Irregular Armed Conflicts and Human Rights. Mokbul Ali Laskar*
|
|
|
- Donna Jefferson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Peace Studies Vol. 10, Issue 1, January-March 2003 Irregular Armed Conflicts and Human Rights Mokbul Ali Laskar* [* Mokbul Ali Laskar is an Associate Scholar with National Institute of Science Communication and Information Resources, New Delhi, India.] The humankind today is haunted by conflicts and violence among and within the weakest states of the world. This intra-state and intra-societal violence has posed grave human rights problems all over the world. Human rights violations by the states have been taken care of by the international human rights regimes and international human rights laws have delineated acceptable limits of behaviour for warring parties. But in recent years, the dynamics of armed engagements have changed and in most of the cases non-state actors have emerged as agents of violence and they are taking on the might of the state through armed insurgencies and subversive activities and violating human rights with little respect for the human rights laws or regimes. The present paper by Mokbul Ali Laskar presents an argument for understanding these conflicts and human rights issues associated with them and goes on to suggest that armed non-state actors should be brought within the ambit of international human rights laws and conventions pertaining to war so that international community and HR regimes can monitor their activities and pressurize these groups to refrain from activities that violate international principle of Human Rights. [Editorial Board] War is in no way a relationship of man with man but a relationship between states, in which individuals are only enemies by accident, not as men, but as soldiers The Social Contract of J. Jacques Rousseau. The above statement is logically followed by another statement of Rousseau: Soldiers may only be fought as long as they themselves are fighting. Once they lay down their weapons they again become mere men. Their lives must be spared. This laid the foundation of the international humanitarian law (IHL), which later developed through the initial efforts of Henry Durant and Francis Lieber. In traditional warfare military casualties were more while civilians suffered less. But the improvement in air-power has enabled strikes well behind enemy lines, at the lines of communication and logistics that kept enemy armies supplied and made civilians much more vulnerable in modern day warfare. This strategy of attacking through air-borne bombers seeks to cut the confronting army off from reinforcements, fuel, and food and ammunitions and thereby contain its ability to fight. This inevitably means strikes at areas that are likely to be populated by civilians as well as civilian labour employed in factories producing weapons, warships and
2 military aircrafts, their armaments and components and in installations producing the fuel to drive vehicle and the raw materials such as steel needed to build ships. The emphasis on target-bombing is thus gradually shifting away from enemy-combatants to the equipments and supplies on which they depend, but at great cost to the enemy s civilian population. Besides, there has been a significant change in the nature of war. Almost 90 percent of the present day wars are intra-state armed conflicts, taking place within the boundaries of the state and in which there are increasing threats to civilians lives and properties. The number of civilian casualties in the present day intra-state conflicts is too high. The wars are becoming irregular and there are widespread violations of IHL and human rights law, both by the states and the non-state actors. Internal armed conflict and its irregular nature In today s world, the war is characterised by conflicts and violence among and within the weakest states of the world. Many of the least developed or developing countries suffer the worst societal violence, which in turn takes the shape of armed conflicts. The latest incidents all over the world confirm that the most dramatic and prevalent threats to the civilians arise in internal armed conflicts. For the period , 56 major armed conflicts were recorded for 44 locations. All but three of the conflicts (Iraq-Kuwait, India-Pakistan, Ethiopia-Eritrea) registered during those 11 years were internal. Of the 25 major armed conflicts recorded in 2002, 23 were internal.[1] Most internal armed conflicts of the last few years often involved communal identity as a source of conflict. Virtually all the conflicts elicited direct political, economic or military involvement of other states and even multinational organisations. The low-intensity conflicts those in which fatalities number less than 1000 and so are often not counted as significant or major conflicts by the organizations who keep records have almost doubled in annual incidence, linking such violence to persistent terrorism and organised international crime. The origin of all such irregular conflicts is diverse and can be found in social, economic, environmental and health factors. These issues are increasingly transcending state borders and are having global repercussions. In fact, as a side effect of globalization, the impact of violent conflicts can no longer be easily contained within specific regions; each conflict carries shock waves of the hostilities in concentric circles to every sphere of transnational activities and across the continents. The salient features of the present day wars are: * A common feature of internal armed conflicts is the widespread violation of IHL and human rights law by state and non-state actors. The threats to civilians have also increased with the proliferation of weapons, especially small arms and landmines and as a result of the organised crime and random violence that occur in these chaotic condition. States appear more and more ineffective and incompetent agents for the implementation of IHL and human rights.
3 * The most disappointing feature of the present day armed conflicts is the presence of armed groups among civilians. It is much harder to establish who is a civilian in modern civil wars where the entire population can be seen as taking part in one way or another[2]. * In contemporary conflicts and warfare civilians suffer disproportionately the ratio of civil to military casualties in warfare is now around 8:1.[3] The belligerents are similarly fragmented in these conflicts and they often include warlords, mercenaries, private sector companies, organised criminal groups, etc. * Most internal armed conflicts rely heavily on external inputs and assistance to maintain their momentum, whether through illicit trafficking, government contracts or other commercial opportunities. Corporate interests in natural/other resources play an increasing part in sustaining armed conflicts and thereby making the situation worse in humanitarian terms. * The domestic conflicts are internationalized in the post-modern era by the media, the growing focus on human rights and IHL and also by the ability of local belligerents in a conflict to operate internationally. Conflicts affect population migration, regional ecosystems, financial markets, commodity markets, etc.; they can no longer be considered isolated events in time or space. Similarly in the case of inter-state armed conflicts or interventionist armed attacks (by military superpowers) the consequences are beyond the norms of international behaviour. These armed attacks or conflicts indeed cause more damage to civilians and civilian objectives. Some have declared their attacks as war for human rights (as NATO proclaimed in Kosovo) or global war against terrorism, but what about the massive/collateral damage to civilian lives and civilian objectives? Are they not against the laws of war? Can these be not characterised as War Crimes or Crimes against humanity? In reality, millions of children, women and men (civilian) are victims of unimaginable atrocities, caused by such irregular violence that deeply shocks the conscience of humanity. Irregular Warfare and human rights issues It is now universally recognized that human development is essential for realizing human rights, and human rights are essential for full human development.[4] According to UNDP Human Development Report, 2000: Human rights are the rights possessed by all persons, by virtue of their common humanity, to live a life of freedom and dignity. They give all people moral claims on the behaviour of individuals and on the designs of social arrangements and are universal, inalienable and indivisible. Human rights express our deepest commitments to ensuring that all persons are secure in their enjoyments of the goods and freedoms that are necessary for dignified living.
4 But irregular warfare has destroyed our sense of respect towards humanity and human beings are unable to enjoy even the basic and most fundamental human rights. In today s anarchic wars we are witnessing that ethnic groups are massacred wholesale, young children are dragged and pressed into military service and civilians (mostly children) are punished by having their limbs amputated (in landmines)[5]. The surge of violence against civilians has increased day by day and the constant images of violence in the media have desensitized human beings the world over to the basic issue of human suffering. The civilian have been displaced, harassed or subjected to extreme forms of violence. An estimated 5 million people died in intrastate conflicts in the 1990s[6]. Globally in 1998, there were more than 10 million refugees and 5 million internally displaced persons. The intensity of intrastate conflicts has increased with the increasing inequalities and the marginalisation of the poor countries and poor people. In the UN Report (titled We, the people: The role of the United Nations in the 21 st century, March 2000) to the Millennium Assembly, United Nations Secretary General Kofi Annan wrote: International conventions have traditionally looked at states to protect civilians, but today this expectation is threatened in several ways. First, states are some times the principal perpetrator of violence against the very citizens that humanitarian law requires them to protect. Second, non-state combatants, particularly in collapsed states are often ignorant or contemptuous of humanitarian law. Third, international conventions do not adequately address the specific needs of vulnerable groups, such as internally displaced persons, or women and children in complex emergencies. According to UNICEF (1999), around 50 per cent of all civilian war casualties currently are children. Unaccompanied children and pregnant women are the most vulnerable to such irregular armed conflicts. Before America attacked Afghanistan there were between 150 and 300 new landmine victims every month and half of them were children[7]. But the deadly cluster bombs dropped by American aircraft have released hundreds of little bombs which are yet to explode; and like landmines, they may kill, maim and make land inaccessible long after the fighting actually would stop. Today, there is no estimation of how many civilians and children will be victim of this added landmines in Afghanistan. Protection of human rights in armed conflicts There is a basic assumption that war will continue to exist as long as there are people who feel that their grievances cannot be redressed by any other means. But we can at least try to reduce the atrocities and mitigate the sufferings of the civilians and the most vulnerable groups in such wars. Based on such assumption there have emerged some basic principles and instruments of IHL, which must be respected by the state and its armed forces.
5 The process began in 1864, with the adoption of the first Geneva Convention. Today, there are four Geneva conventions (of 12 August, 1949) and two additional protocols, which include around 600 articles and they together form the main instrument of IHL. The Article 3 common to the four Geneva Conventions and the additional protocols II gives the various rules and regulations of internal armed conflicts. The basic principle of the series of Geneva Conventions and its Additional Protocols is: the protection and humanitarian treatment of those not (or no longer) participating in an armed conflict, including civilians, the sick, the wounded and prisoners of war Besides Geneva Conventions and its Additional Protocols, today there are many other instruments to deal with humanitarian law; the most recent and notable being the APM treaty and the Rome Statute of International Criminal Court. There are three fundamental principles of IHL, which are to be followed by all the parties in an armed conflict. * Principle of proportionality, which means that there must be a balance between military and humanitarian considerations. Unnecessary military attacks should not be allowed to happen at any costs. Besides, in taking care to protect civilians, soldiers must accept some element of risk to themselves. * Principle of military necessity, which means that only military objectives/targets should be attacked. There is no meaning (at least in military terms) in attacking universities, historical and cultural locations or many other safe havens. * Principles of distinction, which means attacks should be limited to combatants and other military objectives. The civilian population and civilian objects must not be deliberately targeted. The other fundamental rules of humanitarian law applicable in armed conflicts are: * Persons hors de combat (i.e. non-combatant) and those who do not take a direct part in hostilities are entitled to respect for their lives and physical and moral integrity. They shall in all circumstances be protected and treated humanely without any adverse destruction. * It is forbidden to kill or injure an enemy who surrenders or who is hors de combat * The wounded and sick shall be collected and cared for by the party to the conflict, which has them in its power. Protection also covers medical personnel, establishments, transports and material. The emblem of the ICRC is the sign of such protection and must be respected.
6 * Captured combatants and civilians under the authority of an adverse party are entitled to respect for their lives, dignity, personal rights and convictions. They shall be protected against all acts of violence and reprisals. They shall have the right to correspond with their families and to receive relief. * Everyone shall be entitled to benefit from fundamental judicial guarantees. No one shall be held responsible for an act he has not committed. No one shall be subjected to physical mental torture, corporal punishment or cruel or degrading treatment. * Parties to a conflict and member of its armed forces do not have an unlimited choice of means and methods of warfare. It is prohibited to employ weapon or method of warfare of a nature to cause unnecessary losses or excessive sufferings (i.e. blinding weapon, landmines etc are prohibited in a war because they do not kill, but cause unnecessary sufferings). * Besides, state parties should, as far as possible, remove civilians from the vicinity of military objectives; avoid locating military objectives in or near densely populated areas. It is unfortunate that there is evidence that some states do not merely fail to comply with the requirements of international law, but deliberately put military assets close to protected objects or place civilians in military locations with the intentions of protecting military objectives from attack or even in the hope of attracting international condemnation of the enemy if civilians are killed or civilians objects destroyed. Then there are other problems: application of the principle of proportionality is more easily stated than applied in practice, as by adopting a method of attack that would reduce incidental damage, the risk to the attacking troops may be increased. The law is not clear as to the degree of care required of the attacker and the degree of risk that he must be prepared to take. Another great problem of the IHL is the separation of non-international/internal armed conflicts from international one. The decision as regard to the declaration of a war as an internal/non-international armed conflicts rests on the states and till date no country has declared that there is an internal armed conflict. No country is willing to accept that they are having an internal armed conflict, only to avoid the stringent rules to be followed in that circumstance and also to maintain a high sovereign status in the conflict situation. To say in clear terms, there are no stringent rules (of IHL) to deal with the atrocities in the intra-state armed conflicts. The various non-state actors involved in intra-state armed conflicts have never been recognized as part of any international conventions; these non-state armed groups are not aware of the various provisions of the IHL and as such there are gross human rights violation. Conclusion In conclusion it can be said that the origin of the most intra-state/irregular armed conflicts lies in the socio-economic and political set up of a particular country. The globalization of the
7 economy and increasing disparity and inequality and the marginalisation of the poor countries/peoples are the main reasons of these conflicts and their solutions can be found in addressing such issues. There is a need to pay attention to these issues. Besides democracy, good governance and the rule of law can help in eliminating such armed conflicts. The state and its armed forces should be compelled to, through some coercive means, to obey IHL. And the non-state armed groups (those who are fighting and have succeeded in having control over some territory, those who are fighting are in a command position or command structure with a commander and are carrying weapons openly, those belonging to liberation movement and follow the well-established norms or customs of war) operating within or across the states must be given some form of recognition, at least in the above cases, so that they can be given same guidelines to follow IHL and Human rights laws. 1. SIPRI Yearbook 2001, p.52 Endnotes 2. Survey shows fighters don t separate civilians from enemies, Associated press, October 18, International Affairs Vol. 77, No.3, July 2001, pp Human Development Report 2000, UNDP, p A Mission to Protect Non-combatants, International Herald Tribune, October UNDP Human Development Report 2000, p The Economist, November 10, 2001, p Geneva Conventions of August 12, 1949 References 2. Additional Protocol I & II to Geneva Conventions of August 12, 1949 (1977) 3. International Review of the Red Cross (IRRC), June 2001, Vol. 83, No NISCAIR- National Institute of Science Communication and Information Resources.
Attacks on Medical Units in International Humanitarian and Human Rights Law
 Attacks on Medical Units in International Humanitarian and Human Rights Law September 2016 MSF-run hospital in Ma arat al-numan, Idleb Governorate, 15 February 2016 (Photo MSF - www.msf.org) The Syrian
Attacks on Medical Units in International Humanitarian and Human Rights Law September 2016 MSF-run hospital in Ma arat al-numan, Idleb Governorate, 15 February 2016 (Photo MSF - www.msf.org) The Syrian
Explosive weapons in populated areas - key questions and answers
 BACKGROUND PAPER JUNE 2018 Explosive weapons in populated areas - key questions and answers The International Network on Explosive Weapons (INEW) is an NGO partnership calling for immediate action to prevent
BACKGROUND PAPER JUNE 2018 Explosive weapons in populated areas - key questions and answers The International Network on Explosive Weapons (INEW) is an NGO partnership calling for immediate action to prevent
EU GUIDELINES on INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW
 EU GUIDELINES on INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW Contents 1_ Purpose 127 2_ International humanitarian law (IHL) 127 Introduction 127 Evolution and sources of IHL 128 Scope of application 128 International
EU GUIDELINES on INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW Contents 1_ Purpose 127 2_ International humanitarian law (IHL) 127 Introduction 127 Evolution and sources of IHL 128 Scope of application 128 International
1. 4. Legal Framework for United Nations Peacekeeping. L e s s o n
 M o d u l e 1 : A n O v e r v i e w o f U n i t e d N a t i o n s P e a c e k e e p i n g O p e r a t i o n s L e s s o n 1. 4 Legal Framework for United Nations Peacekeeping Relevance Peacekeeping personnel:
M o d u l e 1 : A n O v e r v i e w o f U n i t e d N a t i o n s P e a c e k e e p i n g O p e r a t i o n s L e s s o n 1. 4 Legal Framework for United Nations Peacekeeping Relevance Peacekeeping personnel:
UNITED NATIONS OFFICE OF LEGAL AFFAIRS
 UNITED NATIONS OFFICE OF LEGAL AFFAIRS 36th Annual Seminar on International Humanitarian Law for Legal Advisers and other Diplomats Accredited to the United Nations jointly organized by the International
UNITED NATIONS OFFICE OF LEGAL AFFAIRS 36th Annual Seminar on International Humanitarian Law for Legal Advisers and other Diplomats Accredited to the United Nations jointly organized by the International
Targeting People: Direct Participation in the Conduct of Hostilities DR. GENTIAN ZYBERI NORWEGIAN CENTRE FOR HUMAN RIGHTS UNIVERSITY OF OSLO
 Targeting People: Direct Participation in the Conduct of Hostilities DR. GENTIAN ZYBERI NORWEGIAN CENTRE FOR HUMAN RIGHTS UNIVERSITY OF OSLO Structure: Main Issues Targeting People: Direct Participation
Targeting People: Direct Participation in the Conduct of Hostilities DR. GENTIAN ZYBERI NORWEGIAN CENTRE FOR HUMAN RIGHTS UNIVERSITY OF OSLO Structure: Main Issues Targeting People: Direct Participation
International humanitarian law and the protection of war victims
 International humanitarian law and the protection of war victims Hans-Peter Gasser 1. Why do we need international humanitarian law? War is forbidden. The Charter of the United Nations states clearly that
International humanitarian law and the protection of war victims Hans-Peter Gasser 1. Why do we need international humanitarian law? War is forbidden. The Charter of the United Nations states clearly that
ACT ON THE PUNISHMENT OF CRIMES WITHIN THE JURISDICTION OF THE INTERNATIONAL CRIMINAL COURT
 ACT ON THE PUNISHMENT OF CRIMES WITHIN THE JURISDICTION OF THE INTERNATIONAL CRIMINAL COURT Act on the Punishment of Crimes within the Jurisdiction of the International Criminal Court Enacted on December
ACT ON THE PUNISHMENT OF CRIMES WITHIN THE JURISDICTION OF THE INTERNATIONAL CRIMINAL COURT Act on the Punishment of Crimes within the Jurisdiction of the International Criminal Court Enacted on December
Appraising the Core Principles of International Humanitarian Law By Dr. Arinze Abuah
 ABSTRACT Appraising the Core Principles of International Humanitarian Law By Dr. Arinze Abuah International humanitarian law previously known as the law of wars has principles upon which it is founded.
ABSTRACT Appraising the Core Principles of International Humanitarian Law By Dr. Arinze Abuah International humanitarian law previously known as the law of wars has principles upon which it is founded.
Issue: Measures to ensure continued protection of civilians in war zones
 Forum: Human Rights Council II Issue: Measures to ensure continued protection of civilians in war zones Student Officer: Adam McMahon Position: Deputy Chair 1 Introduction The matter of protecting civilians
Forum: Human Rights Council II Issue: Measures to ensure continued protection of civilians in war zones Student Officer: Adam McMahon Position: Deputy Chair 1 Introduction The matter of protecting civilians
HOSTILITIES UNDER INTERNATIONAL LAW
 An Open Access Journal from The Law Brigade (Publishing) Group 447 HOSTILITIES UNDER INTERNATIONAL LAW Written by Dr. Yeshwant Naik Post-Doctoral Research Fellow, Muenster University, Germany The interrelation
An Open Access Journal from The Law Brigade (Publishing) Group 447 HOSTILITIES UNDER INTERNATIONAL LAW Written by Dr. Yeshwant Naik Post-Doctoral Research Fellow, Muenster University, Germany The interrelation
UNITED NATIONS SECURITY COUNCIL ( )
 2010 2010 (22 December) Resolution 1964 (2010) 2010 (22 December) Resolution 1962 (2010) Hostilities Instability situation "Calls for the immediate cessation of all acts of violence or abuses committed
2010 2010 (22 December) Resolution 1964 (2010) 2010 (22 December) Resolution 1962 (2010) Hostilities Instability situation "Calls for the immediate cessation of all acts of violence or abuses committed
THE POSITION OF WOMEN AND CHILDREN IN THE INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW SYSTEM
 THE POSITION OF WOMEN AND CHILDREN IN THE INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW SYSTEM Hengameh Ghazanfari, Touraj Ahmadi International Law, Department of Law, Islamic Azad University, Khorram Abbad Branch Master
THE POSITION OF WOMEN AND CHILDREN IN THE INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW SYSTEM Hengameh Ghazanfari, Touraj Ahmadi International Law, Department of Law, Islamic Azad University, Khorram Abbad Branch Master
Overview of the ICRC's Expert Process ( )
 1 Overview of the ICRC's Expert Process (2003-2008) 1. The Issue of Civilian Direct Participation in Hostilities The primary aim of international humanitarian law (IHL) is to protect the victims of armed
1 Overview of the ICRC's Expert Process (2003-2008) 1. The Issue of Civilian Direct Participation in Hostilities The primary aim of international humanitarian law (IHL) is to protect the victims of armed
Objectives To explore the meanings of conflict and war. To make deductions and practise reasoning skills.
 H Oxfam Education www.oxfam.org.uk/education Making Sense of World Conflicts Lesson plan 5: Is it war? Age group: 14 17 Objectives To explore the meanings of conflict and war. To make deductions and practise
H Oxfam Education www.oxfam.org.uk/education Making Sense of World Conflicts Lesson plan 5: Is it war? Age group: 14 17 Objectives To explore the meanings of conflict and war. To make deductions and practise
30 YEARS FROM THE ADOPTION OF ADDITIONAL PROTOCOLS I AND II TO THE GENEVA CONVENTIONS
 30 YEARS FROM THE ADOPTION OF ADDITIONAL PROTOCOLS I AND II TO THE GENEVA CONVENTIONS Beatrice Onica Jarka, Nicolae Titulescu University, Law Faculty ABSTRACT The article reflects in a concentrated form
30 YEARS FROM THE ADOPTION OF ADDITIONAL PROTOCOLS I AND II TO THE GENEVA CONVENTIONS Beatrice Onica Jarka, Nicolae Titulescu University, Law Faculty ABSTRACT The article reflects in a concentrated form
penalty proposal violates the American Convention on Human Rights
 PERU @Death penalty proposal violates the American Convention on Human Rights Amnesty International is deeply concerned that the scope of the death penalty in Peru may be extended in the forthcoming new
PERU @Death penalty proposal violates the American Convention on Human Rights Amnesty International is deeply concerned that the scope of the death penalty in Peru may be extended in the forthcoming new
Art. 61. Troops that give no quarter have no right to kill enemies already disabled on the ground, or prisoners captured by other troops.
 Criminalizing War (1) Discovering crimes in war (2) Early attempts to regulate the use of force in war (3) International Military Tribunal (Nuremberg trial) (4) International Military Tribunal for the
Criminalizing War (1) Discovering crimes in war (2) Early attempts to regulate the use of force in war (3) International Military Tribunal (Nuremberg trial) (4) International Military Tribunal for the
Dear students: This presentation is a text version of the presentation that was given in lecture # 1, since presentations with certain animations
 Dear students: This presentation is a text version of the presentation that was given in lecture # 1, since presentations with certain animations cannot be published as PDF-files. The content should be
Dear students: This presentation is a text version of the presentation that was given in lecture # 1, since presentations with certain animations cannot be published as PDF-files. The content should be
International Law and the Use of Armed Force by States
 International Law and the Use of Armed Force by States Abel S. Knottnerus 1 Introduction State violence is defined in this volume as the illegitimate use of force by states against the rights of others.
International Law and the Use of Armed Force by States Abel S. Knottnerus 1 Introduction State violence is defined in this volume as the illegitimate use of force by states against the rights of others.
TOWARDS CONVERGENCE. IHL, IHRL and the Convergence of Norms in Armed Conflict
 TOWARDS CONVERGENCE IHL, IHRL and the Convergence of Norms in Armed Conflict DECISION ON THE DEFENCE MOTION FOR INTERLOCUTORY APPEAL ON JURISDICTION - Tadić As the members of the Security Council well
TOWARDS CONVERGENCE IHL, IHRL and the Convergence of Norms in Armed Conflict DECISION ON THE DEFENCE MOTION FOR INTERLOCUTORY APPEAL ON JURISDICTION - Tadić As the members of the Security Council well
Week # 2 Targeting Principles & Human Shields
 Week # 2 Targeting Principles & Human Shields MILITARY NECESSITY UNNECESSARY SUFFERING PROPORTIONALITY Military Advantage Collateral Damage DISTINCTION Civilian-Combatant Military Objective v. Civilian
Week # 2 Targeting Principles & Human Shields MILITARY NECESSITY UNNECESSARY SUFFERING PROPORTIONALITY Military Advantage Collateral Damage DISTINCTION Civilian-Combatant Military Objective v. Civilian
I. Summary Human Rights Watch August 2007
 I. Summary The year 2007 brought little respite to hundreds of thousands of Somalis suffering from 16 years of unremitting violence. Instead, successive political and military upheavals generated a human
I. Summary The year 2007 brought little respite to hundreds of thousands of Somalis suffering from 16 years of unremitting violence. Instead, successive political and military upheavals generated a human
분쟁과대테러과정에서의인권보호. The Seoul Declaration
 분쟁과대테러과정에서의인권보호 Upholding Human Rights during Conflict and while Countering Terrorism" The Seoul Declaration The Seventh International Conference for National Institutions for the Promotion and Protection
분쟁과대테러과정에서의인권보호 Upholding Human Rights during Conflict and while Countering Terrorism" The Seoul Declaration The Seventh International Conference for National Institutions for the Promotion and Protection
Explosive weapons in populated areas - key questions and answers
 BACKGROUND PAPER AUGUST 2014 Explosive weapons in populated areas - key questions and answers The International Network on Explosive Weapons (INEW) is an NGO partnership calling for immediate action to
BACKGROUND PAPER AUGUST 2014 Explosive weapons in populated areas - key questions and answers The International Network on Explosive Weapons (INEW) is an NGO partnership calling for immediate action to
Lesson 8 Legal Frameworks for Civil-Military-Police Relations
 CC Flickr Photo by Albert Gonzalez Farran, UNAMID Lesson 8 Legal Frameworks for Civil-Military-Police Relations Learning Objectives: At the end of the lesson, participants will be able to: Identify five
CC Flickr Photo by Albert Gonzalez Farran, UNAMID Lesson 8 Legal Frameworks for Civil-Military-Police Relations Learning Objectives: At the end of the lesson, participants will be able to: Identify five
RUSSIA & UKRAINE: INTERNATIONAL LAW AND SELF DETERMINATION. Patrick McGuiness
 RUSSIA & UKRAINE: INTERNATIONAL LAW AND SELF DETERMINATION Patrick McGuiness The Ukraine Conflict How Did it Come to This? Ukrainian Divide The Language Divide A Closer Look The Voting Divide Crimea Be
RUSSIA & UKRAINE: INTERNATIONAL LAW AND SELF DETERMINATION Patrick McGuiness The Ukraine Conflict How Did it Come to This? Ukrainian Divide The Language Divide A Closer Look The Voting Divide Crimea Be
A Need for Greater Restrictions on the Use of Improvised Explosive Devices? A Food for thought paper
 A Need for Greater Restrictions on the Use of Improvised Explosive Devices? A Food for thought paper Geneva, 24 April 2012 Contents INTRODUCTION 1 WHICH WEAPONS ARE WE TALKING ABOUT? 1 UNLAWFUL WEAPONRY
A Need for Greater Restrictions on the Use of Improvised Explosive Devices? A Food for thought paper Geneva, 24 April 2012 Contents INTRODUCTION 1 WHICH WEAPONS ARE WE TALKING ABOUT? 1 UNLAWFUL WEAPONRY
Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons (CCW)
 It resulted in the adoption of treaties which can be labelled humanitarian disarmament. In addition to establishing an absolute ban on the use, production, transfer and stockpiling of certain types of
It resulted in the adoption of treaties which can be labelled humanitarian disarmament. In addition to establishing an absolute ban on the use, production, transfer and stockpiling of certain types of
Teaching International Humanitarian Law
 No. 02 March 2004 The ICRC's mission is to protect and assist the civilian and military victims of armed conflict and internal disturbances on a strictly neutral and impartial basis. Since 1986, the ICRC
No. 02 March 2004 The ICRC's mission is to protect and assist the civilian and military victims of armed conflict and internal disturbances on a strictly neutral and impartial basis. Since 1986, the ICRC
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 1
 Women in Armed Opposition Groups in Africa and the Promotion of International Humanitarian Law and Human Rights Report of a workshop organized in Addis Ababa by Geneva Call and the Program for the Study
Women in Armed Opposition Groups in Africa and the Promotion of International Humanitarian Law and Human Rights Report of a workshop organized in Addis Ababa by Geneva Call and the Program for the Study
THE ICRC'S CLARIFICATION PROCESS ON THE NOTION OF DIRECT PARTICIPATION IN HOSTILITIES UNDER INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW NILS MELZER
 THE ICRC'S CLARIFICATION PROCESS ON THE NOTION OF DIRECT PARTICIPATION IN HOSTILITIES UNDER INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW NILS MELZER Dr. Nils Melzer is legal adviser for the International Committee of
THE ICRC'S CLARIFICATION PROCESS ON THE NOTION OF DIRECT PARTICIPATION IN HOSTILITIES UNDER INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW NILS MELZER Dr. Nils Melzer is legal adviser for the International Committee of
Non-state actors and Direct Participation in Hostilities. Giulio Bartolini University of Roma Tre
 Non-state actors and Direct Participation in Hostilities Giulio Bartolini University of Roma Tre The involvement of non-state actors in armed conflicts. Different kinds of non-state actors : A) Organised
Non-state actors and Direct Participation in Hostilities Giulio Bartolini University of Roma Tre The involvement of non-state actors in armed conflicts. Different kinds of non-state actors : A) Organised
THE ARMS TRADE TREATY AND
 All rights reserved. This publication is copyright, but may be reproduced by any method without fee for advocacy, campaigning and teaching purposes, but not for resale. The copyright holders request that
All rights reserved. This publication is copyright, but may be reproduced by any method without fee for advocacy, campaigning and teaching purposes, but not for resale. The copyright holders request that
PROVISIONS OF THE SPANISH CRIMINAL CODE CONCERNING INTERNATIONAL CRIMES
 PROVISIONS OF THE SPANISH CRIMINAL CODE CONCERNING INTERNATIONAL CRIMES. INTEGRATED TEXT CONTAINING THE AMENDMENTS INTRODUCED BY THE LEY ORGANICA 15/2003 IMPLEMENTING THE STATUTE OF THE INTERNATIONAL CRIMINAL
PROVISIONS OF THE SPANISH CRIMINAL CODE CONCERNING INTERNATIONAL CRIMES. INTEGRATED TEXT CONTAINING THE AMENDMENTS INTRODUCED BY THE LEY ORGANICA 15/2003 IMPLEMENTING THE STATUTE OF THE INTERNATIONAL CRIMINAL
Transfer of the Civilian Population in International Law
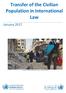 Transfer of the Civilian Population in International Law January 2017 Civilian evacuation of Daraya, 26 August 2016 (Photo AP) An increasing number of localised ceasefire agreements are being agreed between
Transfer of the Civilian Population in International Law January 2017 Civilian evacuation of Daraya, 26 August 2016 (Photo AP) An increasing number of localised ceasefire agreements are being agreed between
INTERNATIONAL CRIMINAL COURT
 INTERNATIONAL CRIMINAL COURT Marta Statkiewicz Department of International and European Law Faculty of Law, Administration and Economics University of Wrocław HISTORY HISTORY establishment of ad hoc international
INTERNATIONAL CRIMINAL COURT Marta Statkiewicz Department of International and European Law Faculty of Law, Administration and Economics University of Wrocław HISTORY HISTORY establishment of ad hoc international
Slovak priorities for the 70th Session of the UN General Assembly
 Slovak priorities for the 70th Session of the UN General Assembly During the 70 th Session of the UN General Assembly Slovakia will promote strengthening of the UN system to effectively respond to global
Slovak priorities for the 70th Session of the UN General Assembly During the 70 th Session of the UN General Assembly Slovakia will promote strengthening of the UN system to effectively respond to global
Economic and Social Council
 UNITED NATIONS E Economic and Social Council Distr. GENERAL E/CN.4/Sub.2/2003/12/Rev.2 26 August 2003 Original: ENGLISH COMMISSION ON HUMAN RIGHTS Sub-Commission on the Promotion and Protection of Human
UNITED NATIONS E Economic and Social Council Distr. GENERAL E/CN.4/Sub.2/2003/12/Rev.2 26 August 2003 Original: ENGLISH COMMISSION ON HUMAN RIGHTS Sub-Commission on the Promotion and Protection of Human
THE DISTINCTION BETWEEN INTERNATIONAL AND NON-INTERNATIONAL ARMED CONFLICTS: CHALLENGES FOR IHL?
 XXXVIII ROUND TABLE ON CURRENT ISSUES OF INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW THE DISTINCTION BETWEEN INTERNATIONAL AND NON-INTERNATIONAL ARMED CONFLICTS: CHALLENGES FOR IHL? SANREMO, 3 rd 5 th SEPTEMBER, 2015
XXXVIII ROUND TABLE ON CURRENT ISSUES OF INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW THE DISTINCTION BETWEEN INTERNATIONAL AND NON-INTERNATIONAL ARMED CONFLICTS: CHALLENGES FOR IHL? SANREMO, 3 rd 5 th SEPTEMBER, 2015
ANNEX I: APPLICABLE INTERNATIONAL LEGAL FRAMEWORK
 ANNEX I: APPLICABLE INTERNATIONAL LEGAL FRAMEWORK The legal framework applicable to the targeting of schools and universities, and the use of schools and universities in support of the military effort,
ANNEX I: APPLICABLE INTERNATIONAL LEGAL FRAMEWORK The legal framework applicable to the targeting of schools and universities, and the use of schools and universities in support of the military effort,
Chapter 8: The Use of Force
 Chapter 8: The Use of Force MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. According to the author, the phrase, war is the continuation of policy by other means, implies that war a. must have purpose c. is not much different from
Chapter 8: The Use of Force MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. According to the author, the phrase, war is the continuation of policy by other means, implies that war a. must have purpose c. is not much different from
Myanmar: International Human Rights Commitments
 Myanmar: International Human Rights Commitments Universal Periodic Review (1 st cycle documentation) 2 nd cycle Deadline for stakeholders and UN submissions 23 March 2015 (tentative) Deadline for national
Myanmar: International Human Rights Commitments Universal Periodic Review (1 st cycle documentation) 2 nd cycle Deadline for stakeholders and UN submissions 23 March 2015 (tentative) Deadline for national
A/HRC/32/L.5/Rev.1. General Assembly. ORAL REVISION 1 July. United Nations
 United Nations General Assembly ORAL REVISION 1 July Distr.: Limited 1 July 2016 Original: English Human Rights Council Thirty-second session Agenda item 4 Human rights situations that require the Council
United Nations General Assembly ORAL REVISION 1 July Distr.: Limited 1 July 2016 Original: English Human Rights Council Thirty-second session Agenda item 4 Human rights situations that require the Council
THE RED CROSS AND THE GENEVA CONVENTIONS 60 YEARS ON
 113 THE RED CROSS AND THE GENEVA CONVENTIONS 60 YEARS ON New Zealand Red Cross * I ORIGINS AND SIGNIFICANCE In 2009, the world marked the 60th anniversary of the Geneva Conventions. Although it is now
113 THE RED CROSS AND THE GENEVA CONVENTIONS 60 YEARS ON New Zealand Red Cross * I ORIGINS AND SIGNIFICANCE In 2009, the world marked the 60th anniversary of the Geneva Conventions. Although it is now
International Humanitarian Law
 International Humanitarian Law Jane Munro Australian Red Cross Henry Dunant The Battle of Solferino, 1859 Memory of Solferino The Geneva Convention 1864 Care for the wounded and dying on the battlefield
International Humanitarian Law Jane Munro Australian Red Cross Henry Dunant The Battle of Solferino, 1859 Memory of Solferino The Geneva Convention 1864 Care for the wounded and dying on the battlefield
HUMAN INTERNATIONAL LAW
 SESSION 7 HUMAN INTERNATIONAL LAW INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW HUMAN INTERNATIONAL LAW SESSION 7 I n t e r n a t i o n a l h u m a n i t a r i a n l a w International humanitarian law also called the
SESSION 7 HUMAN INTERNATIONAL LAW INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW HUMAN INTERNATIONAL LAW SESSION 7 I n t e r n a t i o n a l h u m a n i t a r i a n l a w International humanitarian law also called the
FACT SHEET STOPPING THE USE OF RAPE AS A TACTIC OF
 June 2014 FACT SHEET STOPPING THE USE OF RAPE AS A TACTIC OF WAR: A NEW APPROACH There is a global consensus that the mass rape of girls and women is routinely used as a tactic or weapon of war in contemporary
June 2014 FACT SHEET STOPPING THE USE OF RAPE AS A TACTIC OF WAR: A NEW APPROACH There is a global consensus that the mass rape of girls and women is routinely used as a tactic or weapon of war in contemporary
Published on How does law protect in war? - Online casebook (https://casebook.icrc.org)
 Published on How does law protect in war? - Online casebook (https://casebook.icrc.org) Home > ICRC, Customary International Humanitarian Law A. ICRC Report 1995 [Source: International Humanitarian Law:
Published on How does law protect in war? - Online casebook (https://casebook.icrc.org) Home > ICRC, Customary International Humanitarian Law A. ICRC Report 1995 [Source: International Humanitarian Law:
The Syrian Conflict and International Humanitarian Law
 The Syrian Conflict and International Humanitarian Law Andrew Hall The current situation in Syria is well documented. There is little doubt that a threshold of sustained violence has been reached and that
The Syrian Conflict and International Humanitarian Law Andrew Hall The current situation in Syria is well documented. There is little doubt that a threshold of sustained violence has been reached and that
InternationalHumantarianLawIhLandtheConductofNonInternationalArmedConflictNiac
 Global Journal of HUMANSOCIAL SCIENCE: H Interdisciplinary Volume 15 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN:
Global Journal of HUMANSOCIAL SCIENCE: H Interdisciplinary Volume 15 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN:
Draft of an Act to Introduce the Code of Crimes against International Law
 BMJ, Referat II A 5 - Sa (/VStGB/Entwürfe/RegEntw-fin.doc) As of 28 December 2001 Draft of an Act to Introduce the Code of Crimes against International Law The Federal Parliament has passed the following
BMJ, Referat II A 5 - Sa (/VStGB/Entwürfe/RegEntw-fin.doc) As of 28 December 2001 Draft of an Act to Introduce the Code of Crimes against International Law The Federal Parliament has passed the following
Concluding observations on the combined twentieth to twenty second periodic reports of Bulgaria*
 ADVANCE UNEDITED VERSION Distr.: General 12 May 2017 Original: English Committee on the Elimination of Racial Discrimination Concluding observations on the combined twentieth to twenty second periodic
ADVANCE UNEDITED VERSION Distr.: General 12 May 2017 Original: English Committee on the Elimination of Racial Discrimination Concluding observations on the combined twentieth to twenty second periodic
Resolution adopted by the Human Rights Council on 22 June 2017
 United Nations General Assembly Distr.: General 6 July 2017 A/HRC/RES/35/17 Original: English Human Rights Council Thirty-fifth session 6 23 June 2017 Agenda item 3 Resolution adopted by the Human Rights
United Nations General Assembly Distr.: General 6 July 2017 A/HRC/RES/35/17 Original: English Human Rights Council Thirty-fifth session 6 23 June 2017 Agenda item 3 Resolution adopted by the Human Rights
The Protection of the Civilian Population and NATO Bombing on Yugoslavia: Comments on a Report to the Prosecutor of the ICTY
 EJIL 2001... The Protection of the Civilian Population and NATO Bombing on Yugoslavia: Comments on a Report to the Prosecutor of the ICTY Michael Bothe* Abstract A report to the Prosecutor of the ICTY
EJIL 2001... The Protection of the Civilian Population and NATO Bombing on Yugoslavia: Comments on a Report to the Prosecutor of the ICTY Michael Bothe* Abstract A report to the Prosecutor of the ICTY
Background Paper on Geneva Conventions and Persons Held by U.S. Forces
 Background Paper on Geneva Conventions and Persons Held by U.S. Forces January 29, 2002 Introduction 1. International Law and the Treatment of Prisoners in an Armed Conflict 2. Types of Prisoners under
Background Paper on Geneva Conventions and Persons Held by U.S. Forces January 29, 2002 Introduction 1. International Law and the Treatment of Prisoners in an Armed Conflict 2. Types of Prisoners under
OBSERVATIONS ON THE LEGAL ISSUES RELATED TO THE USE OF CLUSTER MUNITIONS
 GROUP OF GOVERNMENTAL EXPERTS OF THE STATES PARTIES TO THE CONVENTION ON PROHIBITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS ON THE USE OF CERTAIN CONVENTIONAL WEAPONS WHICH MAY BE DEEMED TO BE EXCESSIVELY INJURIOUS OR TO HAVE
GROUP OF GOVERNMENTAL EXPERTS OF THE STATES PARTIES TO THE CONVENTION ON PROHIBITIONS OR RESTRICTIONS ON THE USE OF CERTAIN CONVENTIONAL WEAPONS WHICH MAY BE DEEMED TO BE EXCESSIVELY INJURIOUS OR TO HAVE
Measures undertaken by the Government of Romania in order to disseminate and implement the international humanitarian law
 Measures undertaken by the Government of Romania in order to disseminate and implement the international humanitarian law Romania is party to most of the international humanitarian law treaties, including
Measures undertaken by the Government of Romania in order to disseminate and implement the international humanitarian law Romania is party to most of the international humanitarian law treaties, including
NUCLEAR DISARMAMENT: AN OVERVIEW OF CUSTOMARY INTERNATIONAL LAW
 NUCLEAR DISARMAMENT: AN OVERVIEW OF CUSTOMARY INTERNATIONAL LAW Dr. Gazal Gupta Former Assistant Professor, Lovely Professional University, Punjab International law consists of not only treaties but some
NUCLEAR DISARMAMENT: AN OVERVIEW OF CUSTOMARY INTERNATIONAL LAW Dr. Gazal Gupta Former Assistant Professor, Lovely Professional University, Punjab International law consists of not only treaties but some
Resolution adopted by the General Assembly. [without reference to a Main Committee (A/63/L.48 and Add.1)]
![Resolution adopted by the General Assembly. [without reference to a Main Committee (A/63/L.48 and Add.1)] Resolution adopted by the General Assembly. [without reference to a Main Committee (A/63/L.48 and Add.1)]](/thumbs/90/102229882.jpg) United Nations A/RES/63/138 General Assembly Distr.: General 5 March 2009 Sixty-third session Agenda item 65 Resolution adopted by the General Assembly [without reference to a Main Committee (A/63/L.48
United Nations A/RES/63/138 General Assembly Distr.: General 5 March 2009 Sixty-third session Agenda item 65 Resolution adopted by the General Assembly [without reference to a Main Committee (A/63/L.48
National Action Plan to Implement United Nations Security Council Resolution 1325 Women, Peace and Security in the Republic of Serbia ( )
 National Action Plan to Implement United Nations Security Council Resolution 1325 Women, Peace and Security in the Republic of Serbia () Graphic design and pre-press COMMA communications design Printed
National Action Plan to Implement United Nations Security Council Resolution 1325 Women, Peace and Security in the Republic of Serbia () Graphic design and pre-press COMMA communications design Printed
Accession (a)/ Succession (d) Relevant Laws Constitution of 21 September 1964 Criminal Code of 10 June 1854 Police Act of 10 February 1961
 Country File MALTA Last updated: July 2009 Region Legal system Europe Civil Law/Common Law UNCAT Ratification/ 13 September 1990 (a) Accession (a)/ Succession (d) Relevant Laws Constitution of 21 September
Country File MALTA Last updated: July 2009 Region Legal system Europe Civil Law/Common Law UNCAT Ratification/ 13 September 1990 (a) Accession (a)/ Succession (d) Relevant Laws Constitution of 21 September
Reviewing the legality of new weapons, means and methods of warfare
 Volume 88 Number 864 December 2006 REPORTS AND DOCUMENTS Reviewing the legality of new weapons, means and methods of warfare Kathleen Lawand * Parties to an armed conflict are limited in their choice of
Volume 88 Number 864 December 2006 REPORTS AND DOCUMENTS Reviewing the legality of new weapons, means and methods of warfare Kathleen Lawand * Parties to an armed conflict are limited in their choice of
Legal tools to protect children
 Critical issue module 1 Abuse and exploitation Topic 2 The law and child rights Handout 2 Legal tools to protect children The CRC accords all children, regardless of their legal status, the right to be
Critical issue module 1 Abuse and exploitation Topic 2 The law and child rights Handout 2 Legal tools to protect children The CRC accords all children, regardless of their legal status, the right to be
INTERNATIONAL LAW AND ANTIPERSONNEL LAND MINES
 INTERNATIONAL LAW AND ANTIPERSONNEL LAND MINES Luke T. Lee* I. INTRODUCTION Antipersonnel (A/P) land mines are devastating weapons not only during, but also after, warfare or armed conflicts. There still
INTERNATIONAL LAW AND ANTIPERSONNEL LAND MINES Luke T. Lee* I. INTRODUCTION Antipersonnel (A/P) land mines are devastating weapons not only during, but also after, warfare or armed conflicts. There still
Challenges Facing the Asian-African States in the Contemporary. Era: An Asian-African Perspective
 Challenges Facing the Asian-African States in the Contemporary Era: An Asian-African Perspective Prof. Dr. Rahmat Mohamad At the outset I thank the organizers of this event for inviting me to deliver this
Challenges Facing the Asian-African States in the Contemporary Era: An Asian-African Perspective Prof. Dr. Rahmat Mohamad At the outset I thank the organizers of this event for inviting me to deliver this
Resolution adopted by the General Assembly. [without reference to a Main Committee (A/67/L.63 and Add.1)]
![Resolution adopted by the General Assembly. [without reference to a Main Committee (A/67/L.63 and Add.1)] Resolution adopted by the General Assembly. [without reference to a Main Committee (A/67/L.63 and Add.1)]](/thumbs/87/95409496.jpg) United Nations A/RES/67/262 General Assembly Distr.: General 4 June 2013 Sixty-seventh session Agenda item 33 Resolution adopted by the General Assembly [without reference to a Main Committee (A/67/L.63
United Nations A/RES/67/262 General Assembly Distr.: General 4 June 2013 Sixty-seventh session Agenda item 33 Resolution adopted by the General Assembly [without reference to a Main Committee (A/67/L.63
Global Human Rights Challenges and Solutions THE LAW OF WAR
 Global Human Rights Challenges and Solutions THE LAW OF WAR The State of Nature State vs. State https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/category:thirty_years_war Let Us Beat Swords into Plowshares, a sculpture
Global Human Rights Challenges and Solutions THE LAW OF WAR The State of Nature State vs. State https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/category:thirty_years_war Let Us Beat Swords into Plowshares, a sculpture
HUMANITARIAN LAW IN ARMED CONFLICT
 0 HUMANITARIAN LAW IN ARMED CONFLICT NAME: PRACHI NAIK COURSE: HUMAN RIGHTS S UBJECT: PAPER III 1 War is only a cowardly escape from the problem of peace - By Thomas Mann INTRODUCTION It is indeed a paradox
0 HUMANITARIAN LAW IN ARMED CONFLICT NAME: PRACHI NAIK COURSE: HUMAN RIGHTS S UBJECT: PAPER III 1 War is only a cowardly escape from the problem of peace - By Thomas Mann INTRODUCTION It is indeed a paradox
Obligations of International Humanitarian Law
 Obligations of International Humanitarian Law Knut Doermann It is an understatement to say that armed conflicts fought in densely populated areas can and do cause tremendous human suffering. Civilians
Obligations of International Humanitarian Law Knut Doermann It is an understatement to say that armed conflicts fought in densely populated areas can and do cause tremendous human suffering. Civilians
Summary of the Report on Civilian Casualties in Armed Conflict in 1396
 Afghanistan Independent Human Rights Commission Summary of the Report on Civilian Casualties in Armed Conflict in 1396 Special Investigation Team April 2018 Humanitarian law is a set of rules and principles
Afghanistan Independent Human Rights Commission Summary of the Report on Civilian Casualties in Armed Conflict in 1396 Special Investigation Team April 2018 Humanitarian law is a set of rules and principles
Module 2: LEGAL FRAMEWORK
 Module 2: LEGAL FRAMEWORK Identify the key components of international law governing the UN s mandated tasks in peacekeeping Learning Objectives Understand the relevance of the core legal concepts and
Module 2: LEGAL FRAMEWORK Identify the key components of international law governing the UN s mandated tasks in peacekeeping Learning Objectives Understand the relevance of the core legal concepts and
Less-Lethal Weapons Legislation
 2015 Less-Lethal Weapons Legislation Homeland Security Research Corp. Less-Lethal Weapons Legislation August 2015 Homeland Security Research Corp. (HSRC) is an international market and technology research
2015 Less-Lethal Weapons Legislation Homeland Security Research Corp. Less-Lethal Weapons Legislation August 2015 Homeland Security Research Corp. (HSRC) is an international market and technology research
Comparison of Human Security Definitions
 Internal violence, nuclear weapons, States, individual, nature, mass destruction, repression, gross environment abuses of human rights, the large-scale displacement of civilian populations, international
Internal violence, nuclear weapons, States, individual, nature, mass destruction, repression, gross environment abuses of human rights, the large-scale displacement of civilian populations, international
INTERNATIONAL HUMAN RIGHTS LAW
 INTERNATIONAL HUMAN RIGHTS LAW Nuremburg tried for Crimes of aggression Jus Ad Bellum- determining when it is lawful to resort to force War is Outlawed War is outlawed by the United Nations. Article 2.4
INTERNATIONAL HUMAN RIGHTS LAW Nuremburg tried for Crimes of aggression Jus Ad Bellum- determining when it is lawful to resort to force War is Outlawed War is outlawed by the United Nations. Article 2.4
The University of Edinburgh. From the SelectedWorks of Ray Barquero. Ray Barquero, Mr., University of Edinburgh. Fall October, 2012
 The University of Edinburgh From the SelectedWorks of Ray Barquero Fall October, 2012 International Humanitarian Law Essay: A concise assessment of the interplay between the various sources of international
The University of Edinburgh From the SelectedWorks of Ray Barquero Fall October, 2012 International Humanitarian Law Essay: A concise assessment of the interplay between the various sources of international
Women, armed conflict and international law
 Women, armed conflict and international law HELEN DURHAM* IHL takes a particular male perspective on armed conflict, as a norm against which to measure equality. In a world where women are not equals of
Women, armed conflict and international law HELEN DURHAM* IHL takes a particular male perspective on armed conflict, as a norm against which to measure equality. In a world where women are not equals of
Cordula Droege Legal adviser, ICRC
 DEVELOPMENTS IN THE LEGAL PROTECTION OF INTERNALLY DISPLACED PERSONS 10 YEARS OF EXPERIENCE SINCE THE GUIDING PRINCIPLES Cordula Droege Legal adviser, ICRC It has been 10 years since the then special representative
DEVELOPMENTS IN THE LEGAL PROTECTION OF INTERNALLY DISPLACED PERSONS 10 YEARS OF EXPERIENCE SINCE THE GUIDING PRINCIPLES Cordula Droege Legal adviser, ICRC It has been 10 years since the then special representative
Chapter 3: The Legal Framework
 Chapter 3: The Legal Framework This Chapter provides an overview of the international legal framework that protects persons of concern to UNHCR; highlights the importance of national laws and institutions
Chapter 3: The Legal Framework This Chapter provides an overview of the international legal framework that protects persons of concern to UNHCR; highlights the importance of national laws and institutions
Fallujah and its Aftermath
 OXFORD RESEARCH GROUP International Security Monthly Briefing - November 2004 Fallujah and its Aftermath Professor Paul Rogers Towards the end of October there were numerous reports of a substantial build-up
OXFORD RESEARCH GROUP International Security Monthly Briefing - November 2004 Fallujah and its Aftermath Professor Paul Rogers Towards the end of October there were numerous reports of a substantial build-up
The human rights situation in Sudan
 Human Rights Council Twenty-fourth session Agenda item 10 The human rights situation in Sudan The undersigned organizations urge the Human Rights Council to extend and strengthen the mandate of the Independent
Human Rights Council Twenty-fourth session Agenda item 10 The human rights situation in Sudan The undersigned organizations urge the Human Rights Council to extend and strengthen the mandate of the Independent
Transnationally networked armed conflict. Associate Professor Greg Rose
 Transnationally networked armed conflict Associate Professor Greg Rose Politics, Crime or War? Armed attacks as Politics No problem! Apply laws of asylum Politics, Crime or War? Crime Enforce domestic
Transnationally networked armed conflict Associate Professor Greg Rose Politics, Crime or War? Armed attacks as Politics No problem! Apply laws of asylum Politics, Crime or War? Crime Enforce domestic
CHAPTER 1 BASIC RULES AND PRINCIPLES
 CHAPTER 1 BASIC RULES AND PRINCIPLES Section I. GENERAL 1. Purpose and Scope The purpose of this Manual is to provide authoritative guidance to military personnel on the customary and treaty law applicable
CHAPTER 1 BASIC RULES AND PRINCIPLES Section I. GENERAL 1. Purpose and Scope The purpose of this Manual is to provide authoritative guidance to military personnel on the customary and treaty law applicable
Bearing in mind the report of the Secretary-General on children and armed conflict (S/2002/1299),
 Situation of Human Rights in Myanmar Commission on Human Rights resolution 2003/12 The Commission on Human Rights, Guided by the Charter of the United Nations, the Universal Declaration of Human Rights,
Situation of Human Rights in Myanmar Commission on Human Rights resolution 2003/12 The Commission on Human Rights, Guided by the Charter of the United Nations, the Universal Declaration of Human Rights,
UN Security Council, Report of the Secretary-General on the AU/UN Hybrid Operation in Darfur, 12 July 2013, UN Doc S/2013/420. 2
 Human Rights Situation in Sudan: Amnesty International s joint written statement to the 24th session of the UN Human Rights Council (9 September 27 September 2013) AFR 54/015/2013 29 August 2013 Introduction
Human Rights Situation in Sudan: Amnesty International s joint written statement to the 24th session of the UN Human Rights Council (9 September 27 September 2013) AFR 54/015/2013 29 August 2013 Introduction
Resolution adopted by the General Assembly. [without reference to a Main Committee (A/61/L.45 and Add.1)]
![Resolution adopted by the General Assembly. [without reference to a Main Committee (A/61/L.45 and Add.1)] Resolution adopted by the General Assembly. [without reference to a Main Committee (A/61/L.45 and Add.1)]](/thumbs/90/103662559.jpg) United Nations A/RES/61/133 General Assembly Distr.: General 1 March 2007 Sixty-first session Agenda item 69 Resolution adopted by the General Assembly [without reference to a Main Committee (A/61/L.45
United Nations A/RES/61/133 General Assembly Distr.: General 1 March 2007 Sixty-first session Agenda item 69 Resolution adopted by the General Assembly [without reference to a Main Committee (A/61/L.45
Draft Resolution for Committee Consideration and Recommendation
 Draft Resolution for Committee Consideration and Recommendation Committee A : Civil War and Genocide Draft Resolution Submitted for revision by the delegations to the Model United Nations, College of Charleston,
Draft Resolution for Committee Consideration and Recommendation Committee A : Civil War and Genocide Draft Resolution Submitted for revision by the delegations to the Model United Nations, College of Charleston,
RUSSIAN FEDERATION. Brief summary of concerns about human rights violations in the Chechen Republic RECENT AMNESTY INTERNATIONAL CONCERNS 1
 RUSSIAN FEDERATION Brief summary of concerns about human rights violations in the Chechen Republic RECENT AMNESTY INTERNATIONAL CONCERNS 1 Massive human rights violations have taken place within the context
RUSSIAN FEDERATION Brief summary of concerns about human rights violations in the Chechen Republic RECENT AMNESTY INTERNATIONAL CONCERNS 1 Massive human rights violations have taken place within the context
Identifying the Enemy: Civilian Participation in Armed Conflict
 International Review of the Red Cross (2015), 97 (900), 1507 1511. The evolution of warfare doi:10.1017/s181638311600031x BOOK REVIEW Identifying the Enemy: Civilian Participation in Armed Conflict Emily
International Review of the Red Cross (2015), 97 (900), 1507 1511. The evolution of warfare doi:10.1017/s181638311600031x BOOK REVIEW Identifying the Enemy: Civilian Participation in Armed Conflict Emily
OI Policy Compendium Note on Multi-Dimensional Military Missions and Humanitarian Assistance
 OI Policy Compendium Note on Multi-Dimensional Military Missions and Humanitarian Assistance Overview: Oxfam International s position on Multi-Dimensional Missions and Humanitarian Assistance This policy
OI Policy Compendium Note on Multi-Dimensional Military Missions and Humanitarian Assistance Overview: Oxfam International s position on Multi-Dimensional Missions and Humanitarian Assistance This policy
IMPORTANCE OF PREVENTING CONFLICT THROUGH DEVELOPMENT,
 PRESS RELEASE SECURITY COUNCIL SC/8710 28 APRIL 2006 IMPORTANCE OF PREVENTING CONFLICT THROUGH DEVELOPMENT, DEMOCRACY STRESSED, AS SECURITY COUNCIL UNANIMOUSLY ADOPTS RESOLUTION 1674 (2006) 5430th Meeting
PRESS RELEASE SECURITY COUNCIL SC/8710 28 APRIL 2006 IMPORTANCE OF PREVENTING CONFLICT THROUGH DEVELOPMENT, DEMOCRACY STRESSED, AS SECURITY COUNCIL UNANIMOUSLY ADOPTS RESOLUTION 1674 (2006) 5430th Meeting
INTERNATIONAL LAW AND INSTITUTIONS International Law Regarding the Conduct of War - Mark A. Drumbl INTERNATIONAL LAW REGARDING THE CONDUCT OF WAR
 INTERNATIONAL LAW REGARDING THE CONDUCT OF WAR Mark A. Drumbl Assistant Professor, Washington & Lee University, School of Law, Lexington, Virginia, USA Keywords: Customary international law, environment,
INTERNATIONAL LAW REGARDING THE CONDUCT OF WAR Mark A. Drumbl Assistant Professor, Washington & Lee University, School of Law, Lexington, Virginia, USA Keywords: Customary international law, environment,
UNIDIR RESOURCES IDEAS FOR PEACE AND SECURITY. Explosive Weapons Framing the Problem April Summary
 IDEAS FOR PEACE AND SECURITY UNIDIR RESOURCES Explosive Weapons Framing the Problem April 2010 Background Paper 1 of the Discourse on Explosive Weapons (DEW) project 1 by Maya Brehm and John Borrie Summary
IDEAS FOR PEACE AND SECURITY UNIDIR RESOURCES Explosive Weapons Framing the Problem April 2010 Background Paper 1 of the Discourse on Explosive Weapons (DEW) project 1 by Maya Brehm and John Borrie Summary
Protecting Children in Armed Conflict and Natural Disaster
 Protecting Children in Armed Conflict and Natural Disaster A guide to the Convention on the Rights of the Child, International Humanitarian Law and complementary mechanisms, principles and programmatic
Protecting Children in Armed Conflict and Natural Disaster A guide to the Convention on the Rights of the Child, International Humanitarian Law and complementary mechanisms, principles and programmatic
HUMAN INTERNATIONAL LAW
 SESSION 8 HUMAN INTERNATIONAL LAW HUMAN RIGHTS GENEVA CONVENTIONS HUMAN INTERNATIONAL LAW SESSION 8 Human rights Geneva Conventions Human rights: an overview International human rights law began as a response
SESSION 8 HUMAN INTERNATIONAL LAW HUMAN RIGHTS GENEVA CONVENTIONS HUMAN INTERNATIONAL LAW SESSION 8 Human rights Geneva Conventions Human rights: an overview International human rights law began as a response
STOP KILLING CIVILIANS, START TAKING RESPONSIBILITY: Searching questions about cluster munitions
 STOP KILLING CIVILIANS, START TAKING RESPONSIBILITY: Searching questions about cluster munitions Discussion paper by Dr. Brian Rappert and Richard Moyes B.Rappert@exeter.ac.uk & Richard.Moyes@biscituk.biz
STOP KILLING CIVILIANS, START TAKING RESPONSIBILITY: Searching questions about cluster munitions Discussion paper by Dr. Brian Rappert and Richard Moyes B.Rappert@exeter.ac.uk & Richard.Moyes@biscituk.biz
Conflating Terrorism and Insurgency
 Page 1 of 6 MENU FOREIGN POLICY ESSAY Conflating Terrorism and Insurgency By John Mueller, Mark Stewart Sunday, February 28, 2016, 10:05 AM Editor's Note: What if most terrorism isn t really terrorism?
Page 1 of 6 MENU FOREIGN POLICY ESSAY Conflating Terrorism and Insurgency By John Mueller, Mark Stewart Sunday, February 28, 2016, 10:05 AM Editor's Note: What if most terrorism isn t really terrorism?
Vienna Declaration and Programme of Action
 25 June 1993 Vienna Declaration and Programme of Action Adopted by the World Conference on Human Rights in Vienna on 25 June 1993 The World Conference on Human Rights, Considering that the promotion and
25 June 1993 Vienna Declaration and Programme of Action Adopted by the World Conference on Human Rights in Vienna on 25 June 1993 The World Conference on Human Rights, Considering that the promotion and
A/HRC/WG.6/10/NRU/2. General Assembly. United Nations
 United Nations General Assembly Distr.: General 21 October 2010 Original: English Human Rights Council Working Group on the Universal Periodic Review Tenth session Geneva, 24 January 4 February 2011 Compilation
United Nations General Assembly Distr.: General 21 October 2010 Original: English Human Rights Council Working Group on the Universal Periodic Review Tenth session Geneva, 24 January 4 February 2011 Compilation
SGTM 6C: GENDER AND PEACEKEEPING
 SGTM 6C: GENDER AND PEACEKEEPING The Standard Generic Training Module (SGTM) 6C deals with Gender and Peacekeeping. The 6 th Module groups together a number of sub-modules that all deals with the behavior
SGTM 6C: GENDER AND PEACEKEEPING The Standard Generic Training Module (SGTM) 6C deals with Gender and Peacekeeping. The 6 th Module groups together a number of sub-modules that all deals with the behavior
