Eric M. Uslaner, Inequality, Trust, and Civic Engagement (1)
|
|
|
- Sandra May
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Eric M. Uslaner, Inequality, Trust, and Civic Engagement (1) Inequality, Trust, and Civic Engagement Eric M. Uslaner Department of Government and Politics University of Maryland College Park College Park, MD Telephone: (o) (h)
2 Eric M. Uslaner, Inequality, Trust, and Civic Engagement (2) Project Summary Inequality, Trust, and Civic Engagement Inequality, Trust, and Civic Engagement seeks to explain falling levels of civic engagement in the United States from the 1960s to the present. Fewer Americans are participating in civic life, especially in arenas that demonstrate a strong commitment to one s community such as giving to charity and volunteering time. I argue that rising levels of economic inequality are a key reason why participation has fallen. But the relationship between inequality and declining participation may not be direct. I offer an alternative explanation: Rising inequality makes people less optimistic for the future, which makes them less trusting of others, and thus less likely to take part in activities that bind them to their communities. I shall test this claim through statistical models and present findings to both the scholarly community and to the larger public.
3 Eric M. Uslaner, Inequality, Trust, and Civic Engagement (3) There is widespread agreement that Americans participate less in civic affairs than they once did. Americans have withdrawn from all sorts of civic activities, from voting in elections to joining civic groups to the more demanding forms of engagement such as giving to charity and volunteering time. 1 I suggest in this research that much of the decline in civic engagement can be traced, either directly or indirectly, to rising levels of economic inequality in the United States. The link may be more likely to be indirect. One of the keys to an engaged citizenry is a sense of community, which is reflected in the level of interpersonal trust in a society. Trust leads to civic engagement. And trust has fallen sharply in the United States: In 1960, when the question was first asked in a national survey, 58 percent of Americans said that most people can be trusted. By the mid-to-late 1990s, this figure had dropped to barely more than one-third of Americans. As Americans have become less connected to one another, they should participate less in civic affairs especially in activities that depend heavily upon a sense of community. As I have shown in my book in progress The Moral Foundations of Trust, the principal reason for the drop in trust is the increase in economic inequality in the United States. There has been a 20 percent increase in the value of the Gini index of income inequality (the most widely used measure of 2 disparities in wealth) in the United States from 1960 to I argue that increasing economic inequality leads to a less trusting society and lower trust leads to a society with lower levels of civic engagement. 1. On the decline in membership in voluntary organizations and in political participation, see Robert Putnam, Bowling Alone (New York: Simon and Schuster, in press). On giving to charity and volunteering time, see Eric M. Uslaner, The Moral Foundations of Trust (unpublished manuscript, University of Maryland College Park), ch United States Department of Commerce, Economic and Statistics Administration, Measuring 50 Years of Economic Change (Washington: Bureau of the Census, 1998); and Jared Bernstein et al., Pulling Apart (Washington: Center on Budget and Policy Priorities/Economic Policy Institute, 2000).
4 Eric M. Uslaner, Inequality, Trust, and Civic Engagement (4) Participation in civic life is a sign of people s commitment to their society. The decline of participation in both political and social life bode ill for civil society. And when the decline in participation stems from rising economic inequality, serious questions arise about whether American democracy is becoming less representative. Voices that opt out of participating will not be heard, and public policy will reflect the views of those who are well off even more than it usually does. Focus of the Research This research will establish both the theoretical and empirical foundations of the argument about how economic inequality may lead to waning civic engagement. It will also add to the burgeoning national debate about inequality and its consequences. 3 The claim that income inequality is important for shaping civic engagement is hardly new. Yet, my take on this argument is distinctive. And it has important policy implications: Restoring our civic responsibility depends upon taking action to reduce income disparities. Wealthier people are more likely to take part in a wide range of political and social activities. Well-off people have more education and education is one of the major forces shaping participation in virtually every realm. Additionally, people who have higher paying jobs are more likely to have jobs 4 where they practice skills, such as letter writing and organizing groups to work together. As the income gap between rich and poor has grown over time, there should be a corresponding increase in the class skew of civic engagement. And this simple trend should help account for the decline in many forms of civic engagement in the United States. Yet, some research casts doubt on this 3. See Walter Dean Burnham, Critical Elections and the Mainsprings of American Politics (New York: W.W. Norton, 1970); and Sidney Verba, Kay Lehman Schlozman, and Henry Brady, Voice and Equality (Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 1995). 4. Verba et al., Voice and Equality, p. 457.
5 Eric M. Uslaner, Inequality, Trust, and Civic Engagement (5) explanation, and we need to think again about how inequality might affect participation. 5 For some types of participation, it may be the case that as inequality goes up, participation goes down and the class skew should also increase. This simple relationship should hold for types of 6 participation that are most skewed by class in the first place. Such activities include petitioning public officials, attending public meetings, writing to members of Congress or to newspapers, being an officer in a club, working for a political party, joining a group that works to reform government, and running for office. These are all demanding activities that use skills that are mostly available to the middle and upper classes. There may be a less direct connection between increasing income inequality and other forms of civic engagement. More Americans volunteer their time than write to public officials or to newspapers (among other activities). Two key types of civic engagement, volunteering and giving to charity, depend more upon moral than financial resources. In my book manuscript in progress, The Moral Foundations of Trust, I show that both volunteering and giving to charity depend upon trust in other people even more than upon financial resources. Faith in others is essentially an acceptance of the belief that people who may be different from you are nevertheless part of your moral community. It is the moral glue that holds a society together (what I call the chicken soup of social life ). Volunteering and charitable giving have fallen sharply since the 1960s. These trends track the decline in interpersonal trust much more sharply than they follow trends in economic inequality. Yet, trust itself strongly depends upon economic equality. Trust is a relationship among equals. And it reflects an optimistic view that the world is a good place full of people who share our fundamental 5. Jan E. Leighley and Jonathan Nagler, Socioeconomic Bias in Turnout : The Voters Remain the Same, American Political Science Review (1992): Verba et al., Voice and Equality, passim.
6 Eric M. Uslaner, Inequality, Trust, and Civic Engagement (6) values, that life will continue to get better, and that we can make it so through our own efforts. Mistrust, on the other hand, reflects a pessimistic view of the future and that we are prisoners of forces beyond our 7 control. People become pessimistic as the gap between the rich and the poor gets larger. When inequality is rising, people at the bottom see those at the top as privileged and powerful. Pessimists distrust others and opt out of participation in civic life, especially those activities that reflect a deeper commitment to one s community (and to people unlike yourself) such as giving to charity or volunteering time. Methodology I propose to test these two paths from inequality to civic engagement using both aggregate and individual level data. I first propose to look at aggregate trends in participation (including voting, signing petitions, attending public meetings, writing letters to members of Congress and to newspapers, writing articles, working for political parties, making public speeches, joining good government groups, and serving as an officer in a club) and where data are available, trends in the class skew of participation from the 1970s to the 1990s. The data on aggregate trends in participation come from the Roper Social and Political Trends archive, which asked these questions of national samples from 1974 to Second, I propose to examine the indirect linkage between trust and the forms of civic engagement that depend most on moral resources. Do volunteering and charitable contributions become the 7. See related arguments in Adam B. Seligman, The Problem of Trust (Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1997), pp ; and Robert Putnam, Making Democracy Work (Princeton: Princeton University Press), p On the relationship between trust and inequality, see Uslaner, The Moral Foundations of Trust, chs. 2, 6, and 7; Stephen Knack, Social Capital, Growth, and Poverty: A Survey of the Cross-Country Evidence, Washington: The World Bank, 1999; and John Brehm and Wendy Rahn, "Individual Level Evidence for the Causes and Consequences of Social Capital," American Journal of Political Science, 41:
7 Eric M. Uslaner, Inequality, Trust, and Civic Engagement (7) exclusive province of the handful of trusters in an unequal society? If my hypothesis holds, then mistrusters opt out as the distribution of wealth becomes more unequal and the class skew of civic engagement becomes more worrisome. I shall estimate similar models using trends in charitable contributions obtained from the United Way and from Giving USA and trends in volunteering from the Red Cross and the Roper Social and Political Trends archive. In each case, I shall examine whether there is a direct relationship between civic engagement and trust, or whether the relationship depends upon trust using standard time series regression techniques controlling for other variables such as changes in tax laws and economic conditions. Third, I shall examine whether the level of inequality has a direct or indirect effect on trust as a predictor of political participation and volunteering in the American states over time. I propose to aggregate the levels of volunteering, political participation, and other forms of civic engagement (such as group membership) in the Roper Social and Political Trends archive, surveys by the INDEPENDENT SECTOR, and the General Social Survey to the state level for the decades of the 1970s, 1980s, and 1990s. I shall also aggregate measures of trust across a range of surveys, including the General Social Survey, but also including surveys by the American National Election Study, the Survey Research Center (Quality of Life surveys), the INDEPENDENT SECTOR, the Washington Post, and the New York Times. I shall merge these data with state-level estimates of economic inequality, which are available from the Bureau of the Census. 8 I expect that states with greater levels of inequality will also have fewer trusting citizens. States with higher levels of inequality should also have lower rates of participation, controlling for other standard variables that predict various forms of civic engagement (education levels, income levels, level of political competition, age distribution of the public, etc.). However, the relationship between 8. See Robert D. Putnam, Bowling Alone: The Collapse and Revival of American Community (New York: Simon and Schuster, 2000), ch. 19.
8 Eric M. Uslaner, Inequality, Trust, and Civic Engagement (8) inequality and participation: 1) will vary depending upon the type of participation examined. There may be weak to moderate impacts for many types of political participation such as voting and joining civic associations, but much more powerful impacts for activities that rely upon resources that shape skills (such as writing letters to editors or articles, signing petitions, and serving as an officer in a club) and that rely heavily upon moral resources (such as volunteering). 2) will have an indirect, rather than a direct, impact on most forms of civic engagement. The indirect effect will go through trust. This entails establishing a causal chain (to be estimated by simultaneous equation modeling) from inequality to trust to civic engagement. 3) There is more likely to be a direct effect from inequality to civic participation for actitivies that rely upon skills that are developed through education or resources such as free time that depend upon having enough free time to get involved in political life. These activities include letter writing, petitioning, writing articles, serving as an officer in a club, giving speeches, working for political parties, and attending public meetings. These activities do not depend upon trust at all and may involve the sort of political confrontation that will 9 destroy any existing social trust. On the other hand, certain types of civic engagement do depend upon trust in other people. These are activities that rely more upon moral resources than particular skills: volunteering time and giving to charity. Here I expect only an indirect relationship between civic participation and inequality a connection that is conditioned by trust. The models I shall estimate lead to predictions that: 1) Civic engagement will be lower in states with more trusting citizens and with higher levels of economic equality. 9. See Uslaner, The Moral Foundations of Trust, ch. 7.
9 Eric M. Uslaner, Inequality, Trust, and Civic Engagement (9) 2) As economic inequality in the states has increased, trust has decreased and the level of civic engagement, especially for volunteering, should decrease. While the aggregate trends in most forms of civic engagement have been downward, the various forms of civic participation have not all fallen at similar rates. Nor do they all depend upon either trust or economic equality. There is at least moderate support for this linkage for turnout: As the level of economic inequality has increased across the 50 states and the District of Columbia from 1969 to 1989, turnout in Presidential elections has fallen from 1972 to Figure 1 demonstrates the connection between changes in economic equality and changes in 10 turnout across the 51 states. I would expect even more powerful results for other, more demanding, forms of civic engagement. 3) In states with higher levels of inequality, not only should we see lower rates of civic engagement, but we should also see greater class skews of participation (as measured by Gini indices for participation that can computed from survey data). 4) Does civic engagement really depend upon economic inequality, or upon the level of economic well-being of the citizen? I shall examine this linkage by positing standard models of volunteering and charitable contributions at the individual level (for the 1992 and 1996 American National Election Studies, 1996 General Social Survey and the 1996 INDEPENDENT SECTOR survey), following the analyses I conducted in The Moral Foundations of Trust. In these models, measures of trust are consistently the strongest predictors of volunteering and charitable giving. Economic status is also a consistently strong determinant of charitable giving. I shall then add contextual (statewide) measures of economic inequality to the models, as well as interaction terms between trust and 10. These results and the associated graph were provided by William Evans of the Department of Economics, University of Maryland College Park.
10 Eric M. Uslaner, Inequality, Trust, and Civic Engagement (10) inequality, to see whether the level of economic inequality in a person s environment also shapes (beyond socioeconomic status) whether someone volunteers or gives to charity. My expectation is that state level Gini indices should affect these forms of civic engagement. However, the level of economic inequality should be particularly strong for people who mistrust others or who only trust people like themselves. 5) As economic inequality has increased over time, both the level of participation and the class skew of participation should increase. Thus, we should see a dynamic for inequality and trust over both space (across states) and time. Especially for volunteering, which should depend most heavily upon trust, we should find that the highest levels of participation (and smallest class skews) occurred in the most trusting states (the North Central states such as Minnesota and the Dakotas) when economic inequality was lower (in the 1970s). In contrast, we should see the lowest levels of volunteering (and the greatest class skew) in the least trusting states (the Deep South) when economic inequality is highest (the 1990s). I shall test this claim using simultaneous equation estimation with interaction terms for trust and inequality and for both trust and inequality at different time points. Audiences and Schedule The research will be conducted during the academic years at the University of Maryland. Much of the first academic year will be spent putting the data sets together. I propose to do aggregate analyses by state, but the measures of participation and trust come from large surveys. So I must, with the help of a graduate assistant, create the aggregate measures and build the data sets of state level indicators of participation and trust. Since these measures come from different surveys, there will be a fair amount of data manipulating involved. Some of the data set generation will involve comparing different weighting schemes in the surveys to come up with representative aggregate state-level data sets. Also I shall have to merge the state-level economic inequality data with survey data and this will also be
11 Eric M. Uslaner, Inequality, Trust, and Civic Engagement (11) time consuming. The bulk of the analyses will be done in the summer of 2001 and throughout the academic year and summer. The academic year and summer will be spent writing the manuscript. As data are developed earlier, I shall present papers from the initial result. This research proposal has two intended audiences. The statistical analysis of surveys, of course, will be aimed at the academic community and I shall write conference papers, articles, and a book from the research. There are also important policy implications from this research. I shall present these results to the policy community, as I have done previously--including invitations to give papers at such public meetings as the Communitarian Summit, the Department of State s Secretary s Open Forum, regular coverage of my work by the Washington Post, and media appearances such as interviews on ABC s Good Morning America and on CNN specials. The success of this research depends upon both positive reception by the scholarly community and especially by my success in contributing to the debate over rising economic inequality in the United States. Inequality has become a more prominent issue in political discourse, owing to studies by the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities and has even caught the attention of conservative commentators such as Arianna Huffington. I hope to add to this debate. I expect to write several conference papers that I shall submit for publication, a book, and more popular pieces for newspapers and magazines. For the public audience, I shall submit a paper to the next Communitarian Summit and look for similar forums where I can present my work to a more general audience. Several academic publishers, such as Princeton University Press, the University of Michigan Press, Cambridge University Press, and the University of Chicago Press have long-standing interests in my work and have solicited my manuscript on The Moral Foundations of Trust. In addition, the Brookings Institution Press has also expressed interest in my work and would be particularly keen on a project that has such clear-cut policy implications. I would expect the book to be drafted by the Summer
12 Eric M. Uslaner, Inequality, Trust, and Civic Engagement (12) of I also, as noted, will seek wider publicity for my work through Op-Ed and magazine articles and addresses to public forums. I would expect that my work will be featured prominently in the Washington Post. The polling editor, Richard Morin, writes a semiweekly column, Unconventional Wisdom, where he highlights work from the social sciences. He has devoted considerable space to my work in the past and we maintain an ongoing dialogue about it. I shall also make more contacts with research organizations focusing on economic inequality to engage them in a discussion of additional consequences of the growing gap between the rich and the poor.
13 Eric M. Uslaner, Inequality, Trust, and Civic Engagement (13) Figure 1 Relationship Between Change in Turnout ( ) and Change in Economic Inequality ( ) Across the 50 States and the District of Columbia
14 Eric M. Uslaner, Inequality, Trust, and Civic Engagement (14)
INEQUALITY, TRUST, AND CIVIC ENGAGEMENT
 10.1177/1532673X04271903 AMERICAN Uslaner, Brown / CIVIC ENGAGEMENT POLITICS RESEARCH / NOVEMBER 2005 INEQUALITY, TRUST, AND CIVIC ENGAGEMENT ERIC M. USLANER MITCHELL BROWN University of Maryland, College
10.1177/1532673X04271903 AMERICAN Uslaner, Brown / CIVIC ENGAGEMENT POLITICS RESEARCH / NOVEMBER 2005 INEQUALITY, TRUST, AND CIVIC ENGAGEMENT ERIC M. USLANER MITCHELL BROWN University of Maryland, College
U.S. Family Income Growth
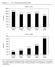 Figure 1.1 U.S. Family Income Growth Growth 140% 120% 100% 80% 60% 115.3% 1947 to 1973 97.1% 97.7% 102.9% 84.0% 40% 20% 0% Lowest Fifth Second Fifth Middle Fifth Fourth Fifth Top Fifth 70% 60% 1973 to
Figure 1.1 U.S. Family Income Growth Growth 140% 120% 100% 80% 60% 115.3% 1947 to 1973 97.1% 97.7% 102.9% 84.0% 40% 20% 0% Lowest Fifth Second Fifth Middle Fifth Fourth Fifth Top Fifth 70% 60% 1973 to
One. After every presidential election, commentators lament the low voter. Introduction ...
 One... Introduction After every presidential election, commentators lament the low voter turnout rate in the United States, suggesting that there is something wrong with a democracy in which only about
One... Introduction After every presidential election, commentators lament the low voter turnout rate in the United States, suggesting that there is something wrong with a democracy in which only about
The very essence of democracy is equality.1
 Political Donations and Democratic Equality in Canada Brianna Carmichael and Paul Howe Equality is a key tenet of democracy. With respect to the financing of federal political parties, one issue relevant
Political Donations and Democratic Equality in Canada Brianna Carmichael and Paul Howe Equality is a key tenet of democracy. With respect to the financing of federal political parties, one issue relevant
Same Day Voter Registration in
 Same Day Voter Registration in Maryland Executive Summary We have analyzed the likely impact on voter turnout should Maryland adopt Same Day Registration (SDR). 1 Under the system proposed in Maryland,
Same Day Voter Registration in Maryland Executive Summary We have analyzed the likely impact on voter turnout should Maryland adopt Same Day Registration (SDR). 1 Under the system proposed in Maryland,
Election Day Voter Registration
 Election Day Voter Registration in IOWA Executive Summary We have analyzed the likely impact of adoption of election day registration (EDR) by the state of Iowa. Consistent with existing research on the
Election Day Voter Registration in IOWA Executive Summary We have analyzed the likely impact of adoption of election day registration (EDR) by the state of Iowa. Consistent with existing research on the
Political Participation
 Political Participation THEME A: POPULAR PARTICIPATION IN ELECTIONS From State to Federal Control Initially, states decided who could vote and for which offices This led to wide variation in federal TIFF
Political Participation THEME A: POPULAR PARTICIPATION IN ELECTIONS From State to Federal Control Initially, states decided who could vote and for which offices This led to wide variation in federal TIFF
Research Thesis. Megan Fountain. The Ohio State University December 2017
 Social Media and its Effects in Politics: The Factors that Influence Social Media use for Political News and Social Media use Influencing Political Participation Research Thesis Presented in partial fulfillment
Social Media and its Effects in Politics: The Factors that Influence Social Media use for Political News and Social Media use Influencing Political Participation Research Thesis Presented in partial fulfillment
Election Day Voter Registration in
 Election Day Voter Registration in Massachusetts Executive Summary We have analyzed the likely impact of adoption of Election Day Registration (EDR) by the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. 1 Consistent with
Election Day Voter Registration in Massachusetts Executive Summary We have analyzed the likely impact of adoption of Election Day Registration (EDR) by the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. 1 Consistent with
THE 2004 YOUTH VOTE MEDIA COVERAGE. Select Newspaper Reports and Commentary
 MEDIA COVERAGE Select Newspaper Reports and Commentary Turnout was up across the board. Youth turnout increased and kept up with the overall increase, said Carrie Donovan, CIRCLE s young vote director.
MEDIA COVERAGE Select Newspaper Reports and Commentary Turnout was up across the board. Youth turnout increased and kept up with the overall increase, said Carrie Donovan, CIRCLE s young vote director.
Jeffrey M. Stonecash Maxwell Professor
 Campbell Public Affairs Institute Inequality and the American Public Results of the Fourth Annual Maxwell School Survey Conducted September, 2007 Jeffrey M. Stonecash Maxwell Professor Campbell Public
Campbell Public Affairs Institute Inequality and the American Public Results of the Fourth Annual Maxwell School Survey Conducted September, 2007 Jeffrey M. Stonecash Maxwell Professor Campbell Public
We have analyzed the likely impact on voter turnout should Hawaii adopt Election Day Registration
 D Ē MOS.ORG ELECTION DAY VOTER REGISTRATION IN HAWAII February 16, 2011 R. Michael Alvarez Jonathan Nagler EXECUTIVE SUMMARY We have analyzed the likely impact on voter turnout should Hawaii adopt Election
D Ē MOS.ORG ELECTION DAY VOTER REGISTRATION IN HAWAII February 16, 2011 R. Michael Alvarez Jonathan Nagler EXECUTIVE SUMMARY We have analyzed the likely impact on voter turnout should Hawaii adopt Election
CIRCLE The Center for Information & Research on Civic Learning & Engagement
 FACT SHEET CIRCLE The Center for Information & Research on Civic Learning & Engagement Religious Service Attendance and Civic Engagement Among 15 to 25 Year Olds By Mark Hugo Lopez, Kumar V. Pratap, and
FACT SHEET CIRCLE The Center for Information & Research on Civic Learning & Engagement Religious Service Attendance and Civic Engagement Among 15 to 25 Year Olds By Mark Hugo Lopez, Kumar V. Pratap, and
THE EFFECT OF EARLY VOTING AND THE LENGTH OF EARLY VOTING ON VOTER TURNOUT
 THE EFFECT OF EARLY VOTING AND THE LENGTH OF EARLY VOTING ON VOTER TURNOUT Simona Altshuler University of Florida Email: simonaalt@ufl.edu Advisor: Dr. Lawrence Kenny Abstract This paper explores the effects
THE EFFECT OF EARLY VOTING AND THE LENGTH OF EARLY VOTING ON VOTER TURNOUT Simona Altshuler University of Florida Email: simonaalt@ufl.edu Advisor: Dr. Lawrence Kenny Abstract This paper explores the effects
Dēmos. Declining Public assistance voter registration and Welfare Reform: Executive Summary. Introduction
 Declining Public assistance voter registration and Welfare Reform: A Response Executive Summary Congress passed the National Voter Registration Act (NVRA) in 1993 in order to increase the number of eligible
Declining Public assistance voter registration and Welfare Reform: A Response Executive Summary Congress passed the National Voter Registration Act (NVRA) in 1993 in order to increase the number of eligible
THE WORKMEN S CIRCLE SURVEY OF AMERICAN JEWS. Jews, Economic Justice & the Vote in Steven M. Cohen and Samuel Abrams
 THE WORKMEN S CIRCLE SURVEY OF AMERICAN JEWS Jews, Economic Justice & the Vote in 2012 Steven M. Cohen and Samuel Abrams 1/4/2013 2 Overview Economic justice concerns were the critical consideration dividing
THE WORKMEN S CIRCLE SURVEY OF AMERICAN JEWS Jews, Economic Justice & the Vote in 2012 Steven M. Cohen and Samuel Abrams 1/4/2013 2 Overview Economic justice concerns were the critical consideration dividing
1. A Republican edge in terms of self-described interest in the election. 2. Lower levels of self-described interest among younger and Latino
 2 Academics use political polling as a measure about the viability of survey research can it accurately predict the result of a national election? The answer continues to be yes. There is compelling evidence
2 Academics use political polling as a measure about the viability of survey research can it accurately predict the result of a national election? The answer continues to be yes. There is compelling evidence
Robert H. Prisuta, American Association of Retired Persons (AARP) 601 E Street, N.W., Washington, D.C
 A POST-ELECTION BANDWAGON EFFECT? COMPARING NATIONAL EXIT POLL DATA WITH A GENERAL POPULATION SURVEY Robert H. Prisuta, American Association of Retired Persons (AARP) 601 E Street, N.W., Washington, D.C.
A POST-ELECTION BANDWAGON EFFECT? COMPARING NATIONAL EXIT POLL DATA WITH A GENERAL POPULATION SURVEY Robert H. Prisuta, American Association of Retired Persons (AARP) 601 E Street, N.W., Washington, D.C.
The Youth Vote 2004 With a Historical Look at Youth Voting Patterns,
 The Youth Vote 2004 With a Historical Look at Youth Voting Patterns, 1972-2004 Mark Hugo Lopez, Research Director Emily Kirby, Research Associate Jared Sagoff, Research Assistant Chris Herbst, Graduate
The Youth Vote 2004 With a Historical Look at Youth Voting Patterns, 1972-2004 Mark Hugo Lopez, Research Director Emily Kirby, Research Associate Jared Sagoff, Research Assistant Chris Herbst, Graduate
CIRCLE The Center for Information & Research on Civic Learning & Engagement
 FACT SHEET CIRCLE The Center for Information & Research on Civic Learning & Engagement Adolescents Trust and Civic Participation in the United States: Analysis of Data from the IEA Civic Education Study
FACT SHEET CIRCLE The Center for Information & Research on Civic Learning & Engagement Adolescents Trust and Civic Participation in the United States: Analysis of Data from the IEA Civic Education Study
All the Cool Kids Are Doing It: The Effects of Group Involvement on Non-electoral Participation
 All the Cool Kids Are Doing It: The Effects of Group Involvement on Non-electoral Participation Aarika P ate I A&S Class of '09 SOC 212, Spring 2008 Vanderbilt University N ashville, TN Abstract Though
All the Cool Kids Are Doing It: The Effects of Group Involvement on Non-electoral Participation Aarika P ate I A&S Class of '09 SOC 212, Spring 2008 Vanderbilt University N ashville, TN Abstract Though
Community Well-Being and the Great Recession
 Pathways Spring 2013 3 Community Well-Being and the Great Recession by Ann Owens and Robert J. Sampson The effects of the Great Recession on individuals and workers are well studied. Many reports document
Pathways Spring 2013 3 Community Well-Being and the Great Recession by Ann Owens and Robert J. Sampson The effects of the Great Recession on individuals and workers are well studied. Many reports document
Class Bias in the U.S. Electorate,
 Class Bias in the U.S. Electorate, 1972-2004 Despite numerous studies confirming the class bias of the electorate, we have only a limited number of studies of changes in class bias over the past several
Class Bias in the U.S. Electorate, 1972-2004 Despite numerous studies confirming the class bias of the electorate, we have only a limited number of studies of changes in class bias over the past several
CHAPTER 8. Trust and the Democratic Temperament. It s difficult to have a civil society when the country is corrupt and criminalized...
 Uslaner, The Moral Foundations of Trust, Chapter 8-1 CHAPTER 8 Trust and the Democratic Temperament It s difficult to have a civil society when the country is corrupt and criminalized... When society is
Uslaner, The Moral Foundations of Trust, Chapter 8-1 CHAPTER 8 Trust and the Democratic Temperament It s difficult to have a civil society when the country is corrupt and criminalized... When society is
public opinion & political behavior D2L is your friend reading material expectations
 public opinion & political behavior PSCI 3051.001 SPRING 2013 EKELEY SCIENCES E1B50 T/TH 12:30 1:45 P.M. DR. JENNIFER WOLAK 131C KETCHUM HALL wolakj@colorado.edu OFFICE HOURS: W 1-3 P.M. & BY APPOINTMENT
public opinion & political behavior PSCI 3051.001 SPRING 2013 EKELEY SCIENCES E1B50 T/TH 12:30 1:45 P.M. DR. JENNIFER WOLAK 131C KETCHUM HALL wolakj@colorado.edu OFFICE HOURS: W 1-3 P.M. & BY APPOINTMENT
National Survey Examines Marriage, Family, Immigration, Health care and Technology in the Age of Trump
 National Survey Examines Marriage, Family, Immigration, Health care and Technology in the Age of Trump Most Americans say biggest problems facing families are economic, but Trump voters are more likely
National Survey Examines Marriage, Family, Immigration, Health care and Technology in the Age of Trump Most Americans say biggest problems facing families are economic, but Trump voters are more likely
Income Distributions and the Relative Representation of Rich and Poor Citizens
 Income Distributions and the Relative Representation of Rich and Poor Citizens Eric Guntermann Mikael Persson University of Gothenburg April 1, 2017 Abstract In this paper, we consider the impact of the
Income Distributions and the Relative Representation of Rich and Poor Citizens Eric Guntermann Mikael Persson University of Gothenburg April 1, 2017 Abstract In this paper, we consider the impact of the
CIRCLE The Center for Information & Research on Civic Learning & Engagement
 FACT SHEET CIRCLE The Center for Information & Research on Civic Learning & Engagement The Youth Vote 2004 By Mark Hugo Lopez, Emily Kirby, and Jared Sagoff 1 July 2005 Estimates from all sources suggest
FACT SHEET CIRCLE The Center for Information & Research on Civic Learning & Engagement The Youth Vote 2004 By Mark Hugo Lopez, Emily Kirby, and Jared Sagoff 1 July 2005 Estimates from all sources suggest
Party Polarization: A Longitudinal Analysis of the Gender Gap in Candidate Preference
 Party Polarization: A Longitudinal Analysis of the Gender Gap in Candidate Preference Tiffany Fameree Faculty Sponsor: Dr. Ray Block, Jr., Department of Political Science/Public Administration ABSTRACT
Party Polarization: A Longitudinal Analysis of the Gender Gap in Candidate Preference Tiffany Fameree Faculty Sponsor: Dr. Ray Block, Jr., Department of Political Science/Public Administration ABSTRACT
2001 Senate Staff Employment Study
 2001 Senate Staff Employment Study Written by Congressional Management Foundation Table of Contents INDIVIDUAL POSITION PROFILES AND ANALYSES Methodology...7 Summary Tables...8 Washington Positions Assistant
2001 Senate Staff Employment Study Written by Congressional Management Foundation Table of Contents INDIVIDUAL POSITION PROFILES AND ANALYSES Methodology...7 Summary Tables...8 Washington Positions Assistant
Comparative Analysis of Inequality, Corruption, and Trust Studies in Modern Societies
 Research Article 2018 Yana Ardelyanova and Olga Obryvalina. This is an open access article licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/).
Research Article 2018 Yana Ardelyanova and Olga Obryvalina. This is an open access article licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/).
Amman, Jordan T: F: /JordanStrategyForumJSF Jordan Strategy Forum
 The Jordan Strategy Forum (JSF) is a not-for-profit organization, which represents a group of Jordanian private sector companies that are active in corporate and social responsibility (CSR) and in promoting
The Jordan Strategy Forum (JSF) is a not-for-profit organization, which represents a group of Jordanian private sector companies that are active in corporate and social responsibility (CSR) and in promoting
Who Votes Now? And Does It Matter?
 Who Votes Now? And Does It Matter? Jan E. Leighley University of Arizona Jonathan Nagler New York University March 7, 2007 Paper prepared for presentation at 2007 Annual Meeting of the Midwest Political
Who Votes Now? And Does It Matter? Jan E. Leighley University of Arizona Jonathan Nagler New York University March 7, 2007 Paper prepared for presentation at 2007 Annual Meeting of the Midwest Political
NUMBERS, FACTS AND TRENDS SHAPING THE WORLD. FOR RELEASE September 12, 2014 FOR FURTHER INFORMATION ON THIS REPORT:
 NUMBERS, FACTS AND TRENDS SHAPING THE WORLD FOR RELEASE September 12, 2014 FOR FURTHER INFORMATION ON THIS REPORT: Carroll Doherty, Director of Political Research Jocelyn Kiley, Associate Director Rachel
NUMBERS, FACTS AND TRENDS SHAPING THE WORLD FOR RELEASE September 12, 2014 FOR FURTHER INFORMATION ON THIS REPORT: Carroll Doherty, Director of Political Research Jocelyn Kiley, Associate Director Rachel
Useful Vot ing Informat ion on Political v. Ente rtain ment Sho ws. Group 6 (3 people)
 Useful Vot ing Informat ion on Political v. Ente rtain ment Sho ws Group 6 () Question During the 2008 election, what types of topics did entertainment-oriented and politically oriented programs cover?
Useful Vot ing Informat ion on Political v. Ente rtain ment Sho ws Group 6 () Question During the 2008 election, what types of topics did entertainment-oriented and politically oriented programs cover?
Race and Economic Opportunity in the United States
 THE EQUALITY OF OPPORTUNITY PROJECT Race and Economic Opportunity in the United States Raj Chetty and Nathaniel Hendren Racial disparities in income and other outcomes are among the most visible and persistent
THE EQUALITY OF OPPORTUNITY PROJECT Race and Economic Opportunity in the United States Raj Chetty and Nathaniel Hendren Racial disparities in income and other outcomes are among the most visible and persistent
Volume 35, Issue 1. An examination of the effect of immigration on income inequality: A Gini index approach
 Volume 35, Issue 1 An examination of the effect of immigration on income inequality: A Gini index approach Brian Hibbs Indiana University South Bend Gihoon Hong Indiana University South Bend Abstract This
Volume 35, Issue 1 An examination of the effect of immigration on income inequality: A Gini index approach Brian Hibbs Indiana University South Bend Gihoon Hong Indiana University South Bend Abstract This
Democracy and Industrial Relations
 I. PRESIDENTIAL ADDRESS Democracy and Industrial Relations Introduction Paula B. Voos Rutgers University Political democracy is thriving in the world. Think about the changes that have occurred in Korea,
I. PRESIDENTIAL ADDRESS Democracy and Industrial Relations Introduction Paula B. Voos Rutgers University Political democracy is thriving in the world. Think about the changes that have occurred in Korea,
Nonvoters in America 2012
 Nonvoters in America 2012 A Study by Professor Ellen Shearer Medill School of Journalism, Media, Integrated Marketing Communications Northwestern University Survey Conducted by Ipsos Public Affairs When
Nonvoters in America 2012 A Study by Professor Ellen Shearer Medill School of Journalism, Media, Integrated Marketing Communications Northwestern University Survey Conducted by Ipsos Public Affairs When
Author(s): Title: Date: Dataset(s): Abstract
 Author(s): Knack, Stephen Title: Social Altruism and Voter Turnout: Evidence from the 1991 NES Pilot Study Date: January 1992 Dataset(s): 1991 Pilot Study Abstract Knack uses data from the 1991 Pilot Study
Author(s): Knack, Stephen Title: Social Altruism and Voter Turnout: Evidence from the 1991 NES Pilot Study Date: January 1992 Dataset(s): 1991 Pilot Study Abstract Knack uses data from the 1991 Pilot Study
THE PUBLIC AND THE CRITICAL ISSUES BEFORE CONGRESS IN THE SUMMER AND FALL OF 2017
 THE PUBLIC AND THE CRITICAL ISSUES BEFORE CONGRESS IN THE SUMMER AND FALL OF 2017 July 2017 1 INTRODUCTION At the time this poll s results are being released, the Congress is engaged in a number of debates
THE PUBLIC AND THE CRITICAL ISSUES BEFORE CONGRESS IN THE SUMMER AND FALL OF 2017 July 2017 1 INTRODUCTION At the time this poll s results are being released, the Congress is engaged in a number of debates
Statistics, Politics, and Policy
 Statistics, Politics, and Policy Volume 1, Issue 1 2010 Article 3 A Snapshot of the 2008 Election Andrew Gelman, Columbia University Daniel Lee, Columbia University Yair Ghitza, Columbia University Recommended
Statistics, Politics, and Policy Volume 1, Issue 1 2010 Article 3 A Snapshot of the 2008 Election Andrew Gelman, Columbia University Daniel Lee, Columbia University Yair Ghitza, Columbia University Recommended
Political Participation and Policy
 Political Participation and Policy PADM-GP.4124, 1.5 Points, 2016 J-term Syllabus Time: Tuesday/Thursdays, 2:30pm to 5:30pm Location: BOBS Room LL138 Dates: 1/7 to 1/21 Professor Aram Hur Puck Building,
Political Participation and Policy PADM-GP.4124, 1.5 Points, 2016 J-term Syllabus Time: Tuesday/Thursdays, 2:30pm to 5:30pm Location: BOBS Room LL138 Dates: 1/7 to 1/21 Professor Aram Hur Puck Building,
Chapter 8:3 The Media
 Chapter 8:3 The Media Rev_13:11 And I beheld another beast coming up out of the earth; and he had two horns like a lamb, and he spake as a dragon. Chapter 8:3 The Media o We will examine the role of the
Chapter 8:3 The Media Rev_13:11 And I beheld another beast coming up out of the earth; and he had two horns like a lamb, and he spake as a dragon. Chapter 8:3 The Media o We will examine the role of the
A Perpetuating Negative Cycle: The Effects of Economic Inequality on Voter Participation. By Jenine Saleh Advisor: Dr. Rudolph
 A Perpetuating Negative Cycle: The Effects of Economic Inequality on Voter Participation By Jenine Saleh Advisor: Dr. Rudolph Thesis For the Degree of Bachelor of Arts in Liberal Arts and Sciences College
A Perpetuating Negative Cycle: The Effects of Economic Inequality on Voter Participation By Jenine Saleh Advisor: Dr. Rudolph Thesis For the Degree of Bachelor of Arts in Liberal Arts and Sciences College
THE LOUISIANA SURVEY 2018
 THE LOUISIANA SURVEY 2018 Criminal justice reforms and Medicaid expansion remain popular with Louisiana public Popular support for work requirements and copayments for Medicaid The fifth in a series of
THE LOUISIANA SURVEY 2018 Criminal justice reforms and Medicaid expansion remain popular with Louisiana public Popular support for work requirements and copayments for Medicaid The fifth in a series of
Strengthening Democracy by Increasing Youth Political Knowledge and Engagement. Laura Langer Bemidji State University
 Strengthening Democracy by Increasing Youth Political Knowledge and Engagement Laura Langer Bemidji State University Political Science Senior Thesis Bemidji State University Dr. Patrick Donnay, Advisor
Strengthening Democracy by Increasing Youth Political Knowledge and Engagement Laura Langer Bemidji State University Political Science Senior Thesis Bemidji State University Dr. Patrick Donnay, Advisor
How s Life in Mexico?
 How s Life in Mexico? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Mexico has a mixed performance across the different well-being dimensions. At 61% in 2016, Mexico s employment rate was below the OECD
How s Life in Mexico? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Mexico has a mixed performance across the different well-being dimensions. At 61% in 2016, Mexico s employment rate was below the OECD
The Future of Inequality
 The Future of Inequality As almost every economic policymaker is aware, the gap between the wages of educated and lesseducated workers has been growing since the early 1980s and that change has been both
The Future of Inequality As almost every economic policymaker is aware, the gap between the wages of educated and lesseducated workers has been growing since the early 1980s and that change has been both
Trend in Redistributive Effects Foreign Remittances in Pakistan in , and
 Fouzia Jamshaid* Abdul Qayyum Mohsin** Ikram Ali Malik*** Trend in Redistributive Effects Foreign Remittances in Pakistan in 2001-02, 2005-06 and 2010-11 ABSTRACT A good chunk of factors affect the economic
Fouzia Jamshaid* Abdul Qayyum Mohsin** Ikram Ali Malik*** Trend in Redistributive Effects Foreign Remittances in Pakistan in 2001-02, 2005-06 and 2010-11 ABSTRACT A good chunk of factors affect the economic
PRESS RELEASE October 15, 2008
 PRESS RELEASE October 15, 2008 Americans Confidence in Their Leaders Declines Sharply Most agree on basic aspects of presidential leadership, but candidate preferences reveal divisions Cambridge, MA 80%
PRESS RELEASE October 15, 2008 Americans Confidence in Their Leaders Declines Sharply Most agree on basic aspects of presidential leadership, but candidate preferences reveal divisions Cambridge, MA 80%
Does Electoral Reform Increase (or Decrease) Political Equality?
 Policy Studies Organization From the SelectedWorks of Elizabeth Rigby 2010 Does Electoral Reform Increase (or Decrease) Political Equality? Elizabeth Rigby, University of Houston - Main Melanie J. Springer
Policy Studies Organization From the SelectedWorks of Elizabeth Rigby 2010 Does Electoral Reform Increase (or Decrease) Political Equality? Elizabeth Rigby, University of Houston - Main Melanie J. Springer
CSES Module 5 Pretest Report: Greece. August 31, 2016
 CSES Module 5 Pretest Report: Greece August 31, 2016 1 Contents INTRODUCTION... 4 BACKGROUND... 4 METHODOLOGY... 4 Sample... 4 Representativeness... 4 DISTRIBUTIONS OF KEY VARIABLES... 7 ATTITUDES ABOUT
CSES Module 5 Pretest Report: Greece August 31, 2016 1 Contents INTRODUCTION... 4 BACKGROUND... 4 METHODOLOGY... 4 Sample... 4 Representativeness... 4 DISTRIBUTIONS OF KEY VARIABLES... 7 ATTITUDES ABOUT
Hungary. Basic facts The development of the quality of democracy in Hungary. The overall quality of democracy
 Hungary Basic facts 2007 Population 10 055 780 GDP p.c. (US$) 13 713 Human development rank 43 Age of democracy in years (Polity) 17 Type of democracy Electoral system Party system Parliamentary Mixed:
Hungary Basic facts 2007 Population 10 055 780 GDP p.c. (US$) 13 713 Human development rank 43 Age of democracy in years (Polity) 17 Type of democracy Electoral system Party system Parliamentary Mixed:
A Transatlantic Divide?
 A Transatlantic Divide? Social Capital in the United States and Europe Pippa Norris and James A. Davis Pippa Norris James A. Davis John F. Kennedy School of Government The Department of Sociology Harvard
A Transatlantic Divide? Social Capital in the United States and Europe Pippa Norris and James A. Davis Pippa Norris James A. Davis John F. Kennedy School of Government The Department of Sociology Harvard
Political Studies, 58(1), 2010, pp
 Inequalities in Non-Institutionalized Forms of Political Participation. A Multilevel Analysis for 25 countries. Sofie Marien Marc Hooghe Ellen Quintelier Political Studies, 58(1), 2010, pp. 187-213. Political
Inequalities in Non-Institutionalized Forms of Political Participation. A Multilevel Analysis for 25 countries. Sofie Marien Marc Hooghe Ellen Quintelier Political Studies, 58(1), 2010, pp. 187-213. Political
A Statistical Abstract Analysis of the Gelman Paradox: Why correlation does not denote. causation in voting outcomes based on regional average incomes
 A Statistical Abstract Analysis of the Gelman Paradox: Why correlation does not denote causation in voting outcomes based on regional average incomes John W, PhD Peru State College Dr. Andrew Gelman Ph.D.
A Statistical Abstract Analysis of the Gelman Paradox: Why correlation does not denote causation in voting outcomes based on regional average incomes John W, PhD Peru State College Dr. Andrew Gelman Ph.D.
Who Really Voted for Obama in 2008 and 2012?
 Who Really Voted for Obama in 2008 and 2012? Helena N. Hlavaty a, Mohamed A. Hussein a, Peter Kiley-Bergen a, Liuxufei Yang a, and Paul M. Sommers a The authors use simple bilinear regression on statewide
Who Really Voted for Obama in 2008 and 2012? Helena N. Hlavaty a, Mohamed A. Hussein a, Peter Kiley-Bergen a, Liuxufei Yang a, and Paul M. Sommers a The authors use simple bilinear regression on statewide
CAMPBELL PUBLIC AFFAIRS INSTITUTE. The Maxwell Poll. Inequality and the American Public: October, 2006 Updated November 15, 2006
 CAMPBELL PUBLIC AFFAIRS INSTITUTE The Maxwell Poll October, 2006 Updated November 15, 2006 Inequality and the American Public: Results of the Third Annual Maxwell Poll Conducted September - October, 2006
CAMPBELL PUBLIC AFFAIRS INSTITUTE The Maxwell Poll October, 2006 Updated November 15, 2006 Inequality and the American Public: Results of the Third Annual Maxwell Poll Conducted September - October, 2006
CITIZEN ADVOCACY CENTER
 CITIZEN ADVOCACY CENTER Young Voters and Civic Participation LESSON PLAN AND ACTIVITIES All rights reserved. No part of this lesson plan may be reproduced in any form or by any electronic or mechanical
CITIZEN ADVOCACY CENTER Young Voters and Civic Participation LESSON PLAN AND ACTIVITIES All rights reserved. No part of this lesson plan may be reproduced in any form or by any electronic or mechanical
The text defines suffrage and franchise as the right to participate. speak. protest. *vote. rally.
 The text defines as the actions of private citizens by which they seek to influence or support government and politics. direct action *political participation unconventional participation conventional
The text defines as the actions of private citizens by which they seek to influence or support government and politics. direct action *political participation unconventional participation conventional
AmericasBarometer Insights: 2010 (No. 37) * Trust in Elections
 AmericasBarometer Insights: 2010 (No. 37) * By Matthew L. Layton Matthew.l.layton@vanderbilt.edu Vanderbilt University E lections are the keystone of representative democracy. While they may not be sufficient
AmericasBarometer Insights: 2010 (No. 37) * By Matthew L. Layton Matthew.l.layton@vanderbilt.edu Vanderbilt University E lections are the keystone of representative democracy. While they may not be sufficient
Response to the Report Evaluation of Edison/Mitofsky Election System
 US Count Votes' National Election Data Archive Project Response to the Report Evaluation of Edison/Mitofsky Election System 2004 http://exit-poll.net/election-night/evaluationjan192005.pdf Executive Summary
US Count Votes' National Election Data Archive Project Response to the Report Evaluation of Edison/Mitofsky Election System 2004 http://exit-poll.net/election-night/evaluationjan192005.pdf Executive Summary
RECOMMENDED CITATION: Pew Research Center, May, 2017, Public Trust in Government Remains Near Historic Lows as Partisan Attitudes Shift
 NUMBERS, FACTS AND TRENDS SHAPING THE WORLD FOR RELEASE MAY 3, 2017 FOR MEDIA OR OTHER INQUIRIES: Carroll Doherty, Director of Political Research Jocelyn Kiley, Associate Director, Research Bridget Johnson,
NUMBERS, FACTS AND TRENDS SHAPING THE WORLD FOR RELEASE MAY 3, 2017 FOR MEDIA OR OTHER INQUIRIES: Carroll Doherty, Director of Political Research Jocelyn Kiley, Associate Director, Research Bridget Johnson,
IPR 40 th Anniversary Distinguished Public Policy Lecture. Rebecca Blank. "Why Does Inequality Matter and What Should We Do About It?
 IPR 40 th Anniversary Distinguished Public Policy Lecture Rebecca Blank "Why Does Inequality Matter and What Should We Do About It?" Robert S. Kerr Senior Fellow, Brookings Institution. Former Dean of
IPR 40 th Anniversary Distinguished Public Policy Lecture Rebecca Blank "Why Does Inequality Matter and What Should We Do About It?" Robert S. Kerr Senior Fellow, Brookings Institution. Former Dean of
The Effect of Political Trust on the Voter Turnout of the Lower Educated
 The Effect of Political Trust on the Voter Turnout of the Lower Educated Jaap Meijer Inge van de Brug June 2013 Jaap Meijer (3412504) & Inge van de Brug (3588408) Bachelor Thesis Sociology Faculty of Social
The Effect of Political Trust on the Voter Turnout of the Lower Educated Jaap Meijer Inge van de Brug June 2013 Jaap Meijer (3412504) & Inge van de Brug (3588408) Bachelor Thesis Sociology Faculty of Social
Content Analysis of Network TV News Coverage
 Supplemental Technical Appendix for Hayes, Danny, and Matt Guardino. 2011. The Influence of Foreign Voices on U.S. Public Opinion. American Journal of Political Science. Content Analysis of Network TV
Supplemental Technical Appendix for Hayes, Danny, and Matt Guardino. 2011. The Influence of Foreign Voices on U.S. Public Opinion. American Journal of Political Science. Content Analysis of Network TV
Youth Voter Turnout has Declined, by Any Measure By Peter Levine and Mark Hugo Lopez 1 September 2002
 Youth Voter has Declined, by Any Measure By Peter Levine and Mark Hugo Lopez 1 September 2002 Measuring young people s voting raises difficult issues, and there is not a single clearly correct turnout
Youth Voter has Declined, by Any Measure By Peter Levine and Mark Hugo Lopez 1 September 2002 Measuring young people s voting raises difficult issues, and there is not a single clearly correct turnout
VoteCastr methodology
 VoteCastr methodology Introduction Going into Election Day, we will have a fairly good idea of which candidate would win each state if everyone voted. However, not everyone votes. The levels of enthusiasm
VoteCastr methodology Introduction Going into Election Day, we will have a fairly good idea of which candidate would win each state if everyone voted. However, not everyone votes. The levels of enthusiasm
Publicizing malfeasance:
 Publicizing malfeasance: When media facilitates electoral accountability in Mexico Horacio Larreguy, John Marshall and James Snyder Harvard University May 1, 2015 Introduction Elections are key for political
Publicizing malfeasance: When media facilitates electoral accountability in Mexico Horacio Larreguy, John Marshall and James Snyder Harvard University May 1, 2015 Introduction Elections are key for political
National Judicial Outreach Week March 4-10, 2018 INFORMATION PACKET
 National Judicial Outreach Week March 4-10, 2018 INFORMATION PACKET American Bar Association Judicial Division Judicial Outreach Network National Judicial Outreach Week 2018 March 4-10, 2018 TABLE OF CONTENTS
National Judicial Outreach Week March 4-10, 2018 INFORMATION PACKET American Bar Association Judicial Division Judicial Outreach Network National Judicial Outreach Week 2018 March 4-10, 2018 TABLE OF CONTENTS
NATIONAL: 2018 HOUSE RACE STABILITY
 Please attribute this information to: Monmouth University Poll West Long Branch, NJ 07764 www.monmouth.edu/polling Follow on Twitter: @MonmouthPoll Released: Friday, November 2, 2018 Contact: PATRICK MURRAY
Please attribute this information to: Monmouth University Poll West Long Branch, NJ 07764 www.monmouth.edu/polling Follow on Twitter: @MonmouthPoll Released: Friday, November 2, 2018 Contact: PATRICK MURRAY
The Impact of the Fall 1997 Debate About Global Warming On American Public Opinion
 The Impact of the Fall 1997 Debate About Global Warming On American Public Opinion Jon A. Krosnick and Penny S. Visser Summary of Findings JULY 28, 1998 -- On October 6, 1997, the White House Conference
The Impact of the Fall 1997 Debate About Global Warming On American Public Opinion Jon A. Krosnick and Penny S. Visser Summary of Findings JULY 28, 1998 -- On October 6, 1997, the White House Conference
Chile s average level of current well-being: Comparative strengths and weaknesses
 How s Life in Chile? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Chile has a mixed performance across the different well-being dimensions. Although performing well in terms of housing affordability
How s Life in Chile? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Chile has a mixed performance across the different well-being dimensions. Although performing well in terms of housing affordability
FOR RELEASE APRIL 26, 2018
 FOR RELEASE APRIL 26, 2018 FOR MEDIA OR OTHER INQUIRIES: Carroll Doherty, Director of Political Research Jocelyn Kiley, Associate Director, Research Bridget Johnson, Communications Associate 202.419.4372
FOR RELEASE APRIL 26, 2018 FOR MEDIA OR OTHER INQUIRIES: Carroll Doherty, Director of Political Research Jocelyn Kiley, Associate Director, Research Bridget Johnson, Communications Associate 202.419.4372
Luxembourg Income Study Working Paper Series
 Luxembourg Income Study Working Paper Series Working Paper No. 385 Economic Inequality and Democratic Political Engagement Frederick Solt July 2004 Luxembourg Income Study (LIS), asbl Abstract Economic
Luxembourg Income Study Working Paper Series Working Paper No. 385 Economic Inequality and Democratic Political Engagement Frederick Solt July 2004 Luxembourg Income Study (LIS), asbl Abstract Economic
The Effect of Ballot Order: Evidence from the Spanish Senate
 The Effect of Ballot Order: Evidence from the Spanish Senate Manuel Bagues Berta Esteve-Volart November 20, 2011 PRELIMINARY AND INCOMPLETE Abstract This paper analyzes the relevance of ballot order in
The Effect of Ballot Order: Evidence from the Spanish Senate Manuel Bagues Berta Esteve-Volart November 20, 2011 PRELIMINARY AND INCOMPLETE Abstract This paper analyzes the relevance of ballot order in
Winning the Economic Argument Report on October National survey: The Economy
 Date: November 3, 2011 To: From: Friends of Democracy Corps and Greenberg Quinlan Rosner Stanley Greenberg, James Carville, and Erica Seifert Winning the Economic Argument Report on October National survey:
Date: November 3, 2011 To: From: Friends of Democracy Corps and Greenberg Quinlan Rosner Stanley Greenberg, James Carville, and Erica Seifert Winning the Economic Argument Report on October National survey:
Who Votes Without Identification? Using Affidavits from Michigan to Learn About the Potential Impact of Strict Photo Voter Identification Laws
 Using Affidavits from Michigan to Learn About the Potential Impact of Strict Photo Voter Identification Laws Phoebe Henninger Marc Meredith Michael Morse University of Michigan University of Pennsylvania
Using Affidavits from Michigan to Learn About the Potential Impact of Strict Photo Voter Identification Laws Phoebe Henninger Marc Meredith Michael Morse University of Michigan University of Pennsylvania
and with support from BRIEFING NOTE 1
 and with support from BRIEFING NOTE 1 Inequality and growth: the contrasting stories of Brazil and India Concern with inequality used to be confined to the political left, but today it has spread to a
and with support from BRIEFING NOTE 1 Inequality and growth: the contrasting stories of Brazil and India Concern with inequality used to be confined to the political left, but today it has spread to a
Income inequality and voter turnout
 Income inequality and voter turnout HORN, Dániel Max Weber Fellow, EUI Hogy áll Magyarország 2012-ben? Konferencia a gazdasági körülményekrıl és a társadalmi kohézióról 2012. November 22-23, Budapest Introduction
Income inequality and voter turnout HORN, Dániel Max Weber Fellow, EUI Hogy áll Magyarország 2012-ben? Konferencia a gazdasági körülményekrıl és a társadalmi kohézióról 2012. November 22-23, Budapest Introduction
YOUNG VOTERS and the WEB of POLITICS. Pathways to Participation in the Youth Engagement and Electoral Campaign Web
 YOUNG VOTERS and the WEB of POLITICS Pathways to Participation in the Youth Engagement and Electoral Campaign Web W. Lance Bennett and Mike Xenos * University of Washington *mxenos@u.washington.edu http://depts.washington.edu/ccce/home.htm
YOUNG VOTERS and the WEB of POLITICS Pathways to Participation in the Youth Engagement and Electoral Campaign Web W. Lance Bennett and Mike Xenos * University of Washington *mxenos@u.washington.edu http://depts.washington.edu/ccce/home.htm
How s Life in Norway?
 How s Life in Norway? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Norway performs very well across the OECD s different well-being indicators and dimensions. Job strain and long-term unemployment are
How s Life in Norway? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Norway performs very well across the OECD s different well-being indicators and dimensions. Job strain and long-term unemployment are
Inequality, cohesion and the middle-class dream
 Essay 193 Broken societies Inequality, cohesion and the middle-class dream Danish academic Christian Larsen challenges traditional accounts of social cohesion by arguing that the degree to which society
Essay 193 Broken societies Inequality, cohesion and the middle-class dream Danish academic Christian Larsen challenges traditional accounts of social cohesion by arguing that the degree to which society
Determinants of Violent Crime in the U.S: Evidence from State Level Data
 12 Journal Student Research Determinants of Violent Crime in the U.S: Evidence from State Level Data Grace Piggott Sophomore, Applied Social Science: Concentration Economics ABSTRACT This study examines
12 Journal Student Research Determinants of Violent Crime in the U.S: Evidence from State Level Data Grace Piggott Sophomore, Applied Social Science: Concentration Economics ABSTRACT This study examines
netw rks The Resurgence of Conservatism, Ronald Reagan s Inauguration Background
 Analyzing Primary Sources Activity Ronald Reagan s Inauguration Background When Ronald Reagan was sworn in as the fortieth president of the United States, the country was facing several crises. The economy
Analyzing Primary Sources Activity Ronald Reagan s Inauguration Background When Ronald Reagan was sworn in as the fortieth president of the United States, the country was facing several crises. The economy
FAVORABLE RATINGS OF LABOR UNIONS FALL SHARPLY
 NEWS Release. 1615 L Street, N.W., Suite 700 Washington, D.C. 20036 Tel (202) 419-4350 Fax (202) 419-4399 FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE: Tuesday, February 23, 2010 FOR FURTHER INFORMATION: Andrew Kohut, Director
NEWS Release. 1615 L Street, N.W., Suite 700 Washington, D.C. 20036 Tel (202) 419-4350 Fax (202) 419-4399 FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE: Tuesday, February 23, 2010 FOR FURTHER INFORMATION: Andrew Kohut, Director
Supplementary Materials A: Figures for All 7 Surveys Figure S1-A: Distribution of Predicted Probabilities of Voting in Primary Elections
 Supplementary Materials (Online), Supplementary Materials A: Figures for All 7 Surveys Figure S-A: Distribution of Predicted Probabilities of Voting in Primary Elections (continued on next page) UT Republican
Supplementary Materials (Online), Supplementary Materials A: Figures for All 7 Surveys Figure S-A: Distribution of Predicted Probabilities of Voting in Primary Elections (continued on next page) UT Republican
Italy s average level of current well-being: Comparative strengths and weaknesses
 How s Life in Italy? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Italy s average performance across the different well-being dimensions is mixed. The employment rate, about 57% in 2016, was among the
How s Life in Italy? November 2017 Relative to other OECD countries, Italy s average performance across the different well-being dimensions is mixed. The employment rate, about 57% in 2016, was among the
POLITICAL CORRUPTION AND IT S EFFECTS ON CIVIC INVOLVEMENT. By: Lilliard Richardson. School of Public and Environmental Affairs
 POLITICAL CORRUPTION AND IT S EFFECTS ON CIVIC INVOLVEMENT By: Lilliard Richardson School of Public and Environmental Affairs Indiana University-Purdue University Indianapolis September 2012 Paper Originally
POLITICAL CORRUPTION AND IT S EFFECTS ON CIVIC INVOLVEMENT By: Lilliard Richardson School of Public and Environmental Affairs Indiana University-Purdue University Indianapolis September 2012 Paper Originally
political participation
 political participation PSCI 5901.003/7901.003 Fall 2007 T 12:30-3:00 P.M. 116 Ketchum webct.colorado.edu Dr. Jennifer Wolak 136 Ketchum Hall wolakj@colorado.edu Hours: W 1-3 P.M. and by appointment Why
political participation PSCI 5901.003/7901.003 Fall 2007 T 12:30-3:00 P.M. 116 Ketchum webct.colorado.edu Dr. Jennifer Wolak 136 Ketchum Hall wolakj@colorado.edu Hours: W 1-3 P.M. and by appointment Why
Chapter 8: Mass Media and Public Opinion Section 1 Objectives Key Terms public affairs: public opinion: mass media: peer group: opinion leader:
 Chapter 8: Mass Media and Public Opinion Section 1 Objectives Examine the term public opinion and understand why it is so difficult to define. Analyze how family and education help shape public opinion.
Chapter 8: Mass Media and Public Opinion Section 1 Objectives Examine the term public opinion and understand why it is so difficult to define. Analyze how family and education help shape public opinion.
PS 5030: Seminar in American Government & Politics Fall 2008 Thursdays 6:15pm-9:00pm Room 1132, Old Library Classroom
 PS 5030: Seminar in American Government & Politics Fall 2008 Thursdays 6:15pm-9:00pm Room 1132, Old Library Classroom Professor: Todd Hartman Phone: (828) 262-6827 Office: 2059 Old Belk Library Classroom
PS 5030: Seminar in American Government & Politics Fall 2008 Thursdays 6:15pm-9:00pm Room 1132, Old Library Classroom Professor: Todd Hartman Phone: (828) 262-6827 Office: 2059 Old Belk Library Classroom
The Youth Vote in 2008 By Emily Hoban Kirby and Kei Kawashima-Ginsberg 1 Updated August 17, 2009
 The Youth Vote in 2008 By Emily Hoban Kirby and Kei Kawashima-Ginsberg 1 Updated August 17, 2009 Estimates from the Census Current Population Survey November Supplement suggest that the voter turnout rate
The Youth Vote in 2008 By Emily Hoban Kirby and Kei Kawashima-Ginsberg 1 Updated August 17, 2009 Estimates from the Census Current Population Survey November Supplement suggest that the voter turnout rate
CONSERVATIVES PULLING AWAY FROM MORIBUND LIBERALS SOME NOTABLE CHANGES IN BROADER OUTLOOK
 www.ekospolitics.ca CONSERVATIVES PULLING AWAY FROM MORIBUND LIBERALS SOME NOTABLE CHANGES IN BROADER OUTLOOK [Ottawa November 25, 2010] In a familiar pattern, the Conservatives are once again establishing
www.ekospolitics.ca CONSERVATIVES PULLING AWAY FROM MORIBUND LIBERALS SOME NOTABLE CHANGES IN BROADER OUTLOOK [Ottawa November 25, 2010] In a familiar pattern, the Conservatives are once again establishing
RECOMMENDED CITATION: Pew Research Center, October, 2015, On Immigration Policy, Wider Partisan Divide Over Border Fence Than Path to Legal Status
 NUMBERS, FACTS AND TRENDS SHAPING THE WORLD FOR RELEASE OCTOBER 8, 2015 FOR FURTHER INFORMATION ON THIS REPORT: Carroll Doherty, Director of Political Research Rob Suls, Research Associate Bridget Jameson,
NUMBERS, FACTS AND TRENDS SHAPING THE WORLD FOR RELEASE OCTOBER 8, 2015 FOR FURTHER INFORMATION ON THIS REPORT: Carroll Doherty, Director of Political Research Rob Suls, Research Associate Bridget Jameson,
Unequal Recovery, Labor Market Polarization, Race, and 2016 U.S. Presidential Election. Maoyong Fan and Anita Alves Pena 1
 Unequal Recovery, Labor Market Polarization, Race, and 2016 U.S. Presidential Election Maoyong Fan and Anita Alves Pena 1 Abstract: Growing income inequality and labor market polarization and increasing
Unequal Recovery, Labor Market Polarization, Race, and 2016 U.S. Presidential Election Maoyong Fan and Anita Alves Pena 1 Abstract: Growing income inequality and labor market polarization and increasing
Chapter 10. Resource Markets and the Distribution of Income. Copyright 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 10 Resource Markets and the Distribution of Income Resource markets differ from markets for consumer goods in several key ways First, the demand for resources comes from firms producing goods and
Chapter 10 Resource Markets and the Distribution of Income Resource markets differ from markets for consumer goods in several key ways First, the demand for resources comes from firms producing goods and
download slides at: Politics Inequality in the United States 1
 Inequality in the United States 1 Political Participation and Income Percent Active 90.0 67.5 45.0 22.5 0 Voting Campaign Work Campaign Contribution under $15,000 $75,000 and over Contact Protest Affiliated
Inequality in the United States 1 Political Participation and Income Percent Active 90.0 67.5 45.0 22.5 0 Voting Campaign Work Campaign Contribution under $15,000 $75,000 and over Contact Protest Affiliated
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF UNDERGRADUATE RESEARCH VOL. 3 NO. 4 (2005)
 , Partisanship and the Post Bounce: A MemoryBased Model of Post Presidential Candidate Evaluations Part II Empirical Results Justin Grimmer Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Wabash College
, Partisanship and the Post Bounce: A MemoryBased Model of Post Presidential Candidate Evaluations Part II Empirical Results Justin Grimmer Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Wabash College
