US Imperialism Practice Questions
|
|
|
- Gregory Barton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the statements below concerning United States foreign policy and on your knowledge of social studies. Speaker A: There was nothing left for us to do but to take the Philippines, to educate the Filipinos, and to uplift, civilize, and Christianize them. Speaker B: If we wish to compete with other nations for foreign possessions, we must have navies and armies like theirs. Happily, the United States has no need to drain its resources in this way. Speaker C: We must insure that a canal across Central America is built. The United States needs an efficient shipping route between the east and west coasts. Speaker D: The principles of the Declaration of Independence should guide United States policy toward other nations. 1 When did this discussion most likely take place? (1) during the American Revolution (2) during the Civil War (3) just after the Spanish-American War (4) just after the announcement of the Good Neighbor policy 2 Which foreign policy action is supported by the statement of Speaker A? (1) assuming the 'White Man's Burden" (2) guaranteeing free trade (3) implementing collective security (4) instituting economic sanctions
2 Base your answers to questions 3 and 4 on the cartoon below and on your knowledge of social studies. 3 The cartoon illustrates the actions of President Theodore Roosevelt in (1) securing the land to build the Panama Canal (2) leading troops in the Spanish-American War (3) ending the war between Russia and Japan (4) improving diplomatic relations with Latin American nations 4 Critics of the actions shown in this cartoon claimed President Theodore Roosevelt was (1) causing environmental damage (2) requiring massive tax increases (3) following a policy of imperialism (4) producing major trade deficits with China
3 5 Which statement best summarizes the United States policy in Latin America in the 20th century? (1) The "big stick" policy was repealed. (2) The main goal of the United States has been to bring about unification of Latin American nations. (3) The United States has actively supported European involvement in Latin American affairs. (4) The United States has intervened in Latin American affairs when United States selfinterest has been involved. 6 Which heading best completes the partial outline below? 10 Base your answer to the following question on the headlines below and on your knowledge of social studies. I. 1 Desire for new markets 2 Creation of a modern navy 3 Belief in Anglo-Saxon superiority (1) Consequences of World War I (2) Results of the Gentlemen's Agreement (3) Events Leading to Neutrality (4) Factors Supporting United States Imperialism 7 In which section of early 19th-century America was the plantation system an important feature? (1) New England (2) the Middle Atlantic states (3) the South (4) the West 8 The practice of yellow journalism most influenced United States entry into which war? (1) War of 1812 (2) Spanish-American War (3) World War II (4) Persian Gulf War 9 "I took the Canal and let Congress debate." Theodore Roosevelt The headlines are an example of (1) the use of journalism as propaganda (2) unbiased news reporting (3) warnings to belligerent nations (4) official reports released to the press This quotation best demonstrates (1) an effort by a President to maintain a policy of isolationism (2) a decline in the use of militarism as a defense policy (3) an increased reliance on the legislative process (4) a Presidential action that achieved a foreign policy objective
4 Base your answers to questions 11 and 12 on the cartoon below and on your knowledge of social studies 11 The primary goal of the United States foreign policy referred to in the cartoon was to (1) build United States factories in the Caribbean region (2) improve relations with Caribbean nations (3) provide defense for nations in the Caribbean (4) protect United States interests in the Caribbean region 12 To carry out the foreign policy referred to in the cartoon, President Theodore Roosevelt added a corollary to the (1) Monroe Doctrine (2) Open Door policy (3) Good Neighbor policy (4) Panama Canal Treaty 13 The United States issued the Open Door policy ( ) primarily to (1) bring democratic government to the Chinese people (2) secure equal trade opportunities in China (3) force China to change its immigration policies (4) use China as a stepping stone to trade with Japan 14 The purpose of the Open Door policy was to (1) encourage European nations to increase their investments in Asian nations (2) announce a change in United States policy toward immigration from Asia (3) improve trading opportunities in China for United States businesses (4) urge China to lower its protective tariffs
5 15 A major reason the United States began to seek colonies during the late 1890's was that the (1) Monroe Doctrine required such action (2) expansion of American industry made acquiring new markets and additional resources desirable (3) population pressures within the United States had become more severe (4) cold-war rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union had heightened 16 Which headline related to the Spanish-American War is an example of yellow journalism? (1) "President McKinley Asks Congress for War Declaration Against Spain" (2) "United States Mobilizes for War with Spain" (3) "United States Demands Response to Spanish Actions" (4) "Spanish Troops Slaughter Innocent Cuban Citizens" 17 The United States supported the Open Door policy toward China mainly to (1) construct military bases (2) bring about democratic government (3) encourage European nations to leave (4) increase trading opportunities 18 The first amendment guarantee of freedom of speech was added to the United States Constitution primarily because its supporters believed it was essential to (1) discourage criticism of government policies (2) ensure the functioning of democracy (3) limit political debate in Congress (4) encourage more candidates to run for office 19 "I have always been fond of the... proverb: 'Speak softly and carry a big stick; you will go far.' " -Theodore Roosevelt This philosophy was used by President Roosevelt primarily to (1) deal with problems of racial segregation (2) conduct his foreign policy (3) expand the western frontier (4) win the Spanish-American War US Imperialism Practice Questions
6 Base your answers to questions 20 and 21 on the headlines below and on your knowledge of social studies. 20 These 1898 headlines are best understood as an example of (1) political advertising (2) yellow journalism (3) public opinion polling (4) isolationist policies 21 The purpose of these headlines was to build public support for (1) efforts to defend the Panama Canal (2) the annexation of Cuba (3) an end to the policy of imperialism (4) the war against Spain 22 President Theodore Roosevelt's Latin American policy was based on his belief that the (1) United States should intervene when necessary to protect its interests in Latin America (2) Monroe Doctrine should be abandoned (3) sovereign rights of other nations should be respected (4) United States and European nations should work together to improve Latin America's economic conditions 23 "U.S. Sponsors Panamanian Revolution" (1903) "U.S. Establishes Military Rule in Dominican Republic" (1916) "CIA Supports Overthrow of Guatemala Regime" (1954) These headlines suggest that (1) United States interests in Latin America have often led to intervention (2) the United States is willing to fight to maintain the independence of Latin American nations (3) Latin American nations have declared war on the United States several times (4) Latin American nations are able to run their governments without United States help
7 Base your answers to questions 24 and 25 on the map below and on your knowledge of social studies. 24 Which conclusion is most clearly supported by information on the map? (1) The United States respected the sovereignty of Latin American nations. (2) United States military action was used to protect American interests. (3) The United States rarely used its armed forces in Latin America before World War II. (4) United States military action in Latin America supported European colonies 25 Which United States foreign policy was most often used to carry out the actions shown on the map? (1) Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine (2) Wilson's Fourteen Points (3) Kellogg-Briand Pact (4) Open Door 26 Maintaining trading opportunities in China for United States businesses was the primary purpose of (1) the Open Door Policy (2) the Roosevelt Corollary (3) the Gentlemen's Agreement (4) Dollar Diplomacy
8 27 What was the primary goal of the Manifest Destiny? (1) the abolition of slavery in territories held by the United States (2) the removal of European influence from South America (3) the expansion of the United States westward to the Pacific Ocean (4) the secession of the Southern states from the Union Base your answers to questions 28 and 29 on the quotation below and on your knowledge of social studies. "... Whether they will or no, Americans must now begin to look outward. The growing production of the country demands it. An increasing volume of public sentiment demands it...." Alfred T. Mahan, The Atlantic Monthly, December Supporters of Mahan s ideas most likely favored a foreign policy that would (1) limit the military arms race (2) acquire foreign markets (3) abandon the Monroe Doctrine (4) establish an international peace organization 29 This statement encouraged popular support among Americans for (1) isolationism (2) protectionism (3) neutrality (4) imperialism 30 Which statement most accurately summarizes United States policies toward Latin American nations during the late 19th and early 20th centuries? (1) As sovereign nations, Latin American countries were never occupied by the United States. (2) Emigration from Latin American nations was encouraged. (3) The United States protected its interests in Latin American countries with military and diplomatic actions. (4) The United States discouraged American investment in Latin American nations. 31 A goal of President Theodore Roosevelt s Big Stick policy and President William Howard Taft s Dollar Diplomacy policy toward Latin America was to (1) Western Hemisphere nations in a military alliance (2) protect American economic and political interests (3) encourage foreign nations to establish colonies (4) raise Latin America s standard of living 32 A major result of the Spanish-American War (1898) was that the United States (1) adopted a policy of isolationism (2) assumed a more prominent role in world affairs (3) gave up control of territories outside the Western Hemisphere (4) increased foreign aid to European allies 33 From 1900 to 1915, a basic aim of United States foreign policy was to (1) develop close economic ties with African nations (2) oppose revolutionary movements in western Europe (3) promote United States influence in Latin America (4) prevent the spread of communism in western Europe and Asia 34 "Hawaiian Planters Urge American Annexation" "U.S. and Germany Negotiate for Control of the Samoan Islands" "US. Gains Control of Wake Island and Guam" Which conclusion can best be drawn from these headlines? (1) The Anti-Imperialist League strongly influenced Congress. (2) Respect for native cultures motivated United States foreign policy. (3) United States territorial expansion increased in the Pacific Ocean. (4) Construction of a railroad to Alaska was a major policy goal.
9 35 Which document is a primary source for information about the Western frontier during the second half of the 1800's? (1) a novel about a farm family in the Dakota Territory (2) a movie presenting a realistic view of cowboys (3) a biography of General George Custer written by one of his descendants (4) a treaty signed by the Sioux Indians and the Federal Government 36 Why was there increased interest in building a canal across Central America in the late 1800s? (1) The United States had acquired colonies in the Pacific region. (2) Tariffs on Chinese and Japanese products had ended. (3) The main source of immigration had shifted from northern Europe to southern Europe. (4) Transcontinental railroads had not yet been completed. US Imperialism Practice Questions
10 Base your answers to questions 37 and 38 on the newspaper headlines below and on your knowledge of social studies. 37 Publication of this and similar news stories encouraged Congress to (1) declare war on Spain (2) improve naval safety (3) pass antiterrorist legislation (4) conduct a criminal investigation 38 The headlines in this newspaper are an example of (1) yellow journalism (2) investigative reporting (3) muckraking literature (4) government censorship 39 In an outline of major developments in United States foreign policy during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, which entry would be the main topic? (1) Emerging Global Involvement (2) Expansion in the Pacific Ocean (3) Building a Two-Ocean Navy (4) Intervention in Latin America 40 The Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine assumed the right of the United States to (1) intervene in the internal affairs of a country in the exercise of international police power (2) grant special privileges to big business in its economic transactions in Latin America (3) grant financial aid to less developed countries (4) disregard any or all parts of the Monroe Doctrine 41 In the late 1800s, an increased demand for raw materials and a desire for new markets contributed to the United States adopting a policy of (1) imperialism (2) pacifism (3) collective security (4) isolationism
11 42 Late in the 19th century, many Americans believed that the United States should establish a colonial empire because (1) additional farmlands were needed to feed the growing American population (2) many sections of the world wanted to become part of the United States (3) American industries needed raw materials and markets (4) colonies would provide cheap labor for southern plantations 43 United States interest in overseas expansion in the late 19th century was based mainly on the desire to (1) achieve greater cultural diversity (2) attain new sources of raw materials and new markets (3) spread Christianity to Latin America and the Philippines (4) acquire new lands to ease population pressures at home 44 By proclaiming the Open Door policy in 1899, the United States was attempting to (1) keep Japan from attacking and colonizing China (2) increase trade between Russia and the United States (3) ensure equal trading opportunities in China (4) prevent European countries from colonizing the Western Hemisphere 45 One result of the Spanish-American War of 1898 was that the United States was (1) recognized as a world power (2) committed to isolationism (3) drawn into World War II (4) forced into an economic depression 46 Which headline is the best example of "yellow journalism," as practiced in the late 1890's? (1) "Maine Sunk in Havana Harbor" (2) "Several Sailors Die in Maine Sinking" (3) "Maine Split by Enemy's Secret Infernal Machine" (4) "Anti-Imperialists Oppose War with Spain" 47 Which United States foreign policy was most directly related to the rise of big business in the late 1800s? (1) containment (2) imperialism (3) détente (4) neutrality 48 Which foreign policy position was held by both President James Monroe and President Theodore Roosevelt? (1) Trade with other nations should be sharply reduced. (2) The United States should follow a policy of isolationism. (3) A special relationship should exist between the United States and the nations of Latin America. (4) The United States should send troops to aid revolutionary movements in European nations. 49 Which United States policy is most closely associated with the annexation of Hawaii and the Philippines? (1) neutrality (2) isolationism (3) imperialism (4) international cooperation 50 In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, United States intervention in Latin America was motivated mainly by the United States desire to (1) suppress Latin American movements for national independence (2) reduce the influence of communism (3) ensure the safety of its growing investments in the area (4) counteract Spain's economic domination of the area 51 Which war is most closely associated with the emergence of the United States as a world power? (1) War of 1812 (2) Mexican War (3) Civil War (4) Spanish-American War
12 52 "No man has a right to fix the boundary of the march of a nation; no man has a right to say to his country: this far you should go and no further." 55 Base your answer on the cartoon below and your knowledge of social studies. The author of this statement would most likely have supported the United States policy of (1) containment (2) manifest destiny (3) sectionalism (4) isolationism 53 "You furnish the pictures and I'll furnish the war." In 1898 when newspaper publisher William Randolph Hearst made this statement to artist Frederic Remington, he was suggesting that (1) artists and writers resented being censored by the government (2) artwork made newspapers more interesting to read (3) journalism could he used to shape opinions and policies (4) journalists valued accuracy and objectivity 54 Which factor is most closely associated with the decision of the United States to declare war on Spain in 1898? (1) isolationist policy (2) labor union pressure (3) yellow journalism (4) unrestricted submarine warfare Which title best describes the message of this cartoon? (1) "Neutrality is the Best Policy" (2) "Isolationism: Our Old Ally" (3) "Temptations of the Imperialist Menu" (4) "The Dangers of Overeating"
13 Base your answers to questions 56 and 57 on the map below and your knowledge of social studies. 56 The main purpose of this map is to illustrate the (1) sources of important natural resources (2) development of United States imperialism (3) growth of the Atlantic slave trade (4) results of the Spanish-American War 57 The conclusion that can best be supported by the information on this map is that construction of the Panama Canal was motivated by the desire of the United States to (1) raise the living standards of Latin American people (2) increase naval mobility and expand overseas markets (3) improve relations with Latin American and Asian nations (4) maintain a policy of collective security
14 58 Base your answer on the cartoon below and on your knowledge of social studies. US Imperialism Practice Questions The main idea of the cartoon is that (1) problems in Central America are very complicated and may not have favorable solutions (2) the ancient civilizations of Central America provide a weak foundation on which to build modern societies (3) Central America is open to ideas from the United States, but not from South American nations (4) the countries of Central America have closed and undemocratic societies
15 Base your answers to questions 59 and 60 on the map below and your knowledge of social studies. US Imperialism Practice Questions 59 The United States government justified most of the actions shown on the map by citing the (1) terms of the Roosevelt corollary to the Monroe Doctrine (2) threats from Germany after World War I (3) desire to stop illegal immigration from Latin America (4) need to protect Latin America from the threat of communism 60 Which title would be the most accurate for this map? (1) Ending Colonization in Latin America (2) Promoting Trade with Latin America (3) Humanitarian Aid in the Western Hemisphere (4) United States Intervention in the Caribbean Area 61 Between the 1890s and the start of World War I, the United States expanded its access to overseas markets and raw materials through the policy of (1) containment (2) imperialism (3) isolationism (4) neutrality 62 The closing of the frontier and the growth of industry in the late 1800s are two factors often associated with the (1) reduction of exports to Asian nations (2) restoration of a plantation economy in the South (3) formation of alliances with other nations (4) rise of United States imperialism
16 63 During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, United States policy toward Latin America was most strongly characterized by (1) friendship and trust (2) intervention and paternalism (3) tolerance and humanitarianism (4) indifference and neglect 64 Some critics believe that the United States has had uneasy relations with much of Latin America because the United States has (1) been too friendly with Cuba (2) allowed a Communist takeover in Mexico (3) stopped the development of natural resources in Latin America (4) placed its own economic and political concerns above the welfare of Latin America 65 Which heading best completes the partial outline below? I. A.Open Door policy B.Panamanian Revolt (1903) C.Roosevelt Corollary D.Truman Doctrine (1) American Domestic Programs (2) Cold War Events (3) United States Interventionism (4) Efforts at Isolationism 66 The Spanish-American War (1898) marked a turning point in United States foreign policy because the United States (1) developed a plan for peaceful coexistence (2) emerged as a major world power (3) pledged neutrality in future European conflicts (4) refused to become a colonial power Base your answers to questions 67 and 68 on the cartoon below and on your knowledge of social studies. 67 Which United States foreign policy is the subject of this 1904 cartoon? (1) imperialism (2) neutrality (3) isolationism (4) containment 68 The cartoonist is expressing concerns about the ability of the United States to (1) accept citizens from foreign countries (2) control territories spread out over vast distances (3) support human rights around the world (4) maintain a trade surplus with new trading partners 69 One foreign policy goal of President Theodore Roosevelt was to (1) create future states by annexing Pacific island territories (2) restrict European intervention in the Western Hemisphere (3) limit United States investment in Latin America (4) encourage independence movements in Africa
17 70 As a result of the Spanish-American War, the United States saw the need to build the Panama Canal because (1) new colonies had been acquired in Africa (2) Spanish opposition to the canal had ended (3) the United States navy could then move more quickly between oceans (4) United States railroads could not transport enough manufactured goods 71 A major reason for the United States decision to build the Panama Canal was the (1) success of the Erie Canal (2) discovery of silver in Nevada (3) need to prevent Mexico from retaking California and Texas (4) desire to increase foreign trade and military security 72 During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, United States intervention in Latin America was motivated by the United States desire to (1) protect its growing investments in Latin America (2) encourage Latin American trade with Europe (3) end Latin American independence movements (4) reduce the influence of communism in Latin America 73 Base your answer to the following question on the speakers' statements below and on your knowledge of social studies. Speaker A: United States expansion should not end when we reach the Pacific Coast. Speaker B: The navy of the United States needs to increase in size to defend our overseas interests. Speaker C: The United States must serve as the military protector of the Western Hemisphere. Speaker D: The United States needs to avoid international commitments in order to protect our national interests. Which president's decision demonstrated a commitment to the idea expressed by Speaker A? (1) James K. Polk going to war with Mexico (2) Abraham Lincoln signing the Homestead Act (3) William McKinley annexing the Hawaiian Islands (4) Woodrow Wilson sending troops to pursue Pancho Villa in Mexico 74 A belief in manifest destiny, the passage of the Dawes Act, and the completion of the transcontinental railroad are most closely associated with the (1) rise of big business (2) growth of the labor movement (3) abolitionist movement (4) expansion and settlement of the West 75 President Theodore Roosevelt's Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine primarily affected Latin America by (1) guaranteeing human rights throughout the Western Hemisphere (2) supporting independence movements in many countries (3) encouraging immigration to the United States (4) increasing United States intervention in the region 76 Early in the 20th century, Presidents William Taft and Woodrow Wilson used the concept of dollar diplomacy to (1) help European nations avoid war (2) expand United States influence in China (3) protect United States investments in Latin America (4) support welfare programs for immigrants to the United States 77 Secretary of State John Hay sent his Open Door Notes ( ) to world powers to (1) keep Chinese workers from coming to America (2) secure a fair settlement in the Russo-Japanese War (3) protect United States trading interests in China (4) bring a peaceful end to the Boxer Rebellion 78 The main purpose of the Open Door policy, announced by the United States in 1899, was to (1) encourage the introduction of modern government into China (2) establish United States domination of Asian affairs (3) increase United States trade with China (4) provide China with military weapons
18 79 During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the intervention of the United States in Latin America was motivated mainly by a desire to (1) reduce the influence of communism (2) control Latin American independence movements (3) promote European colonization of the area (4) protect growing United States investments in Latin America 80 The main reason President Theodore Roosevelt supported a Panamanian rebellion against Colombia in 1903 was to (1) increase the number of democratic nations in Latin America (2) gain the right to complete a canal linking the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans (3) reduce European colonialism in the Western Hemisphere (4) prevent a foreign power from seizing land in Central America 81 The Constitution rides behind And the Big Stick rides before, (Which is the rule of precedent in the reign of Theodore.) 83 By proclaiming the Open Door policy in 1899, the United States was attempting to (1) keep Japan from attacking and colonizing China (2) increase trade between Russia and the United States (3) ensure equal trading opportunities in China (4) prevent European countries from colonizing the Western Hemisphere This rhyme from the early 1900's suggests that President Theodore Roosevelt (1) relied heavily on the advice of his Cabinet and Congress (2) failed to make adequate use of executive power (3) developed strong foreign policies but neglected domestic needs (4) ignored democratic principles in carrying out foreign policy 82 The practice of yellow journalism most directly influenced the (1) purchase of Alaska (2) acquisition of the Mexican Cession (3) start of the Spanish-American War (4) end of the Russo-Japanese War
19 Base your answers to questions 84 and 85 on the map below and on your knowledge of social studies. 84 What is the best title for this map? (1) Eastward Migration (2) Results of the Revolution (3) Territorial Expansion (4) Immigration Before the Civil War 85 Which geographic feature formed the western border of the United States in 1783? (1) Pacific Ocean (2) Mississippi River (3) Great Lakes (4) Rocky Mountains
20 86 This cartoon deals mainly with the concept of (1) imperialism (2) government overspending (3) isolationism (4) free trade 87 The Platt Amendment, the Roosevelt Corollary, and dollar diplomacy are evidence of a United States policy of (1) reducing the number of immigrants from Latin America to the United States (2) cooperating with Great Britain to solve problems in Latin America (3) expanding its interests in Latin America (4) encouraging the independence and sovereignty of Latin American nations 88 The Open Door policy toward China was designed mainly to (1) encourage Chinese emigration to the United States (2) stem the spread of Chinese communism (3) support the development of democracy in China (4) ensure the United States the opportunity to trade with China 89 In the 1890s, the main goal of those who supported United States imperialism was to (1) bring self-government to areas under United States control (2) obtain overseas markets and naval bases (3) defend against attacks by enemy nations (4) spread democracy to Africa and Latin America 90 Which foreign policy position was held by both President James Monroe and President Theodore Roosevelt? (1) Trade with other nations should be sharply reduced. (2) The United States should follow a policy of isolationism. (3) A special relationship should exist between the United States and the nations of Latin America. (4) The United States should send troops to aid revolutionary movements in European nations. 91 One major result of the Spanish-American War was that the United States (1) formed an alliance with England (2) gained recognition as a world power (3) repealed the Monroe Doctrine (4) decreased the size of its navy
21 92 Base your answer to the following question on the cartoon below. 93 Base your answer to the following question on the speakers' statements below and on your knowledge of social studies. Speaker A: The United States has enough problems of its own. We should keep out of the affairs of other countries. Speaker B: If we don't help this country fight off the Communists, the entire region will be overrun by communism. Speaker C: American businesses are producing more than they can sell. We need to acquire overseas markets. Which congressional action led to the Southern viewpoint expressed in this cartoon? (1) passage of the Homestead Act (2) strengthening of the Fugitive Slave Laws (3) military occupation of the former Confederate States (4) ending the Freedmen s Bureau Speaker D: We must not join this international organization. If we do, Congress will lose its power to declare war. Which speaker is most likely an American imperialist of the early 20th century? (1) A (2) B (3) C (4) D 94 During the late 19th century, the growth of capitalism encouraged United States imperialism because of the desire of business to (1) obtain new markets for American products (2) compete with foreign industries (3) provide humanitarian aid to poor nations (4) industrialize underdeveloped nations 95 A study of the application of the Monroe Doctrine from 1823 to the present would most likely show that (1) Latin America continues to be dominated by European country (2) equality has been promoted among the countries of the Western Hemisphere (3) the countries of South America have been united under one government (4) the United States has been a strong influence in Latin America
22 96 The principle that the United States has the right to act as the "policeman of the Western Hemisphere" and intervene in the internal affairs of Latin American nations was established by the (1) Good Neighbor policy (2) Open Door policy (3) Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine (4) Marshall Plan 97 Base your answer on the speakers' statements below and on your knowledge of social studies. Speaker A: In order to maintain the security of the nation, the United States needs colonies in which it can establish naval bases. Speaker B: The United States has problems of its own to be concerned about, so we must focus our attention here at home. Speaker C: If the United States is to compete in a global economy, it needs to look beyond its borders for markets. Speaker D: Supporting an overseas empire would become an enormous burden on the American people. The focus of the speakers' debate is the controversy over the (1) purchase of Alaska (2) policy of imperialism (3) size of the United States military (4) closing of the frontier 98 Yellow journalism contributed to the start of the Spanish-American War (1898) by (1) portraying William McKinley as a pro-war president (2) inciting public outrage over conditions in Cuba (3) showing the need to acquire colonies in the Pacific (4) demanding the repeal of the Gentlemen s Agreement 99 "But today we are raising more than we can consume. Today we are making more than we can use. Today our industrial society is congested; there are more workers than there is work; there is more capital than there is investment. We do not need more money we need more circulation, more employment. Therefore, we must find new markets for our produce, new occupation for our capital, new work for our labor...." Senator Albert J. Beveridge, 1898 This statement provides a reason why political leaders of the late 1800s adopted the policy of (1) imperialism (2) isolationism (3) protectionism (4) collective security 100 In 1899, the United States proclaimed the Open Door policy in an attempt to (1) ensure trading opportunities in China (2) keep the Philippines from attacking China (3) increase trade between Russia and the United States (4) prevent European countries from colonizing Africa 101 During the 1890s, Joseph Pulitzer and William Randolph Hearst used yellow journalism to generate public support for the (1) election of Populist Party candidates (2) presidential candidacy of William McKinley (3) goals of workers in the Pullman strike (4) Spanish-American War 102 President Theodore Roosevelt s Big Stick policy is most closely associated with (1) friendly relations with China after the Boxer Rebellion (2) conservation of natural resources (3) court actions to support business monopolies (4) intervention in Latin American affairs
23 103 Base your answer on the statement below and on your knowledge of social studies....the policy of the government of the United States is to seek a solution which may bring about permanent safety and peace to China, preserve Chinese territorial and administrative entity, protect all rights guaranteed to friendly powers by treaty and international law, and safeguard for the world the principle of equal and impartial trade with all parts of the Chinese Empire... Secretary of State John Hay, Circular Letter, July 3, 1900 This excerpt from John Hay's Circular Letter became part of the (1) Open Door policy (2) Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine (3) policy of Dollar Diplomacy (4) Kellogg-Briand Pact 104 Which United States foreign policy action resulted from the close geographic relationship between the United States and Latin America? (1) Monroe Doctrine (2) Truman Doctrine (3) Marshall Plan (4) Open Door Policy 105 A primary reason for the establishment of the Open Door policy (1899) was to (1) protect United States trade in the Far East (2) gain control of the Panama Canal Zone (3) encourage Chinese immigration to the United States (4) improve relations with Russia 106 The United States promoted its economic interest in China by (1) intervening in the Sino-Japanese War (2) passing the Chinese Exclusion Act (3) encouraging the Boxer Rebellion (4) adopting the Open Door policy 107 In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the United States became involved in Latin America primarily to (1) establish new colonies (2) protect economic and security interests (3) raise the living standards of Latin Americans (4) stop the flow of illegal drugs into the United States 108 Which policy is an expression of economic nationalism? (1) foreign aid (2) protective tariff (3) free trade (4) laissez-faire 109 Which United States foreign policy was most directly related to the rise of big business in the late 1800s? (1) containment (2) imperialism (3) détente (4) neutrality 110 Involvement in the Spanish-American War, acquisition of Hawaii, and introduction of the Open Door policy in China were actions taken by the United States Government to (1) establish military alliances with other nations (2) gain overseas markets and sources of raw materials (3) begin the policy of manifest destiny (4) support isolationist forces in Congress 111 The Big Stick policy and Dollar Diplomacy were attempts to do what? (1) increase United States power in Latin America (2) contain the spread of communism in eastern Europe (3) protect free trade on the Asian continent (4) strengthen political ties with western Europe 112 The Open Door policy of 1899 was originally adopted so that the United States could (1) restrict Chinese immigration (2) gain equal trading rights in China (3) stop Japan from colonizing China (4) encourage the development of democracy in China 113 United States annexation of the Philippines (1898) and military involvement in Vietnam (1960's and 1970's) are similar because in each event the United States (1) achieved its long-range foreign policy objectives (2) put the domino theory into action (3) demonstrated the strength and success of its military power (4) provoked domestic debate about its involvement in the internal affairs of other nations
24 114 Base your answer to the following question on the cartoon below and on your knowledge of social studies. What does the cartoon, which reflects the period from 1898 to 1900, suggest the United States was primarily interested in? (1) increasing its empire (2) improving living standards in poor areas of the world (3) establishing democracies in other countries (4) forming a world peace organization 115 Which title best completes the partial outline below? I. A. No government without consent of the governed B. High cost of defending territories outside the United States C. United States tradition of non-involvement (1) America's New Immigration Policy (2) Reasons for Overseas Expansion (3) Causes of the Spanish-American War (4) Arguments Opposing Imperialism 116 The annexation of Hawaii, the Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine, and Dollar Diplomacy are all associated with United States efforts to (1) meet the demands of antiwar movements (2) isolate itself from international problems (3) expand its power and influence in certain regions of the world (4) implement policies of global cooperation throughout Asia 117 The main reason the United States implemented the Open Door policy in China was to (1) promote immigration (2) expand democratic reforms (3) encourage religious freedom (4) guarantee access to markets 118 President Theodore Roosevelt s Big Stick policy was used by the United States to (1) police the Western Hemisphere (2) expand its colonial empire in Africa (3) isolate itself from European conflicts (4) settle a dispute between Russia and Japan 119 The explosion of the USS Maine and the practice of yellow journalism played a significant role in the (1) public's support for the Spanish-American War (2) creation of the Open Door policy (3) acquisition of Florida (4) purchase of Alaska 120 Why did construction of the Panama Canal become more important to the United States after the Spanish-American War? (1) Congress realized that the key threat to national secmity came from South America. (2) Great Britain had plans to purchase the canal zone and colonize the tenitory. (3) Spain had regained control of its former colonies near the canal route. (4) The navy needed a faster way to move ships between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. 121 The United States established the Open Door policy toward China as a way to (1) promote democracy in Asia (2) secure military bases in East Asia (3) protect United States economic interests (4) end the Boxer Rebellion
25 122 The primary goal of manifest destiny was the (1) abolition of slavery in territories held by the United States (2) removal of European influence from South America (3) expansion of the United States westward to the Pacific Ocean (4) secession of the Southern States from the Union 123 Based on the information in the partial outline below, which is the most appropriate entry for line D? 125 The corporate form of business became dominant in the late 19th century mainly because of the need of business for (1) protective tariffs (2) assembly-line production (3) a supply of cheap labor (4) large amounts of investment capital Base your answers to questions 126 and 127 on the cartoon below and on your knowledge of social studies. (1) United States engaged in civil war. (2) United States became more involved in imperialism. (3) United States built the transcontinental railroad. (4) United States experienced agricultural revolution. 124 Which heading best completes the partial outline below? I. A. Desire for markets and raw materials B. Closing of the western frontier C. Social Darwinism D. Missionary spirit (1) Principles of the Fourteen Points (2) Reasons for United States Imperialism (3) Causes of World War I (4) Adoption of Isolationist Ideals 126 This cartoon reflects foreign policy ideas commonly held by Americans during (1) the Spanish-American War (2) World War I (3) World War II (4) the Korean War 127 The point of view shown in the cartoon; is that the United States had become (1) the world's democratic leader (2) an imperialist country (3) the homeland for immigrants from all nations (4) a self-sufficient country
26 128 Base your answer on the cartoon below and your knowledge of social studies. Which title best describes the message of this cartoon? (1) "Neutrality is the Best Policy" (2) "Isolationism: Our Old Ally" (3) "Temptations of the Imperialist Menu" (4) "The Dangers of Overeating" 129 The government created by the Articles of Confederation was unsuccessful at solving many major problems because (1) unlimited power was given to the Supreme Court (2) most power remained with the state governments (3) members of Congress were elected according to each state s population (4) political parties prevented the passage of legislation 130 The major objective of United States foreign policy toward Latin America during the period from 1900 to 1920 was to (1) improve the standard of living of the people in Latin America (2) support land reform throughout the Western Hemisphere (3) protect the human rights of native peoples in Latin America (4) serve as protector and police officer in the Western Hemisphere
27 131 Why did the United States formulate the Open Door policy toward China? (1) to develop democratic institutions and practices in China (2) to prevent a European and Japanese monopoly of Chinese trade and markets (3) to establish a military presence on the Chinese mainland (4) to support Japanese efforts to industrialize China 132 The principal reason Congress raised tariff rates in the late 1800s and early 1900s was to (1) increase personal income taxes (2) lower prices for American consumers (3) guarantee high wages to American workers (4) protect United States businesses from foreign competition 133 President Theodore Roosevelt's commitment to the proverb, "Speak softly and carry a big stick; you will go far," was most clearly shown when he (1) opposed consumer protection laws (2) intervened in Latin American affairs (3) promoted the conservation of natural resources (4) conducted the Bull Moose campaign of Which United States foreign policy action resulted from the close geographic relationship between the United States and Latin America? (1) Monroe Doctrine (2) Truman Doctrine (3) Marshall Plan (4) Open Door policy 135 Yellow journalists created support for the Spanish-American War by writing articles about the (1) political popularity of William Jennings Bryan (2) efforts of the United States to control Mexico (3) destruction of United States sugar plantations by Hawaiians (4) sinking of the United States battleship Maine in Havana Harbor 136 Late 19th- and early 20th-century expansionists such as Theodore Roosevelt and Alfred Thayer Mahan urged the United States to (1) extend its influence over the Middle East and the subcontinent of India (2) acquire overseas territories, especially in the Pacific (3) seek better trade relations with Latin America (4) negotiate economic and cultural exchange programs with nations in Asia 137 President Theodore Roosevelt's policies toward Latin America were evidence of his belief in (1) noninvolvement in world affairs (2) intervention when American business interests were threatened (3) the sovereign rights of all nations (4) the need for European interference in the Western Hemisphere 138 One major result of the Spanish-American War was that the United States (1) established many foreign-aid programs (2) obtained overseas colonies (3) abandoned the principles of the Monroe Doctrine (4) settled disputes by relying on international peace organizations 139 Which heading best completes the partial outline below? (1) Rise of American Imperialism (2) Causes of World War I (3) Enforcement of the Monroe Doctrine (4) Trade Expansion in East Asia
28 140 Latin American relations with the United States have often been strained as a result of the United States (1) policy of neutrality in Latin American affairs (2) failure to implement the Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine (3) interference on behalf of European colonial powers (4) intervention in the internal affairs of Latin American countries 141 Which heading best completes the partial outline above? (1) Reasons to Declare War on Spain (2) Justification for American Imperialism (3) Theodore Roosevelt's Political Platform (4) Yellow Journalism in Newspapers 142 Which statement best describes President Theodore Roosevelt's foreign policy position toward Latin America in the early 1900's? (1) The United States should reduce its involvement in Latin American affairs. (2) The Monroe Doctrine permits the United States to intervene actively in the affairs of Latin American nations. (3) Latin American nations should form an organization to help them achieve political and economic stability. (4) The United States should give large amounts of financial aid to help the poor of Latin America. 143 The Spanish-American War brought about a major change in United States foreign policy in that the United States (1) gained the Panama Canal (2) lost vast acreage to the Spanish (3) became a colonial power (4) ended its policy of intervention Base your answers to questions 144 and 145 on the quotation below and on your knowledge of social studies. "Chronic wrongdoing... may... ultimately require intervention by some civilized nation, and... adherence... to the Monroe Doctrine may force the United States... to the exercise of an international police power." Theodore Roosevelt, This statement helped provide justification for President Theodore Roosevelt's use of the (1) policy of Dollar Diplomacy (2) Big Stick policy (3) conservation policy (4) Peace Corps 145 Which world region was the focus of the foreign policy expressed in this statement? (1) Middle East (2) Southeast Asia (3) Soviet Union (4) Latin America 146 President Theodore Roosevelt strengthened the Monroe Doctrine by establishing the policy that the United States would (1) require Latin American nations to end trade with Europe (2) reduce Asian influence in Latin America (3) intervene in Latin America to prevent European interference (4) develop military alliances with Pacific naval powers 147 The Roosevelt Corollary (1904) to the Monroe Doctrine proclaimed the right of the United States to (1) intervene in the internal affairs of Latin American nations (2) impose trade restrictions on European imports (3) promote democracy in Africa (4) determine the border between Alaska and Canada
29 148 The early 20th-century policy of dollar diplomacy indicated a United States desire to (1) institute the dollar as an international currency (2) give generous amounts of foreign aid to less developed countries (3) interact with foreign countries in ways profitable to United States corporations (4) give trade preferences to nations that follow a capitalist system 149 In the early 1900s, the United States proposed the Open Door policy to (1) gain new colonies in the Pacific (2) win support for building the Panama Canal (3) improve relations with Europe (4) secure access to markets in China 150 What was a common goal of the Proclamation of Neutrality (1793), the Embargo Act (1807), and the Monroe Doctrine (1823)? (1) forcing Great Britain to grant independence to Canada (2) avoiding conflicts with European nations (3) providing wartime aid to European nations (4) encouraging independence movements in Latin America 151 Which statement is a fact rather than an opinion? (1) Trade barriers will not save American jobs. (2) The Hawley-Smoot Tariff Act set tariffs at the highest level in United States history. (3) High tariffs are the best way to equalize the competition between American workers and their counterparts abroad. (4) Protectionism is a misguided policy and should be opposed. 152 News organizations were engaging in yellow journalism before the Spanish-American War when (1) publishers tried to prevent the war (2) articles about Cuba were fair and balanced (3) editors exaggerated events to build support for war (4) writers ignored the situation in Cuba 153 Base your answer to the following question on the speakers' statements below and on your knowledge of social studies. Speaker A: The United States has enough problems of its own. We should keep out of the affairs of other countries. Speaker B: If we don't help this country fight off the Communists, the entire region will be overrun by communism. Speaker C: American businesses are producing more than they can sell. We need to acquire overseas markets. Speaker D: We must not join this international organization. If we do, Congress will lose its power to declare war. Which speaker is most likely an American imperialist of the early 20th century? (1) A (2) B (3) C (4) D 154 Which statement best describes President Theodore Roosevelt's foreign policy position toward Latin America in the early 1900's? (1) The United States should reduce its involvement in Latin American affairs. (2) The Monroe Doctrine permits the United States to intervene actively in the affairs of Latin American nations. (3) Latin American nations should form an organization to help them achieve political and economic stability. (4) The United States should give large amounts of financial aid to help the poor of Latin America. 155 Which 1890's headline is the best example of yellow journalism? (1) "President Supports Child Labor Legislation" (2) "McKinley Asks Congress To Annex Hawaii" (3) "Populists Demand Change in the Gold Standard" (4) "Spanish Authorities Butcher Innocent Cubans"
30 156 In the late 1800's, which reason led the United States to give greater attention to the world beyond its borders? (1) fear of revolution in Latin America (2) fear of Russian expansion in Alaska (3) interest in finding places to settle surplus population (4) interest in obtaining markets for surplus goods 157 A major reason that Secretary of State John Hay announced the Open Door policy in 1899 was to (1) secure important military bases in Europe (2) encourage more immigration from Europe (3) increase United States access to trade in Asia (4) claim new colonial territories in Africa 158 What was one characteristic of American imperialism in the late 19th and early 20th centuries? (1) avoiding involvement with nations in East Asia (2) supporting independence movements in Africa (3) rejecting the use of military force to gain colonies (4) acquiring territory to promote economic and strategic interests 159 A major way in which the United States has practiced "economic nationalism" has been to (1) implement protective tariffs to help American industry (2) establish social welfare programs to aid the poor (3) pass legislation outlawing most monopolies (4) require industry to provide safe working conditions for employees 160 "... The Pacific is our ocean... And the Pacific is the ocean of the commerce of the future... The power that rules the Pacific, therefore, is the power that rules the world. And, with the Philippines, that power is and will forever be the American Republic." CONGRESSIONAL RECORD, 1900 Which policy is supported by this quotation? (1) imperialism (2) self-determination (3) isolationism (4) humanitarianism 161 The foreign policy actions of Presidents James Monroe, Theodore Roosevelt, and Ronald Reagan were similar in that they all (1) enforced a strict policy of neutrality (2) involved the United States in armed conflict in Europe (3) added to the American colonial empire (4) acted to support United States interests in Latin America 162 The main reason the United States developed the Open Door policy was to (1) allow the United States to expand its trade with China (2) demonstrate the positive features of democracy to Chinese leaders (3) aid the Chinese Nationalists in their struggle with the Chinese Communists (4) encourage Chinese workers to come to the United States 163 Since 1823, which United States policy has limited foreign influence in the Western Hemisphere? (1) the Eisenhower Doctrine (2) popular sovereignty (3) imperialism (4) the Monroe Doctrine 164 In 1823, the Monroe Doctrine was established mainly because the United States wanted to (1) keep control of Alaska and Hawaii (2) establish more colonies in Latin America (3) support England's attempt to keep its empire in Central America (4) warn Europe against any further colonization in Latin America 165 A primary aim of the United States Open Door Policy was to (1) encourage the Chinese to emigrate to other nations (2) prevent European powers from dividing up China (3) develop China's industrial capacity (4) introduce democratic government into China
31 166 Which belief was the basis of President Theodore Roosevelt's foreign policy in the Western Hemisphere? (1) The United States can intervene in the Western Hemisphere to protect political stability and American interests. (2) Each nation in the Western Hemisphere is entitled to full respect for its sovereign rights. (3) The Monroe Doctrine has outlived its usefulness and should be ignored. (4) European nations should be allowed to protect their interests in the Western Hemisphere. 167 Which justification has Congress frequently used for raising United States tariff rates? (1) protecting the jobs of American workers (2) helping American manufacturers to export products (3) increasing the variety and quality of goods available to Americans (4) punishing American industries for their low productivity 168 Base your answer to the following question on the cartoon below and on your knowledge of social studies. 169 The Northwest Ordinance of 1787 set a precedent for other western territories by (1) allowing slavery (2) including voting rights for women (3) providing a method for the creation of new states (4) setting aside land for churches 170 Which argument was used to support United States acquisition of overseas possessions in the late 1800's? (1) The United States needed to obtain raw materials and new markets. (2) The spread of Marxist ideas had to be stopped because they threatened world peace. (3) The United States should be the first world power to build a colonial empire. (4) The doctrine of Manifest Destiny had become obsolete. Which concept is expressed in this cartoon? (1) support for new military alliances (2) support for United States imperialism (3) opposition to the League of Nations (4) opposition to new immigration laws
32 171 Base your answer to the following question on the cartoon below and on your knowledge of social studies. 172 Base your answer on the cartoon below and on your knowledge of social studies. Which goal of United States foreign policy is pictured in the cartoon? (1) allowing China the right to follow a policy of isolation (2) establishing a United States colony in China (3) assisting in the growth of China's industrialization (4) increasing opportunities for the United States to trade with China Which foreign policy is the main issue of this cartoon? (1) containment (2) imperialism (3) internationalism (4) neutrality 173 An important result of the Spanish-American War of 1898 was that the United States (1) acquired territories in Africa (2) became a world power with an overseas empire (3) improved its relations with Germany (4) lost interest in Latin American affairs
33 174 Base your answer on the newspaper headlines below and on your knowledge of social studies. What was a major purpose of these 1898 newspaper headlines? (1) rallying support for a declaration of war against Spain (2) promoting peace between Spain and the United States (3) supporting humanitarian aid for the suffering Cuban people (4) punishing the citizens of Cuba 175 The Panamanian revolt, the Russo-Japanese war, and the creation of the national parks system occurred during the presidency of (1) William McKinley (2) Woodrow Wilson (3) Herbert Hoover (4) Theodore Roosevelt 176 During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, United States foreign policy was marked by (1) declining interest in the Far East (2) increased enforcement of the Monroe Doctrine (3) acceptance of the principle of collective security (4) formation of military alliances with European nations 177 The establishment of the Open Door policy ( ) and the response to the Boxer Rebellion (1900) showed that the United States wanted to (1) curb Russian expansion (2) gain access to Chinese markets (3) build factories in the Far East (4) limit Asian immigration to the United States
U.S. Imperialism Practice Questions
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the map below and on your knowledge of social studies. 1 Which United States foreign policy was most often used to carry out the actions shown on the map? (1)
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the map below and on your knowledge of social studies. 1 Which United States foreign policy was most often used to carry out the actions shown on the map? (1)
Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea
 Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea In the last half of the 1800s, the United States joined the race for control of overseas territories.
Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea In the last half of the 1800s, the United States joined the race for control of overseas territories.
BECOMING A WORLD POWER
 BECOMING A WORLD POWER CHAPTER 10 IMPERIALISM THE PRESSURE TO EXPAND Americans had always sought to expand the size of their nation, and throughout the 19th century they extended their control toward the
BECOMING A WORLD POWER CHAPTER 10 IMPERIALISM THE PRESSURE TO EXPAND Americans had always sought to expand the size of their nation, and throughout the 19th century they extended their control toward the
18 America Claims an Empire QUIT
 18 America Claims an Empire QUIT CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE SECTION 1 Imperialism and America GRAPH MAP SECTION 2 The Spanish-American War SECTION 3 Acquiring New Lands SECTION 4
18 America Claims an Empire QUIT CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE SECTION 1 Imperialism and America GRAPH MAP SECTION 2 The Spanish-American War SECTION 3 Acquiring New Lands SECTION 4
Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism ( )
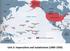 Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism (1890-1930) What is an empire? Is imperialism the same as colonization? Why would the U.S. get involved in this practice? What is the difference between acquiring and
Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism (1890-1930) What is an empire? Is imperialism the same as colonization? Why would the U.S. get involved in this practice? What is the difference between acquiring and
Letter from President Fillmore asking Japan. American ships to stop for supplies safety reasons
 Chapter 19-21 Introduction Japan 1853 Not open to trading with other countries Commodore Matthew Perry went to Japan with a small fleet of warships (Gunboat Diplomacy) Letter from President Fillmore asking
Chapter 19-21 Introduction Japan 1853 Not open to trading with other countries Commodore Matthew Perry went to Japan with a small fleet of warships (Gunboat Diplomacy) Letter from President Fillmore asking
Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War
 Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War 1 Imperialism & Expansion CH 14-1 Imperialism & War Name Reasons why the United States becomes an imperialist nation. 1-New Markets 2-Anglo-Saxonism 3-Modern Navy 4-Into
Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War 1 Imperialism & Expansion CH 14-1 Imperialism & War Name Reasons why the United States becomes an imperialist nation. 1-New Markets 2-Anglo-Saxonism 3-Modern Navy 4-Into
APUSH. U.S. Imperialism REVIEWED! EMPIRE & EXPANSION
 APUSH 1890-1909 EMPIRE & EXPANSION U.S. Imperialism REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 27 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 19 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 21 Important Ideas Since the
APUSH 1890-1909 EMPIRE & EXPANSION U.S. Imperialism REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 27 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 19 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 21 Important Ideas Since the
Unit 8: Imperialism. February 15th & 16th
 Unit 8: Imperialism February 15th & 16th WarmUp - February 15th & 16th Pick up papers from front table Jot down anything that comes to mind when you see the word IMPERIALISM (this is our next topic Unit
Unit 8: Imperialism February 15th & 16th WarmUp - February 15th & 16th Pick up papers from front table Jot down anything that comes to mind when you see the word IMPERIALISM (this is our next topic Unit
Essential Question: How did America s role in the world change from 1890 to 1914?
 Essential Question: How did America s role in the world change from 1890 to 1914? From 1890 to 1914, the United States expanded its role in world affairs and gained new overseas colonies Class Activity:
Essential Question: How did America s role in the world change from 1890 to 1914? From 1890 to 1914, the United States expanded its role in world affairs and gained new overseas colonies Class Activity:
Chapter 17. Becoming a World Power ( )
 Chapter 17 Becoming a World Power (1872 1912) 1 Chapter Overview: During this era, economic and military competition from world powers convinced the United States it must be a world power. The United States
Chapter 17 Becoming a World Power (1872 1912) 1 Chapter Overview: During this era, economic and military competition from world powers convinced the United States it must be a world power. The United States
Female progressives often justified their reformist political activities on the basis of???
 Need to know What was President Roosevelt s Gentlemen s Agreement with Japan? Female progressives often justified their reformist political activities on the basis of??? imperialism Stronger nations dominating
Need to know What was President Roosevelt s Gentlemen s Agreement with Japan? Female progressives often justified their reformist political activities on the basis of??? imperialism Stronger nations dominating
Chapter 17: Becoming a World Power ( )
 Name: Period Page# Chapter 17: Becoming a World Power (1890 1915) Section 1: The Pressure to Expand What factors led to the growth of imperialism around the world? In what ways did the United States begin
Name: Period Page# Chapter 17: Becoming a World Power (1890 1915) Section 1: The Pressure to Expand What factors led to the growth of imperialism around the world? In what ways did the United States begin
Imperalism.notebook March 03, 2015
 Agenda Bell ringer Notability 1 Objective: I can discuss and explain why the United States Foreign Policy changed during the late 19th century. Bell Ringer Notability HW: Due Thursday 2 1 A B C D 3 2 A
Agenda Bell ringer Notability 1 Objective: I can discuss and explain why the United States Foreign Policy changed during the late 19th century. Bell Ringer Notability HW: Due Thursday 2 1 A B C D 3 2 A
Between 1870 and 1900, Europeans had taken over 1/5 of land and 1/10 of population of the world Germany became America s biggest imperialist foe and
 U.S. Imperialism Between 1870 and 1900, Europeans had taken over 1/5 of land and 1/10 of population of the world Germany became America s biggest imperialist foe and largely spurred U.S. into imperialism;
U.S. Imperialism Between 1870 and 1900, Europeans had taken over 1/5 of land and 1/10 of population of the world Germany became America s biggest imperialist foe and largely spurred U.S. into imperialism;
Work Period: Latin America and China Foreign policies Notes President Chart Activity
 USHC 5.0 DEMONSTRATE AN UNDERSTANDING OF DOMESTIC AND FOREIGN DEVELOPMENTS THAT CONTRIBUTED TO THE EMERGENCE OF THE UNITED STATES AS A WORLD POWER IN THE 20 TH CENTURY Opening: Complete pages 185-188 in
USHC 5.0 DEMONSTRATE AN UNDERSTANDING OF DOMESTIC AND FOREIGN DEVELOPMENTS THAT CONTRIBUTED TO THE EMERGENCE OF THE UNITED STATES AS A WORLD POWER IN THE 20 TH CENTURY Opening: Complete pages 185-188 in
Guided Reading and Analysis: Becoming a World Power,
 Name: Class Period: Guided Reading and Analysis: Becoming a World Power, 1865-1917 Amsco Chapter 20 Reading Assignment: Ch. 21 AMSCO Purpose: This guide is intended to provide a space for you to record
Name: Class Period: Guided Reading and Analysis: Becoming a World Power, 1865-1917 Amsco Chapter 20 Reading Assignment: Ch. 21 AMSCO Purpose: This guide is intended to provide a space for you to record
Unit VII Study Guide- American Imperialism
 Unit VII Study Guide- American Imperialism 1. List the ideas that fueled American Imperialism. 2. How were yellow journalists able to influence Americans opinions on foreign policy? 3. The person who urged
Unit VII Study Guide- American Imperialism 1. List the ideas that fueled American Imperialism. 2. How were yellow journalists able to influence Americans opinions on foreign policy? 3. The person who urged
BELLRINGER. Read the abridged platform of the American Anti- Imperialist League. What is the main argument presented against imperialist policies?
 BELLRINGER Read the abridged platform of the American Anti- Imperialist League. What is the main argument presented against imperialist policies? U.S. INTERVENTION ABROAD Ms. Luco IB Hist Americas LEARNING
BELLRINGER Read the abridged platform of the American Anti- Imperialist League. What is the main argument presented against imperialist policies? U.S. INTERVENTION ABROAD Ms. Luco IB Hist Americas LEARNING
Unit 7: America Comes of Age FRQ Outlines
 Prompt: 2. Analyze the extent to which the Spanish-American War was a turning point in American foreign policy. Re-written as a Question: What was the extent to which the Spanish American war a turning
Prompt: 2. Analyze the extent to which the Spanish-American War was a turning point in American foreign policy. Re-written as a Question: What was the extent to which the Spanish American war a turning
Unit 5. US Foreign Policy, Friday, December 9, 11
 Unit 5 US Foreign Policy, 1890-1920 I. American Imperialism A. What is Imperialism? B. Stated motivations (how we were helping others) Helping free countries from foreign domination Spreading Christianity
Unit 5 US Foreign Policy, 1890-1920 I. American Imperialism A. What is Imperialism? B. Stated motivations (how we were helping others) Helping free countries from foreign domination Spreading Christianity
Unit 6: A New Role in the World
 Unit 6: A New Role in the World Study online at quizlet.com/_1fnvlz 1. alliances 5. conscription An agreement between nations to aid and protect each other. 2. Allies A military draft 6. dollar diplomacy
Unit 6: A New Role in the World Study online at quizlet.com/_1fnvlz 1. alliances 5. conscription An agreement between nations to aid and protect each other. 2. Allies A military draft 6. dollar diplomacy
Empire and Expansion. Chapter 27
 Empire and Expansion Chapter 27 Imperialism Stronger nations attempt to create empires by dominating weaker nations. The late 1800s marked the peak of European imperialism, with much of Africa and Asia
Empire and Expansion Chapter 27 Imperialism Stronger nations attempt to create empires by dominating weaker nations. The late 1800s marked the peak of European imperialism, with much of Africa and Asia
STAAR BLITZ: IMPERIALISM, SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR, WWI APRIL 22, 2015
 STAAR BLITZ: IMPERIALISM, SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR, WWI APRIL 22, 2015 AGE OF IMPERIALISM! (1900s- 1914) MILITARY Alfred T. Mahan argued for a strong NAVY in his book Influence of Sea Power Upon History Easier
STAAR BLITZ: IMPERIALISM, SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR, WWI APRIL 22, 2015 AGE OF IMPERIALISM! (1900s- 1914) MILITARY Alfred T. Mahan argued for a strong NAVY in his book Influence of Sea Power Upon History Easier
Unit 4 Take-Home Test Answer Sheet
 Name: Unit 4 Take-Home Test Answer Sheet 1. 11. 21. 31. 41. 2. 12. 22. 32. 42. 3. 13. 23. 33. 43. 4. 14. 24. 34. 44. 5. 15. 25. 35. 45. 6. 16. 26. 36. 46. 7. 17. 27. 37. 47. 8. 18. 28. 38. 48. 9. 19. 29.
Name: Unit 4 Take-Home Test Answer Sheet 1. 11. 21. 31. 41. 2. 12. 22. 32. 42. 3. 13. 23. 33. 43. 4. 14. 24. 34. 44. 5. 15. 25. 35. 45. 6. 16. 26. 36. 46. 7. 17. 27. 37. 47. 8. 18. 28. 38. 48. 9. 19. 29.
Key Term Sheet UNIT #4: IMPERIALISM Chapter 7, Sections 1-3 (Pages )
 Key Term Sheet UNIT #4: IMPERIALISM Chapter 7, Sections 1-3 (Pages 260-276) Name: ANSWER KEY Hour: Term Imperialism Definition Refers to when a larger more powerful country exerts influence over another
Key Term Sheet UNIT #4: IMPERIALISM Chapter 7, Sections 1-3 (Pages 260-276) Name: ANSWER KEY Hour: Term Imperialism Definition Refers to when a larger more powerful country exerts influence over another
U.S. Imperialism s Impact on Other Nations
 U.S. Imperialism s Impact on Other Nations U.S.-Japanese Relations Japan had closed itself to outsiders in the late 1400s; held a strong mistrust of Western cultures In mid-1800s, US businesses began to
U.S. Imperialism s Impact on Other Nations U.S.-Japanese Relations Japan had closed itself to outsiders in the late 1400s; held a strong mistrust of Western cultures In mid-1800s, US businesses began to
The United States Looks Overseas
 The United States Looks Overseas 1853-1915 Interact with History In 1893, American sugar planters in the Kingdom of Hawaii thought they could make more money if Hawaii were an American state. So they staged
The United States Looks Overseas 1853-1915 Interact with History In 1893, American sugar planters in the Kingdom of Hawaii thought they could make more money if Hawaii were an American state. So they staged
American Foreign Policy, : The Good, the Bad, & the Ugly.
 American Foreign Policy, 1880-1920: The Good, the Bad, & the Ugly. Each group will become experts on their assigned country. Create poster showing how U.S. policy toward your respective country was good,
American Foreign Policy, 1880-1920: The Good, the Bad, & the Ugly. Each group will become experts on their assigned country. Create poster showing how U.S. policy toward your respective country was good,
Essential Question: & Latin America? Clicker Review. What role did the United States play as an imperial power in Asia. CPWH Agenda for Unit 10.
 Essential Question: What role did the United States play as an imperial power in Asia & Latin America? CPWH Agenda for Unit 10.8: Clicker Review Imperialism by the USA notes Today s HW: 28.3 Unit 10 Test:
Essential Question: What role did the United States play as an imperial power in Asia & Latin America? CPWH Agenda for Unit 10.8: Clicker Review Imperialism by the USA notes Today s HW: 28.3 Unit 10 Test:
Unit 4: Imperialism. Name: Word Definition Analysis
 Name: Unit 4: Imperialism Word Definition Analysis 1. Imperialism (191) Policy by which strong nations Did America practice imperialism? extend their political, military, If so where? and economic control
Name: Unit 4: Imperialism Word Definition Analysis 1. Imperialism (191) Policy by which strong nations Did America practice imperialism? extend their political, military, If so where? and economic control
Expanding Horizons: Imperialism
 Expanding Horizons: Imperialism In August 1914, World War I broke out in Europe, which drowned out the Progressive Era. Leading up to this, U.S. foreign policy had been drastically changing. IMPERIALISM
Expanding Horizons: Imperialism In August 1914, World War I broke out in Europe, which drowned out the Progressive Era. Leading up to this, U.S. foreign policy had been drastically changing. IMPERIALISM
Imperialism. U.S. Foreign Policy. U.S. Foreign Policy 10/30/13. Chapter 10. Monroe Doctrine. Many Spanish colonies revolting
 Imperialism Chapter 10 U.S. Foreign Policy Monroe Doctrine No new colonization by Europe in western hemisphere U.S. stays out of European affairs If Europe attempts to colonize in the west, U.S. would
Imperialism Chapter 10 U.S. Foreign Policy Monroe Doctrine No new colonization by Europe in western hemisphere U.S. stays out of European affairs If Europe attempts to colonize in the west, U.S. would
Roosevelt Taft Wilson. Big Stick Diplomacy Dollar Diplomacy Moral Diplomacy
 Roosevelt Taft Wilson Big Stick Diplomacy Dollar Diplomacy Moral Diplomacy Definition: The art or practice of conducting international relations, as in negotiating alliances, treaties, and agreements.
Roosevelt Taft Wilson Big Stick Diplomacy Dollar Diplomacy Moral Diplomacy Definition: The art or practice of conducting international relations, as in negotiating alliances, treaties, and agreements.
Imperialism and America
 Chapter 10 America Claims an Empire CHAPTER 10 Section 1 (pages 342-345) Imperialism and America American Expansionism (pages 342-344) Why did Americans support imperialism? In 1893, Queen Liliuokalani
Chapter 10 America Claims an Empire CHAPTER 10 Section 1 (pages 342-345) Imperialism and America American Expansionism (pages 342-344) Why did Americans support imperialism? In 1893, Queen Liliuokalani
Imperialism and America
 CHAPTER 10 Section 1 ( pages 342 345) Imperialism and America BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about Woodrow Wilson. In this section, you will learn how economic activity led to political
CHAPTER 10 Section 1 ( pages 342 345) Imperialism and America BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about Woodrow Wilson. In this section, you will learn how economic activity led to political
Imperialism. Policy in which stronger nations extend their economic, political, or military control over weaker territories
 Imperialism Policy in which stronger nations extend their economic, political, or military control over weaker territories Global Competition European nations had been establishing colonies for years Asia
Imperialism Policy in which stronger nations extend their economic, political, or military control over weaker territories Global Competition European nations had been establishing colonies for years Asia
Let's discuss: to stop human rights abuses under no circumstances
 Let's discuss: When do you think it is appropriate for the US to send soldiers to fight and face death on foreign soil? (Choose up to 3 of the following and briefly explain your choices) to assist an ally
Let's discuss: When do you think it is appropriate for the US to send soldiers to fight and face death on foreign soil? (Choose up to 3 of the following and briefly explain your choices) to assist an ally
throughout the US? Around the world? Why or why not.
 1. Tell what at least three of the symbols you see on this flag represent. 2. Do you think these three symbols would be recognized throughout the US? Around the world? Why or why not. 3. Why would this
1. Tell what at least three of the symbols you see on this flag represent. 2. Do you think these three symbols would be recognized throughout the US? Around the world? Why or why not. 3. Why would this
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e. Chapter Nineteen: From Crisis to Empire
 Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e The Politics of Equilibrium Electoral Stability High Turnout for Elections Cultural Basis of Party Identification Catholics Tended to Vote Democrat 2 The Politics of
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e The Politics of Equilibrium Electoral Stability High Turnout for Elections Cultural Basis of Party Identification Catholics Tended to Vote Democrat 2 The Politics of
Imperialism by the US
 Imperialism by the US Quick Class Discussion: Based on this image, what important changes took place in the United States from 1783 to 1900? 115 years after gaining independence from Britain, the United
Imperialism by the US Quick Class Discussion: Based on this image, what important changes took place in the United States from 1783 to 1900? 115 years after gaining independence from Britain, the United
Chapter 17, Section 1 I. Building Support for Imperialism (pages ) A. Beginning in the 1880s, Americans wanted the United States to become a
 Chapter 17, Section 1 I. Building Support for Imperialism (pages 520 522) A. Beginning in the 1880s, Americans wanted the United States to become a world power. Their change in attitude was a result of
Chapter 17, Section 1 I. Building Support for Imperialism (pages 520 522) A. Beginning in the 1880s, Americans wanted the United States to become a world power. Their change in attitude was a result of
Unit 9 Imperialism and WWI. New US Power and Diplomacy
 Unit 9 Imperialism and WWI New US Power and Diplomacy Attitudes Toward an International Role Arguments for Expansion Economics: new markets/investment opportunities/raw materials Culture: Social Darwinism/Protestant
Unit 9 Imperialism and WWI New US Power and Diplomacy Attitudes Toward an International Role Arguments for Expansion Economics: new markets/investment opportunities/raw materials Culture: Social Darwinism/Protestant
Chapter 27: The Path of Empire, (Pages )
 Chapter 27: The Path of Empire, 1890 1899 (Pages 626 653) I. America Turns Outward A. Motives for overseas expansion 1. Farmers and industrialists Name Per. Date Row 2. The yellow press 3. Role of religion
Chapter 27: The Path of Empire, 1890 1899 (Pages 626 653) I. America Turns Outward A. Motives for overseas expansion 1. Farmers and industrialists Name Per. Date Row 2. The yellow press 3. Role of religion
Imperialism. Creation of the U.S. Empire
 Imperialism Creation of the U.S. Empire Please Note: The images included in this presentation, some of which are copyrighted, are being used under the fair use provision (for educational purposes) of the
Imperialism Creation of the U.S. Empire Please Note: The images included in this presentation, some of which are copyrighted, are being used under the fair use provision (for educational purposes) of the
Chapter 22: America Becomes a World Power
 Chapter 22: America Becomes a World Power Objective: Why did the United States become imperialistic and what were the outcomes? Goal: Students will be able to understand the causes and effects of imperialism
Chapter 22: America Becomes a World Power Objective: Why did the United States become imperialistic and what were the outcomes? Goal: Students will be able to understand the causes and effects of imperialism
Primary Document #1: The Open Door Notes (Policy) ( )
 Primary Document #1: The Open Door Notes (Policy) (1899-1900) By the late 19th century, Japan and the European powers had carved much of China into separate spheres of influence, inside of which each held
Primary Document #1: The Open Door Notes (Policy) (1899-1900) By the late 19th century, Japan and the European powers had carved much of China into separate spheres of influence, inside of which each held
Lesson 9: An Emerging World Power Imperialist = Expansionist (Chapter 9 in Textbook)
 Lesson 9: An Emerging World Power Imperialist = Expansionist (Chapter 9 in Textbook) Time Period: Late 1800s- 1914 Presidents William Mckinley 1897-1901 Theodore Roosevelt 1901-1909 William Howard Taft
Lesson 9: An Emerging World Power Imperialist = Expansionist (Chapter 9 in Textbook) Time Period: Late 1800s- 1914 Presidents William Mckinley 1897-1901 Theodore Roosevelt 1901-1909 William Howard Taft
EOCEP. Release Items by Standard and Indicator. Realigned to 2011 standards in August 2011
 EOCEP Release Items by Standard and Indicator Realigned to 2011 standards in August 2011 Indicator 1.1 (Additional release item for this indicator found in Teacher s Guide) Which colonial region had the
EOCEP Release Items by Standard and Indicator Realigned to 2011 standards in August 2011 Indicator 1.1 (Additional release item for this indicator found in Teacher s Guide) Which colonial region had the
Chapter 18. American Claims an Empire
 Chapter 18 American Claims an Empire Section 1: Imperialism and American Imperialism 1880s U.S. interest in building an Empire builds Imperialism = Stronger : Economic, political, or military control Europeans
Chapter 18 American Claims an Empire Section 1: Imperialism and American Imperialism 1880s U.S. interest in building an Empire builds Imperialism = Stronger : Economic, political, or military control Europeans
America s Path to Empire. APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 8
 America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 8 1890-1892 Foreign Policy The Influence of Sea Power upon History (1890): Alfred Thayer Mahan Sea power throughout history gives advantages US lies
America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 8 1890-1892 Foreign Policy The Influence of Sea Power upon History (1890): Alfred Thayer Mahan Sea power throughout history gives advantages US lies
(Think in reverse for America s products)
 Foreign countries put tariffs on incoming American goods. This made American goods more expensive in those countries and less desirable. Having more control over other countries and their economies would
Foreign countries put tariffs on incoming American goods. This made American goods more expensive in those countries and less desirable. Having more control over other countries and their economies would
IT S STORY TIME! UNIT 4 AMERICAN IMPERIALISM Part 1 The Imperialist Vision Part 2 The Spanish-American War Part 3 New American Diplomacy
 IT S STORY TIME! UNIT 4 AMERICAN IMPERIALISM 1872-1912 Part 1 The Imperialist Vision Part 2 The Spanish-American War Part 3 New American Diplomacy AMERICAN DIPLOMACY in ASIA Each LEASEHOLD became center
IT S STORY TIME! UNIT 4 AMERICAN IMPERIALISM 1872-1912 Part 1 The Imperialist Vision Part 2 The Spanish-American War Part 3 New American Diplomacy AMERICAN DIPLOMACY in ASIA Each LEASEHOLD became center
Define the following: a. Neutrality Policy. b. Louisiana Purchase. c. War of d. Monroe Doctrine. e. Mexican-American War
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Reading Assignment: Chapter 20 in AMSCO or other resource covering the Spanish American War. Directions: 1. Pre-Read: Read the prompts/questions within this guide before
Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Reading Assignment: Chapter 20 in AMSCO or other resource covering the Spanish American War. Directions: 1. Pre-Read: Read the prompts/questions within this guide before
Unit 6 Review Sheets Foreign Policies: Imperialism Isolationism (Spanish-American War Great Depression)
 Speak softly & carry a big stick; you will go far -Theodore Roosevelt Work or fight -National War Labor Board Unit 6 Review Sheets Foreign Policies: Imperialism Isolationism (Spanish-American War Great
Speak softly & carry a big stick; you will go far -Theodore Roosevelt Work or fight -National War Labor Board Unit 6 Review Sheets Foreign Policies: Imperialism Isolationism (Spanish-American War Great
Imperialism Practice Test
 Imperialism Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What did Liliuokalani propose after she became Queen of the Hawaiian Islands?
Imperialism Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What did Liliuokalani propose after she became Queen of the Hawaiian Islands?
Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved.
 Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. US History Immigration and Foreign policy Blizzard Bag 2014-2015 1. In a 1904 address to Congress, President Theodore Roosevelt stated that the United States
Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. US History Immigration and Foreign policy Blizzard Bag 2014-2015 1. In a 1904 address to Congress, President Theodore Roosevelt stated that the United States
U.S. TAKS Review. 11th
 11th U.S. TAKS Review Add a background color or design template to the following slides and use as a Power Point presentation. Print as slides in black and white on colored paper to use as placards for
11th U.S. TAKS Review Add a background color or design template to the following slides and use as a Power Point presentation. Print as slides in black and white on colored paper to use as placards for
Review. Geographic Change Essay. Essay Blocking. Possible Thematic Essays 6/7/2013
 Review Essay Blocking Possible Thematic Essays Study 2 of the following: 5 W s- Who, What, When, Why - Reform Movements (Women, Civil Rights, Progressive Era) - Manifest Destiny ( Louisiana Purchase, Homestead
Review Essay Blocking Possible Thematic Essays Study 2 of the following: 5 W s- Who, What, When, Why - Reform Movements (Women, Civil Rights, Progressive Era) - Manifest Destiny ( Louisiana Purchase, Homestead
Standards US History 10-25
 Standards US History 10-25 Progressivism Progressivism A reform movement focused on improving living conditions, education, working conditions, stopping political corruption, and gain women the right to
Standards US History 10-25 Progressivism Progressivism A reform movement focused on improving living conditions, education, working conditions, stopping political corruption, and gain women the right to
1 U.S. Expansion Pacific to Caribbean 2 Imperialism & Manifest Destiny Imperialism: The quest for colonial empires Manifest Destiny: US was destined
 1 U.S. Expansion Pacific to Caribbean 2 Imperialism & Manifest Destiny Imperialism: The quest for colonial empires Manifest Destiny: US was destined by God to expand from Atlantic coast into Pacific Ocean
1 U.S. Expansion Pacific to Caribbean 2 Imperialism & Manifest Destiny Imperialism: The quest for colonial empires Manifest Destiny: US was destined by God to expand from Atlantic coast into Pacific Ocean
The Age of Empire
 The Age of Empire 1890-1900 Overview Competition for markets Acquisition of land (Primarily in Pacific) Yellow Journalism Spanish American War McKinley vs. Bryan Why Empire? Why Empire? Markets Export
The Age of Empire 1890-1900 Overview Competition for markets Acquisition of land (Primarily in Pacific) Yellow Journalism Spanish American War McKinley vs. Bryan Why Empire? Why Empire? Markets Export
US History Ms. Jones Unit 3 Test
 US History Ms. Jones Unit 3 Test Please read the following instructions carefully. For each question, please select the best answer and fill in the bubble on your answer sheet. Do not write on the test,
US History Ms. Jones Unit 3 Test Please read the following instructions carefully. For each question, please select the best answer and fill in the bubble on your answer sheet. Do not write on the test,
Imperial America The United States in the World
 Imperial America The United States in the World 1890-1914 Gilded Age: A Tale of Today 1873 Novel by Mark Twain and Charles Warner: fictional account of political and economic corruption in the USA gild
Imperial America The United States in the World 1890-1914 Gilded Age: A Tale of Today 1873 Novel by Mark Twain and Charles Warner: fictional account of political and economic corruption in the USA gild
SOCIAL STUDIES AP American History Standard: History
 A. Explain connections between the ideas of Enlightenment and changes in the relationship between citizens and their government. B. Identify the causes of political, economic and social oppression and
A. Explain connections between the ideas of Enlightenment and changes in the relationship between citizens and their government. B. Identify the causes of political, economic and social oppression and
8 TH GRADE UNITS OF INSTRUCTION
 Name Date Per. Social Studies 8 1/3 Review Packet Mrs. Myles McAnally 8 TH GRADE UNITS OF INSTRUCTION Reconstruction: Economic Expansion: a. Immigration b. Industrialization c. US Expansion and Imperialism
Name Date Per. Social Studies 8 1/3 Review Packet Mrs. Myles McAnally 8 TH GRADE UNITS OF INSTRUCTION Reconstruction: Economic Expansion: a. Immigration b. Industrialization c. US Expansion and Imperialism
SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR VOCAB
 SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR VOCAB 1. War of 1812 2. Monroe Doctrine 3. Mexican War 4. Yellow journalism 5. USS Maine 6. Rough Riders 7. San Juan Hill 8. Anti-Imperialist League 9. Platt Amendment 10.Diplomacy
SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR VOCAB 1. War of 1812 2. Monroe Doctrine 3. Mexican War 4. Yellow journalism 5. USS Maine 6. Rough Riders 7. San Juan Hill 8. Anti-Imperialist League 9. Platt Amendment 10.Diplomacy
I. A Brief History of American Foreign Policy
 I. A Brief History of American Foreign Policy A. Isolationism 1. In his Farewell Address in 1796, President George Washington urged Americans to avoid entangling alliances and maintain neutrality. 2. Since
I. A Brief History of American Foreign Policy A. Isolationism 1. In his Farewell Address in 1796, President George Washington urged Americans to avoid entangling alliances and maintain neutrality. 2. Since
2. Transatlantic Encounters and Colonial Beginnings,
 1. Pre-Columbian Societies A. Early inhabitants of the Americas B. American Indian empires in Mesoamerica, the Southwest, and the Mississippi Valley C. American Indian cultures of North America at the
1. Pre-Columbian Societies A. Early inhabitants of the Americas B. American Indian empires in Mesoamerica, the Southwest, and the Mississippi Valley C. American Indian cultures of North America at the
Question of the Day Schedule
 Question of the Day Schedule 2012-2013 Question Dates Topics Subtopics September 3-7 1. Pre-Columbian Societies Early inhabitants of the Americas American Indian empires in Mesoamerica, the Southwest,
Question of the Day Schedule 2012-2013 Question Dates Topics Subtopics September 3-7 1. Pre-Columbian Societies Early inhabitants of the Americas American Indian empires in Mesoamerica, the Southwest,
China Resists Outside Influence
 Name CHAPTER 28 Section 1 (pages 805 809) China Resists Outside Influence BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about imperialism in Asia. In this section, you will see how China dealt with foreign
Name CHAPTER 28 Section 1 (pages 805 809) China Resists Outside Influence BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about imperialism in Asia. In this section, you will see how China dealt with foreign
Imperialism and WWI US History Unit 4. Name:
 Imperialism and WWI US History Unit 4 Name: 2 Imperialism and WWI [all homework assignments must be turned in prior to taking your assessment] 4.1: Due Pages 187-207 1. Imperialism 2. Annexing Hawaii 3.
Imperialism and WWI US History Unit 4 Name: 2 Imperialism and WWI [all homework assignments must be turned in prior to taking your assessment] 4.1: Due Pages 187-207 1. Imperialism 2. Annexing Hawaii 3.
America s Path to Empire. APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 5
 America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 5 Mariam Haider, Emma Tresch, 5th Period America s Path to Empire 1892-1894 Feb 29, 1892: Britain and US sign treaty on seal hunting in the Bering
America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 5 Mariam Haider, Emma Tresch, 5th Period America s Path to Empire 1892-1894 Feb 29, 1892: Britain and US sign treaty on seal hunting in the Bering
1. Commercial/Business Interests. U. S. Foreign Investments:
 1. Commercial/Business Interests U. S. Foreign Investments: 1869-1908 1. Commercial/Business Interests American Foreign Trade: 1870-1914 2. Military/Strategic Interests Alfred T. Mahan The Influence of
1. Commercial/Business Interests U. S. Foreign Investments: 1869-1908 1. Commercial/Business Interests American Foreign Trade: 1870-1914 2. Military/Strategic Interests Alfred T. Mahan The Influence of
Becoming A World Power,
 Becoming A World Power, 1890-1915 United States History Week of April 27, 2015 What Factors Caused Imperialism? Economic factors: need for natural resources, new markets for manufactured goods Nationalistic
Becoming A World Power, 1890-1915 United States History Week of April 27, 2015 What Factors Caused Imperialism? Economic factors: need for natural resources, new markets for manufactured goods Nationalistic
Chapter 12 Section 1 The Imperialist Vision. Click on a hyperlink to view the corresponding slides.
 Chapter 12 Section 1 The Imperialist Vision Click on a hyperlink to view the corresponding slides. Click the Speaker button to listen to the audio again. continued on next slide Guide to Reading Main
Chapter 12 Section 1 The Imperialist Vision Click on a hyperlink to view the corresponding slides. Click the Speaker button to listen to the audio again. continued on next slide Guide to Reading Main
Difficult choice. Republican ideals? Imperial power?
 Difficult choice Republican ideals? Imperial power? Anti-Imperialist League Founded in 1899. Mark Twain, Andrew Carnegie, William James, and William Jennings Bryan among the leaders. Campaigned against
Difficult choice Republican ideals? Imperial power? Anti-Imperialist League Founded in 1899. Mark Twain, Andrew Carnegie, William James, and William Jennings Bryan among the leaders. Campaigned against
5. Base your answer on the map below and on your knowledge of social studies.
 Name: 1. To help pay for World War II, the United States government relied heavily on the 1) money borrowed from foreign governments 2) sale of war bonds 3) sale of United States manufactured goods to
Name: 1. To help pay for World War II, the United States government relied heavily on the 1) money borrowed from foreign governments 2) sale of war bonds 3) sale of United States manufactured goods to
America Past and Present 9 th Edition, AP* Edition 2011
 A Correlation of America Past and Present 9 th Edition, AP* Edition 2011 To the ADVANCED PLACEMENT U.S. HISTORY TOPIC OUTLINE *, Program, AP, and Pre-AP are registered trademarks of the College Board,
A Correlation of America Past and Present 9 th Edition, AP* Edition 2011 To the ADVANCED PLACEMENT U.S. HISTORY TOPIC OUTLINE *, Program, AP, and Pre-AP are registered trademarks of the College Board,
The United States and Latin America
 SECTION3 The United States and Latin America What You Will Learn Main Ideas 1. The United States built the Panama Canal in the early 19s. 2. Theodore Roosevelt changed U.S. policy toward Latin America.
SECTION3 The United States and Latin America What You Will Learn Main Ideas 1. The United States built the Panama Canal in the early 19s. 2. Theodore Roosevelt changed U.S. policy toward Latin America.
UNITED STATES HISTORY SECTION I1 Part A (Suggested writing time-45 minutes) Percent of Section I1 score-45
 UNITED STATES HISTORY SECTION I1 Part A (Suggested writing time-45 minutes) Percent of Section I1 score-45 Directions: The following question requires you to construct a coherent essay that integrates
UNITED STATES HISTORY SECTION I1 Part A (Suggested writing time-45 minutes) Percent of Section I1 score-45 Directions: The following question requires you to construct a coherent essay that integrates
1. How did the Dawes Act aid in destroying the way of life of Native American s?
 Name Period Chapter 4 Reconstruction **List and discuss the failures and successes of Reconstruction concerning political and social rights of African Americans. Make sure and include the Amendments 13,
Name Period Chapter 4 Reconstruction **List and discuss the failures and successes of Reconstruction concerning political and social rights of African Americans. Make sure and include the Amendments 13,
Chapter 19: Republic To Empire
 Chapter 19: Republic To Empire Objectives: o We will examine the policies America implemented in their newly conquered territories after the Spanish American War. o We will examine the various changes
Chapter 19: Republic To Empire Objectives: o We will examine the policies America implemented in their newly conquered territories after the Spanish American War. o We will examine the various changes
Day One U.S. History Review Packet Scavenger Hunt Unit One: Colonial Era
 Day One U.S. History Review Packet Scavenger Hunt Unit One: Colonial Era These two (2) 1. 2. geographic features protect and isolate the United States geographically today? This was the political 3. border
Day One U.S. History Review Packet Scavenger Hunt Unit One: Colonial Era These two (2) 1. 2. geographic features protect and isolate the United States geographically today? This was the political 3. border
ID- Captured Filipino Insurrectionists (642) Summary 1-How many Filipinos died in the three year insurrection against the US? 600,000 Summary 2- How
 Ch 27 P2 Insights 1) Define and explain why the US issued the Open Door Policy 2) Explain how the Open Door Policy changed the United States role in the world. 3) Was the US a good neighbor to Latin America?
Ch 27 P2 Insights 1) Define and explain why the US issued the Open Door Policy 2) Explain how the Open Door Policy changed the United States role in the world. 3) Was the US a good neighbor to Latin America?
Acquiring and Managing Global Power
 1890 1917 Chapter 21 Acquiring and Managing Global Power Were U.S. interventions abroad between 1890 and 1917 motivated more by realism or idealism? 21.1 Introduction On May 1, 1901, the Pan-American Exposition
1890 1917 Chapter 21 Acquiring and Managing Global Power Were U.S. interventions abroad between 1890 and 1917 motivated more by realism or idealism? 21.1 Introduction On May 1, 1901, the Pan-American Exposition
America s Path to Empire. APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 2
 America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 2 Major Events 1890-1892 McKinley Tariff October 1, 1890 Raised the average duty on imports to almost fifty percent Intended to protect domestic industries
America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 2 Major Events 1890-1892 McKinley Tariff October 1, 1890 Raised the average duty on imports to almost fifty percent Intended to protect domestic industries
World History Unit 7 Vocabulary Era of Imperialism ( C.E.)
 World History Unit 7 Vocabulary Era of Imperialism (1800-1914 C.E.) NAME: PERIOD: DATE: For each word: write the definition, create a sentence that displays the meaning of the word, and draw a picture
World History Unit 7 Vocabulary Era of Imperialism (1800-1914 C.E.) NAME: PERIOD: DATE: For each word: write the definition, create a sentence that displays the meaning of the word, and draw a picture
Essential U.S. History
 EOY Revision Sheet Social Studies, Level K Page 1 of 10 Mount Auburn International Academy SABIS School Network Social Studies Level K / Grade 9 EOY Grade 9 Social Studies Revision guide For Essential
EOY Revision Sheet Social Studies, Level K Page 1 of 10 Mount Auburn International Academy SABIS School Network Social Studies Level K / Grade 9 EOY Grade 9 Social Studies Revision guide For Essential
Presidents in general are not lovable. They ve had to do too much to get where they are. But there was one president who was lovable Teddy Roosevelt
 Presidents in general are not lovable. They ve had to do too much to get where they are. But there was one president who was lovable Teddy Roosevelt and I loved him Walter Lippmann Theodore Roosevelt brought
Presidents in general are not lovable. They ve had to do too much to get where they are. But there was one president who was lovable Teddy Roosevelt and I loved him Walter Lippmann Theodore Roosevelt brought
1. AMERICA BECOMES A WORLD POWER
 1. AMERICA BECOMES A WORLD POWER OVERVIEW OF THE VIDEO While Progressive leaders showed their distrust of power in their dealings with large corporations at home, they still grasped the growing need for
1. AMERICA BECOMES A WORLD POWER OVERVIEW OF THE VIDEO While Progressive leaders showed their distrust of power in their dealings with large corporations at home, they still grasped the growing need for
Welcome to History 12 Political and Social History of the U.S. II From 1876 to the present Prof. Valadez
 Welcome to History 12 Political and Social History of the U.S. II From 1876 to the present Prof. Valadez 1 Topics The U.S. as a World Power Progressive Era 2 Becoming a World Power The New Imperialism
Welcome to History 12 Political and Social History of the U.S. II From 1876 to the present Prof. Valadez 1 Topics The U.S. as a World Power Progressive Era 2 Becoming a World Power The New Imperialism
Geneva CUSD 304 Content-Area Curriculum Frameworks Grades 6-12 Social Studies
 Geneva CUSD 304 Content-Area Curriculum Frameworks Grades 6-12 Social Studies Mission Statement It is our belief that Social Studies education is ultimately to prepare students to assume the responsibilities
Geneva CUSD 304 Content-Area Curriculum Frameworks Grades 6-12 Social Studies Mission Statement It is our belief that Social Studies education is ultimately to prepare students to assume the responsibilities
Foreign Policy: Setting a Course of Expansionism
 [Photo: SE19.00] 1796 1896 Chapter 19 Foreign Policy: Setting a Course of Expansionism Was American foreign policy during the 1800s motivated more by realism or idealism? 19.1 Introduction On July 8, 1853,
[Photo: SE19.00] 1796 1896 Chapter 19 Foreign Policy: Setting a Course of Expansionism Was American foreign policy during the 1800s motivated more by realism or idealism? 19.1 Introduction On July 8, 1853,
Name 1. Why were the League of Nations and the United Nations created? A.
 Name 1. Why were the League of Nations and the United Nations created? A. to end world hunger B. to prevent future wars C. to unify the world economy D. to spread democracy in the world 2. How did the
Name 1. Why were the League of Nations and the United Nations created? A. to end world hunger B. to prevent future wars C. to unify the world economy D. to spread democracy in the world 2. How did the
Chapters 18 Review American History
 Chapters 18 Review American History I. Policy of Imperialism: a. Imperialism is a countries policy and practice of creating an empire and maintaining control to expand their control of raw materials, and
Chapters 18 Review American History I. Policy of Imperialism: a. Imperialism is a countries policy and practice of creating an empire and maintaining control to expand their control of raw materials, and
Reasons for American Imperialism
 Name: Reasons for American Introduction: Expansion has always been a part of America s history. At first, expansion headed towards the Pacific within North America. In the 1700 s and 1800 s, European nations
Name: Reasons for American Introduction: Expansion has always been a part of America s history. At first, expansion headed towards the Pacific within North America. In the 1700 s and 1800 s, European nations
4. During the late 1800s, the port of entry for the majority of immigrants was a. Boston b. New York City c. Philadelphia d.
 Chapters 14-18 Presentations Test 1. The cruise of the Great White Fleet showed that a. the Atlantic could be crossed safely. b. Great Britain was a second-rate power. c. the United States was a naval
Chapters 14-18 Presentations Test 1. The cruise of the Great White Fleet showed that a. the Atlantic could be crossed safely. b. Great Britain was a second-rate power. c. the United States was a naval
FB/CCU U.S. HISTORY COURSE DESCRIPTION / LEARNING OBJECTIVES
 FB/CCU U.S. HISTORY COURSE DESCRIPTION / LEARNING OBJECTIVES In the pages that follow, the Focus Questions found at the beginning of each chapter in America: A Narrative History have been reformulated
FB/CCU U.S. HISTORY COURSE DESCRIPTION / LEARNING OBJECTIVES In the pages that follow, the Focus Questions found at the beginning of each chapter in America: A Narrative History have been reformulated
Standards 5.1 and 5.2 Expansionism and the Spanish-American War
 EXPANSIONISM Standards 5.1 and 5.2 Expansionism and the Spanish-American War Westward expansion was motivated by o Led to the establishment of Expansionism in the late 19 th century reached beyond the
EXPANSIONISM Standards 5.1 and 5.2 Expansionism and the Spanish-American War Westward expansion was motivated by o Led to the establishment of Expansionism in the late 19 th century reached beyond the
