PRINCIPLES OF SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT - Vol. II Social Development Information and Knowledge - Marie France Jarret, Règis Mahieu
|
|
|
- Reginald Sherman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SOCIAL DEVELOPMENT INFORMATION AND KNOWLEDGE Marie France Jarret Université du Maine, France Règis Mahieu Université de Versailles, France Keywords: Social development, human development, social indicators, poverty, social sustainability, gender, vulnerability, survey, inequity, deprivation, envy, justice, targeted allocation, universal allocation, social income, social capital, altruism. Contents 1. Introduction 2. Social Development Information 2.1 Social Indicators Single Social Indicators Synthetic Social Indicators Indicators of Poverty The Missing Indicators 2.2 Statistical Basis The Information Sources Inequity, Deprivation, Envy and Justice 3. Knowledge about Social Sustainability, Possibilities and Limits 3.1 The Types of Allocations and Limits of a Poverty Policy Targeted Allocation and Universal Allocation Some Inefficiencies of the Economic Policy Community Societies Individual Societies: Politics of Displacement and Ethnocide The Social Situation may be Analyzed by Poverty but the Analyses have not yet been Accomplished 3.2 Social Sustainability Potential Social Capital and Social Configuration Social Capital as an Effective Advanced Capital Measuring Advanced Social Capital 4. Conclusion Glossary Bibliography Biographical Sketches Summary Social development is firstly a problem of information that will allow the construction of social indicators, either single indicators or synthetic indicators, relating to the quality of life, or finally, indicators relating to poverty. These indicators are incomplete, especially as far as sustainable livelihoods or vulnerability are concerned. It remains very difficult to evaluate such problems as inequity, deprivation, envy, and justice. For
2 this reason, social development is a problem of knowledge, especially concerning social sustainability. How can redistributive, targeted or universal, allocations best be conceptualized? This problem has become more complex when taking into account social capital, implying as it does, the introduction of a compensation principle in social development. 1. Introduction This introductory section starts with a quotation from the World Summit for Social Development held in Copenhagen in 1995: Social development is inseparable from the cultural, ecological, economic, political and spiritual environment in which it takes place. It cannot be pursued as a sectoral initiative. Social development is also clearly linked to the development of peace, freedom, stability and security, both nationally and internationally. To promote social development requires an orientation of values, objectives and priorities towards the well-being of all and the strengthening and promotion of conducive institutions and policies (United Nations 1995). Also, quoting from the World Bank (1999): by promoting socially sustainable development, the World Bank strives to ensure that people, their cultures and societies, and their organizations and institutions are taken into account in the process of economic development. It also helps ensure that development improves the lives of people, especially the poor. These quotations show that social development may be interpreted in several ways: from the strict point of view of social indicators, of well-being, or from a much larger point of view, concerning social life and the state of the society for instance the level of social capital. But social development is highly concerned with the validity of social indicators and especially with the existence of poverty lines. These indicators often depend on hypotheses coming from social knowledge. How can sustainable social development be conceived and precautionary principles be laid down in this field? Social environment is not a priori benevolent and efficient, and the tools of ecological economics cannot be transposed directly into the social environment. 2. Social Development Information Which indicators and which pieces of information are basic to constructing the social dashboard of an economy? This is a problem of priority between social indicators and availability of statistical sources. 2.1 Social Indicators Several kinds of indicator are used: single social indicators relating to one variable, or synthetic social indicators, which refer to several economic and social variables considered together, and indicators of poverty.
3 2.1.1 Single Social Indicators Gross National Product per capita The World Bank s main criterion for classifying economies is gross national product (GNP) per capita. According to the (1997) figures for GNP per capita, economies are divided among four (annual) income groups: low-income ($785 or less), lower middle income ($ ), upper-middle-income ($ ) or high-income ($9656 or more). This indicator is the reference for the mainstream, pro growth school : the larger the pie, the better everyone s share will be. But the inequality approach and the well-known Kuznets law (growth, for a time, may accentuate poverty, Kuznets 1995) contest this. This economic indicator becomes social as soon as considerations about income distribution and consequently on economic and social inequality are taken into account. The most widely used single measure of income inequality is the Gini index; this measures the extent to which the distribution of income (or, in some cases, consumption expenditure) among individuals or households within an economy deviates from a perfectly equal distribution. Another measure of the dispersion of income is the percentage share of income or consumption that accrues to quintiles or deciles of the population ranked by income or consumption. GNP per capita still must be corrected to take into account the marginal utility of the money unit: the dollar utility is very different between the rich and poor. Some methods are used to include this in the equation, which subsequently modifies a lot the comparisons for social development Quality of Life The World Bank considers quality of life through various indicators: growth of private consumption per capita, prevalence of child malnutrition, under-5 mortality rate, life expectancy at birth, adult illiteracy rate, urban population, access to sanitation in urban areas Education and Health Two other social indicators are considered: education, and health. Education is first measured by public expenditure, and then considered in terms of levels of enrolment of children in primary and secondary school or of attainments in the overall educational process. In the same way, health is first a question of public expenditure and then a problem of accessibility to safe water, sanitation, and contraception. Traditional demographic indicators are fertility rate and maternal mortality ratio. Housing and other measures of quality of life such as suicide or criminality, environment management, gender discrimination, appear in the United Nations
4 Development Program (UNDP) annual report and adjust the World Bank indicators toward a human conception of development Synthetic Social Indicators Human Development Index The main indicator is the Human Development Index (HDI), first published by the UNPD in 1990 and since constructed every year, even though there have been a number of changes made to the way it is constructed. The purpose of the HDI is to capture achievements in basic human capabilities (i.e., the basic capacities which enable people to function), which are measured by the average level reached by a country according to three main criteria for human development: longevity, educational attainment and standard of living. Longevity is measured through life expectancy at birth, education as a composite of two thirds of adult illiteracy and one third of enrolment of the children, and standard of living through the gross domestic product (GDP) per capita measured at purchasing power parity rate (PPP). The value of each one of these components is normalized, so that the HDI value ranges from zero to one. The difference between the value achieved by a country and one the maximum possible shows how far the country has to go. One of the main interests of HDI is to rank the countries and to compare them with their ranking according to GDP: the link between economic prosperity and human development is neither automatic, nor obvious. Table 1 indicates the most significant distances between HDI and GDP. Countries Ranking Distance HDI according to HDI HDI/GDP High HDI Canada United States Sweden Australia Switzerland Denmark Luxembourg The most significant negative distances Kuwait Saudi Arabia Oman South Africa Namibia Botswana Gabon
5 The most significant positive distances Cuba Macedonia Georgia Azerbaijan Moldova Tajikistan Mongolia Source: From UNDP 1999 Table 1. The most significant distances between HDI and GDP The Human Development Report (1995) introduced two new measures of human development that highlight the status of women. The Gender-related Development Index (GDI) measures achievement in the same basic capabilities as the HDI does, but takes note of inequality in achievement between women and men. The methodology used imposes a penalty for inequality, such that the GDI falls when the achievement levels of both women and men in a country go down or when the disparity between their achievements increases. The greater the gender disparity in basic capabilities, the lower a country s GDI compared with its HDI. The GDI is simply the HDI discounted, or adjusted downwards, for gender inequality. Thus the GDI reflects gender imbalances in basic health, education and income. The Gender Empowerment Measure (GEM) evaluates progress in advancing women at the political and economic level. It examines whether women and men are able to participate actively in economic and political life and take part in decision-making. While the GDI focuses on expansion of capabilities, the GEM is concerned with the use of those capabilities to take advantage of the opportunities of life Human Poverty Index The Human Poverty Index (HPI) was introduced in 1997 for developing countries and focuses on those groups whose choices are heavily constrained in the three areas of the HDI: longevity, knowledge, and standard of living. Rather than measuring poverty by income, the HPI uses indicators of the most basic dimensions of deprivation: a short life, lack of basic education, and lack of access to public and private resources. The first deprivation relates to survival, the vulnerability to death at a relatively early age, and is represented in the HPI by the percentage of people expected to die before the age of forty. The second dimension relates to knowledge, being excluded from the world of reading and communication, and is measured by the percentage of adults who are illiterate. The third aspect relates to standard of living, in particular, overall economic provisioning.
6 This is represented by a composite of three variables: the percentage of people with access to health services and to safe water, and the percentage of malnourished children under five. UNDP includes unemployment only in the industrialized country poverty index (HPI- 2), calculated since This shows that human poverty does not strike only developing countries, and particularly, that a high HDI does not constitute a guarantee against poverty (for example, in the United States, human poverty strikes 16.5% of the population) Indicators of Poverty Poverty Line Social situation is often summarized by the poverty line drawn between those who fall below this line, the poor and the others, the non-poor, with a norm of real income. For instance, the World Bank underlines the need for a universal poverty line which permits cross-country comparisons. In this objective, the World Bank has estimated a standard threshold of one dollar per person a day, measured in 1985 international prices and adjusted to local currency using PPP conversion factors, according to the method of the basic needs. Basic needs are said to include both minimum requirements of a family for private consumption (food, shelter, clothing), and essential services provided by and for the community (safe water, sanitation facilities, health, education). With an estimation of $370 PPP per person and per year, it has provided a plausible and useful indicator which is simple to understand and apply a dollar a person a day which is not assumed to be applicable to countries other than the poorest. The poverty line only indicates who is poor and who is not. But it is also necessary to know how much poverty there is, both in the country as a whole and among particular groups. This is given by various poverty measures Poverty Head Count The poverty head count is the simplest measure of poverty: it tells how many are poor. According to the World Bank, nearly 1200 million of the world population are poor Poverty Head-Count Ratio The poverty head-count ratio refers to the proportion of the population that falls under the poverty line (25% of the world s population); it provides information on the incidence of poverty among the population. If q is the number of people identified as poor and n the total population, then the head-count ratio is: H = q/n
7 Poverty Gap The poverty gap is calculated as the average income shortfall (I) of the poor from the poverty line, expressed as a percentage of the poverty line. The measure reflects the depth of poverty. ( z = yi ) I 1 q i z where z is the poverty line, and y i is the income of the ith poor (i = 1,, q) where q is the number of poor Poverty Gap Index The poverty gap index (PGI) is defined as the proportionate poverty gap normalized to the total population size. ( z y PGI n i ) = 1 / = H I i z Calculated in this way, the various poverty indicators inform on the different aspects of poverty, but not all at once. A class of comprehensive poverty measures has been developed, which takes into account these components simultaneously, and also, importantly, adds one more: the inequality among the poor Foster, Greer and Thorbecke (FGT) Index The FGT index (P α ) is defined as: P α 1 = n i ( z y z i ) α with y i, q, n and z defined as above, and α the aversion degree against poverty. This index allows estimation of the distribution between the poorest of the poor and the richest of the poor, taking in account the altruistic behavior (sympathy or aversion) aroused by this distribution. The aversion against poverty or propensity to altruism, noted as α, has a normative value that can be set at different levels; a higher α gives more weight to the poorest. The value of α (for instance being materialized by transfers or pluri-activity on segmented markets) determines the position of the index. If there are many FGT indexes, the volatility of the poverty they imply is very high according to the types of allocations. This FGT index enlightens the Smithian linen shirt paradox. In its modern version, this paradox shows that the marginal dollar for assistance will play around the poverty line without any effect on the poorest of the poor.
8 - - - TO ACCESS ALL THE 27 PAGES OF THIS CHAPTER, Visit: Bibliography Atkinson A. B. (1989). Poverty in social economics. The New Palgrave: A Dictionary of Economics, London: Norton and Company. [A classic paper on inequity.] Ballet J. and Mahieu F. R. (2000). Social Capital: an Ambiguous Concept for Development Economics, 25 pp. Cahiers du C3ED. Guyancourt: Centre d économie et d éthique pour l environnement et le développement, Université de Versailles-Saint Quentin en Yvelines. [This paper presents an alternative version of the World Bank theory of social capital.] Becker G. (1974). A theory of social interaction. Journal of Political Economy 82(6), [The seminal paper on social interaction analysis.] Chambers R. (1989). Editorial Introduction: Vulnerability, Coping and Policy. IDS Bulletin, April Vol (20), No 2, 4. Sussex: Institute of Development Studies. [One of the few texts showing the potential opposition between fight against poverty and vulnerability.] Deaton A. (1997). The Analysis of Household Surveys. A Microeconometric Approach to Development Policy, 479 pp. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press (published for The World Bank, Washington). [A classic of the microeconomic analysis of distribution.] Easterly W. and Levine R. (1997). Africa s growth tragedy, policies and ethnic division. Quarterly Journal of Economics 112(4), [One of the first texts on the negative relation between ethnic groups and development.] Foster J. Greer J. and Thorbecke E. (1984). A class of decomposable poverty measures. Econometrica 52(1), [The seminal text on poverty measure.] Gale W. G. and Scholz J. K. (1994). Intergenerational transfers and the accumulation of wealth. Journal of Economic Perspectives 8(4), [The text that revealed the importance of inter vivos transfers in the United States.] Kuznets S. (1955). Economic growth and income inequality. American Economic Review 65, [The seminal text on the relation between economic growth and inequities.] Mahieu F. R. and Rapoport H. (1998). Altruisme: analyses économiques, 294 pp. Paris: Economica. [This book presents the first synthesis in French on altruism.] Rawls J. (1971). A Theory of Justice, 538 pp. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. [The book on economic analysis of justice.] Sen A. K. (1973). On Economic Inequality, 260 pp. Oxford: Oxford University Press. [A classic book on the measure of inequalities.] Sen A. K. (1981). Poverty and Famines: An Essay on Entitlement and Deprivation, 270 pp. New York: Oxford University Press. [This book presents the new theory of famine and more generally of poverty.] United Nations (1995). The Copenhagen Declaration and Program of Action: World Summit for Social Development, 6 12 March New York: UN Department of Publications. [The general conclusions of the Copenhagen World Summit for Social Development are reported.]
9 United Nations Development Programme (1990). Human Development Report: Definition and Measure of Human Development, July, 160 pp. Oxford University Press. [For the first time a presentation of the concept of human development and its measure] World Bank (1999). World Development Report 1998/99, 264 pp. Washington, DC: World Bank. [A comprehensive World Development Report for the year 1998/99.] Biographical Sketches Marie-France Jarret is assistant professor in economics at the University of Maine, France. She teaches development economics, international trade and European integration thought in graduate and postgraduate programs. She obtained a Master of Economics degree at Grenoble-II University and a Ph.D. at the same university, after two years spent at Jawaharlal Nehru University, India. She also taught at the University of Abidjan, Côte d Ivoire, from 1979 to She has written books on economics and public economics, and papers on economic development in academic reviews. She is carrying out research as an associate member of the Centre d économie et d éthique pour l environnement et le développement (C3ED), France. Francois Règis Mahieu is Professeur de Sciences Economiques à l Université de Versailles St Quentin en Yvelines (France). He is professor in economics at the University of Versailles. He teaches development economics, public economics and history of economic thought in graduate and postgraduate programs. He obtained a Master of Economics degree at Paris I-Sorbonne, and a Ph.D. at the University of Paris-Nanterre, and was elected as a full professor in He also taught at the Universities of Abidjan, Côte d Ivoire, from 1979 to 1989, Paris I-Sorbonne (1989), and Lille ( ). He did a six month sabbatical in Louvain la Neuve, Belgium (1994). He has written books on economics, ethics, logic and public economics, and many papers on these topics in academic reviews. He is administrator of two French scientific societies: Association Française de Science Economique, and Association Charles Gide. He is carrying out research at the Centre d économie et d éthique pour l environnement et le développement (C3ED), France.
Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices. Armenia. HDI values and rank changes in the 2014 Human Development Report
 Human Development Report 2014 Sustaining Human Progress: Reducing Vulnerabilities and Building Resilience Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices Armenia HDI values and
Human Development Report 2014 Sustaining Human Progress: Reducing Vulnerabilities and Building Resilience Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices Armenia HDI values and
Sri Lanka. Country coverage and the methodology of the Statistical Annex of the 2015 HDR
 Human Development Report 2015 Work for human development Briefing note for countries on the 2015 Human Development Report Sri Lanka Introduction The 2015 Human Development Report (HDR) Work for Human Development
Human Development Report 2015 Work for human development Briefing note for countries on the 2015 Human Development Report Sri Lanka Introduction The 2015 Human Development Report (HDR) Work for Human Development
Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices. Belarus. HDI values and rank changes in the 2014 Human Development Report
 Human Development Report 2014 Sustaining Human Progress: Reducing Vulnerabilities and Building Resilience Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices Belarus HDI values and
Human Development Report 2014 Sustaining Human Progress: Reducing Vulnerabilities and Building Resilience Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices Belarus HDI values and
The former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia
 Human Development Report 2014 Sustaining Human Progress: Reducing Vulnerabilities and Building Resilience Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices The former Yugoslav HDI
Human Development Report 2014 Sustaining Human Progress: Reducing Vulnerabilities and Building Resilience Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices The former Yugoslav HDI
Venezuela (Bolivarian Republic of)
 Human Development Report 2013 The Rise of the South: Human Progress in a Diverse World Explanatory note on 2013 HDR composite indices Venezuela (Bolivarian HDI values and rank changes in the 2013 Human
Human Development Report 2013 The Rise of the South: Human Progress in a Diverse World Explanatory note on 2013 HDR composite indices Venezuela (Bolivarian HDI values and rank changes in the 2013 Human
Venezuela (Bolivarian Republic of)
 Human Development Report 2014 Sustaining Human Progress: Reducing Vulnerabilities and Building Resilience Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices Venezuela (Bolivarian HDI
Human Development Report 2014 Sustaining Human Progress: Reducing Vulnerabilities and Building Resilience Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices Venezuela (Bolivarian HDI
Human Development Indices and Indicators: 2018 Statistical Update. Eritrea
 Human Development Indices and Indicators: 2018 Statistical Update Briefing note for countries on the 2018 Statistical Update Introduction Eritrea This briefing note is organized into ten sections. The
Human Development Indices and Indicators: 2018 Statistical Update Briefing note for countries on the 2018 Statistical Update Introduction Eritrea This briefing note is organized into ten sections. The
Human Development Indices and Indicators: 2018 Statistical Update. Pakistan
 Human Development Indices and Indicators: 2018 Statistical Update Briefing note for countries on the 2018 Statistical Update Introduction Pakistan This briefing note is organized into ten sections. The
Human Development Indices and Indicators: 2018 Statistical Update Briefing note for countries on the 2018 Statistical Update Introduction Pakistan This briefing note is organized into ten sections. The
Lao People's Democratic Republic
 Human Development Report 2014 Sustaining Human Progress: Reducing Vulnerabilities and Building Resilience Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices Democratic Republic HDI
Human Development Report 2014 Sustaining Human Progress: Reducing Vulnerabilities and Building Resilience Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices Democratic Republic HDI
Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices. Dominican Republic
 Human Development Report 2014 Sustaining Human Progress: Reducing Vulnerabilities and Building Resilience Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices Dominican Republic HDI
Human Development Report 2014 Sustaining Human Progress: Reducing Vulnerabilities and Building Resilience Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices Dominican Republic HDI
Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices. Palestine, State of
 Human Development Report 2014 Sustaining Human Progress: Reducing Vulnerabilities and Building Resilience Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices Palestine, State of HDI
Human Development Report 2014 Sustaining Human Progress: Reducing Vulnerabilities and Building Resilience Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices Palestine, State of HDI
A COMPARATIVE HUMAN DEVELOPMENT INDEX (HDI) AMONG ASEAN COUNTRIES: THE ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT REPERCUSSIONS OF THE 2009 REPORT TO ASEAN COUNTRIES
 A COMPARATIVE HUMAN DEVELOPMENT INDEX (HDI) AMONG ASEAN COUNTRIES: THE ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT REPERCUSSIONS OF THE 2009 REPORT TO ASEAN COUNTRIES Introduction Caroline Mariñas Acosta, Dip. in R&D, MBA, Ph.D.
A COMPARATIVE HUMAN DEVELOPMENT INDEX (HDI) AMONG ASEAN COUNTRIES: THE ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT REPERCUSSIONS OF THE 2009 REPORT TO ASEAN COUNTRIES Introduction Caroline Mariñas Acosta, Dip. in R&D, MBA, Ph.D.
Hong Kong, China (SAR)
 Human Development Report 2014 Sustaining Human Progress: Reducing Vulnerabilities and Building Resilience Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices Hong Kong, China (SAR)
Human Development Report 2014 Sustaining Human Progress: Reducing Vulnerabilities and Building Resilience Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices Hong Kong, China (SAR)
Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices. Cambodia. HDI values and rank changes in the 2014 Human Development Report
 Human Development Report 2014 Sustaining Human Progress: Reducing Vulnerabilities and Building Resilience Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices Cambodia HDI values and
Human Development Report 2014 Sustaining Human Progress: Reducing Vulnerabilities and Building Resilience Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices Cambodia HDI values and
Albania. HDI values and rank changes in the 2013 Human Development Report
 Human Development Report 2013 The Rise of the South: Human Progress in a Diverse World Explanatory note on 2013 HDR composite indices Albania HDI values and rank changes in the 2013 Human Development Report
Human Development Report 2013 The Rise of the South: Human Progress in a Diverse World Explanatory note on 2013 HDR composite indices Albania HDI values and rank changes in the 2013 Human Development Report
Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices. Solomon Islands
 Human Development Report 2014 Sustaining Human Progress: Reducing Vulnerabilities and Building Resilience Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices Solomon Islands HDI values
Human Development Report 2014 Sustaining Human Progress: Reducing Vulnerabilities and Building Resilience Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices Solomon Islands HDI values
Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices. Serbia. HDI values and rank changes in the 2014 Human Development Report
 Human Development Report 2014 Sustaining Human Progress: Reducing Vulnerabilities and Building Resilience Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices Serbia HDI values and rank
Human Development Report 2014 Sustaining Human Progress: Reducing Vulnerabilities and Building Resilience Explanatory note on the 2014 Human Development Report composite indices Serbia HDI values and rank
Hungary. HDI values and rank changes in the 2013 Human Development Report
 Human Development Report 2013 The Rise of the South: Human Progress in a Diverse World Explanatory note on 2013 HDR composite indices Hungary HDI values and rank changes in the 2013 Human Development Report
Human Development Report 2013 The Rise of the South: Human Progress in a Diverse World Explanatory note on 2013 HDR composite indices Hungary HDI values and rank changes in the 2013 Human Development Report
Human Development Indices and Indicators: 2018 Statistical Update. Cambodia
 Human Development Indices and Indicators: 2018 Statistical Update Briefing note for countries on the 2018 Statistical Update Introduction Cambodia This briefing note is organized into ten sections. The
Human Development Indices and Indicators: 2018 Statistical Update Briefing note for countries on the 2018 Statistical Update Introduction Cambodia This briefing note is organized into ten sections. The
Human Development Indices and Indicators: 2018 Statistical Update. Indonesia
 Human Development Indices and Indicators: 2018 Statistical Update Briefing note for countries on the 2018 Statistical Update Introduction Indonesia This briefing note is organized into ten sections. The
Human Development Indices and Indicators: 2018 Statistical Update Briefing note for countries on the 2018 Statistical Update Introduction Indonesia This briefing note is organized into ten sections. The
Lecture 1. Introduction
 Lecture 1 Introduction In this course, we will study the most important and complex economic issue: the economic transformation of developing countries into developed countries. Most of the countries in
Lecture 1 Introduction In this course, we will study the most important and complex economic issue: the economic transformation of developing countries into developed countries. Most of the countries in
Poverty in the Third World
 11. World Poverty Poverty in the Third World Human Poverty Index Poverty and Economic Growth Free Market and the Growth Foreign Aid Millennium Development Goals Poverty in the Third World Subsistence definitions
11. World Poverty Poverty in the Third World Human Poverty Index Poverty and Economic Growth Free Market and the Growth Foreign Aid Millennium Development Goals Poverty in the Third World Subsistence definitions
Measures of Poverty. Foster-Greer-Thorbecke(FGT) index Example: Consider an 8-person economy with the following income distribution
 Foster-Greer-Thorbecke(FGT) index Example: Consider an 8-person economy with the following income distribution Individuals Income 1 0.6 2 0.6 3 0.8 4 0.8 5 2 6 2 7 6 8 6 Poverty line= 1 Recall that Headcount
Foster-Greer-Thorbecke(FGT) index Example: Consider an 8-person economy with the following income distribution Individuals Income 1 0.6 2 0.6 3 0.8 4 0.8 5 2 6 2 7 6 8 6 Poverty line= 1 Recall that Headcount
CIE Economics A-level
 CIE Economics A-level Topic 4: The Macroeconomy c) Classification of countries Notes Indicators of living standards and economic development The three dimensions of the Human Development Index (HDI) The
CIE Economics A-level Topic 4: The Macroeconomy c) Classification of countries Notes Indicators of living standards and economic development The three dimensions of the Human Development Index (HDI) The
INEQUALITY AMONG WOMEN AND ITS IMPACT ON ECONOMIC GROWTH: THE CASE OF MENA
 INEQUALITY AMONG WOMEN AND ITS IMPACT ON ECONOMIC GROWTH: THE CASE OF MENA D. Hosni Associate Professor and Chair, Department of Economics, University of Central Florida, Orlando,USA M. Sandberg and A.
INEQUALITY AMONG WOMEN AND ITS IMPACT ON ECONOMIC GROWTH: THE CASE OF MENA D. Hosni Associate Professor and Chair, Department of Economics, University of Central Florida, Orlando,USA M. Sandberg and A.
Contents. List of Figures List of Maps List of Tables List of Contributors. 1. Introduction 1 Gillette H. Hall and Harry Anthony Patrinos
 Contents List of Figures List of Maps List of Tables List of Contributors page vii ix x xv 1. Introduction 1 Gillette H. Hall and Harry Anthony Patrinos 2. Indigenous Peoples and Development Goals: A Global
Contents List of Figures List of Maps List of Tables List of Contributors page vii ix x xv 1. Introduction 1 Gillette H. Hall and Harry Anthony Patrinos 2. Indigenous Peoples and Development Goals: A Global
Growth and Poverty Reduction: An Empirical Analysis Nanak Kakwani
 Growth and Poverty Reduction: An Empirical Analysis Nanak Kakwani Abstract. This paper develops an inequality-growth trade off index, which shows how much growth is needed to offset the adverse impact
Growth and Poverty Reduction: An Empirical Analysis Nanak Kakwani Abstract. This paper develops an inequality-growth trade off index, which shows how much growth is needed to offset the adverse impact
Online Supplementary Document
 Online Supplementary Document Calu Costa et al. Gender bias in careseeking practices in 57 low and middle income countries J Glob Health 2017;7:010418 Supplementary Table 1 - Careseeking questions in DHS
Online Supplementary Document Calu Costa et al. Gender bias in careseeking practices in 57 low and middle income countries J Glob Health 2017;7:010418 Supplementary Table 1 - Careseeking questions in DHS
The Real Wealth of Nations: Pathways to Human Development
 The Real Wealth of Nations: Pathways to Human Development Quality of Life Indices and Innovations in the 2010 Human Development Report International Society of Quality of Life Studies December 9, 2010,
The Real Wealth of Nations: Pathways to Human Development Quality of Life Indices and Innovations in the 2010 Human Development Report International Society of Quality of Life Studies December 9, 2010,
Inclusive global growth: a framework to think about the post-2015 agenda
 Inclusive global growth: a framework to think about the post-215 agenda François Bourguignon Paris School of Economics Angus Maddison Lecture, Oecd, Paris, April 213 1 Outline 1) Inclusion and exclusion
Inclusive global growth: a framework to think about the post-215 agenda François Bourguignon Paris School of Economics Angus Maddison Lecture, Oecd, Paris, April 213 1 Outline 1) Inclusion and exclusion
Economic and Social Council
 United Nations Economic and Social Council Distr.: General 27 December 2001 E/CN.3/2002/27 Original: English Statistical Commission Thirty-third session 5-8 March 2002 Item 7 (f) of the provisional agenda*
United Nations Economic and Social Council Distr.: General 27 December 2001 E/CN.3/2002/27 Original: English Statistical Commission Thirty-third session 5-8 March 2002 Item 7 (f) of the provisional agenda*
Outline: Poverty, Inequality, and Development
 1 Poverty, Inequality, and Development Outline: Measurement of Poverty and Inequality Economic characteristics of poverty groups Why is inequality a problem? Relationship between growth and inequality
1 Poverty, Inequality, and Development Outline: Measurement of Poverty and Inequality Economic characteristics of poverty groups Why is inequality a problem? Relationship between growth and inequality
REVENUE FROM EXPORTING OIL, INCOME DISTRIBUTION, AND ECONOMIC PROGRESS IN THE MIDDLE EAST
 REVENUE FROM EXPORTING OIL, INCOME DISTRIBUTION, AND ECONOMIC PROGRESS IN THE MIDDLE EAST Mehdi MOHAGHEGH School of Business and Management, Norwich University, 158 Harmon Dr. Northfield, Vermont, 05663,
REVENUE FROM EXPORTING OIL, INCOME DISTRIBUTION, AND ECONOMIC PROGRESS IN THE MIDDLE EAST Mehdi MOHAGHEGH School of Business and Management, Norwich University, 158 Harmon Dr. Northfield, Vermont, 05663,
POVERTY AND INEQUALITY IN SOUTH AFRICA AND THE WORLD
 SOUTH AFRICAN ACTUARIAL JOURNAL 117 60 POVERTY AND INEQUALITY IN SOUTH AFRICA AND THE WORLD By P Govender, N Kambaran, N Patchett, A Ruddle, G Torr and N van Zyl ABSTRACT This article begins with a discussion
SOUTH AFRICAN ACTUARIAL JOURNAL 117 60 POVERTY AND INEQUALITY IN SOUTH AFRICA AND THE WORLD By P Govender, N Kambaran, N Patchett, A Ruddle, G Torr and N van Zyl ABSTRACT This article begins with a discussion
I. Summary. By Ms. Aysegul Tugce BEYCAN
 Ph.D. Thesis Project for Department of Sociology at University of Neuchatel The multidimensional nature of poverty in upper- middle- income countries: How we can improve the poverty indexes? By Ms. Aysegul
Ph.D. Thesis Project for Department of Sociology at University of Neuchatel The multidimensional nature of poverty in upper- middle- income countries: How we can improve the poverty indexes? By Ms. Aysegul
Poverty, Growth and Inequality in Some Arab Countries
 Interim Report for Household Expenditure Patterns in Egypt during the 2000s, IDE-JETRO, 2016 Poverty, Growth and Inequality in Some Arab Countries Dina M. Armanious 1 1. Introduction Poverty eradication
Interim Report for Household Expenditure Patterns in Egypt during the 2000s, IDE-JETRO, 2016 Poverty, Growth and Inequality in Some Arab Countries Dina M. Armanious 1 1. Introduction Poverty eradication
Knowledge. Life expectancy at birth. Adult literacy rate. Adult literacy index. Life expectancy index. Knowledge. Adult illiteracy rate
 TECHNICAL NOTE 1 CALCULATING THE HUMAN DEVELOPMENT INDICES The diagrams here offer a clear overview of how the five human development indices used in the Human Development Report are constructed, highlighting
TECHNICAL NOTE 1 CALCULATING THE HUMAN DEVELOPMENT INDICES The diagrams here offer a clear overview of how the five human development indices used in the Human Development Report are constructed, highlighting
A PERIODICAL CHANGE OF HUMAN DEVELOPMENT IN INDIA IN COMPARISION WITH SURRONDING COUNTRIES
 A PERIODICAL CHANGE OF HUMAN DEVELOPMENT IN INDIA IN COMPARISION WITH SURRONDING Surajit Let Ex-Research Scholar, Dept. of Geography, Visva-Bharati, Santiniketan, W. B. Received Oct. 05, 2017 Accepted
A PERIODICAL CHANGE OF HUMAN DEVELOPMENT IN INDIA IN COMPARISION WITH SURRONDING Surajit Let Ex-Research Scholar, Dept. of Geography, Visva-Bharati, Santiniketan, W. B. Received Oct. 05, 2017 Accepted
THE POLITICAL ECONOMY OF HUMAN DEVELOPMENT: A COMPARATIVE STUDY BETWEEN THE TWELVE MEMBERS OF THE EUROPEAN UNION AND TURKEY
 Ege Akademik Bakış / Ege Academic Review 9 (1) 2009: 231-249 THE POLITICAL ECONOMY OF HUMAN DEVELOPMENT: A COMPARATIVE STUDY BETWEEN THE TWELVE MEMBERS OF THE EUROPEAN UNION AND TURKEY Assist.Prof.Dr.
Ege Akademik Bakış / Ege Academic Review 9 (1) 2009: 231-249 THE POLITICAL ECONOMY OF HUMAN DEVELOPMENT: A COMPARATIVE STUDY BETWEEN THE TWELVE MEMBERS OF THE EUROPEAN UNION AND TURKEY Assist.Prof.Dr.
Briefing Paper Series No Overview of Poverty in Sri Lanka
 Briefing Paper Series No 13 2013 Overview of Poverty in Sri Lanka - 2013 Overview of Poverty in Sri Lanka - 2013 Shakeela Jabbar and Dinushka Senanayake revised by Ishara Rathnayake A Centre for Poverty
Briefing Paper Series No 13 2013 Overview of Poverty in Sri Lanka - 2013 Overview of Poverty in Sri Lanka - 2013 Shakeela Jabbar and Dinushka Senanayake revised by Ishara Rathnayake A Centre for Poverty
Development Report The Rise of the South 13 Analysis on Cambodia
 Development Report 20 Human The Rise of the South 13 Analysis on Cambodia Introduction The concept of human development entails freeing and enlarging people s choices within a society. In principle, these
Development Report 20 Human The Rise of the South 13 Analysis on Cambodia Introduction The concept of human development entails freeing and enlarging people s choices within a society. In principle, these
Human Development Indices and Indicators: Viet Nam s 2018 Statistical updates
 1 Human Development Indices and Indicators: s 2018 Statistical updates Introduction Human Development Indices and Indicators: 2018 Statistical update, released by UNDP Human Development Report Office on
1 Human Development Indices and Indicators: s 2018 Statistical updates Introduction Human Development Indices and Indicators: 2018 Statistical update, released by UNDP Human Development Report Office on
Comparative Economic Development
 Chapter 3 Comparative Economic Development Principles and Concepts 1 I. Common characteristics of developing countries These features in common are on average and with great diversity, in comparison with
Chapter 3 Comparative Economic Development Principles and Concepts 1 I. Common characteristics of developing countries These features in common are on average and with great diversity, in comparison with
Introduction to Development Economics. Q: What is Development Economics?
 Introduction to Development Economics Q: What is Development Economics? Traditional economics, taught in introductory textbooks, is concerned primarily with the efficient, least-cost allocation of scarce
Introduction to Development Economics Q: What is Development Economics? Traditional economics, taught in introductory textbooks, is concerned primarily with the efficient, least-cost allocation of scarce
Test Bank for Economic Development. 12th Edition by Todaro and Smith
 Test Bank for Economic Development 12th Edition by Todaro and Smith Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bankfor-economic-development-12th-edition-by-todaro Chapter 2 Comparative
Test Bank for Economic Development 12th Edition by Todaro and Smith Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bankfor-economic-development-12th-edition-by-todaro Chapter 2 Comparative
8. REGIONAL DISPARITIES IN GDP PER CAPITA
 8. REGIONAL DISPARITIES IN GDP PER CAPITA GDP per capita varies significantly among OECD countries (Figure 8.1). In 2003, GDP per capita in Luxembourg (USD 53 390) was more than double the OECD average
8. REGIONAL DISPARITIES IN GDP PER CAPITA GDP per capita varies significantly among OECD countries (Figure 8.1). In 2003, GDP per capita in Luxembourg (USD 53 390) was more than double the OECD average
Measuring Social Inclusion
 Measuring Social Inclusion Measuring Social Inclusion Social inclusion is a complex and multidimensional concept that cannot be measured directly. To represent the state of social inclusion in European
Measuring Social Inclusion Measuring Social Inclusion Social inclusion is a complex and multidimensional concept that cannot be measured directly. To represent the state of social inclusion in European
ANNEX 1: Human Development Indicators for Bosnia & Herzegovina. Prepared by Maida Fetahagić
 ANNEX 1: Human Development Indicators for Bosnia & Herzegovina Prepared by Maida Fetahagić Sarajevo, April 2013 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Introduction... 2 2 Improving the measurement of Human Development...
ANNEX 1: Human Development Indicators for Bosnia & Herzegovina Prepared by Maida Fetahagić Sarajevo, April 2013 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Introduction... 2 2 Improving the measurement of Human Development...
Global Social Progress Index
 Global Social Progress Index How do we advance society? Economic Development Social Progress www.socialprogressindex.com The Social Progress Imperative defines social progress as: the capacity of a society
Global Social Progress Index How do we advance society? Economic Development Social Progress www.socialprogressindex.com The Social Progress Imperative defines social progress as: the capacity of a society
WELCOME! Professors Jay Aronson, Bernardine Dias, Joe Mertz and Rahul Tongia Fall 2007
 WELCOME! Professors Jay Aronson, Bernardine Dias, Joe Mertz and Rahul Tongia Fall 2007 Instructor Introductions Aronson and Mertz are main instructors for undergraduate version Dias and Tongia are main
WELCOME! Professors Jay Aronson, Bernardine Dias, Joe Mertz and Rahul Tongia Fall 2007 Instructor Introductions Aronson and Mertz are main instructors for undergraduate version Dias and Tongia are main
Mr. Ali Ahmadov Deputy Prime Minister of the Republic of Azerbaijan, Chairman of the National Coordination Council for Sustainable Development
 Mr. Ali Ahmadov Deputy Prime Minister of the Republic of Azerbaijan, Chairman of the National Coordination Council for Sustainable Development 2 Azerbaijan joined the Millennium Declaration in 2000. To
Mr. Ali Ahmadov Deputy Prime Minister of the Republic of Azerbaijan, Chairman of the National Coordination Council for Sustainable Development 2 Azerbaijan joined the Millennium Declaration in 2000. To
Economic Geography Chapter 10 Development
 Economic Geography Chapter 10 Development Development: Key Issues 1. Why Does Development Vary Among Countries? 2. Where Are Inequalities in Development Found? 3. Why Do Countries Face Challenges to Development?
Economic Geography Chapter 10 Development Development: Key Issues 1. Why Does Development Vary Among Countries? 2. Where Are Inequalities in Development Found? 3. Why Do Countries Face Challenges to Development?
Full file at
 Chapter 2 Comparative Economic Development Key Concepts In the new edition, Chapter 2 serves to further examine the extreme contrasts not only between developed and developing countries, but also between
Chapter 2 Comparative Economic Development Key Concepts In the new edition, Chapter 2 serves to further examine the extreme contrasts not only between developed and developing countries, but also between
Poverty and Inequality
 Poverty and Inequality Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () Poverty and Inequality 1 / 50 Sherif Khalifa () Poverty and Inequality 2 / 50 Sherif Khalifa () Poverty and Inequality 3 / 50 Definition Income inequality
Poverty and Inequality Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () Poverty and Inequality 1 / 50 Sherif Khalifa () Poverty and Inequality 2 / 50 Sherif Khalifa () Poverty and Inequality 3 / 50 Definition Income inequality
2010 Human Development Report: 40-year Trends Analysis Shows Poor Countries Making Faster Development Gains
 Strictly embargoed until 4 November 2010, 10:00 AM EDT (New York), 14:00PM GST 2010 Human Development Report: 40-year Trends Analysis Shows Poor Countries Making Faster Development Gains 20th anniversary
Strictly embargoed until 4 November 2010, 10:00 AM EDT (New York), 14:00PM GST 2010 Human Development Report: 40-year Trends Analysis Shows Poor Countries Making Faster Development Gains 20th anniversary
Reducing income inequality by economics growth in Georgia
 Reducing income inequality by economics growth in Georgia Batumi Shota Rustaveli State University Faculty of Economics and Business PhD student in Economics Nino Kontselidze Abstract Nowadays Georgia has
Reducing income inequality by economics growth in Georgia Batumi Shota Rustaveli State University Faculty of Economics and Business PhD student in Economics Nino Kontselidze Abstract Nowadays Georgia has
Access to Food, Poverty and Inequality by Social and Religious groups in India: Estimation with Unit Level Data. Panchanan Das & Anindita Sengupta
 Access to Food, Poverty and Inequality by Social and Religious groups in India: Estimation with Unit Level Data Panchanan Das & Anindita Sengupta Background Food security under trade liberalisation of
Access to Food, Poverty and Inequality by Social and Religious groups in India: Estimation with Unit Level Data Panchanan Das & Anindita Sengupta Background Food security under trade liberalisation of
IMPACT OF GLOBALIZATION ON POVERTY: CASE STUDY OF PAKISTAN
 Romain Pison Prof. Kamal NYU 03/20/06 NYU-G-RP-A1 IMPACT OF GLOBALIZATION ON POVERTY: CASE STUDY OF PAKISTAN INTRODUCTION The purpose of this paper is to examine the effect of globalization in Pakistan
Romain Pison Prof. Kamal NYU 03/20/06 NYU-G-RP-A1 IMPACT OF GLOBALIZATION ON POVERTY: CASE STUDY OF PAKISTAN INTRODUCTION The purpose of this paper is to examine the effect of globalization in Pakistan
CHAPTER 3 SOCIO-ECONOMIC CONDITIONS OF MINORITIES OF INDIA
 CHAPTER 3 SOCIO-ECONOMIC CONDITIONS OF MINORITIES OF INDIA 73 List of Contents S.No. Chapter-3 Socio economic condition of Minorities of India on the Page number basis HDI indicators 3.1 Defination of
CHAPTER 3 SOCIO-ECONOMIC CONDITIONS OF MINORITIES OF INDIA 73 List of Contents S.No. Chapter-3 Socio economic condition of Minorities of India on the Page number basis HDI indicators 3.1 Defination of
Trends in inequality worldwide (Gini coefficients)
 Section 2 Impact of trade on income inequality As described above, it has been theoretically and empirically proved that the progress of globalization as represented by trade brings benefits in the form
Section 2 Impact of trade on income inequality As described above, it has been theoretically and empirically proved that the progress of globalization as represented by trade brings benefits in the form
Panel 1: Multidimensional Poverty Measurement: Uses for a New Understanding of the Meaning of Poverty and Deprivation
 Panel 1: Multidimensional Poverty Measurement: Uses for a New Understanding of the Meaning of Poverty and Deprivation Jeni Klugman, Director of Human Development Report Office (UNDP) Some insights from
Panel 1: Multidimensional Poverty Measurement: Uses for a New Understanding of the Meaning of Poverty and Deprivation Jeni Klugman, Director of Human Development Report Office (UNDP) Some insights from
A comparative analysis of poverty and social inclusion indicators at European level
 A comparative analysis of poverty and social inclusion indicators at European level CRISTINA STE, EVA MILARU, IA COJANU, ISADORA LAZAR, CODRUTA DRAGOIU, ELIZA-OLIVIA NGU Social Indicators and Standard
A comparative analysis of poverty and social inclusion indicators at European level CRISTINA STE, EVA MILARU, IA COJANU, ISADORA LAZAR, CODRUTA DRAGOIU, ELIZA-OLIVIA NGU Social Indicators and Standard
Poverty and Inequality
 Poverty and Inequality Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () Poverty and Inequality 1 / 44 Sherif Khalifa () Poverty and Inequality 2 / 44 Sherif Khalifa () Poverty and Inequality 3 / 44 Definition Income inequality
Poverty and Inequality Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () Poverty and Inequality 1 / 44 Sherif Khalifa () Poverty and Inequality 2 / 44 Sherif Khalifa () Poverty and Inequality 3 / 44 Definition Income inequality
The Demographic Profile of the United Arab Emirates
 UNITED NATIONS The Demographic Profile of the United Arab Emirates Population Trends - Mortality - Fertility - Age Structure - Urbanization - International Migration - Education and Youth Unemployment
UNITED NATIONS The Demographic Profile of the United Arab Emirates Population Trends - Mortality - Fertility - Age Structure - Urbanization - International Migration - Education and Youth Unemployment
How s Life in Denmark?
 How s Life in Denmark? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Denmark generally performs very well across the different well-being dimensions. Although average household net adjusted disposable
How s Life in Denmark? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Denmark generally performs very well across the different well-being dimensions. Although average household net adjusted disposable
In general terms democracy may be defined as a form of governance
 CHAPTER 13 Can Democracy be measured? By Odd R. Hunnes Democracy a matter of governance and culture In general terms democracy may be defined as a form of governance in which rule is of, by and for the
CHAPTER 13 Can Democracy be measured? By Odd R. Hunnes Democracy a matter of governance and culture In general terms democracy may be defined as a form of governance in which rule is of, by and for the
Human development in China. Dr Zhao Baige
 Human development in China Dr Zhao Baige 19 Environment Twenty years ago I began my academic life as a researcher in Cambridge, and it is as an academic that I shall describe the progress China has made
Human development in China Dr Zhao Baige 19 Environment Twenty years ago I began my academic life as a researcher in Cambridge, and it is as an academic that I shall describe the progress China has made
Impact of Economic Freedom and Women s Well-Being
 Impact of Economic Freedom and Women s Well-Being ROSEMARIE FIKE Copyright Copyright 2018 by the Fraser Institute. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced in any manner whatsoever
Impact of Economic Freedom and Women s Well-Being ROSEMARIE FIKE Copyright Copyright 2018 by the Fraser Institute. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced in any manner whatsoever
Chapter 2 Comparative Economic Development
 Chapter 2 Comparative Economic Development Common characteristics of developing countries These features in common are on average and with great diversity, in comparison with developed countries: Lower
Chapter 2 Comparative Economic Development Common characteristics of developing countries These features in common are on average and with great diversity, in comparison with developed countries: Lower
POPULATION AND DEVELOPMENT: CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES Population and Economic Inequality - J.C. Chesnais
 POPULATION AND ECONOMIC INEQUALITY J.C. Senior Research Fellow, Institut National d'etudes Démographiques, Paris, France Keywords: Widening internal and international disparities, hierarchy of living standards
POPULATION AND ECONOMIC INEQUALITY J.C. Senior Research Fellow, Institut National d'etudes Démographiques, Paris, France Keywords: Widening internal and international disparities, hierarchy of living standards
ACHIEVEMENTS IN TERMS OF HUMAN DEVELOPMENT DIMENSIONS
 Yahya Z. ALSHEHHI Faculty of Economics and Business, University of Debrecen ACHIEVEMENTS IN TERMS OF HUMAN DEVELOPMENT DIMENSIONS Case Study Keywords Human development index, Human development indicators,
Yahya Z. ALSHEHHI Faculty of Economics and Business, University of Debrecen ACHIEVEMENTS IN TERMS OF HUMAN DEVELOPMENT DIMENSIONS Case Study Keywords Human development index, Human development indicators,
Social Dimension S o ci al D im en si o n 141
 Social Dimension Social Dimension 141 142 5 th Pillar: Social Justice Fifth Pillar: Social Justice Overview of Current Situation In the framework of the Sustainable Development Strategy: Egypt 2030, social
Social Dimension Social Dimension 141 142 5 th Pillar: Social Justice Fifth Pillar: Social Justice Overview of Current Situation In the framework of the Sustainable Development Strategy: Egypt 2030, social
Poverty and Inequality
 Chapter 4 Poverty and Inequality Problems and Policies: Domestic After completing this chapter, you will be able to 1. Measure poverty across countries using different approaches and explain how poverty
Chapter 4 Poverty and Inequality Problems and Policies: Domestic After completing this chapter, you will be able to 1. Measure poverty across countries using different approaches and explain how poverty
Chapter 5 Poverty, Inequality, and Development
 Chapter 5 Poverty, Inequality, and Development Background Extreme poverty remains widespread in the developing world. More than 1.2 billion people live on less than $1 per day at PPP, More than 2.8 billion,
Chapter 5 Poverty, Inequality, and Development Background Extreme poverty remains widespread in the developing world. More than 1.2 billion people live on less than $1 per day at PPP, More than 2.8 billion,
Volume 36, Issue 1. Impact of remittances on poverty: an analysis of data from a set of developing countries
 Volume 6, Issue 1 Impact of remittances on poverty: an analysis of data from a set of developing countries Basanta K Pradhan Institute of Economic Growth, Delhi Malvika Mahesh Institute of Economic Growth,
Volume 6, Issue 1 Impact of remittances on poverty: an analysis of data from a set of developing countries Basanta K Pradhan Institute of Economic Growth, Delhi Malvika Mahesh Institute of Economic Growth,
Is Global Inequality Really Falling?
 Presentation at session on Global Inequality, WIDER Conference 2018 Is Global Inequality Really Falling? Martin Ravallion Georgetown University 1 Defining global inequality The prevailing approach pools
Presentation at session on Global Inequality, WIDER Conference 2018 Is Global Inequality Really Falling? Martin Ravallion Georgetown University 1 Defining global inequality The prevailing approach pools
Kambhampati / Development and the Developing World Final Proof :53pm page 11. Part I. Defining Development
 Kambhampati / Development and the Developing World Final Proof 2.2.2004 12:53pm page 11 Part I Defining Development Kambhampati / Development and the Developing World Final Proof 2.2.2004 12:53pm page
Kambhampati / Development and the Developing World Final Proof 2.2.2004 12:53pm page 11 Part I Defining Development Kambhampati / Development and the Developing World Final Proof 2.2.2004 12:53pm page
Chapter 1 Definitions and Concepts of Development
 Chapter 1 Definitions and Concepts of Development At the very beginning of this course I want you to picture in your mind how people around the world live their daily life. Try to think of how the three-quarters
Chapter 1 Definitions and Concepts of Development At the very beginning of this course I want you to picture in your mind how people around the world live their daily life. Try to think of how the three-quarters
2. Money Metric Poverty & Expenditure Inequality
 Arab Development Challenges 2. Money Metric Poverty & Expenditure Inequality 1 Chapter Overview Kinds of poverty lines Low money metric poverty but high exposure to economic shock The enigma of inequality
Arab Development Challenges 2. Money Metric Poverty & Expenditure Inequality 1 Chapter Overview Kinds of poverty lines Low money metric poverty but high exposure to economic shock The enigma of inequality
Chapter 2 Overview of Sudanese Economy and the Status of ICT in Sudan
 Chapter 2 Overview of Sudanese Economy and the Status of ICT in Sudan 2.1 Introduction This chapter provides a general overview of the socio-economic characteristics of the Sudanese economy and explains
Chapter 2 Overview of Sudanese Economy and the Status of ICT in Sudan 2.1 Introduction This chapter provides a general overview of the socio-economic characteristics of the Sudanese economy and explains
1. Global Disparities Overview
 1. Global Disparities Overview The world is not an equal place, and throughout history there have always been inequalities between people, between countries and between regions. Today the world s population
1. Global Disparities Overview The world is not an equal place, and throughout history there have always been inequalities between people, between countries and between regions. Today the world s population
Development Economics Lecture 1
 Development Economics Lecture 1 Anne Mikkola Partly using slides of Prof. Haaparanta EXAMS (one of the following) Date: 11.12.2007: Time: 12-14 Place: Porthania II Date: 16.1.2008: Time: 12-14 Place: Economicum
Development Economics Lecture 1 Anne Mikkola Partly using slides of Prof. Haaparanta EXAMS (one of the following) Date: 11.12.2007: Time: 12-14 Place: Porthania II Date: 16.1.2008: Time: 12-14 Place: Economicum
ECONOMIC GROWTH, PUBLIC EXPENDITURE AND HUMAN DEVELOPMENT IN ASIA
 PROSIDING PERKEM IV, JILID 1 (2009) 77-88 ISSN : 2231-962X ECONOMIC GROWTH, PUBLIC EXPENDITURE AND HUMAN DEVELOPMENT IN ASIA FARIASTUTI DJAFAR ABSTRACT This paper has two main objectives. The first objective
PROSIDING PERKEM IV, JILID 1 (2009) 77-88 ISSN : 2231-962X ECONOMIC GROWTH, PUBLIC EXPENDITURE AND HUMAN DEVELOPMENT IN ASIA FARIASTUTI DJAFAR ABSTRACT This paper has two main objectives. The first objective
U.S. Family Income Growth
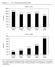 Figure 1.1 U.S. Family Income Growth Growth 140% 120% 100% 80% 60% 115.3% 1947 to 1973 97.1% 97.7% 102.9% 84.0% 40% 20% 0% Lowest Fifth Second Fifth Middle Fifth Fourth Fifth Top Fifth 70% 60% 1973 to
Figure 1.1 U.S. Family Income Growth Growth 140% 120% 100% 80% 60% 115.3% 1947 to 1973 97.1% 97.7% 102.9% 84.0% 40% 20% 0% Lowest Fifth Second Fifth Middle Fifth Fourth Fifth Top Fifth 70% 60% 1973 to
Statistical Yearbook. for Asia and the Pacific
 Statistical Yearbook for Asia and the Pacific 2015 Statistical Yearbook for Asia and the Pacific 2015 Sustainable Development Goal 1 End poverty in all its forms everywhere 1.1 Poverty trends...1 1.2 Data
Statistical Yearbook for Asia and the Pacific 2015 Statistical Yearbook for Asia and the Pacific 2015 Sustainable Development Goal 1 End poverty in all its forms everywhere 1.1 Poverty trends...1 1.2 Data
Visualizing. Rights C E SR. Making Human Rights Accountability More Graphic. Center for Economic and Social Rights. fact sheet no.
 Center for Economic and Social Rights India Making Human Rights Accountability More Graphic This fact sheet is intended to contribute to ongoing monitoring work to hold states accountable for their economic
Center for Economic and Social Rights India Making Human Rights Accountability More Graphic This fact sheet is intended to contribute to ongoing monitoring work to hold states accountable for their economic
The Demographic Profile of Oman
 UNITED NATIONS The Demographic Profile of Oman Population Trends - Mortality - Fertility - Age Structure - Urbanization - International Migration - Education and Youth Unemployment Population Trends Population
UNITED NATIONS The Demographic Profile of Oman Population Trends - Mortality - Fertility - Age Structure - Urbanization - International Migration - Education and Youth Unemployment Population Trends Population
The Demographic Profile of Saudi Arabia
 Infant mortality rate (per 1 live births) UNITED NATIONS The Demographic Profile of Saudi Arabia Population Trends - Mortality - Fertility - Age Structure - Urbanization - International Migration - Education
Infant mortality rate (per 1 live births) UNITED NATIONS The Demographic Profile of Saudi Arabia Population Trends - Mortality - Fertility - Age Structure - Urbanization - International Migration - Education
Poverty and Inequality
 10 Poverty and Inequality Introduction This chapter deals with poverty and inequality which are among South Africa s most intractable development challenges linked to high unemployment. The concepts of
10 Poverty and Inequality Introduction This chapter deals with poverty and inequality which are among South Africa s most intractable development challenges linked to high unemployment. The concepts of
The Ghana Poverty and Inequality Report: Using the 6th Ghana Living Standards Survey 2016
 The Ghana Poverty and Inequality Report: Using the 6th Ghana Living Standards Survey 2016 By Edgar Cooke (Ashesi University College, Ghana); Sarah Hague (Chief of Policy, UNICEF Ghana); Andy McKay (Professor
The Ghana Poverty and Inequality Report: Using the 6th Ghana Living Standards Survey 2016 By Edgar Cooke (Ashesi University College, Ghana); Sarah Hague (Chief of Policy, UNICEF Ghana); Andy McKay (Professor
Inclusion and Gender Equality in China
 Inclusion and Gender Equality in China 12 June 2017 Disclaimer: The views expressed in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views and policies of the Asian Development
Inclusion and Gender Equality in China 12 June 2017 Disclaimer: The views expressed in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views and policies of the Asian Development
PUBLIC POLICIES FOR GREATER EQUALITY: LESSONS LEARNED IN THE ESCWA REGION
 SESSION 4: PUBLIC POLICIES FOR GREATER EQUALITY- INTER-REGIONAL EXPERIENCES PUBLIC POLICIES FOR GREATER EQUALITY: LESSONS LEARNED IN THE ESCWA REGION Economic and Social Commission for Western Asia Oussama
SESSION 4: PUBLIC POLICIES FOR GREATER EQUALITY- INTER-REGIONAL EXPERIENCES PUBLIC POLICIES FOR GREATER EQUALITY: LESSONS LEARNED IN THE ESCWA REGION Economic and Social Commission for Western Asia Oussama
GDP per capita was lowest in the Czech Republic and the Republic of Korea. For more details, see page 3.
 International Comparisons of GDP per Capita and per Hour, 1960 9 Division of International Labor Comparisons October 21, 2010 Table of Contents Introduction.2 Charts...3 Tables...9 Technical Notes.. 18
International Comparisons of GDP per Capita and per Hour, 1960 9 Division of International Labor Comparisons October 21, 2010 Table of Contents Introduction.2 Charts...3 Tables...9 Technical Notes.. 18
Spatial Inequality in Cameroon during the Period
 AERC COLLABORATIVE RESEARCH ON GROWTH AND POVERTY REDUCTION Spatial Inequality in Cameroon during the 1996-2007 Period POLICY BRIEF English Version April, 2012 Samuel Fambon Isaac Tamba FSEG University
AERC COLLABORATIVE RESEARCH ON GROWTH AND POVERTY REDUCTION Spatial Inequality in Cameroon during the 1996-2007 Period POLICY BRIEF English Version April, 2012 Samuel Fambon Isaac Tamba FSEG University
How does development vary amongst regions? How can countries promote development? What are future challenges for development?
 Chapter 9- Development How does development vary amongst regions? How can countries promote development? What are future challenges for development? Human Development Index (HDI) Development process of
Chapter 9- Development How does development vary amongst regions? How can countries promote development? What are future challenges for development? Human Development Index (HDI) Development process of
Application of PPP exchange rates for the measurement and analysis of regional and global inequality and poverty
 Application of PPP exchange rates for the measurement and analysis of regional and global inequality and poverty D.S. Prasada Rao The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia d.rao@uq.edu.au Abstract
Application of PPP exchange rates for the measurement and analysis of regional and global inequality and poverty D.S. Prasada Rao The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia d.rao@uq.edu.au Abstract
How does education affect the economy?
 2. THE ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL BENEFITS OF EDUCATION How does education affect the economy? More than half of the GDP growth in OECD countries over the past decade is related to labour income growth among
2. THE ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL BENEFITS OF EDUCATION How does education affect the economy? More than half of the GDP growth in OECD countries over the past decade is related to labour income growth among
UNDP: Urgent job creation on a mass scale key to stability in the Arab region
 Strictly embargoed until 14 March 2013, 12:00 PM EDT (New York), 4:00 PM GMT (London) UNDP: Urgent job creation on a mass scale key to stability in the Arab region Mexico City, 14 March 2013 Arab States
Strictly embargoed until 14 March 2013, 12:00 PM EDT (New York), 4:00 PM GMT (London) UNDP: Urgent job creation on a mass scale key to stability in the Arab region Mexico City, 14 March 2013 Arab States
The Demographic Profile of the State of Palestine
 UNITED NATIONS The Demographic Profile of the State of Palestine Population Trends - Mortality - Fertility - Age Structure - Urbanization - International Migration - Education and Youth Unemployment Population
UNITED NATIONS The Demographic Profile of the State of Palestine Population Trends - Mortality - Fertility - Age Structure - Urbanization - International Migration - Education and Youth Unemployment Population
How s Life in Belgium?
 How s Life in Belgium? November 2017 Relative to other countries, Belgium performs above or close to the OECD average across the different wellbeing dimensions. Household net adjusted disposable income
How s Life in Belgium? November 2017 Relative to other countries, Belgium performs above or close to the OECD average across the different wellbeing dimensions. Household net adjusted disposable income
