The Possibility of a Social Welfare Function
|
|
|
- Emmeline Ellis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Transactions of the Nebraska Academy of Sciences and Affiliated Societies Nebraska Academy of Sciences 1976 The Possibility of a Social Welfare Function Edward D. Booth University of Nebraska-Lincoln Follow this and additional works at: Booth, Edward D., "The Possibility of a Social Welfare Function" (1976). Transactions of the Nebraska Academy of Sciences and Affiliated Societies This Article is brought to you for free and open access by the Nebraska Academy of Sciences at DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln. It has been accepted for inclusion in Transactions of the Nebraska Academy of Sciences and Affiliated Societies by an authorized administrator of DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln.
2 THE POSSIBILITY OF A SOCIAL WELFARE FUNCTION EDW ARD D. BOOTH Department of Philosophy, University of Nebraska-Lincoln By a social welfare function, or "constitution," or "arbitration scheme,". "conciliation policy," or "amalgamation method," or "voting procedure," 01 _ Iueant a rule which associates to each profile of individual preference I' l)l -derij1"s b a preference ordering for the society itself. Is it possible to articulate such a social welfare function? If we demand that our social welfare (unction satisfy certain ethically acceptable constraints the answer to our yuestion is not immediately obvious. Kenneth Arrow, in his Social Choice and Individual Values, investigated the possibility of specifying a social welfare function which would satisfy certain socially desirable criteria. Antecedent to this specification Arrow demanded of the individuals in the society that they be, in some sense, rational. That is, the individual's preference profile should exhibit transitivity of preference and indifference and connectedness. Arrow's conditions imposed on the social welfare function were these: (1) Unrestricted Domain: The domain of the social welfare function should include all logically possible combinations of individual orderings. (2) The Pareto Principle: If all individuals in the society prefer one option to another or are indifferent as to these two options the social choice should rehect these relationships. (3) The Independence of Irrelevant Alternatives: The introduction of new options should not alter the preference or indifference relationships already established within the individual profiles. (4) Non-dictatorship: There is no individual such that in those situations in which he prefers one option to another society does likewise, regardless of the preferences of the other individuals. Arrow proved his General Impossibility Theorem: If there are at least three options which the members of a society consisting of at least two members may order then every social welfare function satisfying conditions 11), (2) and (3) is dictatorial. This astonishing result provoked three kinds of responses: (1) Arrow's proof is Hawed and therefore a democracy satisfying the conditions which Arrow imposes is possible. (2) Arrow's proof is correct. A democracy satisfying the conditions which Arrow imposes is impossible. (3) Arrow's proof is correct but his conditions fail to capture a notion of a democratic society which we could still, in some sense, accept. This type of democracy, it is hoped, would be Arrow immune. 103
3 Arrow's amended presentation of the proof remains unchallenged. Consequently the first line of attack against the Impossibility Theorem h as been nullified. As a result pessismists were free to accept the second response and champion the death of democracy. However, recalcitrant egalitarians selected the third approach. It is With their general line of attack that we will be concerned. II. In 1951 Arrow wrote, "The viewpoint will be taken here that interpersonal comparison of utilities has no meaning and, in fact, that there is no meaning relevant to welfare comparisons in the measurability of individual utility." (Arrow, 1963:9) Arrow crystallized his attitude here in the form of the Independence of Irrelevant Alternatives condition. It is perhaps not immediately apparent how this condition restricts this sort of utility comparison. But von Neumann and Morgenstern demonstrated that the comparison of two options, between which a relationship of preference had been established, with a third option which was strictly irrelevant to this initial comparison leads to the establishment of a system of numerical utilities permitting linear transforma. tions. This system would permit, though it does not strictly entail, an interpersonal comparison of utilities. Given this opening Arrow's critics have attempted to show that an interpersonal comparison of utilities, if admitted as a condition which a social welfare function should fulfill, would permit a social choice system immune from dictatorial control. The difficulty lies in showing that an interpersonal comparison of utilities is meaningful. Ilmar Waldner's (1972: 102) efforts to establish a meaningful interperson al comparison of utilities have been more serious than most. But finally he is compelled to confess, "My argument has been against the common ~ssumption that it is impossible to have empirical justification for interper sonal utility comparisons. I do not regard myself as having given an empirical justification of the required kind." Arrow never denied this possibility; rather what he denied was that we were now in the possession of such a method of utility measurement. But Arrow, himself, has recently admitted, "that the austerity imposed by this condition (the Independence of Irrelevant Alternatives) is stricter than desirable; in many situations we do have information on preferences for nonfeasible, i.e., irrelevant, alternatives." (Hook, 1967:19). At this point it might be said that Arrow himself had destroyed his own Impossibility Theorem by diluting one of his own conditions. Perhaps 104
4 HISTORY AND PHILOSOPHY Of SCIENCE ArroW'S result is not so disturbing after all. Unfortunately Schwartz (1970:89-106) has shattered this illusion. III. Schwartz adds four conditions to those set forth by Arrow which allow interpersonal comparisons of utilities and even cardinal utility comparisons. \ionetheless, Schwartz proves that even with these drastic alterations in the ~onditions for a social welfare function the resultant function is either inconsistent or despotic. Arrow's critics have been rebuked, again. First we should consider two additional conditions which Schwartz grafts to Arrow's original ones. These so-called decisiveness conditions are ;perative in those situations in which two options are deadlocked. It can occur that the sum of cardinal utilities of all the members of the society, excepting one individual, favoring one particular option is equal to the cardinal utility of that one individual who is opposed to this selection. Schwartz demands, by his decisiveness conditions, that should this one individual's selection over-ride the preference of all the others, for what Schwartz enigmatically refers to as "other reasons," than this unique individual is a despot. Our analysis of Schwartz's program, at least on the positive side, is that Schwartz, perhaps unwittingly, has uncovered another condition which we reasonably expect a social welfare function to fulfill - viz., "decisiveness." Consequently Schwartz has shown us, albeit implicitly, that we may well be hooked on the horns of a new dilemma. Apparently if our society is to act decisively it will do so only under despotic decree or if our society is to act democratically we are propelled towards political deadlock. IV. My proposed solution to the dilemma of despotism or deadlock can, here, be only roughly sketched in. My view is that it is rational for a society which is democratic in a broad sense to permit certain individuals to exercise, for "other reasons," mildly despotic powers. Of course it is well known that certain individuals in the most democratic societies extant exercise powers far in excess of those wielded by ordinary members of that society. The problem is, however, that the people in these societies are persuaded to believe that Arrow's conditions are their basic political birthright while at the same time silent despots steal away with the decision making power. Again it may be protested that what has been just described occurs with such deplorable frequency that a recounting of it here merely cloys. But those obsessed with the problem of despotism seldom explore the obverse of this situation, political deadlock. 105
5 May (1973:85-87) points out that in the United States POlitical deadlock, at least in the presidential elections, was an imminent danger i 1972 and May charges that political amateurs, using an irrationall n conceived system, were responsible. He claims that in 1972 the DemoCrati~ nominating convention selected George McGovern with ample knowledge that McGovern could not win and that his candidacy would be detrimental to other party candidates. May is no mere partisan for he makes it clear that the Republican nominating convention committed the same blunder with their Goldwater nomination in For this reason May believes that current party moves to broaden participation in the nominating conventions aggravates this problem by opening up the conventions to more political amateurs. May's scheme to correct this situation is to lodge the power to nominate candidates for the presidency in the hands of objective party professionals. May proposes that party senators, congressmen, governors, top-ranking state legislative officials and big city mayors, either incumbent or nominee, from marginal or non-marginal states, be allotted from one to three convention votes based on an appropriate mix of these factors. Details of this plan aside we can now give substance to Schwartz's plea for despotic decisiveness based on "other reasons;" at least, for this particular case. Among these "other reasons" are the following. These officials are elected representatives. These officials have political acuity and they will realize that should a candidate for presidency be selected whose chances of winning are slim their own political fortunes may well decline with his defeat. Our point is simply this. We have concluded that a procedure for avoiding deadlock is a reasonable requirement for a political system. An empirical examination of our own presidential nominating conventions gives credence to this demand. May has suggested that a "weighing" of individuals involved in a social decision process will greatly reduce the danger of political deadlock. The general problem facing us now is to sharpen our crude notions of "weight" in some systematic manner. We do not assume that this task is an t(asy one. It may be that several particular social welfare functions are needed. But certainly there is a possibility of finding a social welfare function or functions which will accomodate both democratic and rational demands. To find this is the challenge. REFERENCES CITED Arrow, Kenneth J., Social choice and individual values: New Haven and London, Yale University Press, 124 p. + xi. Hook, Sidney, ed., Human values and economic policy: New York, New York University Press, 268 p. + x. May, John, Up with Dick Daley: Intellectual Digest, 3(7):
6 schwartz, Thomas, On the possibility of rational policy evaluations: Theory and DecIsIOn, (1): Waldner, IImar, The empirical meaningfulness of interpersonal utility comparisons: The Journal of Philosophy, 69(4):
Notes for Session 7 Basic Voting Theory and Arrow s Theorem
 Notes for Session 7 Basic Voting Theory and Arrow s Theorem We follow up the Impossibility (Session 6) of pooling expert probabilities, while preserving unanimities in both unconditional and conditional
Notes for Session 7 Basic Voting Theory and Arrow s Theorem We follow up the Impossibility (Session 6) of pooling expert probabilities, while preserving unanimities in both unconditional and conditional
A NOTE ON THE THEORY OF SOCIAL CHOICE
 A NOTE ON THE THEORY OF SOCIAL CHOICE Professor Arrow brings to his treatment of the theory of social welfare (I) a fine unity of mathematical rigour and insight into fundamental issues of social philosophy.
A NOTE ON THE THEORY OF SOCIAL CHOICE Professor Arrow brings to his treatment of the theory of social welfare (I) a fine unity of mathematical rigour and insight into fundamental issues of social philosophy.
Voting Criteria April
 Voting Criteria 21-301 2018 30 April 1 Evaluating voting methods In the last session, we learned about different voting methods. In this session, we will focus on the criteria we use to evaluate whether
Voting Criteria 21-301 2018 30 April 1 Evaluating voting methods In the last session, we learned about different voting methods. In this session, we will focus on the criteria we use to evaluate whether
Chapter 4: Voting and Social Choice.
 Chapter 4: Voting and Social Choice. Topics: Ordinal Welfarism Condorcet and Borda: 2 alternatives for majority voting Voting over Resource Allocation Single-Peaked Preferences Intermediate Preferences
Chapter 4: Voting and Social Choice. Topics: Ordinal Welfarism Condorcet and Borda: 2 alternatives for majority voting Voting over Resource Allocation Single-Peaked Preferences Intermediate Preferences
Economic philosophy of Amartya Sen Social choice as public reasoning and the capability approach. Reiko Gotoh
 Welfare theory, public action and ethical values: Re-evaluating the history of welfare economics in the twentieth century Backhouse/Baujard/Nishizawa Eds. Economic philosophy of Amartya Sen Social choice
Welfare theory, public action and ethical values: Re-evaluating the history of welfare economics in the twentieth century Backhouse/Baujard/Nishizawa Eds. Economic philosophy of Amartya Sen Social choice
1 Aggregating Preferences
 ECON 301: General Equilibrium III (Welfare) 1 Intermediate Microeconomics II, ECON 301 General Equilibrium III: Welfare We are done with the vital concepts of general equilibrium Its power principally
ECON 301: General Equilibrium III (Welfare) 1 Intermediate Microeconomics II, ECON 301 General Equilibrium III: Welfare We are done with the vital concepts of general equilibrium Its power principally
Chapter 9: Social Choice: The Impossible Dream Lesson Plan
 Lesson Plan For All Practical Purposes An Introduction to Social Choice Majority Rule and Condorcet s Method Mathematical Literacy in Today s World, 9th ed. Other Voting Systems for Three or More Candidates
Lesson Plan For All Practical Purposes An Introduction to Social Choice Majority Rule and Condorcet s Method Mathematical Literacy in Today s World, 9th ed. Other Voting Systems for Three or More Candidates
The Arrow Impossibility Theorem: Where Do We Go From Here?
 The Arrow Impossibility Theorem: Where Do We Go From Here? Eric Maskin Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton Arrow Lecture Columbia University December 11, 2009 I thank Amartya Sen and Joseph Stiglitz
The Arrow Impossibility Theorem: Where Do We Go From Here? Eric Maskin Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton Arrow Lecture Columbia University December 11, 2009 I thank Amartya Sen and Joseph Stiglitz
Computational Social Choice: Spring 2007
 Computational Social Choice: Spring 2007 Ulle Endriss Institute for Logic, Language and Computation University of Amsterdam Ulle Endriss 1 Plan for Today This lecture will be an introduction to voting
Computational Social Choice: Spring 2007 Ulle Endriss Institute for Logic, Language and Computation University of Amsterdam Ulle Endriss 1 Plan for Today This lecture will be an introduction to voting
Comments on Justin Weinberg s Is Government Supererogation Possible? Public Reason Political Philosophy Symposium Friday October 17, 2008
 Helena de Bres Wellesley College Department of Philosophy hdebres@wellesley.edu Comments on Justin Weinberg s Is Government Supererogation Possible? Public Reason Political Philosophy Symposium Friday
Helena de Bres Wellesley College Department of Philosophy hdebres@wellesley.edu Comments on Justin Weinberg s Is Government Supererogation Possible? Public Reason Political Philosophy Symposium Friday
MATH4999 Capstone Projects in Mathematics and Economics Topic 3 Voting methods and social choice theory
 MATH4999 Capstone Projects in Mathematics and Economics Topic 3 Voting methods and social choice theory 3.1 Social choice procedures Plurality voting Borda count Elimination procedures Sequential pairwise
MATH4999 Capstone Projects in Mathematics and Economics Topic 3 Voting methods and social choice theory 3.1 Social choice procedures Plurality voting Borda count Elimination procedures Sequential pairwise
Rationality & Social Choice. Dougherty, POLS 8000
 Rationality & Social Choice Dougherty, POLS 8000 Social Choice A. Background 1. Social Choice examines how to aggregate individual preferences fairly. a. Voting is an example. b. Think of yourself writing
Rationality & Social Choice Dougherty, POLS 8000 Social Choice A. Background 1. Social Choice examines how to aggregate individual preferences fairly. a. Voting is an example. b. Think of yourself writing
Font Size: A A. Eric Maskin and Amartya Sen JANUARY 19, 2017 ISSUE. 1 of 7 2/21/ :01 AM
 1 of 7 2/21/2017 10:01 AM Font Size: A A Eric Maskin and Amartya Sen JANUARY 19, 2017 ISSUE Americans have been using essentially the same rules to elect presidents since the beginning of the Republic.
1 of 7 2/21/2017 10:01 AM Font Size: A A Eric Maskin and Amartya Sen JANUARY 19, 2017 ISSUE Americans have been using essentially the same rules to elect presidents since the beginning of the Republic.
Political Sophistication and Third-Party Voting in Recent Presidential Elections
 Political Sophistication and Third-Party Voting in Recent Presidential Elections Christopher N. Lawrence Department of Political Science Duke University April 3, 2006 Overview During the 1990s, minor-party
Political Sophistication and Third-Party Voting in Recent Presidential Elections Christopher N. Lawrence Department of Political Science Duke University April 3, 2006 Overview During the 1990s, minor-party
Arrow s Impossibility Theorem on Social Choice Systems
 Arrow s Impossibility Theorem on Social Choice Systems Ashvin A. Swaminathan January 11, 2013 Abstract Social choice theory is a field that concerns methods of aggregating individual interests to determine
Arrow s Impossibility Theorem on Social Choice Systems Ashvin A. Swaminathan January 11, 2013 Abstract Social choice theory is a field that concerns methods of aggregating individual interests to determine
Political Sophistication and Third-Party Voting in Recent Presidential Elections
 Political Sophistication and Third-Party Voting in Recent Presidential Elections Christopher N. Lawrence Department of Political Science Duke University April 3, 2006 Overview During the 1990s, minor-party
Political Sophistication and Third-Party Voting in Recent Presidential Elections Christopher N. Lawrence Department of Political Science Duke University April 3, 2006 Overview During the 1990s, minor-party
Problems with Group Decision Making
 Problems with Group Decision Making There are two ways of evaluating political systems: 1. Consequentialist ethics evaluate actions, policies, or institutions in regard to the outcomes they produce. 2.
Problems with Group Decision Making There are two ways of evaluating political systems: 1. Consequentialist ethics evaluate actions, policies, or institutions in regard to the outcomes they produce. 2.
Chapter 9: Social Choice: The Impossible Dream Lesson Plan
 Lesson Plan For ll Practical Purposes Voting and Social hoice Majority Rule and ondorcet s Method Mathematical Literacy in Today s World, 7th ed. Other Voting Systems for Three or More andidates Plurality
Lesson Plan For ll Practical Purposes Voting and Social hoice Majority Rule and ondorcet s Method Mathematical Literacy in Today s World, 7th ed. Other Voting Systems for Three or More andidates Plurality
Mathematics and Social Choice Theory. Topic 4 Voting methods with more than 2 alternatives. 4.1 Social choice procedures
 Mathematics and Social Choice Theory Topic 4 Voting methods with more than 2 alternatives 4.1 Social choice procedures 4.2 Analysis of voting methods 4.3 Arrow s Impossibility Theorem 4.4 Cumulative voting
Mathematics and Social Choice Theory Topic 4 Voting methods with more than 2 alternatives 4.1 Social choice procedures 4.2 Analysis of voting methods 4.3 Arrow s Impossibility Theorem 4.4 Cumulative voting
Robbins as Innovator: the Contribution of An Essay on the Nature and Significance of Economic Science
 1 of 5 4/3/2007 12:25 PM Robbins as Innovator: the Contribution of An Essay on the Nature and Significance of Economic Science Robert F. Mulligan Western Carolina University mulligan@wcu.edu Lionel Robbins's
1 of 5 4/3/2007 12:25 PM Robbins as Innovator: the Contribution of An Essay on the Nature and Significance of Economic Science Robert F. Mulligan Western Carolina University mulligan@wcu.edu Lionel Robbins's
Problems with Group Decision Making
 Problems with Group Decision Making There are two ways of evaluating political systems. 1. Consequentialist ethics evaluate actions, policies, or institutions in regard to the outcomes they produce. 2.
Problems with Group Decision Making There are two ways of evaluating political systems. 1. Consequentialist ethics evaluate actions, policies, or institutions in regard to the outcomes they produce. 2.
Mathematical Thinking. Chapter 9 Voting Systems
 Mathematical Thinking Chapter 9 Voting Systems Voting Systems A voting system is a rule for transforming a set of individual preferences into a single group decision. What are the desirable properties
Mathematical Thinking Chapter 9 Voting Systems Voting Systems A voting system is a rule for transforming a set of individual preferences into a single group decision. What are the desirable properties
ILLINOIS (status quo)
 ILLINOIS KEY POINTS: The state legislature draws congressional districts, subject only to federal constitutional and statutory limitations. The legislature also has the first opportunity to draw state
ILLINOIS KEY POINTS: The state legislature draws congressional districts, subject only to federal constitutional and statutory limitations. The legislature also has the first opportunity to draw state
Chapter 1 Practice Test Questions
 0728 Finite Math Chapter 1 Practice Test Questions VOCABULARY. On the exam, be prepared to match the correct definition to the following terms: 1) Voting Elements: Single-choice ballot, preference ballot,
0728 Finite Math Chapter 1 Practice Test Questions VOCABULARY. On the exam, be prepared to match the correct definition to the following terms: 1) Voting Elements: Single-choice ballot, preference ballot,
CHAPTER 6 IS DEMOCRACY MEANINGLESS? ARROW S CONDITION OF THE INDEPENDENCE OF IRRELEVANT ALTERNATIVES 1
 1 CHAPTER 6 IS DEMOCRACY MEANINGLESS? ARROW S CONDITION OF THE INDEPENDENCE OF IRRELEVANT ALTERNATIVES 1 Introduction. The interpretation that Arrow s Condition I, independence of irrelevant alternatives,
1 CHAPTER 6 IS DEMOCRACY MEANINGLESS? ARROW S CONDITION OF THE INDEPENDENCE OF IRRELEVANT ALTERNATIVES 1 Introduction. The interpretation that Arrow s Condition I, independence of irrelevant alternatives,
Obscenity and Community Standards: A Social Choice Approach
 Obscenity and Community Standards: A Social Choice Approach Alan D. Miller * October 2008 * Division of the Humanities and Social Sciences, Mail Code 228-77, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena,
Obscenity and Community Standards: A Social Choice Approach Alan D. Miller * October 2008 * Division of the Humanities and Social Sciences, Mail Code 228-77, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena,
Write all responses on separate paper. Use complete sentences, charts and diagrams, as appropriate.
 Math 13 HW 5 Chapter 9 Write all responses on separate paper. Use complete sentences, charts and diagrams, as appropriate. 1. Explain why majority rule is not a good way to choose between four alternatives.
Math 13 HW 5 Chapter 9 Write all responses on separate paper. Use complete sentences, charts and diagrams, as appropriate. 1. Explain why majority rule is not a good way to choose between four alternatives.
HARVARD JOHN M. OLIN CENTER FOR LAW, ECONOMICS, AND BUSINESS
 HARVARD JOHN M. OLIN CENTER FOR LAW, ECONOMICS, AND BUSINESS ISSN 1045-6333 ANY NON-WELFARIST METHOD OF POLICY ASSESSMENT VIOLATES THE PARETO PRINCIPLE: REPLY Louis Kaplow Steven Shavell Discussion Paper
HARVARD JOHN M. OLIN CENTER FOR LAW, ECONOMICS, AND BUSINESS ISSN 1045-6333 ANY NON-WELFARIST METHOD OF POLICY ASSESSMENT VIOLATES THE PARETO PRINCIPLE: REPLY Louis Kaplow Steven Shavell Discussion Paper
REPUBLICAN PARTY OF MINNESOTA, 4TH CONGRESSIONAL DISTRICT CONSTITUTION PREAMBLE. ARTICLE I NAME and OBJECTIVE ARTICLE II 4 TH DISTRICT ORGANIZATION
 REPUBLICAN PARTY OF MINNESOTA, 4TH CONGRESSIONAL DISTRICT CONSTITUTION PREAMBLE The Republican Party of Minnesota (hereinafter referred to as the RPM ) welcomes the participation of all Minnesotans who
REPUBLICAN PARTY OF MINNESOTA, 4TH CONGRESSIONAL DISTRICT CONSTITUTION PREAMBLE The Republican Party of Minnesota (hereinafter referred to as the RPM ) welcomes the participation of all Minnesotans who
Analyzing American Democracy
 SUB Hamburg Analyzing American Democracy Politics and Political Science Jon R. Bond Texas A&M University Kevin B. Smith University of Nebraska-Lincoln O Routledge Taylor & Francis Group NEW YORK AND LONDON
SUB Hamburg Analyzing American Democracy Politics and Political Science Jon R. Bond Texas A&M University Kevin B. Smith University of Nebraska-Lincoln O Routledge Taylor & Francis Group NEW YORK AND LONDON
2017 CAMPAIGN FINANCE REPORT
 2017 CAMPAIGN FINANCE REPORT PRINCIPAL AUTHORS: LONNA RAE ATKESON PROFESSOR OF POLITICAL SCIENCE, DIRECTOR CENTER FOR THE STUDY OF VOTING, ELECTIONS AND DEMOCRACY, AND DIRECTOR INSTITUTE FOR SOCIAL RESEARCH,
2017 CAMPAIGN FINANCE REPORT PRINCIPAL AUTHORS: LONNA RAE ATKESON PROFESSOR OF POLITICAL SCIENCE, DIRECTOR CENTER FOR THE STUDY OF VOTING, ELECTIONS AND DEMOCRACY, AND DIRECTOR INSTITUTE FOR SOCIAL RESEARCH,
Decision making and problem solving Lecture 10. Group techniques Voting MAVT for group decisions
 Decision making and problem solving Lecture 10 Group techniques Voting MAVT for group decisions Motivation Thus far we have assumed that Objectives, attributes/criteria, and decision alternatives are given
Decision making and problem solving Lecture 10 Group techniques Voting MAVT for group decisions Motivation Thus far we have assumed that Objectives, attributes/criteria, and decision alternatives are given
Philip Pettit, and Wlodek Rabinowicz for very helpful comments and discussion.
 1 The Impossibility of a Paretian Republican? Some Comments on Pettit and Sen 1 Christian List Department of Government, LSE November 2003 Economics and Philosophy, forthcoming Abstract. Philip Pettit
1 The Impossibility of a Paretian Republican? Some Comments on Pettit and Sen 1 Christian List Department of Government, LSE November 2003 Economics and Philosophy, forthcoming Abstract. Philip Pettit
Any non-welfarist method of policy assessment violates the Pareto principle: A comment
 Any non-welfarist method of policy assessment violates the Pareto principle: A comment Marc Fleurbaey, Bertil Tungodden September 2001 1 Introduction Suppose it is admitted that when all individuals prefer
Any non-welfarist method of policy assessment violates the Pareto principle: A comment Marc Fleurbaey, Bertil Tungodden September 2001 1 Introduction Suppose it is admitted that when all individuals prefer
DEMOCRATS DIGEST. A Monthly Newsletter of the Conference of Young Nigerian Democrats. Inside this Issue:
 DEMOCRATS DIGEST A Monthly Newsletter of the Conference of Young Nigerian Democrats Inside this Issue: Primary Election I INTRODUCTION Primary Election, preliminary election in which voters select a political
DEMOCRATS DIGEST A Monthly Newsletter of the Conference of Young Nigerian Democrats Inside this Issue: Primary Election I INTRODUCTION Primary Election, preliminary election in which voters select a political
Oregon Progressive Party Position on Bill at 2017 Session of Oregon Legislature:
 March 23, 2017 411 S.W. 2nd Avenue Suite 200 Portland, OR 97204 503-548-2797 info@progparty.org Oregon Progressive Party Position on Bill at 2017 Session of Oregon Legislature: HB 2211: Oppose Dear Committee:
March 23, 2017 411 S.W. 2nd Avenue Suite 200 Portland, OR 97204 503-548-2797 info@progparty.org Oregon Progressive Party Position on Bill at 2017 Session of Oregon Legislature: HB 2211: Oppose Dear Committee:
Introduction to Theory of Voting. Chapter 2 of Computational Social Choice by William Zwicker
 Introduction to Theory of Voting Chapter 2 of Computational Social Choice by William Zwicker If we assume Introduction 1. every two voters play equivalent roles in our voting rule 2. every two alternatives
Introduction to Theory of Voting Chapter 2 of Computational Social Choice by William Zwicker If we assume Introduction 1. every two voters play equivalent roles in our voting rule 2. every two alternatives
Testimony of FairVote The Center for Voting and Democracy Jack Santucci, Program for Representative Government. October 16, 2006
 Testimony of FairVote The Center for Voting and Democracy Jack Santucci, Program for Representative Government Given in writing to the Assembly Standing Committee on Governmental Operations and Assembly
Testimony of FairVote The Center for Voting and Democracy Jack Santucci, Program for Representative Government Given in writing to the Assembly Standing Committee on Governmental Operations and Assembly
The California Primary and Redistricting
 The California Primary and Redistricting This study analyzes what is the important impact of changes in the primary voting rules after a Congressional and Legislative Redistricting. Under a citizen s committee,
The California Primary and Redistricting This study analyzes what is the important impact of changes in the primary voting rules after a Congressional and Legislative Redistricting. Under a citizen s committee,
On the Irrelevance of Formal General Equilibrium Analysis
 Eastern Economic Journal 2018, 44, (491 495) Ó 2018 EEA 0094-5056/18 www.palgrave.com/journals COLANDER'S ECONOMICS WITH ATTITUDE On the Irrelevance of Formal General Equilibrium Analysis Middlebury College,
Eastern Economic Journal 2018, 44, (491 495) Ó 2018 EEA 0094-5056/18 www.palgrave.com/journals COLANDER'S ECONOMICS WITH ATTITUDE On the Irrelevance of Formal General Equilibrium Analysis Middlebury College,
Is Majority Rule the Best Voting Method? Partha Dasgupta and Eric Maskin
 Is Majority Rule the Best Voting Method? by Partha Dasgupta and Eric Maskin June 2003 The authors are, respectively, the Frank Ramsey Professor of Economics at the University of Cambridge, UK, and the
Is Majority Rule the Best Voting Method? by Partha Dasgupta and Eric Maskin June 2003 The authors are, respectively, the Frank Ramsey Professor of Economics at the University of Cambridge, UK, and the
Primitivist prioritarianism. Hilary Greaves (Oxford) Value of Equality workshop, Jerusalem, July 2016
 Primitivist prioritarianism Hilary Greaves (Oxford) Value of Equality workshop, Jerusalem, 15-17 July 2016 From the workshop abstract Is inequality bad? The question seems almost trivial a society of equals
Primitivist prioritarianism Hilary Greaves (Oxford) Value of Equality workshop, Jerusalem, 15-17 July 2016 From the workshop abstract Is inequality bad? The question seems almost trivial a society of equals
Lecture 16: Voting systems
 Lecture 16: Voting systems Economics 336 Economics 336 (Toronto) Lecture 16: Voting systems 1 / 18 Introduction Last lecture we looked at the basic theory of majority voting: instability in voting: Condorcet
Lecture 16: Voting systems Economics 336 Economics 336 (Toronto) Lecture 16: Voting systems 1 / 18 Introduction Last lecture we looked at the basic theory of majority voting: instability in voting: Condorcet
Introduction to the Theory of Voting
 November 11, 2015 1 Introduction What is Voting? Motivation 2 Axioms I Anonymity, Neutrality and Pareto Property Issues 3 Voting Rules I Condorcet Extensions and Scoring Rules 4 Axioms II Reinforcement
November 11, 2015 1 Introduction What is Voting? Motivation 2 Axioms I Anonymity, Neutrality and Pareto Property Issues 3 Voting Rules I Condorcet Extensions and Scoring Rules 4 Axioms II Reinforcement
Explaining the Impossible: Kenneth Arrow s Nobel Prize Winning Theorem on Elections
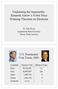 Explaining the Impossible: Kenneth Arrow s Nobel Prize Winning Theorem on Elections Dr. Rick Klima Appalachian State University Boone, North Carolina U.S. Presidential Vote Totals, 2000 Candidate Bush
Explaining the Impossible: Kenneth Arrow s Nobel Prize Winning Theorem on Elections Dr. Rick Klima Appalachian State University Boone, North Carolina U.S. Presidential Vote Totals, 2000 Candidate Bush
Chapter 9: Social Choice: The Impossible Dream
 Chapter 9: Social Choice: The Impossible Dream The application of mathematics to the study of human beings their behavior, values, interactions, conflicts, and methods of making decisions is generally
Chapter 9: Social Choice: The Impossible Dream The application of mathematics to the study of human beings their behavior, values, interactions, conflicts, and methods of making decisions is generally
History of Social Choice and Welfare Economics
 What is Social Choice Theory? History of Social Choice and Welfare Economics SCT concerned with evaluation of alternative methods of collective decision making and logical foundations of welfare economics
What is Social Choice Theory? History of Social Choice and Welfare Economics SCT concerned with evaluation of alternative methods of collective decision making and logical foundations of welfare economics
From The Collected Works of Milton Friedman, compiled and edited by Robert Leeson and Charles G. Palm.
 Value Judgments in Economics * by Milton Friedman In Human Values and Economic Policy, A Symposium, edited by Sidney Hook, pp. 85-93. New York: New York University Press, 1967. NYU Press I find myself
Value Judgments in Economics * by Milton Friedman In Human Values and Economic Policy, A Symposium, edited by Sidney Hook, pp. 85-93. New York: New York University Press, 1967. NYU Press I find myself
Voting rules: (Dixit and Skeath, ch 14) Recall parkland provision decision:
 rules: (Dixit and Skeath, ch 14) Recall parkland provision decision: Assume - n=10; - total cost of proposed parkland=38; - if provided, each pays equal share = 3.8 - there are two groups of individuals
rules: (Dixit and Skeath, ch 14) Recall parkland provision decision: Assume - n=10; - total cost of proposed parkland=38; - if provided, each pays equal share = 3.8 - there are two groups of individuals
Bits and Pieces to Master the Exam Random Thoughts, Trivia, and Other Facts (that may help you be successful AP EXAM)
 Bits and Pieces to Master the Exam Random Thoughts, Trivia, and Other Facts (that may help you be successful AP EXAM) but what is government itself but the greatest of all reflections on human nature?
Bits and Pieces to Master the Exam Random Thoughts, Trivia, and Other Facts (that may help you be successful AP EXAM) but what is government itself but the greatest of all reflections on human nature?
VOTING SYSTEMS AND ARROW S THEOREM
 VOTING SYSTEMS AND ARROW S THEOREM AKHIL MATHEW Abstract. The following is a brief discussion of Arrow s theorem in economics. I wrote it for an economics class in high school. 1. Background Arrow s theorem
VOTING SYSTEMS AND ARROW S THEOREM AKHIL MATHEW Abstract. The following is a brief discussion of Arrow s theorem in economics. I wrote it for an economics class in high school. 1. Background Arrow s theorem
SMALL STATES FIRST; LARGE STATES LAST; WITH A SPORTS PLAYOFF SYSTEM
 14. REFORMING THE PRESIDENTIAL PRIMARIES: SMALL STATES FIRST; LARGE STATES LAST; WITH A SPORTS PLAYOFF SYSTEM The calendar of presidential primary elections currently in use in the United States is a most
14. REFORMING THE PRESIDENTIAL PRIMARIES: SMALL STATES FIRST; LARGE STATES LAST; WITH A SPORTS PLAYOFF SYSTEM The calendar of presidential primary elections currently in use in the United States is a most
The Effects of the Right to Silence on the Innocent s Decision to Remain Silent
 Preliminary Draft of 6008 The Effects of the Right to Silence on the Innocent s Decision to Remain Silent Shmuel Leshem * Abstract This paper shows that innocent suspects benefit from exercising the right
Preliminary Draft of 6008 The Effects of the Right to Silence on the Innocent s Decision to Remain Silent Shmuel Leshem * Abstract This paper shows that innocent suspects benefit from exercising the right
Econ 551 Government Finance: Revenues Fall 2018
 Econ 551 Government Finance: Revenues Fall 2018 Given by Kevin Milligan Vancouver School of Economics University of British Columbia Lecture 2a: Redistribution and Social Choice ECON 551: Lecture 2a 1
Econ 551 Government Finance: Revenues Fall 2018 Given by Kevin Milligan Vancouver School of Economics University of British Columbia Lecture 2a: Redistribution and Social Choice ECON 551: Lecture 2a 1
AGGREGATION OF PREFERENCES AND THE STRUCTURE OF DECISIVE SETS. Donald J. Brown. October 2016 COWLES FOUNDATION DISCUSSION PAPER NO.
 AGGREGATION OF PREFERENCES AND THE STRUCTURE OF DECISIVE SETS By Donald J. Brown October 2016 COWLES FOUNDATION DISCUSSION PAPER NO. 2052 COWLES FOUNDATION FOR RESEARCH IN ECONOMICS YALE UNIVERSITY Box
AGGREGATION OF PREFERENCES AND THE STRUCTURE OF DECISIVE SETS By Donald J. Brown October 2016 COWLES FOUNDATION DISCUSSION PAPER NO. 2052 COWLES FOUNDATION FOR RESEARCH IN ECONOMICS YALE UNIVERSITY Box
1. a person who wants to be elected to a certain position. The candidates for mayor will speak on TV tonight.
 Have you ever heard someone being called an idiot? If you have, what they are really being called is someone who does not vote. The word idiot comes from the Greek word idiotes. In ancient Greece this
Have you ever heard someone being called an idiot? If you have, what they are really being called is someone who does not vote. The word idiot comes from the Greek word idiotes. In ancient Greece this
The Iowa Caucuses. (See Attached Page Below) B R C T R B R R C C B C T T T B
 Date: 9/27/2016 The Iowa Caucuses Part I: Research the Iowa Caucuses and explain how they work. Your response should be a one-page (250-word) narrative. Be sure to include a brief history, how a caucus
Date: 9/27/2016 The Iowa Caucuses Part I: Research the Iowa Caucuses and explain how they work. Your response should be a one-page (250-word) narrative. Be sure to include a brief history, how a caucus
What do you know about how our president is elected?
 What do you know about how our president is elected? The Electoral College When we talk about this election process, we say that our president and vice president are elected by the Electoral College.
What do you know about how our president is elected? The Electoral College When we talk about this election process, we say that our president and vice president are elected by the Electoral College.
Social Choice & Mechanism Design
 Decision Making in Robots and Autonomous Agents Social Choice & Mechanism Design Subramanian Ramamoorthy School of Informatics 2 April, 2013 Introduction Social Choice Our setting: a set of outcomes agents
Decision Making in Robots and Autonomous Agents Social Choice & Mechanism Design Subramanian Ramamoorthy School of Informatics 2 April, 2013 Introduction Social Choice Our setting: a set of outcomes agents
Head-to-Head Winner. To decide if a Head-to-Head winner exists: Every candidate is matched on a one-on-one basis with every other candidate.
 Head-to-Head Winner A candidate is a Head-to-Head winner if he or she beats all other candidates by majority rule when they meet head-to-head (one-on-one). To decide if a Head-to-Head winner exists: Every
Head-to-Head Winner A candidate is a Head-to-Head winner if he or she beats all other candidates by majority rule when they meet head-to-head (one-on-one). To decide if a Head-to-Head winner exists: Every
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SAN DIEGO DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS
 2000-03 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SAN DIEGO DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS JOHN NASH AND THE ANALYSIS OF STRATEGIC BEHAVIOR BY VINCENT P. CRAWFORD DISCUSSION PAPER 2000-03 JANUARY 2000 John Nash and the Analysis
2000-03 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SAN DIEGO DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS JOHN NASH AND THE ANALYSIS OF STRATEGIC BEHAVIOR BY VINCENT P. CRAWFORD DISCUSSION PAPER 2000-03 JANUARY 2000 John Nash and the Analysis
Is Democracy Possible?
 Is Democracy Possible? Nir Oren n.oren @abdn.ac.uk University of Aberdeen March 30, 2012 Nir Oren (Univ. Aberdeen) Democracy March 30, 2012 1 / 30 What are we talking about? A system of government by the
Is Democracy Possible? Nir Oren n.oren @abdn.ac.uk University of Aberdeen March 30, 2012 Nir Oren (Univ. Aberdeen) Democracy March 30, 2012 1 / 30 What are we talking about? A system of government by the
Public Choice. Slide 1
 Public Choice We investigate how people can come up with a group decision mechanism. Several aspects of our economy can not be handled by the competitive market. Whenever there is market failure, there
Public Choice We investigate how people can come up with a group decision mechanism. Several aspects of our economy can not be handled by the competitive market. Whenever there is market failure, there
Competitiveness of Legislative Elections in the United States: Impact of Redistricting Reform and Nonpartisan Elections
 Competitiveness of Legislative Elections in the United States: Impact of Redistricting Reform and Nonpartisan Elections Introduction Anti competitive state laws detract from the power and purpose of elections
Competitiveness of Legislative Elections in the United States: Impact of Redistricting Reform and Nonpartisan Elections Introduction Anti competitive state laws detract from the power and purpose of elections
THE PRESIDENTIAL NOMINATION CONTESTS May 18-23, 2007
 CBS NEWS/NEW YORK TIMES POLL For release: Thursday, May 24, 2007 6:30 P.M. EDT THE PRESIDENTIAL NOMINATION CONTESTS May 18-23, 2007 The current front-runners for their party's Presidential nomination Senator
CBS NEWS/NEW YORK TIMES POLL For release: Thursday, May 24, 2007 6:30 P.M. EDT THE PRESIDENTIAL NOMINATION CONTESTS May 18-23, 2007 The current front-runners for their party's Presidential nomination Senator
Topics on the Border of Economics and Computation December 18, Lecture 8
 Topics on the Border of Economics and Computation December 18, 2005 Lecturer: Noam Nisan Lecture 8 Scribe: Ofer Dekel 1 Correlated Equilibrium In the previous lecture, we introduced the concept of correlated
Topics on the Border of Economics and Computation December 18, 2005 Lecturer: Noam Nisan Lecture 8 Scribe: Ofer Dekel 1 Correlated Equilibrium In the previous lecture, we introduced the concept of correlated
Mathematics of Voting Systems. Tanya Leise Mathematics & Statistics Amherst College
 Mathematics of Voting Systems Tanya Leise Mathematics & Statistics Amherst College Arrow s Impossibility Theorem 1) No special treatment of particular voters or candidates 2) Transitivity A>B and B>C implies
Mathematics of Voting Systems Tanya Leise Mathematics & Statistics Amherst College Arrow s Impossibility Theorem 1) No special treatment of particular voters or candidates 2) Transitivity A>B and B>C implies
Math116Chap1VotingPart2.notebook January 12, Part II. Other Methods of Voting and Other "Fairness Criteria"
 Part II Other Methods of Voting and Other "Fairness Criteria" Plurality with Elimination Method Round 1. Count the first place votes for each candidate, just as you would in the plurality method. If a
Part II Other Methods of Voting and Other "Fairness Criteria" Plurality with Elimination Method Round 1. Count the first place votes for each candidate, just as you would in the plurality method. If a
Definition: Institution public system of rules which defines offices and positions with their rights and duties, powers and immunities p.
 RAWLS Project: to interpret the initial situation, formulate principles of choice, and then establish which principles should be adopted. The principles of justice provide an assignment of fundamental
RAWLS Project: to interpret the initial situation, formulate principles of choice, and then establish which principles should be adopted. The principles of justice provide an assignment of fundamental
Suppose that you must make choices that may influence the well-being and the identities of the people who will
 Priority or Equality for Possible People? Alex Voorhoeve and Marc Fleurbaey Suppose that you must make choices that may influence the well-being and the identities of the people who will exist, though
Priority or Equality for Possible People? Alex Voorhoeve and Marc Fleurbaey Suppose that you must make choices that may influence the well-being and the identities of the people who will exist, though
Elections and Voting Behavior
 Edwards, Wattenberg, and Lineberry Government in America: People, Politics, and Policy Fourteenth Edition Chapter 10 Elections and Voting Behavior How American Elections Work Three types of elections:
Edwards, Wattenberg, and Lineberry Government in America: People, Politics, and Policy Fourteenth Edition Chapter 10 Elections and Voting Behavior How American Elections Work Three types of elections:
TOP TWO CANDIDATES OPEN PRIMARY ACT
 TOP TWO CANDIDATES OPEN PRIMARY ACT BACKGROUND On June 8, 2010, California voters approved Proposition 14, which created the Top Two Candidates Open Primary Act. Allows all voters to choose any candidate
TOP TWO CANDIDATES OPEN PRIMARY ACT BACKGROUND On June 8, 2010, California voters approved Proposition 14, which created the Top Two Candidates Open Primary Act. Allows all voters to choose any candidate
Matthew Adler, a law professor at the Duke University, has written an amazing book in defense
 Well-Being and Fair Distribution: Beyond Cost-Benefit Analysis By MATTHEW D. ADLER Oxford University Press, 2012. xx + 636 pp. 55.00 1. Introduction Matthew Adler, a law professor at the Duke University,
Well-Being and Fair Distribution: Beyond Cost-Benefit Analysis By MATTHEW D. ADLER Oxford University Press, 2012. xx + 636 pp. 55.00 1. Introduction Matthew Adler, a law professor at the Duke University,
Arrow s Impossibility Theorem
 Arrow s Impossibility Theorem Some announcements Final reflections due on Monday. You now have all of the methods and so you can begin analyzing the results of your election. Today s Goals We will discuss
Arrow s Impossibility Theorem Some announcements Final reflections due on Monday. You now have all of the methods and so you can begin analyzing the results of your election. Today s Goals We will discuss
THE CAPABILITY APPROACH AS A HUMAN DEVELOPMENT PARADIGM AND ITS CRITIQUES
 THE CAPABILITY APPROACH AS A HUMAN DEVELOPMENT PARADIGM AND ITS CRITIQUES Nuno Martins Faculty of Economics and Management, Portuguese Catholic University, Porto, Portugal Keywords: capability approach,
THE CAPABILITY APPROACH AS A HUMAN DEVELOPMENT PARADIGM AND ITS CRITIQUES Nuno Martins Faculty of Economics and Management, Portuguese Catholic University, Porto, Portugal Keywords: capability approach,
Ethical Considerations on Quadratic Voting
 Ethical Considerations on Quadratic Voting Ben Laurence Itai Sher March 22, 2016 Abstract This paper explores ethical issues raised by quadratic voting. We compare quadratic voting to majority voting from
Ethical Considerations on Quadratic Voting Ben Laurence Itai Sher March 22, 2016 Abstract This paper explores ethical issues raised by quadratic voting. We compare quadratic voting to majority voting from
Partisan Advantage and Competitiveness in Illinois Redistricting
 Partisan Advantage and Competitiveness in Illinois Redistricting An Updated and Expanded Look By: Cynthia Canary & Kent Redfield June 2015 Using data from the 2014 legislative elections and digging deeper
Partisan Advantage and Competitiveness in Illinois Redistricting An Updated and Expanded Look By: Cynthia Canary & Kent Redfield June 2015 Using data from the 2014 legislative elections and digging deeper
CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web
 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Order Code RS20273 Updated January 17, 2001 The Electoral College: How it Works in Contemporary Presidential Elections Thomas H. Neale Analyst, American
CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Order Code RS20273 Updated January 17, 2001 The Electoral College: How it Works in Contemporary Presidential Elections Thomas H. Neale Analyst, American
Declaration of Conscience. Delivered 1 June 1950
 Margaret Chase Smith Declaration of Conscience Delivered 1 June 1950 Mr. President: I would like to speak briefly and simply about a serious national condition. It is a national feeling of fear and frustration
Margaret Chase Smith Declaration of Conscience Delivered 1 June 1950 Mr. President: I would like to speak briefly and simply about a serious national condition. It is a national feeling of fear and frustration
CRS Report for Congress
 Order Code RS20273 Updated September 8, 2003 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web The Electoral College: How It Works in Contemporary Presidential Elections Thomas H. Neale Government and
Order Code RS20273 Updated September 8, 2003 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web The Electoral College: How It Works in Contemporary Presidential Elections Thomas H. Neale Government and
Politics between Philosophy and Democracy
 Leopold Hess Politics between Philosophy and Democracy In the present paper I would like to make some comments on a classic essay of Michael Walzer Philosophy and Democracy. The main purpose of Walzer
Leopold Hess Politics between Philosophy and Democracy In the present paper I would like to make some comments on a classic essay of Michael Walzer Philosophy and Democracy. The main purpose of Walzer
U.S Presidential Election
 U.S Presidential Election The US has had an elected president since its constitution went into effect in 1789. Unlike in many countries, the Presidential election in the US is rather a year-long process
U.S Presidential Election The US has had an elected president since its constitution went into effect in 1789. Unlike in many countries, the Presidential election in the US is rather a year-long process
What is a political party?
 POLITICAL PARTIES What is a political party? A group of people who work to get candidates nominated to political offices. A political party can be thought of as an organized group that tries to control
POLITICAL PARTIES What is a political party? A group of people who work to get candidates nominated to political offices. A political party can be thought of as an organized group that tries to control
answers to some of the sample exercises : Public Choice
 answers to some of the sample exercises : Public Choice Ques 1 The following table lists the way that 5 different voters rank five different alternatives. Is there a Condorcet winner under pairwise majority
answers to some of the sample exercises : Public Choice Ques 1 The following table lists the way that 5 different voters rank five different alternatives. Is there a Condorcet winner under pairwise majority
A Rawlsian Paradigm Case
 Economic Staff Paper Series Economics 3-1976 A Rawlsian Paradigm Case Ray Gardner Iowa State University Follow this and additional works at: http://lib.dr.iastate.edu/econ_las_staffpapers Part of the Economic
Economic Staff Paper Series Economics 3-1976 A Rawlsian Paradigm Case Ray Gardner Iowa State University Follow this and additional works at: http://lib.dr.iastate.edu/econ_las_staffpapers Part of the Economic
Quiz # 5 Chapter 14 The Executive Branch (President)
 Quiz # 5 Chapter 14 The Executive Branch (President) 1. In a parliamentary system, the voters cannot choose a. their members of parliament. b. their prime minister. c. between two or more parties. d. whether
Quiz # 5 Chapter 14 The Executive Branch (President) 1. In a parliamentary system, the voters cannot choose a. their members of parliament. b. their prime minister. c. between two or more parties. d. whether
Chapter 14. The Causes and Effects of Rational Abstention
 Excerpts from Anthony Downs, An Economic Theory of Democracy. New York: Harper and Row, 1957. (pp. 260-274) Introduction Chapter 14. The Causes and Effects of Rational Abstention Citizens who are eligible
Excerpts from Anthony Downs, An Economic Theory of Democracy. New York: Harper and Row, 1957. (pp. 260-274) Introduction Chapter 14. The Causes and Effects of Rational Abstention Citizens who are eligible
Theorising the Democratic State. Elizabeth Frazer: Lecture 4. Who Rules? I
 Theorising the Democratic State Elizabeth Frazer: http://users.ox.ac.uk/~efrazer/default.htm Lecture 4 Who Rules? I The Elite Theory of Government Democratic Principles 1. Principle of autonomy: Individuals
Theorising the Democratic State Elizabeth Frazer: http://users.ox.ac.uk/~efrazer/default.htm Lecture 4 Who Rules? I The Elite Theory of Government Democratic Principles 1. Principle of autonomy: Individuals
Possible voting reforms in the United States
 Possible voting reforms in the United States Since the disputed 2000 Presidential election, there have numerous proposals to improve how elections are conducted. While most proposals have attempted to
Possible voting reforms in the United States Since the disputed 2000 Presidential election, there have numerous proposals to improve how elections are conducted. While most proposals have attempted to
Main idea: Voting systems matter.
 Voting Systems Main idea: Voting systems matter. Electoral College Winner takes all in most states (48/50) (plurality in states) 270/538 electoral votes needed to win (majority) If 270 isn t obtained -
Voting Systems Main idea: Voting systems matter. Electoral College Winner takes all in most states (48/50) (plurality in states) 270/538 electoral votes needed to win (majority) If 270 isn t obtained -
- 1- CORPORATE GOVERNANCE COMMITTEE CHARTER EFFECTIVE AS OF FEBRUARY 22, 2018
 - 1- CORPORATE GOVERNANCE COMMITTEE CHARTER EFFECTIVE AS OF FEBRUARY 22, 2018 This Corporate Governance Committee Charter (the Charter ) sets out the mandate and responsibilities for the Corporate Governance
- 1- CORPORATE GOVERNANCE COMMITTEE CHARTER EFFECTIVE AS OF FEBRUARY 22, 2018 This Corporate Governance Committee Charter (the Charter ) sets out the mandate and responsibilities for the Corporate Governance
Safe Votes, Sincere Votes, and Strategizing
 Safe Votes, Sincere Votes, and Strategizing Rohit Parikh Eric Pacuit April 7, 2005 Abstract: We examine the basic notion of strategizing in the statement of the Gibbard-Satterthwaite theorem and note that
Safe Votes, Sincere Votes, and Strategizing Rohit Parikh Eric Pacuit April 7, 2005 Abstract: We examine the basic notion of strategizing in the statement of the Gibbard-Satterthwaite theorem and note that
Social Choice Theory. Denis Bouyssou CNRS LAMSADE
 A brief and An incomplete Introduction Introduction to to Social Choice Theory Denis Bouyssou CNRS LAMSADE What is Social Choice Theory? Aim: study decision problems in which a group has to take a decision
A brief and An incomplete Introduction Introduction to to Social Choice Theory Denis Bouyssou CNRS LAMSADE What is Social Choice Theory? Aim: study decision problems in which a group has to take a decision
Federal Primary Election Runoffs and Voter Turnout Decline,
 Federal Primary Election Runoffs and Voter Turnout Decline, 1994-2010 July 2011 By: Katherine Sicienski, William Hix, and Rob Richie Summary of Facts and Findings Near-Universal Decline in Turnout: Of
Federal Primary Election Runoffs and Voter Turnout Decline, 1994-2010 July 2011 By: Katherine Sicienski, William Hix, and Rob Richie Summary of Facts and Findings Near-Universal Decline in Turnout: Of
Strategy in Law and Business Problem Set 1 February 14, Find the Nash equilibria for the following Games:
 Strategy in Law and Business Problem Set 1 February 14, 2006 1. Find the Nash equilibria for the following Games: A: Criminal Suspect 1 Criminal Suspect 2 Remain Silent Confess Confess 0, -10-8, -8 Remain
Strategy in Law and Business Problem Set 1 February 14, 2006 1. Find the Nash equilibria for the following Games: A: Criminal Suspect 1 Criminal Suspect 2 Remain Silent Confess Confess 0, -10-8, -8 Remain
Learning and Belief Based Trade 1
 Learning and Belief Based Trade 1 First Version: October 31, 1994 This Version: September 13, 2005 Drew Fudenberg David K Levine 2 Abstract: We use the theory of learning in games to show that no-trade
Learning and Belief Based Trade 1 First Version: October 31, 1994 This Version: September 13, 2005 Drew Fudenberg David K Levine 2 Abstract: We use the theory of learning in games to show that no-trade
1.6 Arrow s Impossibility Theorem
 1.6 Arrow s Impossibility Theorem Some announcements Homework #2: Text (pages 33-35) 51, 56-60, 61, 65, 71-75 (this is posted on Sakai) For Monday, read Chapter 2 (pages 36-57) Today s Goals We will discuss
1.6 Arrow s Impossibility Theorem Some announcements Homework #2: Text (pages 33-35) 51, 56-60, 61, 65, 71-75 (this is posted on Sakai) For Monday, read Chapter 2 (pages 36-57) Today s Goals We will discuss
American Government & Civics - Course Practices and Skills
 American Government & Civics - Course Practices and Skills I. Civic Participation 1. Demonstrate respect for the rights of others in discussions and classroom; respectfully disagree with other viewpoints
American Government & Civics - Course Practices and Skills I. Civic Participation 1. Demonstrate respect for the rights of others in discussions and classroom; respectfully disagree with other viewpoints
Marist College Institute for Public Opinion Poughkeepsie, NY Phone Fax
 Marist College Institute for Public Opinion Poughkeepsie, NY 12601 Phone 845.575.5050 Fax 845.575.5111 www.maristpoll.marist.edu Hillary Clinton s Re-election Prospects and More EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE:
Marist College Institute for Public Opinion Poughkeepsie, NY 12601 Phone 845.575.5050 Fax 845.575.5111 www.maristpoll.marist.edu Hillary Clinton s Re-election Prospects and More EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE:
Amy Tenhouse. Incumbency Surge: Examining the 1996 Margin of Victory for U.S. House Incumbents
 Amy Tenhouse Incumbency Surge: Examining the 1996 Margin of Victory for U.S. House Incumbents In 1996, the American public reelected 357 members to the United States House of Representatives; of those
Amy Tenhouse Incumbency Surge: Examining the 1996 Margin of Victory for U.S. House Incumbents In 1996, the American public reelected 357 members to the United States House of Representatives; of those
