Rise of the Qin. ! The Qin developed a very effective military state during the Warring States period.
|
|
|
- Julia Sharp
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Classical China
2 Rise of the Qin! The Qin developed a very effective military state during the Warring States period.! The developed a system in which the whole society was mobilized and directed towards the objective of expanding Qin power and conquering other states.! These ideas were first formulated into a political philosophy with emphasis on laws by Shang Yang who was the chief minister of the Qin.
3 Legalism! Han Fei developed these ideas further adding an emphasis on rewards and punishments. Creating the official legalist doctrine! Qin rulers implemented harsh punishments for crime that were universal for all classes of society.
4
5 The Qin Dynasty! The Qin replaced the Zhou Dynasty it employed Legalist ideas to subdue the warring states.! In 221 the the Qin ruler assumed the name Shi Huangdi, which means First Emperor.! Shi Huangdi halted internal battles, defeated invaders, and crushed all resistance to his rule within China.
6 Political opposition! Shi Huangdi employed a policy he call strengthening the trunk and weakening the branches! He commanded all noble families to live in the capital city under his suspicious gaze. This policy uprooted 120,000 noble families.! Seizing their land, the emperor carved China into 36 administrative districts. He sent Qin officials to control them.
7 Qin rule! To prevent criticism, in 214 BCE. Shi Huangdi and his prime minister murdered hundreds of Confucian scholars.! They also burned books of Confucian thinkers and poets.! Shi Huangdi established an autocracy a government that has unlimited power and uses it in an arbitrary manner.
8 The Burning of books and the Burying of Scholars
9 Qin Social Advances Shi Huangdi built a highway network more than 4,000 miles long. He set standards throughout China for writing, law, currency, and weights and measures. Under Shi Huangdi irrigation projects increased farm production and trade blossomed because of the roads system. Trade made the new class of merchants wealthy harsh taxes and repressive government made the Qin regime unpopular
10 The Great Wall! The Great Wall of China arose on the backs of hundreds of thousands of peasants.! The wall builders worked neither for wages nor for love of empire. They faced a terrible choice: work on the wall or die.! Many of the laborers worked on the wall and died anyway, victims of the crushing labor or the harsh winter weather.
11 The Great Wall of China From the Yellow Sea in the east to the Gobi Desert in the west, the Great Wall twisted like a dragon s tail for thousands of miles. Watch towers rose every 200 to 300 yards along the wall. In the time of Shi Huangdi, hundreds of thousands of peasants collected, hauled, and dumped millions of tons of stone, dirt, and rubble to fill the core of the Great Wall. Slabs of cut stone on the outside of the wall enclosed a heap of pebbles and rubble on the inside. Each section of the wall rose to a height of 20 to 25 feet. N 40 The Qin Dynasty, B.C. MONGOLIA KOREA (Approximate) Anyang n g Great Wall He 100 E Qin Dynasty Extent of Zhou Dynasty 0 g 1000 Kilometers TIBET IM AL AYA Ch an gj i Taiwan S Jiang i H East China Sea 120 SKILLBUILDER: Interpreting Visual Sources Luoyang Hao Ch'ang-an (Xi'an) Yellow Sea an Although Shi Huangdi built the earliest unified wall, the wall as it exists today dates from the later Ming Dynasty ( ). e W ei H 500 Miles 0 a Hu N
12 The Fall of the Qin! Three years after the second Qin emperor took office peasants rebelled.! Shi Huangdi s son wasn t a strong ruler and could not suppress these rebellions.! By 202 B.C.E. the Qin gave way to the Han Dynasty
13 Han Dynasty! in 202 B.C. Liu Bang declared himself the first emperor of the Han Dynasty, which ruled China for more than 400 years.! The Han is divided into two periods the former Han ruled for two roughly two centuries until 9 C.E.! After a brief period when the Han were out of power, the Later Han ruled for almost another two centuries.
14 Han China! Lui Bang followed Shi Huangdi s policy of establishing a strong central government.! He destroyed rival kings power and set up a government in which central authority controls the running of the states.! He established hundreds of local provincials called commanderies.
15 Liu Bang! In the western half of the empire Liu Bang appoints officials that governed over provincial territories.! In the East military leaders controlled territories autonomously.! Liu Bang won popular support by departing from the strict legalist practices of Shi Huangdi.! He lowered taxes and softened harsh punishments.
16 Consolidation! By the early 2 nd century BCE. Independently controlled eastern territories became unruly.! Liu family manipulates these leaders against each other and slowly integrates these territories into the imperial system.! By 150 BCE. All eastern territories are under direct imperial authority.
17 Empress Lu! After Liu Bang s death one of his wives seized control through her son.! She outlived her son and retained control by naming an infant king.! Empress Lu was the first female ruler of the Empire
18 The Martial Emperor! Wudi reigned from 141 B.C.E. to 87 B.C.E. Longer than any other Han Emperor.! He was called the Martial Emperor because he adopted the policy of expanding the empire through warfare.! He saw the state as an instrument for good and believed the government should be used to solve problems.! He created Government monopolies on critical commodities like salt alcohol, and iron to regulate pricing against private interest.
19 Confucianism! Mostly, Chinese emperors rewarded loyal followers with government posts.! Others obtained Gov t post by testing their knowledge of Confucianism.! Wudi set up a school where hopeful job applicants from all over China could come to study Confucius s works.
20 Xiongnu! The Xiongnu were fierce nomads that often raided Han s northern territory.! The early Han emperors tried to buy off the Xiongnu by sending them thousands of pounds of silk, rice, alcohol, and money.! When Wudi realized that the bribes were simply making the Xiongnu stronger, he sent more than 100,000 soldiers to fight them.
21 The early Han emperors tried to buy off the Xiongnu by sending them thousands of pounds of silk, rice, alcohol, and money. Usually, the Xiongnu just accepted these gifts and continued their raids. 80 E du sr Dunhuang KA N TAKLIMART DESE T JAPAN an l l o g He w R.) 60 E Kashgar PERSIA ER Yellow Sea H u( Y e. ASIA Lanzhou E 140 Merv E MONGOLIA DES GOBI Kuqa Ctesiphon E Han Dynasty, 200 B.C. A.D. 220 N 40 Luoyang Ch'ang-an Nanjing (Xi'an) H Luoyang ua ll o ng H wr e.) ASIA H e Y Ch'ang-an ( IM AL J z e ian R. g ) Former Han, 200 B.C. AYAS Nanhai (Guangzhou) Ganges R. Pataliputra Yellow Sea (Xi'an) 0 ng Jia.) g R a n g tz e n a C (Y h PACIFIC OCEAN Miles 1,000 Kilometers South China Sea 0 PACIFIC OCEAN g an t Ch ang (Y 1,000 Miles 2,000 Kilometers South China Sea N Han Empire at its greatest extent, A.D. 220 Han protectorate (influence) Xiongnu regions Great Wall Silk Road GEOGRAPHY SKILLBUILDER: Interpreting Maps 1. Place What was the approximate size, in square miles, of the Han Empire at its greatest extent? 2. Location Along which border did the Chinese build the Great Wall? Why did they build it there and not in other places?
22 Change in Policy! Wudi s military adventures and centralized gov t cause severe economic strain on the empire! Han Wudi to finance his ventures he raised taxes confiscated land and personal property from wealthy individuals! After his death in his policies were challenged the Salt and Iron debates of 81 BCE. Led to the dismantling of government monopolies.
23 Wudi s successors! After Wudi s death the Imperial court becomes less engaged in the affairs of administration and leaves the administration of the empire to their officials.! Corruption and exploitation becomes rampant amongst these official who saw opportunities to gain wealth through their political influence.
24 Economic problems! By the first century BCE. Social and economic differences generated serious tensions.! Economic problems forced many small landowners to to sell their property under unfavorable conditions! By the end of the first century BCE land had accumulated in the hands of a relatively small group of individuals who owned vast estates! Poorer classes began to organize rebellions in hopes of attaining a greater share of Han resources.
25 Wang Mang! Wang Mang was a powerful and respected Han administrator.! He he served as regent in the early late first century CE. when a two year old boy inherited the Han imperial throne.! Wang Mang claimed the imperial throne in 9 ce.! Wang Mang tried to implement a system of land redistribution, which was largely up popular among landowners who rebelled infear of losing power.
26 Wang Mang! Wang Mang s life and dynasty were ended in 23 ce. After a coalition of disgruntled landlords and desperate peasants overthrew his empire.! Within two years the a recovered Han dynasty returned to power, but ruled over a much weaker realm.! This period is known as the Later Han
27 cture of d. At the onsidered governors,. They officials, heir red vital to sans and Emperor King Nobles & Scholars State Officials diers, who t the who were oto exhibit e pictures life. Go to Governor Peasants Artisans Merchants Soldiers Slaves
28 Han Gov t! The Han emperor s relied on a complex bureaucracy and a vast imperial army.! He levied taxes to raise money.! Chinese peasants owed part of their yearly crops to the government. Merchants also paid taxes.! Besides taxes, the peasants owed the government a month s worth of labor or military service every year.! With this source of labor, the Han emperors built roads and dug canals and irrigation ditches.
29 Technology! Paper was invented in A.D Before that, books were usually written on silk.! Another technological advance was the collar harness for horses.! The Chinese perfected a plow that was more efficient because it had two blades.! They also improved iron tools, invented the wheelbarrow, and began to use water mills to grind grain.
30 Agriculture and Commerce! During the Han Dynasty, the population of China swelled to 60 million, which created a large demand for agricultural products.! The government established monopolies on the mining of salt, the forging of iron, the minting of coins, and the brewing of alcohol.! Spurred by the worldwide demand for silk, Chinese commerce expanded along the Silk Roads to most of Asia and, through India, all the way to Rome.
31 Women in Han China! Ban Zhao also wrote a guide called Lessons for Women, which called upon women to be humble and obedient but also industrious.! Confucian teachings had dictated that women were to devote themselves to their families.! A few empresses wielded great power. Daoist and later, Buddhist nuns were able to gain an education and lead lives apart from their families.
32 Han decline! During the Han the system of rewarding officials for services in offices through grants of land becomes universal.! Soon individual estates compete in the market and a new aristocratic elite develops.! These aristocrats compete for power and influence within the Han Bureaucracy.
33 The Fall of the Han! According to custom, a family s land was divided equally among all of the father s male heirs.! Small farmers often went into debt and had to borrow money from large landowners, who charged very high interest rates. If the farmer couldn t pay back the debt, the landowner took possession of the farmer s land.! Large landowners were not required to pay taxes, so when their land holdings increased, the amount of land that was left for the government to tax decreased.
34 Decline! Military strongmen also wielded power and competed for influence within the Han Government.! These groups along with Eunuchs within the imperial court caused divisions within the Han government.! In addition Local landowners began to intensify their exploitation of the peasantry.! In 184CE. a major peasant revolt further weakened Imperial authority
35 The Yellow Turban Rebellion Causes: 1. high government taxes used to fund public works projects and garrisons along the Silk Road. 2. Exploitation by wealthy landowners 3. Agrarian crisis and famine in northern territories coupled with Floods along the Yellow River.
36 Outcome of Rebellion! Military gained a glorious victory however the cost was very high.! Government offices were destroyed, magistrates were killed and many districts were cut off from centralized rule.! Military and local leaders gained self-governing status which fueled later feuding and divisions within the empire
37 The Era of the three Kingdoms! In 220 the country divided into three kingdoms ruled independently.! This age is remembered for its great adventure and clever military strategy.
38
1. What were the 7 major states fighting for dominance in China? 2. What advantages did the Qin state have?
 The warring states period in China lasted from 475 when the Zhou Dynasty was divided until 221 1. What were the 7 major states fighting for dominance in China? 2. What advantages did the Qin state have?
The warring states period in China lasted from 475 when the Zhou Dynasty was divided until 221 1. What were the 7 major states fighting for dominance in China? 2. What advantages did the Qin state have?
SHANG DYNASTY BCE
 9/19/2017 SHANG DYNASTY 1766-1122BCE Create bronze tools, weapons, and walled cities, creating a militaristic tradition. Religious traditions are formed to unite the empire Rulers are guided by the
9/19/2017 SHANG DYNASTY 1766-1122BCE Create bronze tools, weapons, and walled cities, creating a militaristic tradition. Religious traditions are formed to unite the empire Rulers are guided by the
A review of China s first five dynasties
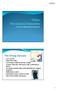 A review of China s first five dynasties The Shang Dynasty 1570 1045 BCE Yellow River Valley Use of tortoise shells for ancestor worship Warriors; built cities with massive walls (30 feet thick in places)
A review of China s first five dynasties The Shang Dynasty 1570 1045 BCE Yellow River Valley Use of tortoise shells for ancestor worship Warriors; built cities with massive walls (30 feet thick in places)
ANCIENT CHINESE DYNASTIES. Notes January 28, 2016
 ANCIENT CHINESE DYNASTIES Notes January 28, 2016 CHINA S FIRST DYNASTIES The Xia (SHAH) Dynasty and The Shang Dynasty The Xia (SHAH) Dynasty This idea of this dynasty has been passed down through Chinese
ANCIENT CHINESE DYNASTIES Notes January 28, 2016 CHINA S FIRST DYNASTIES The Xia (SHAH) Dynasty and The Shang Dynasty The Xia (SHAH) Dynasty This idea of this dynasty has been passed down through Chinese
Geography and Early China
 Geography and Early China China s geographical features separated it from the rest of the world. China is about the size of the United States. The Gobi Desert spreads across the North of China The plains
Geography and Early China China s geographical features separated it from the rest of the world. China is about the size of the United States. The Gobi Desert spreads across the North of China The plains
Classical China. From the Warring States to the Northern and Southern Dynasties
 Classical China From the Warring States to the Northern and Southern Dynasties Oracle Bones: Earliest Writing Geographic Context Farming settlements in China develop on the fertile plains along Yangtze
Classical China From the Warring States to the Northern and Southern Dynasties Oracle Bones: Earliest Writing Geographic Context Farming settlements in China develop on the fertile plains along Yangtze
Classical China. Qin and Han Dynasties
 Classical China Qin and Han Dynasties I. Warring States Period (ca. 481 221 BCE) A. Collapse of Zhou Dynasty B. Several independent, regional states fought for dominance in East central China C. 221 BCE
Classical China Qin and Han Dynasties I. Warring States Period (ca. 481 221 BCE) A. Collapse of Zhou Dynasty B. Several independent, regional states fought for dominance in East central China C. 221 BCE
Chapter 8: The Unification of China. Period of the Warring States: BCE. Qin Dynasty BCE. Former Han Dynasty 206BCE- 9CE
 Chapter 8: The Unification of China Period of the Warring States: 403-221 BCE Qin Dynasty 221-207 BCE Former Han Dynasty 206BCE- 9CE Lao Tse: Wuwei Dao The Way Passive and yielding China Under the Qin
Chapter 8: The Unification of China Period of the Warring States: 403-221 BCE Qin Dynasty 221-207 BCE Former Han Dynasty 206BCE- 9CE Lao Tse: Wuwei Dao The Way Passive and yielding China Under the Qin
Chapters 5 & 8 China
 Chapters 5 & 8 China China is the oldest continuous civilization in the world. Agriculture began in China in the Yellow River Valley. Wheat was the first staple crop. Rice would later be the staple in
Chapters 5 & 8 China China is the oldest continuous civilization in the world. Agriculture began in China in the Yellow River Valley. Wheat was the first staple crop. Rice would later be the staple in
Imperial China REORGANIZING HUMAN SOCIETIES (600 B.C.E. 600 C.E.)
 Imperial China REORGANIZING HUMAN SOCIETIES (600 B.C.E. 600 C.E.) Early China was fragmented, and the Shang & Zhou dynasties ruled for the most part a compact area of northeastern China. Rivalry and fighting
Imperial China REORGANIZING HUMAN SOCIETIES (600 B.C.E. 600 C.E.) Early China was fragmented, and the Shang & Zhou dynasties ruled for the most part a compact area of northeastern China. Rivalry and fighting
A Quick Review: the Shang
 A Quick Review: the Shang 1750-1045 BCE in the Yellow River Valley Use of tortoise shells for worship (oracle bones); ancestor veneration; no organized priesthood Warriors; built cities with massive walls
A Quick Review: the Shang 1750-1045 BCE in the Yellow River Valley Use of tortoise shells for worship (oracle bones); ancestor veneration; no organized priesthood Warriors; built cities with massive walls
ANCIENT CHINA: Chinese River Valley. Unit 11 2/8/16
 ANCIENT CHINA: Chinese River Valley Unit 11 2/8/16 WHAT CONTINENT IS CHINA ON? LOCATED IN ASIA is THE LARGEST COUNTRY LARGER THAN THE U.S.A WHERE IS CHINA? WHERE IS ancient CHINA located? CHINESE River
ANCIENT CHINA: Chinese River Valley Unit 11 2/8/16 WHAT CONTINENT IS CHINA ON? LOCATED IN ASIA is THE LARGEST COUNTRY LARGER THAN THE U.S.A WHERE IS CHINA? WHERE IS ancient CHINA located? CHINESE River
5/21/14. Chapter 2 Classical Civilization: China. Shang Dynasty ( BCE) First documented rule in China after Xia dynasty
 Chapter 2 Classical Civilization: China Shang Dynasty (1600-1046 BCE) First documented rule in China after Xia dynasty Patterns in Classical China 3 dynasties: Zhou, Qin, Han Dynasty Cycle When a dynasty
Chapter 2 Classical Civilization: China Shang Dynasty (1600-1046 BCE) First documented rule in China after Xia dynasty Patterns in Classical China 3 dynasties: Zhou, Qin, Han Dynasty Cycle When a dynasty
China Builds A Bureaucracy*
 China Builds A Bureaucracy* Learning Goal 4: Describe the basic beliefs of legalism, Daoism, and Confucianism and explain how classical Chinese leaders created a strong centralized government based on
China Builds A Bureaucracy* Learning Goal 4: Describe the basic beliefs of legalism, Daoism, and Confucianism and explain how classical Chinese leaders created a strong centralized government based on
Unit II: The Classical Period, 1000 B.C.E. 500 C.E., Uniting Large Regions & Chapter 2 Reading Guide Classical Civilization: CHINA
 Name: Due Date: Unit II: The Classical Period, 1000 B.C.E. 500 C.E., Uniting Large Regions & Chapter 2 Reading Guide Classical Civilization: CHINA UNIT SUMMARY The major development during the classical
Name: Due Date: Unit II: The Classical Period, 1000 B.C.E. 500 C.E., Uniting Large Regions & Chapter 2 Reading Guide Classical Civilization: CHINA UNIT SUMMARY The major development during the classical
中国 Ancient China 古代 中国
 中国 Ancient China 古代中国 Dynasty A line of rulers coming from the same family Name of dynasty name of family Mandate of Heaven Fit to rule according to the heavens Natural disasters = bad ruler Ancient China
中国 Ancient China 古代中国 Dynasty A line of rulers coming from the same family Name of dynasty name of family Mandate of Heaven Fit to rule according to the heavens Natural disasters = bad ruler Ancient China
APWH Notes. How is China Unique? Early Chinese History 9/11/2014. Chapter 2
 APWH Notes Chapter 2 How is China Unique? Geography- wide variety of different landforms, mountain ranges, bodies of water etc. which led to an isolated civilization China has an ability to absorb foreign
APWH Notes Chapter 2 How is China Unique? Geography- wide variety of different landforms, mountain ranges, bodies of water etc. which led to an isolated civilization China has an ability to absorb foreign
CLASSICAL EAST: CHINA QIN & HAN DYNASTIES
 CLASSICAL EAST: CHINA QIN & HAN DYNASTIES Quick Review!! The next few slides are a review from when we last studied China. Read through the slides! Confucianism What dynasty was this created in? Founder?
CLASSICAL EAST: CHINA QIN & HAN DYNASTIES Quick Review!! The next few slides are a review from when we last studied China. Read through the slides! Confucianism What dynasty was this created in? Founder?
Classical Civilization. China
 Classical Civilization China Early China 1200BCE-250BCE Isolated Cultural heritage stressed basic harmony of nature and balance of opposites. Yin/yang Emerged from the classical period as a well integrated
Classical Civilization China Early China 1200BCE-250BCE Isolated Cultural heritage stressed basic harmony of nature and balance of opposites. Yin/yang Emerged from the classical period as a well integrated
Chapter 8. The Unification of China. 2011, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
 Chapter 8 The Unification of China 1 Confucius Kong Fuzi (551-479 B.C.E.) Master philosopher Kong Aristocratic roots Unwilling to compromise principle Decade of unemployment, wandering Returned home a
Chapter 8 The Unification of China 1 Confucius Kong Fuzi (551-479 B.C.E.) Master philosopher Kong Aristocratic roots Unwilling to compromise principle Decade of unemployment, wandering Returned home a
Chapter 8: The Unification of China. Period of the Warring States: BCE. Qin Dynasty BCE. Former Han Dynasty 206BCE- 9CE
 Chapter 8: The Unification of China Period of the Warring States: 403-221 BCE Qin Dynasty 221-207 BCE Former Han Dynasty 206BCE- 9CE Lao Tse: Wuwei Dao The Way Passive and yielding China Under the Qin
Chapter 8: The Unification of China Period of the Warring States: 403-221 BCE Qin Dynasty 221-207 BCE Former Han Dynasty 206BCE- 9CE Lao Tse: Wuwei Dao The Way Passive and yielding China Under the Qin
NAME DATE CLASS. Sea of Japan (East Sea) KOREAN PENINSULA G O B I. Yellow. East. China. Sea. Taiwan. South. China Sea
 Lesson 1 The Birth of Chinese Civilization ESSENTIAL QUESTION What makes a culture unique? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. How have rivers, mountains, and deserts shaped the development of 's civilization? 2. Why
Lesson 1 The Birth of Chinese Civilization ESSENTIAL QUESTION What makes a culture unique? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. How have rivers, mountains, and deserts shaped the development of 's civilization? 2. Why
Classical China THE UNIFICATION OF CHINA
 Classical China 1 THE UNIFICATION OF CHINA ! Kong Fuzi (551-479 BCE)! Master Philosopher Kong Confucius! Aristocratic roots! Unwilling to compromise principle! Decade of unemployment, wandering! Returned
Classical China 1 THE UNIFICATION OF CHINA ! Kong Fuzi (551-479 BCE)! Master Philosopher Kong Confucius! Aristocratic roots! Unwilling to compromise principle! Decade of unemployment, wandering! Returned
Chapter 4 Unification and the Consolidation of Civilization in China
 pp. 80-83 Chapter Summary. The 1 dynasty in the 8th century B.C.E. lost control of its vassals. Internal political disorder was increased by nomadic pressure. The unstable times eventually led to the emergence
pp. 80-83 Chapter Summary. The 1 dynasty in the 8th century B.C.E. lost control of its vassals. Internal political disorder was increased by nomadic pressure. The unstable times eventually led to the emergence
Rise Great Leader Achievements Fall
 Rise Great Leader Achievements Fall Before the Zhou was the Shang 1750-1045 BCE Aristocracy warlords Anyang Oracle bones Human sacrifice Ancestor worship bronze The Enduring Zhou Early Zhou (Western Zhou)
Rise Great Leader Achievements Fall Before the Zhou was the Shang 1750-1045 BCE Aristocracy warlords Anyang Oracle bones Human sacrifice Ancestor worship bronze The Enduring Zhou Early Zhou (Western Zhou)
Chinese Dynasties. Xia to Yuan. E.Q. How did China s imperialistic dynasties transform its government and change its society?
 Chinese Dynasties Xia to Yuan E.Q. How did China s imperialistic dynasties transform its government and change its society? Xia 2200 1750 BCE (approximate) Founded by Yu the Great First Chinese Dynasty
Chinese Dynasties Xia to Yuan E.Q. How did China s imperialistic dynasties transform its government and change its society? Xia 2200 1750 BCE (approximate) Founded by Yu the Great First Chinese Dynasty
China Builds A Bureaucracy
 China Builds A Bureaucracy Learning Goal 4: Describe the basic beliefs of legalism, Daoism, and Confucianism and explain how classical Chinese leaders created a strong centralized government based on Confucian
China Builds A Bureaucracy Learning Goal 4: Describe the basic beliefs of legalism, Daoism, and Confucianism and explain how classical Chinese leaders created a strong centralized government based on Confucian
The Unification of China
 Chapter 8 The Unification of China Mr. McKee Confucius Kong Fuzi (551-479 BCE) Master Philosopher Kong Aristocratic roots Unwilling to compromise principles Decade of unemployment, wandering Returned home
Chapter 8 The Unification of China Mr. McKee Confucius Kong Fuzi (551-479 BCE) Master Philosopher Kong Aristocratic roots Unwilling to compromise principles Decade of unemployment, wandering Returned home
Ladies and gentleman, coming to the ring tonight is something classic... (music plays)
 Classical Civilizations: China WH008 Activity Introduction Ladies and gentleman, coming to the ring tonight is something classic... (music plays) No, no it s better than classical music. I m talking about,
Classical Civilizations: China WH008 Activity Introduction Ladies and gentleman, coming to the ring tonight is something classic... (music plays) No, no it s better than classical music. I m talking about,
2. According to Confucianism, husbands and wives should be supportive of each other.
 True / False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. The civil service system that was created under Han Wudi favored the rich. 2. According to Confucianism, husbands and wives should be supportive
True / False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. The civil service system that was created under Han Wudi favored the rich. 2. According to Confucianism, husbands and wives should be supportive
SY 2017/ nd Final Term Revision. Student s Name: Grade: 10A. Subject: SOCIAL STUDIES. Teacher Signature
 SY 2017/2018 2 nd Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade: 10A Subject: SOCIAL STUDIES Teacher Signature 2nd Term Final Exam SOCIAL STUDIES-10 REVISION Name: Date: CHAPTER 6- SECTION 1-6 ANCIENT CHINA:
SY 2017/2018 2 nd Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade: 10A Subject: SOCIAL STUDIES Teacher Signature 2nd Term Final Exam SOCIAL STUDIES-10 REVISION Name: Date: CHAPTER 6- SECTION 1-6 ANCIENT CHINA:
Three Chinese Philosophies. History Alive Chapter 21
 Three Chinese Philosophies History Alive Chapter 21 21.1 Introduction Three Major Philosophies during the Zhou dynasty Confucianism Daoism (Taoism) Legalism 21.2 Zhou Dynasty In 1045 B.C.E. Zhou dynasty
Three Chinese Philosophies History Alive Chapter 21 21.1 Introduction Three Major Philosophies during the Zhou dynasty Confucianism Daoism (Taoism) Legalism 21.2 Zhou Dynasty In 1045 B.C.E. Zhou dynasty
Classical Civilization: China
 Classical Civilization: China Patterns in Classical China I Three dynastic cycles cover the many centuries of classical China: the Zhou, the Qin, and the Han. I Political instability and frequent invasions
Classical Civilization: China Patterns in Classical China I Three dynastic cycles cover the many centuries of classical China: the Zhou, the Qin, and the Han. I Political instability and frequent invasions
Warm-up Questions. What was the official government policy under Wudi? Who was the peasant emperor of the Han Dynasty?
 Warm-up Questions What was the official government policy under Wudi? Who was the peasant emperor of the Han Dynasty? Ancient China The Han Dynasty Ancient Civilizations Mr. Hollingsworth World History
Warm-up Questions What was the official government policy under Wudi? Who was the peasant emperor of the Han Dynasty? Ancient China The Han Dynasty Ancient Civilizations Mr. Hollingsworth World History
A. A Republic of Farmers 753 B.C.E.-600 C.E Etruscan kings were overthrown in 507 B.C.E. by a senatorial class of large landholders. 2.
 AP World History A. A Republic of Farmers 753 B.C.E.-600 C.E. 1. 7 Etruscan kings were overthrown in 507 B.C.E. by a senatorial class of large landholders. 2. Two Consuls and the Senate. Republic-indirect/representative
AP World History A. A Republic of Farmers 753 B.C.E.-600 C.E. 1. 7 Etruscan kings were overthrown in 507 B.C.E. by a senatorial class of large landholders. 2. Two Consuls and the Senate. Republic-indirect/representative
Classical China. In 221 b.c.e. two centuries of internecine rivalry the Warring States period ended with the rise to centralized power of the Qin
 Chapter 7: China Classical China. In 221 b.c.e. two centuries of internecine rivalry the Warring States period ended with the rise to centralized power of the Qin dynasty, but internal revolt and external
Chapter 7: China Classical China. In 221 b.c.e. two centuries of internecine rivalry the Warring States period ended with the rise to centralized power of the Qin dynasty, but internal revolt and external
QUOTE OF THE DAY. Confucius
 QUOTE OF THE DAY When a country is well governed, poverty and a mean condition are something to be ashamed of. When a country is ill governed riches and honors are something to be ashamed of. Confucius
QUOTE OF THE DAY When a country is well governed, poverty and a mean condition are something to be ashamed of. When a country is ill governed riches and honors are something to be ashamed of. Confucius
Three Chinese Philosophies
 In this Chinese scroll painting, scholars study the Daoist symbol for yin and yang. CHAPTER Three Chinese Philosophies 21.1 Introduction In the last chapter, you read about one of China's earliest dynasties,
In this Chinese scroll painting, scholars study the Daoist symbol for yin and yang. CHAPTER Three Chinese Philosophies 21.1 Introduction In the last chapter, you read about one of China's earliest dynasties,
Ancient China. Hwang Ho River Valley. Hwang Ho River Valley 10/7/2016. Stuff about ancient China and stuff
 Ancient China Stuff about ancient China and stuff Hwang Ho River Valley 4,500 B.C.E. people begin to settle along the Yellow River. They grew millet and soybeans. Animal wise they raised chickens, pigs,
Ancient China Stuff about ancient China and stuff Hwang Ho River Valley 4,500 B.C.E. people begin to settle along the Yellow River. They grew millet and soybeans. Animal wise they raised chickens, pigs,
Chapter 21 Three Chinese Philosophies. How did Confucianism, Daoism, and Legalism influence political rule in ancient China?
 Chapter 21 Three Chinese Philosophies How did Confucianism, Daoism, and Legalism influence political rule in ancient China? 21.1. Introduction One of China s earliest dynasties was the Shang dynasty. China
Chapter 21 Three Chinese Philosophies How did Confucianism, Daoism, and Legalism influence political rule in ancient China? 21.1. Introduction One of China s earliest dynasties was the Shang dynasty. China
China Review. Geographic Features that. separate China/India. separates China & Russia. Confucian - - China s most influential philosopher (thinker).
 China Review Geographic Features that separate China/India separates China & Russia dangerous flooding seasonal winds that bring large amounts of rain Confucian - - China s most influential philosopher
China Review Geographic Features that separate China/India separates China & Russia dangerous flooding seasonal winds that bring large amounts of rain Confucian - - China s most influential philosopher
NAME DATE CLASS. Directions: Select the vocabulary term from the box that best completes each sentence. Write the term(s) in the blank.
 Vocabulary Builder Activity A Content Vocabulary Directions: Select the vocabulary term from the box that best completes each sentence Write the term(s) in the blank warlord aristocrat ancestor pictograph
Vocabulary Builder Activity A Content Vocabulary Directions: Select the vocabulary term from the box that best completes each sentence Write the term(s) in the blank warlord aristocrat ancestor pictograph
understand the attitudes Mongols had about the Chinese and how the Chinese viewed these nomadic
 1 of 5 7/1/2009 11:11 AM Home >> Teachers >> Lesson Plans >> How Shall We Rule China? Lesson Plan: How Shall We Rule China? Role Play Description This role-playing activity focuses on a powerful time in
1 of 5 7/1/2009 11:11 AM Home >> Teachers >> Lesson Plans >> How Shall We Rule China? Lesson Plan: How Shall We Rule China? Role Play Description This role-playing activity focuses on a powerful time in
Chapter 21. Three Chinese Philosophies
 Chapter 21 Three Chinese Philosophies Chapter 21 Three Chinese Philosophies How did Confucianism, Daoism, and Legalism influence political rule in ancient China? 21.1 Introduction One of China's eariiest
Chapter 21 Three Chinese Philosophies Chapter 21 Three Chinese Philosophies How did Confucianism, Daoism, and Legalism influence political rule in ancient China? 21.1 Introduction One of China's eariiest
The Qin Dynasty. Military Power and Mobiliza<on
 China China from 221 B.C.E. to 907 C.E. Conquest, consolida
China China from 221 B.C.E. to 907 C.E. Conquest, consolida
Assessment: Three Chinese Philosophies
 Name Date Mastering the Content Circle the letter next to the best answer. Assessment: Three Chinese Philosophies 1. In the later years of the Zhou dynasty, what condition in China led to new philosophies?
Name Date Mastering the Content Circle the letter next to the best answer. Assessment: Three Chinese Philosophies 1. In the later years of the Zhou dynasty, what condition in China led to new philosophies?
Imperial China. Dynasties and Dragons
 Imperial China Dynasties and Dragons The Mandate of Heaven A Chinese political and religious doctrine used since ancient times to justify the rule of the Emperor of China. Similar to the Medieval European
Imperial China Dynasties and Dragons The Mandate of Heaven A Chinese political and religious doctrine used since ancient times to justify the rule of the Emperor of China. Similar to the Medieval European
Asia ARCTIC OCEAN. The Political Development of Imperial China CHINA. Teachers Curriculum Institute Fourth Proof TCI Arabian Sea.
 G E O G R A P H Y C H A L L E N G E Bl ac 160 W 40 N 180 60 N ARCTIC OCEAN 80 N 140 W Asia ks Caspi an Sea ea E Aral Sea 0 16 Persia Red Sea ng ul f CHINA o pic Tro fc anc er N 20 Arabian Sea Eq u ator
G E O G R A P H Y C H A L L E N G E Bl ac 160 W 40 N 180 60 N ARCTIC OCEAN 80 N 140 W Asia ks Caspi an Sea ea E Aral Sea 0 16 Persia Red Sea ng ul f CHINA o pic Tro fc anc er N 20 Arabian Sea Eq u ator
SHANG DYNASTY BCE
 9/19/2017 SHANG DYNASTY 1766-1122BCE Create bronze tools, weapons, and walled cities, creating a militaristic tradition. Religious traditions are formed to unite the empire Rulers are guided by the
9/19/2017 SHANG DYNASTY 1766-1122BCE Create bronze tools, weapons, and walled cities, creating a militaristic tradition. Religious traditions are formed to unite the empire Rulers are guided by the
CHINESE TIMELINE. Taken From. Tong Sing. The Book of Wisdom based on The Ancient Chinese Almanac. CMG Archives
 CHINESE TIMELINE Taken From Tong Sing The Book of Wisdom based on The Ancient Chinese Almanac CMG Archives http://www.campbellmgold.com (2012) Introduction From the "Tong Sing", The Book of Wisdom based
CHINESE TIMELINE Taken From Tong Sing The Book of Wisdom based on The Ancient Chinese Almanac CMG Archives http://www.campbellmgold.com (2012) Introduction From the "Tong Sing", The Book of Wisdom based
How did Shih Huangdi weaken aristocrats power?
 Ready at the bell, notebook and SIR Card on desk. HW picked up in 3, 2, 1. Notebook heading: Date: 09/12/2013 Topic: Religions continued Unit Question: How do the past and present interact? How did feudalism
Ready at the bell, notebook and SIR Card on desk. HW picked up in 3, 2, 1. Notebook heading: Date: 09/12/2013 Topic: Religions continued Unit Question: How do the past and present interact? How did feudalism
Rome: Republic to Empire
 Ancient Rome Rome: Republic to Empire OBJECTIVES Students will be able to: Identify Cincinnatus, Julius Caesar, Cicero, and Augustus. Describe the government of the Roman Republic, the checks on it, and
Ancient Rome Rome: Republic to Empire OBJECTIVES Students will be able to: Identify Cincinnatus, Julius Caesar, Cicero, and Augustus. Describe the government of the Roman Republic, the checks on it, and
More Ming and Qing. Opium Wars, Boxer Rebellion, Fall of the dynasties
 More Ming and Qing Opium Wars, Boxer Rebellion, Fall of the dynasties The first Ming emperor, Hongwu sought to improve the lives of the peasants through support of agriculture, the development of public
More Ming and Qing Opium Wars, Boxer Rebellion, Fall of the dynasties The first Ming emperor, Hongwu sought to improve the lives of the peasants through support of agriculture, the development of public
DBQ Roman Military Expansion With Notes
 DBQ Roman Military Expansion With Notes KEY Contextualization Thesis / Topic Sentence Summary of Document Tie Back to Thesis Source of Document Evidence Beyond the Document Reasoning Between 200 B.C.E.
DBQ Roman Military Expansion With Notes KEY Contextualization Thesis / Topic Sentence Summary of Document Tie Back to Thesis Source of Document Evidence Beyond the Document Reasoning Between 200 B.C.E.
Russia During the Early- Modern Period
 Russia During the Early- Modern Period Review of Russian History Kievan Rus Dominated by Kiev, but various other principalities throughout Ties with Byzantine Empire Adopted Orthodox Christianity in 900
Russia During the Early- Modern Period Review of Russian History Kievan Rus Dominated by Kiev, but various other principalities throughout Ties with Byzantine Empire Adopted Orthodox Christianity in 900
Chinese regulations ensured China had favorable balance of trade with other nations Balance of trade: difference between how much a country imports
 Chinese regulations ensured China had favorable balance of trade with other nations Balance of trade: difference between how much a country imports and how much it exports By 1800s, western nations were
Chinese regulations ensured China had favorable balance of trade with other nations Balance of trade: difference between how much a country imports and how much it exports By 1800s, western nations were
3. The Roman family consisted of several generations living under the absolute authority of the oldest living male, the paterfamilias.
 Outline Chapter 5: An Age of Empires: Rome and Han China, 753 B.C.E. 330 C.E. I. Rome s Mediterranean Empire, 753 B.C.E. 600 C.E. A. A Republic of Farmers, 753 31 B.C.E. 1. Rome was inhabited at least
Outline Chapter 5: An Age of Empires: Rome and Han China, 753 B.C.E. 330 C.E. I. Rome s Mediterranean Empire, 753 B.C.E. 600 C.E. A. A Republic of Farmers, 753 31 B.C.E. 1. Rome was inhabited at least
Essential Question: How does Chinese history and culture impact China and the world today? Huang He & Chang Jiang Rivers
 Topic World Cultures China Test Study Guide Name: Period: Test Date: Essential Question: How does Chinese history and culture impact China and the world today? Questions 1. Where (meaning around which
Topic World Cultures China Test Study Guide Name: Period: Test Date: Essential Question: How does Chinese history and culture impact China and the world today? Questions 1. Where (meaning around which
China Resists Outside Influence
 Name CHAPTER 28 Section 1 (pages 805 809) China Resists Outside Influence BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about imperialism in Asia. In this section, you will see how China dealt with foreign
Name CHAPTER 28 Section 1 (pages 805 809) China Resists Outside Influence BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about imperialism in Asia. In this section, you will see how China dealt with foreign
Classical China! 500 BCE to 500 CE!
 Teachers notes for the Premium TimeMaps Unit Classical China 500 BCE to 500 CE Contents Introduction: How to use this unit p.2 Section 1: Whole-class presentation notes p.3 Section 2: Student-based enquiry
Teachers notes for the Premium TimeMaps Unit Classical China 500 BCE to 500 CE Contents Introduction: How to use this unit p.2 Section 1: Whole-class presentation notes p.3 Section 2: Student-based enquiry
Chapter 5: Early Societies in Mainland East Asia
 Chapter 5: Early Societies in Mainland East Asia Section 1: Political Organization in Early China Directions: Read the entirety of the above section, including any additional text selections such as Eyewitness
Chapter 5: Early Societies in Mainland East Asia Section 1: Political Organization in Early China Directions: Read the entirety of the above section, including any additional text selections such as Eyewitness
The Rise of Russia. AP World History
 The Rise of Russia AP World History A Newly Independent Russia 1380: Battle of Kulikova (alliance of Russian feudal princes) led to Golden Horde defeat Mongol attempts to subjugate Russians continued for
The Rise of Russia AP World History A Newly Independent Russia 1380: Battle of Kulikova (alliance of Russian feudal princes) led to Golden Horde defeat Mongol attempts to subjugate Russians continued for
SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions.
 SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions. a. Examine absolutism through a comparison of the rules of Louis XIV, Tsar Peter the Great, and Tokugawa Ieyasu. Known as the Sun
SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions. a. Examine absolutism through a comparison of the rules of Louis XIV, Tsar Peter the Great, and Tokugawa Ieyasu. Known as the Sun
Ancient River Valley Civilizations China
 Ancient River Valley Civilizations China http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file:20090529_great_wall_8185.jpg Geography of China India wasn t the only great civilization to emerge in Asia. China developed
Ancient River Valley Civilizations China http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file:20090529_great_wall_8185.jpg Geography of China India wasn t the only great civilization to emerge in Asia. China developed
Essential Question: What was the impact of European imperialism on China?
 Essential Question: What was the impact of European imperialism on China? CPWH Agenda for Unit 10.8: Clicker questions Imperialism in China notes Today s HW: 27.5 Unit 10 Test: Friday, February 22 The
Essential Question: What was the impact of European imperialism on China? CPWH Agenda for Unit 10.8: Clicker questions Imperialism in China notes Today s HW: 27.5 Unit 10 Test: Friday, February 22 The
The Modernization of China: a Historical Perspective. Dong Jingsheng History Department, Peking University, China
 The Modernization of China: a Historical Perspective Dong Jingsheng History Department, Peking University, China MODERNIZATION Modernization is a process by which societies move from rural, agrarian society
The Modernization of China: a Historical Perspective Dong Jingsheng History Department, Peking University, China MODERNIZATION Modernization is a process by which societies move from rural, agrarian society
Athens. Chapter 5 Section 2 Warring City-States
 Where Democracy is Born Unfertile, rocky soil - Sea traders, sailors - Colonies Coined money - 600 BC Easier to buy and sell (Advanced) Chapter 5 Section 2 Warring City-States 1 Chapter 5 Section 2 Warring
Where Democracy is Born Unfertile, rocky soil - Sea traders, sailors - Colonies Coined money - 600 BC Easier to buy and sell (Advanced) Chapter 5 Section 2 Warring City-States 1 Chapter 5 Section 2 Warring
Unit 1: Renaissance and Ming Dynasty
 Unit 1: Renaissance and Ming Dynasty Day 5 Starter: Jan 18th and 19th What do you know about the history of China? Can you name any dynasties? Any inventions? Any famous people? What role did China play
Unit 1: Renaissance and Ming Dynasty Day 5 Starter: Jan 18th and 19th What do you know about the history of China? Can you name any dynasties? Any inventions? Any famous people? What role did China play
Summative: Multiple Choice Questions on the Unit Test and on the AP World History Test in May.
 How Shall We Rule China? Lesson Plan Brad Burzumato- Albemarle High School Context 10 th Grade AP World History Class For homework the night before, the students will have read the Textbook chapter on
How Shall We Rule China? Lesson Plan Brad Burzumato- Albemarle High School Context 10 th Grade AP World History Class For homework the night before, the students will have read the Textbook chapter on
Early China. (a.k.a. - a long list of Dynasties!)
 China Early China (a.k.a. - a long list of Dynasties!) Dynasties of China A dynasty is a series of rulers from the same family Historically, royal rule was descended from father to son Mandate of Heaven:
China Early China (a.k.a. - a long list of Dynasties!) Dynasties of China A dynasty is a series of rulers from the same family Historically, royal rule was descended from father to son Mandate of Heaven:
World History (Survey) Chapter 28: Transformations Around the Globe,
 World History (Survey) Chapter 28: Transformations Around the Globe, 1800 1914 Section 1: China Responds to Pressure from the West In the late 1700s, China was self-sufficient. It had a strong farming
World History (Survey) Chapter 28: Transformations Around the Globe, 1800 1914 Section 1: China Responds to Pressure from the West In the late 1700s, China was self-sufficient. It had a strong farming
Ancient China: Geography
 Ancient China: Geography China is located in East Asia. Like all early civilizations we have discussed, the development of China was greatly influenced by its geography. China was isolated from the rest
Ancient China: Geography China is located in East Asia. Like all early civilizations we have discussed, the development of China was greatly influenced by its geography. China was isolated from the rest
Where is China? A little bit of Chinese history Basic economic facts What does it look like?
 Where is China? A little bit of Chinese history Basic economic facts What does it look like? China World s 4 th -largest country (after Russia, Canada, and US); Mount Everest on the border with Nepal,
Where is China? A little bit of Chinese history Basic economic facts What does it look like? China World s 4 th -largest country (after Russia, Canada, and US); Mount Everest on the border with Nepal,
12. Which foreign religious tradition was absorbed into China during the classical period? A) Hinduism B) The Isis cult C) Buddhism D) Christianity
 Chapter 3 Test 1. Persian political organization included which of the following features? A) An emperor who was merely a figurehead B) A satrap who governed each province C) A civil service examination
Chapter 3 Test 1. Persian political organization included which of the following features? A) An emperor who was merely a figurehead B) A satrap who governed each province C) A civil service examination
A WANING KINGDOM 1/13/2017
 A WANING KINGDOM World History 2017 Mr. Giglio Qing Dynasty began to weaken During the 18 th & 19 th centuries. Opium Wars Taiping Rebellion Sino-Japanese War Spheres of Influence Open-Door Policy REFORM
A WANING KINGDOM World History 2017 Mr. Giglio Qing Dynasty began to weaken During the 18 th & 19 th centuries. Opium Wars Taiping Rebellion Sino-Japanese War Spheres of Influence Open-Door Policy REFORM
All societies, large and small, develop some form of government.
 The Origins and Evolution of Government (HA) All societies, large and small, develop some form of government. During prehistoric times, when small bands of hunter-gatherers wandered Earth in search of
The Origins and Evolution of Government (HA) All societies, large and small, develop some form of government. During prehistoric times, when small bands of hunter-gatherers wandered Earth in search of
Three Chinese Philosophies
 Three Chinese Philosophies How do belief systems compel people to behave and inform how they are governed? Ms. Jeremie Starter What continent is China located on? Name one of the major rivers What isolated
Three Chinese Philosophies How do belief systems compel people to behave and inform how they are governed? Ms. Jeremie Starter What continent is China located on? Name one of the major rivers What isolated
Creates Republican government and codifies Western Law Largest Western Empire Existed for over 1,000 years! Powerful army and great builders Huge
 Creates Republican government and codifies Western Law Largest Western Empire Existed for over 1,000 years! Powerful army and great builders Huge slave culture Adopted much of Greek culture Becomes the
Creates Republican government and codifies Western Law Largest Western Empire Existed for over 1,000 years! Powerful army and great builders Huge slave culture Adopted much of Greek culture Becomes the
Early Chinese Civilization: From Neolithic Origins to 220 C.E.
 CHAPTER 2 Early Chinese Civilization: From Neolithic Origins to 220 C.E. The power of Chinese civilization rests mainly in continuity and accumulation of refinements of institutions begun in the past.
CHAPTER 2 Early Chinese Civilization: From Neolithic Origins to 220 C.E. The power of Chinese civilization rests mainly in continuity and accumulation of refinements of institutions begun in the past.
WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer
 WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer Subject(s) Social Studies Conceptual Lenses Grade/Course 6th grade Values and Beliefs Unit of Study Unit 10 Movement Unit Title China Trade Pacing 14 days Innovation Geography:
WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer Subject(s) Social Studies Conceptual Lenses Grade/Course 6th grade Values and Beliefs Unit of Study Unit 10 Movement Unit Title China Trade Pacing 14 days Innovation Geography:
Eastern European and Russian Absolutism. Ivan IV Ivan the Terrible ( )
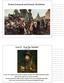 Eastern European and Russian Absolutism Ivan IV Ivan the Terrible (1547-1584) became Tsar at age of 3 and watched rival groups of nobles who sought to control the country when he took charge, he saw treason
Eastern European and Russian Absolutism Ivan IV Ivan the Terrible (1547-1584) became Tsar at age of 3 and watched rival groups of nobles who sought to control the country when he took charge, he saw treason
Populism Made inchina: One Man to Rule Them All
 Populism Made inchina: One Man to Rule Them All A critical overview of one China and one ruler as key images that have shaped power (control, governance) in Chinese Society Paola Voci University of Otago
Populism Made inchina: One Man to Rule Them All A critical overview of one China and one ruler as key images that have shaped power (control, governance) in Chinese Society Paola Voci University of Otago
11/8/2018. Big Idea. Confucianism emerges in ancient China. Essential Question. What are the beliefs of Confucianism?
 Big Idea Confucianism emerges in ancient China. Essential Question What are the beliefs of Confucianism? 1 Let s Set The Stage The Shang Dynasty was the earliest ruling dynasty in China. The Zhou Dynasty
Big Idea Confucianism emerges in ancient China. Essential Question What are the beliefs of Confucianism? 1 Let s Set The Stage The Shang Dynasty was the earliest ruling dynasty in China. The Zhou Dynasty
SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions.
 SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions. a. Examine absolutism through a comparison of the rules of Louis XIV, Tsar Peter the Great, and Tokugawa Ieyasu. EQ: What is characteristics
SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions. a. Examine absolutism through a comparison of the rules of Louis XIV, Tsar Peter the Great, and Tokugawa Ieyasu. EQ: What is characteristics
Absolutism Activity 1
 Absolutism Activity 1 Who is in the painting? What do you think is going on in the painting? Take note of the background. What is the message of the painting? For example, why did the author paint this?
Absolutism Activity 1 Who is in the painting? What do you think is going on in the painting? Take note of the background. What is the message of the painting? For example, why did the author paint this?
The Zhou Dynasty. and New Ideas. If YOU were there... The Zhou Dynasty. How will these teachings affect your life? The Zhou Dynasty SECTION
 ECTION 2 The Zhou Dynasty and New Ideas What You Will Learn Main Ideas 1. The Zhou dynasty expanded China but then declined. 2. Confucius offered ideas to bring order to Chinese society. 3. Daoism and
ECTION 2 The Zhou Dynasty and New Ideas What You Will Learn Main Ideas 1. The Zhou dynasty expanded China but then declined. 2. Confucius offered ideas to bring order to Chinese society. 3. Daoism and
Classical Civilizations of the Mediterranean & Middle East. Persia, Greece & Rome
 Classical Civilizations of the Mediterranean & Middle East Persia, Greece & Rome Common Features of Classical Civilizations China, India, Persia, Greece and Rome developed their own beliefs, lifestyles,
Classical Civilizations of the Mediterranean & Middle East Persia, Greece & Rome Common Features of Classical Civilizations China, India, Persia, Greece and Rome developed their own beliefs, lifestyles,
Geography & Early Republic
 Geography & Early Republic 1. Setting the Stage a. With the defeat of the Persians by Alexander and the eventual decline of the Greek Civilization, power would eventually shift west towards the Italian
Geography & Early Republic 1. Setting the Stage a. With the defeat of the Persians by Alexander and the eventual decline of the Greek Civilization, power would eventually shift west towards the Italian
Ch. 6.3 Radical Period of the French Revolution. leader of the Committee of Public Safety; chief architect of the Reign of Terror
 the right to vote Ch. 6.3 Radical Period of the French Revolution leader of the Committee of Public Safety; chief architect of the Reign of Terror period from September 1793 to July 1794 when those who
the right to vote Ch. 6.3 Radical Period of the French Revolution leader of the Committee of Public Safety; chief architect of the Reign of Terror period from September 1793 to July 1794 when those who
In addition to Greece, a significant classical civilization was ancient Rome. Its history from 500 B.C A.D is known as the Classical Era.
 ROMAN CIVILIZATION In addition to Greece, a significant classical civilization was ancient Rome Its history from 500 B.C.- 600 A.D is known as the Classical Era. Impact of Geography on Rome: Identify 1
ROMAN CIVILIZATION In addition to Greece, a significant classical civilization was ancient Rome Its history from 500 B.C.- 600 A.D is known as the Classical Era. Impact of Geography on Rome: Identify 1
Honors World History
 Honors World History 1. When the Han took over, they a) Completely reinstated the Zhou system b) Completely eradicated all remnants of Qin rule c) Retained the Qin system with minor modifications d) Got
Honors World History 1. When the Han took over, they a) Completely reinstated the Zhou system b) Completely eradicated all remnants of Qin rule c) Retained the Qin system with minor modifications d) Got
French Revolution. Revolution in France (Cause) Estates (Cont) 1/23/ s Feudalist Government. 1 st & 2 nd Estate are Privileged
 French Revolution 1789-1815 Revolution in France (Cause) 1770s Feudalist Government System of the wealthy in power Poor works the land in return for food & protection 3 Estates (Classes of People) 1 st
French Revolution 1789-1815 Revolution in France (Cause) 1770s Feudalist Government System of the wealthy in power Poor works the land in return for food & protection 3 Estates (Classes of People) 1 st
Defining the Republic
 Defining the Republic READ THIS SUMMARY! According to traditional accounts, after chasing the Etruscan king from Rome, the Romans established a new government in the form of a Republic, from Res Publica,
Defining the Republic READ THIS SUMMARY! According to traditional accounts, after chasing the Etruscan king from Rome, the Romans established a new government in the form of a Republic, from Res Publica,
Name Date Mrs. Brannen Global I Emperor Shi Huangdi of China /31
 Name Date Mrs. Brannen Global I Emperor Shi Huangdi of China /31 Objective: Understand how Emperor Shi Huangdi unified China and determine if his rule was overall good or bad. Focus Question: Did Emperor
Name Date Mrs. Brannen Global I Emperor Shi Huangdi of China /31 Objective: Understand how Emperor Shi Huangdi unified China and determine if his rule was overall good or bad. Focus Question: Did Emperor
MRS. OSBORN S APWH CRAM PACKET:
 MRS. OSBORN S APWH CRAM PACKET: Period 5 Industrialization & Global Integration, 1750-1900, chapters 23-29 (20% of APWH Exam) (NOTE: Some material overlaps into Period 6, 1900-1914) Questions of periodization:
MRS. OSBORN S APWH CRAM PACKET: Period 5 Industrialization & Global Integration, 1750-1900, chapters 23-29 (20% of APWH Exam) (NOTE: Some material overlaps into Period 6, 1900-1914) Questions of periodization:
Civilizations in Crisis: Qing China
 Civilizations in Crisis: Qing China 1644-1911 The Qing (Manchu) Dynasty 1644-1912 Though foreign, the Qing continued most Ming policies, including isolationism. Civil Service system was expanded. Patronized
Civilizations in Crisis: Qing China 1644-1911 The Qing (Manchu) Dynasty 1644-1912 Though foreign, the Qing continued most Ming policies, including isolationism. Civil Service system was expanded. Patronized
The Rise of Dictators
 The Rise of Dictators DICTATORS THREATEN WORLD PEACE For many European countries the end of World War I was the beginning of revolutions at home, economic depression and the rise of powerful dictators
The Rise of Dictators DICTATORS THREATEN WORLD PEACE For many European countries the end of World War I was the beginning of revolutions at home, economic depression and the rise of powerful dictators
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 3 The Rise of Napoleon and the Napoleonic Wars ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What causes revolution? How does revolution change society? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary capable having or showing ability
Lesson 3 The Rise of Napoleon and the Napoleonic Wars ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What causes revolution? How does revolution change society? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary capable having or showing ability
Chapter 12. Chapter 12 Section 1 China Resist Outside Influence. Transformations Around The Globe Confucianism. Confucius (K'ung-tzu)
 Chapter 12 Transformations Around The Globe 1800-1914 Chapter 12 Section 1 China Resist Outside Influence Confucius (K'ung-tzu) Kong" 551 BC 479 BC Chinese and social philosopher. emphasized and governmental
Chapter 12 Transformations Around The Globe 1800-1914 Chapter 12 Section 1 China Resist Outside Influence Confucius (K'ung-tzu) Kong" 551 BC 479 BC Chinese and social philosopher. emphasized and governmental
Daily Writing. How did China s dynastic past shape its people s perspective of the world?
 Daily Writing How did China s dynastic past shape its people s perspective of the world? China and the west BRITISH AND CHINESE TRADE Up to this point, China has only one port, Guangzhou, open for trade
Daily Writing How did China s dynastic past shape its people s perspective of the world? China and the west BRITISH AND CHINESE TRADE Up to this point, China has only one port, Guangzhou, open for trade
