Trends in Medicaid and CHIP Eligibility Over Time
|
|
|
- Clinton Harrington
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 REPORT Trends in Medicaid and CHIP Eligibility Over Time August 2015 Prepared by: Samantha Artiga and Elizabeth Cornachione Kaiser Family Foundation
2 Executive Summary... 1 Section 1: Eligibility Trends by Group... 3 Section 2: Eligibility Trends by Geographic Region... 6 Section 3: Eligibility Trends by Medicaid Expansion Status... 9 Section 4: Eligibility Trends by State Health Ranking Conclusion Appendix A Appendix B: Overview of America s Health Rankings... 17
3 Over time eligibility for Medicaid and the Children s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) has expanded to provide a base of coverage for the low-income population, which was most recently strengthened through the Affordable Care Act (ACA) Medicaid expansion as of While eligibility has increased over time, there is significant variation in eligibility levels across states and eligibility groups. This analysis examines trends in Medicaid and CHIP eligibility limits over time for children, pregnant women, parents, and other adults. It also explores how trends in eligibility for these groups vary by several variables, including geographic region, Medicaid expansion status, and state health ranking. (Eligibility levels for all 50 states and DC over time are available at Key findings include the following: Eligibility for children and pregnant women has been consistently higher than for parents and other adults over time. The ACA Medicaid expansion narrowed the gap between medians for these groups, but median eligibility limits for parents and other adults still are lower than those for children and pregnant women. Across eligibility groups, the Northeast generally has had the highest median eligibility limits. The South has the lowest median eligibility limits for all groups, except pregnant women, for whom the West has the lowest median eligibility limits. Over time, the gap between the region with the highest median eligibility limit and the region with the lowest median eligibility increased for children. This gap also widened for other adults when the Medicaid expansion took effect as of January In contrast, the gap between the highest and lowest regions has narrowed for parents and pregnant women over time. States that implemented the Medicaid expansion have higher median eligibility limits compared to nonexpansion states for all eligibility groups, and the gap between expansion and non-expansion states widened for all groups over time. As expected, the largest differences emerged for parents and other adults after implementation of the expansion in However, the difference between the median income limit for children in expansion states and non-expansion states also grew over time. The gap is smaller for pregnant women and has recently begun to narrow. For children, parents, and other adults, states with the lowest health rankings have the lowest median eligibility limits over time, while states with the highest health rankings have the highest median eligibility limits. Gaps between median income eligibility limits for high and low health ranking states are largest for other adults and children. This gap also exists for parents, but it narrowed after implementation of the Medicaid expansion. For pregnant women, middle health ranking states have the highest median eligibility limits. While the high and low health ranking states have lower median eligibility limits compared to the middle health ranking states, the differences in median eligibility limits by health ranking are smaller for pregnant women compared to the other eligibility groups. This analysis is based on 15 years of data collected through a national survey conducted by the Kaiser Commission on Medicaid and the Uninsured with the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, ; and with the Georgetown University Center for Children and Families, The income eligibility limits are reported as a percentage of the federal poverty level (FPL), which is calculated each year by the Department of Health and Human Services. As of 2015, the FPL is $11,770 for an individual and $20,090 for a family of three. The data show changes in eligibility levels by group over time as well as the impact of the ACA on eligibility. Prior to the ACA, states generally could not receive federal Medicaid matching funds to cover non-disabled Trends in Medicaid and CHIP Eligibility Over Time 1
4 adults without dependent children. As enacted, the ACA expanded Medicaid eligibility to adults with incomes at or below 138% FPL beginning in 2014, although this provision was effectively made a state option by the Supreme Court s 2012 ruling on the ACA. Other eligibility changes established by the ACA went into effect across all states as of January 1, 2014, including establishing a new minimum eligibility level of 138% FPL for children of all ages in Medicaid and changing the method for determining financial eligibility for Medicaid for children, pregnant women, parents, and adults and CHIP to a standard based on modified adjusted gross income (MAGI). As such, the changes in eligibility levels between 2013 and 2014 reflect both changes in eligibility policy, including adoption of the Medicaid expansion, as well as the conversion to the MAGI-based standards. While many of the converted 2014 standards appear higher than 2013 levels, the converted thresholds are intended to approximate states existing eligibility levels using different methodology for determining income. Trends in Medicaid and CHIP Eligibility Over Time 2
5 Eligibility for children and pregnant women has been consistently higher than for parents and other adults over time, reflecting both higher federal minimums and state take up of options to expand eligibility for these groups, including coverage under CHIP (Figure 1.1). Median eligibility levels for each eligibility group have increased over time. The Medicaid expansion narrowed the gap between median eligibility limits for parents and other adults and children and pregnant women beginning in 2014, but median eligibility limits for parents and other adults still remain below those for children and pregnant women. Figure 1.1 Median Medicaid/CHIP Eligibility Limits by Group Upper Limit for Children Pregnant Women Parents Other Adults 235% 238% 255% 255% 200% 200% 200% 200% 185% 185% 185% 185% 185% 205% 205% 138% 138% 68% 71% 67% 63% 64% 63% 0% 0% Oct-00 Jan-02 Apr-03 Jul-04 Jul-05 Jul-06 Jan-08 Jan-09 Dec-09 Jan-11 Jan-12 Jan-13 Jan-14 Jan-15 Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, ; and with the Georgetown University Center for Children and Families, Children. For children, the number of states limiting eligibility to less than 200% FPL decreased from 14 to 2 between 2000 and 2015, while the number of states extending eligibility to children with incomes at 250% FPL or higher grew from 11 to 28 over the period (Figure 1.2). Figure 1.2 Upper Medicaid/CHIP Eligibility Limits for Children, October 2000 January 2015 Number of States by Income Eligibility Limit: At or above 250% FPL 200% up to 250% FPL Less than 200% FPL Oct-00 Jan-02 Apr-03 Jul-04 Jul-05 Jul-06 Jan-08 Jan-09 Dec-09 Jan-11 Jan-12 Jan-13 Jan-14 Jan-15 Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, ; and with the Georgetown University Center for Children and Families, Trends in Medicaid and CHIP Eligibility Over Time 3
6 Pregnant women. Similar patterns were observed for pregnant women. The number of states limiting eligibility to less than 200% FPL decreased from 34 to 18 between 2003 and 2015, and the number of states covering pregnant women with incomes at or above 250% FPL rose from 3 to 11 (Figure 1.3). Figure 1.3 Medicaid Eligibility Limits for Pregnant Women, April January 2015 Number of States by Income Eligibility Limit: At or above 250% FPL 200% up to 250% FPL Less than 200% FPL Apr-03 Jul-04 Jul-05 Jul-06 Jan-08 Jan-09 Dec-09 Jan-11 Jan-12 Jan-13 Jan-14 Jan-15 Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, ; and with the Georgetown University Center for Children and Families, Parents. Parent eligibility levels across states remained low and fairly stable over the study period prior to the Medicaid expansion (Figure 1.4). The Medicaid expansion significantly increased the number of states covering parents at or above 138% FPL. However, 14 states that had not implemented the expansion as of January 2015 still had eligibility limits for parents that were less than 50% FPL. Figure 1.4 Medicaid Eligibility Limits for Parents, January 2002 January 2015 Number of States by Income Eligibility Limit: Above 138% FPL Equal to 138% FPL 50% up to 138% FPL Less than 50% FPL Jan-02 Apr-03 Jul-04 Jul-05 Jul-06 Jan-08 Jan-09 Dec-09 Jan-11 Jan-12 Jan-13 Jan-14 Jan-15 NOTE: Washington Eligibility Limit is not reported for January Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, ; and with the Georgetown University Center for Children and Families, Trends in Medicaid and CHIP Eligibility Over Time 4
7 Other adults. Other adults remained ineligible for Medicaid in the majority of states prior to the Medicaid expansion, reflecting the fact that states could not cover these adults through Medicaid prior to the ACA unless they obtained a waiver (Figure 1.5). The Medicaid expansion significantly increased the number of states covering these adults beginning in 2014, but they remained ineligible in all of the non-expansion states, with the exception of Wisconsin, which covers adults up to 100% FPL. Figure 1.5 Medicaid Eligibility Limits for Other Adults, January 2011 January 2015 Number of States by Income Eligibility Limit: Above 138% FPL Equal to 138% FPL Less than 138% FPL No Eligiblity Jan-11 Jan-12 Jan-13 Jan-14 Jan-15 Georgetown University Center for Children and Families, Trends in Medicaid and CHIP Eligibility Over Time 5
8 This section examines trends in eligibility by U.S. Census region, including the Northeast, South, Midwest, and West (Figure 2.1). Across eligibility groups, the Northeast generally has had the highest median eligibility limits over time. The South has had the lowest median eligibility limits for all groups, except pregnant women, for whom the West has the lowest median eligibility limits. Over the study period, the gap between the region with the highest median eligibility limit and the region with the lowest median eligibility increased for children. Similarly, the gap between the region with the highest and lowest median limit widened for other adults when the Medicaid expansion took effect as of January In contrast, this gap between the highest and lowest regions has narrowed for parents and pregnant women over time. Figure 2.1 States by Census Regions WA OR NV CA ID AZ UT MT WY CO NM ND MN WI SD IA NE IL KS MO OK AR MI OH IN KY TN VT NY PA WV VA NC SC ME NH MA CT RI NJ DE MD DC MS AL GA TX LA AK FL HI Northeast (9 states) Midwest (12 states) South (17 states including DC) West (13 states) Source: U.S. Census Bureau. Children. Between 2000 and 2015, median eligibility limits for children increased in all regions, but the increase in the South only reflects the conversion to MAGI-based thresholds beginning as of January 2014 (Figure 2.2). Increases were largest and occurred earliest in the Northeast. Median limits in the West also increased over the period, rising above the U.S. median. Smaller increases occurred in the Midwest, which remains below the U.S. median as of Figure 2.2 Median Upper Medicaid/CHIP Eligibility Limits for Children by Region, October January 2015 Northeast West US Midwest South 300% 300% 300% 319% 319% 250% 250% 250% 235% 238% 221% 235% 205% 219% 200% 200% 200% 200% 200% 265% 265% 255% 255% 253% 251% 217% 217% Oct-00 Jan-02 Apr-03 Jul-04 Jul-05 Jul-06 Jan-08 Jan-09 Dec-09 Jan-11 Jan-12 Jan-13 Jan-14 Jan-15 Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, ; and with the Georgetown University Center for Children and Families, Trends in Medicaid and CHIP Eligibility Over Time 6
9 Pregnant women. Median eligibility limits for pregnant women increased in all regions between 2003 and 2015 (Figure2.3). The largest increase occurred in the West, although the median limit for the region still remains below the U.S. median as of Figure 2.3 Median Medicaid Eligibility Limits for Pregnant Women by Region, April January 2015 Northeast South Midwest US West 214% 214% 200% 200% 200% 200% 200% 193% 193% 185% 185% 185% 185% 185% 175% 175% 208% 205% 205% 201% 204% 190% 190% 133% Apr-03 Jul-04 Jul-05 Jul-06 Jan-08 Jan-09 Dec-09 Jan-11 Jan-12 Jan-13 Jan-14 Jan-15 Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, ; and with the Georgetown University Center for Children and Families, Parents. Changes in median eligibility limits for parents between 2002 and 2015 varied across the regions (Figure 2.4). In the Midwest and West, median eligibility limits for parents significantly increased as of 2014 due to the Medicaid expansion. In the Northeast, the median decreased from 157% FPL to 138% FPL, reflecting Medicaid eligibility reductions in several states when parents above 138% FPL became eligible for new Marketplace coverage options as of In the South, the median eligibility limit remained relatively stable and low, at around half the poverty level, since most states in the region did not adopt the Medicaid expansion. Figure 2.4 Median Medicaid Eligibility Limits for Parents by Region, January January 2015 Northeast West US Midwest South 181% 181% 181% 157% 133% 150% 138% 138% 119% 119% 81% 76% 79% 77% 74% 78% 74% 76% 68% 69% 65% 68% 64% 64% 63% 64% 61% 61% 48% 51% 45% 50% 43% 48% 52% 46% Jan-02 Apr-03 Jul-04 Jul-05 Jul-06 Jan-08 Jan-09 Dec-09 Jan-11 Jan-12 Jan-13 Jan-14 Jan-15 Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, ; and with the Georgetown University Center for Children and Families, Trends in Medicaid and CHIP Eligibility Over Time 7
10 Other adults. Median eligibility limits for other adults substantially increased between 2011 and 2015 in all regions except the South (Figure 2.5). In the Northeast and West, the median limit increased from 0% FPL to 138% FPL, while it increased from 0% to 119% FPL in the Midwest. This reflects adoption of the Medicaid expansion in most states in the Northeast and West and more mixed expansion decisions in the Midwest. In the South, the median eligibility limit remains at 0% FPL since most states in the region have not adopted the expansion. Figure 2.5 Median Medicaid Eligibility Limits for Other Adults by Region, January January 2015 Northeast West US Midwest South 138% 138% 119% 119% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% Jan-11 Jan-12 Jan-13 Jan-14 Jan-15 Georgetown University Center for Children and Families, Trends in Medicaid and CHIP Eligibility Over Time 8
11 This section analyzes trends in eligibility by the status of implementation of the Medicaid expansion as of January 2015, which is the most recent date of the eligibility data in this analysis (Figure 3.1). (As of August 2015, three additional states Indiana, Montana, and Alaska have adopted the Medicaid expansion.) Figure 3.1 Status of the Medicaid Expansion WA OR NV CA ID AZ UT MT* WY CO NM VT ND MN WI NY SD MI PA* IA NE OH IL IN* WV VA KS MO KY NC TN OK AR SC MS AL GA ME MA CT RI NJ DE MD DC TX LA AK* HI FL Implemented as of January 2015 (28 States including DC) Adopted as of July 2015 (3 States) Not Adopting At This Time (20 States) NOTES: *Since January 2015, AK, IN and MT have adopted the expansion as of August Coverage in IN went into effect 2/1/15. AK and MT are still awaiting implementation. SOURCE: Status of State Action on the Medicaid Expansion Decision, KFF State Health Facts, January, States that implemented the Medicaid expansion had higher median eligibility limits compared to nonexpansion states across eligibility groups. Over time, the difference between median eligibility limits for expansion and non-expansion states widened for all eligibility groups. As expected, the largest differences emerged for parents and other adults after implementation of the expansion in However, the difference between the median eligibility limit for children in expansion states and non-expansion states also grew over time. The gap is smaller for pregnant women and has recently begun to narrow. Children. Between 2000 and 2015, median eligibility limits for children increased in Medicaid expansion states (Figure 3.2). The median eligibility limit for non-expansion states remained unchanged, except for the increase in 2014 that reflected the conversion to MAGI-based standards. Figure 3.2 Median Upper Medicaid/CHIP Eligibility Limits for Children by Medicaid Expansion Status, October January 2015 Adopted Medicaid Expansion (30 states including DC) Has Not Adopted Medicaid Expansion (21 states) 305% 305% 265% 265% 243% 250% 250% 228% 200% 200% 200% 200% 200% 200% 200% 200% 200% 200% 200% 200% 214% 215% Oct-00 Jan-02 Apr-03 Jul-04 Jul-05 Jul-06 Jan-08 Jan-09 Dec-09 Jan-11 Jan-12 Jan-13 Jan-14 Jan-15 Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, ; and with the Georgetown University Center for Children and Families, Trends in Medicaid and CHIP Eligibility Over Time 9
12 Pregnant women. Similarly, median eligibility limits for pregnant women increased in expansion states between 2003 and 2015, while there was a smaller increase in non-expansion states (Figure 3.3). This change in the non-expansion states reflected the conversion to MAGI-based standards as of 2014 and the reinstatement of coverage for pregnant women up to 205% FPL in Virginia as of Figure 3.3 Median Medicaid Eligibility Limits for Pregnant Women by Medicaid Expansion Status, April 2003 January 2015 Adopted Medicaid Expansion (30 states including DC) Has Not Adopted Medicaid Expansion (21 states) 213% 213% 200% 200% 200% 200% 200% 200% 199% 201% 185% 185% 185% 185% 185% 185% 185% 185% 185% 185% Apr-03 Jul-04 Jul-05 Jul-06 Jan-08 Jan-09 Dec-09 Jan-11 Jan-12 Jan-13 Jan-14 Jan-15 Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, ; and with the Georgetown University Center for Children and Families, Parents. For parents, median eligibility limits increased in expansion states but declined in non-expansion states between 2002 and 2015 (Figure 3.4). In the Medicaid expansion states, median eligibility limits for parents increased from 100% to 138% FPL, reflecting the fact that many of these states took up options to expand coverage for parents above minimum thresholds prior to the Medicaid expansion. In non-expansion states, the median parent eligibility limit remained low and decreased post-aca, reflecting eligibility reductions in some states. Figure 3.4 Median Medicaid Eligibility Limits for Parents by Medicaid Expansion Status, January 2002 January 2015 Adopted Medicaid Expansion (30 states, including DC) Has Not Adopted Medicaid Expansion (21 states) 138% 138% 100% 87% 87% 87% 88% 92% 96% 89% 95% 95% 98% 62% 59% 57% 56% 54% 52% 52% 49% 50% 49% 48% 47% 45% Jan-02 Apr-03 Jul-04 Jul-05 Jul-06 Jan-08 Jan-09 Dec-09 Jan-11 Jan-12 Jan-13 Jan-14 Jan-15 Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, ; and with the Georgetown University Center for Children and Families, Trends in Medicaid and CHIP Eligibility Over Time 10
13 Other adults. For other adults, the median eligibility limit rose from 0% to 138% FPL in expansion states between 2011 and 2015, while the median limit remains at 0% FPL in non-expansion states (Figure 3.5). Adults without dependent children are ineligible for Medicaid in all of the non-expansions states except Wisconsin, which covers adult up to 100% FPL. Figure 3.5 Median Medicaid Eligibility Limits for Other Adults by Medicaid Expansion Status, January 2011 January 2015 Adopted Medicaid Expansion (30 states including DC) Has Not Adopted Medicaid Expansion (21 states) 138% 138% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% Jan-11 Jan-12 Jan-13 Jan-14 Jan-15 Georgetown University Center for Children and Families, Trends in Medicaid and CHIP Eligibility Over Time 11
14 This section analyzes trends in eligibility over time by state health ranking. State health rankings were based on the 2014 America s Health Rankings report, which included data for all 50 states, but not DC. The rankings are developed based on measures related to four groups of health determinants, including individual behaviors, community and environment, policy, and clinical care, and measures of health outcomes. An overall health score is created for each state based on how they fare on each measure compared to the national average. (See Appendix B for more details.) For this analysis, states were categorized into three groups based on their health ranking scores. A total of 22 states with a negative score were classified as low health ranking states, 15 states with scores between 0 and.39 were grouped as middle health ranking states, and 13 states with scores above.40 were categorized as high health ranking states (Figure 4.1). Figure 4.1 Health Rankings by State, 2014 WA OR NV CA ID AZ UT MT WY CO NM ND MN WI SD IA NE IL KS MO OK AR MS VT NY MI PA OH IN WV VA KY NC TN SC AL GA ME NH MA CT RI NJ DE MD DC TX LA AK FL HI Low Health Ranking (22 states) Middle Health Ranking) (15 states) High Health Ranking (13 states) Note: DC was not ranked. Source: America s Health Ranking by United Health Foundation, American Public Health Association and Partnership for Prevention, 2014, For children, parents, and other adults, states with the lowest health rankings have the lowest median eligibility limits over time, while states with the highest health rankings have the highest median eligibility limits. Gaps between median income eligibility limits for high and low health ranking states are largest for other adults and children. This gap also exists for parents, but it narrowed after implementation of the Medicaid expansion. For pregnant women, middle health ranking states have the highest median eligibility limits. While the high and low health ranking states have lower median eligibility limits compared to the middle health ranking states, the differences in median eligibility limits by health ranking are smaller for pregnant women compared to the other eligibility groups. Trends in Medicaid and CHIP Eligibility Over Time 12
15 Children. Between 2000 and 2015, median eligibility limits for children increased in high and middle ranking states (Figure 4.2). Increases were largest and occurred earlier in high health ranking states compared to the middle health ranking states. Median eligibility limits did not change in the low health ranking states except for the conversion to MAGI-based standards as of January Figure 4.2 Median Upper Medicaid/CHIP Eligibility Limits Children by State Health Ranking, October 2000 January 2015 High Health Ranking (13 states) Middle Health Ranking (15 states) Low Health Ranking (22 states) 280% 280% 280% 300% 300% 300% 300% 250% 250% 250% 250% 305% 305% 266% 266% 200% 200% 200% 200% 200% 200% 200% 200% 200% 200% 200% 200% 217% 217% Oct-00 Jan-02 Apr-03 Jul-04 Jul-05 Jul-06 Jan-08 Jan-09 Dec-09 Jan-11 Jan-12 Jan-13 Jan-14 Jan-15 NOTE: DC is not ranked. SOURCE: Eligibility data based on results from a national survey conducted by the Kaiser Commission on Medicaid and the Uninsured with the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, ; and with the Georgetown University Center for Children and Families, Health rankings based on America s Health Ranking by United Health Foundation, American Public Health Association and Partnership for Prevention, 2014, Pregnant women. Median eligibility limits for pregnant women increased for middle health ranking states between 2003 and 2015 (Figure 4.3). For states with high and low health rankings, the change in median eligibility limits reflect the conversion to MAGI-based standards. Figure 4.3 Median Medicaid Eligibility Limits for Pregnant Women by State Health Ranking, April 2003 January 2015 High Health Ranking (13 states) Middle Health Ranking (15 states) Low Health Ranking (22 states) 217% 217% 193% 200% 200% 200% 200% 203% 202% 202% 201% 185% 185% 185% 185% 185% 185% 185% 185% 185% 185% Apr-03 Jul-04 Jul-05 Jul-06 Jan-08 Jan-09 Dec-09 Jan-11 Jan-12 Jan-13 Jan-14 Jan-15 NOTE: DC is not ranked. SOURCE: Eligibility data based on results from a national survey conducted by the Kaiser Commission on Medicaid and the Uninsured with the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, ; and with the Georgetown University Center for Children and Families, Health Rankings based on America s Health Ranking by United Health Foundation, American Public Health Association and Partnership for Prevention, 2014, Trends in Medicaid and CHIP Eligibility Over Time 13
16 Parents. Median eligibility limits for parents increased between 2002 and 2015 across all three groups of states (Figure 4.4). States with high health rankings started with higher eligibility limits as of 2002 compared to the other middle and low health ranking states, and remained the highest as of The middle and low health ranking states had similar median eligibility limits as of 2002, but the middle health ranking states experienced a larger increase in the median eligibility limit than the low health ranking states over the period. Figure 4.4 Median Medicaid Eligibility Limits for Parents by State Health Ranking, January 2002 January 2015 High Health Ranking (13 states) Middle Health Ranking (15 states) Low Health Ranking (22 states) 138% 138% 105% 94% 86% 100% 100% 100% 100% 69% 67% 66% 64% 62% 60% 85% 74% 100% 100% 100% 81% 81% 81% 78% 100% 105% 62% 62% 61% 57% 57% 55% 53% 56% 56% 51% 53% Jan-02 Apr-03 Jul-04 Jul-05 Jul-06 Jan-08 Jan-09 Dec-09 Jan-11 Jan-12 Jan-13 Jan-14 Jan-15 NOTE: DC is not ranked. SOURCE: Eligibility data based on results from a national survey conducted by the Kaiser Commission on Medicaid and the Uninsured with the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, ; and with the Georgetown University Center for Children and Families, Health Rankings based on America s Health Ranking by United Health Foundation, American Public Health Association and Partnership for Prevention, 2014, 89% 85% Other adults. The high health ranking states were the only group to show an increase in the median eligibility limit for other adults between 2011 and 2015 (Figure 4.5). This increase reflects adoption of the Medicaid expansion in most of the states that have a high health ranking. In contrast, the median eligibility limit for middle and low health ranking states remained at 0% FPL, because more than half of the states in each of these groups did not adopt the Medicaid expansion. Figure 4.5 Median Medicaid Eligibility Limits for Other Adults by State Health Ranking, January 2011 January 2015 High Health Ranking (13 states) Middle Health Ranking (15 states) Low Health Ranking (22 states) 138% 138% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% Jan-11 Jan-12 Jan-13 Jan-14 Jan-15 NOTE: DC is not ranked. SOURCE: Eligibility data based on results from a national survey conducted by the Kaiser Commission on Medicaid and the Georgetown University Center for Children and Families, Health Rankings based on America s Health Ranking by United Health Foundation, American Public Health Association and Partnership for Prevention, 2014, Trends in Medicaid and CHIP Eligibility Over Time 14
17 Together these data show that over time Medicaid and CHIP eligibility levels have increased for all eligibility groups. However, there eligibility levels vary substantially across states and across eligibility groups. Eligibility remains higher for pregnant women and children compared to parents and other adults. Moreover, there generally have been widening disparities in access to coverage across states when examining them by geographic region, Medicaid expansion status, and state health ranking. Trends in Medicaid and CHIP Eligibility Over Time 15
18 South Has Not Adopted Low West Adopted Middle West Implemented Low South Implemented Low West Implemented Middle West Implemented High Northeast Implemented High South Implemented Low South Implemented Not Ranked South Has Not Adopted Low South Has Not Adopted Low West Implemented High West Has Not Adopted Middle Midwest Implemented Low Midwest Implemented (February 2015) Low Midwest Implemented Middle Midwest Has Not Adopted Middle South Implemented Low South Has Not Adopted Low Northeast Has Not Adopted Middle South Implemented Middle Northeast Implemented High Midwest Implemented Low Midwest Implemented High South Has Not Adopted Low Midwest Has Not Adopted Low West Adopted Middle Midwest Has Not Adopted High West Implemented Low Northeast Implemented High Northeast Implemented High West Implemented Low Northeast Implemented Middle South Has Not Adopted Low Midwest Implemented High Midwest Implemented Low South Has Not Adopted Low West Implemented High Northeast Implemented Middle Northeast Implemented Middle South Has Not Adopted Low Midwest Has Not Adopted Middle South Has Not Adopted Low South Has Not Adopted Low West Has Not Adopted High Northeast Implemented High South Has Not Adopted Middle West Implemented High South Implemented Low Midwest Has Not Adopted Middle West Has Not Adopted Middle Sources: Regions based on U.S. Census Bureau, Medicaid expansion based on KCMU analysis, health ranking based on America s Health Ranking state health scores, Trends in Medicaid and CHIP Eligibility Over Time 16
19 America s Health Ranking is published annually by United Health Foundation, American Public Health Association and the Partnership for Prevention ( It develops health scores for states based on four groups of health determinants, including: behaviors, community & environment, policy and clinical care, and several measures of health outcomes. The overall health score is calculated by adding the score of each measure multiplied by the measure weight (see Table 2). The ranking is the order of each state according its overall score; ties in values are assigned equal rankings. The score for each measure is a representation of the number of standard deviations a state is above or below the national mean. The national mean is set at the average value of the states and DC. It is calculated by: Score = (State value National mean)/standard Deviation of all state values. This is commonly known as a Z-score. The score is stated as a decimal ranging from positive to negative 2. Higher scores mean that a state has a higher value than the national average, while lower scores mean that the state has a lower value than the national average. Table 2 shows whether a higher value has a negative or a positive impact on the health ranking. Trends in Medicaid and CHIP Eligibility Over Time 17
20 Smoking (% of adult population) 7.5 Negative Behavioral Risk Factors Surveillance System (BRFSS), 2013 Binge Drinking (% of adult population) 2.5 Negative BRFSS 2013 Drug Deaths (Deaths/100,000) 2.5 Negative National Vital Statistics System, Obesity (% of adult population) 5.0 Negative BRFSS, 2013 Physical Inactivity (%of adult population) 2.5 Negative BRFSS, 2013 High School Graduation (%of incoming 9 th graders) 5.0 Positive National Center for Education Statistics, Violent Crime (Offenses/100,000) 5.0 Negative Federal Bureau of Investigation, 2012 Occupational Fatalities (Deaths/100,000 workers) 2.5 Negative Census of Fatal Occupational Injuries, P&US Bureau of Economic Analysis Infectious Disease (Combined score for Chlamydia, Pertussis, and Salmonella cases/100,000) 5.0 Negative Summary of Notifiable Disease, 2012 & NCHHSTP Atlas, 2012 Children in Poverty (% of children) 5.0 Negative 2014 Annual Social and Economic Supplement, 2013 Air Pollution (Micrograms of fine particles/ cubic meter) 5.0 Negative Environmental Protection Agency, Lack of Health Insurance (% of population) 5.0 Negative American Community Survey, Public Health Funding (Dollars/person) 2.5 Positive Trust for America s Health, Immunization Children (% aged 19 to 35 mos) 2.5 Positive National Immunization Survey, 2013 Immunization Adolescents (% aged 13 to 17 yrs) 2.5 Positive National Immunization Survey, 2013 Low Birthweight (Percent of live births) 3.75 Negative National Vital Statistics System, 2012 Primary Care Physicians (Number/100,000) 3.75 Positive American Medical Association, 2012 Dentists (Number/100,000) 3.75 Positive American Dental Association, 2011 Preventable Hospitalizations (Number /1,000 Medicare beneficiaries) 3.75 Negative Darmouth Atlas, 2012 Diabetes (Percent of adult population) Negative BRFSS, 2013 Poor Mental Health Days (Days in previous 30 days) Poor Physical Health Days (Days in previous 30 days) Disparity in Health Status (Percent difference by education level) Negative BRFSS, Negative BRFSS, Negative BRFSS, 2013 Infant Mortality (Deaths per 1,000 live births) Negative National Vital Statistics System, Cardiovascular Deaths (Deaths/100,000) Negative National Vital Statistics System, Cancer Deaths (Deaths/100,000) Negative National Vital Statistics System, Premature Deaths (Years lost/100,000) Negative National Vital Statistics System, 2012 Trends in Medicaid and CHIP Eligibility Over Time 18
21 the henry j. kaiser family foundation Headquarters 2400 Sand Hill Road Menlo Park, CA Phone Fax Washington Offices and Barbara Jordan Conference Center 1330 G Street, NW Washington, DC Phone Fax This publication (#8762) is available on the Kaiser Family Foundation s website at Filling the need for trusted information on national health issues, the Kaiser Family Foundation is a nonprofit organization based in Menlo Park, California.
Key Facts on Health and Health Care by Race and Ethnicity
 REPORT Key Facts on Health and Health Care by Race and Ethnicity June 2016 Prepared by: Kaiser Family Foundation Disparities in health and health care remain a persistent challenge in the United States.
REPORT Key Facts on Health and Health Care by Race and Ethnicity June 2016 Prepared by: Kaiser Family Foundation Disparities in health and health care remain a persistent challenge in the United States.
Now is the time to pay attention
 Census & Redistricting : Now is the time to pay attention By Kimball Brace, President Election Data Services, Inc. Definitions Reapportionment Allocation of districts to an area Example: Congressional
Census & Redistricting : Now is the time to pay attention By Kimball Brace, President Election Data Services, Inc. Definitions Reapportionment Allocation of districts to an area Example: Congressional
Migrant and Seasonal Head Start. Guadalupe Cuesta Director, National Migrant and Seasonal Head Start Collaboration Office
 Migrant and Seasonal Head Start Guadalupe Cuesta Director, National Migrant and Seasonal Head Start Collaboration Office The Migrant Seasonal Head Start (MSHS) program is one of the largest community based
Migrant and Seasonal Head Start Guadalupe Cuesta Director, National Migrant and Seasonal Head Start Collaboration Office The Migrant Seasonal Head Start (MSHS) program is one of the largest community based
INSTITUTE of PUBLIC POLICY
 INSTITUTE of PUBLIC POLICY Harry S Truman School of Public Affairs University of Missouri ANALYSIS OF STATE REVENUES AND EXPENDITURES Andrew Wesemann and Brian Dabson Summary This report analyzes state
INSTITUTE of PUBLIC POLICY Harry S Truman School of Public Affairs University of Missouri ANALYSIS OF STATE REVENUES AND EXPENDITURES Andrew Wesemann and Brian Dabson Summary This report analyzes state
RULE 1.14: CLIENT WITH DIMINISHED CAPACITY
 American Bar Association CPR Policy Implementation Committee Variations of the ABA Model Rules of Professional Conduct RULE 1.14: CLIENT WITH DIMINISHED CAPACITY (a) When a client's capacity to make adequately
American Bar Association CPR Policy Implementation Committee Variations of the ABA Model Rules of Professional Conduct RULE 1.14: CLIENT WITH DIMINISHED CAPACITY (a) When a client's capacity to make adequately
RULE 1.1: COMPETENCE. As of January 23, American Bar Association CPR Policy Implementation Committee
 American Bar Association CPR Policy Implementation Committee Variations of the ABA Model Rules of Professional Conduct RULE 1.1: COMPETENCE A lawyer shall provide competent representation to a client.
American Bar Association CPR Policy Implementation Committee Variations of the ABA Model Rules of Professional Conduct RULE 1.1: COMPETENCE A lawyer shall provide competent representation to a client.
Mandated Use of Prescription Drug Monitoring Programs (PMPs) Map
 Mandated Use of Prescription Drug Monitoring Programs (PMPs) Map Research Current as of January 2, 2018. This project was supported by Grant No. G1799ONDCP03A, awarded by the Office of National Drug Control
Mandated Use of Prescription Drug Monitoring Programs (PMPs) Map Research Current as of January 2, 2018. This project was supported by Grant No. G1799ONDCP03A, awarded by the Office of National Drug Control
Incarcerated Women and Girls
 Incarcerated and Over the past quarter century, there has been a profound change in the involvement of women within the criminal justice system. This is the result of more expansive law enforcement efforts,
Incarcerated and Over the past quarter century, there has been a profound change in the involvement of women within the criminal justice system. This is the result of more expansive law enforcement efforts,
Uniform Wage Garnishment Act
 Uniform Wage Garnishment Act Agenda What is it? Why do we need it? Major provisions Enactment 1 Who is the ULC? National Conference of Commissioners for Uniform State Laws Uniform Interstate Family Support
Uniform Wage Garnishment Act Agenda What is it? Why do we need it? Major provisions Enactment 1 Who is the ULC? National Conference of Commissioners for Uniform State Laws Uniform Interstate Family Support
a rising tide? The changing demographics on our ballots
 a rising tide? The changing demographics on our ballots OCTOBER 2018 Against the backdrop of unprecedented political turmoil, we calculated the real state of the union. For more than half a decade, we
a rising tide? The changing demographics on our ballots OCTOBER 2018 Against the backdrop of unprecedented political turmoil, we calculated the real state of the union. For more than half a decade, we
WYOMING POPULATION DECLINED SLIGHTLY
 FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Wednesday, December 19, 2018 Contact: Dr. Wenlin Liu, Chief Economist WYOMING POPULATION DECLINED SLIGHTLY CHEYENNE -- Wyoming s total resident population contracted to 577,737 in
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Wednesday, December 19, 2018 Contact: Dr. Wenlin Liu, Chief Economist WYOMING POPULATION DECLINED SLIGHTLY CHEYENNE -- Wyoming s total resident population contracted to 577,737 in
UNIFORM NOTICE OF REGULATION A TIER 2 OFFERING Pursuant to Section 18(b)(3), (b)(4), and/or (c)(2) of the Securities Act of 1933
 Item 1. Issuer s Identity UNIFORM NOTICE OF REGULATION A TIER 2 OFFERING Pursuant to Section 18(b)(3), (b)(4), and/or (c)(2) of the Securities Act of 1933 Name of Issuer Previous Name(s) None Entity Type
Item 1. Issuer s Identity UNIFORM NOTICE OF REGULATION A TIER 2 OFFERING Pursuant to Section 18(b)(3), (b)(4), and/or (c)(2) of the Securities Act of 1933 Name of Issuer Previous Name(s) None Entity Type
State Governments Viewed Favorably as Federal Rating Hits New Low
 APRIL 15, 2013 State Governments Viewed Favorably as Federal Rating Hits New Low FOR FURTHER INFORMATION CONTACT THE PEW RESEARCH CENTER FOR THE PEOPLE & THE PRESS Michael Dimock Director Carroll Doherty
APRIL 15, 2013 State Governments Viewed Favorably as Federal Rating Hits New Low FOR FURTHER INFORMATION CONTACT THE PEW RESEARCH CENTER FOR THE PEOPLE & THE PRESS Michael Dimock Director Carroll Doherty
If you have questions, please or call
 SCCE's 17th Annual Compliance & Ethics Institute: CLE Approvals By State The SCCE submitted sessions deemed eligible for general CLE credits and legal ethics CLE credits to most states with CLE requirements
SCCE's 17th Annual Compliance & Ethics Institute: CLE Approvals By State The SCCE submitted sessions deemed eligible for general CLE credits and legal ethics CLE credits to most states with CLE requirements
Governing Board Roster
 AASA Governance AASA is the national association most directly concerned with public education leadership. Its practicing superintendents and other school system leaders establish and oversee AASA's goals.
AASA Governance AASA is the national association most directly concerned with public education leadership. Its practicing superintendents and other school system leaders establish and oversee AASA's goals.
Admitting Foreign Trained Lawyers. National Conference of Bar Examiners Washington, D.C., April 15, 2016
 Admitting Foreign Trained Lawyers National Conference of Bar Examiners Washington, D.C., April 15, 2016 Professor Laurel S. Terry Carlisle, Pennsylvania LTerry@psu.edu Overview of Remarks Why this issue
Admitting Foreign Trained Lawyers National Conference of Bar Examiners Washington, D.C., April 15, 2016 Professor Laurel S. Terry Carlisle, Pennsylvania LTerry@psu.edu Overview of Remarks Why this issue
CRAIN S CLEVELAND BUSINESS
 PAID CIRCULATION CRAIN S CLEVELAND BUSINESS Cleveland, Ohio 44113 FIELD SERVED: CRAIN S CLEVELAND BUSINESS serves the general business information needs of executives, managers and professionals in the
PAID CIRCULATION CRAIN S CLEVELAND BUSINESS Cleveland, Ohio 44113 FIELD SERVED: CRAIN S CLEVELAND BUSINESS serves the general business information needs of executives, managers and professionals in the
RULE 2.4: LAWYER SERVING
 American Bar Association CPR Policy Implementation Committee Variations of the ABA Model Rules of Professional Conduct RULE 2.4: LAWYER SERVING AS THIRD-PARTY NEUTRAL (a) A lawyer serves as a third-party
American Bar Association CPR Policy Implementation Committee Variations of the ABA Model Rules of Professional Conduct RULE 2.4: LAWYER SERVING AS THIRD-PARTY NEUTRAL (a) A lawyer serves as a third-party
Oregon and STEM+ Migration and Educational Attainment by Degree Type among Young Oregonians. Oregon Office of Economic Analysis
 Oregon and STEM+ Migration and Educational Attainment by Degree Type among Young Oregonians 1 What is STEM and STEM+? STEM refers to college degrees where graduates majored in Science, Technology, Engineering
Oregon and STEM+ Migration and Educational Attainment by Degree Type among Young Oregonians 1 What is STEM and STEM+? STEM refers to college degrees where graduates majored in Science, Technology, Engineering
January 17, 2017 Women in State Legislatures 2017
 January 17, 2017 in State Legislatures 2017 Kelly Dittmar, Ph.D. In 2017, 1832 women (1107D, 703R, 4I, 4Prg, 1WFP, 13NP) hold seats in state legislatures, comprising 24.8% of the 7383 members; 442 women
January 17, 2017 in State Legislatures 2017 Kelly Dittmar, Ph.D. In 2017, 1832 women (1107D, 703R, 4I, 4Prg, 1WFP, 13NP) hold seats in state legislatures, comprising 24.8% of the 7383 members; 442 women
Next Generation NACo Network BYLAWS Adopted by NACo Board of Directors Revised February, 2017
 Next Generation NACo Network BYLAWS Adopted by NACo Board of Directors Revised February, 2017 I. NAME The name of the organization shall be Next Generation NACo Network, hereinafter called NextGen. NACo
Next Generation NACo Network BYLAWS Adopted by NACo Board of Directors Revised February, 2017 I. NAME The name of the organization shall be Next Generation NACo Network, hereinafter called NextGen. NACo
The Youth Vote in 2008 By Emily Hoban Kirby and Kei Kawashima-Ginsberg 1 Updated August 17, 2009
 The Youth Vote in 2008 By Emily Hoban Kirby and Kei Kawashima-Ginsberg 1 Updated August 17, 2009 Estimates from the Census Current Population Survey November Supplement suggest that the voter turnout rate
The Youth Vote in 2008 By Emily Hoban Kirby and Kei Kawashima-Ginsberg 1 Updated August 17, 2009 Estimates from the Census Current Population Survey November Supplement suggest that the voter turnout rate
RULE 3.8(g) AND (h):
 American Bar Association CPR Policy Implementation Committee Variations of the ABA Model Rules of Professional Conduct RULE 3.8(g) AND (h): (g) When a prosecutor knows of new, credible and material evidence
American Bar Association CPR Policy Implementation Committee Variations of the ABA Model Rules of Professional Conduct RULE 3.8(g) AND (h): (g) When a prosecutor knows of new, credible and material evidence
2018 NATIONAL CONVENTION
 Delegate Allocations and Region Formation 2018 NATIONAL CONVENTION HYATT REGENCY, NEW ORLEANS, LA SUNDAY, JULY 1 TUESDAY JULY 3 Written and Prepared By Alicia Mattson Secretary, Libertarian National Committee
Delegate Allocations and Region Formation 2018 NATIONAL CONVENTION HYATT REGENCY, NEW ORLEANS, LA SUNDAY, JULY 1 TUESDAY JULY 3 Written and Prepared By Alicia Mattson Secretary, Libertarian National Committee
RULE 3.1: MERITORIOUS CLAIMS AND CONTENTIONS
 American Bar Association CPR Policy Implementation Committee Variations of the ABA Model Rules of Professional Conduct RULE 3.1: MERITORIOUS CLAIMS AND CONTENTIONS A lawyer shall not bring or defend a
American Bar Association CPR Policy Implementation Committee Variations of the ABA Model Rules of Professional Conduct RULE 3.1: MERITORIOUS CLAIMS AND CONTENTIONS A lawyer shall not bring or defend a
Constitution in a Nutshell NAME. Per
 Constitution in a Nutshell NAME Per Preamble We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defense, promote
Constitution in a Nutshell NAME Per Preamble We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defense, promote
Bylaws of the Prescription Monitoring Information exchange Working Group
 Bylaws of the Prescription Monitoring Information exchange Working Group ` Table of Contents Table of Contents... 2 Article I. Introduction... 6 Article II. Purpose... 6 Article III. Membership... 6 Article
Bylaws of the Prescription Monitoring Information exchange Working Group ` Table of Contents Table of Contents... 2 Article I. Introduction... 6 Article II. Purpose... 6 Article III. Membership... 6 Article
2016 NATIONAL CONVENTION
 Delegate Allocations and Region Formation 2016 NATIONAL CONVENTION ROSEN CENTRE, ORLANDO, FL FRIDAY, MAY 27 MONDAY, MAY 30 Written and Prepared By Alicia Mattson Secretary, Libertarian National Committee
Delegate Allocations and Region Formation 2016 NATIONAL CONVENTION ROSEN CENTRE, ORLANDO, FL FRIDAY, MAY 27 MONDAY, MAY 30 Written and Prepared By Alicia Mattson Secretary, Libertarian National Committee
Presentation Outline
 2016 Elections November 10, 2016 Grant Couch, Director, Government Relations Christina Lavoie, JD, Assistant Director, Public Policy and Operations Jamie Miller, MBA, Director, Government Relations Presentation
2016 Elections November 10, 2016 Grant Couch, Director, Government Relations Christina Lavoie, JD, Assistant Director, Public Policy and Operations Jamie Miller, MBA, Director, Government Relations Presentation
Washington, D.C. Update
 Washington, D.C. Update 2016 AMGA CMO Council March 9, 2016 Chester Speed, J.D., LL.M, Vice-President, Public Policy Presentation Outline AMGA Priority Issues Risk Survey Legislative Agenda Elections 1
Washington, D.C. Update 2016 AMGA CMO Council March 9, 2016 Chester Speed, J.D., LL.M, Vice-President, Public Policy Presentation Outline AMGA Priority Issues Risk Survey Legislative Agenda Elections 1
Representational Bias in the 2012 Electorate
 Representational Bias in the 2012 Electorate by Vanessa Perez, Ph.D. January 2015 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 3 4 2 Methodology 5 3 Continuing Disparities in the and Voting Populations 6-10 4 National
Representational Bias in the 2012 Electorate by Vanessa Perez, Ph.D. January 2015 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 3 4 2 Methodology 5 3 Continuing Disparities in the and Voting Populations 6-10 4 National
New Population Estimates Show Slight Changes For 2010 Congressional Apportionment, With A Number of States Sitting Close to the Edge
 67 Emerywood Court Manassas, Virginia 202 202 789.2004 tel. or 703 580.7267 703 580.6258 fax Info@electiondataservices.com EMBARGOED UNTIL 6:0 P.M. EST, SUNDAY, SEPTEMBER 26, 200 Date: September 26, 200
67 Emerywood Court Manassas, Virginia 202 202 789.2004 tel. or 703 580.7267 703 580.6258 fax Info@electiondataservices.com EMBARGOED UNTIL 6:0 P.M. EST, SUNDAY, SEPTEMBER 26, 200 Date: September 26, 200
Election Cybersecurity, Voter Registration, and ERIC. David Becker Executive Director, CEIR
 Election Cybersecurity, Voter Registration, and ERIC David Becker Executive Director, CEIR SECURING THE VOTER FILE Prevention Detection Mitigation Prevention White-listing IP addresses Limiting
Election Cybersecurity, Voter Registration, and ERIC David Becker Executive Director, CEIR SECURING THE VOTER FILE Prevention Detection Mitigation Prevention White-listing IP addresses Limiting
Graduation and Retention Rates of Nonresidents by State
 Graduation and Retention Rates of Nonresidents by State March 2011 Highlights: California, Illinois, and Texas are the states with the largest numbers of nonresidents. Students from Ohio and Wyoming persist
Graduation and Retention Rates of Nonresidents by State March 2011 Highlights: California, Illinois, and Texas are the states with the largest numbers of nonresidents. Students from Ohio and Wyoming persist
NATIONAL VOTER REGISTRATION DAY. September 26, 2017
 NATIONAL VOTER REGISTRATION DAY September 26, 2017 THE PROBLEM Every year millions of Americans find themselves unable to vote because they miss a registration deadline, don t update their registration,
NATIONAL VOTER REGISTRATION DAY September 26, 2017 THE PROBLEM Every year millions of Americans find themselves unable to vote because they miss a registration deadline, don t update their registration,
The Impact of Wages on Highway Construction Costs
 The Impact of Wages on Highway Construction Costs Updated Analysis Prepared for the Construction Industry Labor-Management Trust and the National Heavy & Highway Alliance by The Construction Labor Research
The Impact of Wages on Highway Construction Costs Updated Analysis Prepared for the Construction Industry Labor-Management Trust and the National Heavy & Highway Alliance by The Construction Labor Research
Dynamic Diversity: Projected Changes in U.S. Race and Ethnic Composition 1995 to December 1999
 Dynamic Diversity: Projected Changes in U.S. Race and Ethnic Composition 1995 to 2050 December 1999 DYNAMIC DIVERSITY: PROJECTED CHANGES IN U.S. RACE AND ETHNIC COMPOSITION 1995 TO 2050 The Minority Business
Dynamic Diversity: Projected Changes in U.S. Race and Ethnic Composition 1995 to 2050 December 1999 DYNAMIC DIVERSITY: PROJECTED CHANGES IN U.S. RACE AND ETHNIC COMPOSITION 1995 TO 2050 The Minority Business
Geek s Guide, Election 2012 by Prof. Sam Wang, Princeton University Princeton Election Consortium
 Geek s Guide, Election 2012 by Prof. Sam Wang, Princeton University Princeton Election Consortium http://election.princeton.edu This document presents a) Key states to watch early in the evening; b) Ways
Geek s Guide, Election 2012 by Prof. Sam Wang, Princeton University Princeton Election Consortium http://election.princeton.edu This document presents a) Key states to watch early in the evening; b) Ways
Reporting and Criminal Records
 A project funded by U.S. Department of Labor and U.S. Department of Justice Reporting and Criminal Records Considerations for Writing about People Who Have Criminal Histories June 13, 2018 Presenters Corinne
A project funded by U.S. Department of Labor and U.S. Department of Justice Reporting and Criminal Records Considerations for Writing about People Who Have Criminal Histories June 13, 2018 Presenters Corinne
2016 us election results
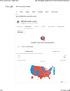 1 of 6 11/12/2016 7:35 PM 2016 us election results All News Images Videos Shopping More Search tools About 243,000,000 results (0.86 seconds) 2 WA OR NV CA AK MT ID WY UT CO AZ NM ND MN SD WI NY MI NE
1 of 6 11/12/2016 7:35 PM 2016 us election results All News Images Videos Shopping More Search tools About 243,000,000 results (0.86 seconds) 2 WA OR NV CA AK MT ID WY UT CO AZ NM ND MN SD WI NY MI NE
Historically, state PM&R societies have operated as independent organizations that advocate on legislative and regulatory proposals.
 PROMOTING STATE PM&R ADVOCACY NEXT STEPS Historically, state PM&R societies have operated as independent organizations that advocate on legislative and regulatory proposals. PROMOTING STATE PM&R ADVOCACY
PROMOTING STATE PM&R ADVOCACY NEXT STEPS Historically, state PM&R societies have operated as independent organizations that advocate on legislative and regulatory proposals. PROMOTING STATE PM&R ADVOCACY
TABLE OF CONTENTS. Introduction. Identifying the Importance of ID. Overview. Policy Recommendations. Conclusion. Summary of Findings
 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction Identifying the Importance of ID Overview Policy Recommendations Conclusion Summary of Findings Quick Reference Guide 3 3 4 6 7 8 8 The National Network for Youth gives
1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction Identifying the Importance of ID Overview Policy Recommendations Conclusion Summary of Findings Quick Reference Guide 3 3 4 6 7 8 8 The National Network for Youth gives
Election 2014: The Midterm Results, the ACA and You
 Election 2014: The Midterm Results, the ACA and You James Slotnick, JD Sun Life Financial AVP, Broker Education Join the conversation on Twitter using #SLFElection2014 The Midterm Results The Outlook for
Election 2014: The Midterm Results, the ACA and You James Slotnick, JD Sun Life Financial AVP, Broker Education Join the conversation on Twitter using #SLFElection2014 The Midterm Results The Outlook for
Congressional Districts Potentially Affected by Shipments to Yucca Mountain, Nevada
 2015 Congressional Districts Potentially Affected by Shipments to Yucca Mountain, Nevada Fred Dilger PhD. Black Mountain Research 10/21/2015 Background On June 16 2008, the Department of Energy (DOE) released
2015 Congressional Districts Potentially Affected by Shipments to Yucca Mountain, Nevada Fred Dilger PhD. Black Mountain Research 10/21/2015 Background On June 16 2008, the Department of Energy (DOE) released
We re Paying Dearly for Bush s Tax Cuts Study Shows Burdens by State from Bush s $87-Billion-Every-51-Days Borrowing Binge
 Citizens for Tax Justice 202-626-3780 September 23, 2003 (9 pp.) Contact: Bob McIntyre We re Paying Dearly for Bush s Tax Cuts Study Shows Burdens by State from Bush s $87-Billion-Every-51-Days Borrowing
Citizens for Tax Justice 202-626-3780 September 23, 2003 (9 pp.) Contact: Bob McIntyre We re Paying Dearly for Bush s Tax Cuts Study Shows Burdens by State from Bush s $87-Billion-Every-51-Days Borrowing
FSC-BENEFITED EXPORTS AND JOBS IN 1999: Estimates for Every Congressional District
 FSC-BENEFITED EXPORTS AND JOBS IN 1999: Estimates for Every Congressional District Prepared for National Foreign Trade Council July 2, 2002 National Economic Consulting FSC-BENEFITED EXPORTS AND JOBS IN
FSC-BENEFITED EXPORTS AND JOBS IN 1999: Estimates for Every Congressional District Prepared for National Foreign Trade Council July 2, 2002 National Economic Consulting FSC-BENEFITED EXPORTS AND JOBS IN
VOCA 101: Allowable/Unallowable Expenses Janelle Melohn, IA Kelly McIntosh, MT
 VOCA 101: Allowable/Unallowable Expenses Janelle Melohn, IA Kelly McIntosh, MT While you re waiting, please visit pollev.com/iowaagcvad so you can participate in this presentation from your phone. Overview
VOCA 101: Allowable/Unallowable Expenses Janelle Melohn, IA Kelly McIntosh, MT While you re waiting, please visit pollev.com/iowaagcvad so you can participate in this presentation from your phone. Overview
RIDE Program Overview
 RIDE Program Overview Table of Contents 1 Program Overview and the E-Verify Process 2 RIDE by the Numbers 3 Filling a Critical Gap and a Glance at Identity Fraud 4 Fact and Fiction? 5 Benefits of Working
RIDE Program Overview Table of Contents 1 Program Overview and the E-Verify Process 2 RIDE by the Numbers 3 Filling a Critical Gap and a Glance at Identity Fraud 4 Fact and Fiction? 5 Benefits of Working
THE POLICY CONSEQUENCES OF POLARIZATION: EVIDENCE FROM STATE REDISTRIBUTIVE POLICY
 THE POLICY CONSEQUENCES OF POLARIZATION: EVIDENCE FROM STATE REDISTRIBUTIVE POLICY Elizabeth Rigby George Washington University Gerald Wright Indiana University Prepared for presentation at the Conference
THE POLICY CONSEQUENCES OF POLARIZATION: EVIDENCE FROM STATE REDISTRIBUTIVE POLICY Elizabeth Rigby George Washington University Gerald Wright Indiana University Prepared for presentation at the Conference
RULE 4.2: COMMUNICATION WITH PERSON REPRESENTED BY COUNSEL
 American Bar Association CPR Policy Implementation Committee Variations of the ABA Model Rules of Professional Conduct RULE 4.2: COMMUNICATION WITH PERSON REPRESENTED BY COUNSEL In representing a client,
American Bar Association CPR Policy Implementation Committee Variations of the ABA Model Rules of Professional Conduct RULE 4.2: COMMUNICATION WITH PERSON REPRESENTED BY COUNSEL In representing a client,
Mineral Availability and Social License to Operate
 Mineral Availability and Social License to Operate Brett Jordan Division of Economics and Business Colorado School of Mines Camp Resources, August 7-9, 2016 Motivation Social License to Operate (SLO) NIMBYism
Mineral Availability and Social License to Operate Brett Jordan Division of Economics and Business Colorado School of Mines Camp Resources, August 7-9, 2016 Motivation Social License to Operate (SLO) NIMBYism
Breakdown of the Types of Specific Criminal Convictions Associated with Criminal Aliens Placed in a Non-Custodial Setting in Fiscal Year 2015
 Breakdown the Types Specific Criminal Associated with Criminal Placed in a Non-Custodial Setting in Fiscal Year 2015 The following table below provides a breakdown the types specific criminal convictions
Breakdown the Types Specific Criminal Associated with Criminal Placed in a Non-Custodial Setting in Fiscal Year 2015 The following table below provides a breakdown the types specific criminal convictions
Prison Price Tag The High Cost of Wisconsin s Corrections Policies
 Prison Price Tag The High Cost of Wisconsin s Corrections Policies November 19, 2015 Wisconsin s overuse of jails and prisons has resulted in outsized costs for state residents. By emphasizing high-cost
Prison Price Tag The High Cost of Wisconsin s Corrections Policies November 19, 2015 Wisconsin s overuse of jails and prisons has resulted in outsized costs for state residents. By emphasizing high-cost
Promoting Second Chances: HR and Criminal Records
 AL AK AZ AR CA CO CT DE DC FL GA HI ID IL IN Adult arrests without charges; records with inaccuracies Only cases of mistaken identity or false accusations are expungeable No expungement or sealing permitted
AL AK AZ AR CA CO CT DE DC FL GA HI ID IL IN Adult arrests without charges; records with inaccuracies Only cases of mistaken identity or false accusations are expungeable No expungement or sealing permitted
Supreme Court Decision What s Next
 Supreme Court Decision What s Next June 3, 2015 Provided by Avalere Disclaimer Organizations may not re use material presented at this AMCP webinar for commercial purposes without the written consent of
Supreme Court Decision What s Next June 3, 2015 Provided by Avalere Disclaimer Organizations may not re use material presented at this AMCP webinar for commercial purposes without the written consent of
Candidate Faces and Election Outcomes: Is the Face-Vote Correlation Caused by Candidate Selection? Corrigendum
 Quarterly Journal of Political Science, 2010, 5: 99 105 Corrigendum Candidate Faces and Election Outcomes: Is the Face-Vote Correlation Caused by Candidate Selection? Corrigendum Matthew D. Atkinson, Ryan
Quarterly Journal of Political Science, 2010, 5: 99 105 Corrigendum Candidate Faces and Election Outcomes: Is the Face-Vote Correlation Caused by Candidate Selection? Corrigendum Matthew D. Atkinson, Ryan
Kansas Legislator Briefing Book 2019
 Kansas Legislator Briefing Book 2019 I-1 Addressing Abandoned Property Using Legal Tools I-2 Administrative Rule and Regulation Legislative Oversight I-3 Board of Indigents Defense Services I-4 Election
Kansas Legislator Briefing Book 2019 I-1 Addressing Abandoned Property Using Legal Tools I-2 Administrative Rule and Regulation Legislative Oversight I-3 Board of Indigents Defense Services I-4 Election
Ballot Questions in Michigan. Selma Tucker and Ken Sikkema
 Ballot Questions in Michigan Selma Tucker and Ken Sikkema PUBLIC SECTOR PUBLIC CONSULTANTS SECTOR CONSULTANTS @PSCMICHIGAN @PSCMICHIGAN PUBLICSECTORCONSULTANTS.COM Presentation Overview History of ballot
Ballot Questions in Michigan Selma Tucker and Ken Sikkema PUBLIC SECTOR PUBLIC CONSULTANTS SECTOR CONSULTANTS @PSCMICHIGAN @PSCMICHIGAN PUBLICSECTORCONSULTANTS.COM Presentation Overview History of ballot
A Dead Heat and the Electoral College
 A Dead Heat and the Electoral College Robert S. Erikson Department of Political Science Columbia University rse14@columbia.edu Karl Sigman Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research sigman@ieor.columbia.edu
A Dead Heat and the Electoral College Robert S. Erikson Department of Political Science Columbia University rse14@columbia.edu Karl Sigman Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research sigman@ieor.columbia.edu
STATISTICAL GRAPHICS FOR VISUALIZING DATA
 STATISTICAL GRAPHICS FOR VISUALIZING DATA Tables and Figures, I William G. Jacoby Michigan State University and ICPSR University of Illinois at Chicago October 14-15, 21 http://polisci.msu.edu/jacoby/uic/graphics
STATISTICAL GRAPHICS FOR VISUALIZING DATA Tables and Figures, I William G. Jacoby Michigan State University and ICPSR University of Illinois at Chicago October 14-15, 21 http://polisci.msu.edu/jacoby/uic/graphics
RIDE Program Overview
 RIDE Program Overview Region IV Annual Conference May 2017 Table of Contents 1 2 3 Program Overview and the E-Verify Process Fact and Fiction Filling a Critical Gap and a Glance at Identity Fraud? 4 RIDE
RIDE Program Overview Region IV Annual Conference May 2017 Table of Contents 1 2 3 Program Overview and the E-Verify Process Fact and Fiction Filling a Critical Gap and a Glance at Identity Fraud? 4 RIDE
Online Appendix. Table A1. Guidelines Sentencing Chart. Notes: Recommended sentence lengths in months.
 Online Appendix Table A1. Guidelines Sentencing Chart Notes: Recommended sentence lengths in months. Table A2. Selection into Sentencing Stage (1) (2) (3) Guilty Plea Dropped Charge Deferred Prosecution
Online Appendix Table A1. Guidelines Sentencing Chart Notes: Recommended sentence lengths in months. Table A2. Selection into Sentencing Stage (1) (2) (3) Guilty Plea Dropped Charge Deferred Prosecution
SPECIAL EDITION 11/6/14
 SPECIAL EDITION 11/6/14 The document below will provide insights on what the new Senate Majority means, as well as a nationwide view of House, Senate and Gubernatorial election results. We will continue
SPECIAL EDITION 11/6/14 The document below will provide insights on what the new Senate Majority means, as well as a nationwide view of House, Senate and Gubernatorial election results. We will continue
How States Can Achieve More Effective Public Safety Policies
 How States Can Achieve More Effective Public Safety Policies Arkansas Legislative Criminal Justice Oversight Task Force and Behavioral Health Treatment Access Task Force July 13, 2015 Marc Pelka, Deputy
How States Can Achieve More Effective Public Safety Policies Arkansas Legislative Criminal Justice Oversight Task Force and Behavioral Health Treatment Access Task Force July 13, 2015 Marc Pelka, Deputy
PREVIEW 2018 PRO-EQUALITY AND ANTI-LGBTQ STATE AND LOCAL LEGISLATION
 PREVIEW 08 PRO-EQUALITY AND ANTI-LGBTQ STATE AND LOCAL LEGISLATION Emboldened by the politics of hate and fear spewed by the Trump-Pence administration, state legislators across the nation have threatened
PREVIEW 08 PRO-EQUALITY AND ANTI-LGBTQ STATE AND LOCAL LEGISLATION Emboldened by the politics of hate and fear spewed by the Trump-Pence administration, state legislators across the nation have threatened
Federal Education: Of Elections &Politics. Oh, and Policy. Noelle Ellerson December 2014
 Federal Education: Of Elections &Politics. Oh, and Policy. Noelle Ellerson December 2014 Climates & To-Do List Funding State and local budgets have yet to reach prerecession levels Sequestration at the
Federal Education: Of Elections &Politics. Oh, and Policy. Noelle Ellerson December 2014 Climates & To-Do List Funding State and local budgets have yet to reach prerecession levels Sequestration at the
50 State Survey of Bad Faith Law. Does your State encourage bad faith?
 A 50 State Survey of Bad Faith Law. Does your State encourage bad faith? Tort Contract Statute/UCPA Tort Contract Assign Statute Tort Statute //Cap AL Ala. Code 1975 Ala. Code 1975 27-12-24 27-12-24 Cap
A 50 State Survey of Bad Faith Law. Does your State encourage bad faith? Tort Contract Statute/UCPA Tort Contract Assign Statute Tort Statute //Cap AL Ala. Code 1975 Ala. Code 1975 27-12-24 27-12-24 Cap
Admitting Foreign-Trained Lawyers. Professor Laurel S. Terry Penn State Dickinson School of Law Carlisle, Pennsylvania
 Admitting Foreign-Trained Lawyers National Conference of Bar Examiners Seattle, May 3, 2014 Professor Laurel S. Terry Penn State Dickinson School of Law Carlisle, Pennsylvania LTerry@psu.edu Overview of
Admitting Foreign-Trained Lawyers National Conference of Bar Examiners Seattle, May 3, 2014 Professor Laurel S. Terry Penn State Dickinson School of Law Carlisle, Pennsylvania LTerry@psu.edu Overview of
Some Change in Apportionment Allocations With New 2017 Census Estimates; But Greater Change Likely by 2020
 FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Date: December 20, 2017 Contact: Kimball W. Brace 6171 Emerywood Court Manassas, Virginia 20112 202 789.2004 tel. or 703 580.7267 703 580.6258 fax Info@electiondataservices.com Tel.:
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Date: December 20, 2017 Contact: Kimball W. Brace 6171 Emerywood Court Manassas, Virginia 20112 202 789.2004 tel. or 703 580.7267 703 580.6258 fax Info@electiondataservices.com Tel.:
Some Change in Apportionment Allocations With New 2017 Census Estimates; But Greater Change Likely by 2020
 FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Date: December 26, 2017 Contact: Kimball W. Brace 6171 Emerywood Court Manassas, Virginia 20112 202 789.2004 tel. or 703 580.7267 703 580.6258 fax Info@electiondataservices.com Tel.:
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Date: December 26, 2017 Contact: Kimball W. Brace 6171 Emerywood Court Manassas, Virginia 20112 202 789.2004 tel. or 703 580.7267 703 580.6258 fax Info@electiondataservices.com Tel.:
By 1970 immigrants from the Americas, Africa, and Asia far outnumbered those from Europe. CANADIAN UNITED STATES CUBAN MEXICAN
 In Search of the American Dream After World War II, millions of immigrants and citizens sought better lives in the United States. More and more immigrants came from Latin America and Asia. Between 940
In Search of the American Dream After World War II, millions of immigrants and citizens sought better lives in the United States. More and more immigrants came from Latin America and Asia. Between 940
Relationship Between Adult and Minor Guardianship Statutes
 RELATIONSHIP DEFINITION STATES TOTAL Integrated Statutory provisions regarding authority over personal AR, DE, FL, IN, IA, KS, KY, MO, NV, NC, OH, OR, 17 matters are applicable to both adults and minors
RELATIONSHIP DEFINITION STATES TOTAL Integrated Statutory provisions regarding authority over personal AR, DE, FL, IN, IA, KS, KY, MO, NV, NC, OH, OR, 17 matters are applicable to both adults and minors
Background and Trends
 Background and Trends Kim English, Division of Criminal Justice Colorado Commission on Criminal and Juvenile Justice February 10, 2017 CCJJ / 02-10-2017 1/14 CCJJ / 02-10-2017 2/14 CCJJ / 02-10-2017 3/14
Background and Trends Kim English, Division of Criminal Justice Colorado Commission on Criminal and Juvenile Justice February 10, 2017 CCJJ / 02-10-2017 1/14 CCJJ / 02-10-2017 2/14 CCJJ / 02-10-2017 3/14
The Progressive Era. 1. reform movement that sought to return control of the government to the people
 Date CHAPTER 17 Form A CHAPTER TEST The Progressive Era Part 1: Main Ideas Write the letter of the term or name that best matches each description. (4 points each) a. Federal Trade Commission f. Susan
Date CHAPTER 17 Form A CHAPTER TEST The Progressive Era Part 1: Main Ideas Write the letter of the term or name that best matches each description. (4 points each) a. Federal Trade Commission f. Susan
Regulating Lawyers in a Global Arena. Conference of Chief Justices Midyear Meeting, Sea Island, Georgia Jan. 28, 2014
 Regulating Lawyers in a Global Arena Conference of Chief Justices Midyear Meeting, Sea Island, Georgia Jan. 28, 2014 Professor Laurel S. Terry Penn State Dickinson School of Law Carlisle, Pennsylvania
Regulating Lawyers in a Global Arena Conference of Chief Justices Midyear Meeting, Sea Island, Georgia Jan. 28, 2014 Professor Laurel S. Terry Penn State Dickinson School of Law Carlisle, Pennsylvania
CA CALIFORNIA. Ala. Code 10-2B (2009) [Transferred, effective January 1, 2011, to 10A ] No monetary penalties listed.
![CA CALIFORNIA. Ala. Code 10-2B (2009) [Transferred, effective January 1, 2011, to 10A ] No monetary penalties listed. CA CALIFORNIA. Ala. Code 10-2B (2009) [Transferred, effective January 1, 2011, to 10A ] No monetary penalties listed.](/thumbs/72/66892882.jpg) AL ALABAMA Ala. Code 10-2B-15.02 (2009) [Transferred, effective January 1, 2011, to 10A-2-15.02.] No monetary penalties listed. May invalidate in-state contracts made by unqualified foreign corporations.
AL ALABAMA Ala. Code 10-2B-15.02 (2009) [Transferred, effective January 1, 2011, to 10A-2-15.02.] No monetary penalties listed. May invalidate in-state contracts made by unqualified foreign corporations.
A contentious election: How the aftermath is impacting education
 Amy L Dagley, Ph.D. University of Alabama Birmingham Brittany Larkin, Ph.D. Auburn University ELA Annual Conference, San Diego, 2017 A contentious election: How the aftermath is impacting education Each
Amy L Dagley, Ph.D. University of Alabama Birmingham Brittany Larkin, Ph.D. Auburn University ELA Annual Conference, San Diego, 2017 A contentious election: How the aftermath is impacting education Each
BYLAWS OF THE NATIONAL STUDENT SPEECH LANGUAGE HEARING ASSOCIATION
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 BYLAWS OF THE NATIONAL STUDENT SPEECH LANGUAGE HEARING ASSOCIATION ARTICLE I Name Section
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 BYLAWS OF THE NATIONAL STUDENT SPEECH LANGUAGE HEARING ASSOCIATION ARTICLE I Name Section
The Law Library: A Brief Guide
 The Law Library: A Brief Guide I. INTRODUCTION Welcome to the Chase Law Library! Law books may at first appear intimidating, but you will gradually find them logical and easy to use. The Reference Staff
The Law Library: A Brief Guide I. INTRODUCTION Welcome to the Chase Law Library! Law books may at first appear intimidating, but you will gradually find them logical and easy to use. The Reference Staff
Effective Dispute Resolution Systems and the Vital Role of Stakeholders
 Effective Dispute Resolution Systems and the Vital Role of Stakeholders Region 4 PTAC Summer Working Meeting June 24-25, 2015 Traverse City, Michigan Philip Moses Associate Director The human brain is
Effective Dispute Resolution Systems and the Vital Role of Stakeholders Region 4 PTAC Summer Working Meeting June 24-25, 2015 Traverse City, Michigan Philip Moses Associate Director The human brain is
State Legislative Competition in 2012: Redistricting and Party Polarization Drive Decrease In Competition
 October 17, 2012 State Legislative Competition in 2012: Redistricting and Party Polarization Drive Decrease In Competition John J. McGlennon, Ph.D. Government Department Chair and Professor of Government
October 17, 2012 State Legislative Competition in 2012: Redistricting and Party Polarization Drive Decrease In Competition John J. McGlennon, Ph.D. Government Department Chair and Professor of Government
Presented by: Ted Bornstein, Dennis Cardoza and Scott Klug
 1 Attorney Advertising Prior results do not guarantee a similar outcome Models used are not clients but may be representative of clients 321 N. Clark Street, Suite 2800,Chicago, IL 60654 312.832.4500 2
1 Attorney Advertising Prior results do not guarantee a similar outcome Models used are not clients but may be representative of clients 321 N. Clark Street, Suite 2800,Chicago, IL 60654 312.832.4500 2
ALASKA BAR ASSOCIATION PRO BONO COMMITTEE RESOLUTION IN SUPPORT OF RECOGNIZING A RIGHT TO COUNSEL FOR INDIGENT INDIVIDUALS IN CERTAIN CIVIL CASES
 ALASKA BAR ASSOCIATION PRO BONO COMMITTEE RESOLUTION IN SUPPORT OF RECOGNIZING A RIGHT TO COUNSEL FOR INDIGENT INDIVIDUALS IN CERTAIN CIVIL CASES WHEREAS, the Alaska Bar Association (AkBA) has made the
ALASKA BAR ASSOCIATION PRO BONO COMMITTEE RESOLUTION IN SUPPORT OF RECOGNIZING A RIGHT TO COUNSEL FOR INDIGENT INDIVIDUALS IN CERTAIN CIVIL CASES WHEREAS, the Alaska Bar Association (AkBA) has made the
the polling company, inc./ WomanTrend On behalf of the Center for Security Policy TOPLINE DATA Nationwide Survey among 1,000 Adults (18+)
 Field Dates: September 23-26, 2014 Margin of Error: ±3% SCREENER 1. Gender (RECORDED BY OBSERVATION) 49% MALE 51% FEMALE the polling company, inc./ WomanTrend On behalf of the Center for Security Policy
Field Dates: September 23-26, 2014 Margin of Error: ±3% SCREENER 1. Gender (RECORDED BY OBSERVATION) 49% MALE 51% FEMALE the polling company, inc./ WomanTrend On behalf of the Center for Security Policy
WLSA&RDC 2014 GARY MONCRIEF
 LESSONS FROM ROSENTHAL WLSA&RDC 2014 GARY MONCRIEF ALAN ROSENTHAL ROSENTHAL S OBSERVATIONS ABOUT LIFE Ask questions Enjoy what you do Have fun Have more fun Keep to yourself that which need not be public
LESSONS FROM ROSENTHAL WLSA&RDC 2014 GARY MONCRIEF ALAN ROSENTHAL ROSENTHAL S OBSERVATIONS ABOUT LIFE Ask questions Enjoy what you do Have fun Have more fun Keep to yourself that which need not be public
Presentation to the Bakery, Confectionery, Tobacco Workers and Grain Millers' International Union. Paul Lemmon July 26, 2010
 Presentation to the Bakery, Confectionery, Tobacco Workers and Grain Millers' International Union Paul Lemmon July 26, 2010 Our Hard Work in 2006 Our Hard Work in 2008 Who We re Fighting Speaker Boehner?
Presentation to the Bakery, Confectionery, Tobacco Workers and Grain Millers' International Union Paul Lemmon July 26, 2010 Our Hard Work in 2006 Our Hard Work in 2008 Who We re Fighting Speaker Boehner?
45 STATES AND THE DISTRICT OF COLUMBIA PERMIT DIRECT PETITIONS TO A COURT FOR TREATMENT FOR A PERSON WITH A SEVERE MENTAL ILLNESS
 45 STATES AND THE DISTRICT OF COLUMBIA PERMIT DIRECT PETITIONS TO A COURT FOR TREATMENT FOR A PERSON WITH A SEVERE MENTAL ILLNESS State Can adults directly petition the court for treatment? Statutory Language
45 STATES AND THE DISTRICT OF COLUMBIA PERMIT DIRECT PETITIONS TO A COURT FOR TREATMENT FOR A PERSON WITH A SEVERE MENTAL ILLNESS State Can adults directly petition the court for treatment? Statutory Language
House Apportionment 2012: States Gaining, Losing, and on the Margin
 House Apportionment 2012: States Gaining, Losing, and on the Margin Royce Crocker Specialist in American National Government August 23, 2013 CRS Report for Congress Prepared for Members and Committees
House Apportionment 2012: States Gaining, Losing, and on the Margin Royce Crocker Specialist in American National Government August 23, 2013 CRS Report for Congress Prepared for Members and Committees
New Ambassador Orientation. Laura Keivel Manager, Grassroots Advocacy
 New Ambassador Orientation Laura Keivel Manager, Grassroots Advocacy Arthritis Foundation Advocacy Advocacy and Access is part of the National Office based in Washington, DC New state advocacy initiatives
New Ambassador Orientation Laura Keivel Manager, Grassroots Advocacy Arthritis Foundation Advocacy Advocacy and Access is part of the National Office based in Washington, DC New state advocacy initiatives
/mediation.htm s/adr.html rograms/adr/
 Alaska Alaska Court System AK http://www.state.ak.us/courts /mediation.htm A variety of programs are offered in courts throughout the state. Alabama Arkansas Alabama Center for AL http://www.alabamaadr.org
Alaska Alaska Court System AK http://www.state.ak.us/courts /mediation.htm A variety of programs are offered in courts throughout the state. Alabama Arkansas Alabama Center for AL http://www.alabamaadr.org
Public and Subsidized Housing as a Platform for Becoming a United States Citizen
 Public and Subsidized Housing as a Platform for Becoming a United States Citizen John I. Carruthers The George Washington University Natasha T. Duncan Mercyhurst College Brigitte S. Waldorf Purdue University
Public and Subsidized Housing as a Platform for Becoming a United States Citizen John I. Carruthers The George Washington University Natasha T. Duncan Mercyhurst College Brigitte S. Waldorf Purdue University
UNTANGLING THE KNOTS What s Possible for Health Reform Efforts
 UNTANGLING THE KNOTS What s Possible for Health Reform Efforts Post-Election ACA Update January 30, 2017 Kathryn Bakich Senior Vice President, National Director Health Care Compliance NCPERS 2017 Legislative
UNTANGLING THE KNOTS What s Possible for Health Reform Efforts Post-Election ACA Update January 30, 2017 Kathryn Bakich Senior Vice President, National Director Health Care Compliance NCPERS 2017 Legislative
Background Checks and Ban the Box Legislation. November 8, 2017
 Background Checks and Ban the Box Legislation November 8, 2017 Presented By Uzo Nwonwu Littler, Kansas City UNwonwu@littler.com, 816.627.4446 Jason Plowman Littler, Kansas City JPlowman@littler.com, 816.627.4435
Background Checks and Ban the Box Legislation November 8, 2017 Presented By Uzo Nwonwu Littler, Kansas City UNwonwu@littler.com, 816.627.4446 Jason Plowman Littler, Kansas City JPlowman@littler.com, 816.627.4435
14 Pathways Summer 2014
 14 Pathways Summer 2014 Pathways Summer 2014 15 Does Immigration Hurt the Poor? By Giovanni Peri The United States has a famously high poverty rate. In recent years, the Great Recession and the slow recovery
14 Pathways Summer 2014 Pathways Summer 2014 15 Does Immigration Hurt the Poor? By Giovanni Peri The United States has a famously high poverty rate. In recent years, the Great Recession and the slow recovery
Unsuccessful Provisional Voting in the 2008 General Election David C. Kimball and Edward B. Foley
 Unsuccessful Provisional Voting in the 2008 General Election David C. Kimball and Edward B. Foley The 2002 Help America Vote Act (HAVA) required most states to adopt or expand procedures for provisional
Unsuccessful Provisional Voting in the 2008 General Election David C. Kimball and Edward B. Foley The 2002 Help America Vote Act (HAVA) required most states to adopt or expand procedures for provisional
The Progressive Era. Part 1: Main Ideas. Write the letter of the best answer. (4 points each)
 Date CHAPTER 9 Form C CHAPTER TEST The Progressive Era Part 1: Main Ideas Write the letter of the best answer. (4 points each) 1. Which of the following was not a result of the introduction of the assembly
Date CHAPTER 9 Form C CHAPTER TEST The Progressive Era Part 1: Main Ideas Write the letter of the best answer. (4 points each) 1. Which of the following was not a result of the introduction of the assembly
QACCI MEDIA ENGAGEMENT
 Overview of Services 03 QACCI MEDIA ENGAGEMENT STATISTI C 1,830,000 INDIVIDUAL S MAKE UP THE HAITIan American MARKET source: 2009 the US Census By any measure: spending power, purchase influence and pass
Overview of Services 03 QACCI MEDIA ENGAGEMENT STATISTI C 1,830,000 INDIVIDUAL S MAKE UP THE HAITIan American MARKET source: 2009 the US Census By any measure: spending power, purchase influence and pass
Immigrant Policy Project. Overview of State Legislation Related to Immigrants and Immigration January - March 2008
 Immigrant Policy Project April 24, 2008 Overview of State Legislation Related to Immigrants and Immigration January - March 2008 States are still tackling immigration related issues in a variety of policy
Immigrant Policy Project April 24, 2008 Overview of State Legislation Related to Immigrants and Immigration January - March 2008 States are still tackling immigration related issues in a variety of policy
RULE 2.10: Judicial Statements on Pending and Impending Cases
 AMERICAN BAR ASSOCIATION CPR POLICY IMPLEMENTATION COMMITTEE COMPARISON OF ABA MODEL CODE OF JUDICIAL CONDUCT AND STATE VARIATIONS RULE 2.10: Judicial Statements on Pending and Impending Cases (A) A judge
AMERICAN BAR ASSOCIATION CPR POLICY IMPLEMENTATION COMMITTEE COMPARISON OF ABA MODEL CODE OF JUDICIAL CONDUCT AND STATE VARIATIONS RULE 2.10: Judicial Statements on Pending and Impending Cases (A) A judge
Geiger Gibson / RCHN Community Health Foundation Research Collaborative. Policy Research Brief # 44
 Geiger Gibson Program in Community Health Policy Geiger Gibson / RCHN Community Health Foundation Research Collaborative Policy Research Brief # 44 How are Migrant Health Centers and their Faring Under
Geiger Gibson Program in Community Health Policy Geiger Gibson / RCHN Community Health Foundation Research Collaborative Policy Research Brief # 44 How are Migrant Health Centers and their Faring Under
