Constitution Day: Federalists vs. Anti-Federalists Introduction Massachusetts History and Social Science Curriculum Frameworks Content Standards
|
|
|
- Job Burke
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Constitution Day: Federalists vs. Anti-Federalists Adapted from the Stanford History Education Group s Federalists and Anti-Federalists Lesson Plan Introduction In this lesson, students will study the debate between Federalists and Anti-Federalists over the ratification of the Constitution, with a focus on representation in Congress. Students will be asked to analyze two primary sources, evaluate a position, debate with their peers, and write a short statement defending their position with evidence from the provided sources. The notes, primary sources, and graphic organizer have been adapted from the Stanford History Education Group s Federalists and Anti-Federalists Lesson Plan, as cited above. This lesson is a great introduction to the ideas covered in the Federalist No. 10. Massachusetts History and Social Science Curriculum Frameworks Content Standards Grade 8: United States and Massachusetts Government and Civic Life Topic 2: The development of the United States government Supporting Question: How did the framers of the Constitution attempt to address issues of power and freedom in the design of the new political system? 2-8. Identify the various leaders of the Constitutional Convention and analyze the major issues (e.g., distribution of political power, rights of individuals, representation and rights of states, slavery ) they debated and how the issues were resolved Compare and contrast key ideas debated between the Federalists and Anti-Federalists over ratification of the Constitution (e.g., federalism, factions, checks and balances, independent judiciary, republicanism, limited government ). United States History I Topic 1: Origins of the Revolution and the Constitution Supporting Question: How did events of the Revolutionary period inform the ideas in the Constitution? 1-8. Describe the Constitutional Convention, the roles of specific individuals (e.g. Benjamin Franklin, Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, George Washington, Roger Sherman, Edmund Randolph), and the conflicts and compromises (e.g., compromises over representation, slavery, the executive branch, and ratification). Guiding Questions 1. What types of governments did Federalists and Anti-Federalists prefer? 2. How should the people of the United States be represented in Congress? 3. How many people should one district in the House of Representatives encompass?
2 4. How fair and effective is the current system of representation in the United States Congress? Learning Objectives 1. Students will be able to identify the Federalist and Anti-Federalist positions on representation during the ratification of the Constitution. 2. Students will be able to analyze primary source documents. 3. Students will be able to debate the Federalist and Anti-Federalist positions on representation. 4. Students will be able to evaluate two opposing positions on the nature of popular representation in government orally and in writing. Materials 1. Sticky notes 2. White board 3. Computer and digital projector 4. Constitution Day: Federalists vs. Anti-Federalists PowerPoint 5. Constitution Day: Federalists vs. Anti-Federalists primary source document excerpts 6. Constitution Day: Federalists vs. Anti-Federalists graphic organizer 7. Constitution Day: Federalists vs. Anti-Federalists student debate handout 8. Constitution Day: Federalists vs. Anti-Federalists post-debate paragraph Assessments : 1. Graphic organizer 2. Post-debate paragraph Key Terms to Know and Identify : 1) Ratify : to give formal consent, making a document official 2) Representative : a member of the House of Representatives who advocates for the people of their district 3) House of Representatives : the lower house of Congress. Representation allotted to states based on population 4) Senate : the upper house of Congress. Representation allocated equally to all states (2 Senators per state) 5) Constitution of 1787 : the document that provides the legal framework for the United States government 6) Yeoman : a small landowning farmer 7) Tyranny : cruel and oppressive rule 8) Direct Democracy : people vote on laws and policies themselves 9) Representative Democracy : people vote for delegates (representatives) to vote on laws and policies on their behalf Estimated Time : 120 minutes
3 Grade Level : 8-12 Lesson Procedures : Activator : (Slide 2) 1. Before students arrive, write the following numbers on the board, outside of the display area of the PowerPoint: a. 1,000 b. 15,000 c. 30,000 d. 100,000 e. 500,000 f. 1,000, Display slide 2 of the Constitution Day: Federalists vs. Anti-Federalists PowerPoint to on the projector. 3. As they arrive, greet students and provide each student with a 3 x 5 sticky note. 4. Display the following question (slide 2 of the lesson PowerPoint) on the board: how many people should be represented by one person in Congress? Please choose one of the following answers and briefly defend your answer. 5. Ask students to answer the question and attach their sticky note to the board under the appropriate number. 6. Read student responses aloud to the class. Ask students to clarify and/or expand open their answers as necessary. 7. Inform students that this issue was a major controversy during the ratification of the Constitution, and that they will be debating this topic today among small groups. Student Inquiry Development (Slides 3-6) 1. Present the guiding questions on slide 3 to the class. 2. Reiterate the question from the activator: how many people should be represented by one person in Congress? 3. Present and discuss the information on slides 4 and In pairs, ask students to generate three to five follow-up questions that build upon the central question above. Ask students to categorize questions as closed (those that can be answered with a yes, no, or simple one word answer) and open (those that cannot be answered with a yes, no, or simple one word answer). 5. Discuss follow-up questions as a class. As you discuss the questions, as students to: a. Prioritize the sustainability of the questions for deeper research/inquiry b. How the questions could be used in preparation of the upcoming debate Lecture/PowerPoint/Video/Brief Discussion (Slides 7-13) 1. Present slides 7-13 of the accompanying PowerPoint presentation. 2. Background lecture should include talking points on the following:
4 a. In 1787, a Constitutional Convention was called to discuss amending the Articles of Confederation, the first document organizing the government of the United States. b. It soon became clear that the delegates needed to draft an entirely new document, what would become the Constitution, the document that still structures the federal (national) government of the United States today. c. One of the most contentious debates was over how representatives from each state should be chosen for the national legislature (Congress). More populous states wanted representation based on population, and less populous states wanted equal representation for each state. d. The Great Compromise (a combination of the New Jersey and Virginia plans) solved this problem. Congress (the national legislature) would have two houses. The lower house, to be called the House of Representatives, would have representation based on population. The upper house, to be called the Senate, would have equal representation (two members from every state, regardless of population). e. After the Constitution was written, it needed to be ratified (approved) by nine states. During this process, a fierce debate emerged. f. The two primary camps in the debate were the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists. The Federalists believed in a strong central government, with one representative per 30,000 people, and believed the Constitution should be ratified as written. Anti-Federalists were concerned the Constitution did not protect the rights and liberties of the people and the states. They also believed representatives should be elected by smaller groups of people, and that states should have more power than the central government. g. Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay were Federalists who collectively authored 85 articles, collectively known as the Federalist Papers, under the pseudonym Publius. Important Anti-Federalist writings were published by Thomas Jefferson, Brutus, and Cato. h. Today, you will be reading excerpts from the debate over ratification in New York. New Hampshire was the ninth state to ratify the Constitution on June 21, 1788, legally establishing the new government. However, as a large and politically diverse state, New York s ratification was seen as necessary for the success of the new Constitution. The debate over ratification in New York was arguably the most heated of any state. Melancton Smith was an Anti-Federalist delegate to the Constitutional Convention from New York. Alexander Hamilton was a Federalist delegate delegate to the Constitutional Convention from New York, and one of the authors of The Federalist Papers. i. New York ratified the Constitution on July 26, 1788, thereby solidifying the new government. While the Anti-Federalists may have lost the battle over ratification in New York, their arguments helped bolster the cause of the Bill of Rights, eventually added to the Constitution as Amendments 1-10 in 1791.
5 j. The result: the Constitution was ratified by all thirteen states, but with the promise that a Bill of Rights be included to protect the rights and liberties of the people and the states. On December 15, 1791, the Bill of Rights was officially ratified, adding Amendments 1-10 to the Constitution. Some of the protections in the Bill of Rights include freedom of speech, freedom of religion, the right to a trial by a jury of peers, and the protection against unreasonable search and seizures. However, the debate over how power should be divided between the federal and state governments has been a constant throughout U.S. history, and is still a source of contention today. Primary Source Document Analysis (Slides 14 and 15) 1. Pre-teach the key terms to know and identify on slide 14 using 7-step process 2. Assign students to small groups (ideally 4 students each) and provide all students with a copy of the primary sources and corresponding graphic organizer. (slide 15) 3. Inform students that they should utilize partner-reading. This is particularly helpful for English Language students. 4. Ask students to complete the graphic organizer within their assigned groups Small Group Debates and Final Paragraph (Slides 16-18) 1. Assign each small group a position and provide all students with a copy of the Student Debate Handout. Inform students that they will have ten minutes with their group to prepare for the debate, using the primary documents, graphic organizer, and lecture notes as sources. Remind students to utilize the inquiry questions they developed earlier in the lesson to help guide their arguments, as well as the questions on slide Pair small groups to debate one another. 3. Monitor debates. Students should be given at least minutes to debate. 4. At the end of the allotted time given to the debates, ask the groups debating each other to arrive at a consensus. Discuss as a class. 5. Ask all students to write one paragraph using evidence from the texts and reasoning from the debate to defend an argument. Students may choose to defend either side of the debate, regardless of their group s consensus. (slide 17) Lesson Extension This lesson provides a great introduction to the ideas discussed in the Federalist Papers #10.
Constitutional Convention
 2014 Delegates Remember a delegate is someone who is chosen to speak for others, or to represent them. The delegates represented each of the states and consisted of: Wealthy and educated landowners, business
2014 Delegates Remember a delegate is someone who is chosen to speak for others, or to represent them. The delegates represented each of the states and consisted of: Wealthy and educated landowners, business
AIM: How did the Articles of Confederation impact the U.S.?
 AIM: How did the Articles of Confederation impact the U.S.? Do Now: How do you think Hale Charter Academy would function if we got rid of the assistant principal, and the dean, and we allowed the individual
AIM: How did the Articles of Confederation impact the U.S.? Do Now: How do you think Hale Charter Academy would function if we got rid of the assistant principal, and the dean, and we allowed the individual
CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION
 CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Objectives Why did the Constitutional Convention draft a new plan for government? How did the rival plans for the new government differ? What other conflicts required the Framers
CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Objectives Why did the Constitutional Convention draft a new plan for government? How did the rival plans for the new government differ? What other conflicts required the Framers
FEDERALISTS, ANTI-FEDERALISTS AND THE CONSTITUTION SS.7.C.1.8
 FEDERALISTS, ANTI-FEDERALISTS AND THE CONSTITUTION SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the ratification of the Constitution and inclusion of a bill of
FEDERALISTS, ANTI-FEDERALISTS AND THE CONSTITUTION SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the ratification of the Constitution and inclusion of a bill of
Chapter 3 Constitution. Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook
 Chapter 3 Constitution Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on www.pknock.com Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from
Chapter 3 Constitution Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on www.pknock.com Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from
Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50
 Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50 The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from religious persecution Economic opportunity Independent
Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50 The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from religious persecution Economic opportunity Independent
Establishing A New Government: Creating a Government. Chapter 4 Concept 2
 Establishing A New Government: Creating a Government Chapter 4 Concept 2 4.2 Creating a Government How did the decisions made at the Constitutional Convention affect the balance of power in the new nation?
Establishing A New Government: Creating a Government Chapter 4 Concept 2 4.2 Creating a Government How did the decisions made at the Constitutional Convention affect the balance of power in the new nation?
Major Problem. Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government.
 The Constitution Major Problem Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government. Why? Feared a government like King George The Constitutional
The Constitution Major Problem Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government. Why? Feared a government like King George The Constitutional
Constitutional Democracy: Promoting Liberty and Self-Government. Chapter 2
 Constitutional Democracy: Promoting Liberty and Self-Government Chapter 2 Before the Constitution: Colonial and Revolutionary Experiences The Rights of Englishmen Life, liberty and property to which all
Constitutional Democracy: Promoting Liberty and Self-Government Chapter 2 Before the Constitution: Colonial and Revolutionary Experiences The Rights of Englishmen Life, liberty and property to which all
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton
 Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
Chapter 5, Section 3 Creating the Constitution. Pages
 Chapter 5, Section 3 Creating the Constitution Pages 163-168 It didn t take long for people to realize that the Articles of Confederation had many weaknesses. By the mid-1780s most political leaders agreed
Chapter 5, Section 3 Creating the Constitution Pages 163-168 It didn t take long for people to realize that the Articles of Confederation had many weaknesses. By the mid-1780s most political leaders agreed
The United States Constitution. The Supreme Law of the Land
 The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land The Articles Prove Unstable Federal gov t could declare war and other foreign affairs Federal gov t have no power to collect taxes, relying only
The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land The Articles Prove Unstable Federal gov t could declare war and other foreign affairs Federal gov t have no power to collect taxes, relying only
Chapter 5 section 3: Creating the Constitution textbook pages
 Chapter 5 section 3: Creating the Constitution textbook pages 163-168 The Big Idea A new constitution provided a framework for a stronger national government. Main Idea 1:The Constitutional Convention
Chapter 5 section 3: Creating the Constitution textbook pages 163-168 The Big Idea A new constitution provided a framework for a stronger national government. Main Idea 1:The Constitutional Convention
OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS
 CHAPTER 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS The colonists brought with them to North America knowledge of the English political system, including three key ideas about government.
CHAPTER 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS The colonists brought with them to North America knowledge of the English political system, including three key ideas about government.
The Constitutional Convention. Chapter 2 Section 4
 The Constitutional Convention Chapter 2 Section 4 Constitutional Convention May 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 74 delegates allowed, 55 attended, 39 signed final Delegates to the Convention Had lots of
The Constitutional Convention Chapter 2 Section 4 Constitutional Convention May 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 74 delegates allowed, 55 attended, 39 signed final Delegates to the Convention Had lots of
Organization & Agreements
 Key Players Key Players Key Players George Washington unanimously chosen to preside over the meetings. Benjamin Franklin now 81 years old. Gouverneur Morris wrote the final draft. James Madison often called
Key Players Key Players Key Players George Washington unanimously chosen to preside over the meetings. Benjamin Franklin now 81 years old. Gouverneur Morris wrote the final draft. James Madison often called
Ratification of the Constitution. Issues
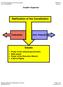 Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
America: The Last Best Hope Chapter 4 Reflection and Choice
 America: The Last Best Hope Chapter 4 Reflection and Choice 1. Under the Articles of Confederation, Congress had all of the following powers EXCEPT A settle disputes between the states B borrow money C
America: The Last Best Hope Chapter 4 Reflection and Choice 1. Under the Articles of Confederation, Congress had all of the following powers EXCEPT A settle disputes between the states B borrow money C
United States Constitution 101
 Constitution 101: An Introduction & Overview to the US Constitution United States Constitution 101 This PPT can be used alone or in conjunction with the Consortium s Goal 1 & 2 lessons, available in the
Constitution 101: An Introduction & Overview to the US Constitution United States Constitution 101 This PPT can be used alone or in conjunction with the Consortium s Goal 1 & 2 lessons, available in the
the states. decisions within its own borders) 1. A central government that would represent all 2. State sovereignty (the power to make
 The United States has operated under two constitutions. The first, The Articles of Confederation, was in effect from March 1, 1781. The Articles tried to balance two very different ideas: 1. A central
The United States has operated under two constitutions. The first, The Articles of Confederation, was in effect from March 1, 1781. The Articles tried to balance two very different ideas: 1. A central
Constitutional Convention Issues
 Constitutional Convention Issues Key Conflicts: Large vs Small States Slave vs Population State vs Federal Authority The debate between states; and the debate between federal verses state governments Constitutional
Constitutional Convention Issues Key Conflicts: Large vs Small States Slave vs Population State vs Federal Authority The debate between states; and the debate between federal verses state governments Constitutional
3. Popular sovereignty - Rule by the people - People give their consent to be governed by government officials - People have the right to revolution
 Unit I Notes Purposes of Government - Maintain social order - Provide public services - Provide security and defense - Provide for the economy - Governments get authority from: o Their legitimacy o Ability
Unit I Notes Purposes of Government - Maintain social order - Provide public services - Provide security and defense - Provide for the economy - Governments get authority from: o Their legitimacy o Ability
1 st United States Constitution. A. loose alliance of states. B. Congress lawmaking body. C. 9 states had to vote to pass laws
 1 st United States Constitution A. loose alliance of states B. Congress lawmaking body C. 9 states had to vote to pass laws D. each state had 1 vote in Congress Northwest Ordinance / Land Ordinance division
1 st United States Constitution A. loose alliance of states B. Congress lawmaking body C. 9 states had to vote to pass laws D. each state had 1 vote in Congress Northwest Ordinance / Land Ordinance division
Unit 4 Writing the Constitution Concepts to Review
 Unit 4 Writing the Constitution Concepts to Review CAUSE AND EFFECTS OF MAJOR ERAS AND EVENTS IN U.S. HISTORY THROUGH 1877 Writing the Constitution Shays Rebellion Philadelphia Convention 1787 Great Compromise
Unit 4 Writing the Constitution Concepts to Review CAUSE AND EFFECTS OF MAJOR ERAS AND EVENTS IN U.S. HISTORY THROUGH 1877 Writing the Constitution Shays Rebellion Philadelphia Convention 1787 Great Compromise
Creating the Constitution
 Creating the Constitution Constitutional Convention Philadelphia 1787 Met in Secret Goal: Alter or abolish fix the old system or create a new one Needed to tweak the articles Focus of Convention Meeting
Creating the Constitution Constitutional Convention Philadelphia 1787 Met in Secret Goal: Alter or abolish fix the old system or create a new one Needed to tweak the articles Focus of Convention Meeting
CHAPTER 7 CREATING A GOVERNMENT
 CHAPTER 7 CREATING A GOVERNMENT The Constitution set out our rules for government. It explains what our government can and cannot do. It reflects are experience as a colony as well as ideas from Europe
CHAPTER 7 CREATING A GOVERNMENT The Constitution set out our rules for government. It explains what our government can and cannot do. It reflects are experience as a colony as well as ideas from Europe
Test - Social Studies Grade 8 Unit 04: Writing the Constitution
 Test - Social Studies Grade 8 Unit 04: Writing the Constitution 2013-2014 5. Use the graphic organizer and your knowledge of social studies to answer the following 1. The Philadelphia Convention of 1787
Test - Social Studies Grade 8 Unit 04: Writing the Constitution 2013-2014 5. Use the graphic organizer and your knowledge of social studies to answer the following 1. The Philadelphia Convention of 1787
A More Perfect Union. Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation
 A More Perfect Union Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation 1. Eleven of the thirteen states adopted state constitutions. Connecticut and Rhode Island kept its colonial charter as its constitution
A More Perfect Union Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation 1. Eleven of the thirteen states adopted state constitutions. Connecticut and Rhode Island kept its colonial charter as its constitution
Life was good in the colonies (Slaves excepted, of
 1. The Origins of the Constitution 2. The Government That Failed: 1776 1787 3. Making a Constitution: The Philadelphia Convention 4. Critical Issues at the Convention 5. The Madisonian System 6. Ratifying
1. The Origins of the Constitution 2. The Government That Failed: 1776 1787 3. Making a Constitution: The Philadelphia Convention 4. Critical Issues at the Convention 5. The Madisonian System 6. Ratifying
Vocabulary for Evolution of Government
 Vocabulary for Evolution of Government Directions Students will make a flash card for each word The flash card must include all the information on the screen (cards will be stamped for completeness) The
Vocabulary for Evolution of Government Directions Students will make a flash card for each word The flash card must include all the information on the screen (cards will be stamped for completeness) The
Federalists and Antifederalists January 25, 2011 Biographies of the Nation Danice Toyias,
 Constitution Debate, pg. 1 of 1 Federalists and Antifederalists January 25, 2011 Biographies of the Nation Danice Toyias, danice.toyias@mchce.net Lesson Topic and Focus This lesson utilizes what I call
Constitution Debate, pg. 1 of 1 Federalists and Antifederalists January 25, 2011 Biographies of the Nation Danice Toyias, danice.toyias@mchce.net Lesson Topic and Focus This lesson utilizes what I call
U.S. Constitution PSCI 1040
 PSCI 1040 Purposes of a Constitution Organize and empower the government Limit the powers of government. Many consider limited government to be the essence of constitutional government. 2 Articles of Confederation
PSCI 1040 Purposes of a Constitution Organize and empower the government Limit the powers of government. Many consider limited government to be the essence of constitutional government. 2 Articles of Confederation
Constitutional Convention. May 1787
 Constitutional Convention May 1787 Annapolis Convention September 11 to September 14, 1786 Annapolis, Maryland Purpose - How to fix the articles of confederation Alexander Hamilton (New York) MUST resolve
Constitutional Convention May 1787 Annapolis Convention September 11 to September 14, 1786 Annapolis, Maryland Purpose - How to fix the articles of confederation Alexander Hamilton (New York) MUST resolve
Chapter 2:4 Constitutional Convention
 Chapter 2:4 Constitutional Convention Psa_119:165 Great peace have they which love thy law: and nothing shall offend them. Objectives: 2:4 Our Political Beginnings o Students will examine the process that
Chapter 2:4 Constitutional Convention Psa_119:165 Great peace have they which love thy law: and nothing shall offend them. Objectives: 2:4 Our Political Beginnings o Students will examine the process that
Articles of Confederation September 18, 2007
 Articles of Confederation September 18, 2007 Powers Given to Congress under the Articles Weaknesses under the Articles Results of the Articles during the Critical Period Use Page 44-46 to analyze the effects
Articles of Confederation September 18, 2007 Powers Given to Congress under the Articles Weaknesses under the Articles Results of the Articles during the Critical Period Use Page 44-46 to analyze the effects
REBELS & FOUNDING FRAMERS: THEIR HUMANITY REVEALED A TWO WEEK UNIT PLAN
 Pamela J. Silva CCC / TAH Seminar Final Project September 25, 2008 REBELS & FOUNDING FRAMERS: THEIR HUMANITY REVEALED A TWO WEEK UNIT PLAN Overview: Many high school students--many Americans in general,
Pamela J. Silva CCC / TAH Seminar Final Project September 25, 2008 REBELS & FOUNDING FRAMERS: THEIR HUMANITY REVEALED A TWO WEEK UNIT PLAN Overview: Many high school students--many Americans in general,
The States: Experiments in Republicanism State constitutions served as experiments in republican government The people demand written constitutions
 The States: Experiments in Republicanism State constitutions served as experiments in republican government The people demand written constitutions provide clear definition of rights describe clear limits
The States: Experiments in Republicanism State constitutions served as experiments in republican government The people demand written constitutions provide clear definition of rights describe clear limits
The Constitutional Convention. Unit 4 (part 2)
 The Constitutional Convention Unit 4 (part 2) Problems and Compromises Struggle for power between the small states and the large states Virginia Plan (James Madison) proposed two houses of Congress based
The Constitutional Convention Unit 4 (part 2) Problems and Compromises Struggle for power between the small states and the large states Virginia Plan (James Madison) proposed two houses of Congress based
American History 11R
 American History 11R Setting of the Philadelphia Convention Early decision to re-write, rather than tinker with the Articles of Confederation Open agreement secretly arrived at--washington's plea Intent
American History 11R Setting of the Philadelphia Convention Early decision to re-write, rather than tinker with the Articles of Confederation Open agreement secretly arrived at--washington's plea Intent
The Constitutional Convention
 The Constitutional Convention Problems like Shay s Rebellion revealed the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation This event convinced many U.S. citizens that our 1 st written plan of government needed
The Constitutional Convention Problems like Shay s Rebellion revealed the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation This event convinced many U.S. citizens that our 1 st written plan of government needed
Creating Our. Constitution. Key Terms. delegates equal representation executive federal system framers House of Representatives judicial
 Lesson 2 Creating Our Constitution Key Terms delegates equal representation executive federal system framers House of Representatives judicial What You Will Learn to Do Explain how the Philadelphia Convention
Lesson 2 Creating Our Constitution Key Terms delegates equal representation executive federal system framers House of Representatives judicial What You Will Learn to Do Explain how the Philadelphia Convention
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes
 Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
WARM UP. 1 Finish the reverse side of the worksheet we began yesterday. 2 It discusses the Articles in the U.S. Constitution
 WARM UP 1 Finish the reverse side of the worksheet we began yesterday 2 It discusses the Articles in the U.S. Constitution 3 You may use your notes or information collected online for the ones that were
WARM UP 1 Finish the reverse side of the worksheet we began yesterday 2 It discusses the Articles in the U.S. Constitution 3 You may use your notes or information collected online for the ones that were
Lesson 13 Writing and Ratifying the Constitution
 Lesson 13 Writing and Ratifying the Constitution Doct r. FRANKLIN looking towards the Presidents Chair, at the back of which a rising sun happened to be painted, observed to a few members near him, that
Lesson 13 Writing and Ratifying the Constitution Doct r. FRANKLIN looking towards the Presidents Chair, at the back of which a rising sun happened to be painted, observed to a few members near him, that
Charles de Montesquieu
 Unit III He first created the idea of consent of the governed where people have a vote in who leads them (democracy). Every person has the right to life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness. John Locke
Unit III He first created the idea of consent of the governed where people have a vote in who leads them (democracy). Every person has the right to life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness. John Locke
SSUSH5 A, B, C & D Creating a New Government
 SSUSH5 A, B, C & D Creating a New Government The Articles of Confederation Formally called the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union, this agreement was created by the leaders of the original thirteen
SSUSH5 A, B, C & D Creating a New Government The Articles of Confederation Formally called the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union, this agreement was created by the leaders of the original thirteen
The American Revolution is over but now the colonists have to decide how they want to frame their government. Take the first 5 minutes of class and
 The American Revolution is over but now the colonists have to decide how they want to frame their government. Take the first 5 minutes of class and imagine that you were a colonist that just fought against
The American Revolution is over but now the colonists have to decide how they want to frame their government. Take the first 5 minutes of class and imagine that you were a colonist that just fought against
The United States Constitution. The Supreme Law of the Land
 The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land Standards SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States
The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land Standards SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States
Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation
 Name: Date: Chapter 8 Study Guide Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation 1. A constitution is a set of basic principles and laws, usually in written form, that state the powers and duties of a government.
Name: Date: Chapter 8 Study Guide Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation 1. A constitution is a set of basic principles and laws, usually in written form, that state the powers and duties of a government.
Chapter 25 Section 1. Section 1. Terms and People
 Chapter 25 Terms and People republic a government in which the people elect their representatives unicameral legislature a lawmaking body with a single house whose representatives are elected by the people
Chapter 25 Terms and People republic a government in which the people elect their representatives unicameral legislature a lawmaking body with a single house whose representatives are elected by the people
THE CONSTITUTION AND ITS HISTORY
 THE CONSTITUTION AND ITS HISTORY 1 CHAPTER Outline I. Introduction II. History Leading up to the Constitution A. Articles of Confederation 1. A firm league of friendship a. Each state was to remain (1)
THE CONSTITUTION AND ITS HISTORY 1 CHAPTER Outline I. Introduction II. History Leading up to the Constitution A. Articles of Confederation 1. A firm league of friendship a. Each state was to remain (1)
Chapter 2 TEST Origins of American Government
 US Government - Ried Chapter 2 TEST Origins of American Government 1)The Magna Carta was originally intended to protect the rights of which group? A. religious leaders B. kings and queens C. common people
US Government - Ried Chapter 2 TEST Origins of American Government 1)The Magna Carta was originally intended to protect the rights of which group? A. religious leaders B. kings and queens C. common people
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Articles of Confederation. Essential Question:
 Articles of Confederation Essential Question: Why was the central government s power too weak under the Articles of Confederation? Objectives Discuss the ideas that guided the new state governments. Describe
Articles of Confederation Essential Question: Why was the central government s power too weak under the Articles of Confederation? Objectives Discuss the ideas that guided the new state governments. Describe
Jeopardy Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400
 Jeopardy 2013-14 Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $500 Q $500 Q $500 Q $500 Final Jeopardy
Jeopardy 2013-14 Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $500 Q $500 Q $500 Q $500 Final Jeopardy
Ch. 6 Creating the Constitution /EQ:
 Ch. 6 Creating the Constitution /EQ: 6.1 Introduction Like Washington, most Americans did not want to be ruled by a monarch. What they did want, though, was an effective government. Articles of Confederation,
Ch. 6 Creating the Constitution /EQ: 6.1 Introduction Like Washington, most Americans did not want to be ruled by a monarch. What they did want, though, was an effective government. Articles of Confederation,
HIST 1301 Part Two. 6: The Republican Experiment
 HIST 1301 Part Two 6: The Republican Experiment The States and the Confederation 1776-1788 During the Revolution, state Governments formed first. 2 min. 40 sec. Each state had a written constitution. Each
HIST 1301 Part Two 6: The Republican Experiment The States and the Confederation 1776-1788 During the Revolution, state Governments formed first. 2 min. 40 sec. Each state had a written constitution. Each
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes
 Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
Constitutional Convention
 Constitutional Convention Members Principles Agreements and compromises The Constitutional Convention, 1787 u 55 delegates attended but on a typical day 35 were present u 29 held college degrees u 34 were
Constitutional Convention Members Principles Agreements and compromises The Constitutional Convention, 1787 u 55 delegates attended but on a typical day 35 were present u 29 held college degrees u 34 were
Ch.8, Sec.2 Creating the Constitution
 ü A al Convention Is Called - during the summer of 1787, 12 states sent delegates to Philadelphia to discuss amending the Articles of Confederation - the example set by Shays Rebellion proved our young
ü A al Convention Is Called - during the summer of 1787, 12 states sent delegates to Philadelphia to discuss amending the Articles of Confederation - the example set by Shays Rebellion proved our young
Origins of American Government Guided Reading Activity Section 1
 Section 1 Read each of the following descriptions, and write who or what is speaking in the space provided. 1. My theories that a republic could only survive if its citizens actively participated in government
Section 1 Read each of the following descriptions, and write who or what is speaking in the space provided. 1. My theories that a republic could only survive if its citizens actively participated in government
Creating the Constitution
 Creating the Constitution 1776-1791 US Timeline 1777-1791 1777 Patriots win Battles of Saratoga. Continental Congress passes the Articles of Confederation. 1781 Articles of Confederation go into effect.
Creating the Constitution 1776-1791 US Timeline 1777-1791 1777 Patriots win Battles of Saratoga. Continental Congress passes the Articles of Confederation. 1781 Articles of Confederation go into effect.
Articles of Confederation
 Articles of Confederation Do Now How is power divided in our country today? SWBAT Analyze government problems under the Articles of Confederation Activity Review the Articles of Confederation chart and
Articles of Confederation Do Now How is power divided in our country today? SWBAT Analyze government problems under the Articles of Confederation Activity Review the Articles of Confederation chart and
The first fighting in the American Revolution happened in in early 1775
 The chief objective of the First Continental Congress was to establish trade relations with foreign powers like France and Germany. select a commander for the Continental Army. draft the U.S. Constitution.
The chief objective of the First Continental Congress was to establish trade relations with foreign powers like France and Germany. select a commander for the Continental Army. draft the U.S. Constitution.
Chapter 5. A Virtuous Republic Creating a Workable Government,
 Chapter 5 A Virtuous Republic Creating a Workable Government, 1783 1789 CHAPTER FIVE: A VIRTUOUS REPUBLIC: CREATING A WORKABLE GOVERNMENT 1783-1789 What did virtue mean to the Founders of the American
Chapter 5 A Virtuous Republic Creating a Workable Government, 1783 1789 CHAPTER FIVE: A VIRTUOUS REPUBLIC: CREATING A WORKABLE GOVERNMENT 1783-1789 What did virtue mean to the Founders of the American
4 th Grade U.S. Government Study Guide
 4 th Grade U.S. Government Study Guide Big Ideas: Imagine trying to make a new country from scratch. You ve just had a war with the only leaders you ve ever known, and now you have to step up and lead.
4 th Grade U.S. Government Study Guide Big Ideas: Imagine trying to make a new country from scratch. You ve just had a war with the only leaders you ve ever known, and now you have to step up and lead.
The Constitutional Convention
 The Constitutional Convention Review Why was the Constitution necessary? Article Text Congress had no power to tax Problem Created Congress had no power to enforce treaties Every state, despite size, had
The Constitutional Convention Review Why was the Constitution necessary? Article Text Congress had no power to tax Problem Created Congress had no power to enforce treaties Every state, despite size, had
The Constitutional Convention
 Early United States I can describe how thirteen colonies evolved into the United States. 4 I can make inferences that go beyond what was taught in class or connect and explain the 3.0 learning targets
Early United States I can describe how thirteen colonies evolved into the United States. 4 I can make inferences that go beyond what was taught in class or connect and explain the 3.0 learning targets
Constitutional Convention
 Constitutional Convention How did the United States overcome the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation and provide for the organization of the new government? What role did compromise play in the
Constitutional Convention How did the United States overcome the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation and provide for the organization of the new government? What role did compromise play in the
2. Divided Convention. 3. Inside the Constitution. Constitution replaced the Articles---becomes the law of the land.
 2. Divided Convention notes7 9/13 states needed to ratify (to approve) Political parties begin Federalists: supported the Constitution The Federalist ---essays support Constitution Anti-Federalists: against
2. Divided Convention notes7 9/13 states needed to ratify (to approve) Political parties begin Federalists: supported the Constitution The Federalist ---essays support Constitution Anti-Federalists: against
Guided Reading Activity
 Guided Reading Activity Lesson 1 Government in Colonial America Review Questions Directions: Read each main idea. Use your text to supply the details that support or explain each main idea. A. Main Idea:
Guided Reading Activity Lesson 1 Government in Colonial America Review Questions Directions: Read each main idea. Use your text to supply the details that support or explain each main idea. A. Main Idea:
Chapter 2 Content Statement
 Content Statement 6 Chapter 2 Content Statement Cite arguments from the Federalist Papers and/or the Anti- Federalist Papers that supported their position on the issue of how well the Constitution upheld
Content Statement 6 Chapter 2 Content Statement Cite arguments from the Federalist Papers and/or the Anti- Federalist Papers that supported their position on the issue of how well the Constitution upheld
1. STUDENTS WILL BE ABLE TO IDENTIFY AND EXPLAIN THE WEAKNESSES OF THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION
 SOUTHWESTERN CHRISTIAN SCHOOL UNITED STATES HISTORY STUDY GUIDE # 7 : CREATING A NEW NATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES STUDENTS WILL BE ABLE TO IDENTIFY AND EXPLAIN THE WEAKNESSES OF THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION
SOUTHWESTERN CHRISTIAN SCHOOL UNITED STATES HISTORY STUDY GUIDE # 7 : CREATING A NEW NATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES STUDENTS WILL BE ABLE TO IDENTIFY AND EXPLAIN THE WEAKNESSES OF THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION
The Constitutional Convention
 The Constitutional Convention Problems like Shay s Rebellion revealed the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation This event convinced many U.S. citizens that our 1 st written plan of government needed
The Constitutional Convention Problems like Shay s Rebellion revealed the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation This event convinced many U.S. citizens that our 1 st written plan of government needed
Shays. Daniel Shay 1784 to 1785, unfair taxes, debt and foreclosure Farmer s rebellion to overthrow Mass. Govt.
 Shays Daniel Shay 1784 to 1785, unfair taxes, debt and foreclosure Farmer s rebellion to overthrow Mass. Govt. 1. Constitutional Convention: May to Sept. 1787 2. Divided Convention 9/13 states needed to
Shays Daniel Shay 1784 to 1785, unfair taxes, debt and foreclosure Farmer s rebellion to overthrow Mass. Govt. 1. Constitutional Convention: May to Sept. 1787 2. Divided Convention 9/13 states needed to
THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION. Compromises Federalists v. Anti-Federalists
 THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Compromises Federalists v. Anti-Federalists QUICK REVIEW: FIND SOMEONE WHO Second Continental Congress Drafting of the Articles of Confederation Weaknesses International Relations
THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Compromises Federalists v. Anti-Federalists QUICK REVIEW: FIND SOMEONE WHO Second Continental Congress Drafting of the Articles of Confederation Weaknesses International Relations
Module 1.2 U.S. Constitutional Framework. Constitutional Trivia! Overview of Lecture 6/4/2008
 Module 1.2 U.S. Constitutional Framework Prof. Bryan McQuide University of Idaho Summer 2008 Constitutional Trivia! Which of the following Presidents signed the U.S. Constitution? George Washington John
Module 1.2 U.S. Constitutional Framework Prof. Bryan McQuide University of Idaho Summer 2008 Constitutional Trivia! Which of the following Presidents signed the U.S. Constitution? George Washington John
Objectives: Students will be able to explain that the success and failures of the articles of confederation and be able to give some examples of each.
 Day 1 Objectives: Students will be able to explain that the success and failures of the articles of confederation and be able to give some examples of each. Procedure: Do Now: Why is it important to have
Day 1 Objectives: Students will be able to explain that the success and failures of the articles of confederation and be able to give some examples of each. Procedure: Do Now: Why is it important to have
Quarter One: Unit Four
 SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will identify the weaknesses of the government under the Articles of Confederation (i.e.,
SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will identify the weaknesses of the government under the Articles of Confederation (i.e.,
FORMING A NEW GOVERNMENT
 FORMING A NEW GOVERNMENT These questions are in random order. They will be in a different order in class tomorrow. Seven Principles Checks & Balances Federalism Individual Rights Limited Government Popular
FORMING A NEW GOVERNMENT These questions are in random order. They will be in a different order in class tomorrow. Seven Principles Checks & Balances Federalism Individual Rights Limited Government Popular
Basic Concepts of Government The English colonists brought 3 ideas that loom large in the shaping of the government in the United States.
 Civics Honors Chapter Two: Origins of American Government Section One: Our Political Beginnings Limited Government Representative government Magna Carta Petition of Right English Bill of Rights Charter
Civics Honors Chapter Two: Origins of American Government Section One: Our Political Beginnings Limited Government Representative government Magna Carta Petition of Right English Bill of Rights Charter
The U.S. Constitution. Ch. 2.4 Ch. 3
 The U.S. Constitution Ch. 2.4 Ch. 3 The Constitutional Convention Philadelphia Five months, from May until September 1787 Secret Meeting, closed to outside. Originally intent to revise the Articles of
The U.S. Constitution Ch. 2.4 Ch. 3 The Constitutional Convention Philadelphia Five months, from May until September 1787 Secret Meeting, closed to outside. Originally intent to revise the Articles of
The Constitution I. Considerations that influenced the formulation and adoption of the Constitution A. Roots 1. Religious Freedom a) Puritan
 The Constitution I. Considerations that influenced the formulation and adoption of the Constitution A. Roots 1. Religious Freedom a) Puritan Theocracy (1) 9 of 13 had state church b) Rhode Island (1) Roger
The Constitution I. Considerations that influenced the formulation and adoption of the Constitution A. Roots 1. Religious Freedom a) Puritan Theocracy (1) 9 of 13 had state church b) Rhode Island (1) Roger
SS.7.C.1.5. Identify how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing of the Constitution
 SS.7.C.1.5. Identify how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing of the Constitution SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the
SS.7.C.1.5. Identify how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing of the Constitution SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the
LESSON TWO: THE FEDERALIST PAPERS
 LESSON TWO: THE FEDERALIST PAPERS OVERVIEW OBJECTIVES Students will be able to: Identify the Articles of Confederation and explain why it failed. Explain the argument over the need for a bill of rights
LESSON TWO: THE FEDERALIST PAPERS OVERVIEW OBJECTIVES Students will be able to: Identify the Articles of Confederation and explain why it failed. Explain the argument over the need for a bill of rights
Name: Articles of Confederation. Problems after the war: 1. What were the problems Facing the 2 nd Continental Congress after the war? 2.
 Articles of Confederation Name: Problems after the war: 1. What were the problems Facing the 2 nd Continental Congress after the war? 2. 3. 4. What are the Articles of Confederation? What were the weaknesses
Articles of Confederation Name: Problems after the war: 1. What were the problems Facing the 2 nd Continental Congress after the war? 2. 3. 4. What are the Articles of Confederation? What were the weaknesses
Creating the Constitution 2.2, 2.3, 2.4
 Creating the Constitution 2.2, 2.3, 2.4 Struggle for Government The creation and signing of the Declaration of Independence did not create a government The founding fathers had many problems Declaration
Creating the Constitution 2.2, 2.3, 2.4 Struggle for Government The creation and signing of the Declaration of Independence did not create a government The founding fathers had many problems Declaration
Wednesday, February 15 th
 Anticipating Constitutional Reform 1 Wednesday, February 15 th Midterm #1: February 14-17 in the Testing Center Monday and Tuesday: No late fee Wednesday: $5 late fee Thursday: $7 late fee and test must
Anticipating Constitutional Reform 1 Wednesday, February 15 th Midterm #1: February 14-17 in the Testing Center Monday and Tuesday: No late fee Wednesday: $5 late fee Thursday: $7 late fee and test must
Quarter One: Unit Four
 SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will identify the weaknesses of the government under the Articles of Confederation (i.e.,
SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will identify the weaknesses of the government under the Articles of Confederation (i.e.,
Essential Question Section 1: The Colonial Period Section 2: Uniting for Independence Section 3: The Articles of Confederation Section 4: The
 Essential Question Section 1: The Colonial Period Section 2: Uniting for Independence Section 3: The Articles of Confederation Section 4: The Constitutional Convention Chapter Summary Content Vocabulary
Essential Question Section 1: The Colonial Period Section 2: Uniting for Independence Section 3: The Articles of Confederation Section 4: The Constitutional Convention Chapter Summary Content Vocabulary
THE CONSTITUTION. Chapter 2
 THE CONSTITUTION Chapter 2 ROOTS OF THE CONSTITUTION 2.1 TRADE AND TAXATION 2.1 Mercantilism Strict import/export controls Widely ignored Costly French and Indian War New taxes on sugar and paper items
THE CONSTITUTION Chapter 2 ROOTS OF THE CONSTITUTION 2.1 TRADE AND TAXATION 2.1 Mercantilism Strict import/export controls Widely ignored Costly French and Indian War New taxes on sugar and paper items
May, 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania ~Independence Hall~ Leader: George Washington
 May, 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania ~Independence Hall~ Leader: George Washington -May 1787 Philadelphia Met in Independence Hall in Philadelphia George Washington leader -12 of 13 states Rhode Island
May, 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania ~Independence Hall~ Leader: George Washington -May 1787 Philadelphia Met in Independence Hall in Philadelphia George Washington leader -12 of 13 states Rhode Island
End of American Revolution and Creation of American government
 End of American Revolution and Creation of American government American Revolution concludes, an independent nation develops, 1781. Articles of Confederation ratified by states March 1781 - framework for
End of American Revolution and Creation of American government American Revolution concludes, an independent nation develops, 1781. Articles of Confederation ratified by states March 1781 - framework for
Creating a Nation Test Review
 Creating a Nation Test Review Question #1: Multiple Choice The Northwest ordinance of 1787 is important because. A. It sent troops to the Northwest to protect the colonies from Native Americans. B. It
Creating a Nation Test Review Question #1: Multiple Choice The Northwest ordinance of 1787 is important because. A. It sent troops to the Northwest to protect the colonies from Native Americans. B. It
The Constitutional Convention formed the plan of government that the United States still has today.
 2 Creating the Constitution MAIN IDEA The states sent delegates to a convention to solve the problems of the Articles of Confederation. WHY IT MATTERS NOW The Constitutional Convention formed the plan
2 Creating the Constitution MAIN IDEA The states sent delegates to a convention to solve the problems of the Articles of Confederation. WHY IT MATTERS NOW The Constitutional Convention formed the plan
Constitution Test Study Guide
 Constitution Test Study Guide Part One: Development of the Constitution Articles of Confederation: America's first government. The 13 states were loosely unified but the government was very weak, with
Constitution Test Study Guide Part One: Development of the Constitution Articles of Confederation: America's first government. The 13 states were loosely unified but the government was very weak, with
DEBATE ON RATIFICATION
 U.S. I Mr. Lanner 100 Point Project DEBATE ON RATIFICATION Should we ratify the new Constitution? Purpose of Lesson: This lesson describes some conflicting points of view of leading Framers about the Constitution.
U.S. I Mr. Lanner 100 Point Project DEBATE ON RATIFICATION Should we ratify the new Constitution? Purpose of Lesson: This lesson describes some conflicting points of view of leading Framers about the Constitution.
Foundations of American Government
 Foundations of American Government Formation of the first governments of the 13 colonies Highly Influenced by: - Contracts, Juries, stare decisis English Tradition Natural rights: Consent of the governed:
Foundations of American Government Formation of the first governments of the 13 colonies Highly Influenced by: - Contracts, Juries, stare decisis English Tradition Natural rights: Consent of the governed:
Unit 2: A New Nation
 Unit 2: A New Nation Establishing a Government Articles of Confederation Nation s first set of laws Limited central gov. Confederation would have more power Ratified in 1781, failed b/c it did not give
Unit 2: A New Nation Establishing a Government Articles of Confederation Nation s first set of laws Limited central gov. Confederation would have more power Ratified in 1781, failed b/c it did not give
New Nation. establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s
 New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
Constitutional Convention
 Constitutional Convention I INTRODUCTION Constitutional Convention, meeting during the summer of 1787 at which delegates from 12 states wrote the Constitution of the United States. At the convention in
Constitutional Convention I INTRODUCTION Constitutional Convention, meeting during the summer of 1787 at which delegates from 12 states wrote the Constitution of the United States. At the convention in
