Journal: The International The Quality of Life. Year: subscriptions.
|
|
|
- Kevin George
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Quality of Life in Ideal typical Welfare Regimes: The Case of the Republic of Korea Journal: Professional Development: The International Journal of Continuing Social Work Education Article Title: The Quality of Life in Ideal typical Welfare Regimes: The Case of the Republic of Korea Author(s): Chang Soo Choe, Michael J. Kelly and Jinman Kyonne Volume and Issue Number: Vol. 16 No. 2 Manuscript ID: Page Number: 65 Year: 2013 Professional Development: The International Journal of Continuing Social Work Education is a refereed journal concerned with publishing scholarly and relevant articles on continuing education, professional development, and training in the field of social welfare. The aims of the journal are too advance the science of professional development and continuing social work education, to foster understanding among educators, practitioners, and researchers, and to promote discussion that represents a broad spectrum of interests in the field. The opinions expressed in this journal are solely those of the contributors and doo not necessarily reflect the policy positions of The University of Texas at Austin s School of Social Work or its Center for Social and Behavioral Research. Professional Development: The International Journal of Continuing Social Work Education is published two times a year (Spring and Winter) by the Center for Social and Behavioral Research at 1 University Station, D3500 Austin, TX Journal subscriptions are $110. Our website at contains additional information regarding submission of publications and subscriptions. Copyright by The University of Texas at Austin ss School of Social Work s Center for Social and Behavioral Research. All rights reserved. Printed in the U.S.A. ISSN: URL:
2 The Quality of Life in Ideal-typical Welfare Regimes: The Case of the Republic of Korea Chang Soo Choe, Michael J. Kelly, & Jinman Kyonne Introduction During the past decades, the Republic of Korea (ROK) achieved a high rate of economic growth. GDP per capita in 1990 was $6,290 and grew in two decades to $21,063 (United Nations Statistical Division, 2012). The economic success of the ROK has been a good model for developing countries and perhaps even for developed countries struggling with the economic crisis since Government policy focused on rapid economic growth has been successful but has also meant that policy has not been concerned with Korea s social needs. The ROK s public social expenditures were 6.5% percent of GDP and lowest among Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) countries (OECD, 2010). It is assumed that the deficiency of public social services reduces Koreans satisfaction with their lives. The mean score of life satisfaction in the ROK was 5.5 (on a 10 point scale) and was below the mean score of 6.7 for all OECD countries. The suicide rate in the ROK was 29 per 100,000 persons, the highest among OECD countries (OECD, 2010). Many Koreans realized the need for a greater emphasis on social welfare and made regime development a critical policy agenda for the 2012 presidential election. See, for example, Commissioner Yi s remarks to the third OCED world forum in 2009 stressing the need to use more socially responsive measures than the GDP to judge progress (Yi, 2009). At the point of designing a welfare state, policy makers should concern themselves with which regime is most appropriate for the Korea s capitalist, democratic society. This study explores the possible choices by looking at the characteristics of ideal-typical welfare regimes. Ideal types represent conceptual approaches to choices between different governmental and social arrange- ments. This study uses Aspalter s (2006) amplification of Esping-Andersen s (1990) classifications of regimes: social democratic, corporatist democratic, liberal, or conservative welfare regimes. In order to conduct a basic test of the people s quality of life (QOL) under different welfare regimes, two simple but contrasting life satisfaction measures were chosen. Life satisfaction was used as the positive indicator of QOL, as it is a widely used measure (Campbell, 1976) and regularly collected by the OECD. The suicide rate was adopted as the negative QOL indicator, since previous research has shown it to have a strong and significant relationship to QOL (Lester, 1984). Comparisons between reported mean scores of each type of regime then suggested which idealtypical regime is more likely to produce QOL through increased life satisfaction scores and with decreased suicide rates. Two test configurations were developed based on which regimes emphasize a strong role for the state/national government versus those which emphasize a strong role for the family. Hofstede (2001) studied which countries were more likely to emphasize a strong role for the state vs. the family in providing social support. Interviewing the employees of a global company regarding the state role for social support, he found that employees in Austria, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, and Norway answered more strongly positive than those in Canada, Japan, Republic of Korea, United Kingdom, and United States. Regarding the family s role in social support, employees in Austria, France, Germany, Japan, and Republic of Korea answered more strongly positive than those in Canada, Denmark, Finland, Norway, United Kingdom, and Chang Soo Choe, PhD is an Associate Professor at Korea University s School of Public Administration. Michael J. Kelly, PhD is a Professor at the University of Missouri at Columbia School of Social Work. Jinman Kyonne, PhD is an Assistant Professor in the Department of Public Administration at Hankuk University of Foreign Studies. 65
3 The Quality of Life in Ideal-typical Welfare Regimes United States. Contrasting the two scales, the findings suggested that the Asian countries, Japan and Republic of Korea, should be categorized as favoring a strong family role with a weak state role. Considering the countries culture and values as the cornerstone, proceeding social construction (Berger & Luckmann, 1966), the categorizations could be used to test the country people s differences of social activities according to their particular characters. Ideal Types of Social Welfare Regimes Esping-Andersen (1990) classified welfare regimes in the three categories: social democratic, corporatist democratic, and liberal welfare states. Each type can be largely contrasted on the roles and responsibilities placed on the state and those expected of the family. Social democratic states are those that provide public services to all citizens, including social insurance, social services, and public employment (Ferragina & Seeleib-Kaiser, 2011). Basically, social democratic regimes stress support rather than free market distribution and actively encourage redistributional policies, especially with regard to social services and public employment. Nations belonging to this category include Norway, Finland, and Denmark (Stephens, 1979). Corporatist democratic states prefer social insurance schemes for occupational social security and social transfers through corporatist institutions such as NGOs (Kersbergen, 1995). Their social assistance and taxation policies emphasize vertical redistribution since they have a high degree of social stratification (Korpi, 1983). The role of the state is strong as is that of family supports, whereas in social democratic welfare states the role of the state is strong but that of the family is weaker. Nations belonging to the classification include Germany, Austria, and France (Aspalter, 2006). Liberal welfare states place a high emphasis on private savings and insurance for helping citizens. This means that they implement a highly limited redistribution of income and value market-friendly systems (Huber & Stephens, 2001). Hence, the government social support is usually only to provide for the basic needs for the poor, a weak state role, with emphasis placed on the individual responsibility. In liberal welfare systems the role of the state is weak, but family roles are also weak (Aspalter, 2006). Liberal states emphasize market-based systems and deemphasize redistribution policies. Kyonne (2008) notes that liberal state social service policies are focused on developing human capital through education services a meritocratic system which values individual effort. Nations in the classification include the United States, United Kingdom, and Canada (Aspalter, 2006). In addition to these three ideal-typical welfare regimes, Aspalter (2006) noted that the welfare model extant in Asian countries could be called the conservative welfare model. In this regime, public investment is focused on social programs that support workers and ensure their ability to enter the labor market. For example, the Republic of Korea s occupational social security system for working classes was put into place to encourage development of the economy. The benefits from the welfare services are quite limited, and preferential treatment of special interest groups is allowed. These welfare programs are economy-friendly welfare programs (Aspalter & Opielka, 2006). In comparison with the other three ideal-typical welfare regimes, the roles of both state and individual are weak whereas the roles of both family and market are strong. The conservative welfare model also depends upon the family to carry out many of the social support functions that governments take in other nations. Nations in this fourth type include the Republic of Korea and Japan (Aspalter, 2006). Quality of Life in Different Welfare States Aspalter s and Esping-Andersen s classification of welfare states are basic to an inquiry into the suitability of different ideal-typical welfare regimes which might increase the peoples expressed quality of life. This analysis is conducted on secondary data from the OECD fact book (2010) concerning expressed life satisfaction scores and the suicide rates (Campbell, 1976; Lester, 1984). The analysis assumes that life satisfaction scores are the positive factor while the reported "suicide rates represent the negative. Regarding life satisfaction, social democratic welfare regimes scored the average of 7.8 (Denmark 8.0, Finland 7.8, Norway 7.6; see Group D of Table 1); liberal welfare regimes scored an average of 7.1 (Canada 7.2, U.S. 7.1, U.K. 7.0; see Group C of Table 1); corporatist democratic welfare regimes scored an average of 7.0 (Austria 7.3, France 7.0, Germany 6.7; see Group B of Table 1); and conservative welfare 66
4 Professional Development: The International Journal of Continuing Social Work Education regimes scored an average of 6.0 (Japan 6.5, Republic of Korea 5.5; see Group A of Table 1). The life satisfaction scores in all four categories were tested. Reported life satisfaction scores in the four ideal-typical welfare regimes representing a wide range of countries were found to have differences, but these differences were not statistically significant. The life satisfaction scores in social democratic welfare regimes were higher (mean = 7.8) than those in conservative welfare regimes (mean = 6.0), but, again, differences were not statistically significant (Chisquare =.978, p >.05). Testing the suicide rate showed social democratic welfare regimes to have an average rate of 13 per 100,000 persons (Denmark 10, Finland 17, Norway 11; see Group D in Table 2), while liberal welfare regimes had an average rate of 9 (Canada 10, U.S. 11, U.K. 6; see Group C of Table 2). Corporatist democratic welfare regimes had an average rate of 12 (Austria 12, France 14, Germany 10; see Group B of Table 2). Conservative welfare regimes had an average rate of 25 (Japan 20, Republic of Korea 30; see Group A of Table 2). Using the Chi-square test, the suicide rates in the four categories were tested, and statistical differences were found (Chi-square =.045, p <.05). The suicide rate in conservative welfare regimes (average rate = 25) was around triple those in liberal welfare regimes (average rate = 9) and around double those in corporatist democratic regimes (average rate = 12) and social democratic welfare regimes (the average rate = 13). In descending order of the mean scores for life satisfaction, social democratic welfare regimes were 7.8, liberal welfare regimes 7.1, corporatist democratic welfare regimes 7.0, and conservative welfare regimes 6.0. In ascending order, the suicide rate in liberal welfare regimes was 9, corporatist democratic welfare regimes 12, social democratic welfare regimes 13, and conservative welfare regimes 25. Based on these outcomes, it is clear that the quality of life (QOL) in conservative welfare regimes is lowest for both positive (life satisfaction) and negative (suicide rate) indicator levels. Which Ideal-type Welfare Regime is best for Korea? Based on the analysis of two QOL indicators, one positive and one negative, the countries with social democratic welfare regimes seem to the best ideal-type welfare states. These regimes scored high levels of life satisfaction with correspondingly low suicide rates. The corporatist democratic and liberal regimes also scored higher levels in quality of life than the conservative welfare regimes in Korea and Japan but were lower 67
5 The Quality of Life in Ideal-typical Welfare Regimes than the social democratic regimes. This suggests that social democratic welfare policies and programs could be a good example for Asian countries. However, other countries welfare regimes cannot be simply adopted due to differences in culture and values. As described by Aspalter (2006), Asians have constructed conservative welfare regimes focusing on insuring an occupational social security system for working classes to develop their economy. This style, emphasizing the roles of both family and market rather than those of state and individual, is not easily changed by policy makers decisions. These systems are deeply involved in the unique values and national culture of Asian states. For example, take the values and culture of Confucianism; built on the premise that parents will provide for their children, even sacrificing their own future welfare, the Confucian value system called for the elderly to end their lives in their children s care and be respected within the family. The government did not need to provide social security schemes, specialized health care, housing and/or nursing homes, or social services, as these were the responsibility of their children. Korea s rapid industrialization has been called the Korean Miracle. Few countries have developed from rural societies to hyper-technical, urbanized industrial societies in so short a time. Howev- er, policies and laws favoring industrialization have resulted in large numbers of elderly people left without income support; Korean law denies welfare to parents whose children are economically able to support them, even when the support is not given. Internal labor mobility often means parents are left in rural areas far from their urbanized children. Not living with the children s families also removes the head of household role so vital to elderly Koreans. The demands of rapid economic success have challenged centuries of Confucianism and, in the last few years, Korea has begun to experience a surge in suicide among the elderly. In order to decrease the suicide rate, Koreans must begin development and redesign of their social systems. They must move from a conservative regime, where the top priority is on economic growth, to corporatist or social democratic regimes which, hopefully, balance economic growth with the social systems needed in economically advanced societies. They must reconsider citizenship from a human rights standpoint rather than just seeing people only as economic resources. This study suggests that a model of welfare regime for Koreans requires movement toward social democratic forms because the QOL is highest in those ideal-typical regimes. Practically, the ROK must increase public social expenditures, develop social service programs for diverse and minority people, 68
6 Professional Development: The International Journal of Continuing Social Work Education and design a redistribution system in both vertical and horizontal ways. These efforts may make Koreans report that they are doing well and, with these social constructions, find their life satisfaction increased and the suicide rate decreased. The Need for a New Model Since culture and values are more difficult to change than is government policy, how can the ROK eventually adopt a social democratic welfare regime? Policy makers must concern themselves with creatively developing social welfare programs, not in ideology but in practice. Uncritical acceptance of any set of welfare policies might lead to crucial side effects. Actually, the ROK s rapid transformation of its social system under industrialization has apparently led to social isolation in a family-centered society. Industrialization emphasizes the individual and is often called Westernization. Social isolation is the critical factor explaining mental health issues such as depression and suicide. Not coincidentally, Korea had the highest suicide rate, with Japan third, among OECD countries (OECD, 2012). Korea must therefore pioneer a new welfare model for assisting the elderly in a hypertechnical, industrial society. The new model should consider a system in which the old are not only recipients of welfare service but also have a role as providers of a highly developed social system. In order to construct a mature society full of vitality, Asian reformers will need to be innovative in designing an economic system in which the old take a role not only as a consumer but also as a main producer. If they concentrate the energy currently expended on economic success on developing a social welfare system in their own ideal-typical regime, the developed Asian countries, including Republic of Korea, can be a new model of a welfare state for developing countries and even for the developed West. Limitations This study depends upon a two variable analysis of the quality of life (QOL) under different idea types of welfare regimes. The ideal-type is itself a conceptual limitation by establishing ideal classifications such that no nation s systems fit perfectly. Another limitation is that the characteristics of conservative welfare regimes have not been studied enough to be compared with those of the other welfare regimes. More importantly, it is hard to find common values and social characteristics even among Asian countries. For example, although China originally embraced Confucianism, their system has become dominated by communist ideas, and their system is quite distinct from democratic-leaning Asian countries. Finally, testing with more indicators of QOL would increase the validity of the research method. In spite of these drawbacks, this study suggests the needs of future study, exploring a new ideal-typical welfare regime for Asian societies, particularly the ROK, that go beyond the Western ideas from Beverage and Bismark. References Aspalter, C. (2006). The East Asian welfare model. International Journal of Social Welfare, 15, Aspalter, C., & Opielka, M. (2006). A new orientation for the welfare state: The defense and development of human, social and cultural capital. New York, NY: Springer Verlag. Berger, L., & Luckmann, T. (1966). The social construction of reality: A treatise on the sociology of knowledge. New York, NY: Anchor Books. Campbell, A. (1976). Subjective measures of well -being. American Journal of Psychology, 31, Esping-Andersen, G. (1990). The three worlds of welfare capitalism. New Jersey: Princeton University Press. Ferragina, E. & Seeleib-Kaiser, M. (2011) 'Welfare regime debate: past, present, futures?', Policy and Politics, Vol. 39, No. 4, pp Hofstede, G. (2001). Culture s consequences: Comparing values, behaviors, institutions and organizations across nations (2nd ed.). CA: Sage Publications. Huber, E., & Stephens, J. (2001). Development and crisis of the welfare state: Parties and policies in global markets. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press. Kersbergen, K. (1995). Social capitalism: A study of Christian democracy and the welfare state. London, England: Routledge. Korpi, W. (1983). The democratic class struggle. 69
7 The Quality of Life in Ideal-typical Welfare Regimes London, England: Routledge. Kyonne, J. (2008). The philosophical origins of the U.S. welfare policy. International Journal of Diversity in Organizations, Communities and Nations, 8(5), Lester, D. (1984). The association between the quality of life and suicide and homicide rates. The Journal of Social Psychology, 124(2), Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD). (2010). OECD factbook Paris, France: OECD Publications. OECD. (2012). OECD factbook Paris, France: OECD Publications. Shinkawa, T. (2004, June). The development and crisis of the Japanese-style welfare regime. Paper presented at the meeting of Korean Political Science, Daejon, Korea. Stephens, J. D. (1979). The transition from capitalism to socialism. London, England: Macmillan. United Nations Statistical Division. (2012). UN commodity trade statistics database. New York, NY: UN Comtrade. Yi, I. (2009, October). Quality of life index in Korea: Why we need it & how to apply. Paper presented at the 3 rd OECD World Forum on Statistics, Knowledge and Policy, Busan, Korea. 70
RESEARCH NOTE The effect of public opinion on social policy generosity
 Socio-Economic Review (2009) 7, 727 740 Advance Access publication June 28, 2009 doi:10.1093/ser/mwp014 RESEARCH NOTE The effect of public opinion on social policy generosity Lane Kenworthy * Department
Socio-Economic Review (2009) 7, 727 740 Advance Access publication June 28, 2009 doi:10.1093/ser/mwp014 RESEARCH NOTE The effect of public opinion on social policy generosity Lane Kenworthy * Department
Inclusive global growth: a framework to think about the post-2015 agenda
 Inclusive global growth: a framework to think about the post-215 agenda François Bourguignon Paris School of Economics Angus Maddison Lecture, Oecd, Paris, April 213 1 Outline 1) Inclusion and exclusion
Inclusive global growth: a framework to think about the post-215 agenda François Bourguignon Paris School of Economics Angus Maddison Lecture, Oecd, Paris, April 213 1 Outline 1) Inclusion and exclusion
8. REGIONAL DISPARITIES IN GDP PER CAPITA
 8. REGIONAL DISPARITIES IN GDP PER CAPITA GDP per capita varies significantly among OECD countries (Figure 8.1). In 2003, GDP per capita in Luxembourg (USD 53 390) was more than double the OECD average
8. REGIONAL DISPARITIES IN GDP PER CAPITA GDP per capita varies significantly among OECD countries (Figure 8.1). In 2003, GDP per capita in Luxembourg (USD 53 390) was more than double the OECD average
Asian American Family Life. Eunju Yoon, Ph.D. Counseling Psychology Loyola University Chicago
 Asian American Family Life Eunju Yoon, Ph.D. Counseling Psychology Loyola University Chicago Outline Demographics Asian values Asian family issues Quotes from Korean immigrant women Q & A Demographics
Asian American Family Life Eunju Yoon, Ph.D. Counseling Psychology Loyola University Chicago Outline Demographics Asian values Asian family issues Quotes from Korean immigrant women Q & A Demographics
OECD Health Data 2009 comparing health statistics across OECD countries
 OECD Centres Germany Berlin (49-3) 288 8353 Japan Tokyo (81-3) 5532-21 Mexico Mexico (52-55) 5281 381 United States Washington (1-22) 785 6323 AUSTRALIA AUSTRIA BELGIUM CANADA CZECH REPUBLIC DENMARK FINLAND
OECD Centres Germany Berlin (49-3) 288 8353 Japan Tokyo (81-3) 5532-21 Mexico Mexico (52-55) 5281 381 United States Washington (1-22) 785 6323 AUSTRALIA AUSTRIA BELGIUM CANADA CZECH REPUBLIC DENMARK FINLAND
Comparative Political Economy. David Soskice Nuffield College
 Comparative Political Economy David Soskice Nuffield College Comparative Political Economy (i) Focus on nation states (ii) Complementarities between 3 systems: Variety of Capitalism (Hall & Soskice) Political
Comparative Political Economy David Soskice Nuffield College Comparative Political Economy (i) Focus on nation states (ii) Complementarities between 3 systems: Variety of Capitalism (Hall & Soskice) Political
DOI: / Lessons in Sustainable Development from Japan and South Korea
 DOI: 10.1057/9781137340986.0001 Lessons in Sustainable Development from Japan and South Korea Comparative Studies of Sustainable Development in Asia Series Editor: Sara Hsu, Assistant Professor, SUNY New
DOI: 10.1057/9781137340986.0001 Lessons in Sustainable Development from Japan and South Korea Comparative Studies of Sustainable Development in Asia Series Editor: Sara Hsu, Assistant Professor, SUNY New
UK Productivity Gap: Skills, management and innovation
 UK Productivity Gap: Skills, management and innovation March 2005 Professor John Van Reenen Director, Centre for Economic Performance, LSE 1 1. Overview The Productivity Gap (output per hour) What is it
UK Productivity Gap: Skills, management and innovation March 2005 Professor John Van Reenen Director, Centre for Economic Performance, LSE 1 1. Overview The Productivity Gap (output per hour) What is it
HIGHLIGHTS. There is a clear trend in the OECD area towards. which is reflected in the economic and innovative performance of certain OECD countries.
 HIGHLIGHTS The ability to create, distribute and exploit knowledge is increasingly central to competitive advantage, wealth creation and better standards of living. The STI Scoreboard 2001 presents the
HIGHLIGHTS The ability to create, distribute and exploit knowledge is increasingly central to competitive advantage, wealth creation and better standards of living. The STI Scoreboard 2001 presents the
Trends in inequality worldwide (Gini coefficients)
 Section 2 Impact of trade on income inequality As described above, it has been theoretically and empirically proved that the progress of globalization as represented by trade brings benefits in the form
Section 2 Impact of trade on income inequality As described above, it has been theoretically and empirically proved that the progress of globalization as represented by trade brings benefits in the form
BRIEFING. International Migration: The UK Compared with other OECD Countries.
 BRIEFING International Migration: The UK Compared with other OECD Countries AUTHOR: DR CARLOS VARGAS-SILVA PUBLISHED: 11/3/214 2nd Revision www.migrationobservatory.ox.ac.uk This briefing uses data from
BRIEFING International Migration: The UK Compared with other OECD Countries AUTHOR: DR CARLOS VARGAS-SILVA PUBLISHED: 11/3/214 2nd Revision www.migrationobservatory.ox.ac.uk This briefing uses data from
Widening of Inequality in Japan: Its Implications
 Widening of Inequality in Japan: Its Implications Jun Saito, Senior Research Fellow Japan Center for Economic Research December 11, 2017 Is inequality widening in Japan? Since the publication of Thomas
Widening of Inequality in Japan: Its Implications Jun Saito, Senior Research Fellow Japan Center for Economic Research December 11, 2017 Is inequality widening in Japan? Since the publication of Thomas
Economic Growth & Welfare Systems. Jean Monnet Chair in European Integration Studies Prof. PASQUALE TRIDICO
 Economic Growth & Welfare Systems Jean Monnet Chair in European Integration Studies Prof. PASQUALE TRIDICO Welfare states and its history Peter Lindert Most of the historical data and the arguments are
Economic Growth & Welfare Systems Jean Monnet Chair in European Integration Studies Prof. PASQUALE TRIDICO Welfare states and its history Peter Lindert Most of the historical data and the arguments are
Upgrading workers skills and competencies: policy strategies
 Federation of Greek Industries Greek General Confederation of Labour CONFERENCE LIFELONG DEVELOPMENT OF COMPETENCES AND QUALIFICATIONS OF THE WORKFORCE; ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES Athens 23-24 24 May 2003
Federation of Greek Industries Greek General Confederation of Labour CONFERENCE LIFELONG DEVELOPMENT OF COMPETENCES AND QUALIFICATIONS OF THE WORKFORCE; ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES Athens 23-24 24 May 2003
Taiwan s Development Strategy for the Next Phase. Dr. San, Gee Vice Chairman Taiwan External Trade Development Council Taiwan
 Taiwan s Development Strategy for the Next Phase Dr. San, Gee Vice Chairman Taiwan External Trade Development Council Taiwan 2013.10.12 1 Outline 1. Some of Taiwan s achievements 2. Taiwan s economic challenges
Taiwan s Development Strategy for the Next Phase Dr. San, Gee Vice Chairman Taiwan External Trade Development Council Taiwan 2013.10.12 1 Outline 1. Some of Taiwan s achievements 2. Taiwan s economic challenges
BUILDING RESILIENT REGIONS FOR STRONGER ECONOMIES OECD
 o: o BUILDING RESILIENT REGIONS FOR STRONGER ECONOMIES OECD Table of Contents Acronyms and Abbreviations 11 List of TL2 Regions 13 Preface 16 Executive Summary 17 Parti Key Regional Trends and Policies
o: o BUILDING RESILIENT REGIONS FOR STRONGER ECONOMIES OECD Table of Contents Acronyms and Abbreviations 11 List of TL2 Regions 13 Preface 16 Executive Summary 17 Parti Key Regional Trends and Policies
The Transmission of Economic Status and Inequality: U.S. Mexico in Comparative Perspective
 The Students We Share: New Research from Mexico and the United States Mexico City January, 2010 The Transmission of Economic Status and Inequality: U.S. Mexico in Comparative Perspective René M. Zenteno
The Students We Share: New Research from Mexico and the United States Mexico City January, 2010 The Transmission of Economic Status and Inequality: U.S. Mexico in Comparative Perspective René M. Zenteno
What Are the Social Outcomes of Education?
 Indicator What Are the Social Outcomes of Education? Adults aged 25 to 64 with higher levels of al attainment are, on average, more satisfied with life, engaged in society and likely to report that they
Indicator What Are the Social Outcomes of Education? Adults aged 25 to 64 with higher levels of al attainment are, on average, more satisfied with life, engaged in society and likely to report that they
HRST Development in China. Mu Rongping Institute of Policy and Management Chinese Academy of Sciences
 2007-8-27 27 HRST Development in China Mu Rongping Institute of Policy and Management Chinese Academy of Sciences Outline I. Introduction II. Demands for HRST in China 1. Quantity/Quality of HRST in China
2007-8-27 27 HRST Development in China Mu Rongping Institute of Policy and Management Chinese Academy of Sciences Outline I. Introduction II. Demands for HRST in China 1. Quantity/Quality of HRST in China
Inclusion and Gender Equality in China
 Inclusion and Gender Equality in China 12 June 2017 Disclaimer: The views expressed in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views and policies of the Asian Development
Inclusion and Gender Equality in China 12 June 2017 Disclaimer: The views expressed in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views and policies of the Asian Development
The Politics of Egalitarian Capitalism; Rethinking the Trade-off between Equality and Efficiency
 The Politics of Egalitarian Capitalism; Rethinking the Trade-off between Equality and Efficiency Week 3 Aidan Regan Democratic politics is about distributive conflict tempered by a common interest in economic
The Politics of Egalitarian Capitalism; Rethinking the Trade-off between Equality and Efficiency Week 3 Aidan Regan Democratic politics is about distributive conflict tempered by a common interest in economic
The Political Economy of Health Inequalities
 The Political Economy of Health Inequalities Dennis Raphael, PhD School of Health Policy and Management, York University, Toronto, Canada Presentation at the Conference Social Policy and Health Inequalities:
The Political Economy of Health Inequalities Dennis Raphael, PhD School of Health Policy and Management, York University, Toronto, Canada Presentation at the Conference Social Policy and Health Inequalities:
OECD ECONOMIC SURVEY OF LITHUANIA 2018 Promoting inclusive growth
 OECD ECONOMIC SURVEY OF LITHUANIA 218 Promoting inclusive growth Vilnius, 5 July 218 http://www.oecd.org/eco/surveys/economic-survey-lithuania.htm @OECDeconomy @OECD 2 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 21 211
OECD ECONOMIC SURVEY OF LITHUANIA 218 Promoting inclusive growth Vilnius, 5 July 218 http://www.oecd.org/eco/surveys/economic-survey-lithuania.htm @OECDeconomy @OECD 2 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 21 211
THE WELFARE STATE AND EDUCATION: A COMPARISON OF SOCIAL AND EDUCATIONAL POLICY IN ADVANCED INDUSTRIAL SOCIETIES
 THE WELFARE STATE AND EDUCATION: A COMPARISON OF SOCIAL AND EDUCATIONAL POLICY IN ADVANCED INDUSTRIAL SOCIETIES Gunther M. Hega Karl G. Hokenmaier Department of Political Science Western Michigan University
THE WELFARE STATE AND EDUCATION: A COMPARISON OF SOCIAL AND EDUCATIONAL POLICY IN ADVANCED INDUSTRIAL SOCIETIES Gunther M. Hega Karl G. Hokenmaier Department of Political Science Western Michigan University
How many students study abroad and where do they go?
 1. EDUCATION LEVELS AND STUDENT NUMBERS How many students study abroad and where do they go? More than 4.1 million tertiary-level students were enrolled outside their country of citizenship in 2010. Australia,
1. EDUCATION LEVELS AND STUDENT NUMBERS How many students study abroad and where do they go? More than 4.1 million tertiary-level students were enrolled outside their country of citizenship in 2010. Australia,
Relationship between Economic Development and Intellectual Production
 Relationship between Economic Development and Intellectual Production 1 Umut Al and Zehra Taşkın 2 1 umutal@hacettepe.edu.tr Hacettepe University, Department of Information Management, 06800, Beytepe Ankara,
Relationship between Economic Development and Intellectual Production 1 Umut Al and Zehra Taşkın 2 1 umutal@hacettepe.edu.tr Hacettepe University, Department of Information Management, 06800, Beytepe Ankara,
Corporatism and the Labour Income Share
 Etica e Economia & Sapienza University Rome, 21 June 2018 Corporatism and the Labour Income Share Econometric Investigation into the Impact of Institutions on the Wage Share of Industrialised Nations by
Etica e Economia & Sapienza University Rome, 21 June 2018 Corporatism and the Labour Income Share Econometric Investigation into the Impact of Institutions on the Wage Share of Industrialised Nations by
Social Economy of Republic of Korea: Conditions of Success and Policy Direction
 Social Economy of Republic of Korea: Conditions of Success and Policy Direction57 Social Economy of Republic of Korea: Conditions of Success and Policy Direction KIM Jong-Gul (Professor, Graduate School
Social Economy of Republic of Korea: Conditions of Success and Policy Direction57 Social Economy of Republic of Korea: Conditions of Success and Policy Direction KIM Jong-Gul (Professor, Graduate School
EDUCATION OUTCOMES EXPENDITURE ON EDUCATION INTERNATIONAL STUDENT ASSESSMENT TERTIARY ATTAINMENT
 EDUCATION OUTCOMES INTERNATIONAL STUDENT ASSESSMENT TERTIARY ATTAINMENT EXPENDITURE ON EDUCATION EXPENDITURE ON TERTIARY EDUCATION PUBLIC AND PRIVATE EDUCATION EXPENDITURE EDUCATION OUTCOMES INTERNATIONAL
EDUCATION OUTCOMES INTERNATIONAL STUDENT ASSESSMENT TERTIARY ATTAINMENT EXPENDITURE ON EDUCATION EXPENDITURE ON TERTIARY EDUCATION PUBLIC AND PRIVATE EDUCATION EXPENDITURE EDUCATION OUTCOMES INTERNATIONAL
TRENDS AND PROSPECTS OF KOREAN ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT: FROM AN INTELLECTUAL POINTS OF VIEW
 TRENDS AND PROSPECTS OF KOREAN ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT: FROM AN INTELLECTUAL POINTS OF VIEW FANOWEDY SAMARA (Seoul, South Korea) Comment on fanowedy@gmail.com On this article, I will share you the key factors
TRENDS AND PROSPECTS OF KOREAN ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT: FROM AN INTELLECTUAL POINTS OF VIEW FANOWEDY SAMARA (Seoul, South Korea) Comment on fanowedy@gmail.com On this article, I will share you the key factors
China s Aid Approaches in the Changing International Aid Architecture
 China s Aid Approaches in the Changing International Aid Architecture Mao Xiaojing Deputy Director, Associate Research Fellow Chinese Academy of International Trade and Economic Cooperation (CAITEC) MOFCOM,
China s Aid Approaches in the Changing International Aid Architecture Mao Xiaojing Deputy Director, Associate Research Fellow Chinese Academy of International Trade and Economic Cooperation (CAITEC) MOFCOM,
INTRODUCTION EB434 ENTERPRISE + GOVERNANCE
 INTRODUCTION EB434 ENTERPRISE + GOVERNANCE why study the company? Corporations play a leading role in most societies Recent corporate failures have had a major social impact and highlighted the importance
INTRODUCTION EB434 ENTERPRISE + GOVERNANCE why study the company? Corporations play a leading role in most societies Recent corporate failures have had a major social impact and highlighted the importance
Why do some societies produce more inequality than others?
 Why do some societies produce more inequality than others? Author: Ksawery Lisiński Word count: 1570 Jan Pen s parade of wealth is probably the most accurate metaphor of economic inequality. 1 Although
Why do some societies produce more inequality than others? Author: Ksawery Lisiński Word count: 1570 Jan Pen s parade of wealth is probably the most accurate metaphor of economic inequality. 1 Although
Civil and Political Rights
 DESIRED OUTCOMES All people enjoy civil and political rights. Mechanisms to regulate and arbitrate people s rights in respect of each other are trustworthy. Civil and Political Rights INTRODUCTION The
DESIRED OUTCOMES All people enjoy civil and political rights. Mechanisms to regulate and arbitrate people s rights in respect of each other are trustworthy. Civil and Political Rights INTRODUCTION The
IMF research links declining labour share to weakened worker bargaining power. ACTU Economic Briefing Note, August 2018
 IMF research links declining labour share to weakened worker bargaining power ACTU Economic Briefing Note, August 2018 Authorised by S. McManus, ACTU, 365 Queen St, Melbourne 3000. ACTU D No. 172/2018
IMF research links declining labour share to weakened worker bargaining power ACTU Economic Briefing Note, August 2018 Authorised by S. McManus, ACTU, 365 Queen St, Melbourne 3000. ACTU D No. 172/2018
Issues in Education and Lifelong Learning: Spending, Learning Recognition, Immigrants and Visible Minorities
 Issues in Education and Lifelong Learning: Spending, Learning Recognition, Immigrants and Visible Minorities Dr. Michael Bloom Executive Director, Strategic Projects, & Director, Education and Learning
Issues in Education and Lifelong Learning: Spending, Learning Recognition, Immigrants and Visible Minorities Dr. Michael Bloom Executive Director, Strategic Projects, & Director, Education and Learning
"Science, Research and Innovation Performance of the EU 2018"
 "Science, Research and Innovation Performance of the EU 2018" Innovation, Productivity, Jobs and Inequality ERAC Workshop Brussels, 4 October 2017 DG RTD, Unit A4 Key messages More robust economic growth
"Science, Research and Innovation Performance of the EU 2018" Innovation, Productivity, Jobs and Inequality ERAC Workshop Brussels, 4 October 2017 DG RTD, Unit A4 Key messages More robust economic growth
Student Mobility: Implications for the ASEAN Labor
 Trends and Patterns of Inter- and Intra-ASEAN Student Mobility: Implications for the ASEAN Labor Market Emily Christi A. Cabegin Paper presented at the Asian Conference on Globalization and Labor Administration:
Trends and Patterns of Inter- and Intra-ASEAN Student Mobility: Implications for the ASEAN Labor Market Emily Christi A. Cabegin Paper presented at the Asian Conference on Globalization and Labor Administration:
WORLDWIDE DISTRIBUTION OF PRIVATE FINANCIAL ASSETS
 WORLDWIDE DISTRIBUTION OF PRIVATE FINANCIAL ASSETS Munich, November 2018 Copyright Allianz 11/19/2018 1 MORE DYNAMIC POST FINANCIAL CRISIS Changes in the global wealth middle classes in millions 1,250
WORLDWIDE DISTRIBUTION OF PRIVATE FINANCIAL ASSETS Munich, November 2018 Copyright Allianz 11/19/2018 1 MORE DYNAMIC POST FINANCIAL CRISIS Changes in the global wealth middle classes in millions 1,250
Chapter 2 Welfare Studies in the West and China
 Chapter 2 Welfare Studies in the West and China This chapter reviews the literature on welfare study both from the West and China. It traces the evolution of ideas and practices of welfare states in Western
Chapter 2 Welfare Studies in the West and China This chapter reviews the literature on welfare study both from the West and China. It traces the evolution of ideas and practices of welfare states in Western
Attitudes and Values. Gill STEEL. Department of Social Psychology University of Tokyo. Disagree Strongly. Agree 36% 60%
 Attitudes and Values 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Disagree Strongly Agree Gill STEEL 4% Department of Social Psychology University of Tokyo 36% 60% My research Public opinion Voting behavior The kind of
Attitudes and Values 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Disagree Strongly Agree Gill STEEL 4% Department of Social Psychology University of Tokyo 36% 60% My research Public opinion Voting behavior The kind of
Assistant Professor, Fall 2013 Current School of Interdisciplinary Global Studies, University of South Florida
 JONGSEOK WOO, Ph. D. Assistant Professor School of Interdisciplinary Global Studies University of South Florida 4202 E. Fowler Ave. SOC107 Tampa, FL 33620 USA Phone: 1-813-974-0842 Email: wooj@usf.edu
JONGSEOK WOO, Ph. D. Assistant Professor School of Interdisciplinary Global Studies University of South Florida 4202 E. Fowler Ave. SOC107 Tampa, FL 33620 USA Phone: 1-813-974-0842 Email: wooj@usf.edu
GERMANY, JAPAN AND INTERNATIONAL PAYMENT IMBALANCES
 Articles Articles Articles Articles Articles CENTRAL EUROPEAN REVIEW OF ECONOMICS & FINANCE Vol. 2, No. 1 (2012) pp. 5-18 Slawomir I. Bukowski* GERMANY, JAPAN AND INTERNATIONAL PAYMENT IMBALANCES Abstract
Articles Articles Articles Articles Articles CENTRAL EUROPEAN REVIEW OF ECONOMICS & FINANCE Vol. 2, No. 1 (2012) pp. 5-18 Slawomir I. Bukowski* GERMANY, JAPAN AND INTERNATIONAL PAYMENT IMBALANCES Abstract
The Mystery of Economic Growth by Elhanan Helpman. Chiara Criscuolo Centre for Economic Performance London School of Economics
 The Mystery of Economic Growth by Elhanan Helpman Chiara Criscuolo Centre for Economic Performance London School of Economics The facts Burundi, 2006 Sweden, 2006 According to Maddison, in the year 1000
The Mystery of Economic Growth by Elhanan Helpman Chiara Criscuolo Centre for Economic Performance London School of Economics The facts Burundi, 2006 Sweden, 2006 According to Maddison, in the year 1000
ISSUE BRIEF: U.S. Immigration Priorities in a Global Context
 Immigration Task Force ISSUE BRIEF: U.S. Immigration Priorities in a Global Context JUNE 2013 As a share of total immigrants in 2011, the United States led a 24-nation sample in familybased immigration
Immigration Task Force ISSUE BRIEF: U.S. Immigration Priorities in a Global Context JUNE 2013 As a share of total immigrants in 2011, the United States led a 24-nation sample in familybased immigration
DETERMINANTS OF THE LONG TERM ECONOMIC GROWTH OF NATIONS IN THE ERA OF THE CRYSTALLIZATION OF THE MODERN WORLD SYSTEM
 DETERMINANTS OF THE LONG TERM ECONOMIC GROWTH OF NATIONS IN THE ERA OF THE CRYSTALLIZATION OF THE MODERN WORLD SYSTEM A Senior Scholars Thesis by NIHAD MANSIMZADA Submitted to Honors and Undergraduate
DETERMINANTS OF THE LONG TERM ECONOMIC GROWTH OF NATIONS IN THE ERA OF THE CRYSTALLIZATION OF THE MODERN WORLD SYSTEM A Senior Scholars Thesis by NIHAD MANSIMZADA Submitted to Honors and Undergraduate
BY Amy Mitchell, Katie Simmons, Katerina Eva Matsa and Laura Silver. FOR RELEASE JANUARY 11, 2018 FOR MEDIA OR OTHER INQUIRIES:
 FOR RELEASE JANUARY 11, 2018 BY Amy Mitchell, Katie Simmons, Katerina Eva Matsa and Laura Silver FOR MEDIA OR OTHER INQUIRIES: Amy Mitchell, Director, Journalism Research Katie Simmons, Associate Director,
FOR RELEASE JANUARY 11, 2018 BY Amy Mitchell, Katie Simmons, Katerina Eva Matsa and Laura Silver FOR MEDIA OR OTHER INQUIRIES: Amy Mitchell, Director, Journalism Research Katie Simmons, Associate Director,
Settling In 2018 Main Indicators of Immigrant Integration
 Settling In 2018 Main Indicators of Immigrant Integration Settling In 2018 Main Indicators of Immigrant Integration Notes on Cyprus 1. Note by Turkey: The information in this document with reference to
Settling In 2018 Main Indicators of Immigrant Integration Settling In 2018 Main Indicators of Immigrant Integration Notes on Cyprus 1. Note by Turkey: The information in this document with reference to
The Danish Welfare State
 The Danish Welfare State The Danish Welfare State A Sociological Investigation Edited by Tea Torbenfeldt Bengtsson, Morten Frederiksen, and J ø rgen Elm Larsen THE DANISH WELFARE STATE Copyright Tea Torbenfeldt
The Danish Welfare State The Danish Welfare State A Sociological Investigation Edited by Tea Torbenfeldt Bengtsson, Morten Frederiksen, and J ø rgen Elm Larsen THE DANISH WELFARE STATE Copyright Tea Torbenfeldt
Briefing Memo Prospect of Demographic Trend, Economic Hegemony and Security: From the mid-21 st to 22 nd Century
 Briefing Memo Prospect of Demographic Trend, Economic Hegemony and Security: From the mid-21 st to 22 nd Century Keishi ONO Chief, Society and Economy Division Security Studies Department The Age of Asia-Pacific
Briefing Memo Prospect of Demographic Trend, Economic Hegemony and Security: From the mid-21 st to 22 nd Century Keishi ONO Chief, Society and Economy Division Security Studies Department The Age of Asia-Pacific
Child and Family Poverty
 Child and Family Poverty Report, November 2009 Highlights In 2007, there were 35,000 (16.7%) children under age 18 living beneath the poverty line (before-tax Low Income Cut-off) in. has the third highest
Child and Family Poverty Report, November 2009 Highlights In 2007, there were 35,000 (16.7%) children under age 18 living beneath the poverty line (before-tax Low Income Cut-off) in. has the third highest
Towards Consensus on a Decent Living Level in South Africa: Inequality beliefs and preferences for redistribution
 Towards Consensus on a Decent Living Level in South Africa: Inequality beliefs and preferences for redistribution Ben Roberts Democracy, Governance & Service Delivery (DSGD), Human Sciences Research Council
Towards Consensus on a Decent Living Level in South Africa: Inequality beliefs and preferences for redistribution Ben Roberts Democracy, Governance & Service Delivery (DSGD), Human Sciences Research Council
FORMS OF WELFARE IN LATIN AMERICA: A COMPARISON ON OIL PRODUCING COUNTRIES. Veronica Ronchi. June 15, 2015
 FORMS OF WELFARE IN LATIN AMERICA: A COMPARISON ON OIL PRODUCING COUNTRIES Veronica Ronchi June 15, 2015 0 Wellness is a concept full of normative and epistemological meanings welfare state is a system
FORMS OF WELFARE IN LATIN AMERICA: A COMPARISON ON OIL PRODUCING COUNTRIES Veronica Ronchi June 15, 2015 0 Wellness is a concept full of normative and epistemological meanings welfare state is a system
U.S. Family Income Growth
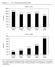 Figure 1.1 U.S. Family Income Growth Growth 140% 120% 100% 80% 60% 115.3% 1947 to 1973 97.1% 97.7% 102.9% 84.0% 40% 20% 0% Lowest Fifth Second Fifth Middle Fifth Fourth Fifth Top Fifth 70% 60% 1973 to
Figure 1.1 U.S. Family Income Growth Growth 140% 120% 100% 80% 60% 115.3% 1947 to 1973 97.1% 97.7% 102.9% 84.0% 40% 20% 0% Lowest Fifth Second Fifth Middle Fifth Fourth Fifth Top Fifth 70% 60% 1973 to
Introduction to Comparative Politics or permission of the instructor.
 Isabela Mares Professor of Political Science 739 International Affairs Building Tel: (212) 854 6513 E-mail: im2195@columbia.edu Office Hours: Wednesdays 5.30 6.30 p.m. TA: Xian Huang Xh2128@columbia.edu
Isabela Mares Professor of Political Science 739 International Affairs Building Tel: (212) 854 6513 E-mail: im2195@columbia.edu Office Hours: Wednesdays 5.30 6.30 p.m. TA: Xian Huang Xh2128@columbia.edu
OECD WORK ON GLOBAL VALUE CHAINS AND TRADE IN VALUE ADDED. Koen De Backer
 OECD WORK ON GLOBAL VALUE CHAINS AND TRADE IN VALUE ADDED Koen De Backer COMPNET meeting, Dublin, 13 March 2013 Global Value Chains case studies Wing box: Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (Japan) Wing ice protection:
OECD WORK ON GLOBAL VALUE CHAINS AND TRADE IN VALUE ADDED Koen De Backer COMPNET meeting, Dublin, 13 March 2013 Global Value Chains case studies Wing box: Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (Japan) Wing ice protection:
Networks and Innovation: Accounting for Structural and Institutional Sources of Recombination in Brokerage Triads
 1 Online Appendix for Networks and Innovation: Accounting for Structural and Institutional Sources of Recombination in Brokerage Triads Sarath Balachandran Exequiel Hernandez This appendix presents a descriptive
1 Online Appendix for Networks and Innovation: Accounting for Structural and Institutional Sources of Recombination in Brokerage Triads Sarath Balachandran Exequiel Hernandez This appendix presents a descriptive
Where are the Middle Class in OECD Countries? Nathaniel Johnson (CUNY and LIS) David Johnson (University of Michigan)
 Where are the Middle Class in OECD Countries? Nathaniel Johnson (CUNY and LIS) David Johnson (University of Michigan) The Middle Class is all over the US Headlines A strong middle class equals a strong
Where are the Middle Class in OECD Countries? Nathaniel Johnson (CUNY and LIS) David Johnson (University of Michigan) The Middle Class is all over the US Headlines A strong middle class equals a strong
How does education affect the economy?
 2. THE ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL BENEFITS OF EDUCATION How does education affect the economy? More than half of the GDP growth in OECD countries over the past decade is related to labour income growth among
2. THE ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL BENEFITS OF EDUCATION How does education affect the economy? More than half of the GDP growth in OECD countries over the past decade is related to labour income growth among
Good Societies Index 2012 Comparing Quality of Life in Relatively Wealthy Societies
 Good Societies Index 2012 Comparing Quality of Life in Relatively Wealthy Societies Ron Anderson University of Minnesota rea@umn.edu For Presentation at the International Society for Quality of Life Studies
Good Societies Index 2012 Comparing Quality of Life in Relatively Wealthy Societies Ron Anderson University of Minnesota rea@umn.edu For Presentation at the International Society for Quality of Life Studies
The impact of democratic transitions on budgeting and public expenditures
 The impact of democratic transitions on budgeting and public expenditures A Latin American perspective Ángel Melguizo OECD Development Centre 4th Annual Meeting of Middle East and North Africa Senior Budget
The impact of democratic transitions on budgeting and public expenditures A Latin American perspective Ángel Melguizo OECD Development Centre 4th Annual Meeting of Middle East and North Africa Senior Budget
CO3.6: Percentage of immigrant children and their educational outcomes
 CO3.6: Percentage of immigrant children and their educational outcomes Definitions and methodology This indicator presents estimates of the proportion of children with immigrant background as well as their
CO3.6: Percentage of immigrant children and their educational outcomes Definitions and methodology This indicator presents estimates of the proportion of children with immigrant background as well as their
Outline. Why is international mobility an important policy issue? The International Mobility of Researchers. IMHE Conference
 The International Mobility of Researchers IMHE Conference 8 and 9 September 28, Paris Ester Basri Science and Technology Policy Division, OECD Contact: ester.basri@oecd.org Outline Why is international
The International Mobility of Researchers IMHE Conference 8 and 9 September 28, Paris Ester Basri Science and Technology Policy Division, OECD Contact: ester.basri@oecd.org Outline Why is international
GDP per capita was lowest in the Czech Republic and the Republic of Korea. For more details, see page 3.
 International Comparisons of GDP per Capita and per Hour, 1960 9 Division of International Labor Comparisons October 21, 2010 Table of Contents Introduction.2 Charts...3 Tables...9 Technical Notes.. 18
International Comparisons of GDP per Capita and per Hour, 1960 9 Division of International Labor Comparisons October 21, 2010 Table of Contents Introduction.2 Charts...3 Tables...9 Technical Notes.. 18
Winner, Theda Skocpol Best Dissertation Award from the Comparative- Historical Sociology Section of the American Sociological Association, 2013
 1 Jaeeun Kim (updated on April 24, 2015) Assistant Professor Department of Sociology Korea Foundation Assistant Professor of Korean Studies Nam Center for Korean Studies University of Michigan, Ann Arbor
1 Jaeeun Kim (updated on April 24, 2015) Assistant Professor Department of Sociology Korea Foundation Assistant Professor of Korean Studies Nam Center for Korean Studies University of Michigan, Ann Arbor
SECTION THREE BENEFITS OF THE JSEPA
 SECTION THREE BENEFITS OF THE JSEPA 1. Section Two described the possible scope of the JSEPA and elaborated on the benefits that could be derived from the proposed initiatives under the JSEPA. This section
SECTION THREE BENEFITS OF THE JSEPA 1. Section Two described the possible scope of the JSEPA and elaborated on the benefits that could be derived from the proposed initiatives under the JSEPA. This section
OECD SKILLS STRATEGY FLANDERS DIAGNOSTIC WORKSHOP
 OECD SKILLS STRATEGY FLANDERS DIAGNOSTIC WORKSHOP Dirk Van Damme Head of Division OECD Centre for Skills Education and Skills Directorate 15 May 218 Use Pigeonhole for your questions 1 WHY DO SKILLS MATTER?
OECD SKILLS STRATEGY FLANDERS DIAGNOSTIC WORKSHOP Dirk Van Damme Head of Division OECD Centre for Skills Education and Skills Directorate 15 May 218 Use Pigeonhole for your questions 1 WHY DO SKILLS MATTER?
Migrants and external voting
 The Migration & Development Series On the occasion of International Migrants Day New York, 18 December 2008 Panel discussion on The Human Rights of Migrants Facilitating the Participation of Migrants in
The Migration & Development Series On the occasion of International Migrants Day New York, 18 December 2008 Panel discussion on The Human Rights of Migrants Facilitating the Participation of Migrants in
HOUSING PRICES. International Comparative Analysis. BDO Consulting Israel September 2017
 HOUSING PRICES International Comparative Analysis BDO Consulting Israel September 2017 OVERVIEW BDO Consulting Israel conducted a comparative analysis of the housing markets among eight observed countries.
HOUSING PRICES International Comparative Analysis BDO Consulting Israel September 2017 OVERVIEW BDO Consulting Israel conducted a comparative analysis of the housing markets among eight observed countries.
Introduction: Summary of the Survey Results
 Introduction: Summary of the Survey Results The following is a chapter-by-chapter summary of the main points that became apparent as a result of this survey. The design of the survey form is similar in
Introduction: Summary of the Survey Results The following is a chapter-by-chapter summary of the main points that became apparent as a result of this survey. The design of the survey form is similar in
Regional and Sectoral Economic Studies
 PRODUCTION BY SECTOR IN THE EUROPEAN UNION: ANALISYS OF FRANCE, GERMANY, ITALY, SPAIN, POLAND AND THE UNITED KINGDOM, 2000-2005 GUISAN, M.C. * AGUAYO, E. Abstract: We analyze the evolution of sectoral
PRODUCTION BY SECTOR IN THE EUROPEAN UNION: ANALISYS OF FRANCE, GERMANY, ITALY, SPAIN, POLAND AND THE UNITED KINGDOM, 2000-2005 GUISAN, M.C. * AGUAYO, E. Abstract: We analyze the evolution of sectoral
JAPAN S WELFARE-STATE REGIME: WELFARE POLITICS, PROVIDER AND REGULATOR*
 DEVELOPMENT AND SOCIETY Volume 34 Number 2, December 2005, pp. 169~190 JAPAN S WELFARE-STATE REGIME: WELFARE POLITICS, PROVIDER AND REGULATOR* SHOGO TAKEGAWA Tokyo University In the late 1990s the Korean
DEVELOPMENT AND SOCIETY Volume 34 Number 2, December 2005, pp. 169~190 JAPAN S WELFARE-STATE REGIME: WELFARE POLITICS, PROVIDER AND REGULATOR* SHOGO TAKEGAWA Tokyo University In the late 1990s the Korean
Finland at the Frontier of Knowledge Economy
 Finland at the Frontier of Knowledge Economy Dr. Timo J. Hämäläinen timo.hamalainen@sitra.fi Sitra, The Finnish Innovation Fund in Knowledge Economy Behind the Scenes Westin Hotel, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia,
Finland at the Frontier of Knowledge Economy Dr. Timo J. Hämäläinen timo.hamalainen@sitra.fi Sitra, The Finnish Innovation Fund in Knowledge Economy Behind the Scenes Westin Hotel, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia,
Human development in China. Dr Zhao Baige
 Human development in China Dr Zhao Baige 19 Environment Twenty years ago I began my academic life as a researcher in Cambridge, and it is as an academic that I shall describe the progress China has made
Human development in China Dr Zhao Baige 19 Environment Twenty years ago I began my academic life as a researcher in Cambridge, and it is as an academic that I shall describe the progress China has made
Brian Duncan (March 2019)
 Brian Duncan (March 2019) Department of Economics University of Colorado Denver Campus Box 181 Denver, CO 80217-3364 Phone: (303) 315-2041 Email: brian.duncan@ucdenver.edu Homepage: www.econ.ucdenver.edu/bduncan
Brian Duncan (March 2019) Department of Economics University of Colorado Denver Campus Box 181 Denver, CO 80217-3364 Phone: (303) 315-2041 Email: brian.duncan@ucdenver.edu Homepage: www.econ.ucdenver.edu/bduncan
Size and Development of the Shadow Economy of 31 European and 5 other OECD Countries from 2003 to 2013: A Further Decline
 January 31, 2013 ShadEcEurope31_Jan2013.doc Size and Development of the Shadow Economy of 31 European and 5 other OECD Countries from 2003 to 2013: A Further Decline by Friedrich Schneider *) In the Tables
January 31, 2013 ShadEcEurope31_Jan2013.doc Size and Development of the Shadow Economy of 31 European and 5 other OECD Countries from 2003 to 2013: A Further Decline by Friedrich Schneider *) In the Tables
Aid spending by Development Assistance Committee donors in 2015
 Aid spending by Development Assistance Committee donors in 2015 Overview of key trends in official development assistance emerging from the provisional 2015 Development Assistance Committee data release
Aid spending by Development Assistance Committee donors in 2015 Overview of key trends in official development assistance emerging from the provisional 2015 Development Assistance Committee data release
Politické vedy / Information
 THE LINGERING PROBLEMS OF THE KNOWLEDGE - BASED SOCIETY DEVELOPMENT IN THE SLOVAK REPUBLIC 1 Daša Adašková Rastislav Kazanský * In the context of the research on the building of knowledge-based society
THE LINGERING PROBLEMS OF THE KNOWLEDGE - BASED SOCIETY DEVELOPMENT IN THE SLOVAK REPUBLIC 1 Daša Adašková Rastislav Kazanský * In the context of the research on the building of knowledge-based society
A GAtewAy to A Bet ter Life Education aspirations around the World September 2013
 A Gateway to a Better Life Education Aspirations Around the World September 2013 Education Is an Investment in the Future RESOLUTE AGREEMENT AROUND THE WORLD ON THE VALUE OF HIGHER EDUCATION HALF OF ALL
A Gateway to a Better Life Education Aspirations Around the World September 2013 Education Is an Investment in the Future RESOLUTE AGREEMENT AROUND THE WORLD ON THE VALUE OF HIGHER EDUCATION HALF OF ALL
Direction of trade and wage inequality
 This article was downloaded by: [California State University Fullerton], [Sherif Khalifa] On: 15 May 2014, At: 17:25 Publisher: Routledge Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number:
This article was downloaded by: [California State University Fullerton], [Sherif Khalifa] On: 15 May 2014, At: 17:25 Publisher: Routledge Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number:
Revista Economica 65:6 (2015) ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT AS AN INTERRELATION BETWEEN WEALTH, COMPETITIVENESS, AND INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL EMPIRICAL EVIDENCES
 ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT AS AN INTERRELATION BETWEEN WEALTH, COMPETITIVENESS, AND INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL EMPIRICAL EVIDENCES Mihaela HERCIU 1 Lucian Blaga University of Sibiu Abstract The present article is
ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT AS AN INTERRELATION BETWEEN WEALTH, COMPETITIVENESS, AND INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL EMPIRICAL EVIDENCES Mihaela HERCIU 1 Lucian Blaga University of Sibiu Abstract The present article is
The Impact of the European Debt Crisis on Trust in Journalism
 The Impact of the European Debt Crisis on Trust in Journalism Andreas Köhler & Kim Otto University of Würzburg, Germany ECREA Conference 11.11.2016, Prague Agenda 1) Problems 2) Theoretical background
The Impact of the European Debt Crisis on Trust in Journalism Andreas Köhler & Kim Otto University of Würzburg, Germany ECREA Conference 11.11.2016, Prague Agenda 1) Problems 2) Theoretical background
How Country Reputation affects investment attraction Italy and its «effective government» growing perception
 How Country Reputation affects investment attraction Italy and its «effective government» growing perception Fabio Ventoruzzo Director - Reputation Institute Rome Investment Forum 2017 December 15 th -16
How Country Reputation affects investment attraction Italy and its «effective government» growing perception Fabio Ventoruzzo Director - Reputation Institute Rome Investment Forum 2017 December 15 th -16
Republic of Korea. (19 session)
 Republic of Korea th (19 session) 347.The Committee considered the third and fourth periodic reports of the Republic of Korea (CEDAW/C/KOR/3 and CEDAW/C/KOR/4) at its 400th and 401st meetings, on 7 July
Republic of Korea th (19 session) 347.The Committee considered the third and fourth periodic reports of the Republic of Korea (CEDAW/C/KOR/3 and CEDAW/C/KOR/4) at its 400th and 401st meetings, on 7 July
Economic Effects in Slovenia within Integration in European Union
 Journal of Empirical Research in Accounting & Auditing ISSN (2384-4787) J. Emp. Res. Acc. Aud. 2, No. 2 (Oct. -2015) Economic Effects in Slovenia within Integration in European Union Amir Imeri AMA International
Journal of Empirical Research in Accounting & Auditing ISSN (2384-4787) J. Emp. Res. Acc. Aud. 2, No. 2 (Oct. -2015) Economic Effects in Slovenia within Integration in European Union Amir Imeri AMA International
India s rank slips to 133 rd in 2018 from 122 nd in 2017 on World Happiness Index 2018 : World Happiness Report 2018
 India s rank slips to 133 rd in 2018 from 122 nd in 2017 on World Happiness Index 2018 : World Happiness Report 2018 UN Sustainable Development Solutions Network's (SDSN) World Happiness Report 2018 notes
India s rank slips to 133 rd in 2018 from 122 nd in 2017 on World Happiness Index 2018 : World Happiness Report 2018 UN Sustainable Development Solutions Network's (SDSN) World Happiness Report 2018 notes
Ideal (and Real) Types of Welfare State #
 Abstract Ideal (and Real) Types of Welfare State # Manuela Arcanjo * April 2006 In the extensive literature that has been dedicated during the past fifteen years to the comparative analysis of the welfare
Abstract Ideal (and Real) Types of Welfare State # Manuela Arcanjo * April 2006 In the extensive literature that has been dedicated during the past fifteen years to the comparative analysis of the welfare
Highly-Skilled Migration and Competitiveness: The Science and Engineering Industries in Japan
 Highly-Skilled Migration and Competitiveness: The Science and Engineering Industries in Japan Migration and Competitiveness: Japan and the United States March 22-23, 2012 Nana Oishi, Sophia University
Highly-Skilled Migration and Competitiveness: The Science and Engineering Industries in Japan Migration and Competitiveness: Japan and the United States March 22-23, 2012 Nana Oishi, Sophia University
Children, Adolescents, Youth and Migration: Access to Education and the Challenge of Social Cohesion
 Children, Adolescents, Youth and Migration: Access to Education and the Challenge of Social Cohesion Turning Migration and Equity Challenges into Opportunities UNICEF s Global Policy Initiative on Children,
Children, Adolescents, Youth and Migration: Access to Education and the Challenge of Social Cohesion Turning Migration and Equity Challenges into Opportunities UNICEF s Global Policy Initiative on Children,
DOI: / Industrial Shift
 Industrial Shift Also by Joe Atikian CUBA UNDER EMBARGO: The Macro Impact SAVING MONEY: The Missing Link Industrial Shift: The Structure of the New World Economy Joe Atikian industrial shift Copyright
Industrial Shift Also by Joe Atikian CUBA UNDER EMBARGO: The Macro Impact SAVING MONEY: The Missing Link Industrial Shift: The Structure of the New World Economy Joe Atikian industrial shift Copyright
American Manufacturing: The Growth since NAFTA*
 American Manufacturing: The Growth since NAFTA* Lindsay Oldenski Discussant Christian Volpe Martincus Inter-American Development Bank Conference Mexico and the United States: Building on the Benefits of
American Manufacturing: The Growth since NAFTA* Lindsay Oldenski Discussant Christian Volpe Martincus Inter-American Development Bank Conference Mexico and the United States: Building on the Benefits of
Chapter 9. East Asia
 Chapter 9 East Asia Map of East Asia Figure 9.1 I. THE GEOGRAPHIC SETTING Differences in language make translation difficult Recent change to Pinyin spelling produced new place names Pinyin: spelling system
Chapter 9 East Asia Map of East Asia Figure 9.1 I. THE GEOGRAPHIC SETTING Differences in language make translation difficult Recent change to Pinyin spelling produced new place names Pinyin: spelling system
POPULATION AND MIGRATION
 POPULATION AND MIGRATION POPULATION TOTAL POPULATION FERTILITY DEPENDENT POPULATION POPULATION BY REGION ELDERLY POPULATION BY REGION INTERNATIONAL MIGRATION IMMIGRANT AND FOREIGN POPULATION TRENDS IN
POPULATION AND MIGRATION POPULATION TOTAL POPULATION FERTILITY DEPENDENT POPULATION POPULATION BY REGION ELDERLY POPULATION BY REGION INTERNATIONAL MIGRATION IMMIGRANT AND FOREIGN POPULATION TRENDS IN
How do the performance and well-being of students with an immigrant background compare across countries? PISA in Focus #82
 How do the performance and well-being of students with an immigrant background compare across countries? PISA in Focus #82 How do the performance and well-being of students with an immigrant background
How do the performance and well-being of students with an immigrant background compare across countries? PISA in Focus #82 How do the performance and well-being of students with an immigrant background
This page intentionally left blank
 JAPAN IN CRISIS This page intentionally left blank JAPAN IN CRISIS WHAT WILL IT TAKE FOR JAPAN TO RISE AGAIN? Edited by Bong Youngshik and T.J. Pempel JAPAN IN CRISIS Copyright The Asan Institute for Policy
JAPAN IN CRISIS This page intentionally left blank JAPAN IN CRISIS WHAT WILL IT TAKE FOR JAPAN TO RISE AGAIN? Edited by Bong Youngshik and T.J. Pempel JAPAN IN CRISIS Copyright The Asan Institute for Policy
Economic Growth and Welfare Systems. Jean Monnet Chair in European Integration Studies Prof. PASQUALE TRIDICO
 Economic Growth and Welfare Systems Jean Monnet Chair in European Integration Studies Prof. PASQUALE TRIDICO The Political Economy of European Welfare Capitalism 1. European Welfare Capitalism in Good
Economic Growth and Welfare Systems Jean Monnet Chair in European Integration Studies Prof. PASQUALE TRIDICO The Political Economy of European Welfare Capitalism 1. European Welfare Capitalism in Good
The Extraordinary Extent of Cultural Consumption in Iceland
 1 Culture and Business Conference in Iceland February 18 2011 Prof. Dr. Ágúst Einarsson Bifröst University PP 1 The Extraordinary Extent of Cultural Consumption in Iceland Prof. Dr. Ágúst Einarsson, Bifröst
1 Culture and Business Conference in Iceland February 18 2011 Prof. Dr. Ágúst Einarsson Bifröst University PP 1 The Extraordinary Extent of Cultural Consumption in Iceland Prof. Dr. Ágúst Einarsson, Bifröst
Labor and Demographic Economics, Applied Econometrics, Economics of Philanthropy, Immigrant Assimilation, and Race/Ethnic Identity.
 Brian Duncan Department of Economics University of Colorado Denver Campus Box 181 Denver, CO 80217-3364 Phone: (303) 315-2041 Fax: (303) 315-2048 E-mail: brian.duncan@ucdenver.edu Web: www.econ.ucdenver.edu/bduncan
Brian Duncan Department of Economics University of Colorado Denver Campus Box 181 Denver, CO 80217-3364 Phone: (303) 315-2041 Fax: (303) 315-2048 E-mail: brian.duncan@ucdenver.edu Web: www.econ.ucdenver.edu/bduncan
Data on gender pay gap by education level collected by UNECE
 United Nations Working paper 18 4 March 2014 Original: English Economic Commission for Europe Conference of European Statisticians Group of Experts on Gender Statistics Work Session on Gender Statistics
United Nations Working paper 18 4 March 2014 Original: English Economic Commission for Europe Conference of European Statisticians Group of Experts on Gender Statistics Work Session on Gender Statistics
Understanding Welcome
 Understanding Welcome Foresight issue 159 VisitBritain Research February 2018 1 Contents Introduction Welcome summary Market summary UK NBI welcome Elements of welcome UK results Market summary heat map
Understanding Welcome Foresight issue 159 VisitBritain Research February 2018 1 Contents Introduction Welcome summary Market summary UK NBI welcome Elements of welcome UK results Market summary heat map
