Deficiencies in the Internet Mass Media. Visualization of U.S. Election Results
|
|
|
- Miles Fowler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Deficiencies in the Internet Mass Media Visualization of U.S. Election Results Soon Tee Teoh Department of Computer Science, San Jose State University San Jose, California, USA Abstract - People are increasingly relying on visualizations on the Internet mass media as their primary source of election results. It is thus crucial for the media to provide accurate, informative, and user-friendly visualizations. However, this is not an easy task because of the complexity of the data. Because elections visualization on the Internet mass media is such an important yet challenging task, it is useful to study its effectiveness. We performed user studies on popular Internet visualizations of the November 2006 U.S. mid-term elections. The results show that these visualizations are alarmingly misleading. A large proportion of users were unable to obtain basic and pertinent information from the visualizations. In contrast, users performed much better on the alternative visualizations that we designed. Keywords: information visualization, Internet media, user study 1 Introduction The Internet news media is an important source of information for many people in the information age. Information visualization is not in widespread use in the news media, whether in print or on the web. One notable exception is the reporting of election results in the United States. Not only is visualization shown by the media during the coverage of the elections, it is also widely noted and studied by consumers of the mass media. The image of blue and red states after the 2000 Bush-Gore elections and the 2004 Bush-Kerry elections has significantly influenced the way Americans view politics and society in their country. In the 2000 U.S. presidential elections, for the first time, all major media outlets used blue to represent Democrats and red to represent Republicans, and the terms `blue states' and `red states' gained ubiquitous status after the 2004 presidential elections'' in mainstream political discussions, indicating the tremendous power and influence of this visualization. Another major reason for the popularity of election visualization on the Internet is because of the real-time coverage it provides. People cannot wait till morning to read the print news, which by that time is outdated by several hours. Because races in recent years have been decided by razor-thin margins, people want to get the latest results. Visualization of election results is very challenging because of the complexity of the data. The data types need to be visualized include: candidate (name, party affiliation, and state), electorate (party affiliation and vote), geographical distribution, balance of power, change in balance of power, margin of victory. The effectiveness of the visualization of election results is therefore very important, since it is the one visualization that people pay strong attention to. On one hand, rather than have users pore through tables of data, an effective visualization of the election results will quickly give users a clear understanding of the situation. On the other hand, a poorly-designed visualization may add more confusion than clarity, and force users to turn to competitor's websites for information. Even worse, some visualizations may potentially lead users to draw incorrect conclusions. We conducted a study on the effectiveness of two of the most popular online visualizations of the November 2006 mid-term elections in the United States from Internet news sources. In these elections, the electorate chose governors, and representatives of the House and the Senate in many but not all the states. We study how easy or difficult it is for the users to get information from the visualizations. We also study whether the users were able to obtain accurate information. Furthermore, we created our own alternative visualizations, and tested whether our visualization is more effective than the two Internet mass media visualizations we studied. The results show that these visualizations are alarmingly misleading and difficult to interpret. A large proportion of users were unable to obtain basic and pertinent information from the visualizations. In contrast, users performed much better on the alternative visualizations that we designed. Such severe deficiency of
2 the Internet mass media is of grave concern because of the widespread dependency of the population on the Internet for checking election results, and the financial impact on the various players in this competitive business. 2 Related Works There are multiple ways of mapping the information in the election results to visual properties. A good mapping is able to convey facts to the user. However, a poorlydesigned visualization may confuse the user, obscure data, or even cause the user to draw false conclusions about the data. As Van Wijk [5] points out, visualization is often subjective, warning of the danger the visualizations can cause the user to gain negative knowledge. Sutcliffe et al. [4] performed user tests on an integrated visual thesaurus and results browser system. They found that although users liked using the system, the system did not actually improve performance. Their work shows an actual instance of the limitations of visualization, as the study found that users were confused by a visual metaphor used in the system. In our study, we are also interested in investigating whether the visual metaphor used in election visualization leads to positive knowledge. Plaisant [3] points out that information visualization techniques are being adopted in mainstream applications but users sometimes still struggle in using them, and stresses the need for studies to guide the more effective deployment of visualization functions. The goal of this paper is to study users' experience of using visualization in mainstream media, with the hope that it will lead to improvements. The effectiveness of using red and blue states of the U.S. map to show election results have been studied. For example, Gastner et al. [2] show alternatives by distorting the map based on population. 3 User Studies on Election Visualization We conduct two between-subjects studies comparing the performance of users using Internet mass media election visualization with the alternative visualization that we designed. We selected webpages from CNN.com and MSNBC.com, since they are the top and third most popular online news sites (excluding the Weather Channel) according to a HitWise study in May The subjects in our studies were all undergraduate students in Anonymous University majoring in Computer Science. They were of ages ranging from 19 to 35. beforehand the number of seats in the U.S. Senate and whether they knew beforehand which color represented which party. This is because their knowledge directly impacts their ability to answer some of the questions. The same users participated in both studies. 4 Study I In Study I, we investigate the effectiveness of Internet mass media visualizations in conveying information about the overall Senate election. There are a total of 100 seats in the U.S. Senate. Democrats need to control 51 seats to get a majority, while Republicans need to control 50 seat (because the Vice-President, not a member of the Senate, who can cast the deciding tie-breaker vote, was Republican at the time of the elections). Not all the seats are up for the elections in November 2006 because they have to serve out the rest of their term. The preceding facts are potentially confusing to people unfamiliar with U.S. politics, and make the visualization challenging. There are a few major issues that people reading the election coverage are concerned about: (1) Who will gain control of the Senate, (2) How many seats switched hands between the parties, and (3) Among the seats that are contested in November 2006, how many did each party win? In this study, subjects were divided into three groups, 9 subjects in Group A, 9 in Group B, and 10 in Group C. Group A viewed the display taken from MSNBC.com showing the Senate balance, Group B viewed table from CNN.com of the same data, while Group C were shown a bar chart visualization that we created. These three difference images are shown in Figures 1 through 3. Image A does not show how many of the seats were up for elections, nor how many seats changed hands. Image C does not show how many seats changed hands. Only Image B has all the information. In our test questions, we want to test how informative the visualizations are. We asked each subject the following questions: 1. How many Senate seats are there altogether? 2. At this time, how many have been decided? 3. Among those decided, how many are in Democrats' hands? 4. At this time, is it conclusive who will have majority in the Senate? We selected these questions based on what we believe is the intention of the Internet visualizations tested in Study I; their intention is to convey to the user the status of the Senate race. These visualizations were meant to tell readers whether the Senate race has been decided, if so who won, and if not what the status is. They also had varying familiarity with the American political system. All subjects were asked if they knew
3 Figure 3: Study I: Visualization of overall Senate race (Group C - Our alternate visualization). This visualization is proposed as an alternate to the visualizations marked ``look here'' in Figures 1 and 2. Users were better able to obtain important information about the status of the Senate race than users of those two Internet media visualizations. Figure 1: Study I: Visualization of overall Senate race (Group A - MSNBC.com). Users were told to look at the area marked ``look here'', which is intended to inform the users of the status of the Senate race (Has anyone won? If so, who won? If not, who is ahead, and by how much?). Because the bar chart lacks vital information, users had difficulty interpreting it. 4.1 Results The average score over all questions for Group A (MSNBC.com), B (CNN.com) and C (our alternate) are 0.7, 0.22 and 0.98 respectively. The average time taken by were 160, 189 and 93 respectively. The Chi Square analysis results are shown in Table 1. Group C users performed significantly better than Group B on Q1, Q2 and Q3, and better than Group A on Q1. Group A users performed significantly better than Group B on Q2 and Q3. Table 1: Chi Square Statistical Analysis of Study I. The threshold at p=0.01 is Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Group A vs. B Group A vs. C Group B vs. C Figure 2: Study I: Visualization of overall Senate race (Group B - CNN.com). Users were told to look at the area marked ``look here'', which is intended to inform the users of the status of the Senate race (Has anyone won? If so, who won? If not, who is ahead, and by how much?). Users had difficulty locating relevant data to make conclusions about the Senate race. Users of the MSNBC.com (Figure 1 for Group A) visualization had difficulty answering Question 1: only 30% of them answered that question correctly. Otherwise, the users of the MSNBC.com visualization were able to accurately obtain the other important information asked in the other questions. The CNN.com (Figure 2 for Group B) visualization fared much more poorly. Although all the information is present in the display, users were unable to understand it. 90% of the subjects failed to answer the first three questions correctly. In other words, they were unable to tell the total
4 number of Senate seats, how many have been decided, and how many the Democrats have won. They did better in the last question, but still, only 60% of the subjects were able to answer the last question correctly. Every subject also answered a survey where they were asked if they had known beforehand the total number of seats in the U.S. Senate. Among those who did not know the answer or got the wrong answer, none of the users of the MSNBC.com or CNN.com visualizations answered Question 1 correctly, while all the users of our alternative visualization got that question right. This result is expected for the MSNBC.com visualization because it failed to present this important piece of information. But it is even more alarming that users of CNN.com also failed to answer this question, because this information is actually available in the CNN.com visualization. This just shows that the CNN.com visualization is too confusing for users to obtain this basic information. In contrast, the new alternative visualization that we came up with (Figure 3 for Group C) was much more effective. Every subject answered questions 1 through 3 correctly, and only one subject did not answer Question 4 correctly. On average, subjects also answered the questions significantly faster than users of the other two visualizations, taking about two-thirds the time of MSNBC.com, and half the time of CNN.com. Note that we did not test the number of seats that changed hands, which is shown in the CNN.com visualization, but not in the other two. The CNN.com visualization would probably have performed better on this question, but we did not test it, because we believed that this is not such crucial information compared to the questions that we asked. 4.2 Statistical Analysis We performed Chi Square Test of significance for each pair of Groups for each of the Questions 1 through 4. The results are shown in Figure 2. The results show that users of our alternative visualization performed significantly better (p<0.01) than the users of the CNN.com visualization on Questions 1, 2 and 3, and significantly better than the users of MSNBC.com on Question 1. The users of MSNBC.com performed significantly better than the users of CNN.com on Questions 2 and 3. Performing ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) on the time taken by users of different groups to answer the questions, we found that the difference observed is statistically significant (p<0.001). Users of our alternative visualization took the shortest time to answer the questions, followed by MSNBC.com, and CNN.com users were the slowest. Figure 4: Bar chart comparing the performance on subjects in Study I. On average, users of our alternative visualization performed the best and most quickly, while users of the CNN.com visualization performed the worst and took the longest time. ANOVA analysis shows that the difference in time taken is statistically significant, at p = Problems with the MSNBC.com Visualization The flaws of the MSNBC.com visualization (Figure 1 for Group A) are obvious. It doesn't tell the total number of seats in the Senate. Therefore, users performed poorly on Question 1, which asks, How many Senate seats are there altogether? That is a crucial question because that determines the outcome of who will have control over the Senate, which is the question on top of many readers' minds. The visualization only shows the balance, and a cryptic number 98. It is not clear whether 98 represents the number of seats in the Senate or the number of seats that have been decided. Without knowing this, readers do not know the aggregate outcome of the elections, or whether the outcome is already known. 4.4 Problems with the CNN.com Visualization The table shown in the CNN.com visualization actually contains a lot more information. However, the information is presented in a confusing and misleading manner. One column is labeled Total. It is unclear what total means; it could refer to (1) the total number of seats won by the party in this election, or (2) the total number of seats controlled by the party (including those not contested in this election). Furthermore, it is not clear how many seats are still undecided. For that, the reader would have to read the fine print above the table, and find out that actually 2 seats were still undecided at that time. Consequently, 90% of users answered Questions 1, 2 and 3 wrongly, which is an unacceptably poor result. Not only that, but users also had to try a lot harder to understand the table,
5 taking twice as much time as those using our alternative visualization. 5 Study II In Study II, we investigate the map of the United States showing which states voted for which party. This is an important visualization because it shows the geographic distribution of the support for each party. The color-coded map visualization used to depict the results of the 2000 presidential elections was very influential in shaping the understanding of the U.S. socio-political landscape because it showed a clear divide between the blue states (those who voted for the Democratic candidate) on the west coast and northeastern states, and the red states (those who voted for the Republican candidate) in the rest of the country another color had to be used to show Independent candidates. Thirdly, the media would like to show which states switched parties; in other words, which states voted for a candidate from a different party from the incumbent. Finally, at the time of reporting, the results of some states were still unknown, and that had to be conveyed in the map. The visualization provided by CNN.com is shown in Figure 5 and our alternative visualization is shown in Figure 6. Each subject was asked the following sequence of questions: 1. Was the Senate seat of Indiana (IN) contested? 2. If yes, which party won? 3. Was the Senate seat of Montana (MT) contested? 4. If yes, which party won? 5. Was the Senate seat of Ohio (OH) contested? 6. If yes, which party won? 7. Was the Senate seat of Oregon (OR) contested? 8. If yes, which party won? 9. Was the Senate seat of Connecticut (CT) contested? 10. If yes, which party won? 11. Was the Senate seat of Hawaii (HI) contested? 12. If yes, which party won? 13. Which states switched parties? Figure 5: Study II Group A were shown this image: Visualization of Senate election results from CNN.com. Misleading and ambiguous legend led to some misunderstanding and misinterpretation of results among users. In the November 2006 elections, the color-coded map was once again used to show the results of the elections. However, the information to be shown is much more complex. In these elections, the terms of the Senate seats of some states were not over, and so those seats were not contested. Therefore, they had to be shown in a different color. In addition, there were some Independent candidates who won seats, whereas in the presidential elections, no states voted for any Independent candidate. Consequently, Figure 6: Study II Group B was shown this image: Our alternative visualization of Senate election results. We use a yellow star symbol to represent states which changed parties, and we made the legend more informative. The above questions all test basic information that users should be able to obtain from the figure. The states mentioned in the questions were all located for all the users so that the time taken by users unfamiliar with the geography of the United States to locate the states would not be a variable in the test. We selected the above six states to question the users because they represent the different
6 categories: Republican (IN), Processing (MT), Democrat/party switch (OH), not contested (OR), Independent (CT) and Democrat (HI). Finally, since this visualization attempts to convey the information about which states switched parties, we test this in Question Results The results of Study II are given in Figure 7. For each question, a wrong answer receives 0, and a correct answer receives 1. Questions 1 through 12 can only either be correct or wrong. For question 13, getting all the states correct receives 1, getting none of the states receives 0, while getting some of the states receives the corresponding fraction of the points. Users of our alternative visualization answered the questions more accurately than users of the CNN.com visualization, except for Question 2 (users of both visualizations performed equally) and Question 9 (users of CNN.com performed slightly better). Users of our alternative visualization also took a shorter time answering the questions. 5.2 Statistical Analysis We performed the Chi Square Test of significance on Questions 1 through 12, since the answers are correct/incorrect and therefore nominal. We performed ANOVA on Question 13 since each participant's answer is given a numerical value of correctly. We found that Questions 6 and 13 shows significant differences (at the p<0.02 and p<0.01 levels respectively) in the performance of the users between the two groups. Figure 7: Bar chart comparing the performance on subjects in Study II. Users of our alternative visualization performed significantly better on Questions 6 and 13. Although the average time spent on our alternative visualization was less than for CNN.com, the difference is not statistically significant. In Question 6, many users of the CNN.com map were confused about the bright blue color. They did not interpret the bright blue color to mean that Ohio was contested, and the Democrats won it from the incumbent Republicans. As for Question 13, many users of CNN.com once again did not understand the bright blue and yellow colors to mean change of control. Although the average time spent on our alternative visualization was less than for CNN.com, ANOVA shows that the difference is not statistically significant. 5.3 Problems with the CNN.com Visualization The CNN.com visualization is confusing because of its lack of a clear legend and its poor choice of color scheme. In the legend, the Democrat (DEM) and Republican (GOP) colors are shown as a lighted blue and red sphere respectively. The problem with lighting the sphere is that the color is non-uniform, and therefore does not match with the actual color in the map. The next problem with the legend is that the symbol for states that are still ``processing'' the votes is shown as a saturated dark green circle with double circular arrows. However, this does not match with the actual color of the states shown on the map (MT and VA), which is a faded light green. Furthermore, on the map of the actual states still processing the results, no symbol containing the double circular arrows is shown: the legend does not match the actual visual image used, which is a very serious error. The decision of CNN.com to indicate party switch with brighter colors causes even more confusion. In this visualization, the states of MO, OH, PA and RI are shown in brighter blue because they are states that have switched from Republican to Democrat in these elections. However, this is confusing because this bright blue color matches with the color of Voting shown in the legend. This can mislead users into thinking that these states are actually still voting. The results of our user study indicate that this choice of a misleading visual mapping indeed causes a significant problem. In Question 13 asking which states switched parties, subjects using the CNN.com visualization on average scored On our alternative visualization, which is to indicate party switch with a star symbol, users on average scored (Note: the star symbol was also used by other mainstream print media to show states that switched parties.) There is also no entry in the legend for Independent candidates. VT and CT were both won by Independent candidates. Because CT was also a party switch, it is shown in a brighter color. CNN.com has chosen to use Yellow to be a brighter version of Beige. This is not an intuitive choice of colors, and it is not universally accepted that Yellow is a brighter version of Beige. Once again, this leads to confusion.
7 There is also no entry in the legend for the states whose Senate seats are not contested. On the map, they are shown in grey, which is a sensible choice. However, because of the poor legend, grey could represent many different things besides being uncontested; for example, they could mean processing, too close to call, or voting. 6 Questionnaire All subjects filled out a questionnaire with questions that correct for any variables in the tests. Subjects were asked if they knew before-hand what the total number of seats in the Senate was. If they claimed that they knew it, they were told to write down that number. This knowledge would enable a subject to answer Question 1 of Study I correctly regardless of the visualization used. The responses of the subjects were recorded and reported in Section 4.1, where we report the results of Study I. Subjects were also tested on their familiarity with U.S. politics, for example, the conventional use of Red to represent the Republicans and Blue to represent the Democrats. All visualizations implicitly assume such knowledge. Also, subjects were asked if they were affiliated in any way to CNN.com and MSNBC.com, since such affiliation may bias their answers. All subjects were sufficiently familiar with U.S. government to know about Republicans, Democrats and their respective colors, and also none of the subjects were affiliated with the companies whose visualizations we tested. 7 Conclusions Through our user studies, we conclude that the two examples we studied of Internet mass media visualizations of the 2006 elections were ineffective and misleading. We showed subjects screenshots of visualizations provided by MSNBC.com and CNN.com, two of the most widely-used Internet news sites. The subjects performed poorly on many of the questions asking about basic information. We have provided a detailed analysis of the users' performance on each question and discussion on why the users did not perform well. In summary, we found that users were unable to answer basic questions about the data because of (1) poor choice of visual cues (colors, symbols) in the visualization, (2) lack of a proper legend to explain the colors and symbols used, (3) misleading, ambiguous or wrong legend, and (4) lack of crucial information (such as total number of seats contested). The users thus performed poorly on the two visualizations tested. Users of the Internet visualizations took a longer time and were less accurate in their responses compared to users of our alternative visualization. Our study also thus shows that it is possible for a welldesigned visualization to convey the same information, and this means that the failure of the Internet mass media visualization is due to poor design, and not because the intrinsic complexity of the underlying data or any intrinsic limitations [1] of using a 2D display to present the data. We believe that Internet visualization of election results is very important because many people depend on the Internet for real-time updates of the election results. Many people check the results frequently on the Internet while the various states report their returns and exit polls. Unlike most news stories, where readers prefer to read textual descriptions, view videos and images, for elections, users like to look at tables, charts, maps and other visualizations to analyze the results. It is therefore very crucial that the Internet mass media provide visualizations that are accurate, user-friendly, and clear. This makes the results of our study particularly alarming, because our study shows that users experience great difficulty in using the visualizations, often drawing wrong conclusions. Furthermore, we have also designed some simple alternative visualizations that are able to convey the same information much more clearly. We hope that the Internet mass media will improve on their election visualizations. 8 References [1] C. Freitas, P. Luzzaerdi, R. Cava, M. Wincker, M. Pimenta, and L. Nedel. Evaluating usability of information visualization techniques. In Proceedings of the 5 th Symposium on Human Factors in Computer Systems (IHC 2002), [2] M. Gastner, C. Shalizi, and M. Newman. Maps and cartograms of the 2004 US presidential election results. Advances in Complex Systems, 8: , [3] C. Plaisant. The challenge of information visualization evalution. In Proceedings of the Working Conference on Advanced Visual Interfaces (AVI 04), pages , [4] A. Sutcliffe, M. Ennis, and J. Hu. Evaluating the effectiveness of visual user interfaces for information retrieval. International Journal on Human-Computer Studies, 53(5): , [5] J.J. van Wijk. The value of visualization. In Proceedings of IEEE Visualization (VIS 05), pages 78-86, 2005.
2016 us election results
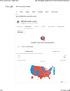 1 of 6 11/12/2016 7:35 PM 2016 us election results All News Images Videos Shopping More Search tools About 243,000,000 results (0.86 seconds) 2 WA OR NV CA AK MT ID WY UT CO AZ NM ND MN SD WI NY MI NE
1 of 6 11/12/2016 7:35 PM 2016 us election results All News Images Videos Shopping More Search tools About 243,000,000 results (0.86 seconds) 2 WA OR NV CA AK MT ID WY UT CO AZ NM ND MN SD WI NY MI NE
The Electoral Process STEP BY STEP. the worksheet activity to the class. the answers with the class. (The PowerPoint works well for this.
 Teacher s Guide Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Projector Copy Instructions: Reading (2 pages; class set) Activity (3 pages; class set) The Electoral Process Learning
Teacher s Guide Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Projector Copy Instructions: Reading (2 pages; class set) Activity (3 pages; class set) The Electoral Process Learning
WISCONSIN SUPREME COURT ELECTIONS WITH PARTISANSHIP
 The Increasing Correlation of WISCONSIN SUPREME COURT ELECTIONS WITH PARTISANSHIP A Statistical Analysis BY CHARLES FRANKLIN Whatever the technically nonpartisan nature of the elections, has the structure
The Increasing Correlation of WISCONSIN SUPREME COURT ELECTIONS WITH PARTISANSHIP A Statistical Analysis BY CHARLES FRANKLIN Whatever the technically nonpartisan nature of the elections, has the structure
The Electoral Process. Learning Objectives Students will be able to: STEP BY STEP. reading pages (double-sided ok) to the students.
 Teacher s Guide Time Needed: One Class Period The Electoral Process Learning Objectives Students will be able to: Materials Needed: Student worksheets Copy Instructions: All student pages can be copied
Teacher s Guide Time Needed: One Class Period The Electoral Process Learning Objectives Students will be able to: Materials Needed: Student worksheets Copy Instructions: All student pages can be copied
Geek s Guide, Election 2012 by Prof. Sam Wang, Princeton University Princeton Election Consortium
 Geek s Guide, Election 2012 by Prof. Sam Wang, Princeton University Princeton Election Consortium http://election.princeton.edu This document presents a) Key states to watch early in the evening; b) Ways
Geek s Guide, Election 2012 by Prof. Sam Wang, Princeton University Princeton Election Consortium http://election.princeton.edu This document presents a) Key states to watch early in the evening; b) Ways
Trump, Populism and the Economy
 Libby Cantrill, CFA October 2016 Trump, Populism and the Economy This material contains the current opinions of the manager and such opinions are subject to change without notice. This material has been
Libby Cantrill, CFA October 2016 Trump, Populism and the Economy This material contains the current opinions of the manager and such opinions are subject to change without notice. This material has been
Election Night Results Guide
 ENR Media Guide Election Night Results Guide North Carolina State Board of Elections Table of Contents Overview of North Carolina Election Night Results... 3 How do I access Election Night Results?...
ENR Media Guide Election Night Results Guide North Carolina State Board of Elections Table of Contents Overview of North Carolina Election Night Results... 3 How do I access Election Night Results?...
SCATTERGRAMS: ANSWERS AND DISCUSSION
 POLI 300 PROBLEM SET #11 11/17/10 General Comments SCATTERGRAMS: ANSWERS AND DISCUSSION In the past, many students work has demonstrated quite fundamental problems. Most generally and fundamentally, these
POLI 300 PROBLEM SET #11 11/17/10 General Comments SCATTERGRAMS: ANSWERS AND DISCUSSION In the past, many students work has demonstrated quite fundamental problems. Most generally and fundamentally, these
Mid Term Elections 2018
 Mid Term Elections 2018 Elections require long and costly preparation. Because of this, extensive planning is required to designate where to geographically campaign based on variables of voter interest.
Mid Term Elections 2018 Elections require long and costly preparation. Because of this, extensive planning is required to designate where to geographically campaign based on variables of voter interest.
NAME CLASS DATE. Section 1 Guided Reading and Review The President s Job Description
 Section 1 Guided Reading and Review The President s Job Description As you read Section 1, fill in a brief description for each of the roles of the President given below. Formal Qualifications for President
Section 1 Guided Reading and Review The President s Job Description As you read Section 1, fill in a brief description for each of the roles of the President given below. Formal Qualifications for President
Who Runs the States?
 Who Runs the States? An in-depth look at historical state partisan control and quality of life indices Part 1: Partisanship of the 50 states between 1992-2013 By Geoff Pallay May 2013 1 Table of Contents
Who Runs the States? An in-depth look at historical state partisan control and quality of life indices Part 1: Partisanship of the 50 states between 1992-2013 By Geoff Pallay May 2013 1 Table of Contents
Introduction to the declination function for gerrymanders
 Introduction to the declination function for gerrymanders Gregory S. Warrington Department of Mathematics & Statistics, University of Vermont, 16 Colchester Ave., Burlington, VT 05401, USA November 4,
Introduction to the declination function for gerrymanders Gregory S. Warrington Department of Mathematics & Statistics, University of Vermont, 16 Colchester Ave., Burlington, VT 05401, USA November 4,
MEASURING THE USABILITY OF PAPER BALLOTS: EFFICIENCY, EFFECTIVENESS, AND SATISFACTION
 PROCEEDINGS of the HUMAN FACTORS AND ERGONOMICS SOCIETY 50th ANNUAL MEETING 2006 2547 MEASURING THE USABILITY OF PAPER BALLOTS: EFFICIENCY, EFFECTIVENESS, AND SATISFACTION Sarah P. Everett, Michael D.
PROCEEDINGS of the HUMAN FACTORS AND ERGONOMICS SOCIETY 50th ANNUAL MEETING 2006 2547 MEASURING THE USABILITY OF PAPER BALLOTS: EFFICIENCY, EFFECTIVENESS, AND SATISFACTION Sarah P. Everett, Michael D.
News English.com Ready-to-use ESL / EFL Lessons
 www.breaking News English.com Ready-to-use ESL / EFL Lessons The Breaking News English.com Resource Book 1,000 Ideas & Activities For Language Teachers http://www.breakingnewsenglish.com/book.html Hillary
www.breaking News English.com Ready-to-use ESL / EFL Lessons The Breaking News English.com Resource Book 1,000 Ideas & Activities For Language Teachers http://www.breakingnewsenglish.com/book.html Hillary
Exposing Media Election Myths
 Exposing Media Election Myths 1 There is no evidence of election fraud. 2 Bush 48% approval in 2004 does not indicate he stole the election. 3 Pre-election polls in 2004 did not match the exit polls. 4
Exposing Media Election Myths 1 There is no evidence of election fraud. 2 Bush 48% approval in 2004 does not indicate he stole the election. 3 Pre-election polls in 2004 did not match the exit polls. 4
A Dead Heat and the Electoral College
 A Dead Heat and the Electoral College Robert S. Erikson Department of Political Science Columbia University rse14@columbia.edu Karl Sigman Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research sigman@ieor.columbia.edu
A Dead Heat and the Electoral College Robert S. Erikson Department of Political Science Columbia University rse14@columbia.edu Karl Sigman Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research sigman@ieor.columbia.edu
Why The National Popular Vote Bill Is Not A Good Choice
 Why The National Popular Vote Bill Is Not A Good Choice A quick look at the National Popular Vote (NPV) approach gives the impression that it promises a much better result in the Electoral College process.
Why The National Popular Vote Bill Is Not A Good Choice A quick look at the National Popular Vote (NPV) approach gives the impression that it promises a much better result in the Electoral College process.
How Should Members of Parliament (and Presidents) Be Elected? E. Maskin Institute for Advanced Study
 How Should Members of Parliament (and Presidents) Be Elected? E. Maskin Institute for Advanced Study What s wrong with this picture? 2005 U.K. General Election Constituency of Croyden Central vote totals
How Should Members of Parliament (and Presidents) Be Elected? E. Maskin Institute for Advanced Study What s wrong with this picture? 2005 U.K. General Election Constituency of Croyden Central vote totals
SPECIAL EDITION 11/6/14
 SPECIAL EDITION 11/6/14 The document below will provide insights on what the new Senate Majority means, as well as a nationwide view of House, Senate and Gubernatorial election results. We will continue
SPECIAL EDITION 11/6/14 The document below will provide insights on what the new Senate Majority means, as well as a nationwide view of House, Senate and Gubernatorial election results. We will continue
To understand the U.S. electoral college and, more generally, American democracy, it is critical to understand that when voters go to the polls on
 To understand the U.S. electoral college and, more generally, American democracy, it is critical to understand that when voters go to the polls on Tuesday, November 8th, they are not voting together in
To understand the U.S. electoral college and, more generally, American democracy, it is critical to understand that when voters go to the polls on Tuesday, November 8th, they are not voting together in
Lab 3: Logistic regression models
 Lab 3: Logistic regression models In this lab, we will apply logistic regression models to United States (US) presidential election data sets. The main purpose is to predict the outcomes of presidential
Lab 3: Logistic regression models In this lab, we will apply logistic regression models to United States (US) presidential election data sets. The main purpose is to predict the outcomes of presidential
ELECTION OVERVIEW. + Context: Mood of the Electorate. + Election Results: Why did it happen? + The Future: What does it mean going forward?
 1 ELECTION OVERVIEW + Context: Mood of the Electorate + Election Results: Why did it happen? + The Future: What does it mean going forward? + Appendix: Polling Post-Mortem 2 2 INITIAL HEADLINES + Things
1 ELECTION OVERVIEW + Context: Mood of the Electorate + Election Results: Why did it happen? + The Future: What does it mean going forward? + Appendix: Polling Post-Mortem 2 2 INITIAL HEADLINES + Things
State Study of Election Methods: A Continuation
 State Study of Election Methods: A Continuation A Summary of Graphics Used in the Committee s Presentations April 2002 THE League of Women Voters of Seattle EDUCATION FUND LWVWA Election Methods Committee
State Study of Election Methods: A Continuation A Summary of Graphics Used in the Committee s Presentations April 2002 THE League of Women Voters of Seattle EDUCATION FUND LWVWA Election Methods Committee
Distorting Democracy: How Gerrymandering Skews the Composition of the House of Representatives
 1 Celia Heudebourg Minju Kim Corey McGinnis MATH 155: Final Project Distorting Democracy: How Gerrymandering Skews the Composition of the House of Representatives Introduction Do you think your vote mattered
1 Celia Heudebourg Minju Kim Corey McGinnis MATH 155: Final Project Distorting Democracy: How Gerrymandering Skews the Composition of the House of Representatives Introduction Do you think your vote mattered
- Bill Bishop, The Big Sort: Why the Clustering of Like-Minded America is Tearing Us Apart, 2008.
 Document 1: America may be more diverse than ever coast to coast, but the places where we live are becoming increasingly crowded with people who live, think and vote like we do. This transformation didn
Document 1: America may be more diverse than ever coast to coast, but the places where we live are becoming increasingly crowded with people who live, think and vote like we do. This transformation didn
Public Opinion and Political Socialization. Chapter 7
 Public Opinion and Political Socialization Chapter 7 What is Public Opinion? What the public thinks about a particular issue or set of issues at any point in time Public opinion polls Interviews or surveys
Public Opinion and Political Socialization Chapter 7 What is Public Opinion? What the public thinks about a particular issue or set of issues at any point in time Public opinion polls Interviews or surveys
The Electoral Process
 Barack Obama speaks at the Democratic National Convention in 2012. Narrowing the Field It s Election Time! Candidates for the larger political parties are chosen at party meetings called conventions. The
Barack Obama speaks at the Democratic National Convention in 2012. Narrowing the Field It s Election Time! Candidates for the larger political parties are chosen at party meetings called conventions. The
ELECTORAL COLLEGE AND BACKGROUND INFO
 ELECTORAL COLLEGE AND BACKGROUND INFO 1. Go to www.270towin.com and select the year 2000 2. How many total popular votes did George W. Bush receive? Al Gore? 3. How many total electoral votes did George
ELECTORAL COLLEGE AND BACKGROUND INFO 1. Go to www.270towin.com and select the year 2000 2. How many total popular votes did George W. Bush receive? Al Gore? 3. How many total electoral votes did George
arxiv: v1 [physics.soc-ph] 13 Mar 2018
![arxiv: v1 [physics.soc-ph] 13 Mar 2018 arxiv: v1 [physics.soc-ph] 13 Mar 2018](/thumbs/80/80574020.jpg) INTRODUCTION TO THE DECLINATION FUNCTION FOR GERRYMANDERS GREGORY S. WARRINGTON arxiv:1803.04799v1 [physics.soc-ph] 13 Mar 2018 ABSTRACT. The declination is introduced in [War17b] as a new quantitative
INTRODUCTION TO THE DECLINATION FUNCTION FOR GERRYMANDERS GREGORY S. WARRINGTON arxiv:1803.04799v1 [physics.soc-ph] 13 Mar 2018 ABSTRACT. The declination is introduced in [War17b] as a new quantitative
The Cook Political Report 2012 Election Outlook
 The Cook Political Report 2012 Election Outlook Presented by: David Wasserman, U.S. House Editor Southwest Ag Issues Summit September 10, 2012 Email: dwasserman@cookpolitical.com Web: http://www.cookpolitical.com
The Cook Political Report 2012 Election Outlook Presented by: David Wasserman, U.S. House Editor Southwest Ag Issues Summit September 10, 2012 Email: dwasserman@cookpolitical.com Web: http://www.cookpolitical.com
What is the Best Election Method?
 What is the Best Election Method? E. Maskin Harvard University Gorman Lectures University College, London February 2016 Today and tomorrow will explore 2 Today and tomorrow will explore election methods
What is the Best Election Method? E. Maskin Harvard University Gorman Lectures University College, London February 2016 Today and tomorrow will explore 2 Today and tomorrow will explore election methods
Supplementary Materials A: Figures for All 7 Surveys Figure S1-A: Distribution of Predicted Probabilities of Voting in Primary Elections
 Supplementary Materials (Online), Supplementary Materials A: Figures for All 7 Surveys Figure S-A: Distribution of Predicted Probabilities of Voting in Primary Elections (continued on next page) UT Republican
Supplementary Materials (Online), Supplementary Materials A: Figures for All 7 Surveys Figure S-A: Distribution of Predicted Probabilities of Voting in Primary Elections (continued on next page) UT Republican
Electing our President with National Popular Vote
 Electing our President with National Popular Vote The current system for electing our president no longer serves America well. Four times in our history, the candidate who placed second in the popular
Electing our President with National Popular Vote The current system for electing our president no longer serves America well. Four times in our history, the candidate who placed second in the popular
The Effect of Electoral Geography on Competitive Elections and Partisan Gerrymandering
 The Effect of Electoral Geography on Competitive Elections and Partisan Gerrymandering Jowei Chen University of Michigan jowei@umich.edu http://www.umich.edu/~jowei November 12, 2012 Abstract: How does
The Effect of Electoral Geography on Competitive Elections and Partisan Gerrymandering Jowei Chen University of Michigan jowei@umich.edu http://www.umich.edu/~jowei November 12, 2012 Abstract: How does
American Dental Association
 American Dental Association May 2, 2016 Bill McInturff SLIDE 1 Heading into the Election Year SLIDE 2 Direction of country remains strongly negative for over a decade. Right Track Wrong Direction WT 80
American Dental Association May 2, 2016 Bill McInturff SLIDE 1 Heading into the Election Year SLIDE 2 Direction of country remains strongly negative for over a decade. Right Track Wrong Direction WT 80
Campaigning in General Elections (HAA)
 Campaigning in General Elections (HAA) Once the primary season ends, the candidates who have won their party s nomination shift gears to campaign in the general election. Although the Constitution calls
Campaigning in General Elections (HAA) Once the primary season ends, the candidates who have won their party s nomination shift gears to campaign in the general election. Although the Constitution calls
The California Primary and Redistricting
 The California Primary and Redistricting This study analyzes what is the important impact of changes in the primary voting rules after a Congressional and Legislative Redistricting. Under a citizen s committee,
The California Primary and Redistricting This study analyzes what is the important impact of changes in the primary voting rules after a Congressional and Legislative Redistricting. Under a citizen s committee,
The Presidential Election. Paul Beck, The Ohio State University Lifelong Learning Institute December 7, 2016
 The Presidential Election Paul Beck, The Ohio State University Lifelong Learning Institute December 7, 2016 1 Introduction: Fundamentals of the 2016 Presidential Contests 2016 presidential results with
The Presidential Election Paul Beck, The Ohio State University Lifelong Learning Institute December 7, 2016 1 Introduction: Fundamentals of the 2016 Presidential Contests 2016 presidential results with
Legal Challege to Winner Take All Jeffrey and Deni Dickler May 9, 2017 Slide 1
 Slide 1 MOPAG Call to Action I m Jeffrey Dickler, part of a small group from MOPAG and MOmentum bringing together resources for a legal challenge to Missouri s method of selecting presidential electors
Slide 1 MOPAG Call to Action I m Jeffrey Dickler, part of a small group from MOPAG and MOmentum bringing together resources for a legal challenge to Missouri s method of selecting presidential electors
THE INDEPENDENT AND NON PARTISAN STATEWIDE SURVEY OF PUBLIC OPINION ESTABLISHED IN 1947 BY MERVIN D. FiElD.
 THE INDEPENDENT AND NON PARTISAN STATEWIDE SURVEY OF PUBLIC OPINION ESTABLISHED IN 1947 BY MERVIN D. FiElD. 234 Front Street San Francisco 94111 (415) 3925763 COPYRIGHT 1982 BY THE FIELD INSTITUTE. FOR
THE INDEPENDENT AND NON PARTISAN STATEWIDE SURVEY OF PUBLIC OPINION ESTABLISHED IN 1947 BY MERVIN D. FiElD. 234 Front Street San Francisco 94111 (415) 3925763 COPYRIGHT 1982 BY THE FIELD INSTITUTE. FOR
VOTING MACHINES AND THE UNDERESTIMATE OF THE BUSH VOTE
 VOTING MACHINES AND THE UNDERESTIMATE OF THE BUSH VOTE VERSION 2 CALTECH/MIT VOTING TECHNOLOGY PROJECT NOVEMBER 11, 2004 1 Voting Machines and the Underestimate of the Bush Vote Summary 1. A series of
VOTING MACHINES AND THE UNDERESTIMATE OF THE BUSH VOTE VERSION 2 CALTECH/MIT VOTING TECHNOLOGY PROJECT NOVEMBER 11, 2004 1 Voting Machines and the Underestimate of the Bush Vote Summary 1. A series of
While viewing this PBS Documentary video answer the following questions. 3. Is voting a Right or a Privilege? (Circle the answer)
 ELECTORAL DYSFUNCTION NAME: While viewing this PBS Documentary video answer the following questions. 1. America is at war over V. The fear of voter fraud and concern over limiting voting for Americans
ELECTORAL DYSFUNCTION NAME: While viewing this PBS Documentary video answer the following questions. 1. America is at war over V. The fear of voter fraud and concern over limiting voting for Americans
dcollege investigation. My dstuden students prior knowl-
 mathematical explorations classroom-ready activities The Electoral College Kimberly A. Markworth and Lara M. Willox Edited by gwen Johnson, gwendolyn.johnson@unt.edu, University of North Texas, Dallas,
mathematical explorations classroom-ready activities The Electoral College Kimberly A. Markworth and Lara M. Willox Edited by gwen Johnson, gwendolyn.johnson@unt.edu, University of North Texas, Dallas,
NEWS RELEASE. Poll Shows Tight Races Obama Leads Clinton. Democratic Primary Election Vote Intention for Obama & Clinton
 NEWS RELEASE FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE: April 18, 2008 Contact: Michael Wolf, Assistant Professor of Political Science, 260-481-6898 Andrew Downs, Assistant Professor of Political Science, 260-481-6691 Poll
NEWS RELEASE FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE: April 18, 2008 Contact: Michael Wolf, Assistant Professor of Political Science, 260-481-6898 Andrew Downs, Assistant Professor of Political Science, 260-481-6691 Poll
Analyzing National Elections of Thailand in 2005, 2007, and 2011 Graphical Approach
 International Journal of Business and Social Science Vol. 3 No. 19; October 2012 Analyzing National Elections of Thailand in 2005, 2007, and 2011 Graphical Approach Attachai Ueranantasun Department of
International Journal of Business and Social Science Vol. 3 No. 19; October 2012 Analyzing National Elections of Thailand in 2005, 2007, and 2011 Graphical Approach Attachai Ueranantasun Department of
What to Do about Turnout Bias in American Elections? A Response to Wink and Weber
 What to Do about Turnout Bias in American Elections? A Response to Wink and Weber Thomas L. Brunell At the end of the 2006 term, the U.S. Supreme Court handed down its decision with respect to the Texas
What to Do about Turnout Bias in American Elections? A Response to Wink and Weber Thomas L. Brunell At the end of the 2006 term, the U.S. Supreme Court handed down its decision with respect to the Texas
Electing a President. The Electoral College
 Electing a President The Electoral College The Original Electoral College System Compromise between allowing Congress to choose a chief executive and direct popular election -Allowing Congress goes against
Electing a President The Electoral College The Original Electoral College System Compromise between allowing Congress to choose a chief executive and direct popular election -Allowing Congress goes against
C H A P T E R 13. CHAPTER 13 The Presidency. What are the President s many roles? What are the formal qualifications necessary to become President?
 Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government CHAPTER 13 The Presidency C H A P T E R 13 The Presidency SECTION 1 The President s Job Description SECTION 2 Presidential Succession and the Vice Presidency
Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government CHAPTER 13 The Presidency C H A P T E R 13 The Presidency SECTION 1 The President s Job Description SECTION 2 Presidential Succession and the Vice Presidency
Key Factors That Shaped 2018 And A Brief Look Ahead
 Key Factors That Shaped 2018 And A Brief Look Ahead November 2018 Bill McInturff SLIDE 1 Yes, it was all about Trump. SLIDE 2 A midterm record said their vote was a message of support or opposition to
Key Factors That Shaped 2018 And A Brief Look Ahead November 2018 Bill McInturff SLIDE 1 Yes, it was all about Trump. SLIDE 2 A midterm record said their vote was a message of support or opposition to
Magruder s American Government
 Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 13 The Presidency 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 13 The Presidency SECTION 1 The President s Job Description SECTION 2 Presidential
Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 13 The Presidency 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 13 The Presidency SECTION 1 The President s Job Description SECTION 2 Presidential
An Assessment of Ranked-Choice Voting in the San Francisco 2005 Election. Final Report. July 2006
 Public Research Institute San Francisco State University 1600 Holloway Ave. San Francisco, CA 94132 Ph.415.338.2978, Fx.415.338.6099 http://pri.sfsu.edu An Assessment of Ranked-Choice Voting in the San
Public Research Institute San Francisco State University 1600 Holloway Ave. San Francisco, CA 94132 Ph.415.338.2978, Fx.415.338.6099 http://pri.sfsu.edu An Assessment of Ranked-Choice Voting in the San
Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems. Voting I 1/36
 Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems Voting I 1/36 Each even year every member of the house is up for election and about a third of the senate seats are up for grabs. Most people do not realize that there
Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems Voting I 1/36 Each even year every member of the house is up for election and about a third of the senate seats are up for grabs. Most people do not realize that there
Inside the Ballot Box
 University at Buffalo Regional Institute POLICY BRIEF March 2009 How did the region vote? Did our voting habits change in 2008? Who voted for whom?, 0 8 Inside the Ballot Box The 2008 presidential election
University at Buffalo Regional Institute POLICY BRIEF March 2009 How did the region vote? Did our voting habits change in 2008? Who voted for whom?, 0 8 Inside the Ballot Box The 2008 presidential election
NATIONAL: 2018 HOUSE RACE STABILITY
 Please attribute this information to: Monmouth University Poll West Long Branch, NJ 07764 www.monmouth.edu/polling Follow on Twitter: @MonmouthPoll Released: Friday, November 2, 2018 Contact: PATRICK MURRAY
Please attribute this information to: Monmouth University Poll West Long Branch, NJ 07764 www.monmouth.edu/polling Follow on Twitter: @MonmouthPoll Released: Friday, November 2, 2018 Contact: PATRICK MURRAY
When should I use the Voting and Elections Collection?
 INTRODUCTION When should I use the Voting and Elections Collection? You can find information and data on: The campaign and election process The electorate, including some demographics, voter turnout and
INTRODUCTION When should I use the Voting and Elections Collection? You can find information and data on: The campaign and election process The electorate, including some demographics, voter turnout and
THE STATE OF VOTING IN 2014
 at New York University School of Law THE STATE OF VOTING IN 2014 By Wendy Weiser and Erik Opsal Executive Summary As we approach the 2014 election, America is still in the midst of a high-pitched and often
at New York University School of Law THE STATE OF VOTING IN 2014 By Wendy Weiser and Erik Opsal Executive Summary As we approach the 2014 election, America is still in the midst of a high-pitched and often
Main idea: Voting systems matter.
 Voting Systems Main idea: Voting systems matter. Electoral College Winner takes all in most states (48/50) (plurality in states) 270/538 electoral votes needed to win (majority) If 270 isn t obtained -
Voting Systems Main idea: Voting systems matter. Electoral College Winner takes all in most states (48/50) (plurality in states) 270/538 electoral votes needed to win (majority) If 270 isn t obtained -
American political campaigns
 American political campaigns William L. Benoit OHIO UNIVERSITY, USA ABSTRACT: This essay provides a perspective on political campaigns in the United States. First, the historical background is discussed.
American political campaigns William L. Benoit OHIO UNIVERSITY, USA ABSTRACT: This essay provides a perspective on political campaigns in the United States. First, the historical background is discussed.
Evaluating the Connection Between Internet Coverage and Polling Accuracy
 Evaluating the Connection Between Internet Coverage and Polling Accuracy California Propositions 2005-2010 Erika Oblea December 12, 2011 Statistics 157 Professor Aldous Oblea 1 Introduction: Polls are
Evaluating the Connection Between Internet Coverage and Polling Accuracy California Propositions 2005-2010 Erika Oblea December 12, 2011 Statistics 157 Professor Aldous Oblea 1 Introduction: Polls are
Candidate Faces and Election Outcomes: Is the Face-Vote Correlation Caused by Candidate Selection? Corrigendum
 Quarterly Journal of Political Science, 2010, 5: 99 105 Corrigendum Candidate Faces and Election Outcomes: Is the Face-Vote Correlation Caused by Candidate Selection? Corrigendum Matthew D. Atkinson, Ryan
Quarterly Journal of Political Science, 2010, 5: 99 105 Corrigendum Candidate Faces and Election Outcomes: Is the Face-Vote Correlation Caused by Candidate Selection? Corrigendum Matthew D. Atkinson, Ryan
Forecasting the 2018 Midterm Election using National Polls and District Information
 Forecasting the 2018 Midterm Election using National Polls and District Information Joseph Bafumi, Dartmouth College Robert S. Erikson, Columbia University Christopher Wlezien, University of Texas at Austin
Forecasting the 2018 Midterm Election using National Polls and District Information Joseph Bafumi, Dartmouth College Robert S. Erikson, Columbia University Christopher Wlezien, University of Texas at Austin
Voting in Maine s Ranked Choice Election. A non-partisan guide to ranked choice elections
 Voting in Maine s Ranked Choice Election A non-partisan guide to ranked choice elections Summary: What is Ranked Choice Voting? A ranked choice ballot allows the voter to rank order the candidates: first
Voting in Maine s Ranked Choice Election A non-partisan guide to ranked choice elections Summary: What is Ranked Choice Voting? A ranked choice ballot allows the voter to rank order the candidates: first
Partisan Advantage and Competitiveness in Illinois Redistricting
 Partisan Advantage and Competitiveness in Illinois Redistricting An Updated and Expanded Look By: Cynthia Canary & Kent Redfield June 2015 Using data from the 2014 legislative elections and digging deeper
Partisan Advantage and Competitiveness in Illinois Redistricting An Updated and Expanded Look By: Cynthia Canary & Kent Redfield June 2015 Using data from the 2014 legislative elections and digging deeper
2008 Legislative Elections
 2008 Legislative Elections By Tim Storey Democrats have been on a roll in legislative elections and increased their numbers again in 2008. Buoyed by the strong campaign of President Barack Obama in many
2008 Legislative Elections By Tim Storey Democrats have been on a roll in legislative elections and increased their numbers again in 2008. Buoyed by the strong campaign of President Barack Obama in many
A Journal of Public Opinion & Political Strategy. Missing Voters in the 2012 Election: Not so white, not so Republican
 THE strategist DEMOCRATIC A Journal of Public Opinion & Political Strategy www.thedemocraticstrategist.org A TDS Strategy Memo: Missing White Voters: Round Two of the Debate By Ruy Teixeira and Alan Abramowitz
THE strategist DEMOCRATIC A Journal of Public Opinion & Political Strategy www.thedemocraticstrategist.org A TDS Strategy Memo: Missing White Voters: Round Two of the Debate By Ruy Teixeira and Alan Abramowitz
The Changing Presidential Race after the Conventions
 Date: September 15, 2008 To: From: Friends of Democracy Corps Stan Greenberg and James Carville The Changing Presidential Race after the Conventions Report on national survey and survey of presidential
Date: September 15, 2008 To: From: Friends of Democracy Corps Stan Greenberg and James Carville The Changing Presidential Race after the Conventions Report on national survey and survey of presidential
Response to the Report Evaluation of Edison/Mitofsky Election System
 US Count Votes' National Election Data Archive Project Response to the Report Evaluation of Edison/Mitofsky Election System 2004 http://exit-poll.net/election-night/evaluationjan192005.pdf Executive Summary
US Count Votes' National Election Data Archive Project Response to the Report Evaluation of Edison/Mitofsky Election System 2004 http://exit-poll.net/election-night/evaluationjan192005.pdf Executive Summary
Do Now. Who do you think has more power a representative/senator, the president, or a Supreme Court justice? Why?
 Do Now Who do you think has more power a representative/senator, the president, or a Supreme Court justice? Why? Political Parties Today, political parties are one of the most important aspects of American
Do Now Who do you think has more power a representative/senator, the president, or a Supreme Court justice? Why? Political Parties Today, political parties are one of the most important aspects of American
CRUZ & KASICH RUN STRONGER AGAINST CLINTON THAN TRUMP TRUMP GOP CANDIDACY COULD FLIP MISSISSIPPI FROM RED TO BLUE
 CRUZ & KASICH RUN STRONGER AGAINST CLINTON THAN TRUMP TRUMP GOP CANDIDACY COULD FLIP MISSISSIPPI FROM RED TO BLUE If Donald Trump wins the Republican presidential nomination, Mississippi and its six electoral
CRUZ & KASICH RUN STRONGER AGAINST CLINTON THAN TRUMP TRUMP GOP CANDIDACY COULD FLIP MISSISSIPPI FROM RED TO BLUE If Donald Trump wins the Republican presidential nomination, Mississippi and its six electoral
By social science convention, negative numbers indicate Republican advantage and positive numbers indicate Democratic advantage.
 Memorandum From: Ruth Greenwood, Senior Legal Counsel To: House Select Committee on Redistricting and Senate Redistricting Committee Date: August 22, 2017 Subject: Proposed 2017 House and Senate Redistricting
Memorandum From: Ruth Greenwood, Senior Legal Counsel To: House Select Committee on Redistricting and Senate Redistricting Committee Date: August 22, 2017 Subject: Proposed 2017 House and Senate Redistricting
Democratic presidential hopeful Senator John Kerry celebrates his primary victory in Manchester, New Hampshire on Tuesday, January 27.
 Election FOCUS JANUARY 28, 2004 U.S. Department of State ISSUE 1 NO 3 Inside This Issue: New Hampshire Primary 2004: The Results..... page 1 A Look Ahead: Seven States Select a Democratic Candidate on
Election FOCUS JANUARY 28, 2004 U.S. Department of State ISSUE 1 NO 3 Inside This Issue: New Hampshire Primary 2004: The Results..... page 1 A Look Ahead: Seven States Select a Democratic Candidate on
TUESDAY, MARCH 22, 2016 ELECTORAL COLLEGE VOTES: 11
 ARIZONA E L E C T I O N D A Y : TUESDAY, MARCH 22, 2016 ELECTORAL COLLEGE VOTES: 11 TOTAL POPULATION (2014): 6,731,484 LATINO POPULATION (2014): 2,056,456 Since 2000, Arizona has seen one particularly
ARIZONA E L E C T I O N D A Y : TUESDAY, MARCH 22, 2016 ELECTORAL COLLEGE VOTES: 11 TOTAL POPULATION (2014): 6,731,484 LATINO POPULATION (2014): 2,056,456 Since 2000, Arizona has seen one particularly
SELA Antenna in the United States SELA Permanent Secretary No th Quarter 2007
 SELA Antenna in the United States SELA Permanent Secretary No. 86 4 th Quarter 2007 SUMMARY: TRADE POLICY AND THE U.S. PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION Impact of the Election on Issues in 2008 Impact of the Election
SELA Antenna in the United States SELA Permanent Secretary No. 86 4 th Quarter 2007 SUMMARY: TRADE POLICY AND THE U.S. PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION Impact of the Election on Issues in 2008 Impact of the Election
Misvotes, Undervotes, and Overvotes: the 2000 Presidential Election in Florida
 Misvotes, Undervotes, and Overvotes: the 2000 Presidential Election in Florida Alan Agresti and Brett Presnell Department of Statistics University of Florida Gainesville, Florida 32611-8545 1 Introduction
Misvotes, Undervotes, and Overvotes: the 2000 Presidential Election in Florida Alan Agresti and Brett Presnell Department of Statistics University of Florida Gainesville, Florida 32611-8545 1 Introduction
An in-depth examination of North Carolina voter attitudes in important current issues. Registered Voters in North Carolina
 An in-depth examination of North Carolina voter attitudes in important current issues Registered Voters in North Carolina January 21-25, 2018 Table of Contents Key Survey Insights... 3 Satisfaction with
An in-depth examination of North Carolina voter attitudes in important current issues Registered Voters in North Carolina January 21-25, 2018 Table of Contents Key Survey Insights... 3 Satisfaction with
CALTECH/MIT VOTING TECHNOLOGY PROJECT A
 CALTECH/MIT VOTING TECHNOLOGY PROJECT A multi-disciplinary, collaborative project of the California Institute of Technology Pasadena, California 91125 and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge,
CALTECH/MIT VOTING TECHNOLOGY PROJECT A multi-disciplinary, collaborative project of the California Institute of Technology Pasadena, California 91125 and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge,
Some Change in Apportionment Allocations With New 2017 Census Estimates; But Greater Change Likely by 2020
 FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Date: December 26, 2017 Contact: Kimball W. Brace 6171 Emerywood Court Manassas, Virginia 20112 202 789.2004 tel. or 703 580.7267 703 580.6258 fax Info@electiondataservices.com Tel.:
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Date: December 26, 2017 Contact: Kimball W. Brace 6171 Emerywood Court Manassas, Virginia 20112 202 789.2004 tel. or 703 580.7267 703 580.6258 fax Info@electiondataservices.com Tel.:
EXPLORING PARTISAN BIAS IN THE ELECTORAL COLLEGE,
 WHS (2009) ISSN: 1535-4738 Volume 9, Issue 4, pp. 2010 Nova Science Publishers, Inc. EXPLORING PARTISAN BIAS IN THE ELECTORAL COLLEGE, 1964-2008 ABSTRACT The purpose of this work is to examine the sources
WHS (2009) ISSN: 1535-4738 Volume 9, Issue 4, pp. 2010 Nova Science Publishers, Inc. EXPLORING PARTISAN BIAS IN THE ELECTORAL COLLEGE, 1964-2008 ABSTRACT The purpose of this work is to examine the sources
Chapter 9 Content Statement
 Content Statement 2 Chapter 9 Content Statement 2. Political parties, interest groups and the media provide opportunities for civic involvement through various means Expectations for Learning Select a
Content Statement 2 Chapter 9 Content Statement 2. Political parties, interest groups and the media provide opportunities for civic involvement through various means Expectations for Learning Select a
ELECTION UPDATE Tom Davis
 ELECTION UPDATE Tom Davis Polarization The Ideological sorting of the parties 1. Redistricting Residential Sorting Voting Rights Act Gerrymandering 2. Media Business Models Cable News Talk Radio Internet
ELECTION UPDATE Tom Davis Polarization The Ideological sorting of the parties 1. Redistricting Residential Sorting Voting Rights Act Gerrymandering 2. Media Business Models Cable News Talk Radio Internet
Data Journalism. What is data journalism? Hurricane Andrew. Bill Dedman: The Color of Money. Michael Friendly Psych 6135
 What is data journalism? Data Journalism Michael Friendly Psych 6135 http://euclid.psych.yorku.ca/www/psy6135 Data journalism reflects the increased role of numerical data for reporting in the digital
What is data journalism? Data Journalism Michael Friendly Psych 6135 http://euclid.psych.yorku.ca/www/psy6135 Data journalism reflects the increased role of numerical data for reporting in the digital
SECTION 1 The President s Job Description. SECTION 2 Presidential Succession and the Vice Presidency
 C H A P T E R 13 The Presidency SECTION 1 The President s Job Description SECTION 2 Presidential Succession and the Vice Presidency SECTION 3 Presidential Selection: The Framers Plan SECTION 4 Presidential
C H A P T E R 13 The Presidency SECTION 1 The President s Job Description SECTION 2 Presidential Succession and the Vice Presidency SECTION 3 Presidential Selection: The Framers Plan SECTION 4 Presidential
The Age of Jackson. A. As you read about the Jacksonian era, write answers to the questions about events that appear on the time line.
 Date CHAPTER Section 3 GUIDED READING The Age of Jackson A. As you read about the Jacksonian era, write answers to the questions about events that appear on the time line. 182 1830 By this point, the Cherokee
Date CHAPTER Section 3 GUIDED READING The Age of Jackson A. As you read about the Jacksonian era, write answers to the questions about events that appear on the time line. 182 1830 By this point, the Cherokee
In the Margins Political Victory in the Context of Technology Error, Residual Votes, and Incident Reports in 2004
 In the Margins Political Victory in the Context of Technology Error, Residual Votes, and Incident Reports in 2004 Dr. Philip N. Howard Assistant Professor, Department of Communication University of Washington
In the Margins Political Victory in the Context of Technology Error, Residual Votes, and Incident Reports in 2004 Dr. Philip N. Howard Assistant Professor, Department of Communication University of Washington
Julie Lenggenhager. The "Ideal" Female Candidate
 Julie Lenggenhager The "Ideal" Female Candidate Why are there so few women elected to positions in both gubernatorial and senatorial contests? Since the ratification of the nineteenth amendment in 1920
Julie Lenggenhager The "Ideal" Female Candidate Why are there so few women elected to positions in both gubernatorial and senatorial contests? Since the ratification of the nineteenth amendment in 1920
By David Lauter. 1 of 5 12/12/2016 9:39 AM
 Clinton won as many votes as Obama in 2012 just not in the states wher... 1 of 5 12/12/2016 9:39 AM Hillary Clinton won the popular vote by at least 2.8 million, according to a final tally. The result
Clinton won as many votes as Obama in 2012 just not in the states wher... 1 of 5 12/12/2016 9:39 AM Hillary Clinton won the popular vote by at least 2.8 million, according to a final tally. The result
US Count Votes. Study of the 2004 Presidential Election Exit Poll Discrepancies
 US Count Votes Study of the 2004 Presidential Election Exit Poll Discrepancies http://uscountvotes.org/ucvanalysis/us/uscountvotes_re_mitofsky-edison.pdf Response to Edison/Mitofsky Election System 2004
US Count Votes Study of the 2004 Presidential Election Exit Poll Discrepancies http://uscountvotes.org/ucvanalysis/us/uscountvotes_re_mitofsky-edison.pdf Response to Edison/Mitofsky Election System 2004
More State s Apportionment Allocations Impacted by New Census Estimates; New Twist in Supreme Court Case
 [Type here] 6171 Emerywood Court Manassas, Virginia 20112 202 789.2004 tel. or 703 580.7267 703 580.6258 fax Info@electiondataservices.com FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Date: December 22, 2015 Contact: Kimball
[Type here] 6171 Emerywood Court Manassas, Virginia 20112 202 789.2004 tel. or 703 580.7267 703 580.6258 fax Info@electiondataservices.com FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Date: December 22, 2015 Contact: Kimball
Young Voters in the 2010 Elections
 Young Voters in the 2010 Elections By CIRCLE Staff November 9, 2010 This CIRCLE fact sheet summarizes important findings from the 2010 National House Exit Polls conducted by Edison Research. The respondents
Young Voters in the 2010 Elections By CIRCLE Staff November 9, 2010 This CIRCLE fact sheet summarizes important findings from the 2010 National House Exit Polls conducted by Edison Research. The respondents
The Alternative Vote Referendum: why I will vote YES. Mohammed Amin
 The Alternative Vote Referendum: why I will vote YES By Mohammed Amin Contents The legislative framework...2 How the first past the post system works...4 How you vote...5 How the votes are counted...5
The Alternative Vote Referendum: why I will vote YES By Mohammed Amin Contents The legislative framework...2 How the first past the post system works...4 How you vote...5 How the votes are counted...5
NEW JERSEY VOTERS TAKE ON 2008
 Contact: PATRICK MURRAY 732-263-5858 (office) 732-979-6769 (cell) pdmurray@monmouth.edu Released: Wednesday, 30, For more information: Monmouth University Polling Institute 400 Cedar Avenue West Long Branch,
Contact: PATRICK MURRAY 732-263-5858 (office) 732-979-6769 (cell) pdmurray@monmouth.edu Released: Wednesday, 30, For more information: Monmouth University Polling Institute 400 Cedar Avenue West Long Branch,
Some Change in Apportionment Allocations With New 2017 Census Estimates; But Greater Change Likely by 2020
 FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Date: December 20, 2017 Contact: Kimball W. Brace 6171 Emerywood Court Manassas, Virginia 20112 202 789.2004 tel. or 703 580.7267 703 580.6258 fax Info@electiondataservices.com Tel.:
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Date: December 20, 2017 Contact: Kimball W. Brace 6171 Emerywood Court Manassas, Virginia 20112 202 789.2004 tel. or 703 580.7267 703 580.6258 fax Info@electiondataservices.com Tel.:
The Electoral College
 The Electoral College Allocating Electors Among The States Each state has electors equal to the number of its Senators and Representatives in the U.S. Congress. In addition, per the Twenty-third Amendment
The Electoral College Allocating Electors Among The States Each state has electors equal to the number of its Senators and Representatives in the U.S. Congress. In addition, per the Twenty-third Amendment
POLI 300 Fall 2010 PROBLEM SET #5B: ANSWERS AND DISCUSSION
 POLI 300 Fall 2010 General Comments PROBLEM SET #5B: ANSWERS AND DISCUSSION Evidently most students were able to produce SPSS frequency tables (and sometimes bar charts as well) without particular difficulty.
POLI 300 Fall 2010 General Comments PROBLEM SET #5B: ANSWERS AND DISCUSSION Evidently most students were able to produce SPSS frequency tables (and sometimes bar charts as well) without particular difficulty.
The University of Akron Bliss Institute Poll: Baseline for the 2018 Election. Ray C. Bliss Institute of Applied Politics University of Akron
 The University of Akron Bliss Institute Poll: Baseline for the 2018 Election Ray C. Bliss Institute of Applied Politics University of Akron Executive Summary The 2018 University of Akron Bliss Institute
The University of Akron Bliss Institute Poll: Baseline for the 2018 Election Ray C. Bliss Institute of Applied Politics University of Akron Executive Summary The 2018 University of Akron Bliss Institute
Survey Research (Polling)
 Survey Research (Polling) Types of Surveys personal (face-to-face) interviews: high response rate, can ask more questions, but... expensive, takes longer to administer telephone interviews: cheaper, fairly
Survey Research (Polling) Types of Surveys personal (face-to-face) interviews: high response rate, can ask more questions, but... expensive, takes longer to administer telephone interviews: cheaper, fairly
2010 Legislative Elections
 2010 Legislative Elections By Tim Storey State Legislative Branch The 2010 state legislative elections brought major change to the state partisan landscape with Republicans emerging in the best position
2010 Legislative Elections By Tim Storey State Legislative Branch The 2010 state legislative elections brought major change to the state partisan landscape with Republicans emerging in the best position
Campaigns & Elections. US Government POS 2041
 Campaigns & Elections US Government POS 2041 Votes for Women, inspired by Katja Von Garner. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lvqnjwk W7gA For Discussion Do you think that democracy is endangered by the
Campaigns & Elections US Government POS 2041 Votes for Women, inspired by Katja Von Garner. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lvqnjwk W7gA For Discussion Do you think that democracy is endangered by the
THE EXECUTIVE BRANCH THE PRESIDENT S ROLES THE PRESIDENT S JOB. The Presidency. Chapter 13. What are the President s many roles?
 THE EXECUTIVE BRANCH The Presidency Chapter 13 THE PRESIDENT S JOB DESCRIPTION What are the President s many roles? What are the formal qualifications necessary to become President? What issues have arisen
THE EXECUTIVE BRANCH The Presidency Chapter 13 THE PRESIDENT S JOB DESCRIPTION What are the President s many roles? What are the formal qualifications necessary to become President? What issues have arisen
Forecasting the 2012 U.S. Presidential Election: Should we Have Known Obama Would Win All Along?
 Forecasting the 2012 U.S. Presidential Election: Should we Have Known Obama Would Win All Along? Robert S. Erikson Columbia University Keynote Address IDC Conference on The Presidential Election of 2012:
Forecasting the 2012 U.S. Presidential Election: Should we Have Known Obama Would Win All Along? Robert S. Erikson Columbia University Keynote Address IDC Conference on The Presidential Election of 2012:
