3. Government and governmental networks
|
|
|
- Gabriella Little
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. Governing in the UK 1.1. Counter-powers: 3. Government and governmental networks In the UK, the Prime Minister has progressively gained more power. As Lord Chancellor Hailsham said: The sovereignty of Parliament has increasingly become, in practice, the sovereignty of the Commons, and the sovereignty of the Government which, in addition to its influence in Parliament, controls the party whips, the party machine, and the Civil Service. This means that what has always been an elective dictatorship in theory, but one in which the component parts operated in practice to control one another, has become a machine in which one of these parts has come to exercise a predominant influence over the rest. (1976) In theory, Parliament is indeed the first institution to present a check on government power in the form of parliamentary reviews or during debates which are often simply ritual exchanges of party political propaganda 1. Parliament may indeed introduce a vote of no confidence to send back the government. MPs and peers can ask their questions during the Prime Minister s Question Time 2, once a week in both houses of Parliament. The attendance rates in both Houses of Parliament, however, are not high: less than 65% for the Commons and less than 50% for the Lords (2008 and 2010 figures). Finally, even the power of the Lords, whose members are mostly politically neutral cross-benchers, has been more and more limited: because Lords are not elected, they are not legitimate enough to oppose elected MPs. Citizens too can oppose government policy by asking for judicial review but the system is complex as they require leave requirement and cost a lot of money, with few results. The authority of the government is contested on a daily basis by Her Majesty s Opposition which consists of the Leader of the Opposition and the Shadow Cabinet. Twenty days a year, during opposition days also known as supply or allotted days the Opposition can set the parliamentary agenda. If a matter is considered important, it may ask the Speaker of the House to organize an adjournement debate. Government policy, in addition, is regularly examined by select committees and standing committees (for more specific matters) whose investigative power remains somewhat limited. Similarly, the Parliamentary Ombudsman has a consultative role only. When a party has the majority in Parliament, it thus becomes difficult to control the government but the Opposition can choose to support it for strategic reasons 3. Backbenchers, furthermore, have a crucial role to play: in spite of the pressure imposed on them by whips, some of them may rebel against their party s policy The Prime Minister: In 1963, as the Consensus years were drawing to a close, Labour MP Richard Crossman declared that the post war epoch has seen the final transformation of the cabinet government into prime ministerial government. Causing even more concern was the emergence, with Thatcher s election in 1979, of conviction politics, a tendency that extended into the 21 st century with T. Blair ( ). Political power became more personalized though at the expense of collective policy-making. It means that the Prime Minister has become more than just primus inter pares. Some of their decisions can be taken without consulting the Cabinet: 1 Weir S. and D. Beetham. Political Power and Democratic Control in Britain. London: Routledge, 1999, A Deputy Prime Minister s Question Time has also existed since : In 1997, before his election, Blair imposed a three-line whip asking Labour MPs not to oppose the 1994 law on criminality because he did not want to appear soft on crime.
2 Refusing the European Exchange Rate Mechanism (EEMR), Thatcher increased the independence the Bank of England without the consultation of Cabinet. Emphasizing that New Labour would not dismantle Thatcherism, Blair s first act of government was coated in Conservatism as he went even beyond Thatcher by granting the Bank of England full control of interest rate policy. The decision took the entire political establishment by surprise and created more dissension within the Labour party. In the context of Blair s decision to wage war on Iraq, his government s key policy decisions were criticized for having been made by a small clique and special advisors (like spin doctors) without proper Cabinet consultation. Blair announced an end to "sofa-style" government, stating that future crises would be dealt with by a formal ad hoc Cabinet committee. The Cameron-Clegg coalition government (2010-5), in retrospect, collective responsibility was more difficult. In this respect, the Coalition Committee was created to coordinate the two partieslib-dem ministers could disagree over some policies such as the raising of tuition fees and nuclear energy policy. It has become clear that cabinet government is not constituted merely by the weekly meeting of the fifteen to twenty plus ministers: to take account of the fact that it covers more than full meetings of the cabinet, concepts such as the core executive or the cabinet system have come to be used in the literature 4. But unlike the American President, the Prime Minister was not directly elected, so he or she might be dismissed by his or her own party The State: To understand how the state works, you have to get acquainted with contractual governance, thereby the people accept to give up certain rights in exchange for protection from the State. In the UK, the word state originally refers to the head of State (the Queen), but it can be extended to government insofar as there exists a Welfare State responsible for social security. More than just protecting, the British state must also be an enabling force, that is to say, it must enable citizens to be responsible for themselves. This trend developed in the 1970s- 80s, as Thatcher sought to roll back the frontiers of the state to make way for the free market. For the same reason, successive British governments have reduced the overall tax rates for businesses and progressively deregulated the market to give managers back the right to manage. Following the so-called Big Bang of 1986, the UK self-regulatory system was placed into a statutory framework 5, reducing the role of the State accordingly and limiting access to allowance policy. Paradoxically enough, as Thatcher reduced state intervention in the economy, social control and regulation became more important, policing those trying to defraud social security. One of the most illustrative example of that tendency was during the miners strike as it generated violent clashes the police. In the 1980s, moreover, the state did not seek the structural causes for the social ills it was trying to combat instead, it sought to change the people directly, invoking individual responsibility 6. The trend did not change in the 1990s and 2000s under Blair s leadership. In fact, the distinction between civil law and criminal law became even more blurry. Such laws as the Prevention of Terrorism Act (2005) and the Terrorism Prevention and Investigation Measures Act (2011) voted by the coalition clearly infringed on individual liberties. 4 In their work on Unlocking the Cabinet, Mackie and Hogwood introduced the term arenas to refer to the different decisionmaking contexts that form part of the cabinet system. 5 Sweeping reform in the regulation of the UK investment industry started with the Financial Services Act (1986) whose comprehensive government regular (the Securities and Investment Board between and the Financial Services Authority since then) was consolidated due to the Financial Services and Markets Act (2000). Following the 2007 financial crisis, the FSA worked with the Bank of England and the Treasury (the Tripartite Authorities) to reform and strengthen the existing UK framework. 6 Family intervention projects, for example, were aimed at helping those seen as antisocial find the cause by themselves.
3 LEA - Civi GB Session Democracy and election system 2.1. First-past-the-post voting: The first-past-the-post voting (FPTP) method is one of the several plurality voting systems: voters indicate on the ballot the candidate they chose, and the candidate who receives more votes in a constituency wins. In that there are some 650 constituencies in the UK, constituency voters may feel better represented. The effect of a system based on single-seat constituencies is that the larger parties gain a disproportionately large share of seats, insuring a working majority while smaller parties are left with a disproportionately small one. The two-party system excluding minority parties, Her Majesty s Opposition in Parliament remains relatively strong, imposing what J.S. Mill called the tyranny of the majority. The winner party, however, is not necessarily the one with more votes: 18 out of 23 general elections since 1922 have produced a single party majority government. In 1951, Labour had some 250,000 more votes than the Conservatives but the latter won more constituencies and Churchill got reelected. Conversely, in 1974, Wilson was reelected because Labour had secured more constituencies than the Conservatives, but had less votes. If there is no majority, there is a hung parliament Reforming the electoral system: The Electoral Reform Society is a British political pressure group which promotes the abolition of FPTP for all national and local elections, arguing it is bad for democracy. Even after the Parliamentary Voting System and Constituencies Act (2011), indeed, the geographical distribution of votes in a constituency remains unfair. In addition, FPTP is usually responsible for tactical voting behaviors. Because a lot of votes are wasted once a candidate has reached the majority of votes (+50%), the British tend to vote against instead of for a candidate. Single transferable voting: After their 2011 referendum on Alternative Vote (AV), Lib-Dems proposed to replace FPTP with single transferable voting: 68% of voters were in favor of electoral reform. But the Conservatives rejected that option and limited the project to preferential voting, or ranked-choice voting (RCV), thereby voters can rank the candidates in order of preference 7. Less votes would be wasted and tactical voting would no longer be necessary, but the project was rejected. Another proposition was the Additional Member System, thereby an elector has two votes: the constituency vote (relative to FPTP) and the regional vote (proportional). 8 This system tends to generate coalition government instead of strong government. Direct democracy: In opposition to representative democracy, direct democracy means citizens acquire power to abide by public decisions and have the right to take part equally and fairly in the entire process that generates these decisions. Direct democracy institutions comprise citizen-initiated mechanisms (CI- MDDs) serving as intermittent safety valves with many different forms: mandatory plebiscites, or obligatory referenda, are one of them (Altman: 1-5). In the UK, participation rates in local elections has decreased since 1950 (80%), reaching 65% in And yet a lot referenda have been organized in recent decades. In 1973, the first UK referendum was organized to settle the question of Northern Ireland s membership in the Union. Successive UK governments, such as G. Brown s ( ), have also encouraged direct democracy initiatives such as citizen s juries (= forums) or e-petitions introduced by the coalition government in the 2010s. In 2011, however, the House of Lords rejected an initiative empowering citizens to elect constables. Unsurprisingly, then, direct action initiatives became more popular: civil disobedience, boycott, blockade etc. 7 The difference is that instant runoff voting (IRV) such as preferential voting is not a proportional voting system, unlike single transferable voting. Like all winner-take-all voting systems, IRV tends to exaggerate the number of seats won by the largest parties. 8 The Scottish Parliament adopted this practice to rectify regional inequality.
4 Ethnic minority and women: British democracy, in many respects, remains quite elitist: in 2010, 7% Britons had been to private schools, against 35% for MPs. Former Prime Minister Cameron comes from Eton College and his former Deputy (N. Clegg), from Westminster School. Both, moreover, studied in Oxbridge, as did 28% of all British MPs. In spite of the Sex Discrimination Act (2002), women, moreover, are still underrepresented. Although technically illegal, political parties may resort to all-women shortlists, as did the Labour Party in 1997, to have more women then nicknamed Blair s Babes serving as MPs. In 2006, the Conservatives adopted a priority list (the A list ) in which half of the candidates had to be women. The fact that T. May was appointed Home Minister in 2010 was the result of the Women2Win campaign group. Ethnic minorities, moreover, are underrepresented too: the first mixed-race Cabinet Minister in Britain was Paul Boateng, whose mother was Scottish and father was Ghanaian and was appointed Chief Secretary to the Treasury in May 2002 only. At the local level, the first ethnic minority woman to be elected as MP was Diane Abbott (with the Labour Party). Other parties like the Lib-Dems or the Conservatives also work towards more diversity as seen with the Ethnic Minority Liberal Democrats or the Priority List adopted by the Conservatives in Critics argue that experience prevails over ethnicity, and that a lot of ethnic minority MPs are but token representatives Renewing democracy: In recent years, the image of the British government has been tarnished by a few political scandals, most notably involving lobbying though not exclusively: the student protests (Nov-Dec. 2010) against further cuts to education, the Belfast City Hall flag protests (2012) revived the tensions between nationalists in Northern Ireland and Unionists, the emergence of the anti-austerity movement (2010-present) or the ongoing mystery surrounding the Westminster paedophile dossier have seriously eroded the population s confidence. According to the British Social Attitudes Survey, moreover, 60% Britons said they did not trust their political leaders. Some laws sought to revive democracy, such as the Freedom of Information Act (2000) but some laws sought to restrict citizens freedom, such as the Identity Cards Act (2006), creating the National Identity Register (NIR), later destroyed as a result of the Identity Documents Act (2010), a bill originally introduced by T. May. The House of Lords: The House of Lords Act (1999) was the first step in the reform of the upper house. Since the recommendations made in the Wakeham report (2000), British officials have managed to agree on the question of whether Lords should be appointed or elected. During the Votes of February 2003, some like T. Blair favored a hybrid House. Blair also created the Department for Constitutional Affairs (DCA) in June so as to debate constitutional reform involving not only the House of Lords, but also the soon-to-be-created Supreme Court. In its September report entitled Constitutional Reform: Next Steps for the House of Lords, the DCA argued in favor a fully appointed house. Discussions reprised early in 2006 in the aftermath of the Cash for Peerages affair concerning the connection between political donations and the award of life peerages 9. Following attempts by the Lords to block (or add safeguards to, according to viewpoint), recent controversial legislation, a short majority of Britons felt that a jury of the general public should decide on the House s future. During the Votes of March 2007, the House of Commons unexpectedly voted by a large majority for an allelected Upper House while, one week later, the House of Lords pronounced in favor of an all-appointed House by a larger majority. It was not until the coalition government that the House of Lords Reform Bill (2012) was drafted and introduced by N. Clegg. Labour called for more scrutiny of the bill and said it would vote against the program motion, along with several Conservative MPs. On 10 July 2012, some 91 Conservative MPs voted against the three-line whip and 19 more abstained. Deputy Prime Minister Nick Clegg had to abandon the bill due to the opposition from Conservative backbench MPs, claiming that their party had broken the coalition contract. In spite of two recent acts voted in 2014 and 2015, allowing Lords to retire, and to expel or suspend members, the debate is still open. 9 To cut a long story short, Blair appointed Lords who were eventually rejected by the Judicial Appointments Commission. It was found that these candidates had given money to finance the Labour Party s campaign.
5 LEA - Civi GB Session 03 The House of Commons: The lower house too was subject to reform. Under the provisions of the Fixed-term Parliament Act (2011), parliamentary elections must be held every five years, beginning in Initially, the Septennial Act (1715) provided that a Parliament expired seven years after it had been summoned this period was reduced to five years by the Parliament Act (1911); though, in any case, Parliament was never allowed to reach its maximum statutory length, as the monarch always dissolved it before its expiry. Before the passage of the 2011 Act, Parliament could thus be dissolved by royal proclamation by virtue of the Royal Prerogative. By the nineteenth century, prime ministers had a great deal of de facto control over the timings of general elections. Furthermore, the Parliamentary Voting System and Constituencies Act (2011) made provisions for both the Alternative Vote referendum and the Sixth Periodic Review of Westminster constituencies. Reviewing is the process by which parliamentary constituencies to the House of Commons are being reviewed by the four boundary commissions (= non-departmental public bodies responsible for determining the boundaries of constituencies for elections to all Parliament, including national ones). At the turn of the 2010s, finally, the Backbench Business Committee was created to give an opportunity to backbenchers to bring forward debates of their choice 10. The Petitions Committee is the body charged with overseeing the e-petitions system. 3. The networks of power 3.1. Interest groups: Business lobbies ( any business-related group that tries to persuade politicians to change sth ): In the UK, big business interests are represented by over 3,000 trade associations such as the Confederation of British Industry (CBI) which has unmatched influence with government. Though originally the CBI tends to work more closely with the Conservatives, T. Blair was the first Labour Prime Minister to intervene in the 1997 annual conference of the Confederation. New Labour has indeed proved to have closer relationships with the business world, like Sir David Simon, former chief executive of BP Oil International, who was appointed Minister for Trade and Competitiveness in Europe, after the 1997 election 11. Some among these businessmen, like Lord Patrick Carter, were even invited to give political advice on issues such health, sports or justice. Moreover, the City of London has eventually become a major contributor to Labour s political campaigns. In 1970, however, the Labour Party had promoted a Companies bill whose provisions would have forced companies to disclose their political contributions. The ensuing Acts of 1976 and 1985 were superseded by the Companies Acts of 2004 and Businessmen generally can access privileged circles of government like the Leader s Group but they may also pay for professional lobbyists to promote community interest companies. Think tanks ( a group of experts brought together, usually by a government, to develop ideas on a particular subject and to make suggestions for action ): Think tanks are ostensibly independent research groups used to promote business interests. The Adam Smith Institute, for instance, campaigned in favor of privatization. Some big businesses, like Group 4 Securicor (G4S), founded in 2004 as a multinational security services company, have had their own think tanks: the Serco Institute was vested with the mission to study competition and contracting in public services. As of 2007, there were over 100 think tanks in the UK. Already in the Thatcher years, the Institute for Economic Affairs would have pushed the government to enact monetarist policy just as in the Blair years, when the Institute for Public Policy Research gave legitimacy to Labour s Third Way politics. Pressure groups ( a group of people who work together to try to influence what other people or the government think about a particular subject, in order to achieve the things they want ): Trade associations such as the British Medical Association, the Law Society or even the Society for the Protection of Birds have more members than political parties. Pressure groups like Liberty (created in 2006) are a means for citizens to make their voices heard. 10 The Committee can consider subjects raised in national or local campaigns, reports by select committees and other groups and issues suggested by constituents, including paper or electronic petitions with no restriction on the number of signatures. 11 Sir David Simon was a leading member of the European Roundtable of Industrialists and former member of the EU's Competitiveness Advisory Group (CAG). One of his first moves as a minister was an -- unsuccessful -- attempt to make Labour MPs vote against a directive to regulate company take-overs. New Labour, he explained, favors self-regulation over legal regulation.
6 3.2. Trade unions and political advisers: Ever since the creation of the Trade Union Congress in 1868, trade unions have had some influence on government policy. In some instances, their influence was so significant that they sapped the government in power at the time, as in 1974 with E. Heath and the National Union of Mineworkers. The fact its membership declined between 2008 (6.5 million) and 2016 (5.8 million) also reflects the fact that their influence has diminished in the last decades, most notably in the Thatcher years: the changing job market, high unemployment, the abolition of the closed shop (= the employer agrees to hire union members only, and employees must remain members of the union at all times in order to remain employed) and picketing (= a form of protest in which picketers congregate outside a place of work or location where an event is taking place). Even during the Blair years, trade unions tended to be removed from the political process. A 2010 report published by the UK s leading (Conservative) think tank Policy Exchange in Sept. even recommended more legislative restrictions to trade unions Media and spin doctors : In the UK, the media tend to have their own commercial and ideological interests. Like other interest groups, some have lost influence: as early as 2006, News of the World, a national red top newspaper published from 1843 to 2011 and one of the biggest-selling English-language newspaper around the globe, became engulfed in allegations of phone hacking. Back in 2000, the populist newspaper had published the names of 150 sexual offenders guilty of child abuse in the wake of the 8-year old Sarah Payne murder. Though the newspaper had to retract from disclosing the name of sex offenders, it continued to lobby for the introduction of a Sarah s Law in the UK that would enable any family to consult the Sex Offenders Register 12. It was not until 2007 that a lighter version of the law was voted, enabling single mothers to consult the registry. Political officials are thus well aware that they need to collaborate with media moguls, as T. Blair with Rupert Murdoch. The so-called Tony press echoing the Tory press however eventually turned the media tide against New Labour. The most recent event to illustrate that phenomenon would be the phone-hacking scandal (2011). Whilst investigations conducted in the mid-2000s limited the paper s phone hacking activities to celebrities, politicians and members of the British Royal Family, in July 2011 it was revealed that the phones of murdered schoolgirl Milly Dowler, relatives of deceased British soldiers and victims of the London bombings (7 July 2005) had also been hacked. The resulting public outcry led to several high-profile resignations, including Murdoch s. The revelation was all the more surprising considering that spin doctors have had an increasing role in British politics. For example, Alastair Campbell, former editor for the Daily Mirror, is remembered as the epitome of the spin doctor for his work as Downing Street Press Secretary ( ), followed by Director of Communications and Strategy (2000 3). His role in the Iraq War ( ) was considerable 13. The same argument goes with special advisers, whose number between 1997 (38) and 2009 (74). There is no legal limit on the number of special advisers, although the current total is less than it was under Blair and Brown. 12 Sarah s Law was inspired from the US Megan s Law with similar provisions. 13 Campbell was involved in the preparation and release of the September Dossier in 2002 and the Iraq Dossier (or Dodgy Dossier ) in February These documents argued the case for concern over possible weapons of mass destruction (WMDs) in Iraq but were criticized as overstating or distorting the actual intelligence findings. Subsequent investigation revealed that the September Dossier had been altered, on Campbell's orders, to be consistent with United States officials.
GOVERNMENT & POLITICS UNIT 1 GLOSSARY
 NAME: GOVERNMENT & POLITICS UNIT 1 GLOSSARY TASK Over the summer holiday complete the definitions for the words for the FOUR topics AND more importantly learn these key words with their definitions! There
NAME: GOVERNMENT & POLITICS UNIT 1 GLOSSARY TASK Over the summer holiday complete the definitions for the words for the FOUR topics AND more importantly learn these key words with their definitions! There
GCE AS 2 Student Guidance Government & Politics. Course Companion Unit AS 2: The British Political System. For first teaching from September 2008
 GCE AS 2 Student Guidance Government & Politics Course Companion Unit AS 2: The British Political System For first teaching from September 2008 For first award of AS Level in Summer 2009 For first award
GCE AS 2 Student Guidance Government & Politics Course Companion Unit AS 2: The British Political System For first teaching from September 2008 For first award of AS Level in Summer 2009 For first award
The United Kingdom: Political Institutions. Lauren Cummings
 The United Kingdom: Political Institutions Lauren Cummings ------------ The UK NORTHERN IRELAND (18) ----------------- SCOTLAND (59) Unitary: Government in which ultimate constitutional authority lies
The United Kingdom: Political Institutions Lauren Cummings ------------ The UK NORTHERN IRELAND (18) ----------------- SCOTLAND (59) Unitary: Government in which ultimate constitutional authority lies
Structure of Governance: The UK
 Structure of Governance: The UK Political Parties The Labour Party Left leaning Political Party Started in early 20th century to support trade unions and workers rights Traditionally connected to Labor
Structure of Governance: The UK Political Parties The Labour Party Left leaning Political Party Started in early 20th century to support trade unions and workers rights Traditionally connected to Labor
House of Lords Reform developments in the 2010 Parliament
 House of Lords Reform developments in the 2010 Parliament Standard Note: SN/PC/7080 Last updated: 12 January 2015 Author: Section Richard Kelly Parliament and Constitution Centre Following the Government
House of Lords Reform developments in the 2010 Parliament Standard Note: SN/PC/7080 Last updated: 12 January 2015 Author: Section Richard Kelly Parliament and Constitution Centre Following the Government
Compare the vote Level 3
 Compare the vote Level 3 Elections and voting Not all elections are the same. We use different voting systems to choose who will represent us in various parliaments and elected assemblies, in the UK and
Compare the vote Level 3 Elections and voting Not all elections are the same. We use different voting systems to choose who will represent us in various parliaments and elected assemblies, in the UK and
Compare the vote Level 1
 Compare the vote Level 1 Elections and voting Not all elections are the same. We use different voting systems to choose who will represent us in various parliaments and elected assemblies, in the UK and
Compare the vote Level 1 Elections and voting Not all elections are the same. We use different voting systems to choose who will represent us in various parliaments and elected assemblies, in the UK and
AS Politics 2017 Revision Guide
 AS Politics 2017 Revision Guide Easter revision guide www.alevelpolitics.com/ukrevision Page 1! Unit 1 Topic Guide Democracy and Participation Definition of democracy Difference between direct and representative
AS Politics 2017 Revision Guide Easter revision guide www.alevelpolitics.com/ukrevision Page 1! Unit 1 Topic Guide Democracy and Participation Definition of democracy Difference between direct and representative
A-Level POLITICS PAPER 1
 A-Level POLITICS PAPER 1 Government and politics of the UK Mark scheme Version 1.0 Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions, by a panel
A-Level POLITICS PAPER 1 Government and politics of the UK Mark scheme Version 1.0 Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions, by a panel
CITIZENS EFFECTING CHANGE
 CITIZENS EFFECTING CHANGE DEMOCRACY In your own words define democracy. What does democracy look like? List ways in which citizens can impact change Pressure groups or interest groups Lobbyists MEDIA
CITIZENS EFFECTING CHANGE DEMOCRACY In your own words define democracy. What does democracy look like? List ways in which citizens can impact change Pressure groups or interest groups Lobbyists MEDIA
2 The Australian. parliamentary system CHAPTER. Australian parliamentary system. Bicameral structure. Separation of powers. Legislative.
 CHAPTER 2 The Australian parliamentary system This chapter explores the structure of the Australian parliamentary system. In order to understand this structure, it is necessary to reflect on the historical
CHAPTER 2 The Australian parliamentary system This chapter explores the structure of the Australian parliamentary system. In order to understand this structure, it is necessary to reflect on the historical
Teaching guidance: Paper 1 Government and politics of the UK
 Teaching guidance: Paper 1 Government and politics of the UK This teaching guidance provides advice for teachers, to help with the delivery of government and politics of the UK content. More information
Teaching guidance: Paper 1 Government and politics of the UK This teaching guidance provides advice for teachers, to help with the delivery of government and politics of the UK content. More information
Model Parliament Unit
 Model Unit Glossary Act of. A bill that has been passed by both the House of Commons and the Senate, has received Royal Assent and has been proclaimed. adjournment. The ending of a sitting of the Senate
Model Unit Glossary Act of. A bill that has been passed by both the House of Commons and the Senate, has received Royal Assent and has been proclaimed. adjournment. The ending of a sitting of the Senate
Paper C: Influencing and Changing Decisions in Society and Government
 Scheme (Results) Summer 207 Pearson Edexcel GCSE in Citizenship Studies Unit 3 (5CS03) Paper C: Influencing and Changing Decisions in Society and Government Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and
Scheme (Results) Summer 207 Pearson Edexcel GCSE in Citizenship Studies Unit 3 (5CS03) Paper C: Influencing and Changing Decisions in Society and Government Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and
Year 11 Citizenship Mock Theme Effective active citizenship
 Year 11 Citizenship Mock 2017 1. Effective active citizenship Theme 1 Mock paper is one hour. It is a unit 3 paper Spend 30 minutes on themes 1 & 2 Spend 30 minutes on the extended writing which is on
Year 11 Citizenship Mock 2017 1. Effective active citizenship Theme 1 Mock paper is one hour. It is a unit 3 paper Spend 30 minutes on themes 1 & 2 Spend 30 minutes on the extended writing which is on
THE SPEAKER S COMMITTEE ON THE ELECTORAL COMMISSION
 POLITICAL PARTIES, ELECTIONS AND REFERENDUMS ACT 2000 THE SPEAKER S COMMITTEE ON THE ELECTORAL COMMISSION THIRD REPORT 2018 Ordered by the House of Commons to be printed 15 November 2018 HC 1727 Published
POLITICAL PARTIES, ELECTIONS AND REFERENDUMS ACT 2000 THE SPEAKER S COMMITTEE ON THE ELECTORAL COMMISSION THIRD REPORT 2018 Ordered by the House of Commons to be printed 15 November 2018 HC 1727 Published
YouGov / Sun Survey Results
 YouGov / Sun Survey Results Sample Size: 2161 GB Adults Fieldwork: 8th - 9th October 2009 For detailed results, click here Headline Voting Intention [Excluding Don't Knows and Wouldn't Votes.] Con 42 42
YouGov / Sun Survey Results Sample Size: 2161 GB Adults Fieldwork: 8th - 9th October 2009 For detailed results, click here Headline Voting Intention [Excluding Don't Knows and Wouldn't Votes.] Con 42 42
Comparing Foreign Political Systems Focus Questions for Unit 1
 Comparing Foreign Political Systems Focus Questions for Unit 1 Any additions or revision to the draft version of the study guide posted earlier in the term are noted in bold. Why should we bother comparing
Comparing Foreign Political Systems Focus Questions for Unit 1 Any additions or revision to the draft version of the study guide posted earlier in the term are noted in bold. Why should we bother comparing
UNITED KINGDOM. Date of Elections: February 28, 1974
 UNITED KINGDOM Date of Elections: February 28, 974 Purpose of Elections General elections were held for the totality of the seats of the House of Commons, which House was dissolved 6 months prematurely.
UNITED KINGDOM Date of Elections: February 28, 974 Purpose of Elections General elections were held for the totality of the seats of the House of Commons, which House was dissolved 6 months prematurely.
4 However, devolution would have better served the people of Wales if a better voting system had been used. At present:
 Electoral Reform Society Wales Evidence to All Wales Convention SUMMARY 1 Electoral Reform Society Wales will support any moves that will increase democratic participation and accountability. Regardless
Electoral Reform Society Wales Evidence to All Wales Convention SUMMARY 1 Electoral Reform Society Wales will support any moves that will increase democratic participation and accountability. Regardless
Political Statistics, Devolution and Electoral Systems
 Political Statistics, Devolution and Electoral Systems John Martyn My interest is in obtaining a better understanding of Scottish devolution and how this might impact on the political integrity of the
Political Statistics, Devolution and Electoral Systems John Martyn My interest is in obtaining a better understanding of Scottish devolution and how this might impact on the political integrity of the
The Labour Government in Westminster and Northern Ireland
 The IRA In the 1920s, 1930s, and 1940s the IRA were not very strong or active in Northern Ireland During World War II, both the Northern Ireland and Irish Free State governments interned IRA members (imprisoned
The IRA In the 1920s, 1930s, and 1940s the IRA were not very strong or active in Northern Ireland During World War II, both the Northern Ireland and Irish Free State governments interned IRA members (imprisoned
Select Committees. Brief Guide
 Select Committees Brief Guide A select committee is a cross-party group of MPs or Lords given a specific remit to investigate and report back to the House that set it up. Select committees gather evidence
Select Committees Brief Guide A select committee is a cross-party group of MPs or Lords given a specific remit to investigate and report back to the House that set it up. Select committees gather evidence
Parliamentary Trends: Statistics about Parliament
 Parliamentary Trends: Statistics about Parliament RESEARCH PAPER 09/69 12 August 2009 This paper provides a summary of statistics about Parliament. It brings together figures about both the House of Commons
Parliamentary Trends: Statistics about Parliament RESEARCH PAPER 09/69 12 August 2009 This paper provides a summary of statistics about Parliament. It brings together figures about both the House of Commons
GCSE CITIZENSHIP STUDIES
 SPECIMEN ASSESSMENT MATERIAL GCSE CITIZENSHIP STUDIES 8100/1 PAPER 1 Draft Mark scheme V1.0 MARK SCHEME GCSE CITIZENSHIP STUDIES 8100/1 SPECIMEN MATERIAL Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment
SPECIMEN ASSESSMENT MATERIAL GCSE CITIZENSHIP STUDIES 8100/1 PAPER 1 Draft Mark scheme V1.0 MARK SCHEME GCSE CITIZENSHIP STUDIES 8100/1 SPECIMEN MATERIAL Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment
ELECTORAL REGULATION RESEARCH NETWORK/DEMOCRATIC AUDIT OF AUSTRALIA JOINT WORKING PAPER SERIES
 ELECTORAL REGULATION RESEARCH NETWORK/DEMOCRATIC AUDIT OF AUSTRALIA JOINT WORKING PAPER SERIES ALTERNATIVE VOTING PLUS: A PROPOSAL FOR THE SOUTH AUSTRALIAN HOUSE OF ASSEMBLY 1 Daniel Messemaker (BA (Hons)
ELECTORAL REGULATION RESEARCH NETWORK/DEMOCRATIC AUDIT OF AUSTRALIA JOINT WORKING PAPER SERIES ALTERNATIVE VOTING PLUS: A PROPOSAL FOR THE SOUTH AUSTRALIAN HOUSE OF ASSEMBLY 1 Daniel Messemaker (BA (Hons)
General Election The Election Results Guide
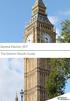 General Election 2017 The Election Results Guide Contents 1. Overview 2. What It Means 3. Electoral Map 4. Meet the New MPs Overview 320 318 261 Conservatives 270 Labour SNP 220 Liberal Democrats 170 DUP
General Election 2017 The Election Results Guide Contents 1. Overview 2. What It Means 3. Electoral Map 4. Meet the New MPs Overview 320 318 261 Conservatives 270 Labour SNP 220 Liberal Democrats 170 DUP
National Quali cations SPECIMEN ONLY SQ38/H/01. Politics *SQ32H01* Date Not applicable Duration 2 hours and 15 minutes.
 H National Quali cations SPECIMEN ONLY SQ38/H/01 Politics Date Not applicable Duration 2 hours and 15 minutes Total marks 60 SECTION 1 POLITICAL THEORY 20 marks Attempt EITHER Question 1(a) OR Question
H National Quali cations SPECIMEN ONLY SQ38/H/01 Politics Date Not applicable Duration 2 hours and 15 minutes Total marks 60 SECTION 1 POLITICAL THEORY 20 marks Attempt EITHER Question 1(a) OR Question
Introduction The forging of a coalition government in May 2010 was a momentous event in British political life. Few of the electorate actively sought
 Introduction The forging of a coalition government in May 2010 was a momentous event in British political life. Few of the electorate actively sought a coalition government. Many indeed believed that such
Introduction The forging of a coalition government in May 2010 was a momentous event in British political life. Few of the electorate actively sought a coalition government. Many indeed believed that such
Reading the local runes:
 Reading the local runes: What the 2011 council elections suggest for the next general election By Paul Hunter Reading the local runes: What the 2011 council elections suggest for the next general election
Reading the local runes: What the 2011 council elections suggest for the next general election By Paul Hunter Reading the local runes: What the 2011 council elections suggest for the next general election
After the Scotland Act (1998) new institutions were set up to enable devolution in Scotland.
 How does devolution work in Scotland? After the Scotland Act (1998) new institutions were set up to enable devolution in Scotland. The Scottish Parliament The Scottish Parliament is made up of 73 MSPs
How does devolution work in Scotland? After the Scotland Act (1998) new institutions were set up to enable devolution in Scotland. The Scottish Parliament The Scottish Parliament is made up of 73 MSPs
The UK Party System and Party Politics Part II: Governance, Ideology and Policy. Patrick Dunleavy
 The UK Party System and Party Politics Part II: Governance, Ideology and Policy Patrick Dunleavy Gv 311: British Politics course, Lecture 10 Michaelmas Term P.J. Dunleavy In governance terms a party system
The UK Party System and Party Politics Part II: Governance, Ideology and Policy Patrick Dunleavy Gv 311: British Politics course, Lecture 10 Michaelmas Term P.J. Dunleavy In governance terms a party system
Women s. Political Representation & Electoral Systems. Key Recommendations. Federal Context. September 2016
 Women s Political Representation & Electoral Systems September 2016 Federal Context Parity has been achieved in federal cabinet, but women remain under-represented in Parliament. Canada ranks 62nd Internationally
Women s Political Representation & Electoral Systems September 2016 Federal Context Parity has been achieved in federal cabinet, but women remain under-represented in Parliament. Canada ranks 62nd Internationally
Audit of Political Engagement
 UK Data Archive Study Number 7373 - Audit of Political Engagement 10, 2012 Audit of Political Engagement Hansard Society General / Core Questions (T) Q1) How would you vote if there were a General Election
UK Data Archive Study Number 7373 - Audit of Political Engagement 10, 2012 Audit of Political Engagement Hansard Society General / Core Questions (T) Q1) How would you vote if there were a General Election
 www.newsflashenglish.com The 4 page 60 minute ESL British English lesson 15/04/15 Election. Voters will go to the polls on Thursday 7 th May 2015. On the same day local elections will also take There are
www.newsflashenglish.com The 4 page 60 minute ESL British English lesson 15/04/15 Election. Voters will go to the polls on Thursday 7 th May 2015. On the same day local elections will also take There are
Contact:
 http://www.iniref.org Contact: info@iniref.org Citizens and Direct Democracy What chance of reform do the major UK political parties offer? The countries of the british isles and the UK as a whole are
http://www.iniref.org Contact: info@iniref.org Citizens and Direct Democracy What chance of reform do the major UK political parties offer? The countries of the british isles and the UK as a whole are
GLOSSARY. Discover Your Legislature Series. Legislative Assembly of British Columbia Victoria British Columbia V8V 1X4
 e GLOSSARY Discover Your Legislature Series Legislative Assembly of British Columbia Victoria British Columbia V8V 1X4 ACT A bill that has passed third reading by the Legislative Assembly and has received
e GLOSSARY Discover Your Legislature Series Legislative Assembly of British Columbia Victoria British Columbia V8V 1X4 ACT A bill that has passed third reading by the Legislative Assembly and has received
SUMMARY REPORT KEY POINTS
 SUMMARY REPORT The Citizens Assembly on Brexit was held over two weekends in September 17. It brought together randomly selected citizens who reflected the diversity of the UK electorate. The Citizens
SUMMARY REPORT The Citizens Assembly on Brexit was held over two weekends in September 17. It brought together randomly selected citizens who reflected the diversity of the UK electorate. The Citizens
Election Statistics: UK
 1 FEBRUARY 2008 Election Statistics: UK 1918-2007 This paper summarises the results of UK elections since 1918. It focuses on elections to Westminster and includes statistics on voting at general and by-elections,
1 FEBRUARY 2008 Election Statistics: UK 1918-2007 This paper summarises the results of UK elections since 1918. It focuses on elections to Westminster and includes statistics on voting at general and by-elections,
COULD THE LIB DEM MARGINAL MELTDOWN MEAN THE TORIES GAIN FROM A.V.? By Lord Ashcroft, KCMG 20 July 2010
 COULD THE LIB DEM MARGINAL MELTDOWN MEAN THE TORIES GAIN FROM A.V.? By Lord Ashcroft, KCMG 20 July 2010 A referendum on the Alternative Vote is currently planned for 5 May 2011. The pollsters have turned
COULD THE LIB DEM MARGINAL MELTDOWN MEAN THE TORIES GAIN FROM A.V.? By Lord Ashcroft, KCMG 20 July 2010 A referendum on the Alternative Vote is currently planned for 5 May 2011. The pollsters have turned
Public Opinion Monitor
 The Public Opinion Monitor The Conservative Party and the Electorate In this third and final special report on the state of the main parties, we look at the Conservative party and their voters in advance
The Public Opinion Monitor The Conservative Party and the Electorate In this third and final special report on the state of the main parties, we look at the Conservative party and their voters in advance
THE ANDREW MARR SHOW INTERVIEW: NICOLA STURGEON, MSP First Minister of Scotland and the Leader of the Scottish National Party APRIL 19TH 2015
 NICOLA STURGEON 1 PLEASE NOTE THE ANDREW MARR SHOW MUST BE CREDITED IF ANY PART OF THIS TRANSCRIPT IS USED THE ANDREW MARR SHOW INTERVIEW: NICOLA STURGEON, MSP First Minister of Scotland and the Leader
NICOLA STURGEON 1 PLEASE NOTE THE ANDREW MARR SHOW MUST BE CREDITED IF ANY PART OF THIS TRANSCRIPT IS USED THE ANDREW MARR SHOW INTERVIEW: NICOLA STURGEON, MSP First Minister of Scotland and the Leader
F2PTP A VOTING SYSTEM FOR EQUALITY OF REPRESENTATION IN A MULTI-PARTY STATE FIRST TWO PAST THE POST. 1 Tuesday, 05 May 2015 David Allen
 A VOTING SYSTEM FOR EQUALITY OF REPRESENTATION IN A MULTI-PARTY STATE 1 Tuesday, 05 May 2015 David Allen TIME FOR CHANGE In 2010, 29,687,604 people voted. The Conservatives received 10,703,654, the Labour
A VOTING SYSTEM FOR EQUALITY OF REPRESENTATION IN A MULTI-PARTY STATE 1 Tuesday, 05 May 2015 David Allen TIME FOR CHANGE In 2010, 29,687,604 people voted. The Conservatives received 10,703,654, the Labour
Factsheet P2 Procedure Series. Contents
 Factsheet P2 Procedure Series Revised August 2010 House of Commons Information Office Departmental Select Committees Contents Background 2 The Chairman and Membership 2 Select Committee staff 3 Meetings
Factsheet P2 Procedure Series Revised August 2010 House of Commons Information Office Departmental Select Committees Contents Background 2 The Chairman and Membership 2 Select Committee staff 3 Meetings
ANDREW MARR SHOW 17 TH DECEMBER DIANE ABBOTT, MP Shadow Home Secretary. AM: I m just looking for specifics. DA: Yeah and specifics.
 1 ANDREW MARR SHOW 17 TH DECEMBER 2017 Shadow Home Secretary AM: Welcome Diane Abbott. Can I just ask you about the Keir Starmer menu as it were for after we leave the EU? He said that we d have a really
1 ANDREW MARR SHOW 17 TH DECEMBER 2017 Shadow Home Secretary AM: Welcome Diane Abbott. Can I just ask you about the Keir Starmer menu as it were for after we leave the EU? He said that we d have a really
YouGov / Mail on Sunday results
 YouGov / Mail on Sunday results Sample: 2,024; fieldwork: June 19-20, 2003 If there were a general election tomorrow, how would you vote? Gen elec Jan 2002 3-4 Jan 2003 16-17 Jan 2003 10-11 April 2003
YouGov / Mail on Sunday results Sample: 2,024; fieldwork: June 19-20, 2003 If there were a general election tomorrow, how would you vote? Gen elec Jan 2002 3-4 Jan 2003 16-17 Jan 2003 10-11 April 2003
UNION LEGISLATURE LOK SABHA, RAJYA SABHA, SPEAKER
 UNION LEGISLATURE LOK SABHA, RAJYA SABHA, SPEAKER FEDERAL SET-UP IN INDIA WHERE WE HAVE A UNION GOVERNMENT AT THE CENTRE AND STATE GOVERNMENT AT EACH STATE LEVEL, BOTH FUNCTIONING THROUGH THE THREE WINGS
UNION LEGISLATURE LOK SABHA, RAJYA SABHA, SPEAKER FEDERAL SET-UP IN INDIA WHERE WE HAVE A UNION GOVERNMENT AT THE CENTRE AND STATE GOVERNMENT AT EACH STATE LEVEL, BOTH FUNCTIONING THROUGH THE THREE WINGS
Legislation. a. Describe the process by which a Bill becomes an Act of Parliament. [15]
![Legislation. a. Describe the process by which a Bill becomes an Act of Parliament. [15] Legislation. a. Describe the process by which a Bill becomes an Act of Parliament. [15]](/thumbs/82/85120810.jpg) Legislation By the end of this unit, you will be able to [AO1]: Describe how a bill becomes an Act of Parliament. Explain the different types of bill and when they might be used Describe what is meant
Legislation By the end of this unit, you will be able to [AO1]: Describe how a bill becomes an Act of Parliament. Explain the different types of bill and when they might be used Describe what is meant
The sure bet by Theresa May ends up in a hung Parliament
 The sure bet by Theresa May ends up in a hung Parliament Vincenzo Emanuele and Bruno Marino June 9, 2017 The decision by the British Prime Minister, Theresa May, to call a snap election to reinforce her
The sure bet by Theresa May ends up in a hung Parliament Vincenzo Emanuele and Bruno Marino June 9, 2017 The decision by the British Prime Minister, Theresa May, to call a snap election to reinforce her
Department of Politics Commencement Lecture
 Department of Politics Commencement Lecture Introduction My aim: to reflect on Brexit in the light of recent British political development; Drawing on the analysis of Developments of British Politics 10
Department of Politics Commencement Lecture Introduction My aim: to reflect on Brexit in the light of recent British political development; Drawing on the analysis of Developments of British Politics 10
21/09/2014 Prepared on behalf of the Mail on Sunday. Referendum Reactions Poll
 Referendum Reactions Poll /0/0 Methodology Fieldwork Dates th September 0 Data Collection Method The survey was conducted via online panel. Invitations to complete surveys were sent out to members of the
Referendum Reactions Poll /0/0 Methodology Fieldwork Dates th September 0 Data Collection Method The survey was conducted via online panel. Invitations to complete surveys were sent out to members of the
A-LEVEL CITIZENSHIP STUDIES
 A-LEVEL CITIZENSHIP STUDIES CIST3 Power and Justice Report on the Examination 2100 June 2015 Version: 1.0 Further copies of this Report are available from aqa.org.uk Copyright 2015 AQA and its licensors.
A-LEVEL CITIZENSHIP STUDIES CIST3 Power and Justice Report on the Examination 2100 June 2015 Version: 1.0 Further copies of this Report are available from aqa.org.uk Copyright 2015 AQA and its licensors.
SECTION 10: POLITICS, PUBLIC POLICY AND POLLS
 SECTION 10: POLITICS, PUBLIC POLICY AND POLLS 10.1 INTRODUCTION 10.1 Introduction 10.2 Principles 10.3 Mandatory Referrals 10.4 Practices Reporting UK Political Parties Political Interviews and Contributions
SECTION 10: POLITICS, PUBLIC POLICY AND POLLS 10.1 INTRODUCTION 10.1 Introduction 10.2 Principles 10.3 Mandatory Referrals 10.4 Practices Reporting UK Political Parties Political Interviews and Contributions
Political snakes and ladders. If you decide to cast your vote in person where do you go?
 How is your privacy ensured when you vote in a polling station? a) Ballot papers are anonymous and polling booths are designed to give you privacy. b) You are required to wear a hat and sunglasses when
How is your privacy ensured when you vote in a polling station? a) Ballot papers are anonymous and polling booths are designed to give you privacy. b) You are required to wear a hat and sunglasses when
US Government Module 3 Study Guide
 US Government Module 3 Study Guide There are 3 branches of government. Module 3 will cover the legislative and execute and module 4 will cover the judicial. 3.01 The Legislative Branch aka Congress Established
US Government Module 3 Study Guide There are 3 branches of government. Module 3 will cover the legislative and execute and module 4 will cover the judicial. 3.01 The Legislative Branch aka Congress Established
House of Lords Reform Bill
 EXPLANATORY NOTES Explanatory notes to the Bill, prepared by the Cabinet Office, are published separately as Bill 2 EN. EUROPEAN CONVENTION ON HUMAN RIGHTS The Deputy Prime Minister has made the following
EXPLANATORY NOTES Explanatory notes to the Bill, prepared by the Cabinet Office, are published separately as Bill 2 EN. EUROPEAN CONVENTION ON HUMAN RIGHTS The Deputy Prime Minister has made the following
Electoral Reform Brief
 2016 Electoral Reform Brief Ron Campbell csm.ron30@yahoo.ca 7/1/2016 Summary We need to look at the cause of the problems that our current system has, in order to know what needs modifying. If we do not
2016 Electoral Reform Brief Ron Campbell csm.ron30@yahoo.ca 7/1/2016 Summary We need to look at the cause of the problems that our current system has, in order to know what needs modifying. If we do not
YouGov / Sunday Times Survey Results Fieldwork: March 15-16, 2007; sample 1,897 electors throughout Great Bitain For full results click here
 YouGov / Sunday Times Survey Results Fieldwork: March 15-16, 2007; sample 1,897 electors throughout Great Bitain For full results click here Voting Intention (excluding don't knows, would not vote) Non
YouGov / Sunday Times Survey Results Fieldwork: March 15-16, 2007; sample 1,897 electors throughout Great Bitain For full results click here Voting Intention (excluding don't knows, would not vote) Non
Members of Parliament The Houses of Parliament The Labour Party
 Politics and youth Task 1: Political people and places Match the people and places in the box with the descriptions below: The Queen The Conservative Party The Prime Minister Members of Parliament The
Politics and youth Task 1: Political people and places Match the people and places in the box with the descriptions below: The Queen The Conservative Party The Prime Minister Members of Parliament The
Union legislature. Lok sabha, rajya sabha, speaker
 Union legislature Lok sabha, rajya sabha, speaker Federal set-up in india A federal setup involves a dual government Where we have a union government at the centre and state government at each state level,
Union legislature Lok sabha, rajya sabha, speaker Federal set-up in india A federal setup involves a dual government Where we have a union government at the centre and state government at each state level,
Transparency of Lobbying, Non Party Campaigning and Trade Union Administration Bill 2013 House of Commons Report Stage and Third Reading
 Transparency of Lobbying, Non Party Campaigning and Trade Union Administration Bill 2013 House of Commons Report Stage and Third Reading Amendment briefing 9 October 2013 This briefing provides our views
Transparency of Lobbying, Non Party Campaigning and Trade Union Administration Bill 2013 House of Commons Report Stage and Third Reading Amendment briefing 9 October 2013 This briefing provides our views
Nineteenth Amendment to the Constitution
 Nineteenth Amendment to the An Act to Amend the of the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka BE it enacted by the Parliament of the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka as follows: Short title
Nineteenth Amendment to the An Act to Amend the of the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka BE it enacted by the Parliament of the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka as follows: Short title
The Three Branches of Government include the executive, the legislative, and the
 Three Branches of the US Government The Three Branches of Government include the executive, the legislative, and the judicial branches. Each branch has a special role in the function of the United States
Three Branches of the US Government The Three Branches of Government include the executive, the legislative, and the judicial branches. Each branch has a special role in the function of the United States
Political strategy CONSULTATION REPORT. Public and Commercial Services Union pcs.org.uk
 Political strategy CONSULTATION REPORT Public and Commercial Services Union pcs.org.uk Introduction In 2015, PCS launched a strategic review in response to the new challenges we face. The central aim of
Political strategy CONSULTATION REPORT Public and Commercial Services Union pcs.org.uk Introduction In 2015, PCS launched a strategic review in response to the new challenges we face. The central aim of
YouGov / Sunday Times Survey Results
 YouGov / Sunday Times Survey Results Sample Size: 1962 Fieldwork: 10th - 11th May 2007 For full results click here Headline Voting Intention Con 38 Lab 34 Lib Dem 15 Other 14 Are you and your family better
YouGov / Sunday Times Survey Results Sample Size: 1962 Fieldwork: 10th - 11th May 2007 For full results click here Headline Voting Intention Con 38 Lab 34 Lib Dem 15 Other 14 Are you and your family better
Canadian electoral reform involves a befuddling
 Feature RAMPing up Parliament An Alternative to Electoral Reform Electoral reform is a complicated proposition, yet the current first-past-the-post (or single member plurality) system has been criticised
Feature RAMPing up Parliament An Alternative to Electoral Reform Electoral reform is a complicated proposition, yet the current first-past-the-post (or single member plurality) system has been criticised
STANDARDS, PROCEDURES AND PUBLIC APPOINTMENTS COMMITTEE INQUIRY INTO LOBBYING SUPPLEMENTARY EVIDENCE FROM APPC
 STANDARDS, PROCEDURES AND PUBLIC APPOINTMENTS COMMITTEE INQUIRY INTO LOBBYING SUPPLEMENTARY EVIDENCE FROM APPC Clarification This supplementary evidence is submitted by Illiam Costain McCade, Chair of
STANDARDS, PROCEDURES AND PUBLIC APPOINTMENTS COMMITTEE INQUIRY INTO LOBBYING SUPPLEMENTARY EVIDENCE FROM APPC Clarification This supplementary evidence is submitted by Illiam Costain McCade, Chair of
Northern Lights. Public policy and the geography of political attitudes in Britain today.
 Northern Lights Public policy and the geography of political attitudes in Britain today #northsouth @Policy_Exchange Image courtesy Andrew Whyte/ LongExposures.co.uk Northern Lights 1. Background to the
Northern Lights Public policy and the geography of political attitudes in Britain today #northsouth @Policy_Exchange Image courtesy Andrew Whyte/ LongExposures.co.uk Northern Lights 1. Background to the
What is the Best Election Method?
 What is the Best Election Method? E. Maskin Harvard University Gorman Lectures University College, London February 2016 Today and tomorrow will explore 2 Today and tomorrow will explore election methods
What is the Best Election Method? E. Maskin Harvard University Gorman Lectures University College, London February 2016 Today and tomorrow will explore 2 Today and tomorrow will explore election methods
Government and Politics GOVP1. General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June People, Politics and Participation
 A Government and Politics General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June 2015 Unit 1 People, Politics and Participation GOVP1 Monday 1 June 2015 9.00 am to 10.30 am For this paper
A Government and Politics General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June 2015 Unit 1 People, Politics and Participation GOVP1 Monday 1 June 2015 9.00 am to 10.30 am For this paper
The British Parliament
 Chapter 1 The Act of Union Ireland had had its own parliament and government in the 1780s but after the Act of Union 1800 Irish Members of Parliament had to travel to London and sit in Westminster with
Chapter 1 The Act of Union Ireland had had its own parliament and government in the 1780s but after the Act of Union 1800 Irish Members of Parliament had to travel to London and sit in Westminster with
ADDENDUM STANDING ORDERS
 ADDENDUM TO STANDING ORDERS PUBLIC BUSINESS 19 October 2017 Reprinted from the Votes and Proceedings of the House of Commons 4 July and 12 September 2017 AMENDMENTS TO STANDING ORDERS 119. European Committees
ADDENDUM TO STANDING ORDERS PUBLIC BUSINESS 19 October 2017 Reprinted from the Votes and Proceedings of the House of Commons 4 July and 12 September 2017 AMENDMENTS TO STANDING ORDERS 119. European Committees
House of Lords Reform: Chronology
 House of Lords Reform: Chronology 1900 2010 This Library Note provides a chronology of key developments in the reform of the House of Lords since 1900. It does not provide a comprehensive account of all
House of Lords Reform: Chronology 1900 2010 This Library Note provides a chronology of key developments in the reform of the House of Lords since 1900. It does not provide a comprehensive account of all
Fixed-term Parliaments Act 2011
 Fixed-term Parliaments Act 2011 CHAPTER 14 CONTENTS 1 Polling days for parliamentary general elections 2 Early parliamentary general elections 3 Dissolution of Parliament 4 General election for Scottish
Fixed-term Parliaments Act 2011 CHAPTER 14 CONTENTS 1 Polling days for parliamentary general elections 2 Early parliamentary general elections 3 Dissolution of Parliament 4 General election for Scottish
AS POLITICS. Government and Politics of the UK. Time allowed: 3 hours SPECIMEN MATERIAL
 SPECIMEN MATERIAL AS POLITICS Government and Politics of the UK Time allowed: 3 hours Materials For this paper you must have: an AQA 12-page answer book. Instructions Use black ink or black ball-point
SPECIMEN MATERIAL AS POLITICS Government and Politics of the UK Time allowed: 3 hours Materials For this paper you must have: an AQA 12-page answer book. Instructions Use black ink or black ball-point
Lobbying. The Art of Political Persuasion. by Lionel Zetter
 A/5094U7 Lobbying The Art of Political Persuasion by Lionel Zetter Contents Preface xxiii Part One - Introduction To Lobbying 1 1.1 Definitions 3 1.2 History 6 1.3 Ethics And Regulation 9 1.4 Funding And
A/5094U7 Lobbying The Art of Political Persuasion by Lionel Zetter Contents Preface xxiii Part One - Introduction To Lobbying 1 1.1 Definitions 3 1.2 History 6 1.3 Ethics And Regulation 9 1.4 Funding And
The Labour Party Manifesto
 The Labour Party Manifesto 14 April 2015 1 The Labour Party Manifesto 1 Overview... 2 2 Key Messages... 3 2.1 Britain can do better... 3 2.2 Fiscal responsibility... 3 2.3 The NHS... 4 2.4 Fighting for
The Labour Party Manifesto 14 April 2015 1 The Labour Party Manifesto 1 Overview... 2 2 Key Messages... 3 2.1 Britain can do better... 3 2.2 Fiscal responsibility... 3 2.3 The NHS... 4 2.4 Fighting for
klm Mark Scheme General Certificate of Education January 2011 Citizenship Studies Power and Justice Unit 3
 klm General Certificate of Education January 2011 Citizenship Studies Power and Justice Unit 3 CIST3 Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner and considered, together with the relevant
klm General Certificate of Education January 2011 Citizenship Studies Power and Justice Unit 3 CIST3 Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner and considered, together with the relevant
Examiners Report January 2011
 Examiners Report January 2011 Edexcel Limited. Registered in England and Wales No. 4496750 Registered Office: One90 High Holborn, London WC1V 7BH 2 Edexcel is one of the leading examining and awarding
Examiners Report January 2011 Edexcel Limited. Registered in England and Wales No. 4496750 Registered Office: One90 High Holborn, London WC1V 7BH 2 Edexcel is one of the leading examining and awarding
Elections and referendums
 Caramani (ed.) Comparative Politics Section III: Structures and institutions Chapter 10: Elections and referendums by Michael Gallagher (1/1) Elections and referendums are the two main voting opportunities
Caramani (ed.) Comparative Politics Section III: Structures and institutions Chapter 10: Elections and referendums by Michael Gallagher (1/1) Elections and referendums are the two main voting opportunities
Do you think the Labour / Conservative Party is united or divided at the present time?
 YouGov / Channel 4 Survey - Interim Results Sample: 2144 electors in 60 seats where Labour's majority (on the new boundaries) was 6-14% over the Conservatives. For detailed s, click here Headline Voting
YouGov / Channel 4 Survey - Interim Results Sample: 2144 electors in 60 seats where Labour's majority (on the new boundaries) was 6-14% over the Conservatives. For detailed s, click here Headline Voting
Chapter 6 Democratic Regimes. Copyright 2015 W.W. Norton, Inc.
 Chapter 6 Democratic Regimes 1. Democracy Clicker question: A state with should be defined as a nondemocracy. A.a hereditary monarch B.an official, state-sanctioned religion C.a legislative body that is
Chapter 6 Democratic Regimes 1. Democracy Clicker question: A state with should be defined as a nondemocracy. A.a hereditary monarch B.an official, state-sanctioned religion C.a legislative body that is
Protection of Freedoms Bill. Delegated Powers - Memorandum by the Home Office. Introduction
 Protection of Freedoms Bill Delegated Powers - Memorandum by the Home Office Introduction 1. This Memorandum identifies the provisions of the Protection of Freedoms Bill which confer powers to make delegated
Protection of Freedoms Bill Delegated Powers - Memorandum by the Home Office Introduction 1. This Memorandum identifies the provisions of the Protection of Freedoms Bill which confer powers to make delegated
A level Government and Politics Scheme of Work 2017 / 2018
 A level Government and Politics Scheme of Work 2017 / 2018 Week 1 Specification Teaching Detail Activities and Extensions 4 th Septemb er Democracy in context in the UK. The features of direct democracy
A level Government and Politics Scheme of Work 2017 / 2018 Week 1 Specification Teaching Detail Activities and Extensions 4 th Septemb er Democracy in context in the UK. The features of direct democracy
Page Report back for Saturday 10th March F16 Reports: Parliamentary Parties of the Liberal Democrats 4
 spring conference conference daily sunday th march 0 Information from the Conference Committee, timings for conference sessions, amendments, emergency motions and questions to reports; report back for
spring conference conference daily sunday th march 0 Information from the Conference Committee, timings for conference sessions, amendments, emergency motions and questions to reports; report back for
National Quali cations
 H 2017 X758/76/11 National Quali cations Politics FRIDAY, 2 JUNE 1:00 PM 3:15 PM Total marks 60 SECTION 1 POLITICAL THEORY 20 marks Attempt Question 1 and EITHER Question 2(a) OR Question 2(b). SECTION
H 2017 X758/76/11 National Quali cations Politics FRIDAY, 2 JUNE 1:00 PM 3:15 PM Total marks 60 SECTION 1 POLITICAL THEORY 20 marks Attempt Question 1 and EITHER Question 2(a) OR Question 2(b). SECTION
Home Rule and Ireland. Ireland at the turn of the century
 Home Rule and Ireland Ireland at the turn of the century Ireland at the turn of the century Was a rural country (60% lived in the country side) Only area with much industry was around Belfast. Since 1800
Home Rule and Ireland Ireland at the turn of the century Ireland at the turn of the century Was a rural country (60% lived in the country side) Only area with much industry was around Belfast. Since 1800
Lisbon Treaty Referendum Bill
 EXPLANATORY NOTES Explanatory notes to the Bill, prepared by the Foreign and Commonwealth Office, are to be published separately EUROPEAN CONVENTION ON HUMAN RIGHTS Mr Secretary Hague has made the following
EXPLANATORY NOTES Explanatory notes to the Bill, prepared by the Foreign and Commonwealth Office, are to be published separately EUROPEAN CONVENTION ON HUMAN RIGHTS Mr Secretary Hague has made the following
Elections and Voting Behaviour. The Political System of the United Kingdom
 Elections and Behaviour The Political System of the United Kingdom Intro Theories of Behaviour in the UK The Political System of the United Kingdom Elections/ (1/25) Current Events The Political System
Elections and Behaviour The Political System of the United Kingdom Intro Theories of Behaviour in the UK The Political System of the United Kingdom Elections/ (1/25) Current Events The Political System
What happens next? Legal Consequences of Brexit FABIAN AMTENBRINK ANASTASIA KARATZIA RENÉ REPASI
 REFERENDUM IN THE UNITED KINGDOM TO LEAVE THE EUROPEAN UNION European Research Centre for Economic and Financial Governance euro-cefg.eu What happens next? Legal Consequences of Brexit FABIAN AMTENBRINK
REFERENDUM IN THE UNITED KINGDOM TO LEAVE THE EUROPEAN UNION European Research Centre for Economic and Financial Governance euro-cefg.eu What happens next? Legal Consequences of Brexit FABIAN AMTENBRINK
DEMOCRATIC AUDIT. How Should We Vote? David Beetham, Associate Director, Democratic Audit
 DEMOCRATIC AUDIT How Should We Vote? David Beetham, Associate Director, Democratic Audit Introduction ELECTIONS constitute a key instrument of representative democracy. They are the mechanism whereby the
DEMOCRATIC AUDIT How Should We Vote? David Beetham, Associate Director, Democratic Audit Introduction ELECTIONS constitute a key instrument of representative democracy. They are the mechanism whereby the
An Update on Brexit. Tim Oliver European University Institute and LSE IDEAS
 An Update on Brexit Tim Oliver European University Institute and LSE IDEAS 1 a. How did Britain vote? b. Why did 52% of Britons vote Leave? 2. What does Brexit mean? a. Britain s Brexit b. UK-EU Brexit
An Update on Brexit Tim Oliver European University Institute and LSE IDEAS 1 a. How did Britain vote? b. Why did 52% of Britons vote Leave? 2. What does Brexit mean? a. Britain s Brexit b. UK-EU Brexit
Commission on Parliamentary Reform
 Consultation response from Dr James Gilmour 1. The voting system used to elected members to the Scottish Parliament should be changed. The Additional Member System (AMS) should be replaced by the Single
Consultation response from Dr James Gilmour 1. The voting system used to elected members to the Scottish Parliament should be changed. The Additional Member System (AMS) should be replaced by the Single
AS Politics. Unit 1 Booklet 1: Democracy and Participation. Powerpoints Handouts
 AS Politics Unit 1 Booklet 1: Democracy and Participation Powerpoints Handouts Politics An Introduction AS Outline 50% Unit 1 People and Politics 50% Unit 2 Governing the UK Edexcel AS Politics An overview
AS Politics Unit 1 Booklet 1: Democracy and Participation Powerpoints Handouts Politics An Introduction AS Outline 50% Unit 1 People and Politics 50% Unit 2 Governing the UK Edexcel AS Politics An overview
Electoral Reform: Making Every Vote Count Equally
 Osgoode Hall Law School of York University From the SelectedWorks of Craig M. Scott September 17, 2016 Electoral Reform: Making Every Vote Count Equally Craig M. Scott Available at: https://works.bepress.com/craig_scott/88/
Osgoode Hall Law School of York University From the SelectedWorks of Craig M. Scott September 17, 2016 Electoral Reform: Making Every Vote Count Equally Craig M. Scott Available at: https://works.bepress.com/craig_scott/88/
The fundamental factors behind the Brexit vote
 The CAGE Background Briefing Series No 64, September 2017 The fundamental factors behind the Brexit vote Sascha O. Becker, Thiemo Fetzer, Dennis Novy In the Brexit referendum on 23 June 2016, the British
The CAGE Background Briefing Series No 64, September 2017 The fundamental factors behind the Brexit vote Sascha O. Becker, Thiemo Fetzer, Dennis Novy In the Brexit referendum on 23 June 2016, the British
Political Parties, Elections and Referendums Act amendments relating to European Parliamentary Elections; and for connected purposes.
 Political Parties, Elections and Referendums Act 2000 2000 Chapter 41 - continued An Act to establish an Electoral Commission; to make provision about the registration and finances of political parties;
Political Parties, Elections and Referendums Act 2000 2000 Chapter 41 - continued An Act to establish an Electoral Commission; to make provision about the registration and finances of political parties;
Counter-Terrorism Bill
 EXPLANATORY NOTES Explanatory notes to the Bill, prepared by the Home Office, will be published separately as HL Bill 6 EN. EUROPEAN CONVENTION ON HUMAN RIGHTS Lord West of Spithead has made the following
EXPLANATORY NOTES Explanatory notes to the Bill, prepared by the Home Office, will be published separately as HL Bill 6 EN. EUROPEAN CONVENTION ON HUMAN RIGHTS Lord West of Spithead has made the following
GRADE 9 Social Studies Canada: Opportunities and Challenges
 GRADE 9 Social Studies Canada: Opportunities and Challenges 9.1 Issues for Canadians: Governance and Rights General Outcome Students will demonstrate an understanding and appreciation of how Canada s political
GRADE 9 Social Studies Canada: Opportunities and Challenges 9.1 Issues for Canadians: Governance and Rights General Outcome Students will demonstrate an understanding and appreciation of how Canada s political
The Case for Electoral Reform: A Mixed Member Proportional System for Canada. Brief by Stephen Phillips, Ph.D.
 1 The Case for Electoral Reform: A Mixed Member Proportional System for Canada Brief by Stephen Phillips, Ph.D. Instructor, Department of Political Science, Langara College Vancouver, BC 6 October 2016
1 The Case for Electoral Reform: A Mixed Member Proportional System for Canada Brief by Stephen Phillips, Ph.D. Instructor, Department of Political Science, Langara College Vancouver, BC 6 October 2016
