LAWS 1072: CONTRACTS
|
|
|
- Victoria Cannon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LAWS1072- CONTRACTS 2- EXAM NOTES: LAWS 1072: CONTRACTS 2 Semester
2 LAWS1072- CONTRACTS 2- EXAM NOTES: 2
3 LAWS1072- CONTRACTS 2- EXAM NOTES: CONSTRUCTION: 1. Express terms: a. Statements made during negotiations b. Written terms + signature c. Terms incorporated by notice d. Incorporation by a history of dealings 2. Extrinsic evidence: a. Parol evidence b. Extrinsic evidence in identifying the terms c. Extrinsic evidence in construing a contract 3. Implied terms: a. Implied in law b. Implied in fact c. Implied by custom d. Implied by statute. 4. Construing the terms: a. TPA b. Construction CASE NOTES STATUTE c. Exclusion clauses 3
4 LAWS1072- CONTRACTS 2- EXAM NOTES: 4
5 LAWS1072- CONTRACTS 2- EXAM NOTES: 1. Express terms: CONSTRUCTION - Terms of a contract are fundamental to determining what the parties have agreed to do by way of performance of their contract. - Use an OBJECTIVE APPROACH- Courts do not inquire into what the parties actually intended, rather courts consider the intention which reasonable persons would have had if placed in the situation of the parties - Reardon Smith Lane v Hansen-Tangen 1976: a. Statements made during negotiations To determine whether oral or other statements form part of a contract, the courts must consider the parties intentions as to the status of the statement; this includes analysis of: (1) The language used.- Codelfa (2) The relevant expertise of the parties. (asymmetry of knowledge)- Oscar Chess v Williams (3) The importance of the statement. Couchman v Hill (4) The timing of the statement.- Harling v Eddy (if the period between the statement and contract formation is brief that it can be assumed that the statement induced entry) (5) The form of the written contract. Statements Promissory or Mere Representation? The common law distinguishes three classes of statements in negotiations: (1) Puff - No legal impact Carlill (2) A Representation- NOT a contractual promise JJ Savage (3) A Contractual Promise- Dick Bentley Dick Bentley Productions v Harold Smith (Motors) If an intelligent bystander would reasonably infer that a warranty was intended, that will suffice. - If a representation is made in the course of dealings for a contract for the very purpose of inducing the other party to act on it, and it actually induces him to act on it by entering into the contract, that is prima facie ground for inferring that the representation was intended as a warranty. - OPINION promise- So far from being a promissory expression an expression of opinion tend against the inference of a promise. JJ Savage & Son v Blakney Reliance does not mean that the term is promissory. JJ Savage & Son v Blakney Innocent misrepresentation that does not amount to a promise or guarantee that the information was accurate does not qualify as a promissory term. Oscar Chess v Williams
6 LAWS1072- CONTRACTS 2- EXAM NOTES: b. Written terms + signature - Given the objective approach to the determination of rights and liabilities of contracting parties signature of a contractual document is irrefragable evidence of agreement. - A signature is widely recognised by the general public as a formal device and its value would be greatly reduced if it could not be treated as conclusive ground of contractual liability at least in all ordinary circumstances. Toll (FGCT) v Alphapharm - General rule= that a party will be bound by the terms contained in a contractual document which has been signed by them, whether or not they have read the document. Signature Binding: Unless Misrepresentation. - a written agreement which is signed by the defendant, the agreement is proved by providing a signature, and, in the absence of fraud, it is wholly immaterial that he has not read the agreement or does not know its contents. - Where no misrepresentation or fraud can be found; Signature is always binding. L Estrange v Graucob 1934 Circumstances in which the effect of signature may be avoided: - The binding nature of a signature is not applicable where the signature was induced by misrepresentation, fraud or mistake. - The rule will also not apply where the document cannot reasonably be considered a contractual document as it has another function- i.e. a receipt. - Any behaviour, by words or conduct, is sufficient to be a misrepresentation if it is such as to mislead the other party about the existence or extent of the exemption- If it conveys a false impression whether it be knowingly (fraudulent misrepresentation) or unwittingly (innocent misrepresentation). Curtis v Chemical Cleaning & Dyeing
7 LAWS1072- CONTRACTS 2- EXAM NOTES: c. Terms incorporated by notice - Parties may allege that the contract contains terms which have been displayed or delivered before or at the time of the transaction. Whether a party is bound depends upon: (1) Whether notice of the terms was given BEFORE the contract was formed (2) Whether reasonable steps were taken to bring the terms to the notice of the party to be bound. (1) Timing of Notice: - Tickets are generally regarded as an offer and the contract is only made through the subsequent acceptance of that offer by the passenger. - Any conditions must be made aware BEFORE the formation of the contract- NOT AFTER - New clause cannot be used UNLESS at the time of the contract the carrier had done all that was reasonably necessary to bring the exemption clause to the passengers notice. Oceanic Sun Line Special Shipping Company v Fay 1988 (2) Knowledge of notice: - If a party knows that the relevant document contains contractual terms, they will be bound regardless of whether they have read them. - In the absence of knowledge, a party will be bound by delivered or displayed terms if they had reasonable notice of the terms. - Reasonable notice is dependants upon the type of contract, nature of the terms and circumstances of the case. Ticket cases: - Conditions thus cannot be printed on ticket as the acceptance has already happened (taking the ticket out of the machine). This is distinguished from ticket cases as it is a machine so the person cannot dispute the terms once they have taken the ticket. Thornton v Shoe Lane Parking 1971: (1) Did the person know there was printing on the ticket? (2) Did they know that the ticket contained or referred to conditions? (3) Did the defendants do what was reasonably possibly in the way of notification of terms and conditions? McCutcheon v David MacBrayne Ltd: Unusual Terms: - It was the appellants responsibility to bring unusual and unexpected terms and conditions at least to the notice of passengers before they were to be bound to them. - The mere presentation of the ticket does not fix acceptance of the terms and conditions if the passenger hasn t had reasonable opportunity to see and agree to them. Baltic Shipping v Dillon (The Mikhail Lermontov) 1991: 7
8 LAWS1072- CONTRACTS 2- EXAM NOTES: d. Incorporation by a history of dealings - Where parties have had a history of dealings, contractual terms introduced in earlier contracts may be incorporated into a subsequent contract. - For a term to be incorporated by a course of dealing, this course of dealing must have been regular and uniform. Henry Kendall & Sons v William Lillico & Sons Ltd The document relied upon in previous transactions must also be reasonably considered a contractual document; nor merely a receipt or docket. Rinaldi & Patroni v Precision Mouldings If there is no express contract, the terms must therefore be implied from the circumstances Balmain New Ferry v Robertson
9 LAWS1072- CONTRACTS 2- EXAM NOTES: 2. Extrinsic evidence: - Extrinsic evidence may be used to show: 1. A contract exists 2. The parties agreed on the integration of the contract 3. The contract is void or voidable because of illegality, fraud, mistake or any other reason. a. Parol evidence - Parol Evidence Rule= Limits to the kind of evidence outside the written document that may be admitted. - When it is proved or admitted that the parties to a contract intended that all the express terms of their agreements should be recorded in a particular document, evidence will be inadmissible (because irrelevant) if it is tendered only for the purpose of adding to, varying, subtracting or contradicting the express terms of that contract.- Codelfa v State Rail NSW RULE:& Only applies to WRITTEN contracts. 1. Extrinsic evidence cannot add to, vary or contradict what is written in the document 2. Evidence which might explain the meaning of terms is limited to only if there is ambiguity. b. Extrinsic evidence in identifying the terms - Presumption that the written document= entire agreement: unless it can be shown that the document was not intended as the complete record of their bargain, Hoyt s v Spencer The mere production of a contractual document, however complete it may look, cannot as a matter of law exclude evidence of oral terms if the other party asserts that such terms were agreed. - The written contract= merely evidence of a contract wholly in writing. - MUST determine whether or not a contract is wholly contained in writing. TEST: 1. Is the contract wholly contained in writing? a. Does the document provide evidence for this? b. What are the extrinsic factors that may provide evidence to show that the contract is/ is not wholly contained in writing? State Rail Authority of NSW v Heath Outdoor
10 LAWS1072- CONTRACTS 2- EXAM NOTES: Exceptions to the Parol Evidence Rule: Exceptions to the parol-evidence rule: (1) Collateral contracts (2) Identify the subject matter (3) Identify the parties (4) Relevant to implied terms (5) Rectification (6) Is there in fact a contract at all/ what is its nature (7) Evidence of the matrix of facts + surrounding circumstances Collateral Contracts: - The Parol Evidence Rule does not apply to exclude evidence of a collateral contract. - Collateral contract= Those statements that are clearly intended to have some significant contractual significance, but that for some reason have been precluded as terms of a contract. - The consideration for this promise/ term is connected to but independent of a main contract and as a consideration for that promise the other party agrees to enter into the main contract. 4 elements: (1) Statement was intended to be relied upon and induce entry into the contract. JJ Savage & Sons v Blackney (2) Reliance by the party alleging the existence of the contract (3) An intention on the part of the maker of the statement to guarantee its truth. (4) The collateral contract must be consistent with the main contract unless it is with a third party Hoyt s Pty Ltd v Spencer. Employment manuals= a common form of collateral documents- the use of one is fairly normal as not every detail of the contract can be dealt with in an interview- Riverwood v McCormick Estoppel: - There are 2 key cases which illustrate the debate as to whether PER excludes the admission of extrinsic evidence for the purpose of establishing an estoppel. Whittet v State Bank of NSW 1991: (a) In order to establish such estoppel it is necessary that there should be clear and convincing proof. (b) The material giving rise to such an estoppel can arise from pre-contract negotiations must give rise to such proof. Australian Co-operative Foods v Norco Co-operative 1999: - The evidence offered to prove estoppel is extensive, discursive and inconclusive and where it is of any value at all it is of less value than written expressions. 10
11 LAWS1072- CONTRACTS 2- EXAM NOTES: c. Extrinsic evidence in construing a contract - Parol Evidence Rule limits the meaning of terms of the contract to be ascertained solely by the words that the parties have used. - Evidence of the meaning subjectively intended by the parties will generally not be admitted. Evidence of the surrounding circumstances: - Evidence of surrounding circumstances is only admissible to assist in the interpretation of a written contract if the language be ambiguous or susceptible to multiple meanings- Codelfa v State Rail NSW. - Construction requires consideration not only of the text of the documents, but also the surrounding circumstances known to the parties and the purpose and object of the transaction- Pacific Carriers Ltd v BNP Paribas Necessary to consider the factual matrix in which the contract was made.- Reardon Smith Line v Hansen Tangen. - The law excludes previous negotiations of the parties and their declarations of subjective intent from what may be considered as admissible background information. - The meaning of a written contract may be illuminated by evidence of facts to which the writing refers. Royal Botanic Gardens and Domain Trust v South Sydney City Council 2002: 11
12 LAWS1072- CONTRACTS 2- EXAM NOTES: 3. Implied terms: a. Implied in law Terms may be implied into a contract: As a matter of law As a matter of fact By Course of dealing By reason of custom By statute - Terms implied in law are terms implied as a legal incident of all contracts of a particular class; eg implied conditions of fitness and merchantable quality on a contract for sale of goods or an implied promise by a banker not to reveal customer s details. - Implication by law can only occur if the term is NOT: o excluded by express provision made by the parties Byrne v Autralian Airlines o inconsistent with the terms of the contract TEST: (1) Is the implication of a particular term necessary for the reasonable or effective operation of the contract? (2) It must be necessary to imply the term because otherwise the enjoyment of the rights conferred by the contract would or could be rendered nugatory, worthless, or, perhaps, be seriously undermined Byrne v Australian Airlines; Frew v Australian Airlines
13 LAWS1072- CONTRACTS 2- EXAM NOTES: b. Implied in fact - Terms in fact are traditionally said to be based on the presumed intentions of the parties concerned and accordingly are unique to the contract in question. Formal Contracts: - If a contract is wholly in writing for a court to imply a term in a contract it must fulfil 5 conditions: (1) It must be reasonable and equitable (2) It must give business efficiency to the contract (i.e. it will not be implied if the contract is efficient without it.). (3) The term must be so obvious it goes without saying (4) It must be capable of clear expression (5) It must not contradict any express term. BP Refinery (Westernport) v Hastings Shire Council 1977 (3) To prove- it goes without saying P must prove that contracting parties would assent to it- Byrne v Australian Airlines - In order to justify the importation of an implied term it is not sufficient that it would be reasonable to imply the term...it clearly must be necessary - A common assumption is not equivalent to the implication of a term. Codelfa Construction Pty Ltd v State Rail Authority of NSW - There is often reluctance to imply terms in non-negotiated contracts. Informal Contracts: - Requirements for an implied term in informal contracts are less strict. - In a case where it is apparent that the parties have not attempted to spell out the full terms of the contract, the court should imply a term by reference to the impute intention of the parties, if, but only if, it can be seen that the implication of the particular term is necessary for the reasonable or effective operation of a contract of that nature in the circumstances of the case Hawkins v Clayton 13
14 LAWS1072- CONTRACTS 2- EXAM NOTES: c. Implied by custom - A term may be implied on the basis of custom where the custom is well known and acquiesced in then everyone making a contract in that situation can reasonably be presumed to have imported that term into the contract. - The custom must be relatively unvariable. The circumstance in which trade, custom or usage may form the basis for the implication of terms into a contract include: (1) The existence of custom is a question of fact (2) There must be evidence that the custom is so well known and acquiesced that everyone in that situation can be presumed to know the term (3) Cannot be contrary to the express terms (4) Don t need knowledge of a custom for it to be implied. Con-Stan Industires of Aus v Norwich Winterthur Insurance d. Terms implied by statute See Trade Practices Act ss69-74: 14
15 LAWS1072- CONTRACTS 2- EXAM NOTES: 4. Construing the terms: a. TPA i. Ss68 and 68A as they apply to ss b. Construction - Construction= Process by which a court determines the meaning and legal effect of the terms of the contract agreed by the parties. - Parties intentions are considered objectively and the meaning of the terms is what would be understood by a reasonable person in the position of the parties. - Court should know the commercial purpose of the contract and this in turn presupposes knowledge of the genesis of the transaction, the background, the context, the market in which the parties are operating. Pacific Carriers v BNP Paribas 2004 c. Exclusion clauses Clause attempts to: (1) Modify the principal obligation(s) arising under a contract of that particular type or; (2) To limit or exclude the liability of a party which would otherwise arise as a result of a breach. - An indemnity clause is similar in that it seeks to exclude the liability of one party by imposing on the other a duty to indemnify the former in respect of any loss incurred. To rely on the protection of an exclusion clause: (1) Clause must be incorporated into the contract. (2) Does the clause apply to exclude/ restrict liability in relation to the issue in dispute? - Exclusion clauses may be construed contra proferentum (against the interests of the party seeking to rely on the clause) where there is ambiguity. - Exclusion clauses must be interpreted by construing the clause according to its natural and ordinary meaning, read in light of the contract as a whole The effect of an exclusion clause must be resolved by construing the language that the parties used, read in its context and with any necessary implications based upon their presumed intentions. Darling Futures v Delco Aust SEE: Trade Practices Act ss A 15
LLB170 - Summary. Content of the parties bargain
 Content of the parties bargain LLB170 - Summary 1. Identifying express terms a. Incorporation of terms: i. By signature:! A party will be bound by all the terms set out in a contractual document if s/he
Content of the parties bargain LLB170 - Summary 1. Identifying express terms a. Incorporation of terms: i. By signature:! A party will be bound by all the terms set out in a contractual document if s/he
Contracts 2 Rose Vassel 2012 CONTRACTS 2 LAWS1072. Rose Vassel
 CONTRACTS 2 LAWS1072 Rose Vassel 1 INCORPORATION BY A COURSE OF DEALINGS This is justified by the idea that by continuing to deal with the party seeking to impose those terms, they have demonstrated a
CONTRACTS 2 LAWS1072 Rose Vassel 1 INCORPORATION BY A COURSE OF DEALINGS This is justified by the idea that by continuing to deal with the party seeking to impose those terms, they have demonstrated a
Identifying the express terms 2
 LAWS1075 CONTRACTS Identifying the express terms 2 Written terms and signature (12.05-40) 2 From notice (12.45-80) 4 From a course of dealing (12.85-100) 6 Parol evidence rule (12.105-180) 9 From statements
LAWS1075 CONTRACTS Identifying the express terms 2 Written terms and signature (12.05-40) 2 From notice (12.45-80) 4 From a course of dealing (12.85-100) 6 Parol evidence rule (12.105-180) 9 From statements
LAWS1072 CONTRACTS II
 UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES LAWS1072 CONTRACTS II SEMESTER II 2012 1 Table of Contents What is a contract?... 9 What are the terms of a contract?... 9 Consent to incorporation of terms in a contract...
UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES LAWS1072 CONTRACTS II SEMESTER II 2012 1 Table of Contents What is a contract?... 9 What are the terms of a contract?... 9 Consent to incorporation of terms in a contract...
LAW OF CONTRACT. LEC Summer 2017/2018 Week 5 Express/Implied Terms
 1 LAW OF CONTRACT LEC Summer 2017/2018 Week 5 Express/Implied Terms Aims and Objectives Lecture 5 2 At the end of this lecture students should understand the following: the circumstances in which pre-contractual
1 LAW OF CONTRACT LEC Summer 2017/2018 Week 5 Express/Implied Terms Aims and Objectives Lecture 5 2 At the end of this lecture students should understand the following: the circumstances in which pre-contractual
Toll, Curtis. Toll, Curtis. Toll (FGCT) Pty v Alphapharm Pty Ltd (2004) 219 CLR 165
 INCORPORATION Which terms are part of a contract, which aren t, and why. Two categories: signed and unsigned Signed documents incorporate terms save fraud but must be objectively contractual Unsigned documents
INCORPORATION Which terms are part of a contract, which aren t, and why. Two categories: signed and unsigned Signed documents incorporate terms save fraud but must be objectively contractual Unsigned documents
Page 7. Capacity. Statute
 Page 1 Contents Capacity... 7 Statute... 7 Minors (Property & Contracts) Act 1970 (NSW)... 7 General Law... 7 Necessaries... 7 Scarborough v Sturzaker (1905) 1 TasLR 117 - Necessaries contracts are enforceable
Page 1 Contents Capacity... 7 Statute... 7 Minors (Property & Contracts) Act 1970 (NSW)... 7 General Law... 7 Necessaries... 7 Scarborough v Sturzaker (1905) 1 TasLR 117 - Necessaries contracts are enforceable
LAW OF CONTRACT. LEC Winter 2016
 LAW OF CONTRACT LEC Winter 2016 Aims and Objectives Lecture 5 At the end of this lecture students should understand the following: the circumstances in which pre-contractual statements amount to terms
LAW OF CONTRACT LEC Winter 2016 Aims and Objectives Lecture 5 At the end of this lecture students should understand the following: the circumstances in which pre-contractual statements amount to terms
TERMS AND THE COMMUNICATING OF THE PARTIES 9
 Contracts TERMS AND THE COMMUNICATING OF THE PARTIES 9 WRITTEN TERMS AND THE EFFECT OF SIGNATURE 10 L ESTRANGE v GRAUCOB [1934] 2 KB 394 10 TOLL (FGCT) v ALPHAPHARM [2004] HCA 52 11 Circumstances in which
Contracts TERMS AND THE COMMUNICATING OF THE PARTIES 9 WRITTEN TERMS AND THE EFFECT OF SIGNATURE 10 L ESTRANGE v GRAUCOB [1934] 2 KB 394 10 TOLL (FGCT) v ALPHAPHARM [2004] HCA 52 11 Circumstances in which
CASE NOTES AND COMMENT
 CASE NOTES AND COMMENT THE HIGH COURT DECISION IN TOLL (FCGT) PTY LTD V ALPHAPHARM PTY LTD & ORS 1 Guy Cumes * INTRODUCTION The question as to whether and how the conduct of the parties constitutes a contract
CASE NOTES AND COMMENT THE HIGH COURT DECISION IN TOLL (FCGT) PTY LTD V ALPHAPHARM PTY LTD & ORS 1 Guy Cumes * INTRODUCTION The question as to whether and how the conduct of the parties constitutes a contract
CONTRACTS. Someone illiterate: may be found to not be bound by signature if they can prove they did not understand it.
 CONTRACTS Class 1.2 Important distinctions between signed and unsigned documents Signed documents: L Estrange Rule -> Signature = bound unless: 1. Equitable relief (Fraud, misrepresentation or rectification)
CONTRACTS Class 1.2 Important distinctions between signed and unsigned documents Signed documents: L Estrange Rule -> Signature = bound unless: 1. Equitable relief (Fraud, misrepresentation or rectification)
INTERPRETATION OF CONTRACTS
 INTERPRETATION OF CONTRACTS ISBN 978-98-3519-11-8 Author: Hamid Ibrahim Binding: Softcover/Extent: 532 pp Publication Price: MYR 210.00 The law is stated as of February 1, 2008 PRINCIPLES & CANONS OF CONSTRUCTION
INTERPRETATION OF CONTRACTS ISBN 978-98-3519-11-8 Author: Hamid Ibrahim Binding: Softcover/Extent: 532 pp Publication Price: MYR 210.00 The law is stated as of February 1, 2008 PRINCIPLES & CANONS OF CONSTRUCTION
Implied Terms: parties have not consciously included these terms in the formation of the contract
 Lecture 6: Implied Terms; Construction of Terms; Exclusion Clauses Implied Terms: parties have not consciously included these terms in the formation of the contract Under which circumstances will a Court
Lecture 6: Implied Terms; Construction of Terms; Exclusion Clauses Implied Terms: parties have not consciously included these terms in the formation of the contract Under which circumstances will a Court
Contractual Interpretation: A Roundabout Approach
 Contractual Interpretation: A Roundabout Approach Paul J Hayes Barrister-at-Law The Victorian Bar, Dever s List (List D) Legalwise Seminar Melbourne 28 March 2014 Introduction Importance? The meaning of
Contractual Interpretation: A Roundabout Approach Paul J Hayes Barrister-at-Law The Victorian Bar, Dever s List (List D) Legalwise Seminar Melbourne 28 March 2014 Introduction Importance? The meaning of
MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2008 question paper 9084 LAW. 9084/03 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2008 question paper 9084 LAW 9084/03 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2008 question paper 9084 LAW 9084/03 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme
Genuineness of Assent
 Genuineness of Assent A party who demonstrates that she did not genuinely assent to the terms of a contract may avoid an otherwise valid contract. Genuine assent may be lacking due to mistake, fraudulent
Genuineness of Assent A party who demonstrates that she did not genuinely assent to the terms of a contract may avoid an otherwise valid contract. Genuine assent may be lacking due to mistake, fraudulent
OVERVIEW OF CONTRACT LAW
 OVERVIEW OF CONTRACT LAW Liability is generally the key issue in regards to contractual disputes. Purpose of K law is to provide the rules which determine when one party is liable to another under or in
OVERVIEW OF CONTRACT LAW Liability is generally the key issue in regards to contractual disputes. Purpose of K law is to provide the rules which determine when one party is liable to another under or in
THE LAW RELATING TO GUARANTEES
 THE LAW RELATING TO GUARANTEES ISBN 978-983-3519-16-3 Author: Nasser Hamid Binding: Softcover / 938 pages Publication Price: MYR 290.00 The law is stated as of March 31, 2009 CONTENTS CHAPTER ONE GUARANTEES
THE LAW RELATING TO GUARANTEES ISBN 978-983-3519-16-3 Author: Nasser Hamid Binding: Softcover / 938 pages Publication Price: MYR 290.00 The law is stated as of March 31, 2009 CONTENTS CHAPTER ONE GUARANTEES
EXCLUSION CLAUSES IN LAW OF CONTRACT
 EXCLUSION CLAUSES IN LAW OF CONTRACT Introduction: a clause means a statement. In relation to contract, it simply means a statement in the contract and that indicate what the parties have agreed on. In
EXCLUSION CLAUSES IN LAW OF CONTRACT Introduction: a clause means a statement. In relation to contract, it simply means a statement in the contract and that indicate what the parties have agreed on. In
BUSINESS LAW GUIDEBOOK
 BUSINESS LAW GUIDEBOOK SECOND EDITION CHARLES YC CHEW CHAPTER 4: CONTRACT: TERMS AND REMEDIES FOR BREACH TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE 1. The terms of a contract may be either express or implied. Explain what is
BUSINESS LAW GUIDEBOOK SECOND EDITION CHARLES YC CHEW CHAPTER 4: CONTRACT: TERMS AND REMEDIES FOR BREACH TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE 1. The terms of a contract may be either express or implied. Explain what is
MLL111- Exam Notes Contract Law (All Topics + Cases)
 1 MLL111- Exam Notes Contract Law (All Topics + Cases) 2 Contents Page Page 8: Formation of Contracts Offer and Acceptance Page 9: Acceptance Communication of Acceptance: Waiver Silence Page 10: Acceptance
1 MLL111- Exam Notes Contract Law (All Topics + Cases) 2 Contents Page Page 8: Formation of Contracts Offer and Acceptance Page 9: Acceptance Communication of Acceptance: Waiver Silence Page 10: Acceptance
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 9084 LAW. 9084/31 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 9084 LAW 9084/31 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme is published
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 9084 LAW 9084/31 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme is published
RECENT DEVELOPMENTS IN EMPLOYMENT DISPUTES: EMPHASISING THE LAW OF CONTRACT. Tom Brennan 1. Barrister, 13 Wentworth Chambers
 RECENT DEVELOPMENTS IN EMPLOYMENT DISPUTES: EMPHASISING THE LAW OF CONTRACT Tom Brennan 1 Barrister, 13 Wentworth Chambers Australian law has shifted from regulating the employer/employee relationship
RECENT DEVELOPMENTS IN EMPLOYMENT DISPUTES: EMPHASISING THE LAW OF CONTRACT Tom Brennan 1 Barrister, 13 Wentworth Chambers Australian law has shifted from regulating the employer/employee relationship
CONTRACT LAW IN THE SOUTH PACIFIC
 CONTRACT LAW IN THE SOUTH PACIFIC Jennifer Corrin Care Senior Lecturer TC Beirne School of Law University of Queensland Cavendish Publishing Limited London Sydney CONTENTS Preface Table of Cases Table
CONTRACT LAW IN THE SOUTH PACIFIC Jennifer Corrin Care Senior Lecturer TC Beirne School of Law University of Queensland Cavendish Publishing Limited London Sydney CONTENTS Preface Table of Cases Table
a) The body of law as made by judges through the determination of cases. d) The system of law that emerged following the Norman Conquest in 1066.
 1. Who of the following was NOT a proponent of natural law? a) Aristotle b) Jeremy Bentham c) St Augustine d) St Thomas Aquinas 2. The term 'common law' has three different meanings. Which of the following
1. Who of the following was NOT a proponent of natural law? a) Aristotle b) Jeremy Bentham c) St Augustine d) St Thomas Aquinas 2. The term 'common law' has three different meanings. Which of the following
Chapter 14 Statute of Frauds and Equitable Exceptions 25-1
 Chapter 14 Statute of Frauds and Equitable Exceptions 25-1 Statute of Frauds for Common Contracts Statute of Frauds: A state statute that requires certain types of contracts to be in writing 14-2 Contracts
Chapter 14 Statute of Frauds and Equitable Exceptions 25-1 Statute of Frauds for Common Contracts Statute of Frauds: A state statute that requires certain types of contracts to be in writing 14-2 Contracts
Surfstone Pty Ltd & Anor v Morgan Consulting Engineers Pty Ltd
 Surfstone Pty Ltd & Anor v Morgan Consulting Engineers Pty Ltd Surfstone Pty Ltd & Anor v Morgan Consulting Engineers Pty Ltd [2016] QCA 213 Supreme Court of Queensland (Court of Appeal) 16 May 2016 and
Surfstone Pty Ltd & Anor v Morgan Consulting Engineers Pty Ltd Surfstone Pty Ltd & Anor v Morgan Consulting Engineers Pty Ltd [2016] QCA 213 Supreme Court of Queensland (Court of Appeal) 16 May 2016 and
Recent Developments in the Canadian Law of Contract
 Honest Performance and Absolutely Everything Else By Ryan P. Krushelnitzky and Sandra L. Corbett QC Recent Developments in the Canadian Law of Contract Bhasin and Sattva represent important changes and
Honest Performance and Absolutely Everything Else By Ryan P. Krushelnitzky and Sandra L. Corbett QC Recent Developments in the Canadian Law of Contract Bhasin and Sattva represent important changes and
CONTRACT LAW. Elements of a Contract
 CONTRACT LAW Contracts: Types and Sources in Australia CONTRACT: An agreement concerning promises made between two or more parties with the intention of creating certain legal rights and obligations upon
CONTRACT LAW Contracts: Types and Sources in Australia CONTRACT: An agreement concerning promises made between two or more parties with the intention of creating certain legal rights and obligations upon
Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Spring Contract Terms
 Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Contract Terms I. Construing and Interpreting Contracts A. Purpose: A court s primary concern is to ascertain
Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Contract Terms I. Construing and Interpreting Contracts A. Purpose: A court s primary concern is to ascertain
Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Spring Contract Terms (Expanded)
 Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Contract Terms (Expanded) I. Construing and Interpreting Contracts A. Purpose: A court s primary concern
Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Contract Terms (Expanded) I. Construing and Interpreting Contracts A. Purpose: A court s primary concern
Contents. Table of Statutes. Table of Secondary Legislation. Table of Cases. The Agreement to Contract
 Contents Table of Statutes Table of Secondary Legislation Table of Cases Chapter 1: The Agreement to Contract 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Elements required for a valid simple contract 1.3 The phenomenon of agreement
Contents Table of Statutes Table of Secondary Legislation Table of Cases Chapter 1: The Agreement to Contract 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Elements required for a valid simple contract 1.3 The phenomenon of agreement
CONTRACTING FOR CONTEXTUALISM HOW CAN PARTIES INFLUENCE THE INTERPRETATION METHOD APPLIED TO THEIR AGREEMENT?
 52 CONTRACTING FOR CONTEXTUALISM HOW CAN PARTIES INFLUENCE THE INTERPRETATION METHOD APPLIED TO THEIR AGREEMENT? NATALIE BYRNE* Since the High Court refusal of leave to appeal against the New South Wales
52 CONTRACTING FOR CONTEXTUALISM HOW CAN PARTIES INFLUENCE THE INTERPRETATION METHOD APPLIED TO THEIR AGREEMENT? NATALIE BYRNE* Since the High Court refusal of leave to appeal against the New South Wales
STATE OF MICHIGAN COURT OF APPEALS
 STATE OF MICHIGAN COURT OF APPEALS TAURUS MOLD, INC, a Michigan Corporation, Plaintiff-Appellant, UNPUBLISHED January 13, 2009 v No. 282269 Macomb Circuit Court TRW AUTOMOTIVE US, LLC, a Foreign LC No.
STATE OF MICHIGAN COURT OF APPEALS TAURUS MOLD, INC, a Michigan Corporation, Plaintiff-Appellant, UNPUBLISHED January 13, 2009 v No. 282269 Macomb Circuit Court TRW AUTOMOTIVE US, LLC, a Foreign LC No.
BARRY ALLAN CONTACT PART II. Introduction 1. OBJECTIVE THEORY OF CONTRACT 2. A MODEL OF CONTRACT
 BARRY ALLAN CONTACT PART II Introduction 1. OBJECTIVE THEORY OF CONTRACT We use the objective principle to decide whether there has been an agreement, consideration and intention to be bound between the
BARRY ALLAN CONTACT PART II Introduction 1. OBJECTIVE THEORY OF CONTRACT We use the objective principle to decide whether there has been an agreement, consideration and intention to be bound between the
Reality of Consent. Reality of Consent. Reality of Consent. Chapter 13
 Reality of Consent Chapter 13 Reality of Consent It is crucial to the economy and commerce that the law be counted on to enforce contracts. However, in some cases there are compelling reasons to permit
Reality of Consent Chapter 13 Reality of Consent It is crucial to the economy and commerce that the law be counted on to enforce contracts. However, in some cases there are compelling reasons to permit
TRIAL DOCUMENTS PROVING, TENDERING AND CROSS-EXAMINATION
 TRIAL DOCUMENTS PROVING, TENDERING AND CROSS-EXAMINATION I take my topic to require a discussion of the use of documents in one s own case evidence in chief and in the opponent s case cross-examination.
TRIAL DOCUMENTS PROVING, TENDERING AND CROSS-EXAMINATION I take my topic to require a discussion of the use of documents in one s own case evidence in chief and in the opponent s case cross-examination.
Revisiting the Rule in L Estrange v F Graucob Ltd
 Bond Law Review Volume 17 Issue 2 Article 10 2005 Revisiting the Rule in L Estrange v F Graucob Ltd Phillip G. Sharp Follow this and additional works at: http://epublications.bond.edu.au/blr This Commentary
Bond Law Review Volume 17 Issue 2 Article 10 2005 Revisiting the Rule in L Estrange v F Graucob Ltd Phillip G. Sharp Follow this and additional works at: http://epublications.bond.edu.au/blr This Commentary
LAW OF CONTRACT. LPAB Summer 2016/2017 Week 6. Alex Kuklik
 LAW OF CONTRACT LPAB Summer 2016/2017 Week 6 Alex Kuklik Aims and Objectives Lecture 6 At the end of this lecture, students should understand the rules and principles by which terms of a contract, especially
LAW OF CONTRACT LPAB Summer 2016/2017 Week 6 Alex Kuklik Aims and Objectives Lecture 6 At the end of this lecture, students should understand the rules and principles by which terms of a contract, especially
FRAUDULENT MISREPRESENTATION
 FRAUDULENT MISREPRESENTATION Author: Nasser Hamid Binding: Softcover, 500 pages Publication Price: MYR 200.00 CONTENTS Chapter 1 STATEMENTS, REPRESENTATIONS AND FRAUD Representation Misrepresentation Fraudulent
FRAUDULENT MISREPRESENTATION Author: Nasser Hamid Binding: Softcover, 500 pages Publication Price: MYR 200.00 CONTENTS Chapter 1 STATEMENTS, REPRESENTATIONS AND FRAUD Representation Misrepresentation Fraudulent
CONTRACT LAW SUMMARY
 CONTRACT LAW SUMMARY LAWSKOOL UK CONTENTS INTRODUCTION TO CONTRACT LAW 6 DEFINITION OF CONTRACT LAW 6 1) The Classical Model of Contract Law 6 INTENTION TO CREATE LEGAL RELATIONS 8 INTRODUCTION TO INTENTION
CONTRACT LAW SUMMARY LAWSKOOL UK CONTENTS INTRODUCTION TO CONTRACT LAW 6 DEFINITION OF CONTRACT LAW 6 1) The Classical Model of Contract Law 6 INTENTION TO CREATE LEGAL RELATIONS 8 INTRODUCTION TO INTENTION
MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9084 LAW. 9084/31 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9084 LAW 9084/31 Paper 3, maximum
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9084 LAW 9084/31 Paper 3, maximum
TABLE OF CONTENTS. Preface... iii Preface to the First Edition... v Table of Cases... TC-1 Table of Statutes... TS-1
 TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE Preface... iii Preface to the First Edition... v Table of Cases... TC-1 Table of Statutes... TS-1 PART I. INTRODUCTION... 1-17 CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION... 1 PART II. ENFORCEABILITY...
TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE Preface... iii Preface to the First Edition... v Table of Cases... TC-1 Table of Statutes... TS-1 PART I. INTRODUCTION... 1-17 CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION... 1 PART II. ENFORCEABILITY...
Chinese Contract Law: A Brief Introduction. ZHANG Xuezhong. Assistant Professor of Law.
 Chinese Contract Law: A Brief Introduction ZHANG Xuezhong Assistant Professor of Law zhangxuezhong@ecupl.edu.cn East China University of Politics and Law Overview 1. In General 2. Principles of Chinese
Chinese Contract Law: A Brief Introduction ZHANG Xuezhong Assistant Professor of Law zhangxuezhong@ecupl.edu.cn East China University of Politics and Law Overview 1. In General 2. Principles of Chinese
LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 LAW OF CONTRACT SUGGESTED ANSWERS - JUNE 2014
 Note to Candidates and Tutors: LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 LAW OF CONTRACT SUGGESTED ANSWERS - JUNE 2014 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students
Note to Candidates and Tutors: LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 LAW OF CONTRACT SUGGESTED ANSWERS - JUNE 2014 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students
LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS JANUARY 2016
 Note to Candidates and Tutors: LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS JANUARY 2016 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students
Note to Candidates and Tutors: LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS JANUARY 2016 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students
MISTAKE. (1) the other party to the contract knew or should have known of the mistake; or
 MISTAKE Mistake of Fact: The parties entered into a contract with different understandings of one or more material facts relating to the contract s performance. Mutual Mistake: A mistake by both contracting
MISTAKE Mistake of Fact: The parties entered into a contract with different understandings of one or more material facts relating to the contract s performance. Mutual Mistake: A mistake by both contracting
J U L Y V O L U M E 6 3
 LEGAL MATTERS J U L Y 2 0 1 6 V O L U M E 6 3 For a contract to be considered valid and binding in South Africa, certain requirements must be met, inter alia, there must be consensus ad idem between the
LEGAL MATTERS J U L Y 2 0 1 6 V O L U M E 6 3 For a contract to be considered valid and binding in South Africa, certain requirements must be met, inter alia, there must be consensus ad idem between the
MLL215 Commercial Law. Exam Notes and Cases
 MLL215 Commercial Law Exam Notes and Cases 1 Topic 1 Creation of Agency Relationship Page 6: Nature of Agency Page 7: Specific Categories of General Agents Page 8: Scope of Agency Page 10: Capacity of
MLL215 Commercial Law Exam Notes and Cases 1 Topic 1 Creation of Agency Relationship Page 6: Nature of Agency Page 7: Specific Categories of General Agents Page 8: Scope of Agency Page 10: Capacity of
APPLICATION FOR COMMERCIAL CREDIT ACCOUNT TRADING TERMS AND CONDITIONS
 APPLICATION FOR COMMERCIAL CREDIT ACCOUNT TRADING TERMS AND CONDITIONS These Trading Terms and Conditions are to be read and understood prior to the execution of the Application for Commercial Credit Account.
APPLICATION FOR COMMERCIAL CREDIT ACCOUNT TRADING TERMS AND CONDITIONS These Trading Terms and Conditions are to be read and understood prior to the execution of the Application for Commercial Credit Account.
REMOTE DEPOSIT ANYWHERE AGREEMENT
 PLEASE READ THIS TIOGA STATE BANK REMOTE DEPOSIT ANYWHERE CAREFULLY AND KEEP A COPY FOR YOUR REFERENCE. 1. DEFINITIONS: In this Agreement, the words "you" or "your" mean the consumer or business that has
PLEASE READ THIS TIOGA STATE BANK REMOTE DEPOSIT ANYWHERE CAREFULLY AND KEEP A COPY FOR YOUR REFERENCE. 1. DEFINITIONS: In this Agreement, the words "you" or "your" mean the consumer or business that has
The Consumer Products Warranties Act
 The Consumer Products Warranties Act being Chapter C-30 of The Revised Statutes of Saskatchewan, 1978 (effective February 26, 1979). NOTE: This consolidation is not official. Amendments have been incorporated
The Consumer Products Warranties Act being Chapter C-30 of The Revised Statutes of Saskatchewan, 1978 (effective February 26, 1979). NOTE: This consolidation is not official. Amendments have been incorporated
Contents. Table of Statutes. Table of Secondary Legislation. Table of Cases. The Agreement to Contract
 Contents Table of Statutes Table of Secondary Legislation Table of Cases Chapter 1: The Agreement to Contract 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Elements required for a valid simple contract 1.3 The phenomenon of agreement
Contents Table of Statutes Table of Secondary Legislation Table of Cases Chapter 1: The Agreement to Contract 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Elements required for a valid simple contract 1.3 The phenomenon of agreement
CONTRACTS. Miscellaneous applications of ACL for Contracts:! 6 PROMISSORY ESTOPPEL! Assumption! Detrimental Reliance!...
 CONTRACTS Miscellaneous applications of ACL for Contracts:! 6 PROMISSORY ESTOPPEL! 7 1. Assumption!... 7 2. Detrimental Reliance!... 7 3. Unconscionability!... 8 Remedy of Promissory Estoppel!... 8 PRIVITY!
CONTRACTS Miscellaneous applications of ACL for Contracts:! 6 PROMISSORY ESTOPPEL! 7 1. Assumption!... 7 2. Detrimental Reliance!... 7 3. Unconscionability!... 8 Remedy of Promissory Estoppel!... 8 PRIVITY!
CONTRACTS COMPLETE EXAM NOTES
 CONTRACTS COMPLETE EXAM NOTES 1 2 LATIN TERMINOLOGY:... 11 1A. OFFER... 14 Offer... 14 RULES AS TO OFFER... 15 UNILATERAL CONTRACT... 15 BILATERAL CONTRACT... 15 OFFERS NEED TO BE DISTINGUISHED FROM THE
CONTRACTS COMPLETE EXAM NOTES 1 2 LATIN TERMINOLOGY:... 11 1A. OFFER... 14 Offer... 14 RULES AS TO OFFER... 15 UNILATERAL CONTRACT... 15 BILATERAL CONTRACT... 15 OFFERS NEED TO BE DISTINGUISHED FROM THE
CONTRACTS AND SALES QUESTION 1
 CONTRACTS AND SALES QUESTION Peter responded to an advertisement placed by Della, a dentist, seeking a dental hygienist. After an interview, Della offered Peter the job and said she would either: () pay
CONTRACTS AND SALES QUESTION Peter responded to an advertisement placed by Della, a dentist, seeking a dental hygienist. After an interview, Della offered Peter the job and said she would either: () pay
Is there a contract?
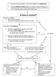 1. te whether this transaction is governed by UCC or the Restatement. 2. Does the Statute of Frauds apply? The contract must be in writing if it is in regard to land, if by its nature it takes more than
1. te whether this transaction is governed by UCC or the Restatement. 2. Does the Statute of Frauds apply? The contract must be in writing if it is in regard to land, if by its nature it takes more than
Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world
 Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk Pearson Education Limited 2014
Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk Pearson Education Limited 2014
Pure economic loss caused by Negligent Misstatement
 Pure economic loss caused by Negligent Misstatement Development of negligent misstatement as a cause of action A negligent misstatement is information or advice which is honestly provided but is inaccurate
Pure economic loss caused by Negligent Misstatement Development of negligent misstatement as a cause of action A negligent misstatement is information or advice which is honestly provided but is inaccurate
CONTRACT DISPUTES: WINNING FROM THE BEGINNING
 Friday, January 27 th, 2017 CONTRACT DISPUTES: WINNING FROM THE BEGINNING Presented By Kimberly Gosling and Christian Andreu-von Euw Senior Associates, Morrison & Foerster, LLP ACC 14th ANNUAL GC ROUNDTABLE
Friday, January 27 th, 2017 CONTRACT DISPUTES: WINNING FROM THE BEGINNING Presented By Kimberly Gosling and Christian Andreu-von Euw Senior Associates, Morrison & Foerster, LLP ACC 14th ANNUAL GC ROUNDTABLE
Drafting Contracts to Avoid (if you can) and Embrace (if you must) Litigation. Amanda M. Quayle
 Drafting Contracts to Avoid (if you can) and Embrace (if you must) Litigation Amanda M. Quayle I. Overview This paper is intended as a general primer for legal practitioners involved in contract negotiating
Drafting Contracts to Avoid (if you can) and Embrace (if you must) Litigation Amanda M. Quayle I. Overview This paper is intended as a general primer for legal practitioners involved in contract negotiating
9084 LAW 9084/32 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9084 LAW 9084/32 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9084 LAW 9084/32 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark
LEVEL 4 - UNIT 1 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS JANUARY 2015
 Note to Candidates and Tutors: LEVEL 4 - UNIT 1 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS JANUARY 2015 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students
Note to Candidates and Tutors: LEVEL 4 - UNIT 1 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS JANUARY 2015 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students
MLL217 MISLEADING CONDUCT AND ECONOMIC TORTS
 MLL217 MISLEADING CONDUCT AND ECONOMIC TORTS Contents FALSE AND MISLEADING STATEMENTS... 5 Other Common Law Torts Regulating False or Misleading Statements... 5 Deceit... 5 Injurious falsehood... 6 Negligent
MLL217 MISLEADING CONDUCT AND ECONOMIC TORTS Contents FALSE AND MISLEADING STATEMENTS... 5 Other Common Law Torts Regulating False or Misleading Statements... 5 Deceit... 5 Injurious falsehood... 6 Negligent
Question 3. Sam hereby agrees that he will not perform interior design services in Town for a period of two years.
 Question 3 Sam decided to sell his interior design business in Town to Betty. While reviewing a purchase agreement drafted by Sam, Betty insisted on a covenant by Sam not to compete with her in the interior
Question 3 Sam decided to sell his interior design business in Town to Betty. While reviewing a purchase agreement drafted by Sam, Betty insisted on a covenant by Sam not to compete with her in the interior
The Objective Principle of a Promise... 2 Intention to Create Legal Relations... 4 Offer and Acceptance... 5
 1 Contents The Objective Principle of a Promise... 2 Intention to Create Legal Relations... 4 Offer and Acceptance... 5 Offer vs. Invitation to Treat... 5 Termination/Lapse of Offer... 6 Acceptance of
1 Contents The Objective Principle of a Promise... 2 Intention to Create Legal Relations... 4 Offer and Acceptance... 5 Offer vs. Invitation to Treat... 5 Termination/Lapse of Offer... 6 Acceptance of
Use of singular and plural; gender. NC General Statutes - Chapter 25 Article 1 1
 Chapter 25. Uniform Commercial Code. Article 1. General Provisions. PART 1. GENERAL PROVISIONS. 25-1-101. Short titles. (a) This Chapter may be cited as the Uniform Commercial Code. (b) This Article may
Chapter 25. Uniform Commercial Code. Article 1. General Provisions. PART 1. GENERAL PROVISIONS. 25-1-101. Short titles. (a) This Chapter may be cited as the Uniform Commercial Code. (b) This Article may
Table of Contents. Preface... Table of Cases...
 Table of Contents Preface... Table of Cases... v xiii Chapter 1 The Sources of the Law... 1 1. Statutory... 1 2. Non-statutory... 6 Chapter 2 The Contract of Sale of Goods... 9 1. Definition... 9 (1) Purchase...
Table of Contents Preface... Table of Cases... v xiii Chapter 1 The Sources of the Law... 1 1. Statutory... 1 2. Non-statutory... 6 Chapter 2 The Contract of Sale of Goods... 9 1. Definition... 9 (1) Purchase...
Recent Developments in English Contract Law
 September 2011 Recent Developments in English Contract Law BY GARRETT HAYES, ROSS MCNAUGHTON & GEORGE WESTON This Stay Current focuses on four significant recent cases in England which may have implications
September 2011 Recent Developments in English Contract Law BY GARRETT HAYES, ROSS MCNAUGHTON & GEORGE WESTON This Stay Current focuses on four significant recent cases in England which may have implications
APPEAL FROM THE CIRCUIT COURT OF TANEY COUNTY. Honorable Eric Eighmy. This case involves the purported 2005 sale of a garage at Pointe Royale
 JOHN WESLEY STRANGE and ) SAUNDRA J. STRANGE, ) ) Plaintiffs-Respondents, ) ) v. ) No. SD35095 ) DANNY L. ROBINSON and ) Filed: June 5, 2018 TAYNIA ROBINSON, ) ) Defendants-Appellants. ) AFFIRMED APPEAL
JOHN WESLEY STRANGE and ) SAUNDRA J. STRANGE, ) ) Plaintiffs-Respondents, ) ) v. ) No. SD35095 ) DANNY L. ROBINSON and ) Filed: June 5, 2018 TAYNIA ROBINSON, ) ) Defendants-Appellants. ) AFFIRMED APPEAL
Legal Liability in Adventure Tourism
 Legal Liability in Adventure Tourism Ross Cloutier Bhudak Consultants Ltd. www.bhudak.com The Legal System in Canada Common Law Records creating a foundation of cases useful as a source of common legal
Legal Liability in Adventure Tourism Ross Cloutier Bhudak Consultants Ltd. www.bhudak.com The Legal System in Canada Common Law Records creating a foundation of cases useful as a source of common legal
A look at UCC 1-103(b) through the lens of Article 2: A practice of liberal supplementation or exclusion?
 A look at UCC 1-103(b) through the lens of Article 2: A practice of liberal supplementation or exclusion? American Bar Association Business Law Section April 15, 2011 Professor Jennifer Martin St. Thomas
A look at UCC 1-103(b) through the lens of Article 2: A practice of liberal supplementation or exclusion? American Bar Association Business Law Section April 15, 2011 Professor Jennifer Martin St. Thomas
17 May Learn With Us: Boilerplate clauses. Jenny Mee, Partner, K&L Gates INTRODUCTION
 17 May 2016 Learn With Us: Boilerplate clauses Jenny Mee, Partner, K&L Gates Copyright 2016 by K&L Gates. All rights reserved. INTRODUCTION 1 WHAT IS A BOILERPLATE CLAUSE? Boilerplate is any text that
17 May 2016 Learn With Us: Boilerplate clauses Jenny Mee, Partner, K&L Gates Copyright 2016 by K&L Gates. All rights reserved. INTRODUCTION 1 WHAT IS A BOILERPLATE CLAUSE? Boilerplate is any text that
TITLE 7 CONTRACTS TABLE OF CONTENTS
 TITLE 7 CONTRACTS TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 7.01 General Provisions 7.0101 Definition 1 7.0102 Essential elements of a contract 1 7.0103 Law of place applied to contracts 1 7.0104 Time of performance 1
TITLE 7 CONTRACTS TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 7.01 General Provisions 7.0101 Definition 1 7.0102 Essential elements of a contract 1 7.0103 Law of place applied to contracts 1 7.0104 Time of performance 1
7/23/2010. The. Contract. Sources of contractual obligations
 Law for Spatial Designers Introduction to the Law of Contract Module 3 Topic 1 Sources of contractual obligations Obligations imposed by law and equity The Contract Statutory obligations The obligations
Law for Spatial Designers Introduction to the Law of Contract Module 3 Topic 1 Sources of contractual obligations Obligations imposed by law and equity The Contract Statutory obligations The obligations
The Impact of Pre-Contractual Conduct on Contractual Interpretation. The Hon Justice Michael Sifris 1
 The Impact of Pre-Contractual Conduct on Contractual Interpretation The Hon Justice Michael Sifris 1 The importance of the written word 1 I would like to begin with a trite proposition, namely, the importance
The Impact of Pre-Contractual Conduct on Contractual Interpretation The Hon Justice Michael Sifris 1 The importance of the written word 1 I would like to begin with a trite proposition, namely, the importance
Although the costs of materials and labor are roughly equal, the primary purpose of the
 Claim 1: Acme Flooring Applicable Law: Although the costs of materials and labor are roughly equal, the primary purpose of the contract was for rendering services because the service component of installation
Claim 1: Acme Flooring Applicable Law: Although the costs of materials and labor are roughly equal, the primary purpose of the contract was for rendering services because the service component of installation
MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2007 question paper 9084 LAW
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2007 question paper 9084 LAW 9084/03 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme is published as an
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2007 question paper 9084 LAW 9084/03 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme is published as an
CQUniversity Division of Higher Education School of Business and Law
 CQUniversity Division of Higher Education School of Business and Law LAWS11062 Contract Law B Topic 2 Misrepresentation and Misleading & Deceptive Conduct Term 2, 2014 Anthony Marinac CQUniversity 2014
CQUniversity Division of Higher Education School of Business and Law LAWS11062 Contract Law B Topic 2 Misrepresentation and Misleading & Deceptive Conduct Term 2, 2014 Anthony Marinac CQUniversity 2014
Business Law Fundamentals Exam #1 Page 1 of 7
 Business Law Fundamentals Exam #1 Page 1 of 7 PRINT name as your signature 1. This Exam #1 must be completed within the allocated time (i.e., 75 minutes). Audible time warnings of 2 minutes, 1 minute,
Business Law Fundamentals Exam #1 Page 1 of 7 PRINT name as your signature 1. This Exam #1 must be completed within the allocated time (i.e., 75 minutes). Audible time warnings of 2 minutes, 1 minute,
IMPORTANT TERMS IN BUSINESS
 CHAPTER 4 CONTRACTS SECTION 1 IMPORTANT TERMS IN BUSINESS ANSWERS TO BUSINESS LAW WHAT S YOUR OPINION? QUESTIONS 1. a) The first agreement was an agreement in respect of land and therefore it had to be
CHAPTER 4 CONTRACTS SECTION 1 IMPORTANT TERMS IN BUSINESS ANSWERS TO BUSINESS LAW WHAT S YOUR OPINION? QUESTIONS 1. a) The first agreement was an agreement in respect of land and therefore it had to be
Question If CapCo files a lawsuit against the Bears seeking damages for breach of contract, who is likely to prevail? Discuss.
 Question 2 CapCo sells baseball caps to youth leagues and recently approached two new teams, the Bears and the Lions. Uncertain how many caps the team would require, the Bears team manager signed a written
Question 2 CapCo sells baseball caps to youth leagues and recently approached two new teams, the Bears and the Lions. Uncertain how many caps the team would require, the Bears team manager signed a written
HIGH COURT OF AUSTRALIA
 HIGH COURT OF AUSTRALIA GLEESON CJ, GUMMOW, HAYNE, CALLINAN AND HEYDON JJ TOLL (FGCT) PTY LIMITED (formerly Finemores GCT Pty Limited) APPELLANT AND ALPHAPHARM PTY LIMITED & ORS RESPONDENTS Toll (FGCT)
HIGH COURT OF AUSTRALIA GLEESON CJ, GUMMOW, HAYNE, CALLINAN AND HEYDON JJ TOLL (FGCT) PTY LIMITED (formerly Finemores GCT Pty Limited) APPELLANT AND ALPHAPHARM PTY LIMITED & ORS RESPONDENTS Toll (FGCT)
WEBSITE TERMS OF USE E-COMMERCE TERMS OF SALE
 DOCUMENT DYNAMIX ABN 30 228 276 249 WEBSITE TERMS OF USE E-COMMERCE TERMS OF SALE 1 TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF USE FOR DOCUMENTDYNAMIX.COM.AU 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 www.documentdynamix.com.au ( the Site ) is
DOCUMENT DYNAMIX ABN 30 228 276 249 WEBSITE TERMS OF USE E-COMMERCE TERMS OF SALE 1 TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF USE FOR DOCUMENTDYNAMIX.COM.AU 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 www.documentdynamix.com.au ( the Site ) is
REVIEW QUESTIONS TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS (CIRCLE THE CORRECT ANSWER)
 REVIEW QUESTIONS TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS (CIRCLE THE CORRECT ANSWER) 1. T F When a court or legislature protects a class, this protection extends to all members of that class in every contractual transaction.
REVIEW QUESTIONS TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS (CIRCLE THE CORRECT ANSWER) 1. T F When a court or legislature protects a class, this protection extends to all members of that class in every contractual transaction.
PROCEDURE & PRINCIPLES: ORDER 26A: ORDER 14 & ORDER 14A
 PROCEDURE & PRINCIPLES: ORDER 26A: ORDER 14 & ORDER 14A ISBN 983-41166-7-5 Author: Nasser Hamid Binding: Softcover/Extent: 650 pp Publication Price: MYR 220.00 The law is stated as of July 1, 2004 Chapter
PROCEDURE & PRINCIPLES: ORDER 26A: ORDER 14 & ORDER 14A ISBN 983-41166-7-5 Author: Nasser Hamid Binding: Softcover/Extent: 650 pp Publication Price: MYR 220.00 The law is stated as of July 1, 2004 Chapter
ROYAL GOVERNMENT OF BHUTAN
 THE NEGOTIABLE INSTRUMENTS ACT OF THE KINGDOM OF BHUTAN 2000 ROYAL GOVERNMENT OF BHUTAN CONTENTS PART I PRELIMINARY 1. Shot title 2. Application of the Act 3. Interpretation clause PART II OF NOTES, BILLS
THE NEGOTIABLE INSTRUMENTS ACT OF THE KINGDOM OF BHUTAN 2000 ROYAL GOVERNMENT OF BHUTAN CONTENTS PART I PRELIMINARY 1. Shot title 2. Application of the Act 3. Interpretation clause PART II OF NOTES, BILLS
STATE OF MICHIGAN COURT OF APPEALS
 STATE OF MICHIGAN COURT OF APPEALS CUSTOM DATA SOLUTIONS, INC., Plaintiff-Appellee, UNPUBLISHED December 19, 2006 v No. 270752 Macomb Circuit Court PREFERRED CAPITAL, INC., LC No. 04-003376-CK Defendant-Appellant.
STATE OF MICHIGAN COURT OF APPEALS CUSTOM DATA SOLUTIONS, INC., Plaintiff-Appellee, UNPUBLISHED December 19, 2006 v No. 270752 Macomb Circuit Court PREFERRED CAPITAL, INC., LC No. 04-003376-CK Defendant-Appellant.
PART 2 FORMATION, TERMS, AND READJUSTMENT OF CONTRACT. (a) A contract or modification thereof is enforceable,
 1 PART 2 FORMATION, TERMS, AND READJUSTMENT OF CONTRACT SECTION 2-201. NO FORMAL REQUIREMENTS. (a) A contract or modification thereof is enforceable, whether or not there is a record signed by a party
1 PART 2 FORMATION, TERMS, AND READJUSTMENT OF CONTRACT SECTION 2-201. NO FORMAL REQUIREMENTS. (a) A contract or modification thereof is enforceable, whether or not there is a record signed by a party
Contractual Interpretation In Singapore: Compatibility With The Evidence Act?
 Contractual Interpretation In Singapore: Compatibility With The Evidence Act? Asst Professor Goh Yihan, Faculty of Law, National University of Singapore Three Distinct but Relevant Questions Before examining
Contractual Interpretation In Singapore: Compatibility With The Evidence Act? Asst Professor Goh Yihan, Faculty of Law, National University of Singapore Three Distinct but Relevant Questions Before examining
ONLINE TRADING AGREEMENT
 ONLINE TRADING AGREEMENT TERMS AND CONDITIONS Phillip Capital Limited ABN 14 002 918 247 AFSL 246827 Phillip Capital Trading Pty Ltd ABN 68 066 066 911 AFSL 246796 Together known as PhillipCapital CLIENT
ONLINE TRADING AGREEMENT TERMS AND CONDITIONS Phillip Capital Limited ABN 14 002 918 247 AFSL 246827 Phillip Capital Trading Pty Ltd ABN 68 066 066 911 AFSL 246796 Together known as PhillipCapital CLIENT
Fundamental Principles in Interpretation of Contract
 Fundamental Principles in Interpretation of Contract Ir. Harrison Cheung Barrister-at-law, Arbitrator, Adjudicator & Mediator Dispute Resolution Advisor FICArb, MHKIE, RPE harrisoncheung.counsel@gmail.com
Fundamental Principles in Interpretation of Contract Ir. Harrison Cheung Barrister-at-law, Arbitrator, Adjudicator & Mediator Dispute Resolution Advisor FICArb, MHKIE, RPE harrisoncheung.counsel@gmail.com
SOLUTION BUSINESS AND CORPORATE LAW NOV 2012
 SOLUTION 1 A. The Lower Courts include: B. i. The circuit courts ii. The magistrate courts; and iii. The National House of Chiefs, Regional houses of chiefs and every traditional council in respect of
SOLUTION 1 A. The Lower Courts include: B. i. The circuit courts ii. The magistrate courts; and iii. The National House of Chiefs, Regional houses of chiefs and every traditional council in respect of
Contractual Clauses That Impact Disputes. By David F. Johnson
 Contractual Clauses That Impact Disputes By David F. Johnson Introduction In the process of drafting contracts, parties can shape the process for resolving their future disputes. They can potentially select
Contractual Clauses That Impact Disputes By David F. Johnson Introduction In the process of drafting contracts, parties can shape the process for resolving their future disputes. They can potentially select
Certified Partner Agreement. THIS AGREEMENT ( Agreement ) is made and entered into on, between the City of Sacramento ( City ) and BACKGROUND
 Certified Partner Agreement THIS AGREEMENT ( Agreement ) is made and entered into on, between the City of Sacramento ( City ) and ( Owner ). BACKGROUND A. City operates a website ( City Website ) that
Certified Partner Agreement THIS AGREEMENT ( Agreement ) is made and entered into on, between the City of Sacramento ( City ) and ( Owner ). BACKGROUND A. City operates a website ( City Website ) that
ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENT TO CHAPTER 15
 C H A P T E R 15 ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENT TO CHAPTER 15 UNIFORM PARTNERSHIP ACT (1914) Part I PRELIMINARY PROVISIONS 1. Name of Act This act may be cited as Uniform Partnership Act. 2. Definition of Terms
C H A P T E R 15 ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENT TO CHAPTER 15 UNIFORM PARTNERSHIP ACT (1914) Part I PRELIMINARY PROVISIONS 1. Name of Act This act may be cited as Uniform Partnership Act. 2. Definition of Terms
GATEKEEPER ABN-DSC SUBSCRIBER AGREEMENT INSTRUCTIONS
 GATEKEEPER ABN-DSC SUBSCRIBER AGREEMENT INSTRUCTIONS Before an Australian Business Number Digital Signature Certificate (ABN-DSC) will be issued to an Applicant, the following criteria must be met: 1.
GATEKEEPER ABN-DSC SUBSCRIBER AGREEMENT INSTRUCTIONS Before an Australian Business Number Digital Signature Certificate (ABN-DSC) will be issued to an Applicant, the following criteria must be met: 1.
Legal & Ethical Applications: Exam #1: Review LAWS 3930 & FoE 1, 3, 4, 9, and 11 & Microecon. & Chapters 5, Page 1 of 8
 Review LAWS 3930 & FoE 1, 3, 4, 9, and 11 & Microecon. & Chapters 5, Page 1 of 8 print name on the line above as your signature INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This Exam #1 must be completed within the allocated time
Review LAWS 3930 & FoE 1, 3, 4, 9, and 11 & Microecon. & Chapters 5, Page 1 of 8 print name on the line above as your signature INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This Exam #1 must be completed within the allocated time
CONTRACT AND ATHLETE SELECTION
 2008 3(1) Australian and New Zealand Sports Law Journal 37 CONTRACT AND ATHLETE SELECTION David Thorpe This paper examines the contractual basis of athlete selection and proposes that the authority to
2008 3(1) Australian and New Zealand Sports Law Journal 37 CONTRACT AND ATHLETE SELECTION David Thorpe This paper examines the contractual basis of athlete selection and proposes that the authority to
THE NEGOTIABLE INSTRUMENTS ACT. [INDIA ACT XXVI, 1881.] (1st March, 1882.)
![THE NEGOTIABLE INSTRUMENTS ACT. [INDIA ACT XXVI, 1881.] (1st March, 1882.) THE NEGOTIABLE INSTRUMENTS ACT. [INDIA ACT XXVI, 1881.] (1st March, 1882.)](/thumbs/88/117199528.jpg) [INDIA ACT XXVI, 1881.] (1st March, 1882.) CHAPTER I. PRELIMINARY. Saving as to paper currency law and of usages relating to hundis, etc. 1. Nothing herein contained affects the law relating to paper currency;
[INDIA ACT XXVI, 1881.] (1st March, 1882.) CHAPTER I. PRELIMINARY. Saving as to paper currency law and of usages relating to hundis, etc. 1. Nothing herein contained affects the law relating to paper currency;
