoga. Continental Congress passes the Articles of Confederation. 1781 Articles of Confederation go into effect.
Creating the Constitution 1776-1791 US Timeline 1777-1791 1777 Patriots win Battles of Saratoga. Continental Congress passes the Articles of Confederation. 1781 Articles of Confederation go into effect.
Early US History Part 1. Your Notes. Goal 9/5/2012. How did the United States became a country?
 Questions / Themes 9/5/2012 Early US History Part 1 How did the United States became a country? Your Notes You will need these notes to prepare for exams. Remember to paraphrase and generalize. Avoid copying
Questions / Themes 9/5/2012 Early US History Part 1 How did the United States became a country? Your Notes You will need these notes to prepare for exams. Remember to paraphrase and generalize. Avoid copying
#1 State Constitutions
 #1 State Constitutions The American Revolution began the process of creating a new nation in a number of different ways. On May 10, 1776, the Continental Congress directed the colonies to suppress royal
#1 State Constitutions The American Revolution began the process of creating a new nation in a number of different ways. On May 10, 1776, the Continental Congress directed the colonies to suppress royal
The Federalist Papers
 The Federalist Papers If men were angels, no government would be necessary. James Madison During the Revolutionary War, Americans set up a new national government. They feared a strong central government.
The Federalist Papers If men were angels, no government would be necessary. James Madison During the Revolutionary War, Americans set up a new national government. They feared a strong central government.
To run away or leave someone in their time of need.
 Desert To run away or leave someone in their time of need. Inflation Rapid rise in prices. Blockade Barrier preventing the movement of troops and supplies. Tributary River or stream that flows into a larger
Desert To run away or leave someone in their time of need. Inflation Rapid rise in prices. Blockade Barrier preventing the movement of troops and supplies. Tributary River or stream that flows into a larger
Test Day. October 3-4
 Test Day October 3-4 Sit Wherever Turn in your Study Guide to me When done with test, Turn in to the correct area up front (follow sticky notes) Pick up outline for Unit 3 Pick up a survey for Unit 3 Pick
Test Day October 3-4 Sit Wherever Turn in your Study Guide to me When done with test, Turn in to the correct area up front (follow sticky notes) Pick up outline for Unit 3 Pick up a survey for Unit 3 Pick
The American Revolution & Confederation. The Birth of the United States
 The American Revolution & Confederation The Birth of the United States 1774-1787 Essential Question Evaluate the extent to which the Revolution fundamentally changed American society. The First Continental
The American Revolution & Confederation The Birth of the United States 1774-1787 Essential Question Evaluate the extent to which the Revolution fundamentally changed American society. The First Continental
We re Free Let s Grow!
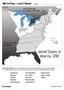 Atlantic Ocean Find Those States! The United States started out with just thirteen states. Use the list below to correctly identify each one on the map. Watch out: Things were a little different back then!
Atlantic Ocean Find Those States! The United States started out with just thirteen states. Use the list below to correctly identify each one on the map. Watch out: Things were a little different back then!
Chapter Seven. The Creation of the United States
 Chapter Seven The Creation of the United States 1776-1786 Part One Introduction The Creation of the United States 1776-1786 What does the painting tell us about who fought for the creation of the United
Chapter Seven The Creation of the United States 1776-1786 Part One Introduction The Creation of the United States 1776-1786 What does the painting tell us about who fought for the creation of the United
The Articles of!confederation
 The Articles of Confederation Our New Nation s First Constitution The Articles of Confederation When the Second Continental Congress appointed a committee to write a Declaration of Independence in 1776,
The Articles of Confederation Our New Nation s First Constitution The Articles of Confederation When the Second Continental Congress appointed a committee to write a Declaration of Independence in 1776,
Understanding Washington s Domestic and Foreign Policies
 1783: Treaty of Paris ended the American Revolution Despite the treaty, Britain: Continued to maintain frontier forts along the Great Lakes Continued their alliances with Native American tribes 1787: The
1783: Treaty of Paris ended the American Revolution Despite the treaty, Britain: Continued to maintain frontier forts along the Great Lakes Continued their alliances with Native American tribes 1787: The
LECTURE 3-2: THE AMERICAN REVOLUTION
 LECTURE 3-2: THE AMERICAN REVOLUTION British attempts to assert tighter control over its North American colonies and the colonial resolve to pursue self-government led to a colonial independence movement
LECTURE 3-2: THE AMERICAN REVOLUTION British attempts to assert tighter control over its North American colonies and the colonial resolve to pursue self-government led to a colonial independence movement
Beginnings of a New Nation
 The period between the Treaty of Paris and the writing of the Constitution, the states were united only by a rope of sand. George Washington Beginnings of a New Nation Officers were disgusted with Congress
The period between the Treaty of Paris and the writing of the Constitution, the states were united only by a rope of sand. George Washington Beginnings of a New Nation Officers were disgusted with Congress
CHAPTER 7 CREATING A GOVERNMENT
 CHAPTER 7 CREATING A GOVERNMENT The Constitution set out our rules for government. It explains what our government can and cannot do. It reflects are experience as a colony as well as ideas from Europe
CHAPTER 7 CREATING A GOVERNMENT The Constitution set out our rules for government. It explains what our government can and cannot do. It reflects are experience as a colony as well as ideas from Europe
CHAPTER 9 THE CONFEDERATION & CONSTITUTION DEFINE REVOLUTION" Slavery after the Revolution 9/22/15 WAS THIS REALLY A REVOLUTION?
 CHAPTER 9 THE CONFEDERATION & CONSTITUTION DEFINE REVOLUTION" A SUDDEN AND MOMENTOUS CHANGE IN A SITUATION THE OVERTHROW AND SUDDEN CHANGE OF A GOVERNMENT WAS THIS REALLY A REVOLUTION? Slavery after the
CHAPTER 9 THE CONFEDERATION & CONSTITUTION DEFINE REVOLUTION" A SUDDEN AND MOMENTOUS CHANGE IN A SITUATION THE OVERTHROW AND SUDDEN CHANGE OF A GOVERNMENT WAS THIS REALLY A REVOLUTION? Slavery after the
US Early Test #1 TEST A
 US Early Test #1 TEST A Matching A. Boston Tea Party B. Bill of Rights C. George Washington D. Railroads E. 13 th Amendment AB. Robert E Lee AC. Nueces AD. Dred Scott AE. Crop Lien BC. Sharecropping BD.
US Early Test #1 TEST A Matching A. Boston Tea Party B. Bill of Rights C. George Washington D. Railroads E. 13 th Amendment AB. Robert E Lee AC. Nueces AD. Dred Scott AE. Crop Lien BC. Sharecropping BD.
ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION TO THE CONSTITUTION
 ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION TO THE CONSTITUTION Articles of Confederation The representatives of the thirteen states agree to create a confederacy called the United States of America, in which each state
ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION TO THE CONSTITUTION Articles of Confederation The representatives of the thirteen states agree to create a confederacy called the United States of America, in which each state
Chapter 9: The Confederation and the Constitution,
 APUSH CH 9+10 Lecture Name: Hour: Chapter 9: The Confederation and the Constitution, 1776-1790 I. From Confederation to Constitution A. The Articles of Confederation: An Attempt at Constitution-Making
APUSH CH 9+10 Lecture Name: Hour: Chapter 9: The Confederation and the Constitution, 1776-1790 I. From Confederation to Constitution A. The Articles of Confederation: An Attempt at Constitution-Making
Chapter 5 Practice Test Forming a Government
 Chapter 5 Practice Test Forming a Government Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of these was a weakness in the Articles of Confederation
Chapter 5 Practice Test Forming a Government Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of these was a weakness in the Articles of Confederation
1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation
 Topic 3 1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg 88-89 They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation agreements 2. How did the British respond to the Boston Tea
Topic 3 1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg 88-89 They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation agreements 2. How did the British respond to the Boston Tea
Underpinnings of the Constitution
 Underpinnings of the Constitution A constitution is a nations basic laws creates political institutions assigns and divides power in government provides certain guarantees to citizens includes unwritten
Underpinnings of the Constitution A constitution is a nations basic laws creates political institutions assigns and divides power in government provides certain guarantees to citizens includes unwritten
SS.8.A.3.2 Explain American colonial reaction to British policy from
 SS.8.C.2.6 Examine the causes, course, and consequences of the French and Indian War. IB Unit 1: No More Kings! SS.8.A.3.1 Explain the consequences of the French and Indian War in British policies for
SS.8.C.2.6 Examine the causes, course, and consequences of the French and Indian War. IB Unit 1: No More Kings! SS.8.A.3.1 Explain the consequences of the French and Indian War in British policies for
netw rks Where in the world? When did it happen? The Federalist Era Lesson 1 The First President ESSENTIAL QUESTION Terms to Know GUIDING QUESTIONS
 Lesson 1 The First President ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the characteristics of a leader? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. What decisions did Washington and the new Congress have to make about the new government?
Lesson 1 The First President ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the characteristics of a leader? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. What decisions did Washington and the new Congress have to make about the new government?
Case Studies Articles of Confederation
 Name Case Studies Articles of Confederation Directions: Read the Case Study given to your group, and answer the questions below. Whose interests were pitted against each other is asking you to think about
Name Case Studies Articles of Confederation Directions: Read the Case Study given to your group, and answer the questions below. Whose interests were pitted against each other is asking you to think about
The Articles of Confederation
 The Articles of Confederation Explain the weaknesses and strengths of the Articles of Confederation. Examine the need for a strong central government. Document that broke the 12 English colonies from British
The Articles of Confederation Explain the weaknesses and strengths of the Articles of Confederation. Examine the need for a strong central government. Document that broke the 12 English colonies from British
Student Reading 10.1: The Story of Ohio s Constitution and Statehood
 Student Reading 10.1: The Story of Ohio s Constitution and Statehood The land that would eventually become Ohio began to grow in the late 1700s. Colonists were encouraged to move and settle in different
Student Reading 10.1: The Story of Ohio s Constitution and Statehood The land that would eventually become Ohio began to grow in the late 1700s. Colonists were encouraged to move and settle in different
The Articles of Confederation
 The Articles of Confederation 1777-1787 During the American Revolution States organized their governments and adopted their own state constitutions. But, Americans needed to establish their own national
The Articles of Confederation 1777-1787 During the American Revolution States organized their governments and adopted their own state constitutions. But, Americans needed to establish their own national
Second Continental Congress May 1775
 Second Continental Congress May 1775 Met in Philadelphia Representatives from each state Continental Congress Went to work on a new government Articles of Confederation (Nov. 1777) Set up a confederation
Second Continental Congress May 1775 Met in Philadelphia Representatives from each state Continental Congress Went to work on a new government Articles of Confederation (Nov. 1777) Set up a confederation
GEORGE WASHINGTON
 GEORGE WASHINGTON 1732-1799 GEORGE WASHINGTON George Washington was the first president of the United States. He served two terms from 1789-1797. He is called the Father of Our Country. REVOLUTIONARY WAR
GEORGE WASHINGTON 1732-1799 GEORGE WASHINGTON George Washington was the first president of the United States. He served two terms from 1789-1797. He is called the Father of Our Country. REVOLUTIONARY WAR
Conceived in Liberty. 5th Grade Social Studies Textbook
 Conceived in Liberty 5th Grade Social Studies Textbook Chapter 9 Creating the Constitution Chapter 9 Creating the Constiution When the American people won their independence, they had to decide what kind
Conceived in Liberty 5th Grade Social Studies Textbook Chapter 9 Creating the Constitution Chapter 9 Creating the Constiution When the American people won their independence, they had to decide what kind
Study Guide: Sunshine State Standards
 å È É Ê Ë Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Í É Î Ë Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ï Ð É Ñ Ñ Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Study Guide: Chapter
å È É Ê Ë Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Í É Î Ë Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ï Ð É Ñ Ñ Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Ì Study Guide: Chapter
THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION
 Tis really astonishing that the same people, who have just emerged from a long and cruel war in defense of liberty, should now agree to fix an elective despotism upon themselves and their posterity. Richard
Tis really astonishing that the same people, who have just emerged from a long and cruel war in defense of liberty, should now agree to fix an elective despotism upon themselves and their posterity. Richard
Ms. Susan M. Pojer Horace Greeley HS Chappaqua, NY
 Ms. Susan M. Pojer Horace Greeley HS Chappaqua, NY On the Eve of the Revolution? Britain Americans Advantages?? Disadvantages?? Loyalist Strongholds Washington s Headaches Only 1/3 of the colonists were
Ms. Susan M. Pojer Horace Greeley HS Chappaqua, NY On the Eve of the Revolution? Britain Americans Advantages?? Disadvantages?? Loyalist Strongholds Washington s Headaches Only 1/3 of the colonists were
Unit Essential Question: How did the strengths and weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation lead to the development of the U.S. Constitution?
 Chapter 7 Creating the Constitution Unit Essential Question: How did the strengths and weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation lead to the development of the U.S. Constitution? Lesson Essential Question:
Chapter 7 Creating the Constitution Unit Essential Question: How did the strengths and weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation lead to the development of the U.S. Constitution? Lesson Essential Question:
7/10/2009. By Mr. Cegielski WARM UP:
 By Mr. Cegielski WARM UP: 1 PREVIEW: George Washington Presidential Accomplishments Washington voluntarily resigned as Commander-in-Chief of the Continental Army in 1783. Because of his victories in the
By Mr. Cegielski WARM UP: 1 PREVIEW: George Washington Presidential Accomplishments Washington voluntarily resigned as Commander-in-Chief of the Continental Army in 1783. Because of his victories in the
The ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION. Mr. P s Class
 The ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION Mr. P s Class ANY NOTES IN YELLOW ARE MAIN POINTS AND GO IN THE LEFT COLUMN OF YOUR NOTES ANY NOTES IN RED ARE SUPPORTING DETAILS AND GO IN THE RIGHT COLUMN OF YOUR NOTES
The ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION Mr. P s Class ANY NOTES IN YELLOW ARE MAIN POINTS AND GO IN THE LEFT COLUMN OF YOUR NOTES ANY NOTES IN RED ARE SUPPORTING DETAILS AND GO IN THE RIGHT COLUMN OF YOUR NOTES
Name: 8 th Grade U.S. History. STAAR Review. Constitution
 8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Constitution FORT BURROWS 2018 VOCABULARY Confederation - A group of loosely connected nations or states that work together for mutual benefit. Republic - A system
8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Constitution FORT BURROWS 2018 VOCABULARY Confederation - A group of loosely connected nations or states that work together for mutual benefit. Republic - A system
The United States Constitution. The Supreme Law of the Land
 The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land Standards SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States
The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land Standards SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States
The New Nation Faces Challenges
 SECTION 2 hat You ill Learn... Main Ideas 1. The United States had difficulties with other nations. 2. Internal economic problems plagued the new nation. 3. Shays s Rebellion pointed out weaknesses in
SECTION 2 hat You ill Learn... Main Ideas 1. The United States had difficulties with other nations. 2. Internal economic problems plagued the new nation. 3. Shays s Rebellion pointed out weaknesses in
South Carolina After the War STATE CONSTITUTION/ ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION. Government
 South Carolina After the War STATE CONSTITUTION/ ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION Government Tensions between the Upcountry and Lowcountry of SC Lowcountry Patriots First area settled in the state and plantation
South Carolina After the War STATE CONSTITUTION/ ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION Government Tensions between the Upcountry and Lowcountry of SC Lowcountry Patriots First area settled in the state and plantation
Articles of Confederation
 Articles of Confederation Do Now How is power divided in our country today? SWBAT Analyze government problems under the Articles of Confederation Activity Review the Articles of Confederation chart and
Articles of Confederation Do Now How is power divided in our country today? SWBAT Analyze government problems under the Articles of Confederation Activity Review the Articles of Confederation chart and
During the, the majority of delegates voted to declare independence from Britain. What is known as the official beginning of the America Revolution?
 What is known as the official beginning of the America Revolution? A. The Stamp Act B. Boston Tea Party C. Quartering Act D. Battle of Lexington and Concord During the, the majority of delegates voted
What is known as the official beginning of the America Revolution? A. The Stamp Act B. Boston Tea Party C. Quartering Act D. Battle of Lexington and Concord During the, the majority of delegates voted
4. After some negotiating, mostly with the promise of the Bill of Rights, the Constitution was ratified.
 Chapter #9: The Confederation and the Constitution Big Picture Ideas 1. The Articles of Confederation, the first government set up after the American Revolution, was structured out of fear of a too-strong
Chapter #9: The Confederation and the Constitution Big Picture Ideas 1. The Articles of Confederation, the first government set up after the American Revolution, was structured out of fear of a too-strong
 1. Which of the following was/were not dispatch rider(s) notifying Americans of British troop movements reported by American surveillance in 1775? (a) Paul Revere (b) William Dawes (c) John Parker (d)
1. Which of the following was/were not dispatch rider(s) notifying Americans of British troop movements reported by American surveillance in 1775? (a) Paul Revere (b) William Dawes (c) John Parker (d)
understanding CONSTITUTION
 understanding the CONSTITUTION Contents The Articles of Confederation The Constitutional Convention The Principles of the Constitution The Preamble The Legislative Branch The Executive Branch The Judicial
understanding the CONSTITUTION Contents The Articles of Confederation The Constitutional Convention The Principles of the Constitution The Preamble The Legislative Branch The Executive Branch The Judicial
The Treaty of Paris in 1783 recognizes the United States independence from England and establishes our borders
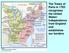 The Treaty of Paris in 1783 recognizes the United States independence from England and establishes our borders AFRICAN-AMERICANS in the AMERICAN REVOLUTION Over 5,000 served in the Continental Army Over
The Treaty of Paris in 1783 recognizes the United States independence from England and establishes our borders AFRICAN-AMERICANS in the AMERICAN REVOLUTION Over 5,000 served in the Continental Army Over
Articles of Condederation Very weak government. Why??? Five pages, 13 articles
 Articles of Condederation Very weak government. Why??? Five pages, 13 articles Establishes the name of the confederation as "The United States of America." Asserts the precedence of the separate states
Articles of Condederation Very weak government. Why??? Five pages, 13 articles Establishes the name of the confederation as "The United States of America." Asserts the precedence of the separate states
LESSON TWO: THE FEDERALIST PAPERS
 LESSON TWO: THE FEDERALIST PAPERS OVERVIEW OBJECTIVES Students will be able to: Identify the Articles of Confederation and explain why it failed. Explain the argument over the need for a bill of rights
LESSON TWO: THE FEDERALIST PAPERS OVERVIEW OBJECTIVES Students will be able to: Identify the Articles of Confederation and explain why it failed. Explain the argument over the need for a bill of rights
The Constitution CHAPTER 5. Table of Contents
 CHAPTER 5 The Constitution ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: Why do people, create, structure, and change governments? How do societies balance individual and community rights? How does social change influence government?
CHAPTER 5 The Constitution ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: Why do people, create, structure, and change governments? How do societies balance individual and community rights? How does social change influence government?
Ancient Greece, Athens had a direct democracy.
 Warm Up 12/7 How did the Baron De Montesquieu believe Gov t should be setup? Did the states lose power under the constitution? What powers did the Federal Gov t Gain? What laws could the states not make?
Warm Up 12/7 How did the Baron De Montesquieu believe Gov t should be setup? Did the states lose power under the constitution? What powers did the Federal Gov t Gain? What laws could the states not make?
american History Semester Exam review (KEY)
 american History Semester Exam review (KEY) 1. Fill in the name of each era and characteristics. Then use the word bank to match the events. 1. Exploration & Colonization 2. American Revolution 3. Creating
american History Semester Exam review (KEY) 1. Fill in the name of each era and characteristics. Then use the word bank to match the events. 1. Exploration & Colonization 2. American Revolution 3. Creating
Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution
 Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution The Articles of Confederation After declaring independence from Britain in 1776, Congress tried to unite the states under one national government. However, many feared
Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution The Articles of Confederation After declaring independence from Britain in 1776, Congress tried to unite the states under one national government. However, many feared
1 st United States Constitution. A. loose alliance of states. B. Congress lawmaking body. C. 9 states had to vote to pass laws
 1 st United States Constitution A. loose alliance of states B. Congress lawmaking body C. 9 states had to vote to pass laws D. each state had 1 vote in Congress Northwest Ordinance / Land Ordinance division
1 st United States Constitution A. loose alliance of states B. Congress lawmaking body C. 9 states had to vote to pass laws D. each state had 1 vote in Congress Northwest Ordinance / Land Ordinance division
NAME DATE CLASS. Directions Select a vocabulary term from the box to complete each of the sentences that follow. Not all the terms will be used.
 Vocabulary Builder A. Content Vocabulary Directions Select a vocabulary term from the box to complete each of the sentences that follow. Not all the terms will be used. proportional Electoral College amendment
Vocabulary Builder A. Content Vocabulary Directions Select a vocabulary term from the box to complete each of the sentences that follow. Not all the terms will be used. proportional Electoral College amendment
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton
 Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
NAME DATE CLASS. Electoral College depression legislative branch checks and balances manumission
 Vocabulary Builder A. Content Vocabulary Directions Select a vocabulary term from the box to complete each of the sentences that follow. Not all of the terms will be used. proportional compromise republic
Vocabulary Builder A. Content Vocabulary Directions Select a vocabulary term from the box to complete each of the sentences that follow. Not all of the terms will be used. proportional compromise republic
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of American Government
 Chapter 2: The Beginnings of American Government United States Government Fall, 2017 Origins of American Political Ideals Colonial Period Where did ideas for government in the colonies come from? Largely,
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of American Government United States Government Fall, 2017 Origins of American Political Ideals Colonial Period Where did ideas for government in the colonies come from? Largely,
A CONFEDERATION Confederation
 A CONFEDERATION I. Unitary System A. Political power is concentrated in a strong central government. B. It was based on the English government. C. Most Americans were suspicious of this form of government.
A CONFEDERATION I. Unitary System A. Political power is concentrated in a strong central government. B. It was based on the English government. C. Most Americans were suspicious of this form of government.
Unit 1: Founding the Nation
 Unit 1: Founding the Nation Name Per Lesson One: Foundations Lesson one has four main assignments. At the end of these assignments you will take a closed note quiz. After these lessons you will be expected
Unit 1: Founding the Nation Name Per Lesson One: Foundations Lesson one has four main assignments. At the end of these assignments you will take a closed note quiz. After these lessons you will be expected
Articles of Confederation
 Confederation Confederation A group of people, countries, organizations, etc., that are joined together in some activity or effort More or less permanently united for common purposes Articles of Confederation
Confederation Confederation A group of people, countries, organizations, etc., that are joined together in some activity or effort More or less permanently united for common purposes Articles of Confederation
