Chapter 9 1/14/2019. Alabama Standard. Ch.9 Section 1 (page #283)
|
|
|
- Byron Jenkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 9 THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION Alabama Standard Describe the impact of technological inventions, conditions of labor and economic theories of capitalism, liberalism, socialism, and Marxism during the the Industrial Revolution of the economies, societies and politics of Europe Identify important inventers in Europe during the Industrial Revolution Comparing the Industrial Revolution in England to later revolutions in Europe Ch.9 Section 1 (page #283) Industrial Revolution Increased production of machine-made goods which began in England in the mid 1700 s Agriculture Revolution Wealthy landowners New agriculture methods Forced small farmers to move or become tenants 1
2 Industrial Revolution in Britain (pg. #283) Enclosures Area where landowners experimented with more productive seeding and harvesting methods with the hope of increasing crop yields Industrial Revolution in Britain (pg. #283) Crop rotations System of growing a different crop in a field each year to preserve the fertility of the land Industrial Revolution in Britain (pg.284) Seed Drill Invented by Jethro Tull Crops in rows and specific depth Robert Bakewell Increased sheep size Only allowed the best sheep to breed 18 to 50 lbs. 2
3 Industrial Revolution in Britain (pg.284) Industrialization Development of industries for the machine production of goods Factors of Production Resources needed to produce goods and services. Land, labor and wealth e.g., Water, coal, iron ore, inland rivers harbors Inventions Spur Industrialization (pg.284) Political Stability No wars on British soil Laws encouraged/protect business ventures Developed banking system Bank loans for machinery investment Inventions Spur Industrialization (pg.286) British Textile Industry Water Frame, Spinning Mule, Power Loom Factories Large building containing machines used to manufacture goods 3
4 Improvements in Transportation (pg.287) Entrepreneur Person who organizes, manages and takes risks of a business Inventions Spur Industrialization (pg.287) Improvements in Transportation Canals: man made waterways Roads (Turnpikes) More Powerful Steam- Engines (Train) Railroads How it works 4
5 Inventions Spur Industrialization (pg.287) Invention of Steam Engine Richard Trevithick (1804) George Stephenson Improved Engine design Built 27 mile railroad (1825) 24 miles per hour (mph) carrying 13 tons Inventions Spur Industrialization (pg.288) Benefits Railroads Sec. 2 Industrialization Changes Life Urbanization Growth of cities and the migration of people into them Many European cities population doubled or quadrupled (4x) Factories built near sources of energy London becomes largest city 5
6 Industrialization Changes Life (page #290) Living Conditions Sewage/sanitation, city planning, police, housing, education Women and Children favored in mines/cheap labor Average life span 17 years for workers Industrialization Changes Life (page #291) Working Conditions 14 hour work day, 6 days a week Worked all year round Class Tensions Grow (page #291) Middle Class Social class of skilled workers, professionals, business people and wealthy farmers Upper middle class: Dr., government employees, lawyers and managers Lower middle class: tool makers, mechanical drafters and printers 6
7 Class Tensions Grow (page #291) Working Class Little improvement in working/living conditions Machines takeover Workers riot Positive Effects Created jobs National wealth grew Increased production Educational opportunities Class Tensions Grow (page #292) Case Study: Child Labor(pg. 292) Children worked with parents Beatings Working class standard of living increased Factory Act 1819 Sec.3 Industrial Development in the United States Industrialization in the U.S U.S same natural resources as Britain Blockade from the War of 1812 caused U.S to manufacture what they were unable to import Britain forbade engineers, mechanics and toolmakers to leave the country 7
8 Sec.3 Industrial Development in the United States Samuel Slater Built spinning machine from memory/partial design Father of American Industrial Revolution Sec.3 Industrial Development in the United States Francis Cabot Lowell Mechanized every stage of cloth manufacturing town in Massachusetts named after he passed Later expansion of U.S Industry Increase in railroads, Light bulb and telephone Sec.3 Industrial Development in the United States Stock Rights to ownership in a company Corporation A business owned by stockholders who share in the profits but are not personally responsible for the debt 8
9 Sec.3 Industrial Development in the United States Standard Oil and Carnegie Steel Company Wanted to control every aspect of their industry to maximize profits by reducing the cost of production Sec.3 Continental Europe Industrializes French Revolution and Napoleonic wars interrupted trade and communication and caused inflation Belgium 1 st European country to copy Great Britain Had rich iron ore deposits British merchants built industrial enterprise in Belgium Sec.3 Continental Europe Industrializes Germany Politically divided, scattered natural resources Coal rich Ruhr Valley industrialized Imported British Engineers and machines Sent Children to Britain to be educated 9
10 Sec.3 Continental Europe Industrializes Spain produced cotton Northern Italy mechanized textile production/silk spinning Serfs ran factories in Russia France s agricultural economy limited their industrialization Sec.3 The Impact of Industrialization Impact of Industrialization Widened inequality between non-industrialized and industrialized countries Industrialized countries seized colonies for economic resources Imperialism Extending a country s rule over another country politically, economically or socially ***T0day in World History*** The first colonial constitution is adopted in Connecticut (1639) Treaty of Paris is ratified, ending the U.S Revolutionary war (1784) Roosevelt begins Japanese-American internment (1942) George Wallace inaugurated as Alabama governor (1963) Diana Ross and the Supremes perform their final concert (1970) Undefeated Dolphins defeat the Redskins in Super Bowl VII (1973) United Nations vote deplores Soviet intervention in Afghanistan (1980) 10
11 Sec.4 The Philosophers of Industrialization Laissez Faire Economic policy letting industry and business set working conditions without interference Sec.4 The Philosophers of Industrialization Adam Smith Wrote Wealth of a Nation (1776) in defense of the idea of a free economy or free markets. He believed economic liberty guaranteed economic progress Sec.4 The Philosophers of Industrialization Wealth of a Nation s 3 natural laws of economics Law of self-interest - People work for their own good Law of competition - Competition forces people to make a better product Law of supply and demand - Enough goods would be produced at the lowest possible price to meet demand in a market economy 11
12 Sec.4 The Philosophers of Industrialization Capitalism Economic system in which factors of production are privately owned and money is invested for a profit An Essay on the Principle of Population (1798) Thomas Malthus Population greater than food supply War & epidemics needed to reduce extra population Sec.4 The Philosophers of Industrialization Principles of Political Economy and Taxation (1817) Malthus Ricardo Underclass will always be poor Lower wages as the population increases Sect.4 The Rise of Socialism Utilitarianism Government action only useful if they promote greatest good for greatest number of people 12
13 Sec.4 Marxism: Radical Socialism Socialism Factors of production are owned by the public and operate for the welfare of all Government should plan economy rather than freemarket capitalism Sec.4 Marxism: Radical Socialism Karl Marx Co-authored the Communist Manifesto Communist Manifesto (1848) Argued that human societies are divided into warring classes. The workers would overthrow the capitalist and would bring economic equality for all people. Sec.4 Marxism: Radical Socialism Communist Manifesto (1848) Argued that human societies are divided into warring classes. The workers would overthrow the capitalist and would economic equality for all people. Bourgeoisie haves Proletariats have nots 13
14 Sec.4 Marxism: Radical Socialism Communism A form of complete socialism. Economic system in which all means of production land, mines, factories, railroads and businesses-- are owned by the people, private property does not exist, and all goods and services are shared equally Sec.4 Labor Unions and Reform Law Union(s) Associations of workers, formed to bargain for better working conditions and higher wages Sec.4 Labor Unions and Reform Law Strike To refuse to work in order to force an employer to meet certain demands 14
15 Section 4 Reforming the Industrial World Reform Laws Factory Act of Ten Hours Act of National Child Labor Committee (1904)- U.S Supreme court- Section 4 Reforming the Industrial World William Wilberforce Led charge to end slavery in British Empire Jane Addams Set up over 10 boarding houses for women in Chicago DO NOT WRITE MEMES 15
I. The Agricultural Revolution
 I. The Agricultural Revolution A. The Agricultural Revolution Paves the Way 1. Wealthy farmers cultivated large fields called enclosures. 2. The enclosure movement caused landowners to try new methods.
I. The Agricultural Revolution A. The Agricultural Revolution Paves the Way 1. Wealthy farmers cultivated large fields called enclosures. 2. The enclosure movement caused landowners to try new methods.
The Beginnings of Industrialization
 Name CHAPTER 25 Section 1 (pages 717 722) The Beginnings of BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about romanticism and realism in the arts. In this section, you will read about the beginning of
Name CHAPTER 25 Section 1 (pages 717 722) The Beginnings of BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about romanticism and realism in the arts. In this section, you will read about the beginning of
Unit 9 Industrial Revolution
 Unit 9 Industrial Revolution Section 1: Beginnings of Industrialization The Industrial Revolution c. 1750/60-1850/60 The Industrial Revolution begins in Britain/England, spreads to other countries, and
Unit 9 Industrial Revolution Section 1: Beginnings of Industrialization The Industrial Revolution c. 1750/60-1850/60 The Industrial Revolution begins in Britain/England, spreads to other countries, and
Chapter 9: The Industrial Revolution,
 Chapter 9: The Industrial Revolution, 1700 1900 The Industrial Revolution begins in Britain, spreads to other countries, and has a strong impact on economics, politics, and society. Rail locomotives began
Chapter 9: The Industrial Revolution, 1700 1900 The Industrial Revolution begins in Britain, spreads to other countries, and has a strong impact on economics, politics, and society. Rail locomotives began
The Early Industrial Revolution Chapter 22 AP World History
 The Early Industrial Revolution 1760-1851 Chapter 22 AP World History Beginnings of Industrialization Main Idea The Industrial Revolution started in England and soon spread to other countries Why It Matters
The Early Industrial Revolution 1760-1851 Chapter 22 AP World History Beginnings of Industrialization Main Idea The Industrial Revolution started in England and soon spread to other countries Why It Matters
Industrialism Changes the World. New Farming Methods Increase Agricultural Production
 Industrialism Changes the World New Farming Methods Increase Agricultural Production Jethro Tull: seed drill crop rotation: planting a different crop in a different field each year the increase in farm
Industrialism Changes the World New Farming Methods Increase Agricultural Production Jethro Tull: seed drill crop rotation: planting a different crop in a different field each year the increase in farm
Industrialization Spreads. Section 9.3
 Industrialization Spreads Section 9.3 England First country to industrialize on huge scale Inspired other countries to industrialize Copy the British miracle Class structure becomes more rigid Raises the
Industrialization Spreads Section 9.3 England First country to industrialize on huge scale Inspired other countries to industrialize Copy the British miracle Class structure becomes more rigid Raises the
The Industrial Revolution. The Start of Mass Production
 The Industrial Revolution The Start of Mass Production Section 1 Beginnings of Industrialization Main Idea The Industrial Revolution started in England and soon spread to other countries Why It Matters
The Industrial Revolution The Start of Mass Production Section 1 Beginnings of Industrialization Main Idea The Industrial Revolution started in England and soon spread to other countries Why It Matters
Summary The Beginnings of Industrialization KEY IDEA The Industrial Revolution started in Great Britain and soon spread elsewhere.
 Summary The Beginnings of Industrialization KEY IDEA The Industrial Revolution started in Great Britain and soon spread elsewhere. In the early 1700s, large landowners in Britain bought much of the land
Summary The Beginnings of Industrialization KEY IDEA The Industrial Revolution started in Great Britain and soon spread elsewhere. In the early 1700s, large landowners in Britain bought much of the land
CHAPTER 25: The Industrial Revolution
 Due Monday, March 24, 2014 NAME Period CHAPTER 25: The Industrial Revolution 25.1: The Beginnings of Industrialization (pg. 717-722) I. Industrial Revolution Begins in England A. What is the definition
Due Monday, March 24, 2014 NAME Period CHAPTER 25: The Industrial Revolution 25.1: The Beginnings of Industrialization (pg. 717-722) I. Industrial Revolution Begins in England A. What is the definition
SSWH 15 Presentation. Describe the impact of industrialization and urbanization.
 SSWH 15 Presentation Describe the impact of industrialization and urbanization. Vocabulary Industrial Revolution Industrialization Adam Smith Capitalism Laissiez-Faire Wealth of Nations Karl Marx Communism
SSWH 15 Presentation Describe the impact of industrialization and urbanization. Vocabulary Industrial Revolution Industrialization Adam Smith Capitalism Laissiez-Faire Wealth of Nations Karl Marx Communism
Industrialization Spreads
 3 Industrialization Spreads MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW TERMS & NAMES EMPIRE BUILDING The industrialization that began in Great Britain spread to other parts of the world. The Industrial Revolution set
3 Industrialization Spreads MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW TERMS & NAMES EMPIRE BUILDING The industrialization that began in Great Britain spread to other parts of the world. The Industrial Revolution set
The Industrial Revolution Begins ( )
 Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter 20, Section World History: Connection to Today Chapter 20 The Industrial Revolution
Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter 20, Section World History: Connection to Today Chapter 20 The Industrial Revolution
Note Taking Study Guide DAWN OF THE INDUSTRIAL AGE
 SECTION 1 DAWN OF THE INDUSTRIAL AGE Focus Question: What events helped bring about the Industrial Revolution? As you read this section in your textbook, complete the following flowchart to list multiple
SECTION 1 DAWN OF THE INDUSTRIAL AGE Focus Question: What events helped bring about the Industrial Revolution? As you read this section in your textbook, complete the following flowchart to list multiple
25.4 Reforming the Industrial World. The Industrial Revolution leads to economic, social, and political reforms.
 25.4 Reforming the Industrial World The Industrial Revolution leads to economic, social, and political reforms. The Philosophers of Industrialization Laissez-faire Economics Laissez faire economic policy
25.4 Reforming the Industrial World The Industrial Revolution leads to economic, social, and political reforms. The Philosophers of Industrialization Laissez-faire Economics Laissez faire economic policy
World History Chapter 25
 World History Chapter 25 Renaissance Reformation Age of Exploration Scientific Revolution Enlightenment The Industrial Revolution starts in England and soon spreads to other countries. Plentiful natural
World History Chapter 25 Renaissance Reformation Age of Exploration Scientific Revolution Enlightenment The Industrial Revolution starts in England and soon spreads to other countries. Plentiful natural
World History Chapter 25
 World History Chapter 25 Renaissance Reformation Age of Exploration Scientific Revolution Enlightenment The Industrial Revolution starts in England and soon spreads to other countries. Plentiful natural
World History Chapter 25 Renaissance Reformation Age of Exploration Scientific Revolution Enlightenment The Industrial Revolution starts in England and soon spreads to other countries. Plentiful natural
Chapter 9 Section 1. The Beginnings of Industrialization
 Chapter 9 Section 1 The Beginnings of Industrialization Industrialization begins in Great Britain Took place between 1760 1840 Before the I.R. hands did most of the work By the mid 1700 s, began using
Chapter 9 Section 1 The Beginnings of Industrialization Industrialization begins in Great Britain Took place between 1760 1840 Before the I.R. hands did most of the work By the mid 1700 s, began using
Why did the Industrial Revolution begin in Great Britain????
 Why did the Industrial Revolution begin in Great Britain???? Read textbook pages 612-615. Write a paragraph explaining why the industrial revolution began in Great Britain. Please include something about
Why did the Industrial Revolution begin in Great Britain???? Read textbook pages 612-615. Write a paragraph explaining why the industrial revolution began in Great Britain. Please include something about
25-1 The Industrial Revolution is tightly connected to the Agricultural Revolution In the early 1700s, the Agricultural Revolution brought several
 25-1 The Industrial Revolution is tightly connected to the Agricultural Revolution In the early 1700s, the Agricultural Revolution brought several changes to farming in Britain including enclosures, crop
25-1 The Industrial Revolution is tightly connected to the Agricultural Revolution In the early 1700s, the Agricultural Revolution brought several changes to farming in Britain including enclosures, crop
Why was the Bank of England important during the Industrial Revolution?
 Why was the Bank of England important during the Industrial Revolution? 1 It allowed for the people of England to take out loans or get credit for various financial transactions 2 What Enlightenment economic
Why was the Bank of England important during the Industrial Revolution? 1 It allowed for the people of England to take out loans or get credit for various financial transactions 2 What Enlightenment economic
Welcome back to WHAP! Thursday 2/15/18
 Welcome back to WHAP! Thursday 2/15/18 Turn your Ch. 17 Skills Activity into the tray- make sure your name is on it You need to have your notes out and something to write with- be ready to take some notes
Welcome back to WHAP! Thursday 2/15/18 Turn your Ch. 17 Skills Activity into the tray- make sure your name is on it You need to have your notes out and something to write with- be ready to take some notes
The Start of the Industrial Revolution
 The Start of the Industrial Revolution I. Agricultural Revolution A. Industrial Revolution changed Europe from a mostly agricultural economy to industrialization- work driven by machinery B. Improved Farm
The Start of the Industrial Revolution I. Agricultural Revolution A. Industrial Revolution changed Europe from a mostly agricultural economy to industrialization- work driven by machinery B. Improved Farm
Essential Question: How did both the government and workers themselves try to improve workers lives?
 Essential Question: How did both the government and workers themselves try to improve workers lives? The Philosophers of Industrialization Rise of Socialism Labor Unions and Reform Laws The Reform Movement
Essential Question: How did both the government and workers themselves try to improve workers lives? The Philosophers of Industrialization Rise of Socialism Labor Unions and Reform Laws The Reform Movement
World History Unit 3 Benchmark Study Guide
 World History Unit 3 Benchmark Study Guide Name Period # Date Directions: Use the textbook to answer the questions below. Every question is directly correlated with the benchmark test that you must pass
World History Unit 3 Benchmark Study Guide Name Period # Date Directions: Use the textbook to answer the questions below. Every question is directly correlated with the benchmark test that you must pass
The Industrial Revolution. Europe s
 The Industrial Revolution Europe 1780-1840s Another Ism Effects Europe: Industrialism Spurs of Industrial Revolution Why Did Industrialization Begin in England First? Industrial Revolution was largely
The Industrial Revolution Europe 1780-1840s Another Ism Effects Europe: Industrialism Spurs of Industrial Revolution Why Did Industrialization Begin in England First? Industrial Revolution was largely
Ch. 15: The Industrial Revolution
 Ch. 15: The Industrial Revolution I. Understanding Economics a. The Three Economic Questions i. People have unlimited wants, but limited resources. ii. 3 basic questions: 1. What should be produced? 2.
Ch. 15: The Industrial Revolution I. Understanding Economics a. The Three Economic Questions i. People have unlimited wants, but limited resources. ii. 3 basic questions: 1. What should be produced? 2.
B. Jethro Tull s seed drill made planting seeds V. Crop A. Years of planting only had B. By planting each year farmers were able to maintain
 The Start of the Industrial Revolution: WHERE, WHY, and HOW *What was the Industrial Revolution? The Industrial Revolution was a period that when humanity really began to *Why? I. Factors of Production
The Start of the Industrial Revolution: WHERE, WHY, and HOW *What was the Industrial Revolution? The Industrial Revolution was a period that when humanity really began to *Why? I. Factors of Production
Chapter 10, Section 1 (Pages ) Economic Growth
 Chapter 10, Section 1 (Pages 304 309) Economic Growth Essential Question What effects did the Industrial Revolution have on the U. S. economy? Directions: As you read, complete a graphic organizer like
Chapter 10, Section 1 (Pages 304 309) Economic Growth Essential Question What effects did the Industrial Revolution have on the U. S. economy? Directions: As you read, complete a graphic organizer like
Laissez-Faire vs. Socialism Who is responsible?
 Laissez-Faire vs. Socialism Who is responsible? Warm-Up In your groups discuss the following question: Should the government be responsible in regulating (controlling) businesses? If not, why? If so, how
Laissez-Faire vs. Socialism Who is responsible? Warm-Up In your groups discuss the following question: Should the government be responsible in regulating (controlling) businesses? If not, why? If so, how
Industrial Cities in Great Britain and Ireland,
 Outline Map Industrial Cities in Great Britain and Ireland, 1800 1850 Directions: Locate and label the following: Bristol, London, Birmingham, Belfast, Liverpool, Manchester, Glasgow, Newcastle, Edinburgh,
Outline Map Industrial Cities in Great Britain and Ireland, 1800 1850 Directions: Locate and label the following: Bristol, London, Birmingham, Belfast, Liverpool, Manchester, Glasgow, Newcastle, Edinburgh,
Unit 8. Innovation Brings Change 1800 s-1850 s
 Unit 8 Innovation Brings Change 1800 s-1850 s Unit Overview: Industrialization Era This unit addresses the development of the economies in the North and the South, innovations in technology and the application
Unit 8 Innovation Brings Change 1800 s-1850 s Unit Overview: Industrialization Era This unit addresses the development of the economies in the North and the South, innovations in technology and the application
Notes on the Industrial Revolution ( ) A. Machines start to replace human & animal power in production and manufacturing of goods
 I. Overview of Industrial Revolution (IR) Notes on the Industrial Revolution (1780-1850) A. Machines start to replace human & animal power in production and manufacturing of goods B. Europe gradually transforms
I. Overview of Industrial Revolution (IR) Notes on the Industrial Revolution (1780-1850) A. Machines start to replace human & animal power in production and manufacturing of goods B. Europe gradually transforms
Industrial Revolution Mechanical Change in the World
 Industrial Revolution Mechanical Change in the World STANDARD WHII.9a The student will demonstrate knowledge of the effects of the Industrial Revolution during the nineteenth century by a) citing scientific,
Industrial Revolution Mechanical Change in the World STANDARD WHII.9a The student will demonstrate knowledge of the effects of the Industrial Revolution during the nineteenth century by a) citing scientific,
The Second Industrial Revolution 13.1
 The Second Industrial Revolution 13.1 Things to know... Westerners in the 1800s worshiped progress due to the amazing material growth from the Second Industrial Revolution. Steel, chemicals, electricity,
The Second Industrial Revolution 13.1 Things to know... Westerners in the 1800s worshiped progress due to the amazing material growth from the Second Industrial Revolution. Steel, chemicals, electricity,
Economic Theory: How has industrial development changed living and working conditions?
 Economic Theory: How has industrial development changed living and working conditions? Adam Smith Karl Marx Friedrich Engels Thomas Malthus BACK David Ricardo Jeremy Bentham Robert Owen Classical Economics:
Economic Theory: How has industrial development changed living and working conditions? Adam Smith Karl Marx Friedrich Engels Thomas Malthus BACK David Ricardo Jeremy Bentham Robert Owen Classical Economics:
MRS. OSBORN S APWH CRAM PACKET:
 MRS. OSBORN S APWH CRAM PACKET: Period 5 Industrialization & Global Integration, 1750-1900, chapters 23-29 (20% of APWH Exam) (NOTE: Some material overlaps into Period 6, 1900-1914) Questions of periodization:
MRS. OSBORN S APWH CRAM PACKET: Period 5 Industrialization & Global Integration, 1750-1900, chapters 23-29 (20% of APWH Exam) (NOTE: Some material overlaps into Period 6, 1900-1914) Questions of periodization:
Industrial Rev Practice
 Name: Industrial Rev Practice 1. A major reason the Industrial Revolution began in England was that England possessed A) a smooth coastline B) abundant coal and iron resources C) many waterfalls D) numerous
Name: Industrial Rev Practice 1. A major reason the Industrial Revolution began in England was that England possessed A) a smooth coastline B) abundant coal and iron resources C) many waterfalls D) numerous
The Industrial Revolution. A new era in human history
 The Industrial Revolution A new era in human history definition The Industrial Revolution is the replacement of human and animal power by other sources Agricultural Revolution Improved farming techniques
The Industrial Revolution A new era in human history definition The Industrial Revolution is the replacement of human and animal power by other sources Agricultural Revolution Improved farming techniques
Labor Unions and Reform Laws
 Labor Unions and Reform Laws Factory workers faced long hours, dirty and dangerous working conditions, and the threat of being laid off. By the 1800s, working people became more active in politics. To
Labor Unions and Reform Laws Factory workers faced long hours, dirty and dangerous working conditions, and the threat of being laid off. By the 1800s, working people became more active in politics. To
Chapter 9 and part of Chapter 8: Transforming the Economy,
 Chapter 9 and part of Chapter 8: Transforming the Economy, 1790-1860 The Big Questions: What were the causes and consequences of the industrial and market revolutions, and how did they change the way ordinary
Chapter 9 and part of Chapter 8: Transforming the Economy, 1790-1860 The Big Questions: What were the causes and consequences of the industrial and market revolutions, and how did they change the way ordinary
2. Entrepreneurs a. People who found new business opportunities and new ways of making profits
 1 World History Name Study Guide Chapter 19 Quiz/Test Industrialization and Nationalism DIRECTIONS Use the three sections that we covered in Chapter 19 (19.1: 614 612; 19.2: 624-626; 19.3: 630 637), your
1 World History Name Study Guide Chapter 19 Quiz/Test Industrialization and Nationalism DIRECTIONS Use the three sections that we covered in Chapter 19 (19.1: 614 612; 19.2: 624-626; 19.3: 630 637), your
Transformation. Society
 Transformation of the Economy & Society in Antebellum America 1820-1860 A09W 10.11.01 Guiding Question Analyze the causes of the transformation of the American economy in the first half of the nineteenth
Transformation of the Economy & Society in Antebellum America 1820-1860 A09W 10.11.01 Guiding Question Analyze the causes of the transformation of the American economy in the first half of the nineteenth
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 1 The Growth of Industrial Prosperity ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How can industrialization affect a country s economy? How are political and social structures influenced by economic changes? Reading HELPDESK
Lesson 1 The Growth of Industrial Prosperity ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How can industrialization affect a country s economy? How are political and social structures influenced by economic changes? Reading HELPDESK
INDUSTRY AND MIGRATION/THE NORTH AND THE SOUTH. pp
 INDUSTRY AND MIGRATION/THE NORTH AND THE SOUTH pp 382-405 What drives history? Table Talk: Brainstorm some things that have driven history forward What do these things have in common? What changes have
INDUSTRY AND MIGRATION/THE NORTH AND THE SOUTH pp 382-405 What drives history? Table Talk: Brainstorm some things that have driven history forward What do these things have in common? What changes have
Adam Smith and the Development of Capitalism Smith argued the world would be an orderly, better place, with increased prosperity if people followed
 Adam Smith and the Development of Capitalism Smith argued the world would be an orderly, better place, with increased prosperity if people followed their own self interests. Another way to say a free economy
Adam Smith and the Development of Capitalism Smith argued the world would be an orderly, better place, with increased prosperity if people followed their own self interests. Another way to say a free economy
netw rks Reading Essentials and Study Guide Mass Society and Democracy Lesson 1 The Growth of Industrial Prosperity
 and Study Guide Lesson 1 The Growth of Industrial Prosperity ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can industrialization affect a country s economy? How are political and social structures influenced by economic changes?
and Study Guide Lesson 1 The Growth of Industrial Prosperity ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can industrialization affect a country s economy? How are political and social structures influenced by economic changes?
CH 17: The European Moment in World History, Revolutions in Industry,
 CH 17: The European Moment in World History, 1750-1914 Revolutions in Industry, 1750-1914 Explore the causes & consequences of the Industrial Revolution Root Europe s Industrial Revolution in a global
CH 17: The European Moment in World History, 1750-1914 Revolutions in Industry, 1750-1914 Explore the causes & consequences of the Industrial Revolution Root Europe s Industrial Revolution in a global
The Industrial Revolution Beginnings. Ways of the World Strayer Chapter 18
 The Industrial Revolution Beginnings Ways of the World Strayer Chapter 18 Explaining the Industrial Revolution The global context for the Industrial Revolution lies in a very substantial increase in human
The Industrial Revolution Beginnings Ways of the World Strayer Chapter 18 Explaining the Industrial Revolution The global context for the Industrial Revolution lies in a very substantial increase in human
Industrial Revolution Essentials
 Industrial Revolution Essentials SSWH15 The student will be able to describe the impact of industrialization, the rise of nationalism, and the major characteristics of worldwide imperialism. Analyze the
Industrial Revolution Essentials SSWH15 The student will be able to describe the impact of industrialization, the rise of nationalism, and the major characteristics of worldwide imperialism. Analyze the
Division of Labor: giving each worker one or two simple jobs.
 Chapter 12 The Nation Grows (1815-1830) Section 1 Industries take Root Industrial Revolution: the growth of industry eventually produced changes so great that this time in history is called the Industrial
Chapter 12 The Nation Grows (1815-1830) Section 1 Industries take Root Industrial Revolution: the growth of industry eventually produced changes so great that this time in history is called the Industrial
Nationalism, Economic Revolution, and Social Change
 Nationalism, Economic Revolution, and Social Change 1800-1860 Nationalism and Economic Growth By 1815, following the end of The War of 1812, America had shown: That it could defend its sovereignty against
Nationalism, Economic Revolution, and Social Change 1800-1860 Nationalism and Economic Growth By 1815, following the end of The War of 1812, America had shown: That it could defend its sovereignty against
Economic Issues and Growth
 Economic Issues and Growth 1800-1848 Tariff of 1816 Passed to protect American industries after War of 1812 What would be advantages and disadvantages of high tariffs? Would different regions of the country
Economic Issues and Growth 1800-1848 Tariff of 1816 Passed to protect American industries after War of 1812 What would be advantages and disadvantages of high tariffs? Would different regions of the country
Reforming the Industrial World
 Reforming the Industrial World 4 MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW TERMS & NAMES ECONOMICS The Industrial Revolution led to economic, social, and political reforms. Many modern social welfare programs developed
Reforming the Industrial World 4 MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW TERMS & NAMES ECONOMICS The Industrial Revolution led to economic, social, and political reforms. Many modern social welfare programs developed
In the early Antebellum era ( ), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that
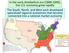 In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that became connected into a national market economy The
In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that became connected into a national market economy The
Unit Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution
 Unit 4 1800-1848 Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution Antebellum America: The Market and Transportation In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The
Unit 4 1800-1848 Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution Antebellum America: The Market and Transportation In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The
Industrialism. Sophia Wright, David Suescun, Oliver Santos, Kayla Gardner
 Industrialism Sophia Wright, David Suescun, Oliver Santos, Kayla Gardner Industrialism- What is It? Before industrialism, mainly farming and agriculture took place in the United States, despite Alexander
Industrialism Sophia Wright, David Suescun, Oliver Santos, Kayla Gardner Industrialism- What is It? Before industrialism, mainly farming and agriculture took place in the United States, despite Alexander
The Industrial Revolution: England s Cities. The factory system changes the way people live and work, introducing a variety of problems.
 The Industrial Revolution: England s Cities The factory system changes the way people live and work, introducing a variety of problems. Last class: Industrial Revolution Industrialization The Industrial
The Industrial Revolution: England s Cities The factory system changes the way people live and work, introducing a variety of problems. Last class: Industrial Revolution Industrialization The Industrial
DRAWING FROM EXPERIENCEII
 Chapter 10, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 306 311 ECONOMIC GROWTH KEY TERMS Industrial Revolution A new way of working and producing goods (page 307) capital Money invested to start new businesses
Chapter 10, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 306 311 ECONOMIC GROWTH KEY TERMS Industrial Revolution A new way of working and producing goods (page 307) capital Money invested to start new businesses
After the War of 1812 THE BEGINNING OF CHANGE IN AMERICAN POLITICS, ECONOMY, AND SOCIETY
 After the War of 1812 THE BEGINNING OF CHANGE IN AMERICAN POLITICS, ECONOMY, AND SOCIETY Consequences of the War of 1812 Why was the War of 1812 fought? Impressment Violation of neutral shipping rights
After the War of 1812 THE BEGINNING OF CHANGE IN AMERICAN POLITICS, ECONOMY, AND SOCIETY Consequences of the War of 1812 Why was the War of 1812 fought? Impressment Violation of neutral shipping rights
Economic Expansion & Nationalism
 Economic Expansion & Nationalism WC Chapter 24 Industrialism Creates a Global Economy How did steam revolutionize transportation? What were its effects? How did the telegraph speed communication? What
Economic Expansion & Nationalism WC Chapter 24 Industrialism Creates a Global Economy How did steam revolutionize transportation? What were its effects? How did the telegraph speed communication? What
The Industrial Revolution
 The Industrial Revolution I. Industrial Revolution: During the 1700s and 1800s, agricultural and industrial innovations led to profound changes in society. The world became more interconnected and industrialization
The Industrial Revolution I. Industrial Revolution: During the 1700s and 1800s, agricultural and industrial innovations led to profound changes in society. The world became more interconnected and industrialization
Industrial Revolution
 Industrial Revolution Industrial Revolution Abraham Darby Richard Arkwright Water Frame Factory System George Stephenson Combination Acts Robert Owen Socialism 1832 Reform Bill People s Charter 1838 Factory
Industrial Revolution Industrial Revolution Abraham Darby Richard Arkwright Water Frame Factory System George Stephenson Combination Acts Robert Owen Socialism 1832 Reform Bill People s Charter 1838 Factory
THE FIRST INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IN THE U.S. How the War of 1812 & Technological Progress Change the Country
 THE FIRST INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IN THE U.S. How the War of 1812 & Technological Progress Change the Country TECHNOLOGY MEANS PROGRESS Developments in technology begin to transform life in the U.S. in the
THE FIRST INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IN THE U.S. How the War of 1812 & Technological Progress Change the Country TECHNOLOGY MEANS PROGRESS Developments in technology begin to transform life in the U.S. in the
Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy?
 Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy? CPUSH Agenda for Unit 4.4: Clickers Questions Market Revolution inquiry activity
Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy? CPUSH Agenda for Unit 4.4: Clickers Questions Market Revolution inquiry activity
Industrial Revolution
 Chapter 9 Economic Transformation Industrial Revolution Division of Labor Industry in America 1790 1820 aided by transportation Industrial Revolution outwork system work done outside of shop modern factory
Chapter 9 Economic Transformation Industrial Revolution Division of Labor Industry in America 1790 1820 aided by transportation Industrial Revolution outwork system work done outside of shop modern factory
Industrial and social revolutions Reforming and reshaping of nations
 Industrial and social revolutions Reforming and reshaping of nations -Switch from manpower to machine power THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION - Great Britain leads the way - factors of production needed for growth:
Industrial and social revolutions Reforming and reshaping of nations -Switch from manpower to machine power THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION - Great Britain leads the way - factors of production needed for growth:
Reforming the Industrial World
 Reforming the Industrial World 4 MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW TERMS & NAMES ECONOMICS The Industrial Revolution led to economic, social, and political reforms. Many modern social welfare programs developed
Reforming the Industrial World 4 MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW TERMS & NAMES ECONOMICS The Industrial Revolution led to economic, social, and political reforms. Many modern social welfare programs developed
Section 4 Notes Window panes
 Term Picture 10 word max summary Answer questions at the end of the section. Section 4 Notes Window panes Laissez-faire Capitalism Utilitarianism Socialism Karl Marx Communism Unions Factory Act of 1883
Term Picture 10 word max summary Answer questions at the end of the section. Section 4 Notes Window panes Laissez-faire Capitalism Utilitarianism Socialism Karl Marx Communism Unions Factory Act of 1883
The textile industry began the industrial age. Changes in farming led to greater production of food but eliminated
 Chapter Review Chapter Summary Section 1: The Dawn of the Industrial Age The textile industry began the industrial age. Changes in farming led to greater production of food but eliminated farming jobs,
Chapter Review Chapter Summary Section 1: The Dawn of the Industrial Age The textile industry began the industrial age. Changes in farming led to greater production of food but eliminated farming jobs,
Starting in England around 1750, the introduction of new
 Economic Theory 1 Starting in England around 1750, the introduction of new machines powered by steam or by running water in streams and rivers changed the ways people had lived and worked for centuries.
Economic Theory 1 Starting in England around 1750, the introduction of new machines powered by steam or by running water in streams and rivers changed the ways people had lived and worked for centuries.
Economic Growth. Guided Reading Activity. Growth and Expansion. Answering Questions DIRECTIONS: As you read the section, answer the questions below.
 Guided Reading Activity Growth and Expansion Section Economic Growth Give yourself enough time to read and understand the text. Don t rush through it. Take your time and pause to reread sections or to
Guided Reading Activity Growth and Expansion Section Economic Growth Give yourself enough time to read and understand the text. Don t rush through it. Take your time and pause to reread sections or to
Originates in France during the French Revolution, after Louis XVI is executed. Spreads across Europe as Napoleon builds his empire by conquering
 Originates in France during the French Revolution, after Louis XVI is executed. Spreads across Europe as Napoleon builds his empire by conquering neighboring nations. Characteristics: Historical Origins:
Originates in France during the French Revolution, after Louis XVI is executed. Spreads across Europe as Napoleon builds his empire by conquering neighboring nations. Characteristics: Historical Origins:
In the first half of the nineteenth century, economic changes called by historians the market revolution transformed the United States.
 1 2 In the first half of the nineteenth century, economic changes called by historians the market revolution transformed the United States. Innovations in transportation and communication sparked these
1 2 In the first half of the nineteenth century, economic changes called by historians the market revolution transformed the United States. Innovations in transportation and communication sparked these
Industrial Revolution: Reform. Key Concept 5.1 Industrialization and Global Capitalism Tuesday March 27, 2018
 Industrial Revolution: Reform Key Concept 5.1 Industrialization and Global Capitalism Tuesday March 27, 2018 Capitalism An economic idea that promoted maximum profit through competition and investment
Industrial Revolution: Reform Key Concept 5.1 Industrialization and Global Capitalism Tuesday March 27, 2018 Capitalism An economic idea that promoted maximum profit through competition and investment
The March of Millions
 The March of Millions Around 1850 the population was doubling every 25 years. By 186 there were 33 states. America was the fourth most populous nation in the world. Cities were rapidly developing as were
The March of Millions Around 1850 the population was doubling every 25 years. By 186 there were 33 states. America was the fourth most populous nation in the world. Cities were rapidly developing as were
Why has our economy grown?
 Review US Economy Why has our economy grown? A large Market Supportive government for business Laissez-faire, no gov t interference in the economy except to maintain law and order Enormous natural resources
Review US Economy Why has our economy grown? A large Market Supportive government for business Laissez-faire, no gov t interference in the economy except to maintain law and order Enormous natural resources
The Industrial Revolution, cont d. S. Anderson World History
 The Industrial Revolution, cont d S. Anderson World History The Industrial Revolution, cont d The Industrial Revolution brought about fundamental changes in the way goods are made. It introduced mass production
The Industrial Revolution, cont d S. Anderson World History The Industrial Revolution, cont d The Industrial Revolution brought about fundamental changes in the way goods are made. It introduced mass production
netw rks Reading Essentials and Study Guide Growth and Division, Lesson 2 Early Industry ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Reading HELPDESK
 and Study Guide Lesson 2 Early Industry ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How did the nation s economy help shape its politics? How did the economic differences between the North and the South cause tension? Reading
and Study Guide Lesson 2 Early Industry ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How did the nation s economy help shape its politics? How did the economic differences between the North and the South cause tension? Reading
Imperialism by the US
 Imperialism by the US Quick Class Discussion: Based on this image, what important changes took place in the United States from 1783 to 1900? 115 years after gaining independence from Britain, the United
Imperialism by the US Quick Class Discussion: Based on this image, what important changes took place in the United States from 1783 to 1900? 115 years after gaining independence from Britain, the United
U.S. History / Geography I Final Exam Review
 U.S. History / Geography I Final Exam Review 1. Laissez-faire relies on to regulate prices and wages. 2. A shortage of workers in California forced the Central-Pacific railroad while building the Trans-Continental
U.S. History / Geography I Final Exam Review 1. Laissez-faire relies on to regulate prices and wages. 2. A shortage of workers in California forced the Central-Pacific railroad while building the Trans-Continental
Characteristics Families Clustered near rivers Regional settlement
 Population 1790 Majority lives East of Appalachian mountains and within a few miles of ocean 1840 1/3 lives between Appalachian mountains and Mississippi River The Sweep West Series of bursts 1790s 1791-1803
Population 1790 Majority lives East of Appalachian mountains and within a few miles of ocean 1840 1/3 lives between Appalachian mountains and Mississippi River The Sweep West Series of bursts 1790s 1791-1803
Industrial Revolution
 ECONOMIC SYSTEM Industrial Revolution During 1760-1820, a period of major industrialization occurred beginning in Britain and then spread throughout the world. New steam and water powered inventions made
ECONOMIC SYSTEM Industrial Revolution During 1760-1820, a period of major industrialization occurred beginning in Britain and then spread throughout the world. New steam and water powered inventions made
UNIT 4: EXPANSION & REFORM LESSON 4.1: EFFECTS OF MANIFEST DESTINY & INDUSTRIALIZATION
 UNIT 4: EXPANSION & REFORM LESSON 4.1: EFFECTS OF MANIFEST DESTINY & INDUSTRIALIZATION ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does expansion and industrialization contribute to growing sectionalism within the United States
UNIT 4: EXPANSION & REFORM LESSON 4.1: EFFECTS OF MANIFEST DESTINY & INDUSTRIALIZATION ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does expansion and industrialization contribute to growing sectionalism within the United States
ECON European Economic History The Industrial Revolution John Lovett $1,600 $1,400 $1,200. (Real GDP/capita) $1,000 $800 $600 $400 $200 $ 0
 ECON 343 European Economic History The Industrial Revolution John Lovett Exam 3 Code Name: In 28 we cover Perry et al instead. Objective Section: 7 pts, 2.5 points each unless noted. ( points This is just
ECON 343 European Economic History The Industrial Revolution John Lovett Exam 3 Code Name: In 28 we cover Perry et al instead. Objective Section: 7 pts, 2.5 points each unless noted. ( points This is just
CHAPTER 11 KEY ISSUE TWO: WHERE IS INDUSTRY DISTRIBUTED?
 CHAPTER 11 KEY ISSUE TWO: WHERE IS INDUSTRY DISTRIBUTED? WORLD INDUSTRIAL REGIONS North America Industrialized areas in North America Changing distribution of U.S. manufacturing Europe Western Europe Eastern
CHAPTER 11 KEY ISSUE TWO: WHERE IS INDUSTRY DISTRIBUTED? WORLD INDUSTRIAL REGIONS North America Industrialized areas in North America Changing distribution of U.S. manufacturing Europe Western Europe Eastern
The Industrial Revolution,
 712 Although this painting shows Canton, China, the flags flying over the fenced-in areas near the shore are those of Spain, the United States, Great Britain, and the Netherlands. Canton was one of only
712 Although this painting shows Canton, China, the flags flying over the fenced-in areas near the shore are those of Spain, the United States, Great Britain, and the Netherlands. Canton was one of only
Today s Lesson A note from me to you
 Today s Lesson A note from me to you I apologize for not being with you today. I have tried to make this a PowerPoint that is easy to follow and one from which you can learn. During the presentation, you
Today s Lesson A note from me to you I apologize for not being with you today. I have tried to make this a PowerPoint that is easy to follow and one from which you can learn. During the presentation, you
World Industrial Regions
 World Industrial Regions North America Industrialized areas in North America Changing distribution of U.S. manufacturing Europe Western Europe Eastern Europe East Asia Manufacturing Regions Fig. 11-3:
World Industrial Regions North America Industrialized areas in North America Changing distribution of U.S. manufacturing Europe Western Europe Eastern Europe East Asia Manufacturing Regions Fig. 11-3:
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism
 Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism Regional Economies Create Differences Samuel Slater brought the Water Frame to Rhode Island from Great Britain in 1789. It was used to spin raw cotton into cotton
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism Regional Economies Create Differences Samuel Slater brought the Water Frame to Rhode Island from Great Britain in 1789. It was used to spin raw cotton into cotton
Conservatism. Belief in strong controls on the population: absolute monarchy censorship strong aristocracy strong church
 Advent of the Isms Conservatism Belief in strong controls on the population: absolute monarchy censorship strong aristocracy strong church Nationalism Patriotism strong sense of national identity & national
Advent of the Isms Conservatism Belief in strong controls on the population: absolute monarchy censorship strong aristocracy strong church Nationalism Patriotism strong sense of national identity & national
20, 2007 HARDSHIPS OF EARLY INDUSTRIAL LIFE
 HARDSHIPS OF EARLY INDUSTRIAL LIFE The New Industrial City urbanization - movement of people to cities - changes in farming, soaring pop. growth, demand for workers led masses of people to migrate from
HARDSHIPS OF EARLY INDUSTRIAL LIFE The New Industrial City urbanization - movement of people to cities - changes in farming, soaring pop. growth, demand for workers led masses of people to migrate from
Trends in Antebellum America:
 Mr. Cegielski Trends in Antebellum America: 1810-1860 Covered last unit: 1. New intellectual and religious movements 2. Social reforms 3. Increase in federal power Marshall Ct. decisions. This Unit: 1.
Mr. Cegielski Trends in Antebellum America: 1810-1860 Covered last unit: 1. New intellectual and religious movements 2. Social reforms 3. Increase in federal power Marshall Ct. decisions. This Unit: 1.
Ch. 4 Industrialization, 5.4 Populism, 6.1 Politics of the Gilded Age Quiz 2011
 Ch. 4 Industrialization, 5.4 Populism, 6.1 Politics of the Gilded Age Quiz 2011 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. IDENTIFYING MAIN IDEAS 1.
Ch. 4 Industrialization, 5.4 Populism, 6.1 Politics of the Gilded Age Quiz 2011 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. IDENTIFYING MAIN IDEAS 1.
Period V ( ): Industrialization and Global Integration
 Period V (1750-1900): Industrialization and Global Integration 5.1 Industrialization and Global Capitalism I. I can describe and explain how industrialism fundamentally changed how goods were produced.
Period V (1750-1900): Industrialization and Global Integration 5.1 Industrialization and Global Capitalism I. I can describe and explain how industrialism fundamentally changed how goods were produced.
The Birth of Unions SE: US 3B. By Brad Harris, Grand Prairie HS
 The Birth of Unions SE: US 3B By Brad Harris, Grand Prairie HS What is a Labor Union? A labor union is an organization of workers who unite to protect the rights of the workers from abusive practices of
The Birth of Unions SE: US 3B By Brad Harris, Grand Prairie HS What is a Labor Union? A labor union is an organization of workers who unite to protect the rights of the workers from abusive practices of
What are fair working conditions?
 What are fair working conditions? You are a 15-year-old living in England where the Industrial Revolution has spurred the growth of thousands of factories. Cheap labor is in great demand. Like millions
What are fair working conditions? You are a 15-year-old living in England where the Industrial Revolution has spurred the growth of thousands of factories. Cheap labor is in great demand. Like millions
Q3/Q4 Sectionalism Vocab
 Q3/Q4 Sectionalism Vocab North: Industrial Revolution Sectionalism: loyalty to one region (section) of the country rather than the whole country Industrial Revolution: period of rapid growth in the use
Q3/Q4 Sectionalism Vocab North: Industrial Revolution Sectionalism: loyalty to one region (section) of the country rather than the whole country Industrial Revolution: period of rapid growth in the use
The Factors Affecting American Economy From : Which Were. The United States economy was stimulated by many factors between
 The Factors Affecting American Economy From 1800 1860: Which Were Most Important And Why William Heegaard Sometime in High School The United States economy was stimulated by many factors between 1800 and
The Factors Affecting American Economy From 1800 1860: Which Were Most Important And Why William Heegaard Sometime in High School The United States economy was stimulated by many factors between 1800 and
Warm-up. The period of rebuilding the nation after the civil war. Why were the Southern States concerned with the election of Lincoln?
 Warm-up The period of rebuilding the nation after the civil war. Why were the Southern States concerned with the election of Lincoln? Objectives Impact of the Industrial Revolution How new innovations
Warm-up The period of rebuilding the nation after the civil war. Why were the Southern States concerned with the election of Lincoln? Objectives Impact of the Industrial Revolution How new innovations
