Sample Examination One Answers RUBRIC FREE RESPO SE QUESTIO S. 1. Political participation in the United States can take place in various forms.
|
|
|
- Ferdinand Fields
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 79 RUBRIC FREE RESPO SE QUESTIO S 1. Political participation in the United States can take place in various forms. a) Other than voting, identify two ways that Americans participate politically. b) Explain one impact that the first type of political participation you identified in (a) might have on the political system. c) Explain one impact that the second type of political participation you identified in (a) might have on the political system. d) Explain one reason why voter turnout among young people is traditionally lower than voter turnout among older people. General Comments This question asks students to demonstrate their knowledge of voter participation, how Americans vote and the impact that the participation has on the system. It also requires students to recognize and explain why young people don t vote in as high of numbers as older voters. In (a) student are required to identify two ways that Americans participate politically, other than voting. In (b) students are required to explain one way that the first type of political participation identified in (a) might have on the political system. In (c) students are required to explain the impact that the second type of political participation in (b) might have on the political system. In (d) students must explain one reason why voter turnout among young people is lower than the voter turnout among older people.. 5 Points total Scoring Guidelines a) Identification of two ways that Americans participate politically, other than voting. = 1 point Note: Two types of participation must be identified to earn 1 point. Some possible ways to participate: Join an interest group Donate to a campaign Work in a campaign Demonstrate for or against an issue Speak out write an editorial, write a letter/ to a politician, give testimony at a public hearing Run for public office
2 80 Section II b) Explain one impact of the first example given in (a) = 1 Point Note: 1 point is earned by an accurate explanation of one impact of the first type of political participation identified in (a). Some possible explanations may include: Interest groups have the impact of representing a view with the power and influence of a group behind it. Interest groups also promote candidates through voter mobilization getting out the vote. Joining an interest group can magnify the influence of one individual. Donating to the campaign of a candidate permits candidates to run for office as it takes money to gain TV time for commercials and pay for a staff. It is expensive to run so this provides candidates with less money some help to overcome candidates with money. Working in a campaign provides needed workers to elect a candidate. It provides political experience for the campaign workers to observe and understand the electoral process. Demonstrations provide a way for citizens who feel passionately about a policy to express their views (positive or negative) with the satisfaction that others also feel as they do. It provides a way to learn political organization in order to stage the demonstration. This sends a message not only to political officials but to other citizens without fear of punishment. Speaking out, such as writing opinions, permits citizens to express their views on a policy or issue without fear of punishment. Letter to Editor can be read not only by politicians who read the paper, but also by other citizens; permits an exchange of ideas and beliefs in the community. Letter to political leaders allows those in power to see the support or disapproval of policy that is being presented and debated and take it into consideration. c) Explain one impact of the second example given in (a) = 1 Point Note: 1 point is earned by an accurate explanation of one impact of the second type of political participation identified in (a). Some possible explanations may include: Can be any of those above but must be two different ones. Demonstrations and speaking out must emphasize the differences between the two.
3 81 Demonstrations are with others, organized and possibly stem from an interest group. Speaking out such as writing editorials or letters to political leaders can be done and motivated by individual motives not necessarily through groups. d) Explain one reason why voter turnout among young people is traditionally lower than voter turnout among older people. = 2 Points Note: 1 or 2 points are earned by an accurate explanation of one reason why voter turnout among young people is traditionally lower than voter turnout among older people. 1 point is earned by a simple description of a difference between young and older voters. 2 points are earned by a response that explains HOW or WHY voter turnout is traditionally lower among young people. Some possible explanations may include: Younger voters: Have not had much political experience and understanding of issues and candidates. Issues don t seem to affect them, ie., Social Security, child care, financial investments, taxes. Busy with beginning their career and more focused on their education and building a career. May be more affected by voter registration process, since they may not have fixed residences. Older voters: Have more political experience and understanding of issues and candidates. Issues more directly affect them, ie., Social Security, child care, financial investments, taxes Either set in their career and have time to study political issues. May be drawn to issues due to their career, ie., education, environment OTE: In order to gain two points for d the student must explain the reason for BOTH young people and older voters. A correct explanation for each group of voters gains a point. If the explanation only addresses young voters the response only gains one point.
4 82 Section II Point Matrix (5 points maximum) ID two ways to participate One impact of participation One impact of participation Explanation voter turnout younger v older 1 point 1 point 1 point 1 or 2 points 1 point maximum 1 point maximum 1 point maximum 2 points maximum 2. The delegates that attended the Constitutional Convention held many different views about what government structure and functions should be included in the Constitution. a) Identify and explain two different issues that caused disagreement among delegates to the Constitutional Convention. b) For each of the issues you identified in (a), identify and describe a compromise made by delegates at the Constitutional Convention. c) Describe one Constitutional provision that resulted from a compromise at the Convention that was amended later in history and explain why it was amended. General Comments This question asks students to demonstrate knowledge concerning the disagreements of the delegates during the Constitutional Convention and how those disagreements led to compromises. It requires students to link issues chosen in part (a) to compromises made by delegates at the Convention in part (b). Students must also provide knowledge of how the compromises sometimes continued to evolve, as evidenced in Constitutional amendments. The explanation in part (c) does not require linkage to the points made in (a) and (b). 6 Points Total Scoring Guidelines: a) Identification and explanation of two issues in which Constitutional delegates disagreed = 2 points Note: 1 point is earned for identification and explanation of one issue that caused disagreement among delegates. 1 point is earned for identification and explanation of a second issue that caused disagreement among delegates.
5 83 Possible identification and explanations: Slavery cannot prohibit it due to the south s dependency on it economically as agricultural workers. Apportionment of members of the House whether to count slaves as people to determine representation in the House of Representatives. Voter requirements states differed on who should vote in determining national property requirements to do so. Representation in the House and Senate based on population or equal representation, large states v small states. Selection of the president by national legislature or popular election. b) Identification and description of a compromise based on the issues explained in (a) = 2 points Note: 1 point is earned for identification and description of one compromise at the Convention. 1 point is earned for identification and description of a second compromise at the Convention. Possible identification and descriptions: 3/5 Compromise 3/5 of the slaves in a state would be counted toward the population that would determine a state s representation in the House of Representatives. Slave Trade importation of slaves cannot be prohibited by Congress for 20 years, until Voter requirements rather than national requirements permit states to determine their own, age, property requirements, gender of citizens permitted to vote. Great Compromise The House to be based on population to satisfy those believing in a more democratic body and large state argument. The Senate to be based on equal representation to satisfy small states to have equal power and authority to protect their interests. Electoral college selection of president by electors chosen by the states. c) Description and explanation of one Constitutional compromise later amended = 2 Points Note: 1 point is earned for the description of a Constitutional provision that resulted from a compromise that was later amended. 1 point is earned for an explanation for why the provision that resulted from a compromise was amended.
6 84 Section II Possible descriptions and explanations 3/5 Compromise 14th Amendment clarified citizenship as those born in U.S. or those naturalized. This made former slaves citizens, who would now be counted 100% as representation for the House. Slave Trade 13th Amendment ended slavery helped by the abolitionist movement and the Civil War. Federal government protection of individual rights, in theory, to end slavery. Great Compromise selection of senators by state legislatures changed to direct popular vote. Voter requirements determined by states: 15th Amendment gave freedmen, or former slaves the right to vote national protection. 19th Amendment gave women the right to vote national standards and protection 26th Amendment guaranteed right of 18 year olds to vote national standards due to pressures of the Vietnam War Point Matrix 6 points maximum ID & Explain ID & Explain ID & Describe ID & Describe Describe & Explain 1 point 1 point 1 point 1 point 1 or 2 points 1 point max. 1 point max. 1 point max. 1 point max. 2 points max 3. Once elected presidents have found that it is difficult to fulfill campaign promises and policy preferences. a) Identify and explain two formal checks that other branches may use to challenge presidential goals. b) Explain two methods (formal or informal) that the president may use to overcome opposition to his policy goals. c) Explain one reason that modern presidents (since 1945) have often found it easier to reach their goals than have presidents of the past. General Comments: This question asks students to demonstrate their knowledge of checks and balances as it relates to the executive branch. In part a students must identify and explain two formal checks that either the legislature or judicial have to challenge presidential goals. In part b students are to explain two methods the president may use to overcome this opposition. The explanation may use either formal or informal powers of the president. In part c students must describe one reason that modern presidents find it easier to
7 85 accomplish their goals than those before This requires students to understand factors that have shaped the modern presidency since Points Total Scoring Guidelines: a) Identification and explanation of 2 formal checks other branches use to check goals of the president = 2 points. Note: 1 point is earned for a correct identification and explanation of one formal check another branch uses to check goals of the president. 1 point is earned for a correct identification and explanation of a second check another branch uses to check goals of the president. Possible identification and explanations may include: Congress may override a presidential veto with 2/3 vote in each house to prevent the president from getting his version of a bill. Congress may refuse to act on a program the president is promoting preventing him from fulfilling a campaign promise. The Senate may refuse to approve his judicial and bureaucratic appointment due to conflicting views between the Senate and the President. Courts may make decisions that support policies that are counter to the president s policies. Federal courts may rule that the president has exceeded his powers that his actions are unconstitutional. b) Explanation of two methods (formal or informal) used by the president to overcome opposition = 2 points. Note: 1 point is earned by an accurate explanation of one method used by the president to overcome opposition. 1 point is earned by an accurate explanation of a second method used by the president to overcome opposition. Possible explanations may include: President may veto a bill that Congress submits to him that does not include his goals. President may take his case to the public through the media in order to gain support for his view.
8 86 Section II President may make a recess appointment to the bureaucracy that does not require immediate Senate approval. President may begin a similar policy initiative that circumvents the Court s decision. President may negotiate with key leaders in Congress to get support for his initiatives. As openings occur in the federal court system, the president may make appointments more in line with his views. c) Explanation of the ability of modern presidents to accomplish this more than past presidents = 2 points Note: 1 or 2 points are earned by an accurate explanation of a reason why modern presidents have often found it easier to reach their goals than have presidents of the past. 1 point is earned for a simple description of a change that has allowed modern presidents to circumvent checks from other branches of government. 2 points are earned for a response that explains HOW or WHY modern presidents are more likely to circumvent checks from other branches of government. Possible explanations may include: Media Past presidents did not have the advantage of communicating with the voters through the media. Modern presidents since 1945 have had the radio, TV and internet to appeal to citizens to promote their views. Modern presidents have use of the bully pulpit. President as Policy-maker Past presidents were not seen as having the power to develop and promote policy but rather to react to the policy sent to them by Congress. Modern presidents are looked to for domestic and foreign goals of their own separate from Congress. Modern presidents must articulate their programs during the campaign and are expected to follow through as campaign promises. Growing interconnections among modern nations. The modern president has a world stage much larger than previous presidents. Point Matrix 6 points total ID & Explain ID & Explain One Method One Method Explanation Modern & Past 1 point 1 point 1 point 1 point 1 or 2 points 1 point maximum 1 point maximum 1 point maximum 1 point maximum 2 points maximum
9 87 AMERICA VIEWS REGARDI G THE EED FOR A THIRD PARTY Parties Adequate Third Party Needed January, June, January, June, January, January, January, Numbers in percentages Source: Gallup.com Question: In your view, do the Republican and Democratic parties do an adequate job of representing the American people, or do they do such a poor job that a third major party is needed? 4. a) Using the data in the chart above, describe the changes in the attitudes of American citizens toward the need for a third party in the American political system. b) Identify and explain two formal impediments to the development of third parties in the United States. c) Describe two contributions that third parties have made to the American political system. General Comments: Students must demonstrate an ability to read and interpret the chart in addition to demonstrating knowledge regarding third parties in the United States. In part a students must interpret the chart as it relates to dissatisfaction with the Republicans and Democrats and support a third party in the United States. In part b students must identify and explain two formal ways that third parties are discouraged in the U.S. system. In part c students must recognize two contributions third parties have made to the American political system.
10 88 Section II 5 Points Total Scoring Guidelines: a) Describe attitude changes of Americans toward need for third party = 1 Point Note: 1 point is earned by an accurate description of attitude changes toward third parties as reflected in the chart. Possible Descriptions may include: The trend from indicates declining satisfaction with the 2 parties until it reached a low of 33% in However as the presidential election approached in 2008 those that felt the two parties were adequate recovered to 47%. General satisfaction with a 2-party system is indicated but from January, 2007 January 2008 over 50% of Americans felt a third party necessary indicating dissatisfaction with the two parties. Satisfaction with the two-party system was never again as high as the 56% that responded in 2004 demonstrating some support for a third party. b) Identification and explanation of two impediments to third parties in American system = 2 points Note: 1 point is earned for correctly identifying and explaining one formal impediment to the development of third parties in the United States. 1 point is earned for correctly identifying and explaining a second formal impediment to the development of third parties in the United States. Possible identifications and explanations may include: Electoral college awards votes with a winner take all making it difficult for third parties to gain votes to win. 50 state ballots with different qualifications make it difficult for a third party, with less organization, to meet those demands and get on all 50 ballots. No national ballot with national guidelines to make it easier for third parties to organize successfully. Winner-take-all electoral system applies to most national elected positions as well as many state and local ones. The U.S. traditionally has had only two parties throughout its history. The U.S. consensual political culture may not leave room for a third party alternative.
11 89 c) Description of two contributions third parties have made to the American system = 2 points Note: 1 point is earned for an accurate description of one contribution that third parties have made to the American political system. 1 point is earned for an accurate description of a second contribution that third parties have made to the American political system. Possible descriptions may include: Third parties may pull more voters into the system increasing the number of voters. Third party candidates may pull enough votes from a candidate to dictate the winner of an election. Third parties may attract disaffected voters bringing them into the political system increasing political participation by the citizens. Third parties bring issues into the political discussion/debates that may not have been presented by the two main parties. Reforms advocated by third parties have been incorporated by one or both of the major political parties. Attitude change Point Matrix 5 Points Total ID & Explain ID & Explain Contribution Contribution 1 Point 1 Point 1 Point 1 Point 1 Point 1 Point Max. 1 Point Max. 1 Point Max. 1 Point Max. 1 Point Max.
RUBRICS FOR FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS
 RUBRICS FOR FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS 1. Using the chart above answer the following: a) Describe an electoral swing state and explain one reason why the U. S. electoral system magnifies the importance of
RUBRICS FOR FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS 1. Using the chart above answer the following: a) Describe an electoral swing state and explain one reason why the U. S. electoral system magnifies the importance of
US Government Module 3 Study Guide
 US Government Module 3 Study Guide There are 3 branches of government. Module 3 will cover the legislative and execute and module 4 will cover the judicial. 3.01 The Legislative Branch aka Congress Established
US Government Module 3 Study Guide There are 3 branches of government. Module 3 will cover the legislative and execute and module 4 will cover the judicial. 3.01 The Legislative Branch aka Congress Established
ORGANIZING TOPIC: NATIONAL GOVERNMENT: SHAPING PUBLIC POLICY STANDARD(S) OF LEARNING
 ORGANIZING TOPIC: NATIONAL GOVERNMENT: SHAPING PUBLIC POLICY STANDARD(S) OF LEARNING GOVT.9 The student will demonstrate knowledge of the process by which public policy is made by a) examining different
ORGANIZING TOPIC: NATIONAL GOVERNMENT: SHAPING PUBLIC POLICY STANDARD(S) OF LEARNING GOVT.9 The student will demonstrate knowledge of the process by which public policy is made by a) examining different
Ch. 5 Test Legislative Branch Government
 Name: Date: 1. In 1998, California had forty-five representatives in the U.S. House of Representatives while Louisiana had seven. What accounts for the difference in these numbers? A. area of the states
Name: Date: 1. In 1998, California had forty-five representatives in the U.S. House of Representatives while Louisiana had seven. What accounts for the difference in these numbers? A. area of the states
Ohio s State Tests ITEM RELEASE SPRING 2015 AMERICAN GOVERNMENT
 Ohio s State Tests ITEM RELEASE SPRING 2015 AMERICAN GOVERNMENT Table of Contents Questions 1 44: Content Summary and Answer Key...iv Question 1: Question and Scoring Guidelines...1 Question 1: Sample
Ohio s State Tests ITEM RELEASE SPRING 2015 AMERICAN GOVERNMENT Table of Contents Questions 1 44: Content Summary and Answer Key...iv Question 1: Question and Scoring Guidelines...1 Question 1: Sample
FORMAL QUALIFICATIONS FOR PRESIDENT TERM AND COMPENSATION
 American Government Chapter 13 Study Guide The Presidency I. Section 1: The President s Job Description 1. I will be able to identify the President s many roles. 2. I will be able to understand the formal
American Government Chapter 13 Study Guide The Presidency I. Section 1: The President s Job Description 1. I will be able to identify the President s many roles. 2. I will be able to understand the formal
Elections and Voting Behavior
 Edwards, Wattenberg, and Lineberry Government in America: People, Politics, and Policy Fourteenth Edition Chapter 10 Elections and Voting Behavior How American Elections Work Three types of elections:
Edwards, Wattenberg, and Lineberry Government in America: People, Politics, and Policy Fourteenth Edition Chapter 10 Elections and Voting Behavior How American Elections Work Three types of elections:
Unit 7 Our Current Government
 Unit 7 Our Current Government Name Date Period Learning Targets (What I need to know): I can describe the Constitutional Convention and two compromises that took place there. I can describe the structure
Unit 7 Our Current Government Name Date Period Learning Targets (What I need to know): I can describe the Constitutional Convention and two compromises that took place there. I can describe the structure
Creating the Constitution
 G e o g r a p h y C h a l l e n g e Creating the Constitution What compromises emerged from the Constitutional Convention? P R E V I E W On a separate sheet of paper, create a T-chart with the heads Articles
G e o g r a p h y C h a l l e n g e Creating the Constitution What compromises emerged from the Constitutional Convention? P R E V I E W On a separate sheet of paper, create a T-chart with the heads Articles
AP United States Government and Politics
 2018 AP United States Government and Politics Scoring Guidelines College Board, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. AP Central
2018 AP United States Government and Politics Scoring Guidelines College Board, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. AP Central
Student Performance Q&A:
 Student Performance Q&A: 2014 AP United States Government and Politics Free-Response Questions The following comments on the 2014 free-response questions for AP United States Government and Politics were
Student Performance Q&A: 2014 AP United States Government and Politics Free-Response Questions The following comments on the 2014 free-response questions for AP United States Government and Politics were
Ohio s State Tests ITEM RELEASE SPRING 2017 AMERICAN GOVERNMENT
 Ohio s State Tests ITEM RELEASE SPRING 2017 AMERICAN GOVERNMENT Table of Contents Questions 1 15: Content Summary and Answer Key... iii Question 1: Question and Scoring Guidelines... 1 Question 1: Sample
Ohio s State Tests ITEM RELEASE SPRING 2017 AMERICAN GOVERNMENT Table of Contents Questions 1 15: Content Summary and Answer Key... iii Question 1: Question and Scoring Guidelines... 1 Question 1: Sample
Guided Notes: Articles of the Constitution. Name: Date: Per: Score: /5
 Name: Date: Per: Score: /5 Directions: Complete the outline of Article 1 of the U.S. Constitution in groups. Then report to the class on your section. ARTICLE 1: The Legislative Branch Article 1: The Legislative
Name: Date: Per: Score: /5 Directions: Complete the outline of Article 1 of the U.S. Constitution in groups. Then report to the class on your section. ARTICLE 1: The Legislative Branch Article 1: The Legislative
The Executive Branch
 The Executive Branch What is the job of the Executive Branch? The Executive Branch is responsible for executing (or carrying out) the laws made by the Congress. Executive Branch The qualifications to be
The Executive Branch What is the job of the Executive Branch? The Executive Branch is responsible for executing (or carrying out) the laws made by the Congress. Executive Branch The qualifications to be
The Electoral College Content-Area Vocabulary
 The Electoral College Content-Area Vocabulary amendment a law or statement added to the Constitution or other document candidates those people running for political offices citizens members of a nation
The Electoral College Content-Area Vocabulary amendment a law or statement added to the Constitution or other document candidates those people running for political offices citizens members of a nation
NAME CLASS DATE. Section 1 Guided Reading and Review The President s Job Description
 Section 1 Guided Reading and Review The President s Job Description As you read Section 1, fill in a brief description for each of the roles of the President given below. Formal Qualifications for President
Section 1 Guided Reading and Review The President s Job Description As you read Section 1, fill in a brief description for each of the roles of the President given below. Formal Qualifications for President
KENNEDY INSTITUTE POLL: AMERICANS SPEAK ON THE UNITED STATES SENATE
 KENNEDY INSTITUTE POLL: AMERICANS SPEAK ON THE UNITED STATES SENATE In an effort to better understand Americans knowledge of and perceptions about the United States Senate, the Edward M. Kennedy Institute
KENNEDY INSTITUTE POLL: AMERICANS SPEAK ON THE UNITED STATES SENATE In an effort to better understand Americans knowledge of and perceptions about the United States Senate, the Edward M. Kennedy Institute
Analysis of Compulsory Voting in Gujarat
 Research Foundation for Governance: in India Analysis of Compulsory Voting in Gujarat ʺCompulsory voting has been introduced in a variety of contexts in the world to address a range of problems, from low
Research Foundation for Governance: in India Analysis of Compulsory Voting in Gujarat ʺCompulsory voting has been introduced in a variety of contexts in the world to address a range of problems, from low
Analyzing American Democracy
 SUB Hamburg Analyzing American Democracy Politics and Political Science Jon R. Bond Texas A&M University Kevin B. Smith University of Nebraska-Lincoln O Routledge Taylor & Francis Group NEW YORK AND LONDON
SUB Hamburg Analyzing American Democracy Politics and Political Science Jon R. Bond Texas A&M University Kevin B. Smith University of Nebraska-Lincoln O Routledge Taylor & Francis Group NEW YORK AND LONDON
Creating the Constitution 1. Teachers Curriculum Institute. The United States, N 70 W 35 N 30 N. 75 W miles
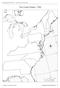 G E O G R A P H Y C H A L L E N G E The United States, 1790 40 N 70 W N W E S 35 N 30 N 0 75 W 100 200 miles 85 W 80 W 0 100 200 kilometers Albers Conic Equal-Area Projection Creating the Constitution
G E O G R A P H Y C H A L L E N G E The United States, 1790 40 N 70 W N W E S 35 N 30 N 0 75 W 100 200 miles 85 W 80 W 0 100 200 kilometers Albers Conic Equal-Area Projection Creating the Constitution
Three Branches of the American Government Packet
 Name: Three es of the American Government Packet THREE BRANCHES OF GOVERNMENT Directions: Use the Civics in Action section in your book to complete the flow chart below by filling in the blanks with words
Name: Three es of the American Government Packet THREE BRANCHES OF GOVERNMENT Directions: Use the Civics in Action section in your book to complete the flow chart below by filling in the blanks with words
Foundations of Government:
 Be able to Define or Explain the following: Foundations of Government: Popular Sovereignty: The idea that government power should belong to the people. Dictatorship: System of government where one ruler
Be able to Define or Explain the following: Foundations of Government: Popular Sovereignty: The idea that government power should belong to the people. Dictatorship: System of government where one ruler
Congressional Institute Reform Study
 Congressional Institute Reform Study Table of Contents Overview 1 Views About Congress 2 Concerns About Congress and Accountability 7 Role of the Media 9 Is Your Voice Heard and tituent Engagement 10 titutional
Congressional Institute Reform Study Table of Contents Overview 1 Views About Congress 2 Concerns About Congress and Accountability 7 Role of the Media 9 Is Your Voice Heard and tituent Engagement 10 titutional
Student Performance Q&A:
 Student Performance Q&A: 2010 AP United States Government and Politics Free-Response Questions The following comments on the 2010 free-response questions for AP United States Government and Politics were
Student Performance Q&A: 2010 AP United States Government and Politics Free-Response Questions The following comments on the 2010 free-response questions for AP United States Government and Politics were
2015 ICCB and CAIT i-pathways.org 1 The GED Mark is a registered trademark of the American Council on Education.
 LESSON 1: MODERN AND HISTORICAL GOVERNMENTS This lesson covers the following information: The different government systems in the world Political ideologies Highlights include the following: Every nation
LESSON 1: MODERN AND HISTORICAL GOVERNMENTS This lesson covers the following information: The different government systems in the world Political ideologies Highlights include the following: Every nation
United States Government End of Course Exam Review
 United States Government End of Course Exam Review Enlightenment Concepts Natural rights- rights that all individuals are born with such as life, liberty, and property. Sovereignty- the idea that the people
United States Government End of Course Exam Review Enlightenment Concepts Natural rights- rights that all individuals are born with such as life, liberty, and property. Sovereignty- the idea that the people
Separation of Powers
 Separation of Powers Separation of Powers: The Legislative Branch The legislative branch of government is Congress. Congress consists of the House of Representatives and the Senate Members of the House
Separation of Powers Separation of Powers: The Legislative Branch The legislative branch of government is Congress. Congress consists of the House of Representatives and the Senate Members of the House
American History 11R
 American History 11R 3 Branches of Government Legislative Branch To Make the Laws Executive Branch To Enforce the Laws Judicial Branch To Interpret the Laws Legislative Branch Article I of the Constitution.
American History 11R 3 Branches of Government Legislative Branch To Make the Laws Executive Branch To Enforce the Laws Judicial Branch To Interpret the Laws Legislative Branch Article I of the Constitution.
AP US Government Top 20 Topics
 AP US Government Top 20 Topics These topics have made up one-third of all mult-choice questions and one-quarter of all free-response questions. Your goal is a 4-5, so you are shooting for getting 62% of
AP US Government Top 20 Topics These topics have made up one-third of all mult-choice questions and one-quarter of all free-response questions. Your goal is a 4-5, so you are shooting for getting 62% of
AP GOVERNMENT AND POLITICS: UNITED STATES 1999 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1! 8 total points possible on this question.
 AP GOVERNMENT AND POLITICS: UNITED STATES 1999 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1! 8 total points possible on this question. Two ways MEDIA have contributed to candidate-centered presidential campaigns: 1 point
AP GOVERNMENT AND POLITICS: UNITED STATES 1999 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1! 8 total points possible on this question. Two ways MEDIA have contributed to candidate-centered presidential campaigns: 1 point
SAMPLE EXAMINATION ONE
 SAMPLE EXAMINATION ONE SECTION I Time 45 minutes 60 Multiple-Choice Questions Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by either four suggested answers or completions.
SAMPLE EXAMINATION ONE SECTION I Time 45 minutes 60 Multiple-Choice Questions Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by either four suggested answers or completions.
AP US GOVERNMENT & POLITICS UNIT 2 REVIEW
 AP US GOVERNMENT & POLITICS UNIT 2 REVIEW POLITICAL BELIEFS & BEHAVIORS Public Opinion vs. Political Ideology Public opinion: the distribution of the population s beliefs about politics and policy issues.
AP US GOVERNMENT & POLITICS UNIT 2 REVIEW POLITICAL BELIEFS & BEHAVIORS Public Opinion vs. Political Ideology Public opinion: the distribution of the population s beliefs about politics and policy issues.
The Electoral College
 Teacher Notes Activity at a Glance Subject: Social Studies Subject Area: American Government Category: The Constitution Topic: The Electoral College The Electoral College Activity 3 Electoral College and
Teacher Notes Activity at a Glance Subject: Social Studies Subject Area: American Government Category: The Constitution Topic: The Electoral College The Electoral College Activity 3 Electoral College and
U.S. Constitution TEST. Notecards
 U.S. Constitution TEST Notecards How many senators does each state have? Two What are the three branches of government? - Legislative Branch - Executive Branch - Judicial Branch Who is known as the Father
U.S. Constitution TEST Notecards How many senators does each state have? Two What are the three branches of government? - Legislative Branch - Executive Branch - Judicial Branch Who is known as the Father
Semester One Exam American Government
 Semester One Exam American Government Directions: Please do not write on the exam! Mark all of your answers on the scantron provided. There are two parts to the exam, a scantron portion as well as two
Semester One Exam American Government Directions: Please do not write on the exam! Mark all of your answers on the scantron provided. There are two parts to the exam, a scantron portion as well as two
Name Class Period. MAIN IDEA PACKET: Political Behavior AMERICAN GOVERNMENT CHAPTERS 5, 6, 7, 8 & 9
 Name Class Period UNIT 3 MAIN IDEA PACKET: Political Behavior AMERICAN GOVERNMENT CHAPTERS 5, 6, 7, 8 & 9 CHAPTER 5 POLITICAL PARTIES Chapter 5 Section 1: Parties and What They Do Political Parties, essential
Name Class Period UNIT 3 MAIN IDEA PACKET: Political Behavior AMERICAN GOVERNMENT CHAPTERS 5, 6, 7, 8 & 9 CHAPTER 5 POLITICAL PARTIES Chapter 5 Section 1: Parties and What They Do Political Parties, essential
Magruder s American Government
 Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 6 Voters and Voter Behavior 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. The History of Voting Rights The Framers of the Constitution purposely left the power
Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 6 Voters and Voter Behavior 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. The History of Voting Rights The Framers of the Constitution purposely left the power
American Government Diagnostic TEST CLE: DOK Level: 1. Which of these is the main function of the legislative branch?
 American Government 2017-18 Diagnostic TEST CLE: Describe the structure of government and the purposes of laws (with emphasis on the federal and state governments) in general. 1. Which of these is the
American Government 2017-18 Diagnostic TEST CLE: Describe the structure of government and the purposes of laws (with emphasis on the federal and state governments) in general. 1. Which of these is the
Constitution Test Study Guide
 Constitution Test Study Guide Part One: Development of the Constitution Articles of Confederation: America's first government. The 13 states were loosely unified but the government was very weak, with
Constitution Test Study Guide Part One: Development of the Constitution Articles of Confederation: America's first government. The 13 states were loosely unified but the government was very weak, with
Article I. Article III. Article IV. Article V. Article VI. Article VII
 Directions: Read the U.S. Constitution and complete the following questions directly on this handout. Be sure to identify the location of each answer in the Constitution (example: Article I, Section 3,
Directions: Read the U.S. Constitution and complete the following questions directly on this handout. Be sure to identify the location of each answer in the Constitution (example: Article I, Section 3,
Student Performance Q&A:
 Student Performance Q&A: 2011 AP United States Government and Politics Free-Response Questions The following comments on the 2011 free-response questions for AP United States Government and Politics were
Student Performance Q&A: 2011 AP United States Government and Politics Free-Response Questions The following comments on the 2011 free-response questions for AP United States Government and Politics were
Quiz # 5 Chapter 14 The Executive Branch (President)
 Quiz # 5 Chapter 14 The Executive Branch (President) 1. In a parliamentary system, the voters cannot choose a. their members of parliament. b. their prime minister. c. between two or more parties. d. whether
Quiz # 5 Chapter 14 The Executive Branch (President) 1. In a parliamentary system, the voters cannot choose a. their members of parliament. b. their prime minister. c. between two or more parties. d. whether
3 Branches of Government
 3 Branches of Government FILL IN THE BLANKS IN THE SENTENCES BELOW 1. What are the 3 branches of our government?,,. 2. The Branch of our government makes the laws. 3. The Branch of our government enforces
3 Branches of Government FILL IN THE BLANKS IN THE SENTENCES BELOW 1. What are the 3 branches of our government?,,. 2. The Branch of our government makes the laws. 3. The Branch of our government enforces
Section Preview. Participation in a Representative Democracy. Section4
 Section Preview As you read, look for: the four factors that influence governments, the requirements to register to vote in Georgia, and vocabulary terms: political party, interest group, lobbyist, general
Section Preview As you read, look for: the four factors that influence governments, the requirements to register to vote in Georgia, and vocabulary terms: political party, interest group, lobbyist, general
Indicate the answer choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Indicate the answer choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. The Electoral College Process 1. According to the diagram, what is Congress s role in the Electoral College process?
Indicate the answer choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. The Electoral College Process 1. According to the diagram, what is Congress s role in the Electoral College process?
Unit #11: The National Government
 Unit #11: The National Government 1. What document defines the current structure and powers of the national government? A. Magna Carta B. Articles of Confederation C. Constitution of the United States
Unit #11: The National Government 1. What document defines the current structure and powers of the national government? A. Magna Carta B. Articles of Confederation C. Constitution of the United States
REPORT ON POLITICAL ATTITUDES & ENGAGEMENT
 THE TEXAS MEDIA &SOCIETY SURVEY REPORT ON POLITICAL ATTITUDES & ENGAGEMENT VS The Texas Media & Society Survey report on POLITICAL ATTITUDES & ENGAGEMENT Released October 27, 2016 Suggested citation: Texas
THE TEXAS MEDIA &SOCIETY SURVEY REPORT ON POLITICAL ATTITUDES & ENGAGEMENT VS The Texas Media & Society Survey report on POLITICAL ATTITUDES & ENGAGEMENT Released October 27, 2016 Suggested citation: Texas
I. Chapter Overview. Roots of Public Opinion Research. A. Learning Objectives
 I. Chapter Overview A. Learning Objectives 11.1 Trace the development of modern public opinion research 11.2 Describe the methods for conducting and analyzing different types of public opinion polls 11.3
I. Chapter Overview A. Learning Objectives 11.1 Trace the development of modern public opinion research 11.2 Describe the methods for conducting and analyzing different types of public opinion polls 11.3
Election Scrapbook Project
 Election Scrapbook Project Materials: Newspapers, magazines, mailers, internet resources and campaign information; paper, scissors, glue, markers Item 1: Meet the Candidate Item 2: Functions of Political
Election Scrapbook Project Materials: Newspapers, magazines, mailers, internet resources and campaign information; paper, scissors, glue, markers Item 1: Meet the Candidate Item 2: Functions of Political
Magruder s American Government
 Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 6 Voters and Voter Behavior 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 6 Voters and Voter Behavior SECTION 1 The Right to Vote SECTION 2 Voter
Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 6 Voters and Voter Behavior 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 6 Voters and Voter Behavior SECTION 1 The Right to Vote SECTION 2 Voter
Chapter 9: Elections, Campaigns, and Voting. American Democracy Now, 4/e
 Chapter 9: Elections, Campaigns, and Voting American Democracy Now, 4/e Political Participation: Engaging Individuals, Shaping Politics Elections, campaigns, and voting are fundamental aspects of civic
Chapter 9: Elections, Campaigns, and Voting American Democracy Now, 4/e Political Participation: Engaging Individuals, Shaping Politics Elections, campaigns, and voting are fundamental aspects of civic
Geer/Schiller/Segal/Herrera, Gateways to Democracy, 3 rd Edition ISBN w/ MindTap PAC: ISBN text alone: ACGM
 ACGM Geer/Schiller/Segal/Herrera, Gateways to Democracy, 3 rd Edition ISBN w/ MindTap PAC: 9781285852904 ISBN text alone: 9781285858548 GOVT 2305 Federal Government LEARNING OUTCOMES Upon successful completion
ACGM Geer/Schiller/Segal/Herrera, Gateways to Democracy, 3 rd Edition ISBN w/ MindTap PAC: 9781285852904 ISBN text alone: 9781285858548 GOVT 2305 Federal Government LEARNING OUTCOMES Upon successful completion
Crash Course U.S. Government
 Crash Course U.S. Government #1: Introduction Crash Course U.S Government & Politics Name 1. What is government? 2. Why study government? 3. What is politics? 4. What is a republic? What is a democracy?
Crash Course U.S. Government #1: Introduction Crash Course U.S Government & Politics Name 1. What is government? 2. Why study government? 3. What is politics? 4. What is a republic? What is a democracy?
Conceived of Compromises: Creating the U.S. Constitution
 Conceived of Compromises: Creating the U.S. Constitution By USHistory.org, adapted by Newsela staff on 05.18.17 Word Count 1,144 Level 1030L The signing of the Constitution at the Constitutional Convention
Conceived of Compromises: Creating the U.S. Constitution By USHistory.org, adapted by Newsela staff on 05.18.17 Word Count 1,144 Level 1030L The signing of the Constitution at the Constitutional Convention
Presentation Pro. American Government CHAPTER 6 Voters and Voter Behavior
 Presentation Pro 1 American Government CHAPTER 6 Voters and Voter Behavior 1 1 CHAPTER 6 Voters and Voter Behavior 2 SECTION 1 The Right to Vote SECTION 2 Voter Qualifications SECTION 3 Suffrage and Civil
Presentation Pro 1 American Government CHAPTER 6 Voters and Voter Behavior 1 1 CHAPTER 6 Voters and Voter Behavior 2 SECTION 1 The Right to Vote SECTION 2 Voter Qualifications SECTION 3 Suffrage and Civil
Course Objectives for The American Citizen
 Course Objectives for The American Citizen Listed below are the key concepts that will be covered in this course. Essentially, this content will be covered in each chapter of the textbook (Richard J. Hardy
Course Objectives for The American Citizen Listed below are the key concepts that will be covered in this course. Essentially, this content will be covered in each chapter of the textbook (Richard J. Hardy
The Critical Period The early years of the American Republic
 The Critical Period 1781-1789 The early years of the American Republic America after the War New Political Ideas: - Greater power for the people Republic: Represent the Public America after the War State
The Critical Period 1781-1789 The early years of the American Republic America after the War New Political Ideas: - Greater power for the people Republic: Represent the Public America after the War State
Unit 2: Political Beliefs and Behaviors Session 2: Political Participation
 Unit 2: Political Beliefs and Behaviors Session 2: Political Participation Learning Targets How do Americans participate politically? How have voting rights been suppressed within the United States How
Unit 2: Political Beliefs and Behaviors Session 2: Political Participation Learning Targets How do Americans participate politically? How have voting rights been suppressed within the United States How
SSUSH10: IDENTIFY LEGAL, POLITICAL, AND SOCIAL DIMENSIONS OF RECONSTRUCTION.
 SSUSH10: IDENTIFY LEGAL, POLITICAL, AND SOCIAL DIMENSIONS OF RECONSTRUCTION. ELEMENT E: Analyze how the Presidential Election of 1876 marked the end of Reconstruction. Overview q The period of Reconstruction
SSUSH10: IDENTIFY LEGAL, POLITICAL, AND SOCIAL DIMENSIONS OF RECONSTRUCTION. ELEMENT E: Analyze how the Presidential Election of 1876 marked the end of Reconstruction. Overview q The period of Reconstruction
Unit IV Test Political Parties, Media & Interest Groups Practice Test
 Unit IV Test Political Parties, Media & Interest Groups Practice Test 1. Ticket-splitting refers to: (A) the procedure used to conduct computerized, automated vote counting. (B) voting for one party for
Unit IV Test Political Parties, Media & Interest Groups Practice Test 1. Ticket-splitting refers to: (A) the procedure used to conduct computerized, automated vote counting. (B) voting for one party for
PRACTICE TEST ANSWER KEY & SCORING GUIDELINES AMERICAN GOVERNMENT
 Ohio s State Tests PRACTICE TEST ANSWER KEY & SCORING GUIDELINES AMERICAN GOVERNMENT Table of Contents Questions 1 23: Content Summary and Answer Key... iii Question 1: Question and Scoring Guidelines...
Ohio s State Tests PRACTICE TEST ANSWER KEY & SCORING GUIDELINES AMERICAN GOVERNMENT Table of Contents Questions 1 23: Content Summary and Answer Key... iii Question 1: Question and Scoring Guidelines...
The worst illiterate is the political illiterate. He hears nothing, sees nothing, takes no part in political life. He doesn't seem to know that the
 The worst illiterate is the political illiterate. He hears nothing, sees nothing, takes no part in political life. He doesn't seem to know that the cost of living, the price of beans, of flour, of rent,
The worst illiterate is the political illiterate. He hears nothing, sees nothing, takes no part in political life. He doesn't seem to know that the cost of living, the price of beans, of flour, of rent,
EDW Chapter 9 Campaigns and Voting Behavior: Nominations, Caucuses
 EDW Chapter 9 Campaigns and Voting Behavior: Nominations, Caucuses 1. Which of the following statements most accurately compares elections in the United States with those in most other Western democracies?
EDW Chapter 9 Campaigns and Voting Behavior: Nominations, Caucuses 1. Which of the following statements most accurately compares elections in the United States with those in most other Western democracies?
Commission on Political. Reform CONGRESS NEEDS TO SPEND MORE TIME IN WASHINGTON BPC S PROPOSAL
 Commission on Political Taking The Pulse Reform of American Democracy Congressional Reform The Commission on Political Reform (CPR), consisting of 29 thought leaders, puts forth recommendations that foster
Commission on Political Taking The Pulse Reform of American Democracy Congressional Reform The Commission on Political Reform (CPR), consisting of 29 thought leaders, puts forth recommendations that foster
FOR RELEASE APRIL 26, 2018
 FOR RELEASE APRIL 26, 2018 FOR MEDIA OR OTHER INQUIRIES: Carroll Doherty, Director of Political Research Jocelyn Kiley, Associate Director, Research Bridget Johnson, Communications Associate 202.419.4372
FOR RELEASE APRIL 26, 2018 FOR MEDIA OR OTHER INQUIRIES: Carroll Doherty, Director of Political Research Jocelyn Kiley, Associate Director, Research Bridget Johnson, Communications Associate 202.419.4372
How do parties contribute to democratic politics?
 Chapter Objectives Evaluate how political parties both contribute to and detract from democratic politics Trace the history of political parties in the U.S. and assess the contemporary system Compare and
Chapter Objectives Evaluate how political parties both contribute to and detract from democratic politics Trace the history of political parties in the U.S. and assess the contemporary system Compare and
Part 1 Role of Mass Media
 Part 1 Role of Mass Media Questions to Ask What is Mass Media? How does the mass media fulfill its role to provide the public with political information? How does the mass media influence politics? What
Part 1 Role of Mass Media Questions to Ask What is Mass Media? How does the mass media fulfill its role to provide the public with political information? How does the mass media influence politics? What
The Executive Branch 8/16/2009
 The Executive Branch 3.5.1 Explain how political parties, interest groups, the media, and individuals can influence and determine the public agenda. 3.5.2 Describe the origin and the evolution of political
The Executive Branch 3.5.1 Explain how political parties, interest groups, the media, and individuals can influence and determine the public agenda. 3.5.2 Describe the origin and the evolution of political
PROFESSIONAL TEACHING STANDARDS BOARD. United States Constitution Study Guide
 PROFESSIONAL TEACHING STANDARDS BOARD United States Constitution Study Guide Section 21-7-304, Wyoming Statutes, 1969--"All persons hereafter applying for certificates authorizing them to become administrators
PROFESSIONAL TEACHING STANDARDS BOARD United States Constitution Study Guide Section 21-7-304, Wyoming Statutes, 1969--"All persons hereafter applying for certificates authorizing them to become administrators
[ 5.1 ] The Presidency An Overview. [ 5.1 ] The Presidency An Overview. The President's Many Roles. [ 5.1 ] The Presidency An Overview
![[ 5.1 ] The Presidency An Overview. [ 5.1 ] The Presidency An Overview. The President's Many Roles. [ 5.1 ] The Presidency An Overview [ 5.1 ] The Presidency An Overview. [ 5.1 ] The Presidency An Overview. The President's Many Roles. [ 5.1 ] The Presidency An Overview](/thumbs/88/117531174.jpg) [ 5.1 ] The Presidency An Overview [ 5.1 ] The Presidency An Overview The President's Many Roles chief of state term for the President as the ceremonial head of the United States, the symbol of all the
[ 5.1 ] The Presidency An Overview [ 5.1 ] The Presidency An Overview The President's Many Roles chief of state term for the President as the ceremonial head of the United States, the symbol of all the
Chapter 5, Section 3 Creating the Constitution. Pages
 Chapter 5, Section 3 Creating the Constitution Pages 163-168 It didn t take long for people to realize that the Articles of Confederation had many weaknesses. By the mid-1780s most political leaders agreed
Chapter 5, Section 3 Creating the Constitution Pages 163-168 It didn t take long for people to realize that the Articles of Confederation had many weaknesses. By the mid-1780s most political leaders agreed
AP GOVERNMENT COOKBOOK
 AP GOVERNMENT COOKBOOK Unit II: Political Beliefs and Behaviors SYLLABUS - Unit Description II. Political Beliefs and Behaviors (10% - 20%) Individual citizens hold a variety of beliefs about their government,
AP GOVERNMENT COOKBOOK Unit II: Political Beliefs and Behaviors SYLLABUS - Unit Description II. Political Beliefs and Behaviors (10% - 20%) Individual citizens hold a variety of beliefs about their government,
AP U.S. Government and Politics
 Advanced Placement AP U.S. Government and Politics AP* U.S. Government and Politics studies the operations and structure of the U.S. government and the behavior of the electorate and politicians. Students
Advanced Placement AP U.S. Government and Politics AP* U.S. Government and Politics studies the operations and structure of the U.S. government and the behavior of the electorate and politicians. Students
Chapter 9 - The Constitution: A More Perfect Union
 Chapter 9 - The Constitution: A More Perfect Union 9.1 - Introduction When the delegates left Independence Hall in September 1787, they each carried a copy of the Constitution. Their task now was to convince
Chapter 9 - The Constitution: A More Perfect Union 9.1 - Introduction When the delegates left Independence Hall in September 1787, they each carried a copy of the Constitution. Their task now was to convince
This assignment must be completed in your own words. Copying or sharing answers is unacceptable and will face academic dishonesty consequences.
 This assignment must be completed in your own words. Copying or sharing answers is unacceptable and will face academic dishonesty consequences. Directions: Read the U.S. Constitution and complete the following
This assignment must be completed in your own words. Copying or sharing answers is unacceptable and will face academic dishonesty consequences. Directions: Read the U.S. Constitution and complete the following
Campaigns & Elections. US Government POS 2041
 Campaigns & Elections US Government POS 2041 Votes for Women, inspired by Katja Von Garner. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lvqnjwk W7gA For Discussion Do you think that democracy is endangered by the
Campaigns & Elections US Government POS 2041 Votes for Women, inspired by Katja Von Garner. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lvqnjwk W7gA For Discussion Do you think that democracy is endangered by the
AP AMERICAN GOVERNMENT UNIT 1 REVIEW
 AP US Government Unit 1 Review Questions 1. What government gets its authority as a result of religious beliefs? 2. What are two distinguishing features of democracy? 3. The town of Davie has called its
AP US Government Unit 1 Review Questions 1. What government gets its authority as a result of religious beliefs? 2. What are two distinguishing features of democracy? 3. The town of Davie has called its
1. Neither slavery nor involuntary servitude, except as a punishment for crime whereof the party shall have been duly convicted, shall exist within
 Amendments 11-27 Amendment 11 - Judicial Limits. Ratified 2/7/1795. The Judicial power of the United States shall not be construed to extend to any suit in law or equity, commenced or prosecuted against
Amendments 11-27 Amendment 11 - Judicial Limits. Ratified 2/7/1795. The Judicial power of the United States shall not be construed to extend to any suit in law or equity, commenced or prosecuted against
Chapter 10: An Organizational Model for Pro-Family Activism
 Chapter 10: An Organizational Model for Pro-Family Activism This chapter is written as a guide to help pro-family people organize themselves into an effective social and political force. It outlines a
Chapter 10: An Organizational Model for Pro-Family Activism This chapter is written as a guide to help pro-family people organize themselves into an effective social and political force. It outlines a
RECONSTRUCTION
 RECONSTRUCTION 1865-1877 Learning Targets Why was it seen as necessary to reconstruct the South following the Civil War? In general terms, what did President Lincoln want to do with the Southern states?
RECONSTRUCTION 1865-1877 Learning Targets Why was it seen as necessary to reconstruct the South following the Civil War? In general terms, what did President Lincoln want to do with the Southern states?
Elections and Voting Behavior
 Elections and Voting Behavior Running for Office: 4 step process Presidential election process: Nomination caucus/primary national convention general election slate of candidates election held with in
Elections and Voting Behavior Running for Office: 4 step process Presidential election process: Nomination caucus/primary national convention general election slate of candidates election held with in
AP U.S. Government and Politics
 Advanced Placement AP U.S. Government and Politics Course materials required. See 'Course Materials' below. studies the operations and structure of the U.S. government and the behavior of the electorate
Advanced Placement AP U.S. Government and Politics Course materials required. See 'Course Materials' below. studies the operations and structure of the U.S. government and the behavior of the electorate
Who attended the Philadelphia Convention? How was it organized? We the People, Unit 3 Lesson 12
 Who attended the Philadelphia Convention? How was it organized? We the People, Unit 3 Lesson 12 A convention has been called to rewrite Redwood school constitution. We need some delegates (representatives).
Who attended the Philadelphia Convention? How was it organized? We the People, Unit 3 Lesson 12 A convention has been called to rewrite Redwood school constitution. We need some delegates (representatives).
INRL CONTEMPORARY STATE SYSTEMS UNITED STATES
 INRL 207 - CONTEMPORARY STATE SYSTEMS UNITED STATES UNITED STATES KEY TERMS FEDERALISM SEPARATION (DIVISION) OF POWERS CHECKS AND BALANCES IMMIGRATION STATE AND FEDERAL SYSTEM Historically state and local
INRL 207 - CONTEMPORARY STATE SYSTEMS UNITED STATES UNITED STATES KEY TERMS FEDERALISM SEPARATION (DIVISION) OF POWERS CHECKS AND BALANCES IMMIGRATION STATE AND FEDERAL SYSTEM Historically state and local
U.S Presidential Election
 U.S Presidential Election The US has had an elected president since its constitution went into effect in 1789. Unlike in many countries, the Presidential election in the US is rather a year-long process
U.S Presidential Election The US has had an elected president since its constitution went into effect in 1789. Unlike in many countries, the Presidential election in the US is rather a year-long process
NEW HAMPSHIRE: CLINTON PULLS AHEAD OF SANDERS
 Please attribute this information to: Monmouth University Poll West Long Branch, NJ 07764 www.monmouth.edu/polling Follow on Twitter: @MonmouthPoll Released: Tuesday, 3, Contact: PATRICK MURRAY 732-979-6769
Please attribute this information to: Monmouth University Poll West Long Branch, NJ 07764 www.monmouth.edu/polling Follow on Twitter: @MonmouthPoll Released: Tuesday, 3, Contact: PATRICK MURRAY 732-979-6769
AP U.S. Government and Politics
 Advanced Placement AP U.S. Government and Politics Course materials required. See 'Course Materials' below. studies the operations and structure of the U.S. government and the behavior of the electorate
Advanced Placement AP U.S. Government and Politics Course materials required. See 'Course Materials' below. studies the operations and structure of the U.S. government and the behavior of the electorate
The Politics of Reconstruction. The Americans, Chapter 12.1, pages
 The Politics of Reconstruction The Americans, Chapter 12.1, pages 376-382. Lincoln s Plan for Reconstruction Reconstruction was the period during which the United States began to rebuild after the Civil
The Politics of Reconstruction The Americans, Chapter 12.1, pages 376-382. Lincoln s Plan for Reconstruction Reconstruction was the period during which the United States began to rebuild after the Civil
Exam. Name. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Max Weber identified which of the following as a characteristic of? A) red tape B) task
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Max Weber identified which of the following as a characteristic of? A) red tape B) task
AP COMPARATIVE GOVERNMENT AND POLITICS 2006 SCORING GUIDELINES. Question 8
 AP COMPARATIVE GOVERNMENT AND POLITICS 2006 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 8 8 points Part (a): 2 points One point is earned for each of two descriptions of measures taken by Iranian political leaders to
AP COMPARATIVE GOVERNMENT AND POLITICS 2006 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 8 8 points Part (a): 2 points One point is earned for each of two descriptions of measures taken by Iranian political leaders to
Standard &
 Standard 12.3.1 & 12.6.4 12.3.1 Explain how civil society provides opportunities for individuals to associate for social, cultural, religious, economic and political purposes. 12.6.4 Describe the means
Standard 12.3.1 & 12.6.4 12.3.1 Explain how civil society provides opportunities for individuals to associate for social, cultural, religious, economic and political purposes. 12.6.4 Describe the means
AP GOPO CHAPTER 9 READING GUIDE
 AP GOPO CHAPTER 9 READING GUIDE 1. Have levels of political participation increased in recent years? 2. Remember what grassroots is. It s come up once or twice before in class. 3. What is a primary? Are
AP GOPO CHAPTER 9 READING GUIDE 1. Have levels of political participation increased in recent years? 2. Remember what grassroots is. It s come up once or twice before in class. 3. What is a primary? Are
Chapter 8: Mass Media and Public Opinion Section 1 Objectives Key Terms public affairs: public opinion: mass media: peer group: opinion leader:
 Chapter 8: Mass Media and Public Opinion Section 1 Objectives Examine the term public opinion and understand why it is so difficult to define. Analyze how family and education help shape public opinion.
Chapter 8: Mass Media and Public Opinion Section 1 Objectives Examine the term public opinion and understand why it is so difficult to define. Analyze how family and education help shape public opinion.
SOL REVIEW STUDY GUIDE
 SOL REVIEW STUDY GUIDE CIVICS AND ECONOMICS 8 Mr. Gaul Name: Directions: Use any notes from class, online search engines (google), and/or the study guides that you were given in class to complete this
SOL REVIEW STUDY GUIDE CIVICS AND ECONOMICS 8 Mr. Gaul Name: Directions: Use any notes from class, online search engines (google), and/or the study guides that you were given in class to complete this
Mark Levin's Eleven proposed Amendments. Amendment I AN AMENDMENT TO ESTABLISH TERM LIMITS FOR MEMBERS OF CONGRESS
 Mark Levin's Eleven proposed Amendments Amendment I AN AMENDMENT TO ESTABLISH TERM LIMITS FOR MEMBERS OF CONGRESS SECTION 1: No person may serve more than twelve years as a member of Congress, whether
Mark Levin's Eleven proposed Amendments Amendment I AN AMENDMENT TO ESTABLISH TERM LIMITS FOR MEMBERS OF CONGRESS SECTION 1: No person may serve more than twelve years as a member of Congress, whether
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying Chapter 10, you should be able to: 1. Explain the functions and unique features of American elections. 2. Describe how American elections have evolved using the presidential
LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying Chapter 10, you should be able to: 1. Explain the functions and unique features of American elections. 2. Describe how American elections have evolved using the presidential
CALIFORNIA GOVERNMENT AND POLITICS TODAY
 TEST BANK AND STUDY GUIDE TO ACCOMPANY CALIFORNIA GOVERNMENT AND POLITICS TODAY THIRTEENTH EDITION BY MONA FIELD Glendale Community College 1 Test Bank and Study Guide to accompany California Government
TEST BANK AND STUDY GUIDE TO ACCOMPANY CALIFORNIA GOVERNMENT AND POLITICS TODAY THIRTEENTH EDITION BY MONA FIELD Glendale Community College 1 Test Bank and Study Guide to accompany California Government
Role of Political and Legal Systems. Unit 5
 Role of Political and Legal Systems Unit 5 Political Labels Liberal call for peaceful and gradual change of the nations political system, would like to see the government involved in the promotion of the
Role of Political and Legal Systems Unit 5 Political Labels Liberal call for peaceful and gradual change of the nations political system, would like to see the government involved in the promotion of the
Do Now. Who do you think has more power a representative/senator, the president, or a Supreme Court justice? Why?
 Do Now Who do you think has more power a representative/senator, the president, or a Supreme Court justice? Why? Political Parties Today, political parties are one of the most important aspects of American
Do Now Who do you think has more power a representative/senator, the president, or a Supreme Court justice? Why? Political Parties Today, political parties are one of the most important aspects of American
Federal Elections, Union Publications. and. Union Websites
 Federal Elections, Union Publications and Union Websites (Produced by the APWU National Postal Press Association) Dear Brother or Sister: Election Day is Tuesday, November 8, 2008. Working families have
Federal Elections, Union Publications and Union Websites (Produced by the APWU National Postal Press Association) Dear Brother or Sister: Election Day is Tuesday, November 8, 2008. Working families have
