A Forgotten War A Forgotten Emergency: The Democratic Republic of Congo
|
|
|
- Osborne Peters
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Forgotten War A Forgotten Emergency: The Democratic Republic of Congo In the Democratic Republic of Congo, a complicated civil war continues to broil, despite the signing of the Lusaka peace accord in July An unofficial front line diagonally cuts the country in two, as heavy artillery and bombings cause thousands in the West of the country to flee in late Smaller-scale attacks, arson and massacres have displaced hundreds of thousands in Province Orientale and North and South Kivu. Neither the DRC government, the rebels, nor their backers in neighbouring countries, show any sign of fully implementing the accord. Statistics in this war are difficult to attain, but non-governmental organisations (NGOs) estimate that more than a million people may have lost their lives in the last two years due to the conflict. The United Nations Office for Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (UN OCHA) estimates that about 33% of the population are now vulnerable. Government spending on health and education have each dropped to less than 1% of government expenditure, leaving nearly a third of the children malnourished, 10% acutely so. Oxfam GB works throughout the country providing clean drinking water and improving hygiene conditions to over half a million people. However, while we work with other humanitarian organisations and the UN agencies to reach the most vulnerable, a large portion of the humanitarian needs are not being met. This is partly because of insecurity, and partly because of restrictive administrative requirements in government-held areas. There have been remarkable improvements in the health of the populations the international community has been able to assist; for example, after the start of a comprehensive water and sanitation programme in the territory of Djugu, cholera has declined from 599 registered cases to 13 cases. However, with chronic shortfalls in funding for humanitarian assistance in the DRC, there are accessible populations in urgent need of assistance that are not being reached. In 2000, donor response to the DRC was weak. The UN consolidated appeal one indicator of funding levels among many had a shortfall of nearly 40%. In 1999 donor governments gave just $8 per person in the DRC, while providing $207 per person in response to the UN appeal for the former Yugoslavia. 1 While it is clear that both regions have significant needs, there is little commitment to universal entitlement to humanitarian assistance. The international community is essentially ignoring what has been deemed Africa s first world war. The DRC remains a forgotten emergency. Falling outside of the media spotlight, and experiencing persistent shortfalls in pledged humanitarian aid, the population of the DRC has been largely abandoned to struggle for their own survival. Aid alone is not enough, however, and political pressure must also be brought to bear in support of the peace agreement and increasing the security throughout the country. This is a forgotten emergency in a forgotten war. It is by no means a simple conflict, and there are no easy answers. However, there will not be peace in the region unless the war in the DRC is fairly and effectively solved. With more than two million people displaced by the conflict, the international community must give this war the attention it deserves. Increased international attention and increased humanitarian aid will be the lifelines for the population of eastern DRC. A war of this magnitude warrants a much stronger and co-ordinated response among agencies, donors and international leaders. To mitigate the effects of this forgotten war and to begin to find a workable solution, Oxfam GB recommends: 1. The international donor community must greatly increase the level of humanitarian aid available to the DRC. This aid should be diversified from merely a focus on food aid, to include human rights, education, and support for primary health. Donations should be increased to levels where international standards for relief such as the Sphere standards can be reliably maintained. 2. There must be concerted international pressure on those in control of the districts with large numbers of displaced people to improve security and eliminate the barriers to the delivery of relief. All belligerents must be pressed to respect humanitarian principles and human rights. 3. Pressure needs to be brought to bear on the DRC government, the warring parties, and on neighbouring countries to abide by the Lusaka accord. The UN should introduce an arms embargo on DRC and all the combatant countries. In addition, arms-producing nations should tighten up export procedures to ensure that shipments of weapons to the region do not further fuel the civil war in the DRC. 1 Oxfam International. An End to Forgotten Emergencies. November
2 Political background: Mobutu Sese-Sekou, one of Africa s longest-ruling and most corrupt leaders, was overthrown by Laurent Kabila in 1997, with the overt support of Rwanda and Uganda. Kabila s government, based in Kinshasa, proved unable to control insurgencies in the eastern part of the country. Rwandan and Ugandan rebels launched guerrilla attacks on their own countries from DRC s border region, terrorising Congolese civilians as well. As relationships between these governments soured, Kabila ordered the withdrawal of all foreign troops from DRC territory in July The current war began in August At present, the Congolese opposition to Kabila consists of the Rassemblement congolais pour la democratie (RCD), and the mouvement pour la liberation du Congo (MLC). The main supporters of these forces are the governments of Rwanda, Uganda and Burundi. The RCD has since split into various factions; the two main groups include one faction loyal to the Rwandan government, known as RCD-Goma, and the other under control of the Ugandan government, known as the RCD- mouvement de liberation (RCD-ML). Angola, Namibia and Zimbabwe have entered the conflict on the side of the government, as did Chad, although the latter withdrew in mid Sudanese government aircraft have been reported to be bombing opposition positions as well. In the East, the unsure political situation and the influx of arms into the region have exacerbated existing ethnic tensions. Fighting that previously took place by machetes and spears is now fought with AK-47s and mortar rounds. Arson, attacks and massacres, particularly between the Hema and Lendu people of Ituri district, have displaced some 180,000 people since July 1999 and killed an estimated 40,000. Although these attacks are ostensibly over land, local authorities are convinced that the power vacuum left by the wider war has led to inter-factional power struggles within the local rebel movement; this has allowed extremists from both sides to manipulate ethnic tensions for their own gains, principally land and resources. While Kabila s military controls the capital, the RCD forces have control of much of the north and east. It has become a military stalemate. Efforts to forge a peace agreement had some success when six countries involved in the war signed a peace accord in Lusaka, Zambia s capital, in July The accord calls for a cease-fire, disarmament of armed factions, the withdrawal of foreign forces, and Congolese political dialogue. However, all warring parties have continued to violate the cease-fire since signing the document. The Lusaka accord also called for the creation of a Joint Military Commission (JMC) to monitor the ceasefire. The UN Security Council authorised the deployment of military liaison officers to prepare for the peacekeeping force MONUC (mission de l organisation des nations unies en Republique democratic de Congo). At present, however, less than a hundred military observers have been dispatched in the DRC, and no armed observers have been allowed to operate. Restrictions on movement and the small numbers mean that the mission is inadequate to monitor the cease-fire. The EU has had an arms embargo on the DRC since The UN has embargoes on UNITA the rebel army in Angola, known to be launching attacks from rear bases in the DRC and on non-governmental Rwandan forces. However, there are no embargoes on the supply of weapons to the governments involved in the conflict, so arms easily flow into the DRC from many sources. After decades of war, the region is awash with weapons. Until May 2000, the UK continued to export military spare parts for aircraft to Zimbabwe despite the latter s participation in the war in the DRC following earlier shipments of Hawk aircraft. Since the unrest in Zimbabwe, however, these shipments have come to a halt. Legislation is currently being considered to tighten up export controls. At present, there is little regulation of arms brokered to the region and little monitoring of the end use of arms exported. Oxfam GB is calling for arms-producing nations to tighten up export procedures to ensure that shipments of weapons to the region do not further fuel DRC s civil war. 2
3 Health and social implications: Although statistics in this region are notoriously difficult to attain, NGOs report that more than a million people may have lost their lives in the two years of conflict. While the vast majority of deaths are due to outbreaks of disease and malnutrition, it is the war that has left these people in such desperate conditions. The highest death rates have been among the two million people internally displaced by the conflict. Violence, fear and intimidation have forced these people into precarious circumstances, often again and again. In addition, over 300,000 Congolese are now refugees in the Republic of Congo, Tanzania, the Central African Republic (CAR), and other countries. 2 Both sides have trouble garnering significant popular support, as there have been massive human rights abuses by all parties to the conflict. 3 This is a war fought with both heavy artillery and small arms. Arson, violence, torture, and arbitrary killings of civilians have been executed with impunity. In addition to the war-related deaths, there has been a breakdown of infrastructure. Government allocated spending on health and education has fallen to less than 1%. 4 Moderate malnutrition affects 32% of the child population, and acute malnutrition hits some 10%. 5 The majority of schools are no longer operational, leaving an entire generation of schoolchildren basically illiterate. The population is left with virtually no government infrastructure or services in most of the country. Many of the displaced people are living with host families, but even these local solutions are reaching a breaking point. An unknown number but estimated to be in the thousands live by their wits in the forest, having been chased from their homes by attacks or fire. They remain too terrified to return, despite precarious living conditions and health problems. As the war simmers on, areas that were once left unaffected by the conflict have become increasingly unable to cope. Economic Situation: The country has thoroughly exhausted its economy after years of war, compounded by decades of corruption and mismanagement. Despite great mineral and hydroelectric potential, the DRC has experienced negative growth in the last decade. Hyperinflation set a world record at 24,000% in Mining has fallen to 10% of its earlier levels, and the formal economy has practically ground to a halt. 7 The export of diamonds was once a major source of funding for the DRC government, but many of these diamonds have now been driven to the black market, through to neighbouring countries. DRC s riches in minerals including gold, copper, cobalt, zinc, and others has exacerbated the ongoing conflict, as local and regional powers vie for control of the resources. On December 1, 2000 the UN General Assembly adopted a resolution on conflict diamonds. They called for all diamond producing, processing, exporting and importing countries to find ways to break the link between illicit transactions and armed conflict. Oxfam GB has lobbied for the implementation of an international certification scheme. This would curb the funding of violence by limiting the illegitimate trade in rough diamonds. In addition, the UN Security Council has mandated a panel of experts to investigate the connection between armed conflict and the illegal exploitation of natural resources in the DRC. Humanitarian funding situation: 2 UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian affairs (UNOCHA). Ms. McAskie s Briefing. 28 November See Amnesty International : Democratic Republic of Congo: Killing Human Decency. 4 Economist Intelligence Unit. Democratic Republic of Congo. (Country profile) World Food Programme (WFP). Brief on WFP Relief Operation: no October Economist Intelligence Unit. 7 Economist Intelligence Unit. 3
4 The UN consolidated inter-agency appeal for 2000 received only 61% of requested funding. 8 In addition, over 82% of financial and in-kind donations was for food security and food assistance. 9 The office of human rights received nothing. Programmes in primary health, epidemic control, child protection, and confidence building received little or no funding at all. This is clearly not an integrated donor strategy in a country with more than 2 million displaced, a collapsed health and education system, and a population exhausted by years of war and decline. Importantly, the lack of funding makes it impossible to monitor human rights abuses, let alone carry out an effective programme of protecting civilians. Even just the presence of international monitors has been known to lower the incidence of abuse, and could initiate a more pro-active international engagement in the human rights situation in the DRC. MONUC, too, needs to be strengthened in numbers of personnel and should have better access to much more of the countryside. Although the World Food Programme (WFP) did receive the majority of its required food in 2000, the agency experienced constraints on the food pipeline. This was mainly due to the delayed pledging and late arrival of donor contributions. The bulk of the food was received after the end of May, delaying emergency operations. WFP reports that this forced the suspension of general distribution programmes in the east. For the whole of the country, however, the UN inter-agency appeal is only part of the picture. The European Community s Humanitarian Organisation (ECHO) donated 20 million Euros from June to December of 2000 and has allocated 35 million Euros for the year The British Government s Department for International Development (DFID) donated 1,322,000 in 1999/ The US government donated $33 million in the fiscal year 2000, of which $13 million is allocated to its Office of Foreign Disaster Assistance (OFDA). 12 Other government bodies have been supporting NGO programmes as well, particularly in the eastern part of the country. While some donors, such as ECHO, have been more generous than others, it is clear that funding levels are still far below what the magnitude of the crisis demands. The humanitarian situation in the DRC requires donors to have a firm commitment to funding projects in all parts of the country. This is not a simple emergency with quick solutions. Donors must work with longer-term strategies when considering assistance for people who have been displaced for over a year. A different kind of approach would incorporate education, health and shelter by working through local structures. UNOCHA s plan for consultative committees in affected communities is a good start in supporting and working through local civil society, including representatives of the displaced. Some donors have objected to increasing their funding because of uncertain security and the consequent difficulties of getting access to those in need. There are very real concerns about security, relating both to the war and to lawlessness. In the Northeast Equateur province, bombings are frequent, forcing thousands to flee to neighbouring CAR or the Republic of Congo-Brazzaville. Banditry and the possibility of riots hamper the security of both local and ex-patriot staff of all the humanitarian organisations across the country. In rebel-controlled areas the difficulties are usually due to insecurity, while in government-held areas restrictive administrative requirements are the main problem. The result is that the people with the most critical needs in the DRC are indeed inaccessible. Forest dwellers and other displaced people in the Kivu provinces, for example, are isolated due to terrain and insecurity. International agencies have made progress in negotiating access, notably for the national immunisation days. These negotiations are rather piece-meal, however, and often rely on the personalities and preferences of the authorities involved. 8 UN OCHA, personal communication. November 30, UN OCHA, UN Consolidated Inter-Agency Appeal for Democratic Republic of the Congo November ECHO. Meeting on DRC November DFID, Statistical Database. 17 November United States Agency for International Development (USAID). Personal communication. 6 December
5 However, there are accessible populations in urgent need of aid that could be reached if more humanitarian assistance was available. Due to the level of financial shortfalls, Oxfam GB and other NGOs have been unable to provide assistance to all those in need who are within reach. In addition, we are unable to provide assistance to the level of internationally-recognised standards for humanitarian aid. These standards, such as Sphere, were agreed upon, along with a humanitarian charter, as the minimum assistance to meet essential needs with impartiality and respect for life with dignity. In the places where we have been able to assist, the improvements are impressive. In Djugu territory, for example, there were 599 cases of cholera in In 2000, after the start of a comprehensive water and sanitation programme, there were only 13 cases. 14 Other water-bourne diseases have declined rapidly as well. Much more could and should be done. Under-funding humanitarian programmes is not an effective solution to the crisis. What is needed is significantly more humanitarian aid, and sustained international attention. Diplomatic pressure on the involved governments and warring parties to improve security, protect the civilian and displaced populations, and reduce the obstacles to delivery are crucial parts of a more effective approach to humanitarian aid and ending the war. 13 Dr. Lobho Romby. Rapport Epidemiologique et Rapport de Service, Dr. Lobho Romby. Situation Humanitaire dans le Zone de Sante Rurale de Rethy, Cases registered up to September
6 To ensure effective humanitarian assistance and to begin to find a long-term solution to DRC s war, Oxfam GB recommends: Donor governments should quickly respond to the war in the DRC, recognising that it is one of the worst humanitarian situations in the world. Donors should immediately support the 2001 UN-OCHA Consolidated Appeal for the DRC, requiring US$139.5 million (about 97 million). To avoid the pipeline problems experienced this year, pledges should come in the early months of the year. Donors should work with international agencies to reach international standards in relief such as the Sphere standards. The international donor community must also diversify their humanitarian aid to ensure that the human rights, primary health, and education have the resources they need. An effective donor strategy would immediately fund the UN Office for Human Rights to monitor abuses, would support educational initiatives for internally displaced children, and would fund nutritional and epidemiological programmes as well. A longer-term approach is needed when working with populations displaced more than a year. International leaders must come together to put intense pressure on the warring parties to adhere to the Lusaka peace accord. UN Security Council members should use their leverage with allies in the region to bring the fighting to a halt. The UN should introduce an arms embargo on DRC and all the combatant countries. In addition, arms-producing nations should tighten up export procedures to ensure that shipments of weapons to the region do not further fuel the civil war in the DRC. All diamond producing, processing, exporting and importing countries should take responsibility for the illicit trade in conflict diamonds fuelling the war in the DRC. Every effort should be made to accelerate the negotiations for an international certification scheme for rough diamonds. The international community must come together to assert concerted pressure on those in control of the districts with large numbers of displaced people to improve security and eliminate the barriers to the delivery of relief. Particularly the government of DRC should be obliged to minimise the administrative procedures hindering relief. The protection of displaced people and civilians from attack, malnutrition or death by curable diseases needs to be prioritised. All belligerents must be pressed to respect humanitarian principles and human rights. Oxfam GB works throughout the country providing clean drinking water and improving hygiene conditions to over half a million people. This US$3.5 million programme includes providing water and sanitation to therapeutic and emergency feeding centres for the displaced, as well as addressing longer-term water and hygiene requirements in urban centres. December 2000 For further information contact: Amelia Bookstein, Policy Advisor, Conflict and Natural Disasters Team Phone: Helen Palmer, Press Officer, Media Unit Phone: First published by Oxfam GB in December Published by Oxfam GB under ISBN in October
Former Rwandan Tutsi-led rebel militia group, and later political party created in 1998
 Forum: Issue: Contemporary Security Council Instability in the Democratic Republic of Congo Student Officers: Yun Kei Chow, Ken Kim Introduction Since achieving independence in 1960, the Democratic Republic
Forum: Issue: Contemporary Security Council Instability in the Democratic Republic of Congo Student Officers: Yun Kei Chow, Ken Kim Introduction Since achieving independence in 1960, the Democratic Republic
Dear Delegates, It is a pleasure to welcome you to the 2016 Montessori Model United Nations Conference.
 Dear Delegates, It is a pleasure to welcome you to the 2016 Montessori Model United Nations Conference. The following pages intend to guide you in the research of the topics that will be debated at MMUN
Dear Delegates, It is a pleasure to welcome you to the 2016 Montessori Model United Nations Conference. The following pages intend to guide you in the research of the topics that will be debated at MMUN
Democratic Republic of the Congo
 Democratic Republic Total requirements: USD 75,035,460 Working environment The context Despite the Goma Conference on peace, stability and development and the signing of a ceasefire agreement in January
Democratic Republic Total requirements: USD 75,035,460 Working environment The context Despite the Goma Conference on peace, stability and development and the signing of a ceasefire agreement in January
DR Congo: waves of displacement follow heightened hopes of peace
 25 October 2004 DR Congo: waves of displacement follow heightened hopes of peace Since the mid-1990s, millions of Congolese have fled their homes to escape fighting between rebel groups and the national
25 October 2004 DR Congo: waves of displacement follow heightened hopes of peace Since the mid-1990s, millions of Congolese have fled their homes to escape fighting between rebel groups and the national
Adopted by the Security Council at its 6792nd meeting, on 27 June 2012
 United Nations S/RES/2053 (2012) Security Council Distr.: General 27 June 2012 Resolution 2053 (2012) Adopted by the Security Council at its 6792nd meeting, on 27 June 2012 The Security Council, Recalling
United Nations S/RES/2053 (2012) Security Council Distr.: General 27 June 2012 Resolution 2053 (2012) Adopted by the Security Council at its 6792nd meeting, on 27 June 2012 The Security Council, Recalling
Burundi Cameroon Central African Republic Congo Democratic Republic of the Congo Gabon Rwanda United Republic of Tanzania
 , Masisi District, Democratic Republic of the Congo. Burundi Cameroon Central African Republic Congo Democratic Republic of the Congo Gabon Rwanda United Republic of Tanzania 2 UNHCRGlobalReport2011 and
, Masisi District, Democratic Republic of the Congo. Burundi Cameroon Central African Republic Congo Democratic Republic of the Congo Gabon Rwanda United Republic of Tanzania 2 UNHCRGlobalReport2011 and
Great Lakes. Major Developments. Burundi Democratic Republic of the Congo Republic of the Congo Rwanda United Republic of Tanzania
 Great Lakes Major Developments The year 2001 saw a positive change in the political and military situation of the Great Lakes Region following the death of President Laurent Desiré Kabila of the Democratic
Great Lakes Major Developments The year 2001 saw a positive change in the political and military situation of the Great Lakes Region following the death of President Laurent Desiré Kabila of the Democratic
Democratic Republic of the Congo
 Democratic Republic Working environment The context It is estimated that the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) hosts more than 156,000 refugees. Most of them live in villages or refugee settlements
Democratic Republic Working environment The context It is estimated that the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) hosts more than 156,000 refugees. Most of them live in villages or refugee settlements
OCHA Regional Office for Central and East Africa Displaced Populations Report January June 2008, ISSUE 3
 OCHA Regional Office for Central and East Africa Displaced Populations Report January, ISSUE 3 United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs Introduction This report contains updated
OCHA Regional Office for Central and East Africa Displaced Populations Report January, ISSUE 3 United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs Introduction This report contains updated
Adopted by the Security Council at its 6324th meeting, on 28 May 2010
 United Nations S/RES/1925 (2010) Security Council Distr.: General 28 May 2010 Resolution 1925 (2010) Adopted by the Security Council at its 6324th meeting, on 28 May 2010 The Security Council, Recalling
United Nations S/RES/1925 (2010) Security Council Distr.: General 28 May 2010 Resolution 1925 (2010) Adopted by the Security Council at its 6324th meeting, on 28 May 2010 The Security Council, Recalling
DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF THE CONGO
 DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF THE CONGO 2013 GLOBAL REPORT Operational highlights Tensions and armed clashes in the Central African Republic (CAR) led to an influx of refugees into the Democratic Republic of
DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF THE CONGO 2013 GLOBAL REPORT Operational highlights Tensions and armed clashes in the Central African Republic (CAR) led to an influx of refugees into the Democratic Republic of
Great Lakes. Major developments. Burundi Democratic Republic of the Congo Republic of the Congo Rwanda United Republic of Tanzania
 Major developments The signing of various peace accords and cease-fire agreements in the period from 2000 to 2002 brought optimism for a resolution of years of instability, especially for the Democratic
Major developments The signing of various peace accords and cease-fire agreements in the period from 2000 to 2002 brought optimism for a resolution of years of instability, especially for the Democratic
AMNESTY INTERNATIONAL PUBLIC APPEAL. Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) Still under the gun: More child soldiers recruited
 PUBLIC AI INDEX: AFR 62/009/2004 JUNE 2004 AMNESTY INTERNATIONAL PUBLIC APPEAL Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) Still under the gun: More child soldiers recruited Armed groups in eastern DRC are still
PUBLIC AI INDEX: AFR 62/009/2004 JUNE 2004 AMNESTY INTERNATIONAL PUBLIC APPEAL Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) Still under the gun: More child soldiers recruited Armed groups in eastern DRC are still
Under-five chronic malnutrition rate is critical (43%) and acute malnutrition rate is high (9%) with some areas above the critical thresholds.
 May 2014 Fighting Hunger Worldwide Democratic Republic of Congo: is economic recovery benefiting the vulnerable? Special Focus DRC DRC Economic growth has been moderately high in DRC over the last decade,
May 2014 Fighting Hunger Worldwide Democratic Republic of Congo: is economic recovery benefiting the vulnerable? Special Focus DRC DRC Economic growth has been moderately high in DRC over the last decade,
Situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo
 P7_TA-PROV(2012)0511 Situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo European Parliament resolution of 13 December 2012 on the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (2012/2907(RSP)) The European
P7_TA-PROV(2012)0511 Situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo European Parliament resolution of 13 December 2012 on the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (2012/2907(RSP)) The European
Rwanda. Main Objectives. Working Environment. Recent Developments. Planning Figures. Total Requirements: USD 8,036,195
 Main Objectives Provide protection and material assistance to refugees, including undertaking refugee status determination (RSD) procedures on behalf of the Government, until such time as the National
Main Objectives Provide protection and material assistance to refugees, including undertaking refugee status determination (RSD) procedures on behalf of the Government, until such time as the National
The RRMP: A Rapid Response
 R R M P The RRMP: A Rapid Response to Population Movement in Eastern DRC Contents 1. Emergency 2. Response 3. Assessment 4. Results 5. Coordination 6. Partnership Please visit the UNICEF DRC blog at www.ponabana.com
R R M P The RRMP: A Rapid Response to Population Movement in Eastern DRC Contents 1. Emergency 2. Response 3. Assessment 4. Results 5. Coordination 6. Partnership Please visit the UNICEF DRC blog at www.ponabana.com
Conflict in the Democratic Republic of the Congo
 Conflict in the Democratic Republic of the Congo Background: The Democratic Republic of the Congo is very wealthy and a sizeable country with rich resources, yet the government has not reaped the benefits
Conflict in the Democratic Republic of the Congo Background: The Democratic Republic of the Congo is very wealthy and a sizeable country with rich resources, yet the government has not reaped the benefits
Important political progress was achieved in some of
 Major developments Important political progress was achieved in some of the seven countries in the region. Insecurity continued however to be a cause for concern in parts of the eastern provinces of the
Major developments Important political progress was achieved in some of the seven countries in the region. Insecurity continued however to be a cause for concern in parts of the eastern provinces of the
The Impact of Armed Conflict on Children in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC)
 The Impact of Armed Conflict on Children in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) June 2003 Watchlist on Children and Armed Conflict 122 East 42 nd Street, 12 th floor New York, NY 10168-1289 Phone: 212.551.3111
The Impact of Armed Conflict on Children in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) June 2003 Watchlist on Children and Armed Conflict 122 East 42 nd Street, 12 th floor New York, NY 10168-1289 Phone: 212.551.3111
Dealing with the fast-changing environment in the eastern DRC. The split in the CNDP
 Henri Boshoff is a military analyst for the Africa Security Analysis Programme at the ISS Pretoria Office Dealing with the fast-changing environment in the eastern DRC Henri Boshoff The split in the CNDP
Henri Boshoff is a military analyst for the Africa Security Analysis Programme at the ISS Pretoria Office Dealing with the fast-changing environment in the eastern DRC Henri Boshoff The split in the CNDP
Council Special Report Congo: Securing Peace, Sustaining Progress
 Council Special Report Congo: Securing Peace, Sustaining Progress Teaching Notes By Anthony W. Gambino Independent Consultant for International Development and Foreign Policy; Former USAID Mission Director,
Council Special Report Congo: Securing Peace, Sustaining Progress Teaching Notes By Anthony W. Gambino Independent Consultant for International Development and Foreign Policy; Former USAID Mission Director,
URGENT NEED TO ASSIST RECENTLY DISPLACED POPULATIONS
 UNICEF HUMANITARIAN ACTION D.R. CONGO DONOR UPDATE 9 JULY 2001 URGENT NEED TO ASSIST RECENTLY DISPLACED POPULATIONS Progress being made toward peace Continued exploitation of natural resources Ethnic conflicts
UNICEF HUMANITARIAN ACTION D.R. CONGO DONOR UPDATE 9 JULY 2001 URGENT NEED TO ASSIST RECENTLY DISPLACED POPULATIONS Progress being made toward peace Continued exploitation of natural resources Ethnic conflicts
ACP-EU JOINT PARLIAMENTARY ASSEMBLY
 ACP-EU JOINT PARLIAMTARY ASSEMBLY ACP-EU 102.583/18/fin. RESOLUTION 1 on the humanitarian crisis in South Sudan The ACP-EU Joint Parliamentary Assembly, meeting in Brussels (Belgium) from 18 to 20 June
ACP-EU JOINT PARLIAMTARY ASSEMBLY ACP-EU 102.583/18/fin. RESOLUTION 1 on the humanitarian crisis in South Sudan The ACP-EU Joint Parliamentary Assembly, meeting in Brussels (Belgium) from 18 to 20 June
Adopted by the Security Council at its 4329th meeting, on 15 June 2001
 United Nations Security Council Distr.: General 15 June 2001 Resolution 1355 (2001) Adopted by the Security Council at its 4329th meeting, on 15 June 2001 The Security Council, Recalling its resolutions
United Nations Security Council Distr.: General 15 June 2001 Resolution 1355 (2001) Adopted by the Security Council at its 4329th meeting, on 15 June 2001 The Security Council, Recalling its resolutions
CENTRAL AFRICA AND THE GREAT LAKES
 CENTRAL AFRICA AND THE GREAT LAKES GLOBAL APPEAL 2015 UPDATE Burundi Cameroon Central African Republic Congo (Republic of the) Democratic Republic of the Congo Gabon Rwanda United Republic of Tanzania
CENTRAL AFRICA AND THE GREAT LAKES GLOBAL APPEAL 2015 UPDATE Burundi Cameroon Central African Republic Congo (Republic of the) Democratic Republic of the Congo Gabon Rwanda United Republic of Tanzania
Natural Resources and Conflict
 20 June 2007 No. 2 Natural Resources and Conflict Expected Council Action On 25 June the Security Council will hold an open debate on the relationship between natural resources and conflict, an initiative
20 June 2007 No. 2 Natural Resources and Conflict Expected Council Action On 25 June the Security Council will hold an open debate on the relationship between natural resources and conflict, an initiative
Democratic Republic of the Congo
 Main objectives Reinforce national institutions dealing with refugees as well as civil society, local communities and their institutions. Organize and facilitate the repatriation of Angolan, Burundian,
Main objectives Reinforce national institutions dealing with refugees as well as civil society, local communities and their institutions. Organize and facilitate the repatriation of Angolan, Burundian,
Democratic Republic of Congo
 Democratic Republic of Congo I Appeal No. MAACD001 08/Sepetember/2008 This report covers the period 1/01/2008 to 30/6/2008. Construction of public latrines at a market in Mbandaka Equateur Province, DRC
Democratic Republic of Congo I Appeal No. MAACD001 08/Sepetember/2008 This report covers the period 1/01/2008 to 30/6/2008. Construction of public latrines at a market in Mbandaka Equateur Province, DRC
DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF THE CONGO
 DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF THE CONGO 2014-2015 GLOBAL APPEAL UNHCR s planned presence 2014 Number of offices 13 Total personnel 338 International staff 62 National staff 240 JPOs 1 UN Volunteers 31 Others
DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF THE CONGO 2014-2015 GLOBAL APPEAL UNHCR s planned presence 2014 Number of offices 13 Total personnel 338 International staff 62 National staff 240 JPOs 1 UN Volunteers 31 Others
RWANDA. Overview. Working environment
 RWANDA 2014-2015 GLOBAL APPEAL UNHCR s planned presence 2014 Number of offices 5 Total personnel 111 International staff 27 National staff 65 UN Volunteers 14 Others 5 Overview Working environment Rwanda
RWANDA 2014-2015 GLOBAL APPEAL UNHCR s planned presence 2014 Number of offices 5 Total personnel 111 International staff 27 National staff 65 UN Volunteers 14 Others 5 Overview Working environment Rwanda
SITUATION REPORT: REFUGEES AND INTERNALLY DISPLACED PEOPLE'S IN AFRICA. Jenny Clover, 2002
 SITUATION REPORT: REFUGEES AND INTERNALLY DISPLACED PEOPLE'S IN AFRICA Jenny Clover, 2002 Technically the term Refugees refers to those who have been displaced across the border of their home States, while
SITUATION REPORT: REFUGEES AND INTERNALLY DISPLACED PEOPLE'S IN AFRICA Jenny Clover, 2002 Technically the term Refugees refers to those who have been displaced across the border of their home States, while
Democratic Republic of Congo Ituri - How many more have to die?
 Democratic Republic of Congo Ituri - How many more have to die? Five years on August 2 2003 marks the fifth anniversary of the start of the conflict in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). While international
Democratic Republic of Congo Ituri - How many more have to die? Five years on August 2 2003 marks the fifth anniversary of the start of the conflict in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). While international
DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF THE CONGO
 DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF THE CONGO INITIAL OBJECTIVES Support the Government in the establishment of the National Eligibility Commission, and to carry out registration exercises of accessible refugees. Provide
DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF THE CONGO INITIAL OBJECTIVES Support the Government in the establishment of the National Eligibility Commission, and to carry out registration exercises of accessible refugees. Provide
Office of the Special Representative for Children and Armed Conflict
 Office of the Special Representative for Children and Armed Conflict Input to the Universal Periodic Review of the Human Rights Council Report on the Democratic Republic of the Congo 13 April 2009 A. Grave
Office of the Special Representative for Children and Armed Conflict Input to the Universal Periodic Review of the Human Rights Council Report on the Democratic Republic of the Congo 13 April 2009 A. Grave
Eastern and Southern Africa
 Eastern and Southern Africa For much of the past decade, millions of children and women in the Eastern and Southern Africa region have endured war, political instability, droughts, floods, food insecurity
Eastern and Southern Africa For much of the past decade, millions of children and women in the Eastern and Southern Africa region have endured war, political instability, droughts, floods, food insecurity
MOTION FOR A RESOLUTION
 European Parliament 2014-2019 Plenary sitting B8-0074/2017 17.1.2017 MOTION FOR A RESOLUTION with request for inclusion in the agenda for a debate on cases of breaches of human rights, democracy and the
European Parliament 2014-2019 Plenary sitting B8-0074/2017 17.1.2017 MOTION FOR A RESOLUTION with request for inclusion in the agenda for a debate on cases of breaches of human rights, democracy and the
During 2005, the Central Africa and the Great
 Recent developments During 2005, the Central Africa and the Great Lakes subregion experienced further stabilization and progress towards peace and democracy. No major refugee crisis occurred in the region
Recent developments During 2005, the Central Africa and the Great Lakes subregion experienced further stabilization and progress towards peace and democracy. No major refugee crisis occurred in the region
Good afternoon and welcome to our Member States briefing on CERF activities in 2013.
 Good afternoon and welcome to our Member States briefing on CERF activities in 2013. So far this year, CERF has allocated more than US$367 million from the Rapid Response and the Underfunded windows to
Good afternoon and welcome to our Member States briefing on CERF activities in 2013. So far this year, CERF has allocated more than US$367 million from the Rapid Response and the Underfunded windows to
Mr. President, Members of the Council,
 Briefing to the Security Council on the Central African Republic Delivered by Mr. Jeffrey Feltman, Under-Secretary-General for Political Affairs 6 January 2014 Members of the Council, The situation in
Briefing to the Security Council on the Central African Republic Delivered by Mr. Jeffrey Feltman, Under-Secretary-General for Political Affairs 6 January 2014 Members of the Council, The situation in
Oxfam (GB) Guiding Principles for Response to Food Crises
 Oxfam (GB) Guiding Principles for Response to Food Crises Introduction The overall goal of Oxfam s Guiding Principles for Response to Food Crises is to provide and promote effective humanitarian assistance
Oxfam (GB) Guiding Principles for Response to Food Crises Introduction The overall goal of Oxfam s Guiding Principles for Response to Food Crises is to provide and promote effective humanitarian assistance
United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) (May 2013 April 2014)
 United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) (May 2013 April 2014) UNHCR s support to New Partnership for Africa s Development (NEPAD) Planning and Coordinating Agency Operational highlights In
United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) (May 2013 April 2014) UNHCR s support to New Partnership for Africa s Development (NEPAD) Planning and Coordinating Agency Operational highlights In
OI Policy Compendium Note on the European Union s Role in Protecting Civilians
 OI Policy Compendium Note on the European Union s Role in Protecting Civilians Overview: Oxfam International s position on the European Union s role in protecting civilians in conflict Oxfam International
OI Policy Compendium Note on the European Union s Role in Protecting Civilians Overview: Oxfam International s position on the European Union s role in protecting civilians in conflict Oxfam International
Scenarios for the Greater Horn of Africa and Great Lakes Region. Humanitarian Partnership Conference Nairobi 15 September, 2015
 Scenarios for the Greater Horn of Africa and Great Lakes Region Humanitarian Partnership Conference Nairobi 15 September, 2015 Background Regional Overview for the Horn of Africa and the Great Lakes Region
Scenarios for the Greater Horn of Africa and Great Lakes Region Humanitarian Partnership Conference Nairobi 15 September, 2015 Background Regional Overview for the Horn of Africa and the Great Lakes Region
COUNTRY OPERATIONS PLAN. Country: Uganda
 COUNTRY OPERATIONS PLAN Country: Uganda Planning Year: 2004 1.1 Context and Beneficiary Populations Part I: Executive - Summary UNHCR s presence in Uganda dates back from the 1960s. Though the earlier
COUNTRY OPERATIONS PLAN Country: Uganda Planning Year: 2004 1.1 Context and Beneficiary Populations Part I: Executive - Summary UNHCR s presence in Uganda dates back from the 1960s. Though the earlier
Resolution UNSC/1.1. UNSC United Nations Security Council
 Resolution UNSC/1.1 Zealand, French Republic, Oriental Republic of Uruguay, Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, Malaysia, People s Republic of China, Kingdom of Spain. Topic: The Democratic Republic of Congo
Resolution UNSC/1.1 Zealand, French Republic, Oriental Republic of Uruguay, Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, Malaysia, People s Republic of China, Kingdom of Spain. Topic: The Democratic Republic of Congo
G8 MIYAZAKI INITIATIVES FOR CONFLICT PREVENTION I. EFFORTS FOR CONFLICT PREVENTION -- A BASIC CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK --
 G8 MIYAZAKI INITIATIVES FOR CONFLICT PREVENTION I. EFFORTS FOR CONFLICT PREVENTION -- A BASIC CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK -- The G8 Heads of State and Government announced last June in Cologne, and we, Foreign
G8 MIYAZAKI INITIATIVES FOR CONFLICT PREVENTION I. EFFORTS FOR CONFLICT PREVENTION -- A BASIC CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK -- The G8 Heads of State and Government announced last June in Cologne, and we, Foreign
$100. million to strengthen humanitarian response in underfunded crises 5.3 M. people. Total $1.51 billion has been allocated since 2006
 2016 CERF (UFE): As of 29 January 2016, in US$ $100 to strengthen humanitarian response in underfunded crises $100 has been approved from the Central Emergency Response Fund (CERF) during the first 2016
2016 CERF (UFE): As of 29 January 2016, in US$ $100 to strengthen humanitarian response in underfunded crises $100 has been approved from the Central Emergency Response Fund (CERF) during the first 2016
UK Policy and Strategic Priorities on Small Arms and Light Weapons
 UK Policy and Strategic Priorities on Small Arms and Light Weapons 2004-2006 The SALW problem: global, national and local The widespread availability of small arms and light weapons in many regions of
UK Policy and Strategic Priorities on Small Arms and Light Weapons 2004-2006 The SALW problem: global, national and local The widespread availability of small arms and light weapons in many regions of
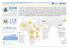
OCHA DRC POPULATION MOVEMENTS IN EASTERN DR CONGO OCTOBER DECEMBER 2009
 OCHA DRC POPULATION MOVEMENTS IN EASTERN DR CONGO OCTOBER DECEMBER January 2010 1 1. OVERVIEW The humanitarian situation and movement of populations in have been heavily influenced by military operations
OCHA DRC POPULATION MOVEMENTS IN EASTERN DR CONGO OCTOBER DECEMBER January 2010 1 1. OVERVIEW The humanitarian situation and movement of populations in have been heavily influenced by military operations
Update on UNHCR s operations in Africa
 Regional update - Africa Executive Committee of the High Commissioner s Programme Sixty-fifth session Geneva, 29 September - 3 October 2014 19 September 2014 English Original: English and French Update
Regional update - Africa Executive Committee of the High Commissioner s Programme Sixty-fifth session Geneva, 29 September - 3 October 2014 19 September 2014 English Original: English and French Update
International Alert. Case study Democratic Republic of Congo * Local Business, Local Peace: the Peacebuilding Potential of the Domestic Private Sector
 International Alert. Local Business, Local Peace: the Peacebuilding Potential of the Domestic Private Sector Case study Democratic Republic of Congo * * This document is an extract from Local Business,
International Alert. Local Business, Local Peace: the Peacebuilding Potential of the Domestic Private Sector Case study Democratic Republic of Congo * * This document is an extract from Local Business,
Somali refugees arriving at UNHCR s transit center in Ethiopia. Djibouti Eritrea Ethiopia Kenya Somalia Uganda. 58 UNHCR Global Appeal
 Somali refugees arriving at UNHCR s transit center in Ethiopia. Djibouti Eritrea Ethiopia Kenya Somalia Uganda 58 UNHCR Global Appeal 2010 11 East and Horn of Africa Working environment UNHCR The situation
Somali refugees arriving at UNHCR s transit center in Ethiopia. Djibouti Eritrea Ethiopia Kenya Somalia Uganda 58 UNHCR Global Appeal 2010 11 East and Horn of Africa Working environment UNHCR The situation
E Distribution: GENERAL WFP/EB.A/2001/4-C 17 April 2001 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH POLICY ISSUES. Agenda item 4
 Executive Board Annual Session Rome, 21-24 May 2001 POLICY ISSUES Agenda item 4 For information* WFP REACHING PEOPLE IN SITUATIONS OF DISPLACEMENT Framework for Action E Distribution: GENERAL WFP/EB.A/2001/4-C
Executive Board Annual Session Rome, 21-24 May 2001 POLICY ISSUES Agenda item 4 For information* WFP REACHING PEOPLE IN SITUATIONS OF DISPLACEMENT Framework for Action E Distribution: GENERAL WFP/EB.A/2001/4-C
ACongolesefarmerrepatriated from DRC ploughs his field in the Ruzizi plain.
 ACongolesefarmerrepatriated from DRC ploughs his field in the Ruzizi plain. Burundi Cameroon Central African Republic Chad (see under Chad-Sudan situation) Congo (Republic of the) Democratic Republic of
ACongolesefarmerrepatriated from DRC ploughs his field in the Ruzizi plain. Burundi Cameroon Central African Republic Chad (see under Chad-Sudan situation) Congo (Republic of the) Democratic Republic of
Africa. Determined leadership and sustained. Working environment
 Working environment Determined leadership and sustained international support in 2006 helped several n countries move towards peace and political stability after years of strife. As a consequence, whether
Working environment Determined leadership and sustained international support in 2006 helped several n countries move towards peace and political stability after years of strife. As a consequence, whether
More than 900 refugees (mostly Congolese) were resettled in third countries.
 RWANDA 2013 GLOBAL REPORT Operational highlights Protection and assistance were offered to more than 73,000 refugees and some 200 asylum-seekers, mostly from the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC).
RWANDA 2013 GLOBAL REPORT Operational highlights Protection and assistance were offered to more than 73,000 refugees and some 200 asylum-seekers, mostly from the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC).
CALL FOR ACTION FINAL 19 May 2017
 Inter-Cluster Operational Responses in South Sudan, Somalia, Yemen, and Nigeria Promoting an Integrated Famine Prevention Package: Breaking Bottlenecks Call for Action Despite extensive efforts to address
Inter-Cluster Operational Responses in South Sudan, Somalia, Yemen, and Nigeria Promoting an Integrated Famine Prevention Package: Breaking Bottlenecks Call for Action Despite extensive efforts to address
Zambia. Operational highlights. Persons of concern
 Operational highlights UNHCR collaborated with the Government of Zambia to repatriate some 9,700 refugees to Angola, Burundi, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), Rwanda and Uganda. Some 2,100 Congolese
Operational highlights UNHCR collaborated with the Government of Zambia to repatriate some 9,700 refugees to Angola, Burundi, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), Rwanda and Uganda. Some 2,100 Congolese
Year: 2017 Last update: 05/07/2017 Version 2 HUMANITARIAN IMPLEMENTATION PLAN (HIP) GREAT LAKES REGION
 HUMANITARIAN IMPLEMENTATION PLAN (HIP) GREAT LAKES REGION The full implementation of this version of the HIP is subject to the adoption of the decision amending Decision C(2016) 8795 final AMOUNT: EUR
HUMANITARIAN IMPLEMENTATION PLAN (HIP) GREAT LAKES REGION The full implementation of this version of the HIP is subject to the adoption of the decision amending Decision C(2016) 8795 final AMOUNT: EUR
117 th Great Lakes Policy Forum Humanitarian Consequences of the Conflict in Katanga" Meeting Report April 6, 2006
 117 th Great Lakes Policy Forum Humanitarian Consequences of the Conflict in Katanga" Meeting Report April 6, 2006 Panelists: Mr. Andrea Lari Advocate, Refugees International Mr. Rick Neal Advocate, Refugees
117 th Great Lakes Policy Forum Humanitarian Consequences of the Conflict in Katanga" Meeting Report April 6, 2006 Panelists: Mr. Andrea Lari Advocate, Refugees International Mr. Rick Neal Advocate, Refugees
Bruxelles, le 14 November 2001
 Bruxelles, le 14 November 2001 Between 1991 and the end of 2001, the European Commission has committed some in aid to Afghan populations in need - implemented through UN agencies, the Red Cross Movement
Bruxelles, le 14 November 2001 Between 1991 and the end of 2001, the European Commission has committed some in aid to Afghan populations in need - implemented through UN agencies, the Red Cross Movement
ACP-EU JOINT PARLIAMENTARY ASSEMBLY
 ACP-EU JOINT PARLIAMTARY ASSEMBLY Committee on Political Affairs 23 September 2003 DRAFT REPORT on conflict prevention, the peace process and post-conflict management Co-Rapporteurs: Philippe Morillon
ACP-EU JOINT PARLIAMTARY ASSEMBLY Committee on Political Affairs 23 September 2003 DRAFT REPORT on conflict prevention, the peace process and post-conflict management Co-Rapporteurs: Philippe Morillon
CONGO (Republic of the)
 CONGO (Republic of the) Operational highlights UNHCR completed the verification of refugees living in the north of the country. More than 131,000 refugees from the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC)
CONGO (Republic of the) Operational highlights UNHCR completed the verification of refugees living in the north of the country. More than 131,000 refugees from the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC)
Central African Republic crisis ECHO CRISIS REPORT N 9
 Central African Republic crisis ECHO CRISIS REPORT N 9 Period covered 10/08/2013 to 17/09/2013 1. Map Time of validity 08:00 (UTC) ECHO Field Office Bangui IDPs in CAR : It is difficult having accurate
Central African Republic crisis ECHO CRISIS REPORT N 9 Period covered 10/08/2013 to 17/09/2013 1. Map Time of validity 08:00 (UTC) ECHO Field Office Bangui IDPs in CAR : It is difficult having accurate
Southern Africa. Recent Developments
 Recent Developments Angola Botswana Comoros Lesotho Madagascar Malawi Mauritius Mozambique Namibia Seychelles South Africa Swaziland Zambia Zimbabwe The positive developments in the Inter-Congolese dialogue
Recent Developments Angola Botswana Comoros Lesotho Madagascar Malawi Mauritius Mozambique Namibia Seychelles South Africa Swaziland Zambia Zimbabwe The positive developments in the Inter-Congolese dialogue
Central African Republic
 Central African Republic Operational highlights Some 9,000 spontaneous returnees from Chad and Cameroon were registered. A technical working group was established for the elaboration of tripartite agreements
Central African Republic Operational highlights Some 9,000 spontaneous returnees from Chad and Cameroon were registered. A technical working group was established for the elaboration of tripartite agreements
1 Summary. We are their meat, their animals. We have nothing to say.
 1 Summary We are their meat, their animals. We have nothing to say. Miner from Shabunda (South Kivu), 28 July 2008 The militarisation of mining in eastern Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) is prolonging
1 Summary We are their meat, their animals. We have nothing to say. Miner from Shabunda (South Kivu), 28 July 2008 The militarisation of mining in eastern Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) is prolonging
Zimbabwe Complex Emergency
 BUREAU FOR DEMOCRACY, CONFLICT, AND HUMANITARIAN ASSISTANCE (DCHA) OFFICE OF U.S. FOREIGN DISASTER ASSISTANCE (OFDA) Zimbabwe Complex Emergency Situation Report #3, Fiscal Year (FY) 2009 February 13, 2009
BUREAU FOR DEMOCRACY, CONFLICT, AND HUMANITARIAN ASSISTANCE (DCHA) OFFICE OF U.S. FOREIGN DISASTER ASSISTANCE (OFDA) Zimbabwe Complex Emergency Situation Report #3, Fiscal Year (FY) 2009 February 13, 2009
SOUTH SUDAN. Working environment
 SOUTH SUDAN GLOBAL APPEAL 2015 UPDATE Planned presence Number of offices 14 Total personnel 477 International staff 123 National staff 322 JPOs 2 UN Volunteers 22 Others 8 2015 plan at a glance* 1.6 million**
SOUTH SUDAN GLOBAL APPEAL 2015 UPDATE Planned presence Number of offices 14 Total personnel 477 International staff 123 National staff 322 JPOs 2 UN Volunteers 22 Others 8 2015 plan at a glance* 1.6 million**
UGANDA. Overview. Working environment
 UGANDA 2014-2015 GLOBAL APPEAL Overview Working environment UNHCR s planned presence 2014 Number of offices 12 Total personnel 202 International staff 18 National staff 145 JPOs 5 UN Volunteers 29 Others
UGANDA 2014-2015 GLOBAL APPEAL Overview Working environment UNHCR s planned presence 2014 Number of offices 12 Total personnel 202 International staff 18 National staff 145 JPOs 5 UN Volunteers 29 Others
Year: 2011 Last update: 27/10/2011 HUMANITARIAN IMPLEMENTATION PLAN (HIP) BURUNDI & TANZANIA
 HUMANITARIAN IMPLEMENTATION PLAN (HIP) BURUNDI & TANZANIA 0. MAJOR CHANGES SINCE PREVIOUS VERSION OF THE HIP At the Tripartite Commission Burundi/Tanzania/UNHCR in May 2011, the Tanzanian authorities have
HUMANITARIAN IMPLEMENTATION PLAN (HIP) BURUNDI & TANZANIA 0. MAJOR CHANGES SINCE PREVIOUS VERSION OF THE HIP At the Tripartite Commission Burundi/Tanzania/UNHCR in May 2011, the Tanzanian authorities have
European Parliament resolution of 17 January 2013 on the situation in the Central African Republic (2013/2514(RSP))
 P7_TA-PROV(2013)0033 Situation in the Central African Republic European Parliament resolution of 17 January 2013 on the situation in the Central African Republic (2013/2514(RSP)) The European Parliament,
P7_TA-PROV(2013)0033 Situation in the Central African Republic European Parliament resolution of 17 January 2013 on the situation in the Central African Republic (2013/2514(RSP)) The European Parliament,
The Role of Diamonds in Fueling Armed Conflict.
 The Role of Diamonds in Fueling Armed Conflict. Introduction As early as 1998, the United Nations (UN) concerned itself with the problem of conflict diamonds and their role in financing armed conflict.
The Role of Diamonds in Fueling Armed Conflict. Introduction As early as 1998, the United Nations (UN) concerned itself with the problem of conflict diamonds and their role in financing armed conflict.
Famine: The end point of a global protection crisis
 POLICY BRIEF Famine: The end point of a global protection crisis The world knew it was coming. The warning signs were there long before an alert was issued in January 2017: an ever-widening gap between
POLICY BRIEF Famine: The end point of a global protection crisis The world knew it was coming. The warning signs were there long before an alert was issued in January 2017: an ever-widening gap between
Central African Republic
 Main objectives Complete the repatriation of those refugees from Sudan and the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) who are willing to return to their country of origin. Provide legal protection and
Main objectives Complete the repatriation of those refugees from Sudan and the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) who are willing to return to their country of origin. Provide legal protection and
Three-Pronged Strategy to Address Refugee Urban Health: Advocate, Support and Monitor
 Urban Refugee Health 1. The issue Many of the health strategies, policies and interventions for refugees are based on past experiences where refugees are situated in camp settings and in poor countries.
Urban Refugee Health 1. The issue Many of the health strategies, policies and interventions for refugees are based on past experiences where refugees are situated in camp settings and in poor countries.
ETHIOPIA HUMANITARIAN FUND (EHF) SECOND ROUND STANDARD ALLOCATION- JULY 2017
 ETHIOPIA HUMANITARIAN FUND (EHF) SECOND ROUND STANDARD ALLOCATION- JULY 2017 I. OVERVIEW 1. This document outlines the strategic objectives of the EHF Second Standard Allocation for 2017. The document
ETHIOPIA HUMANITARIAN FUND (EHF) SECOND ROUND STANDARD ALLOCATION- JULY 2017 I. OVERVIEW 1. This document outlines the strategic objectives of the EHF Second Standard Allocation for 2017. The document
Response to the Somali displacement crisis into Ethiopia, Djibouti and Kenya, 2011
 Response to the Somali displacement crisis into Ethiopia, Djibouti and Kenya, 2011 Donor Relations and Resource Mobilization Service July 2011 Ethiopia, recently arrived Somali refugees waiting to be registered
Response to the Somali displacement crisis into Ethiopia, Djibouti and Kenya, 2011 Donor Relations and Resource Mobilization Service July 2011 Ethiopia, recently arrived Somali refugees waiting to be registered
Discussion Notes, Part Two Humanitarian assistance in the DRC
 Discussion Notes, Part Two Humanitarian assistance in the DRC The DRC is without doubt one of the most dangerous places for humanitarian workers. Humanitarian organisations have to engage with all stakeholders
Discussion Notes, Part Two Humanitarian assistance in the DRC The DRC is without doubt one of the most dangerous places for humanitarian workers. Humanitarian organisations have to engage with all stakeholders
PROFILE OF INTERNAL DISPLACEMENT : DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF THE CONGO
 PROFILE OF INTERNAL DISPLACEMENT : DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF THE CONGO Compilation of the information available in the Global IDP Database of the Norwegian Refugee Council (as of 20 May, 2003) Also available
PROFILE OF INTERNAL DISPLACEMENT : DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF THE CONGO Compilation of the information available in the Global IDP Database of the Norwegian Refugee Council (as of 20 May, 2003) Also available
The Democratic Republic of Congo: Background and Current Developments
 The Democratic Republic of Congo: Background and Current Developments Ted Dagne Specialist in African Affairs July 16, 2009 Congressional Research Service CRS Report for Congress Prepared for Members and
The Democratic Republic of Congo: Background and Current Developments Ted Dagne Specialist in African Affairs July 16, 2009 Congressional Research Service CRS Report for Congress Prepared for Members and
Theo Neethling. Department of Political Studies and Governance Faculty of the Humanities
 Department of Political Studies and Governance Faculty of the Humanities Theo Neethling Post-conflict Reconstruction and Development in the DRC: Revisiting the Main Challenges and the Role of the UN UNIVERSITEIT
Department of Political Studies and Governance Faculty of the Humanities Theo Neethling Post-conflict Reconstruction and Development in the DRC: Revisiting the Main Challenges and the Role of the UN UNIVERSITEIT
Uganda. Main objectives. Working environment. Planning figures. Recent developments. Total requirements: USD 13,363,206
 Main objectives To provide international protection and assistance to refugees whilst pursuing durable solutions for them; To continue to promote a strategy to attain increased self-reliance for Sudanese,
Main objectives To provide international protection and assistance to refugees whilst pursuing durable solutions for them; To continue to promote a strategy to attain increased self-reliance for Sudanese,
FUELLING THE FIRE REPORT CARD ON THE IMPLEMENTATION OF UNSC HUMANITARIAN RESOLUTIONS ON SYRIA IN 2015/2016
 FUELLING THE FIRE REPORT CARD ON THE IMPLEMENTATION OF UNSC HUMANITARIAN RESOLUTIONS ON SYRIA IN 2015/2016 REPORT CARD ON THE IMPLEMENTATION OF UNSC HUMANITARIAN RESOLUTIONS ON SYRIA IN 2015/2016 March
FUELLING THE FIRE REPORT CARD ON THE IMPLEMENTATION OF UNSC HUMANITARIAN RESOLUTIONS ON SYRIA IN 2015/2016 REPORT CARD ON THE IMPLEMENTATION OF UNSC HUMANITARIAN RESOLUTIONS ON SYRIA IN 2015/2016 March
PROFILE OF INTERNAL DISPLACEMENT : DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF THE CONGO
 PROFILE OF INTERNAL DISPLACEMENT : DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF THE CONGO Compilation of the information available in the Global IDP Database of the Norwegian Refugee Council (as of 27 July, 2000) Also available
PROFILE OF INTERNAL DISPLACEMENT : DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF THE CONGO Compilation of the information available in the Global IDP Database of the Norwegian Refugee Council (as of 27 July, 2000) Also available
* Thierry Vircoulon was a technical assistant at the European Union. He writes here in his personal capacity.
 African Security Review 15.1 Institute for Security Studies Anticipating a new and fragile democracy in Central Africa Thierry Vircoulon* The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) became a constitutional
African Security Review 15.1 Institute for Security Studies Anticipating a new and fragile democracy in Central Africa Thierry Vircoulon* The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) became a constitutional
UGANDA. Overview. Working environment GLOBAL APPEAL 2015 UPDATE
 UGANDA GLOBAL APPEAL 2015 UPDATE Overview Working environment The traditional hospitality and generous asylum policies of the Ugandan Government were further demonstrated when fighting erupted in South
UGANDA GLOBAL APPEAL 2015 UPDATE Overview Working environment The traditional hospitality and generous asylum policies of the Ugandan Government were further demonstrated when fighting erupted in South
Responding to conflict in Africa Mark Bowden February 2001
 Responding to conflict in Africa Mark Bowden February 2001 1. In 1990, the Secretary General of the OAU presented a report to the OAU council of Ministers on the changes taking place in the world and their
Responding to conflict in Africa Mark Bowden February 2001 1. In 1990, the Secretary General of the OAU presented a report to the OAU council of Ministers on the changes taking place in the world and their
Peace Agreements Digital Collection
 Peace Agreements Digital Collection Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) >> Ceasefire Agreement Ceasefire Agreement Table of Contents Preamble Article I: The Cease-Fire Article II: Security Concerns Article
Peace Agreements Digital Collection Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) >> Ceasefire Agreement Ceasefire Agreement Table of Contents Preamble Article I: The Cease-Fire Article II: Security Concerns Article
OCHA DRC POPULATION MOVEMENTS IN EASTERN DR CONGO JULY SEPTEMBER 2009
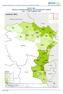 OCHA DRC POPULATION MOVEMENTS IN EASTERN DR CONGO JULY SEPTEMBER 2009 October 2009 1 1. OVERVIEW The humanitarian situation has recently deteriorated in South Kivu where the military operations called
OCHA DRC POPULATION MOVEMENTS IN EASTERN DR CONGO JULY SEPTEMBER 2009 October 2009 1 1. OVERVIEW The humanitarian situation has recently deteriorated in South Kivu where the military operations called
Joint UN rapid assessment mission to Vindza, Kimba, Kindamba districts
 Republic of Congo: Pool Department Situation Report No. 05 (as of 27 April 2018) Highlights At the time of the launch of the HRP 2018, security constraints prevented access to four of the eight districts
Republic of Congo: Pool Department Situation Report No. 05 (as of 27 April 2018) Highlights At the time of the launch of the HRP 2018, security constraints prevented access to four of the eight districts
Central African Republic
 Global Humanitarian Assistance 1 Global Humanitarian Assistance The forgotten crisis Kerry Smith Sophia Swithern December 2013 2 Global Humanitarian Assistance Background Background (CAR) has long been
Global Humanitarian Assistance 1 Global Humanitarian Assistance The forgotten crisis Kerry Smith Sophia Swithern December 2013 2 Global Humanitarian Assistance Background Background (CAR) has long been
AFRICAN DEVELOPMENT BANK GROUP
 AFRICAN DEVELOPMENT BANK GROUP Ministerial Round Table Discussions PANEL 1: The Global Financial Crisis and Fragile States in Africa The 2009 African Development Bank Annual Meetings Ministerial Round
AFRICAN DEVELOPMENT BANK GROUP Ministerial Round Table Discussions PANEL 1: The Global Financial Crisis and Fragile States in Africa The 2009 African Development Bank Annual Meetings Ministerial Round
JoMUN XV INTRODUCTION
 JoMUN XV Forum: Issue: Addressing Famine Student Officer: Natika Bikraj Position: Deputy President INTRODUCTION South Sudan is a country located in north-eastern Africa and is bordered by Sudan, Ethiopia,
JoMUN XV Forum: Issue: Addressing Famine Student Officer: Natika Bikraj Position: Deputy President INTRODUCTION South Sudan is a country located in north-eastern Africa and is bordered by Sudan, Ethiopia,
Special report of the Secretary-General on elections in the Democratic Republic of the Congo I. Introduction
 United Nations Security Council Distr.: General 26 May 2005 Original: English S/2005/320 Special report of the Secretary-General on elections in the Democratic Republic of the Congo I. Introduction 1.
United Nations Security Council Distr.: General 26 May 2005 Original: English S/2005/320 Special report of the Secretary-General on elections in the Democratic Republic of the Congo I. Introduction 1.
FACT SHEET #3, FISCAL YEAR (FY) 2017 MARCH 31, % Humanitarian Coordination & Information Management (11%) 80% 20%
 CENTRAL AFRICAN REPUBLIC - COMPLEX EMERGENCY FACT SHEET #3, FISCAL YEAR (FY) 2017 MARCH 31, 2017 NUMBERS AT A GLANCE 2.2 million People in CAR Requiring Humanitarian Assistance 2017 Humanitarian Needs
CENTRAL AFRICAN REPUBLIC - COMPLEX EMERGENCY FACT SHEET #3, FISCAL YEAR (FY) 2017 MARCH 31, 2017 NUMBERS AT A GLANCE 2.2 million People in CAR Requiring Humanitarian Assistance 2017 Humanitarian Needs
In May 2004, UNHCR resumed the organized
 Recent developments Angola Botswana Comoros Lesotho Madagascar Malawi Mauritius Mozambique Namibia Seychelles South Africa Swaziland Zambia Zimbabwe In May 2004, UNHCR resumed the organized repatriation
Recent developments Angola Botswana Comoros Lesotho Madagascar Malawi Mauritius Mozambique Namibia Seychelles South Africa Swaziland Zambia Zimbabwe In May 2004, UNHCR resumed the organized repatriation
Republic of THE Congo
 Republic of THE Congo Late 2009 and early 2010 saw an influx of some 116,000 refugees from the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) into the northern part of the Republic of the Congo (Congo). The newly
Republic of THE Congo Late 2009 and early 2010 saw an influx of some 116,000 refugees from the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) into the northern part of the Republic of the Congo (Congo). The newly
Emergency response appeal to the situation in the Eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo
 Emergency response appeal to the situation in the Eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo Donor Relations and Resource Mobilization Service September 2012 1 Recently displaced people in North Kivu, waiting
Emergency response appeal to the situation in the Eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo Donor Relations and Resource Mobilization Service September 2012 1 Recently displaced people in North Kivu, waiting
