Unit 4: Statehood SS8H3, SS8H4, SS8H5, SS8CG1, SS8E1, SS8E2. Georgia Studies-Unit 4
|
|
|
- Andrea Barnett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit 4: Statehood SS8H3, SS8H4, SS8H5, SS8CG1, SS8E1, SS8E2
2 Elaborated Unit Focus This unit will focus on the conflicts and changes along with the compromises that led to our country s independence. These will include the economic and technological changes that occurred, and obligations of individual states to create representative governments. The students will see that as the complexity and interaction within our society changed, so, too, did its governance. The students should be able to understand the technological innovations that led to changes in our nation s production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Finally, the student should understand the individuals, groups and institutions that helped produce the changes both within our nation, and more specifically at home in Georgia.
3 What kind of men were they?
4 THE BIG IDEA SS8H3: The student will analyze the role of Georgia in the American Revolution. Analyze: to divide a complex idea into parts or elements- dissect, break down
5 SS8H3a- Revolution SS8H3a: Explain the immediate and long term causes of the American Revolution and their impact on Georgia; include the French and Indian War (i.e., Seven Years war), Proclamation of 1763, Stamp Act, Intolerable Acts, and the Declaration of Independence. Explain: to make understandable, to spell out -illustrate, interpret
6 Causes of the American Revolution SS8H3a Long term (Underlying) Taxation without representation French and Indian War Proclamation of 1763 Duties, smuggling, boycotts Immediate Stamp Act Boston Tea Party Intolerable Acts Declaration of Independence
7 French and Indian War SS8H3a Part of the Seven Years War Great Britain vs. France (G.B. won) After F&I war, relations worsened b/t G.B. and colonies Resulted in G.B. imposing new taxes on the colonies to pay off war debt
8 An argument over territory (of course)
9 After the war
10 Proclamation of 1763 SS8H3a After the end of the F&I War came the proclamation of 1763 Settlers could no longer go West of Appalachian Mountains Redefined GA s borders Temporarily held back westward settlers
11 Stamp Act SS8H3a Required that all printed documents be on paper that was produced in London with an embossed stamp Direct tax on the colonies-1765 Legal documents, magazines, newspapers, etc. Angered colonists, repealed in 1766 American newspapers reacted to the stamp act with images like this one.
12 Boston Tea Party SS8H3b British passed law giving exclusive tea rights to East India Tea co. Colonists angered Dressed as Indians, stormed ship in Boston, threw tea into the harbor Referred to as Boston Tea Party
13 Intolerable Acts G.S. SS8H3a In response to BTP Great Britain passes Coercive Acts Colonists called them Intolerable Acts Port of Boston closed Colonists must quarter British soldiers Protest Groups outlawed Sons of Liberty Liberty Boys
14 How did the British view the colonial revolutionaries? Caption: The Bostonians paying the excise man or Tarring and Feathering.
15 How did the colonial revolutionaries view the British?
16 Declaration of Independence 1 st draft written by Thomas Jefferson Document signed by colonial leaders Adopted: 7/4/1776 Complained about problems w/ the King Declared that colonies were now an independent nation, U.S.A. SS8H3a
17 What kind of men were they?
18 Summary Discussion (H3a) Can you answer the Essential Question now? (H3a) Conflict and Change What were the causes, both immediate and long term, of the American Revolution? Governance How did past experience of the patriots with England s monarchy influence their decisions regarding a new form of government?
19 SS8H3b- Revolutionary War SS8H3b: Analyze the significance of people and events in Georgia on the Revolutionary War; include Loyalists, patriots, Elijah Clarke, Austin Dabney, Nancy Hart, Button Gwinnett, Lyman Hall, George Walton, Battle of Kettle creek, and siege of Savannah. Analyze: to divide a complex idea into parts or elements- dissect, break down
20 Georgia s Signers SS8H3b The three Georgians to sign the Declaration of Independence were Button Gwinnett, Lyman Hall, and George Walton
21 Button Gwinnett SS8H3b Planter who lived on St. Catherine s Island Signed the Declaration of Independence as GA Rep. President (Governor) of GA briefly in 1777 Played key role in getting the GA constitution of 1777 passed
22 Gwinnett vs. McIntosh Button Gwinnett s political rival was Lachlan McIntosh. Gwinnett wanted to lead troops to fight the British in East Florida and secure Georgia s southern border McIntosh got the job The campaign failed, McIntosh blamed Gwinnett, Gwinnett was furious. Gwinnett challenged McIntosh to a duel Both were shot, but Gwinnett died 5/19/1777
23 Lyman Hall SS8H3b Signed the Declaration of Independence as GA Rep. GA representative to the Continental Congress Governor of GA Helped Establish UGA Graduated From Yale and wanted to create Yale of the South 1785
24 George Walton SS8H3b Signed the Declaration of Independence as GA rep. Elected Governor in 1779 Successful lawyer in Savannah and life long politician
25 Loyalist Loyalists vs. Patriots SS8H3b AKA Tories supported the British Patriots AKA Whigs Supported the colonies Loyalist Patriot
26 Battle of Kettle Creek SS8H3b Significant battle of Revolutionary War fought in Georgia Occurred in GA Present day Lincoln County Led by Col John Dooly GA Militia Lt. Col. Elijah Clarke GA Militia Col. Andrew Pickens SC Militia Patriots captured supplies, and rallied more Georgians to the cause
27 Elijah Clarke SS8H3b Hero of Revolutionary war (from GA) Lt. Colonel who led victorious soldiers at the battle of Kettle Creek Clarke county named in his honor Later came to own large amounts of land Illegally tried to establish an independent nation (now known as the Trans Oconee Republic) in an area of GA not open for settlement (Creek Land) When confronted by Governor, said he would not give in Eventually gave in to avoid military action against him Ruined his reputation and died almost bankrupt
28 Mulatto boy, given by his master (Richard Aycock) to the GA militia for the war Fought at Kettle Creek: Fought under Elijah Clarke Only black soldier Severely wounded in the thigh Only black person to be granted land by Georgia for service in the Rev. war After the war he was nursed to health by the Harris family and was loyal to them the rest of his life Paid for son to go to law school Left all of his land to the Harris family Buried with the Harris family Austin Dabney SS8H3b
29 Dabney s Land Grant
30 Nancy Hart G.S. SS8H3b Revolutionary war heroine 5-6 British soldiers invaded her home Demanded a meal She cooked, they drank As they ate, she slipped out their weapons They caught her, she held them at gunpoint Killed 2, held others till husband arrived Remaining soldiers hanged
31 Siege of Savannah G.S. British controlled Savannah SS8H3b Patriots attempted to regain the city British won, held control of city until war s end Casimir Pulaski led the attack
32 Summary Discussion (H3b) Can you answer the Essential Question now? (H3b) Conflict and Change What was the significance of Georgia and its colonists in this conflict? Governance What persons/groups/events were significant to the development of the new government and how? Individuals, Groups, and Institutions What persons/groups/events were significant to the development of the new government of the U.S.A. and of Georgia?
33 Georgia in the Revolution Evaluate the immediate and long term causes of the American Revolution. Which underlying causes do you see as being the most important reasons to fight for independence from Great Britain? Evaluate: to make a judgement as to the worth or value of something; judge, assess SS8H3a
34 Georgia in the Revolution SS8H3a & SS8H3b Evaluate the immediate and long term causes of the American Revolution. Which underlying causes do you see as being the most important reasons to fight for independence from Great Britain? Evaluate: to make a judgement as to the worth or value of something; judge, assess Boston Tea Party Intolerable Acts Stamp Act Taxation without Representation GA in the Revolution Declaration of Independence Liberty Boys/ Sons of Liberty Proclamation of 1763 French and Indian War
35 THE BIG IDEA SS8H4: The student will describe the impact of events that led to the ratification of the United States Constitution and the Bill of Rights. Describe: to represent or give an account of in words- recount, report
36 SS8H4a: Articles of Confederation SS8H4a: Analyze the strengths and weaknesses of both the Georgia Constitution of 1777 and the Articles of Confederation and explain how weaknesses in the Articles of Confederation led to a need to revise the articles Analyze- to divide a complex idea into different parts or elements: dissect, break down
37 Georgia Constitution of 1777 SS8H4a As Georgia s 1 st elected Governor, John Treutlen, had very little executive power Strengths Recognized important ideas: Weaknesses Popular Sovereignty- government s power is in the will of the people Separation of Powers- spread the power out to different branches Appeared to separate power, but legislative was supreme Unicameral legislature: House of Assembly House of Assembly could enact laws and appoint officials for executive and judicial branch
38 Strengths Articles of Confederation Created a Union Representative Government Weaknesses Unicameral legislature Union was weak Congress could not impose taxes Could not regulate trade between states No President No court system SS8H4a
39 Why would the authors of Articles and the GA constitution be inclined to create a weak executive branch?
40 Summary Discussion (H4a) Can you answer the Essential Question now? (H4a) Governance How did past experience of the patriots with England s monarchy influence their decisions regarding a new form of government? What were the strengths and weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation and why was the decision made to write a new document rather than revise them? What were the strengths and weaknesses of the Georgia Constitution of 1777 and how were these weaknesses addressed?
41 SS8H4b: Constitutional Convention SS8H4b: Describe the role of Georgia at the Constitutional Convention of 1787; include the role of Abraham Baldwin and William Few, and reasons why Georgia ratified the new constitution. Describe- to represent or give an account of in words: recount, report
42 A (Weak) New Nation SS8H4b U.S. economy was shaky after the war States taxed products from other states States argued over boundaries States argued over interstate navigation Needed a stronger Central Government Leaders realized that the Articles of Confederation needed to be revised
43 GA s Role at the Constitutional GA sent 4 delegates William Pierce, William Houstoun, William Few, Abraham Baldwin GA s interests: Convention SS8H4b Oppose a ban on slavery Create a strong Central Govt Protection from Creek Indians Started in May and lasted 4 months Windows remained shut, stifling heat Complete secrecy GA representative William Few
44 GA s Role at the Constitutional Convention SS8H4b The debate over equal representation in Congress came to a head on July 2, Both sides were dug in, and delegates from the smaller states were determined to leave the convention if they didn t get equal representation. The roll was called. Georgia voted last. When its turn came, the issue was tied. Georgia s delegation, now down to Baldwin and Houstoun, could break the tie. Houstoun voted with the large states. To many people s surprise, Baldwin voted with the small states. By splitting Georgia s vote, the question remained a tie. The convention had No choice but to turn the matter over to a committee. By his action, Baldwin gave the delegates a chance to fashion what has been called the Great Compromise. Delegates agreed that Congress would consist of two houses a House of Representatives and a Senate. In the House, states would be represented according to their Population. In the Senate, each state would have two senators without regard for the size of its population. The Georgia Studies Book: Our State and Nation (2004) p. 130
45 Baldwin & Few: GA s Signers SS8H4b Abraham Baldwin William Few Houstoun & Baldwin split GA s vote Baldwin voted w/ the small states Tie meant committee was needed Result: Great Compromise 3/5 Compromise Only 3 of every 5 slaves were counted for taxation and representation Commerce Compromise Congress would regulate all trade, and could impose tariffs for the whole country Slave Trade Compromise Congress could not regulate slave trade for 20 years Baldwin and Few were GA s Signers
46 Summary Discussion (H4b) Can you answer the Essential Question now? (H4b) Governance & Individuals, Groups, and Institutions What persons/groups/events were significant to the development of the new government of the U.S.A. and Georgia and how? What role did Georgia play at the Constitutional Convention of 1787 and how did Abraham Baldwin and William Few Influence Georgia s role?
47 Constitutions SS8H4a & SS8H4b Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation and Explain why the United States needed a new Constitution. Evaluate: to make a judgment as to the worth or value of something; judge, assess Describe: to represent or give an account of in wordsrecount, report
48 Constitutions SS8H4a & SS8H4b Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation and Explain why the United States needed a new Constitution. Evaluate: to make a judgment as to the worth or value of something; judge, assess Describe: to represent or give an account of in words- recount, report Weak Executive Power Unicameral Legislature 1777 GA Constitution Baldwin and Few GA in the Revolution Great Compromise Articles of Confederation Constitutional Convention
49 THE BIG IDEA SS8H5: The student will explain significant factors that affected the development of Georgia as part of the growth of the United States between 1789 and Explain- to make understandable, to spell out: illustrate interpret
50 SS8H5a: Establishment SS8H5a: Explain the establishment of the University of Georgia, Louisville, and the spread of Baptist and Methodist churches. Explain- to make understandable, to spell out: illustrate, interpret
51 Establishment of UGA SS8H5a First state chartered university in the United States. Established in 1785 by Abraham Baldwin Baldwin wanted to create the Yale of the South.
52 Louisville SS8H5a GA moved the capital in order to keep it in the middle of the state s population. Louisville was 3rd capital site ( ) one that would be centrally located and accessible to all Georgia residents. 1 st - Savannah, 2 nd- Augusta, 3 rd Louisville, 4 th Milledgeville, 5 th - Atlanta
53 Religion Today According to this Gallup poll from 2011, which region of the United States is the most religious? We can attribute this trend to a 2 nd Great Awakening that helped churches to spread across the Southeast in the early 1800 s
54 Baptist/Methodist Churches SS8H5a As the population grew during the late 18 th and early 19 th century (late 1700 s and early 1800 s) many Baptist and Methodist churches began to pop up across Georgia Circuit riders traveled across the countryside and founded new churches For example: George Whitfield
55 George Whitfield SS8H5a George Whitfield is typical of the type of circuit rider preacher that was typical of this time period. Whitfield was even banned from preaching at many churches because of his non-traditional methods and endorsement of emotionalism in the congregation.
56 Baptist/Methodist Churches SS8H5a
57 By 1855, which of the Protestant religious groups had the largest populations? About this Chart: Approximate church membership and affiliations in This chart includes children and regular church attendees. In the 19 th century church membership requirements were more rigorous than they are today so not all regular attendees were full members.
58 Church Traditions SS8H5a Many of the traditions from this time period still remain in churches (or churches near you). Examples: Primitive Baptists (Calvinists) Foot-Washing Baptists (New-Hope Association, Pleasant Valley Association, Jasper Baptist Association) Shape Note Music Sacred Harp Emotionalism/Spirituality as a part of service Testimonies Extemporaneous preaching instead of prepared sermons Summer revival meetings/tent revivals Times were set (11:00 AM/ 8:00 PM) around an agricultural society Churches meet 1 or 2 Sundays per month Peachers traveled from church to church and congregations visited churches other than their own on the Sunday that their church was not meeting The shape-note system in The Sacred Harp uses a different shape to represent each of the four syllables in the musical scale. This musical phrase is from the hymn "Wondrous Love. Clip Example Sacred Harp singers at the annual Chattahoochee Convention near Carrollton, GA
59 Church Traditions SS8H5a Scenes like this one were once common place in the Southeast. With the growth of indoor baptisteries, this type of baptism is becoming more rare.
60 Summary Discussion (H5a) Can you answer the Essential Question now? (H5a) Individuals, Groups, and Institutions To what extent did the establishment of the University of Georgia, Louisville, and the spread of Baptist and Methodist churches contribute to the overall growth of Georgia? (DOK 4)
61 SS8H5b: Land Policies SS8H5b: Evaluate the impact of land policies pursued by Georgia; include the headright system, land lotteries, and the Yazoo land fraud. Evaluate- to make a value as to the worth or value of something: judge, assess
62 Headright System SS8H5b 1 st method GA used to distribute land Head of family received 100 acres and 50 acres for each additional member
63 Land Lottery SS8H5b Surveyors divided land into square lots. Lots were much smaller than under headright system. Lottery drawing for a prize Those receiving lands were known as fortunate drawers
64 Land Lottery SS8H5b
65 Yazoo Land Fraud SS8H5b In 1795, four private land companies bribed members of the General Assembly to pass a law. This law allowed the companies to buy 35 million acres of GA s western lands near the Yazoo River. They bought it cheap... 2 cents an acre! Georgians found out and were MAD! General Assembly repealed the Yazoo Act and then
66 Yazoo Land Fraud SS8H5b Lawmakers burned the law on the statehouse grounds in public using fire from heaven.
67 Yazoo Land Fraud SS8H5b
68 Summary Discussion (H5b) Can you answer the Essential Question now? (H5b) Individuals, Groups, and Institutions Compare the headright system and the land lottery system of land distribution. To what extent did each impact the growth of Georgia?(DOK 2/3) How did the Yazoo Land Fraud impact the physical boundaries and political landscape of Georgia? (DOK 3)
69 SS8H5c: Technological Developments SS8H5c: Explain how technological developments, including the cotton gin and railroads, had an impact on Georgia s growth. Explain- to make understandable, to spell out: illustrate, interpret
70 Technological Developments SS8H5c Many technological innovations change the way Georgians worked in the late 1700 s. The invention of new products and new modes of transportation make goods move faster New inventions made the plantation grow as the plantation grew so did the economy of GA
71 Cotton Gin SS8H5c Improved by Eli Whitney in 1793 Encouraged economic growth in GA Cotton could be cleaned easier and quicker.
72 Cotton Gin SS8H5c G.S. This roller gin, was built in Farmers have continued to modify the gin since Eli Whitney s improvement on the invention in 1793.
73 Railroads SS8H5c G.S. Building railroads were expensive, money for construction was limited. So, Georgia s General Assembly decided that the state should step in and become a partner in railroad building. As the railroads grew so did the economy. Products could be moved faster East and West Railroad between Cartersville and Cedartown
74 Summary Discussion (H5c) Can you answer the Essential Question now? (H5c) Technological Innovation How did the invention of the Cotton Gin impact Georgia s economy and population? (DOK How did the growth of railroads influence Georgia s growth?
75 SS8H5d: Indian Removal SS8H5d: Analyze the events that led to the removal of Creeks and Cherokees; include the roles of Alexander McGillivray, William McIntosh, Sequoyah, John Ross, Dahlonega Gold Rush, Worcester v. Georgia, Andrew Jackson, John Marshall, and the Trail of Tears. Analyze- to divide a complex idea into parts or elements: dissect, break down
76 Indian Removal SS8H5d Over several years in the early 1800 s there was a systematic removal of Creek and Cherokee Indians in Georgia
77 Creek Indians SS8H5d GA wanted Creek land because of its fertile growing potential Creek were in Southern and Western part of GA Loose confederation of many tribes Spoke variations of Muscogean lang. Divided into Upper Creeks and Lower Creeks Osceola was a leader within the Seminole Indians in South GA and FL. The Seminole were part of the Creek Indians
78 Alexander McGillivray SS8H5d Chief of Upper Creek His Indian name was: Hoboi-Hili-Miko ("Good Child King") Father was a wealthy planter Educated in Charleston, SC (learned Latin and Greek) Fought for British in the Revolutionary War Owned slaves, operated plantation & Fought to keep Creek Land
79 William McIntosh SS8H5d Creek Chief who was bribed to sign a treaty giving up all Creek land. Indian name Tustunnugee Hutkee (White Warrior) Treaty of Indian Springs- sold all remaining Creek lands for $200,000.
80 William McIntosh SS8H5d G.S. The murder of Chief McIntosh Creek people found out about the treaty. Hundreds marched to his house Set house on fire Drug McIntosh out Shot him, and stabbed him to death Also scalped him and used it as an example to other Indians.
81 Cherokee Indians GA wanted Cherokee land mostly because of the gold they believed was underground. Cherokee lived in Northern GA Created the Cherokee Nation with its capital at New Echota near present day Calhoun Georgia Official Newspaper was the Cherokee Phoenix SS8H5d G.S.
82 Sequoyah SS8H5d George Guess Developed a written form of the Cherokee language Syllabary: each character represented a syllable.
83 Sequoyah s Syllabary
84 The Cherokee Phoenix
85 John Ross SS8H5d Chief of the Cherokee Indians Indian Name: Tsan-Usdi (Little John) Not in favor of removal, fought against it. Made several appeals and took petitions to Congress, asking them to honor the treaties with the Cherokee.
86 Dahlonega Gold Rush SS8H5d G.S. Gold discovered in Dahlonega in 1829 and gold fever spread immediately GA took over the land and took all land rights in Dahlonega away from the Cherokee. Cherokee lost their homes, lands, and legal rights.
87 Worcester v. GA SS8H5d White missionaries were living on Cherokee land. They did not want to have to leave. Government said you may stay but must take oath of allegiance to U.S. Missionaries refused to take oath and thus were jailed. Case went to the Supreme Court. John Marshall, supreme court chief justice, ruled that the missionaries should be set free. His ruling U.S./GA law does NOT apply in the Cherokee Nation Samuel Worcester
88 John Marshall SS8H5d Chief Justice of the Supreme Court who delivered the decision in Worcester v. GA Ruled that the laws of the U.S. did NOT apply to the Cherokee Nation
89 Andrew Jackson SS8H5d U.S. President during Indian Removal First solicited the help of Indians, then ordered to have them removed. Famous Indian hater Disagreed with John Marshall. Famously said, John Marshall has rendered his decision, now let him enforce it.
90 Trail of Tears SS8H5d Trail of tears was used to remove 15,000 Cherokee Indians to present day Oklahoma. Cherokee were put in stockades 1 st then forcefully moved. Occurred during winter, many died.
91 Trail of Tears G.S.
92 Trail of Tears SS8H5d
93 Summary Discussion (H5d) Can you answer the Essential Question now? (H5d) Conflict and Change How did the Creeks and Cherokees try to avoid conflict with the settlers? What roles did Alexander McGillivray, William McIntosh, Sequoyah, John Ross, the Dahlonega Gold Rush, Worcester v. Georgia, Andrew Jackson, and John Marshall play in the events leading to the Trail of Tears?
94 Westward Expansion and Indian Removal SS8H5c & SS8H5d Analyze the events that led to the removal of the Creek and Cherokee. Explain how the Indian leaders changed their lifestyles to appease white society. Analyze: to divide a complex idea into parts or elements; dissect, break down Explain: to make understandable, to spell out - illustrate, interpret
95 Westward Expansion and Indian Removal SS8H5c & SS8H5d Analyze the events that led to the removal of the Creek and Cherokee. Explain how the Indian leaders changed their lifestyles to appease white society. Analyze: to divide a complex idea into parts or elements; dissect, break down Dahlonega Gold Rush Trail of Tears Land Lottery Expansion and Indian Removal Yazoo Land Fraud Constitutional Convention Explain: to make understandable, to spell out -illustrate, interpret Cherokee Indians Sequoyah Creek Indians McGillivray McIntosh Cotton Gin and Railroads
96 THE BIG IDEA SS8CG1: The student will describe the role of citizens under Georgia s constitution. Describe- to represent or give an account of in words; recount, report
97 SS8CG1a: GA Constitution SS8CG1a: Explain the basic structure of the Georgia State Constitution Explain- to make understandable, to spell out: illustrate, interpret
98 Basic Structure of GA s Constitution SS8CG1a GA s constitution much like U.S. Constitution however GA s constitution outlines qualifications for voting and running for public office GA s constitution has 10 Articles Several Revisions 1777, 1789, 1798, 1861, 1865, 1868, 1877, 1945, 1976, 1983
99 Basic structure of GA s Constitution Preamble- SS8CG1a Gives reasons for constitution. Article I- Bill of Rights Individual rights, separation of powers, separation of church and state, property rights Article II-Voting and Elections Secret ballot, who is allowed to vote, run offs elections, if public officials commit crimes Article III-Legislative Branch Outlines structure and function of General Assembly How a bill becomes a law Article IV-Constitutional Boards and Commissions Provides for several boards and Commissions (Public Service Comm. Etc) Article V-Executive Branch Qualifications and terms for executive officials, duties and powers of Governor
100 Basic structure of GA s Constitution SS8CG1a Article VI- Judicial Branch Outlines the courts systems and 7 types of Courts: Magistrate, probate, juvenile, state, superior, appeals, and Supreme. Article VII-Taxation and Finance Gives reasons why GA may tax citizens and tells how. Sets tax limits Article VIII-Education Explains how school system is paid for by taxes Outlines the structure of school system at state and local levels Article IX-Counties and Municipal Courts Outlines the roles and functions of county and city governments Article X-Amendments to the Constitution Explains how changes or amendments to the Constitution are made Article XI-Miscellaneous Provisions Talks about how GA s constitutions have been changed over the years
101 Summary Discussion (CG1a) Can you answer the Essential Question now? (CG1a) Governance What is the basic structure of Georgia s Constitution and how does it protect the separation of powers?
102 SS8CG1b: Separating Power SS8CG1b: Explain the concepts of separation of powers and checks and balances Explain- to make understandable, to spell out: illustrate, interpret
103 Separation of Powers SS8CG1b Separation of Powers: Governments power is divided between the branches Each branch has different/distinct jobs.
104 Checks and Balances SS8CG1b Checks and Balances: The ability of one branch to check the power of another branch Keeps any one branch from becoming too powerful
105 Summary Discussion (CG1b) Can you answer the Essential Question now? (CG1b) Governance How did the new government assure citizens that it would not impose the oppression of the past monarchy?
106 SS8CG1c: Citizens SS8CG1c: Describe the rights and responsibilities of citizens Describe- to represent or give an account of in words: recount, report
107 Rights of GA Citizens SS8CG1c Rights standards that keep institutions from harming people's freedoms. Rights of Georgians are in the GA bill of rights in the GA constitution Some include Life, liberty, and property Freedom of speech/press Right to keep and bear arms Right to trial No banishment or whipping for a crime No imprisonment for debt Fishing and hunting
108 Responsibilities of GA Citizens SS8CG1c Responsibilities of GA citizens include: Paying taxes Obeying laws and knowing the consequences of actions Voting Jury Duty
109 Summary Discussion (CG1c) Can you answer the Essential Question now? (CG1c) Governance How did the new government assure citizens that it would not impose the oppression of the past monarchy? What are the rights of American citizens and what responsibilities accompany these basic rights of citizenship?
110 SS8CG1d: Voting SS8CG1d- Explain voting qualifications and elections in Georgia Explain- to make understandable, to spell out: illustrate, interpret
111 Voting Qualifications in GA SS8CG1d To vote in GA you must be registered To register you must be: A U.S. Citizen A legal GA resident and in the county you wish to vote At least 17 ½ years of age (18 when you vote) NOT serving a sentence for a crime of moral turpitude NOT Judicially determined mentally incompetent
112 Voting Qualifications in GA SS8CG1d Griffith-GA Georgia Studies-Unit Studies
113 Summary Discussion (CG1d) Can you answer the Essential Question now? (CG1d) Governance How did the new government assure citizens that it would not impose the oppression of the past monarchy? What are the qualifications to vote in Georgia?
114 SS8CG1e: Political Parties SS8CG1e: Explain the role of political parties in government Explain- to make understandable, to spell out: illustrate, interpret
115 Political Parties SS8CG1e Georgia has 2 major political parties: Democrats and Republicans Voters do not have to join a party but candidates choose one Different parties represent different ideas and interests The candidates job is make those ideas into government policy
116 Summary Discussion (CG1e) Can you answer the Essential Question now? (CG1e) Governance How did the new government assure citizens that it would not impose the oppression of the past monarchy?
117 Role of Georgia Citizens In your notebook: Describe the role of citizens under GA s constitution Describe: to represent or give an account of in words; recount, report SS8CG1
118 Role of Citizens SS8CG1 Describe the role of citizens under GA s constitution Voting Georgia Constitution Separation of Power Describe: to represent or give an account of in words: recount, report Responsibilities Role of Citizens Checks and Balances Rights Political Parties
Georgia & Westward Expansion & Growth
 Georgia & Westward Expansion & Growth I. Government A. The Rules and Regulations was the first state government in Georgia. (only temporary) B. The Rules and Regulations were replaced by the Georgia Constitution
Georgia & Westward Expansion & Growth I. Government A. The Rules and Regulations was the first state government in Georgia. (only temporary) B. The Rules and Regulations were replaced by the Georgia Constitution
One Stop Shop For Educators Eighth Grade Unit 4 Statehood Elaborated Unit Focus conflicts and changes governance
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary for the Eighth Grade Social Studies course. Eighth
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary for the Eighth Grade Social Studies course. Eighth
Intolerable Acts. Taxation without Representation. Unit Essential Questions:
 Intolerable Acts Taxation without Representation History SS8H3 The student will analyze the role of Georgia in the American Revolution. a. Explain the immediate and long-term causes of the American Revolution
Intolerable Acts Taxation without Representation History SS8H3 The student will analyze the role of Georgia in the American Revolution. a. Explain the immediate and long-term causes of the American Revolution
GEORGIA S EARLY STATEHOOD TEST REVIEW. Test is Tuesday
 GEORGIA S EARLY STATEHOOD TEST REVIEW Test is Tuesday 10-21-16 WHAT IS THIS INVENTION? The Cotton Gin WHO CREATED THIS INVENTION? Eli Whitney WHAT DID THIS INVENTION DO? Separated the cotton seeds from
GEORGIA S EARLY STATEHOOD TEST REVIEW Test is Tuesday 10-21-16 WHAT IS THIS INVENTION? The Cotton Gin WHO CREATED THIS INVENTION? Eli Whitney WHAT DID THIS INVENTION DO? Separated the cotton seeds from
Proclamation of French and Indian War. Sugar Act
 Proclamation of 1763 French and Indian War Sugar Act Official announcement made by King George III of England which stopped colonists from settling lands west of the Appalachian Mountains. War fought by
Proclamation of 1763 French and Indian War Sugar Act Official announcement made by King George III of England which stopped colonists from settling lands west of the Appalachian Mountains. War fought by
Study Guide for Test representative government system of government in which voters elect representatives to make laws for them
 Study Guide for Test 4 1. In general, who could vote in the English colonies? Free men, over 21 years old, who owned a certain amount of land. Sometimes had to be church members. 2. representative government
Study Guide for Test 4 1. In general, who could vote in the English colonies? Free men, over 21 years old, who owned a certain amount of land. Sometimes had to be church members. 2. representative government
I. Articles of Confederation
 The New Nation I. Articles of Confederation A. The A.O.C. were the nations 1 st Constitution 1. Adopted by congress during the rev. war 2. Set up a loose alliance among the 13 states 3. it reflects a fear
The New Nation I. Articles of Confederation A. The A.O.C. were the nations 1 st Constitution 1. Adopted by congress during the rev. war 2. Set up a loose alliance among the 13 states 3. it reflects a fear
Revolution in Thought 1607 to 1763
 Revolution in Thought 1607 to 1763 Early settlers found they disliked England America was far from England and isolated Weakened England s authority Produced rugged and independent people Colonies had
Revolution in Thought 1607 to 1763 Early settlers found they disliked England America was far from England and isolated Weakened England s authority Produced rugged and independent people Colonies had
Georgia 4th Grade Clickbook Page-by-Page Outline
 Georgia 4th Grade Clickbook Page-by-Page Outline Special Content Color Key: Related Module(s) Expansion Activity Click & Learn Activity Page Name & Description Unit 1: Geographical Understandings Chapter
Georgia 4th Grade Clickbook Page-by-Page Outline Special Content Color Key: Related Module(s) Expansion Activity Click & Learn Activity Page Name & Description Unit 1: Geographical Understandings Chapter
Dooly County Middle School. Social Studies Georgia Standards of Excellence. 8 th Grade. - Location of Georgia (G1a)
 Dooly County Middle School Social Studies Georgia Standards of Excellence 8 th Grade Social Studies GSE Pacing Guide 2017-2018 8 th Grade First 9 Weeks (July 31, 2017-October 2, 2017) Unit 1: Connecting
Dooly County Middle School Social Studies Georgia Standards of Excellence 8 th Grade Social Studies GSE Pacing Guide 2017-2018 8 th Grade First 9 Weeks (July 31, 2017-October 2, 2017) Unit 1: Connecting
England and the 13 Colonies: Growing Apart
 England and the 13 Colonies: Growing Apart The 13 Colonies: The Basics 1607 to 1776 Image: Public Domain Successful and Loyal Colonies By 1735, the 13 colonies are prosperous and growing quickly Colonists
England and the 13 Colonies: Growing Apart The 13 Colonies: The Basics 1607 to 1776 Image: Public Domain Successful and Loyal Colonies By 1735, the 13 colonies are prosperous and growing quickly Colonists
The American Revolution
 Main Idea The American Revolution Enlightenment ideas led to revolution, independence, and a new government for the United States. Content Statement 6/Learning Goal Describe how Enlightenment thinkers
Main Idea The American Revolution Enlightenment ideas led to revolution, independence, and a new government for the United States. Content Statement 6/Learning Goal Describe how Enlightenment thinkers
The Birth of a Nation
 The Birth of a Nation The student will demonstrate an understanding of the conflicts between regional and national interest in the development of democracy in the United States. Analyze the impact of the
The Birth of a Nation The student will demonstrate an understanding of the conflicts between regional and national interest in the development of democracy in the United States. Analyze the impact of the
AKS M 49 C 30 a-d D 32 a-c D 33 a-c D 34 a-b BUILDING A NEW NATION
 AKS M 49 C 30 a-d D 32 a-c D 33 a-c D 34 a-b BUILDING A NEW NATION The official end of the Revolutionary War was the signing of the Treaty of Paris in 1783. The newly independent US and GA now faced the
AKS M 49 C 30 a-d D 32 a-c D 33 a-c D 34 a-b BUILDING A NEW NATION The official end of the Revolutionary War was the signing of the Treaty of Paris in 1783. The newly independent US and GA now faced the
To run away or leave someone in their time of need.
 Desert To run away or leave someone in their time of need. Inflation Rapid rise in prices. Blockade Barrier preventing the movement of troops and supplies. Tributary River or stream that flows into a larger
Desert To run away or leave someone in their time of need. Inflation Rapid rise in prices. Blockade Barrier preventing the movement of troops and supplies. Tributary River or stream that flows into a larger
4: TELESCOPING THE TIMES
 The Americans (Survey) Chapter 4: TELESCOPING THE TIMES The War for Independence CHAPTER OVERVIEW The colonists clashes with the British government lead them to declare independence. With French aid, they
The Americans (Survey) Chapter 4: TELESCOPING THE TIMES The War for Independence CHAPTER OVERVIEW The colonists clashes with the British government lead them to declare independence. With French aid, they
Section One. A) The Leviathan B) Two Treatises of Government C) Spirit of the Laws D) The Social Contract
 Government Exam Study Guide You will need to be prepared to answer/discuss any of these questions on the exam in various formats. We will complete this study guide in class and review it. Section One 1)
Government Exam Study Guide You will need to be prepared to answer/discuss any of these questions on the exam in various formats. We will complete this study guide in class and review it. Section One 1)
Events Leading to the American Revolution
 Events Leading to the American Revolution Colonization Main Reason was for Mercantilism: Making money for the mother country Joint-stock company: investors share ownership and profits Charters: grants
Events Leading to the American Revolution Colonization Main Reason was for Mercantilism: Making money for the mother country Joint-stock company: investors share ownership and profits Charters: grants
1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation
 Topic 3 1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg 88-89 They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation agreements 2. How did the British respond to the Boston Tea
Topic 3 1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg 88-89 They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation agreements 2. How did the British respond to the Boston Tea
Based on this map where is Georgia located? Hint: You should name the hemisphere(s), continent, country and region
 Based on this map where is Georgia located? Hint: You should name the hemisphere(s), continent, country and region Wednesday August 27, 2014 Most populated region. Known for granite Has rolling hills and
Based on this map where is Georgia located? Hint: You should name the hemisphere(s), continent, country and region Wednesday August 27, 2014 Most populated region. Known for granite Has rolling hills and
THEMATIC UNIT 1 Content Units Date(s) # of Standard(s) Days SS8G1 Describe Georgia s geography and climate. SS8H1
 TCSS 2017 2018 8 th Grade Georgia History Pacing Guide (Quarters 2, 3 and 4) THEMATIC UNIT 1 Date(s): October 9, 2017 December 7, 2017 Total # of : 40 Content Units Date(s) # of Geography Oct 9 Oct 13
TCSS 2017 2018 8 th Grade Georgia History Pacing Guide (Quarters 2, 3 and 4) THEMATIC UNIT 1 Date(s): October 9, 2017 December 7, 2017 Total # of : 40 Content Units Date(s) # of Geography Oct 9 Oct 13
SAVANNAH-CHATHAM COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOL SYSTEM ACADEMIC AFFAIRS: CURRICULUM & INSTRUCTION Curriculum Map and Pacing Guide: 8 th Grade Georgia Studies
 : The focus of this first unit is on the concepts & enduring understandings rather than specific standards 1 Week SS8G1a, b, c MARKING PERIOD 1 SS8H1a SS8G1d 1 Week SS8H1b, c SS8H2a, b, c SS8G1d SS8G2a,
: The focus of this first unit is on the concepts & enduring understandings rather than specific standards 1 Week SS8G1a, b, c MARKING PERIOD 1 SS8H1a SS8G1d 1 Week SS8H1b, c SS8H2a, b, c SS8G1d SS8G2a,
Preview. If you were elected President, who would you put in government positions in the Executive Branch?
 Preview If you were elected President, who would you put in government positions in the Executive Branch? Title your page this! Andrew Jackson a. Nicknamed Old Hickory for his toughness b. Major General
Preview If you were elected President, who would you put in government positions in the Executive Branch? Title your page this! Andrew Jackson a. Nicknamed Old Hickory for his toughness b. Major General
8 th grade American Studies sample test questions
 8 th grade American Studies sample test questions PASS 1.2 Standard 1. The student will develop and practice process skills in social studies. PASS OBJECTIVE 1.2: Identify, analyze, and interpret primary
8 th grade American Studies sample test questions PASS 1.2 Standard 1. The student will develop and practice process skills in social studies. PASS OBJECTIVE 1.2: Identify, analyze, and interpret primary
Unit 2 Part 2 Articles of Confederation
 Unit 2 Part 2 Articles of Confederation Explain how the states new constitutions reflected republican ideals. Describe the structure and powers of the national government under the Articles of Confederation.
Unit 2 Part 2 Articles of Confederation Explain how the states new constitutions reflected republican ideals. Describe the structure and powers of the national government under the Articles of Confederation.
Chapter 4. The American Revolution
 Chapter 4 The American Revolution 1 Raising Taxes Sugar Act- The first tax passed specifically to raise money in the colonies, rather than regulate trade. To crack down on smugglers Help pay for French
Chapter 4 The American Revolution 1 Raising Taxes Sugar Act- The first tax passed specifically to raise money in the colonies, rather than regulate trade. To crack down on smugglers Help pay for French
The Americans (Survey)
 The Americans (Survey) Chapter 7: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OVERVIEW American leaders devise a farsighted policy of improvements as North, South, and West develop
The Americans (Survey) Chapter 7: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OVERVIEW American leaders devise a farsighted policy of improvements as North, South, and West develop
Clickbook Georgia Standards Covered Content Unit 1: Georgia Geography Chapter 1: Know Your State Geography Lesson 1:
 Unit 1: Georgia Geography Chapter 1: Know Your State Geography This lesson reinforces students understandings of maps to meet the 8 th Grade Skills requirement. Where Is Georgia? SS8G1 Describe Georgia
Unit 1: Georgia Geography Chapter 1: Know Your State Geography This lesson reinforces students understandings of maps to meet the 8 th Grade Skills requirement. Where Is Georgia? SS8G1 Describe Georgia
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century)
 The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 2: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Revolution and the Early Republic CHAPTER OVERVIEW Colonists declare their independence and win a war to gain the right
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 2: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Revolution and the Early Republic CHAPTER OVERVIEW Colonists declare their independence and win a war to gain the right
Creating the Constitution
 Creating the Constitution 1776-1791 US Timeline 1777-1791 1777 Patriots win Battles of Saratoga. Continental Congress passes the Articles of Confederation. 1781 Articles of Confederation go into effect.
Creating the Constitution 1776-1791 US Timeline 1777-1791 1777 Patriots win Battles of Saratoga. Continental Congress passes the Articles of Confederation. 1781 Articles of Confederation go into effect.
Learning Goal 5: Students will be able to explain the events which led to the start of the American
 American Revolution Learning Goal 5: Students will be able to explain the events which led to the start of the American Revolution. - Tea Act (Boston Tea Party, British East India Company, Sons of Liberty,
American Revolution Learning Goal 5: Students will be able to explain the events which led to the start of the American Revolution. - Tea Act (Boston Tea Party, British East India Company, Sons of Liberty,
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 2 Uniting for Independence ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why and how did the colonists declare independence? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary draft outline or first copy consent permission or approval
Lesson 2 Uniting for Independence ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why and how did the colonists declare independence? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary draft outline or first copy consent permission or approval
Foundations of the American Government
 Foundations of the American Government 1600s-1770s Each colony was loyal to Great Britain but was responsible for forming its own government, taxing and defending itself. The government and constitution
Foundations of the American Government 1600s-1770s Each colony was loyal to Great Britain but was responsible for forming its own government, taxing and defending itself. The government and constitution
4th 9 weeks study guide.notebook May 19, 2014
 What was the main reason that the Puritans started the Massachusetts Bay Colony? to live according to their religious beliefs What was the main purpose of town meetings in the New England colonies? To
What was the main reason that the Puritans started the Massachusetts Bay Colony? to live according to their religious beliefs What was the main purpose of town meetings in the New England colonies? To
NEW GOVERNMENT: CONFEDERATION TO CONSTITUTION FLIP CARD
 NEW GOVERNMENT: CONFEDERATION TO CONSTITUTION FLIP CARD Big Ideas: Imagine trying to make a new country from scratch. You ve just had a war with the only leaders you ve ever known, and now you have to
NEW GOVERNMENT: CONFEDERATION TO CONSTITUTION FLIP CARD Big Ideas: Imagine trying to make a new country from scratch. You ve just had a war with the only leaders you ve ever known, and now you have to
CCBOE: Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Map 8 th grade Georgia History
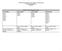 2018-2019 GSE 8 th grade Curriculum Map 1 st 9-weeks 2 nd 9-weeks 3 rd 9-weeks 4 th 9-weeks SS8G1 SS8H4 SS8H7 SS8H11 SS8E1 SS8H5 SS8H8 SS8H12 SS8E2c SS8H6 SS8H9 SS8CG1 SS8H12 SS8H10 SS8CG2 SS8H1 SS8CG3
2018-2019 GSE 8 th grade Curriculum Map 1 st 9-weeks 2 nd 9-weeks 3 rd 9-weeks 4 th 9-weeks SS8G1 SS8H4 SS8H7 SS8H11 SS8E1 SS8H5 SS8H8 SS8H12 SS8E2c SS8H6 SS8H9 SS8CG1 SS8H12 SS8H10 SS8CG2 SS8H1 SS8CG3
Unit 3: Building the New Nation FRQ Outlines. Prompt:Analyze the reasons for the Anti-Federalists opposition to ratifying the Constitution.
 Prompt:Analyze the reasons for the Anti-Federalists opposition to ratifying the Constitution. Re-written as a Question: What were the reasons for the Anti-Federalist opposition to ratifying the constitution?
Prompt:Analyze the reasons for the Anti-Federalists opposition to ratifying the Constitution. Re-written as a Question: What were the reasons for the Anti-Federalist opposition to ratifying the constitution?
7 th Grade Review Sheet for Final Exam.1) What you need to know: What is History? Why do people study history?
 Name: Rondinelli Date: 7 th Grade Review 7 th Grade Review Sheet for Final Exam.1) What you need to know: What is History? Why do people study history? 2) What is Geography? 3) What is archeology? 4.)
Name: Rondinelli Date: 7 th Grade Review 7 th Grade Review Sheet for Final Exam.1) What you need to know: What is History? Why do people study history? 2) What is Geography? 3) What is archeology? 4.)
American History Semester 1 Review - Shorter Answers
 American History Semester 1 Review - Shorter Answers Study online at quizlet.com/_30fd48 1. Name the first three attempts at British Colonies. 2. Which of the first three colonies attempted was settled
American History Semester 1 Review - Shorter Answers Study online at quizlet.com/_30fd48 1. Name the first three attempts at British Colonies. 2. Which of the first three colonies attempted was settled
STAAR STUDY GUIDE 2. Designated materials are the intellectual property of s3strategies, LLC. Permission is granted for internal district use only.
 Dred Scott v. Sandford - Dred Scott, a southern slave, sues for his freedom. Court decision rules that: African Americans had no rights to citizenship & Congress could not limit a slave owner s control
Dred Scott v. Sandford - Dred Scott, a southern slave, sues for his freedom. Court decision rules that: African Americans had no rights to citizenship & Congress could not limit a slave owner s control
Chapter 5 Place & Time: The British Colonies
 Chapter 5 Place & Time: The British Colonies 1763-1776 Lesson 1 No Taxation Without Representation Essential Question: Name: Core: Date: Dealing with Great Britain Enforcing Trade Laws The Sugar Act _
Chapter 5 Place & Time: The British Colonies 1763-1776 Lesson 1 No Taxation Without Representation Essential Question: Name: Core: Date: Dealing with Great Britain Enforcing Trade Laws The Sugar Act _
The American Revolution & Confederation. The Birth of the United States
 The American Revolution & Confederation The Birth of the United States 1774-1787 Essential Question Evaluate the extent to which the Revolution fundamentally changed American society. The First Continental
The American Revolution & Confederation The Birth of the United States 1774-1787 Essential Question Evaluate the extent to which the Revolution fundamentally changed American society. The First Continental
The American Revolution: From Elite Protest to Popular Revolt,
 The American Revolution: From Elite Protest to Popular Revolt, 1763 1783 Breakdown of Political Trust Seven Years War left colonists optimistic about future Most important consequence of Seven Years War
The American Revolution: From Elite Protest to Popular Revolt, 1763 1783 Breakdown of Political Trust Seven Years War left colonists optimistic about future Most important consequence of Seven Years War
Standard 3: Causes of the American Revolution. e. Declaration of Independence
 Name Date Hour U.S. History to 1877 OCCT Review Study Guide Use your notes, your textbook and all of the knowledge gained this year to complete this O.C.C.T. Review Study Guide. This study guide will be
Name Date Hour U.S. History to 1877 OCCT Review Study Guide Use your notes, your textbook and all of the knowledge gained this year to complete this O.C.C.T. Review Study Guide. This study guide will be
Basic Concepts of Government The English colonists brought 3 ideas that loom large in the shaping of the government in the United States.
 Civics Honors Chapter Two: Origins of American Government Section One: Our Political Beginnings Limited Government Representative government Magna Carta Petition of Right English Bill of Rights Charter
Civics Honors Chapter Two: Origins of American Government Section One: Our Political Beginnings Limited Government Representative government Magna Carta Petition of Right English Bill of Rights Charter
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of American Government
 Chapter 2: The Beginnings of American Government United States Government Fall, 2017 Origins of American Political Ideals Colonial Period Where did ideas for government in the colonies come from? Largely,
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of American Government United States Government Fall, 2017 Origins of American Political Ideals Colonial Period Where did ideas for government in the colonies come from? Largely,
1. It disappeared after President James Monroe s landslide election victory in 1816.
 Chapter 10: A Changing Nation 1815-1840 Section 1: Building National Identity 1. It disappeared after President James Monroe s landslide election victory in 1816. 2. You were to put an X on the chart next
Chapter 10: A Changing Nation 1815-1840 Section 1: Building National Identity 1. It disappeared after President James Monroe s landslide election victory in 1816. 2. You were to put an X on the chart next
Early US History Part 1. Your Notes. Goal 9/5/2012. How did the United States became a country?
 Questions / Themes 9/5/2012 Early US History Part 1 How did the United States became a country? Your Notes You will need these notes to prepare for exams. Remember to paraphrase and generalize. Avoid copying
Questions / Themes 9/5/2012 Early US History Part 1 How did the United States became a country? Your Notes You will need these notes to prepare for exams. Remember to paraphrase and generalize. Avoid copying
Washington, Jefferson, Madison, Monroe, Jackson, and Polk Presidencies
 Washington, Jefferson, Madison, Monroe, Jackson, and Polk Presidencies 1. George Washington (1789-1797) - Created a cabinet of advisors 1. Secretary of War - Henry Knox 2. Secretary of the Treasury - Alexander
Washington, Jefferson, Madison, Monroe, Jackson, and Polk Presidencies 1. George Washington (1789-1797) - Created a cabinet of advisors 1. Secretary of War - Henry Knox 2. Secretary of the Treasury - Alexander
8 th Grade Georgia History Sample Assessment Items
 Click on the standard link below to see sample assessment items. The assessment items were obtained from the Georgia Department of Education Georgia History Teacher Notes. SS8H1a. SS8H8a. SS8G1c. SS8CG4e.
Click on the standard link below to see sample assessment items. The assessment items were obtained from the Georgia Department of Education Georgia History Teacher Notes. SS8H1a. SS8H8a. SS8G1c. SS8CG4e.
How Shall We Govern Ourselves?
 How Shall We Govern Ourselves? The Articles of Confederation America s First Constitution What kind of government would the FREEDOM loving Americans create to balance LIBERTY with enough AUTHORITY to get
How Shall We Govern Ourselves? The Articles of Confederation America s First Constitution What kind of government would the FREEDOM loving Americans create to balance LIBERTY with enough AUTHORITY to get
Essential Question Section 1: The Colonial Period Section 2: Uniting for Independence Section 3: The Articles of Confederation Section 4: The
 Essential Question Section 1: The Colonial Period Section 2: Uniting for Independence Section 3: The Articles of Confederation Section 4: The Constitutional Convention Chapter Summary Content Vocabulary
Essential Question Section 1: The Colonial Period Section 2: Uniting for Independence Section 3: The Articles of Confederation Section 4: The Constitutional Convention Chapter Summary Content Vocabulary
Chapter 2:2: Declaring Independence
 Chapter 2:2: Declaring Independence Objectives: 2:2 Our Political Beginnings o Students will explain how the relationship between the colonies and Great Britain changed during the pre- Revolutionary War
Chapter 2:2: Declaring Independence Objectives: 2:2 Our Political Beginnings o Students will explain how the relationship between the colonies and Great Britain changed during the pre- Revolutionary War
Chapter 25 Section 1. Section 1. Terms and People
 Chapter 25 Terms and People republic a government in which the people elect their representatives unicameral legislature a lawmaking body with a single house whose representatives are elected by the people
Chapter 25 Terms and People republic a government in which the people elect their representatives unicameral legislature a lawmaking body with a single house whose representatives are elected by the people
1- England Became Great Britain in the early 1700s. 2- Economic relationships Great Britain imposed strict control over trade.
 1- England Became Great Britain in the early 1700s 2- Economic relationships Great Britain imposed strict control over trade. Great Britain taxed the colonies after the French and Indian War Colonies traded
1- England Became Great Britain in the early 1700s 2- Economic relationships Great Britain imposed strict control over trade. Great Britain taxed the colonies after the French and Indian War Colonies traded
US History Module 1 (A) Lesson 3. A New Nation
 US History Module 1 (A) Lesson 3 A New Nation Forming a New Government Fears and concerns about the form of government affects planning of new government Experimenting with Confederation 1781 Congress
US History Module 1 (A) Lesson 3 A New Nation Forming a New Government Fears and concerns about the form of government affects planning of new government Experimenting with Confederation 1781 Congress
The United States Constitution. The Supreme Law of the Land
 The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land Standards SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States
The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land Standards SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States
SO WHAT EXACTLY HAPPENED? WHY WERE THE COLONIES SO UPSET THEY DECIDED TO OVERTHROW THEIR GOVERNMENT (TAKING JOHN LOCKE S ADVICE)?
 Guided Notes 3: The American Colonies and Great Britain Part II The Revolutionary War began as a disagreement over the way in which Great Britain treated the colonies versus the way the colonies felt they
Guided Notes 3: The American Colonies and Great Britain Part II The Revolutionary War began as a disagreement over the way in which Great Britain treated the colonies versus the way the colonies felt they
CHAPTER 2: REVOLUTION AND THE EARLY REPUBLIC
 CHAPTER 2: REVOLUTION AND THE EARLY REPUBLIC COLONIAL RESISTANCE AND REBELLION SECTION 1 England s Parliament and Big Ben The Proclamation of 1763 sought to halt the westward expansion of the colonist,
CHAPTER 2: REVOLUTION AND THE EARLY REPUBLIC COLONIAL RESISTANCE AND REBELLION SECTION 1 England s Parliament and Big Ben The Proclamation of 1763 sought to halt the westward expansion of the colonist,
Eighth Grade, page 1 rev. May 10, 2011
 Eighth Grade, page 1 rev. May 10, 2011 PROCESS OBJECTIVES--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1 st 9 Weeks 1 st 9 Weeks 1. Explain the political
Eighth Grade, page 1 rev. May 10, 2011 PROCESS OBJECTIVES--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1 st 9 Weeks 1 st 9 Weeks 1. Explain the political
Focus Question: What events led the colonists to declare their independence from Britain?
 US History 1 CP Unit 2: Creating the American Republic The American Revolution 1765-1783 Mr. Mulry Section 2- Declaring Independence pp. 108-112 Objectives -Explain why fighting broke out to begin the
US History 1 CP Unit 2: Creating the American Republic The American Revolution 1765-1783 Mr. Mulry Section 2- Declaring Independence pp. 108-112 Objectives -Explain why fighting broke out to begin the
number of times you used the internet + times you used paper x.42 = $ you owe in taxes every day!
 Unit 2 SSUSH3 Analyze the causes of the Amer ican Revolution. a. Explain how the French and Indian War and the 1763 Treaty of Par is laid the groundwork for the Amer ican Revolution. Warm Up: Stamp Act
Unit 2 SSUSH3 Analyze the causes of the Amer ican Revolution. a. Explain how the French and Indian War and the 1763 Treaty of Par is laid the groundwork for the Amer ican Revolution. Warm Up: Stamp Act
Why Revolution? War of American Independence Clash of Ideology - Cause and Effect
 Why Revolution? War of American Independence Clash of Ideology - Cause and Effect What is your philosophy? 30 second speech DO NOWS! 1. Tag in! Phones away, hoodies/headphones off, greet classmates! 2.
Why Revolution? War of American Independence Clash of Ideology - Cause and Effect What is your philosophy? 30 second speech DO NOWS! 1. Tag in! Phones away, hoodies/headphones off, greet classmates! 2.
Goal 1 Values and Principles of American Democracy
 Practice Test of Goal 1 Values and Principles of American Democracy Note to teachers: These unofficial sample questions were created to help students review Goal 1 content, as well as practice for the
Practice Test of Goal 1 Values and Principles of American Democracy Note to teachers: These unofficial sample questions were created to help students review Goal 1 content, as well as practice for the
Common Sense. A guide to the beginning of American Independence
 Common Sense A guide to the beginning of American Independence List of Events Leading to the American Revolution French & Indian War - fought between Britain and France over land in the Ohio River Valley;
Common Sense A guide to the beginning of American Independence List of Events Leading to the American Revolution French & Indian War - fought between Britain and France over land in the Ohio River Valley;
and France in North America between 1754 and The French and Indian War was the American phase
 1 Vocabulary Unit 2: New Beginnings United States: French & Indian War: French and Indian War definition. A series of military engagements between Britain and France in North America between 1754 and 1763.
1 Vocabulary Unit 2: New Beginnings United States: French & Indian War: French and Indian War definition. A series of military engagements between Britain and France in North America between 1754 and 1763.
[ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals
![[ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals [ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals](/thumbs/77/76341976.jpg) [ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals [ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals Key Terms limited government representative government due process bicameral unicameral [ 2.1 ] Origins of American
[ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals [ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals Key Terms limited government representative government due process bicameral unicameral [ 2.1 ] Origins of American
Age of Jackson. 7 pages
 Age of Jackson 7 pages James Monroe 1817-1825 He is still president U.S. Territory The United States in 1819 (the light orange and light green areas were not then U.S. territory). The Missouri Compromise
Age of Jackson 7 pages James Monroe 1817-1825 He is still president U.S. Territory The United States in 1819 (the light orange and light green areas were not then U.S. territory). The Missouri Compromise
The Boston Tea Party
 American Revolution The Boston Tea Party The Night Boston Harbor Was Turned into a Giant Pot of Tea To learn about the Boston Tea Party, we will be doing a readers theater in class. In groups, you will
American Revolution The Boston Tea Party The Night Boston Harbor Was Turned into a Giant Pot of Tea To learn about the Boston Tea Party, we will be doing a readers theater in class. In groups, you will
MARKING PERIOD 1. Shamokin Area 7 th Grade American History I Common Core I. UNIT 1: THREE WORLDS MEET. Assessments Formative/Performan ce
 Shamokin Area 7 th Grade American History I Common Core Marking Period Content Targets Common Core Standards Objectives Assessments Formative/Performan ce MARKING PERIOD 1 I. UNIT 1: THREE WORLDS MEET
Shamokin Area 7 th Grade American History I Common Core Marking Period Content Targets Common Core Standards Objectives Assessments Formative/Performan ce MARKING PERIOD 1 I. UNIT 1: THREE WORLDS MEET
1. The Stamp Act taxed all legal documents, licenses, dice, playing cards and one other item. What is that other item?
 1. The Stamp Act taxed all legal documents, licenses, dice, playing cards and one other item. What is that other item? 2. Do you think it was fair for the Parliament to expect the colonies to pay to house
1. The Stamp Act taxed all legal documents, licenses, dice, playing cards and one other item. What is that other item? 2. Do you think it was fair for the Parliament to expect the colonies to pay to house
British policy of ignoring the colonies. a replacement of a government by the people of that government. No government/chaos mob rule
 1. Define revolution 2. Define tyranny 3. Define anarchy 4. Define salutary neglect a replacement of a government by the people of that government Total loss of freedom/absolute government power No government/chaos
1. Define revolution 2. Define tyranny 3. Define anarchy 4. Define salutary neglect a replacement of a government by the people of that government Total loss of freedom/absolute government power No government/chaos
Period 3: American Revolution Timeline: The French and Indian War (Seven Years War)
 Period 3: 1754-1800 British imperial attempts to reassert control over its colonies and the colonial reaction to these attempts produced a new American republic, along with struggles over the new nation
Period 3: 1754-1800 British imperial attempts to reassert control over its colonies and the colonial reaction to these attempts produced a new American republic, along with struggles over the new nation
This course focuses on the British perspective:
 Standard 1-Colonization and Revolution 3 countries explore o Spain- Reason: 3 G s (God, Gold, Glory) Area: Central/South America o France- Reason: Fur trapping/trade Area: Northern territories such as
Standard 1-Colonization and Revolution 3 countries explore o Spain- Reason: 3 G s (God, Gold, Glory) Area: Central/South America o France- Reason: Fur trapping/trade Area: Northern territories such as
PAGE 1 Constitution The Set Up Preamble Article I Article II
 PAGE 1 Constitution A constitution establishes the relationship between a government and its people. The structure and powers of state government are defined by the state constitution. Georgia s government
PAGE 1 Constitution A constitution establishes the relationship between a government and its people. The structure and powers of state government are defined by the state constitution. Georgia s government
STANDARD VUS.4c THE POLITICAL DIFFERENCES AMONG THE COLONISTS CONCERNING SEPARATION FROM BRITAIN
 STANDARD VUS.4c THE POLITICAL DIFFERENCES AMONG THE COLONISTS CONCERNING SEPARATION FROM BRITAIN The ideas of the Enlightenment and the perceived unfairness of British policies provoked debate and resistance
STANDARD VUS.4c THE POLITICAL DIFFERENCES AMONG THE COLONISTS CONCERNING SEPARATION FROM BRITAIN The ideas of the Enlightenment and the perceived unfairness of British policies provoked debate and resistance
I. SSUSH1: The student will describe European settlement in North America during the 17th century
 Unit I Review Sheet I. SSUSH1: The student will describe European settlement in North America during the 17th century 1. The Virginia Company A joint stock company. A group of investors share the risk
Unit I Review Sheet I. SSUSH1: The student will describe European settlement in North America during the 17th century 1. The Virginia Company A joint stock company. A group of investors share the risk
American Government. Unit 2 Study Guide
 American Government Unit 2 Study Guide Events leading up the Declaration of Independence: 1) Stamp Act- a tax placed on all printed material a. An attempt to earn money lost in the French and Indian War
American Government Unit 2 Study Guide Events leading up the Declaration of Independence: 1) Stamp Act- a tax placed on all printed material a. An attempt to earn money lost in the French and Indian War
The Critical Period The early years of the American Republic
 The Critical Period 1781-1789 The early years of the American Republic America after the War New Political Ideas: - Greater power for the people Republic: Represent the Public America after the War State
The Critical Period 1781-1789 The early years of the American Republic America after the War New Political Ideas: - Greater power for the people Republic: Represent the Public America after the War State
This review covers 20 questions you ll see on the Civics Midterm exam.
 This review covers 20 questions you ll see on the Civics Midterm exam. The British Empire in the early 1700 s England The Colonies The areas in red are the parts of the world controlled by the British
This review covers 20 questions you ll see on the Civics Midterm exam. The British Empire in the early 1700 s England The Colonies The areas in red are the parts of the world controlled by the British
CHAPTER 7 CREATING A GOVERNMENT
 CHAPTER 7 CREATING A GOVERNMENT The Constitution set out our rules for government. It explains what our government can and cannot do. It reflects are experience as a colony as well as ideas from Europe
CHAPTER 7 CREATING A GOVERNMENT The Constitution set out our rules for government. It explains what our government can and cannot do. It reflects are experience as a colony as well as ideas from Europe
SLIDE 1 Chapter 13: Reconstruction of Georgia and the South
 SLIDE 1 Chapter 13: Reconstruction of Georgia and the South 1863 1877 Racial prejudice, conflicts in government, and lingering bad feelings about the Civil War hurt attempts to rebuild the South and guarantee
SLIDE 1 Chapter 13: Reconstruction of Georgia and the South 1863 1877 Racial prejudice, conflicts in government, and lingering bad feelings about the Civil War hurt attempts to rebuild the South and guarantee
Describe the methods the colonists used to protest British taxes. Understand the significance of the First Continental Congress in 1774.
 Objectives Describe the methods the colonists used to protest British taxes. Understand the significance of the First Continental Congress in 1774. Assess why Congress declared independence and the ideas
Objectives Describe the methods the colonists used to protest British taxes. Understand the significance of the First Continental Congress in 1774. Assess why Congress declared independence and the ideas
Toward Independence: Years of Decision
 Chapter 5 Toward Independence: Years of Decision Salutary Neglect would give way to imperial authority! Problems Begin colonial troops treated poorly governors shared power army in peacetime Distance 1762
Chapter 5 Toward Independence: Years of Decision Salutary Neglect would give way to imperial authority! Problems Begin colonial troops treated poorly governors shared power army in peacetime Distance 1762
WHY DID AMERICAN COLONISTS WANT TO FREE THEMSELVES FROM GREAT BRITAIN?
 6 WHY DID AMERICAN COLONISTS WANT TO FREE THEMSELVES FROM GREAT BRITAIN? LESSON PURPOSE The growth of the American colonies raised issues with the parent country, Great Britain, that were difficult to
6 WHY DID AMERICAN COLONISTS WANT TO FREE THEMSELVES FROM GREAT BRITAIN? LESSON PURPOSE The growth of the American colonies raised issues with the parent country, Great Britain, that were difficult to
Complete the warm-up about Jefferson s quote
 Complete the warm-up about Jefferson s quote The 13 Colonies America: 13 colonies ruled by Great Britain (England) 1620-1783 European settlement initiated by Puritans & people seeking economic opportunities
Complete the warm-up about Jefferson s quote The 13 Colonies America: 13 colonies ruled by Great Britain (England) 1620-1783 European settlement initiated by Puritans & people seeking economic opportunities
LECTURE 3-3: THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION AND THE CONSTITUTION
 LECTURE 3-3: THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION AND THE CONSTITUTION The American Revolution s democratic and republican ideals inspired new experiments with different forms of government. I. Allegiances A.
LECTURE 3-3: THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION AND THE CONSTITUTION The American Revolution s democratic and republican ideals inspired new experiments with different forms of government. I. Allegiances A.
Forming a New Government
 Forming a New Government Why Independent in the First Place? Citizens wanted to limit the power of government Lack of representation No taxation without representation Protect personal freedoms Desired
Forming a New Government Why Independent in the First Place? Citizens wanted to limit the power of government Lack of representation No taxation without representation Protect personal freedoms Desired
Guided Reading Activity 5-1
 Guided Reading Activity 5-1 DIRECTIONS: Recalling the Facts Use the information in your textbook to answer the questions. Use another sheet of paper if necessary. 1. In 1763 how did Great Britain try to
Guided Reading Activity 5-1 DIRECTIONS: Recalling the Facts Use the information in your textbook to answer the questions. Use another sheet of paper if necessary. 1. In 1763 how did Great Britain try to
Name Period Teacher. Wantagh Middle School 7 th Grade Social Studies Final Exam Review Guide
 Name Period Teacher Wantagh Middle School 7 th Grade Social Studies Final Exam Review Guide 1. How did the earliest people migrate to North America? 2. How did Native Americans use the environment around
Name Period Teacher Wantagh Middle School 7 th Grade Social Studies Final Exam Review Guide 1. How did the earliest people migrate to North America? 2. How did Native Americans use the environment around
AMERICAN REVOLUTION. U.S. History Chapter 4
 AMERICAN REVOLUTION U.S. History Chapter 4 The primary cause of economic differences among the colonies in North America was geography. Longer growing season in the South led to an agriculture-based economy.
AMERICAN REVOLUTION U.S. History Chapter 4 The primary cause of economic differences among the colonies in North America was geography. Longer growing season in the South led to an agriculture-based economy.
Grade/Course: Eighth Grade Georgia Studies
 Grade/Course: Eighth Grade Georgia Studies Standards: H1, G1, G2, E1 3 weeks Standards: H1b, c, H2, G1d, E1 4 weeks Standards: H3, H4, E1, E2a 2 weeks Standards: H12a, c, CG1 1 week Unit One focus: Georgia
Grade/Course: Eighth Grade Georgia Studies Standards: H1, G1, G2, E1 3 weeks Standards: H1b, c, H2, G1d, E1 4 weeks Standards: H3, H4, E1, E2a 2 weeks Standards: H12a, c, CG1 1 week Unit One focus: Georgia
The Beginnings of a New American Government
 The Constitution The Beginnings of a New American Government Dissatisfaction grew with the Articles of Confederation as disagreements over control of waterways and trade developed. In 1785 the first meeting
The Constitution The Beginnings of a New American Government Dissatisfaction grew with the Articles of Confederation as disagreements over control of waterways and trade developed. In 1785 the first meeting
Analyze the maps in Setting the Stage. Then answer the following questions and fill out the map as directed.
 Geography Challenge G e o G r a p h y C h a l l e n G e Geography Skills Analyze the maps in Setting the Stage. Then answer the following questions and fill out the map as directed. 1. Label each state
Geography Challenge G e o G r a p h y C h a l l e n G e Geography Skills Analyze the maps in Setting the Stage. Then answer the following questions and fill out the map as directed. 1. Label each state
Foundations. Background to American History
 Foundations Background to American History ISN Set Up! Page Description 1 Table of Contents 2 Gradebook 3 Unit 1 Cover Page 4 Daily Objectives 5-6 Unit Timeline 7-10 Cornell Notes 136 Amendments 137140
Foundations Background to American History ISN Set Up! Page Description 1 Table of Contents 2 Gradebook 3 Unit 1 Cover Page 4 Daily Objectives 5-6 Unit Timeline 7-10 Cornell Notes 136 Amendments 137140
CHAPTER 2 NOTES Government Daily Lecture Notes 2-1 Even though the American colonists got many of their ideas about representative government and
 CHAPTER 2 NOTES Government Daily Lecture Notes 2-1 Even though the American colonists got many of their ideas about representative government and freedom from England, that country has no written constitution.
CHAPTER 2 NOTES Government Daily Lecture Notes 2-1 Even though the American colonists got many of their ideas about representative government and freedom from England, that country has no written constitution.
Colonial Experience with Self-Government
 Read and then answer the questions at the end of the document Section 3 From ideas to Independence: The American Revolution The colonists gathered ideas about government from many sources and traditions.
Read and then answer the questions at the end of the document Section 3 From ideas to Independence: The American Revolution The colonists gathered ideas about government from many sources and traditions.
Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50
 Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50 The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from religious persecution Economic opportunity Independent
Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50 The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from religious persecution Economic opportunity Independent
The Declaration of Independence
 The Declaration of Independence Recap! Mercantilism: economic policy from 1500-1800 in which nations encouraged exports as a means of collecting gold and silver Government controls all trade Colonies ensured
The Declaration of Independence Recap! Mercantilism: economic policy from 1500-1800 in which nations encouraged exports as a means of collecting gold and silver Government controls all trade Colonies ensured
Charter Conservatory Social Studies Curriculum 8 th Aligned to Common Core Georgia Performance Standards
 Content Area: Social Studies Charter Conservatory SOCIAL STUDIES CURRICULUM Course Title: Georgia Studies: My Georgia, My Home Grade Level: 8 Where We Live Prehistoric Period and Geography of Georgia Exploration
Content Area: Social Studies Charter Conservatory SOCIAL STUDIES CURRICULUM Course Title: Georgia Studies: My Georgia, My Home Grade Level: 8 Where We Live Prehistoric Period and Geography of Georgia Exploration
