Chapter 1 Should We Care about Politics?
|
|
|
- Penelope Neal
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 1 Should We Care about Politics? CHAPTER SUMMARY In any form, democracy is both an imperfect system and a complex idea that entails a few basic prerequisites: participation by the people, the willing consent of the people to accept and live by the actions of government, and the recognition that everyone has basic rights that government can t take away. Prerequisites for democracy might not always hold if people choose not to participate, or if they end up unknowingly participating without giving consent. For a democracy, or any political system, to function effectively, there has to be agreement on the rules, as well as on the way the system will be organized, and citizens have to accept the basic principles it s based on. Representative democracy depends heavily on holding free elections and keeping elected officials accountable to the voters. Americans generally respect the authority of a victorious candidate to assume the jurisdiction to act with the authority of the office to which he was elected. Unlike authority, which is granted by virtue of holding an office, legitimacy is partly inherited and partly earned. One source of legitimacy evolves over time and is rooted in the way we come to accept an office and by extension its occupant as being rightful and appropriate. The German sociologist Max Weber suggested this kind of legitimacy is rooted in tradition and law that after hundreds of years, for instance, we have come to accept the presidential winner as the legitimate occupant of that office for a period of four years, under a plan set up long ago in the Constitution. The legitimacy an official inherits is usually at its peak at the start of a term of office and is often the reason for the honeymoon or grace period we tend to give new officials. Political figures can undermine their legitimacy through their actions because, unlike authority, legitimacy is partly earned. When the legitimacy of authority figures is brought into question, doubts about their right to act as they did will naturally arise. Elected officials can use their authority and legitimacy to exercise power, although their ability to do so is hardly automatic. Power is about getting others to act the way you want them to, even if they prefer to act otherwise, in order to determine who gets what, when, and how. The tools of power are resources, which can encompass a wide range of things, such as a politician s personal charm, the information supplied to members of Congress by a lobbyist, or the promise of campaign money. Power relationships are among the most fundamental relationships found at every level of politics from the White House to school boards. Quite often, a mutually beneficial exchange of resources gets others to act in a way they might not have intended. In the American political system, the exercise of power is about mutual benefit. Some people believe that the resources that most influence political officials are concentrated in the hands of a few, giving a small group disproportionate power to determine political outcomes. Others point to the way Americans like to join groups and feel that the resources held by groups with broad memberships greatly influence the decisions that come out of the political process. Pluralism and elitism present divergent and mutually exclusive ways of understanding who holds power. It may be tempting to say that they both describe our political system, but you shouldn t lose sight of the fact that pluralism and elitism assume the system is structured in entirely different ways. 1-1
2 1-2 Study Guide: Chapter 1 Should We Care about Politics? Individuals in American society make choices between liberty and equality. These are normative choices that involve judgments about what to value and what to willingly trade-off to achieve those values. In the United States, many value political equality on the assumption that ensuring everyone the same right to vote and equal rights under the law promotes equal opportunity. In truth, people have neither equality of opportunity nor equality of outcome in America. One place where equal opportunity breaks down is in the unequal economic and social outcomes of women and historically disadvantaged racial and ethnic groups because unequal outcomes are supposed to be a product of our different talents, interests, and abilities, not our physical or ethnic differences. When wealth is more equitably distributed across the population there is less disparity between economic classes. If wealth were equally distributed across the population, there would be no economic classes. In reality, we re very far from equal outcomes in the United States. The top 10 percent of the population dwarfs the bottom 90 percent in average income, and the tope one-tenth of one percent overshadows everyone. Whether you should personally care about politics is a normative judgment. It s also a personal matter that you ll probably approach differently from your friends. You ll make a judgment that depends in part on how much you think politics matters in your life. No one else can make that judgment for you. MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. In theory, democracy requires participation by the people and the recognition that everyone has basic rights. In practice, in the United States A. most people participate all the time. B. some groups have been denied basic political freedoms. C. people do not participate all the time, but they are always aware of when their actions have political consequences. D. people of color, women, and young people have traditionally had a greater say over political decisions than other groups. 2. A political system in which everyone has a personal say in what government does is called a A. direct democracy. B. representative democracy. C. republic. D. social democracy. 3. Which of the following is partly inherited and partly earned? A. power B. legitimacy C. custom legitimacy D. authority 4. The jurisdiction to propose legislation, grant clemency to prisoners, and negotiate a state s budget are all examples of a governor s A. authority. B. power. C. legitimacy. D. resources.
3 Study Guide: Chapter 1 Should We Care about Politics? The public s reaction to George W. Bush following the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001 illustrates A. inherited authority. B. inherited legitimacy. C. earned legitimacy. D. earned authority. 6. Power might be exercised through the use of each of the following except: A. authority. B. coercion. C. promises. D. threats. 7. A person who subscribes to the theory of pluralism believes that power can be exercised by A. bureaucrats. B. corporate leaders. C. military leaders. D. voters. 8. When Thomas Jefferson wrote, all men are created equal, he was referring to A. equality of opportunity. B. equality of outcome. C. equality of outcome for white males of European heritage. D. economic equality. 9. Nations like Norway and Sweden, where government policies attempt to reduce disparities between rich and poor, might be said to value A. elitism. B. equality of opportunity. C. equality of outcome. D. political equality. 10. Absolute liberty: A. would require absolute equality. B. would demand social responsibility. C. would result in chaos. D. would require choices. 11. The concern for the rights of others in society is called A. equality of opportunity. B. equality of outcome. C. liberty. D. social responsibility. 12. People tend to feel strongly about the trade-offs between liberty and social responsibility when A. they engage in power relationships. B. they act like pluralists. C. they make normative judgments. D. their personal liberty is at issue.
4 1-4 Study Guide: Chapter 1 Should We Care about Politics? 13. In 2011, women were paid of what men in comparable jobs were paid a difference that amounts to over $700,000 dollars for the average fulltime woman worker over the course of her working life. A. 42 percent B. 62 percent C. 82 percent D. 92 percent 14. In 2011, the bottom 20 percent of American households combined for only 3.2 percent of all income, while the top 20 percent received more than. A. 50 percent B. 40 percent C. 30 percent D. 20 percent ANSWERS TO MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS # Correct 1. B 2. A 3. B 4. A 5. C 6. A 7. D 8. A 9. C 10. C 11. D 12. D 13. C 14. A TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS 1. A democracy is said to exist in societies where the actions of regular citizens, like voting and joining groups, mask the real power exercised by elites. 2. Political and social satire provide a means for interacting with democracy by encouraging people to think about what government is doing.
5 Study Guide: Chapter 1 Should We Care about Politics? In order for a statement to be classified as being empirical, it must be based on the assessment of data or the analysis of information, without regard to value judgments. 4. Power is exercised when resources other than money are used to achieve a desired outcome. 5. In the American political system, the exercise of power is about mutual benefit, which means that lawyers with expertise and computer firms that make contributions to congressional candidates can be influential if they have resources that are desired by others in the political process. 6. Next to money, information is the lifeblood of many interest groups and it has also become one of the foremost tools of power in today's world because members of Congress and bureaucrats can t survive without it. 7. One way in which a political system can be characterized by pluralism is to have the government respond to the many voices expressed through group membership. 8. A majority of the world's representative democracies typically reject any form of equality of outcome that values using government policy to minimize social class distinctions found in society. 9. Choices between liberty and equality are normative choices that involve judgments about what to value and what to willingly trade off to achieve those values. 10. The great diversity of America is both a strength and a complicating factor for the nation s politics. ANSWERS TO TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS # Correct 1. False 2. True 3. True 4. False 5. True 6. True 7. True 8. False 9. True 10. True
6 1-6 Study Guide: Chapter 1 Should We Care about Politics? GLOSSARY QUIZ 1. The right to act in an official capacity by virtue of holding an office like president or member of Congress. 2. A government created by the people over whom it rules. 3. Democracy without representation, where each eligible individual participates in decision making. 4. Losing or being denied the legal right to vote by intentional or unintentional means. 5. A form of equality of outcome that values using government policy to minimize the economic disparities found in society. 6. The theory that government responds to a small, stable, centralized hierarchy of corporate and academic leaders, military chiefs, people who own big media outlets, and members of a permanent government bureaucracy. 7. Any statement based on the assessment of data or the analysis of information, without regard to value judgments. 8. Widespread public acceptance of the official standing of a political figure or institution. 9. The ability to pursue your ends and objectives, tempered by socially defined boundaries and limited government impediments. 10. Any statement that invokes a judgment or evaluation. 11. The theory that government responds to individuals through their memberships in groups, assuring that government is responsive to a wide range of voices. 12. Establishing political and legal rights on the basis of the individual, so that everyone has the same right to vote and is equal under the law. 13. The process of determining who gets what, when, and how. 14. The ability to make others act in a way that they otherwise might not have done. 15. A form of democracy in which eligible individuals choose others to make decisions on their behalf. 16. Any nation with provisions for the selection of representatives who make decisions on behalf of those who select them. 17. Anything of value to others that can be used to sway another individual. 18. Concern for the protection of the rights of individuals in a community or society, at the expense of some degree of personal liberty. 19. Provides people with comparable advantages for succeeding in life, regardless of the unequal outcomes that may result. 20. Levels the social and economic inequities among people, rather than attempting to give people comparable advantages for succeeding in life.
7 Study Guide: Chapter 1 Should We Care about Politics? 1-7 ANSWERS TO GLOSSARY QUIZ 1. authority The right to act in an official capacity by virtue of holding an office like president or member of Congress. 2. democracy A government created by the people over whom it rules. 3. direct democracy Democracy without representation, where each eligible individual participates in decision making. 4. disenfranchised Losing or being denied the legal right to vote by intentional or unintentional means. 5. economic equality A form of equality of outcome that values using government policy to minimize the economic disparities found in society. 6. elitism The theory that government responds to a small, stable, centralized hierarchy of corporate and academic leaders, military chiefs, people who own big media outlets, and members of a permanent government bureaucracy. 7. empirical Any statement based on the assessment of data or the analysis of information, without regard to value judgments. 8. legitimacy Widespread public acceptance of the official standing of a political figure or institution. 9. liberty The ability to pursue your ends and objectives, tempered by socially defined boundaries and limited government impediments. 10. normative Any statement that invokes a judgment or evaluation. 11. pluralism The theory that government responds to individuals through their memberships in groups, assuring that government is responsive to a wide range of voices.
8 1-8 Study Guide: Chapter 1 Should We Care about Politics? 12. political equality Establishing political and legal rights on the basis of the individual, so that everyone has the same right to vote and is equal under the law. 13. politics The process of determining who gets what, when, and how. 14. power The ability to make others act in a way that they otherwise might not have done. 15. representative democracy A form of democracy in which eligible individuals choose others to make decisions on their behalf. 16. republic Any nation with provisions for the selection of representatives who make decisions on behalf of those who select them. 17. resources Anything of value to others that can be used to sway another individual. 18. social responsibility Concern for the protection of the rights of individuals in a community or society, at the expense of some degree of personal liberty. 19. equality of opportunity Provides people with comparable advantages for succeeding in life, regardless of the unequal outcomes that may result. 20. equality of outcome Levels the social and economic inequities among people, rather than attempting to give people comparable advantages for succeeding in life. SHORT-ANSWER QUESTIONS 1-1. List several activities that constitute ways of directly or indirectly interacting with the political process What prerequisites for democracy was Abraham Lincoln addressing in Gettysburg Address when he spoke of government of the people, by the people, and for the people?
9 Study Guide: Chapter 1 Should We Care about Politics? How does a direct democracy differ from a republic? 1-4. What is authority and how is it derived? 1-5. According to sociologist Max Weber, what is one source of political legitimacy? 1-6. Explain how public officials might undermine their legitimacy Describe how legitimacy differs from authority What is power? 1-9. What is the relationship between power and resources? What is the relationship between power and politics? Provide one example each of an empirical and normative statement Distinguish pluralism from elitism Explain why pluralism and elitism are mutually exclusive ways of understanding who exercises power in society What is equality of opportunity? Explain why Americans tend to value policies that promote equality of opportunity, such as programs that encourage equal access to education How is political equality related to equality of opportunity? How do disparities in outcome based on gender, racial and ethnical characteristics raise questions about whether equality of opportunity works in practice the way it is supposed to work in theory? What is liberty? Identify five types of equality and briefly explain how they relate to liberty Briefly discuss the tension between personal liberty and social responsibility. ANSWERS TO SHORT-ANSWER QUESTIONS 1-1. Examples of activities that constitute ways of interacting with the political process are: voting; consuming political and social satire; joining groups that lobby government officials; obeying (or not obeying) the law; making political contributions; attending college; visiting a national park; paying sales tax on grocery items; utilizing public works like subways, airports or sewer systems. (Section 1.1) 1-2. Lincoln was referring to the basic prerequisites for democracy: participation by the people, the willing consent of the people to accept and live by the actions of government, and the recognition that we all have basic rights that government can t take away. (Section 1.2)
10 1-10 Study Guide: Chapter 1 Should We Care about Politics? 1-3. Every citizen participates in decision-making in a direct democracy. A republic is based on representation, where citizens elect representatives to make decisions on their behalf. (Section 1.3) 1-4. Authority is the right to act in an official capacity. It is derived by holding an office like president or member of Congress after having achieved that office through legitimate means. (Section 1.4) 1-5. According to Weber, legitimacy is rooted in tradition and law, as over time people in a society come to accept an established political office and by extension its occupant as being rightful and appropriate (Section 1.5) 1-6. Public officials can undermine their legitimacy through their actions, especially actions that violate their authority. (Section 1.6) 1-7. Unlike authority, which is granted by virtue of holding an office, legitimacy is partly inherited through tradition and law and partly earned through the behavior of office-holders. (Sections 1.4 through 1.6) 1-8. Power is the ability to make others act in a way they otherwise might not have done. (Section 1.7) 1-9. Resources are the tools of power, which may be used by individuals to achieve a desired outcome. (Section 1.7) If power is the ability to make others act in a way they otherwise might not have done, then it is utilized in relationships among people, and politics is what happens in those relationships the process of determining who gets what, when, and how. (Section 1.7) Any factual statement is empirical (i.e., the American flag contains three colors: red, white and blue). Any value judgment is normative (i.e., the United States is better suited to representative democracy because of its vast size). (Section 1.7a) Pluralism is the theory that government responds to individuals through their membership in groups, assuring that government is responsive to a wide range of voices. Elitism is the theory that government responds to a small, stable, centralized hierarchy of corporate, academic, media and military leaders. (Section 1.7a) Pluralism and elitism present divergent and mutually exclusive ways of understanding who holds power because they assume the system is structured in entirely different ways. People who subscribe to the theory of elitism believe that the actions of regular citizens, like voting and joining groups, simply mask the real power exercised by elites. People who subscribe to the theory of pluralism believe that the wide distribution of resources in society drives the decisions government officials make. (Section 1.7a) Equality of opportunity values giving people comparable advantages in life, regardless of the unequal outcomes that may result. (Section 1.8) Valuing equality of opportunity is consistent with supporting government efforts to make the starting line more equal for people. That s why Americans usually support government programs to help underprivileged kids have access to higher education, because education is considered the gateway to opportunity. (Section 1.8)
11 Study Guide: Chapter 1 Should We Care about Politics? Because equality of opportunity assumes an equal starting point for everyone, it follows that everyone would need the same political rights. This is why Americans generally value political equality and believe that everyone should have the same political and legal rights as everyone else. If all votes count the same and if everyone has the same rights in a court of law, the theory goes, then the playing field isn t tilted toward some groups and away from others. (Section 1.8) In theory, equality of opportunity is supposed to be blind to gender, racial and ethnic characteristics. Unequal outcomes which are the expected result of valuing opportunity over results are supposed to derive from reasons that have no bearing on these differences. When systematic differences in outcome are apparent across gender, racial or ethnic groups, it suggests that some groups face obstacles to achievement or are disadvantaged because they are different. (Section 1.9) Liberty is the ability to pursue your ends and objectives, tempered by socially defined boundaries and limited government impediments. (Section 1.10) Five types of equality were identified: opportunity, outcome, political, social and economic. Equality of opportunity, which requires people to have the freedom to pursue desired ends, necessitates liberty and assumes the level playing field provided by political equality. Equality of outcome restrains liberty through government efforts to reduce social and economic inequities. Therefore, equality of opportunity and political equality are most aligned with liberty, whereas equality of outcome, social equality and economic equality are not. (Section 1.10) Because our actions constantly affect other people, and because it s human nature to want to pursue our desires and objectives despite this, personal self-interest can conflict with the rights of the broader community. These conflicts involve trade-offs between liberty and social responsibility, or the concern for the rights of others in society. Through government, we endeavor to draw the boundaries that determine where individual liberty stops and the needs of society start. (Section 1.11)
19 ECONOMIC INEQUALITY. Chapt er. Key Concepts. Economic Inequality in the United States
 Chapt er 19 ECONOMIC INEQUALITY Key Concepts Economic Inequality in the United States Money income equals market income plus cash payments to households by the government. Market income equals wages, interest,
Chapt er 19 ECONOMIC INEQUALITY Key Concepts Economic Inequality in the United States Money income equals market income plus cash payments to households by the government. Market income equals wages, interest,
Why Does Inequality Matter? T. M. Scanlon. Chapter 8: Unequal Outcomes. It is well known that there has been an enormous increase in inequality in the
 Why Does Inequality Matter? T. M. Scanlon Chapter 8: Unequal Outcomes It is well known that there has been an enormous increase in inequality in the United States and other developed economies in recent
Why Does Inequality Matter? T. M. Scanlon Chapter 8: Unequal Outcomes It is well known that there has been an enormous increase in inequality in the United States and other developed economies in recent
POLI 111: INTRODUCTION TO THE STUDY OF POLITICAL SCIENCE
 POLI 111: INTRODUCTION TO THE STUDY OF POLITICAL SCIENCE Session Two: Basic Concepts of Politics, Part 1 Lecturer: Dr. Evans Aggrey-Darkoh, Department of Political Science Contact information : aggreydarkoh@ug.edu.gh
POLI 111: INTRODUCTION TO THE STUDY OF POLITICAL SCIENCE Session Two: Basic Concepts of Politics, Part 1 Lecturer: Dr. Evans Aggrey-Darkoh, Department of Political Science Contact information : aggreydarkoh@ug.edu.gh
Constructing a Socially Just System of Social Welfare in a Multicultural Society: The U.S. Experience
 Constructing a Socially Just System of Social Welfare in a Multicultural Society: The U.S. Experience Michael Reisch, Ph.D., U. of Michigan Korean Academy of Social Welfare 50 th Anniversary Conference
Constructing a Socially Just System of Social Welfare in a Multicultural Society: The U.S. Experience Michael Reisch, Ph.D., U. of Michigan Korean Academy of Social Welfare 50 th Anniversary Conference
Lesson 10 What Is Economic Justice?
 Lesson 10 What Is Economic Justice? The students play the Veil of Ignorance game to reveal how altering people s selfinterest transforms their vision of economic justice. OVERVIEW Economics Economics has
Lesson 10 What Is Economic Justice? The students play the Veil of Ignorance game to reveal how altering people s selfinterest transforms their vision of economic justice. OVERVIEW Economics Economics has
CHAPTER ONE: INTRODUCING GOVERNMENT IN AMERICA
 CHAPTER ONE: INTRODUCING GOVERNMENT IN AMERICA Chapter 1 PEDAGOGICAL FEATURES p. 4 Figure 1.1: The Political Disengagement of College Students Today p. 5 Figure 1.2: Age and Political Knowledge: 1964 and
CHAPTER ONE: INTRODUCING GOVERNMENT IN AMERICA Chapter 1 PEDAGOGICAL FEATURES p. 4 Figure 1.1: The Political Disengagement of College Students Today p. 5 Figure 1.2: Age and Political Knowledge: 1964 and
Rule of Law: Economic Prosperity Requires the Rule of Law By J. Kenneth Blackwell
 By J. Kenneth Blackwell America is the most prosperous society in the history of mankind, and many factors have contributed to its success. Some credit our unparalleled university system. Others note our
By J. Kenneth Blackwell America is the most prosperous society in the history of mankind, and many factors have contributed to its success. Some credit our unparalleled university system. Others note our
Lincoln asked whether a nation devoted to the values of liberty, equality, justice and opportunity so conceived can long endure.
 What Does it Mean to be an American Citizen? The Hon. Lee H. Hamilton Congressional Conference on Civic Education September 21, 2003 We are here today because the success of any democracy is determined
What Does it Mean to be an American Citizen? The Hon. Lee H. Hamilton Congressional Conference on Civic Education September 21, 2003 We are here today because the success of any democracy is determined
American Political Culture
 American Political Culture Defining the label American can be complicated. What makes someone an American? Citizenship status? Residency? Paying taxes, playing baseball, speaking English, eating apple
American Political Culture Defining the label American can be complicated. What makes someone an American? Citizenship status? Residency? Paying taxes, playing baseball, speaking English, eating apple
Week. 28 Economic Policymaking
 Week Marking Period 1 Week Marking Period 3 1 Introducing American Government 21 The Presidency 2 Introduction American Government 22 The Presidency 3 The Constitution 23 Congress, the President, and the
Week Marking Period 1 Week Marking Period 3 1 Introducing American Government 21 The Presidency 2 Introduction American Government 22 The Presidency 3 The Constitution 23 Congress, the President, and the
Full file at
 Chapter 2 Quiz Poverty and Wealth name 1. Between 1980 and 2007, how has U.S. income changed? a. all categories of the U.S. population saw some rise in average income. b. the gains have been huge for the
Chapter 2 Quiz Poverty and Wealth name 1. Between 1980 and 2007, how has U.S. income changed? a. all categories of the U.S. population saw some rise in average income. b. the gains have been huge for the
Legal development: getting from here to there
 Legal development: getting from here to there How do societies make the shift from repressive law to autonomous law? Why should we care? Helps us understand the past Helps us predict the future Why aren
Legal development: getting from here to there How do societies make the shift from repressive law to autonomous law? Why should we care? Helps us understand the past Helps us predict the future Why aren
Special Interest Groups
 Agenda 1. Interest Groups Notes 2. Interest Groups Book 3. HW: graphs and charts for Chapter 11 Special Interest Groups Lobbying and PACs- Chapter 11 Special Interest Groups An organized group of people
Agenda 1. Interest Groups Notes 2. Interest Groups Book 3. HW: graphs and charts for Chapter 11 Special Interest Groups Lobbying and PACs- Chapter 11 Special Interest Groups An organized group of people
WORKING GROUP OF EXPERTS ON PEOPLE OF AFRICAN DESCENT
 WORKING GROUP OF EXPERTS ON PEOPLE OF AFRICAN DESCENT Recognition through Education and Cultural Rights 12 th Session, Geneva, Palais des Nations 22-26 April 2013 Promotion of equality and opportunity
WORKING GROUP OF EXPERTS ON PEOPLE OF AFRICAN DESCENT Recognition through Education and Cultural Rights 12 th Session, Geneva, Palais des Nations 22-26 April 2013 Promotion of equality and opportunity
CITIZEN ADVOCACY CENTER
 CITIZEN ADVOCACY CENTER Young Voters and Civic Participation LESSON PLAN AND ACTIVITIES All rights reserved. No part of this lesson plan may be reproduced in any form or by any electronic or mechanical
CITIZEN ADVOCACY CENTER Young Voters and Civic Participation LESSON PLAN AND ACTIVITIES All rights reserved. No part of this lesson plan may be reproduced in any form or by any electronic or mechanical
24.03: Good Food 3/13/17. Justice and Food Production
 1. Food Sovereignty, again Justice and Food Production Before when we talked about food sovereignty (Kyle Powys Whyte reading), the main issue was the protection of a way of life, a culture. In the Thompson
1. Food Sovereignty, again Justice and Food Production Before when we talked about food sovereignty (Kyle Powys Whyte reading), the main issue was the protection of a way of life, a culture. In the Thompson
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCING GOVERNMENT IN AMERICA CHAPTER OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCING GOVERNMENT IN AMERICA CHAPTER OUTLINE I. Introduction: Politics and Government Matter (pp. 3 8) A. Many Americans are apathetic about politics and government. B. Political knowledge
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCING GOVERNMENT IN AMERICA CHAPTER OUTLINE I. Introduction: Politics and Government Matter (pp. 3 8) A. Many Americans are apathetic about politics and government. B. Political knowledge
American Government and Politics: Deliberation, Democracy and Citizenship. Joseph M. Bessette John J. Pitney, Jr. PREFACE
 American Government and Politics: Deliberation, Democracy and Citizenship Joseph M. Bessette John J. Pitney, Jr. PREFACE The basic premise of this textbook is that Americans believe in ideals greater than
American Government and Politics: Deliberation, Democracy and Citizenship Joseph M. Bessette John J. Pitney, Jr. PREFACE The basic premise of this textbook is that Americans believe in ideals greater than
Introducing Marxist Theories of the State
 In the following presentation I shall assume that students have some familiarity with introductory Marxist Theory. Students requiring an introductory outline may click here. Students requiring additional
In the following presentation I shall assume that students have some familiarity with introductory Marxist Theory. Students requiring an introductory outline may click here. Students requiring additional
Examiners Report June GCE Government and Politics 6GP01 01
 Examiners Report June 2015 GCE Government and Politics 6GP01 01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the UK s largest awarding body. We provide a wide range
Examiners Report June 2015 GCE Government and Politics 6GP01 01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the UK s largest awarding body. We provide a wide range
ACGM. GOVT 2305 Federal Government LEARNING OUTCOMES Upon successful completion of this course, students will:
 ACGM Geer/Schiller/Segal/ Herrera/Glencross, Gateways to Democracy: The Essentials, 3 rd Edition ISBN w/ MindTap PAC: 9781285852911 ISBN text alone: 9781285858579 GOVT 2305 Federal Government LEARNING
ACGM Geer/Schiller/Segal/ Herrera/Glencross, Gateways to Democracy: The Essentials, 3 rd Edition ISBN w/ MindTap PAC: 9781285852911 ISBN text alone: 9781285858579 GOVT 2305 Federal Government LEARNING
Geer/Schiller/Segal/Herrera, Gateways to Democracy, 3 rd Edition ISBN w/ MindTap PAC: ISBN text alone: ACGM
 ACGM Geer/Schiller/Segal/Herrera, Gateways to Democracy, 3 rd Edition ISBN w/ MindTap PAC: 9781285852904 ISBN text alone: 9781285858548 GOVT 2305 Federal Government LEARNING OUTCOMES Upon successful completion
ACGM Geer/Schiller/Segal/Herrera, Gateways to Democracy, 3 rd Edition ISBN w/ MindTap PAC: 9781285852904 ISBN text alone: 9781285858548 GOVT 2305 Federal Government LEARNING OUTCOMES Upon successful completion
Unit 1: Foundational Concepts of Politics. 1a: Situate the academic discipline of political science within the broader field of social science.
 Unit 1: Foundational Concepts of Politics 1a: Situate the academic discipline of political science within the broader field of social science. 1a.1. Political science is one of several interrelated academic
Unit 1: Foundational Concepts of Politics 1a: Situate the academic discipline of political science within the broader field of social science. 1a.1. Political science is one of several interrelated academic
Reconciling Educational Adequacy and Equity Arguments Through a Rawlsian Lens
 Reconciling Educational Adequacy and Equity Arguments Through a Rawlsian Lens John Pijanowski Professor of Educational Leadership University of Arkansas Spring 2015 Abstract A theory of educational opportunity
Reconciling Educational Adequacy and Equity Arguments Through a Rawlsian Lens John Pijanowski Professor of Educational Leadership University of Arkansas Spring 2015 Abstract A theory of educational opportunity
PART. Why Should We Care About American Democracy? Chapter 1 Should We Care about Politics?
 PART 1 Why Should We Care About American Democracy? Chapter 1 Should We Care about Politics? Chapter 2 The Constitution and Federalism: Setting the Ground Rules for Politics Chapter 1 Should We Care About
PART 1 Why Should We Care About American Democracy? Chapter 1 Should We Care about Politics? Chapter 2 The Constitution and Federalism: Setting the Ground Rules for Politics Chapter 1 Should We Care About
UGBS 105 Introduction to Public Administration
 UGBS 105 Introduction to Public Administration Session 3 Bureaucracy and Public Administration Lecturer: Contact Information: dappiah@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education
UGBS 105 Introduction to Public Administration Session 3 Bureaucracy and Public Administration Lecturer: Contact Information: dappiah@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education
ECONOMICS CHAPTER 11 AND POLITICS. Chapter 11
 CHAPTER 11 ECONOMICS AND POLITICS I. Why Focus on India? A. India is one of two rising powers (the other being China) expected to challenge the global power and influence of the United States. B. India,
CHAPTER 11 ECONOMICS AND POLITICS I. Why Focus on India? A. India is one of two rising powers (the other being China) expected to challenge the global power and influence of the United States. B. India,
To understand the U.S. electoral college and, more generally, American democracy, it is critical to understand that when voters go to the polls on
 To understand the U.S. electoral college and, more generally, American democracy, it is critical to understand that when voters go to the polls on Tuesday, November 8th, they are not voting together in
To understand the U.S. electoral college and, more generally, American democracy, it is critical to understand that when voters go to the polls on Tuesday, November 8th, they are not voting together in
Public Opinion and Government Responsiveness Part II
 Public Opinion and Government Responsiveness Part II How confident are we that the power to drive and determine public opinion will always reside in responsible hands? Carl Sagan How We Form Political
Public Opinion and Government Responsiveness Part II How confident are we that the power to drive and determine public opinion will always reside in responsible hands? Carl Sagan How We Form Political
Quiz # 12 Chapter 17 The Public Policy Process
 Quiz # 12 Chapter 17 The Public Policy Process 1. An interesting psychological characteristic associated with the concept of legitimacy is that most people a. accept what the government does as legitimate.
Quiz # 12 Chapter 17 The Public Policy Process 1. An interesting psychological characteristic associated with the concept of legitimacy is that most people a. accept what the government does as legitimate.
Federal Government (GOVT 2305) Credit: 3 semester credit hours (3 hours lecture) Prerequisite/Co-requisite: None.
 Federal Government (GOVT 2305) Credit: 3 semester credit hours (3 hours lecture) Prerequisite/Co-requisite: None. Course Description Origin and development of the U.S. Constitution, structure and s of
Federal Government (GOVT 2305) Credit: 3 semester credit hours (3 hours lecture) Prerequisite/Co-requisite: None. Course Description Origin and development of the U.S. Constitution, structure and s of
BCGEU surveyed its own members on electoral reform. They reported widespread disaffection with the current provincial electoral system.
 BCGEU SUBMISSION ON THE ELECTORAL REFORM REFERENDUM OF 2018 February, 2018 The BCGEU applauds our government s commitment to allowing British Columbians a direct say in how they vote. As one of the largest
BCGEU SUBMISSION ON THE ELECTORAL REFORM REFERENDUM OF 2018 February, 2018 The BCGEU applauds our government s commitment to allowing British Columbians a direct say in how they vote. As one of the largest
Chapter 1. Introducing Government in America
 Chapter 1 Introducing Government in America Chapter 1: Introducing Government in America Government Politics The Policymaking System Democracy The Scope of Government in America Summary Essential Question(s)
Chapter 1 Introducing Government in America Chapter 1: Introducing Government in America Government Politics The Policymaking System Democracy The Scope of Government in America Summary Essential Question(s)
Support the Voting Rights Advancement Act of 2015 (S / H.R. 2867)
 Legislative Advocacy Day September 16, 2015 Support the Voting Rights Advancement Act of 2015 (S. 1659 / H.R. 2867) As a result of the 2013 Supreme Court decision in Shelby v. Holder, there are currently
Legislative Advocacy Day September 16, 2015 Support the Voting Rights Advancement Act of 2015 (S. 1659 / H.R. 2867) As a result of the 2013 Supreme Court decision in Shelby v. Holder, there are currently
THE WORKMEN S CIRCLE SURVEY OF AMERICAN JEWS. Jews, Economic Justice & the Vote in Steven M. Cohen and Samuel Abrams
 THE WORKMEN S CIRCLE SURVEY OF AMERICAN JEWS Jews, Economic Justice & the Vote in 2012 Steven M. Cohen and Samuel Abrams 1/4/2013 2 Overview Economic justice concerns were the critical consideration dividing
THE WORKMEN S CIRCLE SURVEY OF AMERICAN JEWS Jews, Economic Justice & the Vote in 2012 Steven M. Cohen and Samuel Abrams 1/4/2013 2 Overview Economic justice concerns were the critical consideration dividing
Political Parties. The drama and pageantry of national political conventions are important elements of presidential election
 Political Parties I INTRODUCTION Political Convention Speech The drama and pageantry of national political conventions are important elements of presidential election campaigns in the United States. In
Political Parties I INTRODUCTION Political Convention Speech The drama and pageantry of national political conventions are important elements of presidential election campaigns in the United States. In
I. What is a Theoretical Perspective? The Functionalist Perspective
 I. What is a Theoretical Perspective? Perspectives might best be viewed as models. Each perspective makes assumptions about society. Each one attempts to integrate various kinds of information about society.
I. What is a Theoretical Perspective? Perspectives might best be viewed as models. Each perspective makes assumptions about society. Each one attempts to integrate various kinds of information about society.
Migrants and external voting
 The Migration & Development Series On the occasion of International Migrants Day New York, 18 December 2008 Panel discussion on The Human Rights of Migrants Facilitating the Participation of Migrants in
The Migration & Development Series On the occasion of International Migrants Day New York, 18 December 2008 Panel discussion on The Human Rights of Migrants Facilitating the Participation of Migrants in
First World Summit for the People of Afro Decent
 First World Summit for the People of Afro Decent La Ceiba, Honduras 18-20 August 2011 Panel The Right to Education and Culture Empowering the Afro Descendants through the Right to Education by Kishore
First World Summit for the People of Afro Decent La Ceiba, Honduras 18-20 August 2011 Panel The Right to Education and Culture Empowering the Afro Descendants through the Right to Education by Kishore
Oxfam Education
 Background notes on inequality for teachers Oxfam Education What do we mean by inequality? In this resource inequality refers to wide differences in a population in terms of their wealth, their income
Background notes on inequality for teachers Oxfam Education What do we mean by inequality? In this resource inequality refers to wide differences in a population in terms of their wealth, their income
Julie Lenggenhager. The "Ideal" Female Candidate
 Julie Lenggenhager The "Ideal" Female Candidate Why are there so few women elected to positions in both gubernatorial and senatorial contests? Since the ratification of the nineteenth amendment in 1920
Julie Lenggenhager The "Ideal" Female Candidate Why are there so few women elected to positions in both gubernatorial and senatorial contests? Since the ratification of the nineteenth amendment in 1920
Where do the 12th Congressional District Candidates Stand on Civil Rights and Liberties Issues?
 Where do the 12th Congressional District Candidates Stand on Civil Rights and Liberties Issues? On May 1, 2014, the ACLU of New Jersey and other leading civil rights organization hosted a civil rights
Where do the 12th Congressional District Candidates Stand on Civil Rights and Liberties Issues? On May 1, 2014, the ACLU of New Jersey and other leading civil rights organization hosted a civil rights
The division of society into distinct social classes is one of the most striking manifestations of the modern world... It has often been the source
 The division of society into distinct social classes is one of the most striking manifestations of the modern world... It has often been the source of other kinds of inequality and... the economic dominance
The division of society into distinct social classes is one of the most striking manifestations of the modern world... It has often been the source of other kinds of inequality and... the economic dominance
Definition: Institution public system of rules which defines offices and positions with their rights and duties, powers and immunities p.
 RAWLS Project: to interpret the initial situation, formulate principles of choice, and then establish which principles should be adopted. The principles of justice provide an assignment of fundamental
RAWLS Project: to interpret the initial situation, formulate principles of choice, and then establish which principles should be adopted. The principles of justice provide an assignment of fundamental
How can the changing status of women help improve the human condition? Ph.D. Huseynova Reyhan
 How can the changing status of women help improve the human condition? Ph.D. Huseynova Reyhan Azerbaijan Future Studies Society, Chairwomen Azerbaijani Node of Millennium Project The status of women depends
How can the changing status of women help improve the human condition? Ph.D. Huseynova Reyhan Azerbaijan Future Studies Society, Chairwomen Azerbaijani Node of Millennium Project The status of women depends
LECTURE 1/2: THE GLOBAL POLITICAL ECONOMY OF CAPITALISM
 LECTURE 1/2: THE GLOBAL POLITICAL ECONOMY OF CAPITALISM Dr. Aidan Regan Email: aidan.regan@ucd.ie Blog: www.capitalistdemocracy.wordpress.com Twitter: @aidan_regan Social contract What I expect from you:
LECTURE 1/2: THE GLOBAL POLITICAL ECONOMY OF CAPITALISM Dr. Aidan Regan Email: aidan.regan@ucd.ie Blog: www.capitalistdemocracy.wordpress.com Twitter: @aidan_regan Social contract What I expect from you:
Young Voters in the 2010 Elections
 Young Voters in the 2010 Elections By CIRCLE Staff November 9, 2010 This CIRCLE fact sheet summarizes important findings from the 2010 National House Exit Polls conducted by Edison Research. The respondents
Young Voters in the 2010 Elections By CIRCLE Staff November 9, 2010 This CIRCLE fact sheet summarizes important findings from the 2010 National House Exit Polls conducted by Edison Research. The respondents
Political Parties in the United States (HAA)
 Political Parties in the United States (HAA) Political parties have played an important role in American politics since the early years of the Republic. Yet many of the nation s founders did not approve
Political Parties in the United States (HAA) Political parties have played an important role in American politics since the early years of the Republic. Yet many of the nation s founders did not approve
Strengthening the Foundation for World Peace - A Case for Democratizing the United Nations
 From the SelectedWorks of Jarvis J. Lagman Esq. December 8, 2014 Strengthening the Foundation for World Peace - A Case for Democratizing the United Nations Jarvis J. Lagman, Esq. Available at: https://works.bepress.com/jarvis_lagman/1/
From the SelectedWorks of Jarvis J. Lagman Esq. December 8, 2014 Strengthening the Foundation for World Peace - A Case for Democratizing the United Nations Jarvis J. Lagman, Esq. Available at: https://works.bepress.com/jarvis_lagman/1/
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 1 Expanding Voting Rights ESSENTIAL QUESTION Who should have the right to vote in a democracy? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary device a mechanism designed to serve a special purpose or perform
Lesson 1 Expanding Voting Rights ESSENTIAL QUESTION Who should have the right to vote in a democracy? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary device a mechanism designed to serve a special purpose or perform
Home > Educational Resources > For Educators > Felon Disenfranchisement Is Constitutional, And Justified
 1 of 5 12/7/2012 11:15 AM Search: Go TEMPLETON LECTURE SERIES WELCOME EDUCATORS AND STUDENTS SCHOOL AND GROUP VISITS FOR EDUCATORS The Exchange TAH Grants Lincoln Teacher's Guide Supreme Court Confirmation
1 of 5 12/7/2012 11:15 AM Search: Go TEMPLETON LECTURE SERIES WELCOME EDUCATORS AND STUDENTS SCHOOL AND GROUP VISITS FOR EDUCATORS The Exchange TAH Grants Lincoln Teacher's Guide Supreme Court Confirmation
LECTURE 1/2: THE GLOBAL POLITICAL ECONOMY OF CAPITALISM
 LECTURE 1/2: THE GLOBAL POLITICAL ECONOMY OF CAPITALISM Dr. Aidan Regan Email: aidan.regan@ucd.ie Blog: www.capitalistdemocracy.wordpress.com Twitter: @aidan_regan Social contract What I expect from you:
LECTURE 1/2: THE GLOBAL POLITICAL ECONOMY OF CAPITALISM Dr. Aidan Regan Email: aidan.regan@ucd.ie Blog: www.capitalistdemocracy.wordpress.com Twitter: @aidan_regan Social contract What I expect from you:
Money in Politics: The Impact of Growing Spending on Stakeholders and American. Democracy
 Wang 1 Wenbo Wang The John D. Brademas Center for the Study of Congress Congressional Intern Research Paper The American Association for Justice Money in Politics: The Impact of Growing Spending on Stakeholders
Wang 1 Wenbo Wang The John D. Brademas Center for the Study of Congress Congressional Intern Research Paper The American Association for Justice Money in Politics: The Impact of Growing Spending on Stakeholders
An atlas with a positive message for a European people united in diversity
 Ballas, D., Dorling, D. and Hennig, B.D. (2017) An atlas with a positive message for a European people united in diversity, LSE European Politics and Policy Blog, May 9th, http://blogs.lse.ac.uk/europpblog/2017/05/09/human-atlas-of-europe-united-in-diversity/
Ballas, D., Dorling, D. and Hennig, B.D. (2017) An atlas with a positive message for a European people united in diversity, LSE European Politics and Policy Blog, May 9th, http://blogs.lse.ac.uk/europpblog/2017/05/09/human-atlas-of-europe-united-in-diversity/
netw rks The Resurgence of Conservatism, Ronald Reagan s Inauguration Background
 Analyzing Primary Sources Activity Ronald Reagan s Inauguration Background When Ronald Reagan was sworn in as the fortieth president of the United States, the country was facing several crises. The economy
Analyzing Primary Sources Activity Ronald Reagan s Inauguration Background When Ronald Reagan was sworn in as the fortieth president of the United States, the country was facing several crises. The economy
POLICIES OF STRUCTURAL RACISM AND THE PUBLIC SECTOR State of Georgia U.S. South
 United States of America Submission to the United Nations Universal Periodic Review (UPR) Ninth Session of the Working Group on the UPR Human Rights Council 22 November 3 December 2010 POLICIES OF STRUCTURAL
United States of America Submission to the United Nations Universal Periodic Review (UPR) Ninth Session of the Working Group on the UPR Human Rights Council 22 November 3 December 2010 POLICIES OF STRUCTURAL
AP GOPO CHAPTER 9 READING GUIDE
 AP GOPO CHAPTER 9 READING GUIDE 1. Have levels of political participation increased in recent years? 2. Remember what grassroots is. It s come up once or twice before in class. 3. What is a primary? Are
AP GOPO CHAPTER 9 READING GUIDE 1. Have levels of political participation increased in recent years? 2. Remember what grassroots is. It s come up once or twice before in class. 3. What is a primary? Are
Chapter 1 ( ) The Capitalist Revolution Tue.
 2016 Q2 B Chapter 1 (1.9-1.16) The Capitalist Revolution 2016.06.21 Tue. 1.9 Capitalism as an Economic System Ø Capitalism is an economic system that combines decentralisation with centralisation. Capitalism
2016 Q2 B Chapter 1 (1.9-1.16) The Capitalist Revolution 2016.06.21 Tue. 1.9 Capitalism as an Economic System Ø Capitalism is an economic system that combines decentralisation with centralisation. Capitalism
Texas. SUPER DISTRICT A - FIVE SEATS % 2000 Presidential Vote
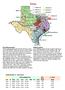 Texas Racial Representation Of the voting population of 6,232,350, 28.7 are Latino and 11.0 are black. Under the current 32-district system, black voters do not make up the majority in any district and
Texas Racial Representation Of the voting population of 6,232,350, 28.7 are Latino and 11.0 are black. Under the current 32-district system, black voters do not make up the majority in any district and
Democracy In The U.S.
 Democracy In The U.S. Objectives Explain the controversy over Texas position on elections and what Federal Act is part of this issue. Explain your position on the political spectrum Explain authoritarian
Democracy In The U.S. Objectives Explain the controversy over Texas position on elections and what Federal Act is part of this issue. Explain your position on the political spectrum Explain authoritarian
Reminders. Please keep phones away. Make sure you are in your seat when the bell rings. Be respectful and listen when others are talking.
 Reminders Please keep phones away Make sure you are in your seat when the bell rings Be respectful and listen when others are talking. Do Now What is Social Stratification? Social Stratification Dimensions
Reminders Please keep phones away Make sure you are in your seat when the bell rings Be respectful and listen when others are talking. Do Now What is Social Stratification? Social Stratification Dimensions
Technocracy, Liberal Democracy and the Division of Our Time
 Technocracy, Liberal Democracy and the Division of Our Time Feb. 15, 2017 The idea that expertise ought to guide our political life is at odds with the principle of national self-determination. By George
Technocracy, Liberal Democracy and the Division of Our Time Feb. 15, 2017 The idea that expertise ought to guide our political life is at odds with the principle of national self-determination. By George
Wyoming Republican Candidate Profile Questionnaire
 Wyoming Republican Candidate Profile Questionnaire Note to All Wyoming State Republican Party Candidates in the 2018 Primary Election, Thank you for filing as a candidate to represent our State and your
Wyoming Republican Candidate Profile Questionnaire Note to All Wyoming State Republican Party Candidates in the 2018 Primary Election, Thank you for filing as a candidate to represent our State and your
SYLLABUS.
 SYLLABUS Pols 001: American Government Office: Clark Hall #406N Ken Nuger Phone: 924-5346, Fall, 2016 email: ken.nuger@sjsu.edu 3 p.m., MW and 6 p.m., M Office Hours: 9:30-10:30, MW, 5-6 M HGH 116 and
SYLLABUS Pols 001: American Government Office: Clark Hall #406N Ken Nuger Phone: 924-5346, Fall, 2016 email: ken.nuger@sjsu.edu 3 p.m., MW and 6 p.m., M Office Hours: 9:30-10:30, MW, 5-6 M HGH 116 and
Release #2475 Release Date: Wednesday, July 2, 2014 WHILE CALIFORNIANS ARE DISSATISFIED
 THE FIELD POLL THE INDEPENDENT AND NON-PARTISAN SURVEY OF PUBLIC OPINION ESTABLISHED IN 1947 AS THE CALIFORNIA POLL BY MERVIN FIELD Field Research Corporation 601 California Street, Suite 210 San Francisco,
THE FIELD POLL THE INDEPENDENT AND NON-PARTISAN SURVEY OF PUBLIC OPINION ESTABLISHED IN 1947 AS THE CALIFORNIA POLL BY MERVIN FIELD Field Research Corporation 601 California Street, Suite 210 San Francisco,
1.Myths and images about families influence our expectations and assumptions about family life. T or F
 Soc of Family Midterm Spring 2016 1.Myths and images about families influence our expectations and assumptions about family life. T or F 2.Of all the images of family, the image of family as encumbrance
Soc of Family Midterm Spring 2016 1.Myths and images about families influence our expectations and assumptions about family life. T or F 2.Of all the images of family, the image of family as encumbrance
When the Blind Rule in Favor of Ignorance; Ignorance is Bliss
 June 26, 2012 When the Blind Rule in Favor of Ignorance; Ignorance is Bliss Section. I. Health Insurance According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics health insurance premiums are defined as Agreed upon
June 26, 2012 When the Blind Rule in Favor of Ignorance; Ignorance is Bliss Section. I. Health Insurance According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics health insurance premiums are defined as Agreed upon
Survey of US Voters Issues and Attitudes June 2014
 Survey of US Voters Issues and Attitudes June 2014 Methodology Three surveys of U.S. voters conducted in late 2013 Two online surveys of voters, respondents reached using recruit-only online panel of adults
Survey of US Voters Issues and Attitudes June 2014 Methodology Three surveys of U.S. voters conducted in late 2013 Two online surveys of voters, respondents reached using recruit-only online panel of adults
Chapter 12 Interest Groups. AP Government
 Chapter 12 Interest Groups AP Government Interest Groups An organized group of individuals or organizations that makes policy-related appeals to government is called an interest group. Why Interest Groups
Chapter 12 Interest Groups AP Government Interest Groups An organized group of individuals or organizations that makes policy-related appeals to government is called an interest group. Why Interest Groups
What is Democratic Socialism?
 What is Democratic Socialism? SOURCE: https://www.dsausa.org/about-us/what-is-democratic-socialism/ What is Democratic Socialism? Democratic socialists believe that both the economy and society should
What is Democratic Socialism? SOURCE: https://www.dsausa.org/about-us/what-is-democratic-socialism/ What is Democratic Socialism? Democratic socialists believe that both the economy and society should
CHAPTER 2: MAJORITARIAN OR PLURALIST DEMOCRACY
 CHAPTER 2: MAJORITARIAN OR PLURALIST DEMOCRACY SHORT ANSWER Please define the following term. 1. autocracy PTS: 1 REF: 34 2. oligarchy PTS: 1 REF: 34 3. democracy PTS: 1 REF: 34 4. procedural democratic
CHAPTER 2: MAJORITARIAN OR PLURALIST DEMOCRACY SHORT ANSWER Please define the following term. 1. autocracy PTS: 1 REF: 34 2. oligarchy PTS: 1 REF: 34 3. democracy PTS: 1 REF: 34 4. procedural democratic
POLITICAL SCIENCE. PS 0200 AMERICAN POLITICS 3 cr. PS 0211 AMERICAN SYSTEM OF CRIMINAL JUSTICE 3 cr. PS 0300 COMPARATIVE POLITICS 3 cr.
 POLITICAL SCIENCE PS 0200 AMERICAN POLITICS 3 cr. Designed to provide students with a basic working knowledge of the basic goals of the constitutional framers, giving students an understanding of the purposes
POLITICAL SCIENCE PS 0200 AMERICAN POLITICS 3 cr. Designed to provide students with a basic working knowledge of the basic goals of the constitutional framers, giving students an understanding of the purposes
Nothing is as permanent as a temporary government program. Milton Friedman
 Nothing is as permanent as a temporary government program. Milton Friedman public policy: an intentional course of action followed by government in dealing with some problem or matter of concern, a term
Nothing is as permanent as a temporary government program. Milton Friedman public policy: an intentional course of action followed by government in dealing with some problem or matter of concern, a term
We the Stakeholders: The Power of Representation beyond Borders? Clara Brandi
 REVIEW Clara Brandi We the Stakeholders: The Power of Representation beyond Borders? Terry Macdonald, Global Stakeholder Democracy. Power and Representation Beyond Liberal States, Oxford, Oxford University
REVIEW Clara Brandi We the Stakeholders: The Power of Representation beyond Borders? Terry Macdonald, Global Stakeholder Democracy. Power and Representation Beyond Liberal States, Oxford, Oxford University
Analyzing American Democracy
 SUB Hamburg Analyzing American Democracy Politics and Political Science Jon R. Bond Texas A&M University Kevin B. Smith University of Nebraska-Lincoln O Routledge Taylor & Francis Group NEW YORK AND LONDON
SUB Hamburg Analyzing American Democracy Politics and Political Science Jon R. Bond Texas A&M University Kevin B. Smith University of Nebraska-Lincoln O Routledge Taylor & Francis Group NEW YORK AND LONDON
THE FEDERAL BUREAUCRACY: EXECUTING THE LAWS
 THE FEDERAL BUREAUCRACY: EXECUTING THE LAWS I. INTRO a. In order to respond quicker to disasters, Carter in 1979 established the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), and it was overhauled in the
THE FEDERAL BUREAUCRACY: EXECUTING THE LAWS I. INTRO a. In order to respond quicker to disasters, Carter in 1979 established the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), and it was overhauled in the
Key Concepts & Research in Political Science and Sociology
 SPS 2 nd term seminar 2015-2016 Key Concepts & Research in Political Science and Sociology By Stefanie Reher and Diederik Boertien Tuesdays, 15:00-17:00, Seminar Room 3 (first session on January, 19th)
SPS 2 nd term seminar 2015-2016 Key Concepts & Research in Political Science and Sociology By Stefanie Reher and Diederik Boertien Tuesdays, 15:00-17:00, Seminar Room 3 (first session on January, 19th)
Collective Action, Interest Groups and Social Movements. Nov. 24
 Collective Action, Interest Groups and Social Movements Nov. 24 Lecture overview Different terms and different kinds of groups Advocacy group tactics Theories of collective action Advocacy groups and democracy
Collective Action, Interest Groups and Social Movements Nov. 24 Lecture overview Different terms and different kinds of groups Advocacy group tactics Theories of collective action Advocacy groups and democracy
AP US Government Syllabus. Desired Results
 AP US Government Syllabus Certificated Teacher: Date: 2017-2018 Course Title: AP United States Government Desired Results Credit: _X One Semester (0.5) Two Semesters (1.0) Estimate of hours per week engaged
AP US Government Syllabus Certificated Teacher: Date: 2017-2018 Course Title: AP United States Government Desired Results Credit: _X One Semester (0.5) Two Semesters (1.0) Estimate of hours per week engaged
Political Inequality Worsens Economic Inequality
 Political Inequality Worsens Economic Inequality Ruy Teixeira is a senior fellow at the Center for American Progress and co-director of a new joint project between the Center and the American Enterprise
Political Inequality Worsens Economic Inequality Ruy Teixeira is a senior fellow at the Center for American Progress and co-director of a new joint project between the Center and the American Enterprise
Chapter 7 5/7/09. Problem 7. Social Inequality. The Cultural Construction of Social Hierarchy
 Chapter 7 The Cultural Construction of Social Hierarchy Problem 7 Why are modern societies characterized by social, political, and economic inequalities? Social Inequality The worth of the 358 richest
Chapter 7 The Cultural Construction of Social Hierarchy Problem 7 Why are modern societies characterized by social, political, and economic inequalities? Social Inequality The worth of the 358 richest
Stratification: Rich and Famous or Rags and Famine? 2015 SAGE Publications, Inc.
 Chapter 7 Stratification: Rich and Famous or Rags and Famine? The Importance of Stratification Social stratification: individuals and groups are layered or ranked in society according to how many valued
Chapter 7 Stratification: Rich and Famous or Rags and Famine? The Importance of Stratification Social stratification: individuals and groups are layered or ranked in society according to how many valued
Community Voices on Causes and Solutions of the Human Rights Crisis in the United States
 Community Voices on Causes and Solutions of the Human Rights Crisis in the United States A Living Document of the Human Rights at Home Campaign (First and Second Episodes) Second Episode: Voices from the
Community Voices on Causes and Solutions of the Human Rights Crisis in the United States A Living Document of the Human Rights at Home Campaign (First and Second Episodes) Second Episode: Voices from the
AP Gov Chapter 1 Outline
 I. POLITICS AND GOVERNMENT Key terms: Politics is the struggle over power or influence within organizations or informal groups that can grant or withhold benefits or privileges, or as Harold Dwight Lasswell
I. POLITICS AND GOVERNMENT Key terms: Politics is the struggle over power or influence within organizations or informal groups that can grant or withhold benefits or privileges, or as Harold Dwight Lasswell
WORKPLACE LEAVE IN A MOVEMENT BUILDING CONTEXT
 WORKPLACE LEAVE IN A MOVEMENT BUILDING CONTEXT How to Win the Strong Policies that Create Equity for Everyone MOVEMENT MOMENTUM There is growing momentum in states and communities across the country to
WORKPLACE LEAVE IN A MOVEMENT BUILDING CONTEXT How to Win the Strong Policies that Create Equity for Everyone MOVEMENT MOMENTUM There is growing momentum in states and communities across the country to
Socio-Legal Course Descriptions
 Socio-Legal Course Descriptions Updated 12/19/2013 Required Courses for Socio-Legal Studies Major: PLSC 1810: Introduction to Law and Society This course addresses justifications and explanations for regulation
Socio-Legal Course Descriptions Updated 12/19/2013 Required Courses for Socio-Legal Studies Major: PLSC 1810: Introduction to Law and Society This course addresses justifications and explanations for regulation
Voters Support Bold Economic Agenda
 Support Bold Economic Agenda Methodology: Demos sponsored an online survey among 1,536 registered voters, conducted June 5 to June 14, 2017. The research included a base sample of registered voters and,
Support Bold Economic Agenda Methodology: Demos sponsored an online survey among 1,536 registered voters, conducted June 5 to June 14, 2017. The research included a base sample of registered voters and,
Officer-Involved Shootings in Fresno, California: Frequency, Fatality, and Disproportionate Impact
 Celia Guo PPD 631: GIS for Policy, Planning, and Development Officer-Involved Shootings in Fresno, California: Frequency, Fatality, and Disproportionate Impact Introduction Since the late 1990s, there
Celia Guo PPD 631: GIS for Policy, Planning, and Development Officer-Involved Shootings in Fresno, California: Frequency, Fatality, and Disproportionate Impact Introduction Since the late 1990s, there
AP U. S. Government and Politics Pacing Guide
 AP U. S. Government and Politics Pacing Guide Strand 1 Introduction to U. S. Government ½ week Vocabulary related to government and politics Differences between government and politics Wilson, Chapter
AP U. S. Government and Politics Pacing Guide Strand 1 Introduction to U. S. Government ½ week Vocabulary related to government and politics Differences between government and politics Wilson, Chapter
Chapter 13: The Presidency. American Democracy Now, 4/e
 Chapter 13: The Presidency American Democracy Now, 4/e Presidential Elections Candidates position themselves years in advance of Election Day. Eligible incumbent presidents are nearly always nominated
Chapter 13: The Presidency American Democracy Now, 4/e Presidential Elections Candidates position themselves years in advance of Election Day. Eligible incumbent presidents are nearly always nominated
VI. Rawls and Equality
 VI. Rawls and Equality A society of free and equal persons Last time, on Justice: Getting What We Are Due 1 Redistributive Taxation Redux Can we justly tax Wilt Chamberlain to redistribute wealth to others?
VI. Rawls and Equality A society of free and equal persons Last time, on Justice: Getting What We Are Due 1 Redistributive Taxation Redux Can we justly tax Wilt Chamberlain to redistribute wealth to others?
Income Inequality in the United States Through the Lens of Other Advanced Economies
 Mia DeSanzo Wealth & Power Major Writing Assignment 3/3/16 Income Inequality in the United States Through the Lens of Other Advanced Economies Income inequality in the United States has become a political
Mia DeSanzo Wealth & Power Major Writing Assignment 3/3/16 Income Inequality in the United States Through the Lens of Other Advanced Economies Income inequality in the United States has become a political
NEW EDITION COMING Student Prices start at $23.95! AMERICAN GOVERNMENT: Your Voice, Your Choice, 5/e Matthew R. Kerbel Villanova University
 AMERICAN GOVERNMENT NEW EDITION COMING Student Prices start at $23.95! AMERICAN GOVERNMENT: Your Voice, Your Choice, 5/e Matthew R. Kerbel Villanova University 2014 (Available July 2013) Approx. 608 pages
AMERICAN GOVERNMENT NEW EDITION COMING Student Prices start at $23.95! AMERICAN GOVERNMENT: Your Voice, Your Choice, 5/e Matthew R. Kerbel Villanova University 2014 (Available July 2013) Approx. 608 pages
Example 8.2 The Economics of Terrorism: Externalities and Strategic Interaction
 Example 8.2 The Economics of Terrorism: Externalities and Strategic Interaction ECONOMIC APPROACHES TO TERRORISM: AN OVERVIEW Terrorism would appear to be a subject for military experts and political scientists,
Example 8.2 The Economics of Terrorism: Externalities and Strategic Interaction ECONOMIC APPROACHES TO TERRORISM: AN OVERVIEW Terrorism would appear to be a subject for military experts and political scientists,
The Problem of the Senate
 The Problem of the Senate by Richard Z. Duffee 1) The problem of the Senate is an example of the fact that one major reason the Constitution is in danger is because it unjustly defends inequities. Those
The Problem of the Senate by Richard Z. Duffee 1) The problem of the Senate is an example of the fact that one major reason the Constitution is in danger is because it unjustly defends inequities. Those
GOVERNMENT & POLITICS UNIT 1 GLOSSARY
 NAME: GOVERNMENT & POLITICS UNIT 1 GLOSSARY TASK Over the summer holiday complete the definitions for the words for the FOUR topics AND more importantly learn these key words with their definitions! There
NAME: GOVERNMENT & POLITICS UNIT 1 GLOSSARY TASK Over the summer holiday complete the definitions for the words for the FOUR topics AND more importantly learn these key words with their definitions! There
THE TARRANCE GROUP. Interested Parties. Brian Nienaber. Key findings from the Battleground Week 6 Survey
 THE TARRANCE GROUP To: From: Re: Interested Parties Ed Goeas Brian Nienaber Key findings from the Battleground Week 6 Survey The Tarrance Group with its partners Lake Research Partners, POLITICO, and George
THE TARRANCE GROUP To: From: Re: Interested Parties Ed Goeas Brian Nienaber Key findings from the Battleground Week 6 Survey The Tarrance Group with its partners Lake Research Partners, POLITICO, and George
Political Parties CHAPTER. Roles of Political Parties
 CHAPTER 9 Political Parties IIN THIS CHAPTERI Summary: Political parties are voluntary associations of people who seek to control the government through common principles based upon peaceful and legal
CHAPTER 9 Political Parties IIN THIS CHAPTERI Summary: Political parties are voluntary associations of people who seek to control the government through common principles based upon peaceful and legal
1. Introduction. Michael Finus
 1. Introduction Michael Finus Global warming is believed to be one of the most serious environmental problems for current and hture generations. This shared belief led more than 180 countries to sign the
1. Introduction Michael Finus Global warming is believed to be one of the most serious environmental problems for current and hture generations. This shared belief led more than 180 countries to sign the
Great comments! (A lot of them could be germs of term papers )
 Phil 290-1: Political Rule February 3, 2014 Great comments! (A lot of them could be germs of term papers ) Some are about the positive view that I sketch at the end of the paper. We ll get to that in two
Phil 290-1: Political Rule February 3, 2014 Great comments! (A lot of them could be germs of term papers ) Some are about the positive view that I sketch at the end of the paper. We ll get to that in two
