Essential Question: What justifies the limitation or promotion of freedom?
|
|
|
- Nathaniel Carpenter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name _ Period Parent Signature (EC) LESSON PACKET - We The People 7 th Social Studies DUE DATE:_ Essential Question: What justifies the limitation or promotion of freedom? Directions: Read the following summary and answer the questions below: Many challenges remained for the new nation after the end of the Revolutionary War. Americans set up a republic, a government in which citizens rule through elected officials. The Articles of Confederation created a weak national government that could not regulate trade, impose taxes to pay debts, or make states obey its laws. Instability followed. In 1787 state delegates met to address the problems. This Constitutional Convention drafted a Constitution calling for a strong central government, including a chief executive to enforce national laws, a court system, and a two-house legislature. One house, called the senate, included two members from each state. The other house, called the House of Representatives, included members from each state based on the state s population. The Framers of the Constitution believed that the government is based on a contract between people and a ruler, and worried about a central government that might become too powerful. To limit government power, they separated the central government into branches and built in checks and balances. Congress, the legislative branch, makes laws. The executive branch, headed by the president, carries out the laws. Courts make up the judicial branch which makes sure that laws passed by lawmakers and signed by the president are constitutional. The Framers left many important powers to the states. Sharing of powers between a national government and states is called federalism. Federalists who supported the Constitution feared that without a strong government there would be chaos. Opponents feared a strong government could take away individual liberties. For the constitution to become law, 9 of the 13 states had to ratify, or approve, it. All 13 states voted to ratify. Antifederalists won guarantees that a bill of rights, protecting individual freedoms, would be added to the Constitutions amendments, or changes. In 1789 George Washington became the 1 st president. That same year Congress created executive departments. The heads of those departments made up the president s cabinet. Congress also set-up the Supreme Court and other federal courts with the powers to reverse state court rulings. In 1791 the Bill of Rights was added to the Constitution. These 10 amendments guaranteed personal liberties. Secretary of the Treasury Alexander Hamilton found ways to pay the government debts and strengthen the nation s economy. Congress also approved a plan for the nations new capitol to be located in the South. Answer the following using the reading above: 1. Word the author chose to show what the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation created? a. Circle the word that could best replace the word the author chose: STRENGTH / CHAOS b. UNDERLINE 3 things the author listed as facts to support his statement. 2. Why did the Constitutional Convention meet in 1787? Circle correct answer a. Go back to being British b. Fix the Problems in the Articles of Confederation c. Make all the states independent countries 3. Why was the government separated into branches? a. The President is to the Executive branch as the is to the Legislative. b. Which 2 branches create laws that the U C I Branch checks to make sure they are Constitutional? 4. Federalist supported the Constitution and feared that without it there would be H S Anti-Federalist feared a strong government could take away individual I T 5. a. In 1789 this happened that would make Federalist happy: b. In 1791 this happened and would make Anti-Federalist happy:
2 Vocabulary 2pts. Each Articles of Confederation* (p. 154) Bicameral* (p. 165)- James Madison (p. 187)- Federalist /Anti-federalist (p. 170)- Ratify(203)- Federalism (pg. 202)- Marbury v. Madison*(p. R32)- Veto (p. 184)- BIG IDEAS: 10pts. Pg. 158 Pg. 163 Pg. 170 Pg. 182 Pg. 216 Foundations of Our Government 5pts. (Read and study the paragraph & cartoon to complete the activity) If men were angels. No government would be necessary, James Madison said. But since the Framers knew that people were not angels, they knew that government had to establish some basic principles under which all people could live. Those principles are stated in our United States Constitution. The rules laid down in the Constitution have shaped our national life for more than 200 years. While the rules have grown and changed as the United States has changed, the basic principles remain unchanged. 1. What principle from the reading is shown in the cartoon: a. Individual Freedom b. Supreme Court 2. James Madison would be considered a (an). a. Framer b. Angel c. Neither 3. A building cannot stand without a(n). a. Supreme Court b. Constitution c. Cornerstone 4. T/F this cartoon and reading say that the U.S. has never had any change.
3 We the People - Lesson Packet OBJ #1: Draw conclusions about the impact on the new Constitution played by compromise and leaders. What was the biggest fear the U.S. had before creating the Articles of Confederation? What weakness of the Articles was a result of the first fear from above? What two governments were battling for POWER? A. Events leading to the Constitution 1. Fear of Strong National (federal) Government a. King had too much power b. States/Colonies didn t want to be told what to do 2. Articles of Confederation (1st National Government) a. VERY WEAK POWERS b. NO LEADER (Ex. President or King) c. Congress only Federal Branch of Government d. STATES HAVE ALL THE POWER -Have their own: Money / Militias / Laws 3. Shays Rebellion a. Took Volunteers to get Militia Ready b. Scares Founding Fathers (Washington) 4. Convention called to Fix Articles a. 12 States send delegates b. GOAL: Fix the Articles c. Result:Throw Away the Articles d. Problems: How much Federal Power? Big States v. Small States B. Father of the Constitution.. James Madison 1. Came Prepared: Studied governments of the world 2. Creates Virginia Plan: 3 Branches of Government 3. Friends with Thomas Jefferson 1. Draw conclusions about the impact on the new Constitution played by compromise and leaders. What man came the most prepared and is called to as the Father of the Constitution. Name two compromises that saved the Constitution, what topics were they about? What group supported the new Constitution and wrote essays to get it ratified? What government did the Constitution replace? (U.S. Ch. 5 pgs & A.J. Ch. 7 pgs )
4 OBJ #1... Continued COMPROMISE means giving a little to get a little, explain what each of the following GAVE to GET BIG STATES: Gave: Get: LITTLESTATES: Gave: Get: Slave States: Gave: Get: Free STATES: Gave: Get: C. Compromises Save the Constitution 1. GREAT COMPROMISE a. Big States and small states fight for power b. New Jersey Plan (Small State) -Kept much of Articles of Conf. -1 house Legislature -Every State Equal in Congress c. Virginia Plan (BIG STATE!) (Madison) -3 Branches of Government (L, E, J) -Bicameral Legislature (2 Houses) -Leg. Decided by Population d. The Great Compromise -3 Branches of Government -Bicameral Legislature (2 Houses) *Senate- 2per state *House of Rep.- By Population *Made Big & Small States Happy -Executive (A leader) & Judicial (Courts) 2. 3/5 COMPROMISE (Slavery) a. South wants to counts slaves as population -Helps raise their House of Rep. # s b. Deal: Every 3 out of 5 slaves will be counted as part of the population D. Federalist & Anti-Federalist 1. Federalist Support Constitution a. Led by Madison, Washington and Hamilton b. Wrote Federalist Papers...essays supporting the Constitution (We need stronger Government) 2. Anti-Federalist DO NOT Like Constitution a. Led by George Mason b. Believed the Constitution did not protect people s rights -Wanted a list of Rights added E. Approving (Ratify) the Constitution! 1. Needed 9 of 13 States to Approve (All 13 impossible) Delaware 1st state to approve Constitution *1788 NH approves (9th State) *1791 Constitution begins *1791 Bill of Rights becomes part of Constitution
5 We the People - Lesson Packet OBJ #2: Differentiate the roles and duties of the 3 branches of government. Federal Power made the country like a F A Republic is like a because Match these 3 words... -Interprets -Makes -Enforces with the following... Executive: Legislative: Judicial:... In Reference to LAWS A. What the branches of Our Government Represent 1. Form of Government a. Republic- People chose the people to lead Them (Not real Democracy!) 2. Federal Power a. Must be more important than State (1 Nation NOT 13 Countries) B. Article I....Legislative Branch 1. Congress (House of Representatives & Senate) a. GREAT COMPROMISE!!!! *House of Representative (Population) *Senate (2 per state -No matter how big or small) 2. Powers of Congress (Article I Section 8) a. Make and Pass Laws (Bills) -Both House and Senate must pass and agree on the same law before sending it to the president for approval b. Declare War c. Provide Money to Executive to run government d. Approve Presidential Appointments (Senate) -Cabinet Members/Judges/Military Officers e. Impose Taxes f. Approve Treaties with other Countries (Senate) C. Article II....Executive Branch 1. Job is to enforce the laws and put someone in the role of a leader (President 2. Differentiate the roles and duties of the three (3) branches of government three in the U.S. Constitution. Name each, its main job, and it s top position. (U.S. Ch. 6 pgs / A.J. Ch. 7 pgs , Civics In Action pgs ) Branch: -Article I -Article II -Article III People: Job:
6 OBJ #2... Continued 2. Powers... Man of Many Hats a. Head of State (Represents U.S. to the World) -Secretary of State is Cabinet member -Allowed to make treaties with other countries b. Commander in Chief (Head of the Military) -Secretary of Defense is Cabinet Member -Commands military c. Chief Law Enforcer (Enforces Laws) -Attorney General is Cabinet member d. Cabinet Members: People hired to run each area while the president does the other jobs -15 today... Washington had 4-1st 4: Treasury, State, War, Attorney General -Newest: Homeland Defense 3. Term in Office a. Elected every 4 yrs. (Can only serve 8) **Electoral College b. Must be born in US / Must be 35 yrs. old D. Article III.... Judicial Branch 1. Reviews laws and disputes. (Supreme Court) a. Supreme Court *Highest Court in the U.S. (What they say goes) b. Lower Courts *Created By Congress *Listen to cases before the Supreme Court (ex. Military/Appeal/District/Maritime/Civil) 2. Judicial Review a. Courts can decide if laws passed and enforced by Congress & President are Constitutional 3. Terms in Office a. President picks judges and the Senate approves b. Life for all judges (Until you die or go crazy) c. 9 Supreme Court Judges
7 We the People - Lesson Packet OBJ #3: Explain the system of Checks and Balances* found in the Constitution. Create an ACROSTIC POEM that explains checks and balances, because it s all about: P O A. Checks & Balances 1. Each branch has power to keep the other from getting too powerful a. President -Picks Judges/Makes Treaties/Hires People -Veto- Can cancel a law passed by Congress b. Congress (Senate) -OK s President s picks (Can say NO!!) -Can Override Veto c. Judicial -Judicial Review.. declare laws unconstitutional or find people accused by government not guilt W E R Letters can be anywhere in word or term 3. Explain the system of Checks and Balances* found in the U.S. Constitution. Give one example for each branch of government in its use of Checks and Balances against the other two. Identify reasons for Checks and Balances. (U.S. Ch. 5 pg. 167 & Ch. 6 pg / A.J. Ch. 7 pgs & Civics In Action Chart pg. 222)
8 We the People - Lesson Packet OBJ #4: Summarize types of rights protected in the Bill of Rights and the imporatnce of being able to add Amendments to the Constitution. The 1 st 10 Amend. were not called the Bill of Rights until many years after they were adopted... What would be another name that might apply? Create a Symbol for these Amendments: **Your Choice # A. *Amendments = Changes to the Constitution (Article 5) 1. Allows country to change without throwing the entire constitution away 2. Two ways to create Amendments #1-2/3 of House & Senate approve or #2-2/3 of State Convention -Then 3/4 of State Legislatures must approve to become part of Constitution Amendments today (last one in 1992) B. Bill of Rights (First 10 Amendments) 1. Guarantees the basic rights that the government cannot take away. a. Protects the MINORITY (people who disagree or have been out voted ) 1. Freedom- Press/Speech/Religion/Assembly 2. Right to bear Arms (Militia?) 3. No Troops in Homes Jefferson 4. Search & Seizure (Rules) V. 5. Rights of Accused (People who are arrested) Madison 6. Right to Speedy Trial & Jury 7. Jury Trial in Civil Cases pg. 204 U.S. 8. Bail & punishment (No Cruel & Unusual) 9. Powers given to the People 10. Powers given to the States 4. Summarize types of rights protected in the Bill of Rights and the imporatnce of being able to add Amendments to the Constitution. How many amendments made up the Bill of Rights? Name two ways amendments can be added. How many amendments have been added to the Constitution today? U.S. Ch. 5 pgs. 173 & Ch. 6 pgs , / A.J. Ch. 7 pgs , Civ. in Act. pg , Constitution pg )
9 We the People - Lesson Packet OBJ #5: Compare the powers of the Federal government to those given to the State governments Identify how an Anti-federalist would fly these two flags on the same flag pole: -Nevada Flag -U.S. Flag A. 1. of power between state & Federal Gov t 2. Constitution gave power to Gov t a. Articles of Conf. gave more power to B. Article II.. Powers to the States 1. Section 8... Powers given to Congress (Federal) -Things the States can do 2. Section Powers DENIED the States C. Article VI Clause 1. Federal Law State Law (if Conflict) 2. State judges must be bound by the supremacy of Federal Law D. Amend. #10- Bill of Rights: Powers given to Federalism: PG. U.S. 201 Powers SHARED between State & Federal Predict which American war in the future would be fought over Federalism? 5. Compare the powers of the Federal government to those given to the State governments in the constitution. Explain the relationship this creates between the federal and state governments? How does this differ from the Articles of Confederation? Explain what flag should fly on top.. U.S. or Nevada? U.S. Ch. 5 pg. 167 & Ch. 6 pgs. 182, 202/ A.J. Ch. 7 pgs. 205, Civ. in Act. pg. 207, Constitution pg. 241)
10 A. Federalism 1. Sharing of power between state & Federal Gov t 2. Constitution gave more power to Federal Gov t a. Articles of Conf. gave more power to States B. Article II.. Powers Denied to the States 1. Section 8... Powers given to Congress (Federal) -Things the States can NOT do 2. Section Powers DENIED the States C. Article VI Supremacy Clause 1. Federal Law OVER RULES State Law (if Conflict) 2. State judges must be bound by the supremacy of Federal Law D. Amend. #10- Bill of Rights: Powers given to STATES FEDERALISM Copy the Federalism Chart on U.S Pg. 201 Powers SHARED between State FEDERAL POWERS & Federal STATE POWERS
11 Name Period Date Shaping the Constitution 7 th Social Studies we The People 80pts. Directions: Choose 3 (TWO) of the following to complete. You may ONLY Choose one of each shape to complete in making your choice pts. Factual, Creative and strove for excellence / 35-30pts. Use of Facts, Complete and finished in final draft format 29-25pts. Complete with Limited Factual Support & Lacking Detail / 24-20pts. Lack of Facts & Missing Major Detail 19-0pts. Incomplete 40 Pts. 40 Pts. 50 Pts. Read & Analyze the JOHN JAY passage. Draw conclusions from the text to answer the questions. Provide line # s to prove your answers Draw a POLITICAL CARTOON about the Great Compromise that should be colored, labeled and in Final Draft format. Follow the directions to complete. Create a COLLAGE of at least 5 newspaper articles/stories that demonstrate the Bill of Rights in real life. Cut out and label the article with the appropriate amendment(s) it pertains to. Give a short 2 sentence summary of the article. Read & Analyze the GEORGE MASON passage. Draw conclusions from the text to answer the questions. Provide line # s to prove your answers With a partner, create A RAP SONG about Checks & Balances. You must include many facts in your song. Be ready to perform! Create a set of FLASH CARDS for the Bill of Rights. Use the 4x6 in cards provided by your teacher to complete this task. Must include a definition and a Picture. Read & Analyze the JAMES MADISON passage. Draw conclusions from the text to answer the questions. Provide line # s to prove your answers Create a 10- QUESTION MULTIPLE CHOICE TEST on the Separation of Powers. Choose good quality questions and answers. Be prepared to quiz a partner! Create a CHILDREN S BOOK demonstrating at least 5 of the Bill of Rights Amendments. Include illustrations. Be sure to write it in language a younger student could understand.
Articles of Confederation
 Articles of Confederation Do Now How is power divided in our country today? SWBAT Analyze government problems under the Articles of Confederation Activity Review the Articles of Confederation chart and
Articles of Confederation Do Now How is power divided in our country today? SWBAT Analyze government problems under the Articles of Confederation Activity Review the Articles of Confederation chart and
Name: 8 th Grade U.S. History. STAAR Review. Constitution
 8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Constitution FORT BURROWS 2018 VOCABULARY Confederation - A group of loosely connected nations or states that work together for mutual benefit. Republic - A system
8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Constitution FORT BURROWS 2018 VOCABULARY Confederation - A group of loosely connected nations or states that work together for mutual benefit. Republic - A system
Constitution Test Study Guide
 Constitution Test Study Guide Part One: Development of the Constitution Articles of Confederation: America's first government. The 13 states were loosely unified but the government was very weak, with
Constitution Test Study Guide Part One: Development of the Constitution Articles of Confederation: America's first government. The 13 states were loosely unified but the government was very weak, with
United States Constitution 101
 Constitution 101: An Introduction & Overview to the US Constitution United States Constitution 101 This PPT can be used alone or in conjunction with the Consortium s Goal 1 & 2 lessons, available in the
Constitution 101: An Introduction & Overview to the US Constitution United States Constitution 101 This PPT can be used alone or in conjunction with the Consortium s Goal 1 & 2 lessons, available in the
Chapter 5 section 3: Creating the Constitution textbook pages
 Chapter 5 section 3: Creating the Constitution textbook pages 163-168 The Big Idea A new constitution provided a framework for a stronger national government. Main Idea 1:The Constitutional Convention
Chapter 5 section 3: Creating the Constitution textbook pages 163-168 The Big Idea A new constitution provided a framework for a stronger national government. Main Idea 1:The Constitutional Convention
Shays. Daniel Shay 1784 to 1785, unfair taxes, debt and foreclosure Farmer s rebellion to overthrow Mass. Govt.
 Shays Daniel Shay 1784 to 1785, unfair taxes, debt and foreclosure Farmer s rebellion to overthrow Mass. Govt. 1. Constitutional Convention: May to Sept. 1787 2. Divided Convention 9/13 states needed to
Shays Daniel Shay 1784 to 1785, unfair taxes, debt and foreclosure Farmer s rebellion to overthrow Mass. Govt. 1. Constitutional Convention: May to Sept. 1787 2. Divided Convention 9/13 states needed to
2. Divided Convention. 3. Inside the Constitution. Constitution replaced the Articles---becomes the law of the land.
 2. Divided Convention notes7 9/13 states needed to ratify (to approve) Political parties begin Federalists: supported the Constitution The Federalist ---essays support Constitution Anti-Federalists: against
2. Divided Convention notes7 9/13 states needed to ratify (to approve) Political parties begin Federalists: supported the Constitution The Federalist ---essays support Constitution Anti-Federalists: against
Unit 7 Our Current Government
 Unit 7 Our Current Government Name Date Period Learning Targets (What I need to know): I can describe the Constitutional Convention and two compromises that took place there. I can describe the structure
Unit 7 Our Current Government Name Date Period Learning Targets (What I need to know): I can describe the Constitutional Convention and two compromises that took place there. I can describe the structure
Analyze the maps in Setting the Stage. Then answer the following questions and fill out the map as directed.
 Geography Challenge G e o G r a p h y C h a l l e n G e Geography Skills Analyze the maps in Setting the Stage. Then answer the following questions and fill out the map as directed. 1. Label each state
Geography Challenge G e o G r a p h y C h a l l e n G e Geography Skills Analyze the maps in Setting the Stage. Then answer the following questions and fill out the map as directed. 1. Label each state
i n t e r a C t i v e s t u d e n t n o t e b o o k Mapping Activity 11/02/17
 Mapping Activity 11/02/17 Geography Skills Analyze the maps in Setting the Stage. Then answer the following questions and fill out the map as directed. 1. Label each state on the map. Which two states
Mapping Activity 11/02/17 Geography Skills Analyze the maps in Setting the Stage. Then answer the following questions and fill out the map as directed. 1. Label each state on the map. Which two states
3. Popular sovereignty - Rule by the people - People give their consent to be governed by government officials - People have the right to revolution
 Unit I Notes Purposes of Government - Maintain social order - Provide public services - Provide security and defense - Provide for the economy - Governments get authority from: o Their legitimacy o Ability
Unit I Notes Purposes of Government - Maintain social order - Provide public services - Provide security and defense - Provide for the economy - Governments get authority from: o Their legitimacy o Ability
SS.7.C.1.5. Identify how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing of the Constitution
 SS.7.C.1.5. Identify how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing of the Constitution SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the
SS.7.C.1.5. Identify how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing of the Constitution SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the
Why do you think the Framers organized the new country as a republic, when most countries in the world (in 1783) were ruled by a king or queen?
 NAME: Date: U.S. History CHAPTER 7 PACKET ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: 1. What is a constitution? 2. What is a republic? 3. What was the Articles of Confederation? 4. How was state and national power divided under
NAME: Date: U.S. History CHAPTER 7 PACKET ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: 1. What is a constitution? 2. What is a republic? 3. What was the Articles of Confederation? 4. How was state and national power divided under
1. STUDENTS WILL BE ABLE TO IDENTIFY AND EXPLAIN THE WEAKNESSES OF THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION
 SOUTHWESTERN CHRISTIAN SCHOOL UNITED STATES HISTORY STUDY GUIDE # 7 : CREATING A NEW NATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES STUDENTS WILL BE ABLE TO IDENTIFY AND EXPLAIN THE WEAKNESSES OF THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION
SOUTHWESTERN CHRISTIAN SCHOOL UNITED STATES HISTORY STUDY GUIDE # 7 : CREATING A NEW NATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES STUDENTS WILL BE ABLE TO IDENTIFY AND EXPLAIN THE WEAKNESSES OF THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION
Debating the Constitution
 SECTION 3 A Bill of Rights A bill of rights is what the people are entitled to against every government on earth, general or particular; and what no just government should refuse or rest on inference.
SECTION 3 A Bill of Rights A bill of rights is what the people are entitled to against every government on earth, general or particular; and what no just government should refuse or rest on inference.
Vocabulary Match-Up. Name Date Period Workbook Activity
 Name Date Period Workbook Activity Vocabulary Match-Up Chapter 2, Lesson 1 7 Part A Directions Match the vocabulary word in Column 1 with its definition in Column 2. Write the correct letter on each line.
Name Date Period Workbook Activity Vocabulary Match-Up Chapter 2, Lesson 1 7 Part A Directions Match the vocabulary word in Column 1 with its definition in Column 2. Write the correct letter on each line.
Civics Study Guide: Final 2015
 Creation of the Constitution: Virginia Plan: Proposal for how the American government should look. Requested 3 branches of government (executive, judicial, legislative) and wanted the legislative branch
Creation of the Constitution: Virginia Plan: Proposal for how the American government should look. Requested 3 branches of government (executive, judicial, legislative) and wanted the legislative branch
The United States Constitution. The Supreme Law of the Land
 The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land The Articles Prove Unstable Federal gov t could declare war and other foreign affairs Federal gov t have no power to collect taxes, relying only
The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land The Articles Prove Unstable Federal gov t could declare war and other foreign affairs Federal gov t have no power to collect taxes, relying only
Unit 4 Writing the Constitution Concepts to Review
 Unit 4 Writing the Constitution Concepts to Review CAUSE AND EFFECTS OF MAJOR ERAS AND EVENTS IN U.S. HISTORY THROUGH 1877 Writing the Constitution Shays Rebellion Philadelphia Convention 1787 Great Compromise
Unit 4 Writing the Constitution Concepts to Review CAUSE AND EFFECTS OF MAJOR ERAS AND EVENTS IN U.S. HISTORY THROUGH 1877 Writing the Constitution Shays Rebellion Philadelphia Convention 1787 Great Compromise
1 st United States Constitution. A. loose alliance of states. B. Congress lawmaking body. C. 9 states had to vote to pass laws
 1 st United States Constitution A. loose alliance of states B. Congress lawmaking body C. 9 states had to vote to pass laws D. each state had 1 vote in Congress Northwest Ordinance / Land Ordinance division
1 st United States Constitution A. loose alliance of states B. Congress lawmaking body C. 9 states had to vote to pass laws D. each state had 1 vote in Congress Northwest Ordinance / Land Ordinance division
A More Perfect Union. Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation
 A More Perfect Union Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation 1. Eleven of the thirteen states adopted state constitutions. Connecticut and Rhode Island kept its colonial charter as its constitution
A More Perfect Union Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation 1. Eleven of the thirteen states adopted state constitutions. Connecticut and Rhode Island kept its colonial charter as its constitution
When were the Bill of Rights ratified? 1791 What is the purpose of the Preamble? KNOW THE Give an introduction and summary of the Constitution
 STUDY GUIDE - CONSTITUTION FLASH CARDS NAME: Background information What was the first national government of the country called? Why was a new Constitution needed? What powers did Congress have under
STUDY GUIDE - CONSTITUTION FLASH CARDS NAME: Background information What was the first national government of the country called? Why was a new Constitution needed? What powers did Congress have under
Vocabulary for Evolution of Government
 Vocabulary for Evolution of Government Directions Students will make a flash card for each word The flash card must include all the information on the screen (cards will be stamped for completeness) The
Vocabulary for Evolution of Government Directions Students will make a flash card for each word The flash card must include all the information on the screen (cards will be stamped for completeness) The
NEW GOVERNMENT: CONFEDERATION TO CONSTITUTION FLIP CARD
 NEW GOVERNMENT: CONFEDERATION TO CONSTITUTION FLIP CARD Big Ideas: Imagine trying to make a new country from scratch. You ve just had a war with the only leaders you ve ever known, and now you have to
NEW GOVERNMENT: CONFEDERATION TO CONSTITUTION FLIP CARD Big Ideas: Imagine trying to make a new country from scratch. You ve just had a war with the only leaders you ve ever known, and now you have to
May, 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania ~Independence Hall~ Leader: George Washington
 May, 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania ~Independence Hall~ Leader: George Washington -May 1787 Philadelphia Met in Independence Hall in Philadelphia George Washington leader -12 of 13 states Rhode Island
May, 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania ~Independence Hall~ Leader: George Washington -May 1787 Philadelphia Met in Independence Hall in Philadelphia George Washington leader -12 of 13 states Rhode Island
Learning Goal. Main Points 10/24/2012. Discuss the philosophical underpinnings of the U.S. Constitution.
 Learning Goal Discuss the philosophical underpinnings of the U.S. Constitution. Main Points The weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the adoption of a new form of government Federalism becomes
Learning Goal Discuss the philosophical underpinnings of the U.S. Constitution. Main Points The weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the adoption of a new form of government Federalism becomes
The United States Constitution. The Supreme Law of the Land
 The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land Standards SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States
The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land Standards SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States
The American Revolution is over but now the colonists have to decide how they want to frame their government. Take the first 5 minutes of class and
 The American Revolution is over but now the colonists have to decide how they want to frame their government. Take the first 5 minutes of class and imagine that you were a colonist that just fought against
The American Revolution is over but now the colonists have to decide how they want to frame their government. Take the first 5 minutes of class and imagine that you were a colonist that just fought against
4 th Grade U.S. Government Study Guide
 4 th Grade U.S. Government Study Guide Big Ideas: Imagine trying to make a new country from scratch. You ve just had a war with the only leaders you ve ever known, and now you have to step up and lead.
4 th Grade U.S. Government Study Guide Big Ideas: Imagine trying to make a new country from scratch. You ve just had a war with the only leaders you ve ever known, and now you have to step up and lead.
Test Day. October 3-4
 Test Day October 3-4 Sit Wherever Turn in your Study Guide to me When done with test, Turn in to the correct area up front (follow sticky notes) Pick up outline for Unit 3 Pick up a survey for Unit 3 Pick
Test Day October 3-4 Sit Wherever Turn in your Study Guide to me When done with test, Turn in to the correct area up front (follow sticky notes) Pick up outline for Unit 3 Pick up a survey for Unit 3 Pick
Major Problem. Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government.
 The Constitution Major Problem Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government. Why? Feared a government like King George The Constitutional
The Constitution Major Problem Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government. Why? Feared a government like King George The Constitutional
The Constitution I. Considerations that influenced the formulation and adoption of the Constitution A. Roots 1. Religious Freedom a) Puritan
 The Constitution I. Considerations that influenced the formulation and adoption of the Constitution A. Roots 1. Religious Freedom a) Puritan Theocracy (1) 9 of 13 had state church b) Rhode Island (1) Roger
The Constitution I. Considerations that influenced the formulation and adoption of the Constitution A. Roots 1. Religious Freedom a) Puritan Theocracy (1) 9 of 13 had state church b) Rhode Island (1) Roger
THE CONSTITUTION. Chapter 2
 THE CONSTITUTION Chapter 2 ROOTS OF THE CONSTITUTION 2.1 TRADE AND TAXATION 2.1 Mercantilism Strict import/export controls Widely ignored Costly French and Indian War New taxes on sugar and paper items
THE CONSTITUTION Chapter 2 ROOTS OF THE CONSTITUTION 2.1 TRADE AND TAXATION 2.1 Mercantilism Strict import/export controls Widely ignored Costly French and Indian War New taxes on sugar and paper items
Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation
 Name: Date: Chapter 8 Study Guide Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation 1. A constitution is a set of basic principles and laws, usually in written form, that state the powers and duties of a government.
Name: Date: Chapter 8 Study Guide Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation 1. A constitution is a set of basic principles and laws, usually in written form, that state the powers and duties of a government.
The U.S. Constitution. Ch. 2.4 Ch. 3
 The U.S. Constitution Ch. 2.4 Ch. 3 The Constitutional Convention Philadelphia Five months, from May until September 1787 Secret Meeting, closed to outside. Originally intent to revise the Articles of
The U.S. Constitution Ch. 2.4 Ch. 3 The Constitutional Convention Philadelphia Five months, from May until September 1787 Secret Meeting, closed to outside. Originally intent to revise the Articles of
THE CONSTITUTION. How do societies balance individual and community rights? How does social change influence government?
 CHAPTER 5 THE CONSTITUTION NGSSS SS.7.C.1.7 Describe how the Constitution limits the powers of government through separation of powers and checks and balances. ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why do people create,
CHAPTER 5 THE CONSTITUTION NGSSS SS.7.C.1.7 Describe how the Constitution limits the powers of government through separation of powers and checks and balances. ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why do people create,
AKS M 49 C 30 a-d D 32 a-c D 33 a-c D 34 a-b BUILDING A NEW NATION
 AKS M 49 C 30 a-d D 32 a-c D 33 a-c D 34 a-b BUILDING A NEW NATION The official end of the Revolutionary War was the signing of the Treaty of Paris in 1783. The newly independent US and GA now faced the
AKS M 49 C 30 a-d D 32 a-c D 33 a-c D 34 a-b BUILDING A NEW NATION The official end of the Revolutionary War was the signing of the Treaty of Paris in 1783. The newly independent US and GA now faced the
The Critical Period The early years of the American Republic
 The Critical Period 1781-1789 The early years of the American Republic America after the War New Political Ideas: - Greater power for the people Republic: Represent the Public America after the War State
The Critical Period 1781-1789 The early years of the American Republic America after the War New Political Ideas: - Greater power for the people Republic: Represent the Public America after the War State
Constitution Unit Test
 Constitution Unit Test Eighth Amendment Excessive fines cannot be imposed. Excessive bail cannot be required. 1. Which sentence completes this diagram? A. People cannot be forced to be witnesses against
Constitution Unit Test Eighth Amendment Excessive fines cannot be imposed. Excessive bail cannot be required. 1. Which sentence completes this diagram? A. People cannot be forced to be witnesses against
CREATING A GOVERNMENT
 Let us not be afraid to view with a steady eye the dangers with which we are surrounded. Are we not on the eve of a war, which is only to be prevented by the hopes from this convention? CREATING A GOVERNMENT
Let us not be afraid to view with a steady eye the dangers with which we are surrounded. Are we not on the eve of a war, which is only to be prevented by the hopes from this convention? CREATING A GOVERNMENT
10/13/14 GOVERNMENT BY THE STATES OPPOSITION TO THE ARTICLES CHAPTER 5 THE CONSTITUTION OF THE UNITED STATES ( )
 1 CHAPTER 5 THE CONSTITUTION OF THE UNITED STATES (1776 1800) Mr. Anderson, M.Ed., J.D. GOVERNMENT BY THE STATES Early Gov t Articles of Confederation Set of laws to govern the U.S. most power w/ the states
1 CHAPTER 5 THE CONSTITUTION OF THE UNITED STATES (1776 1800) Mr. Anderson, M.Ed., J.D. GOVERNMENT BY THE STATES Early Gov t Articles of Confederation Set of laws to govern the U.S. most power w/ the states
Jeopardy Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400
 Jeopardy 2013-14 Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $500 Q $500 Q $500 Q $500 Final Jeopardy
Jeopardy 2013-14 Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $500 Q $500 Q $500 Q $500 Final Jeopardy
understanding CONSTITUTION
 understanding the CONSTITUTION Contents The Articles of Confederation The Constitutional Convention The Principles of the Constitution The Preamble The Legislative Branch The Executive Branch The Judicial
understanding the CONSTITUTION Contents The Articles of Confederation The Constitutional Convention The Principles of the Constitution The Preamble The Legislative Branch The Executive Branch The Judicial
Chapter 5, Section 3 Creating the Constitution. Pages
 Chapter 5, Section 3 Creating the Constitution Pages 163-168 It didn t take long for people to realize that the Articles of Confederation had many weaknesses. By the mid-1780s most political leaders agreed
Chapter 5, Section 3 Creating the Constitution Pages 163-168 It didn t take long for people to realize that the Articles of Confederation had many weaknesses. By the mid-1780s most political leaders agreed
Gov t was needed to maintain peace. Gov t is not all powerful Power is limited to what the people give to it
 Ordered Government Gov t was needed to maintain peace Limited Government*********** Gov t is not all powerful Power is limited to what the people give to it Representative Government Gov t should serve
Ordered Government Gov t was needed to maintain peace Limited Government*********** Gov t is not all powerful Power is limited to what the people give to it Representative Government Gov t should serve
Quarter One: Unit Four
 SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will identify the weaknesses of the government under the Articles of Confederation (i.e.,
SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will identify the weaknesses of the government under the Articles of Confederation (i.e.,
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton
 Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Signing of the Constitution: http://teachingamericanhistory.org/wp-content/themes/tah-main/images/imported/convention/glanzman.jpg Constitution: https://www.whitehouse.gov/sites/whitehouse.gov/files/images/1600/page_masthead/constitution.jpg
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Signing of the Constitution: http://teachingamericanhistory.org/wp-content/themes/tah-main/images/imported/convention/glanzman.jpg Constitution: https://www.whitehouse.gov/sites/whitehouse.gov/files/images/1600/page_masthead/constitution.jpg
Chapter 25 Section 1. Section 1. Terms and People
 Chapter 25 Terms and People republic a government in which the people elect their representatives unicameral legislature a lawmaking body with a single house whose representatives are elected by the people
Chapter 25 Terms and People republic a government in which the people elect their representatives unicameral legislature a lawmaking body with a single house whose representatives are elected by the people
FEDERAL GOVERNMENT GOVT Limited Government & Representative Government September 18, Dr. Michael Sullivan. MoWe 5:30-6:50 MoWe 7-8:30
 Limited Government & Representative Government September 18, 2017 FEDERAL GOVERNMENT GOVT 2305 MoWe 5:30-6:50 MoWe 7-8:30 Dr. Michael Sullivan TODAY S AGENDA Current Events Limited Government Representative
Limited Government & Representative Government September 18, 2017 FEDERAL GOVERNMENT GOVT 2305 MoWe 5:30-6:50 MoWe 7-8:30 Dr. Michael Sullivan TODAY S AGENDA Current Events Limited Government Representative
Quarter One: Unit Four
 SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will identify the weaknesses of the government under the Articles of Confederation (i.e.,
SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will identify the weaknesses of the government under the Articles of Confederation (i.e.,
America: The Last Best Hope Chapter 4 Reflection and Choice
 America: The Last Best Hope Chapter 4 Reflection and Choice 1. Under the Articles of Confederation, Congress had all of the following powers EXCEPT A settle disputes between the states B borrow money C
America: The Last Best Hope Chapter 4 Reflection and Choice 1. Under the Articles of Confederation, Congress had all of the following powers EXCEPT A settle disputes between the states B borrow money C
The Relationship between Britain and its American Colonies Changes
 Packet 3: Page 1 The Relationship between Britain and its American Colonies Changes What were the differing interests of the colonial regions? How and why did the relationship between Britain and the colonies
Packet 3: Page 1 The Relationship between Britain and its American Colonies Changes What were the differing interests of the colonial regions? How and why did the relationship between Britain and the colonies
Unit 2: A New Nation
 Unit 2: A New Nation Establishing a Government Articles of Confederation Nation s first set of laws Limited central gov. Confederation would have more power Ratified in 1781, failed b/c it did not give
Unit 2: A New Nation Establishing a Government Articles of Confederation Nation s first set of laws Limited central gov. Confederation would have more power Ratified in 1781, failed b/c it did not give
[ 3.1 ] An Overview of the Constitution
![[ 3.1 ] An Overview of the Constitution [ 3.1 ] An Overview of the Constitution](/thumbs/86/94779990.jpg) [ 3.1 ] An Overview of the Constitution [ 3.1 ] An Overview of the Constitution Learning Objectives Understand the basic outline of the Constitution. Understand the basic principles of the Constitution:
[ 3.1 ] An Overview of the Constitution [ 3.1 ] An Overview of the Constitution Learning Objectives Understand the basic outline of the Constitution. Understand the basic principles of the Constitution:
I. Making the Constitution: (includes The Articles of Confederation, Preamble, and Federalists vs. Antifederalists )
 Civics 3 rd Quarter Civics Study Guide Page 1 Student Name: Civics 3 rd Quarter Civics Study Guide Date: In completing this study guide, you will need to draw on your knowledge from throughout the 3 rd
Civics 3 rd Quarter Civics Study Guide Page 1 Student Name: Civics 3 rd Quarter Civics Study Guide Date: In completing this study guide, you will need to draw on your knowledge from throughout the 3 rd
STAAR OBJECTIVE: 3. Government and Citizenship
 STAAR OBJECTIVE: 3 Government and Citizenship 1. What is representative government? A. Government that represents the interests of the king. B. Government in which elected officials represent the interest
STAAR OBJECTIVE: 3 Government and Citizenship 1. What is representative government? A. Government that represents the interests of the king. B. Government in which elected officials represent the interest
The Constitution. Karen H. Reeves
 The Constitution Karen H. Reeves Toward a New Union Annapolis Convention (Sept. 1786) Met to determine commercial regulation Nationalists called for Constitutional Convention Constitutional Convention
The Constitution Karen H. Reeves Toward a New Union Annapolis Convention (Sept. 1786) Met to determine commercial regulation Nationalists called for Constitutional Convention Constitutional Convention
The Federalist Papers
 The Federalist Papers If men were angels, no government would be necessary. James Madison During the Revolutionary War, Americans set up a new national government. They feared a strong central government.
The Federalist Papers If men were angels, no government would be necessary. James Madison During the Revolutionary War, Americans set up a new national government. They feared a strong central government.
Ch. 6 Creating the Constitution /EQ:
 Ch. 6 Creating the Constitution /EQ: 6.1 Introduction Like Washington, most Americans did not want to be ruled by a monarch. What they did want, though, was an effective government. Articles of Confederation,
Ch. 6 Creating the Constitution /EQ: 6.1 Introduction Like Washington, most Americans did not want to be ruled by a monarch. What they did want, though, was an effective government. Articles of Confederation,
Name Date Hour. Mid-Term Exam Study Guide
 Name Date Hour Mid-Term Exam Study Guide Following is a list of concepts and terms that may appear on the mid-term exam. Some definitions have been provided. **Exam Tip: Take extra time on graph and reading
Name Date Hour Mid-Term Exam Study Guide Following is a list of concepts and terms that may appear on the mid-term exam. Some definitions have been provided. **Exam Tip: Take extra time on graph and reading
The Articles vs. the Constitution Articles of Confederation. U.S. Constitution A Firm League of Friendship
 USHC 1.4 Analyze how dissatisfactions with the government under the Articles of Confederation were addressed with the writing of the Constitution of 1787, including the debates and compromises reached
USHC 1.4 Analyze how dissatisfactions with the government under the Articles of Confederation were addressed with the writing of the Constitution of 1787, including the debates and compromises reached
Creating a Nation Test Review
 Creating a Nation Test Review Question #1: Multiple Choice The Northwest ordinance of 1787 is important because. A. It sent troops to the Northwest to protect the colonies from Native Americans. B. It
Creating a Nation Test Review Question #1: Multiple Choice The Northwest ordinance of 1787 is important because. A. It sent troops to the Northwest to protect the colonies from Native Americans. B. It
3. What does it mean to be democratic? a government in which the people govern themselves, fair elections
 Civics FINAL EXAM Study Guide Name Class EXAM DATE Topics Covered w/ Textbook location: Citizenship CH3 Types/Forms of Government CH3 Foundations of American Govt. CH4 U.S. Government then and now CH5
Civics FINAL EXAM Study Guide Name Class EXAM DATE Topics Covered w/ Textbook location: Citizenship CH3 Types/Forms of Government CH3 Foundations of American Govt. CH4 U.S. Government then and now CH5
Constitutional Convention Issues
 Constitutional Convention Issues Key Conflicts: Large vs Small States Slave vs Population State vs Federal Authority The debate between states; and the debate between federal verses state governments Constitutional
Constitutional Convention Issues Key Conflicts: Large vs Small States Slave vs Population State vs Federal Authority The debate between states; and the debate between federal verses state governments Constitutional
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of American Government
 Chapter 2: The Beginnings of American Government United States Government Fall, 2017 Origins of American Political Ideals Colonial Period Where did ideas for government in the colonies come from? Largely,
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of American Government United States Government Fall, 2017 Origins of American Political Ideals Colonial Period Where did ideas for government in the colonies come from? Largely,
The Founding of American Democracy By Jessica McBirney 2016
 Name: Class: The Founding of American Democracy By Jessica McBirney 2016 The American colonies rose up in 1776 against Britain with the goal of becoming an independent state. They sent the King of England
Name: Class: The Founding of American Democracy By Jessica McBirney 2016 The American colonies rose up in 1776 against Britain with the goal of becoming an independent state. They sent the King of England
Foundations of American Government
 Foundations of American Government Formation of the first governments of the 13 colonies Highly Influenced by: - Contracts, Juries, stare decisis English Tradition Natural rights: Consent of the governed:
Foundations of American Government Formation of the first governments of the 13 colonies Highly Influenced by: - Contracts, Juries, stare decisis English Tradition Natural rights: Consent of the governed:
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes
 Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
LESSON TWO: THE FEDERALIST PAPERS
 LESSON TWO: THE FEDERALIST PAPERS OVERVIEW OBJECTIVES Students will be able to: Identify the Articles of Confederation and explain why it failed. Explain the argument over the need for a bill of rights
LESSON TWO: THE FEDERALIST PAPERS OVERVIEW OBJECTIVES Students will be able to: Identify the Articles of Confederation and explain why it failed. Explain the argument over the need for a bill of rights
RESULTS OF THE AMERICAN REVOLUTION 3) NO CHANGE FOR WOMEN OR AFRICAN AMERICANS 4) LOST TRADE WITH BRITISH MARKETS
 RESULTS OF THE AMERICAN REVOLUTION 1) NO CHANGE IN POLITICAL POWER 2) NO CHANGE IN ECONOMIC POWER 3) NO CHANGE FOR WOMEN OR AFRICAN AMERICANS 4) LOST TRADE WITH BRITISH MARKETS 5) ECONOMIC DEPRESSION WHAT
RESULTS OF THE AMERICAN REVOLUTION 1) NO CHANGE IN POLITICAL POWER 2) NO CHANGE IN ECONOMIC POWER 3) NO CHANGE FOR WOMEN OR AFRICAN AMERICANS 4) LOST TRADE WITH BRITISH MARKETS 5) ECONOMIC DEPRESSION WHAT
The Big Idea The U.S. Constitution balances the powers of the federal government among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches.
 Understanding the Constitution The Big Idea The U.S. Constitution balances the powers of the federal government among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches. Main Ideas The framers of the Constitution
Understanding the Constitution The Big Idea The U.S. Constitution balances the powers of the federal government among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches. Main Ideas The framers of the Constitution
FEDERALISTS, ANTI-FEDERALISTS AND THE CONSTITUTION SS.7.C.1.8
 FEDERALISTS, ANTI-FEDERALISTS AND THE CONSTITUTION SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the ratification of the Constitution and inclusion of a bill of
FEDERALISTS, ANTI-FEDERALISTS AND THE CONSTITUTION SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the ratification of the Constitution and inclusion of a bill of
Semester 2 CIVICS: What You Will Need to Know! The U.S. Constitution
 The U.S. Constitution The Seven Articles (LEJ RASR) Article I The Legislative Branch o Makes the Laws o Includes a Bicameral Congress with a Senate and House of Representatives Article II The Executive
The U.S. Constitution The Seven Articles (LEJ RASR) Article I The Legislative Branch o Makes the Laws o Includes a Bicameral Congress with a Senate and House of Representatives Article II The Executive
Unit One Reading Guide DEFINING DEMOCRACY
 Name Period Textbook: Chapter One Unit One Reading Guide DEFINING DEMOCRACY Direct Democracy Representative Democracy Core Beliefs of American Democracy Individual liberty Popular consent Equality of opportunity
Name Period Textbook: Chapter One Unit One Reading Guide DEFINING DEMOCRACY Direct Democracy Representative Democracy Core Beliefs of American Democracy Individual liberty Popular consent Equality of opportunity
Types of Government/Roots/Principles/ Goals
 Types of Government/Roots/Principles/ Goals 1. Match the Type of Government to the correct part of the chart. Type of Gov t- put these in the appropriate box Type of Government Definition Monarchy Decisions
Types of Government/Roots/Principles/ Goals 1. Match the Type of Government to the correct part of the chart. Type of Gov t- put these in the appropriate box Type of Government Definition Monarchy Decisions
Land Ordinance of 1785
 Unit 3 SSUSH5 Investigate specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States Constitution. a. Examine the strengths of the Articles of Confederation,
Unit 3 SSUSH5 Investigate specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States Constitution. a. Examine the strengths of the Articles of Confederation,
Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution
 Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution The Articles of Confederation After declaring independence from Britain in 1776, Congress tried to unite the states under one national government. However, many feared
Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution The Articles of Confederation After declaring independence from Britain in 1776, Congress tried to unite the states under one national government. However, many feared
Chapter 2. Government
 Chapter 2 Government The way the United States government is organized, its powers, and its limitations, are based on ideas about government that were brought to these shores by the English colonist. Three
Chapter 2 Government The way the United States government is organized, its powers, and its limitations, are based on ideas about government that were brought to these shores by the English colonist. Three
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes
 Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
What types of things did the new states do to make the governments more democratic?
 Chapter 8 Confederation to Constitution pg. 218 241 8 1 The Confederation Era pg. 221 225 Moving West and New State Governments Into which areas did American settlement expand in the late 1700s? What types
Chapter 8 Confederation to Constitution pg. 218 241 8 1 The Confederation Era pg. 221 225 Moving West and New State Governments Into which areas did American settlement expand in the late 1700s? What types
ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION TO THE CONSTITUTION
 ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION TO THE CONSTITUTION Articles of Confederation The representatives of the thirteen states agree to create a confederacy called the United States of America, in which each state
ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION TO THE CONSTITUTION Articles of Confederation The representatives of the thirteen states agree to create a confederacy called the United States of America, in which each state
Chapter 3: The Constitution
 Chapter 3: The Constitution United States Government Week on October 2, 2017 The Constitution: Structure Pictured: James Madison Structure Preamble: introduction that states why the Constitution was written
Chapter 3: The Constitution United States Government Week on October 2, 2017 The Constitution: Structure Pictured: James Madison Structure Preamble: introduction that states why the Constitution was written
THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION. Compromises Federalists v. Anti-Federalists
 THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Compromises Federalists v. Anti-Federalists QUICK REVIEW: FIND SOMEONE WHO Second Continental Congress Drafting of the Articles of Confederation Weaknesses International Relations
THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Compromises Federalists v. Anti-Federalists QUICK REVIEW: FIND SOMEONE WHO Second Continental Congress Drafting of the Articles of Confederation Weaknesses International Relations
Charles de Montesquieu
 Unit III He first created the idea of consent of the governed where people have a vote in who leads them (democracy). Every person has the right to life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness. John Locke
Unit III He first created the idea of consent of the governed where people have a vote in who leads them (democracy). Every person has the right to life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness. John Locke
New Nation. establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s
 New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
New Nation. establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s
 New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
Module 1.2 U.S. Constitutional Framework. Constitutional Trivia! Overview of Lecture 6/4/2008
 Module 1.2 U.S. Constitutional Framework Prof. Bryan McQuide University of Idaho Summer 2008 Constitutional Trivia! Which of the following Presidents signed the U.S. Constitution? George Washington John
Module 1.2 U.S. Constitutional Framework Prof. Bryan McQuide University of Idaho Summer 2008 Constitutional Trivia! Which of the following Presidents signed the U.S. Constitution? George Washington John
Chapter 6 Citizenship and the Constitution
 Chapter 6 Citizenship and the Constitution Section Notes Understanding the Constitution The Bill of Rights Rights and Responsibilities of Citizenship Quick Facts Separation of Powers Checks and Balances
Chapter 6 Citizenship and the Constitution Section Notes Understanding the Constitution The Bill of Rights Rights and Responsibilities of Citizenship Quick Facts Separation of Powers Checks and Balances
BEGINNINGS: Political essentials and foundational ideas
 BEGINNINGS: Political essentials and foundational ideas 1689 LOCKE S SECOND TREATISE ON GOVERNMENT: Natural Rights: Life, Liberty & Property which existed before government Legitimate government depends
BEGINNINGS: Political essentials and foundational ideas 1689 LOCKE S SECOND TREATISE ON GOVERNMENT: Natural Rights: Life, Liberty & Property which existed before government Legitimate government depends
The Constitution: From Ratification to Amendments. US Government Fall, 2014
 The Constitution: From Ratification to Amendments US Government Fall, 2014 Origins of American Government Colonial Period Where did ideas for government in the colonies come from? Largely, from England
The Constitution: From Ratification to Amendments US Government Fall, 2014 Origins of American Government Colonial Period Where did ideas for government in the colonies come from? Largely, from England
The U.S. Constitution: Who, What, Where, When, Why & How
 The U.S. Constitution: Who, What, Where, When, Why & How 'a ^Va&o/z Fighting between the American colonists and British forces under King George III was in its second year when the Declaration of Independence
The U.S. Constitution: Who, What, Where, When, Why & How 'a ^Va&o/z Fighting between the American colonists and British forces under King George III was in its second year when the Declaration of Independence
Name: Articles of Confederation. Problems after the war: 1. What were the problems Facing the 2 nd Continental Congress after the war? 2.
 Articles of Confederation Name: Problems after the war: 1. What were the problems Facing the 2 nd Continental Congress after the war? 2. 3. 4. What are the Articles of Confederation? What were the weaknesses
Articles of Confederation Name: Problems after the war: 1. What were the problems Facing the 2 nd Continental Congress after the war? 2. 3. 4. What are the Articles of Confederation? What were the weaknesses
Articles of Confederation September 18, 2007
 Articles of Confederation September 18, 2007 Powers Given to Congress under the Articles Weaknesses under the Articles Results of the Articles during the Critical Period Use Page 44-46 to analyze the effects
Articles of Confederation September 18, 2007 Powers Given to Congress under the Articles Weaknesses under the Articles Results of the Articles during the Critical Period Use Page 44-46 to analyze the effects
Ratification of the Constitution. Issues
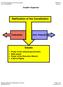 Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
FORMING A NEW GOVERNMENT
 FORMING A NEW GOVERNMENT These questions are in random order. They will be in a different order in class tomorrow. Seven Principles Checks & Balances Federalism Individual Rights Limited Government Popular
FORMING A NEW GOVERNMENT These questions are in random order. They will be in a different order in class tomorrow. Seven Principles Checks & Balances Federalism Individual Rights Limited Government Popular
America: Pathways to the Present. Chapter 5. The Constitution of the United States ( )
 America: Pathways to the Present Chapter 5 The Constitution of the United States (1776 1800) Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey. All
America: Pathways to the Present Chapter 5 The Constitution of the United States (1776 1800) Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey. All
Foundations of Government
 Class: Date: Foundations of Government Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. This is NOT a feature of all the states in today's
Class: Date: Foundations of Government Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. This is NOT a feature of all the states in today's
3: A New Plan of Government. Essential Question: How Do Governments Change?
 3: A New Plan of Government Essential Question: How Do Governments Change? The Constitution s Source Guiding Question: From where did the Framers of the Constitution borrow their ideas about government?
3: A New Plan of Government Essential Question: How Do Governments Change? The Constitution s Source Guiding Question: From where did the Framers of the Constitution borrow their ideas about government?
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 2 The Three Branches of Government ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does the U.S. Constitution structure government and divide power between the national and state governments? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary
Lesson 2 The Three Branches of Government ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does the U.S. Constitution structure government and divide power between the national and state governments? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary
Who attended the Philadelphia Convention? How was it organized? We the People, Unit 3 Lesson 12
 Who attended the Philadelphia Convention? How was it organized? We the People, Unit 3 Lesson 12 A convention has been called to rewrite Redwood school constitution. We need some delegates (representatives).
Who attended the Philadelphia Convention? How was it organized? We the People, Unit 3 Lesson 12 A convention has been called to rewrite Redwood school constitution. We need some delegates (representatives).
