Coyote Economist. The Political Economy of the Occupy Movement. News from the Department of Economics, CSUSB Volume 18, Issue 1..
|
|
|
- Derek O’Brien’
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Coyote Economist News from the Department of Economics, CSUSB Volume 18, Issue 1.. Fall 2011 The Political Economy of the Occupy Movement Inside this Issue: Staying Informed...2 We re on Facebook...5 Tentative Schedule...6 The spectacular growth of the Occupy Movement reflects a deep-seated political sentiment. The movement has grown, in just a little over two months, from an occupation of about 200 people in Zuccotti Park in New York City to a movement that is now represented in over 2,400 cities (according to Occupy Together) and in other formats such as Occupy Colleges and Occupy the Media. Many local communities Riverside, San Bernardino, and Redlands among them have been the sites of Occupy encampments and/or events. What s more, in polls taken by Public Policy Polling, the fraction of voters who support the movement stands at about 33% ( com/main/2011/11/voters-moving-against-occupy-movement.html). Given the traditionally conservative nature of the U.S. electorate, this is a strong sentiment. The Civil Rights movement, for example, did not have this level of support in the late 1950s and early 1960s, and it took years before the Anti-War Movement of the 1960s reached the level of approval currently given to the Occupiers ( com/main/2011/11/voters-moving-against-occupy-movement.html). Clearly, something is happening here. To political economists, what makes this phenomenon interesting is that it represents continued on page 2 Department of Economics CSUSB Facebook: CSUSB Department of Economics Photo: David Shankbone, used under a Creative Commons licence 1
2 Continued from page 1 an attitude that runs against what many claim are the dominant mainstream values in this county. Unlike the Tea Party, which gives voice to these dominant values, the Occupy Movement is giving voice to a contrarian set of norms. While the Tea Party emphasizes private property, individualism, free markets, and a deep suspicion of government and socialist solutions, the Occupy Movement questions the power of corporations and is comfortable with socializing health care and education, redistributing income, and regulating markets specifically financial markets. However, while their encampments emphasize horizontalism, consensus decision-making, and an anarchosocialist perspective, the Occupy movement is not seeking the...the elite have managed to change the legal, economic, and social rules of the game.. overthrow of capitalism. Instead, it appears to seek a more fair form of capitalism. One gets the sense that they would prefer the kind of social democracies found in the Nordic countries (Denmark, Iceland, Norway, Sweden and Finland), where the underlying institutions of private property and markets are regulated to bring about greater equity and a broader access to public services than is common in the United States. The Occupy Movement s simple but powerful slogan, We are the 99%, has captured the imagination of a portion of the public that perceives that public policy in this country is being driven by a wealthy elite that ignores or shuts out the voice of the vast majority of citizens. The government, many in the Occupy Movement claim, has been captured by corporations and wealthy elites, making it less of a democracy and more of a corporatocracy : rule by large corporations and by those who benefit from the ownership and control of these corporations. One consequence of this capture of the government has been that the elite have managed to change the legal, economic, and social rules of the game so that they, the elite, benefit even more than before. This, in turn, has further enhanced the economic and political power of the elite and these elites have used this enhanced power to further tilt the rules of the game even more in their favor. A growing inequality in the distribution of wealth and income is one manifestation of this. Political economists have long drawn attention to the way elites and continued on page 3 Photo: David Shankbone, used under a Creative Commons licence Staying Informed about CSUSB Department of Economics Events and News If you re receiving the Coyote Economist, then you re on our mailing list and everything is as it should be. But, if you know of an Economics Major, or an Econ Fellow Traveler, who is not receiving the Coyote Economist through , then please have him/her inform our Administrative Support Coordinator, Ms. Jacqueline Carrillo, or the Chair of the Economics Department, Professor Mayo Toruño. Our phone number is You can stay informed by consulting: Our Website - Our Facebook Page- Chair of the Economics Department mtoruno@csusb.edu 2
3 Continued from page 2 the business sector shape government. For instance, both Thorstein Veblen and Karl Marx argued that, in capitalist societies, government largely reflects the influence and power of the business class. While the system is formally democratic and allows workers, the overwhelming majority of the electorate, to participate in the choice of legislators and executives, There would not have been a tea party without Fox. it is nevertheless the case that elected officials must be keenly attentive to the needs of business. For instance, if elected officials ignore business interests they might provoke a capital strike in which businesses reduce investment and production which threatens the ouster of offending politicians as the public blames the politicians for the poor economic conditions created by the capital strike. Beyond this, huge corporations and rich elites are able to shape public discourse in this country in ways that benefit these huge corporations and the elites. Consumers of this shaped public discourse often middleclass workers come to believe that their own (middle-class and worker) interests are aligned with the interests of corporations and the elite. Out of this we got the Tea Party, which has provided cover for some in Congress to claim that policies Congress passes (designed to benefit large corporations and elites) are actually the product of the democratic demands of a grassroots and middleclass public movement. Yet the Tea Party s rise to public prominence was not due to grassroots support. As a Tea Party leader Sal Russo admitted in a May 22, 2011 New York Magazine article, There would not have been a tea party without Fox. The current political and economic structure of the United States is something new, but is also a manifestation of long-run tendencies. For instance, Paul Baran and Paul Sweezy, in their 1966 book Monopoly Capital, argued that the rise of the corporate form of business led to a structural transformation of capitalism, from the competitive capital form of the 19th century to the monopoly capital form starting in the 20th century. Monopoly capital economies are dominated by giant corporations that control a majority of the manufacturing and financial assets, and operate in oligopolistic and/or monopolistic markets. Baran and Sweezy argued that this form of capitalism tended to generate profits that were so high that the system had difficulty finding ways to profitably reinvest the profit. This situation, they argued, produced both stagnation in the economy and the potential for growing income for those at the top (and a consequent greater inequality in income and wealth distribution). In a related vein, John Kenneth Galbraith argued in The New Industrial State that the rise of the giant corporation also has important cultural and political effects, creating an ideological environment in which consumer and political choices largely reflect the interests of giant corporations. In short, the Occupy Movement has correctly assessed the broad...the Occupy Movement has correctly assessed the broad outlines of what has been taking place for quite some time... outlines of what has been taking place for quite some time: growing wealth and income inequality and growing influence by the corporate elite. Rising Income and Wealth Inequality The distribution of income and wealth is more unequal now than it was in the 1970s. Consider first the distribution of income. A recent Congressional Budget Office (CBO) studied change in the distribution of household income between 1979 and 2007 (CBO, Trends in the Distribution of Household Income Between 1979 and 2007, October 2011). The study looked at income (from both labor and property ownership) from two different perspectives: first, in terms of income before taxes and transfers; and second, in terms of income after taxes and transfers. The first measure captures the level of income distribution generated by market forces while the second measure captures the continued on page 4 3
4 Continued from page 3 level of income distribution generated by the combination of market forces and particular public policies (i.e., taxes and transfers). As a result, the latter measure provides a better picture of the role of public policy (i.e. neoliberalism) in the distribution of income. The chart below, taken from the CBO study, shows changes in the distribution of income after taxes and transfers for income quintiles from 1979 to Each income quartile includes 20% of households. The lowest quintile includes the 20% of households with the lowest after-tax income, the second-lowest quintile includes the 20% of households who have aftertax income above the lowest quintile but below those in the quintiles above them, and so on. The chart shows, for instance, that in 1979 the after-tax income of the lowest quintile (which includes the 20% of US households who have the lowest income) made up about 8% of the total household incomes in that year. The next bar to the right indicates that in 2007 the lowest quintile s share of after-tax income had fallen to about 6% of all after-tax income earned in that year. Market and political forces operating over 1979 to 2007 led to a shift in income away from the households in the lowest quintile. The chart also shows that between 1979 and 2007 market and political forces caused a shift in after-tax income toward the richest quintile. Between these years, the richest quintile saw their share of the nation s...households in the upper 1% saw dramatic increases in their share of the nation s income. income grow from 43% to 53%. All other quintiles saw their share of income fall over the same period. Yet, a closer look at the chart reveals that the gain to the upper quintile was not shared by all within that quintile. The chart indicates an important fact: the growth in after-tax income for the upper quintile was due exclusively to shifts toward the top 1% of all households. Over 1979 to 2007, then, households in the lower 99% saw their share of the nation s income fall while households in the upper 1% saw dramatic increases in their share of the nation s income. The focus on the 1% by the Occupy Movement seems well-supported by this data. The political and economic force operating within the U.S. granted great benefits for the upper 1%. Certainly some of the other 99% are doing okay financially, but many are falling behind as their incomes have failed to keep up. And the current bad economic conditions have seen many in the lower 99% face grave challenges as they have struggled in the face of layoffs and the lack of appropriate jobs for their education, skills, and abilities. The change in the distribution of wealth follows a similar pattern as seen above for income. The broadest measure of wealth is net worth, which is equal to: value of assets owned minus the value of debt. This measure of net worth includes all assets: both tangible assets (e.g., land, businesses and homes) and financial assets (such as savings accounts, stocks and bonds) continued on page 5 Source: Congressional Budget Office, Trends in the Distribution of Household Income Between 1979 and 2007, October 2011, p. XIII. 4
5 100 Net Wealth Distribution in the US, 1983 and Percent of Wealth Owned Upper 5 Percent Lower 95 Percent Source: based on data taken from Edward N. Wolff, Recent Trends in Household Wealth in the United States: Rising Debt and the Middle-Class Squeeze an Update to 2007, Working Paper No Levy Economics Institute of Bard College, March 2010, p. 44. Continued from page 4 as well as consumptive (such as a car or a home) or productive (such as a farm or factory) assets. Debt includes all forms of debt, such as credit card debt, mortgages, and other forms of loan liabilities. The chart above, based on a recent study by Edward Wolff, shows the distribution net worth in two years, 1983 and Notice that between these two years, the top 5% of all households (the upper red bar) saw their share of net worth grow from 56% to 62%. Over the same period, the rest of the country (the other 95%) saw their share of net wealth decline from 44% to 38%, which represents a decline of 13% in their share of net wealth. It s important to remember that this measure of net worth includes all assets and liabilities and does not distinguish between consumptive and productive assets. If we subtract from this measure the portion of net worth tied to the ownership of the primary residence (the overwhelming contributor to net worth for the bottom 80% of all households) then the inequity in the distribution of net worth is even more dramatic. In recent decades, the US economic and political system has generated a worsening distribution of both income and wealth. Those at the top have...the US economic and political system seems to have been captured by the upper 1%... managed to grab a larger portion of the income generated within the United States and, in parallel, have managed to take hold of a larger portion of wealth that exists within the United States. These changes have occurred slowly, and have been the consequence of a large number of small changes in the US economy and the political and social system within the country. These changes, however, did not become a centerpiece of protest until the financial system (which played a part in the worsening distribution and wealth) failed in the face of a lack of government regulation of this increasingly unrestrained financial system. The consequent high levels of unemployment and the failure of the Congress and the President to pursue the obvious demand-management remedies to this problem have created a large number of people within the US who are willing to stand up and point out the obvious: the US economic and political system has been captured by the upper 1% and the lower 99% are paying the price. We re on Facebook!! Don t forget to check us out on Facebook and say that you like us! You can find the Economics Department at The CSUSB Department of Economics Facebook page. Joining us on Facebook is an important way of keeping up with Departmental news and Department events as well as getting information on political economy. Look for us on Facebook...we re easy to find! 5
6 Tentative SPRING 2012 Schedule of Classes Course Section Title... Time... Days Instructor ECON SOCIAL ISSUES PM MWF ROSE PRIN MICROECON AM MWF STAFF PRIN MICROECON PM MW STAFF PRIN MICROECON PM MW ASHEGHIAN PRIN MICROECON AM TR STAFF PRIN MICROECON PM TR STAFF PRIN MICROECON PM TR STAFF PRIN MACROECON AM MWF STAFF PRIN MACROECON PM MW KONYAR PRIN MACROECON AM TR STAFF PRIN MACROECON PM TR STAFF PRIN MACROECON :50 PM TR NILSSON ECON K PM TR CHARKINS PE OF WOMEN AM MWF ROSE TOOLS EC ANALYSIS PM MWF HARRIS PE OF LGBT :30 PM MWF ROSE BUSINESS CYCLES PM TR HARRIS MONEY & BANKING PM TR STAFF POL ECONOMY PM TR NILSSON GLOBAL ECONOMY PM MW ASHEGHIAN ECONOMETRICS PM MW KONYAR HIST ECON IDEAS PM MWF TORUNO INT ECON ISSUES PM W DULGEROFF 6
CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY SAN BERNARDINO SOCIAL SCIENCE 320: UNDERSTANDING CAPITALISM. Dr. Mayo C. Toruño
 CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY SAN BERNARDINO SOCIAL SCIENCE 320: UNDERSTANDING CAPITALISM Dr. Mayo C. Toruño Spring 2009 Office: SB-209D Phone: 537-5517 Office hours: MW 2-3:50 p.m. email: mtoruno@csusb.edu
CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY SAN BERNARDINO SOCIAL SCIENCE 320: UNDERSTANDING CAPITALISM Dr. Mayo C. Toruño Spring 2009 Office: SB-209D Phone: 537-5517 Office hours: MW 2-3:50 p.m. email: mtoruno@csusb.edu
Chapter 2: The U.S. Economy: A Global View
 Chapter 2: The U.S. Economy: A Global View 1. Approximately how much of the world's output does the United States produce? A. 4 percent. B. 20 percent. C. 30 percent. D. 1.5 percent. The United States
Chapter 2: The U.S. Economy: A Global View 1. Approximately how much of the world's output does the United States produce? A. 4 percent. B. 20 percent. C. 30 percent. D. 1.5 percent. The United States
INEQUALITY: POVERTY AND WEALTH CHAPTER 2
 INEQUALITY: POVERTY AND WEALTH CHAPTER 2 Defining Economic Inequality Social Stratification- rank individuals based on objective criteria, often wealth, power and/or prestige. Human beings have a tendency
INEQUALITY: POVERTY AND WEALTH CHAPTER 2 Defining Economic Inequality Social Stratification- rank individuals based on objective criteria, often wealth, power and/or prestige. Human beings have a tendency
THE COFFEES OF THE SECRETARY-GENERAL JAMES K. GALBRAITH
 THE COFFEES OF THE SECRETARY-GENERAL JAMES K. GALBRAITH 18 June 2010 THE COFFEES OF THE SECRETARY-GENERAL Bringing New Perspectives to the OECD Secretary-General s Speech Writing and Intelligence Outreach
THE COFFEES OF THE SECRETARY-GENERAL JAMES K. GALBRAITH 18 June 2010 THE COFFEES OF THE SECRETARY-GENERAL Bringing New Perspectives to the OECD Secretary-General s Speech Writing and Intelligence Outreach
19 ECONOMIC INEQUALITY. Chapt er. Key Concepts. Economic Inequality in the United States
 Chapt er 19 ECONOMIC INEQUALITY Key Concepts Economic Inequality in the United States Money income equals market income plus cash payments to households by the government. Market income equals wages, interest,
Chapt er 19 ECONOMIC INEQUALITY Key Concepts Economic Inequality in the United States Money income equals market income plus cash payments to households by the government. Market income equals wages, interest,
U.S. Family Income Growth
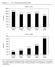 Figure 1.1 U.S. Family Income Growth Growth 140% 120% 100% 80% 60% 115.3% 1947 to 1973 97.1% 97.7% 102.9% 84.0% 40% 20% 0% Lowest Fifth Second Fifth Middle Fifth Fourth Fifth Top Fifth 70% 60% 1973 to
Figure 1.1 U.S. Family Income Growth Growth 140% 120% 100% 80% 60% 115.3% 1947 to 1973 97.1% 97.7% 102.9% 84.0% 40% 20% 0% Lowest Fifth Second Fifth Middle Fifth Fourth Fifth Top Fifth 70% 60% 1973 to
CH 19. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Class: Date: CH 19 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. In the United States, the poorest 20 percent of the household receive approximately
Class: Date: CH 19 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. In the United States, the poorest 20 percent of the household receive approximately
Real Live Transitions from Socialism to Capitalism: Russia
 Real Live Transitions from Socialism to Capitalism: Russia Review from Tues. Why the transition from Socialism to Capitalism? Liberal arguments Inability for socialist economies to grow and modernize Inability
Real Live Transitions from Socialism to Capitalism: Russia Review from Tues. Why the transition from Socialism to Capitalism? Liberal arguments Inability for socialist economies to grow and modernize Inability
Poverty & Inequality
 Sociology 125 Lecture 12/13 Poverty & Inequality October 18 & 23, 2006 Film #2: Bread & Roses 7:00 p.m. Tuesday and Wednesday, October 17 & 18 125 Ag Hall 1450 Linden Drive U.S. Household Income Distribution
Sociology 125 Lecture 12/13 Poverty & Inequality October 18 & 23, 2006 Film #2: Bread & Roses 7:00 p.m. Tuesday and Wednesday, October 17 & 18 125 Ag Hall 1450 Linden Drive U.S. Household Income Distribution
SOCIAL PROBLEMS SOCI 201 1/31/2017. B. Where do Social Problems Come From? 1. Social problems can be though of as objective and subjective.
 SOCI 201 SOCIAL PROBLEMS Professor Kurt reymers, Ph.D. ( Dr. K ) Spring 2017 1. Social problems can be though of as objective and subjective. Objective Condition = Material Reality: the world of physical,
SOCI 201 SOCIAL PROBLEMS Professor Kurt reymers, Ph.D. ( Dr. K ) Spring 2017 1. Social problems can be though of as objective and subjective. Objective Condition = Material Reality: the world of physical,
A 13-PART COURSE IN POPULAR ECONOMICS SAMPLE COURSE OUTLINE
 A 13-PART COURSE IN POPULAR ECONOMICS SAMPLE COURSE OUTLINE By Jim Stanford Canadian Centre for Policy Alternatives, 2008 Non-commercial use and reproduction, with appropriate citation, is authorized.
A 13-PART COURSE IN POPULAR ECONOMICS SAMPLE COURSE OUTLINE By Jim Stanford Canadian Centre for Policy Alternatives, 2008 Non-commercial use and reproduction, with appropriate citation, is authorized.
In a core chapter in their book, Unequal Gains: American Growth. Journal of SUMMER Mark Thornton VOL. 21 N O
 The Quarterly Journal of VOL. 21 N O. 2 158 162 SUMMER 2018 Austrian Economics The Great Leveling: A Note Mark Thornton ABSTRACT: Peter H. Lindert and Jeffrey G. Williamson, in their book Unequal Gains:
The Quarterly Journal of VOL. 21 N O. 2 158 162 SUMMER 2018 Austrian Economics The Great Leveling: A Note Mark Thornton ABSTRACT: Peter H. Lindert and Jeffrey G. Williamson, in their book Unequal Gains:
Social Problems, Census Update, 12e (Eitzen / Baca Zinn / Eitzen Smith) Chapter 2 Wealth and Power: The Bias of the System
 Social Problems, Census Update, 12e (Eitzen / Baca Zinn / Eitzen Smith) Chapter 2 Wealth and Power: The Bias of the System 2.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The authors point out that the problems that
Social Problems, Census Update, 12e (Eitzen / Baca Zinn / Eitzen Smith) Chapter 2 Wealth and Power: The Bias of the System 2.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The authors point out that the problems that
Testimony to the United States Senate Budget Committee Hearing on Opportunity, Mobility, and Inequality in Today's Economy April 1, 2014
 Testimony to the United States Senate Budget Committee Hearing on Opportunity, Mobility, and Inequality in Today's Economy April 1, 2014 Joseph E. Stiglitz University Professor Columbia University The
Testimony to the United States Senate Budget Committee Hearing on Opportunity, Mobility, and Inequality in Today's Economy April 1, 2014 Joseph E. Stiglitz University Professor Columbia University The
CER INSIGHT: Populism culture or economics? by John Springford and Simon Tilford 30 October 2017
 Populism culture or economics? by John Springford and Simon Tilford 30 October 2017 Are economic factors to blame for the rise of populism, or is it a cultural backlash? The answer is a bit of both: economic
Populism culture or economics? by John Springford and Simon Tilford 30 October 2017 Are economic factors to blame for the rise of populism, or is it a cultural backlash? The answer is a bit of both: economic
THERE ARE NO RICH PEOPLE IN THE WORLD
 THERE ARE NO RICH PEOPLE IN THE WORLD There are no rich people in the world, and there are no poor people. There are just people. The rich may have lots of pieces of green paper that many pretend are worth
THERE ARE NO RICH PEOPLE IN THE WORLD There are no rich people in the world, and there are no poor people. There are just people. The rich may have lots of pieces of green paper that many pretend are worth
CAPPELEN DAMM ACCESS UPDATE: THE PERFECT SLOSH
 CAPPELEN DAMM ACCESS UPDATE: THE PERFECT SLOSH 2 The following article about the American Mid-Term elections in 2010 seeks to explain the surprisingly dramatic swings in the way Americans have voted over
CAPPELEN DAMM ACCESS UPDATE: THE PERFECT SLOSH 2 The following article about the American Mid-Term elections in 2010 seeks to explain the surprisingly dramatic swings in the way Americans have voted over
Piketty s Capital in the 21 st Century. Kevin Hassett AEI
 Piketty s Capital in the 21 st Century Kevin Hassett AEI Capital Income Explosion Scenario As K increases, r declines slowly if the elasticity of substitution is >1 Vast direct and indirect literatures
Piketty s Capital in the 21 st Century Kevin Hassett AEI Capital Income Explosion Scenario As K increases, r declines slowly if the elasticity of substitution is >1 Vast direct and indirect literatures
Nathan Glazer on Americans & inequality
 Nathan Glazer on Americans Americans, unlike the citizens of other prosperous democracies, not to mention those of poor countries, do not seem to care much about inequality. One might think that our attitude
Nathan Glazer on Americans Americans, unlike the citizens of other prosperous democracies, not to mention those of poor countries, do not seem to care much about inequality. One might think that our attitude
Political Inequality Worsens Economic Inequality
 Political Inequality Worsens Economic Inequality Ruy Teixeira is a senior fellow at the Center for American Progress and co-director of a new joint project between the Center and the American Enterprise
Political Inequality Worsens Economic Inequality Ruy Teixeira is a senior fellow at the Center for American Progress and co-director of a new joint project between the Center and the American Enterprise
Political Economy of. Post-Communism
 Political Economy of Post-Communism A liberal perspective: Only two systems Is Kornai right? Socialism One (communist) party State dominance Bureaucratic resource allocation Distorted information Absence
Political Economy of Post-Communism A liberal perspective: Only two systems Is Kornai right? Socialism One (communist) party State dominance Bureaucratic resource allocation Distorted information Absence
Oxfam Education
 Background notes on inequality for teachers Oxfam Education What do we mean by inequality? In this resource inequality refers to wide differences in a population in terms of their wealth, their income
Background notes on inequality for teachers Oxfam Education What do we mean by inequality? In this resource inequality refers to wide differences in a population in terms of their wealth, their income
CASE 12: INCOME INEQUALITY, POVERTY, AND JUSTICE
 CASE 12: INCOME INEQUALITY, POVERTY, AND JUSTICE The Big Picture The headline in the financial section of the January 20, 2015 edition of USA Today read, By 2016 1% will have 50% of total global wealth.
CASE 12: INCOME INEQUALITY, POVERTY, AND JUSTICE The Big Picture The headline in the financial section of the January 20, 2015 edition of USA Today read, By 2016 1% will have 50% of total global wealth.
The Wealth of Hispanic Households: 1996 to 2002
 by Rakesh Kochhar October 2004 1919 M Street NW Suite 460 Washington, DC 20036 Tel: 202-452-1702 Fax: 202-785-8282 www.pewhispanic.org CONTENTS Executive Summary 1 1. Introduction 3 2. Median Net Worth
by Rakesh Kochhar October 2004 1919 M Street NW Suite 460 Washington, DC 20036 Tel: 202-452-1702 Fax: 202-785-8282 www.pewhispanic.org CONTENTS Executive Summary 1 1. Introduction 3 2. Median Net Worth
New Ideas About Income Inequality in A Digitalizing World
 October 3, 2018 New Ideas About Income Inequality in A Digitalizing World At a recent INSEAD alumni event in Zurich, Mark Stabile, INSEAD Professor of Economics, spoke about the topic of income inequality,
October 3, 2018 New Ideas About Income Inequality in A Digitalizing World At a recent INSEAD alumni event in Zurich, Mark Stabile, INSEAD Professor of Economics, spoke about the topic of income inequality,
SOCIAL STRATIFICATION. Jennifer L. Fackler, M.A.
 SOCIAL STRATIFICATION Jennifer L. Fackler, M.A. WHAT IS SOCIAL STRATIFICATION? Social Stratification a system by which a society ranks categories of people in a hierarchy. Based on 4 basic principles:
SOCIAL STRATIFICATION Jennifer L. Fackler, M.A. WHAT IS SOCIAL STRATIFICATION? Social Stratification a system by which a society ranks categories of people in a hierarchy. Based on 4 basic principles:
Introduction. Rising inequality
 Introduction Income inequality has risen in much of the world, sending the issue to the top of the policy agenda. The rise of the top 1% gains the lion s share of attention, but there s also concern about
Introduction Income inequality has risen in much of the world, sending the issue to the top of the policy agenda. The rise of the top 1% gains the lion s share of attention, but there s also concern about
Laissez-Faire vs. Socialism Who is responsible?
 Laissez-Faire vs. Socialism Who is responsible? Warm-Up In your groups discuss the following question: Should the government be responsible in regulating (controlling) businesses? If not, why? If so, how
Laissez-Faire vs. Socialism Who is responsible? Warm-Up In your groups discuss the following question: Should the government be responsible in regulating (controlling) businesses? If not, why? If so, how
ECONOMIC SYSTEMS AND DECISION MAKING. Understanding Economics - Chapter 2
 ECONOMIC SYSTEMS AND DECISION MAKING Understanding Economics - Chapter 2 ECONOMIC SYSTEMS Chapter 2, Lesson 1 ECONOMIC SYSTEMS Traditional Market Command Mixed! Economic System organized way a society
ECONOMIC SYSTEMS AND DECISION MAKING Understanding Economics - Chapter 2 ECONOMIC SYSTEMS Chapter 2, Lesson 1 ECONOMIC SYSTEMS Traditional Market Command Mixed! Economic System organized way a society
How s Life in Denmark?
 How s Life in Denmark? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Denmark generally performs very well across the different well-being dimensions. Although average household net adjusted disposable
How s Life in Denmark? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Denmark generally performs very well across the different well-being dimensions. Although average household net adjusted disposable
Whether these changes are good or bad depends in part on how we adapt to them. But, ready or not, here they come.
 Agenda 21 will transform America but into what??? CHANGES ARE COMING ---- Whether these changes are good or bad depends in part on how we adapt to them. But, ready or not, here they come. The United States
Agenda 21 will transform America but into what??? CHANGES ARE COMING ---- Whether these changes are good or bad depends in part on how we adapt to them. But, ready or not, here they come. The United States
a model for economic and social development in Scotland
 The Common Weal a model for economic and social development in Scotland For 30 years public policy in the UK and in Scotland (though to a lesser extent) has been based on one fundamental principle; that
The Common Weal a model for economic and social development in Scotland For 30 years public policy in the UK and in Scotland (though to a lesser extent) has been based on one fundamental principle; that
The Crisis of the European Union. Weakening of the EU Social Model
 The Crisis of the European Union Weakening of the EU Social Model Vincent Navarro and John Schmitt Many observers argue that recent votes unfavorable to the European Union are the result of specific factors
The Crisis of the European Union Weakening of the EU Social Model Vincent Navarro and John Schmitt Many observers argue that recent votes unfavorable to the European Union are the result of specific factors
How s Life in the United Kingdom?
 How s Life in the United Kingdom? November 2017 On average, the United Kingdom performs well across a number of well-being indicators relative to other OECD countries. At 74% in 2016, the employment rate
How s Life in the United Kingdom? November 2017 On average, the United Kingdom performs well across a number of well-being indicators relative to other OECD countries. At 74% in 2016, the employment rate
Foreign Finance, Investment, and. Aid: Controversies and Opportunities
 Chapter 10 Foreign Finance, Investment, and Aid: Controversies and Opportunities Problems and Policies: international and macro 1 The International Flow of Financial Resources A majority of developing
Chapter 10 Foreign Finance, Investment, and Aid: Controversies and Opportunities Problems and Policies: international and macro 1 The International Flow of Financial Resources A majority of developing
Unit 1: Fundamental Economic Concepts. Chapter 2: Economic Choices and Decision Making. Lesson 4: Economic Systems
 Unit 1: Fundamental Economic Concepts Chapter 2: Economic Choices and Decision Making Lesson 4: Economic Systems 1 Your Objectives After this lesson you should be able to: 1. Describe the characteristics
Unit 1: Fundamental Economic Concepts Chapter 2: Economic Choices and Decision Making Lesson 4: Economic Systems 1 Your Objectives After this lesson you should be able to: 1. Describe the characteristics
The Charactaristics & Consequences of a Capitalist Economy. 62 Summer St. Boston, MA,
 The Charactaristics & Consequences of a Capitalist Economy 62 Summer St. Boston, MA, 02110 www.faireconomy.org info@faireconomy.org 617-423-2148 Defining Capitalism An economic system in which a country
The Charactaristics & Consequences of a Capitalist Economy 62 Summer St. Boston, MA, 02110 www.faireconomy.org info@faireconomy.org 617-423-2148 Defining Capitalism An economic system in which a country
How s Life in Finland?
 How s Life in Finland? November 2017 In general, Finland performs well across the different well-being dimensions relative to other OECD countries. Despite levels of household net adjusted disposable income
How s Life in Finland? November 2017 In general, Finland performs well across the different well-being dimensions relative to other OECD countries. Despite levels of household net adjusted disposable income
How s Life in Mexico?
 How s Life in Mexico? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Mexico has a mixed performance across the different well-being dimensions. At 61% in 2016, Mexico s employment rate was below the OECD
How s Life in Mexico? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Mexico has a mixed performance across the different well-being dimensions. At 61% in 2016, Mexico s employment rate was below the OECD
Globalization: It Doesn t Just Happen
 Conference Presentation November 2007 Globalization: It Doesn t Just Happen BY DEAN BAKER* Progressives will not be able to tackle the problems associated with globalization until they first understand
Conference Presentation November 2007 Globalization: It Doesn t Just Happen BY DEAN BAKER* Progressives will not be able to tackle the problems associated with globalization until they first understand
Rising Share of Americans See Conflict Between Rich and Poor
 Social & Demographic Trends Wednesday, Jan 11, 2012 Rising Share of Americans See Conflict Between Rich and Poor Paul Taylor, Director Kim Parker, Associate Director Rich Morin, Senior Editor Seth Motel,
Social & Demographic Trends Wednesday, Jan 11, 2012 Rising Share of Americans See Conflict Between Rich and Poor Paul Taylor, Director Kim Parker, Associate Director Rich Morin, Senior Editor Seth Motel,
Austerity, Poverty and Social Inequalities: Contextualising Health Inequalities in Scotland
 Austerity, Poverty and Social Inequalities: Contextualising Health Inequalities in Scotland Gerry Mooney Faculty of Social Sciences The Open University in Scotland Understanding the Gap: How Research can
Austerity, Poverty and Social Inequalities: Contextualising Health Inequalities in Scotland Gerry Mooney Faculty of Social Sciences The Open University in Scotland Understanding the Gap: How Research can
How s Life in Norway?
 How s Life in Norway? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Norway performs very well across the OECD s different well-being indicators and dimensions. Job strain and long-term unemployment are
How s Life in Norway? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Norway performs very well across the OECD s different well-being indicators and dimensions. Job strain and long-term unemployment are
Lesson 10 What Is Economic Justice?
 Lesson 10 What Is Economic Justice? The students play the Veil of Ignorance game to reveal how altering people s selfinterest transforms their vision of economic justice. OVERVIEW Economics Economics has
Lesson 10 What Is Economic Justice? The students play the Veil of Ignorance game to reveal how altering people s selfinterest transforms their vision of economic justice. OVERVIEW Economics Economics has
From: John Halpin, Center for American Progress Karl Agne, GBA Strategies
 From: John Halpin, Center for American Progress Karl Agne, GBA Strategies To: RE: Interested Parties AMERICAN VOTERS DID NOT ENDORSE TRUMP S EXTREMIST POLICY AGENDA IN 2016 ELECTION The Center for American
From: John Halpin, Center for American Progress Karl Agne, GBA Strategies To: RE: Interested Parties AMERICAN VOTERS DID NOT ENDORSE TRUMP S EXTREMIST POLICY AGENDA IN 2016 ELECTION The Center for American
Economics Of Migration
 Department of Economics and Centre for Macroeconomics public lecture Economics Of Migration Professor Alan Manning Professor of Economics and Director of the Centre for Economic Performance s research
Department of Economics and Centre for Macroeconomics public lecture Economics Of Migration Professor Alan Manning Professor of Economics and Director of the Centre for Economic Performance s research
Capitalism Breeds Reckless Consumption and Starves the Public Sphere
 Page 1 of 5 Capitalism Breeds Reckless Consumption and Starves the Public Sphere Sunday, December 11, 2016 By Mark Karlin (/author/itemlist/user/45664), Truthout Interview Our culture systemically devalues
Page 1 of 5 Capitalism Breeds Reckless Consumption and Starves the Public Sphere Sunday, December 11, 2016 By Mark Karlin (/author/itemlist/user/45664), Truthout Interview Our culture systemically devalues
How s Life in Sweden?
 How s Life in Sweden? November 2017 On average, Sweden performs very well across the different well-being dimensions relative to other OECD countries. In 2016, the employment rate was one of the highest
How s Life in Sweden? November 2017 On average, Sweden performs very well across the different well-being dimensions relative to other OECD countries. In 2016, the employment rate was one of the highest
COMPARE AND CONTRAST CONSERVATISM AND SOCIALISM REFER TO BURKE AND MARX IN YOUR ANSWER
 COMPARE AND CONTRAST CONSERVATISM AND SOCIALISM REFER TO BURKE AND MARX IN YOUR ANSWER CORE FEATURES OF CONSERVATISM TRADITION Tradition refers to values, practices and institutions that have endured though
COMPARE AND CONTRAST CONSERVATISM AND SOCIALISM REFER TO BURKE AND MARX IN YOUR ANSWER CORE FEATURES OF CONSERVATISM TRADITION Tradition refers to values, practices and institutions that have endured though
How s Life in the United States?
 How s Life in the United States? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, the United States performs well in terms of material living conditions: the average household net adjusted disposable income
How s Life in the United States? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, the United States performs well in terms of material living conditions: the average household net adjusted disposable income
How s Life in Poland?
 How s Life in Poland? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Poland s average performance across the different well-being dimensions is mixed. Material conditions are an area of comparative weakness:
How s Life in Poland? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Poland s average performance across the different well-being dimensions is mixed. Material conditions are an area of comparative weakness:
GDP - AN INDICATOR OF PROSPERITY OR A MISLEADING ONE? CRIVEANU MARIA MAGDALENA, PHD STUDENT, UNIVERSITATEA DIN CRAIOVA, ROMANIA
 GDP - AN INDICATOR OF PROSPERITY OR A MISLEADING ONE? CRIVEANU MARIA MAGDALENA, PHD STUDENT, UNIVERSITATEA DIN CRAIOVA, ROMANIA mag_da64 @yahoo.com Abstract The paper presents a comparative analysis of
GDP - AN INDICATOR OF PROSPERITY OR A MISLEADING ONE? CRIVEANU MARIA MAGDALENA, PHD STUDENT, UNIVERSITATEA DIN CRAIOVA, ROMANIA mag_da64 @yahoo.com Abstract The paper presents a comparative analysis of
HOW ECONOMIES GROW AND DEVELOP Macroeconomics In Context (Goodwin, et al.)
 Chapter 17 HOW ECONOMIES GROW AND DEVELOP Macroeconomics In Context (Goodwin, et al.) Chapter Overview This chapter presents material on economic growth, such as the theory behind it, how it is calculated,
Chapter 17 HOW ECONOMIES GROW AND DEVELOP Macroeconomics In Context (Goodwin, et al.) Chapter Overview This chapter presents material on economic growth, such as the theory behind it, how it is calculated,
How s Life in Iceland?
 How s Life in Iceland? November 2017 In general, Iceland performs well across the different well-being dimensions relative to other OECD countries. 86% of the Icelandic population aged 15-64 was in employment
How s Life in Iceland? November 2017 In general, Iceland performs well across the different well-being dimensions relative to other OECD countries. 86% of the Icelandic population aged 15-64 was in employment
The Great Laissez-Faire Experiment
 AP PHOTO/CHARLES REX ARBOGAST The Great Laissez-Faire Experiment American Inequality and Growth from an International Perspective By David R. Howell December 2013 WWW.AMERICANPROGRESS.ORG Section 1: Introduction
AP PHOTO/CHARLES REX ARBOGAST The Great Laissez-Faire Experiment American Inequality and Growth from an International Perspective By David R. Howell December 2013 WWW.AMERICANPROGRESS.ORG Section 1: Introduction
Italy s average level of current well-being: Comparative strengths and weaknesses
 How s Life in Italy? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Italy s average performance across the different well-being dimensions is mixed. The employment rate, about 57% in 2016, was among the
How s Life in Italy? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Italy s average performance across the different well-being dimensions is mixed. The employment rate, about 57% in 2016, was among the
and government interventions, and explain how they represent contrasting political choices
 Chapter 9: Political Economies Learning Objectives After reading this chapter, students should be able to do the following: 9.1: Describe three concrete ways in which national economies vary, the abstract
Chapter 9: Political Economies Learning Objectives After reading this chapter, students should be able to do the following: 9.1: Describe three concrete ways in which national economies vary, the abstract
How s Life in Portugal?
 How s Life in Portugal? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Portugal has a mixed performance across the different well-being dimensions. For example, it is in the bottom third of the OECD in
How s Life in Portugal? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Portugal has a mixed performance across the different well-being dimensions. For example, it is in the bottom third of the OECD in
In class, we have framed poverty in four different ways: poverty in terms of
 Sandra Yu In class, we have framed poverty in four different ways: poverty in terms of deviance, dependence, economic growth and capability, and political disenfranchisement. In this paper, I will focus
Sandra Yu In class, we have framed poverty in four different ways: poverty in terms of deviance, dependence, economic growth and capability, and political disenfranchisement. In this paper, I will focus
Assembly Line For the first time, Henry Ford s entire Highland Park, Michigan automobile factory is run on a continuously moving assembly line when
 Assembly Line For the first time, Henry Ford s entire Highland Park, Michigan automobile factory is run on a continuously moving assembly line when the chassis the automobile s frame is assembled using
Assembly Line For the first time, Henry Ford s entire Highland Park, Michigan automobile factory is run on a continuously moving assembly line when the chassis the automobile s frame is assembled using
How s Life in Germany?
 How s Life in Germany? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Germany performs well across most well-being dimensions. Household net adjusted disposable income is above the OECD average, but household
How s Life in Germany? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Germany performs well across most well-being dimensions. Household net adjusted disposable income is above the OECD average, but household
How s Life in Hungary?
 How s Life in Hungary? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Hungary has a mixed performance across the different well-being dimensions. It has one of the lowest levels of household net adjusted
How s Life in Hungary? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Hungary has a mixed performance across the different well-being dimensions. It has one of the lowest levels of household net adjusted
Introduction to Cultural Anthropology: Class 14 An exploitative theory of inequality: Marxian theory Copyright Bruce Owen 2010 Example of an
 Introduction to Cultural Anthropology: Class 14 An exploitative theory of inequality: Marxian theory Copyright Bruce Owen 2010 Example of an exploitative theory of inequality: Marxian theory the Marxian
Introduction to Cultural Anthropology: Class 14 An exploitative theory of inequality: Marxian theory Copyright Bruce Owen 2010 Example of an exploitative theory of inequality: Marxian theory the Marxian
To: From: Re: December 5, 2011
 December 5, 2011 To: From: Re: Interested Parties Ben Tulchin and Corey O Neil, Tulchin Research California Decline-to-State (DTS) Voters Show Strong Progressive, Pro-Environment Stance Tulchin Research
December 5, 2011 To: From: Re: Interested Parties Ben Tulchin and Corey O Neil, Tulchin Research California Decline-to-State (DTS) Voters Show Strong Progressive, Pro-Environment Stance Tulchin Research
World Inequality Report 2018 : Indian economic inequality widened since 1980
 World Inequality Report 2018 : Indian economic inequality widened since 1980 According to the World Inequality Lab s World Inequality Report 2018, the richest 1% captured twice as much as the poorest 50%
World Inequality Report 2018 : Indian economic inequality widened since 1980 According to the World Inequality Lab s World Inequality Report 2018, the richest 1% captured twice as much as the poorest 50%
Expert group meeting. New research on inequality and its impacts World Social Situation 2019
 Expert group meeting New research on inequality and its impacts World Social Situation 2019 New York, 12-13 September 2018 Introduction In 2017, the General Assembly encouraged the Secretary-General to
Expert group meeting New research on inequality and its impacts World Social Situation 2019 New York, 12-13 September 2018 Introduction In 2017, the General Assembly encouraged the Secretary-General to
LECTURE 23: A SUMMARY OF CAPITAL IN THE 21 ST CENTURY
 LECTURE 23: A SUMMARY OF CAPITAL IN THE 21 ST CENTURY Dr. Aidan Regan Email: aidan.regan@ucd.ie Website: www.aidanregan.com Teaching blog: www.capitalistdemocracy.wordpress.com Twitter: @aidan_regan #CapitalUCD
LECTURE 23: A SUMMARY OF CAPITAL IN THE 21 ST CENTURY Dr. Aidan Regan Email: aidan.regan@ucd.ie Website: www.aidanregan.com Teaching blog: www.capitalistdemocracy.wordpress.com Twitter: @aidan_regan #CapitalUCD
The Inequalities of. Wealth Distribution: its Economic and. Political Consequences. Dr David Rees
 The Inequalities of Wealth Distribution: its Economic and Political Consequences Dr David Rees Wealth Distribution Exercise Your opinion on wealth distribution is based on what you think is 'fair' or 'unfair'
The Inequalities of Wealth Distribution: its Economic and Political Consequences Dr David Rees Wealth Distribution Exercise Your opinion on wealth distribution is based on what you think is 'fair' or 'unfair'
and with support from BRIEFING NOTE 1
 and with support from BRIEFING NOTE 1 Inequality and growth: the contrasting stories of Brazil and India Concern with inequality used to be confined to the political left, but today it has spread to a
and with support from BRIEFING NOTE 1 Inequality and growth: the contrasting stories of Brazil and India Concern with inequality used to be confined to the political left, but today it has spread to a
Losing Middle America:
 New America Foundation Next Social Contract Initiative Policy Brief Losing Middle America: The polarization of jobs in the United States Lauren Damme, Next Social Contract Initiative Valuable research
New America Foundation Next Social Contract Initiative Policy Brief Losing Middle America: The polarization of jobs in the United States Lauren Damme, Next Social Contract Initiative Valuable research
The 1930s Depression & the New Deal
 The 1930s Depression & the New Deal Why was there a Great Depression in the 1930s? Maldistribution of wealth. A major cause of the depression was the inequality of wealth in America. There were some extremely
The 1930s Depression & the New Deal Why was there a Great Depression in the 1930s? Maldistribution of wealth. A major cause of the depression was the inequality of wealth in America. There were some extremely
Community Voices on Causes and Solutions of the Human Rights Crisis in the United States
 Community Voices on Causes and Solutions of the Human Rights Crisis in the United States A Living Document of the Human Rights at Home Campaign (First and Second Episodes) Second Episode: Voices from the
Community Voices on Causes and Solutions of the Human Rights Crisis in the United States A Living Document of the Human Rights at Home Campaign (First and Second Episodes) Second Episode: Voices from the
How s Life in the Netherlands?
 How s Life in the Netherlands? November 2017 In general, the Netherlands performs well across the OECD s headline well-being indicators relative to the other OECD countries. Household net wealth was about
How s Life in the Netherlands? November 2017 In general, the Netherlands performs well across the OECD s headline well-being indicators relative to the other OECD countries. Household net wealth was about
HOLT CHAPTER 22. Section 1: Capitalism Section 2: Socialism Section 3: Communism HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON
 CHAPTER 22 Section 1: Capitalism Section 2: Socialism Section 3: Communism Section 1: Capitalism Objectives: What are the four factors of production? In what way is a free-market economy an essential aspect
CHAPTER 22 Section 1: Capitalism Section 2: Socialism Section 3: Communism Section 1: Capitalism Objectives: What are the four factors of production? In what way is a free-market economy an essential aspect
Korea s average level of current well-being: Comparative strengths and weaknesses
 How s Life in Korea? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Korea s average performance across the different well-being dimensions is mixed. Although income and wealth stand below the OECD average,
How s Life in Korea? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Korea s average performance across the different well-being dimensions is mixed. Although income and wealth stand below the OECD average,
How s Life in France?
 How s Life in France? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, France s average performance across the different well-being dimensions is mixed. While household net adjusted disposable income stands
How s Life in France? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, France s average performance across the different well-being dimensions is mixed. While household net adjusted disposable income stands
Building a Better America One Wealth Quintile at a Time. Forthcoming in Perspectives on Psychological Science
 Building a Better America 1 Building a Better America One Wealth Quintile at a Time Michael I. Norton Harvard Business School Dan Ariely Duke University Forthcoming in Perspectives on Psychological Science
Building a Better America 1 Building a Better America One Wealth Quintile at a Time Michael I. Norton Harvard Business School Dan Ariely Duke University Forthcoming in Perspectives on Psychological Science
How s Life in the Slovak Republic?
 How s Life in the Slovak Republic? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, the average performance of the Slovak Republic across the different well-being dimensions is very mixed. Material conditions,
How s Life in the Slovak Republic? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, the average performance of the Slovak Republic across the different well-being dimensions is very mixed. Material conditions,
REVERSING INEQUALITY
 TRANSFORMATIONS CHUCK COLLINS REVERSING INEQUALITY Unleashing the Transformative Potential of an Equitable Economy SUMMARY August 2017 The US economy s deep systemic inequalities of income, wealth, power,
TRANSFORMATIONS CHUCK COLLINS REVERSING INEQUALITY Unleashing the Transformative Potential of an Equitable Economy SUMMARY August 2017 The US economy s deep systemic inequalities of income, wealth, power,
UNIT 2. Industrialization, Immigration, and the Gilded Age
 UNIT 2 Industrialization, Immigration, and the Gilded Age -Switch from manpower to machine power - Great Britain leads the way; US catches up in latter 19 th century - factors of production needed for
UNIT 2 Industrialization, Immigration, and the Gilded Age -Switch from manpower to machine power - Great Britain leads the way; US catches up in latter 19 th century - factors of production needed for
Economic Systems. Essential Questions. How do different societies around the world meet their economic systems?
 Economic Systems Essential Questions How do different societies around the world meet their economic systems? What are the advantages and disadvantages of each system? Terms to know: Economics Economist
Economic Systems Essential Questions How do different societies around the world meet their economic systems? What are the advantages and disadvantages of each system? Terms to know: Economics Economist
%: Will grow the economy vs. 39%: Will grow the economy.
 Villains and Heroes on the Economy and Government Key Lessons from Opinion Research At Our Story The Hub for American Narratives we take the narrative part literally. Including that villains and heroes
Villains and Heroes on the Economy and Government Key Lessons from Opinion Research At Our Story The Hub for American Narratives we take the narrative part literally. Including that villains and heroes
Persistent Inequality
 Canadian Centre for Policy Alternatives Ontario December 2018 Persistent Inequality Ontario s Colour-coded Labour Market Sheila Block and Grace-Edward Galabuzi www.policyalternatives.ca RESEARCH ANALYSIS
Canadian Centre for Policy Alternatives Ontario December 2018 Persistent Inequality Ontario s Colour-coded Labour Market Sheila Block and Grace-Edward Galabuzi www.policyalternatives.ca RESEARCH ANALYSIS
The Politics of Emotional Confrontation in New Democracies: The Impact of Economic
 Paper prepared for presentation at the panel A Return of Class Conflict? Political Polarization among Party Leaders and Followers in the Wake of the Sovereign Debt Crisis The 24 th IPSA Congress Poznan,
Paper prepared for presentation at the panel A Return of Class Conflict? Political Polarization among Party Leaders and Followers in the Wake of the Sovereign Debt Crisis The 24 th IPSA Congress Poznan,
Starting in England around 1750, the introduction of new
 Economic Theory 1 Starting in England around 1750, the introduction of new machines powered by steam or by running water in streams and rivers changed the ways people had lived and worked for centuries.
Economic Theory 1 Starting in England around 1750, the introduction of new machines powered by steam or by running water in streams and rivers changed the ways people had lived and worked for centuries.
How s Life in the Czech Republic?
 How s Life in the Czech Republic? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, the Czech Republic has mixed outcomes across the different well-being dimensions. Average earnings are in the bottom tier
How s Life in the Czech Republic? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, the Czech Republic has mixed outcomes across the different well-being dimensions. Average earnings are in the bottom tier
How s Life in Turkey?
 How s Life in Turkey? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Turkey has a mixed performance across the different well-being dimensions. At 51% in 2016, the employment rate in Turkey is the lowest
How s Life in Turkey? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Turkey has a mixed performance across the different well-being dimensions. At 51% in 2016, the employment rate in Turkey is the lowest
Economic Geography Chapter 10 Development
 Economic Geography Chapter 10 Development Development: Key Issues 1. Why Does Development Vary Among Countries? 2. Where Are Inequalities in Development Found? 3. Why Do Countries Face Challenges to Development?
Economic Geography Chapter 10 Development Development: Key Issues 1. Why Does Development Vary Among Countries? 2. Where Are Inequalities in Development Found? 3. Why Do Countries Face Challenges to Development?
Employment Regulation and French Unemployment: Were the French Students Right After All? David R. Howell and John Schmitt *
 April 14, 2006 Employment Regulation and French Unemployment: Were the French Students Right After All? David R. Howell and John Schmitt * After weeks of massive demonstrations, the French government has
April 14, 2006 Employment Regulation and French Unemployment: Were the French Students Right After All? David R. Howell and John Schmitt * After weeks of massive demonstrations, the French government has
How s Life in Switzerland?
 How s Life in Switzerland? November 2017 On average, Switzerland performs well across the OECD s headline well-being indicators relative to other OECD countries. Average household net adjusted disposable
How s Life in Switzerland? November 2017 On average, Switzerland performs well across the OECD s headline well-being indicators relative to other OECD countries. Average household net adjusted disposable
Since this chapter looks at economics systems and globalization, we will also be adding Chapter 15 which deals with international trade.
 Monday, January 30 Tuesday, January 31 Since this chapter looks at economics systems and globalization, we will also be adding Chapter 15 which deals with international trade. Three Economic Questions
Monday, January 30 Tuesday, January 31 Since this chapter looks at economics systems and globalization, we will also be adding Chapter 15 which deals with international trade. Three Economic Questions
ECON U.S. Economic History II John Lovett. Exam 1 - Fall 2015
 Exam 1 - Fall 2015 Use a code name to take this exam. Write your real name and your code name on the noc sheet when you leave. Code Name: Objective Section: 70 points 2.0 pts each, unless otherwise noted
Exam 1 - Fall 2015 Use a code name to take this exam. Write your real name and your code name on the noc sheet when you leave. Code Name: Objective Section: 70 points 2.0 pts each, unless otherwise noted
Glasnost and the Intelligentsia
 Glasnost and the Intelligentsia Ways in which the intelligentsia affected the course of events: 1. Control of mass media 2. Participation in elections 3. Offering economic advice. Why most of the intelligentsia
Glasnost and the Intelligentsia Ways in which the intelligentsia affected the course of events: 1. Control of mass media 2. Participation in elections 3. Offering economic advice. Why most of the intelligentsia
INEQUALITY IN BANGLADESH Facts, Sources, Consequences and Policies
 Bangladesh Economists Forum INEQUALITY IN BANGLADESH Facts, Sources, Consequences and Policies Azizur Rahman Khan Qazi Kholiquzzaman Ahmad June 21-22, 2014 1 B E F F i r s t C o n f e r e n c e, H o t
Bangladesh Economists Forum INEQUALITY IN BANGLADESH Facts, Sources, Consequences and Policies Azizur Rahman Khan Qazi Kholiquzzaman Ahmad June 21-22, 2014 1 B E F F i r s t C o n f e r e n c e, H o t
Politics and Prosperity ( )
 America: Pathways to the Present Chapter 14 Politics and Prosperity (1920 1929) Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey. All rights reserved.
America: Pathways to the Present Chapter 14 Politics and Prosperity (1920 1929) Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey. All rights reserved.
Democracy or Dictatorship: Does It Make a Difference?
 Democracy or Dictatorship: Does It Make a Difference? Does regime type make a difference to material well-being? Do democracies produce higher economic growth? Do democracies produce higher economic growth?
Democracy or Dictatorship: Does It Make a Difference? Does regime type make a difference to material well-being? Do democracies produce higher economic growth? Do democracies produce higher economic growth?
GCPH Seminar Series 12 Seminar Summary Paper
 Geoffrey Pleyers FNRS Researcher & Associate Professor of Sociology, Université de Louvain, Belgium and President of the Research Committee 47 Social Classes & Social Movements of the International Sociological
Geoffrey Pleyers FNRS Researcher & Associate Professor of Sociology, Université de Louvain, Belgium and President of the Research Committee 47 Social Classes & Social Movements of the International Sociological
Recession in Japan Part I
 Recession in Japan Part I Deep-rooted problems by Shima M. Yuko April, 2005 Although economic downturns are universal phenomena in recent years, Japan has been suffering from a severe economic recession
Recession in Japan Part I Deep-rooted problems by Shima M. Yuko April, 2005 Although economic downturns are universal phenomena in recent years, Japan has been suffering from a severe economic recession
Ten Economic Lessons from President Obama s State of the Union Address
 Date: March 7, 2013 To: Friends of and Greenberg Quinlan Rosner From: Stan Greenberg, James Carville, and Erica Seifert Ten Economic Lessons from President Obama s State of the Union Address 1. The economy
Date: March 7, 2013 To: Friends of and Greenberg Quinlan Rosner From: Stan Greenberg, James Carville, and Erica Seifert Ten Economic Lessons from President Obama s State of the Union Address 1. The economy
Why do some societies produce more inequality than others?
 Why do some societies produce more inequality than others? Author: Ksawery Lisiński Word count: 1570 Jan Pen s parade of wealth is probably the most accurate metaphor of economic inequality. 1 Although
Why do some societies produce more inequality than others? Author: Ksawery Lisiński Word count: 1570 Jan Pen s parade of wealth is probably the most accurate metaphor of economic inequality. 1 Although
