Letters from the Federal Farmer, No December 1787
|
|
|
- Alberta Stevens
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Letters from the Federal Farmer, No December 1787 Among the hundreds of pamphlets, newspaper articles, and published speeches opposing the new Constitution, a few were judged especially outstanding and have earned enduring fame. Among these, certainly, are the Letters from the Federal Farmer, which were widely read in pamphlet form after appearing initially in the Poughkeepsie Country Journal between November 1787 and January The seventh number developed one of the deepest concerns of many opponents of the Constitution: that the people could not be adequately represented in a single national legislature and, as power gravitated increasingly into federal hands, would end up being ruled by a few great men. Most recent authorities reject the traditional identification of the Federal Farmer as Virginia s Richard Henry Lee. Several suspect that the author may have been Melancton Smith, some of whose speeches in the New York ratifying convention contain close parallels to passages in the letters. But, whoever the author, his concern with an inadequate representation and the creation of a unitary or consolidated central government is necessary background for an understanding of the arguments that would divide the first American parties. 1 Dear Sir, In viewing the various governments instituted by mankind, we see their whole force reducible to two principles force and persuasion. By the former men are compelled, by the latter they are drawn. We denominate a government despotic or free as the one or other principle prevails in it.... In despotic governments one man, or a few men, independent of the people, generally make the laws, command obedience, and enforce it by the sword: one-fourth part of the people are armed and obliged to endure the fatigues of soldiers to oppress the others and keep them subject to the laws. In free governments the people, or their representatives, make the laws; their execution is principally the effect of voluntary consent and aid; the people respect the magistrate, follow their private pursuits, and enjoy the fruits of their labor with very small deductions for the public use. The body of the people must evidently prefer the latter species of government; and it can be only those few who may be well paid for the part they take in enforcing despotism that 1 From Liberty and Order: The First American Party Struggle, ed. and with a Preface by Lance Banning (Indianapolis: Liberty Fund, 2004).
2 can, for a moment, prefer the former. Our true object is to give full efficacy to one principle, to arm persuasion on every side, and to render force as little necessary as possible. Persuasion is never dangerous, not even in despotic governments; but military force, if often applied internally, can never fail to destroy the love and confidence, and break the spirits, of the people, and to render it totally impracticable and unnatural for him or them who govern to hold their places by the peoples elections. The plan proposed will have a doubtful operation between the two principles; and whether it will preponderate towards persuasion or force is uncertain. Government must exist If the persuasive principle be feeble, force is infallibly the next resort. The moment the laws of Congress shall be disregarded they must languish, and the whole system be convulsed that moment we must have recourse to this next resort, and all freedom vanish. It being impracticable for the people to assemble to make laws, they must elect legislators and assign men to the different departments of the government. In the representative branch we must expect chiefly to collect the confidence of the people, and in it to find almost entirely the force of persuasion. In forming this branch, therefore, several important considerations must be attended to. It must possess abilities to discern the situation of the people and of public affairs, a disposition to sympathize with the people, and a capacity and inclination to make laws congenial to their circumstances and condition; it must possess the confidence and have the voluntary support of the people. A fair and equal representation is that in which the interests, feelings, opinions and views of the people are collected in such manner as they would be were the people all assembled. [But] there is no substantial representation of the people provided for in [the new] government, in which the most essential powers, even as to the internal police of the country, are proposed to be
3 lodged. There ought to be an increase of the numbers of representatives: And the elections of them ought to be better secured. The representation is insubstantial and ought to be increased. In matters where there is much room for opinion, you will not expect me to establish my positions with mathematical certainty; you must only expect my observations to be candid and such as are well founded in the mind of the writer. I am in a field where doctors disagree; and as to genuine representation, though no feature in government can be more important, perhaps no one has been less understood, and no one has received so imperfect a consideration by political writers. The ephori in Sparta and the tribunes in Rome were but the shadow [of representation]; the representation in Great Britain is unequal and insecure. In America we have done more in establishing this important branch on its true principles than, perhaps, all the world besides; yet even here, I conceive, that very great improvements in representation may be made. In fixing this branch, the situation of the people must be surveyed and the number of representatives and forms of election apportioned to that situation. When we find a numerous people settled in a fertile and extensive country, possessing equality, and few or none of them oppressed with riches or wants, it ought to be the anxious care of the constitution and laws to arrest them from national depravity and to preserve them in their happy condition. A virtuous people make just laws, and good laws tend to preserve unchanged a virtuous people. A virtuous and happy people, by laws uncongenial to their characters, may easily be gradually changed into servile and depraved creatures. Where the people, or their representatives, make the laws, it is probable they will generally be fitted to the national character and circumstances, unless the representation be partial and the imperfect substitute of the people. [Although] the people may be electors, if the representation be so formed as to give one or more of the natural classes of men in the society an undue ascendancy over the others, it is
4 imperfect; the former will gradually become masters and the latter slaves. It is the first of all among the political balances to preserve in its proper station each of these classes. We talk of balances in the legislature and among the departments of government; we ought to carry them to the body of the people. I have been sensibly struck with a sentence in the Marquis Beccaria s treatise: this sentence was quoted by Congress in 1774, and is as follows: In every society there is an effort continually tending to confer on one part the height of power and happiness and to reduce the others to the extreme of weakness and misery; the intent of good laws is to oppose this effort and to diffuse their influence universally and equally. Add to this Montesquieu s opinion that in a free state every man who is supposed to be a free agent ought to be concerned in his own government; therefore, the legislative should reside in the whole body of the people, or their representatives.... It is deceiving a people to tell them they are electors and can choose their legislators if they cannot, in the nature of things, choose men from among themselves and genuinely like themselves.... These general observations will enable you to discern what I intend by different classes and the general scope of my ideas when I contend for uniting and balancing their interests, feelings, opinions, and views in the legislature; we may not only so unite and balance these as to prevent a change in the government by the gradual exaltation of one part to the depression of others, but we may derive many other advantages from the combination and full representation. A small representation can never be well informed as to the circumstances of the people; the members of it must be too far removed from the people, in general, to sympathize with them, and too few to communicate with them. A representation must be extremely imperfect where the representatives are not circumstanced to make the proper communications to their constituents, and where the constituents in turn cannot, with tolerable convenience, make known their wants, circumstances,
5 and opinions to their representatives. Where there is but one representative to 30,000 or 40,000 inhabitants, it appears to me, he can only mix and be acquainted with a few respectable characters among his constituents; even double the federal representation, and then there must be a very great distance between the representatives and the people in general represented. On the proposed plan, the state of Delaware, the city of Philadelphia, the state of Rhode Island, the province of Maine, the county of Suffolk in Massachusetts will have one representative each; there can be but little personal knowledge, or but few communications, between him and the people at large of either of those districts. It has been observed that mixing only with the respectable men, he will get the best information and ideas from them; he will also receive impressions favorable to their purposes particularly. Many plausible shifts have been made to divert the mind from dwelling on this defective representation. Could we get over all our difficulties respecting a balance of interests and party efforts to raise some and oppress others, the want of sympathy, information, and intercourse between the representatives and the people, an insuperable difficulty will still remain. I mean the constant liability of a small number of representatives to private combinations. The tyranny of the one or the licentiousness of the multitude are, in my mind, but small evils, compared with the factions of the few. It is a consideration well worth pursuing how far this house of representatives will be liable to be formed into private juntos, how far influenced by expectations of appointments and offices, how far liable to be managed by the president and senate, and how far the people will have confidence in them.
Under these impressions, it has been my object to turn your attention to the principal defects in this system.
 Brutus III Brutus November 15, 1787 To the Citizens of the State of New-York. In the investigation of the constitution, under your consideration, great care should be taken, that you do not form your opinions
Brutus III Brutus November 15, 1787 To the Citizens of the State of New-York. In the investigation of the constitution, under your consideration, great care should be taken, that you do not form your opinions
Excerpt From Brutus Essay #1
 Excerpt From Brutus Essay #1 Among the most important of the Anti-Federalist essays is those of Brutus, whose essays were first published in the New York Journal. Brutus, whose identity has never been
Excerpt From Brutus Essay #1 Among the most important of the Anti-Federalist essays is those of Brutus, whose essays were first published in the New York Journal. Brutus, whose identity has never been
Federalist 55 James Madison
 FEDERALIST 319 Federalist James Madison Under the Constitution s original formula, the House would have sixtyfive members. This number was too small according to Anti-Federalists. Publius employs a number
FEDERALIST 319 Federalist James Madison Under the Constitution s original formula, the House would have sixtyfive members. This number was too small according to Anti-Federalists. Publius employs a number
US History, Ms. Brown Website: dph7history.weebly.com
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #70 Aims: SWBAT understand and explain the debate over representation SWBAT identify and explain the Virginia Plan and
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #70 Aims: SWBAT understand and explain the debate over representation SWBAT identify and explain the Virginia Plan and
American Political History, Topic 4: The United States Constitution and Jefferson to Madison (1787)
 Background: The United States Constitution is the God-inspired rubber-and-metal vehicle that carries the American ideals of life, liberty, the pursuit of happiness, equality, justice, and republican government
Background: The United States Constitution is the God-inspired rubber-and-metal vehicle that carries the American ideals of life, liberty, the pursuit of happiness, equality, justice, and republican government
Excerpts from Brutus No. 1
 DOCUMENTS of FREEDOM History, Government & Economics through Primary Sources Primary Source: Excerpts from Brutus No. 1, Annotated Excerpts from Brutus No. 1 18 October 1787 To the Citizens of the State
DOCUMENTS of FREEDOM History, Government & Economics through Primary Sources Primary Source: Excerpts from Brutus No. 1, Annotated Excerpts from Brutus No. 1 18 October 1787 To the Citizens of the State
We The People Packet. Chapter 12- Objective (8.1A,B,C): Describe who attended the Philadelphia Convention & how it was organized.
 We The People Packet Chapter 12- Objective (8.1A,B,C): Describe who attended the Philadelphia Convention & how it was organized. When was the Philadelphia Convention held? What was the intended goal of
We The People Packet Chapter 12- Objective (8.1A,B,C): Describe who attended the Philadelphia Convention & how it was organized. When was the Philadelphia Convention held? What was the intended goal of
American Democracy Now Chapter 2: The Constitution
 American Democracy Now Chapter 2: The Constitution Multiple-Choice Questions: 1. Which of these countries employs an unwritten constitution? a. the United States b. Great Britain c. Venezuela d. Kenya
American Democracy Now Chapter 2: The Constitution Multiple-Choice Questions: 1. Which of these countries employs an unwritten constitution? a. the United States b. Great Britain c. Venezuela d. Kenya
Ratification of the Constitution. Issues
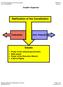 Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
Essay 1. Brutus ESSAY I
 ESSAY I 221 Essay 1 Brutus Supporters of the Constitution dubbed their opponents Anti-Federalists. Opponents resented the label, but it stuck. The Anti-Federalist author Brutus most likely New York lawyer
ESSAY I 221 Essay 1 Brutus Supporters of the Constitution dubbed their opponents Anti-Federalists. Opponents resented the label, but it stuck. The Anti-Federalist author Brutus most likely New York lawyer
Brutus No. 1. Brutus October 18, To the Citizens of the State of New-York.
 Brutus No. 1 Brutus October 18, 1787 To the Citizens of the State of New-York. [1] When the public is called to investigate and decide upon a question in which not only the present members of the community
Brutus No. 1 Brutus October 18, 1787 To the Citizens of the State of New-York. [1] When the public is called to investigate and decide upon a question in which not only the present members of the community
Foundations of American Government
 Foundations of American Government Formation of the first governments of the 13 colonies Highly Influenced by: - Contracts, Juries, stare decisis English Tradition Natural rights: Consent of the governed:
Foundations of American Government Formation of the first governments of the 13 colonies Highly Influenced by: - Contracts, Juries, stare decisis English Tradition Natural rights: Consent of the governed:
ALEXANDER LIBRARY has recently acquired a 1775 edition
 EDMUND BURKE AND THE "PRESENT DISCONTENTS 55 BY NANCY HARPER Dr. Harper is an assistant professor of communication in Rutgers College ALEXANDER LIBRARY has recently acquired a 1775 edition of Edmund Burke's
EDMUND BURKE AND THE "PRESENT DISCONTENTS 55 BY NANCY HARPER Dr. Harper is an assistant professor of communication in Rutgers College ALEXANDER LIBRARY has recently acquired a 1775 edition of Edmund Burke's
Rattfying the Constitution
 Handout 4 (page 1) Part A. Rattfying the Constitution Read the fact sheet, and answer the questions. The Articles of Confederation failed to address several problems confronting the newly formed United
Handout 4 (page 1) Part A. Rattfying the Constitution Read the fact sheet, and answer the questions. The Articles of Confederation failed to address several problems confronting the newly formed United
CREATING A GOVERNMENT
 Let us not be afraid to view with a steady eye the dangers with which we are surrounded. Are we not on the eve of a war, which is only to be prevented by the hopes from this convention? CREATING A GOVERNMENT
Let us not be afraid to view with a steady eye the dangers with which we are surrounded. Are we not on the eve of a war, which is only to be prevented by the hopes from this convention? CREATING A GOVERNMENT
Charles de Montesquieu
 Unit III He first created the idea of consent of the governed where people have a vote in who leads them (democracy). Every person has the right to life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness. John Locke
Unit III He first created the idea of consent of the governed where people have a vote in who leads them (democracy). Every person has the right to life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness. John Locke
Federalists and Antifederalists January 25, 2011 Biographies of the Nation Danice Toyias,
 Constitution Debate, pg. 1 of 1 Federalists and Antifederalists January 25, 2011 Biographies of the Nation Danice Toyias, danice.toyias@mchce.net Lesson Topic and Focus This lesson utilizes what I call
Constitution Debate, pg. 1 of 1 Federalists and Antifederalists January 25, 2011 Biographies of the Nation Danice Toyias, danice.toyias@mchce.net Lesson Topic and Focus This lesson utilizes what I call
James Madison's Defense of the Constitution at the Virginia Convention (1788)
 James Madison's Defense of the Constitution at the Virginia Convention (1788) James Madison, a slight, soft-spoken, and studious man well versed in history, philosophy, and law, was a principal advocate
James Madison's Defense of the Constitution at the Virginia Convention (1788) James Madison, a slight, soft-spoken, and studious man well versed in history, philosophy, and law, was a principal advocate
Creating a Nation Test Review
 Creating a Nation Test Review Question #1: Multiple Choice The Northwest ordinance of 1787 is important because. A. It sent troops to the Northwest to protect the colonies from Native Americans. B. It
Creating a Nation Test Review Question #1: Multiple Choice The Northwest ordinance of 1787 is important because. A. It sent troops to the Northwest to protect the colonies from Native Americans. B. It
Full file at
 Test Questions Multiple Choice Chapter Two Constitutional Democracy: Promoting Liberty and Self-Government 1. The idea that government should be restricted in its lawful uses of power and hence in its
Test Questions Multiple Choice Chapter Two Constitutional Democracy: Promoting Liberty and Self-Government 1. The idea that government should be restricted in its lawful uses of power and hence in its
On the Education of Youth in America By Noah Webster 1788
 Name: Class: On the Education of Youth in America By Noah Webster 1788 Noah Webster (1758-1843), also known as the Father of American Scholarship and Education, was an American textbook pioneer, spelling
Name: Class: On the Education of Youth in America By Noah Webster 1788 Noah Webster (1758-1843), also known as the Father of American Scholarship and Education, was an American textbook pioneer, spelling
Unit 2 Assessment The Development of American Democracy
 Unit 2 Assessment 7 Unit 2 Assessment The Development of American Democracy 1. Which Enlightenment Era thinker stated that everyone is born equal and had certain natural rights of life, liberty, and property
Unit 2 Assessment 7 Unit 2 Assessment The Development of American Democracy 1. Which Enlightenment Era thinker stated that everyone is born equal and had certain natural rights of life, liberty, and property
Explain the key arguments of the Federalists and the process by which the Constitution was finally ratified.
 Explain why the Anti-Federalists opposed ratifying the Constitution. Explain the role of Anti-Federalists in proposing a bill of rights. Explain the key arguments of the Federalists and the process by
Explain why the Anti-Federalists opposed ratifying the Constitution. Explain the role of Anti-Federalists in proposing a bill of rights. Explain the key arguments of the Federalists and the process by
Name: Section: Date:
 Directions: Answer the following multiple choice questions. 1. In 1774, the first Continental Congress took place in what city? a. New York City b. Jamestown c. Philadelphia d. Boston I. The deteriorating
Directions: Answer the following multiple choice questions. 1. In 1774, the first Continental Congress took place in what city? a. New York City b. Jamestown c. Philadelphia d. Boston I. The deteriorating
Major Problem. Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government.
 The Constitution Major Problem Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government. Why? Feared a government like King George The Constitutional
The Constitution Major Problem Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government. Why? Feared a government like King George The Constitutional
Handout B: Madison EXCERPTS FROM FEDERALIST NO. 47 BY JAMES MADISON. DOCUMENTS of FREEDOM History, Government & Economics through Primary Sources
 DOCUMENTS of FREEDOM History, Government & Economics through Primary Sources Unit 2: The Purpose of Government Reading: Separation of Powers and Checks and Balances Activity: Montesquieu and Madison Handout
DOCUMENTS of FREEDOM History, Government & Economics through Primary Sources Unit 2: The Purpose of Government Reading: Separation of Powers and Checks and Balances Activity: Montesquieu and Madison Handout
Learning Goal. Main Points 10/24/2012. Discuss the philosophical underpinnings of the U.S. Constitution.
 Learning Goal Discuss the philosophical underpinnings of the U.S. Constitution. Main Points The weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the adoption of a new form of government Federalism becomes
Learning Goal Discuss the philosophical underpinnings of the U.S. Constitution. Main Points The weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the adoption of a new form of government Federalism becomes
A More Perfect Union. Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation
 A More Perfect Union Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation 1. Eleven of the thirteen states adopted state constitutions. Connecticut and Rhode Island kept its colonial charter as its constitution
A More Perfect Union Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation 1. Eleven of the thirteen states adopted state constitutions. Connecticut and Rhode Island kept its colonial charter as its constitution
3: A New Plan of Government. Essential Question: How Do Governments Change?
 3: A New Plan of Government Essential Question: How Do Governments Change? The Constitution s Source Guiding Question: From where did the Framers of the Constitution borrow their ideas about government?
3: A New Plan of Government Essential Question: How Do Governments Change? The Constitution s Source Guiding Question: From where did the Framers of the Constitution borrow their ideas about government?
The constitution supercedes ordinary law even when the law represents the wishes of a majority of citizens.
 AP Government Chapter 2 The Constitution The constitution supercedes ordinary law even when the law represents the wishes of a majority of citizens. The Constitution is this nation s basic law: It creates
AP Government Chapter 2 The Constitution The constitution supercedes ordinary law even when the law represents the wishes of a majority of citizens. The Constitution is this nation s basic law: It creates
Chapter 5: DEFINING AMERICAN WAR AIMS
 Chapter 5: DEFINING AMERICAN WAR AIMS Objectives: Identify the major debates in the Second Continental Congress, and their outcomes. Assess the impact of Thomas Paine s Common Sense on the colonial view
Chapter 5: DEFINING AMERICAN WAR AIMS Objectives: Identify the major debates in the Second Continental Congress, and their outcomes. Assess the impact of Thomas Paine s Common Sense on the colonial view
WARM UP. 1 Finish the reverse side of the worksheet we began yesterday. 2 It discusses the Articles in the U.S. Constitution
 WARM UP 1 Finish the reverse side of the worksheet we began yesterday 2 It discusses the Articles in the U.S. Constitution 3 You may use your notes or information collected online for the ones that were
WARM UP 1 Finish the reverse side of the worksheet we began yesterday 2 It discusses the Articles in the U.S. Constitution 3 You may use your notes or information collected online for the ones that were
The Constitution. Karen H. Reeves
 The Constitution Karen H. Reeves Toward a New Union Annapolis Convention (Sept. 1786) Met to determine commercial regulation Nationalists called for Constitutional Convention Constitutional Convention
The Constitution Karen H. Reeves Toward a New Union Annapolis Convention (Sept. 1786) Met to determine commercial regulation Nationalists called for Constitutional Convention Constitutional Convention
Federalists versus Anti-Federalists
 Federalists versus Anti-Federalists Overview In this lesson, students will explore the Articles of Confederation and the revisions that created the Constitution of 1787. Students will analyze and assume
Federalists versus Anti-Federalists Overview In this lesson, students will explore the Articles of Confederation and the revisions that created the Constitution of 1787. Students will analyze and assume
WHY DID AMERICAN COLONISTS WANT TO FREE THEMSELVES FROM GREAT BRITAIN?
 6 WHY DID AMERICAN COLONISTS WANT TO FREE THEMSELVES FROM GREAT BRITAIN? LESSON PURPOSE The growth of the American colonies raised issues with the parent country, Great Britain, that were difficult to
6 WHY DID AMERICAN COLONISTS WANT TO FREE THEMSELVES FROM GREAT BRITAIN? LESSON PURPOSE The growth of the American colonies raised issues with the parent country, Great Britain, that were difficult to
During the, the majority of delegates voted to declare independence from Britain. What is known as the official beginning of the America Revolution?
 What is known as the official beginning of the America Revolution? A. The Stamp Act B. Boston Tea Party C. Quartering Act D. Battle of Lexington and Concord During the, the majority of delegates voted
What is known as the official beginning of the America Revolution? A. The Stamp Act B. Boston Tea Party C. Quartering Act D. Battle of Lexington and Concord During the, the majority of delegates voted
Chapter 25 Section 1. Section 1. Terms and People
 Chapter 25 Terms and People republic a government in which the people elect their representatives unicameral legislature a lawmaking body with a single house whose representatives are elected by the people
Chapter 25 Terms and People republic a government in which the people elect their representatives unicameral legislature a lawmaking body with a single house whose representatives are elected by the people
Chapter 02 The Constitution
 Chapter 02 The Constitution Multiple Choice Questions 1. (p. 34) Which of these countries employs an unwritten constitution? A. the United States B. Great Britain C. France D. Sweden E. Germany Difficulty:
Chapter 02 The Constitution Multiple Choice Questions 1. (p. 34) Which of these countries employs an unwritten constitution? A. the United States B. Great Britain C. France D. Sweden E. Germany Difficulty:
A plan for a new government, Introduction. Questions for Discussion
 1 Introduction More than a decade before the Constitutional Convention in 1787 and months before the United States declared independence John Adams wrote a plan for a new form of government for the American
1 Introduction More than a decade before the Constitutional Convention in 1787 and months before the United States declared independence John Adams wrote a plan for a new form of government for the American
The Federalist Papers Summary and Analysis
 The Federalist Papers Summary and Analysis Summary Madison begins perhaps the most famous of the Federalist papers by stating that one of the strongest arguments in favor of the Constitution is the fact
The Federalist Papers Summary and Analysis Summary Madison begins perhaps the most famous of the Federalist papers by stating that one of the strongest arguments in favor of the Constitution is the fact
The United States Constitution. The Supreme Law of the Land
 The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land Standards SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States
The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land Standards SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States
BEGINNINGS: Political essentials and foundational ideas
 BEGINNINGS: Political essentials and foundational ideas 1689 LOCKE S SECOND TREATISE ON GOVERNMENT: Natural Rights: Life, Liberty & Property which existed before government Legitimate government depends
BEGINNINGS: Political essentials and foundational ideas 1689 LOCKE S SECOND TREATISE ON GOVERNMENT: Natural Rights: Life, Liberty & Property which existed before government Legitimate government depends
The U.S. Constitution: Who, What, Where, When, Why & How
 The U.S. Constitution: Who, What, Where, When, Why & How 'a ^Va&o/z Fighting between the American colonists and British forces under King George III was in its second year when the Declaration of Independence
The U.S. Constitution: Who, What, Where, When, Why & How 'a ^Va&o/z Fighting between the American colonists and British forces under King George III was in its second year when the Declaration of Independence
Ratification of the US Constitution in New York, 1788
 Introduction Ratification of the US Constitution in New York, 1788 This unique copy of the US Constitution was printed by Claxton and Babcock in Albany, New York, between February 11 and March 21, 1788.
Introduction Ratification of the US Constitution in New York, 1788 This unique copy of the US Constitution was printed by Claxton and Babcock in Albany, New York, between February 11 and March 21, 1788.
AP American Government
 AP American Government WILSON, CHAPTER 2 The Constitution OVERVIEW The Framers of the Constitution sought to create a government capable of protecting liberty and preserving order. The solution they chose
AP American Government WILSON, CHAPTER 2 The Constitution OVERVIEW The Framers of the Constitution sought to create a government capable of protecting liberty and preserving order. The solution they chose
U.S. Constitution PSCI 1040
 PSCI 1040 Purposes of a Constitution Organize and empower the government Limit the powers of government. Many consider limited government to be the essence of constitutional government. 2 Articles of Confederation
PSCI 1040 Purposes of a Constitution Organize and empower the government Limit the powers of government. Many consider limited government to be the essence of constitutional government. 2 Articles of Confederation
8/25/2011. Serves as a nation s basic law Allocates power within government Structures competition among participants influencing government
 PURPOSES of a CONSTITUTION Serves as a nation s basic law Allocates power within government Structures competition among participants influencing government - May be written or unwritten - May be an accumulation
PURPOSES of a CONSTITUTION Serves as a nation s basic law Allocates power within government Structures competition among participants influencing government - May be written or unwritten - May be an accumulation
Students will understand the characteristics of the Enlightenment by
 Students will understand the characteristics of the Enlightenment by Examining the contributions of Enlightenment era thinkers Examining the parallels between Enlightenment thought and the U.S. Constitution
Students will understand the characteristics of the Enlightenment by Examining the contributions of Enlightenment era thinkers Examining the parallels between Enlightenment thought and the U.S. Constitution
The Constitution I. Considerations that influenced the formulation and adoption of the Constitution A. Roots 1. Religious Freedom a) Puritan
 The Constitution I. Considerations that influenced the formulation and adoption of the Constitution A. Roots 1. Religious Freedom a) Puritan Theocracy (1) 9 of 13 had state church b) Rhode Island (1) Roger
The Constitution I. Considerations that influenced the formulation and adoption of the Constitution A. Roots 1. Religious Freedom a) Puritan Theocracy (1) 9 of 13 had state church b) Rhode Island (1) Roger
Chapter 5 section 3: Creating the Constitution textbook pages
 Chapter 5 section 3: Creating the Constitution textbook pages 163-168 The Big Idea A new constitution provided a framework for a stronger national government. Main Idea 1:The Constitutional Convention
Chapter 5 section 3: Creating the Constitution textbook pages 163-168 The Big Idea A new constitution provided a framework for a stronger national government. Main Idea 1:The Constitutional Convention
The Critical Period The early years of the American Republic
 The Critical Period 1781-1789 The early years of the American Republic America after the War New Political Ideas: - Greater power for the people Republic: Represent the Public America after the War State
The Critical Period 1781-1789 The early years of the American Republic America after the War New Political Ideas: - Greater power for the people Republic: Represent the Public America after the War State
the states. decisions within its own borders) 1. A central government that would represent all 2. State sovereignty (the power to make
 The United States has operated under two constitutions. The first, The Articles of Confederation, was in effect from March 1, 1781. The Articles tried to balance two very different ideas: 1. A central
The United States has operated under two constitutions. The first, The Articles of Confederation, was in effect from March 1, 1781. The Articles tried to balance two very different ideas: 1. A central
Articles of Confederation September 18, 2007
 Articles of Confederation September 18, 2007 Powers Given to Congress under the Articles Weaknesses under the Articles Results of the Articles during the Critical Period Use Page 44-46 to analyze the effects
Articles of Confederation September 18, 2007 Powers Given to Congress under the Articles Weaknesses under the Articles Results of the Articles during the Critical Period Use Page 44-46 to analyze the effects
Constitutional Convention. May 1787
 Constitutional Convention May 1787 Annapolis Convention September 11 to September 14, 1786 Annapolis, Maryland Purpose - How to fix the articles of confederation Alexander Hamilton (New York) MUST resolve
Constitutional Convention May 1787 Annapolis Convention September 11 to September 14, 1786 Annapolis, Maryland Purpose - How to fix the articles of confederation Alexander Hamilton (New York) MUST resolve
The Federalist Papers. Day 1: Constitutional Convention 2/9/2018. In Search of Original Intent
 The Federalist Papers In Search of Original Intent Day 1: Background 10of Constitutional Convention; Purpose of Federalist Papers; Federalist No. 1 Constitutional Convention 1 Facts about the Constitutional
The Federalist Papers In Search of Original Intent Day 1: Background 10of Constitutional Convention; Purpose of Federalist Papers; Federalist No. 1 Constitutional Convention 1 Facts about the Constitutional
Common Sense. Common Sense, 1776
 Chapter 4 Section 3 Common Sense One important document that expressed both levels of the Revolution was Common Sense, a pamphlet written by Thomas Paine. Common Sense first appeared in Philadelphia in
Chapter 4 Section 3 Common Sense One important document that expressed both levels of the Revolution was Common Sense, a pamphlet written by Thomas Paine. Common Sense first appeared in Philadelphia in
Debating the Constitution
 SECTION 3 A Bill of Rights A bill of rights is what the people are entitled to against every government on earth, general or particular; and what no just government should refuse or rest on inference.
SECTION 3 A Bill of Rights A bill of rights is what the people are entitled to against every government on earth, general or particular; and what no just government should refuse or rest on inference.
Creating Our. Constitution. Key Terms. delegates equal representation executive federal system framers House of Representatives judicial
 Lesson 2 Creating Our Constitution Key Terms delegates equal representation executive federal system framers House of Representatives judicial What You Will Learn to Do Explain how the Philadelphia Convention
Lesson 2 Creating Our Constitution Key Terms delegates equal representation executive federal system framers House of Representatives judicial What You Will Learn to Do Explain how the Philadelphia Convention
The Constitution CHAPTER 2 CHAPTER OUTLINE WITH KEYED-IN RESOURCES
 CHAPTER 2 The Constitution CHAPTER OUTLINE WITH KEYED-IN RESOURCES I. The problem of liberty (THEME A: THE POLITICAL PHILOSOPHY OF THE FOUNDERS) A. Colonists were focused on traditional liberties 1. The
CHAPTER 2 The Constitution CHAPTER OUTLINE WITH KEYED-IN RESOURCES I. The problem of liberty (THEME A: THE POLITICAL PHILOSOPHY OF THE FOUNDERS) A. Colonists were focused on traditional liberties 1. The
Blackman High School AP Government & Politics Summer Assignment M. Giacobbi Room D School Year
 Blackman High School AP Government & Politics Summer Assignment M. Giacobbi Room D-02 2017-2018 School Year This college-level course is a challenging course that is meant to be the equivalent of a freshman
Blackman High School AP Government & Politics Summer Assignment M. Giacobbi Room D-02 2017-2018 School Year This college-level course is a challenging course that is meant to be the equivalent of a freshman
May, 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania ~Independence Hall~ Leader: George Washington
 May, 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania ~Independence Hall~ Leader: George Washington -May 1787 Philadelphia Met in Independence Hall in Philadelphia George Washington leader -12 of 13 states Rhode Island
May, 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania ~Independence Hall~ Leader: George Washington -May 1787 Philadelphia Met in Independence Hall in Philadelphia George Washington leader -12 of 13 states Rhode Island
UNITED STATES HISTORY
 UNITED STATES HISTORY SECTION II Part A (Suggested writing time 45 minutes) Percent of Section II score 45 Directions: The following question requires you to construct a coherent essay that integrates
UNITED STATES HISTORY SECTION II Part A (Suggested writing time 45 minutes) Percent of Section II score 45 Directions: The following question requires you to construct a coherent essay that integrates
Chapter 6. APUSH Mr. Muller
 Chapter 6 APUSH Mr. Muller Aim: How is the New Republic tested? Do Now: Thus I consent, sir, to this Constitution, because I expect no better, and because I am not sure that it is not the best. The opinions
Chapter 6 APUSH Mr. Muller Aim: How is the New Republic tested? Do Now: Thus I consent, sir, to this Constitution, because I expect no better, and because I am not sure that it is not the best. The opinions
Unit 3 Section 1 Articles and Early Government.notebook. January 18, Vocabulary. Westward Ho! Need for State and National Government
 8.1 Vocabulary Wilderness Road Republic Articles of Confederation Land Ordinance of 1785 Northwest Territory Northwest Ordinance Shays's Rebellion Chapter Connection: Articles of Confederation were not
8.1 Vocabulary Wilderness Road Republic Articles of Confederation Land Ordinance of 1785 Northwest Territory Northwest Ordinance Shays's Rebellion Chapter Connection: Articles of Confederation were not
Creating the Constitution
 Creating the Constitution 1776-1791 US Timeline 1777-1791 1777 Patriots win Battles of Saratoga. Continental Congress passes the Articles of Confederation. 1781 Articles of Confederation go into effect.
Creating the Constitution 1776-1791 US Timeline 1777-1791 1777 Patriots win Battles of Saratoga. Continental Congress passes the Articles of Confederation. 1781 Articles of Confederation go into effect.
Articles of Confederation
 Articles of Confederation What was the nation facing after the Revolutionary War? -An agrarian or agricultural nation (Farmland) -A Confederate Nation-joined by an agreement or treaty -Debt -Major economic
Articles of Confederation What was the nation facing after the Revolutionary War? -An agrarian or agricultural nation (Farmland) -A Confederate Nation-joined by an agreement or treaty -Debt -Major economic
The United States Constitution. The Supreme Law of the Land
 The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land The Articles Prove Unstable Federal gov t could declare war and other foreign affairs Federal gov t have no power to collect taxes, relying only
The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land The Articles Prove Unstable Federal gov t could declare war and other foreign affairs Federal gov t have no power to collect taxes, relying only
Separation of Powers: History and Theory
 Separation of Powers: History and Theory James E. Hanley Published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International license. This work may be freely reproduced for non-commercial
Separation of Powers: History and Theory James E. Hanley Published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International license. This work may be freely reproduced for non-commercial
Chapter 3 Constitution. Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook
 Chapter 3 Constitution Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on www.pknock.com Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from
Chapter 3 Constitution Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on www.pknock.com Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from
Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution
 Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution The Articles of Confederation After declaring independence from Britain in 1776, Congress tried to unite the states under one national government. However, many feared
Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution The Articles of Confederation After declaring independence from Britain in 1776, Congress tried to unite the states under one national government. However, many feared
Ratifying the Constitution
 Ratifying the Constitution Signing the Constitution Once the debate ended, Governor Morris of New Jersey put the Constitution in its final form. He competed the task of hand-writing 4,300 words in two
Ratifying the Constitution Signing the Constitution Once the debate ended, Governor Morris of New Jersey put the Constitution in its final form. He competed the task of hand-writing 4,300 words in two
The States: Experiments in Republicanism State constitutions served as experiments in republican government The people demand written constitutions
 The States: Experiments in Republicanism State constitutions served as experiments in republican government The people demand written constitutions provide clear definition of rights describe clear limits
The States: Experiments in Republicanism State constitutions served as experiments in republican government The people demand written constitutions provide clear definition of rights describe clear limits
1 st United States Constitution. A. loose alliance of states. B. Congress lawmaking body. C. 9 states had to vote to pass laws
 1 st United States Constitution A. loose alliance of states B. Congress lawmaking body C. 9 states had to vote to pass laws D. each state had 1 vote in Congress Northwest Ordinance / Land Ordinance division
1 st United States Constitution A. loose alliance of states B. Congress lawmaking body C. 9 states had to vote to pass laws D. each state had 1 vote in Congress Northwest Ordinance / Land Ordinance division
A More Perfect Union. Use the text to answer each question below.
 Name Date A More Perfect Union Use the text to answer each question below. 1. John Locke was a 17th-century English philosopher who formulated important theories about governments and humankind. Locke
Name Date A More Perfect Union Use the text to answer each question below. 1. John Locke was a 17th-century English philosopher who formulated important theories about governments and humankind. Locke
4. After some negotiating, mostly with the promise of the Bill of Rights, the Constitution was ratified.
 Chapter #9: The Confederation and the Constitution Big Picture Ideas 1. The Articles of Confederation, the first government set up after the American Revolution, was structured out of fear of a too-strong
Chapter #9: The Confederation and the Constitution Big Picture Ideas 1. The Articles of Confederation, the first government set up after the American Revolution, was structured out of fear of a too-strong
United States Government Chapters 1 and 2
 United States Government Chapters 1 and 2 Chapter 1: Principles of Government Presentation Question 1-1 What do you think it would have been like if, from an early age, you would have been able to do whatever
United States Government Chapters 1 and 2 Chapter 1: Principles of Government Presentation Question 1-1 What do you think it would have been like if, from an early age, you would have been able to do whatever
Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50
 Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50 The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from religious persecution Economic opportunity Independent
Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50 The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from religious persecution Economic opportunity Independent
The Online Library of Liberty
 The Online Library of Liberty A Project Of Liberty Fund, Inc. Lysander Spooner, A Letter to Thomas Bayard: Challenging his right - and that of all the other socalled Senators and Representatives in Congress
The Online Library of Liberty A Project Of Liberty Fund, Inc. Lysander Spooner, A Letter to Thomas Bayard: Challenging his right - and that of all the other socalled Senators and Representatives in Congress
Federalist No. 78. The Judiciary Department. Author: Alexander Hamilton. To the People of the State of New York:
 Federalist No. 78 The Judiciary Department Author: Alexander Hamilton To the People of the State of New York: WE PROCEED now to an examination of the judiciary department of the proposed government. In
Federalist No. 78 The Judiciary Department Author: Alexander Hamilton To the People of the State of New York: WE PROCEED now to an examination of the judiciary department of the proposed government. In
Name: 8 th Grade U.S. History. STAAR Review. Constitution
 8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Constitution FORT BURROWS 2018 VOCABULARY Confederation - A group of loosely connected nations or states that work together for mutual benefit. Republic - A system
8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Constitution FORT BURROWS 2018 VOCABULARY Confederation - A group of loosely connected nations or states that work together for mutual benefit. Republic - A system
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton
 Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
1. According to Washington, what is needed to prevent an uprising like Shays Rebellion? [1]
![1. According to Washington, what is needed to prevent an uprising like Shays Rebellion? [1] 1. According to Washington, what is needed to prevent an uprising like Shays Rebellion? [1]](/thumbs/83/87708147.jpg) Part A Short-Answer Questions Directions: Analyze the documents and answer the short-answer questions that follow each document in the space provided. Document 1 We are fast verging to anarchy and confusion!
Part A Short-Answer Questions Directions: Analyze the documents and answer the short-answer questions that follow each document in the space provided. Document 1 We are fast verging to anarchy and confusion!
CHAPTER 2 ORIGINS OF AMERICAN GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS
 CHAPTER 2 ORIGINS OF AMERICAN GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS Basic Concepts of Government Early settlers brought ideas of government or political systems with them.
CHAPTER 2 ORIGINS OF AMERICAN GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS Basic Concepts of Government Early settlers brought ideas of government or political systems with them.
What do these clips have in common?
 What do these clips have in common? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=salmxkxr5k0 (Avatar) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dlrrewji4so &feature=related (Pirates of the Caribbean) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wlrrbs8jbqo
What do these clips have in common? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=salmxkxr5k0 (Avatar) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dlrrewji4so &feature=related (Pirates of the Caribbean) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wlrrbs8jbqo
The classroom teacher may reproduce materials in this book for classroom use only. The reproduction of any part for an entire school or school system
 AMERICAN GOVERNMENT Gretchen McNulty The classroom teacher may reproduce materials in this book for classroom use only. The reproduction of any part for an entire school or school system is strictly prohibited.
AMERICAN GOVERNMENT Gretchen McNulty The classroom teacher may reproduce materials in this book for classroom use only. The reproduction of any part for an entire school or school system is strictly prohibited.
Chapter 2:4 Constitutional Convention
 Chapter 2:4 Constitutional Convention Psa_119:165 Great peace have they which love thy law: and nothing shall offend them. Objectives: 2:4 Our Political Beginnings o Students will examine the process that
Chapter 2:4 Constitutional Convention Psa_119:165 Great peace have they which love thy law: and nothing shall offend them. Objectives: 2:4 Our Political Beginnings o Students will examine the process that
LETTER XIV. January 17, Dear sir,
 1 of 5 11/4/2007 1:11 PM From the Constitution Society http://www.constitution.org/ LETTER XIV. Dear sir, January 17, 1788. To continue the subject of appointments: Officers, in the fifth place, may be
1 of 5 11/4/2007 1:11 PM From the Constitution Society http://www.constitution.org/ LETTER XIV. Dear sir, January 17, 1788. To continue the subject of appointments: Officers, in the fifth place, may be
Chapter 7, Section 3 A New Plan of Government
 Chapter 7, Section 3 A New Plan of Government (pages 207-213) Setting a Purpose for Reading Think about these questions as you read: What are the roots of the Constitution? How did the Constitution limit
Chapter 7, Section 3 A New Plan of Government (pages 207-213) Setting a Purpose for Reading Think about these questions as you read: What are the roots of the Constitution? How did the Constitution limit
Lesson 13 Writing and Ratifying the Constitution
 Lesson 13 Writing and Ratifying the Constitution Doct r. FRANKLIN looking towards the Presidents Chair, at the back of which a rising sun happened to be painted, observed to a few members near him, that
Lesson 13 Writing and Ratifying the Constitution Doct r. FRANKLIN looking towards the Presidents Chair, at the back of which a rising sun happened to be painted, observed to a few members near him, that
Document-Based Activities
 ACTIVITY 3 Document-Based Activities The Bill of Rights Using Source Materials HISTORICAL CONTEXT The first ten amendments to the U.S. Constitution are known collectively as the Bill of Rights. They were
ACTIVITY 3 Document-Based Activities The Bill of Rights Using Source Materials HISTORICAL CONTEXT The first ten amendments to the U.S. Constitution are known collectively as the Bill of Rights. They were
Guided Reading Activity
 Guided Reading Activity Lesson 1 Government in Colonial America Review Questions Directions: Read each main idea. Use your text to supply the details that support or explain each main idea. A. Main Idea:
Guided Reading Activity Lesson 1 Government in Colonial America Review Questions Directions: Read each main idea. Use your text to supply the details that support or explain each main idea. A. Main Idea:
Activity Three: The Enlightenment ACTIVITY CARD
 ACTIVITY CARD During the 1700 s, European philosophers thought that people should use reason to free themselves from ignorance and superstition. They believed that people who were enlightened by reason
ACTIVITY CARD During the 1700 s, European philosophers thought that people should use reason to free themselves from ignorance and superstition. They believed that people who were enlightened by reason
Declaration of Independence
 Declaration of Independence Second Continental Congress Delegates had been convened in Philadelphia since May 1775 Even though the Colonies were in a state of war with Great Britain, Congress still hoped
Declaration of Independence Second Continental Congress Delegates had been convened in Philadelphia since May 1775 Even though the Colonies were in a state of war with Great Britain, Congress still hoped
Four ENLIGHTENMENT THINKERS
 Four ENLIGHTENMENT THINKERS 1. Thomas Hobbes (1588 1679) 2. John Locke (1632 1704) 3. Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1712 1778) 4. Baron de Montesquieu (1689 1755) State of Nature- Nature is governed by laws such
Four ENLIGHTENMENT THINKERS 1. Thomas Hobbes (1588 1679) 2. John Locke (1632 1704) 3. Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1712 1778) 4. Baron de Montesquieu (1689 1755) State of Nature- Nature is governed by laws such
The Enlightenment Thinkers The Age of Reason
 The Enlightenment Thinkers The Age of Reason The Enlightenment Scholars began to challenge long held beliefs about science, religion, and government. Thinkers were inspired by Galileo and Newton. The method
The Enlightenment Thinkers The Age of Reason The Enlightenment Scholars began to challenge long held beliefs about science, religion, and government. Thinkers were inspired by Galileo and Newton. The method
Chapter 2 The Constitution and the Founding. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 Chapter 2 The Constitution and the Founding A Republic At the close of the Constitutional Convention of 1787, Ben Franklin was queried as he left Independence Hall on the final day of deliberation. In
Chapter 2 The Constitution and the Founding A Republic At the close of the Constitutional Convention of 1787, Ben Franklin was queried as he left Independence Hall on the final day of deliberation. In
SENATE BILL 752. By Beavers. WHEREAS, The Constitution of Tennessee, Article XI, 18, states the following: The
 SENATE BILL 752 By Beavers AN ACT to amend Tennessee Code Annotated, Title 36, relative to the Tennessee Natural Marriage Defense Act. WHEREAS, The Constitution of Tennessee, Article
SENATE BILL 752 By Beavers AN ACT to amend Tennessee Code Annotated, Title 36, relative to the Tennessee Natural Marriage Defense Act. WHEREAS, The Constitution of Tennessee, Article
The Road to Change. From the Declaration of Independence to the Constitution
 The Road to Change From the Declaration of Independence to the Constitution From the Declaration of Independence to the 1776: Colonists sign the Declaration of Independence 1783: Colonists win the American
The Road to Change From the Declaration of Independence to the Constitution From the Declaration of Independence to the 1776: Colonists sign the Declaration of Independence 1783: Colonists win the American
HIST 1301 Part Two. 6: The Republican Experiment
 HIST 1301 Part Two 6: The Republican Experiment The States and the Confederation 1776-1788 During the Revolution, state Governments formed first. 2 min. 40 sec. Each state had a written constitution. Each
HIST 1301 Part Two 6: The Republican Experiment The States and the Confederation 1776-1788 During the Revolution, state Governments formed first. 2 min. 40 sec. Each state had a written constitution. Each
Federalists and anti-federalists The power of subtleties
 Federalists and anti-federalists The power of subtleties The ratification of the Constitution exemplifies the power of subtleties. The two sides in the debate, the Federalists and the Anti-federalists,
Federalists and anti-federalists The power of subtleties The ratification of the Constitution exemplifies the power of subtleties. The two sides in the debate, the Federalists and the Anti-federalists,
