Expert Opinion. On the prohibition of forcible transfer in Susya Village
|
|
|
- Jeremy Lewis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 30 June 2012 Expert Opinion On the prohibition of forcible transfer in Susya Village I the undersigned was requested by Rabbis for Human Rights to provide an expert opinion regarding the legality of execution of demolition orders for the Susya Village buildings, due to its forbidden outcomes, i.e., the expected forcible transfer of the civil population. This opinion is based on the provisions of the international law. I am providing this opinion without remuneration. Background As background to my opinion, I shall note the merits of the facts pertaining to the matter as they were provided to me: In 1986, the residents of Susya were deported from their private lands in ancient Susya, following their expropriated for "public needs", without being offered an alternative residence. They settled on their lands located approximately 500 meters from their village. In 1991 they were deported from that location as well, regarding which it was later claimed, that the deportation was performed due to enforcement of planning and building laws. Consequently, they settled on their agricultural lands, which are until today their place of residence. During 2001 all their houses were demolished for the third time and it was again claimed in respect to this deportation that it was performed due to enforcement of planning and building laws. The residents attempted throughout the years to settle the issue of building permits in the village area by submitting building permit applications etc. On 12 June 2012 notices were distributed regarding the right to submit a demurrer prior to the execution of the demolition of 70 structures in the village which include 24 residential buildings, 21 structures serving as sheep pens and chicken coops, five structures for two solar electricity systems, five outdoor stoves (taboons) which are used as baking stoves for whole families, six latrines, three warehouses, one clinic, one cultural center, one grocery store, one churn and two water cisterns. If these structures are demolished, around 20 structures, which constitute approximately 20 percent of the village houses today (who are also under demolition danger) shall remain in the village. Therefore, the implication of the demolition will be the actual deletion of an entire village including its residential houses, its public institutions, the facilities necessary for it survival on its location, and the sources of livelihood of its residents. As has happened in the past, demolishing the village's structures will force its residents to wander across the area until they find alternative residential locations and sources of livelihood. This time, there is much doubt whether they will be indeed successful to accomplish that, as there is no land which they own left where they are permitted to pitch their tents and rebuild their homes. The legal aspects
2 1. The area in which the residents of Susya village are located is an area under belligerent occupation on which the rules of international law regarding belligerent occupation apply, including the Hague Regulations of 1907 (hereinafter Hague Regulations), the Fourth Geneva Convention regarding protection of civilians during wartime of 1949 (hereinafter Geneva Convention), and the First Additional Protocol to the Geneva Convention of 1977 (hereinafter the Protocol). Israel is not a party to the Hague Regulations, but they are recognized as customary law and therefore bind Israel and also apply in its domestic law. Israel is a party to the Geneva Convention. Article 49 of the Geneva Convention in which my opinion shall focus is accepted among states and by the international jurisprudence as reflecting customary law and therefore it also applies in the Israeli domestic law. Israel is not a party to the Protocol but the provisions discussed in my Opinion are accepted as reflecting customary law and therefore they apply in the Israeli law. For specification of states consistent practice and rulings of the national and international courts see: International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC), Practice Relating to Rule 129. The Act of Displacement A. General 1. Article 49 (1) of the Geneva Convention sets forth: "Individual or mass forcible transfers, as well as deportations of protected persons from occupied territory to the territory of the Occupying Power or to that of any other country, occupied or not, are prohibited, regardless of their motive." As previously stated the above article reflects a customary law which binds the Respondents and which overrides the instructions of the military commander in case of conflict. Not only is the prohibition itself customary, but the sanction for its violation, which is a penal sanction is customary as well. Violation of Article 49 (1) constitutes a grave breach of the Geneva Convention (as noted in Article 147 of the Geneva Convention) which means a "war crime", and the Statute of the International Criminal Court (hereinafter ICC) includes this grave breach among the "war crimes" which are within the jurisdiction of the ICC. This means that anyone who performs an act in an area under belligerent occupation, which result is forcible transfer or deportation is personally responsible for the commission of a war crime. According to the document defining the elements of the offence for purpose of activating the jurisdiction of the ICC, the elements of the crime of forcible transfer or deportation of protected persons include:
3 1. The perpetrator deported or transferred one or more persons to another State or to another location. 2. Such person or persons were protected under one or more of the Geneva Conventions of The perpetrator was aware of the factual circumstances that established that protected status. 4. The conduct took place in the context of and was associated with an international armed conflict. 5. The perpetrator was aware of factual circumstances that established the existence of an armed conflict. Elements of Crime, Article 8 (2) (a) (vii)-1, War crime of unlawful deportation and transfer, available at There is no requirement that the person intended to cause the transfer or deportation, it is sufficient that he was aware that this is an expected outcome of his action. Article 30 of the ICC Constitution sets forth: 1. Unless otherwise provided, a person shall be criminally responsible and liable for punishment for a crime within the jurisdiction of the Court only if the material elements are committed with intent and knowledge. 2. For the purpose of this article, a person has intent where: (a) In relation to conduct, that person means to engage in the conduct; (b) In relation to a consequence, that person means to cause that consequence or is aware that it will occur in the ordinary course of events. 3. For the purposes of this article, "knowledge" means awareness that a circumstance exists or a consequence will occur in the ordinary course of events. "Know" and "Knowingly" shall be construed accordingly. 2. Section 49 (1) of the Convention relates to any transfer of protected population from wherever it is located, whether the issue is a transfer inside the occupied territory, or deportation outside that territory. This clearly arises from the travaux preparatoire of the Geneva Convention. See Final Record of the Diplomatic Conference of Geneva of 1949, Vol. IIa (1949), p. 827:
4 [T]he Committee have [sic] decided on a wording which prohibits individual or mass forcible removals as well as deportations of protected persons from occupied territory to any other country. The unimportance of the distinction between transfer within the occupied territory and deportation beyond the boundaries of the territory was discussed by the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia (ICTY), which stated: 521. Both deportation and forcible transfer relates to the involuntary and unlawful evacuation of individuals from the territory in which they reside. Yet, the two are not synonymous in customary international law. Deportation presumes transfer beyond State borders, whereas forcible transfer relates to displacements within a State However, this distinction has no bearing on the condemnation of such practices in international humanitarian law. Article 2(g) of the Statute, Articles 49 and 147 of the Geneva Convention concerning the Protection of Civilian Persons in Times of War (Fourth Geneva Convention), Article 85 (4) (a) of Additional Protocol I, Article 18 of the ILC Draft Code and Article 7 (1) (d) of the Statute of the International Criminal Court all condemn deportation or forcible transfer of protected persons. Article 17 of Protocol II likewise condemns the "displacement" of civilians In this regard, the Trial Chamber Notes that any forced displacement is by definition a traumatic experience which involves abandoning one's home, losing property and being displaced under duress to another location. ICTY, Prosecutor v. Radislav Krstic, IT T, Trial Chamber, Judgment, (2001) (Footnotes omitted). 3. The prohibition is absolute and has no exception save those which are included in Article 49 (2) and which were intended, at the time of hostilities in the area, to protect the displaced persons themselves, or for imperative military needs, which too are limited by the temporariness of the transfer and the right of the displaced to return immediately upon termination of the hostilities in the area. As determined by the commentator of the International Committee of the Red Cross: The prohibition is absolute and allows no exceptions. See ICRC commentary, available at The significance of the absolute prohibition is that in a situation which is not an actual state of combat, considerations and constraints which are not connected to the security of the displaced protected civilians, or
5 imperative military needs, cannot serve as basis to "balance" vis-à-vis the absolute right of the protected civilians to remain where they are. The absoluteness of the prohibition stems for the dark history of Second World War, where the phenomena of deportation for various reasons were prevalent. As the ICRC commentator states: These mass transfers took place for the greatest possible variety of reasons, mainly as a consequence of the formation of a forced labour service. The thought of the physical and mental suffering endured by these "displaced persons", among whom there were a great many woman, children, old people and sick, can only lead to thankfulness for the prohibition embodied in this paragraph, which is intended to forbid such hateful practices for all time. See ICRC commentary, available at 4. The terms "forcible transfer or deportation" in Article 49 of the Convention should be construed broadly, in order to fulfill the purpose of the Convention, which is the protection of protected persons; and in light of the ability of the occupying army to adversely use different rationales and take diversed indirect measures by manner that causes the protected persons to leave their location. 5. Accordingly it was set forth that the transfer is "forcible" even when it is not accompanied by the exercise of direct physical force on protected persons with the purpose to cause their departure. Creating the circumstances which indirectly cause the departure of protected persons shall be considered as prohibited transfer. See the consistent ruling of the ICTY on this issue: 475. "Forced" is not to be interpreted in a restrictive manner, such as being limited to physical force. It may include the "threat of force or coercion, such as that caused by fear of violence, duress, detention, psychological oppression or abuse of power against such person or persons or another person, or by taking advantage of a coercive environment". The essential element is that the displacement be involuntary in nature, where the relevant persons had no real choice. ICTY, PROSECUTOR v. MILORAD KRNOJELAC, Trial Chamber, Judgment, IT T (2002) (footnotes omitted). Additionally: 519. Transfers motivated by an individual's own genuine wish to leave, are lawful. In determining whether a transfer is based on an individuals [sic] "own wish" the Chamber is assisted by Article 31 of the Geneva Convention IV. It provides for a general prohibition of physical and
6 moral coercion covering pressure that is direct or indirect, obvious or hidden and further holds that this prohibition "applies in so far as the other provisions of the Conventions do not implicitly or explicitly authorise a resort to coercion". The jurisprudence of the Tribunal also supports that the term 'forcible' should not be restricted to physical coercion. [ ] The determination as to whether a transferred person had a "real choice" has to be made in the context of all relevant circumstances on a case by case basis. Forcible transfer is the movement of individuals under duress from where they reside to a place that is not of their choosing. ICTY, PROSECUTOR v. NALETILIC and Vinko MARTINOVIC, IT T, Trial Chamber, Judgment (2003) (footnotes omitted). And also: 281. The term "forced", when used in reference to the crime of deportation, is not to be limited to physical force but includes the threat of force or coercion, such as that caused by fear of violence, duress, detention, psychological oppression or abuse or power against such person or persons or another person, or by taking advantage of a coercive environment. ICTY, PROSECUTOR v. Milomir Stakic, Case No. IT T, Appeals Chamber, Judgment (2006) (footnotes omitted). In another case the Trial Chamber mentions actions such as discharge from workplace, house searches and disconnection of the houses from water, electric power and telephone line as part of the move to create severe living conditions for the residents, which were intended to cause the people to leave their home, which amounts to forcible transfer as previously mentioned: ICTY, PROSECUTOR v. Momčilo Krajišnik Case No. IT T, Trial Chamber I, Judgment (2006), Para In addition to violation of the provisions of Article 49 (1) of the Geneva Convention, the planned demolition of structures is also prohibited by itself. It is contrary to the customary provision that is included in Article 54 of the Protocol that prohibits demolition or damage to structures that are indispensable for the survival of the protected civilian population: 1. Starvation of civilians as a method of warfare is prohibited. 2. It is prohibited to attack, destroy, remove or render useless objects indispensable to the survival of the civilian population, such as foodstuffs, agricultural areas for the production of foodstuffs, crops, livestock, drinking water installations and supplies and irrigation works, for the specific purpose of denying them for their sustenance value to the civilian population or to the adverse Party, whatever the motive, whether in order to starve out civilians, to cause them to move away, or for any other motive.
7 The foregoing Article 54 constitutes a private case to the general rule prohibiting demolition of civilian structures in the occupied territory, which is anchored in Article 53 of the Fourth Geneva Convention: Art. 53. Any destruction by the Occupying Power of real or personal property belonging individually or collectively to private persons, or to the State, or to other public authorities, or to social or cooperative organizations, is prohibited, except where such destruction is rendered absolutely necessary by military operations. See on this issue my opinion regarding the demolition of structure which are indispensable for the survival of the protected civilian population due to the absence of a building permit, which was submitted in the scope of HCJ 5667/11 The Council of Dirat Rafiya Village et al v. the Minister of Defense et al as well as the opinion of Sassoli and Boutruche Expert Opinion on International Humanitarian Law Requiring of the Occupying Power to Transfer Back Planning Authority to Protected Persons Regarding area C of the West Bank by Dr. Theo Boutruche and Prof. Marco Sassoli (hereinafter: "Sassoli Opinion"), that was submitted in the scope of HCJ 5667/11 The council of Dirat Rafiya Village et al v. the Minister of Defense et al 7. The demolition of facilities which are indispensable for protection of the population and without providing it with an alternative protection is contrary to the general duty that is imposed on the Respondents to care for the needs of the protected population under the provisions of Article 43 of the Hague Regulations and the various instructions of the Geneva Convention dealing in assuring the security and welfare of the protected residents in an area under belligerent occupation. This duty also stems from human rights law, which applies in belligerent occupation as well. See on this issue my opinion hereinabove mentioned as well as my book Eyal Benvenisti, The International Law of Occupation (2 nd Ed., 2012). b. Applying the law on the facts of the case 1. The meaning of executing the demolition orders as discussed this Opinion is an actual "transfer" according to its meaning in Article 49 (1) of the Geneva Convention. Despite the fact that this time it is not transfer or deportation through the use of direct force, the aforementioned Article prohibits "transfer" or "deportation" directly or indirectly, of individuals or groups of protected residents. Indirect transfer or deportation are performed in this case by creating the physical conditions that oblige the protected persons to leave the location where they are against their will.
8 This will be the actual situation following the execution of the demolition orders: pursuant the planned demolition of structures, there will be no way to survive in the area of the village without shelter and other facilities that ensure the sustenance and livelihood of the residents. The destruction of all the structures in the village is the de-facto forcible transfer of more than 200 men, woman and children. 2. The transfer is "forcible" in the meaning of Article 49 (1) hereinabove since the residents of a village reside on land that belongs to them. They are not interested in abandoning the lands of their village and in any event have no place to go. 3. In addition to the indirect transfer, the demolition of structures in the village as hereinabove described constitutes demolition of structures which are indispensable for survival of the village residents, which is also prohibited, as provided in Article 6 hereinabove. 4. Of course, logic requires that the prohibition on transfer or deportation shall not apply on evacuation from a location where the protected people settled of their own free will following the beginning of the belligerent occupation and contrary to the local law as applying in the area. That, as long as the evacuation process itself is lawful according to the domestic law and the provisions of the international humanitarian law and human rights law. This condition is not fulfilled in the current case. In addition to the afore described, one should take into consideration that the exercise of planning and building laws by the planning institutions of the civil administration in area C in general and in this case especially, is performed while violating the international humanitarian law and the human rights law. On that issue see: Eyal Benvenisti, The International Law of Occupation 214, 247 (2nd Ed., 2012): Order No. 418 concerning Towns, Villages, and Building Planning Law from 1971 flattened the hierarchical system of the Jordanian building planning law and transferred the authorities of the district planning committees to the central planning council. The latter, manned by appointees of the military commander, among them Jewish settlers, would allow no formal input by the Palestinian inhabitants. This had adverse effects on the possibility of Palestinians obtaining building permits, and turned the permit system into a disciplinary tool of applicants or those many whose frustration with the system prompted them to build without a permit, granting or denying building permits according to the applicants willingness to cooperate. [ ] In principle, the standard practice of occupants should involve the occupied population as much as possible in the administration especially
9 as the occupation lingers on. The long term occupant is required to provide for and pay ample attention to the input of the occupied community regarding the management of the latter s country. (Also see the Sassoli Opinion and my opinion previously mentioned in Article 6 hereinabove). 5. Therefore, my conclusion is that the execution of the demolition orders means in fact the issuance of a deportation order to the residents of the village. This move shall constitute a violation of Article 49 (1) of the Geneva Convention, and will also impose personal criminal liability on those responsible thereof. It shall additionally constitute a violation of the rule prohibiting demolition or damage to structures which are indispensable for the survival of the protected civilian population as well as violation of the duty to ensure the needs of the protected population are provided and human rights law that applies in the area such as the right to family, to adequate standard of living including the right for adequate housing. [signature] Professor Eyal Benvenisti
***Unofficial Translation from Hebrew***
 Expert Opinion: September 5, 2011 Regarding the Destruction of Structures Essential for the Survival of the Protected Civilian Population due to Lack of Construction Permits (HCJ 5667/11) By Professor
Expert Opinion: September 5, 2011 Regarding the Destruction of Structures Essential for the Survival of the Protected Civilian Population due to Lack of Construction Permits (HCJ 5667/11) By Professor
FORCIBLE TRANSFER: ESSENTIAL LEGAL PRINCIPLES A REFERENCE GUIDE FOR PRACTITIONERS AND POLICY-MAKERS
 FORCIBLE TRANSFER: ESSENTIAL LEGAL PRINCIPLES A REFERENCE GUIDE FOR PRACTITIONERS AND POLICY-MAKERS July 2015 About BADIL BADIL Resource Center for Palestinian Residency and Refugee Rights, located in
FORCIBLE TRANSFER: ESSENTIAL LEGAL PRINCIPLES A REFERENCE GUIDE FOR PRACTITIONERS AND POLICY-MAKERS July 2015 About BADIL BADIL Resource Center for Palestinian Residency and Refugee Rights, located in
FORCIBLE TRANSFER: ESSENTIAL LEGAL PRINCIPLES A REFERENCE GUIDE FOR PRACTITIONERS AND POLICY-MAKERS
 FORCIBLE TRANSFER: ESSENTIAL LEGAL PRINCIPLES A REFERENCE GUIDE FOR PRACTITIONERS AND POLICY-MAKERS About BADIL BADIL Resource Center for Palestinian Residency and Refugee Rights, located in Bethlehem
FORCIBLE TRANSFER: ESSENTIAL LEGAL PRINCIPLES A REFERENCE GUIDE FOR PRACTITIONERS AND POLICY-MAKERS About BADIL BADIL Resource Center for Palestinian Residency and Refugee Rights, located in Bethlehem
Setting a time limit: The case for a protocol on prolonged occupation
 Setting a time limit: The case for a protocol on prolonged occupation Itay Epshtain 11 May 2013 Given that international law does not significantly distinguish between short-term and long-term occupation,
Setting a time limit: The case for a protocol on prolonged occupation Itay Epshtain 11 May 2013 Given that international law does not significantly distinguish between short-term and long-term occupation,
Cordula Droege Legal adviser, ICRC
 DEVELOPMENTS IN THE LEGAL PROTECTION OF INTERNALLY DISPLACED PERSONS 10 YEARS OF EXPERIENCE SINCE THE GUIDING PRINCIPLES Cordula Droege Legal adviser, ICRC It has been 10 years since the then special representative
DEVELOPMENTS IN THE LEGAL PROTECTION OF INTERNALLY DISPLACED PERSONS 10 YEARS OF EXPERIENCE SINCE THE GUIDING PRINCIPLES Cordula Droege Legal adviser, ICRC It has been 10 years since the then special representative
Opinion. Guy S. Goodwin-Gill Senior Research Fellow, All Souls College, Oxford Barrister
 Opinion Re Certain Legal Issues Arising from the Application of Israel to become a Member of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development Guy S. Goodwin-Gill Senior Research Fellow, All Souls
Opinion Re Certain Legal Issues Arising from the Application of Israel to become a Member of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development Guy S. Goodwin-Gill Senior Research Fellow, All Souls
entry into force 7 December 1978, in accordance with Article 23
 Protocol Additional to the Geneva Conventions of 12 August 1949, and Relating to the Protection of Victims of Non-International Armed Conflicts (Protocol II) Adopted on 8 June 1977 by the Diplomatic Conference
Protocol Additional to the Geneva Conventions of 12 August 1949, and Relating to the Protection of Victims of Non-International Armed Conflicts (Protocol II) Adopted on 8 June 1977 by the Diplomatic Conference
[on official letterhead of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs Jerusalem, Office of the Director General]
![[on official letterhead of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs Jerusalem, Office of the Director General] [on official letterhead of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs Jerusalem, Office of the Director General]](/thumbs/76/73155402.jpg) [on official letterhead of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs Jerusalem, Office of the Director General] Disclaimer: The following is a non-binding translation of the original Hebrew document. It is provided
[on official letterhead of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs Jerusalem, Office of the Director General] Disclaimer: The following is a non-binding translation of the original Hebrew document. It is provided
Housing, Land and Property Rights and International Criminal Justice. Holding HLP Rights Violators Accountable September 2012
 Housing, Land and Property Rights and International Criminal Justice Holding HLP Rights Violators Accountable September 2012 Foreword Crimes against the home are commonplace in situations of armed conflict,
Housing, Land and Property Rights and International Criminal Justice Holding HLP Rights Violators Accountable September 2012 Foreword Crimes against the home are commonplace in situations of armed conflict,
SUMMARY TABLE OF IHL PROVISIONS
 SUMMARY TABLE OF IHL PROVISIONS SPECIFICALLY APPLICABLE TO CHILDREN Summary table of provisions of international humanitarian law and other provisions of international law specifically applicable to children
SUMMARY TABLE OF IHL PROVISIONS SPECIFICALLY APPLICABLE TO CHILDREN Summary table of provisions of international humanitarian law and other provisions of international law specifically applicable to children
Transfer of the Civilian Population in International Law
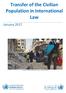 Transfer of the Civilian Population in International Law January 2017 Civilian evacuation of Daraya, 26 August 2016 (Photo AP) An increasing number of localised ceasefire agreements are being agreed between
Transfer of the Civilian Population in International Law January 2017 Civilian evacuation of Daraya, 26 August 2016 (Photo AP) An increasing number of localised ceasefire agreements are being agreed between
Internment in Armed Conflict: Basic Rules and Challenges. International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) Opinion Paper, November 2014
 Internment in Armed Conflict: Basic Rules and Challenges International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) Opinion Paper, November 2014 1. Introduction Deprivation of liberty - detention - is a common and
Internment in Armed Conflict: Basic Rules and Challenges International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) Opinion Paper, November 2014 1. Introduction Deprivation of liberty - detention - is a common and
Iraq, Forced displacement and deliberate destruction
 Published on How does law protect in war? - Online casebook (https://casebook.icrc.org) Home > Iraq, Forced displacement and deliberate destruction Iraq, Forced displacement and deliberate destruction
Published on How does law protect in war? - Online casebook (https://casebook.icrc.org) Home > Iraq, Forced displacement and deliberate destruction Iraq, Forced displacement and deliberate destruction
ANNEX I: APPLICABLE INTERNATIONAL LEGAL FRAMEWORK
 ANNEX I: APPLICABLE INTERNATIONAL LEGAL FRAMEWORK The legal framework applicable to the targeting of schools and universities, and the use of schools and universities in support of the military effort,
ANNEX I: APPLICABLE INTERNATIONAL LEGAL FRAMEWORK The legal framework applicable to the targeting of schools and universities, and the use of schools and universities in support of the military effort,
ACT ON THE PUNISHMENT OF CRIMES WITHIN THE JURISDICTION OF THE INTERNATIONAL CRIMINAL COURT
 ACT ON THE PUNISHMENT OF CRIMES WITHIN THE JURISDICTION OF THE INTERNATIONAL CRIMINAL COURT Act on the Punishment of Crimes within the Jurisdiction of the International Criminal Court Enacted on December
ACT ON THE PUNISHMENT OF CRIMES WITHIN THE JURISDICTION OF THE INTERNATIONAL CRIMINAL COURT Act on the Punishment of Crimes within the Jurisdiction of the International Criminal Court Enacted on December
Draft of an Act to Introduce the Code of Crimes against International Law
 BMJ, Referat II A 5 - Sa (/VStGB/Entwürfe/RegEntw-fin.doc) As of 28 December 2001 Draft of an Act to Introduce the Code of Crimes against International Law The Federal Parliament has passed the following
BMJ, Referat II A 5 - Sa (/VStGB/Entwürfe/RegEntw-fin.doc) As of 28 December 2001 Draft of an Act to Introduce the Code of Crimes against International Law The Federal Parliament has passed the following
EU GUIDELINES on INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW
 EU GUIDELINES on INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW Contents 1_ Purpose 127 2_ International humanitarian law (IHL) 127 Introduction 127 Evolution and sources of IHL 128 Scope of application 128 International
EU GUIDELINES on INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW Contents 1_ Purpose 127 2_ International humanitarian law (IHL) 127 Introduction 127 Evolution and sources of IHL 128 Scope of application 128 International
Command Responsibility. Joaquin G. Bernas, S.J. The death and disappearances of members of media and of people with the same
 Command Responsibility Joaquin G. Bernas, S.J. The death and disappearances of members of media and of people with the same ideological leanings have become an almost daily occurrence and have triggered
Command Responsibility Joaquin G. Bernas, S.J. The death and disappearances of members of media and of people with the same ideological leanings have become an almost daily occurrence and have triggered
THE LAW IN THESE PARTS. Occupation is a legal concept.
 THE LAW IN THESE PARTS Occupation is a legal concept. WHAT IS INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW (IHL)? Part of international law that was adopted to govern relations between states. IHL is a set of rules
THE LAW IN THESE PARTS Occupation is a legal concept. WHAT IS INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW (IHL)? Part of international law that was adopted to govern relations between states. IHL is a set of rules
Implementation of International Humanitarian Law. Dr. Benarji Chakka Associate Professor
 Implementation of International Humanitarian Law Dr. Benarji Chakka Associate Professor International Humanitarian Law: What it is? IHL is a set of rules that seeks, for humanitarian reasons, to limit
Implementation of International Humanitarian Law Dr. Benarji Chakka Associate Professor International Humanitarian Law: What it is? IHL is a set of rules that seeks, for humanitarian reasons, to limit
HAUT-COMMISSARIAT AUX DROITS DE L HOMME OFFICE OF THE HIGH COMMISSIONER FOR HUMAN RIGHTS PALAIS DES NATIONS 1211 GENEVA 10, SWITZERLAND
 HAUT-COMMISSARIAT AUX DROITS DE L HOMME OFFICE OF THE HIGH COMMISSIONER FOR HUMAN RIGHTS PALAIS DES NATIONS 1211 GENEVA 10, SWITZERLAND Mandates of the Special Rapporteur on adequate housing as a component
HAUT-COMMISSARIAT AUX DROITS DE L HOMME OFFICE OF THE HIGH COMMISSIONER FOR HUMAN RIGHTS PALAIS DES NATIONS 1211 GENEVA 10, SWITZERLAND Mandates of the Special Rapporteur on adequate housing as a component
LAW SCHOOL, TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY BEIJING, CHINA PARTICIPANTS: ZHANG XUE, GU XIN, CUINING MEMORIAL FOR THE RESPONDENT
 LAW SCHOOL, TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY BEIJING, CHINA PARTICIPANTS: ZHANG XUE, GU XIN, CUINING MEMORIAL FOR THE RESPONDENT Word Count: 2000 1 TEAM BJIHL1102 MEMORIAL FOR THE RESPONDENT * * OSCOLA (4th edn) as
LAW SCHOOL, TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY BEIJING, CHINA PARTICIPANTS: ZHANG XUE, GU XIN, CUINING MEMORIAL FOR THE RESPONDENT Word Count: 2000 1 TEAM BJIHL1102 MEMORIAL FOR THE RESPONDENT * * OSCOLA (4th edn) as
5 th RED CROSS INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW MOOT. International Criminal Court
 5 th RED CROSS INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW MOOT International Criminal Court THE PROSECUTOR OF THE COURT AGAINST DAVID DABAR MEMORIAL FOR THE APPLICANT Law School, Peking University Jiang Bin & Zhou
5 th RED CROSS INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW MOOT International Criminal Court THE PROSECUTOR OF THE COURT AGAINST DAVID DABAR MEMORIAL FOR THE APPLICANT Law School, Peking University Jiang Bin & Zhou
STATUTE OF THE INTERNATIONAL CRIMINAL TRIBUNAL
 STATUTE OF THE INTERNATIONAL CRIMINAL TRIBUNAL FOR THE FORMER YUGOSLAVIA By Fausto Pocar President of the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia On 6 October 1992, amid accounts of widespread
STATUTE OF THE INTERNATIONAL CRIMINAL TRIBUNAL FOR THE FORMER YUGOSLAVIA By Fausto Pocar President of the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia On 6 October 1992, amid accounts of widespread
PCHR and LAW Position Paper on the Conference of High Contracting Parties to the Fourth Geneva Convention
 PCHR and LAW Position Paper on the Conference of High Contracting Parties to the Fourth Geneva Convention As depositary of the Geneva Conventions, the government of Switzerland has called a conference
PCHR and LAW Position Paper on the Conference of High Contracting Parties to the Fourth Geneva Convention As depositary of the Geneva Conventions, the government of Switzerland has called a conference
CHAPTER 1 BASIC RULES AND PRINCIPLES
 CHAPTER 1 BASIC RULES AND PRINCIPLES Section I. GENERAL 1. Purpose and Scope The purpose of this Manual is to provide authoritative guidance to military personnel on the customary and treaty law applicable
CHAPTER 1 BASIC RULES AND PRINCIPLES Section I. GENERAL 1. Purpose and Scope The purpose of this Manual is to provide authoritative guidance to military personnel on the customary and treaty law applicable
International Environmental Criminal Law. Amissi Melchiade Manirabona Researcher: UdeM/McGill
 International Environmental Criminal Law Amissi Melchiade Manirabona Researcher: UdeM/McGill Thursday 2 July 2009 13h30 16h30 General Considerations: Why Criminal Law in Int l Evtl Matters? Introduction
International Environmental Criminal Law Amissi Melchiade Manirabona Researcher: UdeM/McGill Thursday 2 July 2009 13h30 16h30 General Considerations: Why Criminal Law in Int l Evtl Matters? Introduction
THE ICRC'S CLARIFICATION PROCESS ON THE NOTION OF DIRECT PARTICIPATION IN HOSTILITIES UNDER INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW NILS MELZER
 THE ICRC'S CLARIFICATION PROCESS ON THE NOTION OF DIRECT PARTICIPATION IN HOSTILITIES UNDER INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW NILS MELZER Dr. Nils Melzer is legal adviser for the International Committee of
THE ICRC'S CLARIFICATION PROCESS ON THE NOTION OF DIRECT PARTICIPATION IN HOSTILITIES UNDER INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW NILS MELZER Dr. Nils Melzer is legal adviser for the International Committee of
GENERAL AND SPECIFIC PROTECTION OF WOMEN UNDER INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW
 ANNEX TO THE GUIDANCE DOCUMENT GENERAL AND SPECIFIC PROTECTION OF WOMEN UNDER INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW This Annex includes both the general and specific protection afforded to women under international
ANNEX TO THE GUIDANCE DOCUMENT GENERAL AND SPECIFIC PROTECTION OF WOMEN UNDER INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW This Annex includes both the general and specific protection afforded to women under international
Refugee Law: Introduction. Cecilia M. Bailliet
 Refugee Law: Introduction Cecilia M. Bailliet Mali Refugees Syrian Refugees Syria- Refugees and IDPs International Refugee Organization Refugee: Person who has left, or who is outside of, his country of
Refugee Law: Introduction Cecilia M. Bailliet Mali Refugees Syrian Refugees Syria- Refugees and IDPs International Refugee Organization Refugee: Person who has left, or who is outside of, his country of
Background Paper on Geneva Conventions and Persons Held by U.S. Forces
 Background Paper on Geneva Conventions and Persons Held by U.S. Forces January 29, 2002 Introduction 1. International Law and the Treatment of Prisoners in an Armed Conflict 2. Types of Prisoners under
Background Paper on Geneva Conventions and Persons Held by U.S. Forces January 29, 2002 Introduction 1. International Law and the Treatment of Prisoners in an Armed Conflict 2. Types of Prisoners under
Art. 61. Troops that give no quarter have no right to kill enemies already disabled on the ground, or prisoners captured by other troops.
 Criminalizing War (1) Discovering crimes in war (2) Early attempts to regulate the use of force in war (3) International Military Tribunal (Nuremberg trial) (4) International Military Tribunal for the
Criminalizing War (1) Discovering crimes in war (2) Early attempts to regulate the use of force in war (3) International Military Tribunal (Nuremberg trial) (4) International Military Tribunal for the
EN 32IC/15/19.3 Original: English
 EN 32IC/15/19.3 Original: English 32nd INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE OF THE RED CROSS AND RED CRESCENT Geneva, Switzerland 8-10 December 2015 Sexual and gender-based violence: joint action on prevention and
EN 32IC/15/19.3 Original: English 32nd INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE OF THE RED CROSS AND RED CRESCENT Geneva, Switzerland 8-10 December 2015 Sexual and gender-based violence: joint action on prevention and
No Peace Without Justice in Syria
 Physicians for Human Rights No Peace Without Justice in Syria March 2016 phr.org No Peace Without Justice in Syria 1 About Physicians for Human Rights For 30 years, Physicians for Human Rights (PHR) has
Physicians for Human Rights No Peace Without Justice in Syria March 2016 phr.org No Peace Without Justice in Syria 1 About Physicians for Human Rights For 30 years, Physicians for Human Rights (PHR) has
AN EASY GUIDE TO INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW
 AN EASY GUIDE TO INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW IHL Resource Centre 2015 AN EASY GUIDE TO INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW IN THE OCCUPIED PALESTINIAN TERRITORY IHL Resource Centre May 2015 Published by:
AN EASY GUIDE TO INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW IHL Resource Centre 2015 AN EASY GUIDE TO INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW IN THE OCCUPIED PALESTINIAN TERRITORY IHL Resource Centre May 2015 Published by:
Measures undertaken by the Government of Romania in order to disseminate and implement the international humanitarian law
 Measures undertaken by the Government of Romania in order to disseminate and implement the international humanitarian law Romania is party to most of the international humanitarian law treaties, including
Measures undertaken by the Government of Romania in order to disseminate and implement the international humanitarian law Romania is party to most of the international humanitarian law treaties, including
30 YEARS FROM THE ADOPTION OF ADDITIONAL PROTOCOLS I AND II TO THE GENEVA CONVENTIONS
 30 YEARS FROM THE ADOPTION OF ADDITIONAL PROTOCOLS I AND II TO THE GENEVA CONVENTIONS Beatrice Onica Jarka, Nicolae Titulescu University, Law Faculty ABSTRACT The article reflects in a concentrated form
30 YEARS FROM THE ADOPTION OF ADDITIONAL PROTOCOLS I AND II TO THE GENEVA CONVENTIONS Beatrice Onica Jarka, Nicolae Titulescu University, Law Faculty ABSTRACT The article reflects in a concentrated form
Accession (a)/ Succession (d) Relevant Laws Constitution of 21 September 1964 Criminal Code of 10 June 1854 Police Act of 10 February 1961
 Country File MALTA Last updated: July 2009 Region Legal system Europe Civil Law/Common Law UNCAT Ratification/ 13 September 1990 (a) Accession (a)/ Succession (d) Relevant Laws Constitution of 21 September
Country File MALTA Last updated: July 2009 Region Legal system Europe Civil Law/Common Law UNCAT Ratification/ 13 September 1990 (a) Accession (a)/ Succession (d) Relevant Laws Constitution of 21 September
Implementation of International Humanitarian Law. by Antoine Bouvier Legal Adviser, ICRC Geneva
 Implementation of International Humanitarian Law by Antoine Bouvier Legal Adviser, ICRC Geneva Implementation of International Humanitarian Law Definition and scope Preventive measures to take in peacetime
Implementation of International Humanitarian Law by Antoine Bouvier Legal Adviser, ICRC Geneva Implementation of International Humanitarian Law Definition and scope Preventive measures to take in peacetime
Palestinian prisoners in Israeli jails: Their legal status and their rights
 BRIEFING PAPER 21 May 2012 Palestinian prisoners in Israeli jails: Their legal status and their rights By Dr Abdulrahman Muhammad Ali Introduction The status of prisoners of war is a very complicated issue
BRIEFING PAPER 21 May 2012 Palestinian prisoners in Israeli jails: Their legal status and their rights By Dr Abdulrahman Muhammad Ali Introduction The status of prisoners of war is a very complicated issue
Guénaël Mettraux. The Law of Command Responsibility. Oxford: Oxford University Press, Pp ISBN:
 486 EJIL 21 (2010), 477 499 Guénaël Mettraux. The Law of Command Responsibility. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2009. Pp. 307. 60.00. ISBN: 9780199559329. The doctrine of command responsibility is one
486 EJIL 21 (2010), 477 499 Guénaël Mettraux. The Law of Command Responsibility. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2009. Pp. 307. 60.00. ISBN: 9780199559329. The doctrine of command responsibility is one
Just Convict Everyone! Joint Perpetration: From Tadić to Stakić and Back Again
 International Criminal Law Review 6: 293 302, 2006. 293 2006 Koninklijke Brill NV. Printed in the Netherlands. Just Convict Everyone! Joint Perpetration: From Tadić to Stakić and Back Again MOHAMED ELEWA
International Criminal Law Review 6: 293 302, 2006. 293 2006 Koninklijke Brill NV. Printed in the Netherlands. Just Convict Everyone! Joint Perpetration: From Tadić to Stakić and Back Again MOHAMED ELEWA
...Chapter XI MONITORING AND PROTECTING THE HUMAN RIGHTS OF RETURNEES AND INTERNALLY DISPLACED PERSONS...
 ...Chapter XI MONITORING AND PROTECTING THE HUMAN RIGHTS OF RETURNEES AND INTERNALLY DISPLACED PERSONS... Key concepts United Nations human rights operations have an essential role to fill in monitoring
...Chapter XI MONITORING AND PROTECTING THE HUMAN RIGHTS OF RETURNEES AND INTERNALLY DISPLACED PERSONS... Key concepts United Nations human rights operations have an essential role to fill in monitoring
Attacks on Medical Units in International Humanitarian and Human Rights Law
 Attacks on Medical Units in International Humanitarian and Human Rights Law September 2016 MSF-run hospital in Ma arat al-numan, Idleb Governorate, 15 February 2016 (Photo MSF - www.msf.org) The Syrian
Attacks on Medical Units in International Humanitarian and Human Rights Law September 2016 MSF-run hospital in Ma arat al-numan, Idleb Governorate, 15 February 2016 (Photo MSF - www.msf.org) The Syrian
Resolution 1540: At the crossroads. The Harvard Sussex Draft Convention as a complement to Resolution 1540
 Resolution 1540: At the crossroads The Harvard Sussex Draft Convention as a complement to Resolution 1540 Introduction The Harvard Sussex Draft Convention is an initiative developed by the Harvard Sussex
Resolution 1540: At the crossroads The Harvard Sussex Draft Convention as a complement to Resolution 1540 Introduction The Harvard Sussex Draft Convention is an initiative developed by the Harvard Sussex
PROVISIONS OF THE SPANISH CRIMINAL CODE CONCERNING INTERNATIONAL CRIMES
 PROVISIONS OF THE SPANISH CRIMINAL CODE CONCERNING INTERNATIONAL CRIMES. INTEGRATED TEXT CONTAINING THE AMENDMENTS INTRODUCED BY THE LEY ORGANICA 15/2003 IMPLEMENTING THE STATUTE OF THE INTERNATIONAL CRIMINAL
PROVISIONS OF THE SPANISH CRIMINAL CODE CONCERNING INTERNATIONAL CRIMES. INTEGRATED TEXT CONTAINING THE AMENDMENTS INTRODUCED BY THE LEY ORGANICA 15/2003 IMPLEMENTING THE STATUTE OF THE INTERNATIONAL CRIMINAL
International humanitarian law and the protection of war victims
 International humanitarian law and the protection of war victims Hans-Peter Gasser 1. Why do we need international humanitarian law? War is forbidden. The Charter of the United Nations states clearly that
International humanitarian law and the protection of war victims Hans-Peter Gasser 1. Why do we need international humanitarian law? War is forbidden. The Charter of the United Nations states clearly that
INTERNATIONAL CRIMINAL COURT
 INTERNATIONAL CRIMINAL COURT Marta Statkiewicz Department of International and European Law Faculty of Law, Administration and Economics University of Wrocław HISTORY HISTORY establishment of ad hoc international
INTERNATIONAL CRIMINAL COURT Marta Statkiewicz Department of International and European Law Faculty of Law, Administration and Economics University of Wrocław HISTORY HISTORY establishment of ad hoc international
UNITED NATIONS OFFICE OF LEGAL AFFAIRS
 UNITED NATIONS OFFICE OF LEGAL AFFAIRS 36th Annual Seminar on International Humanitarian Law for Legal Advisers and other Diplomats Accredited to the United Nations jointly organized by the International
UNITED NATIONS OFFICE OF LEGAL AFFAIRS 36th Annual Seminar on International Humanitarian Law for Legal Advisers and other Diplomats Accredited to the United Nations jointly organized by the International
(Statute of the International Tribunal for Rwanda)
 Statute of the International Criminal Tribunal for the Prosecution of Persons Responsible for Genocide and Other Serious Violations of International Humanitarian Law Committed in the Territory of Rwanda
Statute of the International Criminal Tribunal for the Prosecution of Persons Responsible for Genocide and Other Serious Violations of International Humanitarian Law Committed in the Territory of Rwanda
Parallel Report submitted by the Global Initiative for Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (GI-ESCR) to the Country Report Task Force of the Human
 Parallel Report submitted by the Global Initiative for Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (GI-ESCR) to the Country Report Task Force of the Human Rights Committee on the occasion of the consideration
Parallel Report submitted by the Global Initiative for Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (GI-ESCR) to the Country Report Task Force of the Human Rights Committee on the occasion of the consideration
FORMAT FOR NATIONAL REPORTS. Four-year cycle
 FORMAT FOR NATIONAL REPORTS Four-year cycle 2013-2016 National report on the implementation of the Hague Convention of 1954 and its two Protocols (1954 and 1999) This form must be submitted electronically.
FORMAT FOR NATIONAL REPORTS Four-year cycle 2013-2016 National report on the implementation of the Hague Convention of 1954 and its two Protocols (1954 and 1999) This form must be submitted electronically.
INSTITUTE OF INTERNATIONAL LAW Bruges Session Sixteenth Commission. Humanitarian Assistance RESOLUTION
 INSTITUTE OF INTERNATIONAL LAW 02.09.2003 Bruges Session 2003 Sixteenth Commission Humanitarian Assistance Rapporteur: M. Budislav VUKAS RESOLUTION The Institute of International Law, Recalling its Resolutions
INSTITUTE OF INTERNATIONAL LAW 02.09.2003 Bruges Session 2003 Sixteenth Commission Humanitarian Assistance Rapporteur: M. Budislav VUKAS RESOLUTION The Institute of International Law, Recalling its Resolutions
Appendix II Draft comprehensive convention against international terrorism
 Appendix II Draft comprehensive convention against international terrorism Consolidated text prepared by the coordinator for discussion* The States Parties to the present Convention, Recalling the existing
Appendix II Draft comprehensive convention against international terrorism Consolidated text prepared by the coordinator for discussion* The States Parties to the present Convention, Recalling the existing
International Court of Justice
 International Court of Justice Summary 2004/2 9 July 2004 History of the proceedings (paras. 1-12) Legal Consequences of the Construction of a Wall in the Occupied Palestinian Territory (Request for advisory
International Court of Justice Summary 2004/2 9 July 2004 History of the proceedings (paras. 1-12) Legal Consequences of the Construction of a Wall in the Occupied Palestinian Territory (Request for advisory
Non-state actors and Direct Participation in Hostilities. Giulio Bartolini University of Roma Tre
 Non-state actors and Direct Participation in Hostilities Giulio Bartolini University of Roma Tre The involvement of non-state actors in armed conflicts. Different kinds of non-state actors : A) Organised
Non-state actors and Direct Participation in Hostilities Giulio Bartolini University of Roma Tre The involvement of non-state actors in armed conflicts. Different kinds of non-state actors : A) Organised
Counter-Terrorism Measures in Internal Armed Conflicts: The Obligations from International Law
 DPI Briefing Paper Counter-Terrorism Measures in Internal Armed Conflicts: The Obligations from International Law Introduction There is no precise definition of terrorism agreed upon by the international
DPI Briefing Paper Counter-Terrorism Measures in Internal Armed Conflicts: The Obligations from International Law Introduction There is no precise definition of terrorism agreed upon by the international
Cour Pénale Internationale International Criminal Court
 Cour Pénale Internationale International Criminal Court No.: ICC-01/05 Date: 9 September 2005 Original: English TRIAL CHAMBER I Before: International Criminal Court Moot 2005 Pace Law School SITUATION
Cour Pénale Internationale International Criminal Court No.: ICC-01/05 Date: 9 September 2005 Original: English TRIAL CHAMBER I Before: International Criminal Court Moot 2005 Pace Law School SITUATION
COALITION PROVISIONAL AUTHORITY ORDER NUMBER 7 PENAL CODE
 COALITION PROVISIONAL AUTHORITY ORDER NUMBER 7 Pursuant to my authority as head of the Coalition Provisional Authority (CPA), relevant U.N. Security Council resolutions, including Resolution 1483 (2003),
COALITION PROVISIONAL AUTHORITY ORDER NUMBER 7 Pursuant to my authority as head of the Coalition Provisional Authority (CPA), relevant U.N. Security Council resolutions, including Resolution 1483 (2003),
Published on How does law protect in war? - Online casebook (https://casebook.icrc.org)
 Published on How does law protect in war? - Online casebook (https://casebook.icrc.org) Home > ICRC, Customary International Humanitarian Law A. ICRC Report 1995 [Source: International Humanitarian Law:
Published on How does law protect in war? - Online casebook (https://casebook.icrc.org) Home > ICRC, Customary International Humanitarian Law A. ICRC Report 1995 [Source: International Humanitarian Law:
IS DONBAS OCCUPIED? CONTENTS
 IS DONBAS OCCUPIED? CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 2 (1) HOW THE ASSESSMENT OF RUSSIA S ALLEGED OCCUPATION OF DONBAS SHOULD BE APPROACHED. 2 A. LEGAL PROVISION: ARTICLE 42 OF THE HAGUE REGULATIONS... 4 B. FACTUAL
IS DONBAS OCCUPIED? CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 2 (1) HOW THE ASSESSMENT OF RUSSIA S ALLEGED OCCUPATION OF DONBAS SHOULD BE APPROACHED. 2 A. LEGAL PROVISION: ARTICLE 42 OF THE HAGUE REGULATIONS... 4 B. FACTUAL
INTERNATIONAL CRIMES AND THE AD HOC TRIBUNALS BY GUÉNAËL METTRAUX OXFORD: OXFORD DANIEL C. TURACK *
 INTERNATIONAL CRIMES AND THE AD HOC TRIBUNALS BY GUÉNAËL METTRAUX OXFORD: OXFORD DANIEL C. TURACK * Mr. Mettraux brings a wealth of personal experience into the writing of this book, as he worked within
INTERNATIONAL CRIMES AND THE AD HOC TRIBUNALS BY GUÉNAËL METTRAUX OXFORD: OXFORD DANIEL C. TURACK * Mr. Mettraux brings a wealth of personal experience into the writing of this book, as he worked within
A. Yugoslavia/Croatia, Memorandum of Understanding of November 27, 1991
 Published on How does law protect in war? - Online casebook (https://casebook.icrc.org) Home > Former Yugoslavia, Special Agreements between the Parties to the Conflicts A. Yugoslavia/Croatia, Memorandum
Published on How does law protect in war? - Online casebook (https://casebook.icrc.org) Home > Former Yugoslavia, Special Agreements between the Parties to the Conflicts A. Yugoslavia/Croatia, Memorandum
Arrest and Detention of Palestinian Minors in the Occupied Territories Facts and Figures 1. By Attorney Nisreen Alyan and Sapir Slutzker Amran
 Arrest and Detention of Palestinian Minors in the Occupied Territories Introduction 2015 Facts and Figures 1 By Attorney Nisreen Alyan and Sapir Slutzker Amran This document presents the primary findings
Arrest and Detention of Palestinian Minors in the Occupied Territories Introduction 2015 Facts and Figures 1 By Attorney Nisreen Alyan and Sapir Slutzker Amran This document presents the primary findings
GENEVA CONVENTION (IV) RELATIVE TO THE PROTECTION OF CIVILIAN PERSONS IN TIME OF WAR (GENEVA CONVENTION IV)
 GENEVA CONVENTION (IV) RELATIVE TO THE PROTECTION OF CIVILIAN PERSONS IN TIME OF WAR Signed at Geneva, 12 August 1949 The undersigned Plenipotentiaries of the Governments represented at the Diplomatic
GENEVA CONVENTION (IV) RELATIVE TO THE PROTECTION OF CIVILIAN PERSONS IN TIME OF WAR Signed at Geneva, 12 August 1949 The undersigned Plenipotentiaries of the Governments represented at the Diplomatic
NETHERLANDS. International Crimes Act
 NETHERLANDS International Crimes Act 270 Act of 19 June 2003 containing rules concerning serious violations of international humanitarian law (International Crimes Act) We Beatrix, by the Grace of God,
NETHERLANDS International Crimes Act 270 Act of 19 June 2003 containing rules concerning serious violations of international humanitarian law (International Crimes Act) We Beatrix, by the Grace of God,
TOWARDS CONVERGENCE. IHL, IHRL and the Convergence of Norms in Armed Conflict
 TOWARDS CONVERGENCE IHL, IHRL and the Convergence of Norms in Armed Conflict DECISION ON THE DEFENCE MOTION FOR INTERLOCUTORY APPEAL ON JURISDICTION - Tadić As the members of the Security Council well
TOWARDS CONVERGENCE IHL, IHRL and the Convergence of Norms in Armed Conflict DECISION ON THE DEFENCE MOTION FOR INTERLOCUTORY APPEAL ON JURISDICTION - Tadić As the members of the Security Council well
Declaration on the Protection of all Persons from Enforced Disappearance
 Declaration on the Protection of all Persons from Enforced Disappearance Adopted by General Assembly resolution 47/133 of 18 December 1992 The General Assembly, Considering that, in accordance with the
Declaration on the Protection of all Persons from Enforced Disappearance Adopted by General Assembly resolution 47/133 of 18 December 1992 The General Assembly, Considering that, in accordance with the
Fiji Comments on the Discussion Paper on implementation of the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 1 1. Incorporating crimes within the jurisdiction of the Court... 2 (a) genocide... 2 (b) crimes against humanity... 2 (c) war crimes... 3 (d) Implementing other crimes
TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 1 1. Incorporating crimes within the jurisdiction of the Court... 2 (a) genocide... 2 (b) crimes against humanity... 2 (c) war crimes... 3 (d) Implementing other crimes
Israel, Military Prosecutor v. Kassem and Others
 Published on How does law protect in war? - Online casebook (https://casebook.icrc.org) Home > Israel, Military Prosecutor v. Kassem and Others Israel, Military Prosecutor v. Kassem and Others [Source:
Published on How does law protect in war? - Online casebook (https://casebook.icrc.org) Home > Israel, Military Prosecutor v. Kassem and Others Israel, Military Prosecutor v. Kassem and Others [Source:
Israel, Ayub v. Minister of Defence
 Published on How does law protect in war? - Online casebook (https://casebook.icrc.org) Home > Israel, Ayub v. Minister of Defence Israel, Ayub v. Minister of Defence [Source: reproduced as summarized
Published on How does law protect in war? - Online casebook (https://casebook.icrc.org) Home > Israel, Ayub v. Minister of Defence Israel, Ayub v. Minister of Defence [Source: reproduced as summarized
- 1 - Implementing the 1954 Hague Convention and its Protocols: legal and practical implications. Patrick J Boylan, City University London, UK
 - 1 - Implementing the 1954 Hague Convention and its Protocols: legal and practical implications Patrick J Boylan, City University London, UK If and when a State decides to adopt the 1954 Hague Convention
- 1 - Implementing the 1954 Hague Convention and its Protocols: legal and practical implications Patrick J Boylan, City University London, UK If and when a State decides to adopt the 1954 Hague Convention
HUMANITARIAN Access. Handbook on the Normative Framework. in SituationS of armed ConfliCt. Version 1.0
 HUMANITARIAN Access in SituationS of armed ConfliCt Handbook on the Normative Framework Version 1.0 Background and Purpose In light of the challenges in securing and sustaining humanitarian access and
HUMANITARIAN Access in SituationS of armed ConfliCt Handbook on the Normative Framework Version 1.0 Background and Purpose In light of the challenges in securing and sustaining humanitarian access and
Reflections on the Legal Regime of Water during Armed Conflicts
 Reflections on the Legal Regime of Water during Armed Conflicts Paper to be presented at the Fifth Pan-European International Relations Conference (Section 31, Panel 8), The Hague, 9-11 September 2004
Reflections on the Legal Regime of Water during Armed Conflicts Paper to be presented at the Fifth Pan-European International Relations Conference (Section 31, Panel 8), The Hague, 9-11 September 2004
Act of 5 August 2003 on serious violations of international humanitarian law
 Act of 5 August 2003 on serious violations of international humanitarian law CHAPTER I GENERAL PROVISION Article 1 The present Act regulates a matter referred to in article 77 of the Constitution. CHAPTER
Act of 5 August 2003 on serious violations of international humanitarian law CHAPTER I GENERAL PROVISION Article 1 The present Act regulates a matter referred to in article 77 of the Constitution. CHAPTER
FACT SHEET STOPPING THE USE OF RAPE AS A TACTIC OF
 June 2014 FACT SHEET STOPPING THE USE OF RAPE AS A TACTIC OF WAR: A NEW APPROACH There is a global consensus that the mass rape of girls and women is routinely used as a tactic or weapon of war in contemporary
June 2014 FACT SHEET STOPPING THE USE OF RAPE AS A TACTIC OF WAR: A NEW APPROACH There is a global consensus that the mass rape of girls and women is routinely used as a tactic or weapon of war in contemporary
Opinions adopted by the Working Group on Arbitrary Detention at its seventy-ninth session, August 2017
 Advance Edited Version Distr.: General 2 October 2017 Original: English Human Rights Council Working Group on Arbitrary Detention Opinions adopted by the Working Group on Arbitrary Detention at its seventy-ninth
Advance Edited Version Distr.: General 2 October 2017 Original: English Human Rights Council Working Group on Arbitrary Detention Opinions adopted by the Working Group on Arbitrary Detention at its seventy-ninth
Complementarities between International Refugee Law, International Criminal Law and International Human Rights Law. Concept Note
 Complementarities between International Refugee Law, International Criminal Law and International Human Rights Law Concept Note The establishment of the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia
Complementarities between International Refugee Law, International Criminal Law and International Human Rights Law Concept Note The establishment of the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia
INTERNATIONAL LAW AND INSTITUTIONS International Law Regarding the Conduct of War - Mark A. Drumbl INTERNATIONAL LAW REGARDING THE CONDUCT OF WAR
 INTERNATIONAL LAW REGARDING THE CONDUCT OF WAR Mark A. Drumbl Assistant Professor, Washington & Lee University, School of Law, Lexington, Virginia, USA Keywords: Customary international law, environment,
INTERNATIONAL LAW REGARDING THE CONDUCT OF WAR Mark A. Drumbl Assistant Professor, Washington & Lee University, School of Law, Lexington, Virginia, USA Keywords: Customary international law, environment,
In witness whereof the undersigned have signed the present Agreement.
 Agreement for the Prosecution and Punishment of the Major War Criminals of the European Axis, and Charter of the International Military Tribunal. London, 8 August 1945. AGREEMENT Whereas the United Nations
Agreement for the Prosecution and Punishment of the Major War Criminals of the European Axis, and Charter of the International Military Tribunal. London, 8 August 1945. AGREEMENT Whereas the United Nations
A Further Step in the Development of the Joint Criminal Enterprise Doctrine
 HAGUE JUSTICE JOURNAL I JOURNAL JUDICIAIRE DE LA HAYE VOLUME/VOLUME 2 I NUMBER/ NUMÉRO 2 I 2007 A Further Step in the Development of the Joint Criminal Enterprise Doctrine Matteo Fiori 1 1. Introduction
HAGUE JUSTICE JOURNAL I JOURNAL JUDICIAIRE DE LA HAYE VOLUME/VOLUME 2 I NUMBER/ NUMÉRO 2 I 2007 A Further Step in the Development of the Joint Criminal Enterprise Doctrine Matteo Fiori 1 1. Introduction
THE HOSTAGES TRIAL TRIAL OF WILHELM LIST AND OTHERS UNITED STATES MILITARY TRIBUNAL, NUREMBERG. 8 th JULY, 1947, TO 19 th FEBRUARY, 1948
 Published on How does law protect in war? - Online casebook (https://casebook.icrc.org) Home > United States Military Tribunal at Nuremberg, United States v. Wilhelm List [Source: The United Nations War
Published on How does law protect in war? - Online casebook (https://casebook.icrc.org) Home > United States Military Tribunal at Nuremberg, United States v. Wilhelm List [Source: The United Nations War
THE INTERNATIONAL CRIMES (TRIBUNALS) ACT, 1973
 THE INTERNATIONAL CRIMES (TRIBUNALS) ACT, 1973 (ACT NO. XIX OF 1973). [20th July, 1973] An Act to provide for the detention, prosecution and punishment of persons for genocide, crimes against humanity,
THE INTERNATIONAL CRIMES (TRIBUNALS) ACT, 1973 (ACT NO. XIX OF 1973). [20th July, 1973] An Act to provide for the detention, prosecution and punishment of persons for genocide, crimes against humanity,
JCE IN INTERNATIONAL LAW. Dubrovnik, Professor Maja Seršić
 JCE IN INTERNATIONAL LAW Dubrovnik, 29. 03. 2012. Professor Maja Seršić UN Security Council Resolution 827 (1993) - approved report S/25704 of UN Secretary General, with the Statute of the International
JCE IN INTERNATIONAL LAW Dubrovnik, 29. 03. 2012. Professor Maja Seršić UN Security Council Resolution 827 (1993) - approved report S/25704 of UN Secretary General, with the Statute of the International
TO: Members of the Preparatory Committee on the Establishment of an International Criminal Court
 INTERNATIONAL CRIMINAL TRIBUNAL FOR THE FORMER YUGOSLAVIA CHURCHILLPLEIN, 1. P.O. BOX 13888 2501 EW THE HAGUE, NETHERLANDS TELEPHONE 31 70 416-5329 FAX: 31 70416-5307 MEMORANDUM TO: Members of the Preparatory
INTERNATIONAL CRIMINAL TRIBUNAL FOR THE FORMER YUGOSLAVIA CHURCHILLPLEIN, 1. P.O. BOX 13888 2501 EW THE HAGUE, NETHERLANDS TELEPHONE 31 70 416-5329 FAX: 31 70416-5307 MEMORANDUM TO: Members of the Preparatory
Failure to comply could result in the application of disciplinary measures as foreseen in the Staff Regulations.
 FORM A1 OBLIGATIONS OF EEA OFFICIALS AND OTHER SERVANTS UNDER THE STAFF REGULATIONS AND CONDITIONS OF EMPLOYMENT As you commence your duties with the European Environment Agency, your attention is drawn
FORM A1 OBLIGATIONS OF EEA OFFICIALS AND OTHER SERVANTS UNDER THE STAFF REGULATIONS AND CONDITIONS OF EMPLOYMENT As you commence your duties with the European Environment Agency, your attention is drawn
THE DISTINCTION BETWEEN INTERNATIONAL AND NON-INTERNATIONAL ARMED CONFLICTS: CHALLENGES FOR IHL?
 XXXVIII ROUND TABLE ON CURRENT ISSUES OF INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW THE DISTINCTION BETWEEN INTERNATIONAL AND NON-INTERNATIONAL ARMED CONFLICTS: CHALLENGES FOR IHL? SANREMO, 3 rd 5 th SEPTEMBER, 2015
XXXVIII ROUND TABLE ON CURRENT ISSUES OF INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW THE DISTINCTION BETWEEN INTERNATIONAL AND NON-INTERNATIONAL ARMED CONFLICTS: CHALLENGES FOR IHL? SANREMO, 3 rd 5 th SEPTEMBER, 2015
COMMITTEE FOR THE PROTECTION OF CULTURAL PROPERTY IN THE EVENT OF ARMED CONFLICT
 CLT-11/CONF/211/3 Paris, 6 September 2011 Original: English UNITED NATIONS EDUCATIONAL, SCIENTIFIC AND CULTURAL ORGANIZATION COMMITTEE FOR THE PROTECTION OF CULTURAL PROPERTY IN THE EVENT OF ARMED CONFLICT
CLT-11/CONF/211/3 Paris, 6 September 2011 Original: English UNITED NATIONS EDUCATIONAL, SCIENTIFIC AND CULTURAL ORGANIZATION COMMITTEE FOR THE PROTECTION OF CULTURAL PROPERTY IN THE EVENT OF ARMED CONFLICT
DECLARATION OF JUDGE SKOTNIKOV
 DECLARATION OF JUDGE SKOTNIKOV No jurisdiction Respondent had no access to Court when proceedings instituted Relevance of 2004 Legality of Use of Force cases Issue of access to Court not determined in
DECLARATION OF JUDGE SKOTNIKOV No jurisdiction Respondent had no access to Court when proceedings instituted Relevance of 2004 Legality of Use of Force cases Issue of access to Court not determined in
Article. Reference. SASSÒLI, Marco
 Article A plea in defence of Pictet and the inhabitants of territories under invasion: the case for the applicability of the Fourth Geneva Convention during the invasion phase SASSÒLI, Marco Reference
Article A plea in defence of Pictet and the inhabitants of territories under invasion: the case for the applicability of the Fourth Geneva Convention during the invasion phase SASSÒLI, Marco Reference
2012 The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History Excerpts from Ex Parte Quirin (underlining added for emphasis).
 Excerpts from Ex Parte Quirin (underlining added for emphasis). In these causes motions for leave to file petitions for habeas corpus were presented to the United States District Court for the District
Excerpts from Ex Parte Quirin (underlining added for emphasis). In these causes motions for leave to file petitions for habeas corpus were presented to the United States District Court for the District
Convention for the Amelioration of the Condition of the Wounded and Sick in Armies in the Field. Geneva, 27 July (List of Contracting Parties)
 Convention for the Amelioration of the Condition of the Wounded and Sick in Armies in the Field. Geneva, 27 July 1929. (List of Contracting Parties) Being equally animated by the desire to lessen, so far
Convention for the Amelioration of the Condition of the Wounded and Sick in Armies in the Field. Geneva, 27 July 1929. (List of Contracting Parties) Being equally animated by the desire to lessen, so far
Lesson 8 Legal Frameworks for Civil-Military-Police Relations
 CC Flickr Photo by Albert Gonzalez Farran, UNAMID Lesson 8 Legal Frameworks for Civil-Military-Police Relations Learning Objectives: At the end of the lesson, participants will be able to: Identify five
CC Flickr Photo by Albert Gonzalez Farran, UNAMID Lesson 8 Legal Frameworks for Civil-Military-Police Relations Learning Objectives: At the end of the lesson, participants will be able to: Identify five
ICRC POSITION ON. INTERNALLY DISPLACED PERSONS (IDPs) (May 2006)
 ICRC POSITION ON INTERNALLY DISPLACED PERSONS (IDPs) (May 2006) CONTENTS I. Introduction... 2 II. Definition of IDPs and overview of their protection under the law... 2 III. The humanitarian needs of IDPs...
ICRC POSITION ON INTERNALLY DISPLACED PERSONS (IDPs) (May 2006) CONTENTS I. Introduction... 2 II. Definition of IDPs and overview of their protection under the law... 2 III. The humanitarian needs of IDPs...
The Syrian Conflict and International Humanitarian Law
 The Syrian Conflict and International Humanitarian Law Andrew Hall The current situation in Syria is well documented. There is little doubt that a threshold of sustained violence has been reached and that
The Syrian Conflict and International Humanitarian Law Andrew Hall The current situation in Syria is well documented. There is little doubt that a threshold of sustained violence has been reached and that
International Criminal Court (Scotland) Bill
 International Criminal Court (Scotland) Bill [AS AMENDED AT STAGE 2] CONTENTS Section PART 1 OFFENCES Offences 1 Genocide, crimes against humanity and war crimes 2 Conduct ancillary to genocide etc. 3
International Criminal Court (Scotland) Bill [AS AMENDED AT STAGE 2] CONTENTS Section PART 1 OFFENCES Offences 1 Genocide, crimes against humanity and war crimes 2 Conduct ancillary to genocide etc. 3
AFFIRMATION OF THE PRINCIPLES OF INTERNATIONAL LAW
 AFFIRMATION OF THE PRINCIPLES OF INTERNATIONAL LAW RECOGNIZED BY THE CHARTER OF THE NÜRNBERG TRIBUNAL By Antonio Cassese * President of the Special Tribunal for Lebanon 1. Introduction General Assembly
AFFIRMATION OF THE PRINCIPLES OF INTERNATIONAL LAW RECOGNIZED BY THE CHARTER OF THE NÜRNBERG TRIBUNAL By Antonio Cassese * President of the Special Tribunal for Lebanon 1. Introduction General Assembly
Humanitarian Access in situations of armed conflict
 Humanitarian Access in situations of armed conflict Handbook on the Normative Framework Version 1.0 UN Photo/Jorge Aramburu; UN Photo/Olivia Grey Pritchard Background and Purpose In light of the challenges
Humanitarian Access in situations of armed conflict Handbook on the Normative Framework Version 1.0 UN Photo/Jorge Aramburu; UN Photo/Olivia Grey Pritchard Background and Purpose In light of the challenges
7th RED CROSS INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW MOOT. International Criminal Court MEMORIAL FOR THE DEFENSE
 7th RED CROSS INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW MOOT International Criminal Court MEMORIAL FOR THE DEFENSE The Johns Hopkins University-Nanjing University Center for Chinese and American Studies Nathan Fischler
7th RED CROSS INTERNATIONAL HUMANITARIAN LAW MOOT International Criminal Court MEMORIAL FOR THE DEFENSE The Johns Hopkins University-Nanjing University Center for Chinese and American Studies Nathan Fischler
ADVANCED UNEDITED VERSION
 Distr. GENERAL CAT/C/ISR/CO/4 14 May 2009 Original: ENGLISH COMMITTEE AGAINST TORTURE Forty-second session Geneva, 27 April-15 May 2009 ADVANCED UNEDITED VERSION CONSIDERATION OF REPORTS SUBMITTED BY STATES
Distr. GENERAL CAT/C/ISR/CO/4 14 May 2009 Original: ENGLISH COMMITTEE AGAINST TORTURE Forty-second session Geneva, 27 April-15 May 2009 ADVANCED UNEDITED VERSION CONSIDERATION OF REPORTS SUBMITTED BY STATES
