Hear Ye, Hear Ye-Did you hear Me?
|
|
|
- Beatrix Clarke
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hear Ye, Hear Ye-Did you hear Me? A lesson plan for grade 8 History 21 st Century Interdisciplinary Theme: Civic Literacy By: Denise C. Dooley of Albemarle Road Middle School, Charlotte, NC This lesson utilizes documents from the North Carolina State Government Publications Collection. Ensuring Democracy through Digital Access, a NC LSTA- funded grant project. Learning Outcome The students will analyze a letter from President George Washington to the Governor of North Carolina regarding the state s stance on the new Constitution. They will then participate in a mock convention/debate to better understand the issues involved in ratifying the document. Finally the students will pretend they were at the Constitutional Convention as a reporter. The culminating activity will require the students to create a newspaper reporting on the various viewpoints of the Convention in a time-accurate periodical. Type of Activity: Document Analysis, Debate, and Report Materials/Resources Needed 1. Letter from George Washington to the Governor s Council URL: 2. Constitutional Convention Website URL: 3. Constitutional Convention Website (Directed for Debate) URL: 4. Primary Source Document Analysis Sheet URL: 5. Microsoft publisher or blank newspaper template 6. Ice Cream Cone Graphic Organizer URL: Activity Sequence Day 1: 1. For the lesson introduction have the students analyze the primary source document (George Washington to the Governor s Council) without any prior information, other than what they have learned up to this point. 2. Discuss the final question of the analysis which asks what is missing. 3. Explain to the students that North Carolina and Rhode Island refused to sign the Constitution as it was originally written, but DO NOT tell them why. 4. Divide the class up into five groups and pass out the handouts. a. Group 1 Madison and Virginia Plan
2 b. Group 2 Sherman The Connecticut Plan c. Group 3 New Jersey Plan d. Group 4 British Plan e. Group 5- But Group 5. Have each group discuss their plan and each team member complete the ICE CREAM GRAPHIC ORGANIZER. 6. The But group gets all the documents for comparison. They will later be used to entice the class to think about each plan. 7. Each team is to elect a member for the HOT SEAT. 8. Once all groups have completed the graphic organizer have the class arrange their desks in a large circle, students are not to sit next to someone from their original document group. 9. Sit a chair in the center of the circle for the HOT SEAT representatives. 10. Start with the Virginia Plan hot seat representative and have them sit in the center to present their plan. 11. Students can ask questions, if no one opens up it is the responsibility of a member of the BUT group to spur the debate. Day 2 Create the Newspaper Assessment The Newspaper should serve as an assessment of mastery. Author s Notes Students should have studied Shays Rebellion prior to his point and be aware that the Articles of Confederation was too weak a document to govern the United States. North Carolina Essential Standards 8.H.1 Apply historical thinking to understand the creation and development of North Carolina and the United States. 8.H.2 Understand the ways in which conflict, compromise and negotiation have shaped North Carolina and the United States. 8.C&G.1 Analyze how democratic ideals shaped government in North Carolina and the United States. USH.H.2 Analyze key political, economic and social turning points in United States History using historical thinking. USH.H.4 Analyze how conflict and compromise have shaped politics, economics and culture in the United States.
3 Group 1- The Virginia Plan The Virginia Plan The Central Features of the Virginia Plan Text of the Virginia Plan On Tuesday morning, May 29, Edmund Randolph, the tall, 34-year- old governor of Virginia, opened the debate with a long speech decrying the evils that had befallen the country under the Articles of Confederation and stressing the need for creating a strong national government. Randolph then outlined a broad plan that he and his Virginia compatriots had, through long sessions at the Indian Queen tavern, put together in the days preceding the convention. James Madison had such a plan on his mind for years. The proposed government had three branches-- legislative, executive, and judicial--each branch structured to check the other. Highly centralized, the government would have veto power over laws enacted by state legislatures. The plan, Randolph confessed, "meant a strong consolidated union in which the idea of states should be nearly annihilated." This was, indeed, the rat so offensive to Patrick Henry. The introduction of the so-called Virginia Plan at the beginning of the convention was a tactical coup. The Virginians had forced the debate into their own frame of reference and in their own terms. For 10 days the members of the convention discussed the sweeping and, to many delegates, startling Virginia resolutions. The critical issue, described succinctly by Gouverneur Morris on May 30, was the distinction between a federation and a national government, the "former being a mere compact resting on the good faith of the parties; the latter having a compleat and compulsive operation." Morris favored the latter, a "supreme power" capable of exercising necessary authority not merely a shadow government, fragmented and hopelessly ineffective. To correct these deficiencies, the Virginia Plan removed the state legislatures both structurally, and in terms of powers, from any place in the new continental arrangement. Most importantly, 1. The National Legislature should consist of two branches. 2. The people of each State should elect the First Branch of the National Legislature. The Second Branch of the National Legislature should be elected by the first. 3. The National Legislature shall have power "to legislate in all cases to which the separate States are incompetent," and "to negative all laws passed by the States, contravening in the opinion of the National Legislature the articles of Union." 4. The National Legislature shall elect a National Executive. 5. The Executive and a number of National Judiciary will form a Council of Revision. This Council will review laws passed by the National Legislature and have the power to reject the laws, unless the National Legislature can pass the act again. 6. The National Legislature will create the National Judiciary. The structure will consist of one or more supreme tribunals and inferior tribunals. Judges will be appointed for life, during good behavior. 7. State Legislatures, Executives, and Judges are to be bound by oath to support the Articles. 8. The new plan for government should be ratified by the people, through assemblies of representatives chosen by the people.
4 Group 2 The New Jersey Plan The New Jersey Plan This nationalist position revolted many delegates who cringed at the vision of a central government swallowing state sovereignty. On June 13 delegates from smaller states rallied around proposals offered by New Jersey delegate William Paterson. Railing against efforts to throw the states into "hotchpot," Paterson proposed a "union of the States merely federal." The "New Jersey resolutions" called only for a revision of the articles to enable the Congress more easily to raise revenues and regulate commerce. It also provided that acts of Congress and ratified treaties be "the supreme law of the States." For 3 days the convention debated Paterson's plan, finally voting for rejection. With the defeat of the New Jersey resolutions, the convention was moving toward creation of a new government, much to the dismay of many smallstate delegates. The nationalists, led by Madison, appeared to have the proceedings in their grip. In addition, they were able to persuade the members that any new constitution should be ratified through conventions of the people and not by the Congress and the state legislatures- -another tactical coup. Madison and his allies believed that the constitution they had in mind would likely be scuttled in the legislatures, where many state political leaders stood to lose power. The nationalists wanted to bring the issue before "the people," where ratification was more likely.
5 Group 3 - The Connecticut Compromise The Connecticut Compromise The Virginia Plan, introduced on May 29, was "wholly national." Of particular importance is the absence of any structural representation for the states. The general government shall have a bicameral legislative structure with neither branch elected by the states and with neither representing the states. On June 11, the delegates overwhelmingly agreed that the lower house should be based on population and elected by the people. The delegates rejected a proposal by Roger Sherman that supported popular representation in the lower house and equal representation for the states in the upper branch. On 19 June, the New Jersey Plan was defeated. Ellsworth reintroduced the motion of June 11: equal representation for the states in the upper house with proportional representation in the lower house. For the first time, the case for the representation of the states was elevated from one of convenience to one of principle. Ellsworth declared, "We were partly national; partly federal. He trusted that on this middle ground a compromise would take place." On June 30, the youngest delegate, Jonathan Dayton of New Jersey until then a pretty staunch nationalist spoke for the first time: "We were partly federal, partly national in our Union," he declared. "And he did not see why the Govt. might (not) in some respects operate on the States, in others on the people." On July 2, the Ellsworth proposal was defeated on a tie vote: Nevertheless, a Committee of 11 one delegate from each state was created to seek a compromise on the representation question. The key to the Compromise was winning over such former wholly national supporters like Gerry and Mason. An often-overlooked component of the Compromise was the agreement that money bills would originate in the House and could not be amended in the Senate. This feature was vital in winning over Mason and Gerry, as well as Randolph who introduced the wholly national Virginia Plan. These three delegates were willing to buy into the partly national (popular representation in the House), partly federal (equal representation for the states in the Senate) arrangement if the principle of no taxation without popular representation was adhered to. On July 16, the delegates agreed (5-4-1) to the Gerry Committee Report, also known as the Connecticut Compromise. The losing delegates, Madison, Wilson, G. Morris, Pinckney, and King, decided not to challenge the outcome.
6 Group 4 The British Plan Hamilton's Plan On June 18 Alexander Hamilton presented his own ideal plan of government. Erudite and polished, the speech, nevertheless, failed to win a following. It went too far. Calling the British government "the best in the world," Hamilton proposed a model strikingly similar an executive to serve during good behavior or life with veto power over all laws; a senate with members serving during good behavior; the legislature to have power to pass "all laws whatsoever." Hamilton later wrote to Washington that the people were now willing to accept "something not very remote from that which they have lately quitted." What the people had "lately quitted," of course, was monarchy. Some members of the convention fully expected the country to turn in this direction. Hugh Williamson of North Carolina, a wealthy physician, declared that it was "pretty certain... that we should at some time or other have a king." Newspaper accounts appeared in the summer of 1787 alleging that a plot was under way to invite the second son of George III, Frederick, Duke of York, the secular bishop of Osnaburgh in Prussia, to become "king of the United States."
7
8
9 Sources
Chapter 25 Section 1. Section 1. Terms and People
 Chapter 25 Terms and People republic a government in which the people elect their representatives unicameral legislature a lawmaking body with a single house whose representatives are elected by the people
Chapter 25 Terms and People republic a government in which the people elect their representatives unicameral legislature a lawmaking body with a single house whose representatives are elected by the people
Constitutional Convention
 Constitutional Convention I INTRODUCTION Constitutional Convention, meeting during the summer of 1787 at which delegates from 12 states wrote the Constitution of the United States. At the convention in
Constitutional Convention I INTRODUCTION Constitutional Convention, meeting during the summer of 1787 at which delegates from 12 states wrote the Constitution of the United States. At the convention in
The Constitutional Convention. Chapter 2 Section 4
 The Constitutional Convention Chapter 2 Section 4 Constitutional Convention May 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 74 delegates allowed, 55 attended, 39 signed final Delegates to the Convention Had lots of
The Constitutional Convention Chapter 2 Section 4 Constitutional Convention May 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 74 delegates allowed, 55 attended, 39 signed final Delegates to the Convention Had lots of
but given the customs of the time touching personal honor, it made perfect sense. by Charles Wilson
 3 A New Constitution How are you today, my dear General! W ith these words, Gouverneur Morris greeted General George Washington, after slapping him genially on the back. Morris, a Pennsylvania delegate
3 A New Constitution How are you today, my dear General! W ith these words, Gouverneur Morris greeted General George Washington, after slapping him genially on the back. Morris, a Pennsylvania delegate
Creating the Constitution
 Creating the Constitution Constitutional Convention Philadelphia 1787 Met in Secret Goal: Alter or abolish fix the old system or create a new one Needed to tweak the articles Focus of Convention Meeting
Creating the Constitution Constitutional Convention Philadelphia 1787 Met in Secret Goal: Alter or abolish fix the old system or create a new one Needed to tweak the articles Focus of Convention Meeting
Creating Our. Constitution. Key Terms. delegates equal representation executive federal system framers House of Representatives judicial
 Lesson 2 Creating Our Constitution Key Terms delegates equal representation executive federal system framers House of Representatives judicial What You Will Learn to Do Explain how the Philadelphia Convention
Lesson 2 Creating Our Constitution Key Terms delegates equal representation executive federal system framers House of Representatives judicial What You Will Learn to Do Explain how the Philadelphia Convention
A More Perfect Union. Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation
 A More Perfect Union Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation 1. Eleven of the thirteen states adopted state constitutions. Connecticut and Rhode Island kept its colonial charter as its constitution
A More Perfect Union Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation 1. Eleven of the thirteen states adopted state constitutions. Connecticut and Rhode Island kept its colonial charter as its constitution
The Constitutional Convention formed the plan of government that the United States still has today.
 2 Creating the Constitution MAIN IDEA The states sent delegates to a convention to solve the problems of the Articles of Confederation. WHY IT MATTERS NOW The Constitutional Convention formed the plan
2 Creating the Constitution MAIN IDEA The states sent delegates to a convention to solve the problems of the Articles of Confederation. WHY IT MATTERS NOW The Constitutional Convention formed the plan
Convention. Guide to Reading
 Convention and Compromise Main Idea The new Constitution corrected the weaknesses of government under the Articles of Confederation. Key Terms depression, manumission, proportional, compromise 1784 Rhode
Convention and Compromise Main Idea The new Constitution corrected the weaknesses of government under the Articles of Confederation. Key Terms depression, manumission, proportional, compromise 1784 Rhode
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes
 Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
CREATING A GOVERNMENT
 Let us not be afraid to view with a steady eye the dangers with which we are surrounded. Are we not on the eve of a war, which is only to be prevented by the hopes from this convention? CREATING A GOVERNMENT
Let us not be afraid to view with a steady eye the dangers with which we are surrounded. Are we not on the eve of a war, which is only to be prevented by the hopes from this convention? CREATING A GOVERNMENT
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes
 Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
The U.S. Constitution: Who, What, Where, When, Why & How
 The U.S. Constitution: Who, What, Where, When, Why & How 'a ^Va&o/z Fighting between the American colonists and British forces under King George III was in its second year when the Declaration of Independence
The U.S. Constitution: Who, What, Where, When, Why & How 'a ^Va&o/z Fighting between the American colonists and British forces under King George III was in its second year when the Declaration of Independence
Constitutional Convention. May 1787
 Constitutional Convention May 1787 Annapolis Convention September 11 to September 14, 1786 Annapolis, Maryland Purpose - How to fix the articles of confederation Alexander Hamilton (New York) MUST resolve
Constitutional Convention May 1787 Annapolis Convention September 11 to September 14, 1786 Annapolis, Maryland Purpose - How to fix the articles of confederation Alexander Hamilton (New York) MUST resolve
Ch.8, Sec.2 Creating the Constitution
 ü A al Convention Is Called - during the summer of 1787, 12 states sent delegates to Philadelphia to discuss amending the Articles of Confederation - the example set by Shays Rebellion proved our young
ü A al Convention Is Called - during the summer of 1787, 12 states sent delegates to Philadelphia to discuss amending the Articles of Confederation - the example set by Shays Rebellion proved our young
Ratification of the Constitution. Issues
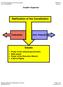 Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
Organization & Agreements
 Key Players Key Players Key Players George Washington unanimously chosen to preside over the meetings. Benjamin Franklin now 81 years old. Gouverneur Morris wrote the final draft. James Madison often called
Key Players Key Players Key Players George Washington unanimously chosen to preside over the meetings. Benjamin Franklin now 81 years old. Gouverneur Morris wrote the final draft. James Madison often called
Chapter 3 Constitution. Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook
 Chapter 3 Constitution Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on www.pknock.com Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from
Chapter 3 Constitution Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on www.pknock.com Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from
The American Revolution is over but now the colonists have to decide how they want to frame their government. Take the first 5 minutes of class and
 The American Revolution is over but now the colonists have to decide how they want to frame their government. Take the first 5 minutes of class and imagine that you were a colonist that just fought against
The American Revolution is over but now the colonists have to decide how they want to frame their government. Take the first 5 minutes of class and imagine that you were a colonist that just fought against
AIM: How did the Articles of Confederation impact the U.S.?
 AIM: How did the Articles of Confederation impact the U.S.? Do Now: How do you think Hale Charter Academy would function if we got rid of the assistant principal, and the dean, and we allowed the individual
AIM: How did the Articles of Confederation impact the U.S.? Do Now: How do you think Hale Charter Academy would function if we got rid of the assistant principal, and the dean, and we allowed the individual
SSUSH5 A, B, C & D Creating a New Government
 SSUSH5 A, B, C & D Creating a New Government The Articles of Confederation Formally called the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union, this agreement was created by the leaders of the original thirteen
SSUSH5 A, B, C & D Creating a New Government The Articles of Confederation Formally called the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union, this agreement was created by the leaders of the original thirteen
Chapter 5 section 3: Creating the Constitution textbook pages
 Chapter 5 section 3: Creating the Constitution textbook pages 163-168 The Big Idea A new constitution provided a framework for a stronger national government. Main Idea 1:The Constitutional Convention
Chapter 5 section 3: Creating the Constitution textbook pages 163-168 The Big Idea A new constitution provided a framework for a stronger national government. Main Idea 1:The Constitutional Convention
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of American Government
 Chapter 2: The Beginnings of American Government United States Government Fall, 2017 Origins of American Political Ideals Colonial Period Where did ideas for government in the colonies come from? Largely,
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of American Government United States Government Fall, 2017 Origins of American Political Ideals Colonial Period Where did ideas for government in the colonies come from? Largely,
The MAKING of the CONSTITUTION
 The MAKING of the CONSTITUTION Americans fought hard to win their freedom. But could they find a way to govern themselves? CAST Sarah Bache, Benjamin Franklin's daughter The delegates: William Davie, North
The MAKING of the CONSTITUTION Americans fought hard to win their freedom. But could they find a way to govern themselves? CAST Sarah Bache, Benjamin Franklin's daughter The delegates: William Davie, North
The Constitutional Convention
 Early United States I can describe how thirteen colonies evolved into the United States. 4 I can make inferences that go beyond what was taught in class or connect and explain the 3.0 learning targets
Early United States I can describe how thirteen colonies evolved into the United States. 4 I can make inferences that go beyond what was taught in class or connect and explain the 3.0 learning targets
Why do you think the Framers organized the new country as a republic, when most countries in the world (in 1783) were ruled by a king or queen?
 NAME: Date: U.S. History CHAPTER 7 PACKET ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: 1. What is a constitution? 2. What is a republic? 3. What was the Articles of Confederation? 4. How was state and national power divided under
NAME: Date: U.S. History CHAPTER 7 PACKET ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: 1. What is a constitution? 2. What is a republic? 3. What was the Articles of Confederation? 4. How was state and national power divided under
Section 4 at a Glance The Constitutional Convention
 Section 4 at a Glance The Constitutional Convention At the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia, delegates debated competing plans the Virginia Plan and the New Jersey Plan for how the new government
Section 4 at a Glance The Constitutional Convention At the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia, delegates debated competing plans the Virginia Plan and the New Jersey Plan for how the new government
Creating the Constitution 2.2, 2.3, 2.4
 Creating the Constitution 2.2, 2.3, 2.4 Struggle for Government The creation and signing of the Declaration of Independence did not create a government The founding fathers had many problems Declaration
Creating the Constitution 2.2, 2.3, 2.4 Struggle for Government The creation and signing of the Declaration of Independence did not create a government The founding fathers had many problems Declaration
CHAPTER 7 CREATING A GOVERNMENT
 CHAPTER 7 CREATING A GOVERNMENT The Constitution set out our rules for government. It explains what our government can and cannot do. It reflects are experience as a colony as well as ideas from Europe
CHAPTER 7 CREATING A GOVERNMENT The Constitution set out our rules for government. It explains what our government can and cannot do. It reflects are experience as a colony as well as ideas from Europe
U.S. Constitution PSCI 1040
 PSCI 1040 Purposes of a Constitution Organize and empower the government Limit the powers of government. Many consider limited government to be the essence of constitutional government. 2 Articles of Confederation
PSCI 1040 Purposes of a Constitution Organize and empower the government Limit the powers of government. Many consider limited government to be the essence of constitutional government. 2 Articles of Confederation
Warm Up. 1 Explain how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to Shays Rebellion:
 Warm Up 1 Explain how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to Shays Rebellion: 2 What was the primary concern of soldier/farmers who supported Daniel Shays? 3 Explain how Shays Rebellion
Warm Up 1 Explain how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to Shays Rebellion: 2 What was the primary concern of soldier/farmers who supported Daniel Shays? 3 Explain how Shays Rebellion
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Articles of Confederation. Essential Question:
 Articles of Confederation Essential Question: Why was the central government s power too weak under the Articles of Confederation? Objectives Discuss the ideas that guided the new state governments. Describe
Articles of Confederation Essential Question: Why was the central government s power too weak under the Articles of Confederation? Objectives Discuss the ideas that guided the new state governments. Describe
THE CONSTITUTION OF THE UNITED STATES
 THE CONSTITUTION OF THE UNITED STATES Presented by Amendment Avenger CONSTITUTIONAL HISTORY The Declaration of Independence Articles of Confederation Critical Period Declaration of Independence Taxation
THE CONSTITUTION OF THE UNITED STATES Presented by Amendment Avenger CONSTITUTIONAL HISTORY The Declaration of Independence Articles of Confederation Critical Period Declaration of Independence Taxation
Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50
 Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50 The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from religious persecution Economic opportunity Independent
Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50 The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from religious persecution Economic opportunity Independent
DISCUSSION QUESTIONS Decision in Philadelphia
 Preface 1. Of all he riches of human life, what is the most highly prized? 2. What do the authors find dismaying about American liberty? a. What are the particulars of this argument? 3. Why have the authors
Preface 1. Of all he riches of human life, what is the most highly prized? 2. What do the authors find dismaying about American liberty? a. What are the particulars of this argument? 3. Why have the authors
Basic Concepts of Government The English colonists brought 3 ideas that loom large in the shaping of the government in the United States.
 Civics Honors Chapter Two: Origins of American Government Section One: Our Political Beginnings Limited Government Representative government Magna Carta Petition of Right English Bill of Rights Charter
Civics Honors Chapter Two: Origins of American Government Section One: Our Political Beginnings Limited Government Representative government Magna Carta Petition of Right English Bill of Rights Charter
Articles of Confederation
 Articles of Confederation What was the nation facing after the Revolutionary War? -An agrarian or agricultural nation (Farmland) -A Confederate Nation-joined by an agreement or treaty -Debt -Major economic
Articles of Confederation What was the nation facing after the Revolutionary War? -An agrarian or agricultural nation (Farmland) -A Confederate Nation-joined by an agreement or treaty -Debt -Major economic
The Constitutional Convention
 The Constitutional Convention Problems like Shay s Rebellion revealed the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation This event convinced many U.S. citizens that our 1 st written plan of government needed
The Constitutional Convention Problems like Shay s Rebellion revealed the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation This event convinced many U.S. citizens that our 1 st written plan of government needed
WARM UP. 1 Using the information from yesterday or new information collected using your ipad create a bubble map on the Constitutional Convention
 WARM UP 1 Using the information from yesterday or new information collected using your ipad create a bubble map on the Constitutional Convention 2 Include people, dates, locations, facts and other information
WARM UP 1 Using the information from yesterday or new information collected using your ipad create a bubble map on the Constitutional Convention 2 Include people, dates, locations, facts and other information
Creators of the Constitution
 Creators of the Constitution After the Revolutionary War, the thirteen former colonies joined together and in November 1777 formed a new government that was bound by an agreement called the Articles of
Creators of the Constitution After the Revolutionary War, the thirteen former colonies joined together and in November 1777 formed a new government that was bound by an agreement called the Articles of
What were the Articles of Confederation? What did America do to create a stronger government in the 1780s?
 2.3 Articles of Confederation What were the Articles of Confederation? Why were the 1780s a critical period in United States history? What did America do to create a stronger government in the 1780s? Section:
2.3 Articles of Confederation What were the Articles of Confederation? Why were the 1780s a critical period in United States history? What did America do to create a stronger government in the 1780s? Section:
BILL OF RIGHTS TERMS. 1. U.S. Constitution 6. Ratify 2. Amendment 7. Petition 3. Citizen 8. Warrant 4. Quartering 9. Due Process 5. Jury 10.
 BILL OF RIGHTS TERMS 1. U.S. Constitution 6. Ratify 2. Amendment 7. Petition 3. Citizen 8. Warrant 4. Quartering 9. Due Process 5. Jury 10. Prohibit A More Perfect Union Chart Person Who What Significance
BILL OF RIGHTS TERMS 1. U.S. Constitution 6. Ratify 2. Amendment 7. Petition 3. Citizen 8. Warrant 4. Quartering 9. Due Process 5. Jury 10. Prohibit A More Perfect Union Chart Person Who What Significance
The Critical Period The early years of the American Republic
 The Critical Period 1781-1789 The early years of the American Republic America after the War New Political Ideas: - Greater power for the people Republic: Represent the Public America after the War State
The Critical Period 1781-1789 The early years of the American Republic America after the War New Political Ideas: - Greater power for the people Republic: Represent the Public America after the War State
Ratifying the Constitution
 Ratifying the Constitution Signing the Constitution Once the debate ended, Governor Morris of New Jersey put the Constitution in its final form. He competed the task of hand-writing 4,300 words in two
Ratifying the Constitution Signing the Constitution Once the debate ended, Governor Morris of New Jersey put the Constitution in its final form. He competed the task of hand-writing 4,300 words in two
Have your notebook out!
 Have your notebook out! Unit 3 Government 10/26/17 Upcountry Vs. Lowcountry Fighting over South Carolina After the war, Upcountry and Lowcountry fought for control over the government and power in South
Have your notebook out! Unit 3 Government 10/26/17 Upcountry Vs. Lowcountry Fighting over South Carolina After the war, Upcountry and Lowcountry fought for control over the government and power in South
Constitutional Convention
 Constitutional Convention How did the United States overcome the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation and provide for the organization of the new government? What role did compromise play in the
Constitutional Convention How did the United States overcome the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation and provide for the organization of the new government? What role did compromise play in the
Chapter 2:4 Constitutional Convention
 Chapter 2:4 Constitutional Convention Psa_119:165 Great peace have they which love thy law: and nothing shall offend them. Objectives: 2:4 Our Political Beginnings o Students will examine the process that
Chapter 2:4 Constitutional Convention Psa_119:165 Great peace have they which love thy law: and nothing shall offend them. Objectives: 2:4 Our Political Beginnings o Students will examine the process that
Chapter 5, Section 3 Creating the Constitution. Pages
 Chapter 5, Section 3 Creating the Constitution Pages 163-168 It didn t take long for people to realize that the Articles of Confederation had many weaknesses. By the mid-1780s most political leaders agreed
Chapter 5, Section 3 Creating the Constitution Pages 163-168 It didn t take long for people to realize that the Articles of Confederation had many weaknesses. By the mid-1780s most political leaders agreed
Constitution Day: Federalists vs. Anti-Federalists Introduction Massachusetts History and Social Science Curriculum Frameworks Content Standards
 Constitution Day: Federalists vs. Anti-Federalists Adapted from the Stanford History Education Group s Federalists and Anti-Federalists Lesson Plan https://sheg.stanford.edu/history-lessons/federalists-and-anti-federalists
Constitution Day: Federalists vs. Anti-Federalists Adapted from the Stanford History Education Group s Federalists and Anti-Federalists Lesson Plan https://sheg.stanford.edu/history-lessons/federalists-and-anti-federalists
STANDARD: CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION. Philadelphia, PA- May 25-September 17, 1787
 STANDARD: 8-3.2 CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Philadelphia, PA- May 25-September 17, 1787 Let s Think? Reasons for a Convention Called to address problems in governing the U.S. In 1787- U.S. was operating
STANDARD: 8-3.2 CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Philadelphia, PA- May 25-September 17, 1787 Let s Think? Reasons for a Convention Called to address problems in governing the U.S. In 1787- U.S. was operating
OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS
 CHAPTER 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS The colonists brought with them to North America knowledge of the English political system, including three key ideas about government.
CHAPTER 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS The colonists brought with them to North America knowledge of the English political system, including three key ideas about government.
A. As You Read. B. Reviewing Key Terms. Section 1 Guided Reading and Review Government and the State
 1 Section 1 Guided Reading and Review Government and the State As you read Section 1, fill in the answers to the following questions. 1. What are the four characteristics of a state? a. b. c. d. 2. What
1 Section 1 Guided Reading and Review Government and the State As you read Section 1, fill in the answers to the following questions. 1. What are the four characteristics of a state? a. b. c. d. 2. What
Origins of American Government. Chapter 2
 Origins of American Government Chapter 2 Section 1 Essential Questions 1) What two principles of government came from the English heritage of the colonists? 2) What documents from England influenced the
Origins of American Government Chapter 2 Section 1 Essential Questions 1) What two principles of government came from the English heritage of the colonists? 2) What documents from England influenced the
The United States Constitution. The Supreme Law of the Land
 The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land The Articles Prove Unstable Federal gov t could declare war and other foreign affairs Federal gov t have no power to collect taxes, relying only
The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land The Articles Prove Unstable Federal gov t could declare war and other foreign affairs Federal gov t have no power to collect taxes, relying only
THE CONSTITUTION AND ITS HISTORY
 THE CONSTITUTION AND ITS HISTORY 1 CHAPTER Outline I. Introduction II. History Leading up to the Constitution A. Articles of Confederation 1. A firm league of friendship a. Each state was to remain (1)
THE CONSTITUTION AND ITS HISTORY 1 CHAPTER Outline I. Introduction II. History Leading up to the Constitution A. Articles of Confederation 1. A firm league of friendship a. Each state was to remain (1)
Quarter One: Unit Four
 SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will identify the weaknesses of the government under the Articles of Confederation (i.e.,
SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will identify the weaknesses of the government under the Articles of Confederation (i.e.,
 Everybody hated this thing. While observing that it was too weak is an oversimplification. The variety of reasons why people were so miserable in the 1780s have everything to do with this document (until
Everybody hated this thing. While observing that it was too weak is an oversimplification. The variety of reasons why people were so miserable in the 1780s have everything to do with this document (until
Vocabulary Match-Up. Name Date Period Workbook Activity
 Name Date Period Workbook Activity Vocabulary Match-Up Chapter 2, Lesson 1 7 Part A Directions Match the vocabulary word in Column 1 with its definition in Column 2. Write the correct letter on each line.
Name Date Period Workbook Activity Vocabulary Match-Up Chapter 2, Lesson 1 7 Part A Directions Match the vocabulary word in Column 1 with its definition in Column 2. Write the correct letter on each line.
Constitutional Convention
 Constitutional Convention Members Principles Agreements and compromises The Constitutional Convention, 1787 u 55 delegates attended but on a typical day 35 were present u 29 held college degrees u 34 were
Constitutional Convention Members Principles Agreements and compromises The Constitutional Convention, 1787 u 55 delegates attended but on a typical day 35 were present u 29 held college degrees u 34 were
HIST 1301 Part Two. 6: The Republican Experiment
 HIST 1301 Part Two 6: The Republican Experiment The States and the Confederation 1776-1788 During the Revolution, state Governments formed first. 2 min. 40 sec. Each state had a written constitution. Each
HIST 1301 Part Two 6: The Republican Experiment The States and the Confederation 1776-1788 During the Revolution, state Governments formed first. 2 min. 40 sec. Each state had a written constitution. Each
It was decided that delegates from the different states would meet during the summer of 1787 in Philadelphia.
 It was decided that delegates from the different states would meet during the summer of 1787 in Philadelphia. Philadelphia has a rich history, as it was at one time America s largest city and former capital.
It was decided that delegates from the different states would meet during the summer of 1787 in Philadelphia. Philadelphia has a rich history, as it was at one time America s largest city and former capital.
Major Problem. Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government.
 The Constitution Major Problem Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government. Why? Feared a government like King George The Constitutional
The Constitution Major Problem Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government. Why? Feared a government like King George The Constitutional
THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION. Compromises Federalists v. Anti-Federalists
 THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Compromises Federalists v. Anti-Federalists QUICK REVIEW: FIND SOMEONE WHO Second Continental Congress Drafting of the Articles of Confederation Weaknesses International Relations
THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Compromises Federalists v. Anti-Federalists QUICK REVIEW: FIND SOMEONE WHO Second Continental Congress Drafting of the Articles of Confederation Weaknesses International Relations
Creating the Constitution
 Creating the Constitution 1776-1791 US Timeline 1777-1791 1777 Patriots win Battles of Saratoga. Continental Congress passes the Articles of Confederation. 1781 Articles of Confederation go into effect.
Creating the Constitution 1776-1791 US Timeline 1777-1791 1777 Patriots win Battles of Saratoga. Continental Congress passes the Articles of Confederation. 1781 Articles of Confederation go into effect.
The States: Experiments in Republicanism State constitutions served as experiments in republican government The people demand written constitutions
 The States: Experiments in Republicanism State constitutions served as experiments in republican government The people demand written constitutions provide clear definition of rights describe clear limits
The States: Experiments in Republicanism State constitutions served as experiments in republican government The people demand written constitutions provide clear definition of rights describe clear limits
Beginnings of a New Nation
 The period between the Treaty of Paris and the writing of the Constitution, the states were united only by a rope of sand. George Washington Beginnings of a New Nation Officers were disgusted with Congress
The period between the Treaty of Paris and the writing of the Constitution, the states were united only by a rope of sand. George Washington Beginnings of a New Nation Officers were disgusted with Congress
the states. decisions within its own borders) 1. A central government that would represent all 2. State sovereignty (the power to make
 The United States has operated under two constitutions. The first, The Articles of Confederation, was in effect from March 1, 1781. The Articles tried to balance two very different ideas: 1. A central
The United States has operated under two constitutions. The first, The Articles of Confederation, was in effect from March 1, 1781. The Articles tried to balance two very different ideas: 1. A central
GOVT 2305: THE ORIGINS OF A NEW NATION:
 GOVT 2305: THE ORIGINS OF A NEW NATION: 1. MERCATILISM (1700s) Private business and economy should benefit the colonial masters the British Crown The British maintained strict control of import/export
GOVT 2305: THE ORIGINS OF A NEW NATION: 1. MERCATILISM (1700s) Private business and economy should benefit the colonial masters the British Crown The British maintained strict control of import/export
2:Forging a New Constitution. Essential Question How do new ideas change the way people live?
 2:Forging a New Constitution Essential Question How do new ideas change the way people live? The Need for Change Bold action helped the nation overcome the serious shortcomings of the Articles of Confederation.
2:Forging a New Constitution Essential Question How do new ideas change the way people live? The Need for Change Bold action helped the nation overcome the serious shortcomings of the Articles of Confederation.
FEDERALISTS, ANTI-FEDERALISTS AND THE CONSTITUTION SS.7.C.1.8
 FEDERALISTS, ANTI-FEDERALISTS AND THE CONSTITUTION SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the ratification of the Constitution and inclusion of a bill of
FEDERALISTS, ANTI-FEDERALISTS AND THE CONSTITUTION SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the ratification of the Constitution and inclusion of a bill of
How Shall We Govern Ourselves?
 How Shall We Govern Ourselves? The Articles of Confederation America s First Constitution What kind of government would the FREEDOM loving Americans create to balance LIBERTY with enough AUTHORITY to get
How Shall We Govern Ourselves? The Articles of Confederation America s First Constitution What kind of government would the FREEDOM loving Americans create to balance LIBERTY with enough AUTHORITY to get
Origins of American Government Guided Reading Activity Section 1
 Section 1 Read each of the following descriptions, and write who or what is speaking in the space provided. 1. My theories that a republic could only survive if its citizens actively participated in government
Section 1 Read each of the following descriptions, and write who or what is speaking in the space provided. 1. My theories that a republic could only survive if its citizens actively participated in government
What types of things did the new states do to make the governments more democratic?
 Chapter 8 Confederation to Constitution pg. 218 241 8 1 The Confederation Era pg. 221 225 Moving West and New State Governments Into which areas did American settlement expand in the late 1700s? What types
Chapter 8 Confederation to Constitution pg. 218 241 8 1 The Confederation Era pg. 221 225 Moving West and New State Governments Into which areas did American settlement expand in the late 1700s? What types
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton
 Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION
 CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Objectives Why did the Constitutional Convention draft a new plan for government? How did the rival plans for the new government differ? What other conflicts required the Framers
CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Objectives Why did the Constitutional Convention draft a new plan for government? How did the rival plans for the new government differ? What other conflicts required the Framers
Module 1.2 U.S. Constitutional Framework. Constitutional Trivia! Overview of Lecture 6/4/2008
 Module 1.2 U.S. Constitutional Framework Prof. Bryan McQuide University of Idaho Summer 2008 Constitutional Trivia! Which of the following Presidents signed the U.S. Constitution? George Washington John
Module 1.2 U.S. Constitutional Framework Prof. Bryan McQuide University of Idaho Summer 2008 Constitutional Trivia! Which of the following Presidents signed the U.S. Constitution? George Washington John
VUS. 5 (pt.1): Building a New Nation: The Constitutional Convention
 Name: Date: Period: VUS 5 (pt1): Building a New Nation: The Constitutional Convention Notes US 5 (pt1): Building a New Nation: The Constitutional Convention 1 Objectives about VUS5: Building a New Nation
Name: Date: Period: VUS 5 (pt1): Building a New Nation: The Constitutional Convention Notes US 5 (pt1): Building a New Nation: The Constitutional Convention 1 Objectives about VUS5: Building a New Nation
The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783!
 Creating a Republic The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783! The treaty ending the war with Britain, more than doubled the territory of the United States!
Creating a Republic The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783! The treaty ending the war with Britain, more than doubled the territory of the United States!
Lesson 13 Writing and Ratifying the Constitution
 Lesson 13 Writing and Ratifying the Constitution Doct r. FRANKLIN looking towards the Presidents Chair, at the back of which a rising sun happened to be painted, observed to a few members near him, that
Lesson 13 Writing and Ratifying the Constitution Doct r. FRANKLIN looking towards the Presidents Chair, at the back of which a rising sun happened to be painted, observed to a few members near him, that
TEACHING AMERICAN HISTORY PROJECT Lesson Title -The Constitutional Convention- Role-Playing Kyra Kasperson
 Grade 7 TEACHING AMERICAN HISTORY PROJECT Lesson Title -The Constitutional Convention- Role-Playing Kyra Kasperson Length of class period Two 42-minute periods Inquiry What were the opposing views regarding
Grade 7 TEACHING AMERICAN HISTORY PROJECT Lesson Title -The Constitutional Convention- Role-Playing Kyra Kasperson Length of class period Two 42-minute periods Inquiry What were the opposing views regarding
The Constitutional Convention
 The Constitutional Convention Problems like Shay s Rebellion revealed the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation This event convinced many U.S. citizens that our 1 st written plan of government needed
The Constitutional Convention Problems like Shay s Rebellion revealed the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation This event convinced many U.S. citizens that our 1 st written plan of government needed
By the mid-1780s many people in the United States recognized that the Articles of
 Constitutional Convention By the mid-1780s many people in the United States recognized that the Articles of Confederation were not taking the country in a desirable direction. Because of this, a convention
Constitutional Convention By the mid-1780s many people in the United States recognized that the Articles of Confederation were not taking the country in a desirable direction. Because of this, a convention
1. STUDENTS WILL BE ABLE TO IDENTIFY AND EXPLAIN THE WEAKNESSES OF THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION
 SOUTHWESTERN CHRISTIAN SCHOOL UNITED STATES HISTORY STUDY GUIDE # 7 : CREATING A NEW NATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES STUDENTS WILL BE ABLE TO IDENTIFY AND EXPLAIN THE WEAKNESSES OF THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION
SOUTHWESTERN CHRISTIAN SCHOOL UNITED STATES HISTORY STUDY GUIDE # 7 : CREATING A NEW NATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES STUDENTS WILL BE ABLE TO IDENTIFY AND EXPLAIN THE WEAKNESSES OF THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION
Chapter 7, Section 2 Convention and Compromise
 Chapter 7, Section 2 Convention and Compromise (pages 199 205) Setting a Purpose for Reading Think about these questions as you read: How did the Constitutional Convention break the deadlock over the form
Chapter 7, Section 2 Convention and Compromise (pages 199 205) Setting a Purpose for Reading Think about these questions as you read: How did the Constitutional Convention break the deadlock over the form
The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783!
 Creating a Republic The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783! The treaty ending the war with Britain, more than doubled the territory of the United States!
Creating a Republic The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783! The treaty ending the war with Britain, more than doubled the territory of the United States!
The Articles of Confederation
 1 The Articles of Confederation Approved by Congress on November 15, 1777, Congress sent to the states for ratification the Articles of Confederation. This was the first governing constitution for the
1 The Articles of Confederation Approved by Congress on November 15, 1777, Congress sent to the states for ratification the Articles of Confederation. This was the first governing constitution for the
understanding CONSTITUTION
 understanding the CONSTITUTION Contents The Articles of Confederation The Constitutional Convention The Principles of the Constitution The Preamble The Legislative Branch The Executive Branch The Judicial
understanding the CONSTITUTION Contents The Articles of Confederation The Constitutional Convention The Principles of the Constitution The Preamble The Legislative Branch The Executive Branch The Judicial
Constitutional Convention
 2014 Delegates Remember a delegate is someone who is chosen to speak for others, or to represent them. The delegates represented each of the states and consisted of: Wealthy and educated landowners, business
2014 Delegates Remember a delegate is someone who is chosen to speak for others, or to represent them. The delegates represented each of the states and consisted of: Wealthy and educated landowners, business
The Convention Leaders
 The Convention Leaders When Thomas Jefferson heard who was attending the Constitutional Convention, he called it an assembly of demigods because the members were so rich in education and political experience.
The Convention Leaders When Thomas Jefferson heard who was attending the Constitutional Convention, he called it an assembly of demigods because the members were so rich in education and political experience.
Gov t was needed to maintain peace. Gov t is not all powerful Power is limited to what the people give to it
 Ordered Government Gov t was needed to maintain peace Limited Government*********** Gov t is not all powerful Power is limited to what the people give to it Representative Government Gov t should serve
Ordered Government Gov t was needed to maintain peace Limited Government*********** Gov t is not all powerful Power is limited to what the people give to it Representative Government Gov t should serve
Full file at
 Test Questions Multiple Choice Chapter Two Constitutional Democracy: Promoting Liberty and Self-Government 1. The idea that government should be restricted in its lawful uses of power and hence in its
Test Questions Multiple Choice Chapter Two Constitutional Democracy: Promoting Liberty and Self-Government 1. The idea that government should be restricted in its lawful uses of power and hence in its
May, 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania ~Independence Hall~ Leader: George Washington
 May, 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania ~Independence Hall~ Leader: George Washington -May 1787 Philadelphia Met in Independence Hall in Philadelphia George Washington leader -12 of 13 states Rhode Island
May, 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania ~Independence Hall~ Leader: George Washington -May 1787 Philadelphia Met in Independence Hall in Philadelphia George Washington leader -12 of 13 states Rhode Island
Constitution Day September 17
 Constitution Day September 17 The Constitution Pages 61-71 How many articles are there? What are each of the first THREE articles about? ( What( it Means boxes) Based on their length, which seems most
Constitution Day September 17 The Constitution Pages 61-71 How many articles are there? What are each of the first THREE articles about? ( What( it Means boxes) Based on their length, which seems most
Name: Date: Block: Notes:
 Chapter 2 Origins of American Government Section 1 a. Our Political Beginnings B. Basic Concepts of a. English brought idea of political system to America i. Ordered Government ii. iii. Restrict Government
Chapter 2 Origins of American Government Section 1 a. Our Political Beginnings B. Basic Concepts of a. English brought idea of political system to America i. Ordered Government ii. iii. Restrict Government
Quarter One: Unit Four
 SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will identify the weaknesses of the government under the Articles of Confederation (i.e.,
SS.7.C.1.5 Articles of Confederation ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Students will identify the weaknesses of the government under the Articles of Confederation (i.e.,
Foundations of American Government
 Foundations of American Government Formation of the first governments of the 13 colonies Highly Influenced by: - Contracts, Juries, stare decisis English Tradition Natural rights: Consent of the governed:
Foundations of American Government Formation of the first governments of the 13 colonies Highly Influenced by: - Contracts, Juries, stare decisis English Tradition Natural rights: Consent of the governed:
Forming a New Government
 Forming a New Government Why Independent in the First Place? Citizens wanted to limit the power of government Lack of representation No taxation without representation Protect personal freedoms Desired
Forming a New Government Why Independent in the First Place? Citizens wanted to limit the power of government Lack of representation No taxation without representation Protect personal freedoms Desired
Articles of Confederation
 Articles of Confederation Do Now How is power divided in our country today? SWBAT Analyze government problems under the Articles of Confederation Activity Review the Articles of Confederation chart and
Articles of Confederation Do Now How is power divided in our country today? SWBAT Analyze government problems under the Articles of Confederation Activity Review the Articles of Confederation chart and
Unit 4 Writing the Constitution Concepts to Review
 Unit 4 Writing the Constitution Concepts to Review CAUSE AND EFFECTS OF MAJOR ERAS AND EVENTS IN U.S. HISTORY THROUGH 1877 Writing the Constitution Shays Rebellion Philadelphia Convention 1787 Great Compromise
Unit 4 Writing the Constitution Concepts to Review CAUSE AND EFFECTS OF MAJOR ERAS AND EVENTS IN U.S. HISTORY THROUGH 1877 Writing the Constitution Shays Rebellion Philadelphia Convention 1787 Great Compromise
Constitutional Convention
 Constitutional Convention 1 The Framers were delegates who went to the Constitutional Convention at the Pennsylvania State House in Philadelphia to draft a new vision of America s system of government.
Constitutional Convention 1 The Framers were delegates who went to the Constitutional Convention at the Pennsylvania State House in Philadelphia to draft a new vision of America s system of government.
