Document A. Montesquieu: Excerpts from The Spirit of the Laws, 1748
|
|
|
- Baldwin Conrad Bradley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Document A Montesquieu: Excerpts from The Spirit of the Laws, 1748 In every government there are three sorts of power; the legislative; the executive, in respect to things dependent on the law of nations; and the executive, in regard to things that depend on the civil law. By virtue of the first, the prince or magistrate enacts temporary or perpetual laws, and amends or abrogates those that have been already enacted. By the second, he makes peace or war, sends or receives embassies; establishes the public security, and provides against invasions. By the third, he punishes criminals, or determines the disputes that arise between individuals. The latter we shall call the judiciary power, and the other simply the executive power of the state. When the legislative and executive powers are united in the same person, or in the same body of magistrates, there can be no liberty; because apprehensions may anse, lest the same monarch or senate should enact tyrannical laws, to execute them in a tyrannical manner. From Montesquieu, The Spirit of the Laws, vol. 1, trans. Thomas Nugent (London: J. Nourse, 1777), pp , passim. 1) What is the main argument/idea? 2) Paraphrase three main points the document makes to support this argument (bullet points) 3) What is the intent of the document? 4) What was the political impact of this document on the development of American Revolution? Connection Historical context Intended Audience Purpose Point of View
2
3 Document B Excerpts from Jean-Jacques Rousseau, The Social Contract (1762) Man is born free; and everywhere he is in chains. One thinks himself the master of others, and still remains a greater slave than they. How did this change come about? I do not know. What can make it legitimate? That question I think I can answer I suppose men to have reached the point at which the obstacles in the way of their preservation in the state of nature show their power of resistance to be greater than the resources at the disposal of each individual for his maintenance in that state. That primitive condition can then subsist no longer; and the human race would perish unless it changed its manner of existence. The clauses of this contract are so determined by the nature of the act that the slightest modification would make them vain and ineffective; so that, although they have perhaps never been formally set forth, they are everywhere the same and everywhere tacitly admitted and recognised, until, on the violation of the social compact, each regains his original rights and resumes his natural liberty, while losing the conventional liberty in favour of which he renounced it. 1) What is the main argument/idea? 2) Paraphrase three main points the document makes to support this argument (bullet points) 3) What is the intent of the document? 4) What was the political impact of this document on the development of American Revolution? Connection Historical context Intended Audience Purpose Point of View
4
5 Document C: John Locke: Excerpts from Two Treatises of Government, 1690 Sec. 87. Man being born, as has been proved, with a title to perfect freedom, and an uncontrouled enjoyment of all the rights and privileges of the law of nature, equally with any other man, or number of men in the world, hath by nature a power, not only to preserve his property, that is, his life, liberty and estate, against the injuries and attempts of other men; but to judge of, and punish the breaches of that law in others, as he is persuaded the offence deserves, even with death itself, in crimes where the heinousness of the fact, in his opinion, requires it. But because no political society can be, nor subsist, without having in itself the power to preserve the property And thus all private judgment of every particular member being excluded, the community comes to be umpire, by settled standing rules, indifferent, and the same to all parties; and by men having authority from the community, for the execution of those rules, decides all the differences that may happen between any members of that society concerning any matter of right; and punishes those offences which any member hath committed against the society, with such penalties as the law has established: whereby it is easy to discern, who are, and who are not, in political society together. Sec. 90. Hence it is evident, that absolute monarchy, which by some men is counted the only government in the world, is indeed inconsistent with civil society, and so can be no form of civil-government at all: for the end of civil society Source: Two Treatises of Government by John Locke (1690) [At Hanover] 2) What is the main argument/idea? 2) Paraphrase three main points the document makes to support this argument (bullet points) 3) What is the intent of the document? 4) What was the political impact of this document on the development of American Revolution? Connection Historical context Intended Audience Purpose Point of View
6
Challenge. Explain 1 difference between Hobbes and Lock's theories of government.
 Challenge Explain 1 difference between Hobbes and Lock's theories of government. 1 Challenge Answer the 3 questions on the handout. Write your answers on the Challenge Sheet. 2 3 Man is born free, and
Challenge Explain 1 difference between Hobbes and Lock's theories of government. 1 Challenge Answer the 3 questions on the handout. Write your answers on the Challenge Sheet. 2 3 Man is born free, and
Fill in the matrix below, giving information for each of the four Enlightenment philosophers profiled in this activity.
 Graphic Organizer Fill in the matrix below, giving information for each of the four Enlightenment philosophers profiled in this activity. Philosopher His Belief About the Nature of Man His Ideal Form of
Graphic Organizer Fill in the matrix below, giving information for each of the four Enlightenment philosophers profiled in this activity. Philosopher His Belief About the Nature of Man His Ideal Form of
Fill in the matrix below, giving information for each of the four Enlightenment philosophers profiled in this activity.
 Graphic Organizer Activity Three: The Enlightenment Fill in the matrix below, giving information for each of the four Enlightenment philosophers profiled in this activity. Philosopher His Belief About
Graphic Organizer Activity Three: The Enlightenment Fill in the matrix below, giving information for each of the four Enlightenment philosophers profiled in this activity. Philosopher His Belief About
Thomas Hobbes. Source: Thomas Hobbes, The Leviathan, published in 1651
 Thomas Hobbes Thomas Hobbes was one of the first English Enlightenment philosophers. He believed in a strong government based on reason. The following is an excerpt from his most famous work The Leviathan.
Thomas Hobbes Thomas Hobbes was one of the first English Enlightenment philosophers. He believed in a strong government based on reason. The following is an excerpt from his most famous work The Leviathan.
Activity Three: The Enlightenment ACTIVITY CARD
 ACTIVITY CARD During the 1700 s, European philosophers thought that people should use reason to free themselves from ignorance and superstition. They believed that people who were enlightened by reason
ACTIVITY CARD During the 1700 s, European philosophers thought that people should use reason to free themselves from ignorance and superstition. They believed that people who were enlightened by reason
Mr. Rarrick. John Locke
 John Locke John Locke was a famous English Enlightenment philosopher that lived from 1632-1704. The following is an excerpt from his Second Treatise on Government. In it, Locke expresses his views on politics
John Locke John Locke was a famous English Enlightenment philosopher that lived from 1632-1704. The following is an excerpt from his Second Treatise on Government. In it, Locke expresses his views on politics
John Locke. Source: John Locke, The Second Treatise of Government published 1689
 John Locke John Locke was a famous English Enlightenment philosopher that lived from 1632-1704. The following is an excerpt from his Second Treatise on Government. In it, Locke expresses his views on politics
John Locke John Locke was a famous English Enlightenment philosopher that lived from 1632-1704. The following is an excerpt from his Second Treatise on Government. In it, Locke expresses his views on politics
*You may bullet-point all responses. John Locke: Second Treatise of Civil Government
 Name: *You may bullet-point all responses. John Locke: Second Treatise of Civil Government Before reading Locke, do some research and discuss the historical context of the Second Treatise. When did he
Name: *You may bullet-point all responses. John Locke: Second Treatise of Civil Government Before reading Locke, do some research and discuss the historical context of the Second Treatise. When did he
Political Society By John Locke From From Second Treatise Of Government, Chapter
 Name: Class: Political Society By John Locke From From Second Treatise Of Government, Chapter 7 1690 John Locke (1632-1704) was an English philosopher regarded as one of the most influential political
Name: Class: Political Society By John Locke From From Second Treatise Of Government, Chapter 7 1690 John Locke (1632-1704) was an English philosopher regarded as one of the most influential political
Enlightenment Philosophers. Great Ideas. Vocabulary: alter = change. initially = at first. resisted = fought against. Discussion Questions:
 Great Ideas Vocabulary: alter = change initially = at first resisted = fought against Discussion Questions: 1. Explain the two sentences at the top of the political cartoon. 2. What is the message of this
Great Ideas Vocabulary: alter = change initially = at first resisted = fought against Discussion Questions: 1. Explain the two sentences at the top of the political cartoon. 2. What is the message of this
The Enlightenment. European thinkers developed new ideas about government and society during the Enlightenment.
 Main Idea The Enlightenment European thinkers developed new ideas about government and society during the Enlightenment. Content Statement 5 /Learning Goal Describe how the Scientific Revolution s impact
Main Idea The Enlightenment European thinkers developed new ideas about government and society during the Enlightenment. Content Statement 5 /Learning Goal Describe how the Scientific Revolution s impact
The Enlightenment. Global History & Geography 2
 The Enlightenment Global History & Geography 2 What was it? A time period when philosophers examined the relationship between humans and their government Key ideas: 17 th & 18 th centuries Extension of
The Enlightenment Global History & Geography 2 What was it? A time period when philosophers examined the relationship between humans and their government Key ideas: 17 th & 18 th centuries Extension of
DBQ FOCUS: The Enlightenment
 NAME: DATE: CLASS: DBQ FOCUS: The Enlightenment Document-Based Question Format Directions: The following question is based on the accompanying Documents (The documents have been edited for the purpose
NAME: DATE: CLASS: DBQ FOCUS: The Enlightenment Document-Based Question Format Directions: The following question is based on the accompanying Documents (The documents have been edited for the purpose
SELECTIONS FROM OF CIVIL GOVERNMENT John Locke ( ) (Primary Source)
 Lesson One Document 1-B SELECTIONS FROM OF CIVIL GOVERNMENT John Locke (1632--1704) The State of Nature To understand political power aright, we must consider what state all men are naturally in, and that
Lesson One Document 1-B SELECTIONS FROM OF CIVIL GOVERNMENT John Locke (1632--1704) The State of Nature To understand political power aright, we must consider what state all men are naturally in, and that
LESSON ONE THE ENGLISH AND FRENCH PHILOSOPHERS
 LESSON ONE THE ENGLISH AND FRENCH PHILOSOPHERS Part One: Thomas Hobbes and John Locke A. OBJECTIVES Students will learn how the ideas of Hobbes and Locke distilled the concepts that developed in the political
LESSON ONE THE ENGLISH AND FRENCH PHILOSOPHERS Part One: Thomas Hobbes and John Locke A. OBJECTIVES Students will learn how the ideas of Hobbes and Locke distilled the concepts that developed in the political
4.6. AP American Government and Politics. John Locke Précis
 John Locke Précis After reading John Locke s Second Treatise of Civil Government, write a précis (a summary of the main ideas and points) about the treatise in 150 words or less. Final product must be
John Locke Précis After reading John Locke s Second Treatise of Civil Government, write a précis (a summary of the main ideas and points) about the treatise in 150 words or less. Final product must be
Students will understand the characteristics of the Enlightenment by
 Students will understand the characteristics of the Enlightenment by Examining the contributions of Enlightenment era thinkers Examining the parallels between Enlightenment thought and the U.S. Constitution
Students will understand the characteristics of the Enlightenment by Examining the contributions of Enlightenment era thinkers Examining the parallels between Enlightenment thought and the U.S. Constitution
Summary of Social Contract Theory by Hobbes, Locke and Rousseau
 Summary of Social Contract Theory by Hobbes, Locke and Rousseau Manzoor Elahi Laskar LL.M Symbiosis Law School, Pune Electronic copy available at: http://ssrn.com/abstract=2410525 Abstract: This paper
Summary of Social Contract Theory by Hobbes, Locke and Rousseau Manzoor Elahi Laskar LL.M Symbiosis Law School, Pune Electronic copy available at: http://ssrn.com/abstract=2410525 Abstract: This paper
AP Government and Politics Summer Assignment
 AP Government and Politics Summer Assignment To the AP Government student: For AP Government, you are required to complete the summer assignment prior to August 15, 2014 of the school year. The purpose
AP Government and Politics Summer Assignment To the AP Government student: For AP Government, you are required to complete the summer assignment prior to August 15, 2014 of the school year. The purpose
Lesson #13-The Enlightenment
 The Enlightenment Lesson #13-The Enlightenment Agenda: Bellwork, Enlightenment Notes, Exit Ticket, Ode to Reason Assignment Bellwork: Begin a new section of notes titles Lesson #13-The Enlightenment. Create
The Enlightenment Lesson #13-The Enlightenment Agenda: Bellwork, Enlightenment Notes, Exit Ticket, Ode to Reason Assignment Bellwork: Begin a new section of notes titles Lesson #13-The Enlightenment. Create
Unit 2 Assessment The Development of American Democracy
 Unit 2 Assessment 7 Unit 2 Assessment The Development of American Democracy 1. Which Enlightenment Era thinker stated that everyone is born equal and had certain natural rights of life, liberty, and property
Unit 2 Assessment 7 Unit 2 Assessment The Development of American Democracy 1. Which Enlightenment Era thinker stated that everyone is born equal and had certain natural rights of life, liberty, and property
Rights, Revolution, and Regicide: John Locke and the Second Treatise on Government (1689) Monday, May 7, 12
 Rights, Revolution, and Regicide: John Locke and the Second Treatise on Government (1689) Biographical Sketch 1632, Born in Wrington, West England. Puritan Family, Pro-Cromwell Patronage of Alexander Popham
Rights, Revolution, and Regicide: John Locke and the Second Treatise on Government (1689) Biographical Sketch 1632, Born in Wrington, West England. Puritan Family, Pro-Cromwell Patronage of Alexander Popham
Foundations of Government Test
 Match each item with its definition. a. democracy b. natural rights c. social contract d. boycott e. repeal 1. an agreement among people in a society with their government 2. to cancel a law 3. a government
Match each item with its definition. a. democracy b. natural rights c. social contract d. boycott e. repeal 1. an agreement among people in a society with their government 2. to cancel a law 3. a government
Four ENLIGHTENMENT THINKERS
 Four ENLIGHTENMENT THINKERS 1. Thomas Hobbes (1588 1679) 2. John Locke (1632 1704) 3. Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1712 1778) 4. Baron de Montesquieu (1689 1755) State of Nature- Nature is governed by laws such
Four ENLIGHTENMENT THINKERS 1. Thomas Hobbes (1588 1679) 2. John Locke (1632 1704) 3. Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1712 1778) 4. Baron de Montesquieu (1689 1755) State of Nature- Nature is governed by laws such
Handout B: Madison EXCERPTS FROM FEDERALIST NO. 47 BY JAMES MADISON. DOCUMENTS of FREEDOM History, Government & Economics through Primary Sources
 DOCUMENTS of FREEDOM History, Government & Economics through Primary Sources Unit 2: The Purpose of Government Reading: Separation of Powers and Checks and Balances Activity: Montesquieu and Madison Handout
DOCUMENTS of FREEDOM History, Government & Economics through Primary Sources Unit 2: The Purpose of Government Reading: Separation of Powers and Checks and Balances Activity: Montesquieu and Madison Handout
Honors US Government & Politics Summer Assignment, 2017
 Honors US Government & Politics Summer Assignment, 2017 Books, etc. 1. Hardball, Chris Mathews. Simon & Schuster, paper. ISBN: 978-0684845593 2. A Guide to the United States Constitution, Ackerman, Ginsburg.
Honors US Government & Politics Summer Assignment, 2017 Books, etc. 1. Hardball, Chris Mathews. Simon & Schuster, paper. ISBN: 978-0684845593 2. A Guide to the United States Constitution, Ackerman, Ginsburg.
Thomas Hobbes. Station 1. Where is he from? What is his view of people (quote examples from Leviathan)?
 Station 1 Thomas Hobbes Where is he from? What is his view of people (quote examples from Leviathan)? What is his view of government (quote examples from Leviathan)? Who would be most likely to like Hobbes
Station 1 Thomas Hobbes Where is he from? What is his view of people (quote examples from Leviathan)? What is his view of government (quote examples from Leviathan)? Who would be most likely to like Hobbes
The Second Treatise on Government
 11 The Second Treatise on Government JOHN LOCKE z BACKGROUND INFORMATION John Locke was an Enlightenment thinker who argued that society was deliberately created and served rational purposes. Like Aristotle,
11 The Second Treatise on Government JOHN LOCKE z BACKGROUND INFORMATION John Locke was an Enlightenment thinker who argued that society was deliberately created and served rational purposes. Like Aristotle,
Excerpt From Brutus Essay #1
 Excerpt From Brutus Essay #1 Among the most important of the Anti-Federalist essays is those of Brutus, whose essays were first published in the New York Journal. Brutus, whose identity has never been
Excerpt From Brutus Essay #1 Among the most important of the Anti-Federalist essays is those of Brutus, whose essays were first published in the New York Journal. Brutus, whose identity has never been
Lesson 7 Enlightenment Ideas / Lesson 8 Founding Documents Views of Government. Topic 1 Enlightenment Movement
 Lesson 7 Enlightenment Ideas / Lesson 8 Founding Documents Views of Government Main Topic Topic 1 Enlightenment Movement Topic 2 Thomas Hobbes (1588 1679) Topic 3 John Locke (1632 1704) Topic 4 Charles
Lesson 7 Enlightenment Ideas / Lesson 8 Founding Documents Views of Government Main Topic Topic 1 Enlightenment Movement Topic 2 Thomas Hobbes (1588 1679) Topic 3 John Locke (1632 1704) Topic 4 Charles
Two Views on Government
 The Enlightenment Two Views on Government Social Contract Hobbes believes that people need a strong government to keep order Leviathan (1651) Observed the horrors of the English Civil War Natural Rights
The Enlightenment Two Views on Government Social Contract Hobbes believes that people need a strong government to keep order Leviathan (1651) Observed the horrors of the English Civil War Natural Rights
Warm-Up: Read the following document and answer the comprehension questions below.
 Lowenhaupt 1 Enlightenment Objective: What were some major ideas to come out of the Enlightenment? How did the thinkers of the Enlightenment change or impact society? Warm-Up: Read the following document
Lowenhaupt 1 Enlightenment Objective: What were some major ideas to come out of the Enlightenment? How did the thinkers of the Enlightenment change or impact society? Warm-Up: Read the following document
Unit 1 Guided Notes: Foundations of Government
 Name: Date: Block: Unit 1: 5 Days (08/01 08/07) Unit 1 Quiz: 08/03 Unit 1 Test: 08/07 Standards for Unit 1: SSGSE 1: Compare and contrast various systems of government. a. Determine how governments differ
Name: Date: Block: Unit 1: 5 Days (08/01 08/07) Unit 1 Quiz: 08/03 Unit 1 Test: 08/07 Standards for Unit 1: SSGSE 1: Compare and contrast various systems of government. a. Determine how governments differ
Table of Contents iii Introduction iv Foundations of U.S Citizen Participation, Campaigns, and E
 AMERICAN GOVERNMENT Gretchen McNulty Table of Contents iii Introduction................................. iv Foundations of U.S................... 1 Citizen Participation, Campaigns, and Elections........
AMERICAN GOVERNMENT Gretchen McNulty Table of Contents iii Introduction................................. iv Foundations of U.S................... 1 Citizen Participation, Campaigns, and Elections........
The Origins of political thought and the Constitution
 The Origins of political thought and the Constitution Social Contract Theory The implied agreement between citizens and the gov t saying that citizens will obey the gov t and give up certain freedoms in
The Origins of political thought and the Constitution Social Contract Theory The implied agreement between citizens and the gov t saying that citizens will obey the gov t and give up certain freedoms in
The Founders Library Books
 The Founders Library Books An Essay Concerning Human Understanding, John Locke, 1690 Locke thinks that human nature is a blank slate on which the environment operates. He states that individuals are responsible
The Founders Library Books An Essay Concerning Human Understanding, John Locke, 1690 Locke thinks that human nature is a blank slate on which the environment operates. He states that individuals are responsible
1. McCulloch#v.#Maryland#(1819)# 17. Regents#of#California#v.#Bakke#(1978)# 2. Gibbons#v.#Ogden#(1824)# 18. Schenck#v.#United#States#(1919)#
 APGovernmentandPolitics SummerAssignment201592016 APGovernmentandPoliticsrequiresdifferentthinkingandwritingskillsthanyouusedinU.S.History.Writingfor governmentrequirestheunderstandingandanalysisofabstractconceptsandprinciples.youwilldependlesson
APGovernmentandPolitics SummerAssignment201592016 APGovernmentandPoliticsrequiresdifferentthinkingandwritingskillsthanyouusedinU.S.History.Writingfor governmentrequirestheunderstandingandanalysisofabstractconceptsandprinciples.youwilldependlesson
Essential Question: What were the key ideas of the Enlightenment?
 Essential Question: What were the key ideas of the Enlightenment? Warm-Up Question: What do you not like about Duluth High? What suggestions do you have to make this school better? From 1650 to 1800, European
Essential Question: What were the key ideas of the Enlightenment? Warm-Up Question: What do you not like about Duluth High? What suggestions do you have to make this school better? From 1650 to 1800, European
AP Government Summer Work Assignment
 AP Government 2016-17 Summer Work Assignment AP U.S. Government is a one-semester class covering seven conceptual units that build a foundational understanding of the formation, workings, and nuances of
AP Government 2016-17 Summer Work Assignment AP U.S. Government is a one-semester class covering seven conceptual units that build a foundational understanding of the formation, workings, and nuances of
Section One. A) The Leviathan B) Two Treatises of Government C) Spirit of the Laws D) The Social Contract
 Government Exam Study Guide You will need to be prepared to answer/discuss any of these questions on the exam in various formats. We will complete this study guide in class and review it. Section One 1)
Government Exam Study Guide You will need to be prepared to answer/discuss any of these questions on the exam in various formats. We will complete this study guide in class and review it. Section One 1)
Why. Government? What are the pros & cons of a government? Why do we need one? What is it for? Could we do without?
 Why do we need one? Why What is it for? What are the pros & cons of a government? Could we do without? Government? How did we setup a government? What happens if we don t have one? Why Government? HOBBES,
Why do we need one? Why What is it for? What are the pros & cons of a government? Could we do without? Government? How did we setup a government? What happens if we don t have one? Why Government? HOBBES,
The Enlightenment. The Age of Reason
 The Enlightenment The Age of Reason Social Contract Theory is the view that persons' moral and/or political obligations are dependent upon a contract or agreement among them to form the society in which
The Enlightenment The Age of Reason Social Contract Theory is the view that persons' moral and/or political obligations are dependent upon a contract or agreement among them to form the society in which
Could the American Revolution Have Happened Without the Age of Enlightenment?
 Could the American Revolution Have Happened Without the Age of Enlightenment? Philosophy in the Age of Reason Annette Nay, Ph.D. Copyright 2001 In 1721 the Persian Letters by Charles de Secondat and Baron
Could the American Revolution Have Happened Without the Age of Enlightenment? Philosophy in the Age of Reason Annette Nay, Ph.D. Copyright 2001 In 1721 the Persian Letters by Charles de Secondat and Baron
Enlightenment with answers Which statement represents a key idea directly associated with John Locke s Two Treatises of
 Enlightenment with answers 1. 2 Supported reforms Believed in natural rights and religious toleration Viewed themselves as servants of their state In the 18th century, European leaders that fit these characteristics
Enlightenment with answers 1. 2 Supported reforms Believed in natural rights and religious toleration Viewed themselves as servants of their state In the 18th century, European leaders that fit these characteristics
Separation of Powers: History and Theory
 Separation of Powers: History and Theory James E. Hanley Published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International license. This work may be freely reproduced for non-commercial
Separation of Powers: History and Theory James E. Hanley Published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International license. This work may be freely reproduced for non-commercial
Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. World History Revolution and Industrialization Blizzard Bag
 Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. World History Revolution and Industrialization Blizzard Bag 2014-2015 The Opium Wars were fought between Britain and China from 1839 to 1860. The wars began
Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. World History Revolution and Industrialization Blizzard Bag 2014-2015 The Opium Wars were fought between Britain and China from 1839 to 1860. The wars began
1.1 Foundations and Constitution. Mr. Desjarlais Allatoona High School
 1.1 Foundations and Constitution Mr. Desjarlais Allatoona High School Standards SSCG1: Compare and contrast various systems of government. SSCG1a: Determine how governments differ in geographic distribution
1.1 Foundations and Constitution Mr. Desjarlais Allatoona High School Standards SSCG1: Compare and contrast various systems of government. SSCG1a: Determine how governments differ in geographic distribution
Rousseau, On the Social Contract
 Rousseau, On the Social Contract Introductory Notes The social contract is Rousseau's argument for how it is possible for a state to ground its authority on a moral and rational foundation. 1. Moral authority
Rousseau, On the Social Contract Introductory Notes The social contract is Rousseau's argument for how it is possible for a state to ground its authority on a moral and rational foundation. 1. Moral authority
Declaration of Independence
 Declaration of Independence Reasons for Independence Over 100 years of the policy of salutary neglect by the British government (relaxed policies, allowed for self government in the colonies) French and
Declaration of Independence Reasons for Independence Over 100 years of the policy of salutary neglect by the British government (relaxed policies, allowed for self government in the colonies) French and
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX: HISTORY CHAPTER: 01: FRENCH REVOLUTION
 INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX: HISTORY CHAPTER: 01: FRENCH REVOLUTION WORKSHEET: 06 1 Discuss the condition of the Monarchy in France on the eve of the Revolution
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX: HISTORY CHAPTER: 01: FRENCH REVOLUTION WORKSHEET: 06 1 Discuss the condition of the Monarchy in France on the eve of the Revolution
****SS.7.C.1.1 The Enlightenment****
 ****SS.7.C.1.1 The Enlightenment**** ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: identify and describe the Enlightenment ideas of separation of powers, natural law, and social contract.
****SS.7.C.1.1 The Enlightenment**** ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: identify and describe the Enlightenment ideas of separation of powers, natural law, and social contract.
THE VIRGINIA DECLARATION OF RIGHTS
 THE VIRGINIA DECLARATION OF RIGHTS The Federalist Papers Project www.thefederalistpapers.org A declaration of rights made by the representatives of the good people of Virginia, assembled in full and free
THE VIRGINIA DECLARATION OF RIGHTS The Federalist Papers Project www.thefederalistpapers.org A declaration of rights made by the representatives of the good people of Virginia, assembled in full and free
Chapter 2:4 Constitutional Convention
 Chapter 2:4 Constitutional Convention Psa_119:165 Great peace have they which love thy law: and nothing shall offend them. Objectives: 2:4 Our Political Beginnings o Students will examine the process that
Chapter 2:4 Constitutional Convention Psa_119:165 Great peace have they which love thy law: and nothing shall offend them. Objectives: 2:4 Our Political Beginnings o Students will examine the process that
****SS.7.C.1.1 The Enlightenment****
 ****SS.7.C.1.1 The Enlightenment**** ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: identify and describe the Enlightenment ideas of separation of powers, natural law, and social contract.
****SS.7.C.1.1 The Enlightenment**** ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: identify and describe the Enlightenment ideas of separation of powers, natural law, and social contract.
Common Core Lesson Plan
 Common Core Lesson Plan Topic: Locke s 2 nd Treatise of Government Title: The Role of Government Resources (primary resource documents, artifacts, material needs, etc.) Excerpts of Locke s 2 nd Treatise
Common Core Lesson Plan Topic: Locke s 2 nd Treatise of Government Title: The Role of Government Resources (primary resource documents, artifacts, material needs, etc.) Excerpts of Locke s 2 nd Treatise
E5 Human Rights Policy. Kelda s Human Rights policy applies to every Kelda employee and is based on the following key principles:
 E5 Kelda s Human Rights policy applies to every Kelda employee and is based on the following key principles: A recognition of international human rights, as set out in the International Bill of Human Rights,
E5 Kelda s Human Rights policy applies to every Kelda employee and is based on the following key principles: A recognition of international human rights, as set out in the International Bill of Human Rights,
Do Now. Review Thomas Paine s Common Sense questions.
 Do Now Review Thomas Paine s Common Sense questions. IB History Paper 1 Question 1 a): worth 3 marks, spend max 5 minutes on. Understanding historical sources - reading comprehension. For 3 marks, give
Do Now Review Thomas Paine s Common Sense questions. IB History Paper 1 Question 1 a): worth 3 marks, spend max 5 minutes on. Understanding historical sources - reading comprehension. For 3 marks, give
Constitutional Foundations
 CHAPTER 2 Constitutional Foundations CHAPTER OUTLINE I. The Setting for Constitutional Change II. The Framers III. The Roots of the Constitution A. The British Constitutional Heritage B. The Colonial Heritage
CHAPTER 2 Constitutional Foundations CHAPTER OUTLINE I. The Setting for Constitutional Change II. The Framers III. The Roots of the Constitution A. The British Constitutional Heritage B. The Colonial Heritage
General and Positive Rights
 General and Positive Rights Fundamental Divide I think the fundamental difference, the difference that defines the difference between American, Anglo-American conservatives and European welfare states,
General and Positive Rights Fundamental Divide I think the fundamental difference, the difference that defines the difference between American, Anglo-American conservatives and European welfare states,
The Enlightenment. Transition from the Scientific Revolution to new ideas in Philosophy, Art, Economics,& Government
 The Enlightenment Transition from the Scientific Revolution to new ideas in Philosophy, Art, Economics,& Government Effects of the Scientific Revolution nduring the Scientific Revolution, people began
The Enlightenment Transition from the Scientific Revolution to new ideas in Philosophy, Art, Economics,& Government Effects of the Scientific Revolution nduring the Scientific Revolution, people began
U1 Pledge of Allegiance, Forms of Government, Political Philosophers
 U1 Pledge of Allegiance, Forms of Government, Political Philosophers SSCG1 Compare and contrast various systems of government. a.determine how governments differ in geographic distribution of power, particularly
U1 Pledge of Allegiance, Forms of Government, Political Philosophers SSCG1 Compare and contrast various systems of government. a.determine how governments differ in geographic distribution of power, particularly
Creating the U.S. Constitution
 Creating the U.S. Constitution Essential Question How did the Americans create a national (federal) government that respected both the independence of the states and the rights of the individuals? Name:
Creating the U.S. Constitution Essential Question How did the Americans create a national (federal) government that respected both the independence of the states and the rights of the individuals? Name:
Forming a New Government
 Forming a New Government FORMING A NEW HIGH SCHOOL Imagine that you re building and opening up a new high school for next year. Create a plan for forming your new high school. With your partner, address
Forming a New Government FORMING A NEW HIGH SCHOOL Imagine that you re building and opening up a new high school for next year. Create a plan for forming your new high school. With your partner, address
FRENCH REVOLUTION. A Child of the Enlightenment
 FRENCH REVOLUTION A Child of the Enlightenment What was the Enlightenment? After the Scientific Revolution, people began to question HOW A RULER GOT HIS POWER AND WHY A GOVERNMENT WAS SET UP The Key word
FRENCH REVOLUTION A Child of the Enlightenment What was the Enlightenment? After the Scientific Revolution, people began to question HOW A RULER GOT HIS POWER AND WHY A GOVERNMENT WAS SET UP The Key word
Thomas Hobbes v. John Locke
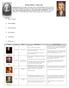 Thomas Hobbes v. John Locke Background: Thomas Hobbes and John Locke were philosophers that wrote about government and theorized about man in the state of nature. They both talked about man s nature and
Thomas Hobbes v. John Locke Background: Thomas Hobbes and John Locke were philosophers that wrote about government and theorized about man in the state of nature. They both talked about man s nature and
AP Government Summer Assignment
 AP Government Summer Assignment AP United States Government and Politics requires all enrolled students to complete summer coursework prior to the the first day of class. Though your class begins in August,
AP Government Summer Assignment AP United States Government and Politics requires all enrolled students to complete summer coursework prior to the the first day of class. Though your class begins in August,
John Locke Natural Rights- Life, Liberty, and Property Two Treaties of Government
 Enlightenment Enlightenment 1500s Enlightenment was the idea that man could use logic and reason to solve the social problems of the day. Philosophers spread this idea of logic and reason to the people
Enlightenment Enlightenment 1500s Enlightenment was the idea that man could use logic and reason to solve the social problems of the day. Philosophers spread this idea of logic and reason to the people
Running Head: Articles of the Confederation and the new Constitution of
 Running Head: Articles of the Confederation and the new Constitution of 1787. 1 Customer inserts his/ her name: Customer inserts his/her course/grade: Customer Inserts name of instructor: History 2 Topic:
Running Head: Articles of the Confederation and the new Constitution of 1787. 1 Customer inserts his/ her name: Customer inserts his/her course/grade: Customer Inserts name of instructor: History 2 Topic:
Jean-Jacques Rousseau ( )
 Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1712-1778) Jean-Jacques Rousseau was born in Geneva, Switzerland. He moved to Paris as a young man to pursue a career as a musician. Instead, he became famous as one of the greatest
Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1712-1778) Jean-Jacques Rousseau was born in Geneva, Switzerland. He moved to Paris as a young man to pursue a career as a musician. Instead, he became famous as one of the greatest
2. According to Pope, what message do voters declare as they vote?
 A Promised Land 1. According to Elder Holland, America may be seen as a sacred place. What determines whether a location is sacred or profane? What must be done in order to maintain a location s sacred
A Promised Land 1. According to Elder Holland, America may be seen as a sacred place. What determines whether a location is sacred or profane? What must be done in order to maintain a location s sacred
Niccolò Machiavelli ( )
 Niccolò Machiavelli (1469-1527) Niccolò Machiavelli, (born May 3, 1469 in Florence, Italy ) was a famous Italian Renaissance political philosopher and statesman, secretary of the Florentine republic. He
Niccolò Machiavelli (1469-1527) Niccolò Machiavelli, (born May 3, 1469 in Florence, Italy ) was a famous Italian Renaissance political philosopher and statesman, secretary of the Florentine republic. He
Unit 2: Age of Revolutions Review. 1st Semester Final Exam Review
 Unit 2: Age of Revolutions Review 1st Semester Final Exam Review The Enlightenment The Enlightenment was an age of reason in which philosophes shared ideas about reason, government, and human nature. Major
Unit 2: Age of Revolutions Review 1st Semester Final Exam Review The Enlightenment The Enlightenment was an age of reason in which philosophes shared ideas about reason, government, and human nature. Major
The classroom teacher may reproduce materials in this book for classroom use only. The reproduction of any part for an entire school or school system
 AMERICAN GOVERNMENT Gretchen McNulty The classroom teacher may reproduce materials in this book for classroom use only. The reproduction of any part for an entire school or school system is strictly prohibited.
AMERICAN GOVERNMENT Gretchen McNulty The classroom teacher may reproduce materials in this book for classroom use only. The reproduction of any part for an entire school or school system is strictly prohibited.
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Enlightenment Philosophy
 Enlightenment Philosophy Objectives Explain how science led to the Enlightenment. Compare the ideas of Hobbes and Locke. Identify the beliefs and contributions of the philosophes. Summarize how economic
Enlightenment Philosophy Objectives Explain how science led to the Enlightenment. Compare the ideas of Hobbes and Locke. Identify the beliefs and contributions of the philosophes. Summarize how economic
Excerpts from Brutus No. 1
 DOCUMENTS of FREEDOM History, Government & Economics through Primary Sources Primary Source: Excerpts from Brutus No. 1, Annotated Excerpts from Brutus No. 1 18 October 1787 To the Citizens of the State
DOCUMENTS of FREEDOM History, Government & Economics through Primary Sources Primary Source: Excerpts from Brutus No. 1, Annotated Excerpts from Brutus No. 1 18 October 1787 To the Citizens of the State
the birth of FREEDOM The Bill of Rights Institute M U S E U M C O N N E C T I O N C R I T I C A L E N G AG E M E N T Q U E S T I O N OV E R V I E W
 the birth of FREEDOM C R I T I C A L E N G AG E M E N T Q U E S T I O N What ideas about rights and freedom interested people before the United States was founded? OV E R V I E W The tree of freedom has
the birth of FREEDOM C R I T I C A L E N G AG E M E N T Q U E S T I O N What ideas about rights and freedom interested people before the United States was founded? OV E R V I E W The tree of freedom has
THE PLURINATIONAL STATE OF BOLIVIA Embassy of The Hague The Netherlands
 THE PLURINATIONAL STATE OF BOLIVIA Embassy of The Hague The Netherlands INFORMATION ON THE PLAN OF ACTION FOR ACHIEVING UNIVERSALITY AND FULL IMPLEMENTATION OF THE ROME STATUTE I. BACKGROUND The International
THE PLURINATIONAL STATE OF BOLIVIA Embassy of The Hague The Netherlands INFORMATION ON THE PLAN OF ACTION FOR ACHIEVING UNIVERSALITY AND FULL IMPLEMENTATION OF THE ROME STATUTE I. BACKGROUND The International
John Locke (29 August, October, 1704)
 John Locke (29 August, 1632 28 October, 1704) John Locke was English philosopher and politician. He was born in Somerset in the UK in 1632. His father had enlisted in the parliamentary army during the
John Locke (29 August, 1632 28 October, 1704) John Locke was English philosopher and politician. He was born in Somerset in the UK in 1632. His father had enlisted in the parliamentary army during the
American Studies First Benchmark Assessment
 American Studies First Benchmark Assessment 2015-2016 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 A federal government is one in which A all power is
American Studies First Benchmark Assessment 2015-2016 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 A federal government is one in which A all power is
Locke. Locke s State of Nature
 Locke 1 Locke s State of Nature Natural condition of humankind is a state of complete liberty Free to conduct one s life as one sees fit Free from interference from others Living among others according
Locke 1 Locke s State of Nature Natural condition of humankind is a state of complete liberty Free to conduct one s life as one sees fit Free from interference from others Living among others according
Leviathan by Thomas Hobbes
 Leviathan by Thomas Hobbes Published in 1651, Thomas Hobbes s book Leviathan discusses the structure of society and legitimate government. In this excerpt from the book, Hobbes describes his idea of a
Leviathan by Thomas Hobbes Published in 1651, Thomas Hobbes s book Leviathan discusses the structure of society and legitimate government. In this excerpt from the book, Hobbes describes his idea of a
Answer the following in your notebook:
 The Enlightenment Answer the following in your notebook: Explain to what extent you agree with the following: 1. At heart people are generally rational and make well considered decisions. 2. The universe
The Enlightenment Answer the following in your notebook: Explain to what extent you agree with the following: 1. At heart people are generally rational and make well considered decisions. 2. The universe
Republican Motherhood
 Republican Motherhood A Crisis of Republican Virtue After the Revolutionary War, how would new Americans born into this country develop civic virtue? How would America instill proper republican values
Republican Motherhood A Crisis of Republican Virtue After the Revolutionary War, how would new Americans born into this country develop civic virtue? How would America instill proper republican values
Unit Portfolio: DBQ-Political Cartoons 15. What is happening in this cartoon? 16. What point is the cartoonist trying to make?
 Unit Portfolio: DBQ-Political Cartoons 15. What is happening in this cartoon? 16. What point is the cartoonist trying to make? Unit 2: Age of Reason Lesson 3: Enlightenment Textbook Correlation: Chapter
Unit Portfolio: DBQ-Political Cartoons 15. What is happening in this cartoon? 16. What point is the cartoonist trying to make? Unit 2: Age of Reason Lesson 3: Enlightenment Textbook Correlation: Chapter
Primary Source Activity: Freedom, Equality, Justice, and the Social Contract Connecting Locke s Ideas to Our Founding Documents
 Primary Source Activity: Freedom, Equality, Justice, and the Social Contract Connecting Locke s Ideas to Our Founding Documents The second step in our Primary Source Activity involves connecting the central
Primary Source Activity: Freedom, Equality, Justice, and the Social Contract Connecting Locke s Ideas to Our Founding Documents The second step in our Primary Source Activity involves connecting the central
Chapter 7 Creating a Republic Notes and Class Activities Packet
 Name: Class: Chapter 7 Creating a Republic 1776-1790 Notes and Class Activities Packet CHAPTER 7Vocabulary Top Ten Vocabulary: These words are in light blue in your book. Remember to write a complete definition
Name: Class: Chapter 7 Creating a Republic 1776-1790 Notes and Class Activities Packet CHAPTER 7Vocabulary Top Ten Vocabulary: These words are in light blue in your book. Remember to write a complete definition
Bill S-8 Bill S-11. An Act respecting the safety of drinking water on First Nation lands
 Clause by Clause Comparison: Bill S-8, An Act respecting the safety of drinking water on First Nation lands (February 29, 2012) and Bill S-11, An Act respecting the safety of drinking water on first nation
Clause by Clause Comparison: Bill S-8, An Act respecting the safety of drinking water on First Nation lands (February 29, 2012) and Bill S-11, An Act respecting the safety of drinking water on first nation
Enlightenment & America
 Enlightenment & America Our Political Beginnings What is a Government? Defined: The institution through which a society makes and enforces its public policies. It is made up of those people who exercise
Enlightenment & America Our Political Beginnings What is a Government? Defined: The institution through which a society makes and enforces its public policies. It is made up of those people who exercise
Political Science 103 Spring, 2018 Dr. Edward S. Cohen INTRODUCTION TO POLITICAL PHILOSOPHY
 Political Science 103 Spring, 2018 Dr. Edward S. Cohen INTRODUCTION TO POLITICAL PHILOSOPHY This course provides an introduction to some of the basic debates and dilemmas surrounding the nature and aims
Political Science 103 Spring, 2018 Dr. Edward S. Cohen INTRODUCTION TO POLITICAL PHILOSOPHY This course provides an introduction to some of the basic debates and dilemmas surrounding the nature and aims
Political Obligation. Dr Simon Beard. Centre for the Study of Existential Risk
 Political Obligation Dr Simon Beard sjb316@cam.ac.uk Centre for the Study of Existential Risk Summary of this lecture What is the aim of these lectures and what are they about? If morality is a social
Political Obligation Dr Simon Beard sjb316@cam.ac.uk Centre for the Study of Existential Risk Summary of this lecture What is the aim of these lectures and what are they about? If morality is a social
Scientific Revolution/Enlightenment Test Review
 Scientific Revolution/Enlightenment Test Review Global History II The authority figures (those in charge) during the 1500-1700s was the Roman Catholic Church and/or absolute monarchs. They came under attack
Scientific Revolution/Enlightenment Test Review Global History II The authority figures (those in charge) during the 1500-1700s was the Roman Catholic Church and/or absolute monarchs. They came under attack
Section 1 What ideas gave birth to the world s first democratic nation?
 After reading answer the questions that follow The Roots of American Democracy Section 1 What ideas gave birth to the world s first democratic nation? Bicentennial celebrations, 1976 On July 4, 1976, Americans
After reading answer the questions that follow The Roots of American Democracy Section 1 What ideas gave birth to the world s first democratic nation? Bicentennial celebrations, 1976 On July 4, 1976, Americans
Political Science 103 Fall, 2015 Dr. Edward S. Cohen INTRODUCTION TO POLITICAL PHILOSOPHY
 Political Science 103 Fall, 2015 Dr. Edward S. Cohen INTRODUCTION TO POLITICAL PHILOSOPHY This course provides an introduction to some of the basic debates and dilemmas surrounding the nature and aims
Political Science 103 Fall, 2015 Dr. Edward S. Cohen INTRODUCTION TO POLITICAL PHILOSOPHY This course provides an introduction to some of the basic debates and dilemmas surrounding the nature and aims
THE FRENCH REVOLUTION
 THE FRENCH REVOLUTION 1) WHEN WAS THE FORTRESS PRISON BASTILLE STORMED? WHAT DID BASTILLE STAND FOR? On the morning of 14th July 1789, Bastille was stormed by a group of several hundred people. It stood
THE FRENCH REVOLUTION 1) WHEN WAS THE FORTRESS PRISON BASTILLE STORMED? WHAT DID BASTILLE STAND FOR? On the morning of 14th July 1789, Bastille was stormed by a group of several hundred people. It stood
Philosophers that Influenced American Government
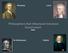 Rousseau Locke Philosophers that Influenced American Government De Montesquieu Hobbes Basic Ideals and Principles of Democracy Consent of the Governed Government gets its power from the people they govern
Rousseau Locke Philosophers that Influenced American Government De Montesquieu Hobbes Basic Ideals and Principles of Democracy Consent of the Governed Government gets its power from the people they govern
Creating a New Form of Government
 Analyzing the Influences of the Enlightenment on the U.S. Constitution Baron von Montesquieu The Spirit of Laws (1748) Book XI To Prevent their abuse, it is necessary from the very nature of things that
Analyzing the Influences of the Enlightenment on the U.S. Constitution Baron von Montesquieu The Spirit of Laws (1748) Book XI To Prevent their abuse, it is necessary from the very nature of things that
Spirit of the Law Letter of the Law Faithful Ministry of the Spirit and Letter of the Law
 The Declaration of Independence, Washington s Farewell Address, and the Constitution of the United States, should be studied by the youth of our country, as their political scriptures.... Emma Willard,
The Declaration of Independence, Washington s Farewell Address, and the Constitution of the United States, should be studied by the youth of our country, as their political scriptures.... Emma Willard,
Essential Question: What were the key ideas of the Enlightenment?
 Essential Question: What were the key ideas of the Enlightenment? Warm-Up Question: What do you not like about South Cobb High? What suggestions do you have to make this school better? From 1650 to 1800,
Essential Question: What were the key ideas of the Enlightenment? Warm-Up Question: What do you not like about South Cobb High? What suggestions do you have to make this school better? From 1650 to 1800,
The Social Contract. Jean-Jacques Rousseau
 The Social Contract Jean-Jacques Rousseau Copyright Jonathan Bennett 2017. All rights reserved [Brackets] enclose editorial explanations. Small dots enclose material that has been added, but can be read
The Social Contract Jean-Jacques Rousseau Copyright Jonathan Bennett 2017. All rights reserved [Brackets] enclose editorial explanations. Small dots enclose material that has been added, but can be read
The Age of Revolution
 The Age of Revolution Timeline Essential Questions Map Age of Reason Scientific Revolution The Enlightenment Enlightened Writers Enlightened Despots Political Revolutions American French Latin American
The Age of Revolution Timeline Essential Questions Map Age of Reason Scientific Revolution The Enlightenment Enlightened Writers Enlightened Despots Political Revolutions American French Latin American
