LEQ: What are the three branches of the United States Federal Government?
|
|
|
- Imogene Thompson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LEQ: What are the three branches of the United States Federal Government? This image of the United States Capitol is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons. This image of the White House s Truman Balcony is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons. This image of the west front of the United States Supreme Court was taken by Robert Housch facing east on July 2, 2009.
2 LEQ: What are the three branches of the United States Federal Government? Legislative Executive Judicial This image of the United States Capitol is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons. This image of the White House s Truman Balcony is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons. This image of the west front of the United States Supreme Court was taken by Robert Housch facing east on July 2, 2009.
3 The Constitution This image is titled: Washington as Statesman at the Constitutional Convention. This image was painted in 1856 by Junius Brutus Stearns ( ). It is courtesy of the Virginia Museum of Fine Arts.
4 LEQ: What are the three branches of the United States Federal Government? This image of the United States Capitol is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons. This image of the White House s Truman Balcony is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons. This image of the west front of the United States Supreme Court was taken by Robert Housch facing east on July 2, 2009.
5 LEQ: What are the three branches of the United States Federal Government? Legislative Executive Judicial This image of the United States Capitol is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons. This image of the White House s Truman Balcony is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons. This image of the west front of the United States Supreme Court was taken by Robert Housch facing east on July 2, 2009.
6 55 delegates from 12 states (not Rhode Island) met in the Pennsylvania State House (Independence Hall) during the summer of The Philadelphia State House (Independence Hall) was constructed from This image by Robert Housch was taken facing southwest at approximately 9:30 AM on Thursday, July 30, 2009.
7 The document that they created has outlived every other constitution in the world, clearly standing the test of time. This image titled Scene at the Signing of the Constitution of the United States depicts George Washington standing on the right and Ben Franklin seated in the center. This image by Howard Chandler Christy ( ) was created in 1940 and is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
8 As the delegates began to write the new Constitution, they drew from a variety of sources. The delegates met in the Assembly Room where the Declaration of Independence had been adopted in This image by Robert Housch was taken facing southeast at approximately 11:30 AM on Thursday, July 30, 2009.
9 In the Native Americans Iroquois League, member nations governed their individual affairs but joined together for defense. An Attack on an Iroquois Fort. This image is from Benson Lossing s Harper s Encyclopedia of United States History published in New York by Harper & Brothers Publishers in 1912.
10 The idea of limiting the power of a ruler was taken from England s Magna Carta of The Magna Carta (originally known as the Charter of Liberties) of 1215 was the first document to limit the power of an English King by his subjects. It was written in iron gall ink on parchment in medieval Latin, using standard abbreviations of the period, authenticated with the Great Seal of King John. The original wax seal was lost over the centuries. This document is held at the British Library and is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
11 The idea of representative government also came from England. This image of Great Britain s House of Commons was produced for Rudolph Ackermann s the Microcosm of London which was produced in three volumes from This image is courtesy of austenonly.com.
12 Enlightenment thinkers believed that people could improve society by using reason. John Locke ( ) was one of the most influential Enlightenment thinkers. This image was painted by Sir Godfrey Kneller ( ) in This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
13 Locke believed all people had natural rights to life, liberty, and property. This pyramid shows that life is the most important of these natural rights. This image is courtesy of nathankey.com.
14 Locke also believed that government should function as a contract between ruler and the ruled. If the government broke that contract, the people had a right to rebel. This image is courtesy of touregypt.net.
15 The concept of separation of powers came from a French enlightenment philosopher, Baron de Montesquieu. Charles-Louis de Secondat, Baron de La Brede et de Montesquieu ( ) was a French lawyer and philosopher. This painting was created by an unknown artist in This image is courtesy of the Palace of Versailles and of Wikimedia Commons.
16 Baron de Montesquieu thought that a government s power should be shared among three branches legislative, executive, and judicial. The Constitution of the United States divides power among the three branches of the federal government. The Legislative Branch is the Congress. The Executive Branch is headed by the President. The Judicial Branch is controlled by the Supreme Court. This image is courtesy of alton.k12.mo.us.
17 The division of power between the national government and state governments is called federalism. A map of the United States showing the 50 states. Only the District of Columbia is abbreviated. This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
18 The powers of the federal government include the power to declare war, to issue money, to regulate trade with other countries and among the states, and to make treaties. President Woodrow Wilson (center) and American Peace Commissioners at the Paris Peace Conference in At the conference they and other countries would sign the Treaty of Versailles, which ended World War I. This image is courtesy of wikimedia.org.
19 According to the Constitution, powers not specifically given to the federal government nor denied to the states are reserved to the states or the people. On August 28, 1963, Civil Rights organizers led the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom. The speeches were held at the Lincoln Memorial where the camera is positioned. In the background is the Washington Monument and the Reflecting Pool. This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
20 Under the Constitution, the state and federal governments share some powers. Both the national government and the state governments build roads. This image was taken at the junction of the Mummasburg Road (right to left) and Howard Avenue at Gettysburg National Military Park. This view by Robert Housch was taken facing east at approximately 4:30 PM on Tuesday, May 12, 2009.
21 The national government has more power than the state governments. This is the east front of the United States Capitol. The Senate meets in the wing on the right (north wing). This image by Robert Housch was taken at approximately 2:15 PM on July 2, 2009.
22 The founding fathers did not believe a single body should make the laws, enforce the laws, and interpret the laws. The Founding Fathers believed that there should be a separation of powers within the federal government. This image is courtesy of constitutionalfights.blogspot.com.
23 LEQ: What are the three branches of the United States Federal Government? This image of the United States Capitol is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons. This image of the White House s Truman Balcony is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons. This image of the west front of the United States Supreme Court was taken by Robert Housch facing east on July 2, 2009.
24 LEQ: What are the three branches of the United States Federal Government? Legislative Executive Judicial This image of the United States Capitol is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons. This image of the White House s Truman Balcony is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons. This image of the west front of the United States Supreme Court was taken by Robert Housch facing east on July 2, 2009.
25 The main responsibility of the legislative branch is to make laws. This photograph shows part of Title 11 of the United States Code (the Bankruptcy Code) on a shelf at a law library in San Francisco. This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
26 Members of the House of Representatives, frequently called Congressmen, are elected to two year terms. This photograph shows the House of Representatives Chamber in the United States Capitol. As the Congressmen face the speaker, the Republicans sit on the left and the Democrats sit on the right. President Barak Obama is speaking to a joint session of Congress on health care reform. This image was taken on September 9, 2009 and is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
27 There are 435 voting Congressmen in the United States. The number of representatives for each state is based on that state s population. The population of the United States is gradually growing in the western and southern states. This image is courtesy of the United States Census Bureau.
28 Your congressman is Scott Perry (R) from Dillsburg, Pennsylvania. Scott Perry (1962-) is the representative (congressman) for Pennsylvania s 4 th Congressional District. This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
29 You live in Pennsylvania s 4 th Congressional District which includes Adams County, York County, and parts of Cumberland and Dauphin counties. This map shows Pennsylvania s 18 Congressional Districts. Each Congressional District in the United States has an average population of 710,767 people. This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
30 Each state has two senators who serve six-year terms. This is a class photograph of the 111 th United States Senate in the Senate Chamber in the United States Capitol. As the Senators face the speaker, the Republicans sit on the left, and the Democrats sit on the right. This image was taken in 2010 and is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
31 Your two United States Senators are Bob Casey Jr. (D) and Pat Toomey (R). Bob Casey Jr. (1960-) (left) is from Scranton, Pennsylvania. Pat Toomey (1961-) (right) is from Allentown, Pennsylvania. These images are courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
32 The Constitution calls for a executive branch to carry out the laws passed by the legislative branch. The President of the United States is the head of the Executive Branch. The President lives at the White House where the helicopter Marine One prepares to land on the South Lawn. This image taken on July 1, 1987 is courtesy of the Department of Defense and Wikimedia Commons.
33 The Judicial Branch includes the Supreme Court, which is the highest court in the land. This is the front entrance (1 st Street Entrance) to the Supreme Court of the United States in Washington, D.C. This image was taken facing east at approximately 3:00 PM by Robert Housch on July 2, 2009.
34 Instead of allowing the people to elect the President directly, the writers of the Constitution developed the idea of an Electoral College. This image shows an Electoral College map for the 2012, 2016, and 2020 Presidential elections. 270 electoral votes are needed to win the election. This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
35 The writers built safeguards into the Constitution to keep each branch from assuming too much authority. This photograph shows the United States Capitol dome as seen from the United States Supreme Court building. This image is courtesy of Wikipedia Commons.
36 An impeachment charge may lead to the removal of the President or a federal judge from office. This drawing shows the 1868 impeachment trial of President Andrew Johnson in the Senate Chamber in the United States Capitol. The Senate is acting as a Court of Impeachment. This image was created by Theodore R. Davis ( ) for Harper s Weekly magazine s April 11, 1868 edition. It is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
37 Federalists favored the Constitution and the strong national government that it created. They wanted to make sure that each state approved or ratified this new Constitution so that it could become the law of the land. The most influential Federalists included from left to right: Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay. This image is courtesy of americanilliterati.blogspot.com.
38 Using pen names, the Federalists wrote a series of essays, called The Federalist Papers, defending the Constitution. The title page of the first printing of the Federalist Papers in The essays, which were part of the collection of the Federalist Papers, were authored by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay. This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
39 Federalists promised that if the states ratified the Constitution, amendments, or additions and changes, would be made to provide a bill of rights to protect the people. There are currently 27 amendments to the United States Constitution. This image is courtesy of Wikipedia Commons.
40 Ratification of the Constitution was to be decided by special conventions to be called in each state. This is the first drawing in a series of cartoons depicting the ratification progress among the States that appeared in the Massachusetts Centinel, beginning on January 16, This image is courtesy of the Library of Congress.
41 New Hampshire ratified the Constitution in June 1788 the ninth state to do so. The Constitution now became law. The cartoon from the Massachusetts Centinel showing that New Hampshire was the ninth state (ninth pillar) to ratify the United States Constitution. This image is courtesy of teachingamericanhistory.org.
42 As promised by the federalists, ten amendments were added to the Constitution. We know the first ten amendments today as the Bill of Rights. The Bill of Rights are the first ten amendments to the United States Constitution. This image is courtesy of arb.ca.gov.
43 Rhode Island became the last of the original 13 states to ratify the Constitution, in The Great Seal of the State of Rhode Island was first adopted in This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
44 LEQ: What are the three branches of the United States Federal Government? This image of the United States Capitol is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons. This image of the White House s Truman Balcony is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons. This image of the west front of the United States Supreme Court was taken by Robert Housch facing east on July 2, 2009.
45 LEQ: What are the three branches of the United States Federal Government? Legislative Executive Judicial This image of the United States Capitol is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons. This image of the White House s Truman Balcony is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons. This image of the west front of the United States Supreme Court was taken by Robert Housch facing east on July 2, 2009.
3: A New Plan of Government. Essential Question: How Do Governments Change?
 3: A New Plan of Government Essential Question: How Do Governments Change? The Constitution s Source Guiding Question: From where did the Framers of the Constitution borrow their ideas about government?
3: A New Plan of Government Essential Question: How Do Governments Change? The Constitution s Source Guiding Question: From where did the Framers of the Constitution borrow their ideas about government?
Chapter 2 TEST Origins of American Government
 US Government - Ried Chapter 2 TEST Origins of American Government 1)The Magna Carta was originally intended to protect the rights of which group? A. religious leaders B. kings and queens C. common people
US Government - Ried Chapter 2 TEST Origins of American Government 1)The Magna Carta was originally intended to protect the rights of which group? A. religious leaders B. kings and queens C. common people
LEQ: The President is in charge of what branch of the U.S. federal government?
 LEQ: The President is in charge of what branch of the U.S. federal government? The south side of the White House decorated for Christmas. This image was taken facing north by Robert Housch on November
LEQ: The President is in charge of what branch of the U.S. federal government? The south side of the White House decorated for Christmas. This image was taken facing north by Robert Housch on November
Vocabulary for Evolution of Government
 Vocabulary for Evolution of Government Directions Students will make a flash card for each word The flash card must include all the information on the screen (cards will be stamped for completeness) The
Vocabulary for Evolution of Government Directions Students will make a flash card for each word The flash card must include all the information on the screen (cards will be stamped for completeness) The
Learning Goal. Main Points 10/24/2012. Discuss the philosophical underpinnings of the U.S. Constitution.
 Learning Goal Discuss the philosophical underpinnings of the U.S. Constitution. Main Points The weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the adoption of a new form of government Federalism becomes
Learning Goal Discuss the philosophical underpinnings of the U.S. Constitution. Main Points The weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the adoption of a new form of government Federalism becomes
LEQ: What Supreme Court Case gave the court more power than it ever had before?
 LEQ: What Supreme Court Case gave the court more power than it ever had before? This image is an inscription on the wall of the United States Supreme Court Building. It is a quote from Chief Justice John
LEQ: What Supreme Court Case gave the court more power than it ever had before? This image is an inscription on the wall of the United States Supreme Court Building. It is a quote from Chief Justice John
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton
 Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS
 CHAPTER 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS The colonists brought with them to North America knowledge of the English political system, including three key ideas about government.
CHAPTER 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS The colonists brought with them to North America knowledge of the English political system, including three key ideas about government.
Why do you think the Framers organized the new country as a republic, when most countries in the world (in 1783) were ruled by a king or queen?
 NAME: Date: U.S. History CHAPTER 7 PACKET ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: 1. What is a constitution? 2. What is a republic? 3. What was the Articles of Confederation? 4. How was state and national power divided under
NAME: Date: U.S. History CHAPTER 7 PACKET ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: 1. What is a constitution? 2. What is a republic? 3. What was the Articles of Confederation? 4. How was state and national power divided under
Major Problem. Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government.
 The Constitution Major Problem Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government. Why? Feared a government like King George The Constitutional
The Constitution Major Problem Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government. Why? Feared a government like King George The Constitutional
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes
 Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
The End of the Confederation Era
 The End of the Confederation Era By 1786 it became clear that the Articles were not working The Philadelphia Convention of 1787 brought leaders from the 12 states (Rhode Island did not attend) to address
The End of the Confederation Era By 1786 it became clear that the Articles were not working The Philadelphia Convention of 1787 brought leaders from the 12 states (Rhode Island did not attend) to address
May, 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania ~Independence Hall~ Leader: George Washington
 May, 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania ~Independence Hall~ Leader: George Washington -May 1787 Philadelphia Met in Independence Hall in Philadelphia George Washington leader -12 of 13 states Rhode Island
May, 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania ~Independence Hall~ Leader: George Washington -May 1787 Philadelphia Met in Independence Hall in Philadelphia George Washington leader -12 of 13 states Rhode Island
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes
 Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
A More Perfect Union. Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation
 A More Perfect Union Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation 1. Eleven of the thirteen states adopted state constitutions. Connecticut and Rhode Island kept its colonial charter as its constitution
A More Perfect Union Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation 1. Eleven of the thirteen states adopted state constitutions. Connecticut and Rhode Island kept its colonial charter as its constitution
LEQ: What were the first two political parties in the United States?
 LEQ: What were the first two political parties in the United States? A symbol for the Federalists became the black and white cockade shown on the left. A black cockade became a symbol for the Federalist
LEQ: What were the first two political parties in the United States? A symbol for the Federalists became the black and white cockade shown on the left. A black cockade became a symbol for the Federalist
LEQ: What are the three branches of the federal government?
 LEQ: What are the three branches of the federal government? The Legislative Branch is divided into two houses. This image is courtesy of nonsensibleshoes.com. LEQ: What are the three branches of the federal
LEQ: What are the three branches of the federal government? The Legislative Branch is divided into two houses. This image is courtesy of nonsensibleshoes.com. LEQ: What are the three branches of the federal
Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings. Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings. Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings. Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings
 Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings The US government has its roots in English history Limited Government The concept that government is limited in what it can and cannot do Representative Government Government
Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings The US government has its roots in English history Limited Government The concept that government is limited in what it can and cannot do Representative Government Government
Magruder s American Government
 Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 Our Political Beginnings
Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 Our Political Beginnings
The constitution supercedes ordinary law even when the law represents the wishes of a majority of citizens.
 AP Government Chapter 2 The Constitution The constitution supercedes ordinary law even when the law represents the wishes of a majority of citizens. The Constitution is this nation s basic law: It creates
AP Government Chapter 2 The Constitution The constitution supercedes ordinary law even when the law represents the wishes of a majority of citizens. The Constitution is this nation s basic law: It creates
TOPIC: HISTORICAL DOCUMENTS. Magna Carta (1215):
 TOPIC: HISTORICAL DOCUMENTS Magna Carta (1215): What was it: One of most important documents in history; What does it mean: The Great Charter in Latin Who issued it: King John of England Why: Served as
TOPIC: HISTORICAL DOCUMENTS Magna Carta (1215): What was it: One of most important documents in history; What does it mean: The Great Charter in Latin Who issued it: King John of England Why: Served as
Chapter 6. APUSH Mr. Muller
 Chapter 6 APUSH Mr. Muller Aim: How is the New Republic tested? Do Now: Thus I consent, sir, to this Constitution, because I expect no better, and because I am not sure that it is not the best. The opinions
Chapter 6 APUSH Mr. Muller Aim: How is the New Republic tested? Do Now: Thus I consent, sir, to this Constitution, because I expect no better, and because I am not sure that it is not the best. The opinions
Name Class Date. MATCHING In the space provided, write the letter of the term or person that matches each description. Some answers will not be used.
 Origins of American Government Section 1 MATCHING In the space provided, write the letter of the term or person that matches each description. Some answers will not be used. 1. Idea that people should
Origins of American Government Section 1 MATCHING In the space provided, write the letter of the term or person that matches each description. Some answers will not be used. 1. Idea that people should
The Constitutional Convention. Unit 4 (part 2)
 The Constitutional Convention Unit 4 (part 2) Problems and Compromises Struggle for power between the small states and the large states Virginia Plan (James Madison) proposed two houses of Congress based
The Constitutional Convention Unit 4 (part 2) Problems and Compromises Struggle for power between the small states and the large states Virginia Plan (James Madison) proposed two houses of Congress based
Forming a New Government
 Forming a New Government Why Independent in the First Place? Citizens wanted to limit the power of government Lack of representation No taxation without representation Protect personal freedoms Desired
Forming a New Government Why Independent in the First Place? Citizens wanted to limit the power of government Lack of representation No taxation without representation Protect personal freedoms Desired
1 st United States Constitution. A. loose alliance of states. B. Congress lawmaking body. C. 9 states had to vote to pass laws
 1 st United States Constitution A. loose alliance of states B. Congress lawmaking body C. 9 states had to vote to pass laws D. each state had 1 vote in Congress Northwest Ordinance / Land Ordinance division
1 st United States Constitution A. loose alliance of states B. Congress lawmaking body C. 9 states had to vote to pass laws D. each state had 1 vote in Congress Northwest Ordinance / Land Ordinance division
The Coming of Independence. Ratifying the Constitution
 C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government 1 SECTION 1 SECTION 2 SECTION 3 SECTION 4 SECTION 5 Our Political Beginnings The Coming of Independence The Critical Period Creating the Constitution Ratifying
C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government 1 SECTION 1 SECTION 2 SECTION 3 SECTION 4 SECTION 5 Our Political Beginnings The Coming of Independence The Critical Period Creating the Constitution Ratifying
Creating the U.S. Constitution
 Creating the U.S. Constitution Essential Question How did the Americans create a national (federal) government that respected both the independence of the states and the rights of the individuals? Name:
Creating the U.S. Constitution Essential Question How did the Americans create a national (federal) government that respected both the independence of the states and the rights of the individuals? Name:
Forming a New Government
 Forming a New Government FORMING A NEW HIGH SCHOOL Imagine that you re building and opening up a new high school for next year. Create a plan for forming your new high school. With your partner, address
Forming a New Government FORMING A NEW HIGH SCHOOL Imagine that you re building and opening up a new high school for next year. Create a plan for forming your new high school. With your partner, address
2. Divided Convention. 3. Inside the Constitution. Constitution replaced the Articles---becomes the law of the land.
 2. Divided Convention notes7 9/13 states needed to ratify (to approve) Political parties begin Federalists: supported the Constitution The Federalist ---essays support Constitution Anti-Federalists: against
2. Divided Convention notes7 9/13 states needed to ratify (to approve) Political parties begin Federalists: supported the Constitution The Federalist ---essays support Constitution Anti-Federalists: against
The Founding of American Democracy By Jessica McBirney 2016
 Name: Class: The Founding of American Democracy By Jessica McBirney 2016 The American colonies rose up in 1776 against Britain with the goal of becoming an independent state. They sent the King of England
Name: Class: The Founding of American Democracy By Jessica McBirney 2016 The American colonies rose up in 1776 against Britain with the goal of becoming an independent state. They sent the King of England
Shays. Daniel Shay 1784 to 1785, unfair taxes, debt and foreclosure Farmer s rebellion to overthrow Mass. Govt.
 Shays Daniel Shay 1784 to 1785, unfair taxes, debt and foreclosure Farmer s rebellion to overthrow Mass. Govt. 1. Constitutional Convention: May to Sept. 1787 2. Divided Convention 9/13 states needed to
Shays Daniel Shay 1784 to 1785, unfair taxes, debt and foreclosure Farmer s rebellion to overthrow Mass. Govt. 1. Constitutional Convention: May to Sept. 1787 2. Divided Convention 9/13 states needed to
The Constitutional Convention. Chapter 2 Section 4
 The Constitutional Convention Chapter 2 Section 4 Constitutional Convention May 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 74 delegates allowed, 55 attended, 39 signed final Delegates to the Convention Had lots of
The Constitutional Convention Chapter 2 Section 4 Constitutional Convention May 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 74 delegates allowed, 55 attended, 39 signed final Delegates to the Convention Had lots of
Chapter 3 Constitution. Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook
 Chapter 3 Constitution Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on www.pknock.com Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from
Chapter 3 Constitution Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on www.pknock.com Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from
LEQ: What were the first two political parties in the United States?
 LEQ: What were the first two political parties in the United States? A symbol for the Federalists became the black and white cockade shown on the left. A black cockade became a symbol for the Federalist
LEQ: What were the first two political parties in the United States? A symbol for the Federalists became the black and white cockade shown on the left. A black cockade became a symbol for the Federalist
Ch. 1 Principles of Government
 Ch. 1 Principles of Government Objectives: 1. Identify the four main purposes of government. 2. Identify and explain the four theories that explain the origin of government. I. What is government? A. Government-
Ch. 1 Principles of Government Objectives: 1. Identify the four main purposes of government. 2. Identify and explain the four theories that explain the origin of government. I. What is government? A. Government-
17. Who becomes President of the United States if the President should die? 22. How many changes or Amendments are there to the Constitution?
 The following are 100 sample U.S. History and Government Questions that may be asked during the Naturalization Exam. 100 Typical Questions 1. What are the colors of our flag? 2. How many stars are there
The following are 100 sample U.S. History and Government Questions that may be asked during the Naturalization Exam. 100 Typical Questions 1. What are the colors of our flag? 2. How many stars are there
THE CONSTITUTION. Chapter 2
 THE CONSTITUTION Chapter 2 ROOTS OF THE CONSTITUTION 2.1 TRADE AND TAXATION 2.1 Mercantilism Strict import/export controls Widely ignored Costly French and Indian War New taxes on sugar and paper items
THE CONSTITUTION Chapter 2 ROOTS OF THE CONSTITUTION 2.1 TRADE AND TAXATION 2.1 Mercantilism Strict import/export controls Widely ignored Costly French and Indian War New taxes on sugar and paper items
Creating the U.S. Constitution Constitutional Convention
 Creating the U.S. Constitution Constitutional Convention Essential Question How did the Americans create a national (federal) government that respected both the independence of the states and the rights
Creating the U.S. Constitution Constitutional Convention Essential Question How did the Americans create a national (federal) government that respected both the independence of the states and the rights
SS.7.C.1.5. Identify how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing of the Constitution
 SS.7.C.1.5. Identify how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing of the Constitution SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the
SS.7.C.1.5. Identify how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing of the Constitution SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the
Ratification of the Constitution. Issues
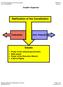 Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
4. After some negotiating, mostly with the promise of the Bill of Rights, the Constitution was ratified.
 Chapter #9: The Confederation and the Constitution Big Picture Ideas 1. The Articles of Confederation, the first government set up after the American Revolution, was structured out of fear of a too-strong
Chapter #9: The Confederation and the Constitution Big Picture Ideas 1. The Articles of Confederation, the first government set up after the American Revolution, was structured out of fear of a too-strong
This cartoon shows that Nullification is just one of the steps leading to Despotism. John C. Calhoun is ascending the steps to reach for the crown.
 LEQ: What was the name given to the right of states to declare federal laws illegal? This cartoon shows that Nullification is just one of the steps leading to Despotism. John C. Calhoun is ascending the
LEQ: What was the name given to the right of states to declare federal laws illegal? This cartoon shows that Nullification is just one of the steps leading to Despotism. John C. Calhoun is ascending the
Chapter 25 Section 1. Section 1. Terms and People
 Chapter 25 Terms and People republic a government in which the people elect their representatives unicameral legislature a lawmaking body with a single house whose representatives are elected by the people
Chapter 25 Terms and People republic a government in which the people elect their representatives unicameral legislature a lawmaking body with a single house whose representatives are elected by the people
Unit 4 Writing the Constitution Concepts to Review
 Unit 4 Writing the Constitution Concepts to Review CAUSE AND EFFECTS OF MAJOR ERAS AND EVENTS IN U.S. HISTORY THROUGH 1877 Writing the Constitution Shays Rebellion Philadelphia Convention 1787 Great Compromise
Unit 4 Writing the Constitution Concepts to Review CAUSE AND EFFECTS OF MAJOR ERAS AND EVENTS IN U.S. HISTORY THROUGH 1877 Writing the Constitution Shays Rebellion Philadelphia Convention 1787 Great Compromise
Constitutional Convention
 2014 Delegates Remember a delegate is someone who is chosen to speak for others, or to represent them. The delegates represented each of the states and consisted of: Wealthy and educated landowners, business
2014 Delegates Remember a delegate is someone who is chosen to speak for others, or to represent them. The delegates represented each of the states and consisted of: Wealthy and educated landowners, business
Quarter One: Unit Four
 SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will identify the weaknesses of the government under the Articles of Confederation (i.e.,
SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will identify the weaknesses of the government under the Articles of Confederation (i.e.,
Constitutional Foundations
 CHAPTER 2 Constitutional Foundations CHAPTER OUTLINE I. The Setting for Constitutional Change II. The Framers III. The Roots of the Constitution A. The British Constitutional Heritage B. The Colonial Heritage
CHAPTER 2 Constitutional Foundations CHAPTER OUTLINE I. The Setting for Constitutional Change II. The Framers III. The Roots of the Constitution A. The British Constitutional Heritage B. The Colonial Heritage
Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50
 Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50 The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from religious persecution Economic opportunity Independent
Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50 The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from religious persecution Economic opportunity Independent
Please update your table of contents. Unit 9:
 Please update your table of contents. Unit 9: Enlightenment & Revolution World History New rule about grades: students will no longer be given grades on classwork/folders. You will only be assessed by
Please update your table of contents. Unit 9: Enlightenment & Revolution World History New rule about grades: students will no longer be given grades on classwork/folders. You will only be assessed by
Constitutional Convention
 Constitutional Convention I INTRODUCTION Constitutional Convention, meeting during the summer of 1787 at which delegates from 12 states wrote the Constitution of the United States. At the convention in
Constitutional Convention I INTRODUCTION Constitutional Convention, meeting during the summer of 1787 at which delegates from 12 states wrote the Constitution of the United States. At the convention in
SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States Constitution.
 Standards SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States Constitution. a. Explain how weaknesses in the Articles of
Standards SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States Constitution. a. Explain how weaknesses in the Articles of
New Nation. establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s
 New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
Photographed by Kandy Hoover Fine Arts Museum, Boston
 Thomas Jefferson The writer of The Declaration of Independence Photographed by Kandy Hoover Fine Arts Museum, Boston 33 year old Thomas Jefferson went to Philadelphia to be a delegate in the 2 nd Continental
Thomas Jefferson The writer of The Declaration of Independence Photographed by Kandy Hoover Fine Arts Museum, Boston 33 year old Thomas Jefferson went to Philadelphia to be a delegate in the 2 nd Continental
Chapter 2. Government
 Chapter 2 Government The way the United States government is organized, its powers, and its limitations, are based on ideas about government that were brought to these shores by the English colonist. Three
Chapter 2 Government The way the United States government is organized, its powers, and its limitations, are based on ideas about government that were brought to these shores by the English colonist. Three
Basic Concepts of Government The English colonists brought 3 ideas that loom large in the shaping of the government in the United States.
 Civics Honors Chapter Two: Origins of American Government Section One: Our Political Beginnings Limited Government Representative government Magna Carta Petition of Right English Bill of Rights Charter
Civics Honors Chapter Two: Origins of American Government Section One: Our Political Beginnings Limited Government Representative government Magna Carta Petition of Right English Bill of Rights Charter
Ratifying the Constitution
 Ratifying the Constitution Signing the Constitution Once the debate ended, Governor Morris of New Jersey put the Constitution in its final form. He competed the task of hand-writing 4,300 words in two
Ratifying the Constitution Signing the Constitution Once the debate ended, Governor Morris of New Jersey put the Constitution in its final form. He competed the task of hand-writing 4,300 words in two
The Federalist Papers
 The Federalist Papers If men were angels, no government would be necessary. James Madison During the Revolutionary War, Americans set up a new national government. They feared a strong central government.
The Federalist Papers If men were angels, no government would be necessary. James Madison During the Revolutionary War, Americans set up a new national government. They feared a strong central government.
Charles de Montesquieu
 Unit III He first created the idea of consent of the governed where people have a vote in who leads them (democracy). Every person has the right to life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness. John Locke
Unit III He first created the idea of consent of the governed where people have a vote in who leads them (democracy). Every person has the right to life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness. John Locke
White. 4. What do the stars on the flag mean? One for each state in the Union. 9. What is the 4th of July? Independence Day. July 4th.
 The following questions are examples of what may be asked of you on your examination for citizenship. You may practice for the exam by attempting to answer them. Your actual test will have ten (10) questions
The following questions are examples of what may be asked of you on your examination for citizenship. You may practice for the exam by attempting to answer them. Your actual test will have ten (10) questions
Ancient Greece, Athens had a direct democracy.
 Warm Up 12/7 How did the Baron De Montesquieu believe Gov t should be setup? Did the states lose power under the constitution? What powers did the Federal Gov t Gain? What laws could the states not make?
Warm Up 12/7 How did the Baron De Montesquieu believe Gov t should be setup? Did the states lose power under the constitution? What powers did the Federal Gov t Gain? What laws could the states not make?
understanding CONSTITUTION
 understanding the CONSTITUTION Contents The Articles of Confederation The Constitutional Convention The Principles of the Constitution The Preamble The Legislative Branch The Executive Branch The Judicial
understanding the CONSTITUTION Contents The Articles of Confederation The Constitutional Convention The Principles of the Constitution The Preamble The Legislative Branch The Executive Branch The Judicial
Convention. Guide to Reading
 Convention and Compromise Main Idea The new Constitution corrected the weaknesses of government under the Articles of Confederation. Key Terms depression, manumission, proportional, compromise 1784 Rhode
Convention and Compromise Main Idea The new Constitution corrected the weaknesses of government under the Articles of Confederation. Key Terms depression, manumission, proportional, compromise 1784 Rhode
American Revolution Vocabulary Matching
 Name: Date: Class: American Revolution Vocabulary Matching Directions: You will need to cut the term out and glue it to the correct definition. This is due at the end of class. War that started due to
Name: Date: Class: American Revolution Vocabulary Matching Directions: You will need to cut the term out and glue it to the correct definition. This is due at the end of class. War that started due to
Civics (History and Government) Questions for the Naturalization Test
 (rev. 01/17) Civics (History and Government) Questions for the Naturalization Test The 100 civics (history and government) questions and answers for the naturalization test are listed below. The civics
(rev. 01/17) Civics (History and Government) Questions for the Naturalization Test The 100 civics (history and government) questions and answers for the naturalization test are listed below. The civics
Civics (History and Government) Questions for the Naturalization Test
 Page 1 of 37 Warning: This material cannot be sold or reproduced by any means It is FREE Disclaimer: I am not responsible for any translation mistake or skipped questions For latest questions, please trust
Page 1 of 37 Warning: This material cannot be sold or reproduced by any means It is FREE Disclaimer: I am not responsible for any translation mistake or skipped questions For latest questions, please trust
Civics (History and Government) Items for the Redesigned Naturalization Test
 Civics (History and Government) Items for the Redesigned Naturalization Test Beginning October 1, 2008, U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) will begin implementation of a redesigned naturalization
Civics (History and Government) Items for the Redesigned Naturalization Test Beginning October 1, 2008, U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) will begin implementation of a redesigned naturalization
Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution
 Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution The Articles of Confederation After declaring independence from Britain in 1776, Congress tried to unite the states under one national government. However, many feared
Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution The Articles of Confederation After declaring independence from Britain in 1776, Congress tried to unite the states under one national government. However, many feared
LEQ: What proclamation said the U.S. would trade with both France and Great Britain?
 LEQ: What proclamation said the U.S. would trade with both France and Great Britain? America s declaration of its official position of neutrality in the war between England and France was declared on February
LEQ: What proclamation said the U.S. would trade with both France and Great Britain? America s declaration of its official position of neutrality in the war between England and France was declared on February
the states. decisions within its own borders) 1. A central government that would represent all 2. State sovereignty (the power to make
 The United States has operated under two constitutions. The first, The Articles of Confederation, was in effect from March 1, 1781. The Articles tried to balance two very different ideas: 1. A central
The United States has operated under two constitutions. The first, The Articles of Confederation, was in effect from March 1, 1781. The Articles tried to balance two very different ideas: 1. A central
Wednesday, February 15 th
 Anticipating Constitutional Reform 1 Wednesday, February 15 th Midterm #1: February 14-17 in the Testing Center Monday and Tuesday: No late fee Wednesday: $5 late fee Thursday: $7 late fee and test must
Anticipating Constitutional Reform 1 Wednesday, February 15 th Midterm #1: February 14-17 in the Testing Center Monday and Tuesday: No late fee Wednesday: $5 late fee Thursday: $7 late fee and test must
FEDERALISTS, ANTI-FEDERALISTS AND THE CONSTITUTION SS.7.C.1.8
 FEDERALISTS, ANTI-FEDERALISTS AND THE CONSTITUTION SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the ratification of the Constitution and inclusion of a bill of
FEDERALISTS, ANTI-FEDERALISTS AND THE CONSTITUTION SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the ratification of the Constitution and inclusion of a bill of
New Nation. establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s
 New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
Constitutional Convention. May 1787
 Constitutional Convention May 1787 Annapolis Convention September 11 to September 14, 1786 Annapolis, Maryland Purpose - How to fix the articles of confederation Alexander Hamilton (New York) MUST resolve
Constitutional Convention May 1787 Annapolis Convention September 11 to September 14, 1786 Annapolis, Maryland Purpose - How to fix the articles of confederation Alexander Hamilton (New York) MUST resolve
Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation
 Name: Date: Chapter 8 Study Guide Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation 1. A constitution is a set of basic principles and laws, usually in written form, that state the powers and duties of a government.
Name: Date: Chapter 8 Study Guide Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation 1. A constitution is a set of basic principles and laws, usually in written form, that state the powers and duties of a government.
American Democracy Now Chapter 2: The Constitution
 American Democracy Now Chapter 2: The Constitution Multiple-Choice Questions: 1. Which of these countries employs an unwritten constitution? a. the United States b. Great Britain c. Venezuela d. Kenya
American Democracy Now Chapter 2: The Constitution Multiple-Choice Questions: 1. Which of these countries employs an unwritten constitution? a. the United States b. Great Britain c. Venezuela d. Kenya
LESSON TWO: THE FEDERALIST PAPERS
 LESSON TWO: THE FEDERALIST PAPERS OVERVIEW OBJECTIVES Students will be able to: Identify the Articles of Confederation and explain why it failed. Explain the argument over the need for a bill of rights
LESSON TWO: THE FEDERALIST PAPERS OVERVIEW OBJECTIVES Students will be able to: Identify the Articles of Confederation and explain why it failed. Explain the argument over the need for a bill of rights
Creating a Nation Test Review
 Creating a Nation Test Review Question #1: Multiple Choice The Northwest ordinance of 1787 is important because. A. It sent troops to the Northwest to protect the colonies from Native Americans. B. It
Creating a Nation Test Review Question #1: Multiple Choice The Northwest ordinance of 1787 is important because. A. It sent troops to the Northwest to protect the colonies from Native Americans. B. It
The Constitutional Convention. Howard Chandler Christy, Scene at the Signing of the Constitution of the United States (1940)
 The Constitutional Convention Howard Chandler Christy, Scene at the Signing of the Constitution of the United States (1940) USHC 1.4 Analyze how dissatisfactions with the government under the Articles
The Constitutional Convention Howard Chandler Christy, Scene at the Signing of the Constitution of the United States (1940) USHC 1.4 Analyze how dissatisfactions with the government under the Articles
Section One. A) The Leviathan B) Two Treatises of Government C) Spirit of the Laws D) The Social Contract
 Government Exam Study Guide You will need to be prepared to answer/discuss any of these questions on the exam in various formats. We will complete this study guide in class and review it. Section One 1)
Government Exam Study Guide You will need to be prepared to answer/discuss any of these questions on the exam in various formats. We will complete this study guide in class and review it. Section One 1)
Weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation 1. Congress could not levy or collect taxes
 Virginia Plan New Jersey Plan The Great Compromise UNIT 2 TEST REVIEW SHEET Strengths of A of C 1- Established Federalism - A system of government where power is divided between a national government and
Virginia Plan New Jersey Plan The Great Compromise UNIT 2 TEST REVIEW SHEET Strengths of A of C 1- Established Federalism - A system of government where power is divided between a national government and
What are Political Concepts in the US Constitution or What are the guiding themes behind our government? Name Page
 Name of the Political Concept and related image. 1.Representative democracy AKA Republicanism Definition of the Political Concept using page 262-265 of your blue text, outside resources or in stations
Name of the Political Concept and related image. 1.Representative democracy AKA Republicanism Definition of the Political Concept using page 262-265 of your blue text, outside resources or in stations
Study Questions for Citizenship. 1. Q. What are the colors of our flag? A. Red, white, and blue. 2. Q. How many stars are there in our flag?
 Study Questions for Citizenship 1. Q. What are the colors of our flag? A. Red, white, and blue 2. Q. How many stars are there in our flag? A. Fifty (50) 3. Q. What colors are the stars on our flag? A.
Study Questions for Citizenship 1. Q. What are the colors of our flag? A. Red, white, and blue 2. Q. How many stars are there in our flag? A. Fifty (50) 3. Q. What colors are the stars on our flag? A.
UNIT 2 TEST REVIEW SHEET. Weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation 1. Congress could not levy or collect taxes
 Virginia Plan New Jersey Plan The Great Compromise UNIT 2 TEST REVIEW SHEET Strengths of A of C 1- Established Federalism - A system of government where power is divided between a national government and
Virginia Plan New Jersey Plan The Great Compromise UNIT 2 TEST REVIEW SHEET Strengths of A of C 1- Established Federalism - A system of government where power is divided between a national government and
AIM: How did the Articles of Confederation impact the U.S.?
 AIM: How did the Articles of Confederation impact the U.S.? Do Now: How do you think Hale Charter Academy would function if we got rid of the assistant principal, and the dean, and we allowed the individual
AIM: How did the Articles of Confederation impact the U.S.? Do Now: How do you think Hale Charter Academy would function if we got rid of the assistant principal, and the dean, and we allowed the individual
2. Which of the following was not one of the rights granted in the Magna Carta?
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 Our Political Beginnings SECTION 2 The Coming of Independence
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 Our Political Beginnings SECTION 2 The Coming of Independence
What types of things did the new states do to make the governments more democratic?
 Chapter 8 Confederation to Constitution pg. 218 241 8 1 The Confederation Era pg. 221 225 Moving West and New State Governments Into which areas did American settlement expand in the late 1700s? What types
Chapter 8 Confederation to Constitution pg. 218 241 8 1 The Confederation Era pg. 221 225 Moving West and New State Governments Into which areas did American settlement expand in the late 1700s? What types
Separation of Powers: History and Theory
 Separation of Powers: History and Theory James E. Hanley Published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International license. This work may be freely reproduced for non-commercial
Separation of Powers: History and Theory James E. Hanley Published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International license. This work may be freely reproduced for non-commercial
How Shall We Govern Ourselves?
 How Shall We Govern Ourselves? The Articles of Confederation America s First Constitution What kind of government would the FREEDOM loving Americans create to balance LIBERTY with enough AUTHORITY to get
How Shall We Govern Ourselves? The Articles of Confederation America s First Constitution What kind of government would the FREEDOM loving Americans create to balance LIBERTY with enough AUTHORITY to get
Chapter 7, Section 3 A New Plan of Government
 Chapter 7, Section 3 A New Plan of Government (pages 207-213) Setting a Purpose for Reading Think about these questions as you read: What are the roots of the Constitution? How did the Constitution limit
Chapter 7, Section 3 A New Plan of Government (pages 207-213) Setting a Purpose for Reading Think about these questions as you read: What are the roots of the Constitution? How did the Constitution limit
Debating the Constitution
 SECTION 3 A Bill of Rights A bill of rights is what the people are entitled to against every government on earth, general or particular; and what no just government should refuse or rest on inference.
SECTION 3 A Bill of Rights A bill of rights is what the people are entitled to against every government on earth, general or particular; and what no just government should refuse or rest on inference.
Explain the key arguments of the Federalists and the process by which the Constitution was finally ratified.
 Explain why the Anti-Federalists opposed ratifying the Constitution. Explain the role of Anti-Federalists in proposing a bill of rights. Explain the key arguments of the Federalists and the process by
Explain why the Anti-Federalists opposed ratifying the Constitution. Explain the role of Anti-Federalists in proposing a bill of rights. Explain the key arguments of the Federalists and the process by
Ch. 6 Creating the Constitution /EQ:
 Ch. 6 Creating the Constitution /EQ: 6.1 Introduction Like Washington, most Americans did not want to be ruled by a monarch. What they did want, though, was an effective government. Articles of Confederation,
Ch. 6 Creating the Constitution /EQ: 6.1 Introduction Like Washington, most Americans did not want to be ruled by a monarch. What they did want, though, was an effective government. Articles of Confederation,
The U.S. Constitution. Ch. 2.4 Ch. 3
 The U.S. Constitution Ch. 2.4 Ch. 3 The Constitutional Convention Philadelphia Five months, from May until September 1787 Secret Meeting, closed to outside. Originally intent to revise the Articles of
The U.S. Constitution Ch. 2.4 Ch. 3 The Constitutional Convention Philadelphia Five months, from May until September 1787 Secret Meeting, closed to outside. Originally intent to revise the Articles of
Federal Constitution Test Review & Study Guide
 Name: AP GOPO 2018-2019 AP United States Government & Politics (AP GOPO) Sumer Work Federal Constitution Test Review & Study Guide AP Government will require you to do a high level of work and to have
Name: AP GOPO 2018-2019 AP United States Government & Politics (AP GOPO) Sumer Work Federal Constitution Test Review & Study Guide AP Government will require you to do a high level of work and to have
Origins of American Government. Chapter 2
 Origins of American Government Chapter 2 Section 1 Essential Questions 1) What two principles of government came from the English heritage of the colonists? 2) What documents from England influenced the
Origins of American Government Chapter 2 Section 1 Essential Questions 1) What two principles of government came from the English heritage of the colonists? 2) What documents from England influenced the
Gov t was needed to maintain peace. Gov t is not all powerful Power is limited to what the people give to it
 Ordered Government Gov t was needed to maintain peace Limited Government*********** Gov t is not all powerful Power is limited to what the people give to it Representative Government Gov t should serve
Ordered Government Gov t was needed to maintain peace Limited Government*********** Gov t is not all powerful Power is limited to what the people give to it Representative Government Gov t should serve
NATIONAL ARCHIVES WELCOME TO THE R-O -T-U-N-D * A WASHINGTON, DC. Exhibition Hall. jpi CONSTITUTION AVE
 WELCOME TO THE NATIONAL ARCHIVES R-O -T-U-N-D * A WASHINGTON, DC Exhibition Hall How is the exhibition area divided? The domed area is the Exhibition Hall, also known as the Rotunda. The exhibit area around
WELCOME TO THE NATIONAL ARCHIVES R-O -T-U-N-D * A WASHINGTON, DC Exhibition Hall How is the exhibition area divided? The domed area is the Exhibition Hall, also known as the Rotunda. The exhibit area around
CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION
 CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Objectives Why did the Constitutional Convention draft a new plan for government? How did the rival plans for the new government differ? What other conflicts required the Framers
CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Objectives Why did the Constitutional Convention draft a new plan for government? How did the rival plans for the new government differ? What other conflicts required the Framers
