Note: Article I, section 2, of the Constitution was modified by section 2 of the 14th amendment.
|
|
|
- Emerald Armstrong
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Apportionment
2 Article 1 Section 2 Representatives and direct Taxes shall be apportioned among the several States which may be included within this Union, according to their respective Numbers, which shall be determined by adding to the whole Number of free Persons, including those bound to Service for a Term of Years, and excluding Indians not taxed, three fifths of all other Persons. The actual Enumeration shall be made within three Years after the first Meeting of the Congress of the United States, and within every subsequent Term of ten Years, in such Manner as they shall by Law direct. The Number of Representatives shall not exceed one for every thirty Thousand, but each State shall have at Least one Representative; and until such enumeration shall be made, the State of New Hampshire shall be entitled to chuse three, Massachusetts eight, Rhode-Island and Providence Plantations one, Connecticut five, New-York six, New Jersey four, Pennsylvania eight, Delaware one, Maryland six, Virginia ten, North Carolina five, South Carolina five, and Georgia three.
3 AMENDMENT XIV Passed by Congress June 13, Ratified July 9, Note: Article I, section 2, of the Constitution was modified by section 2 of the 14th amendment. Section 2. Representatives shall be apportioned among the several States according to their respective numbers, counting the whole number of persons in each State, excluding Indians not taxed. But when the right to vote at any election for the choice of electors for President and Vice-President of the United States, Representatives in Congress, the Executive and Judicial officers of a State, or the members of the Legislature thereof, is denied to any of the male inhabitants of such State, being twenty-one years of age,* and citizens of the United States, or in any way abridged, except for participation in rebellion, or other crime, the basis of representation therein shall be reduced in the proportion which the number of such male citizens shall bear to the whole number of male citizens twenty-one years of age in such State.
4 The problem of actual assignment of the whole number of seats in the United States Congress among necessarily fractional numbers of relative state populations is known as the problem of Apportionment. The Constitution gave Congress three years to come up with a practical solution. Two were submitted right away. One by Alexander Hamilton, the other by Thomas Jefferson. After heated deliberations, Congress opted for the former, but in the very first exercise of the veto power by President of the United States, President Washington blocked the measure. Facing a dangerous stalemate, Congress then adopted Jefferson's method, but with a different number of seats. (It is said that Washington was motivated by the fact that Jefferson's method would allocate one additional seat to his home state of Virginia.)
5 Other Methods Other apportionment methods were submitted by Rep. William Lowndes (1822), Rep. (and, by that time, former President) John Quincy Adams (1832) and Senator Daniel Webster (1832). The latter was eventually adopted in 1842, only to be replaced by Hamilton's method in In 1872, Congress was considering the idea of expanding to 283 seats, because of the agreement of Hamilton's and Webster's methods for this number. As it happened, Congress added 9 additional seats without officially adopting any method. In 1876 Rutherford B. Hayes became President of the United States based on the apportionment (which some say was unconstitutional) of 1872.
6 The Paradoxes In 1880, to everyone's surprise a flaw was discovered in Hamilton's method that is now known as the Alabama paradox. More cracks showed up later. Close to 1900 Hamilton's method was shown to lead to the Population paradox and in 1907, on the occasion of Oklahoma joining the Union, the New-States paradox was also detected. Hamilton's method was replaced by Webster's in 1901, which stayed put until 1941, when Huntington-Hill's method was signed into law by President Roosevelt. Huntington-Hill's method has been used since, although there is much activism going on with the goal of replacing it back with Webster's method.
7 The Paradoxes The Alabama paradox occurs when the total number of seats in the House increases, and some state's number of representatives decreases as a result. The new state paradox occurs when a new state enters the union and all the numbers go up yet some state's number of representatives decreases. The population paradox refers to the situation where the population of some state increases yet their number of representatives decreases.
8 Number of Seats Hamilton's method is the only one that requires fixing the number of seats. All other methods work as well when what is fixed is the ratio of population per seat. Indeed, up until 1842, when Hamilton's method was adopted by Congress, Jefferson's method was used with such a fixed ratio. All apportionment methods, but Hamilton's, violate the Quota Rule if used with the number of seats fixed. However, by the tradition established after 1842, Congress fixes the number of seats up front, with 435 seats being the norm since 1931.
9 Quota Rule All apportionment methods include calculation of the state's standard quota State's population Total number of seats State's Standard Quota =. Total population The Lower Quota is then computed as the integral (floor) part of the standard quota. The Upper Quota is the ceiling (the lower quota plus one) of the standard quota. The Quota Rule stipulates that any fair apportionment should assign to every state either its lower or upper quota.
10 Impossibility Theorem The result known as Balinski and Young's (1982) impossibility theorem states that: If the number of seats to be apportioned is fixed up front, then any apportionment method that does not violate the quota rule must produce paradoxes, and any apportionment method that does not produce paradoxes must violate the Quota Rule. It could be argued that none of the methods at hand violates the Quota Rule when used with a fixed ratio of population per seat, in which case the total number of seats becomes a calculated quantity.
11 House Sizes Due to the population growth and incorporation of new states, the number of Representatives in the House has kept changing: 65 (1787), 105 (1791), 240 (1832), 223 (1842), 234 (1852), 292 (1872), 325 (1882), 386 (1901), 433 (1911), 435 (1931 and since, except when Alaska and Hawaii became states, there was a temporary addition of one seat for each until the apportionment following the 1960 census).
12 Of Local Interest An anecdotal event took place in 1901 when The Bureau of the Census submitted to Congress tables showing apportionment based on Hamilton's method for all size Houses between 350 and 400. In another demonstration of the Alabama paradox, for all sizes between 350 and 400, but 357, the state of Colorado would get three seats, with only two seats in the exceptional case of 357. The opportunity was seized by Rep. Albert Hopkins (IL), at the time the chairman of the House Committee on Apportionment, who submitted a bill to fix the House size at 357 seats. In a display of rationality, the bill was defeated.
13 Hamilton's Method Compute the divisor D = (Total population)/(number of seats) Find and round down state quotas {(State population)/d}. The leftover fractional parts add up to a whole number of seats. Distribute the surplus seats, one per state, starting with the largest leftover fractional part, then proceeding to the next largest, and so on, until all the surplus seats have been dealt with.
14 Hamilton's Problem It's well known that, when the number of seats is fixed in advance, all other methods may occasionally fail. Hamilton's method never fails. This feature that on the first glance might have placed Hamilton's method way ahead of the pack, should have sealed its fate from the very beginning: paradoxically, the method is unsuitable for apportionment of the House seats. The method violates the basic tenet of the Constitution:... according to their respective numbers... Strict proportionality of the representation could be hardly achieved or expected, and hence meant. However, no one would ever question the principle of the equality of the representation: states with equal populations must have equal representations. When other methods can't achieve that they fail. Not so Hamilton's method. The latter will easily distribute 3 seats between 2 states with equal populations. One will get two seats, the other will get only one.
15 Population Paradox State Pop Adams Bethel Carthay Total Adams Bethel Carthay Total Exact Q Lower Q Upper Q Hamilton
16 Jefferson's Method Compute the divisor D = (Total population)/(number of seats) Decrease D by an amount d such that when state allocations {(State population)/(d - d)} are rounded downward, they add up to the exact number of seats.
17 Adam's Method Compute the divisor D = (Total population)/(number of seats) Increase D by an amount d such that when state allocations {(State population)/(d + d)} are rounded upward, they add up to the exact number of seats.
18 Webster's Method Compute the divisor D = (Total population)/(number of seats) Modify D by an amount d, that could be negative, such that when state allocations {(State population)/(d + d)} are rounded in the customary manner, they add up to the exact number of seats. Daniel Webster proposed his apportionment method in 1832.It was adopted by the Congress in 1842, and then replaced by Alexander Hamilton's in It was again adopted in 1901 and reconfirmed in Finally, it was replaced by Huntington-Hill's method in 1941.
19 Huntington-Hill's Method Huntington-Hill's method is the current method of seat apportionment used by the US Congress. It was signed into law by President Roosevelt on November 15, Compute the divisor D = (Total population)/(number of seats) Modify D by an amount d, that could be negative, such that when state allocations {(State population)/(d + d)} are rounded according to the method of equal proportions, they add up to the exact number of seats. With the regular rounding used in the Webster's method the cutoff value is midway between two successive integers. If A is between an integer L and the next integer L+1, then it is rounded down or up depending on whether A is less or greater than the average (L + (L+1))/2. In the method of equal proportions, the cutoff value depends on the magnitude of L = [A] and is equal to the square root of L(L+1).
Chapter 4 The Mathematics of Apportionment
 Quesions on Homework on Voting Methods? Chapter 4 The Mathematics of Apportionment How many representatives should each state have? For California: = 52.59 For Ohio = 16.29 in 2000 census = 17.58 18 Districts
Quesions on Homework on Voting Methods? Chapter 4 The Mathematics of Apportionment How many representatives should each state have? For California: = 52.59 For Ohio = 16.29 in 2000 census = 17.58 18 Districts
Name Chapter 14 Apportionment. 1. What was the Great Compromise in 1787? Populations of 15 states in 1790 as in your book on page 506:
 Name Chapter 14 Apportionment 1. What was the Great Compromise in 1787? Populations of 15 states in 1790 as in your book on page 506: State Population Number Number Number Number Virginia 630,560 Massachusetts
Name Chapter 14 Apportionment 1. What was the Great Compromise in 1787? Populations of 15 states in 1790 as in your book on page 506: State Population Number Number Number Number Virginia 630,560 Massachusetts
Rounding decimals or fractions to whole numbers might seem to be one of the most boring subjects ever.
 Apportionment Rounding decimals or fractions to whole numbers might seem to be one of the most boring subjects ever. However, as we will see, the method used in rounding can be of great significance. Some
Apportionment Rounding decimals or fractions to whole numbers might seem to be one of the most boring subjects ever. However, as we will see, the method used in rounding can be of great significance. Some
Proportional (Mis)representation: The Mathematics of Apportionment
 Proportional (Mis)representation: The Mathematics of Apportionment Vicki Powers Dept. of Mathematics and Computer Science Emory University Kennesaw College Infinite Horizon Series Sept. 27, 2012 What is
Proportional (Mis)representation: The Mathematics of Apportionment Vicki Powers Dept. of Mathematics and Computer Science Emory University Kennesaw College Infinite Horizon Series Sept. 27, 2012 What is
Apportionment. Seven Roads to Fairness. NCTM Regional Conference. November 13, 2014 Richmond, VA. William L. Bowdish
 Apportionment Seven Roads to Fairness NCTM Regional Conference November 13, 2014 Richmond, VA William L. Bowdish Mathematics Department (Retired) Sharon High School Sharon, Massachusetts 02067 bilbowdish@gmail.com
Apportionment Seven Roads to Fairness NCTM Regional Conference November 13, 2014 Richmond, VA William L. Bowdish Mathematics Department (Retired) Sharon High School Sharon, Massachusetts 02067 bilbowdish@gmail.com
In the next few lectures, we consider the problem of dividing indivisible things (say, seats in a legislature) among players (say, states) in
 In the next few lectures, we consider the problem of dividing indivisible things (say, seats in a legislature) among players (say, states) in proportion to something (say, population). If we have 50 identical
In the next few lectures, we consider the problem of dividing indivisible things (say, seats in a legislature) among players (say, states) in proportion to something (say, population). If we have 50 identical
Chapter 4 The Mathematics of Apportionment
 Chapter 4 The Mathematics of Apportionment Typical Problem A school has one teacher available to teach all sections of Geometry, Precalculus and Calculus. She is able to teach 5 courses and no more. How
Chapter 4 The Mathematics of Apportionment Typical Problem A school has one teacher available to teach all sections of Geometry, Precalculus and Calculus. She is able to teach 5 courses and no more. How
12B,C: Voting Power and Apportionment
 12B,C: Voting Power and Apportionment Group Activities 12C Apportionment 1. A college offers tutoring in Math, English, Chemistry, and Biology. The number of students enrolled in each subject is listed
12B,C: Voting Power and Apportionment Group Activities 12C Apportionment 1. A college offers tutoring in Math, English, Chemistry, and Biology. The number of students enrolled in each subject is listed
The Constitution directs Congress to reapportion seats in the House
 12C - Apportionment: The House of Representatives and Beyond For the U.S. House of Representatives, is a process used to divide the available seats among the states. More generally, apportionment is the
12C - Apportionment: The House of Representatives and Beyond For the U.S. House of Representatives, is a process used to divide the available seats among the states. More generally, apportionment is the
Section Apportionment Methods. Copyright 2013, 2010, 2007, Pearson, Education, Inc.
 Section 15.3 Apportionment Methods What You Will Learn Standard Divisor Standard Quota Lower Quota Upper Quota Hamilton s Method The Quota Rule Jefferson s Method Webster s Method Adam s Method 15.3-2
Section 15.3 Apportionment Methods What You Will Learn Standard Divisor Standard Quota Lower Quota Upper Quota Hamilton s Method The Quota Rule Jefferson s Method Webster s Method Adam s Method 15.3-2
Chapter 12: The Math of Democracy 12B,C: Voting Power and Apportionment - SOLUTIONS
 12B,C: Voting Power and Apportionment - SOLUTIONS Group Activities 12C Apportionment 1. A college offers tutoring in Math, English, Chemistry, and Biology. The number of students enrolled in each subject
12B,C: Voting Power and Apportionment - SOLUTIONS Group Activities 12C Apportionment 1. A college offers tutoring in Math, English, Chemistry, and Biology. The number of students enrolled in each subject
The Mathematics of Apportionment
 MATH 110 Week 4 Chapter 4 Worksheet The Mathematics of Apportionment NAME Representatives... shall be apportioned among the several States... according to their respective Numbers. The actual Enumeration
MATH 110 Week 4 Chapter 4 Worksheet The Mathematics of Apportionment NAME Representatives... shall be apportioned among the several States... according to their respective Numbers. The actual Enumeration
The Congressional Apportionment Problem Based on the Census : Basic Divisor Methods
 Humboldt State University Digital Commons @ Humboldt State University Congressional Apportionment Open Educational Resources and Data 10-2015 The Congressional Apportionment Problem Based on the Census
Humboldt State University Digital Commons @ Humboldt State University Congressional Apportionment Open Educational Resources and Data 10-2015 The Congressional Apportionment Problem Based on the Census
Fair Division in Theory and Practice
 Fair Division in Theory and Practice Ron Cytron (Computer Science) Maggie Penn (Political Science) Lecture 3: Apportionment 1 Fair representation We would like to allocate seats proportionally to the 50
Fair Division in Theory and Practice Ron Cytron (Computer Science) Maggie Penn (Political Science) Lecture 3: Apportionment 1 Fair representation We would like to allocate seats proportionally to the 50
Chapter 15 Section 4 - Slide 1
 AND Chapter 15 Section 4 - Slide 1 Chapter 15 Voting and Apportionment Chapter 15 Section 4 - Slide 2 WHAT YOU WILL LEARN Flaws of apportionment methods Chapter 15 Section 4 - Slide 3 Section 4 Flaws of
AND Chapter 15 Section 4 - Slide 1 Chapter 15 Voting and Apportionment Chapter 15 Section 4 - Slide 2 WHAT YOU WILL LEARN Flaws of apportionment methods Chapter 15 Section 4 - Slide 3 Section 4 Flaws of
The Mathematics of Apportionment
 The Place: Philadelphia The Time: Summer 1787 The Players: Delegates from the 13 states The Problem: Draft a Constitution for our new nation The Big Argument: How would the people be represented? What
The Place: Philadelphia The Time: Summer 1787 The Players: Delegates from the 13 states The Problem: Draft a Constitution for our new nation The Big Argument: How would the people be represented? What
Regulating Elections: Districts /252 Fall 2008
 Regulating Elections: Districts 17.251/252 Fall 2008 Major ways that congressional elections are regulated The Constitution Basic stuff (age, apportionment, states given lots of autonomy) Federalism key
Regulating Elections: Districts 17.251/252 Fall 2008 Major ways that congressional elections are regulated The Constitution Basic stuff (age, apportionment, states given lots of autonomy) Federalism key
Presidential Election Democrat Grover Cleveland versus Benjamin Harrison. ************************************ Difference of 100,456
 Presidential Election 1886 Democrat Grover Cleveland versus Benjamin Harrison Cleveland 5,540,309 Harrison 5,439,853 ************************************ Difference of 100,456 Electoral College Cleveland
Presidential Election 1886 Democrat Grover Cleveland versus Benjamin Harrison Cleveland 5,540,309 Harrison 5,439,853 ************************************ Difference of 100,456 Electoral College Cleveland
MATH 1340 Mathematics & Politics
 MATH 1340 Mathematics & Politics Lecture 13 July 9, 2015 Slides prepared by Iian Smythe for MATH 1340, Summer 2015, at Cornell University 1 Apportionment A survey 2 All legislative Powers herein granted
MATH 1340 Mathematics & Politics Lecture 13 July 9, 2015 Slides prepared by Iian Smythe for MATH 1340, Summer 2015, at Cornell University 1 Apportionment A survey 2 All legislative Powers herein granted
Regulating Elections: Districts /252 Fall 2012
 Regulating Elections: Districts 17.251/252 Fall 2012 Throat Clearing Preferences The Black Box of Rules Outcomes Major ways that congressional elections are regulated The Constitution Basic stuff (age,
Regulating Elections: Districts 17.251/252 Fall 2012 Throat Clearing Preferences The Black Box of Rules Outcomes Major ways that congressional elections are regulated The Constitution Basic stuff (age,
Math of Election APPORTIONMENT
 Math of Election APPORTIONMENT Alfonso Gracia-Saz, Ari Nieh, Mira Bernstein Canada/USA Mathcamp 2017 Apportionment refers to any of the following, equivalent mathematical problems: We want to elect a Congress
Math of Election APPORTIONMENT Alfonso Gracia-Saz, Ari Nieh, Mira Bernstein Canada/USA Mathcamp 2017 Apportionment refers to any of the following, equivalent mathematical problems: We want to elect a Congress
Lesson 2.4 More Apportionment Models and Paradoxes
 DM02_Final.qxp:DM02.qxp 5/9/14 2:43 PM Page 82 Lesson 2.4 More Apportionment Models and Paradoxes Dissatisfaction with paradoxes that can occur with the Hamilton model led to its abandonment as a method
DM02_Final.qxp:DM02.qxp 5/9/14 2:43 PM Page 82 Lesson 2.4 More Apportionment Models and Paradoxes Dissatisfaction with paradoxes that can occur with the Hamilton model led to its abandonment as a method
A small country consists of four states. There are 100 seats in the legislature. The populations are: A: 44,800 B: 52,200 C: 49,200 D: 53,800
 Finite Math A Mrs. Leahy Chapter 4 Test Review Practice Questions Vocabulary: Be prepared to identify/define the following terms and methods. Standard Divisor, Standard Quota, Hamilton s Method, Webster
Finite Math A Mrs. Leahy Chapter 4 Test Review Practice Questions Vocabulary: Be prepared to identify/define the following terms and methods. Standard Divisor, Standard Quota, Hamilton s Method, Webster
Chapter Four: The Mathematics of Apportionment
 Chapter Four: The Mathematics of Apportion: to divide and assign in due and proper proportion or according to some plan. 6 New states are being created and Congress is allowing a total of 250 seats to
Chapter Four: The Mathematics of Apportion: to divide and assign in due and proper proportion or according to some plan. 6 New states are being created and Congress is allowing a total of 250 seats to
Should Politicians Choose Their Voters? League of Women Voters of MI Education Fund
 Should Politicians Choose Their Voters? 1 Politicians are drawing their own voting maps to manipulate elections and keep themselves and their party in power. 2 3 -The U.S. Constitution requires that the
Should Politicians Choose Their Voters? 1 Politicians are drawing their own voting maps to manipulate elections and keep themselves and their party in power. 2 3 -The U.S. Constitution requires that the
Constitutional Convention. May 1787
 Constitutional Convention May 1787 Annapolis Convention September 11 to September 14, 1786 Annapolis, Maryland Purpose - How to fix the articles of confederation Alexander Hamilton (New York) MUST resolve
Constitutional Convention May 1787 Annapolis Convention September 11 to September 14, 1786 Annapolis, Maryland Purpose - How to fix the articles of confederation Alexander Hamilton (New York) MUST resolve
Apportionment Problems
 Apportionment Problems Lecture 16 Section 4.1 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Oct 4, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Apportionment Problems Fri, Oct 4, 2013 1 / 15 1 Apportionment
Apportionment Problems Lecture 16 Section 4.1 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Oct 4, 2013 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Apportionment Problems Fri, Oct 4, 2013 1 / 15 1 Apportionment
The Electoral College And
 The Electoral College And National Popular Vote Plan State Population 2010 House Apportionment Senate Number of Electors California 37,341,989 53 2 55 Texas 25,268,418 36 2 38 New York 19,421,055 27 2
The Electoral College And National Popular Vote Plan State Population 2010 House Apportionment Senate Number of Electors California 37,341,989 53 2 55 Texas 25,268,418 36 2 38 New York 19,421,055 27 2
STUDY GUIDE FOR TEST 2
 STUDY GUIDE FOR TEST 2 MATH 303. SPRING 2006. INSTRUCTOR: PROFESSOR AITKEN The test will cover Chapters 4, 5, and 6. Chapter 4: The Mathematics of Voting Sample Exercises: 1, 3, 5, 7, 8, 10, 14, 15, 17,
STUDY GUIDE FOR TEST 2 MATH 303. SPRING 2006. INSTRUCTOR: PROFESSOR AITKEN The test will cover Chapters 4, 5, and 6. Chapter 4: The Mathematics of Voting Sample Exercises: 1, 3, 5, 7, 8, 10, 14, 15, 17,
The House of Representatives Apportionment Formula: An Analysis of Proposals for Change and Their Impact on States
 The House of Representatives Apportionment Formula: An Analysis of Proposals for Change and Their Impact on States Royce Crocker Specialist in American National Government August 26, 2010 Congressional
The House of Representatives Apportionment Formula: An Analysis of Proposals for Change and Their Impact on States Royce Crocker Specialist in American National Government August 26, 2010 Congressional
Mathematics of the Electoral College. Robbie Robinson Professor of Mathematics The George Washington University
 Mathematics of the Electoral College Robbie Robinson Professor of Mathematics The George Washington University Overview Is the US President elected directly? No. The president is elected by electors who
Mathematics of the Electoral College Robbie Robinson Professor of Mathematics The George Washington University Overview Is the US President elected directly? No. The president is elected by electors who
Amendments to the Constitution
 Amendments to the Constitution CONSTITUTION OF THE UNITED STATES ARTICLES IN ADDITION TO, AND AMENDMENT OF, THE CONSTITUTION OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA, PROPOSED BY CONGRESS, AND RATIFIED BY THE LEGISLATURES
Amendments to the Constitution CONSTITUTION OF THE UNITED STATES ARTICLES IN ADDITION TO, AND AMENDMENT OF, THE CONSTITUTION OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA, PROPOSED BY CONGRESS, AND RATIFIED BY THE LEGISLATURES
Lesson 2.3. Apportionment Models
 DM02_Final.qxp:DM02.qxp 5/9/14 2:43 PM Page 72 Lesson 2.3 Apportionment Models The problem of dividing an estate fairly involves discrete objects, but also involves cash. When a fair division problem is
DM02_Final.qxp:DM02.qxp 5/9/14 2:43 PM Page 72 Lesson 2.3 Apportionment Models The problem of dividing an estate fairly involves discrete objects, but also involves cash. When a fair division problem is
HOW TO APPORTION FAIRLY
 Part 1: Representing, electing and ranking École Polytéchnique and CNRS Cornell University September 25, 2007 REPRESENTING, ELECTING, and RANKING REPRESENTING, ELECTING, and RANKING Lecture 1: Why the
Part 1: Representing, electing and ranking École Polytéchnique and CNRS Cornell University September 25, 2007 REPRESENTING, ELECTING, and RANKING REPRESENTING, ELECTING, and RANKING Lecture 1: Why the
Matthew Miller, Bureau of Legislative Research
 Matthew Miller, Bureau of Legislative Research Arkansas (reelection) Georgia (reelection) Idaho (reelection) Kentucky (reelection) Michigan (partisan nomination - reelection) Minnesota (reelection) Mississippi
Matthew Miller, Bureau of Legislative Research Arkansas (reelection) Georgia (reelection) Idaho (reelection) Kentucky (reelection) Michigan (partisan nomination - reelection) Minnesota (reelection) Mississippi
Four reasons we need government
 Four reasons we need government 1. Need for Law and Order - Government makes laws to protect citizens, and punishes those who break the law. Laws provide order in a society. This allows citizens to live
Four reasons we need government 1. Need for Law and Order - Government makes laws to protect citizens, and punishes those who break the law. Laws provide order in a society. This allows citizens to live
1. According to Washington, what is needed to prevent an uprising like Shays Rebellion? [1]
![1. According to Washington, what is needed to prevent an uprising like Shays Rebellion? [1] 1. According to Washington, what is needed to prevent an uprising like Shays Rebellion? [1]](/thumbs/83/87708147.jpg) Part A Short-Answer Questions Directions: Analyze the documents and answer the short-answer questions that follow each document in the space provided. Document 1 We are fast verging to anarchy and confusion!
Part A Short-Answer Questions Directions: Analyze the documents and answer the short-answer questions that follow each document in the space provided. Document 1 We are fast verging to anarchy and confusion!
Apportionment Problems
 Apportionment Problems Lecture 14 Section 4.1 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Feb 20, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Apportionment Problems Fri, Feb 20, 2015 1 / 15 1 Apportioning
Apportionment Problems Lecture 14 Section 4.1 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Feb 20, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Apportionment Problems Fri, Feb 20, 2015 1 / 15 1 Apportioning
Federal Rate of Return. FY 2019 Update Texas Department of Transportation - Federal Affairs
 Federal Rate of Return FY 2019 Update Texas Department of Transportation - Federal Affairs Texas has historically been, and continues to be, the biggest donor to other states when it comes to federal highway
Federal Rate of Return FY 2019 Update Texas Department of Transportation - Federal Affairs Texas has historically been, and continues to be, the biggest donor to other states when it comes to federal highway
Constitution of the United States. Article. I.
 Constitution of the United States Article. I. Section. 1. All legislative Powers herein granted shall be vested in a Congress of the United States, which shall consist of a Senate and House of Representatives.
Constitution of the United States Article. I. Section. 1. All legislative Powers herein granted shall be vested in a Congress of the United States, which shall consist of a Senate and House of Representatives.
Find the winner of the election using majority rule given the results below: Choices (ABC) (ACB) (BAC) (BCA) (CAB) (CBA) Number of Votes
 Voting Theory Majority Rule n If the number of votes n is even, then a majority is 1 2 + n +1 If the number of votes n is odd, then a majority is 2 Example 1 Consider an election with 3 alternatives Candidate
Voting Theory Majority Rule n If the number of votes n is even, then a majority is 1 2 + n +1 If the number of votes n is odd, then a majority is 2 Example 1 Consider an election with 3 alternatives Candidate
Regulating Elections: Districts /252 Spring 2015
 Regulating Elections: Districts 17.251/252 Spring 2015 Arch & Summer Street in Boston Arch & Summer Street in Boston Near this site stood the home of state senator Israel Thorndike, a merchant and privateer.
Regulating Elections: Districts 17.251/252 Spring 2015 Arch & Summer Street in Boston Arch & Summer Street in Boston Near this site stood the home of state senator Israel Thorndike, a merchant and privateer.
We the People of the United States,
 We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defence, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings
We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defence, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings
The Constitutional Convention. Howard Chandler Christy, Scene at the Signing of the Constitution of the United States (1940)
 The Constitutional Convention Howard Chandler Christy, Scene at the Signing of the Constitution of the United States (1940) USHC 1.4 Analyze how dissatisfactions with the government under the Articles
The Constitutional Convention Howard Chandler Christy, Scene at the Signing of the Constitution of the United States (1940) USHC 1.4 Analyze how dissatisfactions with the government under the Articles
TEACHING AMERICAN HISTORY PROJECT The Constitution, Article I Kyra Kasperson
 TEACHING AMERICAN HISTORY PROJECT The Constitution, Article I Kyra Kasperson Grade 7 Length of class period 42 minutes Inquiry What is the composition of the legislative branch under the Constitution and
TEACHING AMERICAN HISTORY PROJECT The Constitution, Article I Kyra Kasperson Grade 7 Length of class period 42 minutes Inquiry What is the composition of the legislative branch under the Constitution and
Notice N HCFB-1. March 25, Subject: FEDERAL-AID HIGHWAY PROGRAM OBLIGATION AUTHORITY FISCAL YEAR (FY) Classification Code
 Notice Subject: FEDERAL-AID HIGHWAY PROGRAM OBLIGATION AUTHORITY FISCAL YEAR (FY) 2009 Classification Code N 4520.201 Date March 25, 2009 Office of Primary Interest HCFB-1 1. What is the purpose of this
Notice Subject: FEDERAL-AID HIGHWAY PROGRAM OBLIGATION AUTHORITY FISCAL YEAR (FY) 2009 Classification Code N 4520.201 Date March 25, 2009 Office of Primary Interest HCFB-1 1. What is the purpose of this
the rules of the republican party
 the rules of the republican party As Adopted by the 2008 Republican National Convention September 1, 2008 *Amended by the Republican National Committee on August 6, 2010 the rules of the republican party
the rules of the republican party As Adopted by the 2008 Republican National Convention September 1, 2008 *Amended by the Republican National Committee on August 6, 2010 the rules of the republican party
NORTH CAROLINA GENERAL ASSEMBLY Legislative Services Office
 NORTH CAROLINA GENERAL ASSEMBLY Legislative Services Office Kory Goldsmith, Interim Legislative Services Officer Research Division 300 N. Salisbury Street, Suite 545 Raleigh, NC 27603-5925 Tel. 919-733-2578
NORTH CAROLINA GENERAL ASSEMBLY Legislative Services Office Kory Goldsmith, Interim Legislative Services Officer Research Division 300 N. Salisbury Street, Suite 545 Raleigh, NC 27603-5925 Tel. 919-733-2578
Redistricting in Michigan
 Dr. Martha Sloan of the Copper Country League of Women Voters Redistricting in Michigan Should Politicians Choose their Voters? Politicians are drawing their own voting maps to manipulate elections and
Dr. Martha Sloan of the Copper Country League of Women Voters Redistricting in Michigan Should Politicians Choose their Voters? Politicians are drawing their own voting maps to manipulate elections and
Hamilton s Method. By: Lauren, Lane, Devonte, Sarah, Hannah A, & Katie H
 Hamilton s Method By: Lauren, Lane, Devonte, Sarah, Hannah A, & Katie H Warm-up: Matrices Review Name the Dimensions 1. [8 3 2] Add the matrices. 2. [ 1 2 3 4] + [-1-2 -3-4] = 3.Find the determinant of
Hamilton s Method By: Lauren, Lane, Devonte, Sarah, Hannah A, & Katie H Warm-up: Matrices Review Name the Dimensions 1. [8 3 2] Add the matrices. 2. [ 1 2 3 4] + [-1-2 -3-4] = 3.Find the determinant of
Why do you think the Framers organized the new country as a republic, when most countries in the world (in 1783) were ruled by a king or queen?
 NAME: Date: U.S. History CHAPTER 7 PACKET ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: 1. What is a constitution? 2. What is a republic? 3. What was the Articles of Confederation? 4. How was state and national power divided under
NAME: Date: U.S. History CHAPTER 7 PACKET ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: 1. What is a constitution? 2. What is a republic? 3. What was the Articles of Confederation? 4. How was state and national power divided under
Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings. Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings. Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings. Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings
 Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings The US government has its roots in English history Limited Government The concept that government is limited in what it can and cannot do Representative Government Government
Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings The US government has its roots in English history Limited Government The concept that government is limited in what it can and cannot do Representative Government Government
Thema Working Paper n Université de Cergy Pontoise, France
 Thema Working Paper n 2011-13 Université de Cergy Pontoise, France A comparison between the methods of apportionment using power indices: the case of the U.S. presidential elections Fabrice Barthelemy
Thema Working Paper n 2011-13 Université de Cergy Pontoise, France A comparison between the methods of apportionment using power indices: the case of the U.S. presidential elections Fabrice Barthelemy
CRS Report for Congress
 Order Code RL30711 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web The House Apportionment Formula in Theory and Practice October 10, 2000 David C. Huckabee Specialist in American National Government
Order Code RL30711 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web The House Apportionment Formula in Theory and Practice October 10, 2000 David C. Huckabee Specialist in American National Government
American Government. Workbook
 American Government Workbook WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Student............................. vii Unit 1: What Is Government? Activity 1 Monarchs of Europe...................... 1 Activity
American Government Workbook WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Student............................. vii Unit 1: What Is Government? Activity 1 Monarchs of Europe...................... 1 Activity
New Population Estimates Show Slight Changes For 2010 Congressional Apportionment, With A Number of States Sitting Close to the Edge
 67 Emerywood Court Manassas, Virginia 202 202 789.2004 tel. or 703 580.7267 703 580.6258 fax Info@electiondataservices.com EMBARGOED UNTIL 6:0 P.M. EST, SUNDAY, SEPTEMBER 26, 200 Date: September 26, 200
67 Emerywood Court Manassas, Virginia 202 202 789.2004 tel. or 703 580.7267 703 580.6258 fax Info@electiondataservices.com EMBARGOED UNTIL 6:0 P.M. EST, SUNDAY, SEPTEMBER 26, 200 Date: September 26, 200
Apportioning Seats in the U.S. House of Representatives Using the 2013 Estimated Citizen Population
 Apportioning Seats in the U.S. House of Representatives Using the Estimated Citizen Royce Crocker Specialist in American National Government October 30, 2015 Congressional Research Service 7-5700 www.crs.gov
Apportioning Seats in the U.S. House of Representatives Using the Estimated Citizen Royce Crocker Specialist in American National Government October 30, 2015 Congressional Research Service 7-5700 www.crs.gov
Delegates: Understanding the numbers and the rules
 Delegates: Understanding the numbers and the rules About 4,051 pledged About 712 unpledged 2472 delegates Images from: https://ballotpedia.org/presidential_election,_2016 On the news I hear about super
Delegates: Understanding the numbers and the rules About 4,051 pledged About 712 unpledged 2472 delegates Images from: https://ballotpedia.org/presidential_election,_2016 On the news I hear about super
THE RULES OF THE REPUBLICAN PARTY 2012 REPUBLICAN NATIONAL CONVENTION
 THE RULES OF THE REPUBLICAN PARTY AS ADOPTED BY THE 2012 REPUBLICAN NATIONAL CONVENTION TAMPA, FLORIDA AUGUST 27, 2012 **AMENDED BY THE REPUBLICAN NATIONAL COMMITTEE ON APRIL 12, 2013 & JANUARY 24, 2014**
THE RULES OF THE REPUBLICAN PARTY AS ADOPTED BY THE 2012 REPUBLICAN NATIONAL CONVENTION TAMPA, FLORIDA AUGUST 27, 2012 **AMENDED BY THE REPUBLICAN NATIONAL COMMITTEE ON APRIL 12, 2013 & JANUARY 24, 2014**
Floor Amendment Procedures
 Floor Action 5-179 Floor Amendment Procedures ills are introduced, but very few are enacted in the same form in which they began. ills are refined as they move through the legislative process. Committees
Floor Action 5-179 Floor Amendment Procedures ills are introduced, but very few are enacted in the same form in which they began. ills are refined as they move through the legislative process. Committees
2010 CENSUS POPULATION REAPPORTIONMENT DATA
 Southern Tier East Census Monograph Series Report 11-1 January 2011 2010 CENSUS POPULATION REAPPORTIONMENT DATA The United States Constitution, Article 1, Section 2, requires a decennial census for the
Southern Tier East Census Monograph Series Report 11-1 January 2011 2010 CENSUS POPULATION REAPPORTIONMENT DATA The United States Constitution, Article 1, Section 2, requires a decennial census for the
2:Forging a New Constitution. Essential Question How do new ideas change the way people live?
 2:Forging a New Constitution Essential Question How do new ideas change the way people live? The Need for Change Bold action helped the nation overcome the serious shortcomings of the Articles of Confederation.
2:Forging a New Constitution Essential Question How do new ideas change the way people live? The Need for Change Bold action helped the nation overcome the serious shortcomings of the Articles of Confederation.
The Mathematics of Apportionment
 The University of Chicago Law School Roundtable Volume 7 Issue 1 Article 9 1-1-2000 The Mathematics of Apportionment Efton Park Follow this and additional works at: http://chicagounbound.uchicago.edu/roundtable
The University of Chicago Law School Roundtable Volume 7 Issue 1 Article 9 1-1-2000 The Mathematics of Apportionment Efton Park Follow this and additional works at: http://chicagounbound.uchicago.edu/roundtable
THE RULES OF THE REPUBLICAN PARTY. As adopted by the 2012 Republican National Convention August 28, 2012
 THE RULES OF THE REPUBLICAN PARTY THE RULES OF THE REPUBLICAN PARTY As adopted by the 2012 Republican National Convention August 28, 2012 *Amended by the Republican National Committee on April 12, 2013
THE RULES OF THE REPUBLICAN PARTY THE RULES OF THE REPUBLICAN PARTY As adopted by the 2012 Republican National Convention August 28, 2012 *Amended by the Republican National Committee on April 12, 2013
CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web
 Order Code RL31074 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web The House of Representatives Apportionment Formula: An Analysis of Proposals for Change and Their Impact on States August 10, 2001
Order Code RL31074 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web The House of Representatives Apportionment Formula: An Analysis of Proposals for Change and Their Impact on States August 10, 2001
More State s Apportionment Allocations Impacted by New Census Estimates; New Twist in Supreme Court Case
 [Type here] 6171 Emerywood Court Manassas, Virginia 20112 202 789.2004 tel. or 703 580.7267 703 580.6258 fax Info@electiondataservices.com FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Date: December 22, 2015 Contact: Kimball
[Type here] 6171 Emerywood Court Manassas, Virginia 20112 202 789.2004 tel. or 703 580.7267 703 580.6258 fax Info@electiondataservices.com FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Date: December 22, 2015 Contact: Kimball
UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE et al. v. MONTANA et al. appeal from the united states district court for the district of montana
 442 OCTOBER TERM, 1991 Syllabus UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE et al. v. MONTANA et al. appeal from the united states district court for the district of montana No. 91 860. Argued March 4, 1992 Decided
442 OCTOBER TERM, 1991 Syllabus UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE et al. v. MONTANA et al. appeal from the united states district court for the district of montana No. 91 860. Argued March 4, 1992 Decided
Democratic Convention *Saturday 1 March 2008 *Monday 25 August - Thursday 28 August District of Columbia Non-binding Primary
 Presidential Primaries, Caucuses, and s Chronologically http://www.thegreenpapers.com/p08/events.phtml?s=c 1 of 9 5/29/2007 2:23 PM Presidential Primaries, Caucuses, and s Chronologically Disclaimer: These
Presidential Primaries, Caucuses, and s Chronologically http://www.thegreenpapers.com/p08/events.phtml?s=c 1 of 9 5/29/2007 2:23 PM Presidential Primaries, Caucuses, and s Chronologically Disclaimer: These
2018 Constituent Society Delegate Apportionment
 Memo to: From: Executive Directors State Medical Associations James L. Madara, MD Date: February 1, Subject: Constituent Society Apportionment I am pleased to provide delegate apportionment figures for.
Memo to: From: Executive Directors State Medical Associations James L. Madara, MD Date: February 1, Subject: Constituent Society Apportionment I am pleased to provide delegate apportionment figures for.
New Census Estimates Show Slight Changes For Congressional Apportionment Now, But Point to Larger Changes by 2020
 [Type here] Emerywood Court Manassas, Virginia 0 0.00 tel. or 0 0. 0 0. fax Info@electiondataservices.com FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Date: December, 0 Contact: Kimball W. Brace Tel.: (0) 00 or (0) 0- Email:
[Type here] Emerywood Court Manassas, Virginia 0 0.00 tel. or 0 0. 0 0. fax Info@electiondataservices.com FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Date: December, 0 Contact: Kimball W. Brace Tel.: (0) 00 or (0) 0- Email:
Major Problem. Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government.
 The Constitution Major Problem Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government. Why? Feared a government like King George The Constitutional
The Constitution Major Problem Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government. Why? Feared a government like King George The Constitutional
THE CALIFORNIA LEGISLATURE: SOME FACTS AND FIGURES. by Andrew L. Roth
 THE CALIFORNIA LEGISLATURE: SOME FACTS AND FIGURES by Andrew L. Roth INTRODUCTION The following pages provide a statistical profile of California's state legislature. The data are intended to suggest who
THE CALIFORNIA LEGISLATURE: SOME FACTS AND FIGURES by Andrew L. Roth INTRODUCTION The following pages provide a statistical profile of California's state legislature. The data are intended to suggest who
Colonies Become States
 Colonies Become States Colonies already had their own individual governments before the 1776 Declaration 11 of 13 colonies had State Constitutions Constitution a document that states rules under which
Colonies Become States Colonies already had their own individual governments before the 1776 Declaration 11 of 13 colonies had State Constitutions Constitution a document that states rules under which
*************************************
 Chapter 75. A Troubling House Vote Hands The Presidency To JQ Adams (1825) Henry Clay (1777-1852) Sections The General Election Ends Without A Winner Sidebar: Detailed Tables From The Election Of 1824
Chapter 75. A Troubling House Vote Hands The Presidency To JQ Adams (1825) Henry Clay (1777-1852) Sections The General Election Ends Without A Winner Sidebar: Detailed Tables From The Election Of 1824
A comparison between the methods of apportionment using power indices: the case of the U.S. presidential election
 A comparison between the methods of apportionment using power indices: the case of the U.S. presidential election Fabrice BARTHÉLÉMY and Mathieu MARTIN THEMA University of Cergy Pontoise 33 boulevard du
A comparison between the methods of apportionment using power indices: the case of the U.S. presidential election Fabrice BARTHÉLÉMY and Mathieu MARTIN THEMA University of Cergy Pontoise 33 boulevard du
7-45. Electronic Access to Legislative Documents. Legislative Documents
 Legislative Documents 7-45 Electronic Access to Legislative Documents Paper is no longer the only medium through which the public can gain access to legislative documents. State legislatures are using
Legislative Documents 7-45 Electronic Access to Legislative Documents Paper is no longer the only medium through which the public can gain access to legislative documents. State legislatures are using
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton
 Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
Expiring Unemployment Insurance Provisions
 Katelin P. Isaacs Analyst in Income Security December 27, 2013 Congressional Research Service 7-5700 www.crs.gov R41508 Summary Several key provisions related to extended federal unemployment benefits
Katelin P. Isaacs Analyst in Income Security December 27, 2013 Congressional Research Service 7-5700 www.crs.gov R41508 Summary Several key provisions related to extended federal unemployment benefits
Please note: Each segment in this Webisode has its own Teaching Guide
 Please note: Each segment in this Webisode has its own Teaching Guide The Articles of Confederation created a union in which the states had the power to pursue their own self-interests, and the central
Please note: Each segment in this Webisode has its own Teaching Guide The Articles of Confederation created a union in which the states had the power to pursue their own self-interests, and the central
Background Information on Redistricting
 Redistricting in New York State Citizens Union/League of Women Voters of New York State Background Information on Redistricting What is redistricting? Redistricting determines the lines of state legislative
Redistricting in New York State Citizens Union/League of Women Voters of New York State Background Information on Redistricting What is redistricting? Redistricting determines the lines of state legislative
Incarcerated America Human Rights Watch Backgrounder April 2003
 Incarcerated America Human Rights Watch Backgrounder April 03 According to the latest statistics from the U.S. Department of Justice, more than two million men and women are now behind bars in the United
Incarcerated America Human Rights Watch Backgrounder April 03 According to the latest statistics from the U.S. Department of Justice, more than two million men and women are now behind bars in the United
Millions to the Polls
 Millions to the Polls PRACTICAL POLICIES TO FULFILL THE FREEDOM TO VOTE FOR ALL AMERICANS THE RIGHT TO VOTE FOR FORMERLY INCARCERATED PERSONS j. mijin cha & liz kennedy THE RIGHT TO VOTE FOR FORMERLY INCARCERATED
Millions to the Polls PRACTICAL POLICIES TO FULFILL THE FREEDOM TO VOTE FOR ALL AMERICANS THE RIGHT TO VOTE FOR FORMERLY INCARCERATED PERSONS j. mijin cha & liz kennedy THE RIGHT TO VOTE FOR FORMERLY INCARCERATED
at New York University School of Law A 50 state guide to redistricting
 at New York University School of Law A 50 state guide to redistricting ABOUT THE BRENNAN CENTER FOR JUSTICE The Brennan Center for Justice at New York University School of Law is a non-partisan public
at New York University School of Law A 50 state guide to redistricting ABOUT THE BRENNAN CENTER FOR JUSTICE The Brennan Center for Justice at New York University School of Law is a non-partisan public
the states. decisions within its own borders) 1. A central government that would represent all 2. State sovereignty (the power to make
 The United States has operated under two constitutions. The first, The Articles of Confederation, was in effect from March 1, 1781. The Articles tried to balance two very different ideas: 1. A central
The United States has operated under two constitutions. The first, The Articles of Confederation, was in effect from March 1, 1781. The Articles tried to balance two very different ideas: 1. A central
U.S. Sentencing Commission Preliminary Crack Retroactivity Data Report Fair Sentencing Act
 U.S. Sentencing Commission Preliminary Crack Retroactivity Data Report Fair Sentencing Act July 2013 Data Introduction As part of its ongoing mission, the United States Sentencing Commission provides Congress,
U.S. Sentencing Commission Preliminary Crack Retroactivity Data Report Fair Sentencing Act July 2013 Data Introduction As part of its ongoing mission, the United States Sentencing Commission provides Congress,
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Articles of Confederation. Essential Question:
 Articles of Confederation Essential Question: Why was the central government s power too weak under the Articles of Confederation? Objectives Discuss the ideas that guided the new state governments. Describe
Articles of Confederation Essential Question: Why was the central government s power too weak under the Articles of Confederation? Objectives Discuss the ideas that guided the new state governments. Describe
FEDERAL ELECTION COMMISSION [NOTICE ] Price Index Adjustments for Contribution and Expenditure Limitations and
![FEDERAL ELECTION COMMISSION [NOTICE ] Price Index Adjustments for Contribution and Expenditure Limitations and FEDERAL ELECTION COMMISSION [NOTICE ] Price Index Adjustments for Contribution and Expenditure Limitations and](/thumbs/76/74112431.jpg) This document is scheduled to be published in the Federal Register on 02/03/2015 and available online at http://federalregister.gov/a/2015-01963, and on FDsys.gov 6715-01-U FEDERAL ELECTION COMMISSION
This document is scheduled to be published in the Federal Register on 02/03/2015 and available online at http://federalregister.gov/a/2015-01963, and on FDsys.gov 6715-01-U FEDERAL ELECTION COMMISSION
U.S. Sentencing Commission 2014 Drug Guidelines Amendment Retroactivity Data Report
 U.S. Sentencing Commission 2014 Drug Guidelines Amendment Retroactivity Data Report October 2017 Introduction As part of its ongoing mission, the United States Sentencing Commission provides Congress,
U.S. Sentencing Commission 2014 Drug Guidelines Amendment Retroactivity Data Report October 2017 Introduction As part of its ongoing mission, the United States Sentencing Commission provides Congress,
PERMISSIBILITY OF ELECTRONIC VOTING IN THE UNITED STATES. Member Electronic Vote/ . Alabama No No Yes No. Alaska No No No No
 PERMISSIBILITY OF ELECTRONIC VOTING IN THE UNITED STATES State Member Conference Call Vote Member Electronic Vote/ Email Board of Directors Conference Call Vote Board of Directors Electronic Vote/ Email
PERMISSIBILITY OF ELECTRONIC VOTING IN THE UNITED STATES State Member Conference Call Vote Member Electronic Vote/ Email Board of Directors Conference Call Vote Board of Directors Electronic Vote/ Email
2008 Changes to the Constitution of International Union UNITED STEELWORKERS
 2008 Changes to the Constitution of International Union UNITED STEELWORKERS MANUAL ADOPTED AT LAS VEGAS, NEVADA July 2008 Affix to inside front cover of your 2005 Constitution CONSTITUTIONAL CHANGES Constitution
2008 Changes to the Constitution of International Union UNITED STEELWORKERS MANUAL ADOPTED AT LAS VEGAS, NEVADA July 2008 Affix to inside front cover of your 2005 Constitution CONSTITUTIONAL CHANGES Constitution
AMENDED AND RESTATED BYLAWS OF CHS INC. (Effective December 3, 2010) ARTICLE I. Membership
 AMENDED AND RESTATED BYLAWS OF CHS INC. (Effective December 3, 2010) ARTICLE I. Membership Section 1 - Qualifications. Producers of agricultural products and associations of producers of agricultural products
AMENDED AND RESTATED BYLAWS OF CHS INC. (Effective December 3, 2010) ARTICLE I. Membership Section 1 - Qualifications. Producers of agricultural products and associations of producers of agricultural products
Number of Bills Passed Per Issue
 04 State Legislative Summary: January through July The 04 legislative session across the fifty states was another active one with 63 bills introduced and 3 enacted or vetoed pertaining to new or updated
04 State Legislative Summary: January through July The 04 legislative session across the fifty states was another active one with 63 bills introduced and 3 enacted or vetoed pertaining to new or updated
The US Constitution of 1787 and Slavery Overview Grade North Carolina Essential Standards (to be implemented in the school year)
 The US Constitution of 1787 and Slavery Overview Students will explore the Preamble to the US Constitution and the liberties and freedoms it sets forth. Students will then discuss the tensions between
The US Constitution of 1787 and Slavery Overview Students will explore the Preamble to the US Constitution and the liberties and freedoms it sets forth. Students will then discuss the tensions between
Ratification of the Constitution. Issues
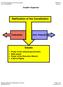 Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
2016 Voter Registration Deadlines by State
 2016 Voter s by Alabama 10/24/2016 https://www.alabamavotes.gov/electioninfo.aspx?m=vote rs Alaska 10/9/2016 (Election Day registration permitted for purpose of voting for president and Vice President
2016 Voter s by Alabama 10/24/2016 https://www.alabamavotes.gov/electioninfo.aspx?m=vote rs Alaska 10/9/2016 (Election Day registration permitted for purpose of voting for president and Vice President
Campaign Finance E-Filing Systems by State WHAT IS REQUIRED? WHO MUST E-FILE? Candidates (Annually, Monthly, Weekly, Daily).
 Exhibit E.1 Alabama Alabama Secretary of State Mandatory Candidates (Annually, Monthly, Weekly, Daily). PAC (annually), Debts. A filing threshold of $1,000 for all candidates for office, from statewide
Exhibit E.1 Alabama Alabama Secretary of State Mandatory Candidates (Annually, Monthly, Weekly, Daily). PAC (annually), Debts. A filing threshold of $1,000 for all candidates for office, from statewide
Fair Division in Theory and Practice
 Fair Division in Theory and Practice Ron Cytron (Computer Science) Maggie Penn (Political Science) Lecture 4: The List Systems of Proportional Representation 1 Saari s milk, wine, beer example Thirteen
Fair Division in Theory and Practice Ron Cytron (Computer Science) Maggie Penn (Political Science) Lecture 4: The List Systems of Proportional Representation 1 Saari s milk, wine, beer example Thirteen
National Latino Peace Officers Association
 National Latino Peace Officers Association Bylaws & SOP Changes: Vote for ADD STANDARD X Posting on Facebook, Instagram, text message and etc.. shall be in compliance to STANDARD II - MISSION NATIONAL
National Latino Peace Officers Association Bylaws & SOP Changes: Vote for ADD STANDARD X Posting on Facebook, Instagram, text message and etc.. shall be in compliance to STANDARD II - MISSION NATIONAL
INTRODUCTION AND SUMMARY
 Gender Parity Index INTRODUCTION AND SUMMARY - 2017 State of Women's Representation Page 1 INTRODUCTION As a result of the 2016 elections, progress towards gender parity stalled. Beyond Hillary Clinton
Gender Parity Index INTRODUCTION AND SUMMARY - 2017 State of Women's Representation Page 1 INTRODUCTION As a result of the 2016 elections, progress towards gender parity stalled. Beyond Hillary Clinton
House Apportionment 2012: States Gaining, Losing, and on the Margin
 House Apportionment 2012: States Gaining, Losing, and on the Margin Royce Crocker Specialist in American National Government August 23, 2013 CRS Report for Congress Prepared for Members and Committees
House Apportionment 2012: States Gaining, Losing, and on the Margin Royce Crocker Specialist in American National Government August 23, 2013 CRS Report for Congress Prepared for Members and Committees
