Answer of the Danish Group
|
|
|
- Fay Jordan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Questionnaire July 2006 Special Committee Q166 Intellectual Property and Genetic Resources, Traditional Knowledge and Folklore On the Requirement of indicating the source and/or country of origin of genetic resources and traditional knowledge in patent applications Answer of the Danish Group by Ejvind CHRISTIANSEN, Bo HAMMER JENSEN, Torsten NØRGAARD etc. Question 1: Is there a legal requirement in your country that the source and/or country of origin of genetic resources and/or traditional knowledge must be indicated in patent applications for inventions based on such genetic resources or traditional knowledge? Answer 1: Yes If yes, please quote the corresponding text from the law/regulations and reply to the following questions, if applicable: Question 1a) Are these regulations found in patent law, general IP laws or in legislation implementing the Convention on Biological Diversity? Answer 1a: Yes, the Implementing Regulations for the Danish Patent Law comprises in 3. 4: If an invention relates to or uses a biological material originating from plants or animals the patent application must comprise information about the geographical origin of the material if the patent applicant has knowledge thereof. If the applicant does not have such knowledge of the geographical origin of the material this must be disclosed in the patent application. Lack of information concerning the geographical origin or the lack of 1
2 knowledge about this does not have any effect on the prosecution of the application or the validity of any of the rights attached to the issued patent. Stk. 4. Hvis en opfindelse angår eller anvender et biologisk materiale af vegetabilsk eller animalsk oprindelse, skal patentansøgningen indeholde oplysninger om materialets geografiske oprindelse, hvis patentansøger er bekendt hermed. Såfremt patentansøger ikke er bekendt med materialets geografiske oprindelse, skal dette fremgå af ansøgningen. Manglende oplysninger om materialets geografiske oprindelse eller om patentansøgers ukendskab herom berører ikke behandlingen af patentansøgningen eller gyldigheden af de rettigheder, som følger af det udstedte patent. Question 1b: Is it clear what the concept of source or country of origin and based on genetic resource/traditional knowledge means and what information must be included in the patent application? Answer 1b: No, the language is geographical origin. The regulation does not state that the name of a country must be indicated, but the general feeling is that this is the meaning, but then again it is not clear it it should be the country of origin as defined in the CBD or the source country meaning where the material was obtained. Question 1c: Are there ways to complement or amend the corresponding text in the patent application? Answer 1c: Yes, Question1d: Is disclosure of prior informed consent and/or agreements on sharing of benefits required? Answer 1d: No Question 1e: Are human genetic resources treated differently or the same way as animal or plant genetic resources falling under the CBD? Answer 1e: Differently. The Implementing Regulation states in 3.5 that: If an invention relates to or uses a biological material of human origin, the patent application must disclose if the person from whom the material originates has consented 2
3 to the filing of the application. The information abut consent does not have any effect on the prosecution of the application or the validity of any of the rights attached to the issued patent. Stk. 5. Hvis en opfindelse angår eller anvender et biologisk materiale af human oprindelse, skal det fremgå af patentansøgningen, om den person, hvorfra det biologiske materiale hidrører, har givet samtykke til ansøgningens indlevering. Oplysningen om samtykke berører ikke behandlingen af patentansøgningen eller gyldigheden af de rettigheder, som følger af det udstedte patent. Question 1f: Is traditional knowledge properly defined, and is the source of traditional knowledge to be indicated only if it is connected to genetic resources (e.g. falling under the CBD) or in general? Answer 1f: No. The Danish legislation does not comprise any issues of traditional knowledge. There is no requirement for the provision of information concerning traditional knowledge. Question 1g: Are sanctions foreseen for non-compliance (e.g. patent invalidation, patent transfer to the owner of the resource, fines, criminal sanctions etc.)? Answer 1g: No specific sanctions are indicated, but it is clear that a violation of the regulation will have no effect on the patentability of the invention or the validity of a patent. A violation of the regulation would be adjudicated under the rules of providing false information to a government administrative body, most likely resulting in a fine. Question 1h: Does the law make a difference depending on whether the genetic resource was obtained by the patent applicant (or by the person/organisation such as a botanical garden, ex situ collection or a collector company from which the patent applicant obtained the resource) before or after the CBD took effect in 1993 [this should be 1994, respondents remark]? Answer 1h: No. Question 2: Do you know of any project of law in your country dealing with the requirement of indicating the source and/or country of origin of genetic resources and/or traditional knowledge in patent applications for inventions based on such genetic resources or traditional knowledge? If yes please provide the corresponding text and review it for the additional questions a) to h) as under 1). Please include also links to websites which would allow to follow the progress on these projects of law. 3
4 Answer 2: No. Question 3: Is your Group of the opinion that the source and/or country of origin of genetic resources should be indicated in patent applications based on such genetic resources? Answer 3: No. The Danish group believes that this information is without relevance for the examination of the application in respect of (i) the patentability, (ii) the inventorship of, and (iii) the ownership of the rights to the disclosed invention. In spite of the opinion as expressed above, the Danish group would like to express its view in respect of the sub questions posed. If yes: Question 3a: Is it sufficient to indicate the source (e.g. the corresponding material was bought from company X, was obtained from the collection of genetic material Y, was collected in the botanical garden in town Z) or must the patent applicant determine and indicate the actual country of origin? Answer 3a: Yes. The Danish group sees no reason for forcing the applicant to make inquiries into the ancestry of the material. Such investigations may be costly and in some cases in vain and they may even result in false indications. The applicant will normally know (through records) where some biological material was obtained from, but even this may not be the situation since records may have been destroyed or they may be lacking or they may be false (intentional or non intentional). This applies for each level of ancestry for biological material and increases the uncertainty as to the correctness of the information obtained and submitted to the Patent authorities. Question 3b: If the patent applicant is not able to indicate the correct source or correct country of origin, is it acceptable that he indicates in the patent application not to know the true source or country of origin? Answer 3b: The Danish group believes that this should be the only indication in this situation. 4
5 Question 3c: Should the requirement of source/country of origin indication be restricted to nonhuman genetic resources (i.e. the resources subject to the CBD) or also apply to human genetic resources? Is it acceptable or even required that the information on the single person or group of persons from which the human genetic material was originally taken, is indicated in the patent application? Answer 3c: The Danish group is of the opinion that any requirement for indicating the origin of biological material in patent application should be limited to material that falls within the scope of the CBD and has been obtained after the entry into force of the CBD. The reason for this is that the demandeurs for such information have indicated that the information is necessary for monitoring sound practices (or rather violations) of the rules of that Convention. Question 3d: What is the sanction if the source/country of origin indication is missing or incorrect? Patent invalidation? Fine? Other sanctions? Should sanctions only apply if the applicant has had an opportunity to correct the omission or the mistake and did not correct it? Should there be no sanction? Answer 3d: The Danish group believes that the sanction in such a situation should at most be fines if the applicant after having unlimited possibilities to correct an omission or an incorrect indication still fails to do so. Question 4: Is your Group of the opinion that the source of traditional knowledge should be indicated in patent applications based on such traditional knowledge? Answer 4: To the extent that holders of traditional knowledge have contributed to the conception/creation of the invention for which protection is applied for, such persons should be indicated as inventors/co-inventors. Furthermore, the applicant should disclose any relevant traditional knowledge that is known to the applicant and is part of the pertinent prior art. Apart from this it is the view of the Danish group that any traditional knowledge conveyed to the inventors, but not forming part of the invention or the pertinent prior art is of no relevance to the examination of the patent application. If holders of traditional knowledge have in some way been involved in the conception/creation of the invention through the provision of secret traditional knowledge, but without any inventive contribution, any mention of this or compensation for having provided this knowledge should be regulated in the agreement between the relevant parties. 5
6 Question 4a: If the patent applicant is not able to indicate the correct source, is it acceptable that he/she indicates in the patent application not to know the true source? Answer 4a: The Danish group does not understand this question. If the applicant has made the invention on the basis of traditional knowledge, but without knowledge of any traditional knowledge forming part of the prior art, he must necessarily have made it on the basis of secret traditional knowledge that has been conveyed to him, and we cannot see how he would not be able to provide such information, unless a contractual obligation prohibits him from disclosing this. The only solution would be to state that contractual obligations prohibits him from making such a disclosure. We believe that such an indication should be acceptable. Please note that there is no question 4b. Question 4c: Should the requirement of source indication be restricted to traditional knowledge in relation to genetic resources (i.e. the traditional knowledge subject to the CBD) or also apply to any traditional knowledge? Answer 4c: Apart from being opposed to such a requirement, the Danish group does not believe that the requirement should be restricted to traditional knowledge related to genetic resources. We further believe that such a restriction would be against the principle of non discrimination of the TRIPs agreement. Question 4d: What is the sanction if the source is missing or incorrect? Patent invalidation? Fine? Other sanctions? Should sanctions only apply if the applicant has had an opportunity to correct the omission or the mistake and did not correct it? Should there be no sanction? Answer 4d: We believe any sanctions should be outside the patent law as it is at present under the Danish law, which in our opinion strikes a fair and manageable balance. Also, it must be secured that the applicant should have the possibility to file such information at any time during the prosecution of the application both in response to an invitation from the Patent Office and voluntarily. Question 5) Is your Group of the opinion that for patent applications based on genetic resources and traditional knowledge proof of prior informed consent (PIC) must be provided? Answer 5: The Danish group is strongly opposed to any requirements in respect of information relating to PIC. Many countries do not have any legislation concerning access to genetic resources or 6
7 traditional knowledge, and it is known that at least some countries do not intend to introduce such special legislation. A patent is a right granted for inventive activity and not a certificate of good behaviour. Question 5a: Is it acceptable to indicate that no person or organisation (e.g. indigenous group) could be or can be identified who has the right to give such consent? Answer 5a: Yes. Question 5b: Is it acceptable to provide proof of prior informed consent after filing the patent application? Answer 5b: Yes, similarly to the situation in question 4d, it must be secured that the applicant should have the possibility to file such proof at any time during the prosecution of the application both in response to an invitation from the Patent Office and voluntarily. Question 5c: What should the sanction be if it turns out that the consent was not actually given or the person/organisation giving consent did not have the right to give consent? Answer 5c: The Danish group believes any sanctions should be outside the patent system and that the issue should be raised by any persons or organisations that allege to have suffered from the incorrect indication. The patent offices do not have the resources, competences or knowledge to investigate the correctness of such information. Question 6) Is your Group of the opinion that for patent applications based on genetic resources and traditional knowledge proof of an agreement sharing benefits with the person or organisation giving access to such genetic resources and/or traditional knowledge must be provided? Answer 6: The Danish group is strongly opposed to any requirements relating to information on benefit sharing. Many countries do not have any legislation concerning benefit sharing in connection with access to genetic resources or traditional knowledge, and it is known that at least some countries do not intend to introduce such special legislation. A patent is a right granted for inventive activity and not a certificate of good behaviour. Question 6a: Is it acceptable to indicate that no person or organisation could be or can be identified who should benefit from it? 7
8 Answer 6a: Yes. Question 6b: Is it acceptable to provide proof of an agreement sharing benefits after filing the patent application? Answer 6b: Yes, similarly to the situation in question 4d, it must be secured that the applicant should have the possibility to file such proof at any time during the prosecution of the application both in response to an invitation from the Patent Office and voluntarily. Question 6c: What should the sanction be if it turns out that the indicated agreement sharing benefits does not benefit the person/organisation that owns the right to such genetic resources or traditional knowledge? Answer 6c: The Danish group believes any sanctions should be outside the patent system and that the issue should be raised by any persons or organisations that allege to have suffered from the incorrect indication. The patent offices do not have the resources, competences or knowledge to investigate the correctness of such information. 8
MATTERS CONCERNING THE INTERGOVERNMENTAL COMMITTEE ON INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND GENETIC RESOURCES, TRADITIONAL KNOWLEDGE AND FOLKLORE (IGC)
 E WO/GA/43/14 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH DATE: AUGUST 14, 2013 WIPO General Assembly Forty-Third (21 st Ordinary) Session Geneva, September 23 to October 2, 2013 MATTERS CONCERNING THE INTERGOVERNMENTAL COMMITTEE
E WO/GA/43/14 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH DATE: AUGUST 14, 2013 WIPO General Assembly Forty-Third (21 st Ordinary) Session Geneva, September 23 to October 2, 2013 MATTERS CONCERNING THE INTERGOVERNMENTAL COMMITTEE
Intergovernmental Committee on Intellectual Property and Genetic Resources, Traditional Knowledge and Folklore
 E ORIGINAL: ENGLISH DATE: JANUARY 31, 2013 Intergovernmental Committee on Intellectual Property and Genetic Resources, Traditional Knowledge and Folklore Twenty-Third Session Geneva, February 4 to 8, 2013
E ORIGINAL: ENGLISH DATE: JANUARY 31, 2013 Intergovernmental Committee on Intellectual Property and Genetic Resources, Traditional Knowledge and Folklore Twenty-Third Session Geneva, February 4 to 8, 2013
The relevance of traditional knowledge to intellectual property law
 Question Q232 National Group: Dutch Group Title: The relevance of traditional knowledge to intellectual property law Contributors: Lucky BELDER, Klaas BISSCHOP, Roderick CHALMERS HOYNCK VAN PAPENDRECHT,
Question Q232 National Group: Dutch Group Title: The relevance of traditional knowledge to intellectual property law Contributors: Lucky BELDER, Klaas BISSCHOP, Roderick CHALMERS HOYNCK VAN PAPENDRECHT,
The relevance of traditional knowledge to intellectual property law
 Question Q232 National Group: The Philippines Title: The relevance of traditional knowledge to intellectual property law Contributors: Aleli Angela G. QUIRINO John Paul M. GABA Antonio Ray A. ORTIGUERA
Question Q232 National Group: The Philippines Title: The relevance of traditional knowledge to intellectual property law Contributors: Aleli Angela G. QUIRINO John Paul M. GABA Antonio Ray A. ORTIGUERA
Guidelines on Access to Genetic Resources For Users in Japan
 Guidelines on Access to Genetic Resources For Users in Japan Second Edition Japan Bioindustry Association (JBA) Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, Japan (METI) March 2012 About the Second Edition
Guidelines on Access to Genetic Resources For Users in Japan Second Edition Japan Bioindustry Association (JBA) Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, Japan (METI) March 2012 About the Second Edition
Questionnaire 2. HCCH Judgments Project
 Questionnaire 2 HCCH Judgments Project Introduction 1) An important current project of the Hague Conference on Private International Law (HCCH) is the development of a convention on the recognition and
Questionnaire 2 HCCH Judgments Project Introduction 1) An important current project of the Hague Conference on Private International Law (HCCH) is the development of a convention on the recognition and
SESSION VIII The Protection of Traditional Knowledge and Genetic Resources in Latin America Case Studies
 SESSION VIII The Protection of Traditional Knowledge and Genetic Resources in Latin America Case Studies Wolfgang L.Ohnes La Paz, BOLIVIA - Efforts in the international context dealing with the discussion
SESSION VIII The Protection of Traditional Knowledge and Genetic Resources in Latin America Case Studies Wolfgang L.Ohnes La Paz, BOLIVIA - Efforts in the international context dealing with the discussion
WORLD INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY ORGANIZATION GENEVA
 WIPO ORIGINAL: English DATE: February 19, 2010 WORLD INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY ORGANIZATION GENEVA E INTERGOVERNMENTAL COMMITTEE ON INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND GENETIC RESOURCES, TRADITIONAL KNOWLEDGE AND FOLKLORE
WIPO ORIGINAL: English DATE: February 19, 2010 WORLD INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY ORGANIZATION GENEVA E INTERGOVERNMENTAL COMMITTEE ON INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND GENETIC RESOURCES, TRADITIONAL KNOWLEDGE AND FOLKLORE
LATVIA Patent Law adopted on 15 February 2007, with the changes of December 15, 2011
 LATVIA Patent Law adopted on 15 February 2007, with the changes of December 15, 2011 TABLE OF CONTENTS Chapter I General Provisions Section 1. Terms used in this Law Section 2. Purpose of this Law Section
LATVIA Patent Law adopted on 15 February 2007, with the changes of December 15, 2011 TABLE OF CONTENTS Chapter I General Provisions Section 1. Terms used in this Law Section 2. Purpose of this Law Section
Effective Mechanisms for Challenging the Validity of Patents
 Effective Mechanisms for Challenging the Validity of Patents Walter Holzer 1 S.G.D.G. Patents are granted with a presumption of validity. 2 A patent examiner simply cannot be aware of all facts and circumstances
Effective Mechanisms for Challenging the Validity of Patents Walter Holzer 1 S.G.D.G. Patents are granted with a presumption of validity. 2 A patent examiner simply cannot be aware of all facts and circumstances
FINLAND Patents Act No. 550 of December 15, 1967 as last amended by Act No. 101/2013 of January 31, 2013 Enter into force on 1 September 2013
 FINLAND Patents Act No. 550 of December 15, 1967 as last amended by Act No. 101/2013 of January 31, 2013 Enter into force on 1 September 2013 TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 General Provisions Section 1 Section
FINLAND Patents Act No. 550 of December 15, 1967 as last amended by Act No. 101/2013 of January 31, 2013 Enter into force on 1 September 2013 TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 General Provisions Section 1 Section
FACILITATING PRIOR INFORMED CONSENT In the Context of Genetic Resources and Traditional Knowledge 1
 Discussion Paper May 19, 2004 FACILITATING PRIOR INFORMED CONSENT In the Context of Genetic Resources and Traditional Knowledge 1 1. Introduction This paper traces the evolution of prior informed consent
Discussion Paper May 19, 2004 FACILITATING PRIOR INFORMED CONSENT In the Context of Genetic Resources and Traditional Knowledge 1 1. Introduction This paper traces the evolution of prior informed consent
Courtesy translation provided by WIPO, 2012
 REPUBLIC OF DJIBOUTI UNITY EQUALITY PEACE ********* PRESIDENCY OF THE REPUBLIC LAW No. 50/AN/09/6 L On the Protection of Industrial Property Courtesy translation provided by WIPO, 2012 THE NATIONAL ASSEMBLY
REPUBLIC OF DJIBOUTI UNITY EQUALITY PEACE ********* PRESIDENCY OF THE REPUBLIC LAW No. 50/AN/09/6 L On the Protection of Industrial Property Courtesy translation provided by WIPO, 2012 THE NATIONAL ASSEMBLY
Questionnaire on Exceptions and Limitations to Patent Rights. The answers to this questionnaire have been provided on behalf of:
 Questionnaire on Exceptions and Limitations to Patent Rights The answers to this questionnaire have been provided on behalf of: Country: Australia... Office: IP Australia... Person to be contacted: Name:
Questionnaire on Exceptions and Limitations to Patent Rights The answers to this questionnaire have been provided on behalf of: Country: Australia... Office: IP Australia... Person to be contacted: Name:
Comparative Analysis of the U.S. Intellectual Property Proposal and Peruvian Law
 !!! Dangers for Access to Medicines in the Trans-Pacific Partnership Agreement: Comparative Analysis of the U.S. Intellectual Property Proposal and Peruvian Law ! Issue US TPPA Proposal Andean Community
!!! Dangers for Access to Medicines in the Trans-Pacific Partnership Agreement: Comparative Analysis of the U.S. Intellectual Property Proposal and Peruvian Law ! Issue US TPPA Proposal Andean Community
[English translation by WIPO] Questionnaire on Exceptions and Limitations to Patent Rights
![[English translation by WIPO] Questionnaire on Exceptions and Limitations to Patent Rights [English translation by WIPO] Questionnaire on Exceptions and Limitations to Patent Rights](/thumbs/90/103688579.jpg) Questionnaire on Exceptions and Limitations to Patent Rights The answers to this questionnaire have been provided on behalf of: Country: Chile... Office: National Institute of Industrial Property (INAPI)...
Questionnaire on Exceptions and Limitations to Patent Rights The answers to this questionnaire have been provided on behalf of: Country: Chile... Office: National Institute of Industrial Property (INAPI)...
DRAFT REPORT. EN United in diversity EN 2012/2135(INI)
 EUROPEAN PARLIAMT 2009-2014 Committee on Development 25.7.2012 2012/2135(INI) DRAFT REPORT on development aspects of intellectual property rights on genetic resources: the impact on poverty reduction in
EUROPEAN PARLIAMT 2009-2014 Committee on Development 25.7.2012 2012/2135(INI) DRAFT REPORT on development aspects of intellectual property rights on genetic resources: the impact on poverty reduction in
New IP Code changes regarding patents, new post-grant opposition and enforcement provisions
 INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY - TURKEY New IP Code changes regarding patents, new post-grant opposition and enforcement provisions AUTHORS Mehmet Nazim Aydin Deriş January 08 2018 Contributed by Deris Avukatlik
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY - TURKEY New IP Code changes regarding patents, new post-grant opposition and enforcement provisions AUTHORS Mehmet Nazim Aydin Deriş January 08 2018 Contributed by Deris Avukatlik
Revision Draft of the Patent Law of the People s Republic of China (For Deliberation)
 Revision Draft of the Patent Law of the People s Republic of China (For Deliberation) (Words in bold font are revised portion) Chapter 1: General Provisions Article 1 This law is enacted for the purpose
Revision Draft of the Patent Law of the People s Republic of China (For Deliberation) (Words in bold font are revised portion) Chapter 1: General Provisions Article 1 This law is enacted for the purpose
EXCO Lisbon 2002 REPORT
 EXCO Lisbon 2002 REPORT Special Committee Q166 Intellectual Property Rights and Genetic Resources, Traditional Knowledge and Folklore Introduction As a result of extensive discussions on intellectual property
EXCO Lisbon 2002 REPORT Special Committee Q166 Intellectual Property Rights and Genetic Resources, Traditional Knowledge and Folklore Introduction As a result of extensive discussions on intellectual property
EVOLUTION OF THE LEGAL ENVIRONMENT OF PLANT BREEDERS RIGHTS.
 EUROPEAN UNION Community Plant Variety Office President EVOLUTION OF THE LEGAL ENVIRONMENT OF PLANT BREEDERS RIGHTS. I Introduction Most national or, as in the case of the European Community, multinational
EUROPEAN UNION Community Plant Variety Office President EVOLUTION OF THE LEGAL ENVIRONMENT OF PLANT BREEDERS RIGHTS. I Introduction Most national or, as in the case of the European Community, multinational
Section 1: General. This question does not imply that the topic of exclusions from patentability is dealt with in this question exhaustively.
 Section 1: General 1. As background for the exceptions and limitations to patents investigated in this questionnaire, what is the legal standard used to determine whether an invention is patentable? If
Section 1: General 1. As background for the exceptions and limitations to patents investigated in this questionnaire, what is the legal standard used to determine whether an invention is patentable? If
3. INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY POLICY & LEGAL FRAMEWORK
 3. INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY POLICY & LEGAL FRAMEWORK This section looks at the key issues and challenges related to the legal and policy framework in LDCs, before setting out a detailed checklist to guide
3. INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY POLICY & LEGAL FRAMEWORK This section looks at the key issues and challenges related to the legal and policy framework in LDCs, before setting out a detailed checklist to guide
ACCESS and USE of Plant Genetic Resources under the Nagoya Protocol A SEED SAVER S DIGEST
 ACCESS and USE of Plant Genetic Resources under the Nagoya Protocol A SEED SAVER S DIGEST Workshop on Nagoya Compliance for Seed Savers Wolkersdorf, 25-26.02.17 SEED SAVERS DIGEST I. USER OBLIGATIONS UNDER
ACCESS and USE of Plant Genetic Resources under the Nagoya Protocol A SEED SAVER S DIGEST Workshop on Nagoya Compliance for Seed Savers Wolkersdorf, 25-26.02.17 SEED SAVERS DIGEST I. USER OBLIGATIONS UNDER
From Law of Patents, Layout Designs of Integrated Circuits, Plant Varieties, and Industrial Designs, Chapter Two:
 Saudi Patent Office Contents Section 1: General... 1 Section 2: Private and/or non-commercial use... 2 Section 3: Experimental use and/or scientific research... 3 Section 4: Preparation of medicines...
Saudi Patent Office Contents Section 1: General... 1 Section 2: Private and/or non-commercial use... 2 Section 3: Experimental use and/or scientific research... 3 Section 4: Preparation of medicines...
GENEVA INTERGOVERNMENTAL COMMITTEE ON INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND GENETIC RESOURCES, TRADITIONAL KNOWLEDGE AND FOLKLORE
 WIPO WIPO/GRTKF/IC/9/INF/3 ORIGINAL: English DATE: March 30, 2006 WORLD INTELLECTUAL PROPERT Y O RGANI ZATION GENEVA E INTERGOVERNMENTAL COMMITTEE ON INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND GENETIC RESOURCES, TRADITIONAL
WIPO WIPO/GRTKF/IC/9/INF/3 ORIGINAL: English DATE: March 30, 2006 WORLD INTELLECTUAL PROPERT Y O RGANI ZATION GENEVA E INTERGOVERNMENTAL COMMITTEE ON INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND GENETIC RESOURCES, TRADITIONAL
[English translation by WIPO] Questionnaire on Exceptions and Limitations to Patent Rights
![[English translation by WIPO] Questionnaire on Exceptions and Limitations to Patent Rights [English translation by WIPO] Questionnaire on Exceptions and Limitations to Patent Rights](/thumbs/90/103895209.jpg) [English translation by WIPO] Questionnaire on Exceptions and Limitations to Patent Rights The answers to this questionnaire have been provided on behalf of: Country: Office: Dominican Republic... National
[English translation by WIPO] Questionnaire on Exceptions and Limitations to Patent Rights The answers to this questionnaire have been provided on behalf of: Country: Office: Dominican Republic... National
DECISION 486 Common Intellectual Property Regime (Non official translation)
 DECISION 486 Common Intellectual Property Regime (Non official translation) THE COMMISSION OF THE ANDEAN COMMUNITY, HAVING SEEN: Article 27 of the Cartagena Agreement and Commission Decision 344; DECIDES:
DECISION 486 Common Intellectual Property Regime (Non official translation) THE COMMISSION OF THE ANDEAN COMMUNITY, HAVING SEEN: Article 27 of the Cartagena Agreement and Commission Decision 344; DECIDES:
America Invents Act: Patent Reform
 America Invents Act: Patent Reform Gunnar Leinberg, Nicholas Gallo, and Gerald Gibbs LeClairRyan December 2011 gunnar.leinberg@leclairryan.com; nicholas.gallo@leclaairryan.com; and gerald.gibbs@leclairryan.com
America Invents Act: Patent Reform Gunnar Leinberg, Nicholas Gallo, and Gerald Gibbs LeClairRyan December 2011 gunnar.leinberg@leclairryan.com; nicholas.gallo@leclaairryan.com; and gerald.gibbs@leclairryan.com
Patent Prosecution Under The AIA
 Patent Prosecution Under The AIA A Practical Guide For Prosecutors William R. Childs, Ph.D., J.D. August 22, 2013 DISCLAIMER These materials are public information and have been prepared solely for educational
Patent Prosecution Under The AIA A Practical Guide For Prosecutors William R. Childs, Ph.D., J.D. August 22, 2013 DISCLAIMER These materials are public information and have been prepared solely for educational
[English translation by WIPO] Questionnaire on Exceptions and Limitations to Patent Rights
![[English translation by WIPO] Questionnaire on Exceptions and Limitations to Patent Rights [English translation by WIPO] Questionnaire on Exceptions and Limitations to Patent Rights](/thumbs/90/103707752.jpg) [English translation by WIPO] Questionnaire on Exceptions and Limitations to Patent Rights The answers to this questionnaire have been provided on behalf of: Country: HONDURAS... Office: DIRECTORATE GENERAL
[English translation by WIPO] Questionnaire on Exceptions and Limitations to Patent Rights The answers to this questionnaire have been provided on behalf of: Country: HONDURAS... Office: DIRECTORATE GENERAL
Innovation Act (H.R. 9) and PATENT Act (S. 1137): A Comparison of Key Provisions
 Innovation Act (H.R. 9) and PATENT Act (S. 1137): A Comparison of Key Provisions TOPIC Innovation Act H.R. 9 PATENT Act S. 1137 Post Grant Review ( PGR ) Proceedings Claim Construction: Each patent claim
Innovation Act (H.R. 9) and PATENT Act (S. 1137): A Comparison of Key Provisions TOPIC Innovation Act H.R. 9 PATENT Act S. 1137 Post Grant Review ( PGR ) Proceedings Claim Construction: Each patent claim
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY OFFICE OF NEW ZEALAND (IPONZ)
 PCT Applicant s Guide National Phase National Chapter Page 1 INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY OFFICE OF NEW ZEALAND (IPO) AS DESIGNATED (OR ELECTED) OFFICE CONTENTS THE ENTRY INTO THE NATIONAL PHASE SUMMARY THE PROCEDURE
PCT Applicant s Guide National Phase National Chapter Page 1 INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY OFFICE OF NEW ZEALAND (IPO) AS DESIGNATED (OR ELECTED) OFFICE CONTENTS THE ENTRY INTO THE NATIONAL PHASE SUMMARY THE PROCEDURE
HUNGARY Patent Act Act XXXIII of 1995 as consolidated on March 01, 2015
 HUNGARY Patent Act Act XXXIII of 1995 as consolidated on March 01, 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS PART I INVENTIONS AND PATENTS Chapter I SUBJECT MATTER OF PATENT PROTECTION Article 1 Patentable inventions Article
HUNGARY Patent Act Act XXXIII of 1995 as consolidated on March 01, 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS PART I INVENTIONS AND PATENTS Chapter I SUBJECT MATTER OF PATENT PROTECTION Article 1 Patentable inventions Article
EXPLANATORY NOTES ON THE PATENT LAW TREATY AND REGULATIONS UNDER THE PATENT LAW TREATY * prepared by the International Bureau
 EXPLANATORY NOTES ON THE PATENT LAW TREATY AND REGULATIONS UNDER THE PATENT LAW TREATY * prepared by the International Bureau * These Notes were prepared by the International Bureau of the World Intellectual
EXPLANATORY NOTES ON THE PATENT LAW TREATY AND REGULATIONS UNDER THE PATENT LAW TREATY * prepared by the International Bureau * These Notes were prepared by the International Bureau of the World Intellectual
COLLABORATIVE RESEARCH AGREEMENT
 PLEASE NOTE: this document represent a standard Collaborative Research Agreement for (BU). Parties interested in pursuing an agreement with BU and/or its employees, representatives, or designees may contact
PLEASE NOTE: this document represent a standard Collaborative Research Agreement for (BU). Parties interested in pursuing an agreement with BU and/or its employees, representatives, or designees may contact
Access and Benefit Sharing (ABS)
 Position Paper Access and Benefit Sharing (ABS) Sixth meeting of the Ad Hoc Open-ended Working Group on Access and Benefit Sharing (WGABS 6) Geneva, Switzerland, 21-25 January, 2008 Introduction The World
Position Paper Access and Benefit Sharing (ABS) Sixth meeting of the Ad Hoc Open-ended Working Group on Access and Benefit Sharing (WGABS 6) Geneva, Switzerland, 21-25 January, 2008 Introduction The World
USPTO Implementation of the America Invents Act. Janet Gongola Patent Reform Coordinator Direct dial:
 USPTO Implementation of the America Invents Act Janet Gongola Patent Reform Coordinator Janet.Gongola@uspto.gov Direct dial: 571-272-8734 Three Pillars of the AIA 11/30/2011 2 Speed Prioritized examination
USPTO Implementation of the America Invents Act Janet Gongola Patent Reform Coordinator Janet.Gongola@uspto.gov Direct dial: 571-272-8734 Three Pillars of the AIA 11/30/2011 2 Speed Prioritized examination
(Translated by the Patent Office of the People's Republic of China. In case of discrepancy, the original version in Chinese shall prevail.
 Patent Law of the People's Republic of China (Adopted at the 4th Session of the Standing Committee of the Sixth National People's Congress on March 12, 1984, Amended by the Decision Regarding the Revision
Patent Law of the People's Republic of China (Adopted at the 4th Session of the Standing Committee of the Sixth National People's Congress on March 12, 1984, Amended by the Decision Regarding the Revision
The Protection of Traditional Knowledge and Traditional Cultural Expressions with a Special Focus on the Traditional in Iranian Handmade Carpets
 The Protection of Traditional Knowledge and Traditional Cultural Expressions with a Special Focus on the Traditional in Iranian Handmade Carpets Wend Wendland, Director, Traditional Knowledge Division,
The Protection of Traditional Knowledge and Traditional Cultural Expressions with a Special Focus on the Traditional in Iranian Handmade Carpets Wend Wendland, Director, Traditional Knowledge Division,
Discovery in a patent infringement suit in Japan particularly about secrecy order (protective order)
 Discovery in a patent infringement suit in Japan particularly about secrecy order (protective order) AIPLA AIPPI Japan/JFBA Joint Meeting April 23, 2009 Hideo Ozaki City-Yuwa Partners http://www.city-yuwa.com/ip-group/en
Discovery in a patent infringement suit in Japan particularly about secrecy order (protective order) AIPLA AIPPI Japan/JFBA Joint Meeting April 23, 2009 Hideo Ozaki City-Yuwa Partners http://www.city-yuwa.com/ip-group/en
EGYPTIAN PATENT OFFICE
 PCT Applicant s Guide National Phase National Chapter EG Page 1 EGYPTIAN PATENT OFFICE AS DESIGNATED (OR ELECTED) OFFICE CONTENTS THE ENTRY INTO THE NATIONAL PHASE SUMMARY THE PROCEDURE IN THE NATIONAL
PCT Applicant s Guide National Phase National Chapter EG Page 1 EGYPTIAN PATENT OFFICE AS DESIGNATED (OR ELECTED) OFFICE CONTENTS THE ENTRY INTO THE NATIONAL PHASE SUMMARY THE PROCEDURE IN THE NATIONAL
ANNEX XVII REFERRED TO IN ARTICLE 5 PROTECTION OF INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY
 ANNEX XVII REFERRED TO IN ARTICLE 5 PROTECTION OF INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY ANNEX XVII REFERRED TO IN ARTICLE 5 PROTECTION OF INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY SECTION I GENERAL PROVISIONS Article 1 Definition of Intellectual
ANNEX XVII REFERRED TO IN ARTICLE 5 PROTECTION OF INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY ANNEX XVII REFERRED TO IN ARTICLE 5 PROTECTION OF INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY SECTION I GENERAL PROVISIONS Article 1 Definition of Intellectual
LUXEMBOURG Patent Law as amended by the law of May 24, 1998 ENTRY INTO FORCE: June 21, 1998
 LUXEMBOURG Patent Law as amended by the law of May 24, 1998 ENTRY INTO FORCE: June 21, 1998 TABLE OF CONTENTS TITLE I GENERAL Art. 1. Definitions Art. 2. International Conventions TITLE II PATENTS FOR
LUXEMBOURG Patent Law as amended by the law of May 24, 1998 ENTRY INTO FORCE: June 21, 1998 TABLE OF CONTENTS TITLE I GENERAL Art. 1. Definitions Art. 2. International Conventions TITLE II PATENTS FOR
STATUS OF. bill in the. Given the is presented. language. ability to would be. completely. of 35 U.S.C found in 35. bills both.
 STATUS OF PATENTT REFORM LEGISLATION On June 23, 2011, the United States House of Representatives approved its patent reform bill, H.R. 1249 (the Leahy-Smith America Invents Act). Thee passage follows
STATUS OF PATENTT REFORM LEGISLATION On June 23, 2011, the United States House of Representatives approved its patent reform bill, H.R. 1249 (the Leahy-Smith America Invents Act). Thee passage follows
How patents work An introduction for law students
 How patents work An introduction for law students 1 Learning goals The learning goals of this lecture are to understand: the different types of intellectual property rights available the role of the patent
How patents work An introduction for law students 1 Learning goals The learning goals of this lecture are to understand: the different types of intellectual property rights available the role of the patent
Please provide to following details on the origin of this report on benefit sharing Contracting Party National Focal Point. and Water Management
 Please provide to following details on the origin of this report on benefit sharing Contracting Party AUSTRIA National Focal Point Full name of the institution: Name and title of contact officer: Mailing
Please provide to following details on the origin of this report on benefit sharing Contracting Party AUSTRIA National Focal Point Full name of the institution: Name and title of contact officer: Mailing
1) Relating to Article 2(1)(m) of the November 2017 Draft Convention:
 National/Regional Group: Ecuador Contributors name(s): Aguirre Johana, Argudo Esteban, Bandre Christian, Burgos Carolina, Gallegos Francisco, Hidalgo Damián, Moreno Saya, Ortega Andres, Puente Geovanna,
National/Regional Group: Ecuador Contributors name(s): Aguirre Johana, Argudo Esteban, Bandre Christian, Burgos Carolina, Gallegos Francisco, Hidalgo Damián, Moreno Saya, Ortega Andres, Puente Geovanna,
Professor Dr Lim Heng Gee Faculty of Law Universiti Teknologi MARA, Shah Alam, Selangor, Malaysia
 Seminar on Intellectual Property and Genetic Resources, Traditional Knowledge and Traditional Cultural Expressions Regional, National and Local Experiences 30 March 1 April 2015 World Intellectual Property
Seminar on Intellectual Property and Genetic Resources, Traditional Knowledge and Traditional Cultural Expressions Regional, National and Local Experiences 30 March 1 April 2015 World Intellectual Property
Note by the Executive Secretary
 CBD AD HOC OPEN-ENDED WORKING GROUP ON ACCESS AND BENEFIT-SHARING Eighth meeting Montreal, 9-15 November 2009 Distr. GENERAL UNEP/CBD/WG-ABS/8/3 9 September 2009 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH COLLATION OF OPERATIVE
CBD AD HOC OPEN-ENDED WORKING GROUP ON ACCESS AND BENEFIT-SHARING Eighth meeting Montreal, 9-15 November 2009 Distr. GENERAL UNEP/CBD/WG-ABS/8/3 9 September 2009 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH COLLATION OF OPERATIVE
Protecting Traditional Knowledge: A framework based on Customary Laws and Bio-Cultural Heritage
 Protecting Traditional Knowledge: A framework based on Customary Laws and Bio-Cultural Heritage Krystyna Swiderska Sustainable Agriculture, Biodiversity and Livelihoods Programme, IIED Paper for the International
Protecting Traditional Knowledge: A framework based on Customary Laws and Bio-Cultural Heritage Krystyna Swiderska Sustainable Agriculture, Biodiversity and Livelihoods Programme, IIED Paper for the International
AUSTRALIA Patents Act 1990 Compilation date: 24 February 2017 Includes amendments up to: Act No. 61, 2016 Registered: 27 February 2017
 AUSTRALIA Patents Act 1990 Compilation date: 24 February 2017 Includes amendments up to: Act No. 61, 2016 Registered: 27 February 2017 TABLE OF CONTENTS Chapter 1. Introductory 1 Short title 2 Commencement
AUSTRALIA Patents Act 1990 Compilation date: 24 February 2017 Includes amendments up to: Act No. 61, 2016 Registered: 27 February 2017 TABLE OF CONTENTS Chapter 1. Introductory 1 Short title 2 Commencement
PATENT ACT (UNOFFICIAL CLEAR TEXT) I. GENERAL PROVISIONS
 PATENT ACT NN 173/03, 31.10.2003. (in force from January 1, 2004) *NN 87/05, 18.07.2005. (in force from July 18, 2005) **NN 76/07, 23.07.2007. (in force from July 31, 2007) ***NN 30/09, 09.03.2009. (in
PATENT ACT NN 173/03, 31.10.2003. (in force from January 1, 2004) *NN 87/05, 18.07.2005. (in force from July 18, 2005) **NN 76/07, 23.07.2007. (in force from July 31, 2007) ***NN 30/09, 09.03.2009. (in
Intellectual Property. EMBL Summer Institute 2010 Dusty Gwinn WVURC
 Intellectual Property EMBL Summer Institute 2010 Dusty Gwinn WVURC Presentation Outline Intellectual Property Patents Trademarks Copyright Trade Secrets Technology Transfer Tech Marketing Tech Assessment
Intellectual Property EMBL Summer Institute 2010 Dusty Gwinn WVURC Presentation Outline Intellectual Property Patents Trademarks Copyright Trade Secrets Technology Transfer Tech Marketing Tech Assessment
Table of Contents I INTERNATIONAL PHASE BEFORE THE RECEIVING OFFICE AND INTERNATIONAL BUREAU.. 14
 Table of Contents I INTERNATIONAL PHASE BEFORE THE RECEIVING OFFICE AND INTERNATIONAL BUREAU.. 14 I.1. Who can file a PCT application?... 19 I.1.1. US law and the applicant (declaration of inventorship)...
Table of Contents I INTERNATIONAL PHASE BEFORE THE RECEIVING OFFICE AND INTERNATIONAL BUREAU.. 14 I.1. Who can file a PCT application?... 19 I.1.1. US law and the applicant (declaration of inventorship)...
Introduction. 1 These materials are public information and have been prepared solely for educational and entertainment purposes to contribute
 Introduction Patent Prosecution Under The AIA William R. Childs, Ph.D., J.D. Drinker Biddle & Reath LLP 1500 K Street, N.W. Washington, DC 20005-1209 (202) 230-5140 phone (202) 842-8465 fax William.Childs@dbr.com
Introduction Patent Prosecution Under The AIA William R. Childs, Ph.D., J.D. Drinker Biddle & Reath LLP 1500 K Street, N.W. Washington, DC 20005-1209 (202) 230-5140 phone (202) 842-8465 fax William.Childs@dbr.com
GERMAN UTILITY MODEL THE UNDERRATED INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT DATE: WEDNESDAY 12 NOVEMBER 2014 LOCATION: GLASGOW, UK
 GERMAN UTILITY MODEL THE UNDERRATED INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT DATE: WEDNESDAY 12 NOVEMBER 2014 LOCATION: GLASGOW, UK INTRODUCTION In Germany the utility model is an unexamined, technical IP right having
GERMAN UTILITY MODEL THE UNDERRATED INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT DATE: WEDNESDAY 12 NOVEMBER 2014 LOCATION: GLASGOW, UK INTRODUCTION In Germany the utility model is an unexamined, technical IP right having
Facilitating International Cooperation for the Protection of Traditional Knowledge: The Relevance of Mutual Recognition Agreements
 Facilitating International Cooperation for the Protection of Traditional Knowledge: The Relevance of Mutual Recognition Agreements by Professor Paul Kuruk 1 I. NEED FOR INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION Traditional
Facilitating International Cooperation for the Protection of Traditional Knowledge: The Relevance of Mutual Recognition Agreements by Professor Paul Kuruk 1 I. NEED FOR INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION Traditional
The person skilled in the art in the context of the inventive step requirement in patent law. Prefatory Statement
 QUESTION Q213 National Group: Title: Contributors: Representative within Working Committee: Philippines The person skilled in the art in the context of the inventive step requirement in patent law Rogelio
QUESTION Q213 National Group: Title: Contributors: Representative within Working Committee: Philippines The person skilled in the art in the context of the inventive step requirement in patent law Rogelio
DRAFT PATENT LAW OF GEORGIA CHAPTER I. GENERAL PROVISIONS
 DRAFT PATENT LAW OF GEORGIA CHAPTER I. GENERAL PROVISIONS ARTICLE 1 This Law regulates property and personal non-property relations formed in connection with the creation, legal protection and usage of
DRAFT PATENT LAW OF GEORGIA CHAPTER I. GENERAL PROVISIONS ARTICLE 1 This Law regulates property and personal non-property relations formed in connection with the creation, legal protection and usage of
RÅDET FOR DEN EUROPÆISKE UNION. Bruxelles, den 2. marts 2012 (06.03) (OR. en) 6051/12 INF 11 API 11 JUR 50
 RÅDET FOR DEN EUROPÆISKE UNION Bruxelles, den 2. marts 2012 (06.03) (OR. en) 6051/12 INF 11 API 11 JUR 50 I/A-PUNKTS-NOTE fra: Informationsgruppen til: Coreper (2. afdeling)/rådet Tidl. dok. nr.: 6050/12
RÅDET FOR DEN EUROPÆISKE UNION Bruxelles, den 2. marts 2012 (06.03) (OR. en) 6051/12 INF 11 API 11 JUR 50 I/A-PUNKTS-NOTE fra: Informationsgruppen til: Coreper (2. afdeling)/rådet Tidl. dok. nr.: 6050/12
Table of Contents. 9 Intellectual Property Policy
 Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers Intellectual Property Policy Extracted from Standards Operations Manual Approved by Board 2012-06-17 Effective 2013-08-05 9 Intellectual Property Policy
Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers Intellectual Property Policy Extracted from Standards Operations Manual Approved by Board 2012-06-17 Effective 2013-08-05 9 Intellectual Property Policy
Note: When any ambiguity of interpretation is found in this provisional translation, the Japanese text shall prevail. Part III Patentability
 Note: When any ambiguity of interpretation is found in this provisional translation, the Japanese text shall prevail. Part III Patent Act (Requirements for ) Article 29(1) Any person
Note: When any ambiguity of interpretation is found in this provisional translation, the Japanese text shall prevail. Part III Patent Act (Requirements for ) Article 29(1) Any person
Questionnaire on Exceptions and Limitations to Patent Rights. The answers to this questionnaire have been provided on behalf of:
 The answers to this questionnaire have been provided on behalf of: Country: Office: Bhutan Intellectual Property Division, Ministry of Economic Affairs, Thimphu Person to be contacted: Name: Mr. Sonam
The answers to this questionnaire have been provided on behalf of: Country: Office: Bhutan Intellectual Property Division, Ministry of Economic Affairs, Thimphu Person to be contacted: Name: Mr. Sonam
Patent Law in Cambodia
 Patent Law in Cambodia September 2012 No 64, St 111 PO Box 172 Phnom Penh Cambodia +855 23 217 510 +855 23 212 740 +855 23 212 840 info@bnglegal.com www.bnglegal.com Patent Law in Cambodia September 2012
Patent Law in Cambodia September 2012 No 64, St 111 PO Box 172 Phnom Penh Cambodia +855 23 217 510 +855 23 212 740 +855 23 212 840 info@bnglegal.com www.bnglegal.com Patent Law in Cambodia September 2012
IP Innovations Class
 IP Innovations Class Pitfalls for Patent Practitioners December 9, 2010 Presented by: Kris Doyle KDoyle@KilpatrickStockton.com 1 PRESERVING FOREIGN PATENT RIGHTS 2 1st Takeaway Absolute novelty is not
IP Innovations Class Pitfalls for Patent Practitioners December 9, 2010 Presented by: Kris Doyle KDoyle@KilpatrickStockton.com 1 PRESERVING FOREIGN PATENT RIGHTS 2 1st Takeaway Absolute novelty is not
Questionnaire Apotex Inc. v Sanofi-Aventis Proposed AIPPI intervention Supreme Court of Canada appeal
 National Group: Hungarian Title: Reporter: Contributors: Questionnaire Apotex Inc. v Sanofi-Aventis Proposed AIPPI intervention Supreme Court of Canada appeal Dr. PETHŐ, Árpád Dr. PETHŐ, Árpád, MOLNÁR,
National Group: Hungarian Title: Reporter: Contributors: Questionnaire Apotex Inc. v Sanofi-Aventis Proposed AIPPI intervention Supreme Court of Canada appeal Dr. PETHŐ, Árpád Dr. PETHŐ, Árpád, MOLNÁR,
WORLD TRADE ORGANIZATION
 WORLD TRADE ORGANIZATION IP/C/W/370 8 August 2002 (02-4356) Council for Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights THE PROTECTION OF TRADITIONAL KNOWLEDGE AND FOLKLORE SUMMARY OF ISSUES RAISED
WORLD TRADE ORGANIZATION IP/C/W/370 8 August 2002 (02-4356) Council for Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights THE PROTECTION OF TRADITIONAL KNOWLEDGE AND FOLKLORE SUMMARY OF ISSUES RAISED
Regulations to the Norwegian Patents Act (The Patent Regulations)
 Regulations to the Norwegian Patents Act (The Patent Regulations) This is an unofficial translation of the regulations to the Norwegian Patents Act. Should there be any differences between this translation
Regulations to the Norwegian Patents Act (The Patent Regulations) This is an unofficial translation of the regulations to the Norwegian Patents Act. Should there be any differences between this translation
Compilation date: 24 February Includes amendments up to: Act No. 61, Registered: 27 February 2017
 Patents Act 1990 No. 83, 1990 Compilation No. 41 Compilation date: 24 February 2017 Includes amendments up to: Act No. 61, 2016 Registered: 27 February 2017 This compilation includes commenced amendments
Patents Act 1990 No. 83, 1990 Compilation No. 41 Compilation date: 24 February 2017 Includes amendments up to: Act No. 61, 2016 Registered: 27 February 2017 This compilation includes commenced amendments
REPUBLIC OF VANUATU BILL FOR THE PATENTS ACT NO. OF 1999
 REPUBLIC OF VANUATU BILL FOR THE PATENTS ACT NO. OF 1999 Arrangement of Sections PART 1 PRELIMINARY PROVISIONS 1. Interpretation PART 2 PATENTABILITY 2. Patentable invention 3. Inventions not patentable
REPUBLIC OF VANUATU BILL FOR THE PATENTS ACT NO. OF 1999 Arrangement of Sections PART 1 PRELIMINARY PROVISIONS 1. Interpretation PART 2 PATENTABILITY 2. Patentable invention 3. Inventions not patentable
SWEDEN PATENTS ACT No.837 of 1967 in the version in force from July 1, 2014
 SWEDEN PATENTS ACT No.837 of 1967 in the version in force from July 1, 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS Chapter 1. General Provisions Article 1 Article 1a Article 1b Article 1c Article 1d Article 2 Article 3 Article
SWEDEN PATENTS ACT No.837 of 1967 in the version in force from July 1, 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS Chapter 1. General Provisions Article 1 Article 1a Article 1b Article 1c Article 1d Article 2 Article 3 Article
Please number your answers with the same numbers used for the corresponding questions.
 Question Q241 National Group: Title: Contributors: Reporter within Working Committee: The Latvian National Group IP licensing and insolvency Vadim MANTROV Vadim MANTROV Date: 19 May 2014 Questions I. Current
Question Q241 National Group: Title: Contributors: Reporter within Working Committee: The Latvian National Group IP licensing and insolvency Vadim MANTROV Vadim MANTROV Date: 19 May 2014 Questions I. Current
INTERGOVERNMENTAL COMMITTEE ON INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND GENETIC RESOURCES, TRADITIONAL KNOWLEDGE AND FOLKLORE (IGC)
 INTERGOVERNMENTAL COMMITTEE ON INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND GENETIC RESOURCES, TRADITIONAL KNOWLEDGE AND FOLKLORE (IGC) EIGHTH SESSION, GENEVA, 6 TO 10 JUNE 2005 PROTECTING TRADITIONAL KNOWLEDGE: MISAPPROPRIATION,
INTERGOVERNMENTAL COMMITTEE ON INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND GENETIC RESOURCES, TRADITIONAL KNOWLEDGE AND FOLKLORE (IGC) EIGHTH SESSION, GENEVA, 6 TO 10 JUNE 2005 PROTECTING TRADITIONAL KNOWLEDGE: MISAPPROPRIATION,
SUDAN Patents Act Act No. 58 of 1971 ENTRY INTO FORCE: October 15, 1971
 SUDAN Patents Act Act No. 58 of 1971 ENTRY INTO FORCE: October 15, 1971 TABLE OF CONTENTS Part I Preliminary Provisions Chapter I 1. Title 2. Definitions Chapter II Terms of Patentability 3. Patentable
SUDAN Patents Act Act No. 58 of 1971 ENTRY INTO FORCE: October 15, 1971 TABLE OF CONTENTS Part I Preliminary Provisions Chapter I 1. Title 2. Definitions Chapter II Terms of Patentability 3. Patentable
INVENTION DISCLOSURE FORM
 INVENTION DISCLOSURE FORM Invention Disclosure Form No. Disclosure Status Send completed form to David Ellis at dgellis@lclark.edu This form may be used as a legal record and should be filled out carefully,
INVENTION DISCLOSURE FORM Invention Disclosure Form No. Disclosure Status Send completed form to David Ellis at dgellis@lclark.edu This form may be used as a legal record and should be filled out carefully,
WHAT HAS CHANGED for TRADEMARKS with THE NEW TURKISH IP CODE?
 1 WHAT HAS CHANGED for TRADEMARKS with THE NEW TURKISH IP CODE? VALIDITY TERM National and international trademark and design applications as well as geographical indication applications made to the Turkish
1 WHAT HAS CHANGED for TRADEMARKS with THE NEW TURKISH IP CODE? VALIDITY TERM National and international trademark and design applications as well as geographical indication applications made to the Turkish
POTENTIAL PATENT APPLICATION QUESTIONNAIRE
 POTENTIAL PATENT APPLICATION QUESTIONNAIRE Prepared by: Date: Your reference for this matter: _ Correspondence information (Questions 1 2) 1. Please provide the correspondence information of the person(s)
POTENTIAL PATENT APPLICATION QUESTIONNAIRE Prepared by: Date: Your reference for this matter: _ Correspondence information (Questions 1 2) 1. Please provide the correspondence information of the person(s)
Intellectual Property Laws Amendment Bill
 The Chairperson: Ms J L Fubbs MP Portfolio Committee Trade & Industry, Parliament Attention: Mr Andre Hermans Tel: 4033776; 0837098482; email: jfubbs@parliament.gov.za 18 October 2010 AFRICAN CENTRE FOR
The Chairperson: Ms J L Fubbs MP Portfolio Committee Trade & Industry, Parliament Attention: Mr Andre Hermans Tel: 4033776; 0837098482; email: jfubbs@parliament.gov.za 18 October 2010 AFRICAN CENTRE FOR
The Protection of Traditional Knowledge: Draft Articles. Facilitators Rev. 2 (December 2, 2016)
 The Protection of Traditional Knowledge: Draft Articles Facilitators Rev. 2 (December 2, 2016) page 2 PREAMBLE/INTRODUCTION Recognize value (i) recognize the [holistic] [distinctive] nature of traditional
The Protection of Traditional Knowledge: Draft Articles Facilitators Rev. 2 (December 2, 2016) page 2 PREAMBLE/INTRODUCTION Recognize value (i) recognize the [holistic] [distinctive] nature of traditional
Foreign Filing Procedures
 Foreign Filing Procedures COSTA RICA 1) Country name: Costa Rica 2) What is language of filing? Spanish only 3) Is this country a member of PCT and/or convention country (yes/no)? Yes 4) National phase:
Foreign Filing Procedures COSTA RICA 1) Country name: Costa Rica 2) What is language of filing? Spanish only 3) Is this country a member of PCT and/or convention country (yes/no)? Yes 4) National phase:
The use of TK-related databases at the EPO: A brief overview. Enrico Luzzatto Director, Pure and Applied Organic Chemistry, Munich
 The use of TK-related databases at the EPO: A brief overview Enrico Luzzatto Director, Pure and Applied Organic Chemistry, Munich WIPO, Geneva June 2015 Specialized TK-related databases available to the
The use of TK-related databases at the EPO: A brief overview Enrico Luzzatto Director, Pure and Applied Organic Chemistry, Munich WIPO, Geneva June 2015 Specialized TK-related databases available to the
PRE-GRANT OPPOSITION POST-GRANT OPPOSITION
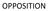 OPPOSITION TYPES OF OPPOSITION PRE-GRANT OPPOSITION [SEC 25(1)] POST-GRANT OPPOSITION [SEC. 25 (2)] REVOCATION[SECs 64 TO 66] GROUNDS FOR OPPOSITION UNDER SECTIONS 25(1) & 25 (2) That the applicant for
OPPOSITION TYPES OF OPPOSITION PRE-GRANT OPPOSITION [SEC 25(1)] POST-GRANT OPPOSITION [SEC. 25 (2)] REVOCATION[SECs 64 TO 66] GROUNDS FOR OPPOSITION UNDER SECTIONS 25(1) & 25 (2) That the applicant for
THE REVISED DRAFT PROVISIONS FOR THE PROTECTION OF TRADITIONAL CULTURAL EXPRESSIONS/ EXPRESSIONS OF FOLKLORE: POLICY OBJECTIVES AND CORE PRINCIPLES
 COMMENTS ON THE REVISED DRAFT PROVISIONS FOR THE PROTECTION OF TRADITIONAL CULTURAL EXPRESSIONS/ EXPRESSIONS OF FOLKLORE: POLICY OBJECTIVES AND CORE PRINCIPLES Submitted by the Emerging Issues Committee
COMMENTS ON THE REVISED DRAFT PROVISIONS FOR THE PROTECTION OF TRADITIONAL CULTURAL EXPRESSIONS/ EXPRESSIONS OF FOLKLORE: POLICY OBJECTIVES AND CORE PRINCIPLES Submitted by the Emerging Issues Committee
ETHIOPIA A PROCLAMATION CONCERNING INVENTIONS, MINOR INVENTIONS AND INDUSTRIAL DESIGNS PROCLAMATION NO. 123/1995 ENTRY INTO FORCE: May 10, 1995
 ETHIOPIA A PROCLAMATION CONCERNING INVENTIONS, MINOR INVENTIONS AND INDUSTRIAL DESIGNS PROCLAMATION NO. 123/1995 ENTRY INTO FORCE: May 10, 1995 TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER ONE General Provisions 1. Short
ETHIOPIA A PROCLAMATION CONCERNING INVENTIONS, MINOR INVENTIONS AND INDUSTRIAL DESIGNS PROCLAMATION NO. 123/1995 ENTRY INTO FORCE: May 10, 1995 TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER ONE General Provisions 1. Short
SUMMARY. Geneva, Switzerland
 THE TRIPS AND WTO NEGOTIATIONS: STAKES FOR AFRICA 1 SUMMARY This paper discusses the current negotiation issues in the context of the Agreement on Trade Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights
THE TRIPS AND WTO NEGOTIATIONS: STAKES FOR AFRICA 1 SUMMARY This paper discusses the current negotiation issues in the context of the Agreement on Trade Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights
11 th Session of the Permanent Forum on Indigenous Issues
 11 th Session of the Permanent Forum on Indigenous Issues Comprehensive Dialogue with the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) May 10, 2012 Outline Introduction key messages What is WIPO? Intellectual
11 th Session of the Permanent Forum on Indigenous Issues Comprehensive Dialogue with the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) May 10, 2012 Outline Introduction key messages What is WIPO? Intellectual
The Consolidate Patents Act
 The Consolidate Patents Act Publication of the Patents Act, cf. Consolidated Act No. 366 of 9 June 1998 as amended by Act No. 412 of 31 May 2000 TABLE OF CONTENTS Sections Part 1: General Provisions...
The Consolidate Patents Act Publication of the Patents Act, cf. Consolidated Act No. 366 of 9 June 1998 as amended by Act No. 412 of 31 May 2000 TABLE OF CONTENTS Sections Part 1: General Provisions...
APPENDIX 8: DECLARATION OF INVENTION DECLARATION OF INVENTION
 APPENDIX 8: DECLARATION OF INVENTION DECLARATION OF INVENTION The purpose of this form is to notify the and CUFA of your potential Invention and any relevant sponsorship and publication history. A copy
APPENDIX 8: DECLARATION OF INVENTION DECLARATION OF INVENTION The purpose of this form is to notify the and CUFA of your potential Invention and any relevant sponsorship and publication history. A copy
[English translation by WIPO] Questionnaire on Exceptions and Limitations to Patent Rights
![[English translation by WIPO] Questionnaire on Exceptions and Limitations to Patent Rights [English translation by WIPO] Questionnaire on Exceptions and Limitations to Patent Rights](/thumbs/90/103497462.jpg) [English translation by WIPO] Questionnaire on Exceptions and Limitations to Patent Rights The answers to this questionnaire have been provided on behalf of: Country: Office: Morocco... Moroccan Industrial
[English translation by WIPO] Questionnaire on Exceptions and Limitations to Patent Rights The answers to this questionnaire have been provided on behalf of: Country: Office: Morocco... Moroccan Industrial
Law on Inventive Activity*
 Law on Inventive Activity* (of October 19, 1972, as amended by the Law of April 16, 1993) TABLE OF CONTENTS** Article Part I: General Provisions... 1 9 Part II: Inventions and Patents 1. Patents... 10
Law on Inventive Activity* (of October 19, 1972, as amended by the Law of April 16, 1993) TABLE OF CONTENTS** Article Part I: General Provisions... 1 9 Part II: Inventions and Patents 1. Patents... 10
ROMANIA Patent Law NO.64/1991 OFFICIAL GAZETTE OF ROMANIA, PART I, NO.613/19 AUGUST 2014
 ROMANIA Patent Law NO.64/1991 OFFICIAL GAZETTE OF ROMANIA, PART I, NO.613/19 AUGUST 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER I - GENERAL PROVISIONS Art. 1 Art. 2 Art. 3 Art. 4 Art. 5 CHAPTER II - PATENTABLE INVENTIONS
ROMANIA Patent Law NO.64/1991 OFFICIAL GAZETTE OF ROMANIA, PART I, NO.613/19 AUGUST 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER I - GENERAL PROVISIONS Art. 1 Art. 2 Art. 3 Art. 4 Art. 5 CHAPTER II - PATENTABLE INVENTIONS
24: Patents: Disclosure Obligations
 24: Patents: Disclosure Obligations Article 29 Conditions on Patent Applicants 1. Members shall require that an applicant for a patent shall disclose the invention in a manner sufficiently clear and complete
24: Patents: Disclosure Obligations Article 29 Conditions on Patent Applicants 1. Members shall require that an applicant for a patent shall disclose the invention in a manner sufficiently clear and complete
Newly Signed U.S. Patent Law Will Overhaul Patent Procurement, Enforcement and Defense
 September 16, 2011 Practice Groups: IP Procurement and Portfolio Management Intellectual Property Litigation Newly Signed U.S. Patent Law Will Overhaul Patent Procurement, Enforcement and Defense On September
September 16, 2011 Practice Groups: IP Procurement and Portfolio Management Intellectual Property Litigation Newly Signed U.S. Patent Law Will Overhaul Patent Procurement, Enforcement and Defense On September
OFFICIAL GAZETTE OF ROMANIA, PART I, NO.613/19 AUGUST 2014 REPUBLICATION PATENT LAW NO.64/1991 1
 OFFICIAL GAZETTE OF ROMANIA, PART I, NO.613/19 AUGUST 2014 REPUBLICATION PATENT LAW NO.64/1991 1 CHAPTER I - GENERAL PROVISIONS Art. 1 - (1) The rights in inventions shall be recognized and protected on
OFFICIAL GAZETTE OF ROMANIA, PART I, NO.613/19 AUGUST 2014 REPUBLICATION PATENT LAW NO.64/1991 1 CHAPTER I - GENERAL PROVISIONS Art. 1 - (1) The rights in inventions shall be recognized and protected on
Economic and Social Council
 UNITED NATIONS E Economic and Social Council Distr. GENERAL 3 July 2001 ENGLISH Original: ENGLISH/SPANISH COMMISSION ON HUMAN RIGHTS Sub-Commission on the Promotion and Protection of Human Rights Fifty-second
UNITED NATIONS E Economic and Social Council Distr. GENERAL 3 July 2001 ENGLISH Original: ENGLISH/SPANISH COMMISSION ON HUMAN RIGHTS Sub-Commission on the Promotion and Protection of Human Rights Fifty-second
THE PATENT LAW 1. GENERAL PROVISIONS. Article 1. This Law shall regulate the legal protection of inventions by means of patents.
 THE PATENT LAW 1. GENERAL PROVISIONS Article 1 This Law shall regulate the legal protection of inventions by means of patents. Article 2 This Law shall also apply to the sea and submarine areas adjacent
THE PATENT LAW 1. GENERAL PROVISIONS Article 1 This Law shall regulate the legal protection of inventions by means of patents. Article 2 This Law shall also apply to the sea and submarine areas adjacent
Options for Incorporating TK and Customary Law into MAT
 Options for Incorporating TK and Customary Law into MAT Preston Hardison Vilm Workshop Tulalip Tribes of Washington July 6, 2009 page 1 Five General Approaches 1. Use existing IPR (trade secrets) 2. Accomodation
Options for Incorporating TK and Customary Law into MAT Preston Hardison Vilm Workshop Tulalip Tribes of Washington July 6, 2009 page 1 Five General Approaches 1. Use existing IPR (trade secrets) 2. Accomodation
CBD. Distr. GENERAL. UNEP/CBD/NP/COP-MOP/2/10 * 3 February 2016 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH
 CBD Distr. GENERAL UNEP/CBD/NP/COP-MOP/2/10 * 3 February 2016 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH CONFERENCE OF THE PARTIES TO THE CONVENTION ON BIOLOGICAL DIVERSITY SERVING AS THE MEETING OF THE PARTIES TO THE NAGOYA PROTOCOL
CBD Distr. GENERAL UNEP/CBD/NP/COP-MOP/2/10 * 3 February 2016 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH CONFERENCE OF THE PARTIES TO THE CONVENTION ON BIOLOGICAL DIVERSITY SERVING AS THE MEETING OF THE PARTIES TO THE NAGOYA PROTOCOL
Utility Models Act. Passed RT I 1994, 25, 407 Entry into force
 Issuer: Riigikogu Type: act In force from: 01.01.2015 In force until: In force Translation published: 23.12.2014 Amended by the following acts Passed 16.03.1994 RT I 1994, 25, 407 Entry into force 23.05.1994
Issuer: Riigikogu Type: act In force from: 01.01.2015 In force until: In force Translation published: 23.12.2014 Amended by the following acts Passed 16.03.1994 RT I 1994, 25, 407 Entry into force 23.05.1994
