The Making of a Nation Program No. 45 Andrew Jackson Part One
|
|
|
- Kelly Bond
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Making of a Nation Program No. 45 Andrew Jackson Part One From VOA Learning English, welcome to The Making of a Nation -- our weekly program of American history for people learning English. I m Steve Ember. Last week in our series, we talked about the election of General Andrew Jackson defeated President John Quincy Adams, after a campaign in which both sides made strong and bitter accusations. On March 4, 1829, Andrew Jackson was sworn in as president. The sky over Washington was cloudy that day. But the clouds parted, and the sun shone through, as Jackson began the ride to the Capitol building. Thousands of cheering supporters saw this change in weather as a good sign. So many people crowded around the Capitol that Jackson had to climb a wall and enter from the back. He walked through the building and into the open area at the front where The Inauguration of Andrew Jackson in 1829 the ceremony would be held. 1 learningenglish.voanews.com Voice of America September 12,
2 The ceremony itself was simple. Jackson made a speech that few in the crowd were able to hear. Then Chief Justice John Marshall swore in the new president. In the crowd was a newspaperman from Kentucky, Amos Kendall. "It is a proud day for the people," Kendall wrote. "General Jackson is their own president." From the Capitol, Jackson rode down Pennsylvania Avenue to the White House. Behind him followed all those who had watched him become the nation's seventh president. The crowds followed him all the way into the White House, where food and drink had been put out for a party. Everyone tried to get in at once. Clothing was torn. Glasses and dishes were broken. Chairs and tables were damaged. Never had there been a party like this at the president s mansion. Jackson stayed for a while. But the crush of people tired him, and he was able to leave. He spent the rest of the day at his hotel room in Virginia. The guests at the White House finally left after drinks were put on the table outside the building. Many of the people left through windows, because the doorways were so crowded. 2 learningenglish.voanews.com Voice of America September 12,
3 Jackson was popular with many voters, who saw him as representing the common man. But Jackson s first term seemed to be mostly a political battle with his own vice president, John C. Calhoun of South Carolina. Calhoun wanted to become the next president. But Jackson preferred his secretary of state, Martin van Buren. John C. Calhoun 1822 Portrait (Age 40) The split between Jackson and Calhoun deepened over another issue. Jackson learned that Calhoun had once called for Jackson's arrest. Calhoun wanted to punish Jackson for his unauthorized military campaign into Spanish Florida in The most important division between the two men was Calhoun's belief about who had more power: the states or the federal government. Calhoun came to believe the rights of the states were stronger than the rights of the federal government. His feelings became well known during a debate on a congressional bill. 3 learningenglish.voanews.com Voice of America September 12,
4 The year before Jackson took office, Congress passed a bill to require taxes on imports. The purpose of the taxes was to protect American industries. The state of South Carolina, Calhoun s state, opposed the measure. South Carolina, like other Southern states, had almost no industry. It was an agricultural area. Import taxes would only raise the price of products the South imported. South Carolina refused to pay the tax. Calhoun wrote a long statement defending South Carolina's action. In the statement, he developed what was called the Doctrine of Nullification. The doctrine declared that the power of the federal government was not supreme. Calhoun argued that, instead, supreme power belonged to the states. He said states did not surrender this power when they approved the Constitution. In any dispute between the states and the federal government, he said, the states should decide what is right. Calhoun argued that if the federal government passed a law that any state thought was not constitutional, or against its interests, that state could temporarily suspend the law. 4 learningenglish.voanews.com Voice of America September 12,
5 The other states of the union, Calhoun said, would then be asked to decide the question of the law's constitutionality. If two-thirds of the states approved the law, the complaining state would have to accept it, or leave the union. If less than two-thirds of the states approved it, then the law would be rejected. None of the states would have to obey it. It would be nullified cancelled. Senators Robert Hayne of South Carolina and Daniel Webster of Massachusetts debated the question of nullification in Congress. Senator Hayne spoke first. He said that there was no greater evil than giving more power to the federal government. The major point of his speech could be put into a few words: liberty first, union afterwards. Senator Webster said Hayne had spoken foolishly. Liberty and union could not be separated, Webster said. It was liberty and union, now and forever, one and inseparable. No one really knew how President Andrew Jackson felt about nullification. He made no public statement during the debate. Leaders in South Carolina developed a plan to get the president's support. They decided to hold a big dinner honoring the memory of Thomas Jefferson. Jackson agreed to attend the dinner. 5 learningenglish.voanews.com Voice of America September 12,
6 The speeches were carefully planned. They began by praising the democratic ideas of Jefferson. Next they discussed South Carolina's opposition to the import tax. Finally, the speeches were finished. It was time for toasts. President Jackson made the first one. He stood up, raised his glass, and looked straight at Vice President John C. Calhoun. He waited for the cheering to stop. "Our union," he said, "it must be preserved." Calhoun rose with the others to drink the toast. He had not expected Jackson's opposition to nullification. His hand shook, and he spilled some of the wine from his glass. Calhoun was called on to make the next toast. "The union," he said, "next to our liberty, most dear." He waited a moment, then, continued. "May we all remember that it can only be preserved by respecting the rights of the states and by giving equally the benefits and burdens of the union." President Jackson left a few minutes later. Most of those at dinner left with him. 6 learningenglish.voanews.com Voice of America September 12,
7 The nation now knew how the president felt. And the people were with him opposed to nullification. But the idea was not dead among some people in South Carolina. The nullifiers held a majority of seats in the state's legislature at that time. They called a special convention. Within five days, convention delegates approved a declaration of nullification. They said citizens of South Carolina need not pay the federal import taxes. The nullifiers also declared that if the federal government tried to use force against South Carolina, then the state would withdraw from the union and form its own independent government. This cut very deeply with Jackson. Jackson was a nationalist. He was a great believer in the federal union. He was a flag-waving patriot. As Jackson saw it, nullification was the beginning of the end of the United States as a nation. That was historian Daniel Feller. He says Jackson believed in a limited federal government. But that did not mean the people of every state should decide what the constitution means. 7 learningenglish.voanews.com Voice of America September 12,
8 That way lies chaos. As Jackson said, Either we have a national government or we don t. And if Congress does pass laws which might prove to be unconstitutional, we have a procedure for dealing with that. We have the Supreme Court, we have the ability of the people and their elected representatives to appeal to Congress to repeal those laws to take them back. But you can t have every state going off on its own and deciding what the Constitution says. Jackson wrote a proclamation answering the nullifiers. In it, he said America's constitution formed a government, not just an association, or group, of sovereign states. South Carolina had no right to cancel a federal law or to withdraw from the union. Jackson explained that it was his duty, as president, to enforce the laws of the land. Even, as Daniel Feller says, if he had to use force. It s going to come to a test of arms, and this I can quote. And it was in italics, underlined, emphasized in the printed version of the proclamation. Disunion by armed force is treason. Are you really read to incur its guilt? Jackson sent eight warships to the port of Charleston, South Carolina, and soldiers to federal military bases in the state. 8 learningenglish.voanews.com Voice of America September 12,
9 While preparing to use force, Jackson offered hope for a peaceful settlement. In a message to Congress, he spoke of reducing the federal import tax that hurt the sale of southern cotton overseas. He said the tax could be reduced, because the national debt would soon be paid. Congress passed a compromise bill to end the import tax by South Carolina's congressmen accepted the compromise. And the state's legislature called another convention. This time, the delegates voted to end the nullification act they had approved earlier. They did not, however, give up their belief in the idea of nullification. Daniel Feller says one reason is because Southern politicians thought they might need to use nullification later. An anti-slavery movement was beginning to grow in the country. Some southerners worried that Congress would one day make laws they did not like against slavery. The issues of slavery and states rights would continue to be areas of conflict. Eventually, they would help start the Civil War in But well before that, President Andrew Jackson would fight a different battle. The struggle over the Bank of the United States will be our story next week. 9 learningenglish.voanews.com Voice of America September 12,
10 I m Steve Ember, inviting you to join us next time for The Making of a Nation American history from VOA Learning English. 10 learningenglish.voanews.com Voice of America September 12,
The Making of a Nation Program No. 43 President John Quincy Adams
 The Making of a Nation Program No. 43 President John Quincy Adams From VOA Learning English, welcome to The Making of a Nation, our weekly program of American history for people learning English. I m Steve
The Making of a Nation Program No. 43 President John Quincy Adams From VOA Learning English, welcome to The Making of a Nation, our weekly program of American history for people learning English. I m Steve
The Making of a Nation Program No. 42
 The Making of a Nation Program No. 42 James Monroe, Part 3: The Election of 1824 From VOA Learning English, welcome to the Making of a Nation, our weekly program of American history for people learning
The Making of a Nation Program No. 42 James Monroe, Part 3: The Election of 1824 From VOA Learning English, welcome to the Making of a Nation, our weekly program of American history for people learning
What four men ran for president and what parts of the country did they represent?
 Chapter 12 The Age of Jackson pg. 366 389 12 1 Politics of the People The Election of 1824 What four men ran for president and what parts of the country did they represent? Why was the election of 1824
Chapter 12 The Age of Jackson pg. 366 389 12 1 Politics of the People The Election of 1824 What four men ran for president and what parts of the country did they represent? Why was the election of 1824
Jackson s Administration
 SECTION2 Jackson s Administration What You Will Learn Main Ideas 1. Regional differences grew during Jackson s presidency. 2. The rights of the states were debated amid arguments about a national tariff.
SECTION2 Jackson s Administration What You Will Learn Main Ideas 1. Regional differences grew during Jackson s presidency. 2. The rights of the states were debated amid arguments about a national tariff.
Warm Up. the north & south. slavery in the southern USA: economic landscape of the United States: 1) Using a Venn Diagram compare and contrast
 Warm Up 1) Using a Venn Diagram compare and contrast the north & south 2) Explain the impact of the cotton gin on slavery in the southern USA: 3) Discuss how industrialization changed the economic landscape
Warm Up 1) Using a Venn Diagram compare and contrast the north & south 2) Explain the impact of the cotton gin on slavery in the southern USA: 3) Discuss how industrialization changed the economic landscape
For a New Nation, Hamilton Seeks a Bank
 For a New Nation, Hamilton Seeks a Bank From VOA Learning English, welcome to The Making of a Nation American history in VOA Special English. I m Steve Ember. This week in our series we continue the story
For a New Nation, Hamilton Seeks a Bank From VOA Learning English, welcome to The Making of a Nation American history in VOA Special English. I m Steve Ember. This week in our series we continue the story
States Rights and the National Bank. The Americans, Chapter 7.4, Pages
 States Rights and the National Bank The Americans, Chapter 7.4, Pages 230-235 A Tariff Raises the States Rights Issue When the war of 1812 ended, British manufacturers wanted to destroy their American
States Rights and the National Bank The Americans, Chapter 7.4, Pages 230-235 A Tariff Raises the States Rights Issue When the war of 1812 ended, British manufacturers wanted to destroy their American
The Jackson Era
 The Jackson Era 1824-1845 Election of 1824- In 1824, four candidates ran for the Presidency: Andrew Jackson John Quincy Adams Henry Clay William Crawford The Results: Harpers Weekly Candidate Popular Votes
The Jackson Era 1824-1845 Election of 1824- In 1824, four candidates ran for the Presidency: Andrew Jackson John Quincy Adams Henry Clay William Crawford The Results: Harpers Weekly Candidate Popular Votes
WARM UP. 1 Get into the Kahoot game on the board. 2 We will review the week & the winner will receive a prize!
 WARM UP 1 Get into the Kahoot game on the board 2 We will review the week & the winner will receive a prize! PRESIDENCY OF JOHN QUINCY ADAMS ELECTION OF 1824 I. Sectionalism replaced nationalism in the
WARM UP 1 Get into the Kahoot game on the board 2 We will review the week & the winner will receive a prize! PRESIDENCY OF JOHN QUINCY ADAMS ELECTION OF 1824 I. Sectionalism replaced nationalism in the
The Big Idea The expansion of voting rights and the election of Andrew Jackson signaled the growing power of the American people.
 Jacksonian Democracy The Big Idea The expansion of voting rights and the election of Andrew Jackson signaled the growing power of the American people. Main Ideas Democracy expanded in the 1820s as more
Jacksonian Democracy The Big Idea The expansion of voting rights and the election of Andrew Jackson signaled the growing power of the American people. Main Ideas Democracy expanded in the 1820s as more
Name Date Class KEY TERMS AND NAMES
 Chapter 8, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 266 272 JACKSONIAN AMERICA KEY TERMS AND NAMES spoils system the practice of appointing people to government jobs on the basis of party loyalty and support
Chapter 8, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 266 272 JACKSONIAN AMERICA KEY TERMS AND NAMES spoils system the practice of appointing people to government jobs on the basis of party loyalty and support
JACKSONIAN DEMOCRACY. Ch. 7 Section 4 & 5
 JACKSONIAN DEMOCRACY Ch. 7 Section 4 & 5 ELECTION OF 1824 The Candidates in the Election of 1824 John Quincy Adams Andrew Jackson Henry Clay Jackson wins plurality of electoral votes (99), but no one wins
JACKSONIAN DEMOCRACY Ch. 7 Section 4 & 5 ELECTION OF 1824 The Candidates in the Election of 1824 John Quincy Adams Andrew Jackson Henry Clay Jackson wins plurality of electoral votes (99), but no one wins
STATES' RIGHTS AND THE NATIONAL BANK. Chapter 7.4
 STATES' RIGHTS AND THE NATIONAL BANK Chapter 7.4 Tariff Raises Issues of States Rights The Nullification Theory British try to flood U.S. with cheap goods Tariff of 1816 curbs cheap imports; tariff raised
STATES' RIGHTS AND THE NATIONAL BANK Chapter 7.4 Tariff Raises Issues of States Rights The Nullification Theory British try to flood U.S. with cheap goods Tariff of 1816 curbs cheap imports; tariff raised
From VOA Learning English, welcome to the Making of a Nation, our weekly program of American history for people learning
 From VOA Learning English, welcome to the Making of a Nation, our weekly program of American history for people learning American English. I m Steve Ember. Last time, we talked about Martin Van Buren.
From VOA Learning English, welcome to the Making of a Nation, our weekly program of American history for people learning American English. I m Steve Ember. Last time, we talked about Martin Van Buren.
Road to Civil War Slavery and the West: Chapter 12, Section 2 Differences in economic, political, and social beliefs and practices can lead to
 Road to Civil War Slavery and the West: Chapter 12, Section 2 Differences in economic, political, and social beliefs and practices can lead to division within a nation and have lasting consequences. The
Road to Civil War Slavery and the West: Chapter 12, Section 2 Differences in economic, political, and social beliefs and practices can lead to division within a nation and have lasting consequences. The
States' Rights and the Economy
 States' Rights and the Economy * * * * * * * * * * * * Focus Question: How did old issues take a new shape in the conflict over a national bank and tariffs? *Jackson believed that common people needed
States' Rights and the Economy * * * * * * * * * * * * Focus Question: How did old issues take a new shape in the conflict over a national bank and tariffs? *Jackson believed that common people needed
CHAPTER 9: THE ASCENSION AND PRESIDENCY OF ANDREW JACKSON
 CHAPTER 9: THE ASCENSION AND PRESIDENCY OF ANDREW JACKSON How did the Panic of 1819, and the Missouri Crisis increase citizens awareness of politics and government? The recession caused by the panic made
CHAPTER 9: THE ASCENSION AND PRESIDENCY OF ANDREW JACKSON How did the Panic of 1819, and the Missouri Crisis increase citizens awareness of politics and government? The recession caused by the panic made
The Role of Politics in Sectionalism
 The Role of Politics in Sectionalism James Monroe 1758 1831 Dem.-Republican 5 th President (1817-25) Last President to have participated in the Revolution Former Gov. of VA, Secretary of State, and Secretary
The Role of Politics in Sectionalism James Monroe 1758 1831 Dem.-Republican 5 th President (1817-25) Last President to have participated in the Revolution Former Gov. of VA, Secretary of State, and Secretary
The Nullification Crisis
 The Nullification Crisis Warm up With your shoulder partner, you need to discuss the questions posted on the next slide. You will be EXPECTED to go to the board and write your answers. What issue is this
The Nullification Crisis Warm up With your shoulder partner, you need to discuss the questions posted on the next slide. You will be EXPECTED to go to the board and write your answers. What issue is this
Issues that Challenged Old Hickory
 Issues that Challenged Old Hickory The Corrupt Bargain The Candidates Andrew Jackson- Democrat John Quincy Adams- Whig Henry Clay- Whig William Crawford- Democrat Jackson won the popular vote, but no candidate
Issues that Challenged Old Hickory The Corrupt Bargain The Candidates Andrew Jackson- Democrat John Quincy Adams- Whig Henry Clay- Whig William Crawford- Democrat Jackson won the popular vote, but no candidate
Jacksonian Democracy
 Jacksonian Democracy 1824-1840 Jackson vs. Adams The Election of 1824 With the breakdown of the Caucus system for choosing candidates, four Republican candidates campaigned for the presidency John Quincy
Jacksonian Democracy 1824-1840 Jackson vs. Adams The Election of 1824 With the breakdown of the Caucus system for choosing candidates, four Republican candidates campaigned for the presidency John Quincy
The Americans (Survey)
 The Americans (Survey) Chapter 7: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OVERVIEW American leaders devise a farsighted policy of improvements as North, South, and West develop
The Americans (Survey) Chapter 7: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OVERVIEW American leaders devise a farsighted policy of improvements as North, South, and West develop
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism
 7 QUIT Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE GRAPH SECTION 1 Regional Economics Create Differences SECTION 2 Nationalism at Center Stage MAP SECTION 3
7 QUIT Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE GRAPH SECTION 1 Regional Economics Create Differences SECTION 2 Nationalism at Center Stage MAP SECTION 3
Binder Page Name Period Andrew Jackson and the Growth of American Democracy
 Binder Page Name Period Andrew Jackson and the Growth of American Democracy Date Chapter 6.1 Jackson Wins the Presidency- (p. 302-312) 1. Democracy was growing in the United States. In other words, the
Binder Page Name Period Andrew Jackson and the Growth of American Democracy Date Chapter 6.1 Jackson Wins the Presidency- (p. 302-312) 1. Democracy was growing in the United States. In other words, the
This cartoon shows that Nullification is just one of the steps leading to Despotism. John C. Calhoun is ascending the steps to reach for the crown.
 LEQ: What was the name given to the right of states to declare federal laws illegal? This cartoon shows that Nullification is just one of the steps leading to Despotism. John C. Calhoun is ascending the
LEQ: What was the name given to the right of states to declare federal laws illegal? This cartoon shows that Nullification is just one of the steps leading to Despotism. John C. Calhoun is ascending the
The Significance of President Andrew Jackson. Josh Liller
 The Significance of President Andrew Jackson Josh Liller FAU AMH4150 March 22, 2012 Andrew Jackson served two terms as President of the United States, elected in 1828 and 1832. Though he remains highly
The Significance of President Andrew Jackson Josh Liller FAU AMH4150 March 22, 2012 Andrew Jackson served two terms as President of the United States, elected in 1828 and 1832. Though he remains highly
James Monroe Leaves Office
 Chapter Time Line Chapter Time Line James Monroe Leaves Office From 1816 and 1824, the US had only one political party The Republicans James Monroe refused to run for a third term Four candidates from
Chapter Time Line Chapter Time Line James Monroe Leaves Office From 1816 and 1824, the US had only one political party The Republicans James Monroe refused to run for a third term Four candidates from
Presidency Chart Andrew Jackson ( )
 Presidency Chart Andrew Jackson (1829-1837) Election of 1824 Four Republicans ran for president. On election day Andrew Jackson of Tennessee led the popular vote and in the Electoral College but did not
Presidency Chart Andrew Jackson (1829-1837) Election of 1824 Four Republicans ran for president. On election day Andrew Jackson of Tennessee led the popular vote and in the Electoral College but did not
How do you think the president should be chosen?
 How do you think the president should be chosen? A. By the current system with an electoral college B. By the popular vote of the people C. By the Congress A. A B. B C. C Chapter 11 The Jackson Era (1824-1845)
How do you think the president should be chosen? A. By the current system with an electoral college B. By the popular vote of the people C. By the Congress A. A B. B C. C Chapter 11 The Jackson Era (1824-1845)
Chapter 9: Jacksonian America
 Chapter 9: Jacksonian America Our Federal Union It Must Be Preserved Andrew Jackson The Rise of Mass Politics Andrew Jackson was sworn in as President on March 4, 1829 and his inauguration marked an era
Chapter 9: Jacksonian America Our Federal Union It Must Be Preserved Andrew Jackson The Rise of Mass Politics Andrew Jackson was sworn in as President on March 4, 1829 and his inauguration marked an era
From VOA Learning English, welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in Special English. I m Steve Ember.
 From VOA Learning English, welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in Special English. I m Steve Ember. Today, we continue our story of the United States Constitution. In recent weeks, we told
From VOA Learning English, welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in Special English. I m Steve Ember. Today, we continue our story of the United States Constitution. In recent weeks, we told
Adams Avoids War with France
 Adams Avoids War with France The Making of a Nation Program No. 28 John Adams Part Two From VOA Learning English, welcome to The Making of a Nation. American history in Special English. I m Steve Ember.
Adams Avoids War with France The Making of a Nation Program No. 28 John Adams Part Two From VOA Learning English, welcome to The Making of a Nation. American history in Special English. I m Steve Ember.
VIDEO OBJECTIVES. 1. Analyze the key characteristics of Jacksonian Democracy and the elections of 1824 and 1828.
 When Jackson wasn t battling Calhoun or his wife, over the Peggy Eaton affair, he was locking horns with Nicholas Biddle, president of the Bank of the United States, over re-charting the Bank of the United
When Jackson wasn t battling Calhoun or his wife, over the Peggy Eaton affair, he was locking horns with Nicholas Biddle, president of the Bank of the United States, over re-charting the Bank of the United
The Age of Jackson. Part 2
 The Age of Jackson Part 2 Old Hickory Jackson was a true folk hero to the masses He had been an orphan but had made himself into a successful politician, war hero, and wealthy plantation owner Jackson
The Age of Jackson Part 2 Old Hickory Jackson was a true folk hero to the masses He had been an orphan but had made himself into a successful politician, war hero, and wealthy plantation owner Jackson
STAAR OBJECTIVE: 3. Government and Citizenship
 STAAR OBJECTIVE: 3 Government and Citizenship 1. What is representative government? A. Government that represents the interests of the king. B. Government in which elected officials represent the interest
STAAR OBJECTIVE: 3 Government and Citizenship 1. What is representative government? A. Government that represents the interests of the king. B. Government in which elected officials represent the interest
Study Guide: Sunshine State Standards
 Chapter 11, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 334 339 JACKSONIAN DEMOCRACY KEY TERMS favorite son Candidates backed by their home states instead of the national party (page 335) majority More than
Chapter 11, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 334 339 JACKSONIAN DEMOCRACY KEY TERMS favorite son Candidates backed by their home states instead of the national party (page 335) majority More than
I was born for a storm and a calm does not suit me.
 I was born for a storm and a calm does not suit me. Reign of King Mob Jacksonian Democracy Today s Non-Negotiable Understand how the election of Andrew Jackson gives rise to mass politics. (e.g. Common
I was born for a storm and a calm does not suit me. Reign of King Mob Jacksonian Democracy Today s Non-Negotiable Understand how the election of Andrew Jackson gives rise to mass politics. (e.g. Common
Lincoln s Election and Southern Secession
 Lincoln s Election and Southern Secession MAIN IDEA The election of Lincoln led the Southern states to secede from the Union. WHY IT MATTERS NOW This was the only time in U.S. history that states seceded
Lincoln s Election and Southern Secession MAIN IDEA The election of Lincoln led the Southern states to secede from the Union. WHY IT MATTERS NOW This was the only time in U.S. history that states seceded
The Declaration of Independence
 The Declaration of Independence From VOA Learning English, this is The Making of a Nation American history in Special English. I'm Steve Ember. This week in our series, we continue the story of the American
The Declaration of Independence From VOA Learning English, this is The Making of a Nation American history in Special English. I'm Steve Ember. This week in our series, we continue the story of the American
This cartoon shows that Nullification is just one of the steps leading to Despotism. John C. Calhoun is ascending the steps to reach for the crown.
 LEQ: What was the name given to the right of states to declare federal laws illegal? This cartoon shows that Nullification is just one of the steps leading to Despotism. John C. Calhoun is ascending the
LEQ: What was the name given to the right of states to declare federal laws illegal? This cartoon shows that Nullification is just one of the steps leading to Despotism. John C. Calhoun is ascending the
Preview. If you were elected President, who would you put in government positions in the Executive Branch?
 Preview If you were elected President, who would you put in government positions in the Executive Branch? Title your page this! Andrew Jackson a. Nicknamed Old Hickory for his toughness b. Major General
Preview If you were elected President, who would you put in government positions in the Executive Branch? Title your page this! Andrew Jackson a. Nicknamed Old Hickory for his toughness b. Major General
Study Guide: Sunshine State Standards
 Chapter 11, Section 1 (continued) 1. How did John Quincy Adams win the election of 1824? The Election of 1828 (pages 335 336) The Republican Party was divided. The Democratic-Republicans supported Jackson.
Chapter 11, Section 1 (continued) 1. How did John Quincy Adams win the election of 1824? The Election of 1828 (pages 335 336) The Republican Party was divided. The Democratic-Republicans supported Jackson.
March 16, Unit 5 Chapter 12.notebook. Wednesday March 4, 2015 What you'll need today: Big Question Who was Andrew Jackson?
 Wednesday March 4, 2015 Big Question for Ch. 12 Start Chapter 12 Fun Fact?: A quater has 119 grooves on its edge. Big Question Using previous knowledge, what we've learned, and what we are going to learn
Wednesday March 4, 2015 Big Question for Ch. 12 Start Chapter 12 Fun Fact?: A quater has 119 grooves on its edge. Big Question Using previous knowledge, what we've learned, and what we are going to learn
Antebellum Politics. Lagniappe. Section2
 Section2 Antebellum Politics Top: Jacques Villere was a Creole who was elected as the second governor of Louisiana. Above: Anglo American Thomas Bolling Robertson was the third governor of the state. As
Section2 Antebellum Politics Top: Jacques Villere was a Creole who was elected as the second governor of Louisiana. Above: Anglo American Thomas Bolling Robertson was the third governor of the state. As
Describe why the election of 1824 was called a Corrupt Bargain by Jackson supporters. Explain one way in which voting rights were expanded.
 The Age of Jackson in United States History: Beginnings to 1877 SWBATs: Describe why the election of 1824 was called a Corrupt Bargain by Jackson supporters. Explain one way in which voting rights were
The Age of Jackson in United States History: Beginnings to 1877 SWBATs: Describe why the election of 1824 was called a Corrupt Bargain by Jackson supporters. Explain one way in which voting rights were
JQA and Jackson
 JQA and Jackson 1824-1840 New parties AFTER ELECTION OF 1824 JACKSONIAN DEMOCRACY The political world changed during the New Democracy and two new political parties emerge: NATIONAL REPUBLICANS 1. Adams,
JQA and Jackson 1824-1840 New parties AFTER ELECTION OF 1824 JACKSONIAN DEMOCRACY The political world changed during the New Democracy and two new political parties emerge: NATIONAL REPUBLICANS 1. Adams,
#9: The Age of Jackson
 #9: The Age of Jackson 1. Part of the "democratizing" of politics during the age of Jackson was the A) direct election of United States senators. B) enfranchisement of women in western states. C) elimination
#9: The Age of Jackson 1. Part of the "democratizing" of politics during the age of Jackson was the A) direct election of United States senators. B) enfranchisement of women in western states. C) elimination
Chapter 11, section 1. Jacksonian Democracy
 Chapter 11, section 1 Jacksonian Democracy 1. Who ran in the election of 1824? Why was there more than one candidate when there was only one party, and which part of the country did each represent? John
Chapter 11, section 1 Jacksonian Democracy 1. Who ran in the election of 1824? Why was there more than one candidate when there was only one party, and which part of the country did each represent? John
Sectionalism:loyalty to one s part or area or region of the country as. opposed to loyalty to the whole country... is it good for me?
 Sectionalism:loyalty to one s part or area or region of the country as opposed to loyalty to the whole country... is it good for me? Southern exports The Main Issues Slavery: Should it exist at all? Should
Sectionalism:loyalty to one s part or area or region of the country as opposed to loyalty to the whole country... is it good for me? Southern exports The Main Issues Slavery: Should it exist at all? Should
1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation
 Topic 3 1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg 88-89 They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation agreements 2. How did the British respond to the Boston Tea
Topic 3 1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg 88-89 They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation agreements 2. How did the British respond to the Boston Tea
Election of Rise of Popular Politics. Republican Candidates. A Democratic Revolution. New Democracy franchise
 Rise of Popular Politics Chapter 10 A Democratic Revolution New Democracy franchise 1810s many states: all white men only place in world laborers, small farmers new western states Republican Candidates
Rise of Popular Politics Chapter 10 A Democratic Revolution New Democracy franchise 1810s many states: all white men only place in world laborers, small farmers new western states Republican Candidates
1. It disappeared after President James Monroe s landslide election victory in 1816.
 Chapter 10: A Changing Nation 1815-1840 Section 1: Building National Identity 1. It disappeared after President James Monroe s landslide election victory in 1816. 2. You were to put an X on the chart next
Chapter 10: A Changing Nation 1815-1840 Section 1: Building National Identity 1. It disappeared after President James Monroe s landslide election victory in 1816. 2. You were to put an X on the chart next
US History Module 1 (A) Lesson 3. A New Nation
 US History Module 1 (A) Lesson 3 A New Nation Forming a New Government Fears and concerns about the form of government affects planning of new government Experimenting with Confederation 1781 Congress
US History Module 1 (A) Lesson 3 A New Nation Forming a New Government Fears and concerns about the form of government affects planning of new government Experimenting with Confederation 1781 Congress
Madison & Monroe. Presidencies
 James James Madison & Monroe Presidencies Where we are March 1797: President John Adams takes office. 1796-1800: XYZ Affair, Quasi-War with France, Alien & Sedition Acts, VA & KY Resolutions 1801-1804:
James James Madison & Monroe Presidencies Where we are March 1797: President John Adams takes office. 1796-1800: XYZ Affair, Quasi-War with France, Alien & Sedition Acts, VA & KY Resolutions 1801-1804:
The Jacksonian Era & the Rise of Sectionalism. (c. 1820s c. 1840s)
 The Jacksonian Era & the Rise of Sectionalism (c. 1820s c. 1840s) SSUSH7 Students will explain the process of economic growth, its regional and national impact in the first half of the 19th century, and
The Jacksonian Era & the Rise of Sectionalism (c. 1820s c. 1840s) SSUSH7 Students will explain the process of economic growth, its regional and national impact in the first half of the 19th century, and
APUSH Reading Quiz 13 The Rise of Mass Democracy ( )
 APUSH Reading Quiz 13 The Rise of Mass Democracy (1824-1840) Period 2 1. Though an ardent advocate for states rights, Andrew Jackson believed that the preservation of the Union was a higher political priority.
APUSH Reading Quiz 13 The Rise of Mass Democracy (1824-1840) Period 2 1. Though an ardent advocate for states rights, Andrew Jackson believed that the preservation of the Union was a higher political priority.
Adams Becomes President
 John Adams Adams Becomes President 1796 campaign Adams was supported by New England and Federalists Defeated Jefferson 71-68 by Electoral College Jefferson becomes VP France and US close to war Jay s Treaty
John Adams Adams Becomes President 1796 campaign Adams was supported by New England and Federalists Defeated Jefferson 71-68 by Electoral College Jefferson becomes VP France and US close to war Jay s Treaty
Chapter 11. Multiple-Choice Questions
 Chapter 11 Multiple-Choice Questions 1a. Correct. Leaders of the revival movement taught that perfection of earthly society would lead to the Second Coming. Therefore, evangelical Protestants became involved
Chapter 11 Multiple-Choice Questions 1a. Correct. Leaders of the revival movement taught that perfection of earthly society would lead to the Second Coming. Therefore, evangelical Protestants became involved
The Triumph of Democracy
 Name: Give Me Liberty!, Chapter 10 Video Guide Big Idea Questions Who wrote The Liberator? What is the cult of domesticity? Guided Notes The Triumph of Democracy Jackson s inauguration Seen as the Man
Name: Give Me Liberty!, Chapter 10 Video Guide Big Idea Questions Who wrote The Liberator? What is the cult of domesticity? Guided Notes The Triumph of Democracy Jackson s inauguration Seen as the Man
Consequences of the War of 1812
 Consequences of the War of 1812 Collapse of Federalist Party Era of Good Feelings Monroe Presidency 18161824 Bring factions togethersimilar to Washington Last of Revolutionary Founding Fathers Appointed
Consequences of the War of 1812 Collapse of Federalist Party Era of Good Feelings Monroe Presidency 18161824 Bring factions togethersimilar to Washington Last of Revolutionary Founding Fathers Appointed
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism
 Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism Regional Economies Create Differences Samuel Slater brought the Water Frame to Rhode Island from Great Britain in 1789. It was used to spin raw cotton into cotton
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism Regional Economies Create Differences Samuel Slater brought the Water Frame to Rhode Island from Great Britain in 1789. It was used to spin raw cotton into cotton
James Monroe and The Era of Good Feelings. The Role of Politics in Sectionalism
 James Monroe and The Era of Good Feelings The Role of Politics in Sectionalism James Monroe 1758 1831 Dem.-Republican 5 th President (1817-25) Last President to have participated in the Revolution Former
James Monroe and The Era of Good Feelings The Role of Politics in Sectionalism James Monroe 1758 1831 Dem.-Republican 5 th President (1817-25) Last President to have participated in the Revolution Former
netw rks Where in the world? When did it happen? The Federalist Era Lesson 1 The First President ESSENTIAL QUESTION Terms to Know GUIDING QUESTIONS
 Lesson 1 The First President ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the characteristics of a leader? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. What decisions did Washington and the new Congress have to make about the new government?
Lesson 1 The First President ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the characteristics of a leader? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. What decisions did Washington and the new Congress have to make about the new government?
The Path to Civil War
 The Path to Civil War It all started at the Constitutional Convention The Three-Fifths Compromise Allowed southern states to count 3/5 of their slave populations for purposes of determining how many representatives
The Path to Civil War It all started at the Constitutional Convention The Three-Fifths Compromise Allowed southern states to count 3/5 of their slave populations for purposes of determining how many representatives
Chapter 10. The Triumph of White Men s Democracy APUSH, Mr. Muller
 Chapter 10 The Triumph of White Men s Democracy APUSH, Mr. Muller Aim: What makes the Jacksonian Democracy different from the previous? Do Now: The political activity that pervades the U.S. must be seen
Chapter 10 The Triumph of White Men s Democracy APUSH, Mr. Muller Aim: What makes the Jacksonian Democracy different from the previous? Do Now: The political activity that pervades the U.S. must be seen
4 th Grade U.S. Government Study Guide
 4 th Grade U.S. Government Study Guide Big Ideas: Imagine trying to make a new country from scratch. You ve just had a war with the only leaders you ve ever known, and now you have to step up and lead.
4 th Grade U.S. Government Study Guide Big Ideas: Imagine trying to make a new country from scratch. You ve just had a war with the only leaders you ve ever known, and now you have to step up and lead.
BellRinger 10/17 Using the maps below, explain how America changed from 1800 to 1830.
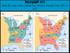 BellRinger 10/17 Using the maps below, explain how America changed from 1800 to 1830. President Jackson Stations Print the following slides and distribute to groups use as stations and have students rotate
BellRinger 10/17 Using the maps below, explain how America changed from 1800 to 1830. President Jackson Stations Print the following slides and distribute to groups use as stations and have students rotate
Division of Labor: giving each worker one or two simple jobs.
 Chapter 12 The Nation Grows (1815-1830) Section 1 Industries take Root Industrial Revolution: the growth of industry eventually produced changes so great that this time in history is called the Industrial
Chapter 12 The Nation Grows (1815-1830) Section 1 Industries take Root Industrial Revolution: the growth of industry eventually produced changes so great that this time in history is called the Industrial
Nuts and Bolts of Civil War/Reconstruction Unit
 Sectionalism Nuts and Bolts of Civil War/Reconstruction Unit Differences between the various regions of the United States had a great impact on the events leading up to the Civil War. The North Industrialized
Sectionalism Nuts and Bolts of Civil War/Reconstruction Unit Differences between the various regions of the United States had a great impact on the events leading up to the Civil War. The North Industrialized
Henry Clay met with Adams, and said he would use his influence as Speaker of the House to elect Adams if Adams named him Sec. of State Adams was
 Election of 1824 Monroe ends 2 nd term, four candidates ran William Crawford Georgia Andrew Jackson Tennessee Henry Clay Kentucky John Quincy Adams Massachusetts each candidate had regional support and
Election of 1824 Monroe ends 2 nd term, four candidates ran William Crawford Georgia Andrew Jackson Tennessee Henry Clay Kentucky John Quincy Adams Massachusetts each candidate had regional support and
Chapter 10 Test: The Age of Jackson
 Chapter 10 Test: The Age of Jackson PRACTICE TEST Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What effect did the Tariff of Abominations have on Andrew
Chapter 10 Test: The Age of Jackson PRACTICE TEST Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What effect did the Tariff of Abominations have on Andrew
The Making of a Nation: James Monroe, Part 1
 The Making of a Nation: James Monroe, Part 1 President James Madison retired after eight years in office. His Republican Party chose another Virginian, James Monroe, as its next presidential candidate.
The Making of a Nation: James Monroe, Part 1 President James Madison retired after eight years in office. His Republican Party chose another Virginian, James Monroe, as its next presidential candidate.
Age of Jackson. 7 pages
 Age of Jackson 7 pages James Monroe 1817-1825 He is still president U.S. Territory The United States in 1819 (the light orange and light green areas were not then U.S. territory). The Missouri Compromise
Age of Jackson 7 pages James Monroe 1817-1825 He is still president U.S. Territory The United States in 1819 (the light orange and light green areas were not then U.S. territory). The Missouri Compromise
The Founding Fathers wanted to make sure they did things correctly. They even spent 3 weeks deciding what to call the President!!!
 The Founding Fathers wanted to make sure they did things correctly. They even spent 3 weeks deciding what to call the President!!! His Excellency, and His Highness were suggested, but Washington was simply
The Founding Fathers wanted to make sure they did things correctly. They even spent 3 weeks deciding what to call the President!!! His Excellency, and His Highness were suggested, but Washington was simply
Key Concept 4.3, I: The US needed a foreign policy and an expansion policy
 Key Concept 4.3, I: The US needed a foreign policy and an expansion policy Key Concept 4.3: U.S. interest in increasing foreign trade, expanding its national borders, and isolating itself from European
Key Concept 4.3, I: The US needed a foreign policy and an expansion policy Key Concept 4.3: U.S. interest in increasing foreign trade, expanding its national borders, and isolating itself from European
Washington, Jefferson, Madison, Monroe, Jackson, and Polk Presidencies
 Washington, Jefferson, Madison, Monroe, Jackson, and Polk Presidencies 1. George Washington (1789-1797) - Created a cabinet of advisors 1. Secretary of War - Henry Knox 2. Secretary of the Treasury - Alexander
Washington, Jefferson, Madison, Monroe, Jackson, and Polk Presidencies 1. George Washington (1789-1797) - Created a cabinet of advisors 1. Secretary of War - Henry Knox 2. Secretary of the Treasury - Alexander
2. An Era of Jacksonian
 The Era of Jacksonian Democracy I've got big shoes to fill. This is my chance to do something. I have to seize the moment. Andrew Jackson, upon entering the Presidency. (1828-1850) 1. The Administration
The Era of Jacksonian Democracy I've got big shoes to fill. This is my chance to do something. I have to seize the moment. Andrew Jackson, upon entering the Presidency. (1828-1850) 1. The Administration
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e. Chapter Nine: Jacksonian America
 Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e Introduction Alexis De Tocqueville Equality of Opportunity 2 The Rise of Mass Politics Jackson s Inauguration Andrew Jackson Travels to Washington (Library of Congress)
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e Introduction Alexis De Tocqueville Equality of Opportunity 2 The Rise of Mass Politics Jackson s Inauguration Andrew Jackson Travels to Washington (Library of Congress)
This Power Point presentation goes with the Mastering the Grade 8 Social Studies TEKS book by Jarrett, Zimmer, and Killoran Chapter 11 The Age of
 This Power Point presentation goes with the Mastering the Grade 8 Social Studies TEKS book by Jarrett, Zimmer, and Killoran Chapter 11 The Age of Hero of the Battle of New Orleans Fought Indians in Georgia
This Power Point presentation goes with the Mastering the Grade 8 Social Studies TEKS book by Jarrett, Zimmer, and Killoran Chapter 11 The Age of Hero of the Battle of New Orleans Fought Indians in Georgia
SMALL FARMERS, FRONTIER SETTLERS & SLAVE HOLDERS
 8 th Grade American Studies Name Unit 6 The New Republic Date Topic: Jacksonian Democracy Period Chapter 10 Section 1 (322 324) & 326-327 & 329-331 Expansion of Democracy In the early 1800 s, how was life
8 th Grade American Studies Name Unit 6 The New Republic Date Topic: Jacksonian Democracy Period Chapter 10 Section 1 (322 324) & 326-327 & 329-331 Expansion of Democracy In the early 1800 s, how was life
White House Transitions Fact Sheet Compiled November 2016
 White House Transitions Fact Sheet Compiled November 2016 1801 Fearing possible violence and recrimination between Federalists and Democratic-Republicans, President John Adams considered resigning several
White House Transitions Fact Sheet Compiled November 2016 1801 Fearing possible violence and recrimination between Federalists and Democratic-Republicans, President John Adams considered resigning several
8-4.3 Notes - Causes of Secession: Why South Carolina Left the Union
 8-4.3 Notes - Causes of Secession: Why South Carolina Left the Union Objectives - Analyze key issues that led to South Carolina s secession from the Union, including the nullification controversy and John
8-4.3 Notes - Causes of Secession: Why South Carolina Left the Union Objectives - Analyze key issues that led to South Carolina s secession from the Union, including the nullification controversy and John
Unit 7 Our Current Government
 Unit 7 Our Current Government Name Date Period Learning Targets (What I need to know): I can describe the Constitutional Convention and two compromises that took place there. I can describe the structure
Unit 7 Our Current Government Name Date Period Learning Targets (What I need to know): I can describe the Constitutional Convention and two compromises that took place there. I can describe the structure
netw rks Reading Essentials and Study Guide Growth and Division, Lesson 1 American Nationalism ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Reading HELPDESK
 and Study Guide Lesson 1 American Nationalism ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How did the nation s economy help shape its politics? How did the economic differences between the North and the South cause tension? Reading
and Study Guide Lesson 1 American Nationalism ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How did the nation s economy help shape its politics? How did the economic differences between the North and the South cause tension? Reading
History 1301 U.S. to Unit 3 - Lecture 1 ~
 History 1301 U.S. to 1877 Unit 3 - Lecture 1 ~ Jacksonian America Jacksonian America: Era of the Common Man: Belief that affluence and property was in reach for all (White) men Growth spawned social, political
History 1301 U.S. to 1877 Unit 3 - Lecture 1 ~ Jacksonian America Jacksonian America: Era of the Common Man: Belief that affluence and property was in reach for all (White) men Growth spawned social, political
The Rise of Mass Democracy
 The Rise of Mass Democracy 1824-1840 The Election of 1824 Four candidates vie for presidency (Monroe ends the Virginia Dynasty): John Quincy Adams MA Henry Clay Kentucky William Crawford Georgia Andrew
The Rise of Mass Democracy 1824-1840 The Election of 1824 Four candidates vie for presidency (Monroe ends the Virginia Dynasty): John Quincy Adams MA Henry Clay Kentucky William Crawford Georgia Andrew
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton
 Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
America s History, Chapter 10: A Democratic Revolution,
 America s History, Chapter 10: A Democratic Revolution, 1800 1844 Key Concept: Innovations in technology, agriculture, and commerce powerfully accelerated the American economy, precipitating profound changes
America s History, Chapter 10: A Democratic Revolution, 1800 1844 Key Concept: Innovations in technology, agriculture, and commerce powerfully accelerated the American economy, precipitating profound changes
REVIEW FOR 4 TH 6 WEEKS COMPREHENSIVE EXAM
 REVIEW FOR 4 TH 6 WEEKS COMPREHENSIVE EXAM 1. What were the main foreign policy issues faced by Washington (include an evaluation of his farewell address)? Keeping the USA neutral during the war between
REVIEW FOR 4 TH 6 WEEKS COMPREHENSIVE EXAM 1. What were the main foreign policy issues faced by Washington (include an evaluation of his farewell address)? Keeping the USA neutral during the war between
Revolution in Thought 1607 to 1763
 Revolution in Thought 1607 to 1763 Early settlers found they disliked England America was far from England and isolated Weakened England s authority Produced rugged and independent people Colonies had
Revolution in Thought 1607 to 1763 Early settlers found they disliked England America was far from England and isolated Weakened England s authority Produced rugged and independent people Colonies had
American Political History, Topic 6: The Civil War Era and the Lincoln-Douglas Debates (1858)
 Background: By 1858, the United States was a house divided against itself in at least two important ways. First, the nation was divided over issues related to sovereignty in the federal system. Should
Background: By 1858, the United States was a house divided against itself in at least two important ways. First, the nation was divided over issues related to sovereignty in the federal system. Should
1. Election of 1828: Andrew Jackson defeats John Quincy Adams. Tariff of 1828 destroyed Adams, negative campaigning occurred for first time.
 1. Election of 1828: Andrew defeats John Quincy Adams. Tariff of 1828 destroyed Adams, negative campaigning occurred for first time. War Hero Nicknames Old Hickory Common Man Born in a Log Cabin Education?
1. Election of 1828: Andrew defeats John Quincy Adams. Tariff of 1828 destroyed Adams, negative campaigning occurred for first time. War Hero Nicknames Old Hickory Common Man Born in a Log Cabin Education?
NEW GOVERNMENT: CONFEDERATION TO CONSTITUTION FLIP CARD
 NEW GOVERNMENT: CONFEDERATION TO CONSTITUTION FLIP CARD Big Ideas: Imagine trying to make a new country from scratch. You ve just had a war with the only leaders you ve ever known, and now you have to
NEW GOVERNMENT: CONFEDERATION TO CONSTITUTION FLIP CARD Big Ideas: Imagine trying to make a new country from scratch. You ve just had a war with the only leaders you ve ever known, and now you have to
The First President. Guide to Reading
 The First President Main Idea President Washington and the first Congress tackled the work of establishing a new government. Key Terms precedent, cabinet, national debt, bond, speculator, unconstitutional,
The First President Main Idea President Washington and the first Congress tackled the work of establishing a new government. Key Terms precedent, cabinet, national debt, bond, speculator, unconstitutional,
Jeopardy. Final Jeopardy. Study Guide Questions. 7.3/7.4 IDs Jackson Government. Random $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300
 Jeopardy 7.3/7.4 IDs Jackson Government Study Guide Questions Random $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 Final Jeopardy
Jeopardy 7.3/7.4 IDs Jackson Government Study Guide Questions Random $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 Final Jeopardy
Chapter 10: The Triumph of White Men s Democracy
 Chapter 10: The Triumph of White Men s Democracy AP United States History Week of December 6, 2015 Democracy in Theory and Practice What is democracy? What is meant by a democratic society? During the
Chapter 10: The Triumph of White Men s Democracy AP United States History Week of December 6, 2015 Democracy in Theory and Practice What is democracy? What is meant by a democratic society? During the
An act which drew an imaginary line down spine of the Appalachian Mountains and closed lands west of the line off for colonial settlement.
 NC Text p. 167-173 Topic: The Road to Revolution Key Vocabulary & People: Pontiac Well respected Ottowa Indian leader (chief) who would organize Native American troops to fight against the British in Pontiac
NC Text p. 167-173 Topic: The Road to Revolution Key Vocabulary & People: Pontiac Well respected Ottowa Indian leader (chief) who would organize Native American troops to fight against the British in Pontiac
Alien and Sedition Acts- Passed by Adams (Federalists) in Issue: What violates freedom of speech? Why were these laws passed?
 Name Alien and Sedition Acts- Passed by Adams (Federalists) in 1798 Issue: What violates freedom of speech? What did the laws do? Alien act- Why were these laws passed? Adams (Federalist reason)- What
Name Alien and Sedition Acts- Passed by Adams (Federalists) in 1798 Issue: What violates freedom of speech? What did the laws do? Alien act- Why were these laws passed? Adams (Federalist reason)- What
Essential Question: What justifies the limitation or promotion of freedom?
 Name _ Period Parent Signature (EC) LESSON PACKET - We The People 7 th Social Studies DUE DATE:_ Essential Question: What justifies the limitation or promotion of freedom? Directions: Read the following
Name _ Period Parent Signature (EC) LESSON PACKET - We The People 7 th Social Studies DUE DATE:_ Essential Question: What justifies the limitation or promotion of freedom? Directions: Read the following
hapter 11 WHAT YOU WILL LEARN:
 Chapter 11 hapter 11 WHAT YOU WILL LEARN: About the Differences between Federalists and Republicans by comparing the ideas of Alexander Hamilton and Thomas Jefferson. Preview CH 11 ISN to page 73 As you
Chapter 11 hapter 11 WHAT YOU WILL LEARN: About the Differences between Federalists and Republicans by comparing the ideas of Alexander Hamilton and Thomas Jefferson. Preview CH 11 ISN to page 73 As you
