CONTRACTS Bartlett Spring 2010
|
|
|
- Dwayne McDowell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Generally... 2 Slide: Components of course... 3 Contract existed (Formation)... 3 Slide: Contract formation... 3 Offer... 4 Interim period: Revocation... 5 Acceptance... 6 Acceptance: Bilateral v. Unilateral... 8 Mutual Assent overview ( so far ) Feb Mutual assent...10 Slide: What is the modern rule of Raffle? Restatement Slide: What meaning have parties attached to a promise? Rst Slide: Mutual Assent & Ambiguous Term Algorithm Statute of Frauds...13 Consideration...14 Slide: Does formality theory ever win? Intent to Be Bound...17 Promissory Estoppel...17 Discerning the [terms of the] agreement...19 Slide: Subjective understandings: Assent (Formation) and Term Interpretation (Discerning) failure = no mutual assent. 20 Illusory promises: Missing promise altogether...20 Form contracts...21 UCC: Add l terms (2-207 analysis): Battle of the Forms Flowchart -- Use This One...23 Parol evidence...24 UCC filler terms: to Duty of Good Faith Performance...26 Implied Warranties...27 Express warranties...28 Contract was breached...29 UCC Rescission and Cure Flowchart...33 Brief review of breach...33 Intentional (Tortious) interference w/ contract...34 Damages...34 Expectation damages...35 Slide: Restatement Reliance damages...37 Restitution...38 Slide: Rounding out Restitution Rescission...41 Limitations on damages...41 Slide: Avoidability doctrine: Wrongfully-discharged employee (Shirley McLaine) UCC Remedies...43 Liquidated damages & penalty clauses...45 Efficient breach...46 Specific performance...47 Defenses...48 Capacity to Assent...48 Assent by Improper Means...49 Slide: Undue influence in California Slide: Analyzing Unconscionability Failure of Basic Assumption...53 Slide: Mistake of Fact: Enforce or Not? Slide: Summary of Contract Defenses General Principles...56 Hypos and Results...58 Seller & Buyer Breach: Common law and UCC (Expectation Damages)
2 Generally I. Generally I.a. I.b. I.c. I.d. I.e. I.f. I.g. Think about: DOCTRINE + FACTS + POLICY Affecting behavior: Morality, Law, Economics, Relational norms Special contract = Express contract: peculiar provisions not ordinarily found in Ks relating to same SM. Public Policy: only when so obviously for or against public health, safety, morals, or welfare that there is virtual unanimity wrt it, that court may constitute itself the voice of community in declaring policy void. i. Shaheen (gives us damages requirement rule) the doctor and patient sterility case. Hit man contract can never be enforceable. Public policy considerations: Incentive Autonomy Institutional competence. i. We want to respect the autonomy of people who enter into contracts. Most of the time... Also, institutional motive: the court (e.g. in Shaheen) wants nothing to do with raising the child. i Elements of pfc in K: (much easier to meet than Negligence standard in Torts) i. A contract existed. Contract was breached 1. tmc: Need to know the terms, man! i Promisee suffered damages as a result. Choice of Law: Hooker test. i. Depends on the nature of the contract and also upon whether dispute in question primarily concerns the goods furnished or the services rendered under the K. UCC Mixed transaction of goods & services. What is the UCC measure of damages?? i Common law: K damages are ordinarily based on injured party s expectation interest and are intended to give him benefit of the bargain by awarding him sum of money that will... put him in as good a position as he would have been in had the contract been performed. iv. 2
3 II.b. MUTUAL ASSENT GENERALLY i. Objective theory of assent. With subjective twist. Look at outward signs and actions to determine. 1. Satisfy 2 conditions: a. Objective assent b. Understanding by other person that it s assent being given. If you re assenting, and you know other party will likely construe your statement as assent, then it s assent. i. The inquiry is context-specific. The issue: Who is the reasonable person?? Any representation looked at must have been made to the plaintiff the target person. A memo to third parties is NOT admissible, since it cannot inform what the target understood those objective actions to mean. Rules. Objective theory of assent, with subjective twist (vague & ambiguous terms become subjective intent of parties standard). i Embry (get your men out, you ll be fine). [I guess there is no question as to acceptance, so focus on the offer to re-employ, for another year. And reliance on that? Yes.] Case gives us objective theory of assent: here, it s ambiguous, but that s what this case is teaching us. You must look at outward signs. Was the assent to the contract objectively manifested? In this case, court holds YES. iv. Lucy v. Zehmer ( high as a Georgia pine ). Despite subjective (internal) intent NOT to form a contract, the outward signs are just SO CLEAR that an offer was being made, that it must be enforced. 1. Also, not incompetent: Court finds overwhelming evidence that D knew exactly what he was doing. 2. And, since it s land specific performance! Offer II.c. OFFER i. Restatement 24 (Offer). Offer = manifestation of willingness to enter into bargain, so made as to justify i iv. another person in understanding that his assent to that bargain is invited and will conclude it. Restatement 26 (Preliminary Negotiations) = manifestation of willingness is NOT offer, if person to whom addressed knows or has reason to know that person making it does NOT intend to conclude bargain, until a further manifestation of assent. 1. cmt a: reason to know = words, conduct, circumstances (incl. previous communications & usages in communities or line of business) 2. cmt c: relevant factors to whether offer is made: terms of any previous inquiry, completeness of the terms of the suggested bargain, and number of persons to whom communication is addressed. a. NUMBER OF PERSONS! Placing a software product on a shelf is for EVERYONE, clearly that s merely a preliminary negotiation. An invitation to receive offers! What is an offer? Nebraska Seed, Leonard v. Pepsico. Completeness Doctrine 1. Restatement 33, and UCC Terms of the offer must be reasonably certain completeness doctrine. 3. But no contract is completely w/r/t everything so some leeway must be left in there. a. UCC seems to give more leeway than Restatement. 4. However BOTH parties must recognize that a contract is being made, the existence of the K hurdles a : must be apparent to the reasonable person. b. Manifestation of intent to form a contract. 6. UCC a. Parties must have intended to make a contract b. There is reasonably certain basis for giving an appropriate remedy. 4
4 v. Nebraska Seed: it was a circular, an advertisement not an offer. Rule Advertisements/circulars are NOT offers generally!! It s merely a preliminary negotiation.!!! Easterbrook!!! Lookie here lookie here!! 1. As a policy matter, you want parties to be able to market their goods so that they can get some offers to buy. (Perhaps this is how one might understand the cases? That... yeah, placing the product on the shelving is NOT an offer;; rather, it s an advertisement! A circular! Or the equivalent thereof!!!) 2. Hurdle 1 was NOT met: no reasonable person could expect this to be an offer. vi. When is written memorial sufficient? Not always: Empro, Texaco. 1. Empro: shoals that wrecked deal are common in business. Wouldn t make sense to hold buyer to the LOI, so NO contract found. Important business terms were lacking, so no intent to be bound when those terms were not present. 2. Texaco: intent to be bound (Getty & Pennzoil) was clear; there WAS a contract, which meant that tortious interference COULD take place, and Texaco was guilty. Well, there was a press release! a. Factors discerning intent to be bound i. Whether party expressly reserved right to be bound only when written agreement is signed Whether there was partial performance by one party that disclaiming party accepted i Whether all essential terms had been agreed upon iv. Whether complexity/magnitude of transaction required formal, executed writing Rule: Written memorial sufficient when it manifests intent to be bound. v Has it been revoked? Dickinson v. Dodds (Friday slip under door, but it was too late. Ct says: yeah, it was revoked. Not an option.) Rst 36 vi But was it an options contract? [which is irrevocable for period]? Rst This would make a difference. Dick. v. Dodds was NOT option. ix. Irrevocable in goods: UCC UCC Interim period: Revocation II.d. INTERIM PERIOD: REVOCATION OF OFFER i. Restatement 35: Offeree s Power of Acceptance 1. Offer gives offeree continuing power to complete by acceptance of offer. i iv. 2. K cannot be created by acceptance after termination method listed in Rst 36 Restatement 36: Methods of Termination of Power of Acceptance 1. Termination by: a. rejection or counter-offer by offeree b. Lapse of time c. Revocation by offeror d. Death/incapacity of offeror or offeree 2. Also, terminated by non-occurrence of condition of acceptance under terms of offer. Restatement 42: Revocation by communication from offeror received by offeree 1. Power of acceptance terminates when offeree receives manifestation of intent not to enter into proposed K. Restatement 43: Indirect communication of revocation 1. Power of acceptance terminated when offeror takes definite action inconsistent with intention to enter into K, AND offeree acquires reliable info to that effect. Dickinson v. Dodds where there was no consideration therefore no binding agreement (to keep K open for a time). a. Consideration can be made by bargaining! Or by payment of some sum. (Bargain theory of consideration!) 5
5 v. Option Contracts: Restatement and UCC are different!! 1. Restatement 25: Option contracts a. = promise which meets requirements for formation of K, AND limits promisor s power to revoke an offer. 2. Restatement 37: Termination of Power of acceptance under option Contract a. Notwithstanding 38-40, power of acceptance under option K NOT terminated by revocation UNLESS requirements met for discharge of contractual duty. vi. Option Contracts: Under UCC common law 1. UCC 2-205: Firm Offers a. Offer to buy/sell goods in signed writing which gives assurance to hold open is not revocable, for lack of consideration. v Example 1. RB s sweatshirt example. Student write, I d like to buy. RB wrote back, Great, give me $10 by Friday, and it s yours. He subsequently sells to Van Houweling. Student sues. What result? a. Common law: There was no consideration to hold it open, therefore NOT option. (The Dickinson v. Dodds result.) b. UCC: No consideration was needed, therefore under it WAS binding. Since it was a good, UCC rules. She can sue. (I hope this is the right answer!) Acceptance II.e. ACCEPTANCE i. Restatement 50: Acceptance of Offer 1. Manifestation of assent to terms thereof, made by offeree in manner invited, or required, by offer. 2. Key: Offeror is the master of the offer. a. Manner invited can be put in a blue envelope under a tree in Switzerland can only accept that way! Restatement 65: Reasonableness of Medium of Acceptance 1. Unless circumstances dictate otherwise, medium of acceptance is reasonable if it is one used by offeror or one customary in similar transactions at time & place the offer is received. i UCC 2-206: Offer & Acceptance in formation of K (basically, same as Restatement) 1. Unless otherwise unambiguously indicated by language or circumstances a. Offer to make K shall be construed as inviting acceptance in any manner & by any medium reasonable in the circumstances. iv. Restatement 63: Time when acceptance takes effect 1. Mailbox Rule: as soon as it s put out of offeree s possession (stuck it in the mailbox = acceptance) a. BUT instantaneous communication: when it s received. b. Policy behind Mailbox Rule: the offeree who accepted can, at moment of putting it in mailbox, rely on that contract. 2. UNLESS option contract. Then, only when it s received by offeror. (policy behind this) v. UCC? Mailbox rule applies because it s a background common law rule. Not replaced by anything in UCC. vi. Careful: that offeree doesn t accidentally terminate his power of acceptance by making a counter-offer! v Mirror Image Rule. Ardente v. Horan (Would house have dining, parlor, furniture? qualified v. absolute acceptance. Based on objective inquiry.) (Must be definite & unequivocal.) Acceptance was not sufficiently clear and his power of acceptance was termination by a rejection or counter-offer! Oopsies, he accidentally terminated his own power of acceptance!! (Restatement 36) 1. Policy: Offeror is entitled to know in clear terms whether the offeree accepts his proposal. a. ** NB: Payment after receiving a counter offer constitutes acceptance and assent to the counter offer! 2. CONTRAST MIRROR IMAGE RULE WITH UCC 2-207: No mirror image required for K to take hold under UCC for goods contracts!!! See below. 3. i.e.: Additional terms are a problem under Restatement because of Mirror Image Rule, but they are not a problem under UCC. 6
6 vi What about Collateral Matter?? 1. Conditional acceptance vs. Absolute acceptance + inquiry regarding collateral matter a. Ardente v. Horan: conditional acceptance (you terminate your power of acceptance) 2. Rule: So long as it is clear that meaning of acceptance is positively & unequivocally to accept offer whether request is gratned or not, a K is formed. Williston. ix. Mailbox Rule [339-40] Rst Offeror cannot revoke after mailing. Speculation is not allowed. 2. In case of delay, there is still a K, but duty to perform is affected. 3. What if revocation arrives prior to acceptance? Well, technically a K still exists, but there s duty to avoid damages, so practical effect might be, No suit by offeror. 4. Options K? Mailbox rule does NOT apply. Only enforceable upon receipt by offeror. WHY? Since there is no right to revoke by offeror (exposure to some risk), we balance that by giving offeror assurance that his offer has actually been accepted (upon receipt). x. Accept by Performance, Unilateral Contracts. 1. Carlill, White v. Corlies & Tifft, Petterson v. Pattberg. 2. = Full performance constitutes acceptance. (Not merely a promise to perform, which is bilateral.) Special problems: notification, revocation, reliance. 3. Finding puppy. Lawn-mowing. a. Carlill: not mere puff because said it was sincere. There was offer, and acceptance was manifested by performance. b. Pepsico: there was no offer to give Harrier Jet. Rather, it was advertisement to receive offers. 4. Performance must be unambiguous & clear. (unlike general builder-like activity in White v. Corlies). to accept unilateral offer. (Objective test) Notification problem. Must be unambiguous notification. 5. Petterson v. Pattberg: Revocation issue. Revocation of unilateral offer can be either I revoke or by some act inconsistent with continuance of offer (like selling mortgage to third party). Court found NO contract, because P was essentially prevented from performing. Rule that kinda sucks, but it is what it is. Tender, part of conditions, was not met. Rst 45 a. But if it s an option contract, then part performance or beginning of tender is fine. b.. Rst 45 c. Restatement 45 covers the Brooklyn Bridge hypothetical. 6. What effect of tender or beginning invited performance? a. If perf = only mode to accept, then tender or beginning performance creates option contract which cannot be revoked by offeror. (Brooklyn Bridge hypothetical). So, offeror is on the hook, but offeree NOT on the hook UNTIL performance is completed. b. If there s a choice to accept either by promise OR performance, then beginning performance = full acceptance, not an option. So, BOTH are on the hook once perf has begun. I think. xi. Acceptance by Silence Rst Hobbs v. Massasoit Whip (received leather, never sent back: court said, had to pay?) 2. Where by single interaction silence does NOT indicate acceptance, in course of dealing acceptance may well be inferred. Look at the prior business relationship to see if silence was enough. a. tmc: Compare 2-207, merchants, silence, etc. re: additional terms. 3. Two ways to infer acceptance by silence: a. Course of dealing (prior business relationship) would give rise to expectation that silence constitutes acceptance. b. In the absence of business relationship, then concrete actions taken by offeree consistent with acceptance constitute acceptance of the bargain. i. Deriving benefit from what was offered DOES constitute evidence of acceptance! Like Register.com case. You CANNOT simply say: Well, you knew what the terms were. You must fine objective manifestation of intent, even in e-commerce! 7
7 x 4. Examples: Software Downloads, electronic license agreements, etc. a. ** We DON T ask whether offeree actually read the terms (that s too subjective! We re looking at objective for mutual assent!) b. Use of the software or website constitutes tacit acceptance of the terms anyway. Will be usually upheld in court. E-Commerce and Mutual Assent: E-Sign Act 1. Register.com rule: If offeree manifests intent to be bound, then takes info and uses to its benefit and was given choice to reject/return but didn t, then assent to be bound is found. a. BUT: A grant of access despite non-acceptance constitutes offeror s consent for offeree to NOT be bound! Acceptance: Bilateral v. Unilateral II.f. ACCEPTANCE SPECIAL CASE: BILATERAL V. UNILATERAL CONTRACTS i. Two Examples 1. Bilateral: uses the formula: I will do X if you agree to do Y. Both sides agree to do something. It s done. It s an exchange of promises. 2. Unilateral: does NOT use agree to in formula: I will do X if you do Y. i.e. if you perform Y. a. Partial performance = promise to fully perform (irrevocable) options K. b. But, you may Contract Around this rule! So you can put a condition: This offer may be revoked at any time. Bilateral: offeror makes promise contained in offer, and offeree makes a promise in return as acceptance 1. Both parties exchange promises and are contractually bound. 2. Offeree liable for any performance deficiencies i Unilateral: Only one promise is made. I ll pay you if you mow my lawn. 1. Offeree renders performance as acceptance. 2. Neither party is bound prior to completion of performance. 3. Partial performance converts into an option contract the offeror cannot revoke, but is NOT liable UNTIL full performance occurs. iv. Restatement 30: Form of Acceptance invited. 1. Offer may invite or require acceptance by affirmative answer in words, OR by performing or refraining from performing a specified act... v. Restatement 54: Acceptance by performance; Necessity of notification. 1. No notice is necessary where offer invites acceptance by performance (unilateral); UNLESS the offer specifically requests such a notification. 2. If offeree knows that offeror has no adequate means of learning of performance w/ promptness & certainty, Contractual duty of offeror is discharged... UNLESS: a. offeree exercises reasonable diligence to notify b. offeror learns of performance within reasonable time c. offer indicates that notification not required. 3. Case: Carlill v. Carbolic Smoke Ball. vi. How much performance is required for acceptance? Several answers: 1. Answer 1 a. Restatement 19: Conduct as manifestation of assent. b. Manifestation of assent, made wholly or partly by written or spoken words or by other acts or by failure to act. c. Conduct of party NOT effective as manifestation, UNLESS he intends to engage in conduct AND knows or has reason to know that other party may infer from conduct that he assents. 8
Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Spring Contract Formation
 Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Contract Formation I. Foundations A. Mutual Assent: Each party to a contract manifests its assent to the
Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Contract Formation I. Foundations A. Mutual Assent: Each party to a contract manifests its assent to the
Chapter 9: Contract Formation. Copyright 2009 South-Western Legal Studies in Business, a part of South-Western Cengage Learning.
 Chapter 9: Contract Formation a Copyright part of South-Western 2009 South-Western Cengage Legal Learning. Studies Business, Introduction is a declaration that something will or will not happen in the
Chapter 9: Contract Formation a Copyright part of South-Western 2009 South-Western Cengage Legal Learning. Studies Business, Introduction is a declaration that something will or will not happen in the
Unilateral Contracts vs. Bilateral Contracts
 Unilateral Contracts vs. Bilateral Contracts A unilateral contract is a promise in exchange for a performance. A bilateral contract is a promise in exchange for a promise. Note: An implied-in-fact contract
Unilateral Contracts vs. Bilateral Contracts A unilateral contract is a promise in exchange for a performance. A bilateral contract is a promise in exchange for a promise. Note: An implied-in-fact contract
Creation of the K a. Statute of Frauds land part performance one year debt 500 b. Offer master of the offer revoke mailbox rule absence of terms
 Contracts outline I. Creation of the K a. Statute of Frauds requires that a sufficient writing, signed by the party to be charged be in existence for the following subject-matter (doesn t apply to restitution
Contracts outline I. Creation of the K a. Statute of Frauds requires that a sufficient writing, signed by the party to be charged be in existence for the following subject-matter (doesn t apply to restitution
QUESTION 1. Carl said, Let me think a moment.
 QUESTION 1 Zena placed an advertisement in a local newspaper: Wanted: Someone to clean my four-bedroom, four-bath house (2500 square feet) once a week for the next month; pay $35 per hour. No interview
QUESTION 1 Zena placed an advertisement in a local newspaper: Wanted: Someone to clean my four-bedroom, four-bath house (2500 square feet) once a week for the next month; pay $35 per hour. No interview
Question If CapCo files a lawsuit against the Bears seeking damages for breach of contract, who is likely to prevail? Discuss.
 Question 2 CapCo sells baseball caps to youth leagues and recently approached two new teams, the Bears and the Lions. Uncertain how many caps the team would require, the Bears team manager signed a written
Question 2 CapCo sells baseball caps to youth leagues and recently approached two new teams, the Bears and the Lions. Uncertain how many caps the team would require, the Bears team manager signed a written
MLL111- Exam Notes Contract Law (All Topics + Cases)
 1 MLL111- Exam Notes Contract Law (All Topics + Cases) 2 Contents Page Page 8: Formation of Contracts Offer and Acceptance Page 9: Acceptance Communication of Acceptance: Waiver Silence Page 10: Acceptance
1 MLL111- Exam Notes Contract Law (All Topics + Cases) 2 Contents Page Page 8: Formation of Contracts Offer and Acceptance Page 9: Acceptance Communication of Acceptance: Waiver Silence Page 10: Acceptance
BAREXAMDOCTOR.COM UNLIMITED ESSAYS AND PTS ONLINE! ESSAY APPROACH. Bar Exam Doctor. CONTRACTS ESSAY
 ESSAY APPROACH www.barexamdoctor.com CONTRACTS ESSAY I. DOES THE UCC APPLY? a. The UCC governs all Ks for the sale of goods b. The UCC also has special rule governing transactions between merchants c.
ESSAY APPROACH www.barexamdoctor.com CONTRACTS ESSAY I. DOES THE UCC APPLY? a. The UCC governs all Ks for the sale of goods b. The UCC also has special rule governing transactions between merchants c.
OVERVIEW OF CONTRACT LAW
 OVERVIEW OF CONTRACT LAW Liability is generally the key issue in regards to contractual disputes. Purpose of K law is to provide the rules which determine when one party is liable to another under or in
OVERVIEW OF CONTRACT LAW Liability is generally the key issue in regards to contractual disputes. Purpose of K law is to provide the rules which determine when one party is liable to another under or in
Simple. CONTRACTS & UCC Outline. NINETY PERCENT of the LAW in NINETY PAGES. Tim Tyler, Ph.D., Attorney at Law
 NAILING THE BAR Simple CONTRACTS & UCC Outline Tim Tyler, Ph.D., Attorney at Law NINETY PERCENT of the LAW in NINETY PAGES NAILING THE BAR Simple CONTRACTS & UCC Outline Table of Contents CHAPTER 1: CONTRACT
NAILING THE BAR Simple CONTRACTS & UCC Outline Tim Tyler, Ph.D., Attorney at Law NINETY PERCENT of the LAW in NINETY PAGES NAILING THE BAR Simple CONTRACTS & UCC Outline Table of Contents CHAPTER 1: CONTRACT
Chapter 3: The Bargain Context
 Chapter 3: The Bargain Context A. Introduction: Contracting parties, no matter how hard they try, cannot negotiate every rule. For example, suppose I agree to sell and you agree to buy my tractor. We agree
Chapter 3: The Bargain Context A. Introduction: Contracting parties, no matter how hard they try, cannot negotiate every rule. For example, suppose I agree to sell and you agree to buy my tractor. We agree
Is there a contract?
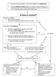 1. te whether this transaction is governed by UCC or the Restatement. 2. Does the Statute of Frauds apply? The contract must be in writing if it is in regard to land, if by its nature it takes more than
1. te whether this transaction is governed by UCC or the Restatement. 2. Does the Statute of Frauds apply? The contract must be in writing if it is in regard to land, if by its nature it takes more than
CONTRACT LAW. Elements of a Contract
 CONTRACT LAW Contracts: Types and Sources in Australia CONTRACT: An agreement concerning promises made between two or more parties with the intention of creating certain legal rights and obligations upon
CONTRACT LAW Contracts: Types and Sources in Australia CONTRACT: An agreement concerning promises made between two or more parties with the intention of creating certain legal rights and obligations upon
Contract Law. 2. Contract formation: a) mutual assent: offer & acceptance b) consideration: need to have an exchange of something.
 Contract Law Jan 18th, 2012: 1. Sources of law: -statutory law: United Commercial Code, uniformed state law; (only for sales of goods, does not require parties to be merchants) -common law; -restatement:
Contract Law Jan 18th, 2012: 1. Sources of law: -statutory law: United Commercial Code, uniformed state law; (only for sales of goods, does not require parties to be merchants) -common law; -restatement:
THIS IS A SAMPLE EXAM. QUESTIONS ARE FOR LEARNING PURPOSES ONLY. THE FINAL EXAM MAY SUBSTANTIALLY DIFFER FROM THIS SAME. EXAM #
 EXAM # FALL 2018 CONTRACTS I (ORANBURG) SAMPLE EXAM INSTRUCTIONS 1. This exam contains one (1) essay question. You will have two (2) hours to write this exam. Do not turn over this instruction page until
EXAM # FALL 2018 CONTRACTS I (ORANBURG) SAMPLE EXAM INSTRUCTIONS 1. This exam contains one (1) essay question. You will have two (2) hours to write this exam. Do not turn over this instruction page until
California Bar Examination
 California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question Betty is a physician. One of her
California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question Betty is a physician. One of her
Spring 2018 Business Law Fundamentals O'Hara 2018 D
 Page 1 of 7 as your signature PRINT your name EXAM #2 Business Law Fundamentals LAWS 3930 sections -001, -002-003 Chapters 1-4, 24, 6, 7, 9-19 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Affix your printed name as your signature
Page 1 of 7 as your signature PRINT your name EXAM #2 Business Law Fundamentals LAWS 3930 sections -001, -002-003 Chapters 1-4, 24, 6, 7, 9-19 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Affix your printed name as your signature
CONTRACT LAW SUMMARY
 CONTRACT LAW SUMMARY LAWSKOOL UK CONTENTS INTRODUCTION TO CONTRACT LAW 6 DEFINITION OF CONTRACT LAW 6 1) The Classical Model of Contract Law 6 INTENTION TO CREATE LEGAL RELATIONS 8 INTRODUCTION TO INTENTION
CONTRACT LAW SUMMARY LAWSKOOL UK CONTENTS INTRODUCTION TO CONTRACT LAW 6 DEFINITION OF CONTRACT LAW 6 1) The Classical Model of Contract Law 6 INTENTION TO CREATE LEGAL RELATIONS 8 INTRODUCTION TO INTENTION
Exam Approach: I. CONTRACT FORMATION
 Exam Approach: 1. On scrap paper, write out all main topics (the purple enumerated topics in this outline) look back at them after reading through the fact pattern to MAKE SURE I haven t missed spotting
Exam Approach: 1. On scrap paper, write out all main topics (the purple enumerated topics in this outline) look back at them after reading through the fact pattern to MAKE SURE I haven t missed spotting
Question 3. Sam hereby agrees that he will not perform interior design services in Town for a period of two years.
 Question 3 Sam decided to sell his interior design business in Town to Betty. While reviewing a purchase agreement drafted by Sam, Betty insisted on a covenant by Sam not to compete with her in the interior
Question 3 Sam decided to sell his interior design business in Town to Betty. While reviewing a purchase agreement drafted by Sam, Betty insisted on a covenant by Sam not to compete with her in the interior
PRINCIPLES OF CONTRACTUAL LIABILITY 1.1. AGREEMENT TEMPLATE: CERTAINTY TEMPLATE:... Error! Bookmark not defined.
 PRINCIPLES OF CONTRACTUAL LIABILITY 1. FORMATION OF CONTRACT:... 2 1.1. AGREEMENT TEMPLATE:... 2 1.2. CAPACITY TEMPLATE:... = Error! Bookmark not defined. 1.3. INTENTION TEMPLATE: (objective test)... Error!
PRINCIPLES OF CONTRACTUAL LIABILITY 1. FORMATION OF CONTRACT:... 2 1.1. AGREEMENT TEMPLATE:... 2 1.2. CAPACITY TEMPLATE:... = Error! Bookmark not defined. 1.3. INTENTION TEMPLATE: (objective test)... Error!
Question 2. Delta has not yet paid for any of the three Model 100 presses despite repeated demands by Press.
 Question 2 Delta Print Co. ( Delta ) ordered three identical Model 100 printing presses from Press Manufacturer Co. ( Press ). Delta s written order form described the items ordered by model number. Delta
Question 2 Delta Print Co. ( Delta ) ordered three identical Model 100 printing presses from Press Manufacturer Co. ( Press ). Delta s written order form described the items ordered by model number. Delta
Contracts I Office: Room 1115 Professor Meyerson Phone: (410)
 Contracts I Office: Room 1115 Professor Meyerson Phone: (410) 837-4550 Fall 2014 E-mail: mmeyerson@ubalt.edu The course packet [available at the Bookstore] contains most of the cases we will be reading
Contracts I Office: Room 1115 Professor Meyerson Phone: (410) 837-4550 Fall 2014 E-mail: mmeyerson@ubalt.edu The course packet [available at the Bookstore] contains most of the cases we will be reading
FULL OUTLINE. Bar Exam Doctor BAREXAMDOCTOR.COM. CONTRACTS
 FULL OUTLINE www.barexamdoctor.com CONTRACTS I. VOCABULARY a. K = legally enforceable agreement (or legally enforceable promise) b. Quasi-K = equitable remedy. NOT K law. i. Elements: 1. P has conferred
FULL OUTLINE www.barexamdoctor.com CONTRACTS I. VOCABULARY a. K = legally enforceable agreement (or legally enforceable promise) b. Quasi-K = equitable remedy. NOT K law. i. Elements: 1. P has conferred
QUESTION What contract rights and remedies, if any, does Olivia have against Juan? Discuss.
 QUESTION 1 Olivia is a florist who specializes in roses. She has a five-year written contract with Juan to sell him as many roses as he needs for his wedding chapel. Over the past three years, Olivia sold
QUESTION 1 Olivia is a florist who specializes in roses. She has a five-year written contract with Juan to sell him as many roses as he needs for his wedding chapel. Over the past three years, Olivia sold
California Bar Examination
 California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question PC manufactures computers. Mart
California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question PC manufactures computers. Mart
Contracts I Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas. Fall 2004
 Contracts I Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Optional HW Assignment #1 - Model Answers 1. Read the attached version of Coakley & Williams, Inc. v.
Contracts I Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Optional HW Assignment #1 - Model Answers 1. Read the attached version of Coakley & Williams, Inc. v.
Beginning Law Essay Writing Part 2 Professor Mary Schofield
 Beginning Law Essay Writing Part 2 Professor Mary Schofield The following pages provide hard copies of the hypothetical used during this session, as well as a copy of the sample answer discussed. I suggest
Beginning Law Essay Writing Part 2 Professor Mary Schofield The following pages provide hard copies of the hypothetical used during this session, as well as a copy of the sample answer discussed. I suggest
Contracts Summary Notes
 Contracts Summary Notes TOPIC ONE: AGREEMENT- OFFER AND ACCEPTANCE There are 4 elements of a contract: Agreement, consideration, intention to create legal relations and certainty The above are all required
Contracts Summary Notes TOPIC ONE: AGREEMENT- OFFER AND ACCEPTANCE There are 4 elements of a contract: Agreement, consideration, intention to create legal relations and certainty The above are all required
TABLE OF CONTENTS. Preface... iii Preface to the First Edition... v Table of Cases... TC-1 Table of Statutes... TS-1
 TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE Preface... iii Preface to the First Edition... v Table of Cases... TC-1 Table of Statutes... TS-1 PART I. INTRODUCTION... 1-17 CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION... 1 PART II. ENFORCEABILITY...
TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE Preface... iii Preface to the First Edition... v Table of Cases... TC-1 Table of Statutes... TS-1 PART I. INTRODUCTION... 1-17 CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION... 1 PART II. ENFORCEABILITY...
CONTRACTS Ponoroff 2016
 A. Contract Law (Overview) a. Contract The promise or set of promises that the law recognizes by way of enforcement. i. Promise The liability involved in contract law is undertaken intentionally by the
A. Contract Law (Overview) a. Contract The promise or set of promises that the law recognizes by way of enforcement. i. Promise The liability involved in contract law is undertaken intentionally by the
Contract Law Final Exam Version C
 Contract Law Final Exam Version C True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Compliance and excuse are valid defenses to a breach of contract action. 2. To have a constructive or implied
Contract Law Final Exam Version C True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Compliance and excuse are valid defenses to a breach of contract action. 2. To have a constructive or implied
California Bar Examination
 California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question On May 1, Owner asked Builder
California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question On May 1, Owner asked Builder
Contracts. Introduction. Introductions Seth C. Oranburg 1. Professor Seth C. Oranburg
 Contracts Professor Seth C. Oranburg Introduction 1. Introductions 2. Overview of Contract Law 3. Which Contract Law Applies? 4. How to Use the IRAC Writing Paradigm? 5. What Is a Contract, Anyway? 6.
Contracts Professor Seth C. Oranburg Introduction 1. Introductions 2. Overview of Contract Law 3. Which Contract Law Applies? 4. How to Use the IRAC Writing Paradigm? 5. What Is a Contract, Anyway? 6.
PART 2 FORMATION, TERMS, AND READJUSTMENT OF CONTRACT. (a) A contract or modification thereof is enforceable,
 1 PART 2 FORMATION, TERMS, AND READJUSTMENT OF CONTRACT SECTION 2-201. NO FORMAL REQUIREMENTS. (a) A contract or modification thereof is enforceable, whether or not there is a record signed by a party
1 PART 2 FORMATION, TERMS, AND READJUSTMENT OF CONTRACT SECTION 2-201. NO FORMAL REQUIREMENTS. (a) A contract or modification thereof is enforceable, whether or not there is a record signed by a party
Page 1 of 7. Fall 2015 Business Law Fundamentals O'Hara 2015 E
 Page 1 of 7 print name as your signature EXAM #2 Business Law Fundamentals LAWS 3930 sections -001-003 Chapters 1-4, 24, 6, 7, 9-18 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Affix your printed name as your signature in the space
Page 1 of 7 print name as your signature EXAM #2 Business Law Fundamentals LAWS 3930 sections -001-003 Chapters 1-4, 24, 6, 7, 9-18 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Affix your printed name as your signature in the space
Genuineness of Assent
 Genuineness of Assent A party who demonstrates that she did not genuinely assent to the terms of a contract may avoid an otherwise valid contract. Genuine assent may be lacking due to mistake, fraudulent
Genuineness of Assent A party who demonstrates that she did not genuinely assent to the terms of a contract may avoid an otherwise valid contract. Genuine assent may be lacking due to mistake, fraudulent
An Introduction to the Law of CONTRACT STEPHEN GRAW
 An Introduction to the Law of CONTRACT by STEPHEN GRAW B.Com., LL.B. (Qld) Solicitor of the Supreme Court of Queensland Associate Professor of Business Law, James Cook University of North Queensland SECOND
An Introduction to the Law of CONTRACT by STEPHEN GRAW B.Com., LL.B. (Qld) Solicitor of the Supreme Court of Queensland Associate Professor of Business Law, James Cook University of North Queensland SECOND
United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods
 United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods ACC International Legal Affairs Committee Legal Quick Hit: November 13, 2014 Presented by: Jeffrey S. Dunn Michael Best & Friedrich
United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods ACC International Legal Affairs Committee Legal Quick Hit: November 13, 2014 Presented by: Jeffrey S. Dunn Michael Best & Friedrich
Answer A to Question 1
 Answer A to Question 1 The issue is whether Pat has a valid contract with Danco and whether Danco has breached such contract, and what damages Pat is entitled to as a result. Service Contract Contracts
Answer A to Question 1 The issue is whether Pat has a valid contract with Danco and whether Danco has breached such contract, and what damages Pat is entitled to as a result. Service Contract Contracts
UNITED NATIONS CONVENTION ON CONTRACTS FOR THE INTERNATIONAL SALE OF GOODS (1980) [CISG]
![UNITED NATIONS CONVENTION ON CONTRACTS FOR THE INTERNATIONAL SALE OF GOODS (1980) [CISG] UNITED NATIONS CONVENTION ON CONTRACTS FOR THE INTERNATIONAL SALE OF GOODS (1980) [CISG]](/thumbs/73/69200382.jpg) Go to CISG Table of Contents Go to Database Directory UNITED NATIONS CONVENTION ON CONTRACTS FOR THE INTERNATIONAL SALE OF GOODS (1980) [CISG] For U.S. citation purposes, the UN-certified English text
Go to CISG Table of Contents Go to Database Directory UNITED NATIONS CONVENTION ON CONTRACTS FOR THE INTERNATIONAL SALE OF GOODS (1980) [CISG] For U.S. citation purposes, the UN-certified English text
CONTRACT LAW IN THE SOUTH PACIFIC
 CONTRACT LAW IN THE SOUTH PACIFIC Jennifer Corrin Care Senior Lecturer TC Beirne School of Law University of Queensland Cavendish Publishing Limited London Sydney CONTENTS Preface Table of Cases Table
CONTRACT LAW IN THE SOUTH PACIFIC Jennifer Corrin Care Senior Lecturer TC Beirne School of Law University of Queensland Cavendish Publishing Limited London Sydney CONTENTS Preface Table of Cases Table
Chinese Contract Law: A Brief Introduction. ZHANG Xuezhong. Assistant Professor of Law.
 Chinese Contract Law: A Brief Introduction ZHANG Xuezhong Assistant Professor of Law zhangxuezhong@ecupl.edu.cn East China University of Politics and Law Overview 1. In General 2. Principles of Chinese
Chinese Contract Law: A Brief Introduction ZHANG Xuezhong Assistant Professor of Law zhangxuezhong@ecupl.edu.cn East China University of Politics and Law Overview 1. In General 2. Principles of Chinese
A) Preliminaries B) Formation
 Contracts Page 1 of 12 A) Preliminaries 1) Governing law The Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) governs transactions that are predominantly for goods (movable property, identifiable to the contract at formation),
Contracts Page 1 of 12 A) Preliminaries 1) Governing law The Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) governs transactions that are predominantly for goods (movable property, identifiable to the contract at formation),
MBE WORKSHOP: CONTRACTS PROFESSOR LISA MCELROY DREXEL UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF LAW
 MBE WORKSHOP: CONTRACTS PROFESSOR LISA MCELROY DREXEL UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF LAW CHAPTER 1: CONTRACTS Editor's Note 1: The below outline is taken from the National Conference of Bar Examiners' website. NOTE:
MBE WORKSHOP: CONTRACTS PROFESSOR LISA MCELROY DREXEL UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF LAW CHAPTER 1: CONTRACTS Editor's Note 1: The below outline is taken from the National Conference of Bar Examiners' website. NOTE:
Law of Contracts. Determining Contractual Intent. Offer. 6 Elements of Legally Enforceable Contracts
 6 Elements of Legally Enforceable Contracts Law of Contracts 1. Offer and Acceptance 2. Genuine Assent 3. Legal Purpose Business Law Chapters 6-11 4. Consideration (Exchange of value) 5. Capacity to Contract
6 Elements of Legally Enforceable Contracts Law of Contracts 1. Offer and Acceptance 2. Genuine Assent 3. Legal Purpose Business Law Chapters 6-11 4. Consideration (Exchange of value) 5. Capacity to Contract
CONTRACTS MID-TERM EXAMINATION December 2006 Santa Barbara/Ventura Colleges of Law Instructor: Craig Smith QUESTION 1
 CONTRACTS MID-TERM EXAMINATION December 2006 Santa Barbara/Ventura Colleges of Law Instructor: Craig Smith QUESTION 1 Moe was a collector of exotic cars. One day he saw an ad in the classified section
CONTRACTS MID-TERM EXAMINATION December 2006 Santa Barbara/Ventura Colleges of Law Instructor: Craig Smith QUESTION 1 Moe was a collector of exotic cars. One day he saw an ad in the classified section
10/29/2007 7:36:00 PM
 10/29/2007 7:36:00 PM I. Article 2 Sales of Goods II. Contractual Assent/Intent & Objective Test A. Contracts are formed by mutual consent. Both parties must intend to enter the contract and agree on its
10/29/2007 7:36:00 PM I. Article 2 Sales of Goods II. Contractual Assent/Intent & Objective Test A. Contracts are formed by mutual consent. Both parties must intend to enter the contract and agree on its
INTERNATIONAL SALE OF GOODS ACT
 c t INTERNATIONAL SALE OF GOODS ACT PLEASE NOTE This document, prepared by the Legislative Counsel Office, is an office consolidation of this Act, current to December 2, 2015. It is intended for information
c t INTERNATIONAL SALE OF GOODS ACT PLEASE NOTE This document, prepared by the Legislative Counsel Office, is an office consolidation of this Act, current to December 2, 2015. It is intended for information
REVIEW QUESTIONS TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS (CIRCLE THE CORRECT ANSWER)
 REVIEW QUESTIONS TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS (CIRCLE THE CORRECT ANSWER) 1. T F The pre-offer phase of a transaction is also known as preliminary negotiation. 2. T F Preliminary negotiation takes place after
REVIEW QUESTIONS TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS (CIRCLE THE CORRECT ANSWER) 1. T F The pre-offer phase of a transaction is also known as preliminary negotiation. 2. T F Preliminary negotiation takes place after
Chapter 1. Bases for Enforcing Promises 1. What is a K? a promise (or set of promises) the law will enforce. The norm in contract law how much money
 Chapter 1. Bases for Enforcing Promises 1. What is a K? a promise (or set of promises) the law will enforce. The norm in contract law how much money will it take to make the injured party WHOLE again.
Chapter 1. Bases for Enforcing Promises 1. What is a K? a promise (or set of promises) the law will enforce. The norm in contract law how much money will it take to make the injured party WHOLE again.
California Bar Examination
 California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question On April 1, Pat, a computer software
California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question On April 1, Pat, a computer software
Business Law & Ethics notes Lec Lecture topic Topic s covered Text book refs. constitution expansion of power interpreting power
 Business Law & Ethics notes Lec Lecture topic Topic s covered Text book refs 1 law, morality and philosophical views of ch 1 meaning of eithics law 2 the source of laws governing constitution expansion
Business Law & Ethics notes Lec Lecture topic Topic s covered Text book refs 1 law, morality and philosophical views of ch 1 meaning of eithics law 2 the source of laws governing constitution expansion
Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Spring Contract Terms (Expanded)
 Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Contract Terms (Expanded) I. Construing and Interpreting Contracts A. Purpose: A court s primary concern
Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Contract Terms (Expanded) I. Construing and Interpreting Contracts A. Purpose: A court s primary concern
CONTRACTS AND SALES QUESTION 1
 CONTRACTS AND SALES QUESTION Peter responded to an advertisement placed by Della, a dentist, seeking a dental hygienist. After an interview, Della offered Peter the job and said she would either: () pay
CONTRACTS AND SALES QUESTION Peter responded to an advertisement placed by Della, a dentist, seeking a dental hygienist. After an interview, Della offered Peter the job and said she would either: () pay
National Paralegal College
 National Paralegal College 6516 North 7 th Street Suite 103, Phoenix, AZ 85014-1263 Tel: 800-371 - 6105 Fax: 866-347-2744 e-mail: info@nationalparalegal.edu Contracts PLG 102 1004 Syllabus and Course Guide
National Paralegal College 6516 North 7 th Street Suite 103, Phoenix, AZ 85014-1263 Tel: 800-371 - 6105 Fax: 866-347-2744 e-mail: info@nationalparalegal.edu Contracts PLG 102 1004 Syllabus and Course Guide
requires a + = WHAT IS IN A CONTRACT? by to another to create.
 UNIT 3 CONTRACTS NBEA STANDARD II: Analyze the relationships between contract law, law of sales, and consumer law. OBJECTIVE: Develop an understanding of contracts: distinguish between express and implied
UNIT 3 CONTRACTS NBEA STANDARD II: Analyze the relationships between contract law, law of sales, and consumer law. OBJECTIVE: Develop an understanding of contracts: distinguish between express and implied
The Objective Principle of a Promise... 2 Intention to Create Legal Relations... 4 Offer and Acceptance... 5
 1 Contents The Objective Principle of a Promise... 2 Intention to Create Legal Relations... 4 Offer and Acceptance... 5 Offer vs. Invitation to Treat... 5 Termination/Lapse of Offer... 6 Acceptance of
1 Contents The Objective Principle of a Promise... 2 Intention to Create Legal Relations... 4 Offer and Acceptance... 5 Offer vs. Invitation to Treat... 5 Termination/Lapse of Offer... 6 Acceptance of
Contents. Table of Statutes. Table of Secondary Legislation. Table of Cases. The Agreement to Contract
 Contents Table of Statutes Table of Secondary Legislation Table of Cases Chapter 1: The Agreement to Contract 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Elements required for a valid simple contract 1.3 The phenomenon of agreement
Contents Table of Statutes Table of Secondary Legislation Table of Cases Chapter 1: The Agreement to Contract 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Elements required for a valid simple contract 1.3 The phenomenon of agreement
Sales and Leases Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Spring Anticipatory Repudiation
 Sales and Leases Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Anticipatory Repudiation I. Doctrinal Basics A. What is a Repudiation?: Despite the fact that his
Sales and Leases Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Anticipatory Repudiation I. Doctrinal Basics A. What is a Repudiation?: Despite the fact that his
Business Law - Contract Law Study Notes
 Business Law - Contract Law Study Notes Comprehensive unit study notes as per Victoria University. 1 Table of Contents Note topic Content page Full semester notes 3-49 How to write IRAC 50-51 response
Business Law - Contract Law Study Notes Comprehensive unit study notes as per Victoria University. 1 Table of Contents Note topic Content page Full semester notes 3-49 How to write IRAC 50-51 response
CHAPTER 2 CONTRACT LAWS INDIAN CONTRACT ACT, A contract is an agreement made between two or more parties which the law will enforce.
 CHAPTER 2 CONTRACT LAWS INDIAN CONTRACT ACT, 1872 Definition of Contract A contract is an agreement made between two or more parties which the law will enforce. Sec 2(h) defines contract as an agreement
CHAPTER 2 CONTRACT LAWS INDIAN CONTRACT ACT, 1872 Definition of Contract A contract is an agreement made between two or more parties which the law will enforce. Sec 2(h) defines contract as an agreement
Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Spring Contract Terms
 Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Contract Terms I. Construing and Interpreting Contracts A. Purpose: A court s primary concern is to ascertain
Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Contract Terms I. Construing and Interpreting Contracts A. Purpose: A court s primary concern is to ascertain
Define genuine agreement and rescission. Identify when duress occurs. Describe how someone may exercise undue influence.
 Define genuine agreement and rescission Identify when duress occurs Describe how someone may exercise undue influence. Genuine Agreement/Assent: meeting of the minds Must be willful and voluntary Must
Define genuine agreement and rescission Identify when duress occurs Describe how someone may exercise undue influence. Genuine Agreement/Assent: meeting of the minds Must be willful and voluntary Must
CONTRACTS TOPIC OUTLINE1
 CONTRACTS TOPIC OUTLINE1 1. OFFER AND ACCEPTANCE a. offer defined b. preliminary negotiations c. advertisements d. unilateral offer e. who may accept an offer f. irrevocable offer g. material terms h.
CONTRACTS TOPIC OUTLINE1 1. OFFER AND ACCEPTANCE a. offer defined b. preliminary negotiations c. advertisements d. unilateral offer e. who may accept an offer f. irrevocable offer g. material terms h.
University of Miami School of Law. CONTRACTS PROFESSOR ROBERT ROSEN Fall Syllabus 1
 University of Miami School of Law CONTRACTS PROFESSOR ROBERT ROSEN Fall 2007 Syllabus 1 [Unless otherwise indicated, all page # s refer to MACAULEY, ET.AL. CONTRACTS: LAW IN ACTION (2 ND ED., 2003)]. YOU
University of Miami School of Law CONTRACTS PROFESSOR ROBERT ROSEN Fall 2007 Syllabus 1 [Unless otherwise indicated, all page # s refer to MACAULEY, ET.AL. CONTRACTS: LAW IN ACTION (2 ND ED., 2003)]. YOU
Foundation Level LAW PRACTICE MANUAL
 Chapter 2:- Offer and Acceptance 2.1 Definition And Essential Elements Of A VALID OFFER 1. The term 'offer or proposal' in legal terms, is defined in (a) Section 2 (a) (b) Section 2 (b) (c) Section 2 (i)
Chapter 2:- Offer and Acceptance 2.1 Definition And Essential Elements Of A VALID OFFER 1. The term 'offer or proposal' in legal terms, is defined in (a) Section 2 (a) (b) Section 2 (b) (c) Section 2 (i)
a) The body of law as made by judges through the determination of cases. d) The system of law that emerged following the Norman Conquest in 1066.
 1. Who of the following was NOT a proponent of natural law? a) Aristotle b) Jeremy Bentham c) St Augustine d) St Thomas Aquinas 2. The term 'common law' has three different meanings. Which of the following
1. Who of the following was NOT a proponent of natural law? a) Aristotle b) Jeremy Bentham c) St Augustine d) St Thomas Aquinas 2. The term 'common law' has three different meanings. Which of the following
UNIDROIT PRINCIPLES OF INTERNATIONAL COMMERCIAL CONTRACTS 2004 (I)
 UNIDROIT PRINCIPLES OF INTERNATIONAL COMMERCIAL CONTRACTS 2004 (I) PREAMBLE (Purpose of the Principles) These Principles set forth general rules for international commercial contracts. They shall be applied
UNIDROIT PRINCIPLES OF INTERNATIONAL COMMERCIAL CONTRACTS 2004 (I) PREAMBLE (Purpose of the Principles) These Principles set forth general rules for international commercial contracts. They shall be applied
TITLE 7 CONTRACTS TABLE OF CONTENTS
 TITLE 7 CONTRACTS TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 7.01 General Provisions 7.0101 Definition 1 7.0102 Essential elements of a contract 1 7.0103 Law of place applied to contracts 1 7.0104 Time of performance 1
TITLE 7 CONTRACTS TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 7.01 General Provisions 7.0101 Definition 1 7.0102 Essential elements of a contract 1 7.0103 Law of place applied to contracts 1 7.0104 Time of performance 1
Article 6. Binding force of contract A contract validly entered into is binding upon the parties.
 Principles of Latin American Contract Law Chapter 1. Preamble Section 1. General provisions Article 1. Scope of Application (1) These principles set forth general rules applicable to domestic and international
Principles of Latin American Contract Law Chapter 1. Preamble Section 1. General provisions Article 1. Scope of Application (1) These principles set forth general rules applicable to domestic and international
7/23/2010. The. Contract. Sources of contractual obligations
 Law for Spatial Designers Introduction to the Law of Contract Module 3 Topic 1 Sources of contractual obligations Obligations imposed by law and equity The Contract Statutory obligations The obligations
Law for Spatial Designers Introduction to the Law of Contract Module 3 Topic 1 Sources of contractual obligations Obligations imposed by law and equity The Contract Statutory obligations The obligations
Foundation Level LAW PRACTICE MANUAL
 Part: - 1 The Indian Contract Act, 1872 Chapter 1:- Nature and Kinds of Contracts 5. The general principles of law of contract applied to all kinds of contract irrespective of their nature. (a) True, as
Part: - 1 The Indian Contract Act, 1872 Chapter 1:- Nature and Kinds of Contracts 5. The general principles of law of contract applied to all kinds of contract irrespective of their nature. (a) True, as
Contracts Final Exam Notes Formation of a contract What is a contract MUST Offer REASONABLE PERSON Acceptance
 Contracts Final Exam Notes Formation of a contract What is a contract - Binding promise between two or more parties, reliant upon several important factors - Offer - Acceptance - Consideration - Certainty
Contracts Final Exam Notes Formation of a contract What is a contract - Binding promise between two or more parties, reliant upon several important factors - Offer - Acceptance - Consideration - Certainty
SALE OF GOODS (VIENNA CONVENTION) ACT 1986 No. 119
 SALE OF GOODS (VIENNA CONVENTION) ACT 1986 No. 119 NEW SOUTH WALES TABLE OF PROVISIONS 1. Short title 2. Commencement 3. Interpretation 4. Act binds Crown 5. Convention to have the force of law 6. Convention
SALE OF GOODS (VIENNA CONVENTION) ACT 1986 No. 119 NEW SOUTH WALES TABLE OF PROVISIONS 1. Short title 2. Commencement 3. Interpretation 4. Act binds Crown 5. Convention to have the force of law 6. Convention
CONTRACT LAW. What is a contract? A promise or set of promises that is legally binding. Why is contract so important? Contract forms the basis for
 CONTRACT LAW What is a contract? A promise or set of promises that is legally binding Why is contract so important? Contract forms the basis for - Commercial transactions - Consumer transactions; and o
CONTRACT LAW What is a contract? A promise or set of promises that is legally binding Why is contract so important? Contract forms the basis for - Commercial transactions - Consumer transactions; and o
CONTRACTS Mid-Term Examination Santa Barbara College of Law Fall 2000 Instructor: Craig Smith. Time Allotted - Two Hours
 CONTRACTS Mid-Term Examination Santa Barbara College of Law Fall 2000 Instructor: Craig Smith Time Allotted - Two Hours An answer should demonstrate your ability to analyze the facts presented by the question,
CONTRACTS Mid-Term Examination Santa Barbara College of Law Fall 2000 Instructor: Craig Smith Time Allotted - Two Hours An answer should demonstrate your ability to analyze the facts presented by the question,
Termination of an Offer
 Termination of an Offer Lapse! If the offer contains a time limit, then it lapses according to the explicit provisions! Offer must be accepted by midnight tonight.! If the offer does not contain a time
Termination of an Offer Lapse! If the offer contains a time limit, then it lapses according to the explicit provisions! Offer must be accepted by midnight tonight.! If the offer does not contain a time
AN INTRODUCTION TO THE LAW OF CONTRACT
 AN INTRODUCTION TO THE LAW OF CONTRACT P. S. ATIYAH Formerly Professor of English Law in the University of Oxford FIFTH EDITION CLARENDON PRESS OXFORD 1995 Contents Table of Cases i. The Development of
AN INTRODUCTION TO THE LAW OF CONTRACT P. S. ATIYAH Formerly Professor of English Law in the University of Oxford FIFTH EDITION CLARENDON PRESS OXFORD 1995 Contents Table of Cases i. The Development of
Although the costs of materials and labor are roughly equal, the primary purpose of the
 Claim 1: Acme Flooring Applicable Law: Although the costs of materials and labor are roughly equal, the primary purpose of the contract was for rendering services because the service component of installation
Claim 1: Acme Flooring Applicable Law: Although the costs of materials and labor are roughly equal, the primary purpose of the contract was for rendering services because the service component of installation
the parties had dealt with each other before and were well acquainted with the timber industry
 Formation of a Contract To start with it needs to be identified whether and which party is alleging a contract. For a contract to be valid it must be: 1.! An agreement 2.! Contractual intention 3.! Consideration
Formation of a Contract To start with it needs to be identified whether and which party is alleging a contract. For a contract to be valid it must be: 1.! An agreement 2.! Contractual intention 3.! Consideration
LAW OF CONTRACT (PART I) Shanila H. Gunawardena LL.B. (Hons.) (Colombo) Attorney-at-Law, CTA (CASL)
 LAW OF CONTRACT (PART I) Shanila H. Gunawardena LL.B. (Hons.) (Colombo) Attorney-at-Law, CTA (CASL) 30-07-2017 MAIN COMPONENTS OF A CONTRACT 1. Intention to create legal relations 2. Agreement between
LAW OF CONTRACT (PART I) Shanila H. Gunawardena LL.B. (Hons.) (Colombo) Attorney-at-Law, CTA (CASL) 30-07-2017 MAIN COMPONENTS OF A CONTRACT 1. Intention to create legal relations 2. Agreement between
Second Look Series AGENCY TABLE OF CONTENTS
 AGENCY TABLE OF CONTENTS I. CREATION OF AGENCY....1 A. GENERALLY..l B. ELEMENTS OF A VALID AGENCY RELATIONSHIP...1 1. Capacity 1 2. Consent. 1 3. Formalities... 1 C. METHODS OF CREATING AN AGENCY RELATIONSHIP.
AGENCY TABLE OF CONTENTS I. CREATION OF AGENCY....1 A. GENERALLY..l B. ELEMENTS OF A VALID AGENCY RELATIONSHIP...1 1. Capacity 1 2. Consent. 1 3. Formalities... 1 C. METHODS OF CREATING AN AGENCY RELATIONSHIP.
Question 1. Is there adequate consideration for Chip Co s agreements above-described with Pam, Dave, Bob and Silicon, Inc.? Discuss.
 Question 1 Ted is the President of Chip Co, a small company that makes computer chips for the secondary personal computer market. In the regular course of Chip Co s business Ted did the following: Ted
Question 1 Ted is the President of Chip Co, a small company that makes computer chips for the secondary personal computer market. In the regular course of Chip Co s business Ted did the following: Ted
Concord University School of Law Practice Essay
 Concord University School of Law Practice Essay Instructions: This is a timed practice, and you should take no more than one hour to complete this exercise. Set a timer and allow no interruptions. Before
Concord University School of Law Practice Essay Instructions: This is a timed practice, and you should take no more than one hour to complete this exercise. Set a timer and allow no interruptions. Before
REVIEW QUESTIONS TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS (CIRCLE THE CORRECT ANSWER)
 REVIEW QUESTIONS TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS (CIRCLE THE CORRECT ANSWER) 1. T F The first step in the contract analysis is to determine the applicable law. 2. T F The second step in the contract analysis is to
REVIEW QUESTIONS TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS (CIRCLE THE CORRECT ANSWER) 1. T F The first step in the contract analysis is to determine the applicable law. 2. T F The second step in the contract analysis is to
THE CYPRUS INSTITUTE OF MARKETING DMM COMMERCIAL LAW
 THE CYPRUS INSTITUTE OF MARKETING DMM COMMERCIAL LAW INTRODUCTION 18 LECTURES CIM BOOKLET + TEXT BOOK ATTENDANCE CONTACT yangos@cima.ac.cy COURSE ASSESSMENT 1. ASSIGNMENT No1. 7.5 % 2. ASSIGNEMENT No2.
THE CYPRUS INSTITUTE OF MARKETING DMM COMMERCIAL LAW INTRODUCTION 18 LECTURES CIM BOOKLET + TEXT BOOK ATTENDANCE CONTACT yangos@cima.ac.cy COURSE ASSESSMENT 1. ASSIGNMENT No1. 7.5 % 2. ASSIGNEMENT No2.
Acceptance of Unilateral Contract Offer Requiring Time in Performance
 SMU Law Review Volume 5 1951 Acceptance of Unilateral Contract Offer Requiring Time in Performance Charles B. Redman Follow this and additional works at: http://scholar.smu.edu/smulr Recommended Citation
SMU Law Review Volume 5 1951 Acceptance of Unilateral Contract Offer Requiring Time in Performance Charles B. Redman Follow this and additional works at: http://scholar.smu.edu/smulr Recommended Citation
Contracts: Offer, Acceptance, and Mutual Assent
 Chapter 7 Contracts: Offer, Acceptance, and Mutual Assent 1 The Purposes of Contract Enforcement When people keep their business promises to one another, good things happen: buildings get built on time
Chapter 7 Contracts: Offer, Acceptance, and Mutual Assent 1 The Purposes of Contract Enforcement When people keep their business promises to one another, good things happen: buildings get built on time
A
 Contracts with Vincent Rougeau in Spring 2008 1. Basic Theories 1.1. Classical Theory - Neutral principles can be instilled from cases 1.1.1. Characteristics 1.1.1.1. Preference for clear rules over general
Contracts with Vincent Rougeau in Spring 2008 1. Basic Theories 1.1. Classical Theory - Neutral principles can be instilled from cases 1.1.1. Characteristics 1.1.1.1. Preference for clear rules over general
CONTRACT VS. PROMISE
 CONTRACT VS. PROMISE Promise: A person s declaration that he will perform or refrain from performing some present or future act. Promisor: The person making the promise. Promisee: The person to whom the
CONTRACT VS. PROMISE Promise: A person s declaration that he will perform or refrain from performing some present or future act. Promisor: The person making the promise. Promisee: The person to whom the
CONTRACTS. A contract is a legally enforceable agreement between two or more parties whereby they make the future more predictable.
 CONTRACTS LESE Spring 2002 O'Hara 1 A contract is a legally enforceable agreement between two or more parties whereby they make the future more predictable. Contracts are in addition to the preexisting,
CONTRACTS LESE Spring 2002 O'Hara 1 A contract is a legally enforceable agreement between two or more parties whereby they make the future more predictable. Contracts are in addition to the preexisting,
United Nations Convention On Contracts For The International Sale Of Goods, 1980 (CISG) United Nations (UN)
 United Nations Convention On Contracts For The International Sale Of Goods, 1980 (CISG) United Nations (UN) Copyright 1980 United Nations (UN) ii Contents Contents PART I - Sphere of Application and General
United Nations Convention On Contracts For The International Sale Of Goods, 1980 (CISG) United Nations (UN) Copyright 1980 United Nations (UN) ii Contents Contents PART I - Sphere of Application and General
Legal & Ethical Applications: Exam #1: Review LAWS 3930 & FoE 1, 3, 4, 9, and 11 & Microecon. & Chapters 5, Page 1 of 8
 Review LAWS 3930 & FoE 1, 3, 4, 9, and 11 & Microecon. & Chapters 5, Page 1 of 8 print name on the line above as your signature INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This Exam #1 must be completed within the allocated time
Review LAWS 3930 & FoE 1, 3, 4, 9, and 11 & Microecon. & Chapters 5, Page 1 of 8 print name on the line above as your signature INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This Exam #1 must be completed within the allocated time
Index. References are to sections.
 Index References are to sections. A Abandonment Anticipatory breach or repudiation, ground for, 12.35 Damages, 12.35, 14.3 Distinguished from rescission, 14.3 Material breach, ground for, 12.37 Mutual,
Index References are to sections. A Abandonment Anticipatory breach or repudiation, ground for, 12.35 Damages, 12.35, 14.3 Distinguished from rescission, 14.3 Material breach, ground for, 12.37 Mutual,
Final Examination in Law 205 (Model Answers) Contracts I-04. Professor Radin
 Final Examination in Law 205 (Model Answers) Contracts I-04 Professor Radin Note: The following are unedited student answers from two different examination papers. Part I 1) Since Alan s contract with
Final Examination in Law 205 (Model Answers) Contracts I-04 Professor Radin Note: The following are unedited student answers from two different examination papers. Part I 1) Since Alan s contract with
ANSON S LAW OF CONTRACT. 29th Edition SIR JACK BEATSON
 ANSON S LAW OF CONTRACT 29th Edition SIR JACK BEATSON DCL, LLD, FBA A Justice of the High Court, Queen's Bench Division sometime Rouse Ball Professor of English Law, University of Cambridge ANDREW BURROWS
ANSON S LAW OF CONTRACT 29th Edition SIR JACK BEATSON DCL, LLD, FBA A Justice of the High Court, Queen's Bench Division sometime Rouse Ball Professor of English Law, University of Cambridge ANDREW BURROWS
Contents. Table of Statutes. Table of Secondary Legislation. Table of Cases. The Agreement to Contract
 Contents Table of Statutes Table of Secondary Legislation Table of Cases Chapter 1: The Agreement to Contract 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Elements required for a valid simple contract 1.3 The phenomenon of agreement
Contents Table of Statutes Table of Secondary Legislation Table of Cases Chapter 1: The Agreement to Contract 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Elements required for a valid simple contract 1.3 The phenomenon of agreement
Contracts - Autonomy Principle
 Contracts - Autonomy Principle THE AUTONOMY PRINCIPLE Enforceable promises are conventionally called contracts. The law of contracts defines the conditions under which people have the legal power to make
Contracts - Autonomy Principle THE AUTONOMY PRINCIPLE Enforceable promises are conventionally called contracts. The law of contracts defines the conditions under which people have the legal power to make
FAQ: Elements of Establishing A Contract
 Question 1: What is the procedure for analyzing a set of facts to establish the existence of a contract? Answer 1: The procedure involves an examination of the facts to determine whether each element of
Question 1: What is the procedure for analyzing a set of facts to establish the existence of a contract? Answer 1: The procedure involves an examination of the facts to determine whether each element of
