Period 8 and Period to Infinity
|
|
|
- Nathaniel Cole
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Period 8 and Period to Infinity
2
3 YOU AND THE DECADES: A TIME OF WONDER AND AMAZEMENT Using the textbook and your massive brains, spend time perusing the decades of the mid-20 th century. It is a tremendous time in US history that would love for you to learn more about it, even more than you will learn in class. Spend a few minutes each night knocking out a few questions and packing in some very solid information. It s a good chance for you and the decades to get to know each other better. Remember waiting until the last minute will not allow you to build the relationship that the decades desire, so be diligent and be the wonderful students that I know you to be. Please note that some questions are asking for your opinion, use that young mind of yours to support those opinions with knowledge. Knowing is half the battle. The other half is not procrastinating. FOCUS ON THE FIFTIES 1. What was McCarthyism? Why did it emerge in the early 1950s? 2. What event brought about McCarthy s downfall and why? 3. How did the United States become involved in the Korean War ( )? Who did we fight against? How was the war resolved? 4. Did President Truman make the right decision to fire General MacArthur in 1951? Why or why not? 5. Who was John Foster Dulles and why was he significant? (besides having an airport named after him) 6. What was Eisenhower s New Look defense policy? What were the goals of this policy? 7. Is the doctrine of massive retaliation (or MAD) a good idea? Why or why not? 8. Why is the Suez Crisis significant in world history, as well as American history? 9. What were the Geneva Accords and how did they pave the way for U.S. entry into the Southeast Asian conflict? 10. What was Eisenhower s greatest domestic achievement that was also a great example of dynamic conservatism? 11. Explain the significance of John Kenneth Galbraith s The Affluent Society and Michael Harrington s The Other America? 12. What two U.S. government initiatives resulted from the Sputnik launch in 1957? What were they designed to do?
4 FOCUS ON THE SIXTIES 1. Who were the major candidates for president in 1960 and why did the election represent a turning point in American political history? 2. Why did the Democrats fail to retain the presidency in the 1968 election? Identify at least two major reasons. 3. What is the Peace Corps and how did it fit with JFK s new approach to the Cold War? 4. What was the result of the Berlin Crisis of 1961? 5. What was the significance of the Bay of Pigs in 1961? How did it contribute to the Cuban Missile Crisis in 1962? 6. What was the Tet Offensive of 1968? How did it mark a turning point in the Vietnam conflict? 7. What was the New Left movement? Why did it gain ground in the late 1960s? 8. What were three major achievements of LBJ s Great Society? 9. What were the two major legislative achievements of the civil rights movement? 10. What was the Black Power movement? Why was it significant? FOCUS ON THE SEVENTIES 1. What was the Republican Party s Southern Strategy? Did it work? 2. What was the Watergate scandal and why did it lead to President Nixon s resignation in 1974? 3. What was the Nixon Doctrine and how did it compare to the Truman Doctrine?
5 4. Why did Nixon order the invasion of Cambodia in 1970? What was the result at home? 5. What was détente and what were some of the results of this policy during Nixon s presidency? Was it a smart approach? 6. What was Jimmy Carter s greatest foreign policy achievement? 7. What were his two greatest foreign policy challenges and why? 8. What is stagflation? How did it challenge Keynesian thinking? 9. What was the significance of Roe v. Wade and the ERA movement? 10. What was the significance of the Love Canal and Three Mile Island incidents? FOCUS ON THE EIGHTIES 1. Why did Ronald Reagan s presidential election victory in 1980 represent a transformation in modern American politics? 2. What was the Moral Majority and what impact did it have on American politics? 3. What is Reaganomics? Describe at least two outcomes of this set of policies. Was this approach a good one for the U.S. economy? 4. What was the Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI) and how did it play a role in the Cold War? 5. What was the Reagan Doctrine? How does it differ from the Truman Doctrine? Identify two cases where it was applied. 6. How did Reagan s approach to the Soviet Union change after 1984? Why? What were two concrete results of this change?
6
7 America in the 1950 s -- Station Guide Post-World War II Domestic Issues What were some of the advances made during WWII that would affect post-war America? What were some of the hindrances to returning to normal life after the war? The Postwar Economy In what ways did WWII contribute to the end of the Depression? (give details) What factors affected the US economy in the years immediately after WWII? What impact did they have on the economy? The Late 1940s What were some adjustments Americans made to adapt to the post WWII era? The Housing Boom Explain the provisions of the GI Bill and how they played out in the post-war economy. Describe the Levittown living experience? Do you think it played a role in creating the America you know today? The Age of the Automobile What was the effect of developments in automobiles and transportation in the late 40 s and early 50 s? Truman s Admin istrat ion Describe some of the successes and failures of the Truman Administration. What do you think was the reason behind and the effect of the Taft-Hartley Act? The 1948 Election What were some of the challenges Truman faced in his bid for re-election in 1948? What factors do you think led to Truman's victory in 1948? What were the major developments of Truman s second term?
8 The 1950 s Give examples supporting the claim that the 1950 s were a decade of both stability and change. The Eisenhower Years What were some challenges Eisenhower faced as he entered office in 1952? Describe some of the changes that took place in America during the Eisenhower years. Women s Roles During WWII women were encouraged to participate in the workplace and over 200,000 even joined the military. What has changed by the 1950 s in the expectations for women? Why do you think these expectations changed? The Late 1950 s What international developments shook America s sense of stability in the 1950 s? What steps did America take to respond to these international challenges? Briefly describe the good and the bad of life in America in the 1950 s
9 Gulf of Tonkin Resolution Guiding Questions Most history books say that the United States war in Vietnam began in 1964, after Congress passed the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution. However, it is no secret that the United States had been very involved in the region for at least a decade before. By the time JFK was assassinated in 1963, the United States had 16,000 military troops in Vietnam. Today we are going to try to answer the question: Was the U.S. planning to go to war in Vietnam before August 1964? Document A According to this document, what did the North Vietnamese do? Why did the United States feel compelled to respond at this point? According to this document, was the U.S. planning to go to war in Vietnam before August 1964? Explain your answer. Document B When was this document written? Who wrote it? What did Bundy suggest to the President? What are three reasons why Bundy made this recommendation? According to this document, was the U.S. planning to go to war in Vietnam before August 1964? Explain your answer. Document C When was this document written? Who wrote it? How did Rusk feel about the South Vietnamese govt s ability to fight the Communists? Support answer with evidence. Why did Rusk think attacking the North Vietnamese is not a smart idea? According to this document, was the U.S. planning to go to war in Vietnam before August 1964? Explain your answer. Document D What type of document is this? How trustworthy do you think this type of document is? What is the dilemma facing President Johnson? According to this document, was the U.S. planning to go to war in Vietnam before August 1964? Explain your answer. Using the docs, on the back of this page write a paragraph in response the question: Was the U.S. planning to go to war in Vietnam before August 1964?
10
11 Civil Rights in the 20 th Century Group Challenges Faced Leaders & Organizations Strategies Accomplishments Deficiencies Women African-Americans
12 Civil Rights in the 20 th Century Group Challenges Faced Leaders & Organizations Strategies Accomplishments Deficiencies Native American Latino
13 Major Events in 1968 Event Define/Explanation Significance/Consequences Tet Offensive Johnson s Decision not to seek 2 nd Term Assassination of Marin Luther King, Jr. Assassination of Robert Kennedy Violence at the Democratic National Convention American Independent Party Soviet suppression of Czech Rebellion
14 US History Period 9 Presidents Name: Directions: Using your book, find information and events that fit in the appropriate boxes. Be sure to give specific details on each individual event that you use. Be thorough and be sure to include details. You ll need them. Years in office President Domestic Policies/Events Foreign Policies/Events Political Economic Social Ronald Reagan Political Party: Vice-President(s): George H. W. Bush Political Party: Vice-President(s): William Clinton Political Party: Vice-President(s): George W. Bush Political Party: Vice-President(s): Barack Obama Political Party: Vice-President(s):
15 THE COLD WAR: Roots of the Cold War U.S. had tried to defeat Bolshevik revolution by invading Russia at Archangel in Communist and democratic/capitalistic ideology non-compatible Failure of Allies to open 2nd front against Germany in 1943 angers Stalin U.S. failure to inform Stalin of A-Bomb until July, 1945 angers Stalin U.S. termination of Lend-Lease to Soviets (while Britain continued to receive aid) angers Stalin Stalin promises free elections for E. Europe at Yalta Stalin refuses free elections for E. Europe at Potsdam, 1945 (angers Allies) Stalin refuses to give E. Germany back (angers Allies) Churchill s Iron Curtain speech (1946): wake up call to Americans vis-à-vis Soviet threat Cold War -- Truman Truman Doctrine, 1947 U.S. pledges to help oppressed people s fight communism; Greece and Turkey are given money and both countries become democracies. Marshall Plan, 1947 Sought to create European economic recovery to prevent communism from taking hold in Europe. Berlin Airlift, U.S. thwarted Soviet blockade of Berlin NATO, 1949 Collective security organization to protect Europe of Soviet threat. Fall of China, 1949; Mao Zedong defeats Chang Kai-shek who flees to Taiwan. Soviets detonate A-Bomb, 1949 Korean War, UN forces led by U.S. prevent communist takeover of South Korea. Cold War--Eisenhower's policies Secretary of State John Foster Dulles: Massive Retaliation ; brinksmanship Soviets develop Hydrogen Bomb in 1953 (U.S. in 1952) End to massive retaliation? Mutual Assured Destruction (MAD) CIA overthrows Moussadegh in Iran, 1953; returns Shah to power (friendly to U.S.)/CIA overthrows leftist leader in Guatemala, 1954 Domino theory : provides aid to France in Vietnam (later to South Vietnam) /Dien Bien Phu, 1954 Geneva Conference, 1954: Vietnam temporarily divided into North and South Dulles forms SEATO (South East Asia Treaty Organization); only a few countries join Ho Chi Minh (leader of Vietminh) vs. Ngo Dinh Diem (leader of S. Vietnam) Peaceful Coexistence with Soviets (Khrushchev); Geneva Summit, 1955 Cold War in Middle East/ U.S intervenes in Suez Crisis, 1956 (along with Soviets)/U.S. troops sent to Lebanon, 1958 Sputnik/ National Education Act (in response to Sputnik) /Space race begins/ NASA (in response to Sputnik) increased arms race U-2 incident: : U.S. spy plane shot down over USSR; Paris Summit breaks down. Plans to overthrow Castro Cold War Kennedy Secretary of State Robert McNamara/Flexible Response Bay of Pigs, 1961 CIA-sponsored invasion by Cuban exiles fails Cuban Missile Crisis, 1962 Krushchev agrees to remove missiles; U.S. agrees not to invade Cuba and remove its missiles in turkey. Nuclear Test Ban Treaty, 1963 Kennedy increases military advisors in S. Vietnam: /Kennedy tacitly approves assassination of Ngo Dinh Diem, 1963
16 Cold War Johnson: Vietnam War Gulf of Tonkin Resolution, 1964 Congress allows LBJ to widen the war in Vietnam. Operation Rolling Thunder Escalation under Johnson: ; 500,000 men in Vietnam by 1968 U.S. Army led by William Westmoreland; body counts ; search and destroy missions; napalm Tet Offensive, 1968: Americans believe war can t be won (begins the end of U.S. involvement) Cold War -- Nixon Secretary of State Henry Kissinger Vietnam War: o 1969, Nixon announces secret plan to end the war but it continues 4 more years/ Vietnamization o 1969, Nixon begins secret bombing in Cambodia, Laos, & N. Vietnam (Ho Chi Minh Trail) o 1970, Nixon announces invasion of Cambodia; mass protests result: Kent State, Jackson State o 1972, Paris Peace Accords result in agreement for ending the war (not accepted until 1973) _ Vietcong retained large areas it gained in South Vietnam; U.S. POWs to be returned in 60 days. o 1973, U.S. pulls out of S. Vietnam/ 1975, communists overrun Saigon and unify Vietnam under communism _ Détente: Nixon (and Ford and Carter) o Kissinger used realpolitik in dealing with Soviets; replaced ideology with practical politics. o Nixon visits China, 1972: Opens new era of improved relations with China. o Nixon visits Moscow, 1972: Plays the China card and gets USSR to help convince North Vietnam to negotiate. o ABM Treaty limited U.S. & USSR to only a few anti-ballistic missiles, o SALT I, 1972: U.S. and USSR agreed to stop making nuclear ballistic missiles and to _ reduce the number of antiballistic missiles to 200 for each power. o Helsinki Conference, 1975: Ended WWII and recognized USSR borders in E. Europe; USSR pledged to improve human rights & increase communication between East & West. o Détente ends with Soviet invasion of Afghanistan in 1979 (during Carter s presidency) _ U.S. boycotts Olympic Games in Moscow, 1980 _ Soviets boycott Olympic Games in Los Angeles, 1984 Cold War: 1980s Reagan (and Bush) _ Reagan begins massive arms build-up _ Economic sanctions on Poland, 1981 In response to communist crackdown on Polish Solidarity movement. _ Star Wars, SDI, 1983: Reagan announced plan to build an anti-missile defense system; _ Soviets became concerned they could not keep up with the arms race _ Evil Empire speech, 1983: -- Justified his military build-up as necessary to thwart aggressive Soviets. _ U.S. aid to Nicaraguan Contras: Sought to overthrow Sandinistas (communists) _ U.S. troops sent to Grenada, 1983: Small Marxist gov t removed by U.S. forces. _ Geneva Summit, 1985 Reagan & Gorbachev meet for first time and lay foundation for future talks. _ INF Treaty, 1987: Banned all intermediate-range missiles from Europe. _ Fall of communism in 1989 in Eastern Europe _ Fall of Soviet Union, 1991
Know how Mao Zedong and the Communists win the Communist Civil War and took over China from Chang Kai Shek?
 U.S HISTORY SECOND SEMESTER REVIEW KNOW THESE MATCHING TERMS: 1. The Berlin airlift 2. Tet Offensive 3. Domino Theory 4. Ho Chi Mihn 5. Freedom Riders 6. Malcolm X 7. Brown v. Board of Education 8. Jackie
U.S HISTORY SECOND SEMESTER REVIEW KNOW THESE MATCHING TERMS: 1. The Berlin airlift 2. Tet Offensive 3. Domino Theory 4. Ho Chi Mihn 5. Freedom Riders 6. Malcolm X 7. Brown v. Board of Education 8. Jackie
Harry Truman Dwight Eisenhower John F. Kennedy
 Harry Truman Dwight Eisenhower John F. Kennedy Years in office Political Party Decisions or Decisions, Acts, or Identify 2 significant social aspects of this era Lyndon Johnson Richard Nixon Gerald Ford
Harry Truman Dwight Eisenhower John F. Kennedy Years in office Political Party Decisions or Decisions, Acts, or Identify 2 significant social aspects of this era Lyndon Johnson Richard Nixon Gerald Ford
Communism. Soviet Union government State (government) controls everything Opposite of democracy and capitalism (USA)
 Cold War VS Communism Soviet Union government State (government) controls everything Opposite of democracy and capitalism (USA) United Nations (UN) Started with 50 member countries Created to promote peace
Cold War VS Communism Soviet Union government State (government) controls everything Opposite of democracy and capitalism (USA) United Nations (UN) Started with 50 member countries Created to promote peace
Chapter 17 Lesson 1: Two Superpowers Face Off. Essential Question: Why did tension between the U.S. and the U.S.S.R increase after WWII?
 Chapter 17 Lesson 1: Two Superpowers Face Off Essential Question: Why did tension between the U.S. and the U.S.S.R increase after WWII? Post WWII Big Three meet in Yalta Divide Germany into 4 zones (U.S.,
Chapter 17 Lesson 1: Two Superpowers Face Off Essential Question: Why did tension between the U.S. and the U.S.S.R increase after WWII? Post WWII Big Three meet in Yalta Divide Germany into 4 zones (U.S.,
Chapter 20. The Vietnam War Era
 Chapter 20 The Vietnam War Era 1954-1975 Ho Chi Minh The most important voice who demanded independence for Vietnam. Communist leader of the Vietminh. Vietminh The term initially used to describe all Vietnamese
Chapter 20 The Vietnam War Era 1954-1975 Ho Chi Minh The most important voice who demanded independence for Vietnam. Communist leader of the Vietminh. Vietminh The term initially used to describe all Vietnamese
World History Chapter 23 Page Reading Outline
 World History Chapter 23 Page 601-632 Reading Outline The Cold War Era: Iron Curtain: a phrased coined by Winston Churchill at the end of World War I when her foresaw of the impending danger Russia would
World History Chapter 23 Page 601-632 Reading Outline The Cold War Era: Iron Curtain: a phrased coined by Winston Churchill at the end of World War I when her foresaw of the impending danger Russia would
Unit 15 Cold War-Present
 Unit 15 Cold War-Present Section 1: Introduction Cold War Definition A cold war in general is a state of political hostility between countries characterized by threats, propaganda, and other measures short
Unit 15 Cold War-Present Section 1: Introduction Cold War Definition A cold war in general is a state of political hostility between countries characterized by threats, propaganda, and other measures short
Chapter 17: Restructuring the Postwar World: 1945-Present I. Cold War: Superpowers Face Off (Section 1) a. Allies Become Enemies i.
 Chapter 17: Restructuring the Postwar World: 1945-Present I. Cold War: Superpowers Face Off (Section 1) a. Allies Become Enemies i. Yalta Conference: A Postwar Plan 1. In February 1945, British, American
Chapter 17: Restructuring the Postwar World: 1945-Present I. Cold War: Superpowers Face Off (Section 1) a. Allies Become Enemies i. Yalta Conference: A Postwar Plan 1. In February 1945, British, American
Unit 7: The Cold War
 Unit 7: The Cold War Standard 7-5 Goal: The student will demonstrate an understanding of international developments during the Cold War era. Vocabulary 7-5.1 OCCUPIED 7-5.2 UNITED NATIONS NORTH ATLANTIC
Unit 7: The Cold War Standard 7-5 Goal: The student will demonstrate an understanding of international developments during the Cold War era. Vocabulary 7-5.1 OCCUPIED 7-5.2 UNITED NATIONS NORTH ATLANTIC
Unit XIII FOCUS QUESTIONS
 Unit XIII FOCUS QUESTIONS The Cold War Begins Chapter 36 pp. 825-866 How and why did the American economy soar from 1950 to 1970? How did population changes shape American society following World War II?
Unit XIII FOCUS QUESTIONS The Cold War Begins Chapter 36 pp. 825-866 How and why did the American economy soar from 1950 to 1970? How did population changes shape American society following World War II?
Early Cold War
 Early Cold War 1945-1972 Capitalism vs. Communism Capitalism Communism Free-Market Economy Upper, Middle and Working Class North Atlantic Treaty Organization Government Controlled Economy Classless Society
Early Cold War 1945-1972 Capitalism vs. Communism Capitalism Communism Free-Market Economy Upper, Middle and Working Class North Atlantic Treaty Organization Government Controlled Economy Classless Society
The Cold War TOWARD A GLOBAL COMMUNITY (1900 PRESENT)
 The Cold War TOWARD A GLOBAL COMMUNITY (1900 PRESENT) Throughout WWII the U.S. and the Soviet Union began to view each other with increasing suspicion. He s a commie, and once made an alliance with Hitler...
The Cold War TOWARD A GLOBAL COMMUNITY (1900 PRESENT) Throughout WWII the U.S. and the Soviet Union began to view each other with increasing suspicion. He s a commie, and once made an alliance with Hitler...
World History: Patterns of Interaction
 Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945-Present The United States and the Soviet Union vie for superiority, and both countries extend their control over other nations. Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945-Present
Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945-Present The United States and the Soviet Union vie for superiority, and both countries extend their control over other nations. Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945-Present
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Cold War Tensions (Chapter 30 Quiz)
 Cold War Tensions (Chapter 30 Quiz) What were the military and political consequences of the Cold War in the Soviet Union, Europe, and the United States? After World War II ended, the United States and
Cold War Tensions (Chapter 30 Quiz) What were the military and political consequences of the Cold War in the Soviet Union, Europe, and the United States? After World War II ended, the United States and
EOC Test Preparation: The Cold War Era
 EOC Test Preparation: The Cold War Era Conflict in Europe Following WWII, tensions were running high between western Allies and USSR US and Great Britain: Allies should not occupy territories they conquered
EOC Test Preparation: The Cold War Era Conflict in Europe Following WWII, tensions were running high between western Allies and USSR US and Great Britain: Allies should not occupy territories they conquered
Ch. 16 Sec. 1: Origins of the Vietnam War
 CHAPTER 16 QUESTIONS 5 sections, and Document Based Questions Ch. 16 Sec. 1: Origins of the Vietnam War 1) French Indochina included which three cultures? 2) How many people lived in Indochina by the end
CHAPTER 16 QUESTIONS 5 sections, and Document Based Questions Ch. 16 Sec. 1: Origins of the Vietnam War 1) French Indochina included which three cultures? 2) How many people lived in Indochina by the end
UNIT Y222 THE COLD WAR IN ASIA
 UNIT Y222 THE COLD WAR IN ASIA 1945-1993 NOTE: BASED ON 2 X 50 MINUTE LESSONS PER WEEK TERMS BASED ON 6 TERM YEAR. Key Topic Term Week Number Indicative Content Extended Content Resources Western Policies
UNIT Y222 THE COLD WAR IN ASIA 1945-1993 NOTE: BASED ON 2 X 50 MINUTE LESSONS PER WEEK TERMS BASED ON 6 TERM YEAR. Key Topic Term Week Number Indicative Content Extended Content Resources Western Policies
THE IRON CURTAIN. From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic an iron curtain has descended across the continent. - Winston Churchill
 COLD WAR 1945-1991 1. The Soviet Union drove the Germans back across Eastern Europe. 2. They occupied several countries along it s western border and considered them a necessary buffer or wall of protection
COLD WAR 1945-1991 1. The Soviet Union drove the Germans back across Eastern Europe. 2. They occupied several countries along it s western border and considered them a necessary buffer or wall of protection
8-1: THE EARLY COLD WAR,
 8-1: THE EARLY COLD WAR, 1945-1963 I. Overview A. The United States responded to an uncertain and unstable postwar world by asserting and working to maintain a position of global leadership, with far-reaching
8-1: THE EARLY COLD WAR, 1945-1963 I. Overview A. The United States responded to an uncertain and unstable postwar world by asserting and working to maintain a position of global leadership, with far-reaching
Ended French rule in Indo-China
 Vietnam Review Dien Bien Phu in 1954 the main French forces were surrounded at this location in the north of Vietnam and forced to surrender. This was a turning point in that it ended the French control
Vietnam Review Dien Bien Phu in 1954 the main French forces were surrounded at this location in the north of Vietnam and forced to surrender. This was a turning point in that it ended the French control
Notes: LG: Analyze how the 1960s changed America.
 Notes: LG: Analyze how the 1960s changed America. USSR Nikita Khrushchev 1953-1964 1. Cold War Abroad in the 1960s a. 1961, Bay of Pigs Invasion (Cuba) i. President Eisenhower and CIA train Cuban
Notes: LG: Analyze how the 1960s changed America. USSR Nikita Khrushchev 1953-1964 1. Cold War Abroad in the 1960s a. 1961, Bay of Pigs Invasion (Cuba) i. President Eisenhower and CIA train Cuban
4/8/2015. April nations met. US and USSR on same side in WW II. Cold War Feb FDR, Churchill, Stalin Postwar issues
 Chapter 26 US and USSR on same side in WW II Not by choice Common enemy Cold War 1946 1991 Feb. 1945 FDR, Churchill, Stalin Postwar issues divide Germany free elections April 1945 50 nations met UN Charter
Chapter 26 US and USSR on same side in WW II Not by choice Common enemy Cold War 1946 1991 Feb. 1945 FDR, Churchill, Stalin Postwar issues divide Germany free elections April 1945 50 nations met UN Charter
What post-war issues caused the Western Allies and the Soviet Union to disagree? What did Churchill mean by an iron curtain has descended?
 The Cold War I. Friend and Foe A. During WWII the US and USSR were. B. The could not have been beaten without the Soviets. C. Near the end of the war the allies met to discuss the. II. The A. Roosevelt,
The Cold War I. Friend and Foe A. During WWII the US and USSR were. B. The could not have been beaten without the Soviets. C. Near the end of the war the allies met to discuss the. II. The A. Roosevelt,
War. Ho Chi Minh. domino theory. Dien Bien Phu SEATO. Vietcong Gulf of Tonkin Resolution. the end of WWII? ce? supporting
 Chapter 29 Section 1 Origins of the Vietnam War Ho Chi Minh domino theory Dien Bien Phu SEATO Vietcong Gulf of Tonkin Resolution 1. Witness History: What countries made up French Indochina? 2. What state
Chapter 29 Section 1 Origins of the Vietnam War Ho Chi Minh domino theory Dien Bien Phu SEATO Vietcong Gulf of Tonkin Resolution 1. Witness History: What countries made up French Indochina? 2. What state
Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present. Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present. Cold War: Superpowers Face Off. Allies Become Enemies
 Restructuring the Postwar World, 9 Present The United States and the Soviet Union vie for superiority, and both countries extend their control over other nations. Restructuring the Postwar World, 9 Present
Restructuring the Postwar World, 9 Present The United States and the Soviet Union vie for superiority, and both countries extend their control over other nations. Restructuring the Postwar World, 9 Present
The Cold War Begins. After WWII
 The Cold War Begins After WWII After WWII the US and the USSR emerged as the world s two. Although allies during WWII distrust between the communist USSR and the democratic US led to the. Cold War tension
The Cold War Begins After WWII After WWII the US and the USSR emerged as the world s two. Although allies during WWII distrust between the communist USSR and the democratic US led to the. Cold War tension
Modern World History Spring Final Exam 09
 1. What was the goal of the Marshall Plan? A. to provide aid to European countries damaged by World War II B. to protect member nations against Soviet Union aggression C. to protect the United States economically
1. What was the goal of the Marshall Plan? A. to provide aid to European countries damaged by World War II B. to protect member nations against Soviet Union aggression C. to protect the United States economically
THE COLD WAR Part Two Teachers Notes by Paul Latham
 THE COLD WAR Part Two Teachers Notes by Paul Latham Notes also available on DVD disc as either a Word document or PDF file. Also available on the website 1 2 The Cold War (Part 2) Teachers Notes CUBA AND
THE COLD WAR Part Two Teachers Notes by Paul Latham Notes also available on DVD disc as either a Word document or PDF file. Also available on the website 1 2 The Cold War (Part 2) Teachers Notes CUBA AND
Making of the Modern World 15. Lecture #10 The Cold War and the American Century
 Making of the Modern World 15 Lecture #10 The Cold War and the American Century Uncle Joe Guess where. Origins of the Cold War US, USSR, Great Britain unnatural allies during World War II Tensions submerged
Making of the Modern World 15 Lecture #10 The Cold War and the American Century Uncle Joe Guess where. Origins of the Cold War US, USSR, Great Britain unnatural allies during World War II Tensions submerged
THE COLD WAR Part One Teachers Notes by Paul Latham
 THE COLD WAR Part One Teachers Notes by Paul Latham Notes also available on DVD disc as either a Word document or PDF file. Also available on the website. 1 2 The Cold War (Part 1) Teachers Notes ORIGINS
THE COLD WAR Part One Teachers Notes by Paul Latham Notes also available on DVD disc as either a Word document or PDF file. Also available on the website. 1 2 The Cold War (Part 1) Teachers Notes ORIGINS
Politics of the Cold War
 Politics of the Cold War Standards SSUSH20 The student will analyze the domestic and international impact of the Cold War on the United States. c. Describe the Cuban Revolution, the Bay of Pigs, and the
Politics of the Cold War Standards SSUSH20 The student will analyze the domestic and international impact of the Cold War on the United States. c. Describe the Cuban Revolution, the Bay of Pigs, and the
Cold War: Superpowers Face Off
 Cold War: Superpowers Face Off ALLIES BECOME ENEMIES What caused the Cold War? The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February 1945, they agreed to divide Germany into
Cold War: Superpowers Face Off ALLIES BECOME ENEMIES What caused the Cold War? The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February 1945, they agreed to divide Germany into
ALLIES BECOME ENEMIES
 Cold War: Super Powers Face Off ALLIES BECOME ENEMIES What caused the Cold War? The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February 1945, they agreed to divide Germany into
Cold War: Super Powers Face Off ALLIES BECOME ENEMIES What caused the Cold War? The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February 1945, they agreed to divide Germany into
Month Content Objectives Standards. Interpret and react to current events relative to the American Studies III course.
 Current Events and September 11, 2011 Sept./Oct. Current Events September 11, 2001 terrorist attack Interpret and react to current events relative to the American Studies III course. CC.8.5.11-12.A. CC.8.5.11-12.B.
Current Events and September 11, 2011 Sept./Oct. Current Events September 11, 2001 terrorist attack Interpret and react to current events relative to the American Studies III course. CC.8.5.11-12.A. CC.8.5.11-12.B.
The War in Vietnam. Chapter 30
 The War in Vietnam Chapter 30 Vietnam A colony of France until after World War II 1954- War for Independence led by Ho Chi Minh Ho Chi Minh The Geneva Accords The Geneva Accords divided the country into
The War in Vietnam Chapter 30 Vietnam A colony of France until after World War II 1954- War for Independence led by Ho Chi Minh Ho Chi Minh The Geneva Accords The Geneva Accords divided the country into
AP UNITED STATES HISTORY 2012 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP UNITED STATES HISTORY 2012 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 5 Compare and contrast the Cold War foreign policies of TWO of the following presidents. Harry Truman (1945 1953) Dwight Eisenhower (1953 1961)
AP UNITED STATES HISTORY 2012 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 5 Compare and contrast the Cold War foreign policies of TWO of the following presidents. Harry Truman (1945 1953) Dwight Eisenhower (1953 1961)
Chapter 33 Summary/Notes
 Chapter 33 Summary/Notes Unit 8 Perspectives on the Present Chapter 33 Section 1. The Cold War Superpowers Face off We learned about the end of WWII. Now we learn about tensions that followed the war.
Chapter 33 Summary/Notes Unit 8 Perspectives on the Present Chapter 33 Section 1. The Cold War Superpowers Face off We learned about the end of WWII. Now we learn about tensions that followed the war.
Domestic Crises
 Domestic Crises 1968-1980 In 1968 conservative Richard Nixon became President. One of Nixon s greatest accomplishments was his 1972 visit to communist China. Visit opened China to American markets and
Domestic Crises 1968-1980 In 1968 conservative Richard Nixon became President. One of Nixon s greatest accomplishments was his 1972 visit to communist China. Visit opened China to American markets and
Topic 5: The Cold War (Compiled from 10 Topic and 6 Topic Format) Revised 2014
 Topic 5: The Cold War (Compiled from 10 Topic and 6 Topic Format) Revised 2014 [Since 1998, the pattern is: two subject specific questions, two questions allowing a choice of examples, and one question
Topic 5: The Cold War (Compiled from 10 Topic and 6 Topic Format) Revised 2014 [Since 1998, the pattern is: two subject specific questions, two questions allowing a choice of examples, and one question
VUS.13b. The Vietnam War. U. S. government s anti- Communist strategy of containment in Asia
 VUS.13b The Vietnam War U. S. government s anti- Communist strategy of containment in Asia Help the French and send some advisors- Increase advisors, send some troops- Escalate- we can not lose a war Peace
VUS.13b The Vietnam War U. S. government s anti- Communist strategy of containment in Asia Help the French and send some advisors- Increase advisors, send some troops- Escalate- we can not lose a war Peace
3/2/2017. Dwight Eisenhower & The Cold War. Election of Adlai Stevenson Democratic Candidate. Dwight D. Eisenhower Ike Republican Candidate
 1 2 3 4 Dwight Eisenhower & The Cold War Election of 1952 Adlai Stevenson Democratic Candidate Dwight D. Eisenhower Ike Republican Candidate 5 6 7 1952 Election Results Dwight D. Eisenhower 34 th President
1 2 3 4 Dwight Eisenhower & The Cold War Election of 1952 Adlai Stevenson Democratic Candidate Dwight D. Eisenhower Ike Republican Candidate 5 6 7 1952 Election Results Dwight D. Eisenhower 34 th President
 . Thanks so much for purchasing this product! Interactive Notebooks are an amazing way to get your students engaged and active in their learning! The graphic organizers and foldables in this resource are
. Thanks so much for purchasing this product! Interactive Notebooks are an amazing way to get your students engaged and active in their learning! The graphic organizers and foldables in this resource are
Topic 5: The Cold War (Compiled from 10 Topic and 6 Topic Format) Revised 2012
 Topic 5: The Cold War (Compiled from 10 Topic and 6 Topic Format) Revised 2012 [Since 1998, the pattern is: two subject specific questions, two questions allowing a choice of examples, and one question
Topic 5: The Cold War (Compiled from 10 Topic and 6 Topic Format) Revised 2012 [Since 1998, the pattern is: two subject specific questions, two questions allowing a choice of examples, and one question
The Cold War
 The Cold War 1945-1989 What is the Cold War It was an intense rivalry between the United States and Russia between West and East and between capitalism and communism that dominated the years following
The Cold War 1945-1989 What is the Cold War It was an intense rivalry between the United States and Russia between West and East and between capitalism and communism that dominated the years following
I Can Statements. Chapter 19: World War II Begins. Chapter 20: America and World War II. American History Part B. America and the World
 I Can Statements American History Part B Chapter 19: World War II Begins America and the World 1. Describe how postwar conditions contributed to the rise of antidemocratic governments in Europe. 2. Explain
I Can Statements American History Part B Chapter 19: World War II Begins America and the World 1. Describe how postwar conditions contributed to the rise of antidemocratic governments in Europe. 2. Explain
The Stormy Sixties. Chapter 38
 The Stormy Sixties Chapter 38 Kennedy Nixon Debates John F Kennedy and Richard Nixon had first presidential debate on TV Kennedy s New Frontier Spirit JFK elected by small margin over Nixon in 1960 Youngest
The Stormy Sixties Chapter 38 Kennedy Nixon Debates John F Kennedy and Richard Nixon had first presidential debate on TV Kennedy s New Frontier Spirit JFK elected by small margin over Nixon in 1960 Youngest
CHAPTER 25. Cold War America. I. Containment and a Divided Global Order. A. Origins of the Cold War. 1. Yalta
 CHAPTER 25 Cold War America 1945 1963 A. Origins of the Cold War 1. Yalta -Big Three (Churchill, FDR, Stalin) met in Feb. 1945, to create a United Nations (the three plus France and China) holding permanent
CHAPTER 25 Cold War America 1945 1963 A. Origins of the Cold War 1. Yalta -Big Three (Churchill, FDR, Stalin) met in Feb. 1945, to create a United Nations (the three plus France and China) holding permanent
The Sixties and Seventies. The Cold War cools down, Civil Rights get complicated, and the Baby Boomers come of age.
 The Sixties and Seventies The Cold War cools down, Civil Rights get complicated, and the Baby Boomers come of age. Learning Targets Describe the Kennedy years, with specific detail covering: The election
The Sixties and Seventies The Cold War cools down, Civil Rights get complicated, and the Baby Boomers come of age. Learning Targets Describe the Kennedy years, with specific detail covering: The election
Standard 8.0- Demonstrate an understanding of social, economic and political issues in contemporary America. Closing: Quiz
 Standard 8.0- Demonstrate an understanding of social, economic and political issues in contemporary America. Opening: Great Society Chart Work Period: Vietnam War Notes Political Cartoon Double Flow Map
Standard 8.0- Demonstrate an understanding of social, economic and political issues in contemporary America. Opening: Great Society Chart Work Period: Vietnam War Notes Political Cartoon Double Flow Map
THEMES. 1) EXPANDING DEMOCRACY: America s mission in Vietnam was to halt the spread of communism-a threat to democracy.
 THEMES 1) EXPANDING DEMOCRACY: America s mission in Vietnam was to halt the spread of communism-a threat to democracy. 2) CONSTITUTIONAL CONCERNS: Among the constitutional issues of the Vietnam War era
THEMES 1) EXPANDING DEMOCRACY: America s mission in Vietnam was to halt the spread of communism-a threat to democracy. 2) CONSTITUTIONAL CONCERNS: Among the constitutional issues of the Vietnam War era
The Americans (Survey)
 The Americans (Survey) Chapter 26: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Cold War Conflicts CHAPTER OVERVIEW After World War II, tensions between the United States and the Soviet Union lead to a war without direct military
The Americans (Survey) Chapter 26: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Cold War Conflicts CHAPTER OVERVIEW After World War II, tensions between the United States and the Soviet Union lead to a war without direct military
Name Period Date. Civil Rights Movement and Vietnam War Unit Test Review. Test Format- 50 questions 15 matching. 5 map, 3 reading a chart, 27 MC
 Name Period Date Civil Rights Movement and Vietnam War Unit Test Review Test Format- 50 questions 15 matching. 5 map, 3 reading a chart, 27 MC 1. What was LBJ s (President Johnson) program to end poverty
Name Period Date Civil Rights Movement and Vietnam War Unit Test Review Test Format- 50 questions 15 matching. 5 map, 3 reading a chart, 27 MC 1. What was LBJ s (President Johnson) program to end poverty
United Nations. Marshall Plan. Israel. Mao Zedong. South Korea
 Unit 9-10 Study Guide 1. What World War II conference between the Potsdam major Allied leaders ultimately triggered the Cold War? 2. Which organization, founded in 1948, replaced the League of Nations
Unit 9-10 Study Guide 1. What World War II conference between the Potsdam major Allied leaders ultimately triggered the Cold War? 2. Which organization, founded in 1948, replaced the League of Nations
How Did President Nixon Get the United States Out of Vietnam?
 How Did President Nixon Get the United States Out of Vietnam? LESSON 2 SECTION 33.2 Text pp. 587 591 Read How Did President Nixon Get the United States Out of Vietnam? (pp. 587-591). Study Exercises Write
How Did President Nixon Get the United States Out of Vietnam? LESSON 2 SECTION 33.2 Text pp. 587 591 Read How Did President Nixon Get the United States Out of Vietnam? (pp. 587-591). Study Exercises Write
OBJECTIVES. Describe and evaluate the events that led to the war between North Vietnam and South Vietnam.
 OBJECTIVES Describe and evaluate the events that led to the war between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. Identify and explain the foreign policy of the United States at this time, and how it relates to
OBJECTIVES Describe and evaluate the events that led to the war between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. Identify and explain the foreign policy of the United States at this time, and how it relates to
The Cold War ( )
 The Cold War (1945-1991) Timeline USSR dissolves WWII Cold War 1939 1945 1989 1991 Revolutions of 1989 What is it US vs. USSR state of tension nuclear arms race Space Race propaganda war fighting through
The Cold War (1945-1991) Timeline USSR dissolves WWII Cold War 1939 1945 1989 1991 Revolutions of 1989 What is it US vs. USSR state of tension nuclear arms race Space Race propaganda war fighting through
The Cold War A bitter rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union, the two superpowers after WWII, that lasted for almost 50 years.
 The Cold War A bitter rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union, the two superpowers after WWII, that lasted for almost 50 years. Satellite Nation: One that is dominated politically and economically
The Cold War A bitter rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union, the two superpowers after WWII, that lasted for almost 50 years. Satellite Nation: One that is dominated politically and economically
Section 4: How did the Cold War develop?
 Section 4: How did the Cold War develop? 1943-56 4 (a) Describe one reason why the Allies met at Yalta in February 1945. 1 1 Simple statement(s) e.g. To discuss what to do with Germany. 2 2 Developed statements
Section 4: How did the Cold War develop? 1943-56 4 (a) Describe one reason why the Allies met at Yalta in February 1945. 1 1 Simple statement(s) e.g. To discuss what to do with Germany. 2 2 Developed statements
Write 3 words you think of when you hear Cold War? THE COLD WAR ( )
 THE Write 3 words you think of when you hear Cold War? COLD WAR (1948-1989) ORIGINS of the Cold War: (1945-1948) Tension or rivalry but NO FIGHTING between the United States and the Soviet Union This rivalry
THE Write 3 words you think of when you hear Cold War? COLD WAR (1948-1989) ORIGINS of the Cold War: (1945-1948) Tension or rivalry but NO FIGHTING between the United States and the Soviet Union This rivalry
Truman & Eisenhower. Chapters 37 & 38
 Truman & Eisenhower Chapters 37 & 38 Worries after World War II Many are still worried about a return to the Great Depression Lots of soldiers returning home would compete for jobs GNP down in 46 and 47
Truman & Eisenhower Chapters 37 & 38 Worries after World War II Many are still worried about a return to the Great Depression Lots of soldiers returning home would compete for jobs GNP down in 46 and 47
THE COLD WAR ( )
 THE COLD WAR (1948-1989) ORIGINS of the Cold War: (1945-1948) Tension or rivalry but NO FIGHTING between the United States and the Soviet Union This rivalry divided the world into two teams (capitalism
THE COLD WAR (1948-1989) ORIGINS of the Cold War: (1945-1948) Tension or rivalry but NO FIGHTING between the United States and the Soviet Union This rivalry divided the world into two teams (capitalism
Introduction to the Cold War
 Introduction to the Cold War What is the Cold War? The Cold War is the conflict that existed between the United States and Soviet Union from 1945 to 1991. It is called cold because the two sides never
Introduction to the Cold War What is the Cold War? The Cold War is the conflict that existed between the United States and Soviet Union from 1945 to 1991. It is called cold because the two sides never
Section 4: How did the Cold War develop?
 Section 4: How did the Cold War develop? 1943 56 Question Number 4 (a) Describe one decision made by the Allies about the war against Germany at the Teheran Conference, 1943. Target: Key features/recall
Section 4: How did the Cold War develop? 1943 56 Question Number 4 (a) Describe one decision made by the Allies about the war against Germany at the Teheran Conference, 1943. Target: Key features/recall
The Cold War. Chap. 18, 19
 The Cold War Chap. 18, 19 Cold War 1945-1991 Political and economic conflict between U.S. and USSR Not fought on battlefield U.S. Vs. USSR Democracy- free elections private ownership Free market former
The Cold War Chap. 18, 19 Cold War 1945-1991 Political and economic conflict between U.S. and USSR Not fought on battlefield U.S. Vs. USSR Democracy- free elections private ownership Free market former
APUSH REVIEWED! THE COLD WAR BEGINS POST WW2, TRUMAN ADMINISTRATION
 APUSH 1945-1952 POST WW2, TRUMAN ADMINISTRATION THE COLD WAR BEGINS REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy) Chapter 36 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 27 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 25-26 Fear
APUSH 1945-1952 POST WW2, TRUMAN ADMINISTRATION THE COLD WAR BEGINS REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy) Chapter 36 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 27 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 25-26 Fear
C. Continuing protests Doves wanted an immediate withdrawal that was complete, unconditional, and irreversible.
 I. VIETNAM WAR spread across 5 presidencies and spanned 25 years Direct U.S involvement from 1963-1973 A. France lost control of Vietnam after the battle of Dien Bien Phu in 1954 1. U.S. by 1954 had financed
I. VIETNAM WAR spread across 5 presidencies and spanned 25 years Direct U.S involvement from 1963-1973 A. France lost control of Vietnam after the battle of Dien Bien Phu in 1954 1. U.S. by 1954 had financed
Preface to Cold War. Preface
 Preface to Cold War Preface I have had the pleasure of teaching IB history for over 20 years, mainly at Malmö Borgarskola in Sweden but also on revision courses in England and in the United States. It
Preface to Cold War Preface I have had the pleasure of teaching IB history for over 20 years, mainly at Malmö Borgarskola in Sweden but also on revision courses in England and in the United States. It
Ch 29-1 The War Develops
 Ch 29-1 The War Develops The Main Idea Concern about the spread of communism led the United States to become increasingly violent in Vietnam. Content Statement/Learning Goal Analyze how the Cold war and
Ch 29-1 The War Develops The Main Idea Concern about the spread of communism led the United States to become increasingly violent in Vietnam. Content Statement/Learning Goal Analyze how the Cold war and
Rise to Globalism: Study Questions IB Government and International Affairs
 Rise to Globalism: Study Questions IB Government and International Affairs Essential Question: How did wartime strategies and developments contribute to the coming Cold War? Chapter 1: The Twisting Path
Rise to Globalism: Study Questions IB Government and International Affairs Essential Question: How did wartime strategies and developments contribute to the coming Cold War? Chapter 1: The Twisting Path
Chapter 19: Going To war in Vietnam
 Heading Towards War Vietnam during WWII After the French were conquered by the Germans, the Nazi controlled government turned the Indochina Peninsula over to their Axis allies, the. returned to Vietnam
Heading Towards War Vietnam during WWII After the French were conquered by the Germans, the Nazi controlled government turned the Indochina Peninsula over to their Axis allies, the. returned to Vietnam
20 th /Raffel The Vietnam War: Containment Leads to Disaster About this Assignment: The Vietnam war was one of the most controversial wars in
 20 th /Raffel The Vietnam War: Containment Leads to Disaster About this Assignment: The Vietnam war was one of the most controversial wars in American history. In retrospect, there were many missed opportunities
20 th /Raffel The Vietnam War: Containment Leads to Disaster About this Assignment: The Vietnam war was one of the most controversial wars in American history. In retrospect, there were many missed opportunities
The Cold War Finally Thaws Out. Korean War ( ) Vietnam War ( ) Afghan War ( )
 The Cold War Finally Thaws Out Korean War (1950-1953) Vietnam War (1963-1973) Afghan War (1979-1989) Korean war Split after WWII between US and USSR Temporary gov ts created in images of their major allies
The Cold War Finally Thaws Out Korean War (1950-1953) Vietnam War (1963-1973) Afghan War (1979-1989) Korean war Split after WWII between US and USSR Temporary gov ts created in images of their major allies
The Potsdam Conference
 The Cold War Begins The United Nations Chartered in April 1945 Replaced the League of Nations as a mediator for international disputes 50 nations joined initially (today, UN has 192 members) In the General
The Cold War Begins The United Nations Chartered in April 1945 Replaced the League of Nations as a mediator for international disputes 50 nations joined initially (today, UN has 192 members) In the General
Cold War: Superpowers Face Off
 Section 1 Cold War: Superpowers Face Off Reading Comprehension Find the name or term in the second column that best matches the description in the first column. Then write the letter of your answer in
Section 1 Cold War: Superpowers Face Off Reading Comprehension Find the name or term in the second column that best matches the description in the first column. Then write the letter of your answer in
Option 26/27 scheme of work
 Option 26/27 scheme of work Superpower relations and the Cold War, 1941 91 GCSE (9-1) History Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in History (1HI0) Introduction This document provides a sample
Option 26/27 scheme of work Superpower relations and the Cold War, 1941 91 GCSE (9-1) History Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in History (1HI0) Introduction This document provides a sample
Post World War II...The Cold War
 Post World War II...The Cold War Thesis Statement The Post WWII era has been dominated by the Cold War and events today are reflective of Cold War dynamics (propaganda, us vs. them, good vs. evil, UN Security
Post World War II...The Cold War Thesis Statement The Post WWII era has been dominated by the Cold War and events today are reflective of Cold War dynamics (propaganda, us vs. them, good vs. evil, UN Security
The Early Cold War: Written by Ms. Susan M. Pojer and modified by J. Christie
 The Early Cold War: 1947-1970 Written by Ms. Susan M. Pojer and modified by J. Christie California Standards Compare the economic and military power shifts caused by the war, including the Yalta Pact,
The Early Cold War: 1947-1970 Written by Ms. Susan M. Pojer and modified by J. Christie California Standards Compare the economic and military power shifts caused by the war, including the Yalta Pact,
The Cold War. Origins - Korean War
 The Cold War Origins - Korean War What is a Cold War? WW II left two nations of almost equal strength but differing goals Cold War A struggle over political differences carried on by means short of direct
The Cold War Origins - Korean War What is a Cold War? WW II left two nations of almost equal strength but differing goals Cold War A struggle over political differences carried on by means short of direct
The Cold War Begins: CHAPTER 39
 The Cold War Begins: 1946-1953 CHAPTER 39 OBJECTIVES Describe the economic transformation of the immediate post-wwii era. Explain the changes in the American population structure brought about the baby
The Cold War Begins: 1946-1953 CHAPTER 39 OBJECTIVES Describe the economic transformation of the immediate post-wwii era. Explain the changes in the American population structure brought about the baby
The Vietnam War Years. B. Domino theory C. Vietcong D. Tonkin Gulf Resolution E. Napalm F. Credibility gap
 study guide Chapter Name The Vietnam War Years Period Due Directions: Write Definitions on a separate sheet of paper. 1. A. Ho Chi Minh B. Domino theory C. Vietcong D. Tonkin Gulf Resolution E. Napalm
study guide Chapter Name The Vietnam War Years Period Due Directions: Write Definitions on a separate sheet of paper. 1. A. Ho Chi Minh B. Domino theory C. Vietcong D. Tonkin Gulf Resolution E. Napalm
World History (Survey) Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present
 World History (Survey) Chapter 33: Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present Section 1: Two Superpowers Face Off The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February
World History (Survey) Chapter 33: Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present Section 1: Two Superpowers Face Off The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February
Chapter 25 Cold War America, APUSH Mr. Muller
 Chapter 25 Cold War America, 1945-1963 APUSH Mr. Muller Aim: How does the U.S. and U.S.S.R. go from allies to rivals? Do Now: Communism holds that the world is so deeply divided into opposing classes that
Chapter 25 Cold War America, 1945-1963 APUSH Mr. Muller Aim: How does the U.S. and U.S.S.R. go from allies to rivals? Do Now: Communism holds that the world is so deeply divided into opposing classes that
Chapter 30-1 CN I. Early American Involvement in Vietnam (pages ) A. Although little was known about Vietnam in the late 1940s and early
 Chapter 30-1 CN I. Early American Involvement in Vietnam (pages 892 894) A. Although little was known about Vietnam in the late 1940s and early 1950s, American officials felt Vietnam was important in their
Chapter 30-1 CN I. Early American Involvement in Vietnam (pages 892 894) A. Although little was known about Vietnam in the late 1940s and early 1950s, American officials felt Vietnam was important in their
Chapter 21 Review. AP World History
 Chapter 21 Review AP World History Essential Question: What led to the Cold War between the United States & Soviet Union? The end of World War II led to important changes in the world: The U.N. United
Chapter 21 Review AP World History Essential Question: What led to the Cold War between the United States & Soviet Union? The end of World War II led to important changes in the world: The U.N. United
Communism. Communism is a form of economy. Everyone gets the same resources. Gov t owns the means of production -so no individuals own the businesses
 The Cold War Communism Communism is a form of economy Everyone gets the same resources Gov t owns the means of production -so no individuals own the businesses Idea of Communism Gov t will work in the
The Cold War Communism Communism is a form of economy Everyone gets the same resources Gov t owns the means of production -so no individuals own the businesses Idea of Communism Gov t will work in the
TRUMAN S ROLE IN VIETNAM. = America is busy!!!!!
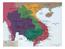 TRUMAN S ROLE IN VIETNAM Saw Vietnam as extension of Cold War - democracy v. communism! France fighting to re-gain Vietnam Truman supported France with money supplies because didn t want Something going
TRUMAN S ROLE IN VIETNAM Saw Vietnam as extension of Cold War - democracy v. communism! France fighting to re-gain Vietnam Truman supported France with money supplies because didn t want Something going
The Atomic Age: Truman & Eisenhower. Post-war Confidence and Anxiety
 The Atomic Age: Truman & Eisenhower Post-war Confidence and Anxiety 1945-1960 The International Impact of the Cold War Origins of the Cold War US President Harry Truman and Soviet Union dictator Joseph
The Atomic Age: Truman & Eisenhower Post-war Confidence and Anxiety 1945-1960 The International Impact of the Cold War Origins of the Cold War US President Harry Truman and Soviet Union dictator Joseph
1969 U.S. troops begin their withdrawal from Vietnam
 Vietnam War Years Timeline 1964 LBJ becomes President 1965 First major combat units arrive in Vietnam 1968 M.L.King and Robert Kennedy are assassinated 1969 U.S. troops begin their withdrawal from Vietnam
Vietnam War Years Timeline 1964 LBJ becomes President 1965 First major combat units arrive in Vietnam 1968 M.L.King and Robert Kennedy are assassinated 1969 U.S. troops begin their withdrawal from Vietnam
Kennedy & Johnson. Chapters 38 & 39
 Kennedy & Johnson Chapters 38 & 39 Kennedy s Presidency Young, inspirational, refreshing Young Cabinet Sec. of Defense - Robert McNamara Attorney General - Robert Kennedy Wanted to target organized crime
Kennedy & Johnson Chapters 38 & 39 Kennedy s Presidency Young, inspirational, refreshing Young Cabinet Sec. of Defense - Robert McNamara Attorney General - Robert Kennedy Wanted to target organized crime
Conflict U.S. War
 Conflict - 1945-1975 U.S. War 1964-1973 Overview of the Vietnam War Why is Vietnam still a painful war to remember? Longest war in U.S. history and only war we lost It showed Americans that our power is
Conflict - 1945-1975 U.S. War 1964-1973 Overview of the Vietnam War Why is Vietnam still a painful war to remember? Longest war in U.S. history and only war we lost It showed Americans that our power is
A International Relations Since A Global History. JOHN YOUNG and JOHN KENT \ \ OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS
 A 371306 International Relations Since 1945 A Global History JOHN YOUNG and JOHN KENT OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Detailed contents Preface List of Abbreviations Introduction v xvii i Part I: The Origins and
A 371306 International Relations Since 1945 A Global History JOHN YOUNG and JOHN KENT OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Detailed contents Preface List of Abbreviations Introduction v xvii i Part I: The Origins and
Bell Ringers - April 21
 WWII: Bell Ringers - April 21 What were the Nuremburg Trials? Trials set up by the Allies (International Military Tribunal) to make sure the NAZIs were punished for their crimes for waging a war of aggression
WWII: Bell Ringers - April 21 What were the Nuremburg Trials? Trials set up by the Allies (International Military Tribunal) to make sure the NAZIs were punished for their crimes for waging a war of aggression
How did African Americans gain more rights and equality during the 1950s-60s?
 Topic: Civil Rights Movement Days: 8 Key Learning: During the 1950s-60s a dramatic change happened with regards to the rights of African Americans. Unit Essential Question(s): How did African Americans
Topic: Civil Rights Movement Days: 8 Key Learning: During the 1950s-60s a dramatic change happened with regards to the rights of African Americans. Unit Essential Question(s): How did African Americans
Chapter 19 GOING TO WAR IN VIETNAM
 Chapter 19 GOING TO WAR IN VIETNAM VIETNAM DURING WWII After the French were conquered by the Germans, the Nazi controlled government turned the Indochina Peninsula over to their Axis allies, the Japanese.
Chapter 19 GOING TO WAR IN VIETNAM VIETNAM DURING WWII After the French were conquered by the Germans, the Nazi controlled government turned the Indochina Peninsula over to their Axis allies, the Japanese.
The Cold War Expands
 The Cold War Expands Arms Race On September 2, 1949, the balance of power between the U.S. and the Soviet Union changed forever. That day, the Soviet Union tested an atomic bomb. H - Bomb In response,
The Cold War Expands Arms Race On September 2, 1949, the balance of power between the U.S. and the Soviet Union changed forever. That day, the Soviet Union tested an atomic bomb. H - Bomb In response,
The Cold War: American Society in the post-war years
 The Cold War: 1945-1952 American Society in the post-war years 1 Post War Economic Anxieties The US experienced a faltering economy after WWII. real GNP dropped with no government price controls, prices
The Cold War: 1945-1952 American Society in the post-war years 1 Post War Economic Anxieties The US experienced a faltering economy after WWII. real GNP dropped with no government price controls, prices
Analyze the political cartoon by writing:
 Bellringer Analyze the political cartoon by writing: 1. Title (make one up of there isn t one): 2. Important Words: 3. Symbols: 4. Action: 5. Message: The Cold War Day 1 Ms. Luco IB Hist Americas Yr 1
Bellringer Analyze the political cartoon by writing: 1. Title (make one up of there isn t one): 2. Important Words: 3. Symbols: 4. Action: 5. Message: The Cold War Day 1 Ms. Luco IB Hist Americas Yr 1
VIETNAM WAR
 VIETNAM WAR 1965-1972 FRENCH CONTROL French controlled Vietnam until World War II Vietnam taken by Japan Ho Chi Minh called for an independence of Vietnam Eight Year war between France and Ho Chi Minh
VIETNAM WAR 1965-1972 FRENCH CONTROL French controlled Vietnam until World War II Vietnam taken by Japan Ho Chi Minh called for an independence of Vietnam Eight Year war between France and Ho Chi Minh
Unit 10 Review Activities
 Unit 10 Review Activities Directions: Listed below are important dates from Unit 10. In each case you should be able to identify the implied event and its significance. 1. 10/29/1929 2. 09/01/1939 3. 12/07/1941
Unit 10 Review Activities Directions: Listed below are important dates from Unit 10. In each case you should be able to identify the implied event and its significance. 1. 10/29/1929 2. 09/01/1939 3. 12/07/1941
Journal # 11 04/30/15 Objective: Students will utilize various
 Journal # 11 04/30/15 Objective: Students will utilize various resources to identify, compare/contrast, and evaluate the origins, development and effects of the Cold War. Agenda: Journal Cold War PPT Guided
Journal # 11 04/30/15 Objective: Students will utilize various resources to identify, compare/contrast, and evaluate the origins, development and effects of the Cold War. Agenda: Journal Cold War PPT Guided
