Type in the following link in your address bar: prefix=mfk&wcsuffix=1000
|
|
|
- Kerry Woods
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 US Studies 1 st Semester Exam Study Guide: The following is a link that goes with our The American Nation textbook. There are selftests with questions that are similar to our test questions and will be helpful to get the past information we ve studied into your mind for the exam. Type in the following link in your address bar: prefix=mfk&wcsuffix=1000 Then, select Chapter 19, Chapter 20, Chapter 21, Chapter 22, Chapter 23 and/or Chapter 24 Then, you ll see the following link for Self-Tests. Click on it. Chapter Self-Test Here are the Summaries & Main Idea Statements for each chapter as seen on the website. Chapter 19 Summary After the Civil War, settlers flooded the West. Miners sought gold and silver. Railroad builders spanned the continent with rail lines. Ranchers raised great herds of cattle. Farmers changed grasslands into fields of wheat and corn. As these westerners gained political influence, they urged government leaders to address their needs and concerns. Native Americans, meanwhile, were driven from their homelands. They struggled to keep their way of life. In the end, however, they were defeated. On reservations, they were forced to learn new ways. Native Americans suffered greatly from the changes that swept the West. Section 1: Indian Peoples of the Great Plains Different Indian peoples lived on the Great Plains, and many relied on the horse and the buffalo as they developed their varied cultures and traditions. Section 2: Mining and Railroading A mining boom changed the West, bringing people and a new means of transportation to the region. Section 3: The Cattle Kingdom Cattle ranching boomed on the open range in the 1870s, producing a Cattle Kingdom of ranchers, cowboys, cattle drives, and cow towns. Section 4: Indian Peoples in Retreat Despite government promises to protect their land, Indian peoples found their way of life threatened as white settlers invaded their territory. Section 5: Farming The Homestead Act opened the West to farmers who struggled to survive the harsh environment of the Great Plains....
2 Chapter 20 Summary After the Civil War, American industry boomed. One reason for this tremendous growth was the rapid increase in the number of railways in the nation. Shrewd, energetic (and sometimes ruthless) business leaders created vast companies. A constant stream of new inventions also helped industry grow. In the new economy, workers often faced long hours, unsafe conditions, and low pay. They soon banded together to win improvements in their lives. Slowly, organized labor became a powerful new force in American society. Section 1: Railroads Spur Industry A boom in railroad building encouraged American industry to grow but gave vast amounts of power to a few railroad owners. Section 2: The Rise of Big Business As industry boomed, American businesses grew and developed new ways of organizing and limiting competition. Section 3: Inventions Change the Nation New technologies transformed American industry and life in the late 1800s. Section 4: The Rise of Organized Labor As workers lost power over their working conditions, they began to organize into unions and fight for better conditions.... Chapter 21 Summary In the 50 years after the Civil War, 25 million immigrants poured into the United States. Most were driven by hunger and poverty and drawn by hope of a better life. They came from places such as Italy, Eastern Europe, Armenia, China, and Mexico. During this time, American cities grew rapidly. Population growth brought problems, including poor housing and strained city services. At the same time, it led to a rich mix of cultures. Cities fostered new leisure-time activities, such as sports. As education improved, newspapers, magazines, and new American fiction gained a larger audience. Section 1: New Immigrants in a Promised Land In the late 1800s, millions of "new immigrants" came to the United States in search of economic opportunity and freedom.
3 Section 2: An Age of Cities Vast numbers of people migrated to cities, changing urban landscapes and creating new problems. Section 3: Life in the Changing Cities A building boom, new technology, and new leisure activities changed the way city dwellers lived. Section 4: Public Education and American Culture The growth of public education was closely linked to other changes in American culture.... Chapter 22 Summary A period of reform known as the Progressive Era took shape in the late 1800s. During this time, Americans worked to fight corruption in government, reduce the power of big business, and improve society. Government became more democratic as people in many states gained the power to pass laws directly. After years of effort, American women finally won the right to vote. From 1901 to 1921, three Presidents played a leading role in reform efforts. African Americans and other minorities also took action against discrimination during the Progressive Era. Despite many setbacks, they laid the groundwork for future progress in civil rights. Section 1: Reform in the Gilded Age During the Gilded Age, reformers worked to end political corruption and limit the power of big business. Section 2: The Progressives Progressive reformers worked to end political corruption and give voters greater power. Section 3: Progressives in the White House During the early 1900s, three Presidents worked for Progressive goals: Theodore Roosevelt, William H. Taft, and Woodrow Wilson. Section 4: Women Win Reforms During the Progressive Era, many women fought for reforms and campaigned to win the right to vote. Section 5: Other Americans Seek Justice African Americans and other Americans created their own communities and struggled for equality during the Progressive Era....
4 Chapter 23 Summary The United States increased its role in world affairs throughout the second half of the nineteenth century. As the nation became an industrial and commercial power, American leaders sought new trade opportunities in Asia. Alaska, Hawaii, and other overseas territories came under United States control. As a result of the Spanish-American War of 1898, the United States acquired an overseas empire. After the war, the United States played an increasing role in the affairs of Latin America. As a result, many Latin Americans began to view the United States with distrust and anger. Outline Section 1: A Pacific Empire At the end of the 1800s, the United States became a world power, acquiring new territories in the Pacific and the Caribbean. Section 2: War With Spain In 1898, the Spanish-American War launched an age of American imperialism in the Caribbean and the Pacific. Section 3: The United States in Latin America Increasing economic ties led the United States to intervene in Latin American affairs.... Chapter 24 - World War I In 1914, long-standing rivalries among European nations exploded into war. At first, President Woodrow Wilson tried to keep the United States neutral. However, after several of Germany's actions affected American citizens, the United States entered the war against Germany in World War I, as the war is now called, cost millions of lives. After the war ended, Wilson worked hard to build a lasting peace. However, because of conflicts at the peace conference and at home, he was unable to achieve all of his goals. Section 1: War in Europe When World War I erupted in 1914, the United States remained neutral. Section 2: From Neutrality to War The United States tried to remain neutral, but the German campaign of submarine warfare finally brought the country into the war.
5 Section 3: Americans in Battle The United States did not enter World War I until 1917, but its fresh troops and supplies helped the Allies to victory. Section 4: The Failed Peace President Woodrow Wilson went to the Paris Peace Conference with high hopes but failed to achieve his goal of a just and lasting peace. Study presidents we ve studied this semester and significant accomplishments or things that we would associate with them. (Hayes - Wilson) Ex: Which President is associated with dollar diplomacy? Taft Know the tools and goals of American Foreign Policy. (Know what they are, about them, and examples.) Goals: National Security, World Peace, Human Rights & Democracy, Trade Tools: Trade Measures, Intelligence, Defense, Diplomacy, Foreign Aid, Alliances What are the 3 types of alliances? Military, Economic, Political; Types of Foreign Aid; Examples of Defense; Examples of Trade Measures Review the Amendments! (Specifically 16-21; know what are, too!) 13 - Abolish Slavery; 14 - Citizenship Rights Extended - not denied based on race; Equal Protection Clause; 15 - Voting Rights Extended - black male citizens legally allowed to vote; 16 - Income tax; 17 - Direct Election of Senators; 18 - Prohibition; 19 - Women s Suffrage; 20 - Presidential Terms & Congress Sessions (President inaugurated on Jan. 20 th ); 21 - Repeal Prohibition
6 Core Concepts It s important for you to know the definitions & about all of the Core Concepts we ve covered so far. If you understand the Core Concepts, you should be able to apply what you know about that concept to other questions and concepts from our studies. You need to think beyond just the definitions. Think about what the concept means so that you can apply it to other questions. Here are a list of the concept cards you should have for 1 st semester. 16 th Amendment - pink (Income Tax - yellow) 17 th Amendment - pink 18 th Amendment - pink 19 th Amendment - pink Acculturation - orange American Federation of Labor - pink Anarchists - yellow Assembly Line - orange Bull Market - yellow Bull Moose Party - pink Chinese Exclusion Act - pink Civil Service Commission - orange (Civil Service - yellow) Clayton Antitrust Act - pink Collective Bargaining - orange Communism - pink Conservation - pink Containment - pink Corporation - Pink Dollar Diplomacy - pink Equal Rights Amendment (ERA) - pink Expansionism - pink Federal Reserve Act - orange Federal Reserve System - pink Federal Trade Commission (FTC) - yellow Foraker Act - orange Gentlemen s Agreement - pink Graduated Income Tax - orange Immigration - pink (Pull Factors - yellow; Push Factors - yellow) Imperialism - pink Initiative - orange Internat l Ladies Garment Workers Union - pink Isolationist/Isolationism - pink Knights of Labor - pink League of Women Voters - pink Mass Production - orange Moral Diplomacy - pink Muckrakers - orange NAACP - pink National Women s Suffrage Assn - pink Nationalism - pink Nativism - pink Nativists - pink Neutrality - pink New Freedom - pink Open Door Policy - pink Platt Amendment - orange Political Bosses - orange Populist/Populism - pink Primary - Orange Progressives/Progressivism - Pink Prohibition - pink (repeal - yellow) Public interest - pink Pure Food & Drug Act - yellow Quota System - pink (quota - yellow) Racism - pink Recall - orange Recession - yellow Referendum - orange Roosevelt Corollary - orange Sabotage (yellow) Settlement Houses - orange (Hull House - yellow) Sherman Antitrust Act - pink Sphere(s) of Influence - pink Square Deal - pink Strike - orange Strikebreaker (Scab) - orange Suburb/Suburbanization - pink Suffrage/Suffragists - pink Tenements - orange The Grange - orange Trade Unions - orange Treaty of Kanagawa - orange Trustbusters - orange Urbanization - pink Vertical Integration - orange Wisconsin Idea - pink Yellow Journalism - orange
7 Topics from book that questions on Exam will be over (In alpha order by chapter) (Your exam is largely made up of questions that will be commonly assessed by all US Studies teachers for all US Studies students... These are the topics... Some are repeated, worded differently depending on the question type. There are 153 commonly assessed questions caqs are multiple choice; 1 extended response.) Chapter 19 Buffalo extinction Buffalo herds Cow Towns Cowhands Dawes Act Exodusters Farm Life in 1800s Free silver Gold, Silver boom Grangers Great Plains farmers Homestead Act Industrial growth in late 1800s Labor Organization Mining Boom Native American Way of life Plains Indian society, Women Plains Indians Railroads Railroads, Populist Party Railroad regulation William Jennings Bryan Chapter 20 Airplane, Wright Brothers Banking system after Civil War Communication devices after the Civil War Corporations George Pullman, Organized Labor George Westinghouse Industrial growth in late 1800s John D. Rockefeller Knights of Labor Labor organization Mass production Organized labor Railroad Rebates Railroad Pools Railroads, Economic growth Railroads, Populist party Standard Oil Standard gauge Standard gauge, Railroads Steel Empires (late 1800s) Thomas Edison Transatlantic cable Transatlantic cable Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire Trusts Women workers late 1800s Chapter 21 Acculturation Building boom in cities (Late 1800s) Chinese Exclusion Act City Settlement (Late 1800s) City settlement patterns (Late 1800s) Compulsory Education Demand for factory workers Immigrants Immigration Interest in sports Kindergarten Mass circulation newspaper (Late 1800s) Migration to cities (Late 1800s) Nativist Pattern of City Settlement (Late 1800s) Popularity of sports (Late 1800s) Population increase in cities (Late 1800s) Public education Push & Pull Factors, Immigration Realist writers Realist writers and painters Reformers, Solving cities problems Settlement House Tenements Vaudeville Women readers, Newspapers Yellow Journalism Chapter 22 African Americans, Ida B. Wells African Americans, Progressive Era Bull Moose/Progressive Party, Election 1912 Chinese Exclusion Act Civil Service Commission Corruption, City government
8 Chapter 22 (Continued) Crusade against alcohol Dawes Act Gentlemen s Agreement Gilded Age Interstate Commerce Act Mexican Americans Mexican Americans Muckrakers Native Americans Opportunities for women (Late 1800s) Progressives Progressive Goals Progressive Reforms Progressives, President Taft Progressives, President Taft Sherman Antitrust Act Society of American Indians Temperance movement Woodrow Wilson, Election of 1912 Women s right to vote Women s suffrage Women s Christian Temperance Union Woodrow Wilson, Progressive Goals Chapter 23 Boxer Rebellion Columbia & Panama Commodore Perry Diseases, Panama Canal Explosion, The Maine George Goethels Hawaii Imperialism Isthmus, Panama Canal John Hay Latin America, Big Stick Mexico, General Francisco Villa Mexico, General Francisco Villa Open Door Policy Panama Canal Panama & Columbia Queen Liliuokalani Roosevelt Corollary Samoa Seward s Folly Spanish American War Spanish American War Theodore Roosevelt Treaty of Kanagawa William Seward, Alaska Be able to describe how industrialization, urbanization, and immigration shaped the US in the late 19 th century (late 1800s). USE THE US STUDIES CHAPTER 24 - WORLD WAR I - LEARNING PACKET TO HELP YOU STUDY FOR THE EXAM ALONG WITH THE ONLINE SELF-TESTS.
8 TH GRADE UNITS OF INSTRUCTION
 Name Date Per. Social Studies 8 1/3 Review Packet Mrs. Myles McAnally 8 TH GRADE UNITS OF INSTRUCTION Reconstruction: Economic Expansion: a. Immigration b. Industrialization c. US Expansion and Imperialism
Name Date Per. Social Studies 8 1/3 Review Packet Mrs. Myles McAnally 8 TH GRADE UNITS OF INSTRUCTION Reconstruction: Economic Expansion: a. Immigration b. Industrialization c. US Expansion and Imperialism
Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea
 Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea In the last half of the 1800s, the United States joined the race for control of overseas territories.
Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea In the last half of the 1800s, the United States joined the race for control of overseas territories.
18 America Claims an Empire QUIT
 18 America Claims an Empire QUIT CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE SECTION 1 Imperialism and America GRAPH MAP SECTION 2 The Spanish-American War SECTION 3 Acquiring New Lands SECTION 4
18 America Claims an Empire QUIT CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE SECTION 1 Imperialism and America GRAPH MAP SECTION 2 The Spanish-American War SECTION 3 Acquiring New Lands SECTION 4
STANDARD VUS.8a. Essential Questions What factors influenced American growth and expansion in the late nineteenth and early twentieth century?
 STANDARD VUS.8a through the early twentieth century by explaining the relationship among territorial expansion, westward movement of the population, new immigration, growth of cities, and the admission
STANDARD VUS.8a through the early twentieth century by explaining the relationship among territorial expansion, westward movement of the population, new immigration, growth of cities, and the admission
1. How did the Dawes Act aid in destroying the way of life of Native American s?
 Name Period Chapter 4 Reconstruction **List and discuss the failures and successes of Reconstruction concerning political and social rights of African Americans. Make sure and include the Amendments 13,
Name Period Chapter 4 Reconstruction **List and discuss the failures and successes of Reconstruction concerning political and social rights of African Americans. Make sure and include the Amendments 13,
Letter from President Fillmore asking Japan. American ships to stop for supplies safety reasons
 Chapter 19-21 Introduction Japan 1853 Not open to trading with other countries Commodore Matthew Perry went to Japan with a small fleet of warships (Gunboat Diplomacy) Letter from President Fillmore asking
Chapter 19-21 Introduction Japan 1853 Not open to trading with other countries Commodore Matthew Perry went to Japan with a small fleet of warships (Gunboat Diplomacy) Letter from President Fillmore asking
CHAPTER 22 CONCEPT CARDS
 CHAPTER 22 CONCEPT CARDS Section 1 CIVIL SERVICE COMMISSION - ORANGE Government agency created by the Pendleton Act of 1863 to fill federal jobs on the basis of merit. - People who scored highest on civil
CHAPTER 22 CONCEPT CARDS Section 1 CIVIL SERVICE COMMISSION - ORANGE Government agency created by the Pendleton Act of 1863 to fill federal jobs on the basis of merit. - People who scored highest on civil
The Progressive Era. America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century
 The Progressive Era America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century Origins of Progressivism As America entered the 20 th century, middle class reformers at the municipal, state, and national levels addressed
The Progressive Era America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century Origins of Progressivism As America entered the 20 th century, middle class reformers at the municipal, state, and national levels addressed
DIOCESE OF HARRISBURG SOCIAL STUDIES CURRICULUM GRADE 7/8 United States History: Westward Expansion to Present Day
 5.1.9 Identify the goals of the constitution and the basic principles of American government. Recognize the Preamble to the Constitution and briefly explain how our government meets each goal. List and
5.1.9 Identify the goals of the constitution and the basic principles of American government. Recognize the Preamble to the Constitution and briefly explain how our government meets each goal. List and
AMERICA SEEKS REFORMS IN THE EARLY 20 TH CENTURY
 AMERICA SEEKS REFORMS IN THE EARLY 20 TH CENTURY ORIGINS OF PROGRESSIVISM As America entered into the 20 th century, middle class reformers addressed many social problems Work conditions, rights for women
AMERICA SEEKS REFORMS IN THE EARLY 20 TH CENTURY ORIGINS OF PROGRESSIVISM As America entered into the 20 th century, middle class reformers addressed many social problems Work conditions, rights for women
The Progressive Era. America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century
 The Progressive Era America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century Origins of Progressivism As America entered the 20 th century, middle class reformers at the municipal, state, and national levels addressed
The Progressive Era America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century Origins of Progressivism As America entered the 20 th century, middle class reformers at the municipal, state, and national levels addressed
Standards US History 10-25
 Standards US History 10-25 Progressivism Progressivism A reform movement focused on improving living conditions, education, working conditions, stopping political corruption, and gain women the right to
Standards US History 10-25 Progressivism Progressivism A reform movement focused on improving living conditions, education, working conditions, stopping political corruption, and gain women the right to
Unit 2: The Rise of Big Government
 Unit 2: The Rise of Big Government Imperialism, the Progressive Era, and the First World War 1898-1920 Unit Overview: By 1896, American industry had caught up with the rest of the world. Since the nation
Unit 2: The Rise of Big Government Imperialism, the Progressive Era, and the First World War 1898-1920 Unit Overview: By 1896, American industry had caught up with the rest of the world. Since the nation
The Progressive Era. America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century
 The Progressive Era America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century Origins of Progressivism As America entered the 20 th century, middle class reformers at the municipal, state, and national levels addressed
The Progressive Era America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century Origins of Progressivism As America entered the 20 th century, middle class reformers at the municipal, state, and national levels addressed
2. COMPARISON -- TWO PHILOSOPHIES:
 THE PROGRESSIVE ERA 1. PROGRESSIVE ERA: Definition = a period of widespread social activism and political reform (1890s-1920s) Also called the Progressive Movement A Progressive = an activist; usually
THE PROGRESSIVE ERA 1. PROGRESSIVE ERA: Definition = a period of widespread social activism and political reform (1890s-1920s) Also called the Progressive Movement A Progressive = an activist; usually
Who were the Progressives?
 Progressive Era Who were the Progressives? Middle class activists urban, college educated, mostly white Leaders of smaller, issue based reform movements Used the power of the national, state and local
Progressive Era Who were the Progressives? Middle class activists urban, college educated, mostly white Leaders of smaller, issue based reform movements Used the power of the national, state and local
The Progressive Presidents
 The Progressive Presidents Main Ideas o The federal government responded to grassroots reform efforts by enacting progressive policies. o Progressive reforms sought to established a greater degree of democratic
The Progressive Presidents Main Ideas o The federal government responded to grassroots reform efforts by enacting progressive policies. o Progressive reforms sought to established a greater degree of democratic
Reforms of the Early 20th Century. (The emergence of government as a problem solver)
 Reforms of the Early 20th Century (The emergence of government as a problem solver) Learning Target Explain the origins of the Populist Party and their impact on American life. Origins of the Populist
Reforms of the Early 20th Century (The emergence of government as a problem solver) Learning Target Explain the origins of the Populist Party and their impact on American life. Origins of the Populist
Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism ( )
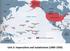 Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism (1890-1930) What is an empire? Is imperialism the same as colonization? Why would the U.S. get involved in this practice? What is the difference between acquiring and
Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism (1890-1930) What is an empire? Is imperialism the same as colonization? Why would the U.S. get involved in this practice? What is the difference between acquiring and
STAAR BLITZ: IMPERIALISM, SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR, WWI APRIL 22, 2015
 STAAR BLITZ: IMPERIALISM, SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR, WWI APRIL 22, 2015 AGE OF IMPERIALISM! (1900s- 1914) MILITARY Alfred T. Mahan argued for a strong NAVY in his book Influence of Sea Power Upon History Easier
STAAR BLITZ: IMPERIALISM, SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR, WWI APRIL 22, 2015 AGE OF IMPERIALISM! (1900s- 1914) MILITARY Alfred T. Mahan argued for a strong NAVY in his book Influence of Sea Power Upon History Easier
netw rks The Progressive Era Lesson 1 The Movement Begins, Continued Mark the Text Identifying Defining 1. Underline the definition of kickbacks.
 Lesson 1 The Movement Begins, Continued Taking on Corruption There were problems in American society in the late 1800s. Many Americans called for reform. Reformers are people who want to change society
Lesson 1 The Movement Begins, Continued Taking on Corruption There were problems in American society in the late 1800s. Many Americans called for reform. Reformers are people who want to change society
Unit 3 Review. Populism and Progressivism
 Unit 3 Review Populism and Progressivism The practice of handing out government jobs to supporters of a winning campaign for federal offices, especially the presidency patronage The practice of handing
Unit 3 Review Populism and Progressivism The practice of handing out government jobs to supporters of a winning campaign for federal offices, especially the presidency patronage The practice of handing
WARM UP. 2 Match the presidential event with the president or presidents that it belongs with
 WARM UP 1 Complete the Progressive Presidential comparison activity 2 Match the presidential event with the president or presidents that it belongs with 3 Research the event if it was not discussed in
WARM UP 1 Complete the Progressive Presidential comparison activity 2 Match the presidential event with the president or presidents that it belongs with 3 Research the event if it was not discussed in
MUCKRAKERS. social, economic, and political injustices. corruption, scandal and injustice to the public view
 THE PROGRESSIVE ERA MUCKRAKERS Journalists focusing on social, economic, and political injustices Known for exposing corruption, scandal and injustice to the public view They investigated governments,
THE PROGRESSIVE ERA MUCKRAKERS Journalists focusing on social, economic, and political injustices Known for exposing corruption, scandal and injustice to the public view They investigated governments,
UNITED STATES HISTORY. Unit 3 THE PROGRESSIVE ERA Aka Power to the People
 UNITED STATES HISTORY Unit 3 THE PROGRESSIVE ERA Aka Power to the People THE ORIGINS OF PROGRESSIVISM Progressivism- reform movement in the U.S. in early 1900s aimed at returning control of the government
UNITED STATES HISTORY Unit 3 THE PROGRESSIVE ERA Aka Power to the People THE ORIGINS OF PROGRESSIVISM Progressivism- reform movement in the U.S. in early 1900s aimed at returning control of the government
US History Mr. Martin Unit 7: The Birth of Modern America Chapters 13-16
 US History Mr. Martin Unit 7: The Birth of Modern America Chapters 13-16 This unit explores the transformation of the US from a rural nation into an industrial, urban nation during the period from 1865
US History Mr. Martin Unit 7: The Birth of Modern America Chapters 13-16 This unit explores the transformation of the US from a rural nation into an industrial, urban nation during the period from 1865
Unit VII Study Guide- American Imperialism
 Unit VII Study Guide- American Imperialism 1. List the ideas that fueled American Imperialism. 2. How were yellow journalists able to influence Americans opinions on foreign policy? 3. The person who urged
Unit VII Study Guide- American Imperialism 1. List the ideas that fueled American Imperialism. 2. How were yellow journalists able to influence Americans opinions on foreign policy? 3. The person who urged
VUS. 8.c&d: Immigration, Discrimination, and The Progressive Era
 Name: Date: Period: VUS 8c&d: Immigration, Discrimination, and The Progressive Era Notes VUS8c&d: Immigration, Discrimination, and the Progressive Era 1 Objectives about Title VUS8 The student will demonstrate
Name: Date: Period: VUS 8c&d: Immigration, Discrimination, and The Progressive Era Notes VUS8c&d: Immigration, Discrimination, and the Progressive Era 1 Objectives about Title VUS8 The student will demonstrate
Populism-agrarian revolt that swept through the Midwest in the late 19 th C.
 The Progressive Era Progressivism Not one single unified movement A wide range of economic, political, social, and moral reforms. Progress to occur through human intervention to solve problems. Origins
The Progressive Era Progressivism Not one single unified movement A wide range of economic, political, social, and moral reforms. Progress to occur through human intervention to solve problems. Origins
Quick Class Discussion: What problems existed within the city, state, and national gov ts?
 During the Gilded Age, city, state, and national governments were in need of reform Corrupt political machines controlled city gov ts Political positions were gained based on patronage not merit Corruption
During the Gilded Age, city, state, and national governments were in need of reform Corrupt political machines controlled city gov ts Political positions were gained based on patronage not merit Corruption
Guided Reading and Analysis: Becoming a World Power,
 Name: Class Period: Guided Reading and Analysis: Becoming a World Power, 1865-1917 Amsco Chapter 20 Reading Assignment: Ch. 21 AMSCO Purpose: This guide is intended to provide a space for you to record
Name: Class Period: Guided Reading and Analysis: Becoming a World Power, 1865-1917 Amsco Chapter 20 Reading Assignment: Ch. 21 AMSCO Purpose: This guide is intended to provide a space for you to record
BELLRINGER. Read the abridged platform of the American Anti- Imperialist League. What is the main argument presented against imperialist policies?
 BELLRINGER Read the abridged platform of the American Anti- Imperialist League. What is the main argument presented against imperialist policies? U.S. INTERVENTION ABROAD Ms. Luco IB Hist Americas LEARNING
BELLRINGER Read the abridged platform of the American Anti- Imperialist League. What is the main argument presented against imperialist policies? U.S. INTERVENTION ABROAD Ms. Luco IB Hist Americas LEARNING
4. During the late 1800s, the port of entry for the majority of immigrants was a. Boston b. New York City c. Philadelphia d.
 Chapters 14-18 Presentations Test 1. The cruise of the Great White Fleet showed that a. the Atlantic could be crossed safely. b. Great Britain was a second-rate power. c. the United States was a naval
Chapters 14-18 Presentations Test 1. The cruise of the Great White Fleet showed that a. the Atlantic could be crossed safely. b. Great Britain was a second-rate power. c. the United States was a naval
CHAPTER 9 THE PROGRESSIVE ERA AMERICA SEEKS REFORMS IN THE EARLY 20 TH CENTURY
 CHAPTER 9 THE PROGRESSIVE ERA AMERICA SEEKS REFORMS IN THE EARLY 20 TH CENTURY ORIGINS OF PROGRESSIVISM As America entered into the 20 th century, middle class reformers addressed many social problems
CHAPTER 9 THE PROGRESSIVE ERA AMERICA SEEKS REFORMS IN THE EARLY 20 TH CENTURY ORIGINS OF PROGRESSIVISM As America entered into the 20 th century, middle class reformers addressed many social problems
The Progressive Era. America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century
 The Progressive Era America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century Goals of Progressive Reformers 1. Protect social welfare (helping the disadvantaged) 2. Promote moral development (making good choices)
The Progressive Era America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century Goals of Progressive Reformers 1. Protect social welfare (helping the disadvantaged) 2. Promote moral development (making good choices)
The Progressive Era AP US History
 The Progressive Era 1900-1920 AP US History Presidents of the Progressive Era Theodore Roosevelt 1901-1909 William H. Taft 1909-1913 Woodrow Wilson 1913-1921 The Progressive Era Defined: Reform movement
The Progressive Era 1900-1920 AP US History Presidents of the Progressive Era Theodore Roosevelt 1901-1909 William H. Taft 1909-1913 Woodrow Wilson 1913-1921 The Progressive Era Defined: Reform movement
Name: ANSWER KEY Date: Mod: Years in Office Political Party Progressive Successes of Administration
 Name: ANSWER KEY Date: Mod: Each of you are now Presidential Historians. In your group, you will be researching and presenting information about the three Progressive Era Presidents Roosevelt, Taft, and
Name: ANSWER KEY Date: Mod: Each of you are now Presidential Historians. In your group, you will be researching and presenting information about the three Progressive Era Presidents Roosevelt, Taft, and
NAME DATE CLASS President McKinley is assassinated
 Lesson 1 The Movement Begins ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why do societies change? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. Which reforms addressed political and economic problems? 2. Why did reformers emerge during this era? Terms
Lesson 1 The Movement Begins ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why do societies change? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. Which reforms addressed political and economic problems? 2. Why did reformers emerge during this era? Terms
Problems Brought About By
 Progressivism Industrialization: Problems Brought About By Industrialization and Urbanization Big Business dominates the economy and monopolies destroy competition; Big Business, with all its wealth and
Progressivism Industrialization: Problems Brought About By Industrialization and Urbanization Big Business dominates the economy and monopolies destroy competition; Big Business, with all its wealth and
All Possible Questions You Will Find in Reading Quiz D
 All Possible Questions You Will Find in Reading Quiz D These questions are used as quizzes. These questions are also 1/3 of the questions for the objective part of the Exam that ends Unit 2, with the other
All Possible Questions You Will Find in Reading Quiz D These questions are used as quizzes. These questions are also 1/3 of the questions for the objective part of the Exam that ends Unit 2, with the other
1. The law that divided reservation land among individual Native Americans
 Loman Honors/US History Midterm Review Chapter 5 1. The law that divided reservation land among individual Native Americans 2. A cattle trail that went from San Antonio, Texas, to rail centers in Kansas
Loman Honors/US History Midterm Review Chapter 5 1. The law that divided reservation land among individual Native Americans 2. A cattle trail that went from San Antonio, Texas, to rail centers in Kansas
U.S. History PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT REVIEWED! THE PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT
 9/28/17 U.S. History 1890-1912 PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT REVIEWED! THE PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT WHY: Industrialization, urbanization, and immigration created significant changes and challenges for the United States.
9/28/17 U.S. History 1890-1912 PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT REVIEWED! THE PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT WHY: Industrialization, urbanization, and immigration created significant changes and challenges for the United States.
American Federation of Labor (AFL) Booker T. Washington. boycotts. child labor. civil rights
 American Federation of Labor (AFL) this was an early union which hoped to organize all working men and women into a single union. This union pursued social reforms like equal pay for equal work, 8 hour
American Federation of Labor (AFL) this was an early union which hoped to organize all working men and women into a single union. This union pursued social reforms like equal pay for equal work, 8 hour
Chapter 17: Becoming a World Power ( )
 Name: Period Page# Chapter 17: Becoming a World Power (1890 1915) Section 1: The Pressure to Expand What factors led to the growth of imperialism around the world? In what ways did the United States begin
Name: Period Page# Chapter 17: Becoming a World Power (1890 1915) Section 1: The Pressure to Expand What factors led to the growth of imperialism around the world? In what ways did the United States begin
Unit 3: The Progressive Era
 Unit 3: The Progressive Era Essential Questions: 1. Can government fix our problems? 2. How did Americans address the problems caused by the Gilded Age? 3. Is a strong president good for our nation? Vocabulary:
Unit 3: The Progressive Era Essential Questions: 1. Can government fix our problems? 2. How did Americans address the problems caused by the Gilded Age? 3. Is a strong president good for our nation? Vocabulary:
APUSH Concept Outline Period 6: 1865 to 1898
 APUSH Concept Outline Period 6: 1865 to 1898 Name Date Overview: The transformation of the United States from an agricultural to an increasingly industrialized and urbanized society brought about significant
APUSH Concept Outline Period 6: 1865 to 1898 Name Date Overview: The transformation of the United States from an agricultural to an increasingly industrialized and urbanized society brought about significant
US History Fall 2013 Final Exam Review
 US History Fall 2013 Final Exam Review Unit 1 - Foundations of Government 1. Define individual rights. Rights, freedom of speech, BILL OF RIGHTS Turn in the Review Sheet on the Day of the Final. 5pts.
US History Fall 2013 Final Exam Review Unit 1 - Foundations of Government 1. Define individual rights. Rights, freedom of speech, BILL OF RIGHTS Turn in the Review Sheet on the Day of the Final. 5pts.
Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved.
 Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. US History Immigration and Foreign policy Blizzard Bag 2014-2015 1. In a 1904 address to Congress, President Theodore Roosevelt stated that the United States
Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. US History Immigration and Foreign policy Blizzard Bag 2014-2015 1. In a 1904 address to Congress, President Theodore Roosevelt stated that the United States
What were the Reconstruction goals of the Radical Republicans? (p.425-6) What organization helped increase literacy rates by 20%? (p.
 American History 11 Final Exam Study Guide Chapter 16: Reconstruction, 1865-1977 Election of 1876? (p.430) Sharecropping (p. 431-2) 14 th Amendment (p.424-5) 15 th Amendment (p.425) What were the Reconstruction
American History 11 Final Exam Study Guide Chapter 16: Reconstruction, 1865-1977 Election of 1876? (p.430) Sharecropping (p. 431-2) 14 th Amendment (p.424-5) 15 th Amendment (p.425) What were the Reconstruction
US History Mr. Martin Unit 7: The Birth of Modern America Chapters 13-16
 US History Mr. Martin Unit 7: The Birth of Modern America Chapters 13-16 This unit explores the transformation of the US from a rural nation into an industrial, urban nation during the period from 1865
US History Mr. Martin Unit 7: The Birth of Modern America Chapters 13-16 This unit explores the transformation of the US from a rural nation into an industrial, urban nation during the period from 1865
Title Student Check Notebook Check Class Notes The West 1890s /15 Class Notes Imperialism (2 days = Double
 In your notebook Title Student Check Notebook Check Class Notes The West 1890s /15 Class Notes Imperialism (2 days = Double /30 Points) Class Notes Philippines Cartoons /15 Class Notes Progressive Era
In your notebook Title Student Check Notebook Check Class Notes The West 1890s /15 Class Notes Imperialism (2 days = Double /30 Points) Class Notes Philippines Cartoons /15 Class Notes Progressive Era
Theodore Roosevelt -rose steadily through gov t ranks. -Spanish American War. -Gov. of NY reform governor. -Vice President of William McKinley
 Theodore Roosevelt -rose steadily through gov t ranks -Spanish American War -Gov. of NY reform governor -Vice President of William McKinley -Became President with McKinley s assassination Square Deal -
Theodore Roosevelt -rose steadily through gov t ranks -Spanish American War -Gov. of NY reform governor -Vice President of William McKinley -Became President with McKinley s assassination Square Deal -
Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War
 Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War 1 Imperialism & Expansion CH 14-1 Imperialism & War Name Reasons why the United States becomes an imperialist nation. 1-New Markets 2-Anglo-Saxonism 3-Modern Navy 4-Into
Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War 1 Imperialism & Expansion CH 14-1 Imperialism & War Name Reasons why the United States becomes an imperialist nation. 1-New Markets 2-Anglo-Saxonism 3-Modern Navy 4-Into
Unit 7: America Comes of Age FRQ Outlines
 Prompt: 2. Analyze the extent to which the Spanish-American War was a turning point in American foreign policy. Re-written as a Question: What was the extent to which the Spanish American war a turning
Prompt: 2. Analyze the extent to which the Spanish-American War was a turning point in American foreign policy. Re-written as a Question: What was the extent to which the Spanish American war a turning
22-1 Study Guide Reform in the Gilded Age, pp
 Soc. St. 8B Name Date Per. Score /10 22-1 Study Guide Reform in the Gilded Age, pp. 630-632 When completed, this assignment will form a study guide for this section of the textbook. You should make corrections
Soc. St. 8B Name Date Per. Score /10 22-1 Study Guide Reform in the Gilded Age, pp. 630-632 When completed, this assignment will form a study guide for this section of the textbook. You should make corrections
APUSH REVIEWED! PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT
 APUSH 1890-1912 PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 28 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 20 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 19-20 THE PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT WHY: Industrialization,
APUSH 1890-1912 PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 28 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 20 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 19-20 THE PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT WHY: Industrialization,
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e. Chapter Nineteen: From Crisis to Empire
 Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e The Politics of Equilibrium Electoral Stability High Turnout for Elections Cultural Basis of Party Identification Catholics Tended to Vote Democrat 2 The Politics of
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e The Politics of Equilibrium Electoral Stability High Turnout for Elections Cultural Basis of Party Identification Catholics Tended to Vote Democrat 2 The Politics of
The Gilded Age. 1870s to 1900s. This Photo by Unknown Author is licensed under CC BY-SA
 The Gilded Age 1870s to 1900s This Photo by Unknown Author is licensed under CC BY-SA Terms to Know civil service system that includes most government jobs, except elected positions, the judiciary, and
The Gilded Age 1870s to 1900s This Photo by Unknown Author is licensed under CC BY-SA Terms to Know civil service system that includes most government jobs, except elected positions, the judiciary, and
The Progressive Era. 1890s-1920
 The Progressive Era 1890s-1920 The Progressive Era A period in history, from 1890 to 1920, where Americans responded to the economic, social and political problems that existed as a result of industrialization
The Progressive Era 1890s-1920 The Progressive Era A period in history, from 1890 to 1920, where Americans responded to the economic, social and political problems that existed as a result of industrialization
Chapter 28: Progressivism and the Republican Roosevelt,
 APUSH CH 28+29 Lecture Name: Hour: Chapter 28: Progressivism and the Republican Roosevelt, 1901-1912 I. The Progressive Era A. What Was It? 1. A time period that focused on correcting political, economic,
APUSH CH 28+29 Lecture Name: Hour: Chapter 28: Progressivism and the Republican Roosevelt, 1901-1912 I. The Progressive Era A. What Was It? 1. A time period that focused on correcting political, economic,
Work Period: Latin America and China Foreign policies Notes President Chart Activity
 USHC 5.0 DEMONSTRATE AN UNDERSTANDING OF DOMESTIC AND FOREIGN DEVELOPMENTS THAT CONTRIBUTED TO THE EMERGENCE OF THE UNITED STATES AS A WORLD POWER IN THE 20 TH CENTURY Opening: Complete pages 185-188 in
USHC 5.0 DEMONSTRATE AN UNDERSTANDING OF DOMESTIC AND FOREIGN DEVELOPMENTS THAT CONTRIBUTED TO THE EMERGENCE OF THE UNITED STATES AS A WORLD POWER IN THE 20 TH CENTURY Opening: Complete pages 185-188 in
The Americans (Survey)
 The Americans (Survey) Chapter 17: TELESCOPING THE TIMES The Progressive Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW In the first two decades of the 1900s, Americans embrace the Progressive movement and many of its reforms.
The Americans (Survey) Chapter 17: TELESCOPING THE TIMES The Progressive Era CHAPTER OVERVIEW In the first two decades of the 1900s, Americans embrace the Progressive movement and many of its reforms.
The Progressive Era. Political, Social, and Economic Reform ( )
 The Progressive Era Political, Social, and Economic Reform (1901-1917) POLITICAL SOCIAL ECONOMIC Expanded Suffrage Decline of Political Machines Increased Party Influence Expanded Workers Rights Assimilation
The Progressive Era Political, Social, and Economic Reform (1901-1917) POLITICAL SOCIAL ECONOMIC Expanded Suffrage Decline of Political Machines Increased Party Influence Expanded Workers Rights Assimilation
Chapter 11 Packet--Dr. Larson
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Chapter 11 Packet--Dr. Larson Matching IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS, PEOPLE, AND PLACES Match each item with the correct statement below. You will not use all the items. a. direct primary
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Chapter 11 Packet--Dr. Larson Matching IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS, PEOPLE, AND PLACES Match each item with the correct statement below. You will not use all the items. a. direct primary
Objective To explain how the progressive movement managed to increase the power of government to regulate business and to protect society from the
 Objective To explain how the progressive movement managed to increase the power of government to regulate business and to protect society from the injustices fostered by big business. What was Progressivism?
Objective To explain how the progressive movement managed to increase the power of government to regulate business and to protect society from the injustices fostered by big business. What was Progressivism?
US History Unit 3 Exam Industrialization, Immigration & Progressive Era 76 Pts
 US History Unit 3 Exam Industrialization, Immigration & Progressive Era 76 Pts Multiple Choice: 1. Which of the following reasons contributed to the success of industrial giants such as John Rockefeller
US History Unit 3 Exam Industrialization, Immigration & Progressive Era 76 Pts Multiple Choice: 1. Which of the following reasons contributed to the success of industrial giants such as John Rockefeller
PROGRESSIVE ERA CCs - CHAPTER 8 (For credit, do not cut and paste. Write in your own handwriting.)
 PROGRESSIVE ERA CCs - CHAPTER 8 (For credit, do not cut and paste. Write in your own handwriting.) PROGRESSIVE PARTY / PROGRESSIVES / PROGRESSIVISM (PINK) Reformers in the late 1800s and early 1900s who
PROGRESSIVE ERA CCs - CHAPTER 8 (For credit, do not cut and paste. Write in your own handwriting.) PROGRESSIVE PARTY / PROGRESSIVES / PROGRESSIVISM (PINK) Reformers in the late 1800s and early 1900s who
Essential U.S. History
 EOY Revision Sheet Social Studies, Level K Page 1 of 10 Mount Auburn International Academy SABIS School Network Social Studies Level K / Grade 9 EOY Grade 9 Social Studies Revision guide For Essential
EOY Revision Sheet Social Studies, Level K Page 1 of 10 Mount Auburn International Academy SABIS School Network Social Studies Level K / Grade 9 EOY Grade 9 Social Studies Revision guide For Essential
CHANGES ON THE WESTERN FRONTIER. Chapter 5
 CHANGES ON THE WESTERN FRONTIER Chapter 5 CULTURES CLASH ON THE PRAIRIE SECTION 1 THE GREAT PLAINS The grasslands in the west-central portion of the U.S. Life centered on the horse and buffalo Great Plains
CHANGES ON THE WESTERN FRONTIER Chapter 5 CULTURES CLASH ON THE PRAIRIE SECTION 1 THE GREAT PLAINS The grasslands in the west-central portion of the U.S. Life centered on the horse and buffalo Great Plains
Unit 6: A New Role in the World
 Unit 6: A New Role in the World Study online at quizlet.com/_1fnvlz 1. alliances 5. conscription An agreement between nations to aid and protect each other. 2. Allies A military draft 6. dollar diplomacy
Unit 6: A New Role in the World Study online at quizlet.com/_1fnvlz 1. alliances 5. conscription An agreement between nations to aid and protect each other. 2. Allies A military draft 6. dollar diplomacy
Chapter Twenty. Commonwealth and Empire
 Chapter Twenty Commonwealth and Empire 1870-1900 Part One: Introduction Commonwealth and Empire What does this painting suggest and American expansion? 3 Chapter Focus Questions What characterized the
Chapter Twenty Commonwealth and Empire 1870-1900 Part One: Introduction Commonwealth and Empire What does this painting suggest and American expansion? 3 Chapter Focus Questions What characterized the
2. How does the Transcontinental Railroad help with the rapid settlement of the West? (p.124)
 U.S. History Fall Semester Exam Review 2015 December 15 th 3 rd and 4 th periods December 16 th 7 th and 8 th periods December 17 th 1 st and 2 nd periods December 18 th 5 th and 6 th periods Westward
U.S. History Fall Semester Exam Review 2015 December 15 th 3 rd and 4 th periods December 16 th 7 th and 8 th periods December 17 th 1 st and 2 nd periods December 18 th 5 th and 6 th periods Westward
How did conditions in eastern Europe in the late 1800s lead to an increase in Jewish immigration?
 Chapter 22 Rise of American Cities 1865-1900 Section 1 Growing Immigration from Europe Ellis Island nationality Thinking Map- Describe Immigration during this time period Who were the new immigrants of
Chapter 22 Rise of American Cities 1865-1900 Section 1 Growing Immigration from Europe Ellis Island nationality Thinking Map- Describe Immigration during this time period Who were the new immigrants of
Welcome to History 12 Political and Social History of the U.S. II From 1876 to the present Prof. Valadez
 Welcome to History 12 Political and Social History of the U.S. II From 1876 to the present Prof. Valadez 1 Topics The U.S. as a World Power Progressive Era 2 Becoming a World Power The New Imperialism
Welcome to History 12 Political and Social History of the U.S. II From 1876 to the present Prof. Valadez 1 Topics The U.S. as a World Power Progressive Era 2 Becoming a World Power The New Imperialism
Imperialism and America
 Chapter 10 America Claims an Empire CHAPTER 10 Section 1 (pages 342-345) Imperialism and America American Expansionism (pages 342-344) Why did Americans support imperialism? In 1893, Queen Liliuokalani
Chapter 10 America Claims an Empire CHAPTER 10 Section 1 (pages 342-345) Imperialism and America American Expansionism (pages 342-344) Why did Americans support imperialism? In 1893, Queen Liliuokalani
The Progressive Movement
 The Progressive Movement Chapter 13 Guided Notes Section 1: I. The Rise of Progressivism (pages 418 420) A. The in American history from about to is known as the. was a collection of different and about
The Progressive Movement Chapter 13 Guided Notes Section 1: I. The Rise of Progressivism (pages 418 420) A. The in American history from about to is known as the. was a collection of different and about
The Progressive Spirit of Reform. Chapter 21 Page 658
 The Progressive Spirit of Reform Chapter 21 Page 658 The Gilded Age and the Progressive Movement Chapter 21 section 1 page 662 Political Corruption In the late 1800s city and county politics were dominated
The Progressive Spirit of Reform Chapter 21 Page 658 The Gilded Age and the Progressive Movement Chapter 21 section 1 page 662 Political Corruption In the late 1800s city and county politics were dominated
The Progressive Era
 The Progressive Era 1890-1920 Bell Work: 10/13/14 (Monday) Now, it is very necessary that we should not flinch from seeing what is vile and debasing. There is filth on the floor, and it must be scraped
The Progressive Era 1890-1920 Bell Work: 10/13/14 (Monday) Now, it is very necessary that we should not flinch from seeing what is vile and debasing. There is filth on the floor, and it must be scraped
Settling the Western Frontier
 Settling the Western Frontier 1860-1890 Library of Congress America Moves West America s desire to expand meant that thousands would migrate to western lands (Manifest Destiny). What are some pull factors?
Settling the Western Frontier 1860-1890 Library of Congress America Moves West America s desire to expand meant that thousands would migrate to western lands (Manifest Destiny). What are some pull factors?
Chapter 22: America Becomes a World Power
 Chapter 22: America Becomes a World Power Objective: Why did the United States become imperialistic and what were the outcomes? Goal: Students will be able to understand the causes and effects of imperialism
Chapter 22: America Becomes a World Power Objective: Why did the United States become imperialistic and what were the outcomes? Goal: Students will be able to understand the causes and effects of imperialism
Ch. 6 & Ch. 7 Test Review COPY OR ADD TO YOUR ANSWERS SO YOU HAVE THE CORRECT INFORMATION TO STUDY FOR YOUR TEST.
 Ch. 6 & Ch. 7 Test Review COPY OR ADD TO YOUR ANSWERS SO YOU HAVE THE CORRECT INFORMATION TO STUDY FOR YOUR TEST. 1. What caused the first boom in the west? 2. Which group of people developed the open-
Ch. 6 & Ch. 7 Test Review COPY OR ADD TO YOUR ANSWERS SO YOU HAVE THE CORRECT INFORMATION TO STUDY FOR YOUR TEST. 1. What caused the first boom in the west? 2. Which group of people developed the open-
Define the following: a. Neutrality Policy. b. Louisiana Purchase. c. War of d. Monroe Doctrine. e. Mexican-American War
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Reading Assignment: Chapter 20 in AMSCO or other resource covering the Spanish American War. Directions: 1. Pre-Read: Read the prompts/questions within this guide before
Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Reading Assignment: Chapter 20 in AMSCO or other resource covering the Spanish American War. Directions: 1. Pre-Read: Read the prompts/questions within this guide before
Progressivism and the Age of Reform
 Progressivism and the Age of Reform This political cartoon shows President Theodore Roosevelt as a hunter who s captured two bears: the good trusts bear he s put on a leash labeled restraint, and the bad
Progressivism and the Age of Reform This political cartoon shows President Theodore Roosevelt as a hunter who s captured two bears: the good trusts bear he s put on a leash labeled restraint, and the bad
Chapter 17. Becoming a World Power ( )
 Chapter 17 Becoming a World Power (1872 1912) 1 Chapter Overview: During this era, economic and military competition from world powers convinced the United States it must be a world power. The United States
Chapter 17 Becoming a World Power (1872 1912) 1 Chapter Overview: During this era, economic and military competition from world powers convinced the United States it must be a world power. The United States
Key Concepts Chart (The Progressive Era)
 Unit 3, Activity 1, Key Concepts Chart Key Concepts Chart (The Progressive Era) Key Concept +? - Explanation Extra Information Knights of Labor American Federation of Labor Industrial Workers of the World
Unit 3, Activity 1, Key Concepts Chart Key Concepts Chart (The Progressive Era) Key Concept +? - Explanation Extra Information Knights of Labor American Federation of Labor Industrial Workers of the World
A Growing Need for Reform
 Progressivism A Growing Need for Reform Tycoons were getting very rich while their workers suffered laissez-faire lack of both business regulation and protection for workers Progressive Era period of much
Progressivism A Growing Need for Reform Tycoons were getting very rich while their workers suffered laissez-faire lack of both business regulation and protection for workers Progressive Era period of much
The Progressive Era
 The Progressive Era 1895 1915 Growing Division Affluence flaunted by the wealthy Progressives Social Darwinism Philosophical approach Big business running small shops out 2% controlled most of the wealth
The Progressive Era 1895 1915 Growing Division Affluence flaunted by the wealthy Progressives Social Darwinism Philosophical approach Big business running small shops out 2% controlled most of the wealth
United States History: 1865 to Present SOL USII. 2 : The student will use maps, globes, photographs, pictures, or tables for explaining:
 United States History: 1865 to Present SOL USII. 2 : The student will use maps, globes, photographs, pictures, or tables for explaining: USII.2a Westward Movement after 1865 : how the physical features
United States History: 1865 to Present SOL USII. 2 : The student will use maps, globes, photographs, pictures, or tables for explaining: USII.2a Westward Movement after 1865 : how the physical features
Progressive Era, Imperialism, and World War 1
 Progressive Era, Imperialism, and World War 1 Section 7.1 Imperialism- a nation desires to gain more territory outside it s borders Reasons for US Imperialism: Economic growth- new people to sell to National
Progressive Era, Imperialism, and World War 1 Section 7.1 Imperialism- a nation desires to gain more territory outside it s borders Reasons for US Imperialism: Economic growth- new people to sell to National
Female progressives often justified their reformist political activities on the basis of???
 Need to know What was President Roosevelt s Gentlemen s Agreement with Japan? Female progressives often justified their reformist political activities on the basis of??? imperialism Stronger nations dominating
Need to know What was President Roosevelt s Gentlemen s Agreement with Japan? Female progressives often justified their reformist political activities on the basis of??? imperialism Stronger nations dominating
Section 1 The Age of Reform
 Section 1 The Age of Reform 1897-1920 Progressivism Video (7 min) DE Streaming with captions. Progressivism A spirit of reform in the early 20 th century Focused on urban problems, poor sanitation, and
Section 1 The Age of Reform 1897-1920 Progressivism Video (7 min) DE Streaming with captions. Progressivism A spirit of reform in the early 20 th century Focused on urban problems, poor sanitation, and
Essential Question: How did America s role in the world change from 1890 to 1914?
 Essential Question: How did America s role in the world change from 1890 to 1914? From 1890 to 1914, the United States expanded its role in world affairs and gained new overseas colonies Class Activity:
Essential Question: How did America s role in the world change from 1890 to 1914? From 1890 to 1914, the United States expanded its role in world affairs and gained new overseas colonies Class Activity:
The Progressive Era. Political Reform
 The Progressive Era Political Reform Progressivism Not one single unified movement A wide range of economic, political, social, and moral reforms. Progress would only occur through human intervention to
The Progressive Era Political Reform Progressivism Not one single unified movement A wide range of economic, political, social, and moral reforms. Progress would only occur through human intervention to
Ch. 4 Industrialization, 5.4 Populism, 6.1 Politics of the Gilded Age Quiz 2011
 Ch. 4 Industrialization, 5.4 Populism, 6.1 Politics of the Gilded Age Quiz 2011 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. IDENTIFYING MAIN IDEAS 1.
Ch. 4 Industrialization, 5.4 Populism, 6.1 Politics of the Gilded Age Quiz 2011 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. IDENTIFYING MAIN IDEAS 1.
Period 6 The Gilded Age and Imperialism Study Guide Chapters 23-26
 Period 6 The Gilded Age and Imperialism Study Guide Chapters 23-26 Chapter #23 Political Paralysis in the Gilded Age Big Picture Themes Name: Date: Hour: 1. President Ulysses S. Grant s administration
Period 6 The Gilded Age and Imperialism Study Guide Chapters 23-26 Chapter #23 Political Paralysis in the Gilded Age Big Picture Themes Name: Date: Hour: 1. President Ulysses S. Grant s administration
The United States Looks Overseas
 The United States Looks Overseas 1853-1915 Interact with History In 1893, American sugar planters in the Kingdom of Hawaii thought they could make more money if Hawaii were an American state. So they staged
The United States Looks Overseas 1853-1915 Interact with History In 1893, American sugar planters in the Kingdom of Hawaii thought they could make more money if Hawaii were an American state. So they staged
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century)
 The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 6: TELESCOPING THE TIMES A New Industrial Age CHAPTER OVERVIEW Technological innovations and the growth of the railroad industry help fuel an
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 6: TELESCOPING THE TIMES A New Industrial Age CHAPTER OVERVIEW Technological innovations and the growth of the railroad industry help fuel an
U.S. Imperialism s Impact on Other Nations
 U.S. Imperialism s Impact on Other Nations U.S.-Japanese Relations Japan had closed itself to outsiders in the late 1400s; held a strong mistrust of Western cultures In mid-1800s, US businesses began to
U.S. Imperialism s Impact on Other Nations U.S.-Japanese Relations Japan had closed itself to outsiders in the late 1400s; held a strong mistrust of Western cultures In mid-1800s, US businesses began to
The Gilded Age leads to the Progressive Era
 The Gilded Age leads to the Progressive Era After the War How do you think the goals of the nation will change after Reconstruction? What innovations or developments are created during the late 1800 s?
The Gilded Age leads to the Progressive Era After the War How do you think the goals of the nation will change after Reconstruction? What innovations or developments are created during the late 1800 s?
Due Friday, 12/ , a k: a. Gilded Age: the time period after the Civil War, between the 1870s and 1890s. Gilded is to coat with a thin layer
 Due Friday, 12/23 644 648, a k: a. Gilded Age: the time period after the Civil War, between the 1870s and 1890s. Gilded is to coat with a thin layer of gold, and the term Gilded Age suggests that beneath
Due Friday, 12/23 644 648, a k: a. Gilded Age: the time period after the Civil War, between the 1870s and 1890s. Gilded is to coat with a thin layer of gold, and the term Gilded Age suggests that beneath
